Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - AGIOS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. | d117444d8k.htm |
| EX-99.2 - EX-99.2 - AGIOS PHARMACEUTICALS, INC. | d117444dex992.htm |

Exhibit 99.1
Agios in 2016
JPMorgan Healthcare Conference
January 11, 2016 David Schenkein, M.D. Chief Executive Officer

Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements
This presentation and various remarks we make during this presentation contain forward-looking statements of Agios Pharmaceuticals, Inc. within the meaning of The Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Such forward-looking statements include those regarding the potential benefits of Agios’ product candidates targeting IDH1/IDH2 or pyruvate kinase-R mutations or other genetic mutations, including AG-221, AG-120, AG-881, AG-348 and AG-519; its plans and timelines for the clinical development of AG-221, AG-120, AG-881, AG-348 and AG-519; its plans regarding future data presentations; its plans regarding its preclinical development activities; and the benefit of its strategic plans and focus. The words “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “plan,” “predict,” “project,” “potential,” “hope,” “could,” “would” and similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements, although not all forward-looking statements contain these identifying words.
Such statements are subject to numerous important factors, risks and uncertainties that may cause actual events or results to differ materially from Agios’ current expectations and beliefs. For example, there can be no guarantee that any product candidate Agios is developing will successfully commence or complete necessary