Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - PLAINS GP HOLDINGS LP | a15-24559_1ex31d2.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - PLAINS GP HOLDINGS LP | a15-24559_1ex32d2.htm |
| EX-12.1 - EX-12.1 - PLAINS GP HOLDINGS LP | a15-24559_1ex12d1.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - PLAINS GP HOLDINGS LP | a15-24559_1ex23d1.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - PLAINS GP HOLDINGS LP | a15-24559_1ex31d1.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - PLAINS GP HOLDINGS LP | a15-24559_1ex32d1.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EX-21.1 - PLAINS GP HOLDINGS LP | a15-24559_1ex21d1.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
x ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015
or
o TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
Commission file number 1-36132
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
|
Delaware |
|
90-1005472 |
|
(State or other jurisdiction of |
|
(I.R.S. Employer |
|
incorporation or organization) |
|
Identification No.) |
|
333 Clay Street, Suite 1600, Houston, Texas |
|
77002 |
|
(Address of principal executive offices) |
|
(Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (713) 646-4100
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
|
Title of Each Class |
|
Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered |
|
Class A Shares, |
|
New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes o No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
|
Large Accelerated Filer x |
|
Accelerated Filer o |
|
|
|
|
|
Non-Accelerated Filer o |
|
Smaller Reporting Company o |
|
(Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
|
|
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No x
The aggregate market value of the Class A shares held by non-affiliates of the registrant (treating all executive officers and directors of the registrant and holders of 10% or more of the Class A shares outstanding, for this purpose, as if they may be affiliates of the registrant) was approximately $5.8 billion on June 30, 2015, based on a closing price of $25.84 per Class A share as reported on the New York Stock Exchange on such date.
As of February 12, 2016, there were 244,203,443 Class A shares outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
NONE
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P. AND SUBSIDIARIES
FORM 10-K—2015 ANNUAL REPORT
FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
All statements included in this report, other than statements of historical fact, are forward-looking statements, including but not limited to statements incorporating the words “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “expect,” “plan,” “intend” and “forecast,” as well as similar expressions and statements regarding our business strategy, plans and objectives for future operations. The absence of such words, expressions or statements, however, does not mean that the statements are not forward-looking. Any such forward-looking statements reflect our current views with respect to future events, based on what we believe to be reasonable assumptions. Certain factors could cause actual results or outcomes to differ materially from the results or outcomes anticipated in the forward-looking statements. The most important of these factors include, but are not limited to:
· our ability to pay distributions to our Class A shareholders;
· our expected receipt of, and amounts of, distributions from Plains AAP, L.P.;
· declines in the volume of crude oil, refined product and NGL shipped, processed, purchased, stored, fractionated and/or gathered at or through the use of our assets, whether due to declines in production from existing oil and gas reserves, failure to develop or slowdown in the development of additional oil and gas reserves, whether from reduced cash flow to fund drilling or the inability to access capital, or other factors;
· the effects of competition;
· failure to implement or capitalize, or delays in implementing or capitalizing, on expansion projects;
· unanticipated changes in crude oil market structure, grade differentials and volatility (or lack thereof);
· environmental liabilities or events that are not covered by an indemnity, insurance or existing reserves;
· fluctuations in refinery capacity in areas supplied by our mainlines and other factors affecting demand for various grades of crude oil, refined products and natural gas and resulting changes in pricing conditions or transportation throughput requirements;
· the occurrence of a natural disaster, catastrophe, terrorist attack or other event, including attacks on our electronic and computer systems;
· tightened capital markets or other factors that increase our cost of capital or limit our ability to obtain debt or equity financing on satisfactory terms to fund additional acquisitions, expansion projects, working capital requirements and the repayment or refinancing of indebtedness;
· the currency exchange rate of the Canadian dollar;
· continued creditworthiness of, and performance by, our counterparties, including financial institutions and trading companies with which we do business;
· maintenance of PAA’s credit rating and ability to receive open credit from suppliers and trade counterparties;
· non-utilization of our assets and facilities;
· weather interference with business operations or project construction, including the impact of extreme weather events or conditions;
· the availability of, and our ability to consummate, acquisition or combination opportunities;
· the successful integration and future performance of acquired assets or businesses and the risks associated with operating in lines of business that are distinct and separate from historical operations;
· increased costs, or lack of availability, of insurance;
· the effectiveness of our risk management activities;
· shortages or cost increases of supplies, materials or labor;
· the impact of current and future laws, rulings, governmental regulations, accounting standards and statements, and related interpretations;
· fluctuations in the debt and equity markets, including the price of PAA’s units at the time of vesting under its long-term incentive plans;
· risks related to the development and operation of our assets, including our ability to satisfy our contractual obligations to our customers;
· inability to recognize current revenue attributable to deficiency payments received from customers who fail to ship or move more than minimum contracted volumes until the related credits expire or are used;
· factors affecting demand for natural gas and natural gas storage services and rates;
· general economic, market or business conditions and the amplification of other risks caused by volatile financial markets, capital constraints and pervasive liquidity concerns; and
· other factors and uncertainties inherent in the transportation, storage, terminalling and marketing of crude oil and refined products, as well as in the storage of natural gas and the processing, transportation, fractionation, storage and marketing of natural gas liquids.
Other factors described herein, as well as factors that are unknown or unpredictable, could also have a material adverse effect on future results. Please read Item 1A “Risk Factors.” Except as required by applicable securities laws, we do not intend to update these forward-looking statements and information.
Items 1 and 2. Business and Properties
General
Plains GP Holdings, L.P. (“PAGP”) is a Delaware limited partnership formed in July 2013 to own an interest in the general partner and incentive distribution rights (“IDRs”) of Plains All American Pipeline, L.P (“PAA”), a publicly traded Delaware limited partnership. Although formed as a limited partnership, PAGP has elected to be taxed as a corporation for United States federal income tax purposes. As used in this Form 10-K and unless the context indicates otherwise (taking into account the fact that PAGP has no operating activities apart from those conducted by PAA and its subsidiaries), the terms “Partnership,” “we,” “us,” “our,” “ours” and similar terms refer to PAGP and its subsidiaries.
Organizational History
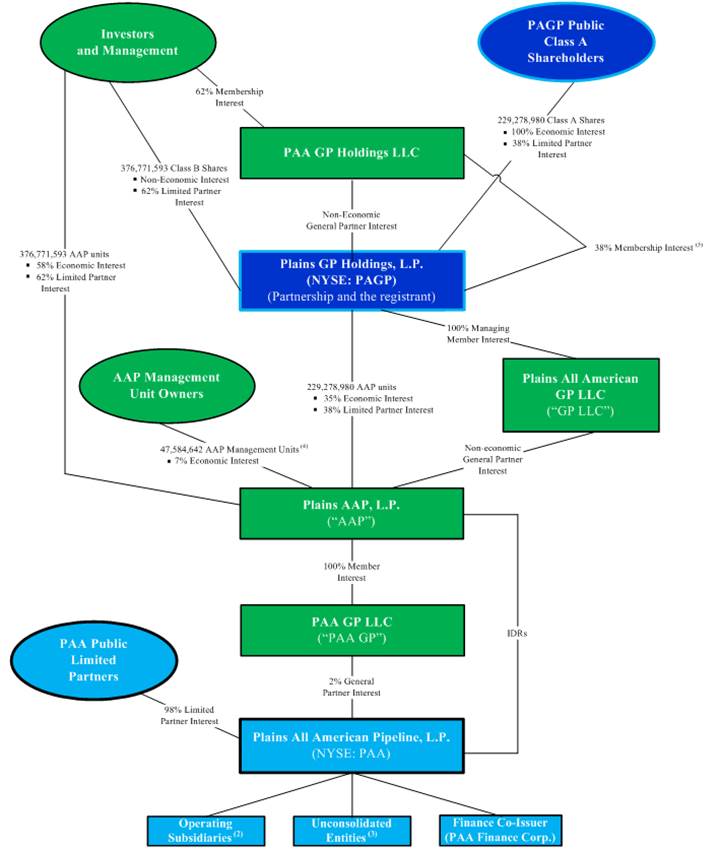
We completed our initial public offering (“IPO”) in October 2013. Immediately prior to completion of our IPO, certain owners of Plains AAP, L.P. (“AAP”) transferred a portion of their interests in AAP to us, resulting in our ownership of a limited partnership interest in AAP. As of December 31, 2015, we owned an approximate 38% limited partner interest in AAP (an approximate 35% economic interest), and the remaining limited partner interests in AAP were held by the owners of AAP immediately prior to our IPO (the “Legacy Owners”). AAP is a Delaware limited partnership that directly owns all of PAA’s IDRs and indirectly owns the 2% general partner interest in PAA. AAP is the sole member of PAA GP LLC (“PAA GP”), a Delaware limited liability company that directly holds the 2% general partner interest in PAA. Plains All American GP LLC (“GP LLC”) is a Delaware limited liability company that holds the general partner interest in AAP. Also, through a series of transactions prior to our IPO with PAA GP Holdings LLC (our general partner) and the owners of GP LLC, GP LLC’s general partner interest in AAP became a non-economic interest and we became the owner of a 100% managing member interest in GP LLC.
PAA is a publicly traded master limited partnership that owns and operates midstream energy infrastructure and provides logistics services for crude oil, natural gas liquids (“NGL”), natural gas and refined products. PAA owns an extensive network of pipeline transportation, terminalling, storage and gathering assets in key crude oil and NGL producing basins and transportation corridors and at major market hubs in the United States and Canada.
Partnership Structure and Management
Our general partner manages our operations and activities and is responsible for exercising on our behalf any rights we have as the sole and managing member of GP LLC, including any rights to appoint members to the board of directors of GP LLC. See Item 10. “Directors and Executive Officers of our General Partner and Corporate Governance.” GP LLC has responsibility for managing the business and affairs of PAA and AAP; however, through our rights as the sole and managing member of GP LLC, we effectively control the business and affairs of AAP and PAA. GP LLC employs all domestic officers and personnel involved in the operation and management of PAA and AAP. PAA’s Canadian officers and personnel are employed by Plains Midstream Canada ULC (“PMC”). Our general partner does not receive a management fee or other compensation in connection with its management of our business.
The two charts below show the structure and ownership of PAGP and certain subsidiaries as of December 31, 2015 in both a summarized and more detailed format. The first chart depicts PAGP’s legal structure in summary format, while the second chart depicts a more comprehensive view of PAGP’s legal structure, including ownership and economic interests and shares and units outstanding.
Summarized Partnership Structure
(as of December 31, 2015) (1)

(1) In January 2016, PAA completed the sale of approximately 61.0 million Series A Convertible Preferred Units representing limited partner interests in PAA. See Note 10 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information.
(2) Board appointment rights limited to non-management investors that own greater than 10% interest in AAP.
(1) In January 2016, PAA completed the sale of approximately 61.0 million Series A Convertible Preferred Units representing limited partner interests in PAA. See Note 10 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information.
(2) PAA holds direct and indirect ownership interests in consolidated operating subsidiaries including, but not limited to, Plains Marketing, L.P., Plains Pipeline, L.P. and PMC.
(3) PAA holds indirect equity interests in unconsolidated entities including BridgeTex Pipeline Company, LLC (“BridgeTex”), Butte Pipe Line Company (“Butte”), Caddo Pipeline LLC (“Caddo”), Diamond Pipeline LLC (“Diamond”), Eagle Ford Pipeline LLC (“Eagle Ford Pipeline”), Eagle Ford Terminals Corpus Christi LLC (“Eagle Ford Terminals”), Frontier Pipeline Company (“Frontier”), Saddlehorn Pipeline Company, LLC (“Saddlehorn”), Settoon Towing, LLC (“Settoon Towing”) and White Cliffs Pipeline LLC (“White Cliffs”).
(4) Represents the number of Class A units of AAP (“AAP units”) for which the Class B units of AAP (referred to herein as the “AAP Management Units”) would be exchangeable, assuming a conversion rate of approximately 0.938 AAP units for each AAP Management Unit as of December 31, 2015. The AAP Management Units are entitled to certain proportionate distributions paid by AAP.
(5) As of December 31, 2015, we owned approximately 38% of the membership interests in our general partner, which percentage corresponds to our ownership percentage of AAP units (approximately 38%, representing an approximate 35% economic interest in AAP, including the dilutive effect of the AAP Management Units).
Our Business
As of December 31, 2015, our only cash-generating assets consisted of 229,278,980 AAP units, which represent an approximate 38% limited partner interest in AAP (approximately 35% economic interest including the dilutive effect of the AAP Management Units). Unless we directly acquire and hold assets or businesses in the future, our cash flows will be generated solely from the cash distributions we receive from AAP. AAP does not own any common units in PAA and currently receives all of its cash flows from distributions on its direct ownership of PAA’s IDRs and its indirect ownership of PAA’s 2% general partner interest. AAP’s ownership of both of these interests entitles it to receive, without duplication:
· 2% of all cash distributed in a quarter until $0.2250 has been distributed in respect of each common unit of PAA for that quarter;
· 15% of all cash distributed in a quarter after $0.2250 has been distributed in respect of each common unit of PAA for that quarter;
· 25% of all cash distributed in a quarter after $0.2475 has been distributed in respect of each common unit of PAA for that quarter; and
· 50% of all cash distributed in a quarter after $0.3375 has been distributed in respect of each common unit of PAA for that quarter.
Such amounts do not take into account temporary and permanent reductions in IDR payments that are currently in place in connection with past PAA acquisition activities, PAA’s January 2016 preferred unit offering, or any reductions that may be implemented with respect to future activities. The cash distributions AAP receives from PAA are tied to (i) PAA’s per unit distribution level, (ii) the number of PAA common units outstanding and (iii) the number of PAA preferred units outstanding. An increase in either factor (assuming the other factor remains constant or increases) will generally, absent additional IDR reductions, result in an increase in the amount of cash distributions AAP receives from PAA, a portion of which we, in turn, receive from AAP. Because the IDRs currently participate at the maximum percentage participation rate, any future growth in distributions we receive from AAP will not result from an increase in the percentage participation rate associated with the IDRs.
Accordingly, our primary business objective is to increase our cash available for distribution to our Class A shareholders through the execution by PAA of its business strategy. In addition, we may facilitate PAA’s growth activities through various means, including, but not limited to, modifying PAA’s IDRs, making loans, purchasing equity interests or providing other forms of financial support to PAA.
PAA’s Business Strategy
PAA’s principal business strategy is to provide competitive and efficient midstream transportation, terminalling, storage, processing, fractionation and supply and logistics services to producers, refiners and other customers. Toward this end, PAA endeavors to address regional supply and demand imbalances for crude oil and NGL in the United States and Canada by combining the strategic location and capabilities of its transportation, terminalling, storage, processing and fractionation assets with its extensive supply, logistics and distribution expertise. We believe PAA’s successful execution of this strategy will enable it to generate sustainable earnings and cash flow. PAA intends to manage and grow its business by:
· commercially optimizing its existing assets and realizing cost efficiencies through operational improvements;
· using its transportation (including pipeline, rail, barge and truck), terminalling, storage, processing and fractionation assets in conjunction with its supply and logistics activities to capitalize on inefficient energy markets and to address physical market imbalances, mitigate inherent risks and increase margin;
· developing and implementing growth projects that (i) address evolving crude oil and NGL needs in the midstream transportation and infrastructure sector and (ii) are well positioned to benefit from long-term industry trends and opportunities; and
· selectively pursuing strategic and accretive acquisitions that complement its existing asset base and distribution capabilities.
PAA’s Competitive Strengths
We believe that the following competitive strengths position PAA to successfully execute its principal business strategy:
· Many of PAA’s assets are strategically located and operationally flexible. The majority of PAA’s primary Transportation segment assets are in crude oil service, are located in well-established crude oil producing regions and other transportation corridors and are connected, directly or indirectly, with PAA’s Facilities segment assets. The majority of PAA’s Facilities segment assets are located at major trading locations and premium markets that serve as gateways to major North American refinery and distribution markets where PAA has strong business relationships. In addition, PAA’s assets include pipeline, rail, barge, truck and storage assets, which provide PAA’s customers and PAA with significant flexibility and optionality to satisfy demand and balance markets, particularly during a dynamic period of changing product flows.
· PAA possesses specialized crude oil and NGL market knowledge. We believe PAA’s business relationships with participants in various phases of the crude oil and NGL distribution chain, from producers to refiners, as well as PAA’s own industry expertise (including PAA’s knowledge of North American crude oil and NGL flows), provide PAA with an extensive understanding of the North American physical crude oil and NGL markets.
· PAA’s supply and logistics activities typically generate a base level of margin with the opportunity to realize incremental margins. We believe the variety of activities executed within PAA’s Supply and Logistics segment in combination with PAA’s risk management strategies provides PAA with a balance that typically provides PAA with the opportunity to generate a base level of margin in a variety of market conditions (subject to the effects of seasonality). In certain circumstances, PAA may be able to realize incremental margins during volatile market conditions.
· PAA has the evaluation, integration and engineering skill sets and the financial flexibility to continue to pursue acquisition and expansion opportunities. Since 1998, PAA has completed and integrated over 85 acquisitions with an aggregate purchase price of approximately $11.7 billion. PAA has also implemented expansion capital projects totaling approximately $10 billion. In addition, considering PAA’s investment grade credit rating, liquidity and capital structure, we believe PAA has the financial resources and strength necessary to finance future strategic expansion and acquisition opportunities. As of December 31, 2015, PAA had approximately $2.3 billion of liquidity available, including cash and cash equivalents and availability under its committed credit facilities, subject to continued covenant compliance.
· PAA has an experienced management team whose interests are aligned with those of its unitholders. PAA’s executive management team has an average of 31 years industry experience, and an average of 18 years with PAA or its predecessors and affiliates. In addition, through their ownership of common units, indirect interests in PAA’s general
partner, grants of phantom units and AAP Management Units, PAA’s management team has a vested interest in PAA’s continued success.
Our Financial Strategy
Our financial strategy is designed to be complementary to PAA’s financial and business strategies. Because our only cash-generating assets consist of our partnership interests in AAP, which currently derives all of its cash flows from PAA’s distributions, we intend to maintain a level of indebtedness at AAP such that it will not be material in relation to PAA’s adjusted EBITDA or other financial metrics used in the evaluation of its business. As of December 31, 2015, AAP had $559 million of debt outstanding under its credit facility. In connection with future PAA equity issuances, we expect AAP may fund any capital contribution required to maintain its indirect 2% general partner interest in PAA with credit facility borrowings. We do not anticipate that additional debt associated with these contributions will be material to our consolidated financial position, as such equity issuances are typically used to pay down existing debt or fund PAA’s growth through acquisitions or organic growth opportunities. We would expect to fund direct acquisitions made by us, if any, with a combination of debt and equity.
PAA’s Financial Strategy
Targeted Credit Profile
We believe that a major factor in PAA’s continued success is its ability to maintain a competitive cost of capital and access to the capital markets. In that regard, PAA intends to maintain a credit profile that it believes is consistent with investment grade credit ratings. PAA has targeted a general credit profile with the following attributes:
· an average long-term debt-to-total capitalization ratio of approximately 50% or less;
· a long-term debt-to-adjusted EBITDA multiple averaging between 3.5x and 4.0x (adjusted EBITDA is earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, equity-indexed compensation plan charges, certain gains and losses from derivative activities and other selected items that impact comparability);
· an average total debt-to-total capitalization ratio of approximately 60% or less; and
· an average adjusted EBITDA-to-interest coverage multiple of approximately 3.3x or better.
The first two of these four metrics include long-term debt as a critical measure. PAA also incurs short-term debt in connection with its supply and logistics activities that involve the simultaneous purchase and forward sale of crude oil, NGL and natural gas. The crude oil, NGL and natural gas purchased in these transactions are hedged. PAA does not consider the working capital borrowings associated with these activities to be part of its long-term capital structure. These borrowings are self-liquidating as they are repaid with sales proceeds. PAA also incurs short-term debt to fund New York Mercantile Exchange (“NYMEX”) and Intercontinental Exchange (“ICE”) margin requirements. In certain market conditions, these routine short-term debt levels may increase significantly above baseline levels.
Typically, for PAA to maintain its targeted credit profile and achieve growth through acquisitions and expansion capital, PAA funds approximately 55% of the capital requirements associated with these activities with equity and cash flow in excess of distributions. During the latter part of 2015, energy industry conditions deteriorated and capital markets access for energy companies was disrupted, which has continued into 2016. To fund PAA’s ongoing capital program and maintain a solid capital structure and significant liquidity, in January 2016, PAA raised $1.6 billion of equity capital through the sale of approximately 61.0 million unregistered Series A Convertible Preferred Units. See Note 10 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information. From time to time, PAA may be outside the parameters of its targeted credit profile as, in certain cases, capital expenditures and acquisitions may be financed initially using debt or there may be delays in realizing anticipated synergies from acquisitions or contributions from expansion capital projects to adjusted EBITDA. As a result of the challenging environment and the impact of the gap in the timing between PAA funding its capital program and the time the assets are placed in service and begin to generate cash flow, PAA expects its long-term debt-to-adjusted EBITDA to be above its target range for the near-term. PAA expects this leverage ratio will improve and return to targeted levels as the industry recovers and PAA realizes EBITDA growth from capital investments.
PAA’s Acquisitions
The acquisition of midstream assets and businesses that are strategic and complementary to PAA’s existing operations constitutes an integral component of its business strategy and growth objectives. Such assets and businesses include crude oil, refined products and NGL logistics assets, natural gas storage assets and other energy assets that have characteristics and provide opportunities similar to its existing business lines and enable PAA to leverage its assets, knowledge and skill sets.
The following table summarizes acquisitions greater than $200 million that PAA has completed over the past five years.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Approximate |
| |
|
Acquisition (1) |
|
Date |
|
Description |
|
Purchase Price (2) |
| |
|
50% Interest in BridgeTex Pipeline Company, LLC (“BridgeTex”) |
|
Nov-2014 |
|
BridgeTex owns a crude oil pipeline that extends from Colorado City, Texas to East Houston |
|
$ |
1,088 |
(3) |
|
US Development Group Crude Oil Rail Terminals |
|
Dec-2012 |
|
Four operating crude oil rail terminals and one terminal under development |
|
$ |
503 |
|
|
BP Canada Energy Company |
|
Apr-2012 |
|
NGL assets located in Canada and the upper-Midwest United States |
|
$ |
1,683 |
(4) |
|
Western Refining, Inc. Pipeline and Storage Assets |
|
Dec-2011 |
|
Multi-product storage facility in Virginia and Crude oil pipeline in southeastern New Mexico |
|
$ |
220 |
(5) |
|
Velocity South Texas Gathering, LLC |
|
Nov-2011 |
|
Crude oil and condensate gathering and transportation assets in South Texas |
|
$ |
349 |
|
|
SG Resources Mississippi, LLC |
|
Feb-2011 |
|
Southern Pines Energy Center natural gas storage facility |
|
$ |
765 |
(6) |
|
Nexen Holdings U.S.A. Inc. Gathering and Transportation Assets |
|
Dec-2010 |
|
Crude oil gathering business and transportation assets in North Dakota and Montana |
|
$ |
229 |
(7) |
(1) Excludes PAA’s acquisition of all of the outstanding publicly-traded common units of PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P. (“PNG”) on December 31, 2013 (referred to herein as the “PNG Merger”), as we historically consolidated PNG into our financial statements for financial reporting purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles in the United States (“GAAP”). As consideration for the PNG Merger, PAA issued approximately 14.7 million of its common units with a value of approximately $760 million.
(2) As applicable, the approximate purchase price includes total cash paid and debt assumed, including amounts for working capital and inventory.
(3) Approximate purchase price of $1.075 billion, net of working capital acquired. PAA accounts for its 50% interest in BridgeTex under the equity method of accounting.
(4) Purchase price includes approximately $17 million of imputed interest. A prepayment of $50 million was made during 2011. Approximate purchase price of $1.192 billion, net of working capital, linefill and long-term inventory acquired.
(5) Includes both transactions with Western.
(6) Approximate purchase price of $750 million, net of cash and other working capital acquired.
(7) Approximate purchase price of $170 million, net of cash, inventory and other working capital acquired.
Ongoing Acquisition and Investment Activities
Consistent with its business strategy, PAA is continuously engaged in the evaluation of potential acquisitions, joint ventures and capital projects. As a part of these efforts, PAA often engages in discussions with potential sellers or other parties regarding the possible purchase of or investment in assets and operations that are strategic and complementary to PAA’s existing operations. In addition, in the past PAA has evaluated and pursued, and intends in the future to evaluate and pursue, the acquisition of or investment in other energy-related assets that have characteristics and provide opportunities similar to PAA’s existing business lines and enable PAA to leverage its assets, knowledge and skill sets. Such efforts may involve participation by PAA in processes that have been made public and involve a number of potential buyers or investors, commonly referred to as “auction” processes, as well as situations in which PAA believes it is the only party or one of a limited number of parties who are in negotiations with the potential seller or other party. These acquisition and investment efforts often involve assets which, if acquired or constructed, could have a material effect on PAA’s financial condition and results of operations.
From time to time, PAA may also sell assets that it regards as non-core or that it believes might be a better fit with the business and/or assets of a third-party buyer.
PAA typically does not announce a transaction until after it has executed a definitive agreement. However, in certain cases in order to protect its business interests or for other reasons, PAA may defer public announcement of a transaction until closing or a later date. Past experience has demonstrated that discussions and negotiations regarding a potential transaction can advance or terminate in a short period of time. Moreover, the closing of any transaction for which PAA has entered into a definitive agreement may be subject to customary and other closing conditions, which may not ultimately be satisfied or waived. Accordingly, PAA can give no assurance that its current or future acquisition, divestiture or investment efforts will be successful. Although PAA expects the acquisitions and investments it makes to be accretive in the long term, PAA can provide no assurance that its expectations will ultimately be realized. See Item 1A. “Risk Factors—Risks Related to PAA’s Business—If PAA does not make acquisitions or if it makes acquisitions that fail to perform as anticipated, its future growth may be limited” and “—Acquisitions involve risks that may adversely affect PAA’s business.”
PAA’s Expansion Capital Projects
PAA’s extensive asset base and its relationships with customers provide it with opportunities for organic growth through the construction of additional assets that are complementary to, and expand or extend, its existing asset base. PAA believes that the diversity and balance of its expansion capital project portfolio (i.e., relatively large number of projects that are small to medium sized and spread across multiple geographic regions) reduces its overall exposure to cost overruns, timing delays and other adverse market developments with respect to a particular project or region. PAA’s 2016 expansion capital plan is representative of the diversity and balance of its overall project portfolio. The following expansion capital projects are included in PAA’s 2016 capital plan as of February 2016:
|
Basin/Region |
|
Project |
|
2016 Plan |
|
Description |
|
Projected |
| |
|
Permian |
|
Permian Basin Area Pipeline Projects |
|
$ |
185 |
|
Multiple projects to increase and expand PAA’s pipeline infrastructure in the Delaware Basin |
|
2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Cactus Pipeline |
|
20 |
|
Installation of two separate valves and pump stations to add 80,000 Bbls/d of additional capacity (increases pipeline capacity to 330,000 Bbls/d) |
|
2016 |
| |
|
Eagle Ford |
|
Eagle Ford JV Project |
|
20 |
|
50% interest in new, 1.2 million barrel terminal in Corpus Christi, TX capable of loading ocean going vessels at a rate of 20,000 barrels per hour |
|
2018 |
| |
|
Central / Mid-Continent |
|
Diamond Pipeline |
|
260 |
|
50% interest in 440 miles of new crude oil pipeline; 200,000 Bbls/d capacity from Cushing, OK to Valero’s refinery in Memphis, TN |
|
2017 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Red River Pipeline (Cushing to Longview) |
|
290 |
|
Approximately 400 miles of new crude oil pipeline; 150,000 Bbls/d capacity from Cushing, OK to Longview, TX |
|
2016 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Cushing Terminal Expansions |
|
35 |
|
Addition of 1.6 million barrels of storage capacity |
|
2016 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
Caddo Pipeline |
|
30 |
|
50% interest in 80 miles of new 12-inch crude oil pipeline; 80,000 Bbls/d capacity between Longview, TX and Shreveport, LA |
|
2016 |
| |
|
Rocky Mountain |
|
Saddlehorn Pipeline |
|
155 |
|
40% of Saddlehorn’s 190,000 Bbls/d of capacity in the 600 miles of new 20-inch crude oil undivided joint interest pipeline from the DJ Basin to Cushing, OK |
|
2016 |
| |
|
Basin/Region |
|
Project |
|
2016 Plan |
|
Description |
|
Projected |
| |
|
Gulf Coast |
|
St. James Terminal Expansions |
|
35 |
|
Addition of 1.5 million barrels of storage capacity with connectivity to the rail and dock facilities |
|
2016 |
| |
|
Canada |
|
Fort Saskatchewan Facility Projects |
|
190 |
|
Multi-phase project, Phase I of which includes (i) development of two new high rate delivery caverns, (ii) conversion of service of two existing caverns, (iii) the addition of 2.4 million barrels of brine capacity and (iv) development of a truck loading facility |
|
Various, throughout 2016 and 2017 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Phase II includes (i) expanding inlet fractionation capacity by 20,000 Bbls/d, (ii) development of two new ethane caverns and a utility cavern, (iii) the addition of 2.7 million barrels of brine capacity and (iv) development of a propane rail loading facility |
|
|
| |
|
Other |
|
Other Projects |
|
280 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
1,500 |
|
|
|
|
|
(1) Represents the portion of the total project cost expected to be incurred during the year. Potential variation to current capital costs estimates may result from (i) changes to project design, (ii) final cost of materials and labor and (iii) timing of incurrence of costs due to uncontrollable factors such as receipt of permits or regulatory approvals and weather.
Global Petroleum Market Overview
The health of the global petroleum market is dependent on the relative supply and demand of hydrocarbons, including crude oil and NGL. These supply and demand economics are greatly influenced by the broader global economic climate, exposing the petroleum market to the challenges and volatility associated with global economic development. For the period from 2004 through 2013, global liquids production increased 7.6 million barrels per day while global liquids consumption increased 8.1 million barrels per day. However, in 2014, global production growth outpaced global consumption growth by 1.1 million barrels per day, with non-OPEC accounting for 104% of the production growth. In 2015, the markets remained oversupplied due to the continuation of the 2014 imbalance. Supply growth in 2015 outpaced demand growth by another 1.0 million barrels per day, resulting in an imbalance of 1.9 million barrels per day. The table below depicts historical OPEC and Non-OPEC liquids production and global liquids consumption and is derived from the EIA Short-Term Energy Outlook, January 2016 (see EIA website at www.eia.doe.gov):
|
|
|
Annual Liquids Production (1) |
|
|
∆ from 2004 |
|
∆ from 2013 |
|
∆ from 2014 |
| ||||||
|
|
|
2004 |
|
2013 |
|
2014 |
|
2015 |
|
|
2013 |
|
2014 |
|
2015 |
|
|
|
|
(in millions of barrels per day) |
| |||||||||||||
|
Production (Supply) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
OPEC |
|
33.6 |
|
37.3 |
|
37.2 |
|
38.3 |
|
|
3.7 |
|
(0.1 |
) |
1.1 |
|
|
Non-OPEC |
|
49.8 |
|
53.7 |
|
56.1 |
|
57.4 |
|
|
3.9 |
|
2.4 |
|
1.3 |
|
|
Total |
|
83.4 |
|
91.0 |
|
93.3 |
|
95.7 |
|
|
7.6 |
|
2.3 |
|
2.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total Consumption (Demand) |
|
83.1 |
|
91.2 |
|
92.4 |
|
93.8 |
|
|
8.1 |
|
1.2 |
|
1.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Global Supply / Demand Balance |
|
0.3 |
|
(0.2 |
) |
0.9 |
|
1.9 |
|
|
(0.5 |
) |
1.1 |
|
1.0 |
|
(1) Amounts are derived from the EIA’s Short-Term Energy Outlook.
This surge in liquids production without a commensurate increase in demand has led to a near-to-medium-term supply imbalance, which has resulted in a reduction to benchmark petroleum prices. Producers, in turn, are scaling back capital programs, which will ultimately reduce supply. This is expected to lead to underinvestment in long lead time projects and stimulate petroleum demand growth, which ultimately should lead to an environment where prices will recover to a level to support future production growth in the U.S.
Crude Oil Market Overview
The definition of a commodity is a “mass-produced unspecialized product” and implies the attribute of fungibility. Crude oil is typically referred to as a commodity; however, it is neither unspecialized nor fungible. The crude slate available to U.S. and world-wide refineries consists of a substantial number of different grades and varieties of crude oil. Each crude oil grade has distinguishing physical properties. For example, specific gravity (generally referred to as light or heavy), sulfur content (generally referred to as sweet or sour) and metals content, along with other characteristics, collectively result in varying economic attributes. In many cases, these factors result in the need for such grades to be batched or segregated in the transportation and storage processes, blended to precise specifications or adjusted in value.
The lack of fungibility of the various grades of crude oil creates logistical transportation, terminalling and storage challenges and inefficiencies associated with regional volumetric supply and demand imbalances. These logistical inefficiencies are created as certain qualities of crude oil are indigenous to particular regions or countries. Also, each refinery has a distinct configuration of process units designed to handle particular grades of crude oil. The relative yields and the cost to obtain, transport and process the crude oil drives the refinery’s choice of feedstock. In addition, from time to time, natural disasters and geopolitical factors such as hurricanes, earthquakes, tsunamis, inclement weather, labor strikes, refinery disruptions, embargoes and armed conflicts may impact supply, demand, transportation and storage logistics.
Our assets and our business strategy are designed to serve our producer and refiner customers by addressing regional crude oil supply and demand imbalances that exist in the United States and Canada. The nature and extent of these imbalances change from time to time as a result of a variety of factors, including regional production declines and/or increases; refinery expansions, modifications and shut-downs; available transportation and storage capacity; and government mandates and related regulatory factors.
From 2011 through 2014, the combination of (i) a significant increase in North American production volumes, (ii) a change in crude oil qualities and related differentials and (iii) high utilization of existing pipeline and terminal infrastructure stimulated multiple industry initiatives to build new pipeline and terminal infrastructure, convert certain pipeline assets to alternative service or reverse flows and expand the use of trucks, rail and barges for the movement of crude oil and condensate. Increased production came from mature producing areas such as the Rockies, the Permian Basin in West Texas and the Mid-Continent region, as well as from less mature, but rapidly growing areas such as the Eagle Ford Shale in South Texas and the Bakken Shale in North Dakota. As a result, North American crude oil production increased 3.6 million barrels per day, or 32%, between 2011 and 2014, with the increases coming primarily from Canada, the Eagle Ford Shale, the Permian Basin and the Bakken Shale. Production increases in all of these regions strained existing transportation, terminalling and downstream infrastructure. This opportunity for new crude oil infrastructure attracted significant investment in midstream oil assets, resulting in excess midstream capacity in the Permian, Eagle Ford, Williston, Midcontinent and Denver Julesburg basins.
However, in the latter half of 2014 crude oil prices fell approximately 50%, and then approximately another 30% during 2015. The reduction in prices precipitated a significant slowdown in drilling activity and plans as producers right-sized their capital budgets to the significantly reduced levels of cash flow resulting from lower prices, a process that is continuing into 2016. The combination of the slowdown of growth in U.S. crude oil production caused by declining prices and the significant commitments for new infrastructure created an environment in which margins have compressed and differentials are less than transportation costs in some cases.
In addition, significant shifts in the type and location of crude oil being produced in North America, relative to the types and location of crude oil being produced five years ago, have led to changes in the utilization of downstream infrastructure. Since reaching a multi-year low in 2009, U.S. net refinery inputs of crude oil have increased to 16.2 million barrels per day in 2015. From 2009 through 2014, refiners increased throughputs to take advantage of discounted domestic production, which led to lower use of imported crude oil by U.S. refineries. This decline in imports was a meaningful change in a multi-year trend where foreign imports of crude oil tripled over an approximately 23-year period from 1985-2007. In 2015, U.S. refinery inputs reached historically high levels fueled by price driven demand growth and exports. U.S. petroleum consumption increased to 19.5 million barrels per day for the twelve month period ended October 2015, the highest levels since 2008. The table below shows the overall domestic petroleum consumption projected through 2017 and is derived from the EIA Short-Term Energy Outlook, January 2016 (see EIA website at www.eia.doe.gov).
|
|
|
Actual |
|
Projected |
| ||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
|
|
|
(In millions of barrels per day) |
| ||||
|
Supply |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Domestic Crude Oil Production |
|
9.4 |
|
8.7 |
|
8.5 |
|
|
Net Imports - Crude Oil |
|
6.9 |
|
7.2 |
|
7.6 |
|
|
Other (Supply Adjustment/Stock Change) |
|
(0.1 |
) |
0.3 |
|
0.2 |
|
|
Crude Oil Input to Domestic Refineries |
|
16.2 |
|
16.2 |
|
16.3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Net Product Imports / (Exports) |
|
(2.2 |
) |
(2.6 |
) |
(2.7 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supply from Renewable Sources |
|
1.1 |
|
1.1 |
|
1.1 |
|
|
Other - (NGL Production, Refinery Processing Gain) |
|
4.4 |
|
4.8 |
|
5.1 |
|
|
Total Domestic Petroleum Consumption |
|
19.5 |
|
19.5 |
|
19.8 |
|
U.S. Crude Oil Exports
At the end of 2015, the U.S. Congress agreed to lift the 40-year ban on exporting U.S. crude oil, providing domestic oil producers the ability to sell into the international market. The immediate impact will most likely not be felt in 2016 as refineries have increased their processing of U.S. crude oil while domestic production output is expected to decline.
NGL Market Overview
NGL primarily includes ethane, propane, normal butane, iso-butane and natural gasoline, and is derived from natural gas production and processing activities as well as crude oil refining processes. Liquefied petroleum gas (“LPG”) primarily includes propane and butane, which liquefy at moderate pressures thus making it easier to transport and store such products as compared to ethane. NGL refers to all NGL products including LPG when used in this Form 10-K.
NGL Demand. Individual NGL products have varying uses. Described below are the five basic NGL components and their typical uses:
· Ethane. Ethane accounts for the largest portion of the NGL barrel and substantially all of the extracted ethane is used as feedstock in the production of ethylene, one of the basic building blocks for a wide range of plastics and other chemical products. When ethane recovery from a wet natural gas stream is uneconomic, ethane is left in the natural gas stream, subject to pipeline specifications.
· Propane. Propane is used as heating fuel, engine fuel and industrial fuel, for agricultural burning and drying and also as petrochemical feedstock for the production of ethylene and propylene.
· Normal butane. Normal butane is principally used for motor gasoline blending and as fuel gas, either alone or in a mixture with propane, and feedstock for the manufacture of ethylene and butadiene, a key ingredient of synthetic rubber. Normal butane is also used as a feedstock for iso-butane production and as a diluent in the transportation of heavy crude oil and bitumen, particularly in Canada.
· Iso-butane. Iso-butane is principally used by refiners to produce alkylates to enhance the octane content of motor gasoline.
· Natural Gasoline. Natural gasoline is principally used as a motor gasoline blend stock, a petrochemical feedstock, or as diluent in the transportation of heavy crude oil and bitumen, particularly in Canada.
NGL Supply. The bulk (approximately 80%) of the United States NGL supply comes from gas processing plants, which separate a mixture of NGL from the dry gas (primarily methane). The NGL mix (also referred to as “Y Grade”) is then either fractionated at the processing site into the five individual NGL components (known as purity products), which may be transported, stored and sold to end use markets or transported as a Y-Grade to a regional fractionation facility.
The majority of gas processing plants in the United States are located along the Gulf Coast, in the West Texas/Oklahoma area, the Marcellus and Utica region and in the Rockies region. In Canada, the vast majority of the processing capacity is located in Alberta, with a much smaller (but increasing) amount in British Columbia and Saskatchewan.
NGL products from refineries represent approximately 17% of the United States supply and are by-products of the refinery conversion processes. Consequently, they have generally already been separated into individual components and do not require further fractionation. NGL products from refineries are principally propane, with lesser amounts of butane, refinery naphthas (products similar to natural gasoline) and ethane. Due to refinery maintenance schedules and seasonal demand considerations, refinery production of propane and butane varies on a seasonal basis.
NGL is also imported into certain regions of the United States from Canada and other parts of the world (approximately 3% of total supply). NGL (primarily propane and butane) is also exported from certain regions of the United States.
NGL Transportation and Trading Hubs. NGL, whether as a mixture or as purity products, is transported by pipelines, barges, railcars and tank trucks. The method of transportation used depends on, among other things, the resources of the transporter, the locations of the production points and the delivery points, cost-efficiency and the quantity of product being transported. Pipelines are generally the most cost-efficient mode of transportation when large, consistent volumes of product are to be delivered.
The major NGL infrastructure and trading hubs in North America are located at Mont Belvieu, Texas; Conway, Kansas; Edmonton, Alberta; and Sarnia, Ontario. Each of these hubs contains a critical mass of infrastructure, including fractionators, storage, pipelines and access to end markets, particularly Mont Belvieu.
NGL Storage. NGL must be stored under pressure to maintain a liquid state. The lighter the product (e.g., ethane), the greater the pressure that must be maintained. Large volumes of NGL are stored in underground caverns constructed in salt or granite. Product is also stored in above ground tanks. Natural gasoline can be stored at relatively low pressures in tankage similar to that used to store motor gasoline. Propane and butane are stored at much higher pressures in steel spheres, cylinders, bullets, salt caverns or other configurations. Ethane is stored at very high pressures, typically in salt caverns. Storage is especially important for NGL as supply and demand can vary materially on a seasonal basis.
NGL Market Outlook. The growth of shale based production in both traditional and new producing areas has resulted in a significant increase in NGL supplies from gas processing plants over the past several years. This has driven extensive expansion and new development of midstream infrastructure in Canada, the Bakken, Marcellus/Utica, and throughout Texas.
The growth of production in non-traditional producing regions has shifted regional basis relationships and the creation of new logistics and infrastructure opportunities. Growing NGL production has meant expansion into new markets, through exports or increased petrochemical demand. The continuation of a relatively low ratio of North American gas and NGL prices to world-wide crude oil prices will mean North American NGL can continue to be competitive on a world scale, either as feedstock for North American based manufacturing or export to overseas markets. In addition to substantially increased exports, a portion of the increased supply of NGL will be absorbed by the domestic petrochemical sector as low-cost feed stocks, as the North American petrochemical industry has enjoyed a supply cost advantage on a world scale.
While a low price environment may stunt production growth, the fundamentals of an accessible resource base and improved midstream infrastructure should mean producers can continue to develop the most economic new supply and be ready to go back to rapid growth as prices recover. The NGL market is, among other things, expected to be driven by:
· the absolute prices of NGL products and their prices relative to natural gas and crude oil;
· drilling activity and wet natural gas production in developing liquids-rich production areas;
· available processing, fractionation, storage and transportation capacity;
· petro-chemical demand;
· diluent requirements for heavy Canadian oil;
· regulatory changes in gasoline specifications affecting demand for butane;
· seasonal demand from refiners;
· seasonal weather related demand; and
· inefficiencies caused by regional supply and demand imbalances.
As a result of these and other factors, the NGL market is complex and volatile, which, along with expected market growth, creates opportunities to solve the logistical inefficiencies inherent in the business.
Natural Gas Storage Market Overview
North American natural gas storage facilities provide a staging and warehousing function for seasonal swings in demand relative to supply, as well as an essential reliability cushion against disruptions in natural gas supply, demand and transportation by allowing natural gas to be injected into, withdrawn from or warehoused in such storage facilities as dictated by market conditions. Natural gas storage serves as the “shock absorber” that balances the market, serving as a source of supply to meet the consumption demands in excess of daily production capacity and a warehouse for gas production in excess of daily demand during low demand periods.
Overall market conditions for natural gas storage have been challenging during the last several years, driven by a variety of factors, including (i) increased natural gas supplies due to production from shale resources, (ii) a shift from Gulf of Mexico production to Northeast production causing less concern over disruptions from tropical weather, (iii) increased availability of storage capacity and (iv) lower basis differentials in certain regions due to expansion and improved connectivity of natural gas transportation infrastructure.
Longer term, we believe several factors will contribute to meaningful growth in North American natural gas demand that will bolster the market need for and the commercial value of natural gas storage. These fundamental factors include (i) exports of North American volumes of LNG, (ii) construction of new gas-fired power plants, (iii) sustained fuel switching from coal to natural gas among existing power plants and (iv) growth in base-level industrial demand. As a result, we remain optimistic about the intermediate- to long-term intrinsic value of our natural gas storage assets.
Projected seasonal spreads for the next few years reflect a directionally similar picture to the challenging market conditions we have experienced during most of the past few years. Continuation of these unfavorable market conditions will adversely impact our hub services activities as well as the rates our customers are willing to pay for firm storage services upon expirations of existing storage agreements.
Description of Segments and Associated Assets
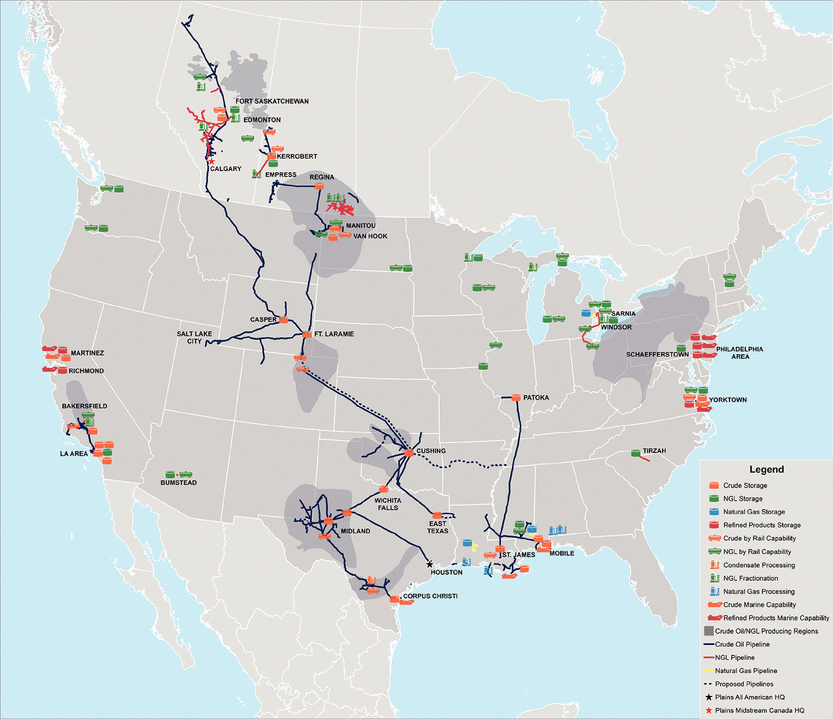
Under GAAP, we consolidate AAP and PAA and its subsidiaries. We currently have no separate operating activities apart from those conducted by PAA. As such, our segment analysis, presentation and discussion is the same as that of PAA, which conducts its operations through three segments—Transportation, Facilities and Supply and Logistics. Accordingly, any references to “we,” “our,” and similar terms describing assets, business characteristics or other related matters are references to assets, business characteristics or other matters involving PAA’s assets and operations. We have an extensive network of pipeline transportation, terminalling, storage and gathering assets in key crude oil and NGL producing basins and transportation corridors and at major market hubs in the United States and Canada. The map below highlights our more significant assets (including certain assets under construction or development) as of December 31, 2015:
Following is a description of the activities and assets for each of our three business segments.
Transportation Segment
Our Transportation segment operations generally consist of fee-based activities associated with transporting crude oil and NGL on pipelines, gathering systems, trucks and barges. We generate revenue through a combination of tariffs, third-party pipeline capacity agreements and other transportation fees. Our Transportation segment also includes equity earnings from our investments in entities that own the BridgeTex, Eagle Ford, White Cliffs, Frontier and Butte pipeline systems as well as Settoon Towing, in which we own interests ranging from 22% to 50%. Additionally, we own interests in entities that are currently constructing and developing pipeline systems, including Caddo, Diamond and Saddlehorn. We account for these investments under the equity method of accounting.
As of December 31, 2015, we employed a variety of owned or, to a much lesser extent, leased long-term physical assets throughout the United States and Canada in this segment, including approximately:
· 18,100 miles of active crude oil and NGL pipelines and gathering systems;
· 30 million barrels of active, above-ground tank capacity used primarily to facilitate pipeline throughput;
· 830 trailers (primarily in Canada); and
· 142 transport and storage barges and 64 transport tugs through our interest in Settoon Towing.
The following is a tabular presentation of our active crude oil and NGL pipeline assets in the United States and Canada as of December 31, 2015, grouped by geographic location:
|
Region / Pipeline and Gathering Systems (1) |
|
Miles |
|
2015 Average Net |
|
|
|
|
|
|
(in thousands) |
|
|
United States Crude Oil Pipelines |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Permian Basin |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Basin / Mesa / Sunrise |
|
696 |
|
829 |
|
|
BridgeTex (3) (4) |
|
408 |
|
103 |
|
|
Cactus |
|
298 |
|
76 |
|
|
Permian Basin Area Systems |
|
2,787 |
|
841 |
|
|
Permian Basin Subtotal |
|
4,189 |
|
1,849 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
South Texas/Eagle Ford |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Eagle Ford Area Systems (4) |
|
670 |
|
306 |
|
|
South Texas/Eagle Ford Subtotal |
|
670 |
|
306 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Western |
|
|
|
|
|
|
All American (5) |
|
138 |
|
14 |
|
|
Line 63 / Line 2000 |
|
314 |
|
120 |
|
|
Other |
|
121 |
|
81 |
|
|
Western Subtotal |
|
573 |
|
215 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Rocky Mountain |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Bakken Area Systems (4) |
|
1,017 |
|
142 |
|
|
Salt Lake City Area Systems (4) |
|
969 |
|
143 |
|
|
White Cliffs (3) (4) |
|
1,054 |
|
43 |
|
|
Other |
|
1,296 |
|
112 |
|
|
Rocky Mountain Subtotal |
|
4,336 |
|
440 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Gulf Coast |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Capline (3) |
|
631 |
|
170 |
|
|
Pascagoula |
|
41 |
|
110 |
|
|
Other |
|
868 |
|
252 |
|
|
Gulf Coast Subtotal |
|
1,540 |
|
532 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Central |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Mid-Continent Area Systems |
|
2,419 |
|
337 |
|
|
Other |
|
137 |
|
76 |
|
|
Central Subtotal |
|
2,556 |
|
413 |
|
|
United States Total |
|
13,864 |
|
3,755 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Canada |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Crude Oil Pipelines |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Manito |
|
556 |
|
47 |
|
|
Rainbow |
|
827 |
|
112 |
|
|
Rangeland |
|
1,171 |
|
59 |
|
|
South Saskatchewan |
|
346 |
|
61 |
|
|
Other |
|
197 |
|
113 |
|
|
Crude Oil Pipelines Subtotal |
|
3,097 |
|
392 |
|
|
NGL Pipelines |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Co-Ed |
|
633 |
|
57 |
|
|
Other |
|
550 |
|
136 |
|
|
NGL Pipelines Subtotal |
|
1,183 |
|
193 |
|
|
Canada Total |
|
4,280 |
|
585 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Grand Total |
|
18,144 |
|
4,340 |
|
(1) Ownership percentage varies on each pipeline and gathering system ranging from approximately 20% to 100%.
(2) Represents average daily volumes for the entire year attributable to our interest. Average daily volumes are calculated as the total volumes (attributable to our interest) for the year divided by the number of days in the year. Volumes reflect tariff movements and thus might be included multiple times as volumes move through our integrated system.
(3) Pipelines operated by a third party.
(4) Includes total mileage and volumes (attributable to our interest) from pipelines owned by unconsolidated entities.
(5) Except for the segment of the All American Pipeline between Pentland and Emidio, the pipeline has been shut down since May 19, 2015, following the Line 901 incident.
United States Pipelines
Permian Basin
Basin Pipeline. We own an 87% undivided joint interest in and are the operator of Basin Pipeline. Basin Pipeline is a primary route for transporting crude oil from the Permian Basin (in west Texas and southern New Mexico) to Cushing, Oklahoma, for further delivery to Mid-Continent and Midwest refining centers. Basin Pipeline also serves as the initial movement for transporting crude oil from the Permian Basin to the Gulf Coast through connections to other carriers at Colorado City, Texas and Wichita Falls, Texas.
Basin Pipeline is an approximate 530-mile mainline, telescoping crude oil pipeline with a capacity ranging from approximately 240,000 barrels per day to 450,000 barrels per day (approximately 208,800 barrels per day to 392,000 barrels per day attributable to our interest), depending on the segment. The pipeline also includes approximately 6 million barrels of storage tankage.
In 2015, we placed into service a 24-inch pipeline loop of Basin Pipeline from Wink to Midland. In addition, we placed into service Phase I of the new Wink South terminal which will handle crude oil from the Delaware Basin and New Mexico, and expect that Phase II of the project will be in service in the second half of 2016. The completion of these projects along with reactivation of a 20-inch pipeline from Wink to Midland during the first half of 2016 will provide 550,000 barrels per day of capacity from Wink to Midland.
Mesa Pipeline. We own a 63% undivided interest in and are the operator of Mesa Pipeline, which transports crude oil from Midland to a refinery at Big Spring, Texas and to connecting carriers at Colorado City. Mesa Pipeline is an 80-mile mainline with capacity of up to 400,000 barrels per day (approximately 252,000 barrels per day attributable to our interest).
Sunrise Pipeline. We own and operate the Sunrise Pipeline, which extends from Midland to connecting carriers at Colorado City. The 84-mile Sunrise Pipeline was placed in service in December 2014, with a capacity of 250,000 barrels per day.
BridgeTex Pipeline. We own a 50% interest in BridgeTex, which is the entity that owns the BridgeTex Pipeline, a 20-inch crude oil pipeline with a capacity of 300,000 barrels per day that extends from Colorado City to East Houston. At Colorado City, the BridgeTex Pipeline is connected to our Basin and Sunrise pipelines. Magellan Midstream Partners, L.P. (“MMP”) owns the remaining 50% interest and serves as the operator of the BridgeTex Pipeline. BridgeTex has entered into a long-term capacity lease agreement with MMP whereby its shippers will have access to capacity on MMP’s pipeline from Houston to Texas City.
Cactus Pipeline. We own and operate the Cactus Pipeline, a 298-mile crude oil pipeline extending from McCamey to Gardendale, Texas. The Cactus Pipeline provides 250,000 barrels per day of takeaway capacity from the Permian Basin, and will be expanded to approximately 330,000 barrels per day when additional pumping equipment is added in 2016.
Permian Basin Area Systems. We operate wholly owned systems of 2,787 miles that aggregate receipts from wellhead gathering lines and bulk truck injection locations into a combination of 4- to 16-inch diameter trunk lines for transportation and delivery into the Basin Pipeline at Jal, Wink and Midland as well as our terminal facilities in Midland. During 2015, we completed construction of several projects, including the Triple Crown gathering system, the Avalon, Texas 12-inch extension to the Triple Crown gathering system, the 20-inch loop of our pipeline from Blacktip to Wink, the 16-inch Wolfbone Ranch pipeline from south Reeves County, Texas to Wink and several gathering projects in Texas’s Upton and Reagan counties.
South Texas/Eagle Ford Area
Eagle Ford Area Systems. We own a 100% interest in and are the operator of several gathering systems that feed into our Gardendale Station, and we also own a 50% interest in Eagle Ford Pipeline, which is the entity that owns the Eagle Ford joint venture pipeline. We serve as operator of the Eagle Ford joint venture pipeline, and our joint venture partner is a subsidiary of Enterprise Products Partners, L.P. (“Enterprise”). Combined, these Eagle Ford Area Systems consist of 670 miles of pipeline that service production in the Eagle Ford shale play of South Texas and include approximately 5 million barrels of operational storage capacity across the system (including the capacity added in 2015, as discussed below). The systems serve the Three Rivers and Corpus Christi, Texas refineries and other markets via marine terminal facilities at Corpus Christi, as well as the Houston market via Enterprise’s connection at Lyssy in Wilson County, Texas.
In 2015, several projects to expand and extend the Eagle Ford joint venture pipeline were completed. Such projects included (i) completion of a connection to our Cactus Pipeline, (ii) completion of a 20-inch pipeline loop of the entire pipeline, as well as expanded pumping capabilities at Three Rivers and (iii) construction of an additional 3 million barrels of operational storage capacity across the system. Combined, these projects increased capacity of the Eagle Ford joint venture pipeline to approximately 600,000 barrels per day. In addition, Eagle Ford Pipeline completed construction of a new condensate gathering system with a capacity of up to 100,000 barrels per day that extends from our station at Three Rivers into Karnes County and Live Oak County.
Western
All American Pipeline. We own and operate the All American Pipeline, which receives crude oil from offshore oil producers at Las Flores, California and at Gaviota, California. The pipeline terminates at our Emidio Station. Between Gaviota and our Emidio Station, the All American Pipeline interconnects with our San Joaquin Valley Gathering System, Line 2000 and Line 63, as well as other third party intrastate pipelines.
In May 2015, we experienced a crude oil release from our Las Flores to Gaviota Pipeline (Line 901) in Santa Barbara County, California. The segment of the pipeline upstream of our Pentland station has been shut down since this incident. See Note 16 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding this incident.
Line 63. We own and operate the Line 63 pipeline that transports crude oil produced in the San Joaquin Valley and California OCS to refineries and terminal facilities in the Los Angeles Basin and in Bakersfield, California. The pipeline is also connected to our crude oil rail terminal at Bakersfield. The Line 63 pipeline consists of a 107-mile trunk pipeline, originating at our Kelley Pump Station in Kern County, California and terminating at our West Hynes Station in Long Beach, California. The trunk pipeline has a capacity of approximately 60,000 barrels per day. The pipeline includes 33 miles of distribution pipelines in the Los Angeles Basin, with a throughput capacity of approximately 20,000 barrels per day, and approximately 117 miles of gathering pipelines in the San Joaquin Valley, with an average throughput capacity of approximately 35,000 barrels per day. We also have approximately 1 million barrels of storage capacity on this pipeline.
In 2009, a 71-mile segment of Line 63 was temporarily taken out of service to allow for certain repairs and realignments to be performed. Line 63 volumes are currently being redirected from the north end of this out-of-service segment to the parallel Line 2000. The product is then batched along Line 2000 until it is re-injected into the active portion of Line 63, which is south of the out-of-service segment, for subsequent delivery to customers. We have commenced a project to place this idle segment in service, which we expect to complete in 2016.
Line 2000. We own and operate the Line 2000 crude oil pipeline that originates at our Emidio Pump Station (part of the All American Pipeline) and transports crude oil produced in the San Joaquin Valley and California OCS to refineries and terminal facilities in the Los Angeles Basin. Line 2000 is an approximately 130-mile, 20-inch trunk pipeline with a throughput capacity of approximately 130,000 barrels per day.
Rocky Mountain
Bakken Area Systems. We own and operate several gathering systems and pipelines that service crude oil production in Eastern Montana and Western North Dakota, and we also own a 22% interest in Butte, which is the entity that owns the Butte Pipeline, a 16-inch crude oil pipeline system extending from Baker, Montana to Guernsey, Wyoming.
Salt Lake City Area Systems. We operate the Salt Lake City and Wahsatch pipelines, in which we own interests ranging between 75% and 100%, and we also own a 50% interest in Frontier, which is the entity that owns the Frontier Pipeline. These pipelines transport crude oil produced in the U.S. Rocky Mountain region and Canada to refiners in Salt Lake City, Utah and to other pipelines at Ft. Laramie, Wyoming.
These pipelines include approximately 970 miles and approximately one million barrels of storage capacity. These pipelines have a maximum throughput capacity of (i) approximately 20,500 barrels per day from Wamsutter, Wyoming to Ft. Laramie, (ii) approximately 47,000 barrels per day from Wamsutter to Wahsatch, Utah, (iii) approximately 95,000 barrels per day from Wahsatch to Salt Lake City and (iv) approximately 75,000 barrels per day from Casper to Ranch Station, Utah.
White Cliffs Pipeline. We own an approximate 36% interest in White Cliffs, the entity that owns the White Cliffs Pipeline, which consists of two 527-mile, 12-inch, crude oil pipelines that move crude out of the DJ Basin to the Cushing, Oklahoma market. Rose Rock Midstream, L.P. serves as the operator of the pipeline, which originates in Platteville, Colorado and terminates in Cushing. In late 2015, the addition of two pump stations increased capacity on the pipeline to approximately 215,000 barrels per day.
Cowboy Pipeline. We recently constructed the Cowboy Pipeline, a 12-inch, 27-mile pipeline that provides 75,000 barrels per day of light sweet crude oil capacity from Cheyenne, Wyoming to our rail loading facility near Carr, Colorado and will be connected to the Saddlehorn Pipeline when it is placed in service. The Cowboy Pipeline includes a new terminal at Cheyenne with approximately 600,000 barrels of storage tank capacity. The Cowboy Pipeline will enable us to source crude oil from our and third party pipeline systems that feed the Guernsey market, through connection to our Cheyenne Pipeline, and deliver to Cushing through connection to the Saddlehorn Pipeline.
Saddlehorn Pipeline. We own a 40% interest in Saddlehorn, which is currently developing the Saddlehorn Pipeline, a 20-inch pipeline that will extend from various receipt points in the Niobrara and DJ Basin to Cushing. The Saddlehorn Pipeline is a joint venture in which Saddlehorn owns an undivided 62.5% interest in the pipeline; Grand Mesa Pipeline, LLC owns the remaining 37.5% interest. Saddlehorn will own 190,000 barrels per day of the capacity in Saddlehorn Pipeline and will have one million barrels of storage capacity at both Platteville and Cushing. The Platteville-to-Cushing segment of the pipeline is expected to be operational in mid-2016 and the Platteville-to-Carr segment is anticipated to be operational by the end of 2016. Saddlehorn has the option to expand the capacity of the pipeline at its sole discretion and cost and would own all of the incremental capacity from any expansion. MMP serves as construction manager and operator of the pipeline.
Gulf Coast
Capline Pipeline. Capline Pipeline, in which we own an aggregate undivided joint interest of approximately 54%, is a 631-mile, 40-inch mainline crude oil pipeline originating in St. James, Louisiana, and terminating in Patoka, Illinois. Marathon Pipeline LLC serves as the operator of the pipeline. Capline has direct connections to a significant amount of crude oil production in the Gulf of Mexico. In addition, it has two active docks capable of handling approximately 600,000-barrel tankers and is connected to the Louisiana Offshore Oil Port and our St. James terminal and transports various grades of crude oil to PADD II. Total designed operating capacity is approximately 1.1 million barrels per day of crude oil, of which our attributable interest is approximately 600,000 barrels per day.
Pascagoula Pipeline. We own and operate the Pascagoula Pipeline, a 41-mile crude oil pipeline that originates at our Ten Mile facility in Alabama and extends to a refinery on the Gulf Coast. Additionally, we have approximately 2 million barrels of storage capacity at our Ten Mile facility that supports the operational needs of the pipeline.
Central
Mid-Continent Area Systems. We own and operate pipeline systems that source crude oil from Western and Central Oklahoma, Southwest Kansas and the Eastern Texas Panhandle. These systems consist of approximately 2,420 miles of pipeline with transportation and delivery into and out of our terminal facilities at Cushing, Oklahoma. In addition, in early 2015 we completed construction of a new receipt facility on the Basin Pipeline in southern Oklahoma to aggregate South Central Oklahoma Oil Province (SCOOP) production.
Diamond Pipeline. We own a 50% interest in Diamond, which is currently developing the Diamond Pipeline, a 20-inch, 440-mile pipeline that will provide 200,000 barrels per day of capacity from our Cushing terminal to Valero’s refinery in Memphis, Tennessee. The Diamond Pipeline project is underpinned by a long-term shipper agreement with Valero and a related contract for storage and terminalling services at our Cushing terminal. In December 2015, Valero exercised its option to become a partner in Diamond and owns the remaining 50% interest. We will serve as operator of the Diamond Pipeline, which is expected to be completed in 2017.
Red River Pipeline (Cushing to Longview). We are currently developing and constructing the Red River Pipeline, which will be a 16-inch crude oil pipeline with an initial takeaway capacity of 150,000 barrels per day extending from Cushing to Longview. The Red River Pipeline is supported by long-term shipper commitments and is expected to be completed in late 2016.
Caddo Pipeline. We own a 50% interest in Caddo, which is constructing the Caddo Pipeline. The Caddo Pipeline is an 80-mile, 12-inch crude oil pipeline with the capacity to move up to 80,000 barrels per day from our terminal in Longview, Texas to supply refineries in the Shreveport, Louisiana area, as well as to an El Dorado, Arkansas refinery through a connection to Delek Logistics Partners, LP’s (“Delek”) pipeline. Delek owns the remaining 50% interest in Caddo. We will serve as operator of the Caddo Pipeline, which is expected to be completed in late 2016.
Canada Pipelines
Crude Oil Pipelines
Manito Pipeline. We own a 100% interest in the Manito heavy oil system. This 556-mile system is comprised of the Manito Pipeline, the North Saskatchewan (“North Sask”) pipeline and the Bodo/Cactus Lake pipeline. Each system consists of a blended crude oil line and a parallel diluent line that delivers condensate to upstream blending locations. The North Sask pipeline is 84 miles in length and originates near Turtleford, Saskatchewan and terminates in Dulwich, Saskatchewan. The Manito Pipeline includes 339 miles of 10-inch blend pipeline. The mainline segment originates at Dulwich and terminates at Kerrobert, Saskatchewan. The Bodo/Cactus Lake pipeline is a 133 mile long, 10-inch blend pipeline that originates in Bodo, Alberta and also terminates at our Kerrobert storage facility. The Kerrobert storage and terminalling facility is connected to the Enbridge pipeline system and can both receive and deliver heavy crude oil from and to the Enbridge pipeline system.
Rainbow System. We own a 100% interest in the Rainbow system. The Rainbow system is comprised of (i) a 480-mile, 20-inch to 24-inch mainline crude oil pipeline, with capacity of approximately 185,000 barrels per day of batched light sweet and heavy sour oil capacity, that extends from the Norman Wells Pipeline connection in Zama, Alberta to Edmonton, Alberta and has 159 miles of associated gathering pipelines and (ii) a 188-mile, 10-inch pipeline to transport diluent north from Edmonton to our Nipisi truck terminal in Northern Alberta.
In late 2015, our Indigo pipeline project, which would have connected to our Rainbow system, was canceled as a result of the committed shipper’s decision to cancel development of its thermal in situ project located in Alberta, Canada. We have been reimbursed for our costs incurred on this project.
Rangeland System. We own a 100% interest in the Rangeland system. The Rangeland system consists of a 670 mile, 8-inch to 16-inch mainline pipeline and approximately 500 miles of 3-inch to 8-inch gathering pipelines. The Rangeland system transports NGL mix, butane, condensate, light sweet crude oil and light sour crude oil either north to Edmonton or south to the U.S./Canadian border near Cutbank, Montana, where it connects to our Western Corridor system.
South Saskatchewan System. We own a 100% interest in the South Saskatchewan system. This system consists of a 160 mile, 16-inch mainline from Cantuar to Regina, Saskatchewan and 186 miles of 4-inch to 12-inch gathering pipelines from the Rapdan area to Cantuar. The South Saskatchewan system has capacity to transport approximately 68,000 barrels per day of heavy crude oil from gathering areas in southern Saskatchewan to Enbridge’s mainline at Regina.
NGL Pipelines
Co-Ed NGL Pipeline System. We own and operate the Co-Ed NGL Pipeline system, which consists of approximately 630 miles of 3-inch to 10-inch pipeline. This pipeline system gathers NGL from approximately 35 field gas processing plants located in Alberta, including all of the NGL produced at the Cochrane Straddle Plant. The Co-Ed NGL Pipeline system has throughput capacity of approximately 72,000 barrels per day to our NGL facilities at Fort Saskatchewan.
Facilities Segment
Our Facilities segment operations generally consist of fee-based activities associated with providing storage, terminalling and throughput services for crude oil, refined products, NGL and natural gas, as well as NGL fractionation and isomerization services and natural gas and condensate processing services. We generate revenue through a combination of month-to-month and multi-year agreements and processing arrangements.
Revenues generated in this segment primarily include (i) fees that are generated from storage capacity agreements, (ii) terminal throughput fees that are generated when we receive crude oil, refined products or NGL from one connecting source and deliver the applicable product to another connecting carrier, (iii) loading and unloading fees at our rail terminals, (iv) fees from NGL fractionation and isomerization services, (v) fees from natural gas and condensate processing services and (vi) fees associated with natural gas park and loan activities, interruptible storage services and wheeling and balancing services.
As of December 31, 2015, we owned, operated or employed a variety of long-term physical assets throughout the United States and Canada in this segment, including:
· approximately 80 million barrels of crude oil and refined products storage capacity primarily at our terminalling and storage locations;
· approximately 25 million barrels of NGL storage capacity;
· approximately 97 Bcf of natural gas storage working capacity;
· approximately 31 Bcf of owned base gas;
· 10 natural gas processing plants located throughout Canada and the Gulf Coast area of the United States;
· a condensate processing facility located in the Eagle Ford area of South Texas with an aggregate processing capacity of approximately 120,000 barrels per day;
· seven fractionation plants located throughout Canada and the United States with an aggregate net processing capacity of approximately 166,300 barrels per day, and an isomerization and fractionation facility in California with an aggregate processing capacity of approximately 15,000 barrels per day;
· 28 crude oil and NGL rail terminals located throughout the United States and Canada. See “Rail Facilities” below for an overview of various terminals and “Supply and Logistics” regarding our use of railcars;
· six major marine facilities in the United States with an aggregate load capacity of 107,000 barrels per hour, including vapor recovery rates, and an aggregate unload capacity of 182,000 barrels per hour; and
· approximately 1,100 miles of active pipelines that support our facilities assets, consisting primarily of NGL and natural gas pipelines.
The following is a tabular presentation of our active Facilities segment storage and service assets in the United States and Canada as of December 31, 2015, grouped by product and service type, with capacity and volume as indicated:
|
Crude Oil and Refined Products Storage Facilities |
|
Total Capacity |
|
|
Cushing |
|
21 |
|
|
LA Basin |
|
8 |
|
|
Martinez and Richmond |
|
5 |
|
|
Mobile and Ten Mile |
|
5 |
|
|
Patoka |
|
6 |
|
|
St. James |
|
11 |
|
|
Yorktown (1) |
|
5 |
|
|
Other (2) |
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
NGL Storage Facilities |
|
Total Capacity |
|
|
Bumstead |
|
4 |
|
|
Fort Saskatchewan |
|
5 |
|
|
Sarnia Area |
|
9 |
|
|
Tirzah |
|
1 |
|
|
Other |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
25 |
|
|
Natural Gas Storage Facilities |
|
Total Capacity |
|
|
Salt-caverns and Depleted Reservoir |
|
97 |
|
|
Natural Gas Processing Facilities (3) |
|
Ownership Interest |
|
Total Gas |
|
Net Gas |
|
|
United States Gulf Coast Area |
|
100 |
% |
0.2 |
|
0.6 |
|
|
Canada |
|
36-100 |
% |
1.1 |
|
5.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1.3 |
|
6.0 |
|
|
Condensate Stabilization Facility |
|
Total Capacity |
|
|
Gardendale |
|
120,000 |
|
|
NGL Fractionation and Isomerization Facilities |
|
Ownership Interest |
|
Total |
|
Net |
|
|
Fort Saskatchewan |
|
21-100 |
% |
26,760 |
|
51,300 |
|
|
Sarnia |
|
62-84 |
% |
60,345 |
|
90,000 |
|
|
Shafter |
|
100 |
% |
6,520 |
|
15,000 |
|
|
Other |
|
82-100 |
% |
9,775 |
|
25,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
103,400 |
|
181,300 |
|
|
Rail Facilities |
|
Ownership Interest |
|
Loading |
|
Unloading |
|
|
Crude Oil Rail Facilities |
|
50-100 |
% |
382,000 |
|
350,000 |
|
|
|
|
Ownership Interest |
|
Number of |
|
Number of |
|
|
NGL Rail Facilities (6) |
|
50-100 |
% |
258 |
|
1,128 |
|
(1) Amount includes approximately 1 million barrels of capacity for which we hold lease options (all of which have been exercised).
(2) Amount includes approximately 2 million barrels of storage capacity associated with our crude oil rail terminal operations.
(3) While natural gas processing inlet volumes and capacity amounts are presented, they currently are not a significant driver of our segment results.
(4) Represents average volumes net to our share for the entire year.
(5) Capacity transported will vary according to specification of product moved.
(6) Our NGL rail terminals are predominately utilized for internal purposes specifically for our supply and logistics activities. See our “Supply and Logistics Segment” discussion following this section for further discussion regarding the use of our rail terminals.
The following discussion contains a detailed description of our more significant Facilities segment assets.
Crude Oil and Refined Products Facilities
Cushing Terminal. Our Cushing, Oklahoma Terminal (the “Cushing Terminal”) is located at the Cushing Interchange, one of the largest wet-barrel trading hubs in the United States and the delivery point for crude oil futures contracts traded on the NYMEX. The Cushing Terminal has been designated by the NYMEX as an approved delivery location for crude oil delivered under the NYMEX light sweet crude oil futures contract. As the NYMEX delivery point and a cash market hub, the Cushing Interchange serves as a source of refinery feedstock for Midwest and Gulf Coast refiners and plays an integral role in establishing and maintaining markets for many varieties of foreign and domestic crude oil. The Cushing Terminal has access to all major inbound and outbound pipelines in Cushing and is designed to handle multiple grades of crude oil while minimizing the interface and enabling deliveries to connecting carriers at their maximum rate.
Since 1999, we have completed multiple expansions that have increased the capacity of the Cushing Terminal to a total of 21 million barrels. In 2015, we added approximately 1.4 million barrels of storage and we expect to add approximately 1.6 million barrels of storage capacity during 2016.
L.A. Basin. We own four crude oil and black oil storage facilities in the Los Angeles area with a total of 8 million barrels of storage capacity in commercial service and a distribution pipeline system of approximately 50 miles of pipeline in the Los Angeles Basin. We use the Los Angeles area storage and distribution system to service the storage and distribution needs of the refining, pipeline and marine terminal industries in the Los Angeles Basin. Our Los Angeles area system’s pipeline distribution assets connect our storage assets with major refineries and third-party pipelines and marine terminals in the Los Angeles Basin.
Martinez and Richmond Terminals. We own two terminals in the San Francisco, California area: a terminal at Martinez (which provides refined product and crude oil service) and a terminal at Richmond (which provides refined product and black oil service). Our San Francisco area terminals have 5 million barrels of combined storage capacity and are connected to area refineries through a network of owned and third-party pipelines that carry crude oil and refined products to and from area refineries. These terminals have dock facilities and our Richmond terminal is also able to receive product by rail.
Mobile and Ten Mile Terminal. We have a marine terminal in Mobile, Alabama (the “Mobile Terminal”) that has current useable capacity of 2 million barrels. Approximately 4 million barrels of additional storage capacity is available at our nearby Ten Mile Facility, which is connected to our Mobile Terminal via a 36-inch pipeline. Of this capacity, approximately 3 million barrels supports our Facilities segment operations, with the remaining storage supporting our Transportation segment assets.
The Mobile Terminal is equipped with a ship/tanker dock, barge dock, truck unloading facilities and various third-party connections for crude oil movements to area refiners. Additionally, the Mobile Terminal serves as a source for imports of foreign crude oil to PADD II refiners through our Mississippi/Alabama pipeline system, which connects to the Capline Pipeline at our station in Liberty, Mississippi. Our Ten Mile Facility is connected to our Pascagoula Pipeline.
Patoka Terminal. Our Patoka Terminal has 6 million barrels of storage capacity and includes an associated manifold and header system at the Patoka Interchange located in southern Illinois. Our terminal has access to all major pipelines and terminals at the Patoka Interchange. Patoka is a growing regional hub with access to domestic and foreign crude oil for certain volumes moving north on the Capline Pipeline as well as Canadian barrels moving south.
St. James Terminal. We have 11 million barrels of crude oil storage capacity at the St. James crude oil interchange in Louisiana, which is one of the three most liquid crude oil interchanges in the United States. The facility is connected to major pipelines and other terminals and includes a manifold and header system that allows for receipts and deliveries with connecting pipelines at their maximum operating capacity. In addition, this facility includes a marine dock that is able to receive from, and load, tankers and barges and is also connected to our rail unloading facility. See “Rail Facilities” below for further discussion. In 2015, we added approximately 1 million barrels of storage capacity to the St. James terminal, and we expect to add approximately 1.5 million barrels of capacity in 2016.
Yorktown Terminal. We have 5 million barrels of storage for crude oil and refined products at our Yorktown facility located in Virginia, including approximately 1 million barrels of capacity for which we hold lease options (all of which have been exercised). The Yorktown facility has its own deep-water port on the York River with the capacity to service the receipt and delivery of product from ships and barges. This facility also has an active truck rack and rail capacity. See “Rail Facilities” below for further discussion.
Corpus Christi. We own a 50% interest in Eagle Ford Terminals, which is currently developing a terminal in Corpus Christi, Texas that will be capable of loading ocean going vessels at a rate of 20,000 barrels per hour. Initial storage capacity of the terminal will be 1.2 million barrels. The facility will have access to production from both the Eagle Ford and the Permian Basin through the Eagle Ford joint venture pipeline and is expected to be placed in service in 2018. Enterprise owns the remaining 50% interest in Eagle Ford Terminals.
NGL Storage Facilities
Bumstead. The Bumstead facility is located at a major rail transit point near Phoenix, Arizona. With 4 million barrels of useable capacity, the facility’s primary assets include three salt-dome storage caverns, a 30-car rail track and six truck racks.
Fort Saskatchewan. The Fort Saskatchewan facility is located approximately 16 miles northeast of Edmonton, Alberta in one of the key North American NGL hubs. The facility is a receipt, storage, fractionation and delivery facility for NGL and is connected to other major NGL plants and pipeline systems in the area. The facility’s primary assets include 22 storage caverns with approximately 5 million barrels in useable storage capacity. The facility includes assets operated by us and assets operated by a third-party. Our ownership in the various facility assets ranges from approximately 21% to 100%. See the section entitled “—NGL Fractionation and Isomerization Facilities” below for additional discussion of this facility.
During 2013, we began upgrading our Fort Saskatchewan storage capacity as part of a multi-phase expansion. The first phase of the expansion will add two new NGL storage caverns each with a capacity of 350,000 barrels and will convert approximately 2.4 million barrels of existing NGL mix storage capacity to propane and condensate storage supported by the addition of approximately 2.4 million barrels of new brine pond capacity. Additionally, as part of the first phase of the project, we expanded our propane truck loading capabilities and added new butane truck loading, which came in service in early 2015. The second phase of the project will see the development of two new ethane caverns totaling 1.6 million barrels of capacity which are supported by long-term commitments from third parties.
Sarnia Area. Our Sarnia Area facility consists of (i) our Sarnia facility, (ii) our Windsor storage terminal and (iii) our St. Clair terminal. The Sarnia facility is a large NGL fractionation, storage and shipping facility located on a 380–acre plant site in the Sarnia Chemical Valley. There are 36 multi-product railcar loading spots, 4 multi-product truck loading racks and a network of 14 pipelines providing product delivery capabilities to our Windsor, St. Clair and Green Springs terminal facilities, in addition to refineries, chemical plants and other pipeline systems in the area. The facility has approximately 4 million barrels of useable storage capacity. In 2012, we initiated a brine disposal program that will facilitate the removal of excess brine via truck from our Sarnia facility. The project increased useable NGL storage capacity at the facility by 1 million barrels in 2015, and is expected to increase capacity by as much as 3 million barrels when completed.
The Windsor storage terminal in Windsor, Canada, is a pipeline hub and underground storage facility. The facility is served by three of our receipt/dispatch pipelines and rail and truck offloading. There are eight storage caverns on site with a useable capacity of approximately 3 million barrels. The terminal assets include 16 multi-product rail tank car loading spots and a propane truck loading rack. In 2014, we initiated a brine disposal program that will facilitate the removal of excess brine via pipeline from our Windsor storage terminal. The project is expected to increase useable NGL storage capacity at the facility by approximately 1 million barrels.
The St. Clair terminal is a propane, isobutane and butane storage and distribution facility located in St. Clair, Michigan and is connected to the Sarnia facility via one of our pipelines. On site are five storage caverns with useable capacity of approximately 2 million barrels and 28 multi-product rail tank car loading spots.
Tirzah. The Tirzah facility is located in South Carolina and consists of an underground granite storage cavern with approximately 1 million barrels of useable capacity. The Tirzah facility is connected to the Dixie Pipeline System (a third-party system) via our 63-mile pipeline.
Natural Gas Storage Facilities
We own three FERC regulated natural gas storage facilities located in the Gulf Coast and Midwest that are permitted for 149 Bcf of working gas capacity, and as of December 31, 2015, we had an aggregate working gas capacity of approximately 97 Bcf in service. Our facilities have aggregate peak daily injection and withdrawal rates of 4.1 Bcf and 6.4 Bcf, respectively.
Our natural gas storage facilities are strategically located and have a diverse group of customers, including utilities, pipelines, producers, power generators, marketers and liquefied natural gas (“LNG”) exporters, whose storage needs vary from traditional seasonal storage services to hourly balancing. We are located near several major market hubs, including the Henry Hub (the delivery point for NYMEX natural gas futures contracts), the Carthage Hub (located in East Texas), the Perryville Hub (located in North Louisiana), and the major market hubs of Chicago, Illinois and Dawn, Ontario. Our facilities have 22 direct interconnects with third party interstate pipelines, industrial facilities and gas fired power plants, serving markets in the Gulf Coast, Midwest, Mid-Atlantic, Northeast, and Southeast regions of the United States and the Southeastern portion of Canada.
Natural Gas Processing Facilities
We own and/or operate four straddle plants and two field gas processing plants located in Western Canada with an aggregate net natural gas processing capacity of approximately 5.4 Bcf per day and long-term liquid supply contracts relating to a third-party owned straddle plant with gross processing capacity of approximately 2.5 Bcf per day. We also own and operate four natural gas processing plants located in Louisiana and Alabama with an aggregate natural gas processing capacity of approximately 0.6 Bcf per day.
NGL Fractionation and Isomerization Facilities
Fort Saskatchewan. Our Fort Saskatchewan facility has a fractionation capacity of approximately 45,000 barrels per day and produces both spec NGL products and NGL mix for delivery to the Sarnia facility via the Enbridge pipeline.
The fractionation feedstock is supplied via the Fort Saskatchewan Pipeline System which connects to the Co-Ed NGL Pipeline System. Through ownership in the Keyera Fort Saskatchewan fractionation plant, we have additional fractionation capacity, net to our share of 6,300 barrels per day.
We recently approved a project to expand our fractionation capacity to provide producers with additional fractionation infrastructure necessary to develop the significant liquids-rich natural gas reserves in western Canada. Upon our target completion date in mid-2017, this expansion will increase capacity to produce a combination of spec NGL products and NGL mix by 20,000 barrels per day. This project is supported by long-term commitments from third parties.
Sarnia. The Sarnia Fractionator is the largest fractionation plant in Eastern Canada and receives NGL feedstock from the Enbridge Pipeline and from refineries, gas plants and chemical plants in the area. The fractionation unit has a net useable capacity of 90,000 barrels per day and produces specification propane, isobutane, normal butane and natural gasoline. Our ownership in the various processing units at the Sarnia Fractionator ranges from 62% to 84%.
Shafter. Our Shafter facility located near Bakersfield, California provides isomerization and fractionation services to producers and customers. The primary assets consist of approximately 200,000 barrels of NGL storage and a processing facility with butane isomerization capacity of approximately 15,000 barrels per day including NGL fractionation capacity of approximately 12,000 barrels per day.
During 2015, we commissioned an approximate 40-mile NGL pipeline system capable of delivering up to 10,000 barrels per day from California Resources Corporation’s Elk Hills Gas plant to our Shafter facility, increased our storage capacity by 30,000 barrels and added 10,000 barrels per day of rail capacity.
Condensate Processing Facility
Our Gardendale condensate processing facility located in La Salle County, Texas is designed to extract natural gas liquids from condensate and is adjacent to our Gardendale terminal and rail facility. We completed an expansion of the facility in the second half of 2015, bringing the total processing capacity of the facility to 120,000 barrels per day. The facility has useable storage capacity of 160,000 barrels. In 2015, we also placed in service a ten mile pipeline that connects to a third party pipeline delivering NGL to Mont Belvieu. Throughput at the Gardendale processing facility is supplied by long-term commitments from producers.
Rail Facilities
Crude Oil Rail Loading Facilities
We own seven active crude oil and condensate rail loading terminals, six of which service production in the Niobrara, Eagle Ford, Permian Basin and Bakken shale formations and have a combined loading capacity of approximately 322,000 barrels per day. These facilities are located in Carr, Colorado; Tampa, Colorado; Gardendale, Texas; McCamey, Texas; Manitou, North Dakota; and Van Hook, North Dakota. Our rail terminal in Western Canada near Kerrobert, Saskatchewan was placed in service in the fourth quarter of 2015, with an initial capacity of approximately 60,000 barrels per day.
Crude Oil Rail Unloading Facilities
We own three active crude oil rail unloading terminals that have a combined unloading capacity of approximately 350,000 barrels per day. Our terminal at St. James, Louisiana is connected to our rail unloading facility that has an unload capacity of 140,000 barrels of sweet crude oil per day. In late 2015, we commissioned a project to enhance our St. James rail facility with capability to receive heavy crude oil. Our Yorktown, Virginia rail facility receives unit trains and has an unload capacity of approximately 140,000 barrels per day, and our Bakersfield, California rail facility receives unit trains and has permitted capacity to unload 70,000 barrels per day.
NGL Rail Facilities
We own 21 operational NGL rail facilities strategically located near NGL storage, pipelines, gas production or propane distribution centers throughout the United States and Canada. Our NGL rail facilities currently have 258 railcar rack spots and 1,128 railcar storage spots and we have the ability to switch our own railcars at six of these terminals.
We have approved a number of expansion projects at our Fort Saskatchewan facility, including a 60 car per day propane rail loading facility, which we plan to place in service in 2016.
Supply and Logistics Segment
Our Supply and Logistics segment operations generally consist of the following merchant-related activities:
· the purchase of U.S. and Canadian crude oil at the wellhead, the bulk purchase of crude oil at pipeline, terminal and rail facilities, and the purchase of cargos at their load port and various other locations in transit;
· the storage of inventory during contango market conditions and the seasonal storage of NGL and natural gas;
· the purchase of NGL from producers, refiners, processors and other marketers;
· the resale or exchange of crude oil and NGL at various points along the distribution chain to refiners or other resellers;
· the transportation of crude oil and NGL on trucks, barges, railcars, pipelines and ocean-going vessels from various delivery points, market hub locations or directly to end users such as refineries, processors and fractionation facilities; and
· the purchase and sale of natural gas.
We characterize a substantial portion of our baseline segment profit generated by our Supply and Logistics segment as fee equivalent. This portion of the segment profit is generated by the purchase and resale of crude oil on an index-related basis, which results in us generating a gross margin for such activities. This gross margin is reduced by the transportation, facilities and other logistical costs associated with delivering the crude oil to market and carrying costs for hedged inventory, as well as any operating and general and administrative expenses. The level of profit associated with a portion of the other activities we conduct in the Supply and Logistics segment is influenced by overall market structure and the degree of market volatility, as well as variable operating expenses. The majority of activities that are carried out within our Supply and Logistics segment are designed to produce stable baseline results in a variety of market conditions, while at the same time providing upside potential associated with opportunities inherent in volatile market conditions (including opportunities to benefit from fluctuating differentials). These activities utilize storage facilities at major interchange and terminalling locations and various hedging strategies. The tankage that is used to support our arbitrage activities positions us to capture margins in various market conditions. See “—Impact of Commodity Price Volatility and Dynamic Market Conditions on Our Business Model” below for further discussion.
In addition to hedged working inventories associated with its merchant activities, as of December 31, 2015, our Supply and Logistics segment also owned significant volumes of crude oil and NGL classified as long-term assets and linefill or minimum inventory requirements and employed a variety of owned or leased physical assets throughout the United States and Canada, including approximately:
· 13 million barrels of crude oil and NGL linefill in pipelines owned by us;
· 5 million barrels of crude oil and NGL linefill in pipelines owned by third parties and other long-term inventory;
· 990 trucks and 1,100 trailers; and
· 10,100 crude oil and NGL railcars.
In connection with its operations, our Supply and Logistics segment secures transportation and facilities services from our other two segments as well as third-party service providers under month-to-month and multi-year arrangements. Intersegment sales are based on posted tariff rates, rates similar to those charged to third parties or rates that we believe approximate market rates. However, certain terminalling and storage rates recognized within our Facilities segment are discounted to our Supply and Logistics segment to reflect the fact that these services may be canceled on short notice to enable the Facilities segment to provide services to third parties, generally under longer term arrangements.
The following table shows the average daily volume of our supply and logistics activities for the year ended December 31, 2015:
|
|
|
Volumes |
|
|
Crude oil lease gathering purchases |
|
943 |
|
|
NGL sales |
|
223 |
|
|
Waterborne cargos |
|
2 |
|
|
Supply and Logistics activities total |
|
1,168 |
|
Crude Oil and NGL Purchases. We purchase crude oil and NGL from multiple producers under contracts and believe that we have established long-term, broad-based relationships with the crude oil and NGL producers in our areas of operations. Our crude oil contracts generally range in term from thirty-day evergreen to five years, with the majority ranging from thirty days to one year and a limited number of contracts with remaining terms extending up to ten years. We utilize our truck fleet, railcars and pipelines as well as leased railcars, third-party pipelines, trucks and barges to transport the crude oil to market. In addition, from time to time, we purchase foreign crude oil. Under these contracts we may purchase crude oil upon delivery in the United States or we may purchase crude oil in foreign locations and transport it on third-party tankers. From time to time, we enter into various types of purchase and exchange transactions including fixed price purchase contracts, collars, financial swaps and crude oil and NGL-related futures contracts as hedging devices.
We purchase NGL from producers, refiners and other NGL marketing companies under contracts that typically have ranged from immediate delivery to one year in term. In the last few years, we have implemented an increasing number of contracts with longer terms to firm up capacity utilization and base-load expansion projects. We utilize our trucking fleet and pipeline network, as well as leased railcars, third-party tank trucks and third-party pipelines to transport NGL.
In addition to purchasing crude oil from producers, we purchase both domestic and foreign crude oil in bulk at major pipeline terminal locations, rail facilities and barge facilities. We also purchase NGL in bulk at major pipeline terminal points and storage facilities from major integrated oil companies, large independent producers or other NGL marketing companies or processors. Crude oil and NGL are purchased in bulk when we believe additional opportunities exist to realize margins further downstream in the crude oil or NGL distribution chain. The opportunities to earn additional margins vary over time with changing market conditions. Accordingly, the margins associated with our bulk purchases will fluctuate from period to period.
Crude Oil and NGL Sales. The activities involved in the supply, logistics and distribution of crude oil and NGL are complex and require current detailed knowledge of crude oil and NGL sources and end markets, as well as a familiarity with a number of factors including grades of crude oil, individual refinery demand for specific grades of crude oil, area market price structures, location of customers, various modes and availability of transportation facilities and timing and costs (including storage) involved in delivering crude oil and NGL to the appropriate customer.
We sell our crude oil to major integrated oil companies, independent refiners and other resellers in various types of sale and exchange transactions. Our crude oil sales contracts generally range in term from thirty-day evergreen to five years, with the majority ranging from thirty days to one year and a limited number of contracts extending up to seven years. We sell NGL primarily to propane and refined product retailers, petrochemical companies and refiners, and limited volumes to other marketers. A majority of our NGL contracts generally range in term from a thirty-day evergreen to one year. With the move to longer term (greater than one year) NGL supply contracts, longer term NGL sale contracts are also becoming more commonplace, usually with flexible pricing mechanisms to ensure the sale remains market-based for both the buyer and seller. We establish a margin for the crude oil and NGL we purchase by entering into physical sales contracts with third parties, or by entering into a future delivery obligation with respect to futures contracts on the NYMEX, ICE or over-the-counter exchanges. Through these transactions, we seek to maintain a position that is substantially balanced between purchases and sales and future delivery obligations. From time to time, we enter into various types of sale and exchange transactions including fixed price delivery contracts, collars, financial swaps and crude oil and NGL-related futures contracts as hedging devices.
Crude Oil and NGL Exchanges. We pursue exchange opportunities to enhance margins throughout the gathering and marketing process. When opportunities arise to increase our margin or to acquire a grade, type or volume of crude oil or NGL that more closely matches our physical delivery requirement, location or the preferences of our customers, we exchange physical crude oil or NGL, as appropriate, with third parties. These exchanges are effected through contracts called exchange or buy/sell agreements. Through an exchange agreement, we agree to buy crude oil or NGL that differs in terms of geographic location, grade of crude oil or type of NGL, or physical delivery schedule from crude oil or NGL we have available for sale. Generally, we enter into exchanges to acquire crude oil or NGL at locations that are closer to our end markets, thereby reducing transportation costs and increasing our margin. We also exchange our crude oil to be physically delivered at a later date, if the exchange is expected to result in a higher margin net of storage costs, and enter into exchanges based on the grade of crude oil, which includes such factors as sulfur content and specific gravity, in order to meet the quality specifications of our physical delivery contracts. See Note 2 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of our accounting for exchange and buy/sell agreements.
Natural Gas Purchase and Sales Activities. We also generate net revenue through the merchant storage activities of our natural gas commercial marketing group, which captures short term market opportunities by utilizing a portion of our natural gas storage capacity and engaging in related commercial marketing activities. Our natural gas merchant storage activities generate revenue through the hedged purchase and sale of natural gas net of any storage-related costs incurred. We utilize physical natural gas storage at our facilities and derivatives to hedge expected margin from these activities. Through these transactions, we seek to maintain a position that is substantially balanced between purchases of natural gas on the one hand and sales or future delivery obligations on the other hand.
In connection with our natural gas merchant storage activities, we incur certain storage-related costs. These costs consist of fees incurred to secure third-party pipeline capacity and natural gas storage and transaction costs associated with managing injection and deliverability capacity at our facilities. Costs associated with our third-party pipeline capacity are subject to variation as the terms of these agreements typically contain certain fees which fluctuate based on actual volumes shipped in addition to monthly reservation fees.
Credit. Our merchant activities involve the purchase of crude oil, NGL and natural gas for resale and require significant extensions of credit by our suppliers. In order to assure our ability to perform our obligations under the purchase agreements, various credit arrangements are negotiated with our suppliers. These arrangements include open lines of credit and, to a lesser extent, standby letters of credit issued under our hedged inventory facility or our senior unsecured revolving credit facility.
When we sell crude oil, NGL and natural gas, we must determine the amount, if any, of the line of credit to be extended to any given customer. We manage our exposure to credit risk through credit analysis, credit approvals, credit limits, prepayment, letters of credit and monitoring procedures.
Because our typical sales transactions can involve large volumes of crude oil and natural gas, the risk of nonpayment and nonperformance by customers is a major consideration in our business. We believe our sales are made to creditworthy entities or entities with adequate credit support. Generally, sales of crude oil and natural gas are settled within 30 days of the month of delivery, and pipeline, transportation and terminalling services settle within 30 days from the date we issue an invoice for the provision of services.
We also have credit risk exposure related to our sales of NGL (principally propane); however, because our sales are typically in relatively small amounts to individual customers, we do not believe that these transactions pose a material concentration of credit risk. Typically, we enter into annual contracts to sell NGL on a forward basis, as well as to sell NGL on a current basis to local distributors and retailers. In certain cases our NGL customers prepay for their purchases, in amounts ranging up to 100% of their contracted amounts.
Certain activities in our Supply and Logistics segment are affected by seasonal aspects, primarily with respect to NGL and natural gas supply and logistics activities.
Impact of Commodity Price Volatility and Dynamic Market Conditions on Our Business Model
Through our three business segments, we are engaged in the transportation, storage, terminalling and marketing of crude oil, NGL and natural gas. The majority of our activities are focused on crude oil, which is the principal feedstock used by refineries in the production of transportation fuels.
Crude oil, NGL, natural gas and refined products commodity prices have historically been very volatile. For example, since the mid-1980s, NYMEX West Texas Intermediate (“WTI”) crude oil benchmark prices have ranged from a low of approximately $10 per barrel during 1986 to a high of over $147 per barrel during 2008. During 2015, West Texas Intermediate crude oil prices traded within a range of approximately $35 to $61 per barrel. There is also volatility within the propane and butane markets as seen through the North American benchmark price located at Mont Belvieu, Texas. Specifically, propane prices have ranged from a low of approximately 39% of the WTI benchmark price for crude oil in 2015 to a high of approximately 81% of the WTI benchmark price for crude oil in 2000. Butane has seen a price range from a low of approximately 52% of the WTI benchmark price for crude oil in 2015 to a high of approximately 93% of the WTI benchmark price for crude oil in 2000.
Absent extended periods of lower crude oil or NGL prices that are below production replacement costs or higher crude oil or NGL prices that have a significant adverse impact on consumption, demand for the services we provide in our fee-based Transportation and Facilities segments and our gross profit from these activities have little correlation to absolute commodity prices. Relative contribution levels will vary from quarter-to-quarter due to seasonal and other similar factors, but our fee-based Transportation and Facilities segments should comprise approximately 70% to 80% of our aggregate base level segment profit.
Base level segment profit from our supply and logistics activities is dependent on our ability to sell crude oil and NGL at prices in excess of our aggregate cost. Although segment profit may be adversely affected during certain transitional periods as discussed further below, our crude oil and NGL supply, logistics and distribution operations are not directly affected by the absolute level of prices, but are affected by overall levels of supply and demand for crude oil and NGL and relative fluctuations in market-related indices.
In developing our business model and allocating our resources among our three segments, we attempt to anticipate the impacts of shifts between supply-driven markets and demand-driven markets, seasonality, cyclicality, regional surpluses and shortages, economic conditions and a number of other influences that can cause volatility and change market dynamics on a short, intermediate and long-term basis. Our objective is to position the Partnership such that our overall annual base level of cash flow is not materially adversely affected by the absolute level of energy prices, shifts between demand-driven markets and supply-driven markets or other similar dynamics. In recent periods, however, the market has experienced impacts from aggressive competition and overbuilt infrastructure in certain regions, which has caused supply and demand imbalances and price volatility. In some of the areas where we operate, there has been significantly increased competition for marginal or incremental volumes from shippers on third party pipelines who have committed to ship more production than they have and are purchasing barrels in the market for shipment on the applicable third party pipeline in satisfaction of their transportation commitments, often doing so at a loss because the loss on sale of the purchased crude oil will be less than the amount of the take-or-pay obligation on the pipeline. This type of activity has put downward pressure on volumes and margins across our three business segments. While recent market conditions have been challenging, we believe the complementary, balanced nature of our business activities and diversification of our asset base among varying regions and demand-driven and supply-driven markets provides us with the opportunity to generate a base level of cash flow in a variety of market scenarios.
In addition to providing the opportunity to generate a base level of cash flow, this approach is also intended to provide opportunities to realize incremental margin during volatile market conditions. For example, if crude oil prices are high relative to historical levels, we may hedge some of our expected pipeline loss allowance barrels, and if crude oil prices are low relative to historical prices, we may hedge a portion of our anticipated diesel purchases needed to operate our trucks and barges. Also, during periods when supply exceeds the demand for crude oil, NGL or natural gas in the near term, the market for such product is often in contango, meaning that the price for future deliveries is higher than current prices. In a contango market, entities that have access to storage at major trading locations can purchase crude oil, NGL or natural gas at current prices for storage and simultaneously sell forward such products for future delivery at higher prices.
The combination of fee-based cash flow from our Transportation and Facilities segments, complemented by a number of diverse, flexible and counter-balanced sources of cash flow within our Supply and Logistics segment is intended to provide us with the opportunity to generate a base level of cash flow and provide upside opportunities. In executing this business model, we employ a variety of financial risk management tools and techniques, predominantly in our Supply and Logistics segment.
During certain transitional periods, such as this extended period of lower crude oil prices, the ability to generate above base line performance is challenging, and taking into account the over-capacity of midstream assets that currently exists in most crude oil producing regions, generating even baseline level performance will be challenging. See “Global Petroleum Market Overview” above for additional discussion regarding market conditions.
Risk Management
In order to hedge margins involving our physical assets and manage risks associated with our various commodity purchase and sale obligations and, in certain circumstances, to realize incremental margin during volatile market conditions, we use derivative instruments. We also use various derivative instruments to manage our exposure to interest rate risk and currency exchange rate risk. In analyzing our risk management activities, we draw a distinction between enterprise level risks and trading-related risks. Enterprise level risks are those that underlie our core businesses and may be managed based on management’s assessment of the cost or benefit in doing so. Conversely, trading-related risks (the risks involved in trading in the hopes of generating an increased return) are not inherent in our core business; rather, those risks arise as a result of engaging in the trading activity. Our policy is to manage the enterprise level risks inherent in our core businesses, rather than trying to profit from trading activity. Our commodity risk management policies and procedures are designed to monitor NYMEX, ICE and over the counter positions, as well as physical volumes, grades, locations, delivery schedules and storage capacity, to help ensure that our hedging activities address our risks. Our interest rate and currency exchange rate risk management policies and procedures are designed to monitor our derivative positions and ensure that those positions are consistent with our objectives and approved strategies. We have a risk management function that has direct responsibility and authority for our risk policies, related controls around commercial activities and procedures and certain other aspects of corporate risk management. Our risk management function also approves all new risk management strategies through a formal process. Our approved strategies are intended to mitigate and manage enterprise level risks that are inherent in our core businesses.
Our policy is generally to structure our purchase and sales contracts so that price fluctuations do not materially affect our operating income, and not to acquire and hold physical inventory or derivatives for the purpose of speculating on outright commodity price changes. Although we seek to maintain a position that is substantially balanced within our supply and logistics activities, we purchase crude oil, NGL and natural gas from thousands of locations and may experience net unbalanced positions for short periods of time as a result of production, transportation and delivery variances as well as logistical issues associated with inclement weather conditions and other uncontrollable events that may occur. When unscheduled physical inventory builds or draws do occur, they are monitored constantly and managed to a balanced position over a reasonable period of time. This activity is monitored independently by our risk management function and must take place within predefined limits and authorizations.
Geographic Data; Financial Information about Segments
See Note 18 to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Customers
Marathon Petroleum Corporation and its subsidiaries accounted for approximately 17%, 17% and 15% of our revenues for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. ExxonMobil Corporation and its subsidiaries accounted for approximately 13%, 15% and 13% of our revenues for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Phillips 66 and its subsidiaries accounted for approximately 11% of our revenues for the year ended December 31, 2013. No other customers accounted for 10% or more of our revenues during any of the three years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013. The majority of revenues from these customers pertain to our supply and logistics operations. The sales to these customers occur at multiple locations and we believe that the loss of these customers would have only a short-term impact on our operating results. There is risk, however, that we would not be able to identify and access a replacement market at comparable margins. For a discussion of customers and industry concentration risk, see Note 13 to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Competition
Competition among pipelines is based primarily on transportation charges, access to producing areas and supply regions and demand for crude oil and NGL by end users. We believe that high capital requirements, environmental considerations and the difficulty in acquiring rights-of-way and related permits, together with the fact that many of the producing basins in the United States and Canada currently have excess take-away capacity (whether by pipeline or rail), make it unlikely that new competing pipeline systems comparable in size and scope to our pipeline systems (and excluding those already publicly announced to be under development or construction) will be built in the foreseeable future. However, to the extent there are already third-party owned pipelines or owners with joint venture pipelines with excess capacity in the vicinity of our operations, we are exposed to significant competition based on the relatively low cost of moving an incremental barrel of crude oil or NGL. In the current environment, such competition for marginal or incremental volumes has been exacerbated in some areas by shippers on third party pipelines who have committed to ship more production than they have and are purchasing barrels in the market and shipping them on the applicable third party pipeline in satisfaction of their commitment. This type of activity reduces the pool of incremental barrels that would otherwise be available for transport on our pipelines. In addition, in areas where additional infrastructure is necessary to accommodate new or increased production or changing product flows, we face competition in providing the required infrastructure solutions as well as the risk of building capacity in excess of sustained demand. Depending upon the specific movement, pipelines, which generally offer the lowest cost of transportation, may also face competition from other forms of transportation, such as rail and barge. Although these alternative forms of transportation are typically higher cost, they can provide access to alternative markets at which a higher price may be realized for the commodity being transported, thereby overcoming the increased transportation cost.
We also face competition with respect to our supply and logistics and facilities services. Our competitors include other crude oil and NGL pipeline companies, other NGL processing and fractionation companies, the major integrated oil companies, their marketing affiliates and independent gatherers, banks that have established a trading platform, brokers and marketers of widely varying sizes, financial resources and experience. Some of these competitors have capital resources greater than ours.
With respect to our natural gas storage operations, the principal elements of competition are rates, terms of service, supply and market access and flexibility of service. An increase in competition in our markets could arise from new ventures or expanded operations from existing competitors. Our natural gas storage facilities compete with several other storage providers, including regional storage facilities and utilities. Certain pipeline companies have existing storage facilities connected to their systems that compete with some of our facilities.
Regulation
Our assets, operations and business activities are subject to extensive legal requirements and regulations under the jurisdiction of numerous federal, state, provincial and local agencies. Many of these agencies are authorized by statute to issue, and have issued, requirements binding on the pipeline industry, related businesses and individual participants. The failure to comply with such legal requirements and regulations can result in substantial fines and penalties, expose us to civil and criminal claims, and cause us to incur significant costs and expenses. In all material respects, we believe that we are in substantial compliance with the various laws, rules and regulations that apply to our assets, operations and business activities; however, we can provide no assurances in that regard. See “Risk Factors—Risks Related to PAA’s Business—PAA’s operations are also subject to laws and regulations relating to protection of the environment and wildlife, operational safety, climate change and related matters that may expose it to significant costs and liabilities.” At any given time there may be proposals, provisional rulings or proceedings in legislation or under governmental agency or court review that could affect our business. The regulatory burden on our assets, operations and activities increases our cost of doing business and, consequently, affects our profitability. We can provide no assurance that the increased costs associated with any new or proposed laws, rules or regulations will not be material. We may at any time also be required to apply significant resources in responding to governmental requests for information and/or enforcement actions. In 2010 we settled by means of separate Consent Decrees, two Department of Justice (“DOJ”)/Environmental Protection Agency (“EPA”) proceedings regarding certain releases of crude oil. One Consent Decree applied to our crude oil pipelines in general and was terminated in November 2013. The remaining Consent Decree applies to a specific system. Although we believe that all material aspects of the injunctive elements of the remaining Consent Decree (costs and operational effects) have been incorporated into our budgeting and planning process, future proceedings could result in additional injunctive remedies, the effect of which would subject us to operational requirements and constraints.
The following is a discussion of certain, but not all, of the laws and regulations affecting our operations.
Environmental, Health and Safety Regulation
General
Our operations involving the storage, treatment, processing and transportation of liquid hydrocarbons, including crude oil, are subject to stringent federal, state, provincial and local laws and regulations governing the discharge of materials into the environment or otherwise relating to protection of the environment. As with the industry generally, compliance with these laws and regulations increases our overall cost of doing business, including our capital costs to construct, maintain and upgrade equipment and facilities. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations could result in the assessment of administrative, civil and criminal penalties, the imposition of investigatory and remedial liabilities and the issuance of injunctions that may subject us to additional operational constraints. Environmental and safety laws and regulations are subject to changes that may result in more stringent requirements, and we cannot provide any assurance that compliance with current and future laws and regulations will not have a material effect on our results of operations or earnings. A discharge of hazardous liquids into the environment could, to the extent such event is not insured, subject us to substantial expense, including both the cost to comply with applicable laws and regulations and any claims made by third parties. The following is a summary of some of the environmental, health and safety laws and regulations to which our operations are subject.
Pipeline Safety/ Integrity Management
A substantial portion of our petroleum pipelines and our storage tank facilities in the United States are subject to regulation by the Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (“PHMSA”) pursuant to the Hazardous Liquids Pipeline Safety Act of 1979, as amended (the “HLPSA”). The HLPSA imposes safety requirements on the design, installation, testing, construction, operation, replacement and management of pipeline and tank facilities. Federal regulations implementing the HLPSA require pipeline operators to adopt measures designed to reduce the environmental impact of oil discharges from onshore oil pipelines, including the maintenance of comprehensive spill response plans and the performance of extensive spill response training for pipeline personnel. These regulations also require pipeline operators to develop and maintain a written qualification program for individuals performing covered tasks on pipeline facilities. Comparable regulation exists in some states in which we conduct intrastate common carrier or private pipeline operations. Regulation in Canada is under the National Energy Board (“NEB”) and provincial agencies.
United States
The HLPSA was amended by the Pipeline Safety Improvement Act of 2002 and the Pipeline Inspection, Protection, Enforcement and Safety Act of 2006. These amendments have resulted in the adoption of rules by the Department of Transportation (“DOT”) that require transportation pipeline operators to implement integrity management programs, including frequent inspections, correction of identified anomalies and other measures, to ensure pipeline safety in “high consequence areas” such as high population areas, areas unusually sensitive to environmental damage, and commercially navigable waterways. In the United States, our costs associated with the inspection, testing and correction of identified anomalies were approximately $107 million in 2015, $107 million in 2014 and $57 million in 2013. Based on currently available information, our preliminary estimate for 2016 is that we will incur approximately $65 million in capital expenditures and approximately $37 million in operational expenditures associated with our required pipeline integrity management program. Significant additional expenses could be incurred if new or more stringently interpreted pipeline safety requirements are implemented. In addition to required activities, our integrity management program includes several voluntary, multi-year initiatives designed to prevent incidents. Costs incurred for such activities were approximately $33 million in 2015, $21 million in 2014 and $22 million in 2013, and our preliminary estimate for 2016 is that we will incur approximately $30 million of such costs.
In 2012, the “Pipeline Safety, Regulatory Certainty, and Job Creation Act of 2011” (the “2011 Act”) became effective. Under the 2011 Act, maximum civil penalties for certain violations have been increased from $100,000 to $200,000 per violation per day, and from a total cap of $1 million to $2 million. In addition, the 2011 Act reauthorized the federal pipeline safety programs of PHMSA through September 30, 2015, and directs the Secretary of Transportation to undertake a number of reviews, studies and reports, some of which may result in additional natural gas and hazardous liquids pipeline safety rulemaking. A number of the provisions of the 2011 Act have the potential to cause owners and operators of pipeline facilities to incur significant capital expenditures and/or operating costs.
The Senate Committee on Commerce, Science & Transportation passed the “Securing America’s Future Energy: Protecting Infrastructure of Pipelines and Enhancing Safety Act” (“Safe Pipes Act”) on December 9, 2015. This bill would (i) reauthorize PHMSA through fiscal year 2019, (ii) require reports to Congress on the status of rulemaking efforts in the areas of integrity management, leak detection and accident and incident notification and, (iii) require PHMSA to initiate new rulemaking for underground natural gas storage facilities and (iv) require PHMSA to define the Great Lakes as an ecological resource under 49 CFR 195.6 (b). The committee has sent the bill to the Senate for further consideration.
In October 2015, PHMSA published a Notice of Proposed Rulemaking (“NPRM”) in the Federal Register proposing to make changes to the hazardous liquid pipeline safety regulations. PHMSA is proposing to make the following changes to the regulations:
· Extend reporting requirements to all hazardous liquid gravity and gathering lines;
· Require inspections of pipelines in areas affected by extreme weather, natural disasters, and other similar events;
· Use of leak detection systems on hazardous liquid pipelines in all locations;
· Modify the provisions for making pipeline repairs;
· Require that all pipelines subject to the Integrity Management requirements be capable of accommodating inline inspection tools within 20 years; and,
· Clarifications to improve certainty and compliance to certain existing regulations.
A number of the provisions of this NPRM have the potential to cause owners and operators of pipeline facilities to incur significant capital expenditures and/or operating costs. It is not known when, or in what form, this proposed rulemaking will become final. More recently, in February 2016, PHMSA issued an advisory bulletin for natural gas storage facility operators in response to the leak at a third-party gas storage facility in Southern California. PHMSA indicated when it issued the advisory bulletin that additional regulations related to safety standards for natural gas storage facilities are likely forthcoming. At this time, we cannot predict the impact of any future regulatory actions in this area.
If approved by PHMSA, states may assume responsibility for enforcing federal interstate pipeline regulations as agents for PHMSA and conduct inspections of interstate pipelines. In practice, states vary in their authority and capacity to address pipeline safety.
The California Governor approved the following three bills on October 8, 2015 related to pipeline safety:
· The Oil Spill Response Bill allows volunteer cleanup crews to be paid as contractors, requires oil skimmers to be placed along the coastline at all times, and prohibits the use of dispersants until EPA issues rules on dispersant safety.
· The Pipeline Safety: Inspections Bill mandates annual pipeline inspections commencing January 1, 2017, with the State Fire Marshal responsible for annually inspecting all intrastate pipelines and operators of intrastate pipelines under the jurisdiction of the State Fire Marshal.
· The Oil Spill Response: Environmentally and Ecologically Sensitive Areas Bill requires automatic shut-offs for pipelines located in environmentally sensitive areas.
Efforts are now underway to draft regulations in order to adopt the provisions of the bills by early 2017. We cannot currently predict the impact and costs of these new laws, and any associated regulations, on our operations.
The DOT has issued guidelines with respect to securing regulated facilities against terrorist attack. We have instituted security measures and procedures in accordance with such guidelines to enhance the protection of certain of our facilities. We cannot provide any assurance that these security measures would fully protect our facilities from an attack.
The DOT has adopted American Petroleum Institute Standard 653 (“API 653”) as the standard for the inspection, repair, alteration and reconstruction of steel aboveground petroleum storage tanks subject to DOT jurisdiction. API 653 requires regularly scheduled inspection and repair of tanks remaining in service. In the United States, our costs associated with this program were approximately $33 million, $32 million and $26 million in 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. For 2016, we have budgeted approximately $34 million in connection with continued API 653 compliance activities and similar new EPA regulations for tanks not regulated by the DOT. Certain storage tanks may be taken out of service if we believe the cost of compliance will exceed the value of the storage tanks or replacement tankage may be constructed.
Canada
In Canada, the NEB and provincial agencies such as the Alberta Energy Regulator (“AER”) and the Saskatchewan Ministry of Economy regulate the safety and integrity management of pipelines and storage tanks used for hydrocarbon transmission. We have incurred and will continue to incur costs related to such regulatory requirements.
In June 2015, the Pipeline Safety Act, SC 2015, c. 21 received royal assent. Upon coming into force in June 2016, it will amend the National Energy Board Act and the Canada Oil and Gas Operations Act in order to strengthen the safety and security of pipelines regulated under those acts. It reinforces the “polluter pays” principle, such that operators of pipelines are liable for costs and damages for all unintended or uncontrolled releases of oil, gas, or other substances. Canada will be the first country to introduce absolute liability, irrespective of fault, for all costs and damages resulting from an uncontrolled release of oil, gas or other commodity from a major pipeline (i.e. with transport capacity over 250,000 barrels per day), or otherwise as prescribed by regulation for pipelines with lower capacity, up to $1 billion. In instances involving fault or negligence, liability will continue to be unlimited. Additionally, operators will be required to maintain the financial resources necessary to meet the applicable absolute liability obligations imposed under the Act. Finally, the Act imposes more stringent requirements with respect to abandoned pipelines, including an obligation to maintain adequate funds to pay for abandonment costs.
In addition to required activities, our Canadian integrity management program includes several voluntary, multi-year programs designed to prevent incidents, such as upgrades to our operating and maintenance programs and systems and upgrades to our pipeline watercourse crossing integrity program. Between such required and elective activities, we spent approximately $66 million, $66 million and $90 million in 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Our preliminary estimate for 2016 is approximately $66 million.
We cannot predict the potential costs associated with additional, future regulation. Significant additional expenses could be incurred, and additional operational requirements and constraints could be imposed, if new or more stringently interpreted pipeline safety requirements are implemented.
Occupational Safety and Health
United States
In the United States, we are subject to the requirements of the Occupational Safety and Health Act, as amended (“OSHA”) and comparable state statutes that regulate the protection of the health and safety of workers. In addition, the OSHA hazard communication standard requires that certain information be maintained about hazardous materials used or produced in operations and that this information be provided to employees, state and local government authorities and citizens. Certain of our facilities are subject to OSHA Process Safety Management (“PSM”) regulations, which are designed to prevent or minimize the consequences of catastrophic releases of toxic, reactive, flammable or explosive chemicals. These regulations apply to any process which involves a chemical at or above specified thresholds or any process that involves 10,000 pounds or more of a flammable liquid or gas in one location.
Canada
Similar regulatory requirements exist in Canada under the federal and provincial Occupational Health and Safety Acts, Regulations and Codes. The agencies with jurisdiction under these regulations are empowered to enforce them through inspection, audit, incident investigation or investigation of a public or employee complaint. In some jurisdictions, the agencies have been empowered to administer penalties for contraventions without the company first being prosecuted. Additionally, under the Criminal Code of Canada, organizations, corporations and individuals may be prosecuted criminally for violating the duty to protect employee and public safety.
Solid Waste
We generate wastes, including hazardous wastes, which are subject to the requirements of the federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, as amended (“RCRA”), and analogous state and provincial laws. Many of the wastes that we generate are not subject to the most stringent requirements of RCRA because our operations generate primarily oil and gas wastes, which currently are excluded from consideration as RCRA hazardous wastes. It is possible, however, that in the future, oil and gas wastes may be included as hazardous wastes under RCRA, in which event our wastes will be subject to more rigorous and costly disposal requirements, resulting in additional capital expenditures or operating expenses.
Hazardous Substances
The federal Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act, as amended (“CERCLA”), also known as “Superfund,” and comparable state laws impose liability, without regard to fault or the legality of the original act, on certain classes of persons that contributed to the release of a “hazardous substance” into the environment. These persons include the owner or operator of the site or sites where the release occurred and companies that disposed of, or arranged for the disposal of, the hazardous substances found at the site. Such persons may be subject to strict, joint and several liability for the costs of cleaning up the hazardous substances that have been released into the environment, for damages to natural resources, and for the costs of certain health studies. It is not uncommon for neighboring landowners and other third parties to file claims for personal injury and property damage allegedly caused by hazardous substances or other pollutants released into the environment. In the course of our ordinary operations, we may generate waste that falls within CERCLA’s definition of a “hazardous substance.” Canadian federal and provincial laws also impose liabilities for releases of certain substances into the environment.
We are subject to the EPA’s Risk Management Plan regulations at certain facilities. These regulations are intended to work with OSHA’s PSM regulations (see “—Occupational Safety and Health” above) to minimize the offsite consequences of catastrophic releases. The regulations require us to develop and implement a risk management program that includes a five-year accident history, an offsite consequence analysis process, a prevention program and an emergency response program.
Environmental Remediation
We currently own or lease, and in the past have owned or leased, properties where hazardous liquids, including hydrocarbons, are or have been handled. These properties and the hazardous liquids or associated wastes disposed thereon may be subject to CERCLA, RCRA and state and Canadian federal and provincial laws and regulations. Under such laws and regulations, we could be required to remove or remediate hazardous liquids or associated wastes (including wastes disposed of or released by prior owners or operators) and to clean up contaminated property (including contaminated groundwater).
We maintain insurance of various types with varying levels of coverage that we consider adequate under the circumstances to cover our operations and properties. The insurance policies are subject to deductibles and retention levels that we consider reasonable and not excessive. Consistent with insurance coverage generally available in the industry, in certain circumstances our insurance policies provide limited coverage for losses or liabilities relating to gradual pollution, with broader coverage for sudden and accidental occurrences.
Assets we have acquired or will acquire in the future may have environmental remediation liabilities for which we are not indemnified. We have in the past experienced and in the future will likely experience releases of crude oil into the environment from our pipeline and storage operations. We may also discover environmental impacts from past releases that were previously unidentified.
Air Emissions
Our United States operations are subject to the United States Clean Air Act (“Clean Air Act”), comparable state laws and associated state and federal regulations. In October 2015, the U.S. EPA promulgated a revised ambient standard for ozone. While full implementation of the standard may take a number of years, the revised standard could make air permit for sources of volatile organic compounds (such as crude oil tank farms) more difficult to obtain in some areas.
Our Canadian operations are subject to federal and provincial air emission regulations. New Canadian standards for air quality and industrial air emissions were implemented in May 2013. The new standards provide more stringent objectives for outdoor air quality, including a long term (annual) target for fine particulate matter. Under these laws, permits may be required before construction can commence on a new or modified source of potentially significant air emissions, and operating permits may be required for sources already constructed.
As a result of the changing requirements in both Canada and the United States such as those mentioned above, we may be required to incur certain capital and operating expenditures in the next several years to install air pollution control equipment and otherwise comply with more stringent federal, state, provincial and regional air emissions control requirements when we attempt to obtain or maintain permits and approvals for sources of air emissions. We can provide no assurance that future compliance obligations will not have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
Climate Change Initiatives
United States
The EPA has adopted rules for the reporting of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases (“GHG”) from certain sources. Fewer than ten of our facilities are presently subject to the federal GHG reporting requirements. These include facilities with combustion GHG emissions and potential fugitive emissions above the reporting thresholds. We import sufficient quantities of finished fuel products into the United States to be required to report that activity as well. We also continue to monitor GHG emissions for our facilities and activities.
The EPA has also promulgated regulations establishing Title V and Prevention of Significant Deterioration permitting requirements for certain large sources of GHGs. Fewer than ten of our existing facilities are potential major sources of GHG subject to these permitting requirements. We may be required to install “best available control technology” or (“BACT”) to limit emissions of GHGs from any new or significantly modified facilities that we may seek to construct in the future if they emit quantities of GHGs that trigger the requirements of these regulations. For facilities such as ours, BACT will normally take the form of enhanced energy efficiency measures rather than post-combustion GHG capture requirements. We do not anticipate that the imposition of enhanced energy efficiency requirements will have a material adverse effect on the cost of our operations.
In 2015, the EPA proposed regulations that, if adopted in 2016 as proposed, would require significant reductions in fugitive methane emissions from certain upstream and midstream oil and gas facilities. We do not expect the cost of complying with these rules to have a material effect on the cost of our operations.
California has implemented a GHG cap-and-trade program, authorized under Assembly Bill 32 (“AB32”). Through 2014, California’s cap-and-trade program has only applied to large industrial facilities. The California Air Resources Board has published a list of facilities that are subject to this program. At this time, the list only includes one of our facilities, the Lone Star Gas Liquids facility in Shafter, California because it is a significant combustion source. As a result, compliance instruments for GHG emissions were purchased in 2015.
On January 1, 2015, the AB32 regulations for the first time cover finished fuel providers and importers. California finished fuels providers (refiners and importers) will be required to purchase GHG emission credits for finished fuel sold in or imported into California. The rules implementing the AB32 program were finalized in December 2011. The compliance requirements of the GHG cap-and-trade program through 2020 are being phased in. The California Air Resources Board is currently developing a scoping plan for AB32 compliance obligations after the year 2020. We will be reporting associated GHG emissions for finished fuels imported and exported across California borders and will be subject to the cap and trade program in 2016.
Executive Order B-30-15 was signed by California’s Governor in mid-year 2015. This Executive Order will require a 40% reduction in GHG emissions from the 1990 baseline level by 2030. The current 2020 goals for GHG emissions reductions are at 15% below the 1990 baseline level. Compliance with this reduction requirement may necessitate the lowering of the threshold for industrial facilities required to participate in the GHG cap and trade program. This may increase the number of PAA facilities subject to this program.
The operations of our refinery and producer customers could also be negatively impacted by current GHG legislation or new regulations resulting in increased operating or compliance costs. Some of the proposed federal and state “cap-and-trade” legislation would require businesses that emit GHGs to buy emission credits from government, other businesses, or through an auction process. In addition, refiners could be required to purchase emission credits for GHG emissions resulting from their refining operations as well as the fuels they sell. While it is not possible at this time to predict the final form of “cap-and-trade” legislation, any new federal or state restrictions on GHG emissions could result in material increased compliance costs, additional operating restrictions and an increase in the cost of feedstock and products produced by our refinery customers.
In December 2015, the Paris Agreement was signed at the 21st annual Conference of Parties to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (“UNFCCC”). The Paris Agreement, upon ratification, will require signatory parties to develop and implement carbon emission reduction policies with a goal of limiting the rise in average global temperatures to 2°C or less. This Agreement is likely to become a significant driver for future potential GHG reduction programs in the United States and Canada.
Although it is not possible at this time to predict how legislation or new regulations that may be adopted to address GHG emissions would impact our business, any such future laws and regulations could result in increased compliance costs or additional operating restrictions, and could have a material adverse effect on our business, demand for our services, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Canada
Federal Regulation. Along with 194 other countries, Canada is a signatory to the UNFCCC, and the previously ratified “Kyoto Protocol”, under which many nations, including Canada, agreed to limit emissions of GHGs. In December 2011, Canada formally withdrew from the Kyoto Protocol and replaced it with the “Durban Platform” committing it to develop a legally binding agreement to reduce GHG emissions, the terms of which are yet to be defined, but are to become effective in 2020.
Since 2004, companies emitting more than 100 thousand tons per year (“kt/y”) of CO2 equivalent (“CO2e”) were required to report their GHG emissions under the Greenhouse Gas Emissions Reporting Program. In 2010, this reporting threshold was reduced to 50 kt/y. Two PMC facilities meet this reporting threshold. In May 2015, the federal government announced plans to reduce its GHG emissions by 30% below 2005 levels by 2030, and formally submitted the plan to the UNFCCC.
Provincial Regulation. In 2014, Alberta introduced the Climate Change and Emissions Management Act, which provides a framework for managing GHG emissions by reducing specified gas emissions, relative to gross domestic product, to an amount that is equal to or less than 50% of 1990 levels by December 31, 2020. The accompanying regulations include the Specified Gas Emitters Regulation (the “SGER”), which imposes GHG emissions limits, the Specified Gas Reporting Regulation (the “SGRR”), which imposes GHG emissions reporting requirements, and the Administrative Penalty Regulation which sets out the penalty for non-compliance with the Climate Change and Emissions Management Act.
The SGER expires on December 31, 2017, to ensure it is reviewed for ongoing relevancy and necessity. The regulation applies to facilities in Alberta that have produced 100,000 or more tonnes of GHG emissions per year, and requires reductions in GHG emissions intensity (i.e., the quantity of GHG emissions per unit of production) from emissions intensity baselines. The SGER establishes these emissions intensity baselines. Since the regulation came into effect, PMC has one facility (Fort Saskatchewan Storage and Fractionation Facility) which currently does not meet the reduction obligation. As such, PMC has been required to submit compliance credits which have been completed by submitting payment to the Climate Change Emissions Management Fund (the “CCEMC”). On June 25, 2015, the Alberta Government announced an amendment to the SGER, which stipulates that the maximum emissions intensity reduction requirement for all facilities will be increased to 15% after January 1, 2016, and then to 20% after January 1, 2017.
Under the SGER, regulated facilities have four ways to comply with the annual emissions intensity reduction requirements: (1) improve emissions intensity at their facilities; (2) purchase Alberta-based offset credits; (3) purchase or use Emission Performance Credits (credits generated by other facilities that have reduced emissions below SGER specifications); or (4) purchase technology offset credits by contributing to Government of Alberta administered CCEMC. Payments into the CCEMC will increase to $20 per tonne of CO2 over a facility’s budget in 2016 and $30 per tonne in 2017, which will increase our operating costs in respect of the Fort Saskatchewan Storage and Fractionation Facility.
In 2015, Alberta’s newly elected Government announced the Specified Gas Emitters Amendment Regulation, which introduced a fifth way for regulated facilities to meet their net emissions intensity limit—the cogeneration compliance adjustment (“CCA”) for the year—which is to be defined in the as of yet unpublished Standard for Completing Greenhouse Gas Compliance Reports.
Following the SGER amendments, the Government of Alberta appointed the Climate Change Advisory Panel to review current climate change policies and consult with public, industry, environmental and First Nations groups on climate change strategies. On November 26, 2015, the Government of Alberta released both the panel’s Climate Leadership Report to Minister (the “Report”) and its Climate Leadership Plan (the “Plan”). The Plan highlights four key strategies to address climate change: (1) completing the phase out of coal-fired sources of electricity by 2030, with cleaner, renewable energy sources in coal’s place; (2) replacing the current emissions intensity carbon pricing program with an emissions performance standard; (3) capping oil sands emissions to 100 megatonnes per year with a carbon price for oil sands facilities; and (4) reducing methane emissions by 45% by 2025.
The Government of Alberta is still developing the details of how the Plan will be implemented, but the Report states that carbon pricing will be central to the new strategy. The Report proposes a Carbon Competitiveness Regulation (“CCR”) to replace the SGER, under which the carbon price would reach $30 per tonne by 2018. The CCR would also include elements of cap-and-trade and carbon tax regimes with distinctions between large industrial emissions (facilities emitting greater than 100,000 tonnes of GHG annually) and end-use emissions (those from transportation and heating fuels). The Report also states that the 100 megatonne limit on oil sands facilities will be subject to exceptions for cogeneration and new upgrading capacity.
The SGRR introduces the Specified Gas Reporting Standard (the “Standard”), a document published by Alberta Environment and Parks, which sets out the minimum emission levels before facility reporting requirements begin. Under the current version of the Standard, the threshold level for submission of a specified gas report is the release of 50,000 tonnes of GHG in a calendar year. Regulated facilities must also report emissions of industrial air pollutants and comply with obligations imposed under permits. Alberta’s 2008 climate change plan set a goal of 14% absolute reduction in GHG emissions below 2005 levels in the province by 2050. Whether or not the impending climate change plan from the new Government of Alberta will align with this goal remains to be seen.
In Saskatchewan, The Management and Reduction of Greenhouse Gases Act (“MRGGA”) received royal assent on May 20, 2010; however, currently, there does not appear to be political will to progress the MRGGA.
Water
The Federal Water Pollution Control Act, as amended, also known as the Clean Water Act (“CWA”), and analogous state and Canadian federal and provincial laws impose restrictions and strict controls regarding the discharge of pollutants into navigable waters of the United States and Canada, as well as state and provincial waters. See “—Pipeline Safety/Pipeline and Storage Tank Integrity Management” above and Note 16 to our Consolidated Financial Statements. Federal, state and provincial regulatory agencies can impose administrative, civil and/or criminal penalties for non-compliance with discharge permits or other requirements of the CWA.
The Oil Pollution Act of 1990 (“OPA”) amended certain provisions of the CWA, as they relate to the release of petroleum products into navigable waters. OPA subjects owners of facilities to strict, joint and potentially unlimited liability for containment and removal costs, natural resource damages and certain other consequences of an oil spill. State and Canadian federal and provincial laws also impose requirements relating to the prevention of oil releases and the remediation of areas affected by releases when they occur.
With respect to our new pipeline construction activities and maintenance on our existing pipelines, Section 404 of the CWA authorizes the Army Corps of Engineers (“Corps”) to permit the discharge of dredged or fill materials into “navigable waters,” which are defined as “the waters of the United States.” Section 404 (e) authorizes the Corps to issue permits on a nationwide basis for categories of discharges that have no more than minimal individual or cumulative environmental effects. For the past 35 years, the Corps has authorized construction, maintenance and repair of pipelines under a streamlined nationwide permit program known as Nationwide Permit 12 (“NWP”). The NWP is supported by strong statutory and regulatory history and was originally approved by Congress in 1977. From time to time, environmental groups have challenged the NWP; however, to date, federal courts have upheld the validity of the NWP under the CWA. We cannot predict whether future lawsuits will be filed to contest the validity of the NWP; however, in the event that a court wholly or partially strikes down the NWP, which we believe to be unlikely, we could face significant delays and financial costs when seeking project approvals from the Corps. In addition, the EPA published a final rule in May 2015 that attempted to clarify federal jurisdiction under the CWA over waters of the United States, but a number of legal challenges to this rule are pending, and implementation of the rule has been stayed nationwide. To the extent the rule expands the scope of the CWA’s jurisdiction, we could face increased costs and delays with respect to obtaining permits for dredge and fill activities in wetland areas.
Endangered Species
New projects may require approvals and environmental analysis under federal, state and provincial laws, including the National Environmental Policy Act and the Endangered Species Act in the United States and the Species at Risk Act in Canada. The resulting costs and liabilities could materially and negatively affect the viability of such projects.
Other Regulation
Transportation Regulation
Our transportation activities are subject to regulation by multiple governmental agencies. Our historical operating costs reflect the recurring costs resulting from compliance with these regulations. The following is a summary of the types of transportation regulation that may impact our operations.
General Interstate Regulation. Our interstate common carrier liquids pipeline operations are subject to rate regulation by the FERC under the Interstate Commerce Act (“ICA”). The ICA requires that tariff rates for liquids pipelines, which include both crude oil pipelines and refined products pipelines, be just and reasonable and non-discriminatory.
State Regulation. Our intrastate liquids pipeline transportation activities are subject to various state laws and regulations, as well as orders of state regulatory bodies, including the Railroad Commission of Texas (“TRRC”) and the California Public Utility Commission (“CPUC”). The CPUC prohibits certain of our subsidiaries from acting as guarantors of our senior notes and credit facilities.
Regulation of OCS Pipelines. The Outer Continental Shelf Lands Act requires that all pipelines operating on or across the OCS provide open access, non-discriminatory transportation service. In June 2008, the Minerals Management Service (now replaced by the Bureau of Ocean Energy Management, Regulation and Enforcement) issued a final rule establishing formal and informal complaint procedures for shippers that believe they have been denied open and nondiscriminatory access to transportation on the OCS.
Energy Policy Act of 1992 and Subsequent Developments. In October 1992, Congress passed the Energy Policy Act of 1992 (“EPAct”), which, among other things, required the FERC to issue rules to establish a simplified and generally applicable ratemaking methodology for petroleum pipelines and to streamline procedures in petroleum pipeline proceedings. The FERC responded to this mandate by establishing a formulaic methodology for petroleum pipelines to change their rates within prescribed ceiling levels that are tied to an inflation index. The FERC reviews the formula every five years. Effective July 1, 2011, the annual index adjustment for the five year period ending June 30, 2016 will equal the producer price index for finished goods for the applicable year plus an adjustment factor of 2.65%. In December 2015, the FERC established an index level of the producer price index for finished goods plus 1.23% for the five-year period commencing July 1, 2016. Pipelines may raise their rates to the rate ceiling level generated by application of the annual index adjustment factor each year; however, a shipper may challenge such increase if the increase in the pipeline’s rates was substantially in excess of the actual cost increases incurred by the pipeline during the relevant year. If the FERC’s annual index adjustment reduces the ceiling level such that it is lower than a pipeline’s filed rate, the pipeline must reduce its rate to conform with the lower ceiling unless doing so would reduce a rate “grandfathered” by the EPAct (see below) to below the grandfathered level. A pipeline must, as a general rule, use the indexing methodology to change its rates. The FERC, however, retained cost-of-service ratemaking, market-based rates and settlement rates as alternatives to the indexing approach that may be used in certain specified circumstances. Because the indexing methodology for the next five-year period is tied to an inflation index and is not based on pipeline-specific costs, the indexing methodology could hamper our ability to recover cost increases.
Under the EPAct, petroleum pipeline rates in effect for the 365-day period ending on the date of enactment of EPAct are deemed to be just and reasonable under the ICA, if such rates had not been subject to complaint, protest or investigation during such 365-day period. Generally, complaints against such “grandfathered” rates may only be pursued if the complainant can show that a substantial change has occurred since the enactment of EPAct in either the economic circumstances of the oil pipeline or in the nature of the services provided that were a basis for the rate. EPAct places no such limit on challenges to a provision of an oil pipeline tariff as unduly discriminatory or preferential.
Canadian Regulation. Our Canadian pipeline assets are subject to regulation by the NEB and by provincial authorities, such as the AER. With respect to a pipeline over which it has jurisdiction, the relevant regulatory authority has the power, upon application by a third party, to determine the rates we are allowed to charge for transportation on, and set other terms of access to, such pipeline. In such circumstances, if the relevant regulatory authority determines that the applicable terms and conditions of service are not just and reasonable, the regulatory authority can impose conditions it considers appropriate.
Our Pipelines. The FERC generally has not investigated rates of liquids pipelines on its own initiative when those rates have not been the subject of a protest or complaint by a shipper. The majority of our Transportation segment profit in the United States is produced by rates that are either grandfathered or set by agreement with one or more shippers.
Trucking Regulation
United States
We operate a fleet of trucks to transport crude oil and oilfield materials as a private, contract and common carrier. We are licensed to perform both intrastate and interstate motor carrier services. As a motor carrier, we are subject to certain safety regulations issued by the DOT. The trucking regulations cover, among other things: (i) driver operations, (ii) log book maintenance, (iii) truck manifest preparations, (iv) safety placard placement on the trucks and trailer vehicles, (v) drug and alcohol testing, (vi) operation and equipment safety and (vii) many other aspects of truck operations. We are also subject to OSHA with respect to our trucking operations.
Canada
Our trucking assets in Canada are subject to regulation by both federal and provincial transportation agencies in the provinces in which they are operated. These regulatory agencies do not set freight rates, but do establish and administer rules and regulations relating to other matters including equipment, facility inspection, reporting and safety. We are licensed to operate both intra- and inter-provincially under the direction of the National Safety Code (“NSC”) that is administered by Transport Canada. Our for-hire service is primarily the transportation of crude oil, condensates and NGL. We are required under the NSC to, among other things, monitor: (i) driver operations, (ii) log book maintenance, (iii) truck manifest preparations, (iv) safety placard placement on the trucks and trailers, (v) operation and equipment safety and (vi) many other aspects of trucking operations. We are also subject to Occupational Health and Safety regulations with respect to our trucking operations.
Railcar Regulation
We own and operate a number of railcar loading and unloading facilities in the United States and Canada. In connection with these rail terminals, we own and lease a significant number of railcars. Our railcar operations are subject to the regulatory jurisdiction of the Federal Railroad Administration of the DOT, the Occupational Safety and Health Administration, as well as other federal and state regulatory agencies and Canadian regulatory agencies for operations in Canada.
Railcar accidents involving trains carrying crude oil from North Dakota’s Bakken shale formation have led to increased regulatory scrutiny. PHMSA issued a safety advisory warning that Bakken crude may be more flammable than other grades of crude oil and reinforcing the requirement to properly test, characterize, classify, and where appropriate sufficiently degasify hazardous materials prior to and during transportation. PHMSA also initiated “Operation Classification”, a compliance initiative involving unannounced inspections and testing of crude oil samples to verify that offerors of the materials have properly classified, described and labeled the hazardous materials before transportation. In May 2015, PHMSA adopted a final rule that, among other things, imposes a new tank car design standard, a phase out by as early as January 2018 for older DOT-111 tank cars that are not retrofitted, and a classification and testing program for unrefined petroleum based products, including crude oil. The rule also includes new operational requirements such as speed restrictions. On December 3, 2015, Congress passed the Fixing America’s Transportation (“FAST”) Act which was subsequently signed by the President on December 7, 2015. This legislation clarified the parameters around the timeline and requirements for railcars hauling crude oil in the United States.
In December 2014, the North Dakota Industrial Commission adopted new standards to improve the safety of Bakken crude oil for transport. The new standard, Commission Order 25417, was effective April 1, 2015, and requires operators/producers to condition Bakken crude oil to certain vapor pressure limits. Under the order, all Bakken crude oil produced in North Dakota will be conditioned with no exceptions. The order requires operators/producers to separate light hydrocarbons from all Bakken crude oil to be transported and prohibits the blending of light hydrocarbons back into oil supplies prior to shipment. We are not directly responsible for the conditioning or stabilization of Bakken crude oil, however, under the order, it is our responsibility to notify the State of North Dakota upon discovering that Bakken crude oil received at our rail facility exceeds certain vapor pressure limits.
Cross Border Regulation
As a result of our cross border activities, including importation of crude oil, NGL and natural gas between the United States and Canada, we are subject to a variety of legal requirements pertaining to such activities including export/import license requirements, tariffs, Canadian and U.S. customs and taxes and requirements relating to toxic substances. U.S. legal requirements relating to these activities include regulations adopted pursuant to the Short Supply Controls of the Export Administration Act, the North American Free Trade Agreement and the Toxic Substances Control Act. In addition, the importation and exportation of natural gas from and to the United States and Canada is subject to regulation by U.S. Customs and Border Protection, U.S. Department of Energy and the NEB. Violations of these licensing, tariff and tax reporting requirements or failure to provide certifications relating to toxic substances could result in the imposition of significant administrative, civil and criminal penalties. Furthermore, the failure to comply with U.S. federal, state and local tax requirements, as well as Canadian federal and provincial tax requirements, could lead to the imposition of additional taxes, interest and penalties.
Market Anti-Manipulation Regulation
In November 2009, the Federal Trade Commission (“FTC”) issued regulations pursuant to the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007, intended to prohibit market manipulation in the petroleum industry. Violators of the regulations face civil penalties of up to $1 million per violation per day. In July 2010, Congress passed the Dodd-Frank Act, which incorporated an expansion of the authority of the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (“CFTC”) to prohibit market manipulation in the markets regulated by the CFTC. This authority, with respect to crude oil swaps and futures contracts, is similar to the anti-manipulation authority granted to the FTC with respect to crude oil purchases and sales. In July 2011, the CFTC issued final rules to implement their new anti-manipulation authority. The rules subject violators to a civil penalty of up to the greater of $1 million or triple the monetary gain to the person for each violation.
Natural Gas Storage Regulation
Our natural gas storage operations are subject to regulatory oversight by numerous federal, state and local regulatory agencies, many of which are authorized by statute to issue, and have issued, rules and regulations binding on the natural gas storage and pipeline industry, related businesses and market participants. The failure to comply with such laws and regulations can result in substantial penalties and fines.
The following is a summary of the kinds of regulation that may impact our natural gas storage operations. However, our unitholders should not rely on such discussion as an exhaustive review of all regulatory considerations affecting our natural gas storage operations.
Our natural gas storage facilities provide natural gas storage services in interstate commerce and are subject to comprehensive regulation by the FERC under the Natural Gas Act of 1938 (“NGA”). Pursuant to the NGA and FERC regulations, storage providers are prohibited from making or granting any undue preference or advantage to any person or subjecting any person to any undue prejudice or disadvantage or from maintaining any unreasonable difference in rates, charges, service, facilities, or in any other respect. The terms and conditions for services provided by our facilities are set forth in natural gas tariffs on file with the FERC. We have been granted market-based rate authorization for the services that our facilities provide. Market-based rate authority allows us to negotiate rates with individual customers based on market demand.
The FERC also has authority over the siting, construction, and operation of United States pipeline transportation and storage facilities and related facilities used in the transportation, storage and sale for resale of natural gas in interstate commerce, including the extension, enlargement or abandonment of such facilities. The FERC’s authority extends to maintenance of accounts and records, terms and conditions of service, acquisition and disposition of facilities, initiation and discontinuation of services, imposition of creditworthiness and credit support requirements applicable to customers and relationships among pipelines and storage companies and certain affiliates. Our natural gas storage entities are required by the FERC to post certain information daily regarding customer activity, capacity and volumes on their respective websites. Additionally, the FERC has jurisdiction to impose rules and regulations applicable to all natural gas market participants to ensure market transparency. FERC regulations require that buyers and sellers of
more than a de minimis volume of natural gas report annual numbers and volumes of relevant transactions to the FERC. Our natural gas storage facilities and related marketing entities are subject to these annual reporting requirements.
Under the Energy Policy Act of 2005 (“EPAct 2005”) and related regulations, it is unlawful in connection with the purchase or sale of natural gas or transportation services subject to FERC jurisdiction to use or employ any device, scheme or artifice to defraud; to make any untrue statement of material fact or omit to make any such statement necessary to make the statements made not misleading; or to engage in any act or practice that operates as a fraud or deceit upon any person. EPAct 2005 gives the FERC civil penalty authority to impose penalties for certain violations of up to $1 million per day for each violation. FERC also has the authority to order disgorgement of profits from transactions deemed to violate the NGA and the EPAct 2005.
The natural gas industry historically has been heavily regulated. New rules, orders, regulations or laws may be passed or implemented that impose additional costs, burdens or restrictions on us. We cannot give any assurance regarding the likelihood of such future rules, orders, regulations or laws or the effect they could have on our business, financial condition, and results of operations or ability to make distributions to our unitholders.
Operational Hazards and Insurance
Pipelines, terminals, trucks or other facilities or equipment may experience damage as a result of an accident or natural disaster. These hazards can cause personal injury and loss of life, severe damage to and destruction of property and equipment, pollution or environmental damage and suspension of operations. Since the time we and our predecessors commenced midstream crude oil activities in the early 1990s, we have maintained insurance of various types and varying levels of coverage that we consider adequate under the circumstances to cover our operations and properties. The insurance policies are subject to deductibles and retention levels that we consider reasonable and not excessive. However, such insurance does not cover every potential risk associated with operating pipelines, terminals and other facilities, including the potential loss of significant revenues. Consistent with insurance coverage generally available to the industry, in certain circumstances our insurance policies provide limited coverage for losses or liabilities relating to gradual pollution, with broader coverage for sudden and accidental occurrences. Over the last several years, our operations have expanded significantly, with total PAA assets increasing over 35 times since the end of 1998. At the same time that the scale and scope of our business activities have expanded, the breadth and depth of the available insurance markets have contracted. The overall cost of such insurance as well as the deductibles and overall retention levels that we maintain have increased. As a result, we have elected to self-insure more activities against certain of these operating hazards and expect this trend will continue in the future. Due to the events of September 11, 2001, insurers have excluded acts of terrorism and sabotage from our insurance policies. We have elected to purchase a separate insurance policy for acts of terrorism and sabotage.
Since the terrorist attacks, the United States Government has issued numerous warnings that energy assets, including our nation’s pipeline infrastructure, may be future targets of terrorist organizations. These developments expose our operations and assets to increased risks. We have instituted security measures and procedures in conformity with DOT guidance. We will institute, as appropriate, additional security measures or procedures indicated by the DOT or the Transportation Safety Administration. However, there can be no assurance that these or any other security measures would protect our facilities from an attack. Any future terrorist attacks on our facilities, those of our customers and, in some cases, those of our competitors, could have a material adverse effect on our business, whether insured or not.
The occurrence of a significant event not fully insured, indemnified or reserved against, or the failure of a party to meet its indemnification obligations, could materially and adversely affect our operations and financial condition. We believe we are adequately insured for third-party liability and property damage to others with respect to our operations. With respect to all of our coverage, no assurance can be given that we will be able to maintain adequate insurance in the future at rates we consider reasonable, or that we have established adequate reserves to the extent that such risks are not insured.
Title to Properties and Rights-of-Way
Our real property holdings are generally comprised of: (i) parcels of land that we own in fee, (ii) surface leases, underground storage leases and (iii) easements, rights-of-way, permits, crossing agreements or licenses from landowners or governmental authorities permitting the use of certain lands for our operations. We believe we have satisfactory title or the right to use the sites upon which our significant facilities are located, subject to customary liens, restrictions or encumbrances. Except for challenges that we do not regard as material relative to our overall operations, we have no knowledge of any challenge to the underlying fee title of any material fee, lease, easement, right-of-way, permit or license held by us or to our rights pursuant to any material deed, lease, easement, right-of-way, permit or license, and we believe that we have satisfactory rights pursuant to all of our material leases, easements, rights-of-way, permits and licenses. Some of our real property rights (mainly for pipelines) may be subject to termination under agreements
that provide for one or more of: periodic payments, term periods, renewal rights, revocation by the licensor or grantor and possible relocation obligations.
Employees and Labor Relations
Through GP LLC or its affiliates, we employed approximately 5,400 employees at December 31, 2015. None of these employees were subject to a collective bargaining agreement, except for nine employees covered by an agreement scheduled for renegotiation in September 2016 and another nine employees covered by a separate agreement scheduled for renegotiation in September 2018. Also, a first collective agreement is being negotiated for 66 employees who recently unionized in Canada. We consider employee relations to be good.
Summary of Tax Considerations
The following is a summary of material U.S. federal income tax consequences, tax considerations, and in the case of a non-U.S. holder, estate tax consequences related to the purchase, ownership and disposition of our Class A shares by a taxpayer that holds our Class A shares as a “capital asset” (generally property held for investment). This summary is based on the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (“the Code”), U.S. Treasury regulations and administrative rulings and judicial decisions, all as in effect on the date hereof, and all of which are subject to change, possibly with retroactive effect. We have not sought any ruling from the Internal Revenue Service, or the IRS, with respect to the statements made and the conclusions reached in the following summary, and there can be no assurance that the IRS will agree with such statements and conclusions.
This summary does not address all aspects of U.S. federal income and estate taxation or the tax considerations arising under the laws of any non-U.S., state, or local jurisdiction, or under U.S. federal gift tax laws. In addition, this summary does not address tax considerations applicable to investors that may be subject to special treatment under the U.S. federal income tax laws. The tax consequences of ownership of Class A shares depends in part on the owner’s individual tax circumstances. It is the responsibility of each shareholder, either individually or through a tax advisor, to investigate the legal and tax consequences, under the laws of pertinent U.S. federal, states and localities, as well as Canada and the Canadian provinces, of the shareholder’s investment in us. Further, it is the responsibility of each shareholder to file all U.S. federal, Canadian, state, provincial and local tax returns that may be required of the shareholder. Also see Item 1A. “Risk Factors—Tax Risks.”
Corporate Status
Although we are a Delaware limited partnership, we have elected to be treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes. As a result, we are subject to tax as a corporation and distributions on the Class A shares will be treated as distributions on corporate stock for federal income tax purposes. No Schedule K-1s will be issued with respect to the Class A shares, but instead holders of Class A shares will receive a Form 1099 from us with respect to distributions received on the Class A shares.
Consequences to U.S. Holders
The discussion in this section is addressed to holders of our Class A shares who are U.S. holders for U.S. federal income tax purposes. A U.S. holder for purposes of this discussion is a beneficial owner of our Class A shares and who is, for U.S. federal income tax purposes:
· an individual citizen or resident of the United States;
· a corporation, or other entity taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, that was created or organized in or under the laws of the United States, any state thereof or the District of Columbia;
· an estate whose income is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source; or
· a trust if (i) a U.S. court can exercise primary supervision over the trust’s administration and one or more United States persons are authorized to control all substantial decisions of the trust or (ii) certain circumstances apply and the trust has validly elected to be treated as a United States person.
Distributions
Distributions with respect to our Class A shares will constitute dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes to the extent paid from our current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles. To the extent that the amount of a distribution with respect to our Class A shares exceeds our current and accumulated earnings and profits, such distribution will be treated first as a tax-free return of capital to the extent of the U.S. holder’s adjusted tax basis in such Class A shares, which reduces such basis dollar-for-dollar, and thereafter as capital gain. Such gain will be long-term capital gain provided that the U.S. holder has held such Class A shares for more than one year as of the time of the distribution. Non-corporate holders that receive distributions on our Class A shares that are treated as dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes generally would be subject to U.S. federal income tax at a maximum tax rate of 20% on such dividends provided certain holding period requirements are met.
Both AAP and PAA have made elections permitted by Section 754 of the Code. As a result, our initial acquisition of interests in AAP resulted in basis adjustments with respect to our interest in the assets of AAP (and indirectly in PAA). Such adjustments resulted in depreciation and amortization deductions that we anticipate will offset a substantial portion of our taxable income for an extended period of time. In addition, future exchanges of retained interests in AAP and Class B shares in us for our Class A shares will result in additional basis adjustments with respect to our interest in the assets of AAP (and indirectly in PAA). We expect to benefit from additional tax deductions resulting from those adjustments, the amount of which will vary depending on the value of the Class A shares at the time of the exchange.
We do not expect to have any earnings and profits for an extended period of time, which we estimate will include, at a minimum, each of the periods ending December 31, 2016 and 2017 and we may not have sufficient earnings and profits during future tax years for any distributions on our Class A shares to qualify as dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes. If a distribution on our Class A shares fails to qualify as a dividend for U.S. federal income tax purposes, U.S. corporate holders would be unable to utilize the corporate dividends-received deduction.
Prospective investors in our Class A shares are encouraged to consult their tax advisors as to the tax consequences of receiving distributions on our Class A shares that do not qualify as dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes, including, in the case of prospective corporate investors, the inability to claim the corporate dividends received deduction with respect to such distributions.
Gain on Disposition of Class A Shares
A U.S. holder generally will recognize capital gain or loss on a sale, exchange, certain redemptions, or other taxable disposition of our Class A shares equal to the difference, if any, between the amount realized upon the disposition of such Class A shares and the U.S. holder’s adjusted tax basis in those shares. A U.S. holder’s tax basis in the shares generally will be equal to the amount paid for such shares reduced (but not below zero) by distributions received on such shares that are not treated as dividends for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Such capital gain or loss generally will be long-term capital gain or loss if the U.S. holder’s holding period for the shares sold or disposed of is more than one year. Long-term capital gains of individuals generally are subject to a reduced maximum U.S. federal income tax rate of 20%. The deductibility of net capital losses is subject to limitations.
Backup Withholding and Information Reporting
Information returns generally will be filed with the IRS with respect to distributions on our Class A shares and the proceeds from a disposition of our Class A shares. U.S. holders may be subject to backup withholding on distributions with respect to our Class A shares and on the proceeds of a disposition of our Class A shares unless such U.S. holders furnish the applicable withholding agent with a taxpayer identification number, certified under penalties of perjury, and certain other information, or otherwise establish, in the manner prescribed by law, an exemption from backup withholding. Penalties apply for failure to furnish correct information and for failure to include reportable payments in income.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld under the backup withholding rules will be creditable against a U.S. holder’s U.S. federal income tax liability, and the U.S. holder may be entitled to a refund, provided the U.S. holder timely furnishes the required information to the IRS. U.S. holders are urged to consult their own tax advisors regarding the application of the backup withholding rules to their particular circumstances and the availability of, and procedure for, obtaining an exemption from backup withholding.
Consequences to Non-U.S. Holders
The discussion in this section is addressed to holders of our Class A shares who are non-U.S. holders for U.S. federal income tax purposes. For purposes of this discussion, a non-U.S. holder is a beneficial owner of our Class A shares that is an individual, corporation, estate or trust that is not a U.S. holder as defined above.
Distributions
Generally, a distribution treated as a dividend paid to a non-U.S. holder on our Class A shares will be subject to U.S. withholding tax at a rate of 30% of the gross amount of the distribution, or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty. To the extent a distribution exceeds our current and accumulated earnings and profits, such distribution will reduce the non-U.S. holder’s adjusted tax basis in its Class A shares (but not below zero). The amount of any such distribution in excess of the non-U.S. holder’s adjusted tax basis in its Class A shares will be treated as gain from the sale of such shares and will have the tax consequences described below under “Gain on Disposition of Class A Shares.” The rules applicable to distributions by “USRPHCs” (as defined below) to non-U.S. persons that exceed current and accumulated earnings and profits are not clear. As a result, it is possible that U.S. federal income tax at a rate not less than 10% (or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty for distributions from a USRPHC) may be withheld from distributions received by non-U.S. holders that exceed our current and accumulated earnings and profits. To receive the benefit of a reduced treaty rate on distributions, a non-U.S. holder must provide the withholding agent with an IRS W-8BEN (or other appropriate form) certifying qualification for the reduced rate.
Non-U.S. holders are encouraged to consult their tax advisors regarding the withholding rules applicable to distributions on our Class A shares, the requirement for claiming treaty benefits, and any procedures required to obtain a refund of any overwithheld amounts.
Distributions treated as dividends that are paid to a non-U.S. holder and are effectively connected with a trade or business conducted by the non-U.S. holder in the United States (and, if required by an applicable tax treaty, are attributable to a permanent establishment maintained by the non-U.S. holder in the United States) generally will be taxed on a net income basis at the rates and in the manner generally applicable to U.S. persons (as defined under the Code). Effectively connected dividend income will not be subject to U.S. withholding tax if the non-U.S. holder satisfies certain certification requirements by providing to the withholding agent a properly executed IRS Form W-8ECI (or successor form) certifying eligibility for the exemption. If the non-U.S. holder is a corporation, that portion of the corporation’s earnings and profits for the taxable year, as adjusted for certain items, that is effectively connected with its U.S. trade or business (and, if required by applicable income tax treaty, is attributable to a permanent establishment maintained by the corporate non-U.S. holder in the United States) may also be subject to a “branch profits tax” at a 30% rate or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable tax treaty.
Gain on Disposition of Class A Shares
A non-U.S. holder generally will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax on any gain realized upon the sale or other disposition of our Class A shares unless:
· the non-U.S. holder is an individual who is present in the United States for a period or periods aggregating 183 days or more during the calendar year in which the sale or disposition occurs and certain other conditions are met;
· the gain is effectively connected with a trade or business conducted by the non-U.S. holder in the United States (and, if required by an applicable tax treaty, is attributable to a permanent establishment maintained by the non-U.S. holder in the United States); or
· our Class A shares constitute a U.S. real property interest by reason of our status as a United States real property holding corporation, or USRPHC, for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
A non-U.S. holder described in the first bullet point above will be subject to tax at a rate of 30% (or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable tax treaty) on the amount of such gain (which may be offset by U.S. source capital losses).
A non-U.S. holder whose gain is described in the second bullet point above will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on any gain recognized on a net income basis at the same graduated rates generally applicable to U.S. persons unless an applicable tax treaty provides otherwise. Corporate non-U.S. holders may also be subject to a branch profits tax equal to 30% (or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable tax treaty) of their effectively connected earnings and profits attributable to such gain, as adjusted for certain items.
Generally, a corporation is a USRPHC if the fair market value of its U.S. real property interests equals or exceeds 50% of the sum of the fair market value of its worldwide real property interests and its other assets used or held for use in a trade or business. We believe that we currently are, and expect to remain for the foreseeable future, a USRPHC for U.S. federal income tax purposes. However, as long as our Class A shares are “regularly traded on an established securities market,” a non-U.S. holder will be taxable on gain recognized on the disposition of our Class A shares as a result of our status as a USRPHC only if the non-U.S. holder actually or constructively owns, or owned at any time during the five-year period ending on the date of the disposition or, if shorter, the non-U.S. holder’s holding period for the Class A shares, more than 5% of our Class A shares. If our Class A shares were not considered to be regularly traded on an established securities market, all non-U.S. holders would be subject to U.S. federal income tax on a disposition of our Class A shares, and a 10% withholding tax would apply to the gross proceeds from the sale of our Class A shares by such non-U.S. holder. Non-U.S. holders should consult their tax advisors with respect to the application of the foregoing rules to their ownership and disposition of our Class A shares.
U.S. Federal Estate Tax
Our Class A shares beneficially owned or treated as owned by an individual who is not a citizen or resident of the United States (as defined for U.S. federal estate tax purposes) at the time of death generally will be includable in the decedent’s gross estate for U.S. federal estate tax purposes, unless an applicable estate tax treaty provides otherwise, and therefore may be subject to U.S. federal estate tax.
Backup Withholding and Information Reporting
Generally, we must report annually to the IRS and to each non-U.S. holder the amount of dividends paid to such holder, the name and address of the recipient, and the amount, if any, of tax withheld with respect to those dividends. These information reporting requirements apply even if withholding was not required. Pursuant to tax treaties or other agreements, the IRS may make such reports available to tax authorities in the recipient’s country of residence.
Payments of dividends to a non-U.S. holder generally will not be subject to backup withholding if the non-U.S. holder establishes an exemption by properly certifying its non-U.S. status on an IRS Form W-8BEN or another appropriate version of IRS Form W-8, provided that the withholding agent does not have actual knowledge, or reason to know, that the beneficial owner is a U.S. person that is not an exempt recipient.
Payments of the proceeds from a sale or other disposition by a non-U.S. holder of our Class A shares effected by or through a U.S. office of a broker generally will be subject to information reporting and backup withholding (at the applicable rate) unless the non-U.S. holder establishes an exemption by properly certifying its non-U.S. status on an IRS Form W-8BEN or another appropriate version of IRS Form W-8 and certain other conditions are met or the non-U.S. holder otherwise establishes an exemption. Information reporting and backup withholding generally will not apply to any payment of the proceeds from a sale or other disposition of our Class A shares effected outside the United States by a foreign office of a broker. However, unless such broker has documentary evidence in its records that the holder is a non-U.S. holder and certain other conditions are met, or the non-U.S. holder otherwise establishes an exemption, information reporting will apply to a payment of the proceeds of the disposition of our Class A shares effected outside the United States by such a broker if it has certain relationships within the United States.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Rather, the U.S. income tax liability (if any) of persons subject to backup withholding will be reduced by the amount of tax withheld. If withholding results in an overpayment of taxes, a refund may be obtained, provided that certain required information is timely furnished to the IRS.
Legislation Affecting Class A Shares Held Through Foreign Accounts
Legislation enacted in 2010 imposes a 30% withholding tax on any dividends on our Class A shares and on the gross proceeds from a disposition of our Class A shares in each case if paid to a foreign financial institution or a non-financial foreign entity (including, in some cases, when such foreign financial institution or entity is acting as an intermediary), unless (i) in the case of a foreign financial institution, such institution enters into an agreement with the U.S. government to withhold on certain payments, and to collect and provide to the U.S. tax authorities substantial information regarding U.S. account holders of such institution (which includes certain equity and debt holders of such institution, as well as certain account holders that are foreign entities with U.S. owners), (ii) in the case of a non-financial foreign entity, such entity certifies that it does not have any substantial U.S. owners or provides the withholding agent with a certification identifying the direct and indirect substantial U.S. owners of the entity, or (iii) the foreign financial institution or non-financial foreign entity otherwise qualifies for an exemption from these rules. Under certain circumstances, a holder might be eligible for refunds or credits of such taxes.
Payments subject to withholding tax under this law generally include dividends paid on Class A shares after June 30, 2014, and gross proceeds from sales or redemptions of such Class A shares after December 31, 2016. Non-U.S. holders are encouraged to consult their tax advisors regarding the possible implications of this law.
3.8% Tax on Unearned Income
Certain holders that are individuals, trusts or estates will be subject to an additional 3.8% Medicare tax on unearned income, which generally will include dividends received and gain recognized with respect to our Class A shares. For individual U.S. holders, the additional Medicare tax applies to the lesser of (i) “net investment income,” or (ii) the excess of “modified adjusted gross income” over $200,000 ($250,000 if married and filing jointly or $125,000 if married and filing separately). “Net investment income” generally equals a holder’s gross investment income reduced by the deductions that are allocable to such income. Investment income generally includes passive income such as interest, dividends, annuities, royalties, rents and capital gains. Holders are urged to consult their own tax advisors regarding the application of this additional Medicare tax to their particular circumstances.
Available Information
We make available, free of charge on our Internet website at ir.paagp.com, our annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) or 15(d) of the Exchange Act as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file the material with, or furnish it to, the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”).
Risks Inherent in an Investment in Us
Our cash flow will be entirely dependent upon the ability of PAA to make cash distributions to AAP, and the ability of AAP to make cash distributions to us.
The source of our earnings and cash flow currently consist exclusively of cash distributions from AAP, which currently consist exclusively of cash distributions from PAA. The amount of cash that PAA will be able to distribute to its partners, including AAP, each quarter principally depends upon the amount of cash it generates from its business. For a description of certain factors that can cause fluctuations in the amount of cash that PAA generates from its business, please read “—Risks Related to PAA’s Business” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” PAA may not have sufficient available cash each quarter to continue paying distributions at its current level or at all. If PAA reduces its per unit distribution, either because of reduced operating cash flow, higher expenses, capital requirements or otherwise, we will have less cash available for distribution and would likely be required to reduce our per share distribution. The amount of cash PAA has available for distribution depends primarily upon PAA’s cash flow, including cash flow from the release of financial reserves as well as borrowings, and is not solely a function of profitability, which will be affected by non-cash items. As a result, PAA may make cash distributions during periods when it records losses and may not make cash distributions during periods when it records profits.
Furthermore, AAP’s ability to distribute cash to us and our ability to distribute cash received from AAP to our Class A shareholders is limited by a number of factors, including:
· AAP’s payment of costs and expenses associated with our operations, and the operations of GP LLC, including expenses we incur as a result of being a public company, to the extent they are not subject to reimbursement by PAA;
· our payment of any income taxes;
· interest expense and principal payments on any indebtedness incurred by AAP or us;
· restrictions on distributions contained in AAP’s and PAA’s respective credit facilities and any future debt agreements entered into by AAP, PAA or us;
· reserves necessary for us to pay a ratable amount to AAP as necessary to permit AAP to make required capital contributions to PAA to maintain AAP’s indirect 2% general partner interest in PAA, as required by the partnership agreement of PAA upon the issuance of additional partnership interests by PAA; and
· reserves our general partner establishes for the proper conduct of our business, to comply with applicable law or any agreement binding on us or our subsidiaries (exclusive of PAA and its subsidiaries), which reserves are not subject to a limit pursuant to our partnership agreement.
A material increase in amounts paid or reserved with respect to any of these factors could restrict our ability to pay quarterly distributions to our Class A shareholders.
The IDRs AAP is entitled to receive may be limited or modified without the consent of our shareholders, which may reduce cash distributions to our Class A shareholders.
At December 31, 2015, we owned an approximate 38% limited partner interest in AAP, which owns all of PAA’s IDRs, which entitle AAP to receive increasing percentages (up to a maximum of 48%, to the extent not modified) of any cash distributed by PAA in excess of $0.225 per PAA common unit in any quarter. The vast majority of the cash flow we receive from AAP is derived from its ownership of these IDRs.
PAA, like other publicly traded partnerships, will generally only undertake an acquisition or expansion capital project if, after giving effect to related costs and expenses, the transaction would be expected to be accretive, meaning it would increase cash distributions per unit in future periods. Because AAP currently participates in the IDRs at all levels, including the highest sharing level of 48%, to the extent not modified, it is harder for an acquisition or capital project to show accretion for the common unitholders of PAA than if the IDRs received less incremental cash flow. We therefore expect that AAP may determine, in certain cases, to propose a reduction to the IDRs to facilitate a particular acquisition or expansion capital project. Any such reduction of IDRs will reduce the amount of cash that would have otherwise been distributed by AAP to us, which will in turn reduce the cash distributions we would otherwise be able to pay to our Class A shareholders. Our shareholders will not be able to vote on, or otherwise prohibit our general partner from taking, similar actions in the future and our general partner may elect to modify the IDRs without considering the interests of the holders of the Class A shares. In addition, there can be no guarantee that the expected benefits of any IDR modification will be realized.
A reduction in PAA’s distributions below certain levels will lead to a disproportionately greater reduction in the amount of cash distributions to which AAP is currently entitled.
AAP’s ownership of PAA’s IDRs entitle it to receive increasing percentages, ranging from 13% up to 48%, to the extent not modified, of all cash distributed by PAA in excess of $0.225 per PAA common unit per quarter. A decrease in the amount of distributions paid by PAA to less than $0.3375 per PAA common unit per quarter would reduce AAP’s percentage of incremental cash distributions in excess of $0.225 per PAA common unit per quarter from 48% to as low as 13%. As a result, any such reduction in quarterly cash distributions from PAA would have the effect of disproportionately reducing the amount of distributions that AAP receives from PAA in respect of the IDRs as compared to cash distributions PAA makes with respect to its 2% general partner interest and common units.
If distributions on our Class A shares are not paid with respect to any fiscal quarter, our Class A shareholders will not be entitled to receive that quarter’s payments in the future.
Our distributions to our Class A shareholders are not cumulative. Consequently, if distributions on our Class A shares are not paid with respect to any fiscal quarter, our Class A shareholders will not be entitled to receive that quarter’s payments in the future.
The amount of cash that we and PAA distribute each quarter may limit our ability to grow.
Because we distribute all of our available cash, our growth may not be as fast as the growth of businesses that reinvest their available cash to expand ongoing operations. In fact, because currently our cash flow is generated solely from distributions we receive from AAP, which are derived from AAP’s direct and indirect partnership interests in PAA, our growth will initially be completely dependent upon PAA. The amount of distributions received by AAP is based on PAA’s per unit distribution paid on each PAA common unit and the number of PAA common units outstanding. If we issue additional Class A shares or we were to incur debt or are required to pay taxes, the payment of distributions on those additional Class A shares, or interest on such debt or payment of such taxes could increase the risk that we will be unable to maintain or increase our cash distribution levels.
Our rate of growth may be reduced to the extent we purchase equity interests from PAA, which will reduce the relative percentage of the cash we receive from the IDRs.
Our business strategy includes, where appropriate, supporting the growth of PAA by making loans, purchasing equity interests or providing other forms of financial support to PAA to provide funding for the acquisition of a business or asset or for an internal growth project. To the extent we purchase equity interests from PAA that are not entitled to distributions or do not receive distributions at the same rates as the IDRs, the rate of our distribution growth may be reduced, at least in the short term, as less of our cash distributions will come from our ownership of IDRs, with respect to which distributions increase at a faster rate than PAA’s common units and any similar equity interests PAA may issue in the future.
Restrictions in AAP’s and PAA’s respective credit facilities could limit AAP’s ability to make distributions to us, thereby limiting our ability to make distributions to our Class A shareholders.
AAP’s and PAA’s respective credit facilities contain various operating and financial restrictions and covenants. AAP’s and PAA’s respective ability to comply with these restrictions and covenants may be affected by events beyond their control, including prevailing economic, financial and industry conditions. If AAP or PAA is unable to comply with these restrictions and covenants, any indebtedness under these credit facilities may become immediately due and payable and AAP’s and PAA’s respective lenders’ commitment to make further loans under these credit facilities may terminate. AAP or PAA might not have, or be able to obtain, sufficient funds to make these accelerated payments. In addition, AAP’s credit facility limits our ability to pay distributions to our Class A shareholders during an event of default or if an event of default would result from the distribution.
For more information regarding AAP’s and PAA’s credit facilities, please read “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources.” For information regarding risks related to PAA’s credit facilities, please see “—Risks Related to PAA’s Business—The terms of PAA’s indebtedness may limit its ability to borrow additional funds or capitalize on business opportunities. In addition, PAA’s future debt level may limit its future financial and operating flexibility.”
Substantially all of AAP’s assets, including the IDRs and its indirect 2% general partner interest in PAA, are pledged under AAP’s credit facility.
Substantially all of AAP’s assets, including the IDRs and its indirect 2% general partner interest in PAA, are pledged as security under AAP’s credit facility. AAP’s credit facility contains customary and other events of default. Upon an event of default, the lenders under AAP’s credit facility could foreclose on AAP’s assets, including the IDRs and its indirect 2% general partner interest in PAA, which are the only assets from which our cash flows are derived. This would have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
Our shareholders do not elect or have the power to remove our general partner and until certain conditions are met will not vote in the election of our general partner’s directors. The Class B shareholders own a sufficient number of shares to allow them to prevent the removal of our general partner.
Our shareholders have only limited voting rights on matters affecting our business and, therefore, limited ability to influence management’s decisions regarding our business. The board of directors of our general partner, including our independent directors, have been designated and elected by the Legacy Owners or their designees. Our shareholders do not currently have the ability to elect our general partner or the members of the board of directors of our general partner. However, when the overall direct and indirect economic interest of the Legacy Owners and their permitted transferees in AAP falls below 40% (calculated as described below), subject to certain time and other limitations, which we refer to as a “trigger date,” our shareholders will have the right to elect certain of our general partner’s directors. The 40% threshold referred to above will be calculated on a fully diluted basis that takes into account any Class A shares owned by the Legacy Owners and their affiliates and permitted transferees, assumes the exchange of all AAP Management Units for AAP units based on the applicable conversion factor and attributes the ownership of such AAP units to the Legacy Owners. However, as a result of our resulting governance arrangements, including a staggered board of directors, limitations on director nomination rights and the 20% voting limitation in our partnership agreement, it will be difficult for one or more of our shareholders to gain control of our general partner’s board of directors. Moreover, a period of up to three years, in certain circumstances, may lapse between the occurrence of a trigger date and the first meeting of shareholders called to elect members of our board of directors.
In addition, if our Class A shareholders are dissatisfied with the performance of our general partner, they have little ability to remove our general partner. Our general partner may only be removed by vote of the holders of at least 66 2/3% of our outstanding
shares (including both Class A and Class B shares). At December 31, 2015, the Legacy Owners owned approximately 62% of our outstanding shares. This ownership level enables the Legacy Owners to prevent our general partner’s removal.
As a result of these provisions, the price at which our shares trade may be lower because of the absence or reduction of a takeover premium in the trading price.
Our general partner may cause us to issue additional Class A shares or other equity securities, including equity securities that are senior to our Class A shares, or cause AAP to issue additional securities, in each case without shareholder approval, which may adversely affect our shareholders.
Our general partner may cause us to issue an unlimited number of additional Class A shares or other equity securities of equal rank with the Class A shares, or cause AAP to issue additional securities, in each case without shareholder approval. In addition, we may issue an unlimited number of shares that are senior to our Class A shares in right of distribution, liquidation and voting. Except for Class A shares issued in connection with the exercise of an Exchange Right, which will result in the cancellation of an equivalent number of Class B shares and therefore have no effect on the total number of outstanding shares, the issuance of additional Class A shares or our other equity securities of equal or senior rank, or the issuance by AAP of additional securities, will have the following effects:
· each shareholder’s proportionate ownership interest in us may decrease;
· the amount of cash available for distribution on each Class A share may decrease;
· the relative voting strength of each previously outstanding Class A share may be diminished;
· the ratio of taxable income to distributions may increase; and
· the market price of the Class A shares may decline.
If PAA’s unitholders remove PAA GP, AAP may be required to sell or exchange its indirect general partner interest and its IDRs and we would lose the ability to manage and control PAA.
We currently manage our investment in PAA through our membership interest in GP LLC, the general partner of AAP. PAA’s partnership agreement, however, gives unitholders of PAA the right to remove PAA GP upon the affirmative vote of holders of 66 2/3% of PAA’s outstanding units. If PAA GP withdraws as general partner in compliance with PAA’s partnership agreement or is removed as general partner of PAA where cause (as defined in PAA’s partnership agreement) does not exist and a successor general partner is elected in accordance with PAA’s partnership agreement, AAP could elect to receive cash in exchange for its 2% general partner interest and the IDRs (if then owned by AAP). If PAA GP withdraws in circumstances other than those described in the preceding sentence and a successor general partner is elected in accordance with PAA’s partnership agreement, the successor general partner will have the option to purchase the 2% general partner interest and the IDRs (if then owned by AAP) for their fair market value. If PAA GP or the successor general partner do not exercise their options, PAA GP’s interests would be converted into common units based on an independent valuation. In each case, PAA GP would also lose its ability to manage PAA.
In addition, if PAA GP is removed as general partner of PAA, we would face an increased risk of being deemed an investment company. Please read “—If in the future we cease to manage and control PAA, we may be deemed to be an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940.”
Shareholders may not have limited liability if a court finds that shareholder action constitutes control of our business.
Under Delaware law, our shareholders could be held liable for our obligations to the same extent as a general partner if a court determined that the right or the exercise of the right by our shareholders as a group to remove or replace our general partner, to approve some amendments to the partnership agreement or to take other action under our partnership agreement constituted participation in the “control” of our business. Additionally, the limitations on the liability of holders of limited partner interests for the liabilities of a limited partnership have not been clearly established in many jurisdictions.
Furthermore, Section 17-607 of the Delaware Revised Uniform Limited Partnership Act provides that, under some circumstances, a shareholder may be liable to us for the amount of a distribution for a period of three years from the date of the distribution.
If in the future we cease to manage and control PAA, we may be deemed to be an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940.
If we cease to indirectly manage and control PAA and are deemed to be an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940, we would either have to register as an investment company under the Investment Company Act of 1940, obtain exemptive relief from the SEC or modify our organizational structure or our contractual rights to fall outside the definition of an investment company. Registering as an investment company could, among other things, materially limit our ability to engage in transactions with affiliates, including the purchase and sale of certain securities or other property to or from our affiliates, restrict the ability of PAA and us to borrow funds or engage in other transactions involving leverage, require us to add additional directors who are independent of us and our affiliates, and adversely affect the price of our Class A shares.
Our partnership agreement restricts the rights of shareholders owning 20% or more of our shares.
Our shareholders’ voting rights are restricted by the provision in our partnership agreement generally providing that any shares held by a person or group that owns 20% or more of any class of shares then outstanding, other than our general partner, the Legacy Owners (or certain transferees in private, non-exchange transactions), their respective affiliates and persons who acquired such shares with the prior approval of our general partner’s board of directors, cannot be voted on any matter. In addition, our partnership agreement contains provisions limiting the ability of our shareholders to call meetings or to acquire information about our operations, as well as other provisions limiting our shareholders’ ability to influence the manner or direction of our management. As a result, the price at which our Class A shares will trade may be lower because of the absence or reduction of a takeover premium in the trading price.
If PAA’s general partner, which is owned by AAP, is not fully reimbursed or indemnified for obligations and liabilities it incurs in managing the business and affairs of PAA, its value, and, therefore, the value of our Class A shares, could decline.
AAP, GP LLC and their affiliates may make expenditures on behalf of PAA for which PAA GP will seek reimbursement from PAA. Under Delaware partnership law, PAA GP has unlimited liability for the obligations of PAA, such as its debts and environmental liabilities, except for those contractual obligations of PAA that are expressly made without recourse to the general partner. To the extent PAA GP incurs obligations on behalf of PAA, it is entitled to be reimbursed or indemnified by PAA. If PAA is unable or unwilling to reimburse or indemnify PAA GP, PAA GP may be required to satisfy those liabilities or obligations, which would reduce AAP’s cash flows to us.
The price of our Class A shares may be volatile, and holders of our Class A shares could lose a significant portion of their investments.
The market price of our Class A shares could be volatile, and our shareholders may not be able to resell their Class A shares at or above the price at which they purchased such Class A shares due to fluctuations in the market price of the Class A shares, including changes in price caused by factors unrelated to our operating performance or prospects or the operating performance or prospects of PAA. The following factors, among others, could affect our Class A share price:
· PAA’s operating and financial performance and prospects and the trading price of its common units;
· the level of PAA’s quarterly distributions and our quarterly distributions;
· quarterly variations in the rate of growth of our financial indicators, such as distributable cash flow per Class A share, net income and revenues;
· changes in revenue or earnings and distribution estimates or publication of research reports by analysts;
· speculation by the press or investment community;
· sales of our Class A shares by our shareholders;
· the exercise by the Legacy Owners of their exchange rights with respect to any retained AAP units;
· announcements by PAA or its competitors of significant contracts, acquisitions, strategic partnerships, joint ventures, securities offerings or capital commitments;
· general market conditions, including conditions in financial markets;
· changes in accounting standards, policies, guidance, interpretations or principles;
· adverse changes in tax laws or regulations;
· domestic and international economic, legal and regulatory factors related to PAA’s performance; and
· other factors described in these “Risk Factors.”
An increase in interest rates may cause the market price of our shares to decline.
Like all equity investments, an investment in our Class A shares is subject to certain risks. In exchange for accepting these risks, investors may expect to receive a higher rate of return than would otherwise be obtainable from lower-risk investments. Accordingly, as interest rates rise, the ability of investors to obtain higher risk-adjusted rates of return by purchasing government-backed debt securities may cause a corresponding decline in demand for riskier investments generally, including yield-based equity investments such as publicly traded limited partnership interests. Reduced demand for our Class A shares resulting from investors seeking other more favorable investment opportunities may cause the trading price of our Class A shares to decline.
Future sales of our Class A shares in the public market could reduce our Class A share price, and any additional capital raised by us through the sale of equity or convertible securities may have a dilutive effect on our shareholders.
Subject to certain limitations and exceptions, holders of AAP units may exchange their AAP units (together with a corresponding number of Class B shares) for Class A shares (on a one-for-one basis, subject to customary conversion rate adjustments for equity splits and reclassification and other similar transactions) and then sell those Class A shares. We may also issue additional Class A shares or convertible securities in subsequent public or private offerings.
We cannot predict the size of future issuances of our Class A shares or securities convertible into Class A shares or the effect, if any, that future issuances and sales of our Class A shares will have on the market price of our Class A shares. Sales of substantial amounts of our Class A shares (including shares issued in connection with an acquisition), or the perception that such sales could occur, may adversely affect prevailing market prices of our Class A shares.
The Legacy Owners hold a majority of the combined voting power of our Class A and Class B shares.
At December 31, 2015, the Legacy Owners held approximately 62% of the combined voting power of our Class A and Class B shares. The Legacy Owners are entitled to act separately in their own respective interests with respect to their partnership interests in us, and collectively they currently have the ability to (i) determine the outcome of all matters requiring shareholder approval, including certain mergers and other material transactions and (ii) cause or prevent a change in the composition of our board of directors or a change in control of our company that could deprive our shareholders of an opportunity to receive a premium for their Class A shares as part of a sale of our company. So long as the Legacy Owners continue to own a significant amount of our outstanding shares, even if such amount is less than 50%, they will continue to be able to strongly influence all matters requiring shareholder approval, regardless of whether or not other shareholders believe that such matters are in their own best interests.
A valuation allowance on our deferred tax asset could reduce our earnings.