preclinical and clinical development phases, or that development of any of Agios’ product candidates will successfully continue. There can be no guarantee that any positive developments in Agios’ business will result in stock price appreciation. Management’s expectations and, therefore, any forward-looking statements in this presentation or the various remarks made during this presentation could also be affected by risks and uncertainties relating to a number of other important factors, including: Agios’ results of clinical trials and preclinical studies, including subsequent analysis of existing data and new data received from ongoing and future studies; the content and timing of decisions made by the U.S. FDA and other regulatory authorities, investigational review boards at clinical trial sites and publication review bodies; Agios’ ability to obtain and maintain requisite regulatory approvals and to enroll patients in its planned clinical trials; unplanned cash requirements and expenditures; competitive factors; Agios’ ability to obtain, maintain and enforce patent and other intellectual property protection for any product candidates it is developing; Agios’ ability to maintain key collaborations, such as its agreement with Celgene; and general economic and market conditions. These and other risks are described in greater detail under the caption “Risk Factors” included in Agios’ Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2015, and other filings that Agios may make with the Securities and Exchange Commission in the future.
Any forward-looking statements contained in this presentation or in remarks made during this presentation speak only as of the date hereof, and Agios expressly disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or, except as required by law.

We Are Driven By a Clear Vision and Values
RARE GENETIC DISORDERS OF METABOLISM CANCER METABOLISM DYSREGULATED METABOLISM
VISION
Agios is passionately committed to the fundamental transformation of patients’ lives through scientific leadership in the field of cancer metabolism and rare genetic disorders of metabolism
3
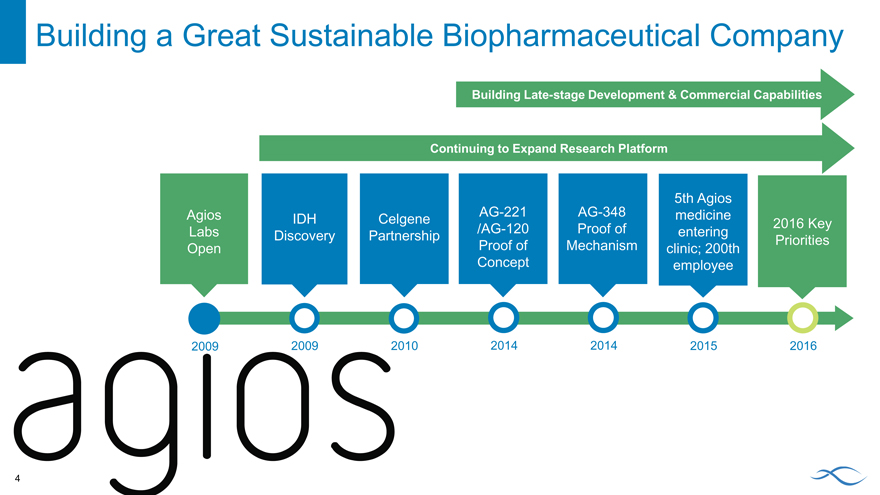
Building a Great Sustainable Biopharmaceutical Company
Building Late-stage Development & Commercial Capabilities
Continuing to Expand Research Platform
5th Agios
Agios IDH Celgene AG-221 AG-348 medicine 2016 Key
Labs Discovery Partnership /AG-120 Proof of entering Priorities
Open Proof of Mechanism clinic; 200th
Concept employee
2009 2009 2010 2014 2014 2015 2016
4
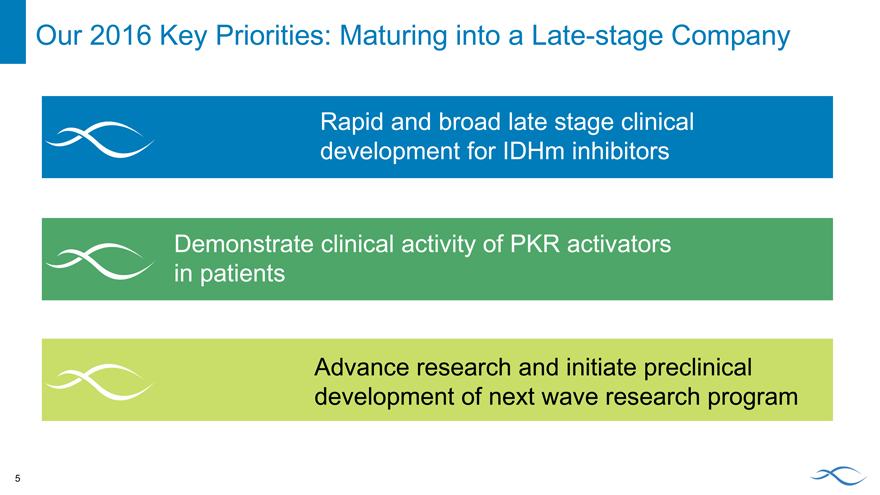
Our 2016 Key Priorities: Maturing into a Late-stage Company
Rapid and broad late stage clinical development for IDHm inhibitors
Demonstrate clinical activity of PKR activators in patients
Advance research and initiate preclinical development of next wave research program
5
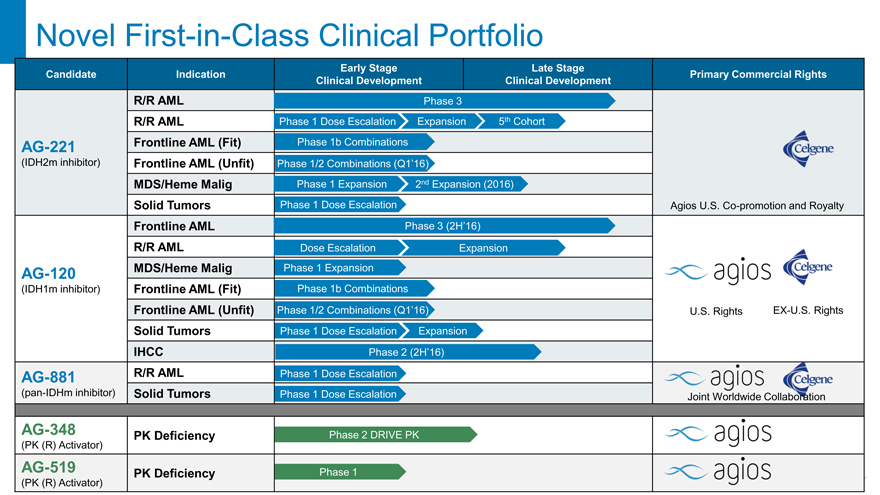
Novel First-in-Class Clinical Portfolio
Early Stage Late Stage
Candidate Indication Primary Commercial Rights
Clinical Development Clinical Development
R/R AML Phase 3
R/R AML Phase 1 Dose Escalation Expansion 5th Cohort
AG-221 Frontline AML (Fit) Phase 1b Combinations
(IDH2m inhibitor) Frontline AML (Unfit) Phase 1/2 Combinations (Q1’16)
MDS/Heme Malig Phase 1 Expansion 2nd Expansion (2016)
Solid Tumors Phase 1 Dose Escalation Agios U.S. Co-promotion and Royalty
Frontline AML Phase 3 (2H’16)