A deferred tax asset of approximately $1.8 billion, that is being amortized, was recorded on our books as a result of certain of the transactions that took place in connection with our 2013 initial public offering, our November 2014 secondary offering and exchanges by Legacy Owners of AAP units and Class B shares into Class A shares. GAAP requires that a valuation allowance must be established for deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not that they will not be realized. We believe that the deferred tax asset we recorded will be realized and that a valuation allowance is not required. However, if we were to determine that a valuation allowance was appropriate for our deferred tax asset, we would be required to take an immediate charge to earnings with a corresponding reduction of partners’ capital and increase in balance sheet leverage as measured by debt-to-total capitalization.
The New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) does not require a limited partnership like us to comply with certain of its corporate governance requirements.
Because we are a limited partnership, the NYSE does not require our general partner to have a majority of independent directors on its board of directors or to establish a compensation committee or a nominating and corporate governance committee. Accordingly, our shareholders do not have the same protections afforded to certain corporations that are subject to all of the NYSE corporate governance requirements. In addition, as a limited partnership we are not required to seek shareholder approval for issuances of Class A shares, including issuances in excess of 20% of our outstanding equity securities, or for issuances of equity to certain affiliates.
We may incur liability as a result of our ownership of our and PAA’s general partner.
Under Delaware law, a general partner of a limited partnership is generally liable for the debts and liabilities of the partnership for which it serves as general partner, subject to the terms of any indemnification agreements contained in the partnership agreement and except to the extent the partnership’s contracts are non-recourse to the general partner. As a result of our structure, we indirectly own and control the general partner of PAA and own a portion of our general partner’s membership interests. Our percentage ownership of our general partner is expected to increase over time as the Legacy Owners exercise their exchange rights. To the extent the indemnification provisions in the applicable partnership agreement or non-recourse provisions in our contracts are not sufficient to protect us from such liability, we may in the future incur liabilities as a result of our ownership of these general partner entities.
Risks Related to Conflicts of Interest
Our existing organizational structure and the relationships among us, PAA, our respective general partners, the Legacy Owners and affiliated entities present the potential for conflicts of interest. Moreover, additional conflicts of interest may arise in the future among us and the entities affiliated with any general partner or similar interests we acquire or among PAA and such entities.
Conflicts of interest may arise as a result of our organizational structure and the relationships among us, PAA, our respective general partners, the Legacy Owners and affiliated entities.
Our partnership agreement defines the duties of our general partner (and, by extension, its officers and directors). Our general partner’s board of directors or its conflicts committee will have authority on our behalf to resolve any conflict involving us and they have broad latitude to consider the interests of all parties to the conflict.
Conflicts of interest may arise between us and our shareholders, on the one hand, and our general partner and its owners and affiliated entities, on the other hand, or between us and our shareholders, on the one hand, and PAA and its unitholders, on the other hand. The resolution of these conflicts may not always be in our best interest or that of our shareholders.
Our partnership agreement defines our general partner’s duties to us and contains provisions that reduce the remedies available to our shareholders for actions that might otherwise be challenged as breaches of fiduciary or other duties under state law.
Our partnership agreement contains provisions that substantially reduce the standards to which our general partner would otherwise be held by state fiduciary duty law. For example, our partnership agreement:
· permits our general partner to make a number of decisions in its individual capacity, as opposed to in its capacity as our general partner. This entitles our general partner to consider only the interests and factors that it desires, and it has no duty or obligation to give any consideration to any interest of, or factors affecting, us, the Legacy Owners, our affiliates or any limited partner. Examples include its right to vote membership interests in our general partner held by us, the exercise of its limited call right, its rights to transfer or vote any shares it may own, and its determination whether or not to consent to any merger or consolidation of our partnership or amendment to our partnership agreement;
· generally provides that our general partner will not have any liability to us or our shareholders for decisions made in its capacity as a general partner so long as it acted in good faith which, pursuant to our partnership agreement, requires a subjective belief that the determination, or other action or anticipated result thereof is in, or not opposed to, our best interests;
· generally provides that any resolution or course of action adopted by our general partner and its affiliates in respect of a conflict of interest will be permitted and deemed approved by all of our partners, and will not constitute a breach of our partnership agreement or any duty stated or implied by law or equity if the resolution or course of action in respect of such conflict of interest is:
· approved by a majority of the members of our general partner’s conflicts committee after due inquiry, based on a subjective belief that the course of action or determination that is the subject of such approval is fair and reasonable to us;
· approved by majority vote of our Class A shares and Class B shares (excluding shares owned by our general partner and its affiliates, but including shares owned by the Legacy Owners) voting together as a single class;
· determined by our general partner (after due inquiry) to be on terms no less favorable to us than those generally being provided to or available from unrelated third parties; or
· determined by our general partner (after due inquiry) to be fair and reasonable to us, which determination may be made taking into account the circumstances and the relationships among the parties involved (including our short-term or long-term interests and other arrangements or relationships that could be considered favorable or advantageous to us).
· provides that, to the fullest extent permitted by law, in connection with any action or inaction of, or determination made by, our general partner or the conflicts committee of our general partner’s board of directors with respect to any matter relating to us, it shall be presumed that our general partner or the conflicts committee of our general partner’s board of directors acted in a manner that satisfied the contractual standards set forth in our partnership agreement, and in any proceeding brought by any limited partner or by or on behalf of such limited partner or any other limited partner or our partnership challenging any such action or inaction of, or determination made by, our general partner, the person bringing or prosecuting such proceeding shall have the burden of overcoming such presumption; and
· provides that our general partner and its officers and directors will not be liable for monetary damages to us, our limited partners or assignees for any acts or omissions unless there has been a final and non-appealable judgment entered by a court of competent jurisdiction determining that our general partner or those other persons acted in bad faith or engaged in fraud or willful misconduct or, in the case of a criminal matter, acted with knowledge that such person’s conduct was criminal.
The Legacy Owners may have interests that conflict with holders of our Class A shares.
At December 31, 2015, the Legacy Owners owned approximately 62% of our outstanding shares and approximately 62% of the AAP units. As a result, the Legacy Owners may have conflicting interests with holders of Class A shares. For example, the Legacy Owners may have different tax positions from us which could influence their decisions regarding whether and when to cause us to dispose of assets.
Furthermore, conflicts of interest could arise in the future between us, on the one hand, and the Legacy Owners, on the other hand, concerning among other things, a decision whether to modify or limit the IDRs in the future or potential competitive business activities or business opportunities. These conflicts of interest may not be resolved in our favor.
If we are presented with business opportunities, PAA has the first right to pursue such opportunities.
Pursuant to the administrative agreement, we have agreed to certain business opportunity arrangements to address potential conflicts with respect to business opportunities that may arise among us, our general partner, PAA, PAA GP, AAP and GP LLC. If a business opportunity is presented to us, our general partner, PAA, PAA GP, AAP or GP LLC, then PAA will have the first right to pursue such business opportunity. We have the right to pursue and/or participate in such business opportunity if invited to do so by PAA, or if PAA abandons the business opportunity and GP LLC so notifies our general partner. Accordingly, the terms of the administrative agreement limit our ability to pursue business opportunities.
Our general partner’s affiliates and the Legacy Owners may compete with us.
Our partnership agreement provides that our general partner will be restricted from engaging in any business activities other than acting as our general partner and those activities incidental to its ownership of interests in us. The restrictions contained in our general partner’s limited liability company agreement are subject to a number of exceptions. Affiliates of our general partner and the Legacy Owners will not be prohibited from engaging in other businesses or activities that might be in direct competition with us except to the extent they compete using our confidential information.
Our general partner has a call right that may require our shareholders to sell their Class A shares at an undesirable time or price.
If at any time more than 80% of our outstanding Class A shares and Class B shares on a combined basis (including Class A shares issuable upon the exchange of Class B shares) are owned by our general partner, the Legacy Owners (or certain transferees in private, non-exchange transactions) or their respective affiliates, our general partner will have the right (which it may assign to any of its affiliates, the Legacy Owners or us), but not the obligation, to acquire all, but not less than all, of the remaining Class A shares held by public shareholders at a price equal to the greater of (x) the current market price of such shares as of the date three days before notice of exercise of the call right is first mailed and (y) the highest price paid by our general partner, the Legacy Owners (or certain transferees in private, non-exchange transactions) or their respective affiliates for such shares during the 90 day period preceding the date such notice is first mailed. As a result, holders of our Class A shares may be required to sell such Class A shares at an undesirable time or price and may not receive any return of or on their investment. Class A shareholders may also incur a tax liability upon a sale of their Class A shares. At December 31, 2015, the Legacy Owners owned approximately 62% of the Class A shares and Class B shares on a combined basis.
Risks Related to PAA’s Business
PAA may not be able to fully implement or capitalize upon planned growth projects.
PAA has a number of organic growth projects that involve the construction of new midstream energy infrastructure assets or the expansion or modification of existing assets. Many of these projects involve numerous regulatory, environmental, commercial, economic, weather-related, political and legal uncertainties that are beyond its control, including the following:
· As these projects are undertaken, required approvals, permits and licenses may not be obtained, may be delayed or may be obtained with conditions that materially alter the expected return associated with the underlying projects;
· PAA may face opposition to its planned growth projects from environmental groups, landowners, local groups and other advocates, including lawsuits or other actions designed to disrupt or delay PAA’s planned projects;
· PAA may not be able to secure, or PAA may be significantly delayed in obtaining, all of the rights of way or other real property interests it needs to complete such projects, or the costs PAA incurs in order to obtain such rights of way or other interests may be greater than PAA anticipated;
· Despite the fact that PAA will expend significant amounts of capital during the construction phase of these projects, revenues associated with these organic growth projects will not materialize until the projects have been completed and placed into commercial service, and the amount of revenue generated from these projects could be significantly lower than anticipated for a variety of reasons;
· PAA may construct pipelines, facilities or other assets in anticipation of market demand that dissipates or market growth that never materializes;
· Due to unavailability or costs of materials, supplies, power, labor or equipment, the cost of completing these projects could turn out to be significantly higher than PAA budgeted and the time it takes to complete construction of these projects and place them into commercial service could be significantly longer than planned; and
· The completion or success of PAA’s projects may depend on the completion or success of third-party facilities over which PAA have no control.
As a result of these uncertainties, the anticipated benefits associated with PAA’s capital projects may not be achieved or could be delayed. In turn, this could negatively impact PAA’s cash flow and its ability to make or increase cash distributions to its partners.
PAA’s profitability depends on the volume of crude oil, refined product, natural gas and NGL shipped, processed, purchased, stored, fractionated and/or gathered at or through the use of its facilities, which can be negatively impacted by a variety of factors outside of its control.
PAA’s profitability could be materially impacted by a decline in the volume of crude oil, natural gas, refined product and NGL transported, gathered, stored or processed at its facilities. A material decrease in crude oil or natural gas production or crude oil refining, as a result of depressed commodity prices, natural decline rates attributable to crude oil and natural gas reservoirs, a decrease in exploration and development activities, supply disruptions, economic conditions or otherwise, could result in a decline in the volume of crude oil, natural gas, refined product or NGL handled by PAA’s facilities and other energy logistics assets.
During the latter half of 2014 and continuing throughout 2015, benchmark crude oil prices declined significantly; as a result, many of the companies that produce oil and gas reduced capital expenditures for 2015 and announced further reductions for 2016. Such reduced expenditure levels, coupled with high decline rates for many horizontal wells in the shale resource plays, is beginning to lead to production declines in the Lower 48 United States (excluding Gulf of Mexico production). Other factors that could adversely impact production include reduced capital market access, increased capital raising costs for producers or adverse governmental or regulatory action. In turn, such developments could lead to reduced throughput on PAA’s pipelines and at PAA’s other facilities, which, depending on the level of production declines, could have a material adverse effect on PAA’s business.
Also, except with respect to some of our recently constructed pipeline assets, third-party shippers generally do not have long-term contractual commitments to ship crude oil on PAA’s pipelines. A decision by a shipper to substantially reduce or cease to ship volumes of crude oil on PAA’s pipelines could cause a significant decline in its revenues.
To maintain the volumes of crude oil PAA purchases in connection with its operations, PAA must continue to contract for new supplies of crude oil to offset volumes lost because of reduced drilling activity by producers, natural declines in crude oil production from depleting wells or volumes lost to competitors. If production declines, competitors with under-utilized assets could impair PAA’s ability to secure additional supplies of crude oil.
Fluctuations in supply and demand, which can be caused by a variety of factors outside of PAA’s control, can negatively affect its operating results.
Supply and demand for crude oil and other hydrocarbon products PAA handles is dependent upon a variety of factors, including price, the impact of future economic conditions, fuel conservation measures, alternative fuel requirements, governmental regulation, including climate change regulations, and technological advances in fuel economy and energy generation devices. For example, the adoption of legislation or regulatory programs to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases could increase the cost of consuming crude oil and other hydrocarbon products, thereby causing a reduction in the demand for such products. Demand also depends on the ability and willingness of shippers having access to PAA’s transportation assets to satisfy their demand by deliveries through those assets. The supply of crude oil depends on a variety of global political and economic factors, including the reliance of foreign governments on petroleum revenues. Excess global supply of crude oil may negatively impact PAA’s operating results by decreasing the price of crude oil and making production and transportation less profitable in areas PAA services.
Fluctuations in demand for crude oil, such as those caused by refinery downtime or shutdowns, can have a negative effect on PAA’s operating results. Specifically, reduced demand in an area serviced by PAA’s transportation systems will negatively affect the throughput on such systems. Although the negative impact may be mitigated or overcome by PAA’s ability to capture differentials created by demand fluctuations, this ability is dependent on location and grade of crude oil, and thus is unpredictable.
Fluctuations in demand for NGL products, whether because of general or industry specific economic conditions, new government regulations, global competition, reduced demand by consumers for products made with NGL products, increased competition from petroleum-based feedstocks due to pricing differences, mild winter weather for some NGL products, particularly propane, or other reasons, could result in a decline in the volume of NGL products PAA handles or a reduction of the fees it charges for its services. Also, increased supply of NGL products could reduce the value of NGL PAA handles and reduce the margins realized by it.
NGL and products produced from NGL also compete with products from global markets. Any reduced demand or increased supply for ethane, propane, normal butane, iso-butane or natural gasoline in the markets PAA accesses for any of the reasons stated above could adversely affect demand for the services PAA provides as well as NGL prices, which could negatively impact its operating results.
PAA’s results of operations are influenced by the overall forward market for crude oil, and certain market structures or the absence of pricing volatility may adversely impact its results.
Results from PAA’s Supply and Logistics segment are influenced by the overall forward market for crude oil. A contango market is favorable to commercial strategies that are associated with storage capacity as it allows a party to simultaneously purchase crude oil at current prices for storage and sell at higher prices for future delivery. Wide contango spreads combined with price structure volatility generally have a favorable impact on PAA’s results. A backwardated market (meaning that the price of crude oil for future deliveries is lower than current prices) can have a positive impact on lease gathering margins because in certain circumstances crude oil gatherers can capture a premium for prompt deliveries; however, in this environment there is little incentive to store crude oil as current prices are above future delivery prices. In either case, margins can be improved when prices are volatile. The periods between these two market structures are referred to as transition periods. If the market is in a backwardated to transitional structure, PAA’s results from its Supply and Logistics segment may be less than those generated during the more favorable contango market conditions. Additionally, a prolonged transition period or a lack of volatility in the pricing structure may further negatively impact PAA’s results. Depending on the overall duration of these transition periods, how PAA has allocated its assets to particular strategies and the time length of its crude oil purchase and sale contracts and storage agreements, these transition periods may have either an adverse or beneficial effect on its aggregate segment profit. A prolonged transition from a backwardated market to a contango market, or vice versa (essentially a market that is neither in pronounced backwardation nor contango), represents the least beneficial environment for PAA’s Supply and Logistics segment.
A natural disaster, catastrophe, terrorist attack, process safety failure or other event, including pipeline or facility accidents and attacks on PAA’s electronic and computer systems, could interrupt its operations and/or result in severe personal injury, property damage and environmental damage, which could have a material adverse effect on its financial position, results of operations and cash flows.
Some of PAA’s operations involve risks of personal injury, property damage and environmental damage, which could curtail its operations and otherwise materially adversely affect its cash flow. Virtually all of PAA’s operations are exposed to potential natural disasters, including hurricanes, tornadoes, storms, floods and/or earthquakes. The location of some of PAA’s assets and its customers’ assets in the U.S. Gulf Coast region makes them particularly vulnerable to hurricane or tropical storm risk. PAA’s facilities and operations are also vulnerable to accidents caused by process safety failures, equipment failures or human error. In addition, since the September 11, 2001 terrorist attacks, the U.S. government has issued warnings that energy assets, specifically the nation’s pipeline infrastructure, may be future targets of terrorist organizations. Terrorists may target PAA’s physical facilities and hackers may attack its electronic and computer systems.
If one or more of PAA’s facilities, including electronic and computer systems, or any facilities or businesses that deliver products, supplies or services to PAA or that it relies on in order to operate its business, are damaged by severe weather or any other disaster, accident, catastrophe, terrorist attack or event, its operations could be significantly interrupted. These interruptions could involve significant damage or injury to people, property or the environment, and repairs could take from a week or less for minor incidents to six months or more for major interruptions. Any such event that interrupts the revenues generated by its operations, or which causes PAA to make significant expenditures not covered by insurance, could reduce its cash available for paying distributions to its partners and, accordingly, adversely affect its financial condition and the market price of its securities.
PAA may also suffer damage (including reputational damage) as a result of a disaster, accident, catastrophe, terrorist attack or other such event. The occurrence of such an event, or a series of such events, especially if one or more of them occurs in a highly populated or sensitive area, could negatively impact public perception of PAA’s operations and/or make it more difficult for PAA to obtain the approvals, permits, licenses or real property interests PAA needs in order to operate its assets or complete planned growth projects.
PAA may not be able to compete effectively in its transportation, facilities and supply and logistics activities, and PAA’s business is subject to various risks associated with the risk general capacity overbuild of midstream energy infrastructure in some of the areas where it operates.
PAA faces competition in all aspects of its business and can give no assurances that it will be able to compete effectively against its competitors. In general, competition comes from a wide variety of participants in a wide variety of contexts, including new entrants and existing participants and in connection with day-to-day business, expansion capital projects, acquisitions and joint venture activities. Some of PAA’s competitors have capital resources many times greater than PAA’s and control greater supplies of crude oil, natural gas or NGL.
A significant driver of competition in some of the markets where PAA operates (including, for example, the Eagle Ford, Permian Basin, and Rockies/Bakken areas) stems from the rapid development of new midstream energy infrastructure capacity that was driven by the combination of (i) significant increases in oil and gas production and development in the applicable production areas, both actual and anticipated, (ii) relatively low barriers to entry and (iii) generally widespread access to relatively low cost capital. While this environment presented opportunities for PAA, many of these areas have become overbuilt, resulting in an excess of midstream energy infrastructure capacity. In addition, as an established participant in some markets, PAA also faces competition from aggressive new entrants to the market that are willing to provide services at a discount in order to establish relationships and gain a foothold in the market. Current expectations for oil and gas development in many of the areas where PAA operates are not as robust as they were during the last few years. This adversely impacts both PAA’s existing assets and growth projects in such areas. PAA also faces competition for incremental volumes from shippers on third party pipelines who overcommitted relative to their actual production and are now purchasing barrels on the open market and shipping them on such third party pipelines in order to satisfy their minimum commitment levels. This puts downward pressure on PAA’s throughput and margins and, together with other adverse competitive effects, could have a significant adverse impact on PAA’s financial position, cash flows and ability to pay or increase distributions to its partners.
With respect to PAA’s crude oil activities, its competitors include other crude oil pipelines, the major integrated oil companies, their marketing affiliates, refiners, industrial companies, independent gatherers, brokers and marketers of widely varying sizes, financial resources and experience. PAA competes against these companies on the basis of many factors, including geographic proximity to production areas, market access, rates, terms of service, connection costs and other factors.
With respect to PAA’s natural gas storage operations, the principal elements of competition are rates, terms of service, supply and market access and flexibility of service. PAA’s natural gas storage facilities compete with several other storage providers, including regional storage facilities and utilities. Certain pipeline companies have existing storage facilities connected to their systems that compete with some of PAA’s facilities.
With regard to PAA’s NGL operations, it competes with large oil, natural gas and natural gas liquids companies that may, relative to PAA, have greater financial resources and access to supplies of natural gas and NGL. The principal elements of competition are rates, processing fees, geographic proximity to the natural gas or NGL mix, available processing and fractionation capacity, transportation alternatives and their associated costs, and access to end user markets.
PAA’s growth strategy requires access to new capital. Tightened capital markets or other factors that increase its cost of capital could impair its ability to grow.
PAA continuously considers potential acquisitions and opportunities for expansion capital projects. Acquisition transactions can be effected quickly, may occur at any time and may be significant in size relative to its existing assets and operations. PAA’s ability to fund its capital projects and make acquisitions depends on whether it can access the necessary financing to fund these activities. Any limitations on its access to capital or increase in the cost of that capital could significantly impair its growth strategy. PAA’s ability to maintain its targeted credit profile, including maintaining its credit ratings, could affect PAA’s cost of capital as well as its ability to execute its growth strategy. In addition, a variety of factors beyond its control could impact the availability or cost of capital, including domestic or international economic conditions, increases in key benchmark interest rates and/or credit spreads, the adoption of new or amended banking or capital market laws or regulations, the re-pricing of market risks and volatility in capital and financial markets. In the latter half of 2015, the depth and availability of conventional public equity and debt markets contracted while the costs of accessing such markets rose significantly.
Due to these factors, PAA cannot be certain that funding for its capital needs will be available from bank credit arrangements, capital markets or other sources on acceptable terms. If funding is not available when needed, or is available only on unfavorable terms, PAA may be unable to implement its development plans, enhance its existing business, complete acquisitions and construction projects, take advantage of business opportunities or respond to competitive pressures, any of which could have a material adverse effect on its revenues and results of operations.
Loss of PAA’s investment grade credit rating or the ability to receive open credit could negatively affect its ability to purchase crude oil, NGL and natural gas supplies or to capitalize on market opportunities.
PAA believes that, because of its strategic asset base and complementary business model, PAA will continue to benefit from swings in market prices and shifts in market structure during periods of volatility in the crude oil, NGL and natural gas markets. The extent to which PAA is able to capture that benefit, however, is subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including whether PAA will be able to maintain an attractive credit rating and continue to receive open credit from its suppliers and trade counterparties. PAA’s senior unsecured debt is currently rated as “investment grade” by Standard & Poor’s and Moody’s Investors Service. A downgrade below PAA’s current ratings levels by either of such rating agencies could increase its borrowing costs, reduce its borrowing capacity and cause its counterparties to reduce the amount of open credit it receives from them. This could negatively impact PAA’s ability to capitalize on market opportunities. For example, PAA’s ability to utilize its crude oil storage capacity for merchant activities to capture contango market opportunities is dependent upon having adequate credit facilities, both in terms of the total amount of credit facilities and the cost of such credit facilities, which enables PAA to finance the storage of the crude oil from the time it completes the purchase of the crude oil until the time it completes the sale of the crude oil.
PAA is exposed to the credit risk of its customers in the ordinary course of its business activities.
Risks of nonpayment and nonperformance by customers are a significant consideration in PAA’s business And are of increased concern in the current low commodity price environment. Although PAA has credit risk management policies and procedures that are designed to mitigate and limit its exposure in this area, there can be no assurance that PAA has adequately assessed and managed the creditworthiness of its existing or future counterparties or that there will not be an unanticipated deterioration in their creditworthiness or unexpected instances of nonpayment or nonperformance, all of which could have an adverse impact on PAA’s cash flow and its ability to pay or increase its cash distributions to its partners.
PAA has a number of minimum volume commitment contracts that support pipelines in its Transportation segment. In addition, certain of the pipelines in which PAA owns a joint venture interest have minimum volume commitment contracts. Pursuant to such contracts, shippers are obligated to pay for a minimum volume of transportation service regardless of whether such volume is actually shipped (typically referred to as a deficiency payment), subject to the receipt of credits that typically expire if not used by a certain date. While such contracts provide greater revenue certainty, if the applicable shipper fails to transport the minimum required volume and is required to make a deficiency payment, under applicable accounting rules, the revenue associated with such deficiency payment may not be recognized until the applicable transportation credit has expired or has been used. Deferred revenue associated with non-performance by shippers under minimum volume contracts could be significant and could adversely affect PAA’s profitability and earnings.
In addition, in those cases in which PAA provides division order services for crude oil purchased at the wellhead, it may be responsible for distribution of proceeds to all parties. In other cases, PAA pays all of or a portion of the production proceeds to an operator who distributes these proceeds to the various interest owners. These arrangements expose PAA to operator credit risk, and there can be no assurance that PAA will not experience losses in dealings with such operators and other parties.
Further, to the extent one or more of PAA’s major customers experiences financial distress or commences bankruptcy proceedings, contracts with such customers (including contracts that are supported by acreage dedications) may be subject to renegotiation or rejection under applicable provisions of the United States Bankruptcy Code. Any such renegotiation or rejection could have an adverse effect on PAA’s revenue and cash flows and its ability to make cash distributions to its partners.
If PAA does not make acquisitions or if it makes acquisitions that fail to perform as anticipated, its future growth may be limited.
PAA’s ability to grow its distributions depends in part on its ability to make acquisitions that result in an increase in operating surplus per unit. If PAA is unable to make such accretive acquisitions either because PAA is (i) unable to identify attractive acquisition candidates or negotiate acceptable purchase contracts with the sellers, (ii) unable to raise financing for such acquisitions on economically acceptable terms or (iii) outbid by competitors, PAA’s future growth will be limited. As a result, PAA may not be able to grow as quickly as it has historically.
In evaluating acquisitions, PAA generally prepares one or more financial cases based on a number of business, industry, economic, legal, regulatory, and other assumptions applicable to the proposed transaction. Although PAA expects a reasonable basis will exist for those assumptions, the assumptions will generally involve current estimates of future conditions. Realization of many of the assumptions will be beyond PAA’s control. Moreover, the uncertainty and risk of inaccuracy associated with any financial projection will increase with the length of the forecasted period. Some acquisitions may not be accretive in the near term, and will be accretive in the long term only if PAA is able to timely and effectively integrate the underlying assets and such assets perform at or near the levels anticipated in its acquisition projections.
Acquisitions involve risks that may adversely affect PAA’s business.
Any acquisition involves potential risks, including:
· performance from the acquired businesses or assets that is below the forecasts PAA used in evaluating the acquisition;
· a significant increase in PAA’s indebtedness and working capital requirements;
· the inability to timely and effectively integrate the operations of recently acquired businesses or assets;
· the incurrence of substantial unforeseen environmental and other liabilities arising out of the acquired businesses or assets for which PAA is either not indemnified, or the indemnity is not from a credit-worthy party, including liabilities arising from the operation of the acquired businesses or assets prior to PAA’s acquisition;
· risks associated with operating in lines of business that are distinct and separate from PAA’s historical operations;
· customer or key employee loss from the acquired businesses; and
· the diversion of management’s attention from other business concerns.
Any of these factors could adversely affect PAA’s ability to achieve anticipated levels of cash flows from its acquisitions, realize other anticipated benefits and its ability to pay distributions to its partners or meet its debt service requirements.
PAA’s risk policies cannot eliminate all risks. In addition, any non-compliance with its risk policies could result in significant financial losses.
Generally, it is PAA’s policy to establish a margin for crude oil or other products it purchases by selling such products for physical delivery to third-party users, or by entering into a future delivery obligation under derivative contracts. Through these transactions, PAA seeks to maintain a position that is substantially balanced between purchases on the one hand, and sales or future delivery obligations on the other hand. PAA’s policy is not to acquire and hold physical inventory or derivative products for the purpose of speculating on commodity price changes. These policies and practices cannot, however, eliminate all risks. For example, any event that disrupts PAA’s anticipated physical supply of crude oil or other products could expose it to risk of loss resulting from price changes. PAA is also exposed to basis risk when crude oil or other products are purchased against one pricing index and sold against a different index. Moreover, PAA is exposed to some risks that are not hedged, including risks on certain of its inventory, such as linefill, which must be maintained in order to transport crude oil on its pipelines. In an effort to maintain a balanced position, specifically authorized personnel can purchase or sell crude oil, refined products and NGL, up to predefined limits and authorizations. Although this activity is monitored independently by PAA’s risk management function, it exposes PAA to commodity price risks within these limits.
In addition, PAA’s operations involve the risk of non-compliance with its risk policies. PAA has taken steps within its organization to implement processes and procedures designed to detect unauthorized trading; however, PAA can provide no assurance that these steps will detect and prevent all violations of its risk policies and procedures, particularly if deception, collusion or other intentional misconduct is involved.
PAA’s operations are also subject to laws and regulations relating to protection of the environment and wildlife, operational safety, climate change and related matters that may expose it to significant costs and liabilities.
PAA’s operations involving the storage, treatment, processing, and transportation of liquid hydrocarbons, including crude oil, NGL and refined products, as well as PAA’s operations involving the storage of natural gas, are subject to stringent federal, state, and local laws and regulations governing the discharge of materials into the environment. PAA’s operations are also subject to laws and regulations relating to protection of the environment and wildlife, operational safety, climate change and related matters. Compliance with all of these laws and regulations increases its overall cost of doing business, including its capital costs to construct, maintain and upgrade equipment and facilities. For example, the adoption of legislation or regulatory programs to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases, including cap and trade programs, could require PAA to incur increased operating costs, such as costs to purchase and operate emissions control systems, to acquire emissions allowances or comply with new regulatory or reporting requirements. In addition, with respect to our railcar operations, the adoption of new regulations designed to enhance the overall safety of crude oil and natural gas liquids transportation by rail, including new regulations requiring that existing railcars be retrofitted or upgraded to improve integrity, could result in increased operating costs and potentially involve substantial capital expenditures. Also, the failure to comply with any such laws and regulations could result in the assessment of administrative, civil, and criminal penalties, the imposition of investigatory and remedial liabilities, the issuance of injunctions that may subject PAA to additional operational requirements and constraints, or claims of damages to property or persons resulting from its operations. The laws and regulations applicable to PAA’s operations are subject to change and interpretation by the relevant governmental agency, including the possibility that exemptions it currently qualifies for may be modified or changed in ways that require PAA to incur significant additional compliance costs. Any such change or interpretation adverse to PAA could have a material adverse effect on its operations, revenues, expenses and profitability.
PAA has a history of incremental additions to the miles of pipelines it owns, both through acquisitions and expansion capital projects. PAA has also increased its terminal and storage capacity and operate several facilities on or near navigable waters and domestic water supplies. Although PAA has implemented programs intended to maintain the integrity of its assets (discussed below), as it acquires additional assets it historically has observed an increase in the number of releases of liquid hydrocarbons into the environment. These releases expose PAA to potentially substantial expense, including clean-up and remediation costs, fines and penalties, and third party claims for personal injury or property damage related to past or future releases. Some of these expenses could increase by amounts disproportionately higher than the relative increase in pipeline mileage and the increase in revenues associated therewith. PAA’s refined products terminal assets are also subject to significant compliance costs and liabilities. In addition, because of their increased volatility and tendency to migrate farther and faster than crude oil, releases of refined products into the environment can have a more significant impact than crude oil and require significantly higher expenditures to respond and remediate. The incurrence of such expenses not covered by insurance, indemnity or reserves could materially adversely affect PAA’s results of operations.
PAA currently devotes substantial resources to comply with DOT-mandated pipeline integrity rules. The 2006 Pipeline Safety Act requires the DOT to issue regulations for certain pipelines that were not previously subject to regulation. The DOT regulations include requirements for the establishment of pipeline integrity management programs and for protection of “high consequence areas” where a pipeline leak or rupture could produce significant adverse consequences. PAA has also developed and implemented certain pipeline integrity measures that it believes go beyond regulatory mandates. See Items 1 and 2 “Business and Properties—Regulation.”
For 2016 and beyond, PAA will continue to focus on pipeline integrity management as a primary operational emphasis. In that regard, PAA has implemented programs intended to maintain the integrity of its assets, with a focus on risk reduction through testing, enhanced corrosion control, leak detection, and damage prevention. PAA has an internal review process pursuant to which it examines various aspects of its pipeline and gathering systems that are not subject to the DOT pipeline integrity management mandate. The purpose of this process is to review the surrounding environment, condition and operating history of these pipeline and gathering assets to determine if such assets warrant additional investment or replacement. Accordingly, in addition to potential cost increases related to unanticipated regulatory changes or injunctive remedies resulting from regulatory agency enforcement actions, PAA may elect (as a result of its own internal initiatives) to spend substantial sums to enhance the integrity of and upgrade its pipeline systems to maintain environmental compliance and, in some cases, PAA may take pipelines out of service if it believes the cost of upgrades will exceed the value of the pipelines. PAA cannot provide any assurance as to the ultimate amount or timing of future pipeline integrity expenditures but any such expenditures could be significant. See Item 3 “Legal Proceedings—Environmental—General.” In addition, despite PAA’s pipeline and facility integrity management efforts, it can provide no assurance that its pipelines and facilities will not experience leaks or releases or that PAA will be able to fully comply with all of the federal, state and local laws and regulations applicable to the operation of PAA’s pipelines or facilities; any such leaks or releases could be material and could have a significant adverse impact on PAA’s reputation, financial position, cash flows and ability to pay or increase distributions to its partners.
PAA’s assets are subject to federal, state and provincial regulation. Rate regulation or a successful challenge to the rates PAA charges on its U.S. and Canadian pipeline systems may reduce the amount of cash it generates.
PAA’s U.S. interstate common carrier liquids pipelines are subject to regulation by the FERC under the ICA. The ICA requires that tariff rates for liquids pipelines be just and reasonable and non-discriminatory. PAA is also subject to the Pipeline Safety Regulations of the DOT. PAA’s intrastate pipeline transportation activities are subject to various state laws and regulations as well as orders of regulatory bodies.
For PAA’s U.S. interstate common carrier liquids pipelines subject to FERC regulation under the ICA, shippers may protest its pipeline tariff filings, file complaints against its existing rates, or the FERC can investigate on its own initiative. Under certain circumstances, the FERC could limit PAA’s ability to set rates based on its costs, or could order PAA to reduce its rates and could require the payment of reparations to complaining shippers for up to two years prior to the complaint. Natural gas storage facilities are subject to regulation by the FERC and certain state agencies.
PAA’s Canadian pipelines are subject to regulation by the NEB and by provincial authorities. Under the National Energy Board Act, the NEB could investigate the tariff rates or the terms and conditions of service relating to a jurisdictional pipeline on its own initiative upon the filing of a toll or tariff application, or upon the filing of a written complaint. If the NEB found the rates or terms of service relating to such pipeline to be unjust or unreasonable or unjustly discriminatory, the NEB could require PAA to change its rates, provide access to other shippers, or change its terms of service. A provincial authority could, on the application of a shipper or other interested party, investigate the tariff rates or PAA’s terms and conditions of service relating to its provincially regulated proprietary pipelines. If it found PAA’s rates or terms of service to be contrary to statutory requirements, it could impose conditions it considers appropriate. A provincial authority could declare a pipeline to be a common carrier pipeline, and require PAA
to change its rates, provide access to other shippers, or otherwise alter its terms of service. Any reduction in PAA’s tariff rates would result in lower revenue and cash flows.
Some of PAA’s operations cross the U.S./Canada border and are subject to cross-border regulation.
PAA’s cross border activities subject it to regulatory matters, including import and export licenses, tariffs, Canadian and U.S. customs and tax issues and toxic substance certifications. Such regulations include the Short Supply Controls of the Export Administration Act, the North American Free Trade Agreement and the Toxic Substances Control Act. Violations of these licensing, tariff and tax reporting requirements could result in the imposition of significant administrative, civil and criminal penalties.
PAA’s sales of crude oil, natural gas, NGL and other energy commodities, and related transportation and hedging activities, expose it to potential regulatory risks.
The FTC, the FERC and the CFTC hold statutory authority to monitor certain segments of the physical and futures energy commodities markets. These agencies have imposed broad regulations prohibiting fraud and manipulation of such markets. With regard to PAA’s physical sales of oil, natural gas, NGL or other energy commodities, and any related transportation and/or hedging activities that it undertakes, PAA is required to observe the market-related regulations enforced by these agencies, which hold substantial enforcement authority. PAA’s sales may also be subject to certain reporting and other requirements. Additionally, to the extent that PAA enters into transportation contracts with natural gas pipelines that are subject to FERC regulation, it is subject to FERC requirements related to the use of such capacity. Any failure on PAA’s part to comply with the regulations and policies of the FERC, the FTC or the CFTC could result in the imposition of civil and criminal penalties. Failure to comply with such regulations, as interpreted and enforced, could have a material adverse effect on PAA’s business, results of operations, financial condition and its ability to make cash distributions to its partners.
The enactment and implementation of derivatives legislation could have an adverse impact on PAA’s ability to use derivative instruments to reduce the effect of commodity price, interest rate and other risks associated with its business and increase the working capital requirement to conduct these hedging activities.
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd Frank Act”), enacted on July 21, 2010, established federal oversight and regulation of derivative markets and entities, such as PAA, that participate in those markets. The Dodd Frank Act requires the CFTC and the SEC to promulgate rules and regulations implementing the Dodd Frank Act. Although the CFTC has finalized certain regulations, others remain to be finalized or implemented and it is not possible at this time to predict when this will be accomplished.
In October 2011, the CFTC issued regulations to set position limits for certain futures and option contracts in the major energy markets. The initial position limits rule was vacated by the United States District Court for the District of Columbia in September 2012. However, in November 2013, the CFTC proposed new rules that would place limits on positions in certain core futures and equivalent swaps contracts for, or linked to, certain physical commodities, subject to exceptions for certain bona fide hedging transactions. As these new position limit rules are not yet final, the impact of those provisions on PAA is uncertain at this time.
The CFTC has designated certain interest rate swaps and credit default swaps for mandatory clearing, and the associated rules require PAA, in connection with covered derivative activities, to comply with clearing and trade-execution requirements or take steps to qualify for an exemption from such requirements. PAA does not utilize credit default swaps and PAA qualifies for, and expects to continue to qualify for, the end-user exception from the mandatory clearing requirements for swaps entered into to hedge its interest rate risks. Should the CFTC designate commodity derivatives for mandatory clearing, PAA would expect to qualify for an end-user exception from the mandatory clearing requirements for swaps entered into to hedge its commodity price risk. However, the majority of PAA’s financial derivative transactions used for hedging commodity price risks are currently executed and cleared over exchanges that require the posting of margin or letters of credit based on initial and variation margin requirements. Pursuant to the Dodd Frank Act, however, the CFTC or federal banking regulators may require the posting of collateral with respect to uncleared interest rate and commodity derivative transactions.
Certain banking regulators and the CFTC have adopted final rules establishing minimum margin requirements for uncleared swaps. Although PAA qualifies for the end-user exception from margin requirements for swaps entered into to hedge commercial risks, if any of PAA’s swaps do not qualify for the commercial end-user exception, a requirement to post additional cash margin or collateral could reduce PAA’s ability to execute hedges necessary to reduce commodity price exposures and protect cash flows. Posting of additional cash margin or collateral could affect PAA’s liquidity (defined as unrestricted cash on hand plus available capacity under its credit facilities) and reduce PAA’s ability to use cash for capital expenditures or other partnership purposes.
Even if PAA itself is not required to post additional cash margin or collateral for its derivative contracts, the banks and other derivatives dealers who are PAA’s contractual counterparties will be required to comply with other new requirements under the Dodd Frank Act and related rules. The costs of such compliance may be passed on to customers such as PAA, thus decreasing the benefits to PAA of hedging transactions or reducing its profitability. In addition, implementation of the Dodd Frank Act and related rules and regulations could reduce the overall liquidity and depth of the markets for financial and other derivatives PAA utilizes in connection with its business, which could expose PAA to additional risks or limit the opportunities PAA is able to capture by limiting the extent to which PAA is able to execute its hedging strategies.
Finally, the Dodd Frank Act was intended, in part, to reduce the volatility of oil and gas prices, which some legislators attributed to speculative trading in derivatives and commodity instruments related to oil and gas. PAA’s financial results could be adversely affected if a consequence of the Dodd Frank Act and implementing regulations is lower commodity prices.
The full impact of the Dodd Frank Act and related regulatory requirements upon PAA’s business will not be known until the regulations are implemented and the market for derivatives contracts has adjusted. The Dodd Frank Act and any new regulations could significantly increase the cost of derivative contracts, materially alter the terms of derivative contracts, reduce the availability of derivatives to protect against risks PAA encounters, reduce PAA’s ability to monetize or restructure its existing derivative contracts. If PAA reduces its use of derivatives as a result of the Dodd Frank Act and regulations implementing the Dodd Frank Act, PAA’s results of operations may become more volatile and its cash flows may be less predictable. Any of these consequences could have a material adverse effect on PAA, its financial condition and its results of operations.
Legislation and regulatory initiatives relating to hydraulic fracturing could reduce domestic production of crude oil and natural gas.
Hydraulic fracturing is an important and common practice that is used to stimulate production of hydrocarbons from unconventional geological formations. Recent advances in hydraulic fracturing techniques have resulted in significant increases in crude oil and natural gas production in many basins in the United States and Canada. The process involves the injection of water, sand and chemicals under pressure into the formation to fracture the surrounding rock and stimulate production, and it is typically regulated by state and provincial oil and gas commissions. We do not perform hydraulic fracturing, but many of the producers using our pipelines do. Hydraulic fracturing has been subject to increased scrutiny due to public concerns that it could result in contamination of drinking water supplies, and there have been a variety of legislative and regulatory proposals to prohibit, restrict, or more closely regulate various forms of hydraulic fracturing. Any legislation or regulatory initiatives that curtail hydraulic fracturing could reduce the production of crude oil and natural gas in the United States or Canada, and could thereby reduce demand for PAA’s transportation, terminalling and storage services as well as its supply and logistics services.
PAA may in the future encounter increased costs related to, and lack of availability of, insurance.
Over the last several years, as the scale and scope of PAA’s business activities has expanded, the breadth and depth of available insurance markets has contracted. As a result of these factors and other market conditions, as well as the fact that PAA has experienced several incidents over the last 3 to 5 years, premiums and deductibles for certain insurance policies have increased substantially. Accordingly, PAA can give no assurance that it will be able to maintain adequate insurance in the future at rates or on other terms PAA considers commercially reasonable. In addition, although PAA believes that it currently maintains adequate insurance coverage, insurance will not cover many types of interruptions or events that might occur and will not cover all risks associated with its operations. In addition, the proceeds of any such insurance may not be paid in a timely manner and may be insufficient if such an event were to occur. The occurrence of a significant event, the consequences of which are either not covered by insurance or not fully insured, or a significant delay in the payment of a major insurance claim, could materially and adversely affect PAA’s financial position, results of operations and cash flows.
The terms of PAA’s indebtedness may limit its ability to borrow additional funds or capitalize on business opportunities. In addition, PAA’s future debt level may limit its future financial and operating flexibility.
As of December 31, 2015, the principal amount of PAA’s consolidated debt outstanding was approximately $11.5 billion, consisting of approximately $10.5 billion principal amount of long-term debt (including senior notes and long-term commercial paper borrowings) and approximately $1.0 billion of short-term borrowings. As of December 31, 2015, PAA had approximately $2.3 billion of liquidity available, including cash and cash equivalents and available borrowing capacity under its senior unsecured revolving credit facility, its senior secured hedged inventory facility and its senior unsecured 364-day credit facility, subject to continued covenant compliance. Lower adjusted EBITDA could increase PAA’s leverage ratios and effectively reduce its ability to incur additional indebtedness.
The amount of PAA’s current or future indebtedness could have significant effects on its operations, including, among other things:
· a significant portion of PAA’s cash flow will be dedicated to the payment of principal and interest on its indebtedness and may not be available for other purposes, including the payment of distributions on its units and capital expenditures;
· credit rating agencies may view PAA’s debt level negatively;
· covenants contained in PAA’s existing debt arrangements will require it to continue to meet financial tests that may adversely affect its flexibility in planning for and reacting to changes in its business;
· PAA’s ability to obtain additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions and general partnership purposes may be limited;
· PAA may be at a competitive disadvantage relative to similar companies that have less debt; and
· PAA may be more vulnerable to adverse economic and industry conditions as a result of its significant debt level.
PAA’s credit agreements prohibit distributions on, or purchases or redemptions of, units if any default or event of default is continuing. In addition, the agreements contain various covenants limiting PAA’s ability to, among other things, incur indebtedness if certain financial ratios are not maintained, grant liens, engage in transactions with affiliates, enter into sale-leaseback transactions, and sell substantially all of its assets or enter into a merger or consolidation. PAA’s credit facility treats a change of control as an event of default and also requires PAA to maintain a certain debt coverage ratio. PAA’s senior notes do not restrict distributions to unitholders, but a default under its credit agreements will be treated as a default under the senior notes. Please read Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Credit Agreements, PAA Commercial Paper Program and Indentures.”
PAA’s ability to access capital markets to raise capital on favorable terms will be affected by its debt level, its operating and financial performance, the amount of its current maturities and debt maturing in the next several years, and by prevailing market conditions. Moreover, if the rating agencies were to downgrade PAA’s credit ratings, then it could experience an increase in its borrowing costs, face difficulty accessing capital markets or incurring additional indebtedness, be unable to receive open credit from its suppliers and trade counterparties, be unable to benefit from swings in market prices and shifts in market structure during periods of volatility in the crude oil market or suffer a reduction in the market price of its common units. If PAA is unable to access the capital markets on favorable terms at the time a debt obligation becomes due in the future, it might be forced to refinance some of its debt obligations through bank credit, as opposed to long-term public debt securities or equity securities, or sell assets. The price and terms upon which PAA might receive such extensions or additional bank credit, if at all, could be more onerous than those contained in existing debt agreements. Any such arrangements could, in turn, increase the risk that PAA’s leverage may adversely affect its future financial and operating flexibility and thereby impact its ability to pay cash distributions at expected rates.
Increases in interest rates could adversely affect PAA’s business and the trading price of its units.
As of December 31, 2015, PAA had approximately $11.5 billion in principal amount of consolidated debt, of which approximately $9.8 billion was at fixed interest rates and approximately $1.7 billion was at variable interest rates. PAA is exposed to market risk due to the short-term nature of its commercial paper borrowings and the floating interest rates on its credit facilities. PAA’s results of operations, cash flows and financial position could be adversely affected by significant increases in interest rates above current levels. Additionally, increases in interest rates could adversely affect PAA’s Supply and Logistics segment results by increasing interest costs associated with the storage of hedged crude oil and NGL inventory. Further, the trading price of PAA’s common units may be sensitive to changes in interest rates and any rise in interest rates could adversely impact such trading price.
Changes in currency exchange rates could adversely affect PAA’s operating results.
Because PAA is a U.S. dollar reporting company and also conducts operations in Canada, it is exposed to currency fluctuations and exchange rate risks that may adversely affect the U.S. dollar value of its earnings, cash flow and partners’ capital under applicable accounting rules. For example, as the U.S. dollar appreciates against the Canadian dollar, the U.S. dollar value of PAA’s Canadian dollar denominated earnings is reduced for U.S. reporting purposes.
An impairment of long-term assets could reduce PAA’s earnings.
At December 31, 2015, PAA had approximately $13.5 billion of net property and equipment, $2.4 billion of goodwill, $2.0 billion of investments accounted for under the equity method of accounting and $0.3 billion of net intangible assets capitalized on its balance sheet. GAAP requires an assessment for impairment on an annual basis or in certain circumstances, including when there is an indication that the carrying value of property and equipment may not be recoverable or a determination that it is more likely than not that a reporting unit’s carrying value is in excess of the reporting unit’s fair value. If PAA was to determine that any of its property and equipment, goodwill, intangibles or equity method investments was impaired, it could be required to take an immediate charge to earnings, which could adversely impact its operating results, with a corresponding reduction of partners’ capital and increase in balance sheet leverage as measured by debt-to-total capitalization.
Rail and marine transportation of crude oil have inherent operating risks.
PAA’s supply and logistics operations include purchasing crude oil that is carried on railcars, tankers or barges. Such cargos are at risk of being damaged or lost because of events such as derailment, marine disaster, inclement weather, mechanical failures, grounding or collision, fire, explosion, environmental accidents, piracy, terrorism and political instability. Such occurrences could result in death or injury to persons, loss of property or environmental damage, delays in the delivery of cargo, loss of revenues, termination of contracts, governmental fines, penalties or restrictions on conducting business, higher insurance rates and damage to PAA’s reputation and customer relationships generally. Although certain of these risks may be covered under PAA’s insurance program, any of these circumstances or events could increase its costs or lower its revenues.
PAA is dependent on use of third-party assets for certain of its operations.
Certain of PAA’s business activities require the use of third-party assets over which it may have little or no control. For example, a portion of PAA’s storage and distribution business conducted in the Los Angeles basin receives waterborne crude oil through dock facilities operated by a third party in the Port of Long Beach. If at any time PAA’s access to this dock was denied, and if access to an alternative dock could not be arranged, the volume of crude oil that it presently receives from its customers in the Los Angeles basin may be reduced, which could result in a reduction of PAA’s Facilities segment revenue and cash flow.
Non-utilization of certain assets, such as PAA’s leased railcars, could significantly reduce its profitability due to fixed costs incurred to obtain the right to use such assets.
From time to time in connection with its business, PAA may lease or otherwise secure the right to use certain third party assets (such as railcars, trucks, barges, ships, pipeline capacity, storage capacity and other similar assets) with the expectation that the revenues it generates through the use of such assets will be greater than the fixed costs it incurs pursuant to the applicable leases or other arrangements. However, when such assets are not utilized or are under-utilized, PAA’s profitability could be negatively impacted because the revenues it earns are either non-existent or reduced, but it remains obligated to continue paying any applicable fixed charges, in addition to the potential of incurring other costs attributable to the non-utilization of such assets. For example, in connection with PAA’s rail operations, it leases substantially all of its railcars, typically pursuant to multi-year leases that obligate PAA to pay the applicable lease rate without regard to utilization. If business conditions are such that a portion of PAA’s rail fleet is not utilized for any period of time due to reduced demand for the services they provide, PAA will still be obligated to pay the applicable fixed lease rate for such railcars. In addition, during the period of time that PAA is not utilizing such railcars, it will incur incremental costs associated with the cost of storing such railcars and will continue to incur costs for maintenance and upkeep. Non-utilization of its leased railcars and other similar assets in connection with PAA’s business could have a significant negative impact on PAA’s profitability and cash flows.
For various operating and commercial reasons, PAA may not be able to perform all of its obligations under its contracts, which could lead to increased costs and negatively impact financial results.
Various operational and commercial factors could result in an inability on PAA’s part to satisfy its contractual commitments and obligations. For example, in connection with the provision of firm storage services and hub services to its natural gas storage customers, PAA enters into contracts that obligate PAA to honor its customers’ requests to inject gas into its storage facilities, withdraw gas from its facilities and wheel gas through its facilities, in each case subject to volume, timing and other limitations set forth in such contracts. The following factors could adversely impact PAA’s ability to perform its obligations under these contracts:
· a failure on the part of PAA’s storage facilities to perform as expected, whether due to malfunction of equipment or facilities or realization of other operational risks;
· the operating pressure of PAA’s storage facilities (affected in varying degree, depending on the type of storage cavern, by total volume of working and base gas, and temperature);
· a variety of commercial decisions PAA makes from time to time in connection with the management and operation of its storage facilities. Examples include, without limitation, decisions with respect to matters such as (i) the aggregate amount of commitments PAA is willing to make with respect to wheeling, injection, and withdrawal services, which could exceed PAA’s capabilities at any given time for various reasons, (ii) the timing of scheduled and unplanned maintenance or repairs, which can impact equipment availability and capacity, (iii) the schedule for and rate at which PAA conducts opportunistic leaching activities at its facilities in connection with the expansion of existing salt caverns, which can impact the amount of storage capacity PAA has available to satisfy its customers’ requests, (iv) the timing and aggregate volume of any base gas park and/or loan transactions PAA consummates, which can directly affect the operating pressure of PAA’s storage facilities and (v) the amount of compression capacity and other gas handling equipment that PAA installs at its facilities to support gas wheeling, injection and withdrawal activities; and
· adverse operating conditions due to hurricanes, extreme weather events or conditions, and operational problems or issues with third-party pipelines, storage or production facilities.
Although PAA manages and monitors all of these various factors in connection with the ongoing operation of its natural gas storage facilities with the goal of performing all of its contractual commitments and obligations and optimizing revenue, one or more of the above factors may adversely impact PAA’s ability to satisfy its injection, withdrawal or wheeling obligations under its storage contracts. In such event, PAA may be liable to its customers for losses or damages they suffer and/or PAA may need to incur costs or expenses in order to permit it to satisfy its obligations.
Cost reimbursements due to PAA’s general partner may be substantial and will reduce PAA’s cash available for distribution to its partners.
Prior to making any distribution to its partners, PAA will reimburse PAA GP and its affiliates, including officers and directors, for all expenses incurred on PAA’s behalf (other than expenses related to the AAP Management Units). The reimbursement of expenses and the payment of fees could adversely affect PAA’s ability to make distributions to its partners. PAA GP has sole discretion to determine the amount of these expenses. In addition, PAA GP and its affiliates may provide PAA with services for which PAA will be charged reasonable fees as determined by its general partner.
Cash distributions are not guaranteed and may fluctuate with PAA’s performance and the establishment of financial reserves.
Because distributions on PAA’s partnership interests are dependent on the amount of cash it generates, distributions to PAA’s common unitholders may fluctuate based on PAA’s performance, which will result in fluctuations in the amount of distributions ultimately received by AAP. The actual amount of cash that is available to be distributed each quarter will depend on numerous factors, some of which are beyond PAA’s control and the control of PAA GP. Cash distributions are dependent primarily on cash flow, including cash flow from financial reserves and working capital borrowings, and not solely on profitability, which is affected by non-cash items. Therefore, cash distributions might be made during periods when PAA records losses and might not be made during periods when it records profits.
PAA’s preferred units have rights, preferences and privileges that are not held by, and are preferential to the rights of, holders of PAA’s common units.
PAA’s Series A Preferred Units (the “PAA preferred units”), issued in January 2016, rank senior to all of PAA’s other classes or series of equity securities with respect to distribution rights and rights upon liquidation. These preferences could adversely affect the market price for PAA’s common units, or could make it more difficult for PAA to sell common units in the future.
Distributions on the PAA preferred units accrue and are cumulative, at the rate of 8% per annum on the original issue price and are convertible into PAA common units by the holders of such units or by PAA in certain circumstances. PAA’s obligation to pay distributions on its preferred units, or on the common units issued following the conversion of such preferred units, could impact its liquidity and reduce the amount of cash flow available for working capital, capital expenditures, growth opportunities, acquisitions, and other general partnership purposes. PAA’s obligations to the holders of preferred units could also limit its ability to obtain additional financing or increase our borrowing costs, which could have an adverse effect on PAA’s financial condition.
Tax Risks
As our only cash-generating assets consist of our partnership interest in AAP and its related direct and indirect interests in PAA, our tax risks are primarily derivative of the tax risks associated with an investment in PAA.
The tax treatment of PAA depends on its status as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes, as well as it not being subject to a material amount of additional entity-level taxation by individual states. If the Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) were to treat PAA as a corporation for federal income tax purposes or if PAA becomes subject to additional amounts of entity-level taxation for state or foreign tax purposes, it would reduce the amount of cash available for distribution to us and increase the portion of our distributions treated as taxable dividends.
At December 31, 2015, we owned an approximate 38% limited partner interest in AAP, which indirectly owns PAA’s 2% general partner interest, and directly owns all of PAA’s IDRs. Accordingly, the value of our indirect investment in PAA, as well as the anticipated after-tax economic benefit of an investment in our Class A shares, depends largely on PAA being treated as a partnership for federal income tax purposes, which requires that 90% or more of PAA’s gross income for every taxable year consist of qualifying income, as defined in Section 7704 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”). The IRS issued proposed regulations on which activities give rise to qualifying income within the meaning of Section 7704 on May 5, 2015, but are not yet final. However, finalized regulations could modify the amount of PAA’s gross income that PAA is able to treat as qualifying income for the purposes of the qualifying income requirement.
Despite the fact that PAA is a limited partnership under Delaware law and, unlike us, has not elected to be treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes, it is possible, under certain circumstances, for PAA to be treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes. Although we do not believe, based on its current operations, that PAA will be so treated, a change in PAA’s business could cause it to be treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes or otherwise subject it to federal income taxation as an entity.
Current law may change, causing PAA to be treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes or otherwise subjecting PAA to additional entity-level taxation. In addition, several states are evaluating ways to subject partnerships to entity-level taxation through the imposition of state income, franchise and other forms of taxation. For example, PAA is subject to entity-level tax on the portion of its income apportioned to Texas in the prior year. Imposition of any similar taxes on PAA in additional states will reduce its cash available for distribution to its partners.
If PAA were treated as a corporation for federal income tax purposes, it would pay federal income tax on its taxable income at the corporate tax rate, which is currently a maximum of 35%, and would likely pay state income taxes at varying rates. Distributions to PAA’s partners, including AAP, would generally be taxed again as corporate distributions, and no income, gains, losses or deductions would flow through to PAA’s partners. Because a tax would be imposed upon PAA as a corporation, its cash available for distribution would be substantially reduced. Therefore, treatment of PAA as a corporation would result in a material reduction in the anticipated cash flow and after-tax return to us, likely causing a substantial reduction in the value of our Class A shares.
PAA’s partnership agreement provides that if a law is enacted or existing law is modified or interpreted in a manner that subjects PAA to taxation as a corporation or otherwise subjects PAA to entity-level taxation for federal income tax purposes, PAA’s minimum quarterly distribution and target distribution amounts will be adjusted downward by a percentage that is based on the applicable entity-level tax rate, including both federal and state tax burdens. Although it is impossible to make an accurate assessment of the impact without the specific details of any such new law or modification, in such event, it is likely the amount of distributions AAP receives from PAA and our resulting cash flows could be reduced substantially, which would adversely affect our ability to pay distributions to our shareholders.
Moreover, if PAA were treated as a corporation we would not be entitled to the deductions associated with our initial acquisition of interests in AAP or subsequent exchanges of retained AAP interests and Class B shares for our Class A shares. As a result, if PAA were treated as a corporation, (i) our liability for taxes would likely be higher, further reducing our cash available for distribution, and (ii) a greater portion of the cash we are able to distribute will be treated as a taxable dividend.
The tax treatment of publicly traded partnerships such as PAA could be subject to potential legislative, judicial or administrative changes and differing interpretations, possibly on a retroactive basis.
Legislative changes to the IRS audit rules, starting with partnership tax years beginning after 2017, will allow the IRS to assess and collect tax on audit adjustments at the partnership level as opposed to the partner level unless the partnership makes an election or exercises certain alternatives. Changes were also made to limit partner representation in the event of an audit.
The Bipartisan Budget Act of 2015 (H.R. 1315) (“Act”), effective for partnership tax years beginning after December 31, 2017, repeals the partnership audit rules of the Tax Equity and Fiscal Responsibility Act of 1982 (“TEFRA”) and replaces the TEFRA provisions with new provisions that allow for the IRS to assess and collect taxes associated with audit adjustments, referred to as an “imputed underpayment”, at the partnership entity level rather than the partner level in the year the partnership adjustment is made, the “adjustment year”, as opposed to the year the adjustment relates, the “reviewed year”. The imputed underpayment is calculated using the highest tax rate in effect for the reviewed year. The implications of an imputed underpayment are that current partners could be liable for a liability of former partners. If an audit adjustment did result in a material imputed underpayment the partnership would need to determine whether to pay the imputed underpayment or to avail itself of one of three alternative provisions under the Act that can shift the partnership level tax liability back onto the prior tax year partners. The first alternative, an opt-out election, is not available to PAA as a publicly traded partnership because PAA does not meet the criteria of 100 or fewer partners. The second alternative would require the partnership to submit audit adjustment information to the affected partners and to the IRS as well as ensure amended return compliance by our partners within 270 days after receipt of the proposed audit adjustment. From an administrative standpoint, considering the number of PAA’s partners, as a publicly traded partnership, the second alternative is not a viable option to PAA. The third alternative is an election by PAA that would require the partnership, not later than 45 days after the date of the notice of final partnership adjustment, to furnish to each affected partner and to the IRS a statement of each partner’s share of any adjustment to income, gain, loss, deduction, or credit. Under this alternative, reviewed year partners calculate their share of additional tax due and pay the additional amount with their respective current year individual tax returns. An election under this provision, however, because the reviewed year is older increases the applicable imputed underpayment interest rate by two percentage points. If PAA was required to pay taxes, penalties and interest as the result of audit adjustments, cash available for distribution to their unitholders may be substantially reduced. In addition, because payment would be due for the taxable year in which the audit is completed, unitholders during that taxable year would bear the expense of the adjustment even if they were not unitholders during the audited taxable year.
Also for partnership tax years beginning after 2017, the Act eliminated rights that certain individual partners might previously have had in the audit process by now restricting it to a single “partnership representative”
The present U.S. federal income tax treatment of publicly traded partnerships, including PAA, may be modified by administrative, legislative or judicial changes or differing interpretations at any time. For example, the Obama administration’s budget proposal for fiscal year 2016 recommends that certain publicly traded partnerships earning income from activities related to fossil fuels be taxed as corporations beginning in 2021. From time to time, members of Congress propose and consider such substantive changes to the existing federal income tax laws that affect publicly traded partnerships. If successful, the Obama administration’s proposal or other similar proposals could eliminate the qualifying income exception to the treatment of all publicly-traded partnerships as corporations upon which PAA relies for its treatment as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
Any modification to the U.S. federal income tax laws may be applied retroactively and could make it more difficult or impossible for PAA to meet the exception for certain publicly traded partnerships to be treated as partnerships for U.S. federal income tax purposes. We are unable to predict whether any of these changes or other proposals will ultimately be enacted. Any such changes could negatively impact the value of our indirect investment in PAA.
Taxable gain or loss on the sale of our Class A shares could be more or less than expected.
If a holder sells our Class A shares, the holder will recognize a gain or loss equal to the difference between the amount realized and the holder’s tax basis in those Class A shares. To the extent that the amount of our distributions exceeds our current and accumulated earnings and profits, the distributions will be treated as a tax free return of capital and will reduce a holder’s tax basis in the Class A shares. We did not have any earnings and profits in 2015 and we do not expect to have any earnings and profits for an extended period of time, which we estimate will include, at a minimum, each of the periods ending December 31, 2016 and 2017. Because our distributions in excess of our earnings and profits decrease a holder’s tax basis in Class A shares, such excess distributions will result in a corresponding increase in the amount of gain, or a corresponding decrease in the amount of loss, recognized by the holder upon the sale of the Class A shares. Please read “Summary of Tax Considerations—Gain on Disposition of Class A Shares” for a further discussion of the foregoing.
Our current tax treatment may change, which could affect the value of our Class A shares or reduce our cash available for distribution.
Our expectation that tax deductions associated with our initial and subsequent acquisitions of interests in AAP (as a result of the exercise by Legacy Owners of their exchange rights) will offset all of our current taxable income for an extended period of time, and thus result in our distributions not constituting taxable dividends for an extended period of time, is based on current law with respect to the amortization of basis adjustments associated with our acquisition of interests in AAP. Changes in federal income tax law relating to such tax treatment could result in (i) our being subject to additional taxation at the entity level with the result that we would have less cash available for distribution, and (ii) a greater portion of our distributions being treated as taxable dividends. Moreover, we are subject to tax in numerous jurisdictions. Changes in current law in these jurisdictions, particularly relating to the treatment of deductions attributable to acquisitions of interests in AAP, could result in our being subject to additional taxation at the entity level with the result that we would have less cash available for distribution.
Any decrease in our Class A share price could adversely affect our amount of cash available for distribution.
Changes in certain market conditions may cause our Class A share price to decrease. If our Legacy Owners exchange their retained interests in AAP and Class B shares in us for our Class A shares at a point in time when our Class A share price is below the price at which Class A shares were sold in our initial public offering or in any subsequent exchange, the ratio of our income tax deductions to gross income would decline. This decline could result in our being subject to tax sooner than expected, our tax liability being greater than expected, or a greater portion of our distributions being treated as taxable dividends.
The IRS Forms 1099-DIV that our shareholders receive from their brokers may over-report dividend income with respect to our shares for U.S. federal income tax purposes, and failure to report dividend income in a manner consistent with the IRS Forms 1099-DIV may cause the IRS to assert audit adjustments to a shareholder’s U.S. federal income tax return. For non-U.S. holders of our shares, brokers or other withholding agents may overwithhold taxes from dividends paid, in which case a shareholder generally would have to timely file a U.S. tax return or an appropriate claim for refund in order to claim a refund of the overwithheld taxes.
Distributions we pay with respect to our shares will constitute “dividends” for U.S. federal income tax purposes only to the extent of our current and accumulated earnings and profits. Distributions we pay in excess of our earnings and profits will not be treated as “dividends” for U.S. federal income tax purposes; instead, they will be treated first as a tax-free return of capital to the extent of a shareholder’s tax basis in their shares and then as capital gain realized on the sale or exchange of such shares. We may be unable to timely determine the portion of our distributions that is a “dividend” for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
For a U.S. holder of our shares, the IRS Forms 1099-DIV may not be consistent with our determination of the amount that constitutes a “dividend” for U.S. federal income tax purposes or a shareholder may receive a corrected IRS Form 1099-DIV (and may therefore need to file an amended federal, state or local income tax return). We will attempt to timely notify our shareholders of available information to assist with income tax reporting (such as posting the correct information on our website). However, the information that we provide to our shareholders may be inconsistent with the amounts reported by a broker on IRS Form 1099-DIV, and the IRS may disagree with any such information and may make audit adjustments to a shareholder’s tax return.
For a non-U.S. holder of our shares, “dividends” for U.S. federal income tax purposes will be subject to withholding of U.S. federal income tax at a 30% rate (or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty) unless the dividends are effectively connected with conduct of a U.S. trade or business. Please read “Summary of Tax Considerations—Consequences to Non-U.S. Holders.” In the event that we are unable to timely determine the portion of our distributions that is a “dividend” for U.S. federal income tax purposes, or a shareholder’s broker or withholding agent chooses to withhold taxes from distributions in a manner inconsistent with our determination of the amount that constitutes a “dividend” for such purposes, a shareholder’s broker or other withholding agent may overwithhold taxes from distributions paid. In such a case, a shareholder generally would have to timely file a U.S. tax return or an appropriate claim for refund in order to obtain a refund of the overwithheld tax.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
Loss Contingencies — General
To the extent we are able to assess the likelihood of a negative outcome for a contingency, our assessments of such likelihood range from remote to probable. If we determine that a negative outcome is probable and the amount of loss is reasonably estimable, we accrue an undiscounted liability equal to the estimated amount. If a range of probable loss amounts can be reasonably estimated and no amount within the range is a better estimate than any other amount, then we accrue an undiscounted liability equal to the minimum amount in the range. In addition, we estimate legal fees that we expect to incur associated with loss contingencies and accrue those costs when they are material and probable of being incurred.
We do not record a contingent liability when the likelihood of loss is probable but the amount cannot be reasonably estimated or when the likelihood of loss is believed to be only reasonably possible or remote. For contingencies where an unfavorable outcome is reasonably possible and the impact would be material to our consolidated financial statements, we disclose the nature of the contingency and, where feasible, an estimate of the possible loss or range of loss.
Legal Proceedings — General
In the ordinary course of business, we are involved in various legal proceedings, including those arising from regulatory and environmental matters. Although we are insured against various risks to the extent we believe it is prudent, there is no assurance that the nature and amount of such insurance will be adequate, in every case, to fully protect us from losses arising from current or future legal proceedings.
Taking into account what we believe to be all relevant known facts and circumstances, and based on what we believe to be reasonable assumptions regarding the application of those facts and circumstances to existing laws and regulations, we do not believe that the outcome of the legal proceedings in which we are currently involved (including those described below) will, individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Environmental — General
Although over the course of the last several years we have made significant investments in our maintenance and integrity programs, and have hired additional personnel in those areas, we have experienced (and likely will experience future) releases of hydrocarbon products into the environment from our pipeline, rail, storage and other facility operations. These releases can result from accidents or from unpredictable man-made or natural forces and may reach surface water bodies, groundwater aquifers or other sensitive environments. Damages and liabilities associated with any such releases from our existing or future assets could be significant and could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
We record environmental liabilities when environmental assessments and/or remedial efforts are probable and the amounts can be reasonably estimated. Generally, our recording of these accruals coincides with our completion of a feasibility study or our commitment to a formal plan of action. We do not discount our environmental remediation liabilities to present value. We also record environmental liabilities assumed in business combinations based on the estimated fair value of the environmental obligations caused by past operations of the acquired company. We record receivables for amounts recoverable from insurance or from third parties under indemnification agreements in the period that we determine the costs are probable of recovery.
Environmental expenditures that pertain to current operations or to future revenues are expensed or capitalized consistent with our capitalization policy for property and equipment. Expenditures that result from the remediation of an existing condition caused by past operations and that do not contribute to current or future profitability are expensed.
At December 31, 2015, our estimated undiscounted reserve for environmental liabilities (including liabilities related to the Line 901 incident, as discussed further below) totaled $185 million, of which $81 million was classified as short-term and $104 million was classified as long-term. At December 31, 2014, our estimated undiscounted reserve for environmental liabilities totaled $82 million, of which $13 million was classified as short-term and $69 million was classified as long-term. The short- and long-term environmental liabilities referenced above are reflected in “Accounts payable and accrued liabilities” and “Other long-term liabilities and deferred credits,” respectively, on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, we had recorded receivables totaling $161 million and $8 million, respectively, for amounts probable of recovery under insurance and from third parties under indemnification agreements, which are predominantly reflected in “Trade accounts receivable and other receivables, net” on our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
In some cases, the actual cash expenditures associated with these liabilities may not occur for three years or longer. Our estimates used in determining these reserves are based on information currently available to us and our assessment of the ultimate outcome. Among the many uncertainties that impact our estimates are the necessary regulatory approvals for, and potential modification of, our remediation plans, the limited amount of data available upon initial assessment of the impact of soil or water contamination, changes in costs associated with environmental remediation services and equipment and the possibility of existing or future legal claims giving rise to additional liabilities. Therefore, although we believe that the reserve is adequate, actual costs incurred (which may ultimately include costs for contingencies that are currently not reasonably estimable or costs for contingencies where the likelihood of loss is currently believed to be only reasonably possible or remote) may be in excess of the reserve and may potentially have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Specific Legal, Environmental or Regulatory Matters
Line 901 Incident. In May 2015, we experienced a crude oil release from our Las Flores to Gaviota Pipeline (Line 901) in Santa Barbara County, California. A portion of the released crude oil reached the Pacific Ocean at Refugio State Beach through a drainage culvert. Following the release, we shut down the pipeline and initiated our emergency response plan. A Unified Command, which includes the United States Coast Guard, the EPA, the California Office of Spill Prevention and Response and the Santa Barbara Office of Emergency Management, was established for the response effort. Clean-up and remediation operations with respect to impacted shoreline and other areas has been determined by the Unified Command to be complete, subject to continued shoreline monitoring. The cause of the release remains under investigation. Our current “worst case” estimate of the amount of oil spilled, representing the maximum volume of oil that we believed could have been spilled based on relevant facts, data and information, is approximately 2,935 barrels.
As a result of the Line 901 incident, several governmental agencies and regulators have initiated investigations into the Line 901 incident, various claims have been made against us and a number of lawsuits have been filed against us. We may be subject to additional claims, investigations and lawsuits, which could materially impact the liabilities and costs we currently expect to incur as a result of the Line 901 incident. Set forth below is a brief summary of actions and matters that are currently pending:
On May 21, 2015, we received a corrective action order from the United States Department of Transportation’s Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (“PHMSA”), the governmental agency that has jurisdiction over the operation of Line 901 as well as over a second stretch of pipeline extending from Gaviota Pump Station in Santa Barbara County to Emidio Pump Station in Kern County, California (Line 903), requiring us to shut down, purge, review, remediate and test Line 901. On June 3, 2015, the corrective action order was amended to require us to take additional corrective actions with respect to both Lines 901 and 903, and on November 13, 2015, the corrective action order was further amended to require the purge and shutdown of Line 903 between Gaviota and Pentland (as amended, the “CAO”). Among other requirements, the CAO also obligates us to conduct a root cause failure analysis with respect to Line 901 and present remedial work plans and restart plans to PHMSA prior to returning Line 901 and 903 to service; the CAO also imposes a pressure restriction on Line 903 and requires us to take other specified actions with respect to both Lines 901 and 903. We intend to continue to comply with the CAO and to cooperate with any other governmental investigations relating to or arising out of the release. Excavation and removal of the affected section of the pipeline was completed on May 28, 2015. No timeline has been established for the restart of Line 901 or Line 903. On February 17, 2016, PHMSA issued a Preliminary Factual Report of the Line 901 failure, which contains PHMSA’s preliminary findings regarding factual information about the events leading up to the accident and the technical analysis that has been conducted to date. By virtue of its statutory authority, PHMSA has the power and authority to impose fines and penalties on us and cause civil or criminal charges to be brought against us. While to date PHMSA has not imposed any such fines or penalties or pursued any such civil or criminal charges with respect to the Line 901 release, there can be no assurance that such fines or penalties will not be imposed upon us, or that such civil or criminal charges will not be brought against us, in the future.
On September 11, 2015, we received a Notice of Probable Violation and Proposed Compliance Order from PHMSA arising out of its inspection of Lines 901 and 903 in August, September and October of 2013 (the “2013 Audit NOPV”). The 2013 Audit NOPV alleges that the Partnership committed probable violations of various federal pipeline safety regulations by failing to document, or inadequately documenting, certain activities. On October 12, 2015, the Partnership filed a response to the 2013 Audit NOPV. To date, PHMSA has not issued a final order with respect to the 2013 Audit NOPV, nor has it assessed any fines or penalties with respect thereto; however, we cannot provide any assurances that any such fines or penalties will not be assessed against us.
In late May of 2015, on behalf of the EPA, the United States Attorney for the Department of Justice, Central District of California, Environmental Crimes Section (“DOJ”) began an investigation into whether there were any violations of federal criminal statutes in connection with the Line 901 incident, including potential violations of the federal Clean Water Act. We are cooperating with the DOJ’s investigation by responding to their requests for documents and access to our employees. The DOJ has already spoken to several of our employees and has expressed an interest in talking to other employees; consistent with the terms of our governing organizational documents, we are funding our employees’ defense costs, including the costs of separate counsel engaged to represent such individuals. In addition to the DOJ, the California Attorney General’s Office and the District Attorney’s Office for the County of Santa Barbara are also investigating the Line 901 incident to determine whether any applicable state or local laws have been violated. On August 26, 2015, we also received a Request for Information from the EPA relating to Line 901 and we are in the process of responding to such request. While to date no civil or criminal charges with respect to the Line 901 release have been brought against PAA or any of its affiliates, officers or employees by PHMSA, DOJ, EPA, California Attorney General or Santa Barbara County District Attorney, and no fines or penalties have been imposed by such governmental agencies, there can be no assurance that such fines or penalties will not be imposed upon us, our officers or our employees, or that such civil or criminal charges will not be brought against us, our officers or our employees in the future, whether by those or other governmental agencies.
Shortly following the Line 901 incident, we established a claims line and encouraged any parties that were damaged by the release to contact us to discuss their damage claims. We have received a number of claims through the claims line and we are processing those claims as we receive them. In addition, we have also had seven class action lawsuits filed against us, all of which have been administratively consolidated into a single proceeding in the United States District Court for the Central District of California. In general, the plaintiffs are seeking to establish different classes of claimants that have allegedly been damaged by the release, including potential classes such as persons that derive a significant portion of their income through commercial fishing and harvesting activities in the waters adjacent to Santa Barbara County or from businesses that are dependent on marine resources from Santa Barbara County, retail businesses located in historic downtown Santa Barbara, certain owners of oceanfront and/or beachfront property on the Pacific Coast of California, and other classes of individuals and businesses that were allegedly impacted by the release.
There have also been two securities law class action lawsuits filed on behalf of certain purported investors in PAA and/or PAGP against PAA, PAGP and/or certain of their respective officers, directors and underwriters. Both of these lawsuits have been consolidated into a single proceeding in the United States District Court for the Southern District of Texas. In general, these lawsuits allege that the various defendants violated securities laws by misleading investors regarding the integrity of PAA’s pipelines and related facilities through false and misleading statements, omission of material facts and concealing of the true extent of the spill. The plaintiffs claim unspecified damages as a result of the reduction in value of their investments in PAA and PAGP, which they attribute to the alleged wrongful acts of the defendants. PAA and PAGP, and the other defendants, deny the allegations in these lawsuits and intend to respond accordingly. Consistent with and subject to the terms of our governing organizational documents (and to the extent applicable, insurance policies), we are indemnifying and funding the defense costs of our officers and directors in connection with these lawsuits; we are also indemnifying and funding the defense costs of our underwriters pursuant to the terms of the underwriting agreements we previously entered into with such underwriters.
In addition, three unitholder derivative lawsuits have been filed by certain purported investors in PAA against PAA, certain of its affiliates and certain officers and directors. Two of these lawsuits were filed in the United States District Court for the Southern District of Texas and the other was filed in State District Court in Harris County, Texas. In general, these lawsuits allege that the various defendants breached their fiduciary duties, engaged in gross mismanagement and made false and misleading statements, among other similar allegations, in connection with their management and oversight of PAA during the period of time leading up to and following the Line 901 release. The plaintiffs claim that PAA suffered unspecified damages as a result of the actions of the various defendants and seek to hold the defendants liable for such damages, in addition to other remedies. The defendants deny the allegations in these lawsuits and intend to respond accordingly. Consistent with and subject to the terms of our governing organizational documents (and to the extent applicable, insurance policies), we are indemnifying and funding the defense costs of our officers and directors in connection with these lawsuits.
In addition to the foregoing, as the “responsible party” for the Line 901 incident we are liable for various costs and for certain natural resource damages under the Oil Pollution Act, and we also have exposure to the payment of additional fines, penalties and costs under other applicable federal, state and local laws, statutes and regulations. To the extent any such costs are reasonably estimable, we have included an estimate of such costs in the loss accrual described below.
Taking the foregoing into account, as of December 31, 2015, we estimate that the aggregate total costs we have incurred or will incur with respect to the Line 901 incident will be approximately $269 million, which estimate includes actual and projected emergency response and clean-up costs, natural resource damage assessments and certain third party claims settlements, as well as estimates for fines, penalties and certain legal fees.This estimate considers our prior experience in environmental investigation and remediation matters and available data from, and in consultation with, our environmental and other specialists, as well as currently available facts and presently enacted laws and regulations. We have made assumptions for (i) the expected number of days that monitoring services will be required, (ii) the duration of the natural resource damage assessment and the ultimate amount of damages determined, (iii) the resolution of certain third party claims and lawsuits, but excluding claims and lawsuits with respect to which losses are not probable and reasonably estimable, and excluding future claims and lawsuits, (iv) the determination and calculation of fines and penalties, but excluding fines and penalties that are not probable and reasonably estimable and (v) the nature, extent and cost of legal services that will be required in connection with all lawsuits, claims and other matters requiring legal or expert advice associated with the Line 901 incident. Our estimate does not include any lost revenue associated with the shutdown of Line 901 or 903 and does not include any liabilities or costs that are not reasonably estimable at this time or that relate to contingencies where we currently regard the likelihood of loss as being only reasonably possible or remote. We believe we have accrued adequate amounts for all probable and reasonably estimable costs; however, this estimate is subject to uncertainties associated with the assumptions that we have made. For example, the amount of time it takes for us to resolve all of the current and future lawsuits, claims and investigations that relate to the Line 901 incident could turn out to be significantly longer than we have assumed, and as a result the costs we incur for legal services could be significantly higher than we have estimated. In addition, with respect to fines and penalties, the ultimate amount of any fines and penalties assessed against us depends on a wide variety of factors, many of which are not estimable at this time. Where fines and penalties are probable and estimable, we have included them in our estimate, although such estimates could turn out to be wrong. Accordingly, our assumptions and estimates may turn out to be inaccurate and our total costs could turn out to be materially higher; therefore, we can provide no assurance that we will not have to accrue significant additional costs in the future with respect to the Line 901 incident.
We have accrued such estimate of aggregate total costs to “Field operating costs” on our Consolidated Statement of Operations. As of December 31, 2015, we had a remaining undiscounted gross liability of $116 million related to this event, the majority of which is presented as a current liability in “Accounts payable and accrued liabilities” on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. We maintain insurance coverage, which is subject to certain exclusions and deductibles, in the event of such environmental liabilities. Subject to such exclusions and deductibles, we believe that our coverage is adequate to cover the current estimated total emergency response and clean-up costs, claims settlement costs and remediation costs and we believe that this coverage is also adequate to cover any potential increase in the estimates for these costs that exceed the amounts currently identified. Through December 31, 2015, we had collected, subject to customary reservations, $31 million out of the approximate $186 million of release costs that we believe are probable of recovery from insurance carriers, net of deductibles. We recovered an additional $69 million of proceeds from insurance carriers in January 2016. As of December 31, 2015, we have recognized a receivable of approximately $155 million for the portion of the release costs that we believe is probable of recovery from insurance, net of deductibles and amounts already collected. A majority of this receivable has been recognized as a current asset in “Trade accounts receivable and other receivables, net” on our Consolidated Balance Sheets with the offset reducing “Field operating costs” on our Consolidated Statement of Operations. We have substantially completed the clean-up and remediation efforts, excluding long-term site monitoring activities; however, we expect to make payments for additional costs associated with restoration and monitoring of the area, as well as natural resource damage assessment, legal, professional and regulatory costs, in addition to fines and penalties, during future periods.
MP29 Release. On July 10, 2015, we experienced a crude oil release of approximately 100 barrels at our Pocahontas Pump Station near the border of Bond and Madison Counties in Illinois, approximately 40 miles from St. Louis, Missouri. The Pocahontas Station is part of the Capwood pipeline that runs from our Patoka Station to Wood River, Illinois. A portion of the released crude oil was contained within our Pocahontas facility, but some of the released crude oil entered a nearby waterway where it was contained with booms. On July 14, 2015, PHMSA issued a corrective action order requiring us to take various actions in response to the release, including remediation, reporting and other actions. As of December 18, 2015, we had submitted all requested information and reports required by the corrective action order and are currently awaiting PHMSA’s comment or approval. On August 10, 2015, we received a Notice of Violation from the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency (the “Agency”) alleging violations relating to the release and outlining the activities recommended by the Agency to resolve the alleged violations, including the completion of an investigation and various remediation activities. The Agency approved a work plan describing remediation activities proposed for remaining hydrocarbons at Pocahontas Station and affected waterways. Remediation activities under this work plan have effectively been completed, and on December 17, 2015, we entered into a Compliance Commitment Agreement with the Agency, which provides the framework for final completion and documentation of the remediation effort. To date, no fines or penalties have been assessed in this matter; however, it is possible that fines and penalties could be assessed in the future. In connection with this incident, we have also had one class action lawsuit filed against us in the United States District Court for the Southern District of Illinois, which was subsequently voluntarily dismissed by the plantiff. We estimate that the aggregate total costs associated with this release will be less than $10 million.
Cushing Tank Cathodic Protection. On May 22, 2015, PHMSA issued a Final Order relating to an April 2013 Notice of Probable Violation and Proposed Compliance Order alleging that we did not maintain adequate cathodic protection for certain tanks at our Cushing Terminal. In its 2013 Notice of Probable Violation, PHMSA maintained that the proprietary cathodic protection system utilized by us for certain of our storage tanks at our Cushing, Oklahoma facility was not contemplated by applicable regulations. In response to the notice, we provided extensive documentation and supporting information regarding the effectiveness of the technology we were utilizing, including past communications with PHMSA regarding the topic. At a hearing in August 2013, we gave a formal presentation on the technology, provided empirical data confirming its effectiveness and also had a third party corrosion expert witness speak to the effectiveness of the technology. Almost two years later, PHMSA issued the Final Order and Compliance Order dated May 22, 2015 ruling against our position, assessing a penalty of $102,900 and specifying certain corrective actions to be completed by us. We chose not to further contest this matter and paid the penalty on June 5, 2015.
In the Matter of Bakersfield Crude Terminal LLC et al. On April 30, 2015, the EPA issued a Finding and Notice of Violation (“NOV”) to Bakersfield Crude Terminal LLC, our subsidiary, for alleged violations of the Clean Air Act, as amended. The NOV, which cites 10 separate rule violations, questions the validity of construction and operating permits issued to our Bakersfield rail unloading facility in 2012 and 2014 by the San Joaquin Valley Air Pollution Control District (the “SJV District”). We believe we fully complied with all applicable regulatory requirements and that the permits issued to us by the SJV District are valid. To date, no fines or penalties have been assessed in this matter; however, it is possible that fines and penalties could be assessed in the future.
Mesa to Basin Pipeline. On January 6, 2016, PHMSA issued a Notice of Probable Violation and Proposed Civil Penalty relating to an approximate 500 barrel release of crude oil that took place on January 1, 2015 on our Mesa to Basin 12” pipeline in Midland, Texas. PHMSA conducted an accident investigation and reviewed documentation related to the incident, and concluded that we had committed probable violations of certain pipeline safety regulations. In the Notice, PHMSA maintains that we failed to carry out our written damage prevention program and to follow our pipeline excavation/ditching and backfill procedures on four separate occasions, and that such failures resulted in outside force damage that led to the January 1, 2015 release. PHMSA’s compliance officer has recommended that we be assessed a civil penalty of $190,000. We have formally responded to PHMSA regarding this matter, but at this point we can provide no assurance regarding the final disposition of this matter or the final amount of any civil penalties.
National Energy Board Audit. In the third quarter of 2014, the National Energy Board (“NEB”) of Canada notified PMC that various corrective actions from a 2010 audit had not been completed to the satisfaction of the NEB. The NEB initiated a process to assess PMC’s approach to compliance with the NEB’s Onshore Pipeline Regulations, which resulted in the issuance by the NEB of an order on January 15, 2015 that imposed six conditions on PMC designed to enhance PMC’s ability to operate its pipelines in a manner that protects the public and the environment. The conditions include the filing of certain safety critical tasks, controls and programs with the NEB, external audits of certain PMC programs and systems, and periodic update meetings with NEB staff regarding the status and progress of corrective actions. In early February 2015, the NEB imposed a penalty on PMC of $76,000 CAD related to these issues. It is possible that additional fines and penalties may be assessed against PMC in the future related to this matter.
Kemp River Pipeline Releases. In May and June 2013, two separate releases were discovered on our Kemp River pipeline in Northern Alberta, Canada that, in the aggregate, resulted in the release of approximately 700 barrels of condensate and light crude oil. Clean-up and remediation activities are being conducted in cooperation with the applicable regulatory agencies. Final investigation by the Alberta Energy Regulator is not complete. To date, no charges, fines or penalties have been assessed against PMC with respect to these releases; however, it is possible that fines or penalties may be assessed against PMC in the future. We estimate that the aggregate clean-up and remediation costs associated with these releases will be $15 million. Through December 31, 2015, we spent $9 million in connection with clean-up and remediation activities.
Bay Springs Pipeline Release. In February 2013, we experienced a crude oil release of approximately 120 barrels on a portion of one of our pipelines near Bay Springs, Mississippi. Most of the released crude oil was contained within our pipeline right of way, but some of the released crude oil entered a nearby waterway where it was contained with booms. The EPA has issued an administrative order requiring us to take various actions in response to the release, including remediation, reporting and other actions. We have satisfied the requirements of the administrative order; however, we may be subjected to a civil penalty. The aggregate cost to clean up and remediate the site was $6 million.
Environmental Remediation
We currently own or lease, and in the past have owned and leased, properties where hazardous liquids, including hydrocarbons, are or have been handled. These properties and the hazardous liquids or associated wastes disposed thereon may be subject to CERCLA, RCRA and state and Canadian federal and provincial laws and regulations. Under such laws and regulations, we could be required to remove or remediate hazardous liquids or associated wastes (including wastes disposed of or released by prior owners or operators) and to clean up contaminated property (including contaminated groundwater).
We maintain insurance of various types with varying levels of coverage that we consider adequate under the circumstances to cover our operations and properties. The insurance policies are subject to deductibles and retention levels that we consider reasonable and not excessive. Consistent with insurance coverage generally available in the industry, in certain circumstances our insurance policies provide limited coverage for losses or liabilities relating to gradual pollution, with broader coverage for sudden and accidental occurrences.
Assets we have acquired or will acquire in the future may have environmental remediation liabilities for which we are not indemnified. We have in the past experienced and in the future likely will experience releases of crude oil into the environment from our pipeline and storage operations. We also may discover environmental impacts from past releases that were previously unidentified.
Insurance
A pipeline, terminal or other facility may experience damage as a result of an accident, natural disaster or terrorist activity. These hazards can cause personal injury and loss of life, severe damage to and destruction of property and equipment, pollution or environmental damage and suspension of operations. We maintain various types of insurance that we consider adequate to cover our operations and certain assets. The insurance policies are subject to deductibles or self-insured retentions that we consider reasonable. Our insurance does not cover every potential risk associated with operating pipelines, terminals and other facilities, including the potential loss of significant revenues.
The occurrence of a significant event not fully insured, indemnified or reserved against, or the failure of a party to meet its indemnification obligations, could materially and adversely affect our operations and financial condition. We believe we are adequately insured for third-party liability and property damage with respect to our operations. In the future, we may not be able to maintain insurance at levels that we consider adequate for rates we consider reasonable. As a result, we may elect to self-insure or utilize higher deductibles in certain insurance programs. For example, the market for hurricane- or windstorm-related property damage coverage has remained difficult the last few years. The amount of coverage available has been limited, costs have increased substantially and deductibles have increased as well.
Our assessment of the current availability of coverage and associated rates for hurricane insurance has led us to the decision to self-insure this risk. This decision does not affect our third-party liability insurance, which still covers hurricane-related liability claims and which we have maintained at our historic coverage levels. In addition, although we believe that we have established adequate reserves to the extent such risks are not insured, costs incurred in excess of these reserves may be higher and may potentially have a material adverse effect on our financial conditions, results of operations or cash flows.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not applicable.
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Shares, Related Shareholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Our Class A shares are listed and traded on the New York Stock Exchange (“NYSE”) under the symbol “PAGP.” As of February 12, 2016, the closing market price for our Class A shares was $6.04 per share and there were approximately 29,000 record holders and beneficial owners (held in street name). As of February 12, 2016, there were 244,203,443 Class A shares outstanding.
The following table sets forth high and low sales prices for our Class A shares and the cash distributions declared per Class A share for the periods indicated:
|
|
|
Class A share |
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
Price Range |
|
Cash |
| |||||
|
|
|
High |
|
Low |
|
Distributions (1) |
| |||
|
2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
4th Quarter |
|
$ |
19.49 |
|
$ |
7.18 |
|
$ |
0.23100 |
|
|
3rd Quarter |
|
$ |
26.64 |
|
$ |
16.28 |
|
$ |
0.23100 |
|
|
2nd Quarter |
|
$ |
29.87 |
|
$ |
25.81 |
|
$ |
0.22700 |
|
|
1st Quarter |
|
$ |
28.96 |
|
$ |
24.01 |
|
$ |
0.22200 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
2014 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
4th Quarter |
|
$ |
30.75 |
|
$ |
22.51 |
|
$ |
0.20300 |
|
|
3rd Quarter |
|
$ |
32.26 |
|
$ |
28.48 |
|
$ |
0.19075 |
|
|
2nd Quarter |
|
$ |
32.58 |
|
$ |
27.00 |
|
$ |
0.18340 |
|
|
1st Quarter |
|
$ |
29.00 |
|
$ |
24.38 |
|
$ |
0.17055 |
|
(1) Cash distributions associated with the quarter presented. These distributions were declared and paid in the following calendar quarter. See the “Cash Distribution Policy” section below for a discussion of our policy regarding distribution payments.
Our Class B shares are not listed or traded on any stock exchange.
Our Class A shares are also used as a form of compensation to our employees and directors. Additional information regarding our equity-indexed compensation plans is included in Part III of this report under Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.”
See Item 12. “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters” for information regarding securities authorized for issuance under equity compensation plans.
Cash Distribution Policy
Our partnership agreement requires that, within 55 days following the end of each quarter, we distribute all of our available cash to Class A shareholders of record on the applicable record date. Available cash generally means, for any quarter ending prior to liquidation, all cash on hand at the date of determination of available cash for the distribution in respect of such quarter (including expected distributions from AAP in respect of such quarter), less the amount of cash reserves established by our general partner, which will not be subject to a cap, to:
· comply with applicable law or any agreement binding upon us or our subsidiaries (exclusive of PAA and its subsidiaries);
· provide funds for distributions to shareholders;
· provide for future capital expenditures, debt service and other credit needs as well as any federal, state, provincial or other income tax that may affect us in the future;
· permit us to pay a ratable amount to AAP as necessary to permit AAP to make required capital contributions to PAA to maintain PAA GP’s 2% general partner interest upon the issuance of additional partnership securities by PAA; or
· provide for the proper conduct of our business;
As of December 31, 2015, our only cash-generating assets consisted of our indirect partnership interests in PAA through our approximate 38% limited partner interest in AAP. AAP currently receives all of its cash flows from its direct ownership of all of PAA’s IDRs and its indirect ownership of the 2% general partner interest in PAA. Therefore, our cash flow and resulting ability to make distributions will be completely dependent upon the ability of PAA to make distributions to AAP in respect of those partnership interests. The actual amount of cash that PAA, and correspondingly AAP, will have available for distribution will primarily depend on the amount of cash PAA generates from its operations. Also, under the terms of the agreements governing AAP and PAA’s debt, they are prohibited from declaring or paying any distribution to unitholders if a default or event of default (as defined in such agreements) exists. No such default has occurred. See Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Credit Agreements, PAA Commercial Paper Program and Indentures.”
In January 2016, PAA completed the private placement of approximately 61.0 million Series A Convertible Preferred Units representing limited partner interests in PAA (the “PAA preferred units”). The PAA preferred units rank senior to all classes or series of equity securities in PAA with respect to distribution rights. AAP will be entitled to participate in distributions on the PAA preferred units equal to its 2% general partner interest in PAA.
Although not required to do so, in response to past requests by PAA management in connection with PAA’s acquisition activities, AAP has, from time to time, agreed to reduce the amounts due to it as incentive distributions. Such modifications were implemented with a view toward enhancing PAA’s competitiveness for such acquisitions and managing the overall cost of equity capital while achieving an appropriate balance between short-term and long-term accretion to PAA’s limited partners and the holders of its general partner interest and IDRs. During 2015, 2014 and 2013, AAP’s incentive distributions were reduced by approximately $22 million, $23 million and $15 million, respectively. These reductions were agreed to in connection with the BP NGL Acquisition and the PNG Merger. In addition, AAP has agreed to reduce the amount of its incentive distribution by $5.0 million per quarter in 2016 and $3.75 million per quarter thereafter. See Note 1 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of the PNG Merger. In connection with PAA’s January 2016 private placement of preferred units, AAP agreed to further modify its IDRs such that when the PAA preferred units convert into PAA common units, the IDRs associated with the resulting PAA common units will only participate in distribution growth above an annualized PAA distribution level of $2.80 per converted PAA common unit. See Note 10 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of PAA’s preferred unit issuance.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
In connection with our IPO and related transactions, the former owners of Plains All American GP LLC (the “Legacy Owners”) acquired the following interests (collectively, the “Stapled Interests”): (i) AAP units representing an economic limited partner interest in AAP; (ii) general partner units representing a non-economic membership interest in our general partner; and (iii) Class B shares representing a non-economic limited partner interest in us. The Legacy Owners and any permitted transferees of their Stapled Interests have the right to exchange (the “Exchange Right”) all or a portion of such Stapled Interests for an equivalent number of Class A shares. In connection with the exercise of the Exchange Right, the Stapled Interests are transferred to us and the applicable Class B shares are canceled. Although we issue one Class A share for each Stapled Interest that is exchanged, we also receive one AAP unit and one general partner unit. As a result, the exercise by Legacy Owners of the Exchange Right is not dilutive. During the three months ended December 31, 2015, certain Legacy Owners or their permitted transferees exercised the Exchange Right, which resulted in the issuance of 2,074,022 Class A shares. The issuance of Class A shares in connection with the exercise of the Exchange Rights was exempt from the registration requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, pursuant to Section 4(2) thereof.
Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
We did not repurchase any of our Class A shares during the fourth quarter of 2015, and we do not have any announced or existing plans to repurchase any of our Class A shares.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The following tables set forth selected historical consolidated financial and other information for PAGP as of the dates and for the periods indicated. The selected consolidated statements of operations data for the year ended December 31, 2013 include results attributable to PAGP from October 21, 2013 (the date of closing PAGP’s IPO) through December 31, 2013, plus results for Plains All American GP LLC (“GP LLC”), the predecessor entity to PAGP, prior to October 21, 2013.
The selected historical statements of operations and cash flow data for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014, 2013, 2012 and 2011 and balance sheet data as of December 31, 2015, 2014, 2013 and 2012 is derived from the audited financial statements of
PAGP (and GP LLC as discussed above) included elsewhere in this document. The selected balance sheet data as of December 31, 2011 is derived from the unaudited financial statements of GP LLC that are not included elsewhere in this document.
The selected financial data should be read in conjunction with the Consolidated Financial Statements, including the notes thereto, and Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
Amounts for 2011 through 2014 have been retroactively restated to reflect the impact of our adoption of revised debt issuance costs guidance issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”). See Note 2 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information.
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
2012 |
|
2011 |
| |||||
|
|
|
(in millions, except per unit data) |
| |||||||||||||
|
Statement of operations data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Total revenues |
|
$ |
23,152 |
|
$ |
43,464 |
|
$ |
42,249 |
|
$ |
37,797 |
|
$ |
34,275 |
|
|
Operating income |
|
$ |
1,258 |
|
$ |
1,791 |
|
$ |
1,734 |
|
$ |
1,433 |
|
$ |
1,305 |
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
809 |
|
$ |
1,328 |
|
$ |
1,374 |
|
$ |
1,118 |
|
$ |
987 |
|
|
Net income attributable to PAGP |
|
$ |
118 |
|
$ |
70 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
$ |
3 |
|
$ |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Per unit data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Basic net income per Class A share (1) |
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
$ |
0.48 |
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
| ||
|
Diluted net income per Class A share (1) |
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
$ |
0.47 |
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
| ||
|
Declared distributions per common unit (2) |
|
$ |
0.88 |
|
$ |
0.67 |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Balance sheet data (at end of period): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
$ |
13,493 |
|
$ |
12,292 |
|
$ |
10,841 |
|
$ |
9,664 |
|
$ |
7,763 |
|
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
24,142 |
|
$ |
23,923 |
|
$ |
21,411 |
|
$ |
19,219 |
|
$ |
15,388 |
|
|
Long-term debt |
|
$ |
10,932 |
|
$ |
9,238 |
|
$ |
7,188 |
|
$ |
6,480 |
|
$ |
4,694 |
|
|
Total debt |
|
$ |
11,931 |
|
$ |
10,525 |
|
$ |
8,301 |
|
$ |
7,566 |
|
$ |
5,380 |
|
|
Partners’ capital / Members’ equity: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Partners’ capital / Members’ equity (excluding Noncontrolling interests) |
|
$ |
1,762 |
|
$ |
1,657 |
|
$ |
1,035 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Noncontrolling interests |
|
$ |
7,472 |
|
$ |
7,724 |
|
$ |
7,244 |
|
$ |
6,968 |
|
$ |
5,794 |
|
|
Total Partners’ capital / Members’ equity |
|
$ |
9,234 |
|
$ |
9,381 |
|
$ |
8,279 |
|
$ |
6,968 |
|
$ |
5,794 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Other data: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
$ |
1,333 |
|
$ |
1,988 |
|
$ |
1,948 |
|
$ |
1,232 |
|
$ |
2,357 |
|
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
$ |
(2,530 |
) |
$ |
(3,296 |
) |
$ |
(1,653 |
) |
$ |
(3,392 |
) |
$ |
(2,020 |
) |
|
Net cash provided by/(used in) financing activities |
|
$ |
827 |
|
$ |
1,672 |
|
$ |
(274 |
) |
$ |
2,159 |
|
$ |
(337 |
) |
|
Capital expenditures: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Acquisition capital |
|
$ |
105 |
|
$ |
1,099 |
|
$ |
19 |
|
$ |
2,286 |
|
$ |
1,404 |
|
|
Expansion capital |
|
$ |
2,170 |
|
$ |
2,026 |
|
$ |
1,622 |
|
$ |
1,185 |
|
$ |
531 |
|
|
Maintenance capital |
|
$ |
220 |
|
$ |
224 |
|
$ |
176 |
|
$ |
170 |
|
$ |
120 |
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| ||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
2012 |
|
2011 |
|
|
Volumes (3) (4) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Transportation segment (average daily volumes in thousands of barrels per day): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tariff activities |
|
4,340 |
|
3,952 |
|
3,595 |
|
3,373 |
|
2,942 |
|
|
Trucking |
|
113 |
|
127 |
|
117 |
|
106 |
|
105 |
|
|
Transportation segment total volumes |
|
4,453 |
|
4,079 |
|
3,712 |
|
3,479 |
|
3,047 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Facilities segment: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Crude oil, refined products and NGL terminalling and storage (average monthly capacity in millions of barrels) |
|
100 |
|
95 |
|
94 |
|
90 |
|
70 |
|
|
Rail load / unload volumes (average volumes in thousands of barrels per day) |
|
210 |
|
231 |
|
221 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
Natural gas storage (average monthly working capacity in billions of cubic feet) |
|
97 |
|
97 |
|
96 |
|
84 |
|
71 |
|
|
NGL fractionation (average volumes in thousands of barrels per day) |
|
103 |
|
96 |
|
96 |
|
79 |
|
14 |
|
|
Facilities segment total volumes (average monthly volumes in millions of barrels) |
|
126 |
|
121 |
|
120 |
|
106 |
|
82 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Supply and Logistics segment (average daily volumes in thousands of barrels per day): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Crude oil lease gathering purchases |
|
943 |
|
949 |
|
859 |
|
818 |
|
742 |
|
|
NGL sales |
|
223 |
|
208 |
|
215 |
|
182 |
|
103 |
|
|
Waterborne cargos |
|
2 |
|
— |
|
4 |
|
3 |
|
21 |
|
|
Supply and Logistics segment total volumes |
|
1,168 |
|
1,157 |
|
1,078 |
|
1,003 |
|
866 |
|
(1) Basic and diluted net income per Class A share for 2013 were calculated based on net income attributable to PAGP for the period following the closing of our initial public offering on October 21, 2013 and basic weighted average Class A shares outstanding weighted for the same period.
(2) Represents cash distributions declared and paid during the year presented.
(3) Average volumes are calculated as the total volumes (attributable to our interest) for the year divided by the number of days or months in the year.
(4) Facilities segment total is calculated as the sum of: (i) crude oil, refined products and NGL terminalling and storage capacity; (ii) rail load and unload volumes multiplied by the number of days in the year and divided by the number of months in the year; (iii) natural gas storage working capacity divided by 6 to account for the 6:1 thousand cubic feet (“mcf”) of natural gas to crude British thermal unit (“Btu”) equivalent ratio and further divided by 1,000 to convert to monthly volumes in millions; and (iv) NGL fractionation volumes multiplied by the number of days in the year and divided by the number of months in the year.
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Introduction
The following discussion is intended to provide investors with an understanding of our financial condition and results of our operations, including periods prior to the closing of our IPO on October 21, 2013. Such analysis should be read in conjunction with our historical consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes. For ease of reference, we refer to the historical results of Plains All American GP LLC (“GP LLC”) prior to our IPO as being “our” historical financial results. Unless the context otherwise requires, references to “we,” “us,” “our,” and “PAGP” are intended to mean the business and operations of PAGP and its consolidated subsidiaries since October 21, 2013. When used in the historical context (i.e. prior to October 21, 2013), these terms are intended to mean the business and operations of GP LLC and its consolidated subsidiaries.
Our discussion and analysis includes the following:
· Executive Summary
· Acquisitions and Capital Projects
· Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
· Recent Accounting Pronouncements
· Results of Operations
· Outlook
· Liquidity and Capital Resources
Executive Summary
Company Overview
We are a Delaware limited partnership formed on July 17, 2013 to own an interest in the general partner and incentive distribution rights (“IDRs”) of Plains All American Pipeline, L.P (“PAA”), a publicly traded Delaware limited partnership. Although we were formed as a limited partnership, we have elected to be taxed as a corporation for United States federal income tax purposes. As of December 31, 2015, we owned an approximate 38% limited partner interest in AAP, and the remaining limited partner interests in AAP were held by the owners of AAP immediately prior to our IPO (the “Legacy Owners”). AAP is a Delaware limited partnership that directly owns all of PAA’s incentive distribution rights and indirectly owns the 2% general partner interest in PAA. AAP is the sole member of PAA GP LLC (“PAA GP”), a Delaware limited liability company that directly holds the 2% general partner interest in PAA.
Through a series of transactions prior to our IPO with our general partner and the owners of GP LLC, a Delaware limited liability company formed on May 2, 2001 that manages the business and affairs of PAA and AAP, GP LLC’s general partner interest in AAP became a non-economic interest, and we became the owner of a 100% managing member interest in GP LLC. Since we are the managing member of and control GP LLC, which in turn effectively controls PAA, we reflect our ownership in PAA, as well as its subsidiaries, on a consolidated basis in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. Accordingly, our financial results are combined with those of GP LLC and PAA as well as with their subsidiaries. As such, our results of operations as discussed below do not differ materially from the results of operations of PAA.
PAA owns and operates midstream energy infrastructure and provides logistics services for crude oil, NGL, natural gas and refined products. PAA owns an extensive network of pipeline transportation, terminalling, storage, and gathering assets in key crude oil and NGL producing basins and transportation corridors and at major market hubs in the United States and Canada.
Overview of Operating Results, Capital Investments and Other Significant Activities
Primarily as a result of advances in drilling and completion techniques and their application to a number of large-scale shale and resource plays, which occurred contemporaneously with attractive petroleum prices, during the approximately three year period through the end of 2014, U.S. crude oil and liquids production in the lower 48 states increased rapidly. Additionally, during this period, the crude oil market experienced high levels of volatility in location and quality differentials as a result of the confluence of regional infrastructure constraints in North America, rapid and unexpected changes in crude oil qualities, international supply issues, and regional downstream operating issues. During 2014 (albeit to a lesser degree than previous years), these market conditions had a positive impact on our profitability as our business strategy and asset base positioned us to capitalize on opportunities created by the volatile environment. However, the combination during such period of surging North American liquids production, relatively flat liquids production for the rest of the world and relatively modest growth in global liquids demand led to a supply imbalance, which in turn led to a significant and rapid reduction in petroleum prices during the second half of 2014 and throughout 2015.
While we believe that our business model and asset base have minimal direct exposure to petroleum prices, our performance is influenced by certain differentials and overall North American production levels, which in turn are impacted by major price movements. The meaningful decrease in crude oil price levels during the second half of 2014 and throughout 2015 relative to the levels experienced during 2013 and the first half of 2014 have led many producers, including North American producers, to significantly scale back capital programs. As a result, during 2015, the rate of growth of North American crude oil production slowed significantly and began to decrease in some areas as producers have taken rigs out of service and deferred completions at an increased rate. The slowdown in North American production coupled with increases in infrastructure led to a compression of basis differentials in a number of locations. This transitioning crude oil market created a challenging environment for our business model and asset base in 2015. We recognized net income of $809 million in 2015 as compared to net income of $1.328 billion recognized in 2014. The year-over-year decrease was driven by:
· Lower operating results, primarily from our Supply and Logistics segment, as increased competition and compressed differentials from the market conditions discussed above drove lower unit margins in this part of our business. See further discussion of our segment operating results in the “—Results of Operations—Analysis of Operating Segments” section below;
· Costs and lost revenue associated with the Line 901 incident; and
· Higher depreciation and amortization expense and interest expense associated with our growing asset base and related financing activities; partially offset by
· Lower income tax expense resulting from the deferred income tax impact associated with fluctuations in the derivative mark-to-market valuation in our Canadian operations.
We executed a $2.2 billion capital program during 2015. We expect the majority of the capital invested will contribute to growth in our fee-based Transportation and Facilities segments in future years. To fund the 2015 capital expansion activities, PAA executed multiple financings, including raising an aggregate of approximately $2.1 billion of long-term debt and equity capital. In addition, we paid approximately $1.7 billion of cash distributions to our Class A shareholders and noncontrolling interests during 2015.
Acquisitions and Capital Projects
We completed a number of acquisitions and capital projects in 2015, 2014 and 2013 that have impacted our results of operations. The following table summarizes our expenditures for acquisition capital, expansion capital and maintenance capital for the periods indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
Acquisition capital (1) (2) |
|
$ |
105 |
|
$ |
1,099 |
|
$ |
19 |
|
|
Expansion capital (3) |
|
2,170 |
|
2,026 |
|
1,622 |
| |||
|
Maintenance capital (3) |
|
220 |
|
224 |
|
176 |
| |||
|
|
|
$ |
2,495 |
|
$ |
3,349 |
|
$ |
1,817 |
|
(1) Acquisitions of initial investments or additional interests in unconsolidated entities are included in “Acquisition capital.” Subsequent contributions to unconsolidated entities related to expansion projects of such entities are recognized in “Expansion capital.” We account for our investments in such entities under the equity method of accounting.
(2) Excludes the PNG Merger completed on December 31, 2013, as we historically consolidated PNG into our financial statements for financial reporting purposes in accordance with GAAP. As consideration for the PNG Merger, we issued approximately 14.7 million PAA common units with a value of approximately $760 million. See Note 1 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of the PNG Merger.
(3) Capital expenditures made to expand the existing operating and/or earnings capacity of our assets are classified as expansion capital. Capital expenditures for the replacement of partially or fully depreciated assets in order to maintain the operating and/or earnings capacity of our existing assets are classified as maintenance capital.
Acquisitions
Acquisitions are financed using a combination of equity and debt, including borrowings under the PAA commercial paper program or credit facilities and the issuance of PAA senior notes. Businesses acquired impact our results of operations commencing on the closing date of each acquisition. Our acquisition and capital expansion activities are discussed further in “—Liquidity and Capital Resources.” Information regarding acquisitions completed in 2015, 2014 and 2013 is set forth in the table below (in millions):
|
|
|
Effective |
|
Acquisition |
|
|
| |
|
Acquisition |
|
Date |
|
Price |
|
Operating Segment |
| |
|
2015 Total |
|
Various |
|
$ |
105 |
|
Transportation and Facilities |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
BridgeTex Acquisition (50% interest) (1) |
|
11/14/2014 |
|
$ |
1,088 |
|
Transportation |
|
|
Other |
|
Various |
|
11 |
|
Facilities |
| |
|
2014 Total |
|
|
|
$ |
1,099 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2013 Total (2) |
|
09/01/2013 |
|
$ |
19 |
|
Transportation |
|
(1) We account for our 50% interest in BridgeTex under the equity method of accounting. See Note 7 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of our equity method investments.
(2) Excludes the PNG Merger completed on December 31, 2013, as we historically consolidated PNG into our financial statements for financial reporting purposes in accordance with GAAP. As consideration for the PNG Merger, we issued approximately 14.7 million PAA common units with a value of approximately $760 million. See Note 1 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion of the PNG Merger.
Expansion Capital Projects
Our 2015 projects primarily included the construction and expansion of pipeline systems and storage and terminal facilities. The following table summarizes our 2015, 2014 and 2013 projects (in millions):
|
Projects |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
Permian Basin Area Projects (1) |
|
$ |
470 |
|
$ |
378 |
|
$ |
59 |
|
|
Rail Terminal Projects (2) |
|
294 |
|
239 |
|
149 |
| |||
|
Fort Saskatchewan Facility Projects / NGL Line (1) |
|
272 |
|
142 |
|
73 |
| |||
|
Red River Pipeline (Cushing to Longview) (1) |
|
143 |
|
— |
|
— |
| |||
|
Cactus Pipeline (1) |
|
134 |
|
350 |
|
64 |
| |||
|
Saddlehorn Pipeline (1) (3) |
|
103 |
|
— |
|
— |
| |||
|
Eagle Ford JV Project (1) (4) |
|
93 |
|
117 |
|
60 |
| |||
|
Cowboy Pipeline (Cheyenne to Carr) (1) |
|
47 |
|
— |
|
— |
| |||
|
Eagle Ford Area Projects (5) |
|
45 |
|
10 |
|
86 |
| |||
|
St. James Terminal Expansions (1) |
|
45 |
|
25 |
|
51 |
| |||
|
Cushing Terminal Expansions (1) |
|
39 |
|
13 |
|
38 |
| |||
|
Diamond Pipeline (1) (4) |
|
6 |
|
29 |
|
3 |
| |||
|
Mississippian Lime Pipeline |
|
— |
|
58 |
|
163 |
| |||
|
Pascagoula Pipeline |
|
— |
|
26 |
|
125 |
| |||
|
Other Projects |
|
479 |
|
639 |
|
751 |
| |||
|
Total |
|
$ |
2,170 |
|
$ |
2,026 |
|
$ |
1,622 |
|
(1) These projects will continue into 2016. See “—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Acquisitions, Capital Expenditures and Distributions Paid to Our Class A Shareholders and Noncontrolling Interests—2016 Capital Projects.”
(2) Includes railcar purchases, as well as rail projects near St. James, LA; Tampa, CO; Bakersfield, CA; Carr, CO; Manitou, ND; Van Hook, ND; Yorktown, VA; and Kerrobert, Canada rail projects.
(3) Represents contributions related to our 40% investment interest in Saddlehorn.
(4) Represents contributions related to our 50% investment interest.
(5) Includes pipeline, tankage and condensate stabilization.
The overall increase in our expansion capital expenditures over the periods presented was primarily driven by our investment in midstream infrastructure projects to address the need for additional takeaway capacity in regions impacted by the increase in crude oil and liquids-rich gas production growth in North America, as well as the long-term needs of both the upstream and downstream sectors of the crude oil space. A majority of the expansion capital spent in the years presented was invested in our fee-based Transportation and Facilities segments.
We currently expect to spend approximately $1.5 billion for expansion capital in 2016. See “—Liquidity and Capital Resources—Acquisitions, Capital Expenditures and Distributions Paid to Our Class A Shareholders and Noncontrolling Interests—2016 Capital Projects” and “—Outlook” for additional information.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Critical Accounting Policies
We have adopted various accounting policies to prepare our consolidated financial statements in accordance with GAAP. These critical accounting policies are discussed in Note 2 to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Critical Accounting Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP and rules and regulations of the SEC requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, as well as the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities, at the date of the financial statements. Such estimates and assumptions also affect the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Although we believe these estimates are reasonable, actual results could differ from these estimates. On a regular basis, we evaluate our assumptions, judgments and estimates. We also discuss our critical accounting policies and estimates with the Audit Committee of the Board of Directors.
We believe that the assumptions, judgments and estimates involved in the accounting for our (i) purchase and sales accruals, (ii) estimated fair value of assets and liabilities acquired and identification of associated goodwill and intangible assets, (iii) fair value of derivatives, (iv) accruals and contingent liabilities, (v) equity-indexed compensation plan accruals, (vi) property and equipment, depreciation expense and asset retirement obligations, (vii) allowance for doubtful accounts and (viii) inventory valuations have the greatest potential impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements. These areas are key components of our results of operations and are based on complex rules which require us to make judgments and estimates, so we consider these to be our critical accounting estimates. Such critical accounting estimates are discussed further as follows:
Purchase and Sales Accruals. We routinely make accruals based on estimates for certain components of our revenues and purchases and related costs due to the timing of compiling billing information, receiving third-party information and reconciling our records with those of third parties. Where applicable, these accruals are based on nominated volumes expected to be purchased, transported and subsequently sold. Uncertainties involved in these estimates include levels of production at the wellhead, access to certain qualities of crude oil, pipeline capacities and delivery times, utilization of truck fleets to transport volumes to their destinations, weather, market conditions and other forces beyond our control. These estimates are generally associated with a portion of the last month of each reporting period. For the year ended December 31, 2015, we estimate that approximately 2% of annual revenues and purchases and related costs were recorded using sales and purchase estimates. Accordingly, a hypothetical variance of 10% from both of these estimates, either up or down in tandem, would impact annual revenues, purchases and related costs, operating income and net income by less than 1% on an annual basis. Although the resolution of these uncertainties has not historically had a material impact on our reported results of operations or financial condition, because of the high volume, low margin nature of our business, we cannot provide assurance that actual amounts will not vary significantly from estimated amounts. Variances from estimates are reflected in the period actual results become known, typically in the month following the estimate.
Fair Value of Assets and Liabilities Acquired and Identification of Associated Goodwill and Intangible Assets. In accordance with FASB guidance regarding business combinations, with each acquisition, we allocate the cost of the acquired entity to the assets and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair values at the date of acquisition. If the initial accounting for the business combination is incomplete when the combination occurs, an estimate will be recorded. Any subsequent adjustments to this estimate, if material, will be recognized retroactive to the date of acquisition. With exception to acquisitions of equity method investments, we also expense the transaction costs as incurred in connection with each acquisition. In addition, we are required to recognize intangible assets separately from goodwill. Intangible assets with finite lives are amortized over their estimated useful life as determined by management. Goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite lives are not amortized but instead are periodically assessed for impairment.
Determining the fair value of assets and liabilities acquired, as well as intangible assets that relate to such items as customer relationships, contracts and industry expertise, involves professional judgment and is ultimately based on acquisition models and management’s assessment of the value of the assets acquired and, to the extent available, third party assessments. Impairment testing entails estimating future net cash flows relating to the business, based on management’s estimate of future revenues, future cash flows and market conditions including pricing, demand, competition, operating costs and other factors, such as weighted average cost of capital. Uncertainties associated with these estimates include changes in production decline rates, production interruptions, fluctuations in refinery capacity or product slates, economic obsolescence factors in the area and potential future sources of cash flow. Although the resolution of these uncertainties has not historically had a material impact on our results of operations or financial condition, we cannot provide assurance that actual amounts will not vary significantly from estimated amounts. Further, significant negative variances in the assumptions and estimates utilized in our forecasts, such as a continued decline in petroleum commodity prices or a sustained multi-year low petroleum commodity price environment that results in lower volumes and cash flows or further increases in our weighted average cost of capital assumption, could result in reporting unit carrying values in excess of fair values. See Note 6 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for a further discussion of goodwill.
Fair Value of Derivatives. The fair value of a derivative at a particular period end does not reflect the end results of a particular transaction, and will most likely not reflect the gain or loss at the conclusion of a transaction. We reflect estimates for these items based on our internal records and information from third parties. The valuations of our derivatives that are exchange traded are based on market prices on the applicable exchange on the last day of the period. For our derivatives that are not exchange traded, the estimates we use are based on indicative broker quotations or an internal valuation model. Our valuation models utilize market observable inputs such as price, volatility, correlation and other factors and may not be reflective of the price at which they can be settled due to the lack of a liquid market. Less than 1% of total annual revenues are based on estimates derived from internal valuation models. Although the resolution of these uncertainties has not historically had a material impact on our results of operations or financial condition, we cannot provide assurance that actual amounts will not vary significantly from estimated amounts. See Note 11 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion regarding our derivatives and risk management activities.
Accruals and Contingent Liabilities. We record accruals or liabilities for, among other things, environmental remediation, natural resource damage assessments, governmental fines and penalties, potential legal claims and fees for legal services associated with loss contingencies, and bonuses. Accruals are made when our assessment indicates that it is probable that a liability has occurred and the amount of liability can be reasonably estimated. Our estimates are based on all known facts at the time and our assessment of the ultimate outcome. Among the many uncertainties that impact our estimates are the necessary regulatory approvals for, and potential modification of, our environmental remediation plans, the limited amount of data available upon initial assessment of the impact of soil or water contamination, changes in costs associated with environmental remediation services and equipment, the duration of the natural resource damage assessment and the ultimate amount of damages determined, the determination and calculation of fines and penalties, the possibility of existing legal claims giving rise to additional claims and the nature, extent and cost of legal services that will be required in connection with lawsuits, claims and other matters. Our estimates for contingent liability accruals are increased or decreased as additional information is obtained or resolution is achieved. A hypothetical variance of 5% in our aggregate estimate for the accruals and contingent liabilities discussed above would have an impact on earnings of up to approximately $14 million. Although the resolution of these uncertainties has not historically had a material impact on our results of operations or financial condition, we cannot provide assurance that actual amounts will not vary significantly from estimated amounts.
Equity-Indexed Compensation Plan Accruals. We accrue compensation expense (referred to herein as equity-indexed compensation expense) for outstanding equity-indexed compensation awards. Under GAAP, we are required to estimate the fair value of our outstanding equity-indexed compensation awards and recognize that fair value as compensation expense over the service period. For equity-indexed compensation awards that contain a performance condition, the fair value of the award is recognized as equity-indexed compensation expense only if the attainment of the performance condition is considered probable. Uncertainties involved in this estimate include the actual unit price at time of vesting, whether or not a performance condition will be attained and the continued employment of personnel with outstanding equity-indexed compensation awards. We cannot provide assurance that the actual fair value of our equity-indexed compensation awards will not vary significantly from estimated amounts.
We recognized equity-indexed compensation expense of $27 million, $99 million and $116 million in 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, related to awards granted under our various equity-indexed compensation plans. A hypothetical variance of 5% in our aggregate estimate for the equity-indexed compensation expense would have an impact on net income of less than 1%. See Note 15 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion regarding our equity-indexed compensation plans.
Property and Equipment, Depreciation Expense and Asset Retirement Obligations. We compute depreciation using the straight-line method based on estimated useful lives. These estimates are based on various factors including condition, manufacturing specifications, technological advances and historical data concerning useful lives of similar assets. Uncertainties that impact these estimates include changes in laws and regulations relating to restoration and abandonment requirements, economic conditions and supply and demand in the area. When assets are put into service, we make estimates with respect to useful lives and salvage values that we believe are reasonable. However, subsequent events could cause us to change our estimates, thus impacting the future calculation of depreciation and amortization.
We record retirement obligations associated with tangible long-lived assets based on estimates related to the costs associated with cleaning, purging and in some cases, completely removing the assets and returning the land to its original state. In addition, our estimates include a determination of the settlement date or dates for the potential obligation, which may or may not be determinable. Uncertainties that impact these estimates include the costs associated with these activities and the timing of incurring such costs.
We periodically evaluate property and equipment for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying value of these assets may not be recoverable. Any evaluation is highly dependent on the underlying assumptions of related cash flows. We consider the fair value estimate used to calculate impairment of property and equipment a critical accounting estimate. In determining the existence of an impairment of carrying value, we make a number of subjective assumptions as to:
· whether there is an event or circumstance that may be indicative of an impairment;
· the grouping of assets;
· the intention of “holding”, “abandoning” or “selling” an asset;
· the forecast of undiscounted expected future cash flow over the asset’s estimated useful life; and
· if an impairment exists, the fair value of the asset or asset group.
We did not recognize any material impairment of long-lived assets during the three years ending December 31, 2015. See Note 5 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion regarding impairments.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts. We perform credit evaluations of our customers and grant credit based on past payment history, financial conditions and anticipated industry conditions. Customer payments are regularly monitored and a provision for doubtful accounts is established based on specific situations and overall industry conditions. Our history of bad debt losses has been minimal (less than $2 million in the aggregate over the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013) and generally limited to specific customer circumstances; however, credit risks can change suddenly and without notice. See Note 2 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional discussion.
Inventory Valuations. Inventory, including long-term inventory, primarily consists of crude oil, NGL and natural gas and is valued at the lower of cost or market, with cost determined using an average cost method within specific inventory pools. At the end of each reporting period, we assess the carrying value of our inventory and use estimates and judgment when making any adjustments necessary to reduce the carrying value to net realizable value. Among the uncertainties that impact our estimates are the applicable quality and location differentials to include in our net realizable value analysis. Additionally, we estimate the upcoming liquidation timing of the inventory. Changes in assumptions made as to the timing of a sale can materially impact net realizable value. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, we recorded charges of $117 million, $289 million and $7 million, respectively, related to the valuation adjustment of our crude oil, NGL and natural gas inventory due to declines in prices. See Note 4 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion regarding inventory.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
See Note 2 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for information regarding the effect of recent accounting pronouncements on our consolidated financial statements, including the impact of our adoption of revised debt issuance costs guidance on prior period financial statements.
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth an overview of our consolidated financial results calculated in accordance with GAAP (in millions, except per share amounts):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Favorable/(Unfavorable) Variance |
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
2015-2014 |
|
2014-2013 |
| ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|
$ |
|
% |
|
$ |
|
% |
| |||||
|
Transportation segment profit |
|
$ |
917 |
|
$ |
925 |
|
$ |
729 |
|
|
$ |
(8 |
) |
(1 |
)% |
$ |
196 |
|
27 |
% |
|
Facilities segment profit |
|
579 |
|
584 |
|
616 |
|
|
(5 |
) |
(1 |
)% |
(32 |
) |
(5 |
)% | |||||
|
Supply and Logistics segment profit |
|
381 |
|
782 |
|
822 |
|
|
(401 |
) |
(51 |
)% |
(40 |
) |
(5 |
)% | |||||
|
Total segment profit |
|
1,877 |
|
2,291 |
|
2,167 |
|
|
(414 |
) |
(18 |
)% |
124 |
|
6 |
% | |||||
|
Unallocated general and administrative expenses |
|
(3 |
) |
(6 |
) |
(1 |
) |
|
3 |
|
50 |
% |
(5 |
) |
(500 |
)% | |||||
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
(433 |
) |
(386 |
) |
(368 |
) |
|
(47 |
) |
(12 |
)% |
(18 |
) |
(5 |
)% | |||||
|
Interest expense, net |
|
(443 |
) |
(357 |
) |
(319 |
) |
|
(86 |
) |
(24 |
)% |
(38 |
) |
(12 |
)% | |||||
|
Other income/(expense), net |
|
(7 |
) |
(2 |
) |
1 |
|
|
(5 |
) |
(250 |
)% |
(3 |
) |
(300 |
)% | |||||
|
Income tax expense |
|
(182 |
) |
(212 |
) |
(106 |
) |
|
30 |
|
14 |
% |
(106 |
) |
(100 |
)% | |||||
|
Net income |
|
809 |
|
1,328 |
|
1,374 |
|
|
(519 |
) |
(39 |
)% |
(46 |
) |
(3 |
)% | |||||
|
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
(691 |
) |
(1,258 |
) |
(1,359 |
) |
|
567 |
|
45 |
% |
101 |
|
7 |
% | |||||
|
Net income attributable to PAGP |
|
$ |
118 |
|
$ |
70 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
|
$ |
48 |
|
69 |
% |
$ |
55 |
|
367 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Basic net income per Class A share (1) |
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
$ |
0.48 |
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
|
$ |
0.05 |
|
10 |
% |
$ |
0.38 |
|
380 |
% |
|
Diluted net income per Class A share (1) |
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
$ |
0.47 |
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
|
$ |
0.06 |
|
13 |
% |
$ |
0.37 |
|
370 |
% |
|
Basic weighted average Class A shares outstanding (1) |
|
222 |
|
145 |
|
132 |
|
|
77 |
|
53 |
% |
13 |
|
10 |
% | |||||
|
Diluted weighted average Class A shares outstanding (1) |
|
222 |
|
650 |
|
132 |
|
|
(428 |
) |
(66 |
)% |
518 |
|
392 |
% | |||||
(1) For the 2013 period, basic and diluted net income per Class A share were calculated based on net income attributable to PAGP for the period following the closing of our initial public offering on October 21, 2013 and basic weighted average Class A shares outstanding weighted for the same period.
Analysis of Operating Segments
We manage our operations through three operating segments: Transportation, Facilities and Supply and Logistics. Our Chief Operating Decision Maker (our Chief Executive Officer) evaluates segment performance based on a variety of measures including segment profit, segment volumes, segment profit per barrel and maintenance capital investment. See Note 18 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for a definition of segment profit (including an explanation of why this is a performance measure) and a reconciliation of segment profit to net income attributable to PAGP.
Our segment analysis involves an element of judgment relating to the allocations between segments. In connection with its operations, the Supply and Logistics segment secures transportation and facilities services from our other two segments as well as third-party service providers under month-to-month and multi-year arrangements. Intersegment transportation service rates are conducted at posted tariff rates, rates similar to those charged to third parties or rates that we believe approximate market. Facilities segment services are also obtained at rates generally consistent with rates charged to third parties for similar services; however, certain terminalling and storage rates are discounted to our Supply and Logistics segment to reflect the fact that these services may be canceled on short notice to enable the Facilities segment to provide services to third parties. Intersegment activities are eliminated in consolidation and we believe that the estimates with respect to these rates are reasonable. Also, our segment operating and general and administrative expenses reflect direct costs attributable to each segment; however, we also allocate certain operating expenses and general and administrative overhead expenses between segments based on management’s assessment of the business activities for the period. The proportional allocations by segment require judgment by management and may be adjusted in the future based on the business activities that exist during each period. We believe that the estimates with respect to these allocations are reasonable.
Revenues and expenses from our Canadian based subsidiaries, which use CAD as their functional currency, are translated at the prevailing average exchange rates for each month.
Transportation Segment
Our Transportation segment operations generally consist of fee-based activities associated with transporting crude oil and NGL on pipelines, gathering systems, trucks and barges. The Transportation segment generates revenue through a combination of tariffs, third-party pipeline capacity agreements and other transportation fees.
The following tables set forth our operating results from our Transportation segment for the periods indicated:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Favorable/(Unfavorable) Variance |
| |||||||||||
|
Operating Results (1) |
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
2015-2014 |
|
2014-2013 |
| |||||||||||||
|
(in millions, except per barrel data) |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|
$ |
|
% |
|
$ |
|
% |
| |||||
|
Revenues |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Tariff activities |
|
$ |
1,439 |
|
$ |
1,447 |
|
$ |
1,293 |
|
|
$ |
(8 |
) |
(1 |
)% |
$ |
154 |
|
12 |
% |
|
Trucking |
|
155 |
|
208 |
|
205 |
|
|
(53 |
) |
(25 |
)% |
3 |
|
1 |
% | |||||
|
Total transportation revenues |
|
1,594 |
|
1,655 |
|
1,498 |
|
|
(61 |
) |
(4 |
)% |
157 |
|
10 |
% | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Costs and Expenses |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Trucking costs |
|
(108 |
) |
(151 |
) |
(147 |
) |
|
43 |
|
28 |
% |
(4 |
) |
(3 |
)% | |||||
|
Field operating costs (2) |
|
(652 |
) |
(560 |
) |
(528 |
) |
|
(92 |
) |
(16 |
)% |
(32 |
) |
(6 |
)% | |||||
|
Equity-indexed compensation expense - operations |
|
(5 |
) |
(15 |
) |
(18 |
) |
|
10 |
|
67 |
% |
3 |
|
17 |
% | |||||
|
Segment general and administrative expenses (2) (3) |
|
(89 |
) |
(83 |
) |
(101 |
) |
|
(6 |
) |
(7 |
)% |
18 |
|
18 |
% | |||||
|
Equity-indexed compensation expense - general and administrative |
|
(6 |
) |
(29 |
) |
(39 |
) |
|
23 |
|
79 |
% |
10 |
|
26 |
% | |||||
|
Equity earnings in unconsolidated entities |
|
183 |
|
108 |
|
64 |
|
|
75 |
|
69 |
% |
44 |
|
69 |
% | |||||
|
Segment profit |
|
$ |
917 |
|
$ |
925 |
|
$ |
729 |
|
|
$ |
(8 |
) |
(1 |
)% |
$ |
196 |
|
27 |
% |
|
Maintenance capital |
|
$ |
144 |
|
$ |
165 |
|
$ |
123 |
|
|
$ |
21 |
|
13 |
% |
$ |
(42 |
) |
(34 |
)% |
|
Segment profit per barrel |
|
$ |
0.56 |
|
$ |
0.62 |
|
$ |
0.54 |
|
|
$ |
(0.06 |
) |
(10 |
)% |
$ |
0.08 |
|
15 |
% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Favorable/(Unfavorable) Variance |
| ||||||
|
Average Daily Volumes |
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
|
2015-2014 |
|
2014-2013 |
| ||||||||
|
(in thousands of barrels per day) (4) |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
|
Volumes |
|
% |
|
Volumes |
|
% |
|
|
Tariff activities volumes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Crude oil pipelines (by region): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Permian Basin (5) |
|
1,849 |
|
1,512 |
|
1,299 |
|
|
337 |
|
22 |
% |
213 |
|
16 |
% |
|
South Texas / Eagle Ford (5) |
|
306 |
|
227 |
|
102 |
|
|
79 |
|
35 |
% |
125 |
|
123 |
% |
|
Western |
|
215 |
|
260 |
|
247 |
|
|
(45 |
) |
(17 |
)% |
13 |
|
5 |
% |
|
Rocky Mountain (5) |
|
440 |
|
426 |
|
398 |
|
|
14 |
|
3 |
% |
28 |
|
7 |
% |
|
Gulf Coast |
|
532 |
|
492 |
|
442 |
|
|
40 |
|
8 |
% |
50 |
|
11 |
% |
|
Central |
|
413 |
|
450 |
|
405 |
|
|
(37 |
) |
(8 |
)% |
45 |
|
11 |
% |
|
Canada |
|
392 |
|
399 |
|
384 |
|
|
(7 |
) |
(2 |
)% |
15 |
|
4 |
% |
|
Crude oil pipelines |
|
4,147 |
|
3,766 |
|
3,277 |
|
|
381 |
|
10 |
% |
489 |
|
15 |
% |
|
NGL pipelines |
|
193 |
|
186 |
|
250 |
|
|
7 |
|
4 |
% |
(64 |
) |
(26 |
)% |
|
Refined products pipelines |
|
— |
|
— |
|
68 |
|
|
— |
|
N/A |
|
(68 |
) |
(100 |
)% |
|
Tariff activities total volumes |
|
4,340 |
|
3,952 |
|
3,595 |
|
|
388 |
|
10 |
% |
357 |
|
10 |
% |
|
Trucking volumes |
|
113 |
|
127 |
|
117 |
|
|
(14 |
) |
(11 |
)% |
10 |
|
9 |
% |
|
Transportation segment total volumes |
|
4,453 |
|
4,079 |
|
3,712 |
|
|
374 |
|
9 |
% |
367 |
|
10 |
% |
(1) Revenues and costs and expenses include intersegment amounts.
(2) Field operating costs and Segment general and administrative expenses exclude equity-indexed compensation expense, which is presented separately in the table above.
(3) Segment general and administrative expenses reflect direct costs attributable to each segment and an allocation of other expenses to the segments. The proportional allocations by segment require judgment by management and are based on the business activities that exist during each period.
(4) Average daily volumes are calculated as the total volumes (attributable to our interest) for the year divided by the number of days in the year.
(5) Area systems include volumes (attributable to our interest) from pipelines owned by unconsolidated entities.
Tariffs and other fees on our pipeline systems vary by receipt point and delivery point. The segment profit generated by our tariff and other fee-related activities depends on the volumes transported on the pipeline and the level of the tariff and other fees charged as well as the fixed and variable field costs of operating the pipeline. As is common in the pipeline transportation industry, our tariffs incorporate a loss allowance factor that is intended to offset losses due to evaporation, measurement and other losses in transit. We value the variance of allowance volumes to actual losses at the estimated net realizable value (including the impact of gains and losses from derivative-related activities) at the time the variance occurred and the result is recorded as either an increase or decrease to tariff activities revenues. Revenue from our pipeline capacity agreements generally reflects a negotiated amount.
The following is a discussion of items impacting Transportation segment profit and segment profit per barrel for the periods indicated.
Net Operating Revenues, Equity Earnings and Volumes. As noted in the table above, our total Transportation segment revenues, net of trucking costs, decreased for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, but increased for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013. Equity earnings in unconsolidated entities and average daily volumes increased year-over-year for each of the comparative periods presented. The following table presents the net revenue and equity earnings variances by type of revenue, product and region for the comparative periods presented:
|
|
|
Favorable/(Unfavorable) Variance |
|
Favorable/(Unfavorable) Variance |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
2015 - 2014 |
|
2014 - 2013 |
| |||||||||
|
(in millions) |
|
Net Revenues |
|
Equity Earnings |
|
|
Net Revenues |
|
Equity Earnings |
| ||||
|
Tariff activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Permian Basin region |
|
$ |
75 |
|
$ |
52 |
|
|
$ |
66 |
|
$ |
9 |
|
|
South Texas / Eagle Ford region |
|
12 |
|
19 |
|
|
24 |
|
28 |
| ||||
|
Western region |
|
(24 |
) |
— |
|
|
3 |
|
— |
| ||||
|
Canada |
|
(16 |
) |
— |
|
|
40 |
|
— |
| ||||
|
NGL pipelines |
|
(1 |
) |
— |
|
|
(14 |
) |
— |
| ||||
|
Refined products pipelines |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
(28 |
) |
— |
| ||||
|
Other (including pipeline loss allowance revenue) |
|
(54 |
) |
4 |
|
|
63 |
|
7 |
| ||||
|
Tariff activities total |
|
(8 |
) |
75 |
|
|
154 |
|
44 |
| ||||
|
Trucking |
|
(10 |
) |
— |
|
|
(1 |
) |
— |
| ||||
|
Transportation segment total |
|
$ |
(18 |
) |
$ |
75 |
|
|
$ |
153 |
|
$ |
44 |
|
· Tariff activities —
· Permian Basin region. The increase in revenues for 2015 over 2014 was primarily driven by results from (i) our Cactus pipeline, which was placed in service in April 2015, and (ii) higher volumes related to increased production, primarily associated with the expansion of our pipeline system in the Delaware Basin.
Revenues increased for 2014 over 2013 primarily due to (i) higher volumes related to increased production and new pipeline connections and (ii) higher pumpover movements at our Basin pipeline terminal.
The increase in equity earnings for each of the comparative periods presented was driven by earnings from our interest in BridgeTex, which we acquired in November 2014.
· South Texas / Eagle Ford region. Revenues increased for each of the comparative periods due to higher volumes driven by increased production and the extension of our gathering system.
Equity earnings increased for each of the comparative periods presented due to higher earnings from our interest in Eagle Ford Pipeline LLC, primarily driven by higher throughput on the Eagle Ford pipeline system. The higher throughput in 2015 compared to 2014 was due to a combination of (i) the connection to our Cactus pipeline in April
2015, (ii) the completion of an expansion of the pipeline system in August 2015 and (iii) increased crude oil production in the Eagle Ford region. The higher throughput for 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily due to increased crude oil production in the Eagle Ford region.
· Western region. Revenues and volumes decreased for 2015 as compared to 2014 primarily due to pipeline downtime on our All American Pipeline associated with the Line 901 incident that occurred in the second quarter of 2015. See Note 16 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding this incident.
· Canada. Revenues decreased for 2015 as compared to 2014 due to unfavorable foreign exchange impacts of $38 million, which more than offset revenue increases from higher tariff rates on certain of our pipelines and related system assets.
Revenues increased for 2014 over 2013 primarily due to (i) rate increases on certain of our pipelines and related system assets, (ii) additional revenues from a reclassification of certain storage facilities from our Facilities segment to our Transportation segment during the second quarter of 2014, (iii) higher revenues from our Rangeland and South Saskatchewan pipelines, as they were shut down in the second and third quarters of 2013 due to high river flow rates and flooding in the surrounding area and (iv) incremental volumes and revenues from our Wascana pipeline, which was reactivated during the second quarter of 2014 and was connected to our Bakken North pipeline system. Such increases were partially offset by unfavorable foreign exchange impacts of $16 million.
· NGL pipelines. Revenues and volumes from our NGL pipelines were relatively consistent for 2015 compared to 2014, as higher revenue from tariff rate increases was substantially offset by unfavorable foreign exchange impacts of $12 million.
Revenues and volumes from our NGL pipelines decreased for 2014 as compared to 2013 primarily due to (i) the discontinuation of a capacity lease arrangement in the fourth quarter of 2013, (ii) the impact of netting joint venture related volumes to our share on a pipeline during 2014, which did not affect revenues and (iii) estimated unfavorable foreign exchange impacts of $7 million. Such unfavorable impacts were partially offset by higher revenues from our Co-Ed pipeline due to tariff rate increases and the shutdown of the pipeline in the second and third quarters of 2013 due to high river flow rates and flooding in the surrounding area.
· Refined products pipelines. We sold our refined products pipeline systems and related assets in 2013.
· Other. The variances for the comparative periods presented were primarily related to pipeline loss allowance revenue. Loss allowance revenue decreased by $62 million for 2015 compared to 2014 primarily due to a lower average realized price per barrel, partially offset by higher volumes. Loss allowance revenue increased by $46 million for 2014 over 2013 and was primarily driven by higher volumes.
· Trucking — Net revenues from our trucking operations decreased for 2015 as compared to 2014 due to unfavorable foreign exchange impacts of $8 million and lower producer volumes.
Field Operating Costs. The increase in field operating costs (excluding equity-indexed compensation expense) for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 was primarily due to estimated costs of $83 million recognized during 2015 associated with the Line 901 incident, net of amounts we believe are probable of recovery from insurance. See Note 16 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding this incident. The increase in field operating costs was also driven by (i) higher salary and related expenses and property tax expense primarily associated with new assets placed in service in 2015 and (ii) higher maintenance and repairs cost, partially offset by favorable foreign exchange impacts of $22 million.
Field operating costs (excluding equity-indexed compensation expense) increased during the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013 primarily due to (i) a change in classification of $14 million of certain costs from general and administrative expenses, (ii) increased asset integrity spending, (iii) higher property tax expense due to capital expansion and (iv) higher utility costs associated with increased throughput volumes. Such increases were partially offset by a reduction in environmental remediation costs and an $11 million favorable foreign exchange impact.
General and Administrative Expenses. The increase in general and administrative expenses (excluding equity-indexed compensation expenses) for the year ended December 31, 2015 over the year ended December 31, 2014 was primarily due to
increased salaries, benefits and other costs associated with the growth in the segment, partially offset by a $4 million favorable foreign exchange impact.
General and administrative expenses (excluding equity-indexed compensation expenses) decreased during the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013 due to a change in classification of $14 million of certain costs to field operating costs and a $5 million favorable impact of foreign exchange.
Equity-Indexed Compensation Expense. A majority of our equity-indexed compensation awards (including the AAP Management Units) contain performance conditions contingent upon achieving certain distribution levels. For awards with performance conditions (such as distribution targets), expense is accrued over the service period only if the performance condition is considered probable of occurring. When awards with performance conditions that were previously considered improbable become probable, we incur additional expense in the period that our probability assessment changes. This is necessary to bring the accrued liability associated with these awards up to the level it would have been if we had been accruing for these awards since the grant date. At December 31, 2015, a PAA distribution level of $2.90 per common unit was deemed probable of occurring in the reasonably foreseeable future (and was initially determined to be probable in the fourth quarter of 2014). Furthermore, a change in PAA unit price impacts the fair value of our liability-classified awards. See Note 15 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information regarding our equity-indexed compensation plans.
On a consolidated basis, equity-indexed compensation expense decreased by $72 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, primarily due to the impact of the decrease in PAA unit price during the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the impact of the decrease in PAA unit price during the year ended December 31, 2014. On a consolidated basis, equity-indexed compensation expense decreased by $17 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013 primarily due to the impact of the decrease in PAA unit price during the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the impact of the increase in PAA unit price during the year ended December 31, 2013.
Maintenance Capital. Maintenance capital consists of capital expenditures for the replacement of partially or fully depreciated assets in order to maintain the operating and/or earnings capacity of our existing assets. The decrease in maintenance capital in 2015 compared to 2014 was primarily due to a reclassification of certain maintenance capital costs from our Facilities segment during the 2014 period. In addition, the decrease in maintenance capital was impacted by the depreciation of CAD relative to USD.
The increase in maintenance capital in 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily due to pipeline replacement projects and increased investments in pipeline integrity and a reclassification of certain maintenance capital costs from our Facilities segment during the 2014 period.
Facilities Segment
Our Facilities segment operations generally consist of fee-based activities associated with providing storage, terminalling and throughput services for crude oil, refined products, NGL and natural gas, as well as NGL fractionation and isomerization services and natural gas and condensate processing services. The Facilities segment generates revenue through a combination of month-to-month and multi-year agreements and processing arrangements.
The following tables set forth our operating results from our Facilities segment for the periods indicated:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Favorable/(Unfavorable) Variance |
| ||||||||||||
|
Operating Results (1) |
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
2015-2014 |
|
2014-2013 |
| ||||||||||||||
|
(in millions, except per barrel data) |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
$ |
|
% |
|
$ |
|
% |
| ||||||
|
Revenues |
|
$ |
1,050 |
|
$ |
1,127 |
|
$ |
1,075 |
|
|
$ |
(77 |
) |
(7 |
)% |
$ |
52 |
|
5 |
% |
|
Natural gas sales (2) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
302 |
|
|
— |
|
N/A |
|
(302 |
) |
(100 |
)% | |||||
|
Natural gas related storage costs |
|
(24 |
) |
(55 |
) |
(16 |
) |
|
31 |
|
56 |
% |
(39 |
) |
(244 |
)% | |||||
|
Natural gas sales costs (2) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(296 |
) |
|
— |
|
N/A |
|
296 |
|
100 |
% | |||||
|
Field operating costs (3) |
|
(377 |
) |
(404 |
) |
(362 |
) |
|
27 |
|
7 |
% |
(42 |
) |
(12 |
)% | |||||
|
Equity-indexed compensation expense - operations |
|
— |
|
(4 |
) |
(2 |
) |
|
4 |
|
100 |
% |
(2 |
) |
(100 |
)% | |||||
|
Segment general and administrative expenses (3) (4) |
|
(65 |
) |
(60 |
) |
(63 |
) |
|
(5 |
) |
(8 |
)% |
3 |
|
5 |
% | |||||
|
Equity-indexed compensation expense - general and administrative |
|
(5 |
) |
(20 |
) |
(22 |
) |
|
15 |
|
75 |
% |
2 |
|
9 |
% | |||||
|
Segment profit |
|
$ |
579 |
|
$ |
584 |
|
$ |
616 |
|
|
$ |
(5 |
) |
(1 |
)% |
$ |
(32 |
) |
(5 |
)% |
|
Maintenance capital |
|
$ |
68 |
|
$ |
52 |
|
$ |
38 |
|
|
$ |
(16 |
) |
(31 |
)% |
$ |
(14 |
) |
(37 |
)% |
|
Segment profit per barrel |
|
$ |
0.38 |
|
$ |
0.40 |
|
$ |
0.43 |
|
|
$ |
(0.02 |
) |
(5 |
)% |
$ |
(0.03 |
) |
(7 |
)% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Favorable/(Unfavorable) Variance |
| |||||||
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
2015-2014 |
|
2014-2013 |
| |||||||||
|
Volumes (5) |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
Volumes |
|
% |
|
Volumes |
|
% |
| |
|
Crude oil, refined products and NGL terminalling and storage (average monthly capacity in millions of barrels) |
|
100 |
|
95 |
|
94 |
|
|
5 |
|
5 |
% |
1 |
|
1 |
% |
|
Rail load / unload volumes (average volumes in thousands of barrels per day) |
|
210 |
|
231 |
|
221 |
|
|
(21 |
) |
(9 |
)% |
10 |
|
5 |
% |
|
Natural gas storage (average monthly working capacity in billions of cubic feet) |
|
97 |
|
97 |
|
96 |
|
|
— |
|
— |
% |
1 |
|
1 |
% |
|
NGL fractionation (average volumes in thousands of barrels per day) |
|
103 |
|
96 |
|
96 |
|
|
7 |
|
7 |
% |
— |
|
— |
% |
|
Facilities segment total volumes (average monthly volumes in millions of barrels) (6) |
|
126 |
|
121 |
|
120 |
|
|
5 |
|
4 |
% |
1 |
|
1 |
% |
(1) Revenues and costs and expenses include intersegment amounts.
(2) Effective January 1, 2014, our natural gas sales and costs, primarily attributable to the activities performed by our natural gas storage commercial optimization group, are reported in our Supply and Logistics segment.
(3) Field operating costs and Segment general and administrative expenses exclude equity-indexed compensation expense, which is presented separately in the table above.
(4) Segment general and administrative expenses reflect direct costs attributable to each segment and an allocation of other expenses to the segments. The proportional allocations by segment require judgment by management and are based on the business activities that exist during each period.
(5) Average monthly volumes are calculated as total volumes for the year divided by the number of months in the year.
(6) Facilities segment total is calculated as the sum of: (i) crude oil, refined products and NGL terminalling and storage capacity; (ii) rail load and unload volumes multiplied by the number of days in the year and divided by the number of months in the year; (iii) natural gas storage working capacity divided by 6 to account for the 6:1 mcf of natural gas to crude Btu equivalent ratio and further divided by 1,000 to convert to monthly volumes in millions; and (iv) NGL fractionation volumes multiplied by the number of days in the year and divided by the number of months in the year.
The following is a discussion of items impacting Facilities segment profit and segment profit per barrel for the periods indicated.
Net Operating Revenues and Volumes. As noted in the table above, our Facilities segment revenues, net of related costs, decreased by $46 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014, but increased by $7 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 over the comparable 2013 period. Total volumes increased for each of the comparative periods presented. Variances in net revenues and average monthly volumes between the comparative periods are discussed below:
· Rail Terminals — For the year ended December 31, 2015, revenues decreased by $26 million compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 due to lower volumes and lower rail fees related to the movement of certain volumes of Bakken crude oil, partially offset by revenues from our Bakersfield rail terminal that came online in the fourth quarter of 2014.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, revenues increased by $3 million over the year ended December 31, 2013 due to new rail terminals that came on line in the fourth quarter of 2013 and in 2014, substantially offset by the unfavorable impact of rail delays and lower volumes at certain of our existing rail terminals during 2014 and weather-related issues at certain of our terminals during the first quarter of 2014.
· Natural Gas Storage Operations — Net revenues decreased by $12 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 and by $43 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013 primarily due to (i) declines in market rates for natural gas storage, which resulted in lower rates on new contracts replacing expiring contracts and (ii) reduced hub services opportunities. The 2014 period was further unfavorably impacted by costs incurred to manage deliverability requirements in conjunction with the extended period of severe cold weather experienced during the first quarter of 2014.
· Gulf Coast Gas Processing — Revenues decreased by $13 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to 2014 primarily due to lower volumes and decreased margins driven by lower commodity prices.
· NGL Storage, NGL Fractionation and Canadian Gas Processing — Revenues decreased by $7 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014. This decrease was primarily due to estimated unfavorable foreign exchange impacts of $41 million, which offset revenue increases from higher facility fees for the 2015 period. These impacts were largely offset in our Supply and Logistics segment results.
Revenues from our NGL storage, NGL fractionation and Canadian gas processing activities increased by $31 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 over the year ended December 31, 2013 largely driven by higher facility fee revenues due to rate increases at certain of our storage and fractionation facilities, partially offset by lower physical processing gains. Such increases were partially offset by estimated unfavorable foreign exchange impacts of $18 million. These impacts were largely offset in our Supply and Logistics segment results.
· Crude Oil Storage — For the year ended December 31, 2015, revenues increased by $9 million over the year ended December 31, 2014 primarily due to capacity expansions of approximately 1 million barrels and higher marine access activity at our St. James terminal.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, crude oil storage revenues increased by $8 million over the year ended December 31, 2013 primarily due to increased throughput at our Cushing, Yorktown and Mobile/Ten Mile terminals and a 1.2 million barrel capacity expansion at our St. James terminal, partially offset by lower revenues from certain storage facilities in California and the East Coast due to underutilization resulting from decreased demand, as well decreased revenues of $12 million due to the reclassification of certain of our Canadian storage facilities to our Transportation segment during the second quarter of 2014.
· Condensate Processing — Revenues increased by $8 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to 2013 due to the benefit from the start-up and subsequent expansion of our Gardendale condensate processing facility. Revenues were relatively consistent for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014.
Field Operating Costs. The decrease in field operating costs (excluding equity-indexed compensation expenses) for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 was primarily due to (i) decreased maintenance and repairs cost, (ii) lower gas and power costs largely associated with our NGL fractionation and Canadian gas processing activities and (iii) favorable foreign exchange impacts of $19 million. Such decreases were partially offset by an increase in expenses associated with new assets placed in service.
Field operating costs (excluding equity-indexed compensation expenses) increased during the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013 due to (i) an increase in costs for rail activities, primarily due to new rail terminals that came online in the fourth quarter of 2013 and in 2014 as discussed above, (ii) a change in classification of $8 million of certain costs from general and administrative expenses, (iii) an increase in brine disposal costs associated with our NGL storage caverns, (iv) higher gas and power costs and (v) increased costs associated with the cancellation of certain capital projects. The effect of these increases was reduced by a $9 million favorable impact of foreign exchange.
General and Administrative Expenses. The increase in general and administrative expenses (excluding equity-indexed compensation expenses) for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 was primarily due to increased salaries and benefits, partially offset by a $3 million favorable foreign exchange impact.
General and administrative expenses (excluding equity-indexed compensation expenses) decreased during the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013. These results reflect the net impact of a decrease due to a change in classification of $8 million of certain costs to field operating costs during the 2014 period, partially offset by increased expenses resulting from overall growth in the segment.
Maintenance Capital. The increase in maintenance capital in 2015 over 2014 was primarily due to various tank and facility projects and timing of equipment replacements, as well as the impact from a change in classification of certain maintenance capital costs to our Transportation segment in the 2014 period. The increase in maintenance capital in 2014 from 2013 is primarily due to the timing of maintenance projects for tanks and other facility assets, partially offset by a change in classification of certain maintenance capital costs to our Transportation segment in the 2014 period.
Supply and Logistics Segment
Our revenues from supply and logistics activities reflect the sale of gathered and bulk-purchased crude oil, as well as sales of NGL volumes purchased from suppliers and natural gas sales attributable to the activities performed by our natural gas storage commercial optimization group. Generally, our segment profit is impacted by (i) increases or decreases in our Supply and Logistics segment volumes (which consist of lease gathering crude oil purchase volumes, NGL sales volumes and waterborne cargos), (ii) demand for lease gathering services we provide producers and (iii) the overall volatility and strength or weakness of market conditions and the allocation of our assets among our various risk management strategies. In addition, the execution of our risk management strategies in conjunction with our assets can provide upside in certain markets. Although segment profit may be adversely affected during certain transitional periods as discussed further below, our crude oil and NGL supply, logistics and distribution operations are not directly affected by the absolute level of prices, but are affected by overall levels of supply and demand for crude oil and NGL and relative fluctuations in market-related indices.
The following tables set forth our operating results from our Supply and Logistics segment for the periods indicated:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Favorable/(Unfavorable) Variance |
| ||||||||||||
|
Operating Results (1) (2) |
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
2015-2014 |
|
2014-2013 |
| ||||||||||||||
|
(in millions, except per barrel data) |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
$ |
|
% |
|
$ |
|
% |
| ||||||
|
Revenues |
|
$ |
21,945 |
|
$ |
42,150 |
|
$ |
40,696 |
|
|
$ |
(20,205 |
) |
(48 |
)% |
$ |
1,454 |
|
4 |
% |
|
Purchases and related costs (3) |
|
(21,018 |
) |
(40,752 |
) |
(39,315 |
) |
|
19,734 |
|
48 |
% |
(1,437 |
) |
(4 |
)% | |||||
|
Field operating costs (4) |
|
(433 |
) |
(481 |
) |
(422 |
) |
|
48 |
|
10 |
% |
(59 |
) |
(14 |
)% | |||||
|
Equity-indexed compensation expense - operations |
|
— |
|
(2 |
) |
(3 |
) |
|
2 |
|
100 |
% |
1 |
|
33 |
% | |||||
|
Segment general and administrative expenses (4) (5) |
|
(102 |
) |
(105 |
) |
(102 |
) |
|
3 |
|
3 |
% |
(3 |
) |
(3 |
)% | |||||
|
Equity-indexed compensation expense - general and administrative |
|
(11 |
) |
(28 |
) |
(32 |
) |
|
17 |
|
61 |
% |
4 |
|
13 |
% | |||||
|
Segment profit |
|
$ |
381 |
|
$ |
782 |
|
$ |
822 |
|
|
$ |
(401 |
) |
(51 |
)% |
$ |
(40 |
) |
(5 |
)% |
|
Maintenance capital |
|
$ |
8 |
|
$ |
7 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
|
$ |
(1 |
) |
(14 |
)% |
$ |
8 |
|
53 |
% |
|
Segment profit per barrel |
|
$ |
0.89 |
|
$ |
1.85 |
|
$ |
2.09 |
|
|
$ |
(0.96 |
) |
(52 |
)% |
$ |
(0.24 |
) |
(11 |
)% |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Favorable (Unfavorable) Variance |
| |||||||
|
Average Daily Volumes |
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
2015-2014 |
|
2014-2013 |
| |||||||||
|
(in thousands of barrels per day) |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
Volume |
|
% |
|
Volume |
|
% |
| |
|
Crude oil lease gathering purchases |
|
943 |
|
949 |
|
859 |
|
|
(6 |
) |
(1 |
)% |
90 |
|
10 |
% |
|
NGL sales |
|
223 |
|
208 |
|
215 |
|
|
15 |
|
7 |
% |
(7 |
) |
(3 |
)% |
|
Waterborne cargos |
|
2 |
|
— |
|
4 |
|
|
2 |
|
N/A |
|
(4 |
) |
(100 |
)% |
|
Supply and Logistics segment total volumes |
|
1,168 |
|
1,157 |
|
1,078 |
|
|
11 |
|
1 |
% |
79 |
|
7 |
% |
(1) Revenues and costs include intersegment amounts.
(2) Prior to January 1, 2014, natural gas sales and costs attributable to the activities performed by our natural gas storage commercial optimization group were reported in our Facilities segment.
(3) Purchases and related costs include interest expense (related to hedged inventory purchases) of $6 million, $12 million and $30 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
(4) Field operating costs and Segment general and administrative expenses exclude equity-indexed compensation expense, which is presented separately in the table above.
(5) Segment general and administrative expenses reflect direct costs attributable to each segment and an allocation of other expenses to the segments. The proportional allocations by segment require judgment by management and are based on the business activities that exist during each period.
The following table presents the range of the NYMEX West Texas Intermediate benchmark price of crude oil during the periods indicated:
|
|
|
NYMEX WTI |
| ||||
|
|
|
Crude Oil Price |
| ||||
|
During the Year Ended December 31, |
|
Low |
|
High |
| ||
|
2015 |
|
$ |
35 |
|
$ |
61 |
|
|
2014 |
|
$ |
53 |
|
$ |
107 |
|
|
2013 |
|
$ |
87 |
|
$ |
111 |
|
Because the commodities that we buy and sell are generally indexed to the same pricing indices for both sales and purchases, revenues and costs related to purchases will fluctuate with market prices. However, the margins related to those sales and purchases will not necessarily have a corresponding increase or decrease. The absolute amount of our revenues and purchases decreased for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 due to lower crude oil and NGL prices during the 2015 period. The increase of the absolute amount of our revenues and purchases for the year ended December 31, 2014 over the year ended December 31, 2013 primarily resulted from higher crude oil volumes in the 2014 period, partially offset by lower crude oil prices relative to 2013, particularly in the fourth quarter.
Generally, we expect a base level of earnings from our Supply and Logistics segment from the assets employed by this segment. This base level may be optimized and enhanced when there is a high level of market volatility, favorable basis differentials and/or a steep contango or backwardated market structure. Also, our NGL marketing operations are sensitive to weather-related demand, particularly during the approximate five-month peak heating season of November through March, and temperature differences from period-to-period may have a significant effect on NGL demand and thus our financial performance.
The following is a discussion of items impacting Supply and Logistics segment profit and segment profit per barrel for the periods indicated.
Net Operating Revenues and Volumes. Our Supply and Logistics segment revenues, net of purchases and related costs, decreased by $471 million for the year ended December 31, 2015 as compared to the 2014 period, of which $389 million related to the mark-to-market impact of certain derivatives (see discussion and table below) and long-term inventory costing adjustments (see discussion below). For the 2014 period, segment revenues, net of purchases and related costs, increased by $17 million over the comparable 2013 period. The following summarizes the more significant items impacting the comparative periods:
· Crude Oil Operations — Net revenues from our crude oil supply and logistics activities decreased for the year ended December 31, 2015 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 primarily due to (i) the compression of certain differentials during the 2015 period, which resulted in fewer opportunities to capture above-baseline margins as compared to 2014 and (ii) increased competition, largely due to overbuilt infrastructure in certain areas that has negatively impacted our lease gathering unit margins and volumes, most notably during the second half of 2015. However, such unfavorable results were partially offset by revenues from opportunities created by the contango market structure during 2015.
Net revenues from our crude oil supply and logistics activities increased slightly for 2014 as compared to 2013 primarily due to favorable impacts from the widening of certain differentials, most notably in the second and third quarters of 2014, that allowed for more opportunities to capture above-baseline margins as compared to 2013.
· NGL Operations — Net revenues from our NGL operations increased for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014. The increase was primarily driven by higher margins due to the lower cost of inventory carried over from 2014 year end and higher sales volumes.
Net revenues from our NGL marketing operations decreased for the year ended December 31, 2014 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013. This decrease was driven by higher NGL purchases and related costs in the 2014 periods, primarily due to a higher weighted average inventory cost and increased facility fees. Additionally, NGL margins were further impacted by less favorable market conditions, most notably during (i) the second quarter of 2014, as market pricing was stronger in the comparable 2013 period due to heating requirements during a winter season that extended into the second quarter and greater petrochemical demand for propane and (ii) the fourth quarter of 2014, due to less demand for crop drying as compared to the 2013 period.
· Natural Gas Storage Commercial Optimization — During the first quarter of 2014, our natural gas storage commercial optimization activities were unfavorably impacted by costs incurred to manage deliverability requirements in conjunction with the extended period of severe cold weather experienced. We did not incur similar costs during 2015 or 2013.
· Impact from Certain Derivative Activities, Net of Inventory Valuation Adjustments — The mark-to-market of certain of our derivative activities impacted our net revenues as shown in the table below for the periods indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
|
Variance |
| ||||||||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
|
2015-2014 |
|
2014-2013 |
| ||||||
|
Gains/(losses) from certain derivative activities, net of inventory valuation adjustments (1) |
|
$ |
(114 |
) |
$ |
261 |
|
$ |
(59 |
) |
|
$ |
(375 |
) |
$ |
320 |
|
(1) Includes mark-to-market and other gains and losses resulting from certain derivative instruments that are related to underlying activities in another period (or the reversal of mark-to-market gains and losses from a prior period), gains and losses on certain derivatives that are related to investing activities (such as the purchase of linefill) and inventory valuation adjustments, as applicable. See Note 11 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for a comprehensive discussion regarding our derivatives and risk management activities.
· Long-Term Inventory Costing Adjustments — Our operating results are impacted by changes in the weighted average cost of our crude oil and NGL inventory pools that result from price movements during the periods. Such costing adjustments resulted in unfavorable impacts of $99 million and $85 million for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, due to price decreases during each year. These costing adjustments related to long-term inventory necessary to meet our minimum inventory requirements in third-party assets and other working inventory that was needed for our commercial operations. We consider this inventory necessary to conduct our operations and we intend to carry this inventory for the foreseeable future.
· Foreign Exchange Impacts — Our results are impacted by fluctuations in the value of CAD to USD, resulting in foreign exchange gains and losses on U.S. denominated net assets within our Canadian operations. The impact of such gains and losses resulted in a favorable variance of $38 million for 2015 compared to 2014 and an unfavorable variance of $16 million for 2014 to 2013.
Furthermore, the depreciation of CAD relative to USD resulted in lower net USD costs of approximately $41 million for 2015 compared to 2014 and by $15 million for 2014 compared to 2013. Such costs are primarily associated with intercompany facility fees and are largely offset in our Facilities segment results.
Field Operating Costs. The decrease in field operating costs (excluding equity-indexed compensation expenses) for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 was primarily due to the decreased use of third party trucking services as pipeline expansion projects were placed into service.
The increase in field operating costs (excluding equity-indexed compensation expenses) for the year ended December 31, 2014 over the year ended December 31, 2013 was primarily due to an increase in trucking costs associated with higher lease gathering volumes.
Maintenance Capital. The decrease in maintenance capital in 2014 compared to 2013 was primarily due to reduced spending on trucking assets.
Other Income and Expenses
Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation and amortization expense increased during the 2015 period over the comparable 2014 period primarily due to various capital expansion projects completed during 2015, partially offset by favorable impacts from the depreciation of CAD relative to USD.
Depreciation and amortization expense increased during the 2014 period over the comparable 2013 period primarily due to various recently completed capital expansion projects, as well as an acceleration of depreciation on certain pipeline assets to reflect a change in their estimated useful lives. These increases were partially offset by a reduction in amortization expense due to declining-balance amortization used for certain of our intangible assets acquired in recent years.
Interest Expense
Interest expense is primarily impacted by:
· our weighted average debt balances;
· the level and maturity of fixed rate debt and interest rates associated therewith;
· market interest rates and our interest rate hedging activities on floating rate debt; and
· interest capitalized on capital projects and included in purchases and related costs.
The following table summarizes the components impacting the interest expense variance for the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 (in millions, except for percentages):
|
|
|
|
|
Average |
|
Weighted Average |
| |
|
Interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2013 |
|
$ |
319 |
|
0.2 |
% |
4.4 |
% |
|
Impact of issuance of PAA senior notes (2) (5) |
|
51 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Impact of interest included in purchases and related costs (3) |
|
18 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Impact of retirement of PAA senior notes (4) |
|
(13 |
) |
|
|
|
| |
|
Impact of capitalized interest |
|
(10 |
) |
|
|
|
| |
|
Other |
|
(8 |
) |
|
|
|
| |
|
Interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2014 |
|
$ |
357 |
|
0.1 |
% |
4.3 |
% |
|
Impact of issuance of PAA senior notes (5) (6) |
|
88 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Impact of interest included in purchases and related costs (3) |
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Impact of retirement of PAA senior notes (7) |
|
(9 |
) |
|
|
|
| |
|
Impact of capitalized interest |
|
(9 |
) |
|
|
|
| |
|
Other |
|
10 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
443 |
|
0.2 |
% |
4.4 |
% |
(1) Excludes commitment and other fees.
(2) In August 2013, PAA completed the issuance of $700 million of 3.85% senior notes due 2023.
(3) Interest costs attributable to borrowings for hedged inventory purchases are included in purchases and related costs in our Supply and Logistics segment profit as we consider interest on these borrowings a direct cost to storing the inventory. These costs were $6 million, $12 million and $30 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
(4) In December 2013, PAA’s $250 million, 5.63% senior notes matured.
(5) In April 2014, PAA completed the issuance of $700 million of 4.70% senior notes due 2044; in September 2014, PAA completed the issuance of $750 million of 3.60% senior notes due 2024; and in December 2014, PAA completed the issuance of $500 million of 2.60% senior notes due 2019 and $650 million of 4.90% senior notes due 2045.
(6) In August 2015, PAA completed the issuance of $1.0 billion of 4.65% senior notes due 2025.
(7) PAA’s $150 million, 5.25% senior notes and $400 million, 3.95% senior notes matured in June 2015 and September 2015, respectively.
Other Income/(Expense), Net
Other income/(expense), net in each of the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 was primarily comprised of foreign currency gains or losses related to revaluations of CAD-denominated interest receivables associated with intercompany notes and the impact of related foreign currency hedges.
Income Tax Expense
Income tax expense decreased for the year ended December 31, 2015 compared to the year ended December 31, 2014 primarily due to the deferred income tax impact associated with fluctuations in the derivative mark-to-market valuation in our Canadian operations during the 2015 and 2014 periods. This benefit was partially offset by (i) higher deferred income tax expense associated with the amortization of our deferred tax asset, (ii) an Alberta, Canada provincial tax rate increase of 2% enacted during the second quarter of 2015 and (iii) higher current income tax expense resulting from increased year-over-year taxable earnings from our Canadian operations. The 2015 period was also favorably impacted by the depreciation of CAD relative to USD.
Income tax expense increased for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013 primarily as a result of the amortization of the deferred tax asset created in connection with our October 2013 IPO and November 2014 secondary offering, as well as higher deferred income tax expense associated with derivative mark-to-market gains in our Canadian operations. The increased deferred income tax expense was partially offset by lower current income tax expense as a result of decreased year-over-year taxable earnings from our Canadian operations.
Outlook
Primarily as a result of advances in drilling and completion techniques and their application to a number of large-scale shale and resource plays, which occurred contemporaneously with attractive crude oil and liquids prices, during the approximately three year period through the end of 2014, U.S. crude oil and liquids production in the lower 48 states increased rapidly. This was particularly true for light crudes and condensates. Similar resource development activities in Canada and ongoing oil sands development activities also led to increased Canadian crude oil production during this period. Additionally, during this period, the crude oil market experienced high levels of volatility in location and quality differentials as a result of the confluence of regional infrastructure constraints in North America, rapid and unexpected changes in crude oil qualities, international supply issues, and regional downstream operating issues. During 2013 and to a lesser degree 2014, these market conditions had a positive impact on our profitability as our business strategy and asset base positioned us to capitalize on opportunities created by the volatile environment.
However, the combination during such period of surging North American liquids production, relatively flat liquids production for the rest of the world and relatively modest growth in global liquids demand led to a supply imbalance, which in turn led to a significant and rapid reduction in petroleum prices. While we believe that our business model and asset base have minimal direct exposure to petroleum prices, our performance is influenced by certain differentials and overall North American production levels, which in turn are impacted by major price movements. The meaningful decrease in crude oil price levels during the second half of 2014 and throughout 2015 relative to the levels experienced during 2013 and the first half of 2014 have led many producers, including North American producers, to significantly scale back capital programs. As a result, during 2015, the rate of growth of North American crude oil production has slowed significantly and began to decrease in some areas as producers have taken rigs out of service and deferred completions at an increased rate. While we believe that the large North American resource base remains intact and will be developed, such production will likely take place at a slower pace and previously anticipated peak production levels will likely be reduced. The slowdown in North American production coupled with increases in infrastructure has led to a compression of basis differentials in a number of locations. This transitioning crude oil market presents challenges to our business model and asset base and will likely impact the rate of cash flow and distribution growth that we would have otherwise experienced over the next several years. In addition, increased competition and compressed differentials may drive lower volumes and lower unit margins in parts of our business, particularly our Supply and Logistics segment.
While we believe that these recent market developments will continue to slow down crude oil supply growth and contribute toward bringing the markets back to equilibrium, there can be no assurance that such equilibrium will be achieved or that we will not be negatively impacted by declining crude oil supply, low level of volatility or challenging capital markets conditions. Additionally, construction of additional infrastructure by us and our competitors will likely create excess takeaway capacity in certain areas at least for the near to medium term, which could further reduce unit margins in our various segments, and which may be exacerbated by declining levels of crude oil production. Finally, we cannot be certain that our expansion efforts will generate targeted returns or that any future acquisition activities will be successful. See Item 1A. “Risk Factors — Risks Related to PAA’s Business.”
Liquidity and Capital Resources
General
On a consolidated basis, our primary sources of liquidity are (i) cash flow from operating activities as further discussed below in the section entitled “—Cash Flow from Operating Activities,” (ii) borrowings under the credit facilities or the PAA commercial paper program and (iii) funds received from PAA’s sales of equity and debt securities. Our primary cash requirements include, but are not limited to, (i) ordinary course of business uses, such as the payment of amounts related to the purchase of crude oil, NGL and other products and other expenses and interest payments on outstanding debt, (ii) expansion and maintenance activities, (iii) acquisitions of assets or businesses, (iv) repayment of principal on long-term debt and (v) distributions to our Class A shareholders and noncontrolling interests. We generally expect to fund our short-term cash requirements through cash flow generated from operating activities and/or borrowings under the PAA commercial paper program or the credit facilities. In addition, we generally expect to fund our long-term needs, such as those resulting from expansion activities or acquisitions and refinancing long-term debt, through a variety of sources (either separately or in combination), which may include the sources mentioned above as funding for short-term needs and/or the issuance of additional PAA equity or debt securities. As of December 31, 2015, we had a working capital deficit of $437 million and approximately $2.4 billion of liquidity available to meet our ongoing operating, investing and financing needs, subject to continued covenant compliance, as noted below (in millions):
|
|
|
As of |
| |
|
Availability under PAA senior unsecured revolving credit facility (1) (2) |
|
$ |
1,583 |
|
|
Availability under PAA senior secured hedged inventory facility (1) (2) |
|
1,071 |
| |
|
Availability under PAA senior unsecured 364-day revolving credit facility |
|
1,000 |
| |
|
Amounts outstanding under PAA commercial paper program |
|
(1,368 |
) | |
|
Subtotal |
|
2,286 |
| |
|
Availability under AAP senior secured revolving credit facility |
|
116 |
| |
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
30 |
| |
|
Total |
|
$ |
2,432 |
|
(1) Represents availability prior to giving effect to amounts outstanding under the PAA commercial paper program, which reduce available capacity under the facilities.
(2) Available capacity under the PAA senior unsecured revolving credit facility and the PAA senior secured hedged inventory facility was reduced by outstanding letters of credit of $17 million and $29 million, respectively.
During the latter part of 2015, energy industry conditions deteriorated and capital markets access for energy companies was disrupted, which has continued into 2016. To fund its ongoing capital program and maintain a solid capital structure and significant liquidity, in January 2016, PAA raised $1.6 billion of equity capital through the sale of approximately 61.0 million unregistered Series A Convertible Preferred Units. See Note 10 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional information.
We believe that we have, and will continue to have, the ability to access the PAA commercial paper program and the credit facilities, which we use to meet our short-term cash needs. We believe that our financial position remains strong and we have sufficient liquidity; however, extended disruptions in the financial markets and/or energy price volatility that adversely affect our business may have a materially adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations or cash flows. Also, see Item 1A. “Risk Factors” for further discussion regarding such risks that may impact our liquidity and capital resources. Usage of the PAA credit facilities, which provide the backstop for the PAA commercial paper program, and the AAP credit facility is subject to ongoing compliance with covenants. As of December 31, 2015, PAA and AAP were in compliance with all such covenants.
Cash Flow from Operating Activities
The primary drivers of cash flow from operating activities are (i) the collection of amounts related to the sale of crude oil, NGL and other products, the transportation of crude oil and other products for a fee, and storage and terminalling services provided for a fee and (ii) the payment of amounts related to the purchase of crude oil, NGL and other products and other expenses, principally field operating costs, general and administrative expenses and interest expense.
Cash flow from operating activities can be materially impacted by the storage of crude oil in periods of a contango market, when the price of crude oil for future deliveries is higher than current prices. In the month we pay for the stored crude oil, we borrow under the credit facilities or the PAA commercial paper program (or use cash on hand) to pay for the crude oil, which negatively impacts operating cash flow. Conversely, cash flow from operating activities increases during the period in which we collect the cash from the sale of the stored crude oil. Similarly, the level of NGL and other product inventory stored and held for resale at period end affects our cash flow from operating activities.
In periods when the market is not in contango, we typically sell our crude oil during the same month in which we purchase it and we do not rely on borrowings under the credit facilities or the PAA commercial paper program to pay for the crude oil. During such market conditions, our accounts payable and accounts receivable generally move in tandem as we make payments and receive payments for the purchase and sale of crude oil in the same month, which is the month following such activity. In periods during which we build inventory, regardless of market structure, we may rely on the credit facilities or the PAA commercial paper program to pay for the inventory. In addition, we use derivative instruments to manage the risks associated with the purchase and sale of our commodities. Therefore, our cash flow from operating activities may be impacted by the margin deposit requirements related to our derivative activities and/or the timing of settlement of our derivative activities. For example, gains and losses from settled instruments that qualify as effective cash flow hedges are deferred in accumulated other comprehensive income/loss, but may impact operating cash flow in the period settled. See Note 11 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion regarding our derivatives and risk management activities.
Net cash provided by operating activities for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 was approximately $1.3 billion, $2.0 billion and $1.95 billion, respectively, and primarily resulted from earnings from our operations. Additionally, as discussed further below, changes in our inventory levels during these years impacted our cash flow from operating activities.
During 2015, we increased the amount of our inventory; however, these volumetric increases were largely offset by lower prices for our inventory stored at the end of the year compared to prior year amounts.
During 2014, we decreased the volume of our crude oil inventory that we held. The decreased inventory levels were further impacted by lower prices for such inventory stored at the end of the year compared to prior year amounts. In addition, our margin balances fluctuated from a net cash outflow to a net cash inflow. A portion of the net proceeds received from the liquidation of such inventory and the positive cash flow associated with our margin balance activities were used to repay borrowings under the PAA commercial paper program and favorably impacted cash flow from operating activities. These overall decreases were partially offset by an increase in the amount of NGL inventory stored at December 31, 2014 compared to prior year amounts, which was primarily financed through borrowings under the PAA commercial paper program.
During 2013, we decreased the amount of our inventory, primarily due to the sale of crude oil inventory that had been stored during the contango market, as well as the sale of NGL inventory due to end users’ increased demand for product used for heating and crop drying during the latter half of 2013. The net proceeds received from liquidation of such inventory during the year were used to repay borrowings under the credit facilities or the PAA commercial paper program and favorably impacted cash flow from operating activities. These decreases in inventory were partially offset by an increase in natural gas inventory whereby we retained more capacity for our own use. We primarily used borrowings under the credit facilities to pay for the stored natural gas, which negatively impacted our cash flow from operating activities. Also, a significant portion of our 2013 natural gas sales occurred in December 2013, with cash collections on these sales occurring in January 2014.
Credit Agreements, PAA Commercial Paper Program and Indentures
At December 31, 2015, PAA had four primary credit arrangements. These include a $1.6 billion senior unsecured revolving credit facility maturing in 2020, a $1.4 billion senior secured hedged inventory facility maturing in 2018 and a $1.0 billion, 364-day senior unsecured credit facility maturing in August 2016. Additionally, PAA has a $3.0 billion unsecured commercial paper program that is backstopped by its revolving credit facility and its hedged inventory facility. The PAA credit agreements (which impact the ability to access the PAA commercial paper program because they provide the backstop that supports PAA’s short-term credit ratings) and the indentures governing PAA’s senior notes contain cross-default provisions. A default under PAA’s credit agreements would permit the lenders to accelerate the maturity of the outstanding debt. As long as PAA is in compliance with the provisions in its credit agreements, PAA’s ability to make distributions of available cash is not restricted. PAA was in compliance with the covenants contained in its credit agreements and indentures as of December 31, 2015. In addition, AAP has a credit agreement which includes a $550 million term loan facility and a $125 million senior secured revolving credit facility, both maturing in 2020. AAP was in compliance with the covenants contained in its credit agreement as of December 31, 2015.
Equity and Debt Financing Activities
On a consolidated basis, our financing activities primarily relate to funding expansion capital projects, acquisitions and refinancing of debt maturities, as well as short-term working capital and hedged inventory borrowings related to our NGL business and contango market activities. Our financing activities have primarily consisted of PAA equity offerings, PAA senior notes offerings and borrowings and repayments under the credit facilities or the PAA commercial paper program, as well as payment of distributions to our Class A shareholders and noncontrolling interests.
PAA Registration Statements. PAA periodically accesses the capital markets for both equity and debt financing. PAA has filed with the SEC a universal shelf registration statement that, subject to effectiveness at the time of use, allows PAA to issue up to an aggregate of $2.0 billion of debt or equity securities (“Traditional Shelf”). All issuances of PAA equity securities associated with PAA’s continuous offering program have been issued pursuant to the Traditional Shelf. At December 31, 2015, PAA had approximately $2.0 billion of unsold securities available under the Traditional Shelf. PAA also has access to a universal shelf registration statement (“WKSI Shelf”), which provides it with the ability to offer and sell an unlimited amount of debt and equity securities, subject to market conditions and capital needs. PAA’s March 2015 underwritten equity offering and PAA’s August 2015 senior notes issuance were conducted under the WKSI shelf. See “PAA Common Unit Issuances” and “PAA Senior Notes” below.
PAA Common Unit Issuances. The following table summarizes the issuance of PAA’s common units during the three years ended December 31, 2015 (net proceeds in millions):
|
Year |
|
Type of Offering |
|
Units Issued |
|
Net Proceeds (1) |
| |
|
2015 |
|
Continuous Offering Program |
|
1,133,904 |
|
$ |
58 |
(2) |
|
2015 |
|
Underwritten Offering |
|
21,000,000 |
|
1,041 |
(3) | |
|
2015 Total |
|
|
|
22,133,904 |
|
$ |
1,099 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2014 Total |
|
Continuous Offering Program |
|
15,375,810 |
|
$ |
848 |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2013 Total |
|
Continuous Offering Program |
|
8,644,807 |
|
$ |
468 |
(2) |
(1) Amounts are net of costs associated with the offerings.
(2) PAA pays commissions to its sales agents in connection with common unit issuances under its Continuous Offering Program. PAA paid $1 million, $9 million and $5 million of such commissions during 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The net proceeds from these offerings were used for general partnership purposes.
(3) A portion of the net proceeds from such offering was used to repay borrowings under the PAA commercial paper program and the remaining net proceeds were used for general partnership purposes, including expenditures for our 2015 capital program.