R/R AML Dose Escalation Expansion
AG-120 MDS/Heme Malig Phase 1 Expansion
(IDH1m inhibitor) Frontline AML (Fit) Phase 1b Combinations
Frontline AML (Unfit) Phase 1/2 Combinations (Q1’16) U.S. Rights EX-U.S. Rights
Solid Tumors Phase 1 Dose Escalation Expansion
IHCC Phase 2 (2H’16)
AG-881 R/R AML Phase 1 Dose Escalation
(pan-IDHm inhibitor) Solid Tumors Phase 1 Dose Escalation Joint Worldwide Collaboration
AG-348 PK Deficiency Phase 2 DRIVE PK
(PK (R) Activator)
AG-519 PK Deficiency Phase 1
(PK (R) Activator)
Celgene agios

Today’s Key 2016 Milestone Announcements
IDHm Inhibitors
Complete enrollment in AG-221 and AG-120 expansion arms in 2H Initiate Phase 3 study of AG-120 in frontline AML in 2H
Initiate MDS expansion arm for AG-221
Initiate randomized Phase 2 study of AG-120 in cholangiocarcinoma in 2H
PKR Activators
Present first data from DRIVE PK trial of AG-348 in 1H
Present first data from AG-519 Phase 1 healthy volunteer study in 1H Present new findings from Natural History Study of PK deficiency in 2H
Outline clinical development plans for PKR activators in beta-thalassemia in 2H
Research
Initiate preclinical development activities and publish on a new cancer metabolism program

Cancer Metabolism: IDH
Using a pill once a day to repair a cancer cell
agios
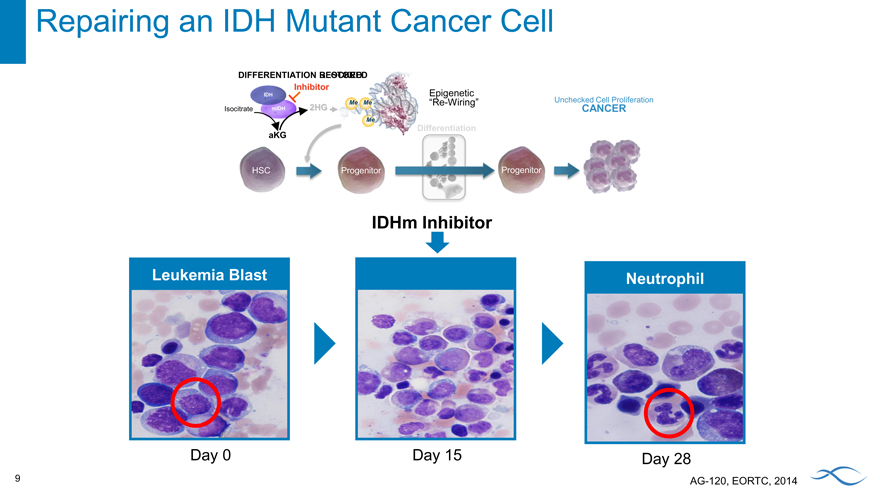
Repairing an IDH Mutant Cancer Cell
DIFFERENTIATION RESTORED BLO
Inhibitor
IDH Epigenetic
“Re-Wiring” Unchecked Cell Proliferation
Isocitrate mIDH 2HG CANCER
Differentiation aKG
HSC Progenitor Progenitor
IDHm Inhibitor
Leukemia Blast Neutrophil
Day 0 Day 15 Day 28
AG-120, EORTC, 2014
9
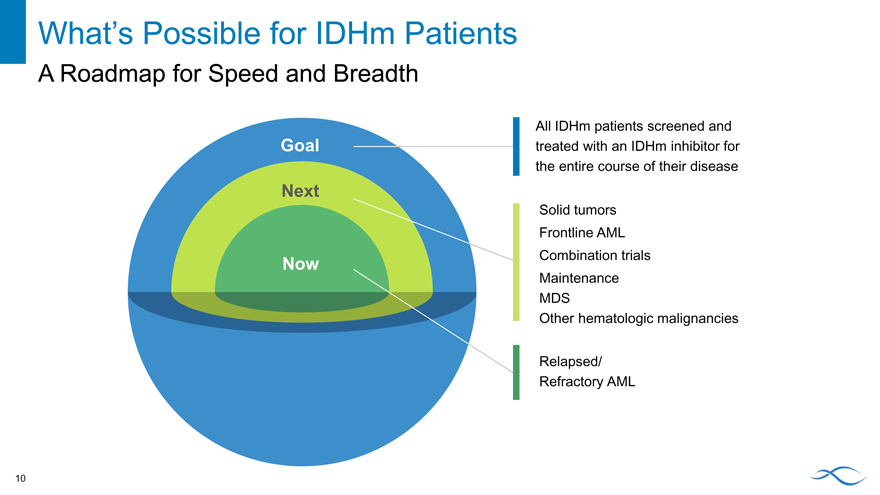
What’s Possible for IDHm Patients
A Roadmap for Speed and Breadth
Goal