PAA Preferred Unit Issuance. In January 2016, PAA completed the private placement of approximately 61.0 million PAA preferred units at a price of $26.25 per unit resulting in total net proceeds, after deducting offering expenses and the 2% transaction fee due to the purchasers, of approximately $1.6 billion. We intend to use the net proceeds for capital expenditures, repayment of debt and general partnership purposes.
The PAA preferred units rank senior to all classes or series of equity securities in PAA with respect to distribution rights. The holders of the PAA preferred units are entitled to receive quarterly distributions, subject to customary anti-dilution adjustments, of $0.525 per unit ($2.10 per unit annualized), commencing with the quarter ending March 31, 2016. With respect to any quarter ending on or prior to December 31, 2017, PAA may elect to pay distributions on the PAA preferred units in additional preferred units, in cash or in a combination of both. AAP will be entitled to participate in distributions on the PAA preferred units equal to its 2% general partner interest in PAA.
After two years, the preferred units are convertible at the purchasers’ option into common units on a one-for-one basis, subject to certain conditions, and are convertible at PAA’s option in certain circumstances after three years.
Distribution of Net Proceeds from our IPO. In October 2013, we completed our IPO of 132,382,094 Class A shares representing limited partner interests at a price of $22.00 per Class A share, generating net proceeds, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and direct offering expenses, of approximately $2.8 billion. We distributed these net proceeds to certain owners of AAP who, prior to our IPO, sold a portion of their interests in AAP to us in exchange for the right to receive an amount equal to the net proceeds of the IPO.
PAA Senior Notes. During the last three years, PAA issued senior unsecured notes as summarized in the table below (in millions):
|
Year |
|
Description |
|
Maturity |
|
Face Value |
|
Gross |
|
Net |
| |||
|
2015 |
|
4.65% Senior Notes issued at 99.846% of face value (3) |
|
October 2025 |
|
$ |
1,000 |
|
$ |
998 |
|
$ |
990 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
2014 |
|
2.60% Senior Notes issued at 99.813% of face value (4) |
|
December 2019 |
|
$ |
500 |
|
$ |
499 |
|
$ |
495 |
|
|
2014 |
|
4.90% Senior Notes issued at 99.876% of face value (4) |
|
February 2045 |
|
$ |
650 |
|
$ |
649 |
|
$ |
643 |
|
|
2014 |
|
3.60% Senior Notes issued at 99.842% of face value (3) |
|
November 2024 |
|
$ |
750 |
|
$ |
749 |
|
$ |
743 |
|
|
2014 |
|
4.70% Senior Notes issued at 99.734% of face value (3) |
|
June 2044 |
|
$ |
700 |
|
$ |
698 |
|
$ |
691 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
2013 |
|
3.85% Senior Notes issued at 99.792% of face value (3) |
|
October 2023 |
|
$ |
700 |
|
$ |
699 |
|
$ |
693 |
|
(1) Face value of notes less the applicable premium or discount (before deducting for initial purchaser discounts, commissions and offering expenses).
(2) Face value of notes less the applicable premium or discount, initial purchaser discounts, commissions and offering expenses.
(3) The net proceeds from this offering were used to repay outstanding borrowings under the PAA credit facilities or the PAA commercial paper program and for general partnership purposes.
(4) The net proceeds from this offering were used to repay outstanding borrowings under the PAA commercial paper program (a portion of which was used to fund the acquisition of a 50% interest in BridgeTex). See Note 7 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion.
PAA’s $150 million, 5.25% senior notes and $400 million, 3.95% senior notes matured in June 2015 and September 2015, respectively, and were repaid with borrowings under the PAA commercial paper program.
In December 2013, PAA’s $250 million, 5.63% senior notes matured and were repaid with borrowings under the PAA commercial paper program.
Acquisitions, Capital Expenditures and Distributions Paid to Our Class A Shareholders and Noncontrolling Interests
In addition to our operating needs discussed above, on a consolidated basis, we also use cash for acquisition activities, capital projects and distributions paid to our Class A shareholders and noncontrolling interests. Historically, we have financed these expenditures primarily with cash generated by operations and the financing activities discussed above. See “—Acquisitions and Capital Projects” for further discussion of such capital expenditures.
Acquisitions and Divestitures. The price of acquisitions includes cash paid, assumed liabilities and net working capital items. Because of the non-cash items included in the total price of the acquisition and the timing of certain cash payments, the net cash paid may differ significantly from the total price of the acquisitions completed during the year. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, we paid cash of $105 million, $1,098 million and $28 million, respectively, for acquisitions.
During the first quarter of 2016, we entered into binding agreements for the sale of various non-core assets for total consideration of approximately $325 million. We expect these transactions to close in the first half of 2016.
2016 Capital Projects. We expect the majority of funding for our 2016 capital program will be provided by the proceeds from PAA’s January 2016 preferred unit offering. Our capital program is highlighted by a large number of small-to-medium sized projects spread across multiple geographic regions/resource plays. We believe the diversity of our program mitigates the impact of delays, cost overruns or adverse market developments with respect to a particular project or geographic region/resource play. The majority of our 2016 expansion capital program will be invested in our fee-based Transportation and Facilities segments. We expect that our investments will have minimal contributions to our 2016 results, but will provide growth for 2017 and beyond. Our 2016 capital program includes the following projects as of February 2016 with the estimated cost for the entire year (in millions):
|
Projects |
|
2016 |
|
|
Red River Pipeline (Cushing to Longview) |
|
$290 |
|
|
Diamond Pipeline |
|
260 |
|
|
Fort Saskatchewan Facility Projects |
|
190 |
|
|
Permian Basin Area Pipeline Projects |
|
185 |
|
|
Saddlehorn Pipeline |
|
155 |
|
|
Cushing Terminal Expansions |
|
35 |
|
|
St. James Terminal Expansions |
|
35 |
|
|
Caddo Pipeline |
|
30 |
|
|
Cactus Pipeline |
|
20 |
|
|
Eagle Ford JV Project |
|
20 |
|
|
Other Projects |
|
280 |
|
|
|
|
$1,500 |
|
|
Potential Adjustments for Timing / Scope Refinement (1) |
|
-$100 + $100 |
|
|
Total Projected Expansion Capital Expenditures |
|
$1,400 - $1,600 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Maintenance Capital Expenditures |
|
$190 - $210 |
|
(1) Potential variation to current capital costs estimates may result from (i) changes to project design, (ii) final cost of materials and labor and (iii) timing of incurrence of costs due to uncontrollable factors such as receipt of permits or regulatory approvals and weather.
Distributions to our Class A shareholders. We distribute 100% of our available cash within 55 days following the end of each quarter to Class A shareholders of record. Available cash is generally defined as all of our cash and cash equivalents on hand at the end of each quarter less reserves established in the discretion of our general partner for future requirements. On February 12, 2016, we paid a quarterly distribution of $0.231 per Class A share. This distribution represents a year-over-year distribution increase of approximately 13.8%. See Note 10 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for details of distributions paid. Also, see Item 5. “Market for Registrant’s Shares, Related Shareholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities—Cash Distribution Policy” for additional discussion regarding distributions.
Distributions to noncontrolling interests. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, distributions of approximately $1.5 billion, $1.3 billion and $1.5 billion, respectively, were paid to noncontrolling interests. These amounts represent distributions paid on interests in PAA, AAP and SLC Pipeline LLC that were not owned by us. Of the amount distributed during the year ended December 31, 2013, $296 million related to distributions paid for the noncontrolling interests’ proportionate share of the net proceeds from the increase in AAP’s term loan. See Note 10 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion.
We believe that we have sufficient liquid assets, cash flow from operations and borrowing capacity under the credit agreements to meet our financial commitments, debt service obligations, contingencies and anticipated capital expenditures. We are, however, subject to business and operational risks that could adversely affect our cash flow. A prolonged material decrease in our cash flows would likely produce an adverse effect on our borrowing capacity.
Contingencies
For a discussion of contingencies that may impact us, see Note 16 to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Commitments
Contractual Obligations. In the ordinary course of doing business, we purchase crude oil and NGL from third parties under contracts, the majority of which range in term from thirty-day evergreen to five years, with a limited number of contracts with remaining terms extending up to ten years. We establish a margin for these purchases by entering into various types of physical and financial sale and exchange transactions through which we seek to maintain a position that is substantially balanced between purchases on the one hand and sales and future delivery obligations on the other. In addition, we enter into similar contractual obligations in conjunction with our natural gas operations. The table below includes purchase obligations related to these activities. Where applicable, the amounts presented represent the net obligations associated with our counterparties (including giving effect to netting buy/sell contracts and those subject to a net settlement arrangement). We do not expect to use a significant amount of internal capital to meet these obligations, as the obligations will be funded by corresponding sales to entities that we deem creditworthy or who have provided credit support we consider adequate.
The following table includes our best estimate of the amount and timing of these payments as well as others due under the specified contractual obligations as of December 31, 2015 (in millions):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2021 and |
|
|
| |||||||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2018 |
|
2019 |
|
2020 |
|
Thereafter |
|
Total |
| |||||||
|
Long-term debt, including current maturities and related interest payments (1) |
|
$ |
1,335 |
|
$ |
858 |
|
$ |
1,031 |
|
$ |
1,247 |
|
$ |
1,400 |
|
$ |
11,040 |
|
$ |
16,911 |
|
|
Leases (2) |
|
200 |
|
184 |
|
154 |
|
128 |
|
108 |
|
427 |
|
1,201 |
| |||||||
|
Other obligations (3) |
|
680 |
|
364 |
|
145 |
|
149 |
|
146 |
|
581 |
|
2,065 |
| |||||||
|
Subtotal |
|
2,215 |
|
1,406 |
|
1,330 |
|
1,524 |
|
1,654 |
|
12,048 |
|
20,177 |
| |||||||
|
Crude oil, natural gas, NGL and other purchases (4) |
|
3,837 |
|
2,142 |
|
1,592 |
|
1,127 |
|
914 |
|
2,694 |
|
12,306 |
| |||||||
|
Total |
|
$ |
6,052 |
|
$ |
3,548 |
|
$ |
2,922 |
|
$ |
2,651 |
|
$ |
2,568 |
|
$ |
14,742 |
|
$ |
32,483 |
|
(1) Includes debt service payments, interest payments due on PAA’s senior notes, interest payments on long-term borrowings outstanding under the AAP credit agreement, the commitment fee on assumed available capacity under the PAA credit facilities and long-term borrowings under the PAA commercial paper program. Although there may be short-term borrowings under the PAA credit facilities and the PAA commercial paper program, we historically repay and borrow at varying amounts. As such, we have included only the maximum commitment fee (as if no short-term borrowings were outstanding on the PAA credit facilities or the PAA commercial paper program) in the amounts above. For additional information regarding our debt obligations, see Note 9 to our Consolidated Financial Statements.
(2) Leases are primarily for (i) surface rentals, (ii) office rent, (iii) pipeline assets and (iv) trucks, trailers and railcars. Includes both capital and operating leases as defined by FASB guidance.
(3) Includes (i) other long-term liabilities (excluding approximately $33 million related to derivative activity included in Crude oil, natural gas, NGL and other purchases), (ii) storage, processing and transportation agreements and (iii) non-cancelable commitments related to our capital expansion projects, including projected contributions for our share of the capital spending of our equity method investments. The transportation agreements include approximately $930 million associated with an agreement to transport crude oil on a pipeline that is owned by an equity method investee, in which we own a 50% interest. Our commitment to transport is supported by crude oil buy/sell agreements with third parties (including Oxy) with commensurate quantities.
(4) Amounts are primarily based on estimated volumes and market prices based on average activity during December 2015. The actual physical volume purchased and actual settlement prices will vary from the assumptions used in the table. Uncertainties involved in these estimates include levels of production at the wellhead, weather conditions, changes in market prices and other conditions beyond our control.
Letters of Credit. In connection with supply and logistics activities, we provide certain suppliers with irrevocable standby letters of credit to secure our obligation for the purchase of crude oil, NGL and natural gas. Our liabilities with respect to these purchase obligations are recorded in accounts payable on our balance sheet in the month the product is purchased. Generally, these letters of credit are issued for periods of up to seventy days and are terminated upon completion of each transaction. Additionally, we issue letters of credit to support insurance programs, derivative transactions and construction activities. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, we had outstanding letters of credit of approximately $46 million and $87 million, respectively.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We have no off-balance sheet arrangements as defined by Item 303 of Regulation S-K.
Investments in Unconsolidated Entities
We have invested in entities that are not consolidated in our financial statements. Certain of these entities are borrowers under credit facilities. We are neither a co-borrower nor a guarantor under any such facilities. We may elect at any time to make additional capital contributions to any of these entities. The following table sets forth selected information regarding these entities as of December 31, 2015 (unaudited, dollars in millions):
|
Entity |
|
Type of Operation |
|
Our |
|
Total Entity |
|
Total Cash |
|
Total Entity |
| |||
|
Settoon Towing, LLC |
|
Barge Transportation Services |
|
50 |
% |
$ |
337 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
226 |
|
|
BridgeTex Pipeline Company, LLC |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
50 |
% |
$ |
857 |
|
$ |
26 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Caddo Pipeline LLC |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
50 |
% |
$ |
54 |
|
$ |
2 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Diamond Pipeline LLC |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
50 |
% |
$ |
178 |
|
$ |
100 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Eagle Ford Terminals Corpus Christi LLC |
|
Crude Oil Terminal and Dock |
|
50 |
% |
$ |
62 |
|
$ |
4 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Eagle Ford Pipeline LLC |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
50 |
% |
$ |
768 |
|
$ |
14 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Frontier Pipeline Company |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
50 |
% |
$ |
26 |
|
$ |
4 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Saddlehorn Pipeline Company, LLC |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
40 |
% |
$ |
365 |
|
$ |
51 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
White Cliffs Pipeline, LLC |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
36 |
% |
$ |
592 |
|
$ |
24 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Butte Pipe Line Company |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
22 |
% |
$ |
28 |
|
$ |
3 |
|
$ |
— |
|
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
We are exposed to various market risks, including (i) commodity price risk, (ii) interest rate risk and (iii) currency exchange rate risk. We use various derivative instruments to manage such risks and, in certain circumstances, to realize incremental margin during volatile market conditions. Our risk management policies and procedures are designed to help ensure that our hedging activities address our risks by monitoring our exchange-cleared and over-the-counter positions, as well as physical volumes, grades, locations, delivery schedules and storage capacity. We have a risk management function that has direct responsibility and authority for our risk policies, related controls around commercial activities and certain aspects of corporate risk management. Our risk management function also approves all new risk management strategies through a formal process. The following discussion addresses each category of risk.
Commodity Price Risk
We use derivative instruments to hedge price risk associated with the following commodities:
· Crude oil
We utilize crude oil derivatives to hedge commodity price risk inherent in our Supply and Logistics and Transportation segments. Our objectives for these derivatives include hedging anticipated purchases and sales, stored inventory, and storage capacity utilization. We manage these exposures with various instruments including exchange-traded and over-the-counter futures, forwards, swaps and options.
· Natural gas
We utilize natural gas derivatives to hedge commodity price risk inherent in our Supply and Logistics and Facilities segments. Our objectives for these derivatives include hedging anticipated purchases and sales and managing our anticipated base gas requirements. We manage these exposures with various instruments including exchange-traded futures, swaps and options.
· NGL and other
We utilize NGL derivatives, primarily butane and propane derivatives, to hedge commodity price risk inherent in our Supply and Logistics segment. Our objectives for these derivatives include hedging anticipated purchases and sales and stored inventory. We manage these exposures with various instruments including exchange-traded and over-the-counter futures, forwards, swaps and options.
See Note 11 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion regarding our hedging strategies and objectives.
The fair value of our commodity derivatives and the change in fair value as of December 31, 2015 that would be expected from a 10% price increase or decrease is shown in the table below (in millions):
|
|
|
|
|
Effect of 10% |
|
Effect of 10% |
| |||
|
|
|
Fair Value |
|
Price Increase |
|
Price Decrease |
| |||
|
Crude oil |
|
$ |
128 |
|
$ |
(56 |
) |
$ |
56 |
|
|
Natural gas |
|
4 |
|
$ |
(4 |
) |
$ |
4 |
| |
|
NGL and other |
|
95 |
|
$ |
(20 |
) |
$ |
20 |
| |
|
Total fair value |
|
$ |
227 |
|
|
|
|
| ||
The fair values presented in the table above reflect the sensitivity of the derivative instruments only and do not include the effect of the underlying hedged commodity. Price-risk sensitivities were calculated by assuming an across-the-board 10% increase or decrease in price regardless of term or historical relationships between the contractual price of the instruments and the underlying commodity price. In the event of an actual 10% change in near-term commodity prices, the fair value of our derivative portfolio would typically change less than that shown in the table as changes in near-term prices are not typically mirrored in delivery months further out.
Interest Rate Risk
Our use of variable rate debt and any forecasted issuances of fixed rate debt expose us to interest rate risk. Therefore, from time to time we use interest rate derivatives to hedge interest rate risk associated with anticipated interest payments and, in certain cases, outstanding debt instruments. All of PAA’s senior notes are fixed rate notes and thus are not subject to interest rate risk. Our variable rate debt outstanding at December 31, 2015, approximately $2.2 billion, is subject to interest rate re-sets that range from less than one week to two months. The average interest rate on variable rate debt that was outstanding during the year ended December 31, 2015 was 1.1%, based upon rates in effect during the year. The fair value of our interest rate derivatives was a liability of $49 million as of December 31, 2015. A 10% increase in the forward LIBOR curve as of December 31, 2015 would have resulted in an increase of $47 million to the fair value of our interest rate derivatives. A 10% decrease in the forward LIBOR curve as of December 31, 2015 would have resulted in a decrease of $47 million to the fair value of our interest rate derivatives. See Note 11 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion of our interest rate risk hedging activities.
Currency Exchange Rate Risk
We use foreign currency derivatives to hedge foreign currency exchange rate risk associated with our exposure to fluctuations in the USD-to-CAD exchange rate. Because a significant portion of our Canadian business is conducted in CAD and, at times, a portion of our debt is denominated in CAD, we use certain financial instruments to minimize the risks of unfavorable changes in exchange rates. These instruments include foreign currency exchange contracts, forwards and options. The fair value of our foreign currency derivatives was a liability of $8 million as of December 31, 2015. A 10% increase in the exchange rate (USD-to-CAD) would have resulted in a decrease of $19 million to the fair value of our foreign currency derivatives. A 10% decrease in the exchange rate (USD-to-CAD) would have resulted in an increase of $19 million to the fair value of our foreign currency derivatives. See Note 11 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion of our currency exchange rate risk hedging.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
See “Index to the Consolidated Financial Statements” on page F-1.
Item 9. Changes In and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
We maintain written disclosure controls and procedures, which we refer to as our “DCP.” Our DCP is designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in reports that we file under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”) is (i) recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and (ii) accumulated and communicated to management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Applicable SEC rules require an evaluation of the effectiveness of our DCP. Management, under the supervision and with the participation of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our DCP as of December 31, 2015, the end of the period covered by this report, and, based on such evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer have concluded that our DCP is effective.
Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. “Internal control over financial reporting” is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, and effected by our Board of Directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with GAAP. Our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief Financial Officer, has evaluated the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015. See Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting on page F-2 of our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Our independent registered public accounting firm, PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting, as stated in the firm’s report. See “Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm” on page F-3 of our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes in our internal control over financial reporting during the fourth quarter of 2015 that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Certifications
The certifications of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a) are filed with this report as Exhibits 31.1 and 31.2. The certifications of our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. 1350 are furnished with this report as Exhibits 32.1 and 32.2.
There was no information that was required to be disclosed in a report on Form 8-K during the fourth quarter of 2015 that has not previously been reported.
Item 10. Directors and Executive Officers of Our General Partner and Corporate Governance
Our Management and Governance
We own a 100% managing member interest in Plains All American GP LLC (“GP LLC”), the general partner of Plains AAP, L.P. (“AAP”). As of December 31, 2015, we also owned a 38% limited partner interest in AAP, which directly owns all of the incentive distribution rights and indirectly owns the 2% general partner interest in Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. (“PAA”). AAP is the sole member of PAA GP LLC, which is the general partner of PAA. GP LLC’s general partner interest in AAP is a non-economic interest.
Our general partner, PAA GP Holdings LLC (“GP Holdings”), manages our operations and activities. Class A shareholders are limited partners and do not participate in the management of our operations. As a general partner, GP Holdings is liable for all of our debts (to the extent not paid from our assets), except for indebtedness or other obligations that are made specifically non-recourse to it. Our general partner has the sole discretion to incur indebtedness or other obligations on our behalf on a non-recourse basis to the general partner.
We and our general partner have no employees. All of our officers and other personnel necessary for our business to function (to the extent not out-sourced) are employed by GP LLC. Pursuant to the Administrative Agreement described below under “Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence—Related Party Transactions—Administrative Agreement”, AAP, on our behalf, pays GP LLC an annual fee for general and administrative services. In addition, the Administrative Agreement provides that any direct expenses incurred by PAGP, GP Holdings and AAP (other than income taxes payable by PAGP) are borne by AAP. These direct expenses include costs related to (i) compensation for our independent directors, (ii) incremental director and officer liability insurance, (iii) listing on the NYSE, (iv) investor relations, (v) legal, (vi) tax and (vii) accounting.
In addition to the fee and expenses described above, AAP also reimburses GP LLC for expenses incurred (i) on our behalf; (ii) on behalf of our general partner; or (iii) for any other purpose related to our business and activities or those of our general partner. AAP also reimburses our general partner for any additional expenses incurred on our behalf or to maintain our legal existence and good standing. There is no limit on the amount of fees and expenses AAP may be required to pay to affiliates of our general partner on our behalf pursuant to the Administrative Agreement.
All of the officers and a majority of the directors of our general partner are also officers or directors of GP LLC. Our general partner’s executive officers spend the substantial majority of their time managing the business of PAA, which benefits us as PAA’s performance will determine our success. We estimate that these officers spend less than 10% of their time on our business, as distinct from PAA’s business. The actual time devoted by these officers to managing our business as well as PAA’s will fluctuate as a result of the relative activity level between the two entities. The amount of incremental time spent by non-officer directors who serve on both boards will depend to some extent on committee assignments, but our general partner estimates that such directors spend less than 20% more time by serving on the board of directors of our general partner. One of our independent directors also serves as an independent director of GP LLC.
Election of Directors
Initial Election of Directors. Our general partner’s limited liability company agreement provides for a board of directors consisting of seven members. For so long as each of EMG Investment, LLC (an affiliate of The Energy & Minerals Group), KAFU Holdings, L.P. (an affiliate of Kayne Anderson Investment Management Inc.) and Oxy Holding Company (Pipeline), Inc. (a subsidiary of Occidental Petroleum Corporation), together with their respective affiliates, which we refer to as the “original designating parties,” own at least a 10% limited partner interest in AAP (excluding for this purpose the AAP Management Units but including any indirect ownership interest in AAP through ownership of Class A shares), such party will be entitled to designate one director to our general partner’s board of directors. In addition, any other person or group that acquires and maintains a 20% or greater limited partner interest in AAP, which we refer to a “subsequent designating person,” will be entitled to designate one director to our general partner’s board of directors. We refer to this 10% ownership interest
requirement for the original designating parties and this 20% ownership interest requirement for a subsequent designating person as the “minimum ownership requirement,” and we refer to the original designating parties and a subsequent designating person collectively as the “designating parties.” In no event will more than three designating parties be entitled to designate a director to our general partner’s board of directors at any point in time. In the event that any designating party’s ownership level falls below the minimum ownership requirement, such party will automatically forfeit its designation right, and the director then designated by such party will be replaced by a director elected by (i) a majority vote of the remaining directors if such forfeiture takes place prior to the date that the overall direct and indirect economic interest of the Legacy Owners and their permitted transferees in AAP falls below 40% (calculated as described below), which we refer to as the “trigger date,” and (ii) our Class A and Class B shareholders voting together as a single class if such forfeiture takes place after the trigger date. The 40% threshold referred to above will be calculated on a fully diluted basis that takes into account any Class A shares owned by the Legacy Owners and their affiliates and permitted transferees, assumes the exchange of all AAP Management Units for AAP units based on the applicable conversion factor and attributes the ownership of such AAP units to the Legacy Owners.
The limited liability company agreement of our general partner further provides that the Chief Executive Officer of our general partner will serve as a director and Chairman of the Board of our general partner. All three of the remaining members of our general partner’s board of directors must be “independent” (as defined in applicable NYSE and SEC rules) and eligible to serve on the audit committee. Because we are a limited partnership, the listing standards of the NYSE do not require that our general partner’s board of directors include a majority of independent directors. At least two directors on our general partner’s board of directors must meet the criteria for service on a conflicts committee in accordance with our partnership agreement. Any successors to the three independent directors will be elected by our general partner’s board of directors (rather than the members of our general partner), until such time as our shareholders are entitled to vote in the election of directors as described below.
Election of Directors Following Substantial Reduction in Legacy Owners’ Ownership. Our general partner’s limited liability company agreement contains provisions linking the ownership of the membership interests in our general partner to the ownership of the outstanding AAP units. Membership interests in our general partner cannot be transferred without transferring the same number of AAP units and vice versa. The membership interests in our general partner generally may not be transferred in private (non-exchange) transactions other than in the case of specified permitted transfers. Any other transfers would be subject to a right of first refusal in favor of the other owners of our general partner, including us or our designee.
Our general partner’s limited liability company agreement provides that as the Legacy Owners reduce their ownership in AAP (through their exchange of AAP units and Class B shares for Class A shares), they will be contractually obligated to contribute to us a percentage of membership interests in our general partner that corresponds to the percentage of AAP units being exchanged by such Legacy Owner. As a result, as the Legacy Owners reduce their ownership of AAP units and membership interests in our general partner, our ownership of our general partner will increase in the same proportion. Moreover, as a result of these provisions, holders of our Class A shares will not have the ability to acquire the contractual right to designate a director through the acquisition of Class A shares in market purchases. Following the trigger date, the following governance arrangements will occur: (i) within a certain period of time, our general partner’s board of directors will be staggered into three classes; (ii) within a certain time period and subject to certain limitations, our Class A and Class B shareholders, voting together as a single class, will have the right to elect certain of our directors; and (iii) any person that owns of record at least 10% of our combined Class A and Class B shares will be entitled to nominate a single director for election at an annual meeting.
Board Leadership Structure and Role in Risk Oversight
Our CEO also serves as Chairman of the Board. The board of directors of our general partner has no policy with respect to the separation of the offices of chairman and CEO; rather, that relationship is currently defined and governed by our general partner’s limited liability company agreement, which currently requires coincidence of the offices. However, pursuant to the terms of our general partner’s limited liability company agreement, if and when our general partner’s board of directors elects a successor to our current CEO, by majority vote our general partner’s board of directors may determine to separate the offices of CEO and Chairman of the Board. We do not have a lead independent director.
The management of enterprise-level risk (ELR) may be defined as the process of identifying, managing and monitoring events that present opportunities and risks with respect to creation of value for our Class A shareholders. The GP LLC board has delegated to PAA management the primary responsibility for ELR management, while the GP LLC board has retained responsibility for oversight of management in that regard. Management provides an ELR assessment to the GP LLC board at least once every year.
Non-Management Executive Sessions and Shareholder Communications
NYSE listing standards require regular executive sessions of the non-management directors of a listed company, and an executive session for independent directors at least once a year. Only the members of our audit committee qualify as “independent.” Our audit committee routinely holds discussions with no other directors or members of management present. Our non-management directors also meet in executive session in connection with each regular board meeting, which are held in conjunction with meetings of the board of directors of GP LLC. On a rotating basis (determined alphabetically by last name), one of the non-management directors acts as presiding director at each such executive session.
Interested parties can communicate directly with non-management directors by mail in care of the General Counsel and Secretary or in care of the Vice President of Internal Audit at Plains GP Holdings, L.P., 333 Clay Street, Suite 1600, Houston, Texas 77002. Such communications should specify the intended recipient or recipients. Commercial solicitations or communications will not be forwarded.
Independence Determinations and Audit Committee
Because we are a limited partnership, the listing standards of the NYSE do not require that we establish or maintain a nominating or compensation committee of the board. We are, however, required to have an audit committee consisting of at least three members, all of whom are required to be “independent” as defined by the NYSE.
To be considered independent under NYSE listing standards, our board of directors must determine that a director has no material relationship with us other than as a director. The standards specify the criteria by which the independence of directors will be determined, including guidelines for directors and their immediate family members with respect to employment or affiliation with us or with our independent public accountants.
We have an audit committee that reviews our external financial reporting, engages our independent auditors, and reviews the adequacy of our internal accounting controls. The charter of our audit committee is available on our website. See “—Meetings and Other Information” for information on how to access or obtain copies of this charter. The board of directors of our general partner has determined that each member of our audit committee (Messrs. Burk, Goyanes and Shackouls) is “independent” under applicable NYSE rules and that Messrs. Burk and Goyanes are each an “Audit Committee Financial Expert,” as that term is defined in Item 407 of Regulation S-K.
None of the members of our audit committee has any relationships with us or our general partner, other than as a director and shareholder. Mr. Goyanes also serves as a director and chairman of the audit committee of the board of directors of GP LLC. For additional information regarding the experience and qualifications of our directors, please read the biographical descriptions under “—Directors and Executive Officers of our General Partner” below.
Other Committees
Applicable NYSE listing standards do not require that we or our general partner have a compensation committee or a nominating committee. Our general partner’s board of directors performs the functions of a compensation committee and administers our Long-Term Incentive Plan. Our general partner’s board of directors did not retain any compensation consultants during 2015.
Our partnership agreement provides for the establishment of a conflicts committee as circumstances warrant to review conflicts of interest between us and our general partner or the owners of our general partner or
between us and PAA or its affiliates. Such committee would consist of a minimum of two members, none of whom can be officers or employees of our general partner or directors, officers or employees of its affiliates and each of whom must meet the independence standards established by the NYSE and the SEC for service on an audit committee. Any matters approved by the conflicts committee will be conclusively deemed to be fair and reasonable to us, approved by all of our partners, and not a breach by our general partner of any duties owed to us or our shareholders. See Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence—Review, Approval or Ratification of Transactions with Related Persons.”
Meetings and Other Information
During the last fiscal year, our board of directors held nine meetings and our audit committee held eight meetings. All directors have access to members of management, and a substantial amount of information transfer and informal communication occurs between meetings. None of our directors attended fewer than 75% of the aggregate number of meetings of the board of directors and committees of the board on which the director served.
As discussed above, our general partner manages our operations and activities under the direction of our board of directors, whose members are currently either designated or appointed by members of our general partner. Accordingly, our Class A shareholders have only limited voting rights on matters affecting our business or governance. As a result, we do not hold regular annual meetings of shareholders for the purpose of electing directors or soliciting approval of any other routine matters prior to the trigger date.
Our audit committee charter and governance guidelines, as well as our Code of Business Conduct and our Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers (which applies to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer and principal accounting officer) are available under the Structure and Governance tab under “Company Information” in the Investor Relations section of our Internet website at http://www.plainsallamerican.com. We intend to disclose any amendment to or waiver of the Code of Ethics for Senior Financial Officers and any waiver of our Code of Business Conduct on behalf of an executive officer or director either on our Internet website or in an 8-K filing.
Audit Committee Report
The audit committee of our general partner’s board of directors oversees the Partnership’s financial reporting process on behalf of the board of directors. Management has the primary responsibility for the financial statements and the reporting process, including the systems of internal controls.
In fulfilling its oversight responsibilities, the audit committee reviewed and discussed with management the audited financial statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
The Partnership’s independent registered public accounting firm, PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, is responsible for expressing an opinion on the conformity of the audited financial statements with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The audit committee reviewed with PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP the firm’s judgment as to the quality, not just the acceptability, of the Partnership’s accounting principles and such other matters as are required to be discussed with the audit committee under generally accepted auditing standards.
The audit committee discussed with PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP the matters required to be discussed by Public Company Accounting Oversight Board Auditing Standard No. 16, Communications with Audit Committees. The audit committee received written disclosures and the letter from PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP required by applicable requirements of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board regarding PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP’s communications with the audit committee concerning independence, and has discussed with PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP its independence from management and the Partnership.
Based on the reviews and discussions referred to above, the audit committee recommended to the board of directors that the audited financial statements be included in the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2015 for filing with the SEC.
|
|
Everardo Goyanes, Chairman |
|
|
Victor Burk |
|
|
Bobby S. Shackouls |
Directors and Executive Officers of Our General Partner
The following table sets forth certain information with respect to the directors and executive officers (for purposes of Item 401(b) of Regulation S-K) of our general partner. Directors are elected annually and all executive officers are appointed by the board of directors of our general partner. There is no family relationship between any executive officer and director. As discussed above, three of the owners of membership interests in our general partner each have the right to separately designate a member of our board of directors, and such designee in turn automatically becomes a member of the GP LLC board (as does the CEO). For additional information regarding the contractual designation of directors to our general partner’s board, please read “Election of Directors” above.
|
Name |
|
Age (as of |
|
Position(1) |
|
Greg L. Armstrong(2) |
|
57 |
|
Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer and Director |
|
Harry N. Pefanis |
|
58 |
|
President and Chief Operating Officer |
|
Wilfred (Willie) C. Chiang |
|
55 |
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer (U.S.) |
|
Mark J. Gorman |
|
61 |
|
Executive Vice President—Operations and Engineering |
|
Phillip D. Kramer |
|
59 |
|
Executive Vice President |
|
Richard K. McGee |
|
54 |
|
Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary |
|
Al Swanson |
|
51 |
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
|
John P. vonBerg |
|
61 |
|
Executive Vice President—Commercial Activities |
|
W. David Duckett |
|
60 |
|
Chief Executive Officer, Plains Midstream Canada |
|
Chris Herbold |
|
43 |
|
Vice President—Accounting and Chief Accounting Officer |
|
Victor Burk |
|
66 |
|
Director and Member of Audit Committee |
|
Bernard (Ben) Figlock(2) |
|
55 |
|
Director |
|
Everardo Goyanes(2) |
|
71 |
|
Director and Member of Audit Committee* |
|
John T. Raymond(2) |
|
45 |
|
Director |
|
Bobby S. Shackouls |
|
65 |
|
Director and Member of Audit Committee |
|
Robert V. Sinnott(2) |
|
66 |
|
Director |
* Indicates chairman of committee.
(1) Unless otherwise described, the position indicates the position held with GP LLC.
(2) These individuals also serve as members of the GP LLC board of directors.
Greg L. Armstrong has served as Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer of our general partner since July 2013 and as Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer of PAA’s general partner since PAA’s formation in 1998. He has also served as a director of PAA’s general partner or former general partner since PAA’s formation. In addition, he was President, Chief Executive Officer and director of Plains Resources Inc. from 1992 to May 2001. He previously served Plains Resources as: President and Chief Operating Officer from October to December 1992; Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from June to October 1992; Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from 1991 to 1992; Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from 1984 to 1991; Corporate Secretary from 1981 to 1988; and Treasurer from 1984 to 1987. Mr. Armstrong is a director of the Federal Reserve Bank of Dallas, and a director of National Oilwell Varco, Inc. Mr. Armstrong is also a member of the advisory board of the Maguire Energy Institute at the Cox School of Business at Southern Methodist University, the National Petroleum Council and the Foundation for The Council on Alcohol and Drugs Houston.
Harry N. Pefanis has served as President and Chief Operating Officer of our general partner since July 2013 and as President and Chief Operating Officer of PAA’s general partner since PAA’s formation in 1998. He was also a director of PAA’s former general partner. In addition, he was Executive Vice President—Midstream of Plains Resources from May 1998 to May 2001. He previously served Plains Resources as: Senior Vice President from February 1996 until May 1998; Vice President—Products Marketing from 1988 to February 1996; Manager of Products Marketing from 1987 to 1988; and Special Assistant for Corporate Planning from 1983 to 1987. Mr. Pefanis was also President of several former midstream subsidiaries of Plains Resources until PAA’s formation. Mr. Pefanis is a director of Settoon Towing.
Wilfred (Willie) C. Chiang has served as Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer (U.S.) of our general partner and of PAA’s general partner since August 2015. Prior to joining Plains, Mr. Chiang served as Executive Vice President — Operations for Occidental Petroleum Corporation from 2012 until 2015. From 1996 until 2012, he served in various positions at ConocoPhillips, including most recently as Senior Vice President — Refining, Marketing, Transportation and Commercial.
Mark J. Gorman has served as Executive Vice President — Operations and Engineering of our general partner and of PAA’s general partner since December 2015. He served as Executive Vice President—Operations and Business Development of our general partner from July 2013 until December 2015 and as Executive Vice President—Operations and Business Development of PAA’s general partner from February 2013 until December 2015. He previously served as Senior Vice President—Operations and Business Development from August 2008 until February 2013, and as Vice President from November 2006 until August 2008. Prior to joining Plains, he was with Genesis Energy in differing capacities as a Director, President and CEO, and Executive Vice President and COO from 1996 through August 2006. From 1992 to 1996, he served as a President for Howell Crude Oil Company. Mr. Gorman began his career with Marathon Oil Company, spending 13 years in various disciplines. Mr. Gorman is also a director of Settoon Towing and Butte.
Phillip D. Kramer has served as Executive Vice President of our general partner since July 2013 and as Executive Vice President of PAA’s general partner since November 2008. He previously served as Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from PAA’s formation in 1998 until November 2008. In addition, he was Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of Plains Resources from May 1998 to May 2001. He previously served Plains Resources as Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from May 1997 until May 1998; Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from 1992 to 1997; Vice President from 1988 to 1992; Treasurer from 1987 to 2001; and Controller from 1983 to 1987.
Richard K. McGee has served as Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary of our general partner since July 2013 and as Executive Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary of PAA’s general partner since February 2013. He served as Vice President, General Counsel and Secretary from March 2012 until February 2013 and served as Vice President and Deputy General Counsel from August 2011 through March 2012. He also served as Vice President—Legal and Business Development of PAA’s natural gas storage business from September 2009 through March 2012. From January 1999 to July 2009, he was employed by Duke Energy, serving as President of Duke Energy International from October 2001 through July 2009 and serving as general counsel of Duke Energy Services from January 1999 through September 2001. He previously spent 12 years at Vinson & Elkins L.L.P., where he was a partner with a focus on acquisitions, divestitures and development work for various clients in the energy industry.
Al Swanson has served as Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of our general partner since July 2013 and as Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of PAA’s general partner since February 2011. He previously served as Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer from November 2008 through February 2011, as Senior Vice President—Finance from August 2008 until November 2008 and as Senior Vice President—Finance and Treasurer from August 2007 until August 2008. He served as Vice President—Finance and Treasurer from August 2005 to August 2007, as Vice President and Treasurer from February 2004 to August 2005 and as Treasurer from May 2001 to February 2004. In addition, he held finance related positions at Plains Resources including Treasurer from February 2001 to May 2001 and Director of Treasury from November 2000 to February 2001. Prior to joining Plains Resources, he served as Treasurer of Santa Fe Snyder Corporation from 1999 to October 2000 and in various capacities at Snyder Oil Corporation including Director of
Corporate Finance from 1998, Controller—SOCO Offshore, Inc. from 1997, and Accounting Manager from 1992. Mr. Swanson began his career with Apache Corporation in 1986 serving in internal audit and accounting.
John P. vonBerg has served as Executive Vice President—Commercial Activities of our general partner since February 2014 and served as Senior Vice President—Commercial Activities of our general partner from July 2013 until February 2014. He has also served as Executive Vice President—Commercial Operations of PAA’s general partner since February 2014. Previously he served as Senior Vice President—Commercial Activities of PAA’s general partner from August 2008 until February 2014, as Vice President—Commercial Activities from August 2007 until August 2008 and as Vice President—Trading from May 2003 until August 2007. He served as Director of these activities from January 2002 until May 2003. Prior to joining us in January 2002, he was with Genesis Energy in differing capacities as a Director, Vice Chairman, President and CEO from 1996 through 2001, and from 1993 to 1996 he served as a Vice President and a Crude Oil Manager for Phibro Energy USA. Mr. vonBerg began his career with Marathon Oil Company, spending 13 years in various disciplines.
W. David Duckett has served as Chief Executive Officer of Plains Midstream Canada since January 1, 2016. He served as President of Plains Midstream Canada from June 2003 through December 2015, and served as Executive Vice President of Plains Midstream Canada from July 2001 to June 2003. Mr. Duckett was with CANPET Energy Group Inc. (“CANPET”) from 1985 to 2001, where he served in various capacities, including most recently as President, Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board.
Chris Herbold has served as Vice President—Accounting and Chief Accounting Officer of our general partner since July 2013 and as Vice President—Accounting and Chief Accounting Officer of PAA’s general partner since August 2010. He served as Controller of PAA from 2008 until August 2010. He previously served as Director of Operational Accounting from 2006 to 2008, Director of Financial Reporting and Accounting from 2003 to 2006 and Manager of SEC and Financial Reporting from 2002 to 2003. Prior to joining PAA in April 2002, Mr. Herbold spent seven years working for the accounting firm Arthur Andersen LLP.
Victor Burk has served as a director of our general partner since January 2014. He has been a Managing Director for Alvarez and Marsal, a privately owned professional services firm since April 2009. From 2005 to 2009, Mr. Burk was the global energy practice leader for Spencer Stuart, a privately owned executive recruiting firm. Prior to joining Spencer Stuart, Mr. Burk served as managing partner of Deloitte & Touche’s global oil and natural gas group from 2002 to 2005. He began his professional career in 1972 with Arthur Andersen and served as managing partner of Arthur Andersen’s global oil and natural gas group from 1989 until 2002. Mr. Burk is on the board of directors of EV Management, LLC, the ultimate general partner of EV Energy Partners, L.P., a publicly traded limited partnership engaged in the acquisition, development and production of oil and natural gas. Mr. Burk served as a director and as chairman of the audit committee of PNGS GP LLC, the general partner of PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P., from April 2010 through December 2013. Mr. Burk also serves as a board member of the Independent Petroleum Association of America (Southeast Texas Region) and the Sam Houston Area Council of the Boy Scouts of America. He received a BBA in Accounting from Stephen F. Austin State University, graduating with highest honors. The board of directors of our general partner has determined that Mr. Burk is “independent” under applicable NYSE rules and qualifies as an “Audit Committee Financial Expert.” We believe that Mr. Burk’s background, spanning over 30 years of extensive public accounting and consulting in the energy industry, coupled with his demonstrated leadership abilities, brings valuable expertise and insight to the board.
Bernard (Ben) Figlock has served as a director of our general partner since January 2015. He has also served as a director of PAA’s general partner since January 2015. Mr. Figlock currently serves as Vice President and Treasurer at Oxy, where he directs and oversees management of Oxy’s treasury and risk management functions including finance, investments, insurance and operational risk, commodities trading credit and market risk, and currencies. Mr. Figlock joined Oxy in 1987, advancing to positions of increasing responsibility in Internal Audit, Corporate Finance Planning & Analysis, Corporate Development, and Treasury. Mr. Figlock holds a BS in Accounting from Wake Forest University and an MBA from Loyola Marymount University. We believe that Mr. Figlock’s financial and analytical background provides the board a distinctive and valuable perspective.
Everardo Goyanes has served as a director of our general partner since October 2013. He has served as a director of PAA’s general partner or former general partner since May 1999. He is Founder of Ex Cathedra LLC (a consulting firm). Mr. Goyanes served as Chairman of Liberty Natural Resources from April 2009 until August 2011. From May 2000 to April 2009, he was President and Chief Executive Officer of Liberty Energy Holdings, LLC (an energy investment firm). From 1999 to May 2000, he was a financial consultant specializing in natural resources. From 1989 to 1999, he was Managing Director of the Natural Resources Group of ING Barings Furman Selz (a banking firm). He was a financial consultant from 1987 to 1989 and was Vice President—Finance of Forest Oil Corporation from 1983 to 1987. From 1967 to 1982, Mr. Goyanes served in various financial and management capacities at Chase Bank, where his major emphasis was international and corporate finance to large independent and major oil companies. Mr. Goyanes received a BA in Economics from Cornell University and a Masters degree in Finance (honors) from Babson Institute. The board of directors of our general partner has determined that Mr. Goyanes is “independent” under applicable NYSE rules and qualifies as an “Audit Committee Financial Expert.” Mr. Goyanes’ qualifications as an Audit Committee Financial Expert are supplemented by extensive experience comprising direct involvement in the energy sector over a span of more than 30 years. We believe that this experience, coupled with the leadership qualities demonstrated by his executive background bring important experience and skill to the board.
John T. Raymond has served as a director of our general partner since October 2013. He has served as a director of PAA’s general partner since December 2010. Mr. Raymond is an owner and founder of The Energy & Minerals Group, which is the management company for a series of specialized private equity funds. EMG was founded in 2006 and focuses on investing across various facets of the global natural resource industry including the upstream and midstream segments of the energy complex. As of September 30, 2015, EMG has approximately $16.5 billion of regulatory assets under management and approximately $9.4 billion in commitments have been allocated across the energy sector since inception. Previous to that time, Mr. Raymond held leadership positions with various energy companies, including President and CEO of Plains Resources Inc. (the predecessor entity for Vulcan Energy), President and Chief Operating Officer of Plains Exploration and Production Company and Director of Development for Kinder Morgan, Inc. Mr. Raymond has been a direct or indirect owner of PAA’s general partner since 2001 and served on the board of PAA’s general partner from 2001 to 2005. Mr. Raymond serves on numerous other boards, including NGL Energy Holdings LLC, the general partner of NGL Energy Partners, L.P., Tallgrass MLP GP, LLC, the general partner of Tallgrass Energy Partners, L.P. and Tallgrass Management, LLC, the general partner of Tallgrass Energy GP, LP. Mr. Raymond received a BSM degree from the A.B. Freeman School of Business at Tulane University with dual concentrations in finance and accounting. We believe that Mr. Raymond’s experience with investment in and management of a variety of upstream and midstream assets and operations provides a valuable resource to the board.
Bobby S. Shackouls has served as a director of our general partner since January 2014. Mr. Shackouls served as Chairman of Burlington Resources Inc. from 1997 until its acquisition by ConocoPhillips in 2006, and continued to serve on the ConocoPhillips Board of Directors until his retirement in May 2011. Prior thereto, Mr. Shackouls served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Meridian Oil, Inc, a wholly owned subsidiary of Burlington Resources, from 1994-1995, and as President and Chief Executive Officer of Burlington Resources from 1995 until 2006. Mr. Shackouls currently serves as a director and member of the audit and corporate governance committees of The Kroger Co. and as a director and member of the compensation committee of Oasis Petroleum. He served as a director and member of the audit committee of PNGS GP LLC, the general partner of PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P., from April 2010 through December 2013. The board of directors of our general partner has determined that Mr. Shackouls is “independent” under applicable NYSE rules. We believe that Mr. Shackouls’ extensive experience within the energy industry offers valuable perspective and, in tandem with his long history of leadership as the CEO of a public company, make him highly qualified to serve as a member of the board.
Robert V. Sinnott has served as a director of our general partner since October 2013. He has served as a director of PAA’s general partner or former general partner since September 1998. Mr. Sinnott is President, Chief Executive Officer and Chief Investment Officer of Kayne Anderson Capital Advisors, L.P. (an investment management firm). He also served as a Managing Director from 1992 to 1996 and as a Senior Managing Director from 1996 until assuming his CEO role in 2010. He is also President of Kayne Anderson Investment Management, Inc., the general partner of Kayne Anderson Capital Advisors, L.P. Mr. Sinnott served as a director of Kayne Anderson Energy Development Company from 2006 through June 2013. He was Vice President and Senior Securities Officer of the Investment Banking Division of Citibank from 1986 to 1992, and previously held positions with United Energy Resources, a pipeline company, and Bank of America in its oil and gas finance department. Mr.
Sinnott also serves as a director of California Resources Corporation. Mr. Sinnott received a BA from the University of Virginia and an MBA from Harvard. Mr. Sinnott’s extensive investment management background includes his current role of managing approximately $16 billion of energy-related investments. Coupled with his direct involvement in the energy sector, spanning more than 30 years, the breadth of his current market and industry knowledge is enhanced by the depth of his knowledge of the various cycles in the energy sector. We believe that as a result of his background and knowledge, as well as the attributes of leadership demonstrated by his executive experience, Mr. Sinnott brings substantial experience and skill to the board.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Section 16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 requires directors, executive officers and persons who beneficially own more than ten percent of a registered class of our equity securities to file with the SEC and the NYSE initial reports of ownership and reports of changes in ownership of such equity securities. Such persons are also required to furnish us with copies of all Section 16(a) forms that they file. Such reports are accessible on or through our Internet website at http://www.plainsallamerican.com.
Based solely upon a review of the copies of Forms 3 and 4 furnished to us, or written representations from certain reporting persons that no Forms 5 were required, we believe that our executive officers and directors complied with all filing requirements with respect to transactions in our equity securities during 2015.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
Compensation Committee Report
Our general partner’s board of directors performs the functions of a compensation committee. Accordingly, the board of directors of our general partner has reviewed and discussed with management the compensation discussion and analysis contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Based on those reviews and discussions, the board of directors has recommended that the compensation discussion and analysis be included in the Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2015 for filing with the SEC.
|
|
Greg L. Armstrong |
|
|
Victor Burk |
|
|
Ben Figlock |
|
|
Everardo Goyanes |
|
|
John T. Raymond |
|
|
Bobby S. Shackouls |
|
|
Robert V. Sinnott |
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
Our general partner’s board of directors performs the functions of a compensation committee. Mr. Armstrong, our Chief Executive Officer, also serves as a director and executive officer of GP LLC. No other member of our general partner’s board of directors serves as an executive officer of us or PAA. Mr. Goyanes serves as a director of GP LLC and as chairman of its audit committee, Messrs. Figlock, Raymond and Sinnott serve as directors of GP LLC, and Messrs. Raymond and Sinnott serve as members of GP LLC’s compensation committee. Mr. Raymond is associated with EMG, Mr. Sinnott is associated with Kayne Anderson and its affiliates, and Mr. Figlock is associated with Oxy. We have relationships with these entities. See Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence—Related Party Transactions.”
Compensation Discussion and Analysis
We and our general partner were formed in July 2013. As such, neither we nor our general partner accrued any obligations with respect to compensation for our executive officers or directors for any period prior to completion of our initial public offering in October 2013.
Neither we nor our general partner have employees. All of our officers and other personnel necessary for our business to function (to the extent not out-sourced) are employed by GP LLC, and AAP, on our behalf, pays GP LLC an annual fee for general and administrative services. See Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence—Related Party Transactions—Administrative Agreement.” Applicable disclosure rules require us to discuss certain aspects of the compensation of any of our “Named Executive Officers,” which include our Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”), our Chief Financial Officer (“CFO”), and the four other most highly compensated executive officers who received compensation in excess of $100,000 during the previous fiscal year. For 2015, references within this Compensation Discussion and Analysis to our Named Executive Officers and to PAA’s Named Executive Officers refer to Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Chiang, Swanson, Duckett and vonBerg.
We do not separately compensate our Named Executive Officers; rather, their management of our business is part of the service provided by GP LLC under the Administrative Agreement. Moreover, substantially all responsibility and authority for compensation-related decisions resides with the compensation committee of GP LLC. Our Named Executive Officers participate in the employee benefit plans and arrangements of GP LLC and PAA, including plans that may be established in the future. Neither we nor our general partner have entered into any employment or benefits-related agreements with any individual who provides executive officer services to us, and, except for the LTIP and potential awards under such plan, we do not anticipate entering into any such agreement in the future. The Administrative Agreement, which governs the reimbursement of GP LLC by AAP for AAP’s allocable share of costs and expenses borne or incurred by GP LLC for the benefit of AAP, us or our general partner does not cover any costs we may incur that are attributable to any future awards we may grant under the LTIP. Any such costs will be borne by AAP as determined by our general partner’s board of directors, who is responsible for the administration of our LTIP, the issuance of any awards thereunder and approval of any compensation payable to our general partner’s non-employee directors.
The compensation information set forth in this section discloses the compensation discussion and analysis of PAA for the year ended December 31, 2015. This section will provide insight into GP LLC’s compensation philosophy and policies that governed the compensation of our Named Executive Officers as it relates to their services performed on behalf of PAA during the 2015 fiscal year.
PAA Background
All of PAA’s officers and employees (other than Canadian personnel) are employed by GP LLC. PAA’s Canadian personnel are employed by Plains Midstream Canada, which is a wholly owned subsidiary. Under its partnership agreement, PAA is required to reimburse its general partner and its general partner’s affiliates for all employment-related costs, including compensation for executive officers, other than expenses related to the AAP Management Units (which are borne entirely by AAP).
Objectives
Since PAA’s inception, it has employed a compensation philosophy that emphasizes pay for performance, both on an individual and entity level, and places the majority of each Named Executive Officer’s (defined in the Summary Compensation Table below) compensation at risk. The primary long-term measure of PAA’s performance is its ability to increase its sustainable quarterly distribution to its unitholders. PAA believes its pay-for-performance approach aligns the interests of its executive officers with that of its equity holders, and at the same time enables PAA to maintain a lower level of base overhead in the event operating and financial performance is below expectations. PAA’s executive compensation is designed to attract and retain individuals with the background and skills necessary to successfully execute PAA’s business model in a demanding environment, to motivate those individuals to reach near-term and long-term goals in a way that aligns their interest with that of PAA’s unitholders, and to reward success in reaching such goals. PAA uses three primary elements of compensation to fulfill that design—salary, cash bonus and long-term equity incentive awards. Cash bonuses and equity incentives (as opposed to salary)
represent the performance driven elements. They are also flexible in application and can be tailored to meet PAA’s objectives. The determination of specific individuals’ cash bonuses is based on their relative contribution to achieving or exceeding annual goals and the determination of specific individuals’ long-term incentive awards is based on their expected contribution in respect of longer term performance objectives. PAA does not maintain a defined benefit or pension plan for its executive officers as PAA believes such plans primarily reward longevity and not performance. PAA provides a basic benefits package generally to all employees, which includes a 401(k) plan and health, disability and life insurance. In instances considered necessary for the execution of their job responsibilities, PAA also reimburses certain Named Executive Officers and other employees for club dues and similar expenses. PAA considers these benefits and reimbursements to be typical of other employers, and does not believe they are distinctive of its compensation program.
Elements of Compensation
Salary. PAA does not “benchmark” salary or bonus amounts. In practice, PAA believes its salaries are generally competitive with the narrower universe of large-cap master limited partnerships, but are moderate relative to the broad spectrum of energy industry competitors for similar talent.
Cash Bonuses. PAA’s cash bonuses include annual discretionary bonuses in which all of its current domestic Named Executive Officers potentially participate, as well as a quarterly bonus program in which Mr. vonBerg participates. Mr. Duckett participates in an annual and quarterly bonus program that is specific to activities managed by PAA’s Canadian personnel.
Long-Term Incentive Awards. The primary long-term measure of PAA’s performance is its ability to increase sustainable quarterly distribution to its unitholders. Historically, PAA has used performance-indexed phantom unit grants issued under its Long-Term Incentive Plans to encourage and reward timely achievement of targeted distribution levels and align the long-term interests of its Named Executive Officers with those of its unitholders. These grants also require minimum service periods as further described below in order to encourage long-term retention. A phantom unit is the right to receive, upon the satisfaction of vesting criteria specified in the grant, a common unit (or cash equivalent). PAA does not use options as a form of incentive compensation. Unlike “vesting” of an option, vesting of a phantom unit results in delivery of a common unit or cash of equivalent value as opposed to a right to exercise. Terms of historical phantom unit grants have varied, but generally phantom units vest upon the later of achievement of targeted distribution threshold levels and continued employment for periods ranging from two to five years. These distribution performance thresholds are generally consistent with PAA’s targeted range for distribution growth. To encourage accelerated performance, if PAA meets certain distribution thresholds prior to meeting the minimum service requirement for vesting, PAA’s current Named Executive Officers have the right to receive distributions on phantom units prior to vesting in the underlying common units (referred to as distribution equivalent rights, or “DERs”).
In 2007, the owners of AAP authorized the creation of “Class B” units of AAP (“AAP Management Units”), each of which represents a “profits interest” in AAP, and authorized GP LLC’s compensation committee to issue grants of AAP Management Units to create additional long-term incentives for PAA’s management designed to attract talent and encourage retention over an extended period of time. The entire economic burden of the AAP Management Units is borne solely by AAP, and does not impact PAA’s cash or units outstanding.
The AAP Management Units are subject to restrictions on transfer and generally become incrementally “earned” (entitled to receive a portion of the distributions that would otherwise be paid to holders of AAP units) upon achievement of certain performance thresholds related to achievement of targeted PAA distribution levels, which are aligned with the interests of PAA’s common unitholders. As of February 15, 2016, 100% of the outstanding AAP Management Units granted in 2007, 2009, 2010 and 2011 (including those held by Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett and vonBerg) had been earned, 75% of the AAP Management Units granted in 2013 had been earned, and 25% of the AAP Management Units granted in 2014 had been earned. None of the AAP Management Units issued in 2015 (including those held by Mr. Chiang) have been earned. No AAP Management Units were granted in 2008 or 2012.
To encourage retention following achievement of these performance benchmarks, AAP retained a call right to purchase any earned AAP Management Units at a discount to fair market value that is generally exercisable upon the termination of a holder’s employment with GP LLC and its affiliates (other than termination under certain
circumstances such as a termination without cause or by the employee for good reason) prior to certain stated dates. If a holder of an AAP Management Unit remains employed past such designated date (or prior to such date such holder is terminated without cause or quits for good reason), any earned units are no longer subject to the call right and are deemed to have “vested.” As of January 1, 2016, AAP Management Units granted in 2007 and 2009 (including those held by Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett and vonBerg) are no longer subject to such call right and have vested. The applicable vesting dates for the remaining AAP Management Unit grants range from January 1, 2017 for AAP Management Units granted in 2010 to January 1, 2023 for AAP Management Units granted in 2015. In order to encourage retention, the size of the discount to fair market value reflected in the potential call right purchase price decreases over time pursuant to a formula set forth in each AAP Management Unit grant agreement. AAP Management Unit grants also provide that all earned AAP Management Units and a portion of any unearned and unvested AAP Management Units will vest upon a change of control. All earned AAP Management Units will also vest if AAP does not timely exercise its call right.
As long as our Class A shares are publicly traded, each vested AAP Management Unit may be converted into AAP units and a like number of our Class B shares based on a conversion ratio calculated in accordance with the AAP limited partnership agreement (which conversion ratio will not be more than one-to-one and was approximately 0.938 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit as of December 31, 2015 and approximately 0.940 as of February 15, 2016). Following any such conversion, the resulting AAP units and Class B shares are exchangeable for our Class A shares on a one-for-one basis as provided in the AAP limited partnership agreement. As of February 15, 2016, approximately 44.9 million AAP Management Units had vested, of which 18.8 million have been converted into 17.7 million AAP units and Class B shares. A portion of the resulting AAP units and Class B shares was subsequently exchanged for an aggregate of 11.4 million Class A shares. See Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence—AAP Management Units.”
Relation of Compensation Elements to Compensation Objectives
PAA’s compensation program is designed to motivate, reward and retain its executive officers. Cash bonuses serve as a near-term motivation and reward for achieving the annual goals established at the beginning of each year. Phantom unit awards (and associated DERs) and AAP Management Units provide motivation and reward over both the near-term and long-term for achieving performance thresholds necessary for earning and vesting. The level of annual bonus and phantom unit awards reflect the moderate salary profile and the significant weighting towards performance based, at-risk compensation. Salaries and cash bonuses (particularly quarterly bonuses), as well as currently payable DERs associated with unvested phantom units and earned AAP Management Units subject to AAP’s call right, serve as near-term retention tools. Longer-term retention is facilitated by the minimum service periods of up to five years associated with phantom unit awards, the long-term vesting profile of the AAP Management Units and, in the case of certain executives directly involved in activities that generate partnership earnings, annual bonuses that are payable over a three-year period. To facilitate GP LLC’s compensation committee in reviewing and making recommendations, a compensation “tally sheet” is prepared by GP LLC’s CEO and General Counsel and provided to the compensation committee.
PAA stresses performance-based compensation elements to attempt to create a performance-driven environment in which its executive officers are (i) motivated to perform over both the short term and the long term, (ii) appropriately rewarded for their services and (iii) encouraged to remain with PAA even after meeting long-term performance thresholds in order to meet the minimum service periods and by the potential for rewards yet to come. PAA believes its compensation philosophy as implemented by application of the three primary compensation elements (i) aligns the interests of PAA’s Named Executive Officers with its unitholders, (ii) positions PAA to achieve its business goals, and (iii) effectively encourages the exercise of sound judgment and risk-taking that is conducive to creating and sustaining long-term value. PAA believes the processes employed by the GP LLC compensation committee and board in applying the elements of compensation (as discussed in more detail below) provide an adequate level of oversight with respect to the degree of risk being taken by management to achieve short-term performance goals. See “Relation of Compensation Policies and Practices to Risk Management.”
PAA believes its compensation program has been instrumental in its achievement of stated objectives. Over the five-year period ended December 31, 2015, PAA’s annual distribution per common unit has grown at a compound annual rate of 8.1% and the total return realized by PAA’s unitholders for that period averaged approximately (1)%
per annum as compared to the AMZ total return of 2%. During this period, PAA has enjoyed a very high rate of retention among executive officers.
Application of Compensation Elements
Salary. PAA does not make systematic annual adjustments to the salaries of its Named Executive Officers. PAA does, however, make salary adjustments as necessary to maintain hierarchical relationships among senior management levels after new senior management members are added to keep pace with overall growth. Since the date of PAA’s initial public offering in 1998 (or date of employment, if later) through December 31, 2015, Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis and vonBerg have each received one salary adjustment, Mr. Duckett has received small salary adjustments in line with other Canadian personnel, and Mr. Swanson has received four salary adjustments in connection with taking on increasing responsibilities and promotions.
Annual Discretionary Bonuses. Annual discretionary bonuses are determined based on PAA’s performance relative to its annual plan forecast and public guidance (typically provided quarterly in conjunction with release of earnings), distribution growth targets, and other quantitative and qualitative goals established at the beginning of each year. Such annual objectives are discussed and reviewed with the board of directors in conjunction with the review and authorization of the annual plan.
At the end of each year, the CEO performs a quantitative and qualitative assessment of PAA’s performance relative to goals. Key quantitative measures include earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization, excluding items affecting comparability (“adjusted EBITDA”), relative to established guidance, as well as the growth in the annualized quarterly distribution level per common unit relative to annual growth targets. PAA’s primary performance metric is its ability to generate increasing and sustainable cash distributions to its unitholders. Accordingly, although net income and net income per unit are monitored to highlight inconsistencies with primary performance metrics, as is PAA’s market performance relative to its MLP peers and major indices, these metrics are considered secondary performance measures. The CEO’s written analysis of PAA’s performance examines PAA’s accomplishments, shortfalls and overall performance against opportunity, taking into account controllable and non-controllable factors encountered during the year.
The resulting document and supporting detail is submitted to the board of directors of GP LLC for review and comment. Based on the conclusions set forth in the annual performance review, the CEO submits recommendations to the GP LLC compensation committee for bonuses to PAA’s other Named Executive Officers taking into account the relative contribution of the individual officer. There are no set formulas for determining the annual discretionary bonus for PAA’s Named Executive Officers; however, pursuant to his employment agreement, Mr. Chiang is entitled to a minimum bonus of $500,000 for 2015 and $1.25 million for each of 2016 and 2017. Factors considered by the CEO in determining the level of bonus in general include (i) whether or not PAA achieved the goals established for the year and any notable shortfalls relative to expectations; (ii) the level of difficulty associated with achieving such objectives based on the opportunities and challenges encountered during the year; (iii) current year operating and financial performance relative to both public guidance and prior year’s performance; (iv) significant transactions or accomplishments for the period not included in the goals for the year; (v) PAA’s relative prospects at the end of the year with respect to future growth and performance; and (vi) PAA’s positioning at the end of the year with respect to its targeted credit profile. The CEO takes these factors into consideration as well as the relative contributions of each Named Executive Officer to the year’s performance in developing his recommendations for bonus amounts.
These recommendations are discussed with the GP LLC compensation committee, adjusted as appropriate, and submitted to the GP LLC board of directors for its review and approval. Similarly, the GP LLC compensation committee typically assesses the CEO’s contribution toward meeting PAA’s goals, and recommends a bonus for the CEO it believes to be commensurate with such contribution. In several historical instances, the CEO and the President have requested that the bonus amount recommended by the GP LLC compensation committee be reduced to maintain a closer relationship to bonuses awarded to the other Named Executive Officers. With respect to 2015, PAA’s CEO and President have indicated that neither of them will request or accept a bonus. Accordingly, the typical practice of having the CEO submit to the GP LLC compensation committee a preliminary draft of bonus recommendations with the amount for the CEO left blank was modified for 2015 in that bonus recommendations were not included for either the CEO or the
President. The CEO and the GP LLC compensation committee discussed such preliminary draft, which was then revised to include any changes or adjustments in the formal submittal to the GP LLC compensation committee for review and recommendation to the GP LLC board.
U.S. Bonus based on Adjusted EBITDA. Mr. vonBerg and certain other members of PAA’s U.S.-based senior management team are directly involved in activities that generate partnership earnings. These individuals, along with other employees in PAA’s marketing and business development groups participate in a quarterly bonus pool, the size of which is based on adjusted EBITDA, which directly rewards for quarterly performance the commercial and asset managing employees who participate. This quarterly incentive provides a direct incentive to optimize quarterly performance even when, on an annual basis, other factors might negatively affect bonus potential. The size of the bonus pool, and the allocation of quarterly bonus amounts among all participants based on relative contribution, is recommended by Mr. Pefanis and reviewed, modified and approved by Mr. Armstrong, as appropriate. Messrs. Pefanis and Armstrong do not participate in the quarterly bonus pool. The quarterly bonus amounts for Mr. vonBerg are taken into consideration in determining the recommended annual discretionary bonus submitted by the CEO to the GP LLC compensation committee.
Annual Bonus and Quarterly Bonus based on Adjusted EBITDA (Canada). Substantially all of the personnel employed by Plains Midstream Canada (including Mr. Duckett) or involved in Canadian operations participate in a bonus pool under a program established at the time of PAA’s entry into Canada in 2001 in connection with the CANPET acquisition. The program encompasses a bonus pool consisting of 10% of adjusted EBITDA for Canadian-based operations (reduced by the carrying cost of inventory in excess of base-level requirements and by the cost of capital associated with growth capital and acquisitions). Participation in the program is recommended by Mr. Duckett and reviewed, adjusted if warranted, and approved by Mr. Pefanis. Mr. Pefanis does not participate in the bonus pool. Mr. Duckett receives a quarterly bonus equal to approximately 40% of his participation level for the first three fiscal quarters of the year. He receives an annual bonus consisting of 60% of his participation in the first three quarters and 100% of his participation in the fourth quarter.
Long-Term Incentive Awards. PAA does not make systematic annual grants of phantom unit awards to its Named Executive Officers. Instead, PAA’s objective is to time the granting of awards such that the creation of new long-term incentives coincides with the satisfaction of performance thresholds under existing awards. Thus, performance is rewarded by relatively greater frequency of awards, and lack of performance by relatively lesser frequency of awards. Generally, PAA believes that a grant cycle of approximately three years (and extended time-vesting requirements) provides a balance between a meaningful retention period for PAA and a visible, reachable reward for the executive officer. Achievement of performance targets does not shorten the minimum service period requirement. If top performance targets on outstanding awards are achieved in the early part of this cycle, new awards are granted with higher performance thresholds, and the minimum service periods of the new awards are generally synchronized with the remaining time-vesting requirements of outstanding awards in a manner designed to encourage extended retention of PAA’s Named Executive Officers. Accordingly, these new arrangements inherently take into account the value of awards where performance levels have been achieved but have not yet vested due to ongoing service period requirements, but do not take into consideration previous awards that have fully vested.
AAP Management Units (each of which represents a “profits interest” in AAP) provide an additional longer-term, performance-based officer incentive. These AAP Management Units are limited to 52,125,935 authorized units, of which 50,722,830 were outstanding as of December 31, 2015 pursuant to individual restricted unit agreements between AAP and certain members of PAA’s management. As of December 31, 2015, PAA’s Named Executive Officers held 29,931,571 of the restricted AAP Management Units. As noted above under “Elements of Compensation,” a significant portion of the outstanding AAP Management Units vested as of January 1, 2016 and a portion of such vested AAP Management Units has been converted into AAP units and our Class B shares. As a result, as of February 15, 2016, the number of AAP Management Units outstanding was 31,878,821, of which 20,676,096 were held by PAA’s Named Executive Officers. The remaining available AAP Management Units are administered at the discretion of the GP LLC compensation committee (subject to limited authority delegated to the CEO to approve awards to employees other than executive officers) and may be awarded upon advancement, exceptional performance or other change in circumstance of an existing member of management, or upon the addition of a new individual to the management team.
Application in 2015
At the beginning of 2015, PAA established four public goals with paraphrased versions of these goals overlapping three of its five internal goals.
The four public goals for the year were to:
1. Deliver operating and financial performance in line with or above guidance;
2. Successfully execute PAA’s 2015 capital program and set the stage for continued growth in 2016 and beyond;
3. Increase PAA’s November 2015 annualized distribution level by 7% over the November 2014 annualized distribution level; and
4. Selectively pursue strategic and accretive acquisitions.
Additionally, PAA’s internal qualitative goals included (a) advancing multi-year programs and initiatives and preparing the organization for future growth, and (b) continuing to promote a culture of safety and environmental responsibility throughout the organization.
Industry conditions deteriorated throughout 2015 as crude oil and natural gas prices decreased and capital expenditures by producers were reduced. As a result, crude oil production volumes were below expectations and competition within the midstream crude oil sector increased due to excess pipeline capacity and shipper over-commitments under minimum volume contracts. Primarily as a result of the challenging industry conditions, PAA reduced its 2015 guidance and made a number of other mid-course corrections to its strategies and plans. Additionally, PAA’s 2015 reported results were impacted by an accidental release of approximately 2,935 barrels of crude oil near Santa Barbara, California. This event resulted in an accrual as of December 31, 2015 of estimated total costs that PAA has incurred or expects to incur in connection with such incident of $269 million ($83 million, net of expected insurance reimbursements) (See Item 3. “Legal Proceedings—Specific Legal, Environmental or Regulatory Matters”).
Summarized below are the more significant shortfalls and accomplishments for the year relative to PAA’s public and internal goals:
Shortfalls:
· PAA reported approximately $2.2 billion of adjusted EBITDA and $1.5 billion of distributable cash flow, slightly below its revised guidance, but approximately 8% and 10%, respectively, below the midpoint of initial guidance;
· PAA increased its annualized distribution rate by 6% over the November 2014 exit rate, and generated distribution coverage for the year of approximately 88%;
Accomplishments:
· PAA executed a $2.2 billion expansion capital program timely and cost effectively, and commissioned and integrated multiple new assets into its operations;
· PAA completed transactions associated with two of its pipeline projects that reduced its funding requirements while essentially maintaining the long-term earnings capacity of such projects;
· PAA executed two key financings on attractive terms that enabled it to maintain solid liquidity and financial strength, including raising approximately $1.1 billion of common equity capital and $1.0 billion in long-term debt;
· PAA initiated a $1.6 billion preferred equity placement that was completed in January 2016; and
· PAA made significant progress with respect to the implementation of multiple initiatives to strengthen and sustain the organization and promote a culture of safety and environmental responsibility throughout.
For 2015, the elements of compensation were applied as described below.
Salary. No salary adjustments for Named Executive Officers were recommended or made in 2015. See “—Employment Contracts” for additional information regarding the base salaries of PAA’s Named Executive Officers with employment contracts.
Cash Bonuses. In light of PAA’s overall 2015 performance, PAA’s CEO and President have indicated that neither of them will request or accept a bonus. Additionally, pursuant to Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement, his bonus for 2015 will not be less than $500,000. The CEO’s annual bonus recommendations for the remaining Named Executive Officers were based on his assessment of PAA’s performance as well as the individual’s performance against goals, opportunities and challenges, taking into consideration both controllable and non-controllable factors. Based on the CEO’s annual performance review and recommendations, the GP LLC compensation committee recommended to the GP LLC board of directors and the GP LLC board of directors approved the annual bonuses reflected in the Summary Compensation Table and notes thereto.
Long-Term Incentive Awards. Other than the grant of 120,000 phantom units and 1,000,000 AAP Management Units to Mr. Chiang in connection with his employment as described below, there were no grants of long-term incentive awards to Named Executive Officers in 2015.
Mr. Chiang’s phantom units will vest 40% on the later of the August 2018 distribution date and the date PAA pays an annualized quarterly distribution of $2.90 per common unit; 30% on the later of the August 2019 distribution date and the date PAA pays an annualized quarterly distribution of $3.10 per common unit; and 30% on the later of the August 2020 distribution date and the date PAA pays an annualized quarterly distribution of $3.30 per common unit. The phantom units also vest upon termination of employment under certain circumstances described under “—Employment Contracts” and “—Potential Payments Upon Termination or Change-in-Control” below. Any phantom units that have not vested as of the August 2021 distribution date will be forfeited. Upon vesting, the phantom units are payable on a one-for-one basis in common units. Mr. Chiang’s phantom units have associated DERs that are currently vested and payable in cash on each distribution payment date.
Mr. Chiang’s AAP Management Units become earned in 25% increments upon payment by PAA of annualized quarterly distributions of $2.90, $3.15, $3.30 and $3.50 per common unit, respectively. Mr. Chiang’s AAP Management Units are subject to a call right in the event his employment is terminated under certain circumstances prior to December 31, 2022. If Mr. Chiang remains employed after such date, his AAP Management Units will be deemed to have vested. Mr. Chiang’s AAP Management Units also vest upon his termination of employment under certain circumstances described below under “—Employment Contracts” and “—Potential Payments Upon Termination or Change-in-Control.”
Other Compensation Related Matters
Equity Ownership. PAA’s Named Executive Officers collectively own substantial equity in PAA as well as its general partner. Although PAA encourages its Named Executive Officers to acquire and retain ownership in PAA, it does not have a policy requiring maintenance of a specified equity ownership level. PAA’s policies prohibit its Named Executive Officers from using puts, calls or options to hedge the economic risk of their ownership. As of February 15, 2016, PAA’s Named Executive Officers beneficially owned, in the aggregate, (i) approximately 2.6 million PAA common units (excluding any unvested equity awards), (ii) through their ownership of interests in PAA Management, L.P., an approximate 1.9% indirect ownership interest (approximate 1.8% economic interest) in AAP, (iii) 20,676,096 AAP Management Units, which represent an approximate 3.0% aggregate economic interest in AAP, and (iv) 10,102,845 of our Class A shares. Based on the market price of PAA’s common units and our Class A shares at February 15, 2016 and assuming the conversion of all earned AAP Management Units into AAP units at a conversion factor of approximately 0.940 and the exchange of AAP units for an equivalent number of our Class A shares, the value of the equity ownership of these individuals was significantly greater than the combined aggregate salaries and bonuses of these individuals for 2015.
Recovery of Prior Awards. Except as provided by applicable laws and regulations, PAA does not have a policy with respect to adjustment or recovery of awards or payments if relevant company performance measures upon which previous awards were based are restated or otherwise adjusted in a manner that would have reduced the size of such award or payment if previously known.
Section 162(m). With respect to the deduction limitations under Section 162(m) of the Code, PAA is a limited partnership and does not fall within the definition of a “corporation” under Section 162(m).
Change in Control Triggers. The employment agreements for Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis and Chiang, the long-term incentive plan grants to PAA’s Named Executive Officers, and the AAP Management Unit grant agreements to which PAA’s Named Executive Officers are a party include severance payment provisions or accelerated vesting triggered upon a change of control, as defined in the respective agreements. In the case of the long-term incentive plan grants, the provision becomes operative only if the change in control is accompanied by a change in status (such as the termination of employment by GP LLC). PAA believes this “double trigger” arrangement is appropriate because it provides assurance to the executive, but does not offer a windfall to the executive when there has been no real change in employment status. The provisions in the employment agreements for Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis become operative only if the executive terminates employment within three months of the change in control. Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis agreed to a conditional waiver of these provisions with respect to Vulcan Energy Corporation’s (“Vulcan Energy”) sale of its 50.1% general partner interest in December 2010 and with respect to the completion of our initial public offering in October 2013. The AAP Management Unit grant agreements generally call for vesting upon a change in control of any units that have already been earned, plus the next increment of units that could be earned at the next distribution threshold. Any remaining AAP Management Units would be forfeited (unless waived at the discretion of the general partner or acquirer as the case may be). As a result of significant participation (i.e., purchases) by existing general partner owners or their affiliates in the December 2010 sale of Vulcan Energy’s 50.1% ownership in the general partner, the change of control provisions of the AAP Management Unit grant agreements were not triggered. In addition, the completion of our initial public offering in October 2013 did not constitute a change of control pursuant to the terms of the AAP Management Unit grant agreements. Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement provides for accelerated vesting of his long-term incentive plan grant and AAP Management Unit grant in the event of a change of control prior to December 31, 2018 if, in connection therewith, he is not designated to receive a promotion to the top leadership position of GP LLC and terminates his employment within a period of 90 days following such change of control. See “—Employment Contracts” and “—Potential Payments Upon Termination or Change-in-Control.” The provision of severance or equity acceleration for certain terminations and change of control help to create a retention tool by assuring the executive that the benefit of the employment arrangement will be at least partially realized despite the occurrence of an event that would materially alter the employment arrangement.
Relation of Compensation Policies and Practices to Risk Management
PAA’s compensation policies and practices are designed to provide rewards for short-term and long-term performance, both on an individual basis and at the entity level. In general, optimal financial and operational performance, particularly in a competitive business, requires some degree of risk-taking. Accordingly, the use of compensation as an incentive for performance can foster the potential for management and others to take unnecessary or excessive risks to reach the performance thresholds. For PAA, such risks would primarily attach to certain commercial activities conducted in its supply and logistics segment as well as to the execution of capital expansion projects and acquisitions and the realization of associated returns.
From a risk management perspective, PAA’s policy is to conduct its commercial activities within pre-defined risk parameters that are closely monitored and are structured in a manner intended to control and minimize the potential for unwarranted risk-taking. See “Impact of Commodity Price Volatility and Dynamic Market Conditions on Our Business Model—Risk Management” in Part I of this annual report. PAA also routinely monitors and measures the execution and performance of its capital projects and acquisitions relative to expectations.
PAA’s compensation arrangements contain a number of design elements that serve to minimize the incentive for unwarranted risk-taking to achieve short-term, unsustainable results, including delaying the reward and subjecting such rewards to forfeiture for terminations related to violations of PAA’s risk management policies and
practices or of PAA’s Code of Business Conduct. In addition, PAA’s long-term incentive awards typically include vesting criteria based on payment of distributions from currently available cash. See “Compensation Discussion and Analysis—Relation of Compensation Elements to Compensation Objectives.”
In combination with PAA’s risk-management practices, PAA does not believe that risks arising from its compensation policies and practices for its employees are reasonably likely to have a material adverse effect on it.
Summary Compensation Table
The following table sets forth certain compensation information for PAA’s Named Executive Officers. PAA reimburses its general partner and its affiliates for expenses incurred on PAA’s behalf, including the costs of officer compensation (excluding the costs of the obligations represented by the AAP Management Units). Mr. Chiang joined PAA in August 2015; therefore, his salary and bonus amounts reflect a partial year of payment.
|
Name and Principal |
|
Year |
|
Salary |
|
Bonus |
|
Stock |
|
All Other |
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Greg L. Armstrong |
|
2015 |
|
375,000 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
17,340 |
|
392,340 |
|
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
|
2014 |
|
375,000 |
|
3,900,000 |
|
— |
|
17,040 |
|
4,292,040 |
|
|
|
2013 |
|
375,000 |
|
4,400,000 |
|
2,662,378 |
|
16,740 |
|
7,454,118 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Harry N. Pefanis |
|
2015 |
|
300,000 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
17,340 |
|
317,340 |
|
|
President and Chief Operating Officer |
|
2014 |
|
300,000 |
|
3,800,000 |
|
— |
|
17,040 |
|
4,117,040 |
|
|
|
2013 |
|
300,000 |
|
4,250,000 |
|
2,396,140 |
|
16,740 |
|
6,962,880 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wilfred (Willie) C. Chiang |
|
2015 |
|
89,102 |
|
500,000 |
|
5,330,830 |
|
5,886 |
|
5,925,818 |
|
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer (U.S.) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Al Swanson |
|
2015 |
|
250,000 |
|
900,000 |
|
— |
|
17,340 |
|
1,167,340 |
|
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
|
2014 |
|
250,000 |
|
1,650,000 |
|
— |
|
17,040 |
|
1,917,040 |
|
|
|
2013 |
|
250,000 |
|
1,800,000 |
|
1,774,919 |
|
16,740 |
|
3,841,659 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
W. David Duckett(3) |
|
2015 |
|
222,543 |
|
2,665,224 |
|
— |
|
99,173 |
|
2,986,940 |
|
|
Chief Executive Officer—Plains Midstream Canada |
|
2014 |
|
257,571 |
|
3,244,686 |
|
— |
|
101,472 |
|
3,603,729 |
|
|
|
2013 |
|
276,666 |
|
3,887,652 |
|
1,774,919 |
|
102,936 |
|
6,042,173 |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
John P. vonBerg |
|
2015 |
|
250,000 |
|
3,650,000 |
(4) |
— |
|
17,340 |
|
3,917,340 |
|
|
Executive Vice President—Commercial Activities |
|
2014 |
|
250,000 |
|
4,175,000 |
(4) |
— |
|
17,040 |
|
4,442,040 |
|
|
|
2013 |
|
250,000 |
|
5,255,000 |
(4) |
1,331,189 |
|
16,740 |
|
6,852,929 |
|
(1) Grant date fair values are presented for (i) LTIP phantom unit grants awarded to Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett and vonBerg in 2013, (ii) LTIP phantom unit grants awarded to Mr. Chiang in 2015, and (iii) AAP Management Unit grants awarded to Mr. Chiang in 2015. Dollar amounts in the table represent the aggregate grant date fair value of phantom units and AAP Management Units awarded based on the probable outcome of underlying performance conditions pursuant to FASB ASC Topic 718. For LTIP phantom units granted in 2013, the performance threshold for the first tranche of vesting was deemed probable of occurring on the grant date. The maximum grant date fair values of phantom unit grants awarded in 2013, assuming that the highest level of performance conditions will be met, are: $7,562,664 for Mr. Armstrong; $6,806,398 for Mr. Pefanis; $5,041,776 for Mr. Swanson; $5,041,776 for Mr. Duckett and $3,781,332 for Mr. vonBerg. For LTIP phantom unit grants and AAP Management Unit grants awarded in 2015, the performance threshold for the first tranche of vesting was deemed probable of occurring on the grant date. The aggregate maximum grant date fair value of phantom unit grants and AAP
Management Unit grants awarded to Mr. Chiang in 2015, assuming that the highest level of performance conditions will be met, was $17,197,332. See Note 15 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for further discussion regarding the calculation of grant date fair values.
(2) GP LLC matches 100% of employees’ contributions to its 401(k) plan in cash, subject to certain limitations in the plan. All Other Compensation for each of Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson and vonBerg includes $15,900 ($5,346 for Mr. Chiang) in such contributions for 2015. The remaining amount for each represents premium payments on behalf of such Named Executive Officer for group term life insurance. All Other Compensation for Mr. Duckett includes, for 2015, employer contributions to the Plains Midstream Canada savings plan of $28,931, group term life insurance premiums of $30,891, automobile lease payments of $33,128 and club dues of $6,223.
(3) Salary, bonus and all other compensation amounts for Mr. Duckett are presented in U.S. dollar equivalent based on the exchange rates in effect on the dates payments were made or approved.
(4) Includes quarterly bonuses aggregating $2,750,000, $2,275,000 and $3,355,000 and annual bonuses of $900,000, $1,900,000 and $1,900,000 in 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The annual bonuses are payable 60% at the time of award and 20% in each of the two succeeding years.
Grants of Plan-Based Awards Table
The following table sets forth summary information regarding all grants of plan-based awards made to PAA’s Named Executive Officers during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015:
|
|
|
|
|
All Other |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Stock |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Awards: |
|
Grant Date |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Number |
|
Fair Value |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Shares Of |
|
Stock and |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Stock or |
|
Option |
| |
|
|
|
Grant |
|
Units |
|
Awards |
| |
|
Name |
|
Date |
|
(#) |
|
($)(3) |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Wilfred (Willie) C. Chiang |
|
8/24/15 |
|
120,000 |
(1) |
$ |
1,519,680 |
|
|
|
|
8/24/15 |
|
1,000,000 |
(2) |
$ |
3,811,150 |
|
(1) These phantom units will vest 40% on the later of the August 2018 distribution date and the date PAA pays an annualized quarterly distribution of $2.90 per common unit; 30% on the later of the August 2019 distribution date and the date PAA pays an annualized quarterly distribution of $3.10 per common unit; and 30% on the later of the August 2020 distribution date and the date PAA pays an annualized quarterly distribution of $3.30 per common unit. The phantom units also vest upon termination of employment under certain circumstances described under “—Employment Contracts” and “—Potential Payments Upon Termination or Change-in-Control” below. Any phantom units that have not vested as of the August 2021 distribution date will be forfeited. Upon vesting, the phantom units are payable on a one-for-one basis in common units. The phantom units have associated DERs that are currently vested and payable in cash on each distribution payment date.
(2) These AAP Management Units become earned in 25% increments upon payment by PAA of annualized quarterly distributions of $2.90, $3.15, $3.30 and $3.50 per common unit, respectively. These AAP Management Units are subject to a call right in the event Mr. Chiang’s employment is terminated under certain circumstances prior to December 31, 2022. If Mr. Chiang remains employed after such date, his AAP Management Units will be deemed to have vested. Mr. Chiang’s AAP Management Units also vest upon his termination of employment under certain circumstances described under “—Employment Contracts” and “—Potential Payments Upon Termination or Change-in-Control” below.
(3) Represents the grant date fair values of LTIP phantom units and AAP Management Units based on the probable outcome of underlying performance conditions pursuant to FASB ASC Topic 718. The performance threshold for the first tranche of vesting of the LTIP phantom units and AAP Management Units was deemed
probable of occurring on the grant date. The aggregate maximum grant date fair value of phantom unit grants and AAP Management Unit grants awarded in 2015, assuming that the highest level of performance conditions will be met, was $17,197,332.
Narrative Disclosure to Summary Compensation Table
A narrative description of all material factors necessary to an understanding of the information included in the above Summary Compensation Table is included in “—Compensation Discussion and Analysis” and in the footnotes to such tables.
Employment Contracts
Mr. Armstrong is employed as PAA’s Chairman and Chief Executive Officer. The initial three-year term of Mr. Armstrong’s employment agreement commenced on June 30, 2001, and is automatically extended for one year on June 30 of each year (such that the term is reset to three years) unless Mr. Armstrong receives notice from the chairman of the GP LLC compensation committee that the board of directors has elected not to extend the agreement. Mr. Armstrong has agreed, during the term of the agreement and for five years thereafter, not to disclose (subject to typical exceptions, including, but not limited to, requirement of law or prior disclosure by a third party) any confidential information obtained by him while employed under the agreement. The agreement provided for a base salary of $330,000 per year, subject to annual review. In 2005, Mr. Armstrong’s annual salary was increased to $375,000. For 2016, Mr. Armstrong has unilaterally elected to forego approximately 90% of his annual base salary.
Mr. Pefanis is employed as PAA’s President and Chief Operating Officer. The initial three-year term of Mr. Pefanis’ employment agreement commenced on June 30, 2001, and is automatically extended for one year on June 30 of each year (such that the term is reset to three years) unless Mr. Pefanis receives notice from the Chairman of the Board of GP LLC that the board of directors has elected not to extend the agreement. Mr. Pefanis has agreed, during the term of the agreement and for one year thereafter, not to disclose (subject to typical exceptions) any confidential information obtained by him while employed under the agreement. The agreement provided for a base salary of $235,000 per year, subject to annual review. In 2005, Mr. Pefanis’ annual salary was increased to $300,000.
In connection with Mr. Chiang’s employment in August 2015, GP LLC and Mr. Chiang entered into an agreement setting forth the terms of his employment. The agreement, which may be terminated by either party at any time, provides for a base salary of $250,000 per year, and a minimum bonus of $500,000 for 2015 and $1.25 million for each of 2016 and 2017. GP LLC’s obligation to pay the minimum bonus is subject to Mr. Chiang’s continued employment through the bonus payment date. Mr. Chiang was hired with the expectation that, contingent on his performance, he would be offered the top executive leadership position of GP LLC (the “Executive Promotion”) no later than December 31, 2018 (the “Reference Date”). Consistent with such expectation and as an inducement to Mr. Chiang, Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement provides for the accelerated vesting of his phantom units and AAP Management Units in the event his employment is terminated under certain circumstances prior to the Reference Date. These circumstances include the following: (i) if Mr. Chiang has not received the Executive Promotion and is terminated other than for cause prior to the Reference Date; (ii) if Mr. Chiang has not received the Executive Promotion by the Reference Date and Mr. Chiang resigns within 90 days thereafter or if Mr. Chiang has not received the Executive Promotion and terminates his employment for “good reason” prior to the Reference Date; and (iii) if a change of control occurs prior to the Reference Date and in connection therewith Mr. Chiang is not designated to receive the Executive Promotion and terminates his employment within 90 days of such change of control. Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement also provides that in the event of his death or disability prior to the second anniversary of his employment date under circumstances where less than 500,000 of his AAP Management Units have previously become “earned”, he will immediately vest in such number of AAP Management Units as may be necessary to cause the number of vested AAP Management Units to equal 500,000. Mr. Chiang also entered into ancillary agreements pursuant to which he has agreed to maintain confidentiality and not to solicit customers, assets or employees for a period of two years following termination of his employment.
See “—Compensation Discussion and Analysis” for a discussion of how PAA uses salary and bonus to achieve compensation objectives. See “—Potential Payments upon Termination or Change-In-Control” for a discussion of the provisions in Messrs. Armstrong’s, Pefanis’ and Chiang’s employment agreements related to termination, change of control and related payment obligations.
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End
The following table sets forth certain information regarding outstanding equity awards at December 31, 2015 with respect to PAA’s Named Executive Officers:
|
|
|
Unit Awards |
| ||||||
|
Name |
|
Number of |
|
Market |
|
Equity |
|
Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Greg L. Armstrong |
|
10,425,791 |
(2) |
92,428,125 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
150,000 |
(3) |
3,465,000 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Harry N. Pefanis |
|
7,819,344 |
(2) |
69,321,099 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
135,000 |
(3) |
3,118,500 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wilfred (Willie) C. Chiang |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1,000,000 |
(4) |
8,865,338 |
|
|
|
|
— |
|
— |
|
120,000 |
(5) |
2,772,000 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Al Swanson |
|
2,606,448 |
(2) |
23,107,036 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
100,000 |
(3) |
2,310,000 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
W. David Duckett |
|
4,430,961 |
(2) |
39,281,949 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
100,000 |
(3) |
2,310,000 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
John P. vonBerg |
|
3,649,027 |
(2) |
32,349,845 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
75,000 |
(3) |
1,732,500 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(1) Market value of phantom units reported in these columns is calculated by multiplying the closing market price ($23.10) of PAA’s common units at December 31, 2015 (the last trading day of the fiscal year) by the number of units. No discount is applied for remaining performance threshold or service period requirements. Market value of AAP Management Units is calculated by (i) assuming that such AAP Management Units are converted into AAP units based on the December 31, 2015 conversion factor of approximately 0.938 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit, (ii) assuming the exchange of the resulting AAP units and our Class B shares for our Class A shares on a one-for-one basis, and (iii) multiplying such resulting number of our Class A shares by the closing market price ($9.45) of our Class A shares at December 31, 2015 (the last trading day of the fiscal year).
(2) Represents the pre-conversion number of AAP Management Units held by the applicable individual, each of which represents a “profits interest” in AAP, entitling the holder to participate in future profits and losses from operations, current distributions from operations, and an interest in future appreciation or depreciation in AAP’s asset values, but does not represent an interest in the capital of AAP on the applicable grant date of the AAP Management Units. Despite the fact that 100% of the AAP Management Units held by PAA’s Named Executive Officers (other than Mr. Chiang) had been earned as of December 31, 2015 (i.e., all relevant performance benchmarks have been satisfied), all such AAP Management Units are treated as stock that has not vested for purposes of this table due to the fact that, as of December 31, 2015, they remained subject to a “call right” held by AAP. Such call right expired on January 1, 2016 and the AAP Management Units held by Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett and vonBerg are now vested. As long as our Class A shares are publicly traded, each vested AAP Management Unit may be converted into AAP units and a like number of our Class B shares based on a conversion ratio calculated in accordance with the AAP limited partnership agreement (which conversion ratio will not be
more than one-to-one and was approximately 0.938 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit as of December 31, 2015). Following any such conversion, the resulting AAP units and Class B shares are exchangeable for our Class A shares on a one-for-one basis as provided in our limited partnership agreement. In January and February 2016, Messrs. Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett and vonBerg converted all or a portion of their AAP Management Units into AAP units and our Class B shares and then exchanged all of their respective resulting AAP units and Class B shares for our Class A shares. For additional information regarding the AAP Management Units, please read Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence—AAP Management Units.”
(3) Represents phantom units granted in 2013 under PAA’s Long-Term Incentive Plan. All performance thresholds have been met. Accordingly, subject to continued employment, these phantom units will vest as follows: (i) one-third will vest on the August 2016 distribution date, (ii) one third will vest on the August 2017 distribution date, and (iii) one-third will vest on the August 2018 distribution date. Upon vesting, the phantom units are payable on a one-for-one basis in PAA common units. All of the DERs associated with these phantom units are currently payable. The DERs expire when the associated phantom units vest.
(4) Represents the pre-conversion number of AAP Management Units held by Mr. Chiang, each of which represents a “profits interest” in AAP, entitling him to participate in future profits and losses from operations, current distributions from operations, and an interest in future appreciation or depreciation in AAP’s asset values, but does not represent an interest in the capital of AAP on the applicable grant date of the AAP Management Units. These AAP Management Units become earned in 25% increments upon payment by PAA of annualized quarterly distributions of $2.90, $3.15, $3.30 and $3.50 per common unit, respectively. These AAP Management Units are subject to a call right in the event Mr. Chiang’s employment is terminated under certain circumstances prior to December 31, 2022. If Mr. Chiang remains employed after such date, his AAP Management Units will be deemed to have vested. Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement provides for the accelerated vesting of his AAP Management Units under certain circumstances prior to December 31, 2018. See “—Employment Contracts” and “—Potential Payments Upon Termination or Change-in-Control.”
(5) Represents phantom units granted in 2015 under PAA’s Long-Term Incentive Plan. These phantom units will vest 40% on the later of the August 2018 distribution date and the date PAA pays an annualized quarterly distribution of $2.90 per common unit; 30% on the later of the August 2019 distribution date and the date PAA pays an annualized quarterly distribution of $3.10 per common unit; and 30% on the later of the August 2020 distribution date and the date PAA pays an annualized quarterly distribution of $3.30 per common unit. The phantom units also vest upon termination of employment under certain circumstances. See “—Employment Contracts” and “—Potential Payments Upon Termination or Change-in-Control.” Any phantom units that have not vested as of the August 2021 distribution date will be forfeited. Upon vesting, the phantom units are payable on a one-for-one basis in common units. The phantom units have associated DERs that are currently vested and payable in cash on each distribution payment date.
Option Exercises and Units Vested
The following table sets forth certain information regarding the vesting of phantom units during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2015 with respect to PAA’s Named Executive Officers.
|
|
|
Unit Awards |
| ||
|
Name |
|
Number of Units |
|
Value Realized on |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Greg L. Armstrong |
|
120,000 |
(1) |
5,818,800 |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Harry N. Pefanis |
|
80,000 |
(1) |
3,879,200 |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wilfred (Willie) C. Chiang |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Al Swanson |
|
40,000 |
(1) |
1,939,600 |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
W. David Duckett |
|
50,000 |
(1) |
2,424,500 |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
John P. vonBerg |
|
36,000 |
(1) |
1,745,640 |
(2) |
(1) Represents the gross number of phantom units that vested during the year ended December 31, 2015. The actual number of units delivered was net of income tax withholding.
(2) Consistent with the terms of PAA’s Long-Term Incentive Plan, the value realized upon vesting is computed by multiplying the closing market price ($48.49) of PAA’s common units on May 14, 2015 (the date preceding the vesting date) by the number of units that vested.
Pension Benefits
PAA sponsors a 401(k) plan that is available to all U.S. employees, but it does not maintain a pension or defined benefit program.
Nonqualified Deferred Compensation and Other Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Plans
PAA does not have a nonqualified deferred compensation plan or program for its officers or employees.
Potential Payments upon Termination or Change-in-Control
The following table sets forth potential amounts payable to PAA’s Named Executive Officers upon termination of employment under various circumstances, and as if terminated on December 31, 2015.
|
|
|
By Reason of |
|
By Reason of |
|
By Company |
|
By Executive |
|
In |
|
|
Greg L. Armstrong |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Salary and Bonus |
|
9,550,000 |
(1) |
9,550,000 |
(1) |
9,550,000 |
(1) |
9,550,000 |
(1) |
14,325,000 |
(2) |
|
Equity Compensation |
|
3,465,000 |
(3) |
3,465,000 |
(3) |
3,465,000 |
(4) |
3,465,000 |
(4) |
3,465,000 |
(5) |
|
Health Benefits |
|
N/A |
|
33,708 |
(6) |
33,708 |
(6) |
33,708 |
(6) |
33,708 |
(6) |
|
Tax Gross-up |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
884,755 |
(7) |
|
AAP Management Units |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
23,107,031 |
(8) |
23,107,031 |
(8) |
23,107,031 |
(9) |
|
Total |
|
13,015,000 |
|
13,048,708 |
|
36,155,739 |
|
36,155,739 |
|
41,815,494 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Harry N. Pefanis |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Salary and Bonus |
|
9,100,000 |
(1) |
9,100,000 |
(1) |
9,100,000 |
(1) |
9,100,000 |
(1) |
13,650,000 |
(2) |
|
Equity Compensation |
|
3,118,500 |
(3) |
3,118,500 |
(3) |
3,118,500 |
(4) |
3,118,500 |
(4) |
3,118,500 |
(5) |
|
Health Benefits |
|
N/A |
|
52,412 |
(6) |
52,412 |
(6) |
52,412 |
(6) |
52,412 |
(6) |
|
Tax Gross-up |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
1,333,497 |
(7) |
|
AAP Management Units |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
17,330,275 |
(8) |
17,330,275 |
(8) |
17,330,275 |
(9) |
|
Total |
|
12,218,500 |
|
12,270,912 |
|
29,601,187 |
|
29,601,187 |
|
35,484,684 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wilfred (Willie) C. Chiang (10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity Compensation |
|
1,108,800 |
(3) |
1,108,800 |
(3) |
2,772,000 |
(4) |
2,772,000 |
(4) |
2,772,000 |
(5) |
|
AAP Management Units |
|
4,432,669 |
(11) |
4,432,669 |
(11) |
8,865,338 |
(8) |
8,865,338 |
(8) |
8,865,338 |
(9) |
|
Total |
|
5,541,469 |
|
5,541,469 |
|
11,637,338 |
|
11,637,338 |
|
11,637,338 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Al Swanson (10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity Compensation |
|
2,310,000 |
(3) |
2,310,000 |
(3) |
2,310,000 |
(4) |
N/A |
|
2,310,000 |
(5) |
|
AAP Management Units |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
5,776,759 |
(8) |
5,776,759 |
(8) |
5,776,759 |
(9) |
|
Total |
|
2,310,000 |
|
2,310,000 |
|
8,086,759 |
|
5,776,759 |
|
8,086,759 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
W. David Duckett (10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity Compensation |
|
2,310,000 |
(3) |
2,310,000 |
(3) |
2,310,000 |
(4) |
N/A |
|
2,310,000 |
(5) |
|
AAP Management Units |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
9,820,487 |
(8) |
9,820,487 |
(8) |
9,820,487 |
(9) |
|
Total |
|
2,310,000 |
|
2,310,000 |
|
12,130,487 |
|
9,820,487 |
|
12,310,487 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
John P. vonBerg (10) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity Compensation |
|
1,732,500 |
(3) |
1,732,500 |
(3) |
1,732,500 |
(4) |
N/A |
|
1,732,500 |
(5) |
|
AAP Management Units |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
8,087,461 |
(8) |
8,087,461 |
(8) |
8,087,461 |
(9) |
|
Total |
|
1,732,500 |
|
1,732,500 |
|
9,819,961 |
|
8,087,461 |
|
9,819,961 |
|
(1) The employment agreements between GP LLC and Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis provide that if (i) their employment with GP LLC is terminated as a result of their death, (ii) they terminate their employment with GP LLC (a) because of a disability (as defined in Section 409A of the Code) or (b) for good reason (as defined below), or (iii) GP LLC terminates their employment without cause (as defined below), they are entitled to a lump-sum amount equal to the product of (1) the sum of their (a) highest annual base salary paid prior to their date of termination and (b) highest annual bonus paid or payable for any of the three years prior to the date of termination, and (2) the lesser of (i) two or (ii) the number of days remaining in the term of their employment agreement divided by 360. The amount provided in the table assumes for each executive a termination date of December 31, 2015, and also assumes a highest annual base salary of $375,000 and highest annual bonus of $4,400,000 for Mr. Armstrong, and a highest annual base salary of $300,000 and highest annual bonus of $4,250,000 for Mr. Pefanis.
The employment agreements between GP LLC and Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis define “cause” as (i) willfully engaging in gross misconduct, or (ii) conviction of a felony involving moral turpitude. Notwithstanding, no act, or failure to act, on their part is “willful” unless done, or omitted to be done, not in good faith and without reasonable belief that such act or omission was in the best interest of GP LLC or otherwise likely to result in no material injury to GP LLC. However, neither Mr. Armstrong nor Mr. Pefanis will be deemed to have been terminated for cause unless and until there is delivered to them a copy of a resolution of the board of directors of GP LLC at a meeting held for that purpose (after reasonable notice and an opportunity to be heard), finding that Mr. Armstrong or Mr. Pefanis, as applicable, was guilty of the conduct described above, and specifying the basis for that finding. If Mr. Armstrong or Mr. Pefanis were terminated for cause, GP LLC would be obligated to pay base salary through the date of termination, with no other payment obligations triggered by the termination under the employment agreement or other employment arrangement.
The employment agreements between GP LLC and Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis define “good reason” as the occurrence of any of the following circumstances: (i) removal by GP LLC from, or failure to re-elect them to, the positions to which Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis were appointed pursuant to their respective employment agreements, except in connection with their termination for cause (as defined above); (ii) (a) a reduction in their rate of base salary (other than in connection with across-the-board salary reductions for all executive officers of GP LLC) unless such reduction reduces their base salary to less than 85% of their current base salary, (b) a material reduction in their fringe benefits, or (c) any other material failure by GP LLC to comply with its obligations under their employment agreements to pay their annual salary and bonus, reimburse their business expenses, provide for their participation in certain employee benefit plans and arrangements, furnish them with suitable office space and support staff, or allow them no less than 15 business days of paid vacation annually; or (iii) the failure of GP LLC to obtain the express assumption of the employment agreements by a successor entity (whether direct or indirect, by purchase, merger, consolidation or otherwise) to all or substantially all of the business and/or assets of GP LLC.
(2) Pursuant to their employment agreements, if Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis terminate their employment with GP LLC within three (3) months of a change in control (as defined below), they are entitled to a lump-sum payment in an amount equal to the product of (i) three and (ii) the sum of (a) their highest annual base salary previously paid to them and (b) their highest annual bonus paid or payable for any of the three years prior to the date of such termination. The amount provided in the table assumes a change in control and
termination date of December 31, 2015, and also assumes a highest annual base salary of $375,000 and highest annual bonus of $4,400,000 for Mr. Armstrong, and a highest annual base salary of $300,000 and highest annual bonus of $4,250,000 for Mr. Pefanis.
“Change in control” was originally defined in their employment agreements to mean (i) the acquisition by a person or group (other than Vulcan Energy or a wholly owned subsidiary thereof) of beneficial ownership, directly or indirectly, of 50% or more of the membership interest of GP LLC or (ii) the owners of the membership interests of GP LLC on June 30, 2001 ceasing to beneficially own, directly or indirectly, more than 50% of the membership interests of GP LLC.
In August 2005, Vulcan Energy increased its interest in GP LLC from approximately 44% to greater than 50%. The consummation of the transaction constituted a change in control under the employment agreements with Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis. However, Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis entered into agreements with GP LLC waiving their rights to payments under their employment agreements in connection with the change in control, contingent on the execution and performance by Vulcan Energy of a voting agreement with GP LLC that restricted certain of Vulcan’s voting rights. The December 2010 sale by Vulcan Energy of its interest in GP LLC also constituted a change in control under the employment agreements and resulted in the termination of the voting agreement. Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis executed new agreements waiving their rights to payments under their employment agreements with respect to the December 2010 transaction and voting agreement termination.
Our initial public offering and certain related transactions in October 2013 would have constituted a change in control as originally defined under the employment agreements, which would have allowed Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis to terminate their employment and become entitled to certain separation benefits. Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis executed agreements waiving their rights to terminate employment and receive such benefits. In connection with such waivers, the definition of “Change in Control” in the employment agreements was also modified to mean, and will be deemed to occur upon, one or more of the following events: (i) any person (other than PAGP or its wholly owned subsidiaries), including any partnership, limited partnership, syndicate or other group deemed a “person” for purposes of Section 13(d) or 14(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, becomes the beneficial owner, directly or indirectly, of 50% or more of the membership interest in GP LLC or 50% or more of the outstanding limited partnership interests of PAGP; (ii) any person (other than PAGP or its wholly owned subsidiaries), including any partnership, limited partnership, syndicate or other group deemed a “person” for purposes of Section 13(d) or 14(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, becomes the beneficial owner, directly or indirectly, of 50% or more of the membership interest in GP Holdings; (iii) PAGP ceases to beneficially own, directly or indirectly, more than 50% of the membership interest in GP LLC; (iv) KAFU Holdings, L.P. and its affiliates, Lynx Holdings I, LLC and its affiliates, Oxy Holding Company (Pipeline), Inc. and its affiliates, Mark Strome and his affiliates, Windy, LLC and its affiliates, PAA Management, L.P. and its affiliates, PAGP and its affiliates, and various individual investors (collectively, the “Owner Affiliates”), cease to beneficially own, directly or indirectly, more than 50% of the membership interest in GP Holdings; or (v) there has been a direct or indirect transfer, sale, exchange or other disposition in a single transaction or series of transactions (whether by merger or otherwise) of all or substantially all of the assets of PAGP or PAA to one or more persons who are not affiliates of PAGP (“third party or parties”), other than a transaction in which the Owner Affiliates continue to beneficially own, directly or indirectly, more than 50% of the issued and outstanding voting securities of such third party or parties immediately following such transaction.
(3) The letters evidencing phantom unit grants awarded to PAA’s Named Executive Officers provide that in the event of their death or disability (as defined below), all of their then outstanding phantom units and associated DERs will be deemed nonforfeitable, and (i) any unvested phantom units that had satisfied all of the vesting criteria as of the date of their termination but for the passage of time would vest on the next following distribution date and (ii) the remaining unvested outstanding phantom units will vest on the distribution date on which the vesting criteria is met. For this purpose, “disability” means a physical or mental infirmity that impairs the ability substantially to perform duties for a period of eighteen (18) months or that the general partner otherwise determines constitutes a disability.
Assuming death or disability occurred on December 31, 2015, all of the phantom unit grants and associated DERs held by PAA’s Named Executive Officers would have become nonforfeitable effective as of December 31, 2015, and would vest on the February 2016 distribution date to the extent the vesting criteria had been satisfied (other than the passage of time) or, if the vesting criteria had not been satisfied, at the times described in the footnotes to the “Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End” table. For the 2015 grants, any units not vested by August 2021 would expire. That portion of the dollar value given that is attributable to PAA phantom units assumes that all performance thresholds will be timely achieved if deemed probable of occurrence as of December 31, 2015, and is based on the market value of PAA’s common units on December 31, 2015 ($23.10 per unit) without discount for service period. At December 31, 2015, an annualized distribution level of $2.90 was deemed probable of occurrence. All outstanding 2013 grants and 40% of the 2015 grants (Mr. Chiang) were assumed to eventually vest as a result. The balance of the 2015 grants is assumed to expire unvested in August 2021.
(4) Pursuant to the phantom unit grants held by PAA’s Named Executive Officers, in the event their employment is terminated other than in connection with a change of control (as defined in footnote 5 below) or by reason of death, disability (as defined in footnote 3 above) or retirement, all of the phantom units and associated DERs (regardless of vesting) then outstanding under such phantom unit grants would automatically be forfeited as of the date of termination; provided, however, that if GP LLC terminated their employment other than for cause (as defined in footnote 5 below), any unvested phantom units that had satisfied all of the vesting criteria as of the date of their termination but for the passage of time would be deemed nonforfeitable and would vest on the next following distribution date. Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement also provides that his phantom unit grants will vest in full if he has not received the Executive Promotion and is terminated by GP LLC other than for cause or he terminates his employment for good reason prior to December 31, 2018 (see “—Employment Contracts” for additional information regarding Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement). The dollar value amount provided assumes that (i) PAA’s Named Executive Officers (other than Mr. Chiang) were terminated without cause on December 31, 2015, and (ii) Mr. Chiang had not received the Executive Promotion and was terminated without cause or terminated his employment for good reason on December 31, 2015. As a result, all of the phantom unit grants held by Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett, vonBerg and Chiang would be deemed nonforfeitable and would vest on the February 2016 distribution date. That portion of the dollar value given that is attributable to PAA phantom units is based on the market value of PAA’s common units on December 31, 2015 ($23.10 per unit), without discount for service period. In addition to the foregoing, under Canadian law, Mr. Duckett could have a claim for additional payment if inadequate notice were given for a termination without cause.
Under the waiver signed in 2010 by Mr. Armstrong and Mr. Pefanis (see footnote 2 above), upon a termination of employment by GP LLC without cause or by the executive for good reason (in each case as defined in the relevant employment agreement), all of the executive’s outstanding awards under PAA’s Long-Term Incentive Plan would immediately vest.
(5) The letters evidencing phantom unit grants awarded to PAA’s Named Executive Officers provide that in the event of a change in status (as defined below), all of the then outstanding phantom units and associated DERs will be deemed nonforfeitable, and such phantom units will vest in full (i.e., the phantom units will become payable in the form of one common unit per phantom unit) upon the next following distribution date. Additionally, Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement provides that his phantom unit grants will vest in full if he terminates his employment within 90 days after a change of control (as defined below) prior to December 31, 2018 and in connection therewith he does not receive the Executive Promotion (see “—Employment Contracts” for additional information regarding Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement). Assuming (i) that a change in status occurred on December 31, 2015, (ii) that a change of control occurred 90 days prior to December 31, 2015, and (iii) that, in connection with the change of control, Mr. Chiang did not receive the Executive Promotion and terminated his employment on December 31, 2015, all outstanding phantom units and the associated DERs would have become nonforfeitable as of December 31, 2015, and such phantom units would vest on the February 2016 distribution date. That portion of the dollar value given that is attributable to PAA phantom units is based on the market value of PAA’s common units on December 31, 2015 ($23.10 per unit), without discount for service period.
The phrase “change in status” means, with respect to a Named Executive Officer, the occurrence, during the period beginning two and a half months prior to and ending one year following a change of control (as defined below), of any of the following: (A) the termination of employment by GP LLC other than a termination for cause (as defined below), or (B) the termination of employment by the Named Executive Officer due to the occurrence, without the Named Executive Officer’s written consent, of (i) any material diminution in the Named Executive Officer’s authority, duties or responsibilities, (ii) any material reduction in the Named Executive Officer’s base salary or (iii) any other action or inaction that would constitute a material breach of the agreement by GP LLC.
The phrase “change of control” is defined in the phantom unit grants awarded to PAA’s Named Executive Officers other than Mr. Chiang to mean, and is deemed to have occurred upon the occurrence of, one or more of the following events: (i) GP LLC ceasing to be the general partner of PAA’s general partner; (ii) any sale, lease, exchange or other transfer (in one transaction or a series of related transactions) of all or substantially all of the assets of PAA or GP LLC to any person and/or its affiliates, other than to PAA or GP LLC, including any employee benefit plan thereof; (iii) the consolidation, reorganization, merger, or any other similar transaction involving (A) a person other than PAA or GP LLC and (B) PAA, GP LLC or both; (iv) the persons who own membership interests in GP LLC as of the grant date ceasing to beneficially own, directly or indirectly, more than 50% of the membership interests of GP LLC; or (v) any person, including any partnership, limited partnership, syndicate or other group deemed a “person” for purposes of Section 13(d) or 14(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, becoming the beneficial owner, directly or indirectly, of more than 49.9% of the membership interest in GP LLC. Notwithstanding the definition of change of control, no change of control is deemed to have occurred in connection with a restructuring or reorganization related to the securitization and sale to the public of direct or indirect equity interests in the general partner if (x) GP LLC retains direct or indirect control over the general partner and (y) the current members of GP LLC continue to own more than 50% of the member interest in GP LLC. Our initial public offering did not constitute a change of control under the phantom unit grant letters. The term “cause” means (i) the failure to perform the duties and responsibilities of a position at an acceptable level as reasonably determined in good faith by the CEO of GP LLC (or by the board in the case of the CEO), or (ii) the violation of GP LLC’s Code of Business Conduct (unless waived in accordance with the terms thereof), in each case, with the specific failure or violation described in writing.
With respect to Mr. Chiang’s phantom units, “Change of Control” means the determination by the board that one of the following events has occurred: (i) the Persons who owned member interests in GP Holdings immediately following the closing of our initial public offering, including PAGP, and the respective Affiliates of such Persons (such owners and Affiliates being referred to as the “Owner Affiliates”), cease to own directly or indirectly at least 50% of the membership interests of such entity; (ii) (x) a “person” or “group” other than the Owner Affiliates becomes the “beneficial owner” directly or indirectly of 25% or more of the member interest in our general partner, and (y) the member interest beneficially owned by such “person” or “group” exceeds the aggregate member interest in our general partner beneficially owned, directly or indirectly, by the Owner Affiliates; or (iii) a direct or indirect transfer, sale, exchange or other disposition in a single transaction or series of transaction (whether by merger or otherwise) of all or substantially all of the assets of PAGP or PAA to one or more Persons who are not Affiliates of PAGP (“third party or parties”), other than a transaction in which the Owner Affiliates continues to beneficially own, directly or indirectly, more than 50% of the issued and outstanding voting securities of such third party or parties immediately following such transaction. “Cause” is defined in Mr. Chiang’s phantom unit grant agreement as (i) substantial failure to perform the duties and responsibilities of his position at an acceptable level as reasonably determined in good faith by the CEO and President-COO of GP LLC (or if Mr. Chiang is the CEO, by vote of the board of directors) and after written notice specifying such failure in detail and after a reasonable period under the circumstances (determined by the CEO, or alternatively the board of directors, in good faith) such failure has continued without full correction by the executive, (ii) the executive’s conviction of or guilty plea to the committing of an act or acts constituting a felony under the laws of the United States or any state thereof or any misdemeanor involving moral turpitude, or (iii) violation of GP LLC’s Code of Business Conduct (unless waived in accordance with the terms thereof), in each case with the specific failure or violation described in writing.
(6) Pursuant to their employment agreements with GP LLC, if Messrs. Armstrong or Pefanis are terminated other than (i) for cause (as defined in footnote 1 above), (ii) by reason of death or (iii) by resignation (unless such resignation is due to a disability or for good reason (each as defined in footnote 1 above)), then they are entitled to continue to participate, for a period which is the lesser of two years from the date of termination or the remaining term of the employment agreement, in such health and accident plans or arrangements as are made available by GP LLC to its executive officers generally. The amounts provided in the table assume a termination date of December 31, 2015.
(7) Pursuant to their employment agreements, Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis will be reimbursed for any excise tax due under Section 4999 of the Code as a result of compensation (parachute) payments made under their respective employment agreements. The values provided for this benefit assume that Messrs. Armstrong and Pefanis were terminated in connection with a change in control effective as of December 31, 2015.
(8) Pursuant to the AAP Management Unit grant agreements of each of our Named Executive Officers, to encourage retention following the achievement of applicable performance benchmarks, AAP retained a call right to purchase any earned AAP Management Units for an amount equal to 75% of fair market value (which is referred to in the AAP Management Unit grant agreements as the “Call Value” as defined below) of such AAP Management Units, which call right is exercisable upon the termination of such Named Executive Officer’s employment with GP LLC and its affiliates prior to January 1, 2016 (January 1, 2023 for Mr. Chiang); provided, however, that such call right is not applicable (i) in the case of the termination of such Named Executive Officer’s employment without cause (defined below), (ii) in the event of a resignation by such Named Executive Officer with good reason (defined below), and (iii) in Mr. Chiang’s case, in the event of his death or disability. Additionally, Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement provides that his AAP Management Units will vest in full if he has not received the Executive Promotion and is terminated by GP LLC other than for cause (as defined below) or he terminates his employment for good reason prior to December 31, 2018 (see “—Employment Contracts” for additional information regarding Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement). If the Named Executive Officers are terminated without cause or terminate their employment for good reason, or if such Named Executive Officer remains employed past December 31, 2015 (December 31, 2022 for Mr. Chiang), any earned AAP Management Units are no longer subject to the call right and are deemed to have “vested.” As of December 31, 2015, 100% of the AAP Management Units held by Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett and vonBerg had been earned, but all of such AAP Management Units remained subject to AAP’s call right, and none of the AAP Management Units held by Mr. Chiang had been earned. Assuming a termination of employment without cause or for good reason on December 31, 2015 and assuming that Mr. Chiang had not received the Executive Promotion prior to that date, all of the AAP Management Units held by Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett, vonBerg and Chiang would become vested and would no longer be subject to the call right. Because the call right provides for a discounted purchase price equal to 75% of fair market value, in such event the applicable Named Executive Officer would “benefit” by virtue of the fact that such officer’s AAP Management Units could no longer be purchased by AAP at a 25% discount. The value reflected in the table above for Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett and vonBerg represents the implied value of such “benefit” to the applicable Named Executive Officer, calculated as of December 31, 2015 by (i) assuming that such officer’s AAP Management Units are converted into AAP units based on the December 31, 2015 conversion factor of approximately 0.938 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit, (ii) assuming the exchange of the resulting AAP units and our Class B shares for our Class A shares on a one-for-one basis, and (iii) multiplying such resulting number of our Class A shares by an amount equal to 25% of the closing market price ($9.45) of our Class A shares at December 31, 2015 (the last trading day of the fiscal year). The value reflected in the table above for Mr. Chiang represents the implied value of such “benefit”, calculated as of December 31, 2015 by (i) assuming that Mr. Chiang’s AAP Management Units are converted into AAP units based on the December 31, 2015 conversion factor of approximately 0.938 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit, (ii) assuming the exchange of the resulting AAP units and our Class B shares for our Class A shares on a one-for-one basis, and (iii) multiplying such resulting number of our Class A shares by an amount equal to 100% of the closing market price ($9.45) of our Class A shares at December 31, 2015 (the last trading day of the fiscal year). The entire economic burden of the AAP Management Units is borne solely by AAP.
“Cause” is defined in the AAP Management Unit grant agreements of PAA’s Named Executive Officers other than Mr. Chiang as (i) a finding by the board of GP LLC that the executive has substantially failed to perform the duties and responsibilities of his position at an acceptable level and after written notice specifying such failure in detail and after a reasonable period under the circumstances (determined by the board in good faith) such failure has continued without full correction by the executive, (ii) the executive’s conviction of or guilty plea to the committing of an act or acts constituting a felony under the laws of the United States or any state thereof or any misdemeanor involving moral turpitude, or (iii) any action by the executive involving personal dishonesty, theft or fraud in connection with executive’s duties as an employee of GP LLC or its affiliates. For Mr. Chiang, “Cause” is defined as (i) substantial failure to perform the duties and responsibilities of his position at an acceptable level as reasonably determined in good faith by the CEO and President-COO of GP LLC (or if Mr. Chiang is the CEO, by vote of the board of directors) and after written notice specifying such failure in detail and after a reasonable period under the circumstances (determined by the CEO, or alternatively the board of directors, in good faith) such failure has continued without full correction by the executive, (ii) the executive’s conviction of or guilty plea to the committing of an act or acts constituting a felony under the laws of the United States or any state thereof or any misdemeanor involving moral turpitude, or (iii) violation of GP LLC’s Code of Business Conduct (unless waived in accordance with the terms thereof), in each case with the specific failure or violation described in writing.
“Good Reason” is defined in the AAP Management Unit grant agreements as (i) any material breach by AAP of executive’s AAP Management Unit grant agreement, (ii) the failure of any successor of AAP to assume executive’s AAP Management Unit grant agreement, or (iii) any material overall reduction the executive’s authority, responsibilities or duties.
“Call Value” is defined in the AAP Management Unit grant agreements as the product of the applicable conversion factor and the closing sales price of our Class A shares on the applicable date.
(9) Pursuant to the AAP Management Unit grant agreements, upon the occurrence of a Change in Control, any earned AAP Management Units (and any AAP Management Units that will become earned in less than 180 days) become vested units and, to the extent any AAP Management Units remain unearned, an incremental 25% of the number of AAP Management Units originally granted becomes vested. Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement also provides that his AAP Management Units will vest in full if he terminates his employment within 90 days after a change of control prior to December 31, 2018 and in connection therewith he does not receive the Executive Promotion (see “—Employment Contracts” for additional information regarding Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement). As of December 31, 2015, 100% of the AAP Management Units held by Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett and vonBerg had been earned, and none of the AAP Management Units held by Mr. Chiang had been earned. Accordingly, assuming that a Change in Control occurred on December 31, 2015 (or in the case of Mr. Chiang, 90 days prior to December 31, 2015) and that in connection with such Change in Control, Mr. Chiang had not received the Executive Promotion, all of the AAP Management Units held by Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett, vonBerg and Chiang would become vested and would no longer be subject to the call right. Because the call right provides for a discounted purchase price equal to 75% of fair market value as described above, the applicable Named Executive Officer would “benefit” from a Change in Control by virtue of the fact that such officer’s AAP Management Units could no longer be purchased by AAP at a 25% discount. The value reflected in the table above for Messrs. Armstrong, Pefanis, Swanson, Duckett and vonBerg represents the implied value of such “benefit” to the applicable Named Executive Officer, calculated as of December 31, 2015 by (i) assuming that such officer’s AAP Management Units are converted into AAP units based on the December 31, 2015 conversion factor of approximately 0.938 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit, (ii) assuming the exchange of the resulting AAP units and our Class B shares for our Class A shares on a one-for-one basis, and (iii) multiplying such resulting number of our Class A shares by an amount equal to 25% of the closing market price ($9.45) of our Class A shares at December 31, 2015 (the last trading day of the fiscal year). The value reflected in the table above for Mr. Chiang represents the implied value of such “benefit”, calculated as of December 31, 2015 by (i) assuming that Mr. Chiang’s AAP Management Units are converted into AAP units based on the December 31, 2015 conversion factor of approximately 0.938 AAP
units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit, (ii) assuming the exchange of the resulting AAP units and our Class B shares for our Class A shares on a one-for-one basis, and (iii) multiplying such resulting number of our Class A shares by an amount equal to 100% of the closing market price ($9.45) of our Class A shares at December 31, 2015 (the last trading day of the fiscal year). The entire economic burden of the AAP Management Units is borne solely by AAP.
“Change in Control” means the determination by the board that one of the following events has occurred: (i) the Persons who own member interests in GP Holdings immediately following the closing of the GP IPO, including PAGP, and the respective Affiliates of such Persons (such owners and Affiliates being referred to as the “Owner Affiliates”), cease to own directly or indirectly at least 50% of the membership interests of such entity; (ii) (x) a “person” or “group” other than the Owner Affiliates becomes the “beneficial owner” directly or indirectly of 25% or more of the member interest in the general partner of PAGP, and (y) the member interest beneficially owned by such “person” or “group” exceeds the aggregate member interest in the general partner of PAGP beneficially owned, directly or indirectly, by the Owner Affiliates; or (iii) a direct or indirect transfer, sale, exchange or other disposition in a single transaction or series of transaction (whether by merger or otherwise) of all or substantially all of the assets of PAGP or PAA to one or more Persons who are not Affiliates of PAGP (“third party or parties”), other than a transaction in which the Owner Affiliates continues to beneficially own, directly or indirectly, more than 50% of the issued and outstanding voting securities of such third party or parties immediately following such transaction.
(10) If Messrs. Swanson, Duckett, vonBerg or Chiang were terminated for cause, GP LLC would be obligated to pay base salary through the date of termination, with no other payment obligation triggered by the termination under any employment arrangement.
(11) Mr. Chiang’s employment agreement provides that in the event of his death or disability prior to December 31, 2018, if less than 500,000 of his AAP Management Units have been earned, he shall vest in such number of additional AAP Management Units as may be necessary to cause the total number of vested AAP Management Units to equal 500,000. Mr. Chiang’s AAP Management Unit grant agreement also provides that in the event of his death or disability, AAP will not have a call right and all of his earned AAP Management Units will vest. As of December 31, 2015, none of Mr. Chiang’s AAP Management Units had been earned. The dollar value given assumes Mr. Chiang’s death or disability on December 31, 2015 and represents the implied value of such “benefit,” calculated as of December 31, 2015 by (i) assuming that Mr. Chiang’s vested AAP Management Units are converted into AAP units based on the December 31, 2015 conversion factor of approximately 0.938 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit, (ii) assuming the exchange of the resulting AAP units and our Class B shares for our Class A shares on a one-for-one basis, and (iii) multiplying such resulting number of our Class A shares by the closing market price ($9.45) of our Class A shares at December 31, 2015 (the last trading day of the fiscal year). The entire economic burden of the AAP Management Units is borne solely by AAP.
Confidentiality, Non-Compete and Non-Solicitation Arrangements
Pursuant to his employment agreement, Mr. Armstrong has agreed to maintain the confidentiality of PAA information for a period of five years after the termination of his employment. Mr. Pefanis has agreed to a similar restriction for a period of one year following the termination of his employment. Mr. Duckett has agreed to maintain confidentiality following termination of his employment for a period of two years with respect to customer lists. He has also agreed not to compete in a specified geographic area for a period of two years after termination of his employment. Mr. vonBerg has agreed to maintain confidentiality and not to solicit customers for a period of one year following termination of his employment. Mr. Chiang has agreed to maintain confidentiality and not to solicit customers, assets and employees for two years following termination of his employment.
Compensation of GP LLC Directors
The following table sets forth a summary of the compensation paid to each person who served as a non-employee director of GP LLC in 2015:
|
Name |
|
Fees |
|
Stock |
|
Total ($) |
|
|
Ben Figlock (2) |
|
45,000 |
|
n/a |
|
45,000 |
|
|
Everardo Goyanes |
|
75,000 |
|
179,200 |
|
254,200 |
|
|
Gary R. Petersen |
|
45,000 |
|
89,600 |
|
134,600 |
|
|
John T. Raymond |
|
45,000 |
|
89,600 |
|
134,600 |
|
|
Robert V. Sinnott |
|
47,000 |
|
89,600 |
|
136,600 |
|
|
J. Taft Symonds |
|
62,000 |
|
179,200 |
|
241,200 |
|
|
Christopher M. Temple |
|
60,000 |
|
179,200 |
|
239,200 |
|
(1) The dollar value of LTIPs granted during 2015 is based on the grant date fair value computed in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718. See Note 15 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional discussion regarding the calculation of grant date fair values. In connection with the August 2015 vesting of director LTIP awards, Messrs. Goyanes, Symonds and Temple each were granted 5,000 units, and Messrs. Petersen, Raymond and Sinnott each were granted 2,500 units by virtue of the automatic re-grant feature of the vested awards. Upon vesting of the director LTIP awards in August 2015 (other than the incremental audit committee awards), a cash payment of $145,050 was made to Oxy as directed by Mr. Figlock. Such cash payment was based on the unit value of Mr. Sinnott’s award on the previous year’s vesting date. As of December 31, 2015, the number of outstanding LTIPs held by GP LLC’s directors was as follows: Goyanes - 20,000; Petersen - 10,000; Raymond - 10,000; Sinnott - 10,000; Symonds - 20,000; and Temple - 20,000.
(2) Mr. Figlock’s compensation is assigned to Oxy.
Each director of GP LLC who is not an employee of GP LLC is reimbursed for any travel, lodging and other out-of-pocket expenses related to meeting attendance or otherwise related to service on the GP LLC board (including, without limitation, reimbursement for continuing education expenses). Each GP LLC non-employee director is currently paid an annual retainer fee of $45,000; however, the annual retainer fee for the director designated by Oxy is paid to Oxy. Mr. Armstrong is otherwise compensated for his services as an employee and therefore receives no separate compensation for his services as a director. In addition to the annual retainer, each committee chairman (other than the chairman of the GP LLC audit committee) receives $2,000 annually. The chairman of the GP LLC audit committee receives $30,000 annually, and the other members of the GP LLC audit committee receive $15,000 annually, in each case, in addition to the annual retainer. During 2015, Messrs. Sinnott, Goyanes and Symonds served as chairmen of the GP LLC compensation, audit and governance committees, respectively.
GP LLC’s non-employee directors receive LTIP awards or cash equivalent awards as part of their compensation. The LTIP awards vest annually in 25% increments over a four-year period and have an automatic re-grant feature such that as they vest, an equivalent amount is granted. The awards have associated distribution equivalent rights that are payable quarterly. The three non-employee directors who serve on the audit committee (Messrs. Goyanes, Symonds and Temple) each have outstanding a grant of 20,000 units (vesting 5,000 units per year). Messrs. Petersen, Raymond and Sinnott each have outstanding a grant of 10,000 units (vesting 2,500 units per year). Upon vesting of the director LTIPs (other than the incremental audit committee awards), a cash payment will be made to Oxy as directed by the Oxy designee. Such cash payment is based on the unit value of Mr. Sinnott’s award on the previous year’s vesting date.
All LTIP awards held by a GP LLC director vest in full upon the next following distribution date after the death or disability (as determined in good faith by the board) of the director. For audit committee grants, the awards also vest in full if such director (i) retires (no longer with full-time employment and no longer serving as an officer
or director of any public company) or (ii) is removed from the board of directors or is not reelected to the board of directors, unless such removal or failure to reelect is for “good cause,” as defined in the letter granting the units.
Compensation of PAA GP Holdings LLC Directors
The following table sets forth a summary of the compensation paid to each person who served as a non-employee director of GP Holdings in 2015:
|
Name |
|
Fees |
|
Stock |
|
Total ($) |
|
|
Victor Burk |
|
40,000 |
|
222,720 |
|
262,720 |
|
|
Ben Figlock (2) |
|
n/a |
|
n/a |
|
n/a |
|
|
Everardo Goyanes |
|
n/a |
|
133,632 |
|
133,632 |
|
|
John T. Raymond (2) |
|
n/a |
|
n/a |
|
n/a |
|
|
Bobby Shackouls |
|
40,000 |
|
222,720 |
|
262,720 |
|
|
Robert V. Sinnott (2) |
|
n/a |
|
n/a |
|
n/a |
|
(1) The dollar value of LTIPs granted during 2015 is based on the grant date fair value computed in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718. See Note 15 to our Consolidated Financial Statements for additional discussion regarding the calculation of grant date fair values. In connection with the February 2015 vesting of director LTIP awards, Messrs. Burk and Shackouls each were granted 8,000 phantom Class A shares and Mr. Goyanes was granted 4,800 phantom Class A shares by virtue of the automatic re-grant feature of the vested awards. As of December 31, 2015, the number of outstanding LTIPs held by our directors was as follows: Burk — 32,000; Goyanes — 19,200; and Shackouls — 32,000.
(2) Messrs. Figlock, Raymond and Sinnott served on both the GP LLC board and the GP Holdings board during 2015. They were compensated by GP LLC and did not receive additional compensation for service on the GP Holdings board.
Messrs. Figlock, Raymond and Sinnott serve on both our general partner’s board of directors and GP LLC’s board of directors. They are compensated by GP LLC and do not receive additional compensation for service on our general partner’s board of directors. Mr. Armstrong is otherwise compensated for his services as an employee by GP LLC and receives no separate compensation for his services as a director of our general partner.
Messrs. Burk and Shackouls each receive an annual retainer of $40,000 for service on our general partner’s board and the audit committee. Messrs. Burk and Shackouls each also received initial equity compensation in the form of an LTIP award for 32,000 phantom Class A shares that, subject to continued service as a director, vests in 25% increments over a four-year period and includes an automatic re-grant feature such that as they vest, an equivalent amount is granted.
Mr. Goyanes serves on our general partner’s board as well as on GP LLC’s board and also serves as chairman of the audit committee of both boards. Mr. Goyanes is compensated by GP LLC for his service as a director and chairman of the audit committee of the GP LLC board. See “— Compensation of GP LLC Directors” above. Mr. Goyanes does not receive any cash consideration for his service as a director and chairman of the audit committee of our general partner’s board, but received initial equity compensation in the form of an LTIP award for 19,200 phantom Class A shares that, subject to continued service as a director, vests in 25% increments over a four-year period and includes an automatic re-grant feature such that as they vest, an equivalent amount is granted. Mr. Goyanes’ annual compensation represents roughly one-half of the value of the total annual compensation paid to each of Messrs. Burk and Shackouls.
The LTIP awards granted to Messrs. Burk, Goyanes and Shackouls also have associated distribution equivalent rights that are payable quarterly and entitle the holder to receive a cash payment for each phantom Class A share equal in amount to the distribution paid on our Class A shares. The LTIP awards held by Messrs. Burk, Goyanes and Shackouls vest in full upon the distribution date immediately following the date such
director (i) dies or is determined by the board to be disabled, (ii) retires, or (iii) is removed from the board of directors or is not re-elected to the board of directors, unless such removal or failure to re-elect is for “cause” as defined in the limited liability company agreement of our general partner.
Each director will be indemnified for his actions associated with being a director to the fullest extent permitted under Delaware law.
Reimbursement of Expenses of PAA’s General Partner and its Affiliates
PAA does not pay its general partner a management fee, but it does reimburse its general partner for all direct and indirect costs of services provided to PAA, incurred on PAA’s behalf, including the costs of employee, officer and director compensation (other than expenses related to the AAP Management Units) and benefits allocable to PAA, as well as all other expenses necessary or appropriate to the conduct of PAA’s business, allocable to PAA. PAA records these costs on the accrual basis in the period in which PAA’s general partner incurs them. PAA’s partnership agreement provides that its general partner will determine the expenses that are allocable to PAA in any reasonable manner determined by its general partner in its sole discretion.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters
Plains GP Holdings, L.P.
The following tables set forth certain information regarding the beneficial ownership of our Class A shares and Class B shares as of February 15, 2016 by:
· each person who is known to us to beneficially own more than 5% of the Class A shares;
· each person who is known to us to beneficially own more than 5% of the Class B shares;
· the Named Executive Officers of our general partner;
· each of the directors of our general partner; and
· all of the directors and executive officers of our general partner as a group.
All information with respect to beneficial ownership has been furnished by the respective directors, officers or 5% or more shareholders, as the case may be. Unless otherwise noted, the address of each beneficial owner named in the chart below is 333 Clay Street, Suite 1600, Houston, Texas 77002.
|
Name and Address of Beneficial Owner |
|
Class A Shares |
|
Percentage of |
|
Class B Shares |
|
Percentage of |
|
|
Waddell & Reed Financial, Inc. (3) 6300 Lamar Avenue Overland Park, KS 66202 |
|
16,263,938 |
|
6.1 |
% |
— |
|
— |
|
|
Salient Capital Advisors (4) 4265 San Felipe, 8th Floor Houston, TX 77027 |
|
15,883,779 |
|
6.0 |
% |
— |
|
— |
|
|
Kayne Anderson Capital Advisors, L.P./Richard A. Kayne(5) 1800 Avenue of the Stars, 3rd Floor Los Angeles, CA 90067 |
|
13,219,681 |
|
5.0 |
% |
— |
|
— |
|
|
EMG Investment, LLC 811 Main, Suite 4200 Houston, TX 77002 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
121,516,879 |
|
31.3 |
% |
|
KAFU Holdings, L.P. et al 1800 Avenue of the Stars, 3rd Floor Los Angeles, CA 90067 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
81,060,157 |
|
20.9 |
% |
|
Name and Address of Beneficial Owner |
|
Class A Shares |
|
Percentage of |
|
Class B Shares |
|
Percentage of |
|
|
Oxy Holding Company (Pipeline), Inc. 5 Greenway Plaza Houston, TX 77046 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
79,830,161 |
|
20.6 |
% |
|
Greg L. Armstrong |
|
1,200,000 |
|
* |
|
15,317,555 |
(6) |
3.9 |
% |
|
Harry N. Pefanis |
|
489,065 |
|
* |
|
10,026,960 |
(7) |
2.6 |
% |
|
Al Swanson |
|
2,445,189 |
|
* |
|
1,154,716 |
(8) |
* |
|
|
W. David Duckett |
|
2,345,327 |
|
* |
|
3,147,251 |
(9) |
* |
|
|
John P. vonBerg |
|
3,423,264 |
|
1.3 |
% |
917,262 |
(10) |
* |
|
|
Wilfred (Willie) C. Chiang |
|
200,000 |
|
* |
|
940,002 |
(11) |
* |
|
|
Victor Burk |
|
19,000 |
|
* |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
Ben Figlock |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
Everardo Goyanes |
|
54,600 |
|
* |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
John T. Raymond |
|
573,954 |
|
* |
|
129,993,681 |
(12) |
33.5 |
% |
|
Bobby S. Shackouls |
|
16,000 |
|
* |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
Robert V. Sinnott |
|
3,274,488 |
|
1.2 |
% |
74,903,838 |
(13) |
19.3 |
% |
|
All directors and executive officers of our general partner as a group (16 persons) (15) |
|
15,752,519 |
|
5.9 |
% |
240,056,223 |
(14) |
61.8 |
% |
* Less than 1%.
(1) Class A shares beneficially owned do not include any Class A shares issuable in connection with the exchange of any Class B shares, whether such Class B shares are currently outstanding or issuable following the conversion of any AAP Management Units. Although holders of our Class B shares have the right, at any time and from time to time, to immediately exchange (the “Exchange Right”) their Class B shares, together with a like number of AAP units and general partner units, for our Class A shares on a one-for-one basis, the fact that such Exchange Right may be settled in cash at AAP’s option results in such Class A shares not being deemed to be beneficially owned by the holders of our Class B shares.
(2) As long as our Class A shares are publicly traded, a holder of vested AAP Management Units will be entitled to convert such AAP Management Units into Class B shares and a like number of AAP units based on a conversion ratio calculated in accordance with the AAP limited partnership agreement (which conversion ratio will not be more than one-to-one and was approximately 0.940 AAP units (and Class B shares) for each AAP Management Unit as of February 15, 2016). Accordingly, figures presented for Class B shares beneficially owned and percentage of Class B shares beneficially owned are presented on a fully diluted basis and include Class B shares to be issued upon the conversion of all outstanding AAP Management Units based on such 0.940 conversion ratio.
(3) This information has been derived from a Schedule 13G filed with the SEC on February 12, 2016.
(4) This information has been derived from a Schedule 13G filed with the SEC on January 12, 2016.
(5) Richard A. Kayne is Chief Executive Officer and Director of Kayne Anderson Investment Management, Inc., which is the general partner of Kayne Anderson Capital Advisors, L.P. (“KACALP”). Various accounts under the management or control of KACALP own 12,718,240 Class A shares. Mr. Kayne may be deemed to beneficially own such shares. In addition, Mr. Kayne directly owns or has sole voting and dispositive power over 501,441 Class A shares. Mr. Kayne disclaims beneficial ownership of any of our Class A shares other than Class A shares held by him or attributable to him by virtue of his interests in the accounts that own our Class A shares.
(6) Represents the number of Class B shares beneficially owned by Mr. Armstrong through his (i) direct and indirect ownership of an approximately 25.3% interest in PAA Management, L.P., which entity owns 21,835,922 Class B shares, and (ii) beneficial ownership of 9,800,262 AAP units and Class B shares, based on an assumed conversion ratio of 0.940 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit.
(7) Represents the number of Class B shares beneficially owned by Mr. Pefanis through his (i) direct and indirect ownership of an approximately 14.4% interest in PAA Management, L.P., which entity owns 21,835,922 Class B shares, and (ii) beneficial ownership of 6,880,196 AAP units and Class B shares, based on an assumed conversion ratio of 0.940 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit.
(8) Represents the number of Class B shares beneficially owned by Mr. Swanson through his direct and indirect ownership of an approximately 5.3% interest in PAA Management, L.P., which entity owns 21,835,922 Class B shares.
(9) Represents the number of Class B shares beneficially owned by Mr. Duckett through his (i) direct and indirect ownership of an approximately 6.1% interest in PAA Management, L.P., which entity owns 21,835,922 Class B shares, and (ii) beneficial ownership of 1,815,107 AAP units and Class B shares, based on an assumed conversion ratio of 0.940 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit.
(10) Represents the number of Class B shares beneficially owned by Mr. vonBerg through his direct and indirect ownership of an approximately 4.2% interest in PAA Management, L.P., which entity owns 21,835,922 Class B shares.
(11) Represents the number of Class B shares beneficially owned by Mr. Chiang through his beneficial ownership of 940,002 AAP units and Class B shares, based on an assumed conversion ratio of 0.940 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit.
(12) Mr. Raymond is (i) the sole member of the general partner of the manager of EMG Investment, LLC, which entity owns 121,516,879 Class B shares, and (ii) the sole member of Lynx Holdings I, LLC, which entity owns 8,476,802 Class B shares. As such, Mr. Raymond has sole voting and dispositive power over the Class B shares owned by each of EMG Investment, LLC and Lynx Holdings I, LLC. Mr. Raymond disclaims any deemed beneficial ownership of the interests owned by EMG Investment, LLC beyond his pecuniary interest therein.
(13) Mr. Sinnott has shared voting and dispositive power over the Class B shares owned by (i) KAFU Holdings, L.P. (“KAFU”), which entity owns 3,305,189 Class B shares, (ii) KAFU Holdings (QP), L.P. (“KAFU QP”), which entity owns 64,803,104 Class B shares, and (iii) KAFU Holdings II, L.P. (“KAFU II”), which entity owns 6,795,545 Class B shares. Mr. Sinnott disclaims any deemed beneficial ownership of the interests owned by KAFU, KAFU QP and KAFU II beyond his pecuniary interest therein.
(14) The executive officers of our general partner as a group directly and indirectly own (i) an approximately 65.3% interest in PAA Management, L.P., which entity owns 21,835,922 Class B shares, and (ii) 20,905,607 AAP units and Class B shares based on an assumed conversion ratio of 0.940 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit. Amount shown in table represents the number of Class B shares beneficially owned by this group by virtue of such interests.
(15) As of February 15, 2016, no Class A shares or Class B shares were pledged by directors or Named Executive Officers.
Beneficial Ownership of Plains AAP, L.P.
The following table sets forth the percentage ownership of each of the Class A limited partners of AAP and the resulting economic interest of each such limited partner and the holders of the AAP Management Units as a group, in each case as of February 15, 2016:
|
Name of Owner and Address (in the case of Owners of more than 5%) |
|
Percentage |
|
Economic |
|
|
Plains GP Holdings, L.P. |
|
42.5 |
% |
40.6 |
% |
|
EMG Investment, LLC |
|
19.5 |
% |
18.6 |
% |
|
KAFU Holdings, L.P. and Affiliates |
|
13.0 |
% |
12.4 |
% |
|
Oxy Holding Company (Pipeline), Inc. |
|
12.8 |
% |
12.2 |
% |
|
PAA Management, L.P. (2) |
|
3.5 |
% |
3.3 |
% |
|
Strome PAA, L.P. and Affiliate |
|
2.9 |
% |
2.8 |
% |
|
Windy, L.L.C. |
|
2.9 |
% |
2.7 |
% |
|
Lynx Holdings I, LLC |
|
1.4 |
% |
1.3 |
% |
|
Various Individual Investors (3) |
|
1.5 |
% |
1.5 |
% |
|
AAP Management Unitholders (4) |
|
— |
|
4.6 |
% |
(1) AAP owns a 100% member interest in PAA GP LLC, which owns PAA’s 2% general partner interest. AAP has pledged its member interest, as well as its interest in PAA’s incentive distribution rights, as security for its obligations under the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of September 26, 2013 among AAP, Citibank, N.A. and the lenders party thereto (as amended, the “Plains AAP Credit Agreement”). A default by AAP under the Plains AAP Credit Agreement could result in a change in control of PAA’s general partner.
(2) PAA Management, L.P. is owned entirely by certain current and former members of PAA senior management, including Messrs. Armstrong (approximately 25%), Pefanis (approximately 14%), Duckett (approximately 6%), vonBerg (approximately 4%) and Swanson (approximately 5%). Other than Mr. Armstrong, none of our directors own any interest in PAA Management, L.P. Executive officers of PAA as a group own approximately 65% of PAA Management, L.P. Mr. Armstrong disclaims any beneficial ownership of the general partner interest except to the extent of his ownership interest in PAA Management, L.P.
(3) Includes certain current and former members of management who have converted AAP Management Units into AAP units and our Class B shares.
(4) Represents a profits interest in AAP in the form of AAP Management Units owned by certain members of management. On January 1, 2016, a significant number of AAP Management Units vested and a portion thereof was converted into AAP units and our Class B shares. Additionally, a portion of the resulting AAP units and Class B shares was exchanged for our Class A shares. As a result of such conversions and exchanges as well as open market purchases, as of February 15, 2016, Named Executive Officers and executive officers as a group owned the following AAP Management Units, AAP units and Class A shares (other than Mr. Armstrong, none of our directors own any AAP Management Units):
|
Name of Owner |
|
AAP Management |
|
AAP Units |
|
Class A |
|
|
Greg L. Armstrong |
|
10,425,791 |
|
— |
|
1,200,000 |
|
|
Harry N. Pefanis |
|
7,319,344 |
|
— |
|
489,065 |
|
|
Wilfred (Willie) C. Chiang |
|
1,000,000 |
|
— |
|
200,000 |
|
|
Al Swanson |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2,445,189 |
|
|
W. David Duckett |
|
1,930,961 |
|
— |
|
2,345,327 |
|
|
John vonBerg |
|
— |
|
— |
|
3,423,264 |
|
|
All executive officers as a group |
|
22,239,965 |
|
2,689,707 |
|
11,814,477 |
|
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table sets forth certain information with respect to our equity compensation plan as of December 31, 2015. For a description, see Item 13. “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence—Plains GP Holdings, L.P. Long Term Incentive Plan.”
|
Plan |
|
Number of Shares |
|
Weighted Average |
|
Number of Shares |
|
|
Equity compensation plans approved by shareholders: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Long Term Incentive Plan |
|
83,200 |
(1) |
N/A |
|
9,896,000 |
(1) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Equity compensation plans not approved by shareholders |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
(1) The Plains GP Holdings, L.P. Long Term Incentive Plan (the “LTIP”) was adopted by our general partner in connection with our IPO in October 2013. The LTIP contemplates the issuance or delivery of up to 10,000,000 Class A shares to satisfy awards under the LTIP. In accordance with Item 201(d) of Regulation S-K, column (c) excludes the securities disclosed in column (a). However, any phantom Class A shares represented in column (a) that are not satisfied by the issuance of Class A shares become “available for future issuance.”
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
For a discussion of director independence, see Item 10. “Directors and Executive Officers of Our General Partner and Corporate Governance.”
Our General Partner
Our general partner manages our operations and activities. We and our general partner have no employees. All of our officers and other personnel necessary for our business to function (the the extent not outsourced) are employed by GP LLC. Pursuant to the Administrative Agreement described below under “—Related Party Transactions—Administrative Agreement,” AAP, on our behalf, pays GP LLC an annual fee for general and administrative services. AAP also reimburses our general partner and its affiliates for expenses incurred in managing and operating us and our general partner. AAP also reimburses GP LLC for expenses incurred (i) on our behalf, (ii) on behalf of our general partner, or (iii) for any other purpose related to our business and activities or those of our general partner. AAP also reimburses our general partner for any additional expenses incurred on our behalf or to maintain our legal existence and good standing.
Our general partner owns a non-economic general partner interest in us, which does not entitle it to receive cash distributions. We own a portion of the membership interest in our general partner.
Plains GP Holdings, L.P. Long Term Incentive Plan
In connection with our initial public offering, our general partner adopted the Plains GP Holdings, L.P. Long Term Incentive Plan (the “LTIP”) on our behalf for (i) the employees of our general partner and its affiliates who perform services for us and (ii) the non-employee directors of our general partner. Awards that may be granted under the LTIP include restricted shares, phantom shares, options and share appreciation rights. The LTIP limits the number of shares that may be delivered pursuant to awards to 10,000,000 Class A shares (subject to any adjustment due to recapitalization, reorganization or a similar event permitted under the LTIP). Shares (other than restricted
shares) that are forfeited or withheld to satisfy exercise price or tax withholding obligations are available for delivery pursuant to other awards. As of December 31, 2015, grants of 83,200 unvested phantom Class A shares were outstanding under the LTIP.
The LTIP is administered by the board of directors of our general partner. The board of directors of our general partner has the right to terminate or amend the LTIP or any part of the LTIP from time to time, including increasing the number of shares that may be granted, subject to shareholder approval as may be required by the exchange upon which the Class A shares are listed at that time, if any. No change may be made in any outstanding grant that would materially reduce the benefits of the participant without the consent of the participant. The LTIP will expire upon the earlier of the termination of the LTIP by the board of directors of our general partner or the date that no shares remain available under the LTIP for awards. Upon termination of the LTIP, awards then outstanding will continue pursuant to the terms of their grants.
Class A shares to be delivered in settlement of awards under the LTIP may be newly issued Class A shares, Class A shares acquired in the open market, Class A shares acquired from any other person, or any combination of the foregoing.
Awards
Restricted Shares. A restricted share is a Class A share that vests over a period of time and that during such time is subject to forfeiture. The board of directors will determine the period over which restricted shares granted to participants will vest. The board of directors, in its discretion, may base its determination upon the achievement of performance metrics. Distributions made on restricted shares may be subjected to the same vesting provisions as the restricted share. If a grantee’s employment or membership on the board of directors terminates for any reason, the grantee’s restricted shares will be automatically forfeited unless, and to the extent, the board of directors or the terms of the award agreement provide otherwise.
We intend the restricted shares under the LTIP to serve as a means of incentive compensation for performance and not primarily as an opportunity to participate in the equity appreciation of our Class A shares. Therefore, participants will not pay any consideration for the Class A shares they receive, and we will receive no remuneration for the shares.
Phantom Shares. A phantom share entitles the grantee to receive a Class A share upon the vesting of the phantom share or, in the discretion of the board of directors, cash equivalent to the value of a Class A share. The board of directors will determine the period over which phantom shares granted to participants will vest. The board of directors, in its discretion, may base its determination upon the achievement of performance metrics. If a grantee’s employment or membership on the board of directors terminates for any reason, the grantee’s phantom shares will be automatically forfeited unless, and to the extent, the board of directors or the terms of the award agreement provide otherwise.
The board of directors, in its discretion, may grant distribution equivalent rights, which we refer to as DERs, with respect to a phantom share. DERs entitle the grantee to receive an amount in cash equal to the cash distributions made on a Class A share during the period the related award is outstanding. The board of directors will establish whether the DERs are paid currently, when the tandem phantom share vests or on some other basis.
We intend the issuance of any Class A shares upon vesting of the phantom shares under the LTIP to serve as a means of incentive compensation for performance and not primarily as an opportunity to participate in the equity appreciation of our Class A shares. Therefore, plan participants will not pay any consideration for the Class A shares they receive, and we will receive no remuneration for the shares.
Options. An option provides a participant with the option to acquire Class A shares at a specified price. The exercise price of each option granted under the LTIP will be stated in the option agreement and may vary between participants; provided, however, that the exercise price for an option must not be less than 100% of the fair market value per Class A share as of the date of grant of the option. Options may be exercised in the manner and at such times as the board of directors determines for each option. The board of directors will determine the methods
and form of payment for the exercise price of an option and the methods and forms in which Class A shares will be delivered to a participant. The board of directors, in its discretion, may grant DERs with respect to an option.
Share Appreciation Rights. A share appreciation right is an award that, upon exercise, entitles the holder to receive the excess, if any, of the fair market value of a Class A share on the exercise date over the grant price of the share appreciation right. The excess may be paid in cash and/or in Class A shares, as determined by the board of directors in its discretion. The board of directors will have the authority to determine to whom share appreciation rights will be granted, the number of Class A shares to be covered by each grant, and the conditions and limitations applicable to the exercise of the share appreciation right. The grant price per share appreciation right will be determined by the board of directors at the time the share appreciation right is granted, but each share appreciation right must have an exercise price that is not less than the fair market value of the Class A shares on the date of grant. The board of directors will determine the time or times at which a share appreciation right may be exercised in whole or in part. Unless otherwise waived by the board of directors, or set forth in an award agreement, outstanding share appreciation rights awarded to a participant will be automatically forfeited upon a termination of the individual’s employment or membership on the board of directors terminates for any reason. The board of directors, in its discretion, may grant DERs with respect to a share appreciation right.
Other LTIP Provisions
Tax Withholding. Unless other arrangements are made, our general partner and its affiliates will be authorized to withhold from any award, from any payment due under any award, or from any compensation or other amount owing to a participant the amount (in cash, shares, shares that would otherwise be issued pursuant to such award, or other property) of any applicable taxes payable with respect to the grant of an award, its settlement, its exercise, the lapse of restrictions applicable to an award or in connection with any payment relating to an award or the transfer of an award and to take such other actions as may be necessary to satisfy the withholding obligations with respect to an award.
Anti-Dilution Adjustments. Upon the occurrence of any “equity restructuring” event that could result in an additional compensation expense under Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification Topic 718 (“FASB ASC Topic 718”) if adjustments to awards with respect to such event were discretionary, the board of directors will equitably adjust the number and type of shares covered by each outstanding award and the terms and conditions of such award to equitably reflect the restructuring event, and the board of directors will adjust the number and type of shares with respect to which future awards may be granted. With respect to a similar event that would not result in a FASB ASC Topic 718 accounting charge if adjustment to awards were discretionary, the board of directors shall have complete discretion to adjust awards in the manner it deems appropriate.
Change of Control. If specifically provided in an award agreement, upon a change of control (as defined in the award agreement), the award may automatically vest and be payable or become exercisable in full, as the case may be.
Transferability of Awards. Options and share appreciation rights are only exercisable by the participant during the participant’s lifetime, or by the person to whom the participant’s rights pass by will or the laws of descent and distribution. No award or right granted under the LTIP may be assigned, alienated, pledged, attached, sold or otherwise transferred or encumbered and any such purported transfer shall be void and unenforceable. Notwithstanding the foregoing, the board of directors may, in its discretion, allow a participant to transfer an option or a share appreciation right without consideration to an immediate family member or a related family trust, limited partnership, or similar entity on the terms and conditions established by the board of directors from time to time.
AAP Management Units
In August 2007, the owners of AAP authorized the creation and issuance of AAP Management Units and authorized the compensation committee of GP LLC to issue grants of AAP Management Units to create long-term incentives for PAA’s management. The entire economic burden of the AAP Management Units, which are equity classified, is borne solely by AAP. PAA is not obligated to reimburse AAP for any costs attributable to the AAP Management Units. The amount of cash available for distribution by AAP to us will be reduced by amounts to which the AAP Management Units are entitled, which will reduce the cash available for distribution to our Class A shareholders. Each AAP Management Unit represents a “profits interest” in AAP, which entitles the holder to participate in future profits and losses from operations, current distributions from operations, and an interest in future appreciation or depreciation in AAP’s asset values. Up to 52,125,935 AAP Management Units are authorized
for issuance. As of December 31, 2015, 50,722,830 AAP Management Units were issued and outstanding, which, based on the conversion ratio of approximately 0.938 AAP units for each AAP Management Unit as of December 31, 2015, would equate to 47,584,642 AAP units. On January 1, 2016, a significant portion of the outstanding AAP Management Units vested and a portion of such vested AAP Management Units has been converted into AAP units and our Class B shares. As a result, as of February 15, 2016, the number of AAP Management Units outstanding was 31,878,821 (29,966,147 on an as converted basis).
The outstanding AAP Management Units are subject to restrictions on transfer and generally become “earned” (entitled to receive a portion of the distributions that would otherwise be paid to holders of AAP units) in percentage increments when the annualized quarterly distributions on PAA’s common units equal or exceed certain thresholds. Upon achievement of these performance thresholds (or, in some cases, within six months thereafter), the AAP Management Units will be entitled to their proportionate share of all quarterly cash distributions made by AAP in excess of $11 million per quarter (as adjusted for debt service costs and excluding special distributions funded by debt). Assuming all authorized AAP Management Units are issued, the maximum participation would be approximately 8% of the amount in excess of $11 million per quarter, as adjusted. As of February 15, 2016, approximately 93% of the outstanding AAP Management Units had been earned or will be earned within 180 days. The remaining AAP Management Units will be earned in 25% increments upon or six months after PAA’s payment of annualized quarterly distributions ranging from $2.85 to $3.50 per unit.
To encourage retention following achievement of these performance benchmarks, AAP retained a call right to purchase any earned AAP Management Units at a discount to fair market value that is generally exercisable upon the termination of a holder’s employment with GP LLC and its affiliates (other than termination under certain circumstances such as a termination without cause or by the employee for good reason) prior to certain stated dates. If a holder of an AAP Management Unit remains employed past such designated date (or prior to such date such holder is terminated without cause or quits for good reason), any earned units are no longer subject to the call right and are deemed to have “vested.” As of January 1, 2016, AAP Management Units granted in 2007 and 2009 are no longer subject to such call right and have vested. The applicable vesting dates for the remaining AAP Management Unit grants range from January 1, 2017 for AAP Management Units granted in 2010 to January 1, 2023 for AAP Management Units granted in 2015. In order to encourage retention, the size of the discount to fair market value reflected in the potential call right purchase price decreases over time pursuant to a formula set forth in each AAP Management Unit grant agreement. AAP Management Unit grants also provide that all earned AAP Management Units and a portion of any unearned and unvested AAP Management Units will vest upon a change of control. All earned AAP Management Units will also vest if AAP does not timely exercise its call right.
As long as our Class A shares are publicly traded, each vested AAP Management Unit may be converted into AAP units and a like number of our Class B shares based on a conversion ratio calculated in accordance with the AAP limited partnership agreement (which conversion ratio will not be more than one-to-one and was approximately 0.940 AAP units and Class B shares for each AAP Management Unit as of February 15, 2016). Following any such conversion, the resulting AAP units and Class B shares are exchangeable for Class A shares on a one-for-one basis as provided in the AAP limited partnership agreement. As of February 15, 2016, approximately 44.9 million AAP Management Units had vested, of which 18.8 million have been converted into 17.7 million AAP units and Class B shares. A portion of the resulting AAP units and Class B shares were subsequently exchanged for an aggregate of 11.4 million Class A shares.
Related Party Transactions
Administrative Agreement
In connection with the closing of our IPO in October 2013, we entered into an administrative agreement (the “Administrative Agreement”) with PAA, our general partner, AAP, PAA GP LLC and GP LLC to address, among other things, potential conflicts with respect to business opportunities that may arise among us, our general partner, AAP, PAA, PAA GP LLC and GP LLC. The agreement provides that if any business opportunity is presented to us, our general partner, AAP, PAA, PAA GP LLC or GP LLC, then PAA will have the first right to pursue such business opportunity. We will have the right to pursue and/or participate in such business opportunity if invited to do so by PAA, or if PAA abandons the business opportunity and GP LLC so notifies our general partner.
Pursuant to the Administrative Agreement, all of our officers and other personnel necessary for our business to function (to the extent not out-sourced) are employed by GP LLC, and AAP pays GP LLC an annual fee
for general and administrative services performed on our behalf. During 2015, the annual fee paid by AAP to GP LLC totaled $1.5 million. This fee is subject to adjustment on an annual basis based on the Consumer Price Index. The fee is also subject to adjustment if a material event occurs that impacts the general and administrative services provided to us, such as acquisitions, entering into new lines of business or changes in laws, regulations, listing requirements or accounting rules.
In addition, the Administrative Agreement provides that any direct expenses incurred by us, our general partner and AAP (other than income taxes payable by us) are borne by AAP. These direct expenses include costs related to (i) compensation for our independent directors, (ii) incremental director and officer liability insurance, (iii) listing on the NYSE, (iv) investor relations, (v) legal, (vi) tax and (vii) accounting.
In addition to the fee and expenses described above, the Administrative Agreement requires AAP to reimburse GP LLC for any additional expenses incurred by GP LLC and certain of its affiliates (i) on our behalf, (ii) on behalf of our general partner, or (iii) for any other purpose related to our business and activities or those of our general partner. AAP is also required to reimburse our general partner for any additional expenses incurred by it on our behalf or to maintain our legal existence and good standing. There is no limit on the amount of fees and expenses AAP may be required to pay to affiliates of our general partner on our behalf pursuant to the Administrative Agreement.
Pursuant to the Administrative Agreement, PAA has also granted us a license to use the names “PAA” and “Plains” and any associated or related marks.
Capital Structure
As of December 31, 2015, our sole assets consisted of (i) a 100% member interest in GP LLC, which holds a non-economic general partner interest in AAP, (ii) 229,278,980 AAP units (representing 38% of the limited partner interests in AAP, and an approximate 35% economic interest (including the dilutive effect of the AAP Management Units) in AAP, which directly or indirectly owns all of the IDRs and the 2% general partner interest in PAA), and (iii) 229,278,980 general partner units representing 38% of the membership interests in our general partner.
In accordance with the AAP partnership agreement, holders of AAP Management Units are allocated gross income equal to the amount of any distributions paid with respect to such units and the remaining net profits and net losses of AAP are generally allocated to the other holders of AAP units on a pro rata basis in accordance with their relative number of AAP units held. In addition, through our control of GP LLC, we have the right to determine when distributions will be made to the holders of AAP units and the amount of any such distributions. If we cause a distribution to be made, such distribution will, subject to certain limitations on the amount of distributions to be made with respect to AAP Management Units, be made to the holders of AAP units on a pro rata basis in accordance with their relative number of AAP units held.
Prior to the trigger date, GP LLC must remain the sole general partner of AAP, and may not withdraw, transfer its general partner interest or be replaced, unless the holders of two-thirds of the AAP units consent. In addition, no (i) entry into new material related party transactions, (ii) issuance of AAP securities to us or (iii) change in AAP’s tax election may occur prior to the expiration of a 30-day notice period in favor of the holders of AAP units.
For purposes of any transfer or exchange of AAP units initially owned by the Legacy Owners and our Class B shares, the AAP partnership agreement, our general partner’s limited liability company agreement and our partnership agreement contain provisions linking each such AAP unit with one of our Class B shares and a general partner unit. Our Class B shares and general partner units cannot be transferred without transferring an equal number of AAP units and vice versa.
The Legacy Owners and any permitted transferees of their AAP units each have the right to exchange (the “Exchange Right”) all or a portion of their AAP units into Class A shares at an exchange ratio of one Class A share for each AAP unit exchanged. The above Exchange Right may be exercised only if, simultaneously therewith, an equal number of our Class B shares and general partner units are transferred by the exercising party to us. We are
obligated to facilitate such exchange through a contribution of Class A shares to AAP or alternatively we have the right to acquire the subject AAP units, Class B shares and general partner units directly from the AAP unitholder exercising the Exchange Right. At AAP’s option, AAP may give the exchanging AAP unitholder cash in an amount equal to the market value of the Class A shares instead. Prior to the trigger date, no change to the one-for-one exchange ratio may be made without the prior approval of the holders of two-thirds of the AAP units, and only after the expiration of a 30-day notice period.
As long as the Class A shares are publicly traded, a holder of vested AAP Management Units will be entitled to convert his or her AAP Management Units into AAP units and a like number of our Class B shares based on a conversion ratio calculated in accordance with the AAP limited partnership agreement (which conversion ratio will not be more than one-to-one and is approximately 0.940 AAP units for each AAP Management Unit as of February 15, 2016). Following any such conversion, the holder will have the Exchange Right for our Class A shares. Holders of AAP Management Units who convert into AAP units and Class B shares will not receive general partner units and thus will not need to include any general partner units in a transfer or the exercise of their Exchange Right.
The above mechanisms are subject to customary conversion rate adjustments for equity splits, equity dividends and reclassifications.
In addition, pursuant to our partnership agreement and the AAP partnership agreement, our capital structure and the capital structure of AAP generally replicate one another and provide for customary antidilution mechanisms in order to maintain the one-for-one exchange ratio between the AAP units, Class B shares and general partner units, on the one hand, and our Class A shares, on the other hand.
Registration Rights Agreement
In connection with the closing of our IPO in October 2013, we entered into a shareholder and registration rights agreement, which we refer to as the registration rights agreement, with the Legacy Owners. Pursuant to the registration rights agreement, we agreed to register the resale of all Class A shares issuable upon exercise of the Exchange Right (the “Registrable Securities”) held by the parties to the registration rights agreement under certain circumstances. Additionally, upon the vesting of the AAP Management Units, we have agreed to amend the registration rights agreement to include any Class A shares issuable upon exercise of the Exchange Right with respect to such vested AAP Management Units as Registrable Securities, so long as the holder of such units agrees to be bound by the terms and conditions of the registration rights agreement.
Shelf Registration Statement
Under the Registration Rights Agreement, we agreed to file and maintain a shelf registration statement on Form S-3 covering the resale of all of the Registrable Securities. We are obligated to maintain the effectiveness of any such registration statement until the date on which all Registrable Securities covered by such shelf registration statement (i) have been sold thereunder in accordance with the plan and method of distribution disclosed in the prospectus included in the shelf registration statement, or (ii) otherwise cease to be Registrable Securities under the registration rights agreement. A shelf registration statement on Form S-3 covering the resale of the Registrable Securities was filed and declared effective in December 2014.
Demand and Piggyback Rights
Subject to any applicable lock-up arrangements, certain of the Legacy Owners will have the right to require that we register their Registrable Securities and/or facilitate an underwritten offering of their Registrable Securities. There is no aggregate limit on the number of such demand requests; however, the demand rights of these holders are subject to a number of size, frequency and other limitations. Occidental exercised its demand rights in connection with its underwritten secondary offering of Class A shares in November 2014.
In the event we propose to conduct an underwritten offering of Registrable Securities, then the holders of Registrable Securities will generally have customary rights to participate in such offering, subject to customary offering size limitations and related allocation provisions and other limitations. Similarly, in the event that eligible holders demand that we conduct an underwritten offering of their Registrable Securities, then we will generally have
customary rights to participate in such offering, subject to customary offering size limitations and related allocation provisions and other limitations.
Delay Rights
We will not be required to comply with any demand request, and may suspend the holders’ ability to use any shelf registration statement, following our delivery of written notice to the holders of customary blackout periods and deferral events.
Expenses
All selling expenses, including any underwriting discounts and selling commissions, relating to the sale of securities registered pursuant to the registration rights agreement, will be borne by the holders of such securities. We will cause all other registration expenses in connection with our obligations under the registration rights agreement to be borne by AAP.
Other
In January 2016, PAA sold approximately 61.0 million unregistered Series A Convertible Preferred Units (the “Preferred Units”) in a private placement offering to a group of purchasers that included affiliates of EnCap, KAFU and EMG. Net proceeds to PAA of the sale, after deducting offering expenses and a transaction fee due to the purchasers and including the 2% equity contribution of PAA’s general partner, were approximately $1.6 billion.
In connection with the closing of PAA’s private placement of Preferred Units, PAA entered into a Registration Rights Agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”) with the purchasers of the Preferred Units relating to the registered resale of the PAA common units issuable upon conversion of the Preferred Units. Pursuant to the Registration Rights Agreement, PAA is required to file or cause to be filed a registration statement for such registered resale and is required to cause the registration statement to become effective no later than two years after the closing. In certain circumstances, the holders of registrable securities (as defined in the Registration Rights Agreement) will have piggyback registration rights on offerings initiated by other holders, and certain purchasers will have rights to request an underwritten offering as described in the Registration Rights Agreement. Holders of registrable securities will cease to have registration rights under the Registration Rights Agreement on the later of (i) the fourth anniversary of the date on which all Preferred Units have been converted into PAA common units pursuant to PAA’s partnership agreement and (ii) the earlier of (x) the date on which such holder is no longer an “affiliate” as such term is defined in Rule 144 promulgated under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and (y) the tenth anniversary of the closing.
During 2015, PAA recognized sales and transportation and storage revenues of approximately $0.9 billion from companies affiliated with Occidental. During 2015, PAA also purchased approximately $41 million of petroleum products from companies affiliated with Occidental. These transactions were conducted at posted tariff rates or prices that PAA believes approximate market. A portion of these transactions was conducted under a crude oil buy/sell agreement that includes a multi-year minimum volume commitment. These amounts do not include revenues from unconsolidated equity investments.
During 2015, PAA recognized sales and transportation and storage revenues of approximately $38 million from companies affiliated with EMG. During 2015, PAA also purchased approximately $165 million of oil from companies affiliated with EMG. These transactions were conducted at posted tariff rates or prices that PAA believes approximate market.
During 2015, PAA purchased approximately $17.5 million of oil from companies owned and controlled by funds managed by KACALP. PAA pays the same amount per barrel to these companies that it pays to other producers in the area.
An employee in PAA’s marketing department is the son of Phil Kramer, one of our executive officers. Mr. Kramer’s son’s total compensation for 2015 (which amount includes the grant date fair value of LTIPs awarded to him on terms consistent with all eligible employees) was approximately $284,000.
An employee with PAA’s Canadian operations is the son of W. David Duckett, one of our executive officers. Mr. Duckett’s son’s total compensation for 2015 (which amount includes the grant date fair value of LTIPs awarded to him on terms consistent with all eligible employees) was approximately $501,000.
Another employee with PAA’s Canadian operations is the daughter of W. David Duckett, one of our executive officers. Mr. Duckett’s daughter’s total compensation for 2015 (which amount includes the grant date fair value of LTIPs awarded to her on terms consistent with all eligible employees) was approximately $129,000.
An employee in PAA’s facilities department is the son of John vonBerg, one of our executive officers. Mr. vonBerg’s son’s total compensation for 2015 (which amount includes the grant date fair value of LTIPs awarded to him on terms consistent with all eligible employees) was approximately $120,000.
Review, Approval or Ratification of Transactions with Related Persons
Pursuant to our Governance Guidelines, a director is expected to bring to the attention of the CEO or the board any conflict or potential conflict of interest that may arise between the director, his or her family members or any affiliate of the director, on the one hand, and the Partnership or our general partner on the other. The resolution of any such conflict or potential conflict should, at the discretion of the board in light of the circumstances, be determined by a majority of the disinterested directors.
If a conflict or potential conflict of interest arises between the Partnership and our general partner, the resolution of any such conflict or potential conflict should be addressed by the board in accordance with the provisions of the Partnership Agreement. At the discretion of the board in light of the circumstances, the resolution may be determined by the board of directors of our general partner or by a “conflicts committee” meeting the definitional requirements for such a committee under the Partnership Agreement. Such resolution may include resolution of any derivative conflicts created by an executive officer’s ownership of interests in our general partner of any of its affiliates or a director’s appointment to the board of our general partner by an owner of interests in our general partner.
Pursuant to our Code of Business Conduct, any executive officer must avoid conflicts of interest unless approved by the board of directors of our general partner.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The following table details the aggregate fees billed for professional services rendered by our independent auditor for services provided to us and to our subsidiaries (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
Audit fees (1) |
|
$ |
4.8 |
|
$ |
4.7 |
|
|
Audit-related fees (2) |
|
0.1 |
|
0.1 |
| ||
|
Tax fees (3) |
|
1.5 |
|
1.8 |
| ||
|
Total |
|
$ |
6.4 |
|
$ |
6.6 |
|
(1) Audit fees include those related to (a) our annual audit (including internal control evaluation and reporting); (b) the audit of certain joint ventures of which we are the operator, and (c) work performed on our registration of publicly held debt and equity.
(2) Audit-related fees are for an audit of our benefit plan.
(3) Tax fees are related to tax processing as well as the preparation of Forms K-1 for PAA unitholders and international tax planning work associated with the structure of our Canadian investment.
Pre-Approval Policy
As discussed above, we have an audit committee that reviews our external financial reporting, engages our independent auditors and reviews the adequacy of our internal accounting controls. Our consolidated subsidiary, PAA, also has an audit committee that performs similar functions on PAA’s behalf. All services provided by our independent auditor are subject to pre-approval by our audit committee or the audit committee of PAA (for services provided to PAA).
The audit committees have instituted policies that describe certain pre-approved non-audit services. We believe that the descriptions of services are designed to be sufficiently detailed as to particular services provided, such that (i) management is not required to exercise judgment as to whether a proposed service fits within the description and (ii) the audit committee knows what services it is being asked to pre-approve. The audit committees are informed of each engagement of the independent auditor to provide services under the respective policy. Except as noted above, all services provided by our independent auditor during the years ended December 31, 2015 and 2014 were approved in advance by the applicable audit committee.
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
(a) (1) Financial Statements
See “Index to the Consolidated Financial Statements” set forth on Page F-1.
(2) Financial Statement Schedules
All schedules are omitted because they are either not applicable or the required information is shown in the Consolidated Financial Statements or notes thereto.
(3) Exhibits
The exhibits listed on the accompanying Exhibit Index are filed or incorporated by reference as part of this report, and such Exhibit Index is incorporated herein by reference.
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
|
|
|
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P. | |
|
|
|
By: |
PAA GP HOLDINGS LLC, |
|
|
|
|
its general partner |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
By: |
/s/ Greg L. Armstrong |
|
|
|
|
Greg L. Armstrong, |
|
|
|
|
Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer |
|
|
|
|
and Director of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
|
|
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
By: |
/s/ Al Swanson |
|
|
|
|
Al Swanson, |
|
|
|
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer |
|
|
|
|
of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
|
|
|
(Principal Financial Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
By: |
/s/ Chris Herbold |
|
|
|
|
Chris Herbold, |
|
|
|
|
Vice President—Accounting and Chief Accounting Officer of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
|
|
|
(Principal Accounting Officer) |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
|
|
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
|
Name |
|
Title |
|
Date |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Greg L. Armstrong |
|
Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer and Director of PAA GP Holdings LLC (Principal Executive Officer) |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
Greg L. Armstrong |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Harry N. Pefanis |
|
President and Chief Operating Officer of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
Harry N. Pefanis |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Al Swanson |
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of PAA GP Holdings LLC (Principal Financial Officer) |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
Al Swanson |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Chris Herbold |
|
Vice President—Accounting and Chief Accounting Officer of PAA GP Holdings LLC (Principal Accounting Officer) |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
Chris Herbold |
|
|
| |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Victor Burk |
|
Director of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
Victor Burk |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Bernard Figlock |
|
Director of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
Bernard Figlock |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Everardo Goyanes |
|
Director of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
Everardo Goyanes |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ John T. Raymond |
|
Director of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
John T. Raymond |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Bobby S. Shackouls |
|
Director of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
Bobby S. Shackouls |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Robert V. Sinnott |
|
Director of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
Robert V. Sinnott |
|
|
|
|
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P. AND SUBSIDIARIES
INDEX TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
|
|
Page |
|
Consolidated Financial Statements |
|
|
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting |
F-2 |
|
F-3 | |
|
Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 |
F-4 |
|
Consolidated Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 |
F-5 |
|
Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 |
F-6 |
|
F-6 | |
|
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 |
F-7 |
|
F-8 | |
|
F-9 | |
|
F-9 | |
|
F-10 | |
|
F-15 | |
|
F-17 | |
|
F-18 | |
|
F-19 | |
|
F-20 | |
|
F-21 | |
|
F-23 | |
|
F-27 | |
|
F-30 | |
|
F-37 | |
|
F-39 | |
|
F-40 | |
|
F-41 | |
|
F-45 | |
|
F-51 | |
|
F-51 |
MANAGEMENT’S REPORT ON INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
Plains GP Holdings, L.P.’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles.
Internal control over financial reporting has inherent limitations. Internal control over financial reporting is a process that involves human diligence and compliance and is subject to lapses in judgment and breakdowns resulting from human failures. Internal control over financial reporting also can be circumvented by collusion or improper management override. Because of such limitations, there is a risk that material misstatements may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis by internal control over financial reporting. However, these inherent limitations are known features of the financial reporting process. Therefore, it is possible to design into the process safeguards to reduce, though not eliminate, this risk.
Management has used the framework set forth in the report entitled “Internal Control—Integrated Framework” (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (“COSO”) to evaluate the effectiveness of the Partnership’s internal control over financial reporting. Based on that evaluation, management has concluded that the Partnership’s internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2015.
The effectiveness of the Partnership’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015 has been audited by PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report which appears on Page F-3.
|
|
/s/ Greg L. Armstrong |
|
|
Greg L. Armstrong |
|
|
Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer and Director of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
|
(Principal Executive Officer) |
|
|
|
|
|
/s/ Al Swanson |
|
|
Al Swanson |
|
|
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer of PAA GP Holdings LLC |
|
|
(Principal Financial Officer) |
|
|
|
|
February 25, 2016 |
|
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors of the General Partner and Shareholders of
Plains GP Holdings, L.P.:
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and the related consolidated statements of operations, of comprehensive income, of changes in accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss), of changes in partners’ capital, and of cash flows present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Plains GP Holdings, L.P. and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2015 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Partnership maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2015, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (2013) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Partnership’s management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements and on the Partnership’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audits (which were integrated audits in 2015 and 2014). We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audits to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audits of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audits also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinions.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
|
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP |
|
Houston, Texas |
|
February 25, 2016 |
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P. AND SUBSIDIARIES
(in millions, except share data)
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
CURRENT ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Cash and cash equivalents |
|
$ |
30 |
|
$ |
404 |
|
|
Trade accounts receivable and other receivables, net |
|
1,785 |
|
2,615 |
| ||
|
Inventory |
|
916 |
|
891 |
| ||
|
Other current assets |
|
241 |
|
271 |
| ||
|
Total current assets |
|
2,972 |
|
4,181 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT |
|
15,695 |
|
14,219 |
| ||
|
Accumulated depreciation |
|
(2,202 |
) |
(1,927 |
) | ||
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
13,493 |
|
12,292 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
OTHER ASSETS |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Goodwill |
|
2,405 |
|
2,465 |
| ||
|
Investments in unconsolidated entities |
|
2,027 |
|
1,735 |
| ||
|
Deferred tax asset |
|
1,835 |
|
1,705 |
| ||
|
Linefill and base gas |
|
898 |
|
930 |
| ||
|
Long-term inventory |
|
129 |
|
186 |
| ||
|
Other long-term assets, net |
|
383 |
|
429 |
| ||
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
24,142 |
|
$ |
23,923 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
LIABILITIES AND PARTNERS’ CAPITAL |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
CURRENT LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
|
$ |
2,040 |
|
$ |
2,987 |
|
|
Short-term debt |
|
999 |
|
1,287 |
| ||
|
Other current liabilities |
|
370 |
|
482 |
| ||
|
Total current liabilities |
|
3,409 |
|
4,756 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
LONG-TERM LIABILITIES |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Senior notes, net of unamortized discounts and debt issuance costs |
|
9,698 |
|
8,699 |
| ||
|
Other long-term debt, net of unamortized debt issuance costs |
|
1,234 |
|
539 |
| ||
|
Other long-term liabilities and deferred credits |
|
567 |
|
548 |
| ||
|
Total long-term liabilities |
|
11,499 |
|
9,786 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES (NOTE 16) |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
PARTNERS’ CAPITAL |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Class A Shareholders (229,278,980 and 206,933,274 shares outstanding, respectively) |
|
1,762 |
|
1,657 |
| ||
|
Class B Shareholders (376,771,593 and 399,096,499 shares outstanding, respectively) |
|
— |
|
— |
| ||
|
Noncontrolling interests |
|
7,472 |
|
7,724 |
| ||
|
Total partners’ capital |
|
9,234 |
|
9,381 |
| ||
|
Total liabilities and partners’ capital |
|
$ |
24,142 |
|
$ |
23,923 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in millions, except per share data)
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
REVENUES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Supply and Logistics segment revenues |
|
$ |
21,927 |
|
$ |
42,114 |
|
$ |
40,692 |
|
|
Transportation segment revenues |
|
697 |
|
774 |
|
701 |
| |||
|
Facilities segment revenues |
|
528 |
|
576 |
|
856 |
| |||
|
Total revenues |
|
23,152 |
|
43,464 |
|
42,249 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
COSTS AND EXPENSES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Purchases and related costs |
|
19,726 |
|
39,500 |
|
38,465 |
| |||
|
Field operating costs |
|
1,454 |
|
1,456 |
|
1,322 |
| |||
|
General and administrative expenses |
|
281 |
|
331 |
|
360 |
| |||
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
433 |
|
386 |
|
368 |
| |||
|
Total costs and expenses |
|
21,894 |
|
41,673 |
|
40,515 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
OPERATING INCOME |
|
1,258 |
|
1,791 |
|
1,734 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
OTHER INCOME/(EXPENSE) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Equity earnings in unconsolidated entities |
|
183 |
|
108 |
|
64 |
| |||
|
Interest expense (net of capitalized interest of $57, $48 and $38, respectively) |
|
(443 |
) |
(357 |
) |
(319 |
) | |||
|
Other income/(expense), net |
|
(7 |
) |
(2 |
) |
1 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
INCOME BEFORE TAX |
|
991 |
|
1,540 |
|
1,480 |
| |||
|
Current income tax expense |
|
(84 |
) |
(71 |
) |
(100 |
) | |||
|
Deferred income tax expense |
|
(98 |
) |
(141 |
) |
(6 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
NET INCOME |
|
809 |
|
1,328 |
|
1,374 |
| |||
|
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
(691 |
) |
(1,258 |
) |
(1,359 |
) | |||
|
NET INCOME ATTRIBUTABLE TO PAGP |
|
$ |
118 |
|
$ |
70 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
BASIC NET INCOME PER CLASS A SHARE (1) |
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
$ |
0.48 |
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
DILUTED NET INCOME PER CLASS A SHARE (1) |
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
$ |
0.47 |
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
BASIC WEIGHTED AVERAGE CLASS A SHARES OUTSTANDING |
|
222 |
|
145 |
|
132 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
DILUTED WEIGHTED AVERAGE CLASS A SHARES OUTSTANDING |
|
222 |
|
650 |
|
132 |
| |||
(1) For the 2013 period, basic and diluted net income per Class A share were calculated based on net income attributable to PAGP for the period following the closing of our initial public offering on October 21, 2013 and basic weighted average Class A shares outstanding weighted for the same period. See Note 3, “Net Income Per Class A Share”.
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
(in millions)
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
Net income |
|
$ |
809 |
|
$ |
1,328 |
|
$ |
1,374 |
|
|
Other comprehensive loss |
|
(614 |
) |
(370 |
) |
(176 |
) | |||
|
Comprehensive income |
|
195 |
|
958 |
|
1,198 |
| |||
|
Comprehensive income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
(82 |
) |
(890 |
) |
(1,183 |
) | |||
|
Comprehensive income attributable to PAGP |
|
$ |
113 |
|
$ |
68 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN ACCUMULATED
OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME/(LOSS)
(in millions)
|
|
|
Derivative |
|
Translation |
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
Instruments |
|
Adjustments |
|
Total |
| |||
|
Balance at December 31, 2012 |
|
$ |
(121 |
) |
$ |
200 |
|
$ |
79 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Reclassification adjustments |
|
(66 |
) |
— |
|
(66 |
) | |||
|
Deferred gain on cash flow hedges, net of tax |
|
110 |
|
— |
|
110 |
| |||
|
Currency translation adjustments |
|
— |
|
(220 |
) |
(220 |
) | |||
|
2013 Activity |
|
44 |
|
(220 |
) |
(176 |
) | |||
|
Balance at December 31, 2013 |
|
$ |
(77 |
) |
$ |
(20 |
) |
$ |
(97 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Reclassification adjustments |
|
4 |
|
— |
|
4 |
| |||
|
Deferred loss on cash flow hedges, net of tax |
|
(86 |
) |
— |
|
(86 |
) | |||
|
Currency translation adjustments |
|
— |
|
(288 |
) |
(288 |
) | |||
|
2014 Activity |
|
(82 |
) |
(288 |
) |
(370 |
) | |||
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
$ |
(159 |
) |
$ |
(308 |
) |
$ |
(467 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Reclassification adjustments |
|
(45 |
) |
— |
|
(45 |
) | |||
|
Deferred gain on cash flow hedges, net of tax |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
1 |
| |||
|
Currency translation adjustments |
|
— |
|
(570 |
) |
(570 |
) | |||
|
2015 Activity |
|
(44 |
) |
(570 |
) |
(614 |
) | |||
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
(203 |
) |
$ |
(878 |
) |
$ |
(1,081 |
) |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in millions)
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Net income |
|
$ |
809 |
|
$ |
1,328 |
|
$ |
1,374 |
|
|
Reconciliation of net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
433 |
|
386 |
|
368 |
| |||
|
Equity-indexed compensation expense |
|
27 |
|
99 |
|
116 |
| |||
|
Inventory valuation adjustments |
|
117 |
|
289 |
|
7 |
| |||
|
Deferred income tax expense |
|
98 |
|
141 |
|
6 |
| |||
|
Settlement of terminated interest rate hedging instruments |
|
(48 |
) |
(7 |
) |
8 |
| |||
|
Equity earnings in unconsolidated entities |
|
(183 |
) |
(108 |
) |
(64 |
) | |||
|
Distributions from unconsolidated entities |
|
214 |
|
105 |
|
54 |
| |||
|
Other |
|
(20 |
) |
24 |
|
6 |
| |||
|
Changes in assets and liabilities, net of acquisitions: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Trade accounts receivable and other |
|
803 |
|
1,177 |
|
(185 |
) | |||
|
Inventory |
|
(90 |
) |
(129 |
) |
134 |
| |||
|
Accounts payable and other current liabilities |
|
(827 |
) |
(1,317 |
) |
124 |
| |||
|
Net cash provided by operating activities |
|
1,333 |
|
1,988 |
|
1,948 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Cash paid in connection with acquisitions, net of cash acquired (Note 7) |
|
(105 |
) |
(1,098 |
) |
(28 |
) | |||
|
Investments in unconsolidated entities (Note 7) |
|
(253 |
) |
(158 |
) |
(133 |
) | |||
|
Additions to property, equipment and other |
|
(2,079 |
) |
(1,932 |
) |
(1,613 |
) | |||
|
Cash paid for purchases of linefill and base gas |
|
(133 |
) |
(161 |
) |
(122 |
) | |||
|
Proceeds from sales of assets |
|
5 |
|
28 |
|
200 |
| |||
|
Other investing activities |
|
35 |
|
25 |
|
43 |
| |||
|
Net cash used in investing activities |
|
(2,530 |
) |
(3,296 |
) |
(1,653 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Net borrowings/(repayments) under PAA senior secured hedged inventory facility (Note 9) |
|
300 |
|
— |
|
(660 |
) | |||
|
Net repayments under PAA senior unsecured revolving credit facility (Note 9) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(92 |
) | |||
|
Net repayments under PNG credit agreement |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(382 |
) | |||
|
Net borrowings/(repayments) under PAA commercial paper program (Note 9) |
|
631 |
|
(366 |
) |
1,110 |
| |||
|
Net borrowings/(repayments) under AAP senior secured revolving credit facility (Note 9) |
|
(27 |
) |
21 |
|
15 |
| |||
|
Proceeds from AAP term loan (Note 9) |
|
50 |
|
— |
|
300 |
| |||
|
Proceeds from the issuance of PAA senior notes (Note 9) |
|
998 |
|
2,595 |
|
699 |
| |||
|
Repayments of PAA senior notes (Note 9) |
|
(549 |
) |
— |
|
(250 |
) | |||
|
Net proceeds from the sale of common units by subsidiaries (Note 10) |
|
1,099 |
|
848 |
|
505 |
| |||
|
Contributions from noncontrolling interests related to the sale of common units by subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
— |
|
10 |
| |||
|
Proceeds received from initial public offering (Note 10) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2,825 |
| |||
|
Distribution of proceeds received from initial public offering (Note 10) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(2,825 |
) | |||
|
Distributions paid to Class A shareholders (Note 10) |
|
(195 |
) |
(91 |
) |
— |
| |||
|
Distributions paid to members (Note 10) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(6 |
) | |||
|
Distributions paid to noncontrolling interests (Note 10) |
|
(1,465 |
) |
(1,305 |
) |
(1,494 |
) | |||
|
Other financing activities |
|
(15 |
) |
(30 |
) |
(29 |
) | |||
|
Net cash provided by/(used in) financing activities |
|
827 |
|
1,672 |
|
(274 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Effect of translation adjustment on cash |
|
(4 |
) |
(3 |
) |
(3 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Net increase/(decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
|
(374 |
) |
361 |
|
18 |
| |||
|
Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of period |
|
404 |
|
43 |
|
25 |
| |||
|
Cash and cash equivalents, end of period |
|
$ |
30 |
|
$ |
404 |
|
$ |
43 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Cash paid for: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Interest, net of amounts capitalized |
|
$ |
405 |
|
$ |
344 |
|
$ |
312 |
|
|
Income taxes, net of amounts refunded |
|
$ |
50 |
|
$ |
159 |
|
$ |
37 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P. AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN PARTNERS’ CAPITAL/MEMBERS’ EQUITY
(in millions)
|
|
|
Members’ Equity |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Total |
| |||||
|
|
|
(Excluding |
|
Partners’ Capital |
|
|
|
Partners’ |
| |||||||
|
|
|
Noncontrolling |
|
(Excluding Noncontrolling Interests) |
|
Noncontrolling |
|
Capital/ |
| |||||||
|
|
|
Interests) |
|
Class A |
|
Class B |
|
Interests |
|
Members’ Equity |
| |||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2012 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
6,968 |
|
$ |
6,968 |
|
|
Net income |
|
3 |
|
12 |
|
— |
|
1,359 |
|
1,374 |
| |||||
|
Distributions |
|
(6 |
) |
— |
|
— |
|
(1,494 |
) |
(1,500 |
) | |||||
|
Transfer of ownership interest in connection with reorganization prior to initial public offering (Note 10) |
|
3 |
|
(51 |
) |
— |
|
48 |
|
— |
| |||||
|
Issuance of Class A shares to the public, net of offering and other costs (Note 10) |
|
— |
|
2,825 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
2,825 |
| |||||
|
Distribution of net proceeds of initial public offering (Note 10) |
|
|
|
(2,825 |
) |
— |
|
— |
|
(2,825 |
) | |||||
|
Deferred tax asset (Note 12) |
|
— |
|
1,076 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1,076 |
| |||||
|
Change in ownership interest in connection with Exchange Right exercises (Note 10) |
|
|
|
(1 |
) |
|
|
1 |
|
— |
| |||||
|
Sale of common units by subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
508 |
|
508 |
| |||||
|
Other comprehensive loss |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
(176 |
) |
(176 |
) | |||||
|
Other |
|
— |
|
(1 |
) |
— |
|
30 |
|
29 |
| |||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2013 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
1,035 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
7,244 |
|
$ |
8,279 |
|
|
Net income |
|
— |
|
70 |
|
— |
|
1,258 |
|
1,328 |
| |||||
|
Distributions |
|
— |
|
(91 |
) |
— |
|
(1,305 |
) |
(1,396 |
) | |||||
|
Deferred tax asset (Note 12) |
|
— |
|
675 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
675 |
| |||||
|
Change in ownership interest in connection with Exchange Right exercises (Note 10) |
|
— |
|
(31 |
) |
— |
|
31 |
|
— |
| |||||
|
Sale of common units by subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
848 |
|
848 |
| |||||
|
Other comprehensive loss |
|
— |
|
(2 |
) |
— |
|
(368 |
) |
(370 |
) | |||||
|
Other |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
16 |
|
17 |
| |||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
1,657 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
7,724 |
|
$ |
9,381 |
|
|
Net income |
|
— |
|
118 |
|
— |
|
691 |
|
809 |
| |||||
|
Distributions |
|
— |
|
(195 |
) |
— |
|
(1,465 |
) |
(1,660 |
) | |||||
|
Deferred tax asset (Note 12) |
|
— |
|
205 |
|
— |
|
— |
|
205 |
| |||||
|
Change in ownership interest in connection with Exchange Right exercises (Note 10) |
|
— |
|
(6 |
) |
— |
|
6 |
|
— |
| |||||
|
Sale of common units by subsidiaries |
|
— |
|
— |
|
— |
|
1,099 |
|
1,099 |
| |||||
|
Other comprehensive loss |
|
— |
|
(5 |
) |
— |
|
(609 |
) |
(614 |
) | |||||
|
Other |
|
— |
|
(12 |
) |
— |
|
26 |
|
14 |
| |||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
1,762 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
7,472 |
|
$ |
9,234 |
|
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
PLAINS GP HOLDINGS, L.P. AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO THE CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1—Organization and Basis of Consolidation and Presentation
Organization
Plains GP Holdings, L.P. (“PAGP”) is a Delaware limited partnership formed on July 17, 2013 to own an interest in the general partner and incentive distribution rights (“IDRs”) of Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. (“PAA”), a publicly traded Delaware limited partnership. PAGP has elected to be treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes. As used in this Form 10-K and unless the context indicates otherwise (taking into account the fact that PAGP has no operating activities apart from those conducted by PAA and its subsidiaries), the terms “Partnership,” “we,” “us,” “our,” “ours” and similar terms refer to PAGP and its subsidiaries.
We completed our initial public offering (“IPO”) on October 21, 2013. As of December 31, 2015, our sole assets consisted of (i) a 100% managing member interest in Plains All American GP LLC (“GP LLC”) and (ii) an approximate 38% limited partner interest in Plains AAP, L.P. (“AAP”) through our ownership of 229,278,980 Class A units of AAP (“AAP units”). See Note 10 for additional discussion of our IPO and transactions involving our ownership interests in AAP and GP LLC. GP LLC is a Delaware limited liability company that holds the general partner interest in AAP. AAP is a Delaware limited partnership that directly owns all of PAA’s IDRs and indirectly owns the 2% general partner interest in PAA. AAP is the sole member of PAA GP LLC (“PAA GP”), a Delaware limited liability company that directly holds the 2% general partner interest in PAA. Plains GP Holdings LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, is our general partner.
GP LLC manages the business and affairs of PAA and AAP. Except for certain matters relating to PAA that require the approval of the limited partners of PAA, and certain matters relating to AAP that require the approval of the limited partners of AAP or of us as the sole member of GP LLC, either pursuant to the governing documents of PAA, AAP or GP LLC, or as may be required by non-waivable provisions of applicable law, GP LLC has full and complete authority, power and discretion to manage and control the business, affairs and property of PAA and AAP, to make all decisions regarding those matters and to perform any and all other acts or activities customary or incident to the management of PAA and AAP’s business, including the execution of contracts and management of litigation. GP LLC employs all domestic officers and personnel involved in the operation and management of PAA and AAP. PAA’s Canadian officers and personnel are employed by Plains Midstream Canada ULC (“PMC”).
PAA is a publicly traded master limited partnership that owns and operates midstream energy infrastructure and provides logistics services for crude oil, natural gas liquids (“NGL”), natural gas and refined products. PAA owns an extensive network of pipeline transportation, terminalling, storage and gathering assets in key crude oil and NGL producing basins and transportation corridors and at major market hubs in the United States and Canada. Our business activities are conducted through three operating segments: Transportation, Facilities and Supply and Logistics. See Note 18 for further discussion of our operating segments.
Definitions
Additional defined terms are used in the following notes and shall have the meanings indicated below:
|
AOCI |
|
= |
|
Accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) |
|
Bcf |
|
= |
|
Billion cubic feet |
|
Btu |
|
= |
|
British thermal unit |
|
CAD |
|
= |
|
Canadian dollar |
|
CERCLA |
|
= |
|
Federal Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act, as amended |
|
DERs |
|
= |
|
Distribution equivalent rights |
|
EBITDA |
|
= |
|
Earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization |
|
EPA |
|
= |
|
United States Environmental Protection Agency |
|
FASB |
|
= |
|
Financial Accounting Standards Board |
|
GAAP |
|
= |
|
Generally accepted accounting principles in the United States |
|
ICE |
|
= |
|
Intercontinental Exchange |
|
IDR |
|
= |
|
Incentive distribution right |
|
IPO |
|
= |
|
Initial public offering |
|
LTIP |
|
= |
|
Long-term incentive plan |
|
Mcf |
|
= |
|
Thousand cubic feet |
|
MQD |
|
= |
|
Minimum quarterly distribution |
|
NGL |
|
= |
|
Natural gas liquids, including ethane, propane and butane |
|
NYMEX |
|
= |
|
New York Mercantile Exchange |
|
NYSE |
|
= |
|
New York Stock Exchange |
|
Oxy |
|
= |
|
Occidental Petroleum Corporation or its subsidiaries |
|
PLA |
|
= |
|
Pipeline loss allowance |
|
PNG |
|
= |
|
PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P. |
|
RCRA |
|
= |
|
Federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, as amended |
|
USD |
|
= |
|
United States dollar |
|
WTI |
|
= |
|
West Texas Intermediate |
Basis of Consolidation and Presentation
The accompanying financial statements and related notes present and discuss our consolidated financial position as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, and the consolidated results of our operations, cash flows, changes in partners’ capital/members’ equity, comprehensive income and changes in accumulated other comprehensive income/(loss) for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013. All significant intercompany transactions have been eliminated in consolidation, and certain reclassifications have been made to information from previous years to conform to the current presentation. These reclassifications do not affect net income attributable to PAGP. The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of PAGP and all of its wholly owned subsidiaries and those entities that it controls. Under GAAP, we consolidate PAA, AAP and GP LLC. Amounts associated with the interests in these entities not owned by us are reflected in our results of operations as net income attributable to noncontrolling interests and on our balance sheet in the partners’ capital section as noncontrolling interests. Investments in entities over which we have significant influence but not control are accounted for by the equity method.
The Consolidated Statement of Changes in Partners’ Capital for the period ended December 31, 2015 includes an adjustment of $19 million to correct the misclassifications in prior periods of amounts allocated between our Class A shareholders and noncontrolling interests. We have assessed the impact of the misclassification on current and prior periods and have determined the impacts are not material in any period.
For periods prior to our IPO, the accompanying consolidated financial statements reflect the financial statements of GP LLC, the predecessor of PAGP, and are based on the historical ownership percentages of GP LLC and AAP. These financial statements, to the extent they relate to periods prior to our IPO, have been prepared from the separate financial records maintained by GP LLC and may not necessarily be indicative of the actual results of operations that might have occurred if PAGP had operated separately during those periods.
Subsequent events have been evaluated through the financial statements issuance date and have been included in the following footnotes where applicable.
PNG Merger
On December 31, 2013, with the approval of PNG’s common unitholders, PNG became PAA’s wholly-owned subsidiary through a unit-for-unit exchange (referred to herein as the “PNG Merger”). PAA issued 0.445 PAA common units for each outstanding PNG common unit (the “Merger Exchange Ratio”) held by unitholders other than PAA, plus cash in lieu of any fractional PAA common units otherwise issuable in the PNG Merger. Also in conjunction with the PNG Merger, AAP agreed to reduce the amount of its incentive distributions. See Note 10 for further discussion. Since we historically consolidated PNG for financial reporting purposes, the PNG Merger did not change the basis of consolidation of our historical financial statements.
Note 2—Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. We make significant estimates with respect to (i) purchases and sales accruals, (ii) estimated fair value of assets and liabilities acquired and identification of associated goodwill and intangible assets, (iii) fair value of derivatives, (iv) accruals and contingent liabilities, (v) equity-indexed compensation plan accruals, (vi) property and equipment, depreciation expense and asset retirement obligations, (vii) allowance for doubtful accounts and (viii) inventory valuations. Although we believe these estimates are reasonable, actual results could differ from these estimates.
Revenue Recognition
Supply and Logistics Segment Revenues. Revenues from sales of crude oil, NGL and natural gas are recognized at the time title to the product sold transfers to the purchaser, which occurs upon delivery of the product to the purchaser or its designee. Sales of crude oil and NGL consist of outright sales contracts. Inventory purchases and sales under buy/sell transactions are treated as inventory exchanges. The sales under these exchanges are netted to zero in Supply and Logistics segment revenues in our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Additionally, we may utilize derivatives in connection with the transactions described above. For commodity derivatives that are designated as cash flow hedges, derivative gains and losses are deferred in AOCI and recognized in revenues in the periods during which the underlying physical hedged transaction impacts earnings. Also, the ineffective portion of the change in fair value of cash flow hedges is recognized in revenues each period along with the change in fair value of derivatives that do not qualify for or are not designated for hedge accounting.
Transportation Segment Revenues. Our Transportation segment operations generally consist of fee-based activities associated with transporting crude oil and NGL on pipelines, gathering systems, trucks and barges. Revenues from pipeline tariffs and fees are associated with the transportation of crude oil and NGL at a published tariff, as well as revenues associated with agreements for committed space on various assets. Tariff revenues are recognized either at the point of delivery or at the point of receipt pursuant to specifications outlined in the regulated and non-regulated tariffs. Revenues associated with fees are recognized in the month to which the fee applies. The majority of our pipeline tariff and fee revenues are based on actual volumes and rates. As is common in the pipeline transportation industry, our tariffs incorporate a loss allowance factor that is intended to offset losses due to evaporation, measurement and other losses in transit. We value the variance of allowance volumes to actual losses at the estimated net realizable value (including the impact of gains and losses from derivative related activities) at the time the variance occurred and the result is recorded as either an increase or decrease to tariff revenues.
Facilities Segment Revenues. Our Facilities segment operations generally consist of fee-based activities associated with providing storage, terminalling and throughput services for crude oil, refined products, NGL and natural gas, as well as NGL fractionation and isomerization services and natural gas and condensate processing services. Revenues generated in this segment include (i) fees that are generated from storage capacity agreements, (ii) terminal throughput fees that are generated when we receive crude oil, refined products or NGL from one connecting source and deliver the applicable product to another connecting carrier, (iii) loading and unloading fees at our rail terminals, (iv) fees from NGL fractionation and isomerization, (v) fees from natural gas and condensate processing services and (vi) fees associated with natural gas park and loan activities, interruptible storage services and wheeling and balancing services.
We generate revenue through a combination of month-to-month and multi-year agreements and processing arrangements. Storage fees resulting from short-term and long-term contracts are typically recognized in revenue ratably over the term of the contract regardless of the actual storage capacity utilized. Terminal fees (including throughput and rail fees) are recognized as the crude oil, NGL or refined product enters or exits the terminal and is received from or delivered to the connecting carrier or third-party terminal, as applicable. Hub service fees are recognized in the period the natural gas moves across our header system. Fees from NGL fractionation, isomerization services and gas processing services are recognized in the period when the services are performed.
Minimum Volume Commitments. We have certain agreements that require counterparties to deliver, transport or throughput a minimum volume over an agreed upon period. Some of these agreements include make-up rights if the minimum volume is not met. At December 31, 2015, counterparty deficiencies associated with agreements that include minimum volume commitments totaled $33 million.
We record a receivable from the counterparty in the period that services are provided or when the transaction occurs, including amounts for deficiency obligations from counterparties associated with minimum volume commitments. If a counterparty has a make-up right associated with a deficiency, we defer the revenue attributable to the counterparty make-up right and subsequently recognize the revenue at the earlier of when the deficiency volume is delivered or shipped, when the make-up right expires or when it is determined that the counterparty’s ability to utilize the make-up right is remote.
As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, we had deferred revenue associated with minimum volume commitments of $17 million and $4 million, respectively. In addition to the amounts recorded as deferred revenue, as of December 31, 2015, there was $16 million of accrued deficiencies for which the counterparties had not met their contractual minimum commitments, but we had not yet billed or collected such amounts.
Purchases and Related Costs
Purchases and related costs include (i) the cost of crude oil, NGL and natural gas obtained in outright purchases, (ii) fees incurred for third-party storage and transportation, whether by pipeline, truck, rail, ship or barge, (iii) interest cost attributable to borrowings for inventory stored in a contango market and (iv) performance-related bonus costs. These costs are recognized when incurred except in the case of products purchased, which are recognized at the time title transfers to us. Purchases that are part of exchanges under buy/sell transactions are netted with the related sales, with any margin presented in “Purchases and related costs” in our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
Field Operating Costs and General and Administrative Expenses
Field operating costs consist of various field operating expenses, including fuel and power costs (including the impact of gains and losses from derivative related activities), telecommunications, payroll and benefit costs (including equity-indexed compensation expense) for truck drivers and field and other operations personnel, third-party trucking transportation costs for our U.S. crude oil operations, maintenance and integrity management costs, regulatory compliance, environmental remediation, insurance, vehicle leases, and property taxes. General and administrative expenses consist primarily of payroll and benefit costs (including equity-indexed compensation expense), certain information systems and legal costs, office rent, contract and consultant costs and audit and tax fees.
Foreign Currency Transactions/Translation
Certain of our subsidiaries use the Canadian dollar as their functional currency. Assets and liabilities of subsidiaries with a Canadian dollar functional currency are translated at period-end rates of exchange, and revenues and expenses are translated at average exchange rates prevailing for each month. The resulting translation adjustments are made directly to a separate component of other comprehensive income, which is reflected in Partners’ Capital on our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Certain of our subsidiaries also enter into transactions and have monetary assets and liabilities that are denominated in a currency other than the entities’ respective functional currencies. Gains and losses from the revaluation of foreign currency transactions and monetary assets and liabilities are included in the Consolidated Statements of Operations. The revaluation of foreign currency transactions and monetary assets and liabilities resulted in a net gain of $21 million for the year ended December 31, 2015, a net loss of $13 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 and a net gain of $1 million for the year ended December 31, 2013.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
Cash and cash equivalents consist of all unrestricted demand deposits and funds invested in highly liquid instruments with original maturities of three months or less and typically exceed federally insured limits. We periodically assess the financial condition of the institutions where these funds are held and believe that our credit risk is minimal.
In accordance with our policy, outstanding checks are classified as accounts payable rather than negative cash. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, accounts payable included $60 million and $94 million, respectively, of outstanding checks that were reclassified from cash and cash equivalents.
Accounts Receivable
Our accounts receivable are primarily from purchasers and shippers of crude oil and, to a lesser extent, purchasers of NGL and natural gas. These purchasers include, but are not limited to, refiners, producers, marketing and trading companies and financial institutions that are active in the physical and financial commodity markets. The majority of our accounts receivable relate to our crude oil supply and logistics activities that can generally be described as high volume and low margin activities, in many cases involving exchanges of crude oil volumes.
The sustained decrease in commodity prices since late 2014 has caused liquidity issues throughout the energy industry, which in turn has increased the potential credit risks associated with certain counterparties with which we do business. To mitigate credit risk related to our accounts receivable, we utilize a rigorous credit review process. We closely monitor market conditions to make a determination with respect to the amount, if any, of open credit to be extended to any given customer and the form and amount of financial performance assurances we require. Such financial assurances are commonly provided to us in the form of advance cash payments, standby letters of credit or parental guarantees. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, we had received $88 million and $180 million, respectively, of advance cash payments from third parties to mitigate credit risk. We also received $36 million and $198 million as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively, of standby letters of credit to support obligations due from third parties, a portion of which applies to future business. The decrease in standby letters of credit and advance cash payments from third parties as of December 31, 2015 compared to December 31, 2014 was largely due to a decrease in exposure to various customers requiring letters of credit. Additionally, in an effort to mitigate credit risk, a significant portion of our transactions with counterparties are settled on a net-cash basis. Furthermore, we also enter into netting agreements (contractual agreements that allow us to offset receivables and payables with those counterparties against each other on our balance sheet) for a majority of such arrangements.
We review all outstanding accounts receivable balances on a monthly basis and record a reserve for amounts that we expect will not be fully recovered. We do not apply actual balances against the reserve until we have exhausted substantially all collection efforts. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, substantially all of our trade accounts receivable (net of allowance for doubtful accounts) were less than 30 days past their scheduled invoice date. Our allowance for doubtful accounts receivable totaled $4 million at both December 31, 2015 and 2014. Although we consider our allowance for doubtful accounts receivable to be adequate, actual amounts could vary significantly from estimated amounts.
Noncontrolling Interests
We account for noncontrolling interests in subsidiaries in accordance with FASB guidance, which requires all entities to report noncontrolling interests in subsidiaries as a component of equity in the consolidated financial statements. Noncontrolling interest represents the portion of assets and liabilities in a consolidated subsidiary that is owned by a third-party. See Note 10 for additional discussion regarding our noncontrolling interests.
Asset Retirement Obligations
FASB guidance establishes accounting requirements for retirement obligations associated with tangible long-lived assets, including estimates related to (i) the time of the liability recognition, (ii) initial measurement of the liability, (iii) allocation of asset retirement cost to expense, (iv) subsequent measurement of the liability and (v) financial statement disclosures. FASB guidance also requires that the cost for asset retirement should be capitalized as part of the cost of the related long-lived asset and subsequently allocated to expense using a systematic and rational method.
Some of our assets, primarily related to our Transportation and Facilities segments, have contractual or regulatory obligations to perform remediation and, in some instances, dismantlement and removal activities when the assets are abandoned. These obligations include varying levels of activity including disconnecting inactive assets from active assets, cleaning and purging assets, and in some cases, completely removing the assets and returning the land to its original state. These assets have been in existence for many years and with regular maintenance will continue to be in service for many years to come. It is not possible to predict when demand for these transportation or storage services will cease, and we do not believe that such demand will cease for the foreseeable future. Accordingly, we believe the date when these assets will be abandoned is indeterminate. With no reasonably determinable abandonment date, we cannot reasonably estimate the fair value of the associated asset retirement obligations. We will record asset retirement obligations for these assets in the period in which sufficient information becomes available for us to reasonably determine the settlement dates.
A small portion of our contractual or regulatory obligations is related to assets that are inactive or that we plan to take out of service and, although the ultimate timing and costs to settle these obligations are not known with certainty, we have recorded a reasonable estimate of these obligations. We have estimated that the fair value of these obligations was $35 million and $36 million, respectively, at December 31, 2015 and 2014.
Fair Value Measurements
Financial assets and liabilities are classified in their entirety based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement. Our assessment of the significance of a particular input to the fair value measurement requires judgment, which affects the placement of assets and liabilities within the fair value hierarchy levels. The determination of the fair values includes not only the credit standing of the counterparties involved and the impact of credit enhancements (such as cash deposits and letters of credit) but also the impact of our nonperformance risk on our liabilities. The fair value of our commodity derivatives, interest rate derivatives and foreign currency derivatives includes adjustments for credit risk. Our credit adjustment methodology uses market observable inputs and requires judgment. There were no changes to any of our valuation techniques during the period. See Note 11 for further discussion.
Other Significant Accounting Policies
See the respective footnotes for our accounting policies regarding (i) net income per Class A share, (ii) inventory, linefill and base gas and long-term inventory, (iii) property and equipment, (iv) goodwill, (v) investments in unconsolidated entities, (vi) other long-term assets, net, (vii) derivatives and risk management activities, (viii) income taxes, (ix) equity-indexed compensation and (x) legal and environmental matters.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In November 2015, the FASB issued guidance to simplify the balance sheet classification of deferred taxes by requiring that deferred tax liabilities and assets be classified as noncurrent. This guidance is effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, with early adoption permitted, and may be applied prospectively or retrospectively to all periods presented. We early adopted this guidance during the fourth quarter of 2015, with prospective application. Prior period amounts presented have not been retrospectively adjusted. Our adoption did not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In September 2015, the FASB issued guidance to simplify the accounting for measurement-period adjustments for provisional amounts recognized in a business combination by eliminating the requirement for an acquirer to retrospectively account for measurement-period adjustments. Under the updated guidance, the acquirer must recognize adjustments in the reporting period in which the adjustment amounts are determined and the effect on earnings as a result of the change to the provisional amounts must be calculated as if the accounting had been completed at the acquisition date. This guidance will become effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2015, with early adoption permitted, and must be applied prospectively. We adopted this guidance on January 1, 2016. Our adoption did not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In July 2015, the FASB issued guidance to simplify the measurement of inventory. This updated guidance requires entities to measure inventory at the lower of cost and net realizable value; however, inventory measured using last-in, first-out and the retail inventory method is unchanged by this update. This guidance will become effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016, with prospective application required. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period. We expect to adopt this guidance on January 1, 2017, and we do not anticipate that our adoption will have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In April 2015, the FASB issued guidance to simplify the presentation of debt issuance costs in entities’ financial statements. This updated guidance requires entities to present certain debt issuance costs as a direct deduction from the related debt liability, consistent with debt discounts. Additionally, amortization of debt issuance costs is required to be reported as interest expense. This guidance became effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2015, with retrospective application required for all prior periods presented and early adoption permitted. We early adopted this guidance during the fourth quarter of 2015 and have retroactively adjusted all prior period information presented in this Form 10-K. Our adoption of this guidance resulted in the reclassification of $60 million of unamortized debt issuance costs from “Other long-term assets, net” to “Senior notes, net of unamortized discounts and debt issuance costs” and “Other long-term debt, net of unamortized discounts” in our accompanying Consolidated Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2014. Additionally, for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, we reclassified $8 million and $10 million, respectively, from “Depreciation and amortization” to “Interest expense, net” in our accompanying Consolidated Statement of Operations related to the presentation of the amortization of debt issuance costs. Our adoption of this guidance did not impact our Consolidated Statements of Comprehensive Income, Cash Flows or Changes in Partners’ Capital.
In February 2015, the FASB issued guidance that revises the analysis that a reporting entity must perform to determine whether it should consolidate certain types of legal entities. All legal entities are subject to reevaluation under the revised consolidation model. Among other things, this guidance (i) modifies the evaluation of whether limited partnerships and similar legal entities are variable interest entities or voting interest entities, (ii) eliminates the presumption that a general partner should consolidate a limited partnership and (iii) affects the consolidation analysis of reporting entities that are involved with variable interest entities, particularly those that have fee arrangements and related party relationships. This guidance will become effective for interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2015. Early adoption is permitted, including adoption in an interim period. We adopted this guidance on January 1, 2016. Our adoption did not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
In May 2014, the FASB issued guidance regarding the recognition of revenue from contracts with customers with the underlying principle that an entity will recognize revenue to reflect amounts expected to be received in exchange for the provision of goods and services to customers upon the transfer of those goods or services. The guidance also requires additional disclosures about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and the related cash flows. This guidance can be adopted either with a full retrospective approach or a modified retrospective approach with a cumulative-effect adjustment as of the date of adoption. In August 2015, the FASB issued guidance deferring the effective date to interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2017. Therefore, we expect to adopt this guidance on January 1, 2018, and we are currently evaluating which transition approach to apply and the impact that adopting this guidance will have on our financial position, results of operations and cash flows.
In April 2014, the FASB issued guidance that modifies the criteria under which assets to be disposed of are evaluated to determine if such assets qualify as a discontinued operation and requires new disclosures for both discontinued operations and certain other disposals that do not meet the definition of a discontinued operation. This guidance is effective prospectively for annual and interim reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2014. We adopted this guidance on January 1, 2015. Our adoption did not have a material impact on our financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Note 3—Net Income Per Class A Share
Basic net income per Class A share is determined by dividing net income attributable to PAGP by the weighted-average number of Class A shares outstanding during the period. Class B shares do not share in the earnings of the Partnership. Accordingly, basic and diluted net income per Class B share has not been presented.
Diluted net income per Class A share is determined by dividing net income attributable to PAGP by the diluted weighted-average number of Class A shares outstanding during the period. For purposes of calculating diluted net income per Class A share, both the net income attributable to PAGP and the diluted weighted-average number of Class A shares outstanding consider the impact of possible future exchanges of (i) AAP units and the associated Class B shares into our Class A shares and (ii) certain Class B units of AAP (referred to herein as “AAP Management Units”) into our Class A shares. In addition, the calculation of the diluted weighted average number of Class A shares outstanding considers the effect of potentially dilutive awards under the Plains GP Holdings, L.P. Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “PAGP LTIP”).
All AAP Management Units that have satisfied the applicable performance conditions are considered potentially dilutive. Exchanges of potentially dilutive AAP units and AAP Management Units are assumed to have occurred at the beginning of the period and the incremental income attributable to PAGP resulting from the assumed exchanges is representative of the incremental income that would have been attributable to PAGP if the assumed exchanges occurred on that date. See Note 10 for information regarding exchanges of AAP units and AAP Management Units. PAGP LTIP awards that are deemed to be dilutive are reduced by a hypothetical share repurchase based on the remaining unamortized fair value, as prescribed by the treasury stock method in guidance issued by the FASB. See Note 15 for a complete discussion of PAGP LTIP awards.
For the year ended December 31, 2015, the possible exchange of any AAP units and certain AAP Management Units would have had an antidilutive effect on basic net income per Class A share. For the year ended December 31, 2014, the possible exchange of any AAP units and certain AAP Management Units would have had a dilutive effect on basic net income per Class A share. For the same periods, our PAGP LTIP awards were dilutive; however, there were less than 0.1 million dilutive LTIP awards for each period, which did not change the presentation of weighted average Class A shares outstanding or net income per Class A share. For the year ended December 31, 2013, the possible exchange of any AAP units and certain AAP Management Units would have had an antidilutive effect on net income per Class A share. The following tables illustrate the calculation of basic and diluted net income per Class A share for the periods indicated (in millions, except per share data):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
Basic Net Income per Class A Share |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Net income attributable to PAGP |
|
$ |
118 |
|
$ |
70 |
|
|
Basic weighted average Class A shares outstanding |
|
222 |
|
145 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Basic net income per Class A share |
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
$ |
0.48 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Diluted Net Income per Class A Share |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Net income attributable to PAGP |
|
$ |
118 |
|
$ |
70 |
|
|
Incremental net income attributable to PAGP resulting from assumed exchange of AAP units and AAP Management Units |
|
— |
|
235 |
| ||
|
Net income attributable to PAGP including incremental net income from assumed exchange of AAP units and AAP Management Units |
|
$ |
118 |
|
$ |
305 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Basic weighted average Class A shares outstanding |
|
222 |
|
145 |
| ||
|
Dilutive shares resulting from assumed exchange of AAP units and AAP Management Units |
|
— |
|
505 |
| ||
|
Diluted weighted average Class A shares outstanding |
|
222 |
|
650 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Diluted net income per Class A share |
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
$ |
0.47 |
|
|
|
|
October 21, 2013 |
| |
|
Basic and Diluted Net Income per Class A Share |
|
|
| |
|
Net income attributable to PAGP |
|
$ |
15 |
|
|
Less: Net income attributable to PAGP for the period from January 1, 2013 to October 20, 2013 |
|
(3 |
) | |
|
Net income attributable to PAGP for the period from October 21, 2013 to December 31, 2013 |
|
$ |
12 |
|
|
Basic and diluted weighted average Class A shares outstanding (1) |
|
132 |
| |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Basic and diluted net income per Class A share |
|
$ |
0.10 |
|
(1) Basic weighted average Class A shares outstanding is weighted for the period following the closing of our IPO. Approximately 128 million Class A shares were issued upon closing of our IPO with approximately 4 million additional Class A shares issued through the exercise in October 2013 of an over-allotment option. Subsequent conversions of AAP units were immaterial.
Note 4—Inventory, Linefill and Base Gas and Long-term Inventory
Inventory primarily consists of crude oil, NGL and natural gas in pipelines, storage facilities and railcars that are valued at the lower of cost or market, with cost determined using an average cost method within specific inventory pools. At the end of each reporting period, we assess the carrying value of our inventory and make any adjustments necessary to reduce the carrying value to the applicable net realizable value. Any resulting adjustments are a component of “Purchases and related costs” on our accompanying Consolidated Statements of Operations. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, we recorded charges of $117 million, $289 million and $7 million, respectively, related to the writedown of our crude oil, NGL and natural gas inventory due to declines in prices. In addition, the charges recorded during the year ended December 31, 2014 included the writedown of our natural gas inventory that was purchased in conjunction with managing natural gas storage deliverability requirements during the extended period of severe cold weather in the first quarter of 2014. A portion of these adjustments was offset by the recognition of gains on derivative instruments being utilized to hedge the future sales of our crude oil and NGL inventory. Substantially all of such gains were recorded to “Supply and Logistics segment revenues” in our accompanying Consolidated Statement of Operations. See Note 11 for discussion of our derivative and risk management activities.
Linefill and base gas and minimum working inventory requirements in assets we own are recorded at historical cost and consist of crude oil, NGL and natural gas. We classify as linefill or base gas (i) our proportionate share of barrels used to fill a pipeline that we own such that when an incremental barrel is pumped into or enters a pipeline it forces product out at another location, (ii) barrels that represent the minimum working requirements in tanks and caverns that we own and (iii) natural gas required to maintain the minimum operating pressure of natural gas storage facilities we own. Linefill and base gas carrying amounts are reviewed for impairment in accordance with FASB guidance with respect to accounting for the impairment or disposal of long-lived assets. Carrying amounts that are not expected to be recoverable through future cash flows are written down to estimated fair value. See Note 5 for further discussion regarding impairment of long-lived assets. During 2015, 2014 and 2013, we did not recognize any impairments of linefill and base gas, but we did recognize gains of less than $1 million, $8 million and $7 million, respectively, on the sale of linefill and base gas for proceeds of $1 million, $24 million and $40 million, respectively.
Minimum working inventory requirements in third-party assets and other working inventory in our assets that are needed for our commercial operations are included within specific inventory pools in inventory (a current asset) in determining the average cost of operating inventory. At the end of each period, we reclassify the inventory not expected to be liquidated within the succeeding twelve months out of inventory, at the average cost of the applicable inventory pools, and into long-term inventory, which is reflected as a separate line item in “Other assets” on our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Inventory, linefill and base gas and long-term inventory consisted of the following as of the dates indicated (barrels and natural gas volumes in thousands and carrying value in millions):
|
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
December 31, 2014 |
| ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Volumes |
|
Unit of |
|
Carrying |
|
Price/ |
|
Volumes |
|
Unit of |
|
Carrying |
|
Price/ |
| ||||
|
Inventory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Crude oil |
|
16,345 |
|
barrels |
|
$ |
608 |
|
$ |
37.20 |
|
6,465 |
|
barrels |
|
$ |
304 |
|
$ |
47.02 |
|
|
NGL |
|
13,907 |
|
barrels |
|
218 |
|
$ |
15.68 |
|
13,553 |
|
barrels |
|
454 |
|
$ |
33.50 |
| ||
|
Natural gas |
|
22,080 |
|
Mcf |
|
53 |
|
$ |
2.40 |
|
32,317 |
|
Mcf |
|
102 |
|
$ |
3.16 |
| ||
|
Other |
|
N/A |
|
|
|
37 |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
|
|
31 |
|
N/A |
| ||||
|
Inventory subtotal |
|
|
|
|
|
916 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
891 |
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Linefill and base gas |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Crude oil |
|
12,298 |
|
barrels |
|
713 |
|
$ |
57.98 |
|
11,810 |
|
barrels |
|
744 |
|
$ |
63.00 |
| ||
|
NGL |
|
1,348 |
|
barrels |
|
44 |
|
$ |
32.64 |
|
1,212 |
|
barrels |
|
52 |
|
$ |
42.90 |
| ||
|
Natural gas |
|
30,812 |
|
Mcf |
|
141 |
|
$ |
4.58 |
|
28,612 |
|
Mcf |
|
134 |
|
$ |
4.68 |
| ||
|
Linefill and base gas subtotal |
|
|
|
|
|
898 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
930 |
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Long-term inventory |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Crude oil |
|
3,417 |
|
barrels |
|
106 |
|
$ |
31.02 |
|
2,582 |
|
barrels |
|
136 |
|
$ |
52.67 |
| ||
|
NGL |
|
1,652 |
|
barrels |
|
23 |
|
$ |
13.92 |
|
1,681 |
|
barrels |
|
50 |
|
$ |
29.74 |
| ||
|
Long-term inventory subtotal |
|
|
|
|
|
129 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
186 |
|
|
| ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Total |
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
1,943 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
2,007 |
|
|
| ||
(1) Price per unit of measure is comprised of a weighted average associated with various grades, qualities and locations. Accordingly, these prices may not coincide with any published benchmarks for such products.
In accordance with our capitalization policy, expenditures made to expand the existing operating and/or earnings capacity of our assets are capitalized. We also capitalize certain costs directly related to the construction of such assets, including related internal labor costs, engineering costs and interest costs. For the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, capitalized interest was $57 million, $48 million and $38 million, respectively. We also capitalize expenditures for the replacement of partially or fully depreciated assets in order to maintain the operating and/or earnings capacity of our existing assets. Repair and maintenance expenditures incurred in order to maintain the day to day operation of our existing assets are expensed as incurred.
Property and equipment, net is stated at cost and consisted of the following as of the dates indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
Estimated Useful |
|
December 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
Lives (Years) |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
Pipelines and related facilities |
|
10 - 70 |
|
$ |
8,436 |
|
$ |
7,044 |
|
|
Storage, terminal and rail facilities |
|
30 - 70 |
|
5,012 |
|
4,853 |
| ||
|
Trucking equipment and other |
|
3 - 15 |
|
392 |
|
198 |
| ||
|
Construction in progress |
|
- |
|
1,217 |
|
1,545 |
| ||
|
Office property and equipment |
|
2 - 50 |
|
196 |
|
156 |
| ||
|
Land and other |
|
N/A |
|
442 |
|
423 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
15,695 |
|
14,219 |
| ||
|
Accumulated depreciation |
|
|
|
(2,202 |
) |
(1,927 |
) | ||
|
Property and equipment, net |
|
|
|
$ |
13,493 |
|
$ |
12,292 |
|
We calculate our depreciation using the straight-line method, based on estimated useful lives and salvage values of our assets. Depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 was $381 million, $321 million and $262 million, respectively. We also classify gains and losses on sales of assets and asset impairments as a component of “Depreciation and amortization” in our Consolidated Statements of Operations. See “Impairment of Long-Lived Assets” below for a discussion of our policy for the recognition of asset impairments.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
Long-lived assets with recorded values that are not expected to be recovered through future cash flows are written down to estimated fair value in accordance with FASB guidance with respect to the accounting for the impairment or disposal of long-lived assets. Under this guidance, a long-lived asset is tested for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that its carrying value may not be recoverable. The carrying value of a long-lived asset is not recoverable if it exceeds the sum of the undiscounted cash flows expected to result from the use and eventual disposition of the asset. If the carrying value exceeds the sum of the undiscounted cash flows, an impairment loss equal to the amount by which the carrying value exceeds the fair value of the asset is recognized.
We periodically evaluate property and equipment and other long-lived assets for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying value of these assets may not be recoverable. The evaluation is highly dependent on the underlying assumptions of related cash flows. The subjective assumptions used to determine the existence of an impairment in carrying value include:
· whether there is an indication of impairment;
· the grouping of assets;
· the intention of “holding,” “abandoning” or “selling” an asset;
· the forecast of undiscounted expected future cash flow over the asset’s estimated useful life; and
· if an impairment exists, the fair value of the asset or asset group.
We did not recognize any impairments during the year ended December 31, 2015. During the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, we recognized impairments of $10 million and $20 million, respectively, primarily related to assets that were taken out of service.
Goodwill represents the future economic benefits arising from assets acquired in a business combination that are not individually identified and separately recognized.
In accordance with FASB guidance, we test goodwill to determine whether an impairment has occurred at least annually (as of June 30) and on an interim basis if it is more likely than not that a reporting unit’s fair value is less than its carrying value. Goodwill is tested for impairment at a level of reporting referred to as a reporting unit. A reporting unit is an operating segment or one level below an operating segment for which discrete financial information is available and regularly reviewed by segment management. Our reporting units are our operating segments. FASB guidance requires a two-step, quantitative approach to testing goodwill for impairment; however, we may first assess certain qualitative factors to determine whether it is necessary to perform the two-step goodwill impairment test. We did not elect to apply this qualitative assessment during our 2015 annual goodwill impairment test, but proceeded directly to the two-step, quantitative test. In Step 1, we compare the fair value of the reporting unit with the respective book values, including goodwill, by using an income approach based on a discounted cash flow analysis. This approach requires us to make long-term forecasts of future revenues, expenses and other expenditures. Those forecasts require the use of various assumptions and estimates, the most significant of which are net revenues (total revenues less purchases and related costs), operating expenses, general and administrative expenses and the weighted average cost of capital. Fair value of the reporting units is determined using significant unobservable inputs, or Level 3 inputs in the fair value hierarchy. When the fair value is greater than book value, then the reporting unit’s goodwill is not considered impaired. If the book value is greater than fair value, then we proceed to Step 2. In Step 2, we compare the implied fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill to the book value. A goodwill impairment loss is recognized if the carrying amount exceeds its fair value.
Through Step 1 of our annual testing of goodwill for potential impairment, which also includes a sensitivity analysis regarding the excess of our reporting unit’s fair value over book value, we determined that the fair value of each reporting unit was substantially greater than its respective book value; therefore, goodwill was not considered impaired. We did not recognize any material impairments of goodwill during the last three years.
As of December 31, 2015, as a result of industry conditions, we considered qualitative factors to determine whether a triggering event had occurred, which would require that a Step 1 impairment test be performed as of the end of the year. A triggering event is a determination that it is more likely than not that the fair value of any reporting unit was less than its carrying value. Based on our assessment, we concluded that a triggering event had not occurred as of December 31, 2015. However, significant negative variances in the assumptions and estimates utilized in our forecasts, such as a continued decline in petroleum commodity prices or a sustained multi-year low petroleum commodity price environment that results in lower volumes and cash flows or further increases in our weighted average cost of capital assumption, could result in reporting unit carrying values in excess of fair values.
Goodwill by segment and changes in goodwill is reflected in the following table (in millions):
|
|
|
Transportation |
|
Facilities |
|
Supply and Logistics |
|
Total |
| ||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2013 |
|
$ |
878 |
|
$ |
1,162 |
|
$ |
463 |
|
$ |
2,503 |
|
|
Acquisitions |
|
— |
|
1 |
|
— |
|
1 |
| ||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
(24 |
) |
(11 |
) |
(4 |
) |
(39 |
) | ||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
$ |
854 |
|
$ |
1,152 |
|
$ |
459 |
|
$ |
2,465 |
|
|
Acquisitions (1) |
|
3 |
|
8 |
|
— |
|
11 |
| ||||
|
Foreign currency translation adjustments |
|
(42 |
) |
(19 |
) |
(10 |
) |
(71 |
) | ||||
|
Other |
|
— |
|
(54 |
) |
54 |
|
— |
| ||||
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
$ |
815 |
|
$ |
1,087 |
|
$ |
503 |
|
$ |
2,405 |
|
(1) Goodwill is recorded at the acquisition date based on a preliminary fair value determination. This preliminary goodwill balance may be adjusted when the fair value determination is finalized.
Note 7—Investments in Unconsolidated Entities
Investments in entities over which we have significant influence but not control are accounted for by the equity method. We do not consolidate any part of the assets or liabilities of our equity investees. Our share of net income or loss is reflected as one line item on our Consolidated Statements of Operations entitled “Equity earnings in unconsolidated entities” and will increase or decrease, as applicable, the carrying value of our investments in unconsolidated entities on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. In addition, as applicable, we include a proportionate share of our equity method investees’ unrealized gains and losses in other comprehensive income on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. We also adjust our investment balances in these investees by the like amount. We evaluate our equity investments for impairment in accordance with FASB guidance with respect to the equity method of accounting for investments in common stock. An impairment of an equity investment results when factors indicate that the investment’s fair value is less than its carrying value and the reduction in value is other than temporary in nature.
Our investments in the following entities are accounted for under the equity method of accounting:
|
Entity |
|
Type of Operation |
|
Our Ownership |
|
|
Settoon Towing, LLC |
|
Barge Transportation Services |
|
50 |
% |
|
BridgeTex Pipeline Company, LLC (“BridgeTex”) |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
50 |
% |
|
Caddo Pipeline LLC (“Caddo”) (1) |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline (2) |
|
50 |
% |
|
Diamond Pipeline LLC (“Diamond”) (1) |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline (2) |
|
50 |
% |
|
Eagle Ford Pipeline LLC |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
50 |
% |
|
Eagle Ford Terminals Corpus Christi LLC (“Eagle Ford Terminals”) (1) |
|
Crude Oil Terminal and Dock (2) |
|
50 |
% |
|
Frontier Pipeline Company |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
50 |
% |
|
Saddlehorn Pipeline Company, LLC (“Saddlehorn”) (1) |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline (2) |
|
40 |
% |
|
White Cliffs Pipeline, LLC |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
36 |
% |
|
Butte Pipe Line Company |
|
Crude Oil Pipeline |
|
22 |
% |
(1) Our initial investment in the entity occurred in 2015.
(2) Asset is currently under construction by the entity and has not yet been placed in service.
In November 2014, we acquired a 50% interest in BridgeTex from Oxy. BridgeTex owns a 300,000 barrel-per-day crude oil pipeline that extends from Colorado City in West Texas to a crude oil terminal in East Houston, which we believe is complementary to our existing West Texas assets. We paid cash of $1.088 billion, including working capital adjustments of $13 million, for our interest in BridgeTex.
We consider distributions received from unconsolidated entities as returns on investment in those entities to the extent of cumulative net operating cash flows, and therefore classify these distributions as cash flows from operating activities in our Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows. We define cumulative net operating cash flows as cumulative net income adjusted for certain non-cash items such as depreciation and amortization expense. Other distributions received from unconsolidated entities would be considered a return of the investment and classified as cash flows from investing activities on the Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows.
We generally fund our portion of development, construction or capital expansion projects of our equity method investees through capital contributions. Our contributions to these entities increase the carrying value of our investments and are reflected in our Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows as cash used in investing activities. During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, we made cash contributions of $253 million, $158 million and $133 million, respectively, to certain of our equity method investees. The contributions amount for 2015 is net of $53 million of cash received as a return of our investment. We anticipate that we will make additional contributions related to ongoing projects at Diamond, Saddlehorn, Eagle Ford Terminals and Caddo over the next several years.
Our investments in unconsolidated entities exceeded our share of the underlying equity in the net assets of such entities by $760 million and $763 million at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. Such basis differences are included in the carrying values of our investments on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. The portion of the basis differences attributable to depreciable or amortizable assets is amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful life of the related assets, which reduces “Equity earnings in unconsolidated entities” on our Consolidated Statements of Operations. The portion of the basis differences attributable to goodwill is not amortized. The basis difference is primarily related to our acquisition of an interest in BridgeTex.
Summarized Financial Information of Unconsolidated Entities
Combined summarized financial information for all of our unconsolidated entities is shown in the tables below (in millions):
|
|
|
December 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
Current assets |
|
$ |
365 |
|
$ |
184 |
|
|
Noncurrent assets |
|
$ |
2,901 |
|
$ |
2,303 |
|
|
Current liabilities |
|
$ |
231 |
|
$ |
142 |
|
|
Noncurrent liabilities |
|
$ |
184 |
|
$ |
222 |
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
Revenues |
|
$ |
769 |
|
$ |
531 |
|
$ |
344 |
|
|
Operating income |
|
$ |
441 |
|
$ |
301 |
|
$ |
181 |
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
424 |
|
$ |
285 |
|
$ |
172 |
|
Note 8—Other Long-Term Assets, Net
Other long-term assets, net of accumulated amortization, consisted of the following as of the dates indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
December 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
Intangible assets |
|
$ |
610 |
|
$ |
644 |
|
|
Fair value of derivative instruments |
|
9 |
|
27 |
| ||
|
Other |
|
91 |
|
59 |
| ||
|
|
|
710 |
|
730 |
| ||
|
Accumulated amortization |
|
(327 |
) |
(301 |
) | ||
|
|
|
$ |
383 |
|
$ |
429 |
|
Amortization expense for finite-lived intangible assets for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 was $49 million, $57 million and $85 million, respectively.
Intangible assets that have finite lives are tested for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying value may not be recoverable. Our intangible assets that have finite lives consisted of the following as of the dates indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
December 31, 2014 |
| ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
Estimated Useful |
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
|
|
|
Accumulated |
|
|
| ||||||
|
|
|
Lives (Years) |
|
Cost |
|
Amortization |
|
Net |
|
Cost |
|
Amortization |
|
Net |
| ||||||
|
Customer contracts and relationships |
|
1 – 20 |
|
$ |
537 |
|
$ |
(301 |
) |
$ |
236 |
|
$ |
565 |
|
$ |
(277 |
) |
$ |
288 |
|
|
Property tax abatement |
|
7 – 13 |
|
38 |
|
(22 |
) |
16 |
|
38 |
|
(18 |
) |
20 |
| ||||||
|
Other agreements |
|
25 – 70 |
|
28 |
|
(4 |
) |
24 |
|
33 |
|
(4 |
) |
29 |
| ||||||
|
Emission reduction credits (1) |
|
N/A |
|
7 |
|
— |
|
7 |
|
8 |
|
— |
|
8 |
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
$ |
610 |
|
$ |
(327 |
) |
$ |
283 |
|
$ |
644 |
|
$ |
(299 |
) |
$ |
345 |
|
(1) Emission reduction credits, once surrendered in exchange for environmental permits, are finite-lived.
We estimate that our amortization expense related to finite-lived intangible assets for the next five years will be as follows (in millions):
|
2016 |
|
$ |
44 |
|
|
2017 |
|
$ |
41 |
|
|
2018 |
|
$ |
36 |
|
|
2019 |
|
$ |
33 |
|
|
2020 |
|
$ |
31 |
|
Debt consisted of the following as of the dates indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
December 31, |
|
December 31, |
| ||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
SHORT-TERM DEBT |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
PAA commercial paper notes, bearing a weighted-average interest rate of 1.1% and 0.46%, respectively (1) |
|
$ |
696 |
|
$ |
734 |
|
|
PAA senior secured hedged inventory facility, bearing a weighted-average interest rate of 1.4% (1) |
|
300 |
|
— |
| ||
|
PAA senior notes: |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
5.25% senior notes due June 2015 |
|
— |
|
150 |
| ||
|
3.95% senior notes due September 2015 |
|
— |
|
400 |
| ||
|
Other |
|
3 |
|
3 |
| ||
|
Total short-term debt |
|
999 |
|
1,287 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
LONG-TERM DEBT |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
PAA senior notes: |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
5.88% senior notes due August 2016 (2) |
|
175 |
|
175 |
| ||
|
6.13% senior notes due January 2017 |
|
400 |
|
400 |
| ||
|
6.50% senior notes due May 2018 |
|
600 |
|
600 |
| ||
|
8.75% senior notes due May 2019 |
|
350 |
|
350 |
| ||
|
2.60% senior notes due December 2019 |
|
500 |
|
500 |
| ||
|
5.75% senior notes due January 2020 |
|
500 |
|
500 |
| ||
|
5.00% senior notes due February 2021 |
|
600 |
|
600 |
| ||
|
3.65% senior notes due June 2022 |
|
750 |
|
750 |
| ||
|
2.85% senior notes due January 2023 |
|
400 |
|
400 |
| ||
|
3.85% senior notes due October 2023 |
|
700 |
|
700 |
| ||
|
3.60% senior notes due November 2024 |
|
750 |
|
750 |
| ||
|
4.65% senior notes due October 2025 |
|
1,000 |
|
— |
| ||
|
6.70% senior notes due May 2036 |
|
250 |
|
250 |
| ||
|
6.65% senior notes due January 2037 |
|
600 |
|
600 |
| ||
|
5.15% senior notes due June 2042 |
|
500 |
|
500 |
| ||
|
4.30% senior notes due January 2043 |
|
350 |
|
350 |
| ||
|
4.70% senior notes due June 2044 |
|
700 |
|
700 |
| ||
|
4.90% senior notes due February 2045 |
|
650 |
|
650 |
| ||
|
Unamortized discounts and debt issuance costs |
|
(77 |
) |
(76 |
) | ||
|
PAA senior notes, net of unamortized discounts and debt issuance costs |
|
9,698 |
|
8,699 |
| ||
|
PAA commercial paper notes, bearing a weighted-average interest rate of 1.1% (2) |
|
672 |
|
— |
| ||
|
AAP term loan, bearing a weighted-average interest rate of 2.0% and 1.8%, respectively |
|
550 |
|
500 |
| ||
|
AAP senior secured revolving credit facility, bearing a weighted-average interest rate of 2.0% and 1.8%, respectively |
|
9 |
|
36 |
| ||
|
Unamortized debt issuance costs |
|
(2 |
) |
(2 |
) | ||
|
Other |
|
5 |
|
5 |
| ||
|
Total long-term debt |
|
10,932 |
|
9,238 |
| ||
|
Total debt (3) |
|
$ |
11,931 |
|
$ |
10,525 |
|
(1) We classified these PAA commercial paper notes and credit facility borrowings as short-term at December 31, 2015 and 2014, as these notes and borrowings were primarily designated as working capital borrowings, were required to be repaid within one year and were primarily for hedged NGL and crude oil inventory and NYMEX and ICE margin deposits.
(2) As of December 31, 2015, we have classified PAA’s $175 million, 5.88% senior notes due August 2016 and a portion of PAA’s commercial paper notes as long-term based on PAA’s ability and intent to refinance such amounts on a long-term basis under its credit agreements.
(3) PAA’s fixed-rate senior notes (including current maturities) had a face value of approximately $9.8 billion and $9.3 billion as of December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively. We estimated the aggregate fair value of these notes as of December 31, 2015 and 2014 to be approximately $8.6 billion and $9.9 billion, respectively. PAA’s fixed-rate senior notes are traded among institutions, and these trades are routinely published by a reporting service. Our determination of fair value is based on reported trading activity near year end. We estimate that the carrying value of outstanding borrowings under the credit agreements and the PAA commercial paper program approximates fair value as interest rates reflect current market rates. The fair value estimates for the PAA senior notes, the credit agreements and the PAA commercial paper program are based upon observable market data and are classified in Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy.
PAA Commercial Paper Program
PAA has a commercial paper program under which it may issue (and have outstanding at any time) up to $3.0 billion in the aggregate of privately placed, unsecured commercial paper notes. Such notes are backstopped by the PAA senior unsecured revolving credit facility and the PAA senior secured hedged inventory facility; as such, any borrowings under the PAA commercial paper program reduce the available capacity under these facilities.
Credit Agreements
PAA senior secured hedged inventory facility. The PAA senior secured hedged inventory facility has a committed borrowing capacity of $1.4 billion, of which $400 million is available for the issuance of letters of credit. Subject to obtaining additional or increased lender commitments, the committed amount of the facility may be increased to $1.9 billion. Proceeds from the facility are primarily used to finance purchased or stored hedged inventory, including NYMEX and ICE margin deposits. Such obligations under the committed facility are secured by the financed inventory and the associated accounts receivable and are repaid from the proceeds of the sale of the financed inventory. Borrowings accrue interest based, at PAA’s election, on either the Eurocurrency Rate or the Base Rate, in each case plus a margin based on PAA’s credit rating at the applicable time. The agreement also provides for one or more one-year extensions, subject to applicable approval. In August 2015, PAA extended the maturity date of the facility to August 2018.
PAA senior unsecured revolving credit facility. The PAA senior unsecured revolving credit facility has a committed borrowing capacity of $1.6 billion and contains an accordion feature that enables us to increase the committed capacity to $2.1 billion, subject to obtaining additional or increased lender commitments. The credit agreement also provides for the issuance of letters of credit. Borrowings accrue interest based, at PAA’s election, on the Eurocurrency Rate, the Base Rate or the Canadian Prime Rate, in each case plus a margin based on PAA’s credit rating at the applicable time. The agreement also provides for one or more one-year extensions, subject to applicable approval. In August 2015, PAA extended the maturity date of the facility to August 2020.
PAA senior unsecured 364-day revolving credit facility. In January 2015, PAA entered into an agreement for a 364-day senior unsecured revolving credit facility with a borrowing capacity of $1.0 billion. In August 2015, PAA amended this agreement to extend the maturity date to August 2016. Borrowings accrue interest based, at PAA’s election, on either the Eurocurrency Rate or the Base Rate, as defined in the agreement, in each case plus a margin based on PAA’s credit rating at the applicable time.
AAP senior secured credit agreement. In August 2015, AAP amended its credit agreement to, among other things, (i) increase its term loan commitments from $500 million to $550 million, (ii) increase the aggregate commitments under its senior secured revolving credit facility from $75 million to $125 million and (iii) extend the maturity date of the term loan and senior secured revolving credit facility to August 2020 through the exercise of the option included in the current credit agreement. In addition, the amendment provides for a $50 million accordion feature, which may be used to expand the term loan and/or revolving credit facility commitments. We pay a quarterly commitment fee on the revolver that is based on AAP’s Consolidated Indebtedness to Consolidated EBITDA ratio (“Leverage Ratio”), as defined in the AAP credit agreement. The commitment fee can range from 0.175% to 0.35% and is payable on the daily average unused amount of the revolver. Borrowings accrue interest based, at AAP’s election, on the Alternative Base Rate (the greater of the Base Rate or Federal Funds Effective Rate) or the Eurodollar Rate, in each case plus a margin as determined by AAP’s Leverage Ratio.
PAA Senior Notes
PAA’s senior notes are co-issued, jointly and severally, by Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. and a 100%-owned consolidated finance subsidiary (neither of which have independent assets or operations) and are unsecured senior obligations of such entities and rank equally in right of payment with existing and future senior indebtedness of the issuers. PAA may, at its option, redeem any series of senior notes at any time in whole or from time to time in part, prior to maturity, at the redemption prices described in the indentures governing the senior notes. PAA’s senior notes are not guaranteed by any of its subsidiaries.
PAA Senior Notes Issuances
The table below summarizes PAA’s issuances of senior unsecured notes during 2015, 2014 and 2013 (in millions):
|
Year |
|
Description |
|
Maturity |
|
Face Value |
|
Interest Payment Dates |
| |
|
2015 |
|
4.65% Senior Notes issued at 99.846% of face value |
|
October 2025 |
|
$ |
1,000 |
|
April 15 and October 15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2014 |
|
2.60% Senior Notes issued at 99.813% of face value |
|
December 2019 |
|
$ |
500 |
|
June 15 and December 15 |
|
|
2014 |
|
4.90% Senior Notes issued at 99.876% of face value |
|
February 2045 |
|
$ |
650 |
|
February 15 and August 15 |
|
|
2014 |
|
3.60% Senior Notes issued at 99.842% of face value |
|
November 2024 |
|
$ |
750 |
|
May 1 and November 1 |
|
|
2014 |
|
4.70% Senior Notes issued at 99.734% of face value |
|
June 2044 |
|
$ |
700 |
|
June 15 and December 15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2013 |
|
3.85% Senior Notes issued at 99.792% of face value |
|
October 2023 |
|
$ |
700 |
|
April 15 and October 15 |
|
PAA Senior Note Repayments
The PAA $150 million, 5.25% senior notes and $400 million, 3.95% senior notes were repaid in June 2015 and September 2015, respectively. We utilized cash on hand and available capacity under the PAA commercial paper program to repay these notes.
On December 13, 2013, PAA repaid its $250 million, 5.63% senior notes. We utilized cash on hand and available capacity under the PAA commercial paper program to repay these notes.
Maturities
The weighted average maturity of our long-term debt outstanding at December 31, 2015 was approximately 11 years. The following table presents the aggregate contractually scheduled maturities for the next five years and thereafter. The amounts presented exclude unamortized discounts and debt issuance costs.
|
|
|
Payment |
| |
|
Calendar Year |
|
(in millions) |
| |
|
2016 |
|
$ |
847 |
|
|
2017 |
|
400 |
| |
|
2018 |
|
600 |
| |
|
2019 |
|
850 |
| |
|
2020 |
|
1,059 |
| |
|
Thereafter |
|
7,255 |
| |
Covenants and Compliance
PAA Credit Agreements. PAA’s credit agreements (which impact the ability to access the PAA commercial paper program because they provide the backstop that supports PAA’s short-term credit ratings) and the indentures governing PAA’s senior notes contain cross-default provisions. PAA’s credit agreements prohibit declaration or payments of distributions on, or purchases or redemptions of, units if any default or event of default is continuing. In addition, PAA’s credit agreements contain various covenants limiting PAA’s ability to, among other things:
· grant liens on certain property;
· incur indebtedness, including capital leases;
· sell substantially all of its assets or enter into a merger or consolidation;
· engage in certain transactions with affiliates; and
· enter into certain burdensome agreements.
The credit agreements for the PAA senior unsecured revolving credit facility, the PAA senior secured hedged inventory facility and the PAA senior unsecured 364-day revolving credit facility treat a change of control as an event of default and also require PAA to maintain a debt-to-EBITDA coverage ratio that, on a trailing four-quarter basis, will not be greater than 5.00 to 1.00 (or 5.50 to 1.00 on all outstanding debt during an acquisition period (generally, the period consisting of three fiscal quarters following an acquisition greater than $150 million)). For covenant compliance purposes, Consolidated EBITDA may include certain adjustments, including those for material projects and certain non-recurring expenses. Additionally, letters of credit and borrowings to fund hedged inventory and margin requirements are excluded when calculating the debt coverage ratio.
A default under PAA’s credit facilities would permit the lenders to accelerate the maturity of the outstanding debt. As long as PAA is in compliance with its credit agreements, PAA’s ability to make distributions of available cash is not restricted. As of December 31, 2015, PAA was in compliance with the covenants contained in its credit agreements and indentures.
AAP Credit Agreement. To secure the AAP credit agreement, AAP pledged 100% of (i) its incentive distribution rights in PAA and (ii) its interest in PAA GP. The AAP credit agreement contains various covenants limiting AAP’s ability to, among other things:
· incur additional indebtedness;
· grant liens;
· make fundamental changes as defined;
· make restrictive payments as defined; and
· enter into restrictive agreements.
The AAP credit agreement also requires AAP to maintain a Leverage Ratio of no greater than 4.0 to 1.0. As of December 31, 2015, AAP was in compliance with the covenants contained in its credit agreement.
Borrowings and Repayments
Total borrowings under the credit agreements and the PAA commercial paper program for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 were approximately $62.3 billion, $71.0 billion and $31.5 billion, respectively. Total repayments under the credit agreements and the PAA commercial paper program were approximately $61.4 billion, $71.3 billion and $31.2 billion for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The variance in total gross borrowings and repayments is impacted by various business and financial factors including, but not limited to, the timing, average term and method of general partnership borrowing activities.
Letters of Credit
In connection with our supply and logistics activities, we provide certain suppliers with irrevocable standby letters of credit to secure our obligation for the purchase of crude oil, NGL and natural gas. These letters of credit are issued under the PAA senior unsecured revolving credit facility and the PAA senior secured hedged inventory facility, and our liabilities with respect to these purchase obligations are recorded in accounts payable on our balance sheet in the month the crude oil, NGL or natural gas is purchased. Generally, these letters of credit are issued for periods of up to seventy days and are terminated upon completion of each transaction. Additionally, we issue letters of credit to support insurance programs, derivative transactions and construction activities. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, we had outstanding letters of credit of $46 million and $87 million, respectively.
Debt Issuance Costs
Costs incurred in connection with the issuance of senior notes and long-term debt under credit agreements are recorded as a direct deduction from the related debt liability and are amortized using the straight-line method over the term of the related debt. Use of the straight-line method does not differ materially from the “effective interest” method of amortization.
Note 10—Partners’ Capital and Distributions
Class A and Class B Shares
Our Class A shares and Class B shares represent limited partner interests in us. The holders of our Class A and Class B shares are entitled to exercise the rights or privileges available to limited partners under our partnership agreement, but only holders of Class A shares are entitled to participate in our distributions.
Initial Public Offering
Immediately prior to our IPO, the general partner interest in AAP held by GP LLC was converted into a non-economic interest and, through a series of transactions with our general partner and the owners of GP LLC, we issued 473,647,679 Class B shares and an equal number of units of our general partner to such owners and received a 100% managing member interest in GP LLC. Also prior to our IPO, certain owners of AAP (the “Selling Owners”) sold a portion of their interests in AAP to us in exchange for the right to receive an amount equal to the net proceeds of the IPO, resulting in our ownership of AAP units representing limited partnership interests in AAP.
On October 21, 2013, we completed our IPO of 132,382,094 Class A shares representing limited partner interests in us at a price of $22.00 per Class A share, generating net proceeds, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and direct offering expenses, of approximately $2.8 billion. We distributed the net proceeds of the IPO to the Selling Owners.
Exchange Rights
Holders of AAP units and their permitted transferees each have the right to exchange all or a portion of their AAP units for Class A shares at an exchange ratio of one Class A share for each AAP unit exchanged (referred to herein as their “Exchange Right”). This Exchange Right may be exercised only if, simultaneously therewith, an equal number of Class B shares and general partner units are transferred by the exercising party to us. Additionally, beginning after December 31, 2015, a holder of vested AAP Management Units will be entitled to convert his or her AAP Management Units into AAP units and a like number of our Class B shares based on a conversion ratio calculated in accordance with the AAP limited partnership agreement (which conversion ratio will not be more than one-to-one and was approximately 0.938 AAP units for each AAP Management Unit as of December 31, 2015). Following any such conversion, the holder will have the Exchange Right for our Class A shares. Holders of AAP Management Units who convert such units into AAP units and Class B shares will not receive general partner units and thus will not need to include any general partner units in a transfer or the exercise of their Exchange Right. See Note 15 for additional information regarding the AAP Management Units.
Shares Outstanding
The following table presents the activity for our Class A shares and Class B shares for the periods indicated:
|
|
|
Class B Shares |
|
Class A Shares |
|
|
Balance at October 21, 2013 (IPO date) |
|
— |
|
— |
|
|
Shares issued in connection with the reorganization and IPO |
|
473,647,679 |
|
132,382,094 |
|
|
Shares (exchanged)/issued in connection with Exchange Right exercises |
|
(1,451,543 |
) |
1,451,543 |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2013 |
|
472,196,136 |
|
133,833,637 |
|
|
Shares (exchanged)/issued in connection with Exchange Right exercises (1) |
|
(73,099,637 |
) |
73,099,637 |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
399,096,499 |
|
206,933,274 |
|
|
Shares (exchanged)/issued in connection with Exchange Right exercises |
|
(22,324,906 |
) |
22,324,906 |
|
|
Shares issued in connection with PAGP LTIP award vestings |
|
— |
|
20,800 |
|
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
376,771,593 |
|
229,278,980 |
|
(1) Includes 69,000,000 Class A shares issued to Oxy immediately preceding the sale of such shares in an underwritten secondary public offering. See Note 14 for further discussion.
Distributions
We distribute 100% of our available cash within 55 days following the end of each quarter to Class A shareholders of record. Available cash is generally defined as all cash on hand at the date of determination of available cash for the distribution in respect to such quarter (including expected distributions from AAP in respect of such quarter), less reserves established by our general partner for future requirements.
The following table details the distributions paid to Class A shareholders during the periods indicated (in millions, except per share data):
|
Year |
|
Distributions Paid |
|
Distributions per Class A Share |
| ||
|
2015 |
|
$ |
195 |
|
$ |
0.88300 |
|
|
2014 (1) |
|
$ |
91 |
|
$ |
0.66975 |
|
(1) The distribution paid to our Class A shareholders in the first quarter of 2014 was based on the prorated distribution received from AAP attributable to the period beginning on the date of the closing of our IPO through the end of the fourth quarter of 2013.
On January 12, 2016, we declared a cash distribution of $0.231 per outstanding Class A share. This distribution of $55 million was paid on February 12, 2016 to shareholders of record at the close of business on January 29, 2016, for the period October 1, 2015 through December 31, 2015.
Distributions Prior to our IPO. During the year ended December 31, 2013, $6 million was distributed to the owners of GP LLC. Of the amount distributed during the year ended December 31, 2013, $3 million related to distributions received from AAP of the net proceeds from the increase in AAP’s term loan, as discussed under “AAP Distributions” below.
Consolidated Subsidiaries
Noncontrolling Interests in Subsidiaries
As of December 31, 2015, noncontrolling interests in our subsidiaries consisted of (i) a 98% limited partner interest in PAA, (ii) an approximate 62% limited partner interest in AAP that consists of Class A units and AAP Management Units (a profits interest) and (iii) a 25% interest in SLC Pipeline LLC.
Subsidiary Distributions
PAA Distributions. PAA distributes 100% of its available cash within 45 days following the end of each quarter to unitholders of record and to AAP. Available cash is generally defined as all of PAA’s cash and cash equivalents on hand at the end of each quarter, less reserves established by its general partner for future requirements.
AAP is entitled to receive (i) distributions representing its 2% indirect general partner interest in PAA and (ii) incentive distributions if the amount PAA distributes with respect to any quarter exceeds levels specified in PAA’s partnership agreement. Under the quarterly distribution provisions, AAP is entitled, without duplication, to 2% of amounts PAA distributes up to $0.2250 per unit, referred to as the MQD, 15% of amounts PAA distributes in excess of $0.2250 per unit, 25% of the amounts PAA distributes in excess of $0.2475 per unit and 50% of amounts PAA distributes in excess of $0.3375 per unit.
During the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, AAP’s incentive distributions were reduced by approximately $22 million, $23 million and $15 million, respectively. These reductions were agreed to in connection with the BP NGL Acquisition and the PNG Merger. In addition, AAP has agreed to reduce the amount of its incentive distribution by $5.0 million per quarter in 2016 and $3.75 million per quarter thereafter. In connection with PAA’s January 2016 private placement of preferred units, as discussed further in “Issuance of Units by Subsidiaries” below, AAP agreed to further modify its IDRs such that when the preferred units convert into PAA common units, the IDRs associated with the resulting common units will only participate in distribution growth above an annualized PAA distribution level of $2.80 per converted PAA common unit.
The following table details distributions, net of reductions in AAP’s incentive distributions, paid during periods indicated (in millions, except per unit data):
|
|
|
Distributions Paid |
|
Distributions per |
| |||||||||
|
Year |
|
Common Unitholders |
|
AAP |
|
Total |
|
common unit |
| |||||
|
2015 |
|
$ |
1,081 |
|
$ |
590 |
|
$ |
1,671 |
|
|
$ |
2.755 |
|
|
2014 |
|
$ |
934 |
|
$ |
473 |
|
$ |
1,407 |
|
|
$ |
2.550 |
|
|
2013 |
|
$ |
791 |
|
$ |
369 |
|
$ |
1,160 |
|
|
$ |
2.325 |
|
On January 12, 2016, PAA declared a cash distribution of $0.70 per unit on PAA’s outstanding common units. The distribution was paid on February 12, 2016 to unitholders of record on January 29, 2016, for the period October 1, 2015 through December 31, 2015. The total distribution paid was $433 million, with $278 million paid to PAA’s common unitholders and $155 million paid to AAP for its 2% general partner and incentive distribution interests.
AAP Distributions. AAP distributes all of the cash received from PAA distributions on a quarterly basis, less reserves established in the discretion of its general partner for future requirements. Generally, distributions are paid to its partners in proportion to their percentage interest in AAP. The following table details the distributions to AAP’s partners paid during the periods indicated from distributions received from PAA (in millions):
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Distributions to AAP’s Partners |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
Distributions Received |
|
Cash |
|
|
|
Noncontrolling |
|
|
| |||||
|
Year |
|
by AAP from PAA |
|
Reserves |
|
Total |
|
Interests |
|
PAGP |
| |||||
|
2015 |
|
$ |
590 |
|
$ |
(14 |
) |
$ |
576 |
|
$ |
380 |
|
$ |
196 |
|
|
2014 (1) |
|
$ |
473 |
|
$ |
(14 |
) |
$ |
459 |
|
$ |
368 |
|
$ |
91 |
|
|
2013 |
|
$ |
369 |
|
$ |
(8 |
) |
$ |
361 |
|
$ |
358 |
|
$ |
3 |
(2) |
(1) The distribution paid by AAP in the first quarter of 2014 was prorated as of the date of the consummation of our IPO, such that the owners of AAP prior to our IPO received the portion of the distribution attributable to the period prior to our IPO, and the owners of AAP at the date of record of January 31, 2014, including us, received the portion of the distribution attributable to the period beginning on the date of the IPO through the end of the fourth quarter of 2013.
(2) Represents distributions paid by AAP to our predecessor, GP LLC, prior to our IPO.
On February 12, 2016, AAP distributed $151 million of the distributions received from PAA, net of cash reserves of $4 million, to its partners. Of this amount, $96 million was distributed to noncontrolling interests and $55 million was distributed to us.
In September 2013, the AAP credit agreement was amended to increase the amount of the term loan by $300 million. Upon receipt, the net term loan proceeds of $299 million were distributed to AAP’s limited partners, excluding AAP Management Unit holders, and GPLLC in proportion to their respective ownership interests.
Other Distributions. During each of the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, distributions of $3 million were paid to noncontrolling interests in SLC Pipeline LLC. During the year ended December 31, 2013, distributions of $46 million were paid to noncontrolling interests in PNG.
Issuance of Units by Subsidiaries
PAA Common Unit Issuances. PAA has entered into several equity distribution agreements under its Continuous Offering Program, pursuant to which PAA may offer and sell, through sales agents, common units representing limited partner interests. In addition to its Continuous Offering Program, PAA may sell common units through overnight or underwritten offerings.
The following table summarizes PAA’s issuance of common units in connection with its Continuous Offering Program and underwritten offerings during the periods indicated (net proceeds in millions):
|
Year |
|
Type of Offering |
|
Units Issued |
|
Net Proceeds (1) |
| |
|
2015 |
|
Continuous Offering Program |
|
1,133,904 |
|
$ |
58 |
(2) |
|
2015 |
|
Underwritten Offering |
|
21,000,000 |
|
1,041 |
| |
|
2015 Total |
|
|
|
22,133,904 |
|
$ |
1,099 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2014 Total |
|
Continuous Offering Program |
|
15,375,810 |
|
$ |
848 |
(2) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |
|
2013 Total |
|
Continuous Offering Program |
|
8,644,807 |
|
$ |
468 |
(2) |
(1) Amounts are net of costs associated with the offerings.
(2) PAA pays commissions to sales agents in connection with common unit issuances under its Continuous Offering Program. PAA paid $1 million, $9 million and $5 million of such commissions during 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
PAA Preferred Unit Issuance. In January 2016, PAA completed the private placement of approximately 61.0 million Series A Convertible Preferred Units representing limited partner interests in PAA (the “PAA preferred units”), for a cash purchase price of $26.25 per unit (the “Issue Price”), resulting in total net proceeds, after deducting offering expenses and the 2% transaction fee due to the purchasers, of approximately $1.6 billion. Certain of the purchasers or their affiliates are related parties. See Note 14 for additional information.
The PAA preferred units are a new class of equity security in PAA that rank senior to all classes or series of equity securities in PAA with respect to distribution rights and rights upon liquidation. The holders of the PAA preferred units will receive quarterly distributions, subject to customary anti-dilution adjustments, equal to an annual rate of 8% of the Issue Price ($2.10 per unit annualized). AAP will be entitled to participate in distributions on the PAA preferred units equal to its 2% general partner interest.
PNG Unit Issuances. PNG issued approximately 1.9 million common units during the year ended December 31, 2013. As a result of PNG’s common unit issuances, we recorded an increase in noncontrolling interest of $40 million in 2013.
Contributions from Noncontrolling Interests
Contributions from noncontrolling interests consists of contributions from the owners of AAP (other than us) to reimburse AAP for its capital contribution required to maintain its indirect 2% general partner interest in PAA following PAA’s issuance of common units.
Note 11—Derivatives and Risk Management Activities
We identify the risks that underlie our core business activities and use risk management strategies to mitigate those risks when we determine that there is value in doing so. Our policy is to use derivative instruments for risk management purposes and not for the purpose of speculating on hydrocarbon commodity (referred to herein as “commodity”) price changes. We use various derivative instruments to (i) manage our exposure to commodity price risk, as well as to optimize our profits, (ii) manage our exposure to interest rate risk and (iii) manage our exposure to currency exchange rate risk. Our commodity risk management policies and procedures are designed to help ensure that our hedging activities address our risks by monitoring our derivative positions, as well as physical volumes, grades, locations, delivery schedules and storage capacity. Our interest rate and currency exchange rate risk management policies and procedures are designed to monitor our derivative positions and ensure that those positions are consistent with our objectives and approved strategies. When we apply hedge accounting, our policy is to formally document all relationships between hedging instruments and hedged items, as well as our risk management objectives for undertaking the hedge. This process includes specific identification of the hedging instrument and the hedged transaction, the nature of the risk being hedged and how the hedging instrument’s effectiveness will be assessed. Both at the inception of the hedge and throughout the hedging relationship, we assess whether the derivatives employed are highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows of anticipated hedged transactions.
Commodity Price Risk Hedging
Our core business activities involve certain commodity price-related risks that we manage in various ways, including through the use of derivative instruments. Our policy is to (i) only purchase inventory for which we have a market, (ii) structure our sales contracts so that price fluctuations do not materially affect our operating income and (iii) not acquire and hold physical inventory or
derivatives for the purpose of speculating on commodity price changes. The material commodity-related risks inherent in our business activities can be divided into the following general categories:
Commodity Purchases and Sales — In the normal course of our operations, we purchase and sell commodities. We use derivatives to manage the associated risks and to optimize profits. As of December 31, 2015, net derivative positions related to these activities included:
· An average of 92,100 barrels per day net long position (total of 2.9 million barrels) associated with our crude oil purchases, which was unwound ratably during January 2016 to match monthly average pricing.
· A net short time spread position averaging 11,500 barrels per day (total of 5.6 million barrels), which hedges a portion of our anticipated crude oil lease gathering purchases through April 2017.
· An average of 8,000 barrels per day (total of 3.7 million barrels) of crude oil grade spread positions through December 2016. These derivatives allow us to lock in grade basis differentials.
· A net short position of 18.9 Bcf through May 2016 related to anticipated sales of natural gas inventory and base gas requirements.
· A net short position of 29.7 million barrels through January 2018 related to anticipated net sales of our crude oil and NGL inventory.
Pipeline Loss Allowance Oil — As is common in the pipeline transportation industry, our tariffs incorporate a loss allowance factor that is intended to, among other things, offset losses due to evaporation, measurement and other losses in transit. We utilize derivative instruments to hedge a portion of the anticipated sales of the allowance oil that is to be collected under our tariffs. As of December 31, 2015, our material PLA hedges included a long call option position of approximately 1.6 million barrels through December 2018.
Natural Gas Processing/NGL Fractionation — We purchase natural gas for processing and operational needs. Additionally, we purchase NGL mix for fractionation and sell the resulting individual specification products (including ethane, propane, butane and condensate). In conjunction with these activities, we hedge the price risk associated with the purchase of the natural gas and the subsequent sale of the individual specification products. As of December 31, 2015, we had a long natural gas position of 5.7 Bcf through December 2016, a short propane position of 1.2 million barrels through December 2016, a short butane position of 0.4 million barrels through December 2016 and a short WTI position of 0.1 million barrels through December 2016. In addition, we had a long power position of 0.4 million megawatt hours which hedges a portion of our power supply requirements at our Canadian natural gas processing and fractionation plants through December 2018.
Physical commodity contracts that meet the definition of a derivative but are ineligible, or not designated, for the normal purchases and normal sales scope exception are recorded on the balance sheet at fair value, with changes in fair value recognized in earnings. We have determined that substantially all of our physical commodity contracts qualify for the normal purchases and normal sales scope exception.
Interest Rate Risk Hedging
We use interest rate derivatives to hedge interest rate risk associated with anticipated and outstanding interest payments occurring as a result of debt issuances. The derivative instruments we use to manage this risk consist of forward starting interest rate swaps and treasury locks. As of December 31, 2015, AOCI includes deferred losses of $183 million that relate to open and terminated interest rate derivatives that were designated as cash flow hedges. The terminated interest rate derivatives were cash-settled in connection with the issuance or refinancing of debt agreements. The deferred loss related to these instruments is being amortized to interest expense over the terms of the hedged debt instruments.
We have entered into forward starting interest rate swaps to hedge the underlying benchmark interest rate related to forecasted interest payments through 2049. The following table summarizes the terms of our forward starting interest rate swaps as of December 31, 2015 (notional amounts in millions):
|
Hedged Transaction |
|
Number and Types of |
|
Notional |
|
Expected |
|
Average Rate |
|
Accounting |
| |
|
Anticipated interest payments |
|
8 forward starting swaps |
|
$ |
200 |
|
6/15/2016 |
|
3.06 |
% |
Cash flow hedge |
|
|
Anticipated interest payments |
|
8 forward starting swaps |
|
$ |
200 |
|
6/15/2017 |
|
3.14 |
% |
Cash flow hedge |
|
|
Anticipated interest payments |
|
8 forward starting swaps |
|
$ |
200 |
|
6/15/2018 |
|
3.20 |
% |
Cash flow hedge |
|
|
Anticipated interest payments |
|
8 forward starting swaps |
|
$ |
200 |
|
6/14/2019 |
|
2.83 |
% |
Cash flow hedge |
|
The following table summarizes activity related to terminated interest rate derivatives (all of which were designated as cash flow hedges) for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013 (notional amounts and cash received/(paid) in millions):
|
Hedged Transaction |
|
Number and Types of |
|
Notional |
|
Cash |
|
Average Rate |
| ||
|
August 2015 PAA senior note issuance |
|
10 forward starting swaps (30-year) |
|
$ |
250 |
|
$ |
(31 |
) |
3.60 |
% |
|
August 2015 PAA senior note issuance |
|
7 forward starting swaps (30-year) |
|
$ |
250 |
|
$ |
(21 |
) |
3.03 |
% |
|
April 2014 PAA senior note issuance |
|
5 treasury lock agreements |
|
$ |
250 |
|
$ |
(7 |
) |
3.62 |
% |
|
August 2013 PAA senior note issuance |
|
5 forward starting swaps (30-year) |
|
$ |
125 |
|
$ |
11 |
|
3.39 |
% |
Currency Exchange Rate Risk Hedging
Because a significant portion of our Canadian business is conducted in CAD and, at times, a portion of our debt is denominated in CAD, we use foreign currency derivatives to minimize the risk of unfavorable changes in exchange rates. These instruments include foreign currency exchange contracts and forwards.
As of December 31, 2015, our outstanding foreign currency derivatives include derivatives we use to (i) hedge currency exchange risk associated with USD-denominated commodity purchases and sales in Canada and (ii) hedge currency exchange risk created by the use of USD-denominated commodity derivatives to hedge commodity price risk associated with CAD-denominated commodity purchases and sales.
The following table summarizes our open forward exchange contracts as of December 31, 2015 (in millions):
|
|
|
|
|
USD |
|
CAD |
|
Average Exchange Rate |
| ||
|
Forward exchange contracts that exchange CAD for USD: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
$ |
150 |
|
$ |
207 |
|
$1.00 - $1.38 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Forward exchange contracts that exchange USD for CAD: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
2016 |
|
$ |
219 |
|
$ |
291 |
|
$1.00 - $1.33 |
|
Summary of Financial Impact
We record all open derivatives on the balance sheet as either assets or liabilities measured at fair value. Changes in the fair value of derivatives are recognized currently in earnings unless specific hedge accounting criteria are met. For derivatives that qualify as cash flow hedges, changes in fair value of the effective portion of the hedges are deferred in AOCI and recognized in earnings in the periods during which the underlying physical transactions are recognized in earnings. Derivatives that do not qualify for hedge accounting and the portion of cash flow hedges that are not highly effective in offsetting changes in cash flows of the hedged items are recognized in earnings each period. Cash settlements associated with our derivative activities are classified within the same category as the related hedged item in our Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows.
A summary of the impact of our derivative activities recognized in earnings for the periods indicated is as follows (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, 2015 |
| ||||||||
|
Location of Gain/(Loss) |
|
Derivatives in |
|
Derivatives |
|
Total |
| ||||
|
Commodity Derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Supply and Logistics segment revenues |
|
$ |
56 |
|
$ |
152 |
|
|
$ |
208 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Transportation segment revenues |
|
— |
|
8 |
|
|
8 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Field operating costs |
|
— |
|
(18 |
) |
|
(18 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Interest Rate Derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Interest expense |
|
(11 |
) |
— |
|
|
(11 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Foreign Currency Derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Supply and Logistics segment revenues |
|
— |
|
(31 |
) |
|
(31 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Total Gain/(Loss) on Derivatives Recognized in Net Income |
|
$ |
45 |
|
$ |
111 |
|
|
$ |
156 |
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, 2014 |
| ||||||||
|
Location of Gain/(Loss) |
|
Derivatives in |
|
Derivatives |
|
Total |
| ||||
|
Commodity Derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Supply and Logistics segment revenues |
|
$ |
(1 |
) |
$ |
206 |
|
|
$ |
205 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Field operating costs |
|
— |
|
(21 |
) |
|
(21 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Interest Rate Derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Interest expense |
|
(5 |
) |
— |
|
|
(5 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Foreign Currency Derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Supply and Logistics segment revenues |
|
— |
|
(28 |
) |
|
(28 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Other income/(expense), net |
|
2 |
|
— |
|
|
2 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Total Gain/(Loss) on Derivatives Recognized in Net Income |
|
$ |
(4 |
) |
$ |
157 |
|
|
$ |
153 |
|
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, 2013 |
| ||||||||
|
Location of Gain/(Loss) |
|
Derivatives in |
|
Derivatives |
|
Total |
| ||||
|
Commodity Derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Supply and Logistics segment revenues |
|
$ |
77 |
|
$ |
(116 |
) |
|
$ |
(39 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Facilities segment revenues |
|
(11 |
) |
— |
|
|
(11 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Field operating costs |
|
— |
|
8 |
|
|
8 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Interest Rate Derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Interest expense |
|
(4 |
) |
— |
|
|
(4 |
) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Foreign Currency Derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Other income/(expense), net |
|
5 |
|
— |
|
|
5 |
| |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Total Gain/(Loss) on Derivatives Recognized in Net Income |
|
$ |
67 |
|
$ |
(108 |
) |
|
$ |
(41 |
) |
The following table summarizes the derivative assets and liabilities on our Consolidated Balance Sheets on a gross basis as of December 31, 2015 (in millions):
|
|
|
Asset Derivatives |
|
Liability Derivatives |
| |||||||
|
|
|
Balance Sheet |
|
Fair |
|
Balance Sheet |
|
Fair |
| |||
|
|
|
Location |
|
Value |
|
Location |
|
Value |
| |||
|
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Commodity derivatives |
|
Other current assets |
|
$ |
4 |
|
|
Other current assets |
|
$ |
(2 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Interest rate derivatives |
|
Other long-term assets, net |
|
1 |
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
(17 |
) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other long-term liabilities and deferred credits |
|
(33 |
) | ||
|
Total derivatives designated as hedging instruments |
|
|
|
$ |
5 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
(52 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Commodity derivatives |
|
Other current assets |
|
$ |
265 |
|
|
Other current assets |
|
$ |
(35 |
) |
|
|
|
Other long-term assets, net |
|
10 |
|
|
Other long-term assets, net |
|
(1 |
) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
(13 |
) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other long-term liabilities and deferred credits |
|
(1 |
) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Foreign currency derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
(8 |
) | ||
|
Total derivatives not designated as hedging instruments |
|
|
|
$ |
275 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
(58 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Total derivatives |
|
|
|
$ |
280 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
(110 |
) |
The following table summarizes the derivative assets and liabilities on our Consolidated Balance Sheets on a gross basis as of December 31, 2014 (in millions):
|
|
|
Asset Derivatives |
|
|
Liability Derivatives |
| ||||||
|
|
|
Balance Sheet |
|
Fair |
|
|
Balance Sheet |
|
Fair |
| ||
|
|
|
Location |
|
Value |
|
|
Location |
|
Value |
| ||
|
Derivatives designated as hedging instruments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Commodity derivatives |
|
Other current assets |
|
$ |
23 |
|
|
Other current assets |
|
$ |
(12 |
) |
|
|
|
Other long-term assets, net |
|
8 |
|
|
Other long-term assets, net |
|
(1 |
) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Interest rate derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
(44 |
) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other long-term liabilities and deferred credits |
|
(26 |
) | ||
|
Total derivatives designated as hedging instruments |
|
|
|
$ |
31 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
(83 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Derivatives not designated as hedging instruments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Commodity derivatives |
|
Other current assets |
|
$ |
439 |
|
|
Other current assets |
|
$ |
(246 |
) |
|
|
|
Other long-term assets, net |
|
23 |
|
|
Other long-term assets, net |
|
(3 |
) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
(35 |
) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other long-term liabilities and deferred credits |
|
(5 |
) | ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Foreign currency derivatives |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
(12 |
) | ||
|
Total derivatives not designated as hedging instruments |
|
|
|
$ |
462 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
(301 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Total derivatives |
|
|
|
$ |
493 |
|
|
|
|
$ |
(384 |
) |
Our derivative transactions are governed through ISDA (International Swaps and Derivatives Association) master agreements and clearing brokerage agreements. These agreements include stipulations regarding the right of set off in the event that we or our counterparty default on performance obligations. If a default were to occur, both parties have the right to net amounts payable and receivable into a single net settlement between parties.
Our accounting policy is to offset derivative assets and liabilities executed with the same counterparty when a master netting arrangement exists. Accordingly, we also offset derivative assets and liabilities with amounts associated with cash margin. Our exchange-traded derivatives are transacted through clearing brokerage accounts and are subject to margin requirements as established by the respective exchange. On a daily basis, our account equity (consisting of the sum of our cash balance and the fair value of our open derivatives) is compared to our initial margin requirement resulting in the payment or return of variation margin. As of December 31, 2015, we had a net broker payable of $156 million (consisting of initial margin of $91 million reduced by $247 million of variation margin that had been returned to us). As of December 31, 2014, we had a net broker payable of $133 million (consisting of initial margin of $126 million reduced by $259 million of variation margin that had been returned to us).
The following table presents information about derivative financial assets and liabilities that are subject to offsetting, including enforceable master netting arrangements as of the dates indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
December 31, 2015 |
|
December 31, 2014 |
| |||||||||
|
|
|
Derivative |
|
Derivative |
|
Derivative |
|
Derivative |
| |||||
|
|
|
Asset Positions |
|
Liability Positions |
|
Asset Positions |
|
Liability Positions |
| |||||
|
Netting Adjustments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Gross position - asset/(liability) |
|
$ |
280 |
|
$ |
(110 |
) |
|
$ |
493 |
|
$ |
(384 |
) |
|
Netting adjustment |
|
(38 |
) |
38 |
|
|
(262 |
) |
262 |
| ||||
|
Cash collateral received |
|
(156 |
) |
— |
|
|
(133 |
) |
— |
| ||||
|
Net position - asset/(liability) |
|
$ |
86 |
|
$ |
(72 |
) |
|
$ |
98 |
|
$ |
(122 |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Balance Sheet Location After Netting Adjustments: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Other current assets |
|
$ |
76 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
$ |
71 |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Other long-term assets, net |
|
10 |
|
— |
|
|
27 |
|
— |
| ||||
|
Other current liabilities |
|
— |
|
(38 |
) |
|
— |
|
(91 |
) | ||||
|
Other long-term liabilities and deferred credits |
|
— |
|
(34 |
) |
|
— |
|
(31 |
) | ||||
|
|
|
$ |
86 |
|
$ |
(72 |
) |
|
$ |
98 |
|
$ |
(122 |
) |
As of December 31, 2015, there was a net loss of $203 million deferred in AOCI. The deferred net loss recorded in AOCI is expected to be reclassified to future earnings contemporaneously with (i) the earnings recognition of the underlying hedged commodity transaction or (ii) interest expense accruals associated with underlying debt instruments. Of the total net loss deferred in AOCI at December 31, 2015, we expect to reclassify a net loss of $3 million to earnings in the next twelve months. The remaining deferred loss of $200 million is expected to be reclassified to earnings through 2049. A portion of these amounts is based on market prices as of December 31, 2015; thus, actual amounts to be reclassified will differ and could vary materially as a result of changes in market conditions.
The net deferred gain/(loss), including tax effects, recognized in AOCI for derivatives for the periods indicated was as follows (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
Commodity derivatives, net |
|
$ |
33 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
$ |
37 |
|
|
Interest rate derivatives, net |
|
(32 |
) |
(103 |
) |
73 |
| |||
|
Foreign currency derivatives, net |
|
— |
|
2 |
|
— |
| |||
|
Total |
|
$ |
1 |
|
$ |
(86 |
) |
$ |
110 |
|
At December 31, 2015 and December 31, 2014, none of our outstanding derivatives contained credit-risk related contingent features that would result in a material adverse impact to us upon any change in our credit ratings. Although we may be required to post margin on our cleared derivatives as described above, we do not require our non-cleared derivative counterparties to post collateral with us.
Recurring Fair Value Measurements
Derivative Financial Assets and Liabilities
The following table sets forth by level within the fair value hierarchy our financial assets and liabilities that were accounted for at fair value on a recurring basis as of the dates indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
Fair Value as of December 31, 2015 |
|
Fair Value as of December 31, 2014 |
| |||||||||||||||||||||
|
Recurring Fair Value Measures (1) |
|
Level 1 |
|
Level 2 |
|
Level 3 |
|
Total |
|
Level 1 |
|
Level 2 |
|
Level 3 |
|
Total |
| |||||||||
|
Commodity derivatives |
|
$ |
126 |
|
$ |
90 |
|
$ |
11 |
|
$ |
227 |
|
|
$ |
(85 |
) |
$ |
261 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
$ |
191 |
|
|
Interest rate derivatives |
|
— |
|
(49 |
) |
— |
|
(49 |
) |
|
— |
|
(70 |
) |
— |
|
(70 |
) | ||||||||
|
Foreign currency derivatives |
|
— |
|
(8 |
) |
— |
|
(8 |
) |
|
— |
|
(12 |
) |
— |
|
(12 |
) | ||||||||
|
Total net derivative asset/(liability) |
|
$ |
126 |
|
$ |
33 |
|
$ |
11 |
|
$ |
170 |
|
|
$ |
(85 |
) |
$ |
179 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
$ |
109 |
|
(1) Derivative assets and liabilities are presented above on a net basis but do not include related cash margin deposits.
Level 1
Level 1 of the fair value hierarchy includes exchange-traded commodity derivatives such as futures and options. The fair value of exchange-traded commodity derivatives is based on unadjusted quoted prices in active markets.
Level 2
Level 2 of the fair value hierarchy includes exchange-cleared commodity derivatives and over-the-counter commodity, interest rate and foreign currency derivatives that are traded in active markets. In addition, it includes certain physical commodity contracts. The fair value of these derivatives is based on broker price quotations which are corroborated with market observable inputs.
Level 3
Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy includes certain physical commodity contracts. The fair value of our Level 3 physical commodity contracts is based on a valuation model utilizing broker-quoted forward commodity prices, and timing estimates, which involve management judgment. The significant unobservable inputs used in the fair value measurement of our Level 3 derivatives are forward prices obtained from brokers. A significant increase or decrease in these forward prices could result in a material change in fair value to our Level 3 derivatives. We report unrealized gains and losses associated with Level 3 commodity derivatives in our Consolidated Statements of Operations as Supply and Logistics segment revenues.
To the extent any transfers between levels of the fair value hierarchy occur, our policy is to reflect these transfers as of the beginning of the reporting period in which they occurred.
Rollforward of Level 3 Net Asset/(Liability)
The following table provides a reconciliation of changes in fair value of the beginning and ending balances for our derivatives classified as Level 3 for the periods indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
Beginning Balance |
|
$ |
15 |
|
$ |
(3 |
) |
|
Gains for the period included in earnings |
|
1 |
|
— |
| ||
|
Settlements |
|
(14 |
) |
3 |
| ||
|
Derivatives entered into during the period |
|
9 |
|
15 |
| ||
|
Ending Balance |
|
$ |
11 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Change in unrealized gains included in earnings relating to Level 3 derivatives still held at the end of the period |
|
$ |
10 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
Income tax expense is estimated using the tax rate in effect or to be in effect during the relevant periods in the jurisdictions in which we operate. Deferred income tax assets and liabilities are recognized for temporary differences between the basis of assets and liabilities for financial reporting and tax purposes and are stated at enacted tax rates expected to be in effect when taxes are actually paid or recovered. To the extent we do not consider it more likely than not that a deferred tax asset will be recovered, a valuation allowance is established. Changes in tax legislation are included in the relevant computations in the period in which such changes are effective. We review contingent tax liabilities for estimated exposures on a more likely than not standard related to our current tax positions.
Pursuant to FASB guidance related to accounting for uncertainty in income taxes, we must recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position only if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained upon examination by the taxing authorities, based on the technical merits of the tax position and also the past administrative practices and precedents of the taxing authority. As of December 31, 2015 and 2014, we had not recognized any material amounts in connection with uncertainty in income taxes.
U.S. Federal and State Taxes
Although we are organized as a limited partnership, we have elected to be treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes and are therefore subject to both U. S. federal and state income taxes.
Canadian Federal and Provincial Taxes
All of our Canadian operations are conducted by entities that are treated as corporations for Canadian tax purposes (flow through for U.S. tax purposes) and that are subject to Canadian federal and provincial taxes. Additionally, payments of interest and dividends from our Canadian entities to other Plains entities are subject to Canadian withholding tax that is treated as income tax expense.
Tax Components
Components of income tax expense for the periods indicated are as follows (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
Current income tax expense: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
State income tax |
|
$ |
1 |
|
$ |
1 |
|
$ |
1 |
|
|
Canadian federal and provincial income tax |
|
83 |
|
70 |
|
99 |
| |||
|
Total current income tax expense |
|
$ |
84 |
|
$ |
71 |
|
$ |
100 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Deferred income tax expense/(benefit): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Federal income tax |
|
$ |
75 |
|
$ |
38 |
|
$ |
7 |
|
|
State income tax |
|
7 |
|
3 |
|
— |
| |||
|
Canadian federal and provincial income tax |
|
16 |
|
100 |
|
(1 |
) | |||
|
Total deferred income tax expense |
|
$ |
98 |
|
$ |
141 |
|
$ |
6 |
|
|
Total income tax expense |
|
$ |
182 |
|
$ |
212 |
|
$ |
106 |
|
The difference between income tax expense based on the statutory federal income tax rate and our effective income tax expense is summarized for the periods indicated as follows (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
Income before tax |
|
$ |
991 |
|
$ |
1,540 |
|
$ |
1,480 |
|
|
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
(691 |
) |
(1,258 |
) |
(1,359 |
) | |||
|
Income taxes attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
(100 |
) |
(171 |
) |
(99 |
) | |||
|
|
|
$ |
200 |
|
$ |
111 |
|
$ |
22 |
|
|
Federal statutory income tax rate |
|
35 |
% |
35 |
% |
35 |
% | |||
|
Income tax at statutory rate |
|
$ |
70 |
|
$ |
39 |
|
$ |
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Federal benefit of state income tax |
|
$ |
(3 |
) |
$ |
(1 |
) |
$ |
(1 |
) |
|
Deferred tax rate adjustment |
|
8 |
|
— |
|
— |
| |||
|
State income tax |
|
7 |
|
3 |
|
— |
| |||
|
Income taxes attributable to noncontrolling interests: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Canadian federal and provincial income tax |
|
$ |
85 |
|
$ |
154 |
|
$ |
79 |
|
|
Canadian withholding tax |
|
14 |
|
16 |
|
19 |
| |||
|
State income tax |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
| |||
|
Total income tax expense |
|
$ |
182 |
|
$ |
212 |
|
$ |
106 |
|
Deferred tax assets and liabilities are aggregated by the applicable tax paying entity and jurisdiction and result from the following as of the dates indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
December 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
Deferred tax assets: |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Investment in partnerships |
|
$ |
1,730 |
|
$ |
1,651 |
|
|
Net operating losses |
|
105 |
|
54 |
| ||
|
Book accruals in excess of current tax deductions |
|
20 |
|
29 |
| ||
|
Total deferred tax assets |
|
1,855 |
|
1,734 |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Deferred tax liabilities: |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Derivative instruments |
|
(30 |
) |
(71 |
) | ||
|
Property and equipment in excess of tax values |
|
(312 |
) |
(322 |
) | ||
|
Other |
|
(41 |
) |
(49 |
) | ||
|
Total deferred tax liabilities |
|
(383 |
) |
(442 |
) | ||
|
Net deferred tax assets |
|
$ |
1,472 |
|
$ |
1,292 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Balance sheet classification of deferred tax assets/(liabilities): |
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Deferred tax asset |
|
$ |
1,835 |
|
$ |
1,705 |
|
|
Other current liabilities |
|
— |
|
(64 |
) | ||
|
Other long-term liabilities and deferred credits |
|
(363 |
) |
(349 |
) | ||
|
|
|
$ |
1,472 |
|
$ |
1,292 |
|
In connection with the transfer of the ownership interest in AAP in connection with our IPO in October 2013 and subsequent transfers in 2013, 2014 and 2015, a deferred tax asset was created. These transfers of ownership were accounted for at the historical carrying basis for GAAP accounting purposes, but were recorded at the fair market value of the Class A shares at the time of exchange for U.S. federal income tax purposes. The resulting basis difference resulted in a deferred tax asset that was recorded as a component of partners’ capital as it results from transactions among shareholders. The deferred tax asset is amortized to deferred income tax expense as the associated basis step-up is realized on our tax returns.
As of December 31, 2015, we had net operating loss carryforwards for (i) U.S. federal income tax purposes of $264 million, which will expire from 2033 to 2035, (ii) state income tax purposes of $90 million, which will expire from 2018 to 2035, and (iii) foreign income tax purposes of $11 million, which will expire from 2034 to 2035. As of December 31, 2015, we had foreign tax credits for U.S. federal income tax purposes of $6 million, which will expire in 2024.
Generally, tax returns for our Canadian entities are open to audit from 2008 through 2015. Our U.S. and state tax years are generally open to examination from 2012 to 2015.
Note 13—Major Customers and Concentration of Credit Risk
Marathon Petroleum Corporation and its subsidiaries accounted for 17%, 17% and 15% of our revenues for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. ExxonMobil Corporation and its subsidiaries accounted for 13%, 15% and 13% of our revenues for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. Phillips 66 and its subsidiaries accounted for 11% of our revenues for the year ended December 31, 2013. No other customers accounted for 10% or more of our revenues during any of the three years ended December 31, 2015. The majority of revenues from these customers pertain to our supply and logistics operations. The sales to these customers occur at multiple locations and we believe that the loss of these customers would have only a short-term impact on our operating results. There is risk, however, that we would not be able to identify and access a replacement market at comparable margins.
Financial instruments that potentially subject us to concentrations of credit risk consist principally of trade receivables. Our accounts receivable are primarily from purchasers and shippers of crude oil and, to a lesser extent, purchasers of NGL and natural gas. This industry concentration has the potential to impact our overall exposure to credit risk in that the customers may be similarly affected by changes in economic, industry or other conditions. We review credit exposure and financial information of our counterparties and generally require letters of credit for receivables from customers that are not considered creditworthy, unless the credit risk can otherwise be reduced. See Note 2 for additional discussion of our accounts receivable and our review of credit exposure.
Note 14—Related Party Transactions
Transactions with Oxy
As of December 31, 2015, Oxy owned approximately 13% of the limited partner interests in AAP and had a representative on the board of directors of GP LLC and our general partner. During the three years ended December 31, 2015, we recognized sales and transportation revenues and purchased petroleum products from Oxy. These transactions were conducted at posted tariff rates or prices that we believe approximate market. A portion of these transactions was conducted under a crude oil buy/sell agreement that includes a multi-year minimum volume commitment. The impact to our Consolidated Statements of Operations from those transactions is included below (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
Revenues |
|
$ |
866 |
|
$ |
1,212 |
|
$ |
1,309 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||
|
Purchases and related costs (1) |
|
$ |
41 |
|
$ |
925 |
|
$ |
863 |
|
(1) Purchases and related costs include crude oil buy/sell transactions that are accounted for as inventory exchanges and are presented net in our Consolidated Statements of Operations.
We currently have a netting arrangement with Oxy. Our gross receivable and payable amounts with Oxy on our Consolidated Balance Sheets were as follows as of the dates indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
December 31, |
| ||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
Trade accounts receivable and other receivables |
|
$ |
405 |
|
$ |
489 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||
|
Accounts payable |
|
$ |
363 |
|
$ |
441 |
|
In November 2014, we purchased Oxy’s 50% interest in BridgeTex. See Note 7 for further discussion. Also in November 2014, Oxy exercised its Exchange Right, pursuant to which Oxy received 69,000,000 Class A shares in exchange for an equal number of Class B shares, general partner units and AAP units. Immediately following the exercise of the Exchange Right, we completed an underwritten secondary public offering of the Class A shares received by Oxy. We did not receive any of the proceeds from the offering.
Transactions with Equity Method Investees
We also have transactions with companies in which we hold an investment accounted for under the equity method of accounting (see Note 7 for information related to these investments). We recorded revenues of $17 million, $3 million and $33 million during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. During the three years ended December 31, 2015, we utilized transportation services and purchased petroleum products provided by these companies. Costs related to these services totaled $164 million, $75 million and $79 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively. These transactions were conducted at posted tariff rates or contracted rates or prices that we believe approximate market. Receivables from our equity method investees totaled $14 million at December 31, 2015 and less than $1 million at December 31, 2014. Accounts payable to our equity method investees were $25 million and $6 million at December 31, 2015 and 2014, respectively.
In addition, we have an agreement to transport crude oil at posted tariff rates on a pipeline that is owned by an equity method investee, in which we own a 50% interest. Our commitment to transport is supported by crude oil buy/sell agreements with third parties (including Oxy) with commensurate quantities.
PAA Preferred Unit Issuance
In January 2016, PAA completed a private placement of preferred units. Certain of the purchasers of the PAA preferred units or their affiliates are related parties. Kayne Anderson Capital Advisors, L.P. and certain of its affiliates and an affiliate of The Energy Minerals Group hold ownership interests in AAP. In addition, certain of the current directors of GP LLC and our general partner are affiliated with certain of the purchasers. See Note 10 for additional information.
Note 15—Equity-Indexed Compensation Plans
PAGP Long-Term Incentive Plan Awards
In connection with our IPO in October 2013, our general partner adopted the PAGP LTIP, which is intended to align the interests of employees and directors with those of our shareholders by providing such employees and directors incentive compensation awards that reward achievement of targeted distribution levels and other business objectives. The PAGP LTIP provides for awards of options, restricted shares, phantom shares and share appreciation rights. Certain awards may also include distribution equivalent rights (“DERs”), which, subject to applicable vesting criteria, entitle the grantee to a cash payment equal to the cash distribution paid on an outstanding Class A share. The PAGP LTIP authorizes the issuance of up to 10 million Class A shares deliverable upon vesting. In February 2014, an aggregate of 83,200 phantom Class A shares were issued to our directors. These awards vest annually in February in 25% increments and have an automatic re-grant feature such that as they vest, an equivalent amount is granted.
Activity for awards under the PAGP LTIP is summarized in the following table for the periods indicated (shares in millions):
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted Average |
| |
|
|
|
|
|
Grant Date |
| |
|
|
|
PAGP Shares |
|
Fair Value per Share |
| |
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2013 |
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Granted |
|
0.1 |
|
$ |
27.84 |
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2014 |
|
0.1 |
|
$ |
27.84 |
|
|
Granted (1) |
|
— |
|
$ |
27.84 |
|
|
Vested (2) |
|
— |
|
$ |
27.84 |
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
|
0.1 |
|
$ |
27.84 |
|
(1) During the year ended December 31, 2015, less than 0.1 million PAGP LTIP awards were granted under the automatic re-grant feature for awards issued to our directors.
(2) During the year ended December 31, 2015, less than 0.1 million PAGP LTIP awards vested. These awards were settled in Class A shares.
PAA Long-Term Incentive Plan Awards
Plains All American 2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan. In November 2013, PAA’s common unitholders approved the Plains All American 2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “PAA 2013 LTIP”), which consolidated PAA’s three previous long-term incentive plans (the Plains All American GP LLC 1998 Long-Term Incentive Plan, as amended, the Plains All American 2005 Long-Term Incentive Plan, as amended, and the Plains All American PPX Successor Long-Term Incentive Plan, as amended) into a single plan. The PAA 2013 LTIP authorizes the issuance of an aggregate of approximately 13.1 million PAA common units deliverable upon vesting. Although other types of awards are contemplated under the PAA 2013 LTIP, currently outstanding awards are limited to “phantom units,” which mature into the right to receive common units of PAA (or cash equivalent) upon vesting. Some awards also include DERs, which, subject to applicable vesting criteria, entitle the grantee to a cash payment equal to the cash distribution paid on an outstanding PAA common unit.
Plains All American PNG Successor Long-Term Incentive Plan. In conjunction with the PNG Merger on December 31, 2013, PAA’s general partner adopted and assumed the PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P. 2010 Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “PNG 2010 LTIP”) and changed the plan name to the Plains All American PNG Successor Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “PNG Successor LTIP”). Additionally, as a result of the PNG Merger, outstanding awards of PNG phantom units issued under the PNG 2010 LTIP were converted into comparable awards of phantom units representing the right to receive PAA common units by applying the Merger Exchange Ratio to each outstanding phantom unit and rounding down to the nearest PAA phantom unit for any fractions. See Note 1 for further discussion of the PNG Merger. The PNG Successor LTIP authorizes the issuance of an aggregate of 1.3 million PAA common units deliverable upon vesting. Although other types of awards are contemplated under the PNG Successor LTIP, currently outstanding awards are limited to “phantom units,” which mature into the right to receive common units of PAA (or cash equivalent) upon vesting. Some awards also include DERs, which, subject to applicable vesting criteria, entitle the grantee to a cash payment equal to the cash distribution paid on an outstanding PAA common unit.
Plains All American GP LLC 2006 Long-Term Incentive Tracking Unit Plan. PAA’s general partner has adopted the Plains All American GP LLC 2006 Long-Term Incentive Tracking Unit Plan (the “2006 Plan”) for non-officer employees. The 2006 Plan authorizes the grant of approximately 4.2 million “tracking units” which, upon vesting, represent the right to receive a cash payment in an amount based upon the market value of a PAA common unit at the time of vesting.
At December 31, 2015, the following LTIP awards, denominated in PAA units, were outstanding (units in millions):
|
PAA |
|
PAA |
|
Probable Awards |
|
Not Yet |
| |||||||||||
|
LTIP Units |
|
Distribution |
|
Estimated Unit Vesting Date |
|
Probable |
| |||||||||||
|
Outstanding (1) (2) |
|
Required (3) |
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2018 |
|
2019 |
|
Thereafter |
|
Total |
|
Awards (4) |
| |
|
6.9 |
|
$ |
2.075-$3.300 |
|
1.9 |
|
1.5 |
|
1.0 |
|
0.8 |
|
0.5 |
|
5.7 |
|
1.2 |
|
(1) Approximately 2.7 million of the 6.9 million outstanding PAA LTIP awards also include DERs, of which 2.4 million had vested as of December 31, 2015.
(2) LTIP units outstanding do not include AAP Management Units or PAGP LTIP awards.
(3) These LTIP awards have performance conditions requiring the attainment of an annualized PAA distribution of between $2.075 and $3.30 and vest upon the later of a certain date or the attainment of such levels. If the performance conditions are not attained while the grantee remains employed by us, or the grantee does not meet employment requirements, these awards will be forfeited. For purposes of this disclosure, vesting dates are based on an estimate of future distribution levels and assume that all grantees remain employed by us through the vesting date. As of December 31, 2015, a distribution of $2.90 per PAA common unit was deemed probable of occurring in the reasonably foreseeable future (and was initially determined to be probable in the fourth quarter of 2014).
(4) The achievement of the applicable performance conditions (distributions greater than $2.90 per PAA common unit) was not deemed to be probable as of December 31, 2015 and, therefore, no expense has been recognized related to these awards.
PAA’s LTIP awards include both liability-classified and equity-classified awards. In accordance with FASB guidance regarding share-based payments, the fair value of liability-classified LTIP awards is calculated based on the closing market price of the underlying PAA unit at each balance sheet date and adjusted for the present value of any distributions that are estimated to occur on the underlying units over the vesting period that will not be received by the award recipients. The fair value of equity-classified LTIP awards is calculated based on the closing market price of the underlying PAA unit on the respective grant dates and adjusted for the present value of any distributions that are estimated to occur on the underlying units over the vesting period that will not be received by the award recipient. This fair value is recognized as compensation expense over the service period.
PAA’s LTIP awards typically contain performance conditions based on the attainment of certain PAA annualized distribution levels and vest upon the later of a certain date or the attainment of such levels. For awards with performance conditions (such as distribution targets), expense is accrued over the service period only if the performance condition is considered probable of occurring. When awards with performance conditions that were previously considered improbable become probable, we incur additional expense in the period that the probability assessment changes. This is necessary to bring the accrued obligation associated with these awards up to the level it would be if we had been accruing for these awards since the grant date. DER awards typically contain performance conditions based on the attainment of certain PAA annualized distribution levels and become earned upon the attainment of such levels. The DERs terminate with the vesting or forfeiture of the underlying LTIP award. For liability-classified awards, we recognize DER payments in the period the payment is earned as compensation expense. For equity-classified awards, we recognize DER payments in the period they are paid as a reduction of noncontrolling interest in partners’ capital.
Our accrued liability at December 31, 2015 related to all outstanding liability-classified PAA LTIP awards and DERs was $33 million, of which $20 million was classified as short-term and $13 million was classified as long-term. These short- and long-term accrued LTIP liabilities are reflected in “Accounts payable and accrued liabilities” and “Other long-term liabilities and deferred credits,” respectively, on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. These liabilities include accruals associated with our assessment that an annualized PAA distribution of $2.90 per unit is probable of occurring in the reasonably foreseeable future (which was initially determined to be probable in the fourth quarter of 2014). At December 31, 2014, the accrued liability was $101 million, of which $57 million was classified as short-term and $44 million was classified as long-term.
Activity for LTIP awards under our equity-indexed compensation plans denominated in PAA and PNG units is summarized in the following table for the periods indicated (units in millions):
|
|
|
PAA Units (1) (2) |
|
PNG Units |
| ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
Weighted Average |
|
|
|
Weighted Average |
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
Grant Date |
|
|
|
Grant Date |
| ||
|
|
|
Units |
|
Fair Value per Unit |
|
Units |
|
Fair Value per Unit |
| ||
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2012 |
|
6.0 |
|
$ |
25.55 |
|
0.9 |
|
$ |
17.49 |
|
|
Granted |
|
4.1 |
|
$ |
47.60 |
|
0.4 |
|
$ |
17.51 |
|
|
Vested (3) |
|
(1.8 |
) |
$ |
24.79 |
|
— |
|
$ |
18.88 |
|
|
Cancelled or forfeited (4) |
|
(0.3 |
) |
$ |
36.70 |
|
(0.3 |
) |
$ |
21.62 |
|
|
Conversion of PNG unit-denominated awards into PAA unit-denominated awards (5) |
|
0.4 |
|
$ |
40.54 |
|
(1.0 |
) |
$ |
16.41 |
|
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2013 |
|
8.4 |
|
$ |
36.97 |
|
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
|
Granted |
|
1.2 |
|
$ |
47.68 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Vested |
|
(1.9 |
) |
$ |
25.49 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Cancelled or forfeited |
|
(0.4 |
) |
$ |
40.14 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2014 |
|
7.3 |
|
$ |
41.45 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Granted |
|
2.1 |
|
$ |
28.76 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Vested |
|
(2.1 |
) |
$ |
28.91 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Cancelled or forfeited |
|
(0.4 |
) |
$ |
44.56 |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
Outstanding at December 31, 2015 |
|
6.9 |
|
$ |
41.23 |
|
|
|
|
| |
(1) Amounts do not include AAP Management Units or PAGP LTIP awards.
(2) Approximately 0.5 million, 0.6 million and 0.5 million PAA common units were issued, net of tax withholding of approximately 0.3 million, 0.3 million and 0.3 million units during 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, in connection with the settlement of vested awards. The remaining PAA awards (approximately 1.3 million, 1.0 million and 1.0 million units) that vested during 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively, were settled in cash.
(3) Less than 0.1 million PNG units vested during the year ended December 31, 2013.
(4) The unvested portion of grants of PNG phantom unit awards other than those granted under the PNG 2010 LTIP was surrendered on December 31, 2013 in connection with the closing of the PNG Merger.
(5) As a result of the PNG Merger on December 31, 2013, outstanding awards of PNG phantom units issued under the PNG 2010 LTIP were converted into comparable awards of PAA phantom units representing the right to receive PAA common units by applying the Merger Exchange Ratio to each outstanding PNG phantom unit and rounding down to the nearest PAA phantom unit for any fractions.
AAP Management Units
In August 2007, the owners of AAP authorized the issuance of AAP Management Units (a profits interest) in order to provide additional long-term incentives and encourage retention for certain members of our senior management. AAP Management Units become earned in various increments upon the achievement of certain performance thresholds related to achievement of targeted PAA distribution levels. As of December 31, 2015, 2.2 million AAP Management Units were unearned; however, these unearned AAP Management Units will become earned in 25% increments upon or 180 days after the achievement of annualized PAA distribution levels of between $2.85 and $3.50. When earned, the AAP Management Units are entitled to participate in distributions paid by AAP in excess of $11 million (as adjusted for debt service costs and excluding special distributions funded by debt) per quarter. Up to approximately 52.1 million AAP Management Units are authorized for issuance. Assuming all 52.1 million AAP Management Units were granted and earned, the maximum participation would be approximately 8% of AAP’s distribution in excess of $11 million (as adjusted) each quarter.
Additionally, beginning after December 31, 2015, a holder of vested AAP Management Units will be entitled to convert his or her AAP Management Units into AAP units and a like number of our Class B shares based on a conversion ratio calculated in accordance with the AAP limited partnership agreement. Following any such conversion, the holder will have the Exchange Right for our Class A shares. See Note 10 for additional information.
The following is a summary of activity of AAP Management Units for the periods indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
Reserved for |
|
Outstanding |
|
Outstanding |
|
Grant Date |
| ||
|
Balance at December 31, 2013 |
|
3.5 |
|
48.6 |
|
47.0 |
|
|
$ |
51 |
|
|
Granted |
|
(0.5 |
) |
0.5 |
|
— |
|
|
13 |
| |
|
Earned |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
0.8 |
|
|
N/A |
| |
|
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
|
3.0 |
|
49.1 |
|
47.8 |
|
|
$ |
64 |
|
|
Granted |
|
(1.6 |
) |
1.6 |
|
— |
|
|
24 |
| |
|
Earned |
|
N/A |
|
N/A |
|
0.7 |
|
|
N/A |
| |
|
Balance at December 31, 2015 |
|
1.4 |
|
50.7 |
|
48.5 |
|
|
$ |
88 |
|
(1) Of the $88 million grant date fair value, $56 million had been recognized through December 31, 2015 on a cumulative basis. Of this amount, $1 million, $7 million and $5 million was recognized as expense during the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
As the intent of the AAP Management Units is to provide a performance incentive and encourage retention for certain members of PAA’s senior management, we recognize the grant date fair value of the AAP Management Units as compensation expense over the service period, with a corresponding credit to noncontrolling interest in partners’ capital on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
Other Consolidated Equity-Indexed Compensation Plan Information
We refer to all of the LTIPs and AAP Management Units collectively as our “equity-indexed compensation plans.” The table below summarizes the expense recognized and the value of vested LTIP awards (settled in PAA common units, PAGP shares and cash) under our equity-indexed compensation plans and includes both liability-classified and equity-classified awards for the periods indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
Equity-indexed compensation expense |
|
$ |
27 |
|
$ |
99 |
|
$ |
116 |
|
|
LTIP unit- or share-settled vestings |
|
$ |
37 |
|
$ |
53 |
|
$ |
48 |
|
|
LTIP cash-settled vestings |
|
$ |
66 |
|
$ |
53 |
|
$ |
61 |
|
|
DER cash payments |
|
$ |
8 |
|
$ |
8 |
|
$ |
8 |
|
Based on the December 31, 2015 fair value measurement and probability assessment regarding future distributions, we expect to recognize $74 million of additional expense over the life of outstanding awards related to the remaining unrecognized fair value. Actual amounts may differ materially as a result of a change in the market price of PAA’s units and PAGP’s shares and/or probability assessments regarding future distributions. We estimate that the remaining fair value will be recognized in expense as shown below (in millions):
|
Year |
|
Equity-Indexed |
| |
|
2016 |
|
$ |
37 |
|
|
2017 |
|
22 |
| |
|
2018 |
|
11 |
| |
|
2019 |
|
3 |
| |
|
2020 |
|
1 |
| |
|
Total |
|
$ |
74 |
|
(1) Amounts do not include fair value associated with awards containing performance conditions that are not considered to be probable of occurring at December 31, 2015.
(2) Includes unamortized fair value associated with AAP Management Units and PAGP LTIP awards.
Note 16—Commitments and Contingencies
Commitments
We have commitments, some of which are leases, related to real property, equipment and operating facilities. We also incur costs associated with leased land, rights-of-way, permits and regulatory fees. Future non-cancelable commitments related to these items at December 31, 2015, are summarized below (in millions):
|
|
|
2016 |
|
2017 |
|
2018 |
|
2019 |
|
2020 |
|
Thereafter |
|
Total |
| |||||||
|
Leases (1) |
|
$ |
200 |
|
$ |
184 |
|
$ |
154 |
|
$ |
128 |
|
$ |
108 |
|
$ |
427 |
|
$ |
1,201 |
|
|
Other commitments (2) |
|
150 |
|
152 |
|
133 |
|
127 |
|
129 |
|
487 |
|
1,178 |
| |||||||
|
Total |
|
$ |
350 |
|
$ |
336 |
|
$ |
287 |
|
$ |
255 |
|
$ |
237 |
|
$ |
914 |
|
$ |
2,379 |
|
(1) Includes capital and operating leases as defined by FASB guidance. Lease expense for 2015, 2014 and 2013 was $164 million, $145 million and $132 million, respectively.
(2) Primarily includes third-party storage and transportation agreements and pipeline throughput agreements, as well as approximately $930 million associated with an agreement to transport crude oil on a pipeline that is owned by an equity method investee, in which we own a 50% interest. Our commitment to transport is supported by crude oil buy/sell agreements with third parties (including Oxy) with commensurate quantities.
Loss Contingencies — General
To the extent we are able to assess the likelihood of a negative outcome for a contingency, our assessments of such likelihood range from remote to probable. If we determine that a negative outcome is probable and the amount of loss is reasonably estimable, we accrue an undiscounted liability equal to the estimated amount. If a range of probable loss amounts can be reasonably estimated and no amount within the range is a better estimate than any other amount, then we accrue an undiscounted liability equal to the minimum amount in the range. In addition, we estimate legal fees that we expect to incur associated with loss contingencies and accrue those costs when they are material and probable of being incurred.
We do not record a contingent liability when the likelihood of loss is probable but the amount cannot be reasonably estimated or when the likelihood of loss is believed to be only reasonably possible or remote. For contingencies where an unfavorable outcome is reasonably possible and the impact would be material to our consolidated financial statements, we disclose the nature of the contingency and, where feasible, an estimate of the possible loss or range of loss.
Legal Proceedings — General
In the ordinary course of business, we are involved in various legal proceedings, including those arising from regulatory and environmental matters. Although we are insured against various risks to the extent we believe it is prudent, there is no assurance that the nature and amount of such insurance will be adequate, in every case, to fully protect us from losses arising from current or future legal proceedings.
Taking into account what we believe to be all relevant known facts and circumstances, and based on what we believe to be reasonable assumptions regarding the application of those facts and circumstances to existing laws and regulations, we do not believe that the outcome of the legal proceedings in which we are currently involved (including those described below) will, individually or in the aggregate, have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Environmental — General
Although over the course of the last several years we have made significant investments in our maintenance and integrity programs, and have hired additional personnel in those areas, we have experienced (and likely will experience future) releases of hydrocarbon products into the environment from our pipeline, rail, storage and other facility operations. These releases can result from accidents or from unpredictable man-made or natural forces and may reach surface water bodies, groundwater aquifers or other sensitive environments. Damages and liabilities associated with any such releases from our existing or future assets could be significant and could have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
We record environmental liabilities when environmental assessments and/or remedial efforts are probable and the amounts can be reasonably estimated. Generally, our recording of these accruals coincides with our completion of a feasibility study or our commitment to a formal plan of action. We do not discount our environmental remediation liabilities to present value. We also record environmental liabilities assumed in business combinations based on the estimated fair value of the environmental obligations caused by past operations of the acquired company. We record receivables for amounts recoverable from insurance or from third parties under indemnification agreements in the period that we determine the costs are probable of recovery.
Environmental expenditures that pertain to current operations or to future revenues are expensed or capitalized consistent with our capitalization policy for property and equipment. Expenditures that result from the remediation of an existing condition caused by past operations and that do not contribute to current or future profitability are expensed.
At December 31, 2015, our estimated undiscounted reserve for environmental liabilities (including liabilities related to the Line 901 incident, as discussed further below) totaled $185 million, of which $81 million was classified as short-term and $104 million was classified as long-term. At December 31, 2014, our estimated undiscounted reserve for environmental liabilities totaled $82 million, of which $13 million was classified as short-term and $69 million was classified as long-term. The short- and long-term environmental liabilities referenced above are reflected in “Accounts payable and accrued liabilities” and “Other long-term liabilities and deferred credits,” respectively, on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. At December 31, 2015 and 2014, we had recorded receivables totaling $161 million and $8 million, respectively, for amounts probable of recovery under insurance and from third parties under indemnification agreements, which are predominantly reflected in “Trade accounts receivable and other receivables, net” on our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
In some cases, the actual cash expenditures associated with these liabilities may not occur for three years or longer. Our estimates used in determining these reserves are based on information currently available to us and our assessment of the ultimate outcome. Among the many uncertainties that impact our estimates are the necessary regulatory approvals for, and potential modification of, our remediation plans, the limited amount of data available upon initial assessment of the impact of soil or water contamination, changes in costs associated with environmental remediation services and equipment and the possibility of existing or future legal claims giving rise to additional liabilities. Therefore, although we believe that the reserve is adequate, actual costs incurred (which may ultimately include costs for contingencies that are currently not reasonably estimable or costs for contingencies where the likelihood of loss is currently believed to be only reasonably possible or remote) may be in excess of the reserve and may potentially have a material adverse effect on our consolidated financial condition, results of operations or cash flows.
Specific Legal, Environmental or Regulatory Matters
Line 901 Incident. In May 2015, we experienced a crude oil release from our Las Flores to Gaviota Pipeline (Line 901) in Santa Barbara County, California. A portion of the released crude oil reached the Pacific Ocean at Refugio State Beach through a drainage culvert. Following the release, we shut down the pipeline and initiated our emergency response plan. A Unified Command, which includes the United States Coast Guard, the EPA, the California Office of Spill Prevention and Response and the Santa Barbara Office of Emergency Management, was established for the response effort. Clean-up and remediation operations with respect to impacted shoreline and other areas has been determined by the Unified Command to be complete, subject to continued shoreline monitoring. The cause of the release remains under investigation. Our current “worst case” estimate of the amount of oil spilled, representing the maximum volume of oil that we believed could have been spilled based on relevant facts, data and information, is approximately 2,935 barrels.
As a result of the Line 901 incident, several governmental agencies and regulators have initiated investigations into the Line 901 incident, various claims have been made against us and a number of lawsuits have been filed against us. We may be subject to additional claims, investigations and lawsuits, which could materially impact the liabilities and costs we currently expect to incur as a result of the Line 901 incident. Set forth below is a brief summary of actions and matters that are currently pending:
On May 21, 2015, we received a corrective action order from the United States Department of Transportation’s Pipeline and Hazardous Materials Safety Administration (“PHMSA”), the governmental agency that has jurisdiction over the operation of Line 901 as well as over a second stretch of pipeline extending from Gaviota Pump Station in Santa Barbara County to Emidio Pump Station in Kern County, California (Line 903), requiring us to shut down, purge, review, remediate and test Line 901. On June 3, 2015, the corrective action order was amended to require us to take additional corrective actions with respect to both Lines 901 and 903, and on November 13, 2015, the corrective action order was further amended to require the purge and shutdown of Line 903 between Gaviota and Pentland (as amended, the “CAO”). Among other requirements, the CAO also obligates us to conduct a root cause failure analysis with respect to Line 901 and present remedial work plans and restart plans to PHMSA prior to returning Line 901 and 903 to service; the CAO also imposes a pressure restriction on Line 903 and requires us to take other specified actions with respect to both Lines 901 and 903. We intend to continue to comply with the CAO and to cooperate with any other governmental investigations relating to or arising out of the release. Excavation and removal of the affected section of the pipeline was completed on May 28, 2015. No timeline has been established for the restart of Line 901 or Line 903. On February 17, 2016, PHMSA issued a Preliminary Factual Report of the Line 901 failure, which contains PHMSA’s preliminary findings regarding factual information about the events leading up to the accident and the technical analysis that has been conducted to date. By virtue of its statutory authority, PHMSA has the power and authority to impose fines and penalties on us and cause civil or criminal charges to be brought against us. While to date PHMSA has not imposed any such fines or penalties or pursued any such civil or criminal charges with respect to the Line 901 release, there can be no assurance that such fines or penalties will not be imposed upon us, or that such civil or criminal charges will not be brought against us, in the future.
On September 11, 2015, we received a Notice of Probable Violation and Proposed Compliance Order from PHMSA arising out of its inspection of Lines 901 and 903 in August, September and October of 2013 (the “2013 Audit NOPV”). The 2013 Audit NOPV alleges that the Partnership committed probable violations of various federal pipeline safety regulations by failing to document, or inadequately documenting, certain activities. On October 12, 2015, the Partnership filed a response to the 2013 Audit NOPV. To date, PHMSA has not issued a final order with respect to the 2013 Audit NOPV, nor has it assessed any fines or penalties with respect thereto; however, we cannot provide any assurances that any such fines or penalties will not be assessed against us.
In late May of 2015, on behalf of the EPA, the United States Attorney for the Department of Justice, Central District of California, Environmental Crimes Section (“DOJ”) began an investigation into whether there were any violations of federal criminal statutes in connection with the Line 901 incident, including potential violations of the federal Clean Water Act. We are cooperating with the DOJ’s investigation by responding to their requests for documents and access to our employees. The DOJ has already spoken to several of our employees and has expressed an interest in talking to other employees; consistent with the terms of our governing organizational documents, we are funding our employees’ defense costs, including the costs of separate counsel engaged to represent such individuals. In addition to the DOJ, the California Attorney General’s Office and the District Attorney’s Office for the County of Santa Barbara are also investigating the Line 901 incident to determine whether any applicable state or local laws have been violated. On August 26, 2015, we also received a Request for Information from the EPA relating to Line 901 and we are in the process of responding to such request. While to date no civil or criminal charges with respect to the Line 901 release have been brought against PAA or any of its affiliates, officers or employees by PHMSA, DOJ, EPA, California Attorney General or Santa Barbara County District Attorney, and no fines or penalties have been imposed by such governmental agencies, there can be no assurance that such fines or penalties will not be imposed upon us, our officers or our employees, or that such civil or criminal charges will not be brought against us, our officers or our employees in the future, whether by those or other governmental agencies.
Shortly following the Line 901 incident, we established a claims line and encouraged any parties that were damaged by the release to contact us to discuss their damage claims. We have received a number of claims through the claims line and we are processing those claims as we receive them. In addition, we have also had seven class action lawsuits filed against us, all of which have been administratively consolidated into a single proceeding in the United States District Court for the Central District of California. In general, the plaintiffs are seeking to establish different classes of claimants that have allegedly been damaged by the release, including potential classes such as persons that derive a significant portion of their income through commercial fishing and harvesting activities in the waters adjacent to Santa Barbara County or from businesses that are dependent on marine resources from Santa Barbara County, retail businesses located in historic downtown Santa Barbara, certain owners of oceanfront and/or beachfront property on the Pacific Coast of California, and other classes of individuals and businesses that were allegedly impacted by the release.
There have also been two securities law class action lawsuits filed on behalf of certain purported investors in PAA and/or PAGP against PAA, PAGP and/or certain of their respective officers, directors and underwriters. Both of these lawsuits have been consolidated into a single proceeding in the United States District Court for the Southern District of Texas. In general, these lawsuits allege that the various defendants violated securities laws by misleading investors regarding the integrity of PAA’s pipelines and related facilities through false and misleading statements, omission of material facts and concealing of the true extent of the spill. The plaintiffs claim unspecified damages as a result of the reduction in value of their investments in PAA and PAGP, which they attribute to the alleged wrongful acts of the defendants. PAA and PAGP, and the other defendants, deny the allegations in these lawsuits and intend to respond accordingly. Consistent with and subject to the terms of our governing organizational documents (and to the extent applicable, insurance policies), we are indemnifying and funding the defense costs of our officers and directors in connection with these lawsuits; we are also indemnifying and funding the defense costs of our underwriters pursuant to the terms of the underwriting agreements we previously entered into with such underwriters.
In addition, three unitholder derivative lawsuits have been filed by certain purported investors in PAA against PAA, certain of its affiliates and certain officers and directors. Two of these lawsuits were filed in the United States District Court for the Southern District of Texas and the other was filed in State District Court in Harris County, Texas. In general, these lawsuits allege that the various defendants breached their fiduciary duties, engaged in gross mismanagement and made false and misleading statements, among other similar allegations, in connection with their management and oversight of PAA during the period of time leading up to and following the Line 901 release. The plaintiffs claim that PAA suffered unspecified damages as a result of the actions of the various defendants and seek to hold the defendants liable for such damages, in addition to other remedies. The defendants deny the allegations in these lawsuits and intend to respond accordingly. Consistent with and subject to the terms of our governing organizational documents (and to the extent applicable, insurance policies), we are indemnifying and funding the defense costs of our officers and directors in connection with these lawsuits.
In addition to the foregoing, as the “responsible party” for the Line 901 incident we are liable for various costs and for certain natural resource damages under the Oil Pollution Act, and we also have exposure to the payment of additional fines, penalties and costs under other applicable federal, state and local laws, statutes and regulations. To the extent any such costs are reasonably estimable, we have included an estimate of such costs in the loss accrual described below.
Taking the foregoing into account, as of December 31, 2015, we estimate that the aggregate total costs we have incurred or will incur with respect to the Line 901 incident will be approximately $269 million, which estimate includes actual and projected emergency response and clean-up costs, natural resource damage assessments and certain third party claims settlements, as well as estimates for fines, penalties and certain legal fees. This estimate considers our prior experience in environmental investigation and remediation matters and available data from, and in consultation with, our environmental and other specialists, as well as currently available facts and presently enacted laws and regulations. We have made assumptions for (i) the expected number of days that monitoring services will be required, (ii) the duration of the natural resource damage assessment and the ultimate amount of damages determined, (iii) the resolution of certain third party claims and lawsuits, but excluding claims and lawsuits with respect to which losses are not probable and reasonably estimable, and excluding future claims and lawsuits, (iv) the determination and calculation of fines and penalties, but excluding fines and penalties that are not probable and reasonably estimable and (v) the nature, extent and cost of legal services that will be required in connection with all lawsuits, claims and other matters requiring legal or expert advice associated with the Line 901 incident. Our estimate does not include any lost revenue associated with the shutdown of Line 901 or 903 and does not include any liabilities or costs that are not reasonably estimable at this time or that relate to contingencies where we currently regard the likelihood of loss as being only reasonably possible or remote. We believe we have accrued adequate amounts for all probable and reasonably estimable costs; however, this estimate is subject to uncertainties associated with the assumptions that we have made. For example, the amount of time it takes for us to resolve all of the current and future lawsuits, claims and investigations that relate to the Line 901 incident could turn out to be significantly longer than we have assumed, and as a result the costs we incur for legal services could be significantly higher than we have estimated. In addition, with respect to fines and penalties, the ultimate amount of any fines and penalties assessed against us depends on a wide variety of factors, many of which are not estimable at this time. Where fines and penalties are probable and estimable, we have included them in our estimate, although such estimates could turn out to be wrong. Accordingly, our assumptions and estimates may turn out to be inaccurate and our total costs could turn out to be materially higher; therefore, we can provide no assurance that we will not have to accrue significant additional costs in the future with respect to the Line 901 incident.
We have accrued such estimate of aggregate total costs to “Field operating costs” on our Consolidated Statement of Operations. As of December 31, 2015, we had a remaining undiscounted gross liability of $116 million related to this event, the majority of which is presented as a current liability in “Accounts payable and accrued liabilities” on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. We maintain insurance coverage, which is subject to certain exclusions and deductibles, in the event of such environmental liabilities. Subject to such exclusions and deductibles, we believe that our coverage is adequate to cover the current estimated total emergency response and clean-up costs, claims settlement costs and remediation costs and we believe that this coverage is also adequate to cover any potential increase in the estimates for these costs that exceed the amounts currently identified. Through December 31, 2015, we had collected, subject to customary reservations, $31 million out of the approximate $186 million of release costs that we believe are probable of recovery from insurance carriers, net of deductibles. We recovered an additional $69 million of proceeds from insurance carriers in January 2016. As of December 31, 2015, we have recognized a receivable of approximately $155 million for the portion of the release costs that we believe is probable of recovery from insurance, net of deductibles and amounts already collected. A majority of this receivable has been recognized as a current asset in “Trade accounts receivable and other receivables, net” on our Consolidated Balance Sheets with the offset reducing “Field operating costs” on our Consolidated Statement of Operations. We have substantially completed the clean-up and remediation efforts, excluding long-term site monitoring activities; however, we expect to make payments for additional costs associated with restoration and monitoring of the area, as well as natural resource damage assessment, legal, professional and regulatory costs, in addition to fines and penalties, during future periods.
MP29 Release. On July 10, 2015, we experienced a crude oil release of approximately 100 barrels at our Pocahontas Pump Station near the border of Bond and Madison Counties in Illinois, approximately 40 miles from St. Louis, Missouri. The Pocahontas Station is part of the Capwood pipeline that runs from our Patoka Station to Wood River, Illinois. A portion of the released crude oil was contained within our Pocahontas facility, but some of the released crude oil entered a nearby waterway where it was contained with booms. On July 14, 2015, PHMSA issued a corrective action order requiring us to take various actions in response to the release, including remediation, reporting and other actions. As of December 18, 2015, we had submitted all requested information and reports required by the corrective action order and are currently awaiting PHMSA’s comment or approval. On August 10, 2015, we received a Notice of Violation from the Illinois Environmental Protection Agency (the “Agency”) alleging violations relating to the release and outlining the activities recommended by the Agency to resolve the alleged violations, including the completion of an investigation and various remediation activities. The Agency approved a work plan describing remediation activities proposed for remaining hydrocarbons at Pocahontas Station and affected waterways. Remediation activities under this work plan have effectively been completed, and on December 17, 2015, we entered into a Compliance Commitment Agreement with the Agency, which provides the framework for final completion and documentation of the remediation effort. To date, no fines or penalties have been assessed in this matter; however, it is possible that fines and penalties could be assessed in the future. In connection with this incident, we have also had one class action lawsuit filed against us in the United States District Court for the Southern District of Illinois, which was subsequently voluntarily dismissed by the plaintiff. We estimate that the aggregate total costs associated with this release will be less than $10 million.
Cushing Tank Cathodic Protection. On May 22, 2015, PHMSA issued a Final Order relating to an April 2013 Notice of Probable Violation and Proposed Compliance Order alleging that we did not maintain adequate cathodic protection for certain tanks at our Cushing Terminal. In its 2013 Notice of Probable Violation, PHMSA maintained that the proprietary cathodic protection system utilized by us for certain of our storage tanks at our Cushing, Oklahoma facility was not contemplated by applicable regulations. In response to the notice, we provided extensive documentation and supporting information regarding the effectiveness of the technology we were utilizing, including past communications with PHMSA regarding the topic. At a hearing in August 2013, we gave a formal presentation on the technology, provided empirical data confirming its effectiveness and also had a third party corrosion expert witness speak to the effectiveness of the technology. Almost two years later, PHMSA issued the Final Order and Compliance Order dated May 22, 2015 ruling against our position, assessing a penalty of $102,900 and specifying certain corrective actions to be completed by us. We chose not to further contest this matter and paid the penalty on June 5, 2015.
In the Matter of Bakersfield Crude Terminal LLC et al. On April 30, 2015, the EPA issued a Finding and Notice of Violation (“NOV”) to Bakersfield Crude Terminal LLC, our subsidiary, for alleged violations of the Clean Air Act, as amended. The NOV, which cites 10 separate rule violations, questions the validity of construction and operating permits issued to our Bakersfield rail unloading facility in 2012 and 2014 by the San Joaquin Valley Air Pollution Control District (the “SJV District”). We believe we fully complied with all applicable regulatory requirements and that the permits issued to us by the SJV District are valid. To date, no fines or penalties have been assessed in this matter; however, it is possible that fines and penalties could be assessed in the future.
Mesa to Basin Pipeline. On January 6, 2016, PHMSA issued a Notice of Probable Violation and Proposed Civil Penalty relating to an approximate 500 barrel release of crude oil that took place on January 1, 2015 on our Mesa to Basin 12” pipeline in Midland, Texas. PHMSA conducted an accident investigation and reviewed documentation related to the incident, and concluded that we had committed probable violations of certain pipeline safety regulations. In the Notice, PHMSA maintains that we failed to carry out our written damage prevention program and to follow our pipeline excavation/ditching and backfill procedures on four separate occasions, and that such failures resulted in outside force damage that led to the January 1, 2015 release. PHMSA’s compliance officer has recommended that we be assessed a civil penalty of $190,000. We have formally responded to PHMSA regarding this matter, but at this point we can provide no assurance regarding the final disposition of this matter or the final amount of any civil penalties.
National Energy Board Audit. In the third quarter of 2014, the National Energy Board (“NEB”) of Canada notified PMC that various corrective actions from a 2010 audit had not been completed to the satisfaction of the NEB. The NEB initiated a process to assess PMC’s approach to compliance with the NEB’s Onshore Pipeline Regulations, which resulted in the issuance by the NEB of an order on January 15, 2015 that imposed six conditions on PMC designed to enhance PMC’s ability to operate its pipelines in a manner that protects the public and the environment. The conditions include the filing of certain safety critical tasks, controls and programs with the NEB, external audits of certain PMC programs and systems, and periodic update meetings with NEB staff regarding the status and progress of corrective actions. In early February 2015, the NEB imposed a penalty on PMC of $76,000 CAD related to these issues. It is possible that additional fines and penalties may be assessed against PMC in the future related to this matter.
Kemp River Pipeline Releases. In May and June 2013, two separate releases were discovered on our Kemp River pipeline in Northern Alberta, Canada that, in the aggregate, resulted in the release of approximately 700 barrels of condensate and light crude oil. Clean-up and remediation activities are being conducted in cooperation with the applicable regulatory agencies. Final investigation by the Alberta Energy Regulator is not complete. To date, no charges, fines or penalties have been assessed against PMC with respect to these releases; however, it is possible that fines or penalties may be assessed against PMC in the future. We estimate that the aggregate clean-up and remediation costs associated with these releases will be $15 million. Through December 31, 2015, we spent $9 million in connection with clean-up and remediation activities.
Bay Springs Pipeline Release. In February 2013, we experienced a crude oil release of approximately 120 barrels on a portion of one of our pipelines near Bay Springs, Mississippi. Most of the released crude oil was contained within our pipeline right of way, but some of the released crude oil entered a nearby waterway where it was contained with booms. The EPA has issued an administrative order requiring us to take various actions in response to the release, including remediation, reporting and other actions. We have satisfied the requirements of the administrative order; however, we may be subjected to a civil penalty. The aggregate cost to clean up and remediate the site was $6 million.
Environmental Remediation
We currently own or lease, and in the past have owned and leased, properties where hazardous liquids, including hydrocarbons, are or have been handled. These properties and the hazardous liquids or associated wastes disposed thereon may be subject to CERCLA, RCRA and state and Canadian federal and provincial laws and regulations. Under such laws and regulations, we could be required to remove or remediate hazardous liquids or associated wastes (including wastes disposed of or released by prior owners or operators) and to clean up contaminated property (including contaminated groundwater).
We maintain insurance of various types with varying levels of coverage that we consider adequate under the circumstances to cover our operations and properties. The insurance policies are subject to deductibles and retention levels that we consider reasonable and not excessive. Consistent with insurance coverage generally available in the industry, in certain circumstances our insurance policies provide limited coverage for losses or liabilities relating to gradual pollution, with broader coverage for sudden and accidental occurrences.
Assets we have acquired or will acquire in the future may have environmental remediation liabilities for which we are not indemnified. We have in the past experienced and in the future likely will experience releases of crude oil into the environment from our pipeline and storage operations. We also may discover environmental impacts from past releases that were previously unidentified.
Insurance
A pipeline, terminal or other facility may experience damage as a result of an accident, natural disaster or terrorist activity. These hazards can cause personal injury and loss of life, severe damage to and destruction of property and equipment, pollution or environmental damage and suspension of operations. We maintain various types of insurance that we consider adequate to cover our operations and certain assets. The insurance policies are subject to deductibles or self-insured retentions that we consider reasonable. Our insurance does not cover every potential risk associated with operating pipelines, terminals and other facilities, including the potential loss of significant revenues.
The occurrence of a significant event not fully insured, indemnified or reserved against, or the failure of a party to meet its indemnification obligations, could materially and adversely affect our operations and financial condition. We believe we are adequately insured for third-party liability and property damage with respect to our operations. In the future, we may not be able to maintain insurance at levels that we consider adequate for rates we consider reasonable. As a result, we may elect to self-insure or utilize higher deductibles in certain insurance programs. For example, the market for hurricane- or windstorm-related property damage coverage has remained difficult the last few years. The amount of coverage available has been limited, costs have increased substantially and deductibles have increased as well.
Our assessment of the current availability of coverage and associated rates for hurricane insurance has led us to the decision to self-insure this risk. This decision does not affect our third-party liability insurance, which still covers hurricane-related liability claims and which we have maintained at our historic coverage levels. In addition, although we believe that we have established adequate reserves to the extent such risks are not insured, costs incurred in excess of these reserves may be higher and may potentially have a material adverse effect on our financial conditions, results of operations or cash flows.
Note 17—Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
|
|
|
First |
|
Second |
|
Third |
|
Fourth |
|
|
| |||||
|
|
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
Quarter |
|
Total (1) |
| |||||
|
|
|
(in millions, except per share data) |
| |||||||||||||
|
2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Total revenues |
|
$ |
5,942 |
|
$ |
6,663 |
|
$ |
5,551 |
|
$ |
4,996 |
|
$ |
23,152 |
|
|
Gross margin (2) (3) |
|
$ |
449 |
|
$ |
290 |
|
$ |
394 |
|
$ |
405 |
|
$ |
1,539 |
|
|
Operating income (3) |
|
$ |
370 |
|
$ |
210 |
|
$ |
334 |
|
$ |
343 |
|
$ |
1,258 |
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
262 |
|
$ |
103 |
|
$ |
228 |
|
$ |
216 |
|
$ |
809 |
|
|
Net income attributable to PAGP |
|
$ |
31 |
|
$ |
30 |
|
$ |
32 |
|
$ |
25 |
|
$ |
118 |
|
|
Basic net income per Class A share |
|
$ |
0.14 |
|
$ |
0.14 |
|
$ |
0.14 |
|
$ |
0.11 |
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
|
Diluted net income per Class A share |
|
$ |
0.14 |
|
$ |
0.14 |
|
$ |
0.14 |
|
$ |
0.11 |
|
$ |
0.53 |
|
|
Cash distributions per Class A share (4) |
|
$ |
0.20300 |
|
$ |
0.22200 |
|
$ |
0.22700 |
|
$ |
0.23100 |
|
$ |
0.88300 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
2014 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| |||||
|
Total revenues |
|
$ |
11,684 |
|
$ |
11,195 |
|
$ |
11,127 |
|
$ |
9,459 |
|
$ |
43,464 |
|
|
Gross margin (2) (3) |
|
$ |
584 |
|
$ |
457 |
|
$ |
484 |
|
$ |
599 |
|
$ |
2,122 |
|
|
Operating income (3) |
|
$ |
494 |
|
$ |
366 |
|
$ |
405 |
|
$ |
529 |
|
$ |
1,791 |
|
|
Net income |
|
$ |
372 |
|
$ |
275 |
|
$ |
311 |
|
$ |
370 |
|
$ |
1,328 |
|
|
Net income attributable to PAGP |
|
$ |
14 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
$ |
16 |
|
$ |
24 |
|
$ |
70 |
|
|
Basic net income per Class A share |
|
$ |
0.11 |
|
$ |
0.11 |
|
$ |
0.12 |
|
$ |
0.14 |
|
$ |
0.48 |
|
|
Diluted net income per Class A share |
|
$ |
0.11 |
|
$ |
0.11 |
|
$ |
0.12 |
|
$ |
0.13 |
|
$ |
0.47 |
|
|
Cash distributions per Class A share (4) (5) |
|
$ |
0.12505 |
|
$ |
0.17055 |
|
$ |
0.18340 |
|
$ |
0.19075 |
|
$ |
0.66975 |
|
(1) The sum of the four quarters may not equal the total year due to rounding.
(2) Gross margin is calculated as Total revenues less (i) Purchases and related costs, (ii) Field operating costs and (iii) Depreciation and amortization.
(3) Amounts reported in prior periods have been retroactively restated to reflect the impact of our adoption of revised debt issuance costs guidance issued by the FASB. See Note 2 for additional information.
(4) Represents cash distributions declared and paid in the period presented.
(5) The distribution paid during the first quarter of 2014 was prorated for the partial quarter following the closing of our IPO on October 21, 2013.
We manage our operations through three operating segments: Transportation, Facilities and Supply and Logistics. See “Revenue Recognition” in Note 2 for a summary of the types of products and services from which each segment derives its revenues. Our Chief Operating Decision Maker (our Chief Executive Officer) evaluates segment performance based on measures including segment profit and maintenance capital investment. We define segment profit as revenues and equity earnings in unconsolidated entities less (a) purchases and related costs, (b) field operating costs and (c) segment general and administrative expenses. Each of the items above excludes depreciation and amortization. Maintenance capital consists of capital expenditures for the replacement of partially or fully depreciated assets in order to maintain the operating and/or earnings capacity of our existing assets.
We look at each period’s earnings before non-cash depreciation and amortization as an important measure of segment performance. The exclusion of depreciation and amortization expense could be viewed as limiting the usefulness of segment profit as a performance measure because it does not account in current periods for the implied reduction in value of our capital assets, such as crude oil pipelines and facilities, caused by age-related decline and wear and tear. We compensate for this limitation by recognizing that depreciation and amortization are largely offset by repair and maintenance investments, which act to partially offset the aging and wear and tear in the value of our principal fixed assets. These maintenance investments are a component of field operating costs included in segment profit or in maintenance capital, depending on the nature of the cost. Capital expenditures made to expand the existing operating and/or earnings capacity of our assets are classified as expansion capital. Capital expenditures for the replacement of partially or fully depreciated assets in order to maintain the operating and/or earnings capacity of our existing assets are classified as maintenance capital, which is deducted in determining “available cash”. Repair and maintenance expenditures incurred in order to maintain the day to day operation of our existing assets are charged to expense as incurred.
The following table reflects certain financial data for each segment for the periods indicated (in millions):
|
|
|
Transportation |
|
Facilities |
|
Supply and Logistics |
|
Total |
| ||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Revenues (1): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
External customers |
|
$ |
697 |
|
$ |
528 |
|
$ |
21,927 |
|
$ |
23,152 |
|
|
Intersegment (2) |
|
897 |
|
522 |
|
18 |
|
1,437 |
| ||||
|
Total revenues of reportable segments |
|
$ |
1,594 |
|
$ |
1,050 |
|
$ |
21,945 |
|
$ |
24,589 |
|
|
Equity earnings in unconsolidated entities |
|
$ |
183 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
183 |
|
|
Segment profit (3) (4) |
|
$ |
917 |
|
$ |
579 |
|
$ |
381 |
|
$ |
1,877 |
|
|
Capital expenditures (5) |
|
$ |
1,278 |
|
$ |
813 |
|
$ |
184 |
|
$ |
2,275 |
|
|
Maintenance capital |
|
$ |
144 |
|
$ |
68 |
|
$ |
8 |
|
$ |
220 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
As of December 31, 2015 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
11,272 |
|
$ |
7,645 |
|
$ |
5,225 |
|
$ |
24,142 |
|
|
Investments in unconsolidated entities |
|
$ |
1,998 |
|
$ |
29 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
2,027 |
|
|
|
|
Transportation |
|
Facilities |
|
Supply and Logistics |
|
Total |
| ||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2014 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Revenues (1): |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
External customers |
|
$ |
774 |
|
$ |
576 |
|
$ |
42,114 |
|
$ |
43,464 |
|
|
Intersegment (2) |
|
881 |
|
551 |
|
36 |
|
1,468 |
| ||||
|
Total revenues of reportable segments |
|
$ |
1,655 |
|
$ |
1,127 |
|
$ |
42,150 |
|
$ |
44,932 |
|
|
Equity earnings in unconsolidated entities |
|
$ |
108 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
108 |
|
|
Segment profit (3) (4) |
|
$ |
925 |
|
$ |
584 |
|
$ |
782 |
|
$ |
2,291 |
|
|
Capital expenditures (5) |
|
$ |
2,483 |
|
$ |
582 |
|
$ |
60 |
|
$ |
3,125 |
|
|
Maintenance capital |
|
$ |
165 |
|
$ |
52 |
|
$ |
7 |
|
$ |
224 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
As of December 31, 2014 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
10,441 |
|
$ |
7,137 |
|
$ |
6,345 |
|
$ |
23,923 |
|
|
Investments in unconsolidated entities |
|
$ |
1,735 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
1,735 |
|
|
|
|
Transportation |
|
Facilities |
|
Supply and Logistics |
|
Total |
| ||||
|
Year Ended December 31, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Revenues: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
External Customers |
|
$ |
701 |
|
$ |
856 |
|
$ |
40,692 |
|
$ |
42,249 |
|
|
Intersegment (2) |
|
797 |
|
521 |
|
4 |
|
1,322 |
| ||||
|
Total revenues of reportable segments |
|
$ |
1,498 |
|
$ |
1,377 |
|
$ |
40,696 |
|
$ |
43,571 |
|
|
Equity earnings in unconsolidated entities |
|
$ |
64 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
64 |
|
|
Segment profit (3) (4) |
|
$ |
729 |
|
$ |
616 |
|
$ |
822 |
|
$ |
2,167 |
|
|
Capital expenditures (5) |
|
$ |
1,046 |
|
$ |
549 |
|
$ |
46 |
|
$ |
1,641 |
|
|
Maintenance capital |
|
$ |
123 |
|
$ |
38 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
$ |
176 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
As of December 31, 2013 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
| ||||
|
Total assets |
|
$ |
7,726 |
|
$ |
6,741 |
|
$ |
6,944 |
|
$ |
21,411 |
|
|
Investments in unconsolidated entities |
|
$ |
485 |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
— |
|
$ |
485 |
|
(1) Effective January 1, 2014, our natural gas sales and costs, primarily attributable to the activities performed by our natural gas storage commercial optimization group, are reported in the Supply and Logistics segment. Such items were previously reported in the Facilities segment.
(2) Segment revenues include intersegment amounts that are eliminated in Purchases and related costs and Field operating costs in our Consolidated Statements of Operations. Intersegment sales are conducted at posted tariff rates, rates similar to those charged to third parties or rates that we believe approximate market at the time the agreement is executed or renegotiated.
(3) Supply and Logistics segment profit includes interest expense (related to hedged inventory purchases) of $6 million, $12 million and $30 million for the years ended December 31, 2015, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
(4) The following table reconciles segment profit to net income attributable to PAGP (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
|
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
Segment profit |
|
$ |
1,877 |
|
$ |
2,291 |
|
$ |
2,167 |
|
|
Unallocated general and administrative expenses |
|
(3 |
) |
(6 |
) |
(1 |
) | |||
|
Depreciation and amortization |
|
(433 |
) |
(386 |
) |
(368 |
) | |||
|
Interest expense, net |
|
(443 |
) |
(357 |
) |
(319 |
) | |||
|
Other income/(expense), net |
|
(7 |
) |
(2 |
) |
1 |
| |||
|
Income before tax |
|
991 |
|
1,540 |
|
1,480 |
| |||
|
Income tax expense |
|
(182 |
) |
(212 |
) |
(106 |
) | |||
|
Net income |
|
809 |
|
1,328 |
|
1,374 |
| |||
|
Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests |
|
(691 |
) |
(1,258 |
) |
(1,359 |
) | |||
|
Net income attributable to PAGP |
|
$ |
118 |
|
$ |
70 |
|
$ |
15 |
|
(5) Expenditures for acquisition capital and expansion capital, including investments in unconsolidated entities.
Geographic Data
We have operations in the United States and Canada. Set forth below are revenues and long-lived assets attributable to these geographic areas (in millions):
|
|
|
Year Ended December 31, |
| |||||||
|
Revenues (1) |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
|
2013 |
| |||
|
United States |
|
$ |
18,701 |
|
$ |
34,860 |
|
$ |
32,924 |
|
|
Canada |
|
4,451 |
|
8,604 |
|
9,325 |
| |||
|
|
|
$ |
23,152 |
|
$ |
43,464 |
|
$ |
42,249 |
|
(1) Revenues are primarily attributed to each region based on where the services are provided or the product is shipped.
|
|
|
December 31, |
| ||||
|
Long-Lived Assets (1) |
|
2015 |
|
2014 |
| ||
|
United States |
|
$ |
15,958 |
|
$ |
14,360 |
|
|
Canada |
|
3,368 |
|
3,650 |
| ||
|
|
|
$ |
19,326 |
|
$ |
18,010 |
|
(1) Excludes long-term derivative assets and long-term deferred tax assets.
EXHIBIT INDEX
|
2.1 * |
|
— |
|
Share Purchase Agreement dated December 1, 2011 by and among Amoco Canada International Holdings B.V. and Plains Midstream Canada ULC (the schedules and exhibits have been omitted pursuant to Item 601(b)(2) of Regulation S-K) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2.2 |
|
— |
|
Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of October 21, 2013, by and among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Acquisition Company LLC, PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P. and PNGS GP LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 2.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 24, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.1 |
|
— |
|
Certificate of Limited Partnership of Plains GP Holdings, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (333-190227) filed July 29, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.2 |
|
— |
|
Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of Plains GP Holdings, L.P. dated as of October 21, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.3 |
|
— |
|
Certificate of Formation of PAA GP Holdings LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1 (333-190227) filed July 29, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.4 |
|
— |
|
Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of PAA GP Holdings LLC dated as of October 21, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.5 |
|
— |
|
Amendment No. 1 dated as of December 31, 2013 to the Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of PAA GP Holdings LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 31, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.6 |
|
— |
|
Fifth Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. dated as of January 28, 2016 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 2, 2016). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.7 |
|
— |
|
Sixth Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Plains All American GP LLC dated October 21, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.4 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.8 |
|
— |
|
Amendment No. 1 dated January 28, 2016 to the Sixth Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement of Plains All American GP LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 2, 2016). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.9 |
|
— |
|
Seventh Amended and Restated Limited Partnership Agreement of Plains AAP, L.P. dated October 21, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.10 |
|
— |
|
Amendment No. 1 dated December 31, 2013 to the Seventh Amended and Restated Limited Partnership Agreement of Plains AAP, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 31, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3.11 |
|
— |
|
Limited Liability Company Agreement of PAA GP LLC dated December 28, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.3 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 4, 2008). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.1 |
|
— |
|
Indenture dated September 25, 2002 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp. and Wachovia Bank, National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2002). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.2 |
|
— |
|
Fourth Supplemental Indenture (Series A and Series B 5.875% Senior Notes due 2016) dated August 12, 2004 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein and Wachovia Bank, National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.5 to PAA’s Registration Statement on Form S-4, File No. 333-121168). |
|
4.3 |
|
— |
|
Sixth Supplemental Indenture (Series A and Series B 6.70% Senior Notes due 2036) dated May 12, 2006 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein and Wachovia Bank, National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 12, 2006). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.4 |
|
— |
|
Ninth Supplemental Indenture (Series A and Series B 6.125% Senior Notes due 2017) dated October 30, 2006 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 30, 2006). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.5 |
|
— |
|
Tenth Supplemental Indenture (Series A and Series B 6.650% Senior Notes due 2037) dated October 30, 2006 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 30, 2006). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.6 |
|
— |
|
Thirteenth Supplemental Indenture (Series A and Series B 6.50% Senior Notes due 2018) dated April 23, 2008 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed April 23, 2008). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.7 |
|
— |
|
Fifteenth Supplemental Indenture (8.75% Senior Notes due 2019) dated April 20, 2009 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed April 20, 2009). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.8 |
|
— |
|
Seventeenth Supplemental Indenture (5.75% Senior Notes due 2020) dated September 4, 2009 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed September 4, 2009). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.9 |
|
— |
|
Nineteenth Supplemental Indenture (5.00% Senior Notes due 2021) dated January 14, 2011 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., the Subsidiary Guarantors named therein and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 11, 2011). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.10 |
|
— |
|
Twentieth Supplemental Indenture (3.65% Senior Notes due 2022) dated March 22, 2012 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 26, 2012). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.11 |
|
— |
|
Twenty-First Supplemental Indenture (5.15% Senior Notes due 2042) dated March 22, 2012 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 26, 2012). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.12 |
|
— |
|
Twenty-Second Supplemental Indenture (2.85% Senior Notes due 2023) dated December 10, 2012, by and among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 12, 2012). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.13 |
|
— |
|
Twenty-Third Supplemental Indenture (4.30% Senior Notes due 2043) dated December 10, 2012, by and among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 12, 2012). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.14 |
|
— |
|
Twenty-Fourth Supplemental Indenture (3.85% Senior Notes due 2023) dated August 15, 2013, by and among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 15, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.15 |
|
— |
|
Twenty-Fifth Supplemental Indenture (4.70% Senior Notes due 2044) dated April 23, 2014, by and among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed April 29, 2014). |
|
4.16 |
|
— |
|
Twenty-Sixth Supplemental Indenture (3.60% Senior Notes due 2024) dated September 9, 2014, by and among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp. and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed September 11, 2014). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.17 |
|
— |
|
Twenty-Seventh Supplemental Indenture (2.60% Senior Notes due 2019) dated December 9, 2014, by and among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 11, 2014). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.18 |
|
— |
|
Twenty-Eighth Supplemental Indenture (4.90% Senior Notes due 2045) dated December 9, 2014, by and among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.3 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 11, 2014). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.19 |
|
— |
|
Twenty-Ninth Supplemental Indenture (4.65% Senior Notes due 2025) dated August 24, 2015, by and among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Finance Corp., and U.S. Bank National Association, as trustee (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 26, 2015). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
4.20 |
|
— |
|
Shareholder and Registration Rights Agreement dated October 21, 2013 by and among Plains GP Holdings, L.P. and the other parties signatory thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.1 |
|
— |
|
Credit Agreement dated as of August 19, 2011 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., as Borrower; certain subsidiaries of Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. from time to time party thereto, as Designated Borrowers; Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent; and the other Lenders party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 25, 2011). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.2 |
|
— |
|
First Amendment to Credit Agreement dated as of June 27, 2012, among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. and Plains Midstream Canada ULC, as Borrowers; Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer; Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as an L/C Issuer; and the other Lenders party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 3, 2012). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.3 |
|
— |
|
Second Amendment to Credit Agreement dated as of August 16, 2013, among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. and Plains Midstream Canada ULC, as Borrowers; Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer; Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as an L/C Issuer; and the other Lenders party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 20, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.4 |
|
— |
|
Contribution, Assignment and Amendment Agreement dated as of June 27, 2001, among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., Plains Marketing, L.P., All American Pipeline, L.P., Plains AAP, L.P., Plains All American GP LLC and Plains Marketing GP Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 27, 2001). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.5 |
|
— |
|
Contribution, Assignment and Amendment Agreement dated as of June 8, 2001, among Plains All American Inc., Plains AAP, L.P. and Plains All American GP LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 11, 2001). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.6 |
|
— |
|
Separation Agreement dated as of June 8, 2001 among Plains Resources Inc., Plains All American Inc., Plains All American GP LLC, Plains AAP, L.P. and Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 11, 2001). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.7 ** |
|
— |
|
Pension and Employee Benefits Assumption and Transition Agreement dated as of June 8, 2001 among Plains Resources Inc., Plains All American Inc. and Plains All American GP LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 11, 2001). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.8 ** |
|
— |
|
Plains All American GP LLC 2005 Long-Term Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 26, 2005). |
|
10.9 ** |
|
— |
|
Plains All American GP LLC 1998 Long-Term Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to Registration Statement on Form S-8, File No. 333-74920) as amended June 27, 2003 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2003). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.10** |
|
— |
|
Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between Plains All American GP LLC and Greg L. Armstrong dated as of June 30, 2001 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2001). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.11** |
|
— |
|
Amended and Restated Employment Agreement between Plains All American GP LLC and Harry N. Pefanis dated as of June 30, 2001 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to PAA’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2001). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.12 |
|
— |
|
Asset Purchase and Sale Agreement dated February 28, 2001 between Murphy Oil Company Ltd. and Plains Marketing Canada, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 10, 2001). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.13 |
|
— |
|
Transportation Agreement dated July 30, 1993, between All American Pipeline Company and Exxon Company, U.S.A. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.9 to PAA’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed September 23, 1998, File No. 333-64107). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.14 |
|
— |
|
Transportation Agreement dated August 2, 1993, among All American Pipeline Company, Texaco Trading and Transportation Inc., Chevron U.S.A. and Sun Operating Limited Partnership (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to PAA’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 filed September 23, 1998, File No. 333-64107). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.15 |
|
— |
|
Contribution, Conveyance and Assumption Agreement among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P. and certain other parties dated as of November 23, 1998. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1998). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.16 |
|
— |
|
First Amendment to Contribution, Conveyance and Assumption Agreement dated as of December 15, 1998 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1998). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.17 |
|
— |
|
Agreement for Purchase and Sale of Membership Interest in Scurlock Permian LLC between Marathon Ashland LLC and Plains Marketing, L.P. dated as of March 17, 1999 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.16 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 1998). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.18** |
|
— |
|
PMC (Nova Scotia) Company Bonus Program (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.20 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2004). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.19** |
|
— |
|
Quarterly Bonus Program Summary (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.20** |
|
— |
|
Form of LTIP Grant Letter (independent directors) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 23, 2005). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.21** |
|
— |
|
Form of LTIP Grant Letter (designated directors) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 23, 2005). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.22 |
|
— |
|
Membership Interest Purchase Agreement by and between Sempra Energy Trading Corporation and PAA/Vulcan Gas Storage, LLC dated August 19, 2005 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 1.2 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed September 19, 2005). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.23** |
|
— |
|
Waiver Agreement dated as of December 23, 2010 between Plains All American GP LLC and Greg L. Armstrong (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.31 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.24** |
|
— |
|
Waiver Agreement dated as of December 23, 2010 between Plains All American GP LLC and Harry N. Pefanis (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.32 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010). |
|
10.25** |
|
— |
|
Employment Agreement between Plains All American GP LLC and John P. vonBerg dated December 18, 2001 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.40 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.26** |
|
— |
|
Form of LTIP Grant Letter (audit committee members) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 23, 2006). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.27** |
|
— |
|
Plains All American PPX Successor Long-Term Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.45 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2006). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.28** |
|
— |
|
Form of Plains AAP, L.P. Class B Restricted Units Agreement (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 4, 2008). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.29 |
|
— |
|
Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of August 19, 2011 by and among Plains Marketing, L.P., as Borrower, Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., as Guarantor, Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, and the other Lenders party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 25, 2011). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.30 |
|
— |
|
First Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of June 27, 2012, among Plains Marketing, L.P. and Plains Midstream Canada ULC, as Borrowers; Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., as Guarantor; Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer; and the other Lenders and L/C Issuers party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 3, 2012). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.31 |
|
— |
|
Second Amendment to Third Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of August 16, 2013, among Plains Marketing, L.P. and Plains Midstream Canada ULC, as Borrowers; Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., as Guarantor; Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent, Swing Line Lender and L/C Issuer; Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as an L/C Issuer; and the other Lenders and L/C Issuers party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 20, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.32 |
|
— |
|
Contribution and Assumption Agreement dated December 28, 2007, by and between Plains AAP, L.P. and PAA GP LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 4, 2008). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.33** |
|
— |
|
First Amendment to Amended and Restated Employment Agreement dated December 4, 2008 between Plains All American GP LLC and Greg L. Armstrong (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.49 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.34** |
|
— |
|
First Amendment to Amended and Restated Employment Agreement dated December 4, 2008 between Plains All American GP LLC and Harry N. Pefanis (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.50 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.35** |
|
— |
|
First Amendment to Plains All American GP LLC 2005 Long-Term Incentive Plan dated December 4, 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.51 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.36** |
|
— |
|
Second Amendment to Plains All American GP LLC 1998 Long-Term Incentive Plan dated December 4, 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.52 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.37** |
|
— |
|
Form of Amendment to LTIP grant letters (executive officers) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.53 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.38** |
|
— |
|
Form of Amendment to LTIP grant letters (directors) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.54 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.39 |
|
— |
|
Contribution Agreement dated as of April 29, 2010 by and among PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P., PNGS GP LLC, Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA Natural Gas Storage, LLC, PAA/Vulcan Gas Storage, LLC, Plains Marketing, L.P. and Plains Marketing GP Inc. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PNG’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 4, 2010). |
|
10.40 |
|
— |
|
Omnibus Agreement dated May 5, 2010 by and among Plains All American GP LLC, Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PNGS GP LLC and PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PNG’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 11, 2010). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.41** |
|
— |
|
Form of 2010 LTIP Grant Letters (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.58 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.42** |
|
— |
|
Director Compensation Summary (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.45 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2011). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.43** |
|
— |
|
Form of PAA LTIP Grant Letter for Officers (February 2013) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.44 |
|
— |
|
Administrative Agreement dated October 21, 2013, by and among Plains GP Holdings, L.P., PAA GP Holdings LLC, Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., PAA GP LLC, Plains AAP, L.P. and Plains All American GP LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.45 |
|
— |
|
Contribution Agreement dated October 21, 2013, by and among Plains GP Holdings, L.P., PAA GP Holdings LLC and the other parties signatory thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.46** |
|
— |
|
Plains GP Holdings, L.P. Long Term Incentive Plan, (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.47** |
|
— |
|
Waiver Agreement dated October 21, 2013 to the Amended and Restated Employment Agreement dated June 30, 2001 of Greg L. Armstrong (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.48** |
|
— |
|
Waiver Agreement dated October 21, 2013 to the Amended and Restated Employment Agreement dated June 30, 2001 of Harry N. Pefanis (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.49** |
|
— |
|
Form of Amendment to the Plains AAP, L.P. Class B Restricted Units Agreement, dated October 18, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed October 25, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.50 |
|
— |
|
Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement among Plains AAP, L.P., as Borrower, Citibank, N.A. as Administrative Agent, and the other Lenders party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.46 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1A (333-190227) filed October 2, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.51 |
|
— |
|
First Amendment to Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of August 14, 2015 among Plains AAP, L.P., as Borrower, Citibank, N.A. as Administrative Agent, and the other Lenders party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 14, 2015). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.52** |
|
— |
|
Plains All American 2013 Long-Term Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit A to PAA’s Definitive Proxy Statement filed on October 3, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.53** |
|
— |
|
Plains All American PNG Successor Long-Term Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to PAA’s Registration Statement on Form S-8 (333-19319) filed December 31, 2013). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.54** |
|
— |
|
PAA Natural Gas Storage, L.P. 2010 Long-Term Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to PNG’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed May 11, 2010). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.55 |
|
— |
|
364-Day Credit Agreement dated January 16, 2015 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., as Borrower; Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent; Citibank, N.A., JPMorgan Chase Bank N.A. and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Co-Syndication Agents; DNB Bank ASA, New York Branch and Mizuho Bank, Ltd., as Co-Documentation Agents; the other Lenders party thereto; and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, Citigroup Global Markets Inc., DNB Markets, Inc., J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Mizuho Bank, Ltd. and Wells Fargo Securities, LLC, as Joint Lead Arrangers and Joint Bookrunners (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 20, 2015). |
|
10.56 |
|
— |
|
First Amendment to 364-Day Credit Agreement dated August 14, 2015 among Plains All American Pipeline, L.P., as Borrower; Bank of America, N.A., as Administrative Agent; Citibank, N.A., JPMorgan Chase Bank N.A. and Wells Fargo Bank, National Association, as Co-Syndication Agents; DNB Bank ASA, New York Branch and Mizuho Bank, Ltd., as Co-Documentation Agents; the other Lenders party thereto; and Merrill Lynch, Pierce, Fenner & Smith Incorporated, Citigroup Global Markets Inc., DNB Markets, Inc., J.P. Morgan Securities LLC, Mizuho Bank, Ltd. and Wells Fargo Securities, LLC, as Joint Lead Arrangers and Joint Bookrunners (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to PAA’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 14, 2015). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.57** |
|
— |
|
Form of LTIP Grant Letter (PAGP Audit Committee Members) (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2014). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.58** |
|
— |
|
Employment Agreement between Plains All American GP LLC and Willie Chiang dated July 10, 2015 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.53 to PAA’s Annual Report on Form 10-K filed February 25, 2016). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
12.1 † |
|
— |
|
Computation of Ratio of Earnings to Fixed Charges. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
21.1 † |
|
— |
|
List of Subsidiaries of Plains GP Holdings, L.P. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23.1 † |
|
— |
|
Consent of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.1 † |
|
— |
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
31.2 † |
|
— |
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a). |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.1 †† |
|
— |
|
Certification of Principal Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. 1350. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
32.2 †† |
|
— |
|
Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. 1350. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101. INS† |
|
— |
|
XBRL Instance Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.SCH† |
|
— |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.CAL† |
|
— |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.DEF† |
|
— |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.LAB† |
|
— |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
101.PRE† |
|
— |
|
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document |
† Filed herewith.
†† Furnished herewith.
* Certain confidential portions of this exhibit have been omitted pursuant to an Application for Confidential Treatment under Rule 24b-2 under the Exchange Act. This exhibit, with the omitted language, has been filed separately with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
** Management compensatory plan or arrangement.