Next
Now
All IDHm patients screened and treated with an IDHm inhibitor for the entire course of their disease
Solid tumors Frontline AML Combination trials Maintenance MDS
Other hematologic malignancies
Relapsed/ Refractory AML
10
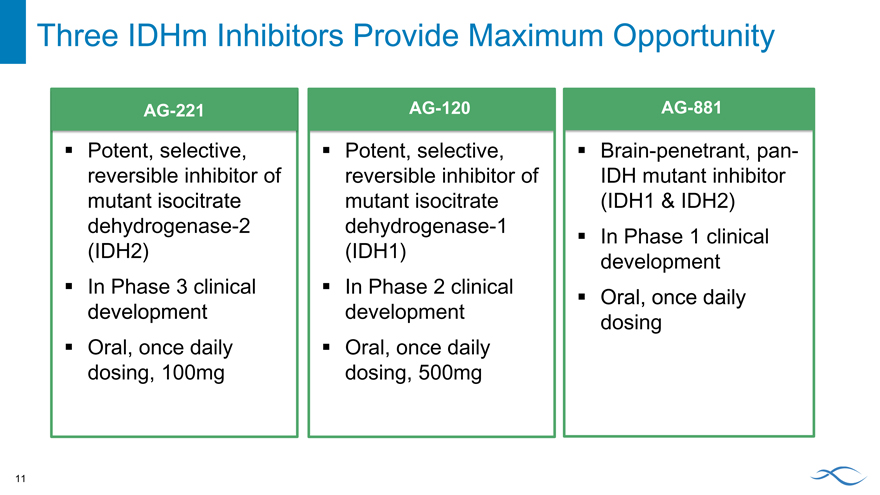
Three IDHm Inhibitors Provide Maximum Opportunity
AG-221
Potent, selective, reversible inhibitor of mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase-2 (IDH2) In Phase 3 clinical development Oral, once daily dosing, 100mg
AG -120
Potent, selective, reversible inhibitor of mutant isocitrate dehydrogenase-1 (IDH1) In Phase 2 clinical development Oral, once daily dosing, 500mg
AG-881
Brain-penetrant, pan-IDH mutant inhibitor (IDH1 & IDH2) In Phase 1 clinical development Oral, once daily dosing
11
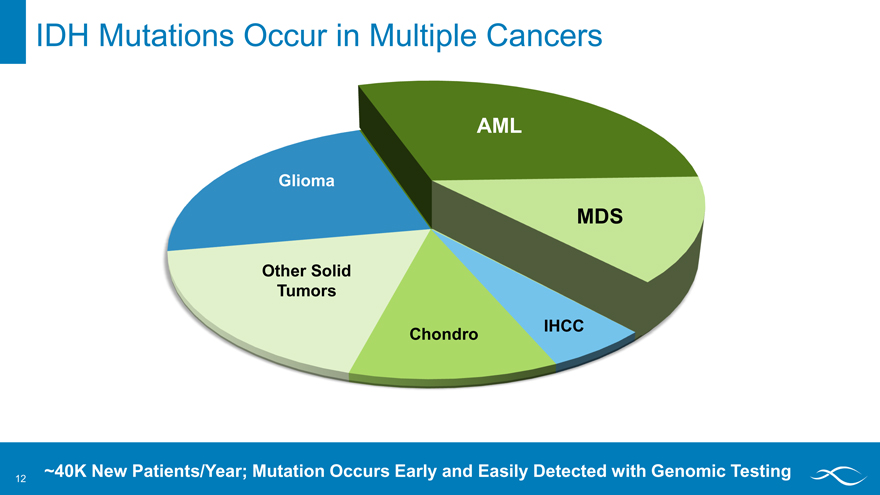
IDH Mutations Occur in Multiple Cancers
AML
MDS
IHCC
Chondro
Other solid tumors
Glioma
~40K New Patients/Year; Mutation Occurs Early and Easily Detected with Genomic Testing
12
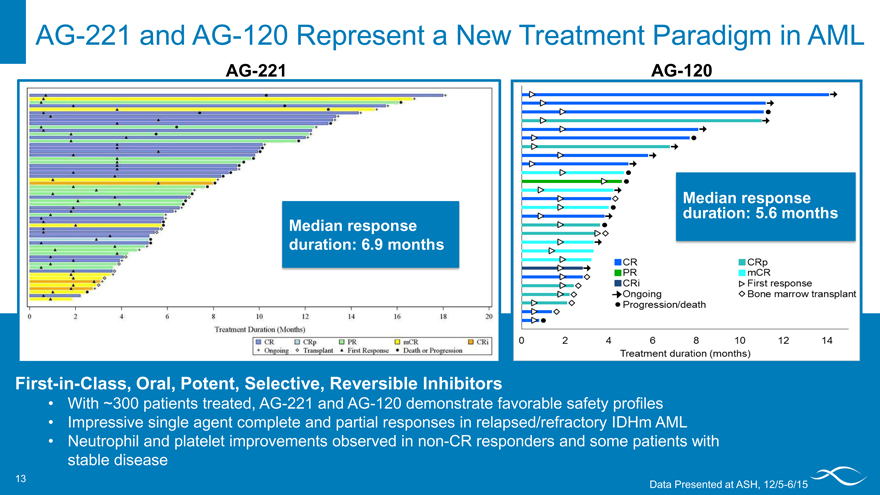
AG-221 and AG-120 Represent a New Treatment Paradigm in AML
AG-221 AG-120
Median response duration: 5.6 months Median response duration: 6.9 months
CR PR CRI Ongoing Progression/death crp mcr first response bone marrow transplant treatment suration (months) death or Progression transplant
First-in-Class, Oral, Potent, Selective, Reversible Inhibitors
With ~300 patients treated, AG-221 and AG-120 demonstrate favorable safety profiles Impressive single agent complete and partial responses in relapsed/refractory IDHm AML
Neutrophil and platelet improvements observed in non-CR responders and some patients with stable disease
Data Presented at ASH, 12/5-6/15
13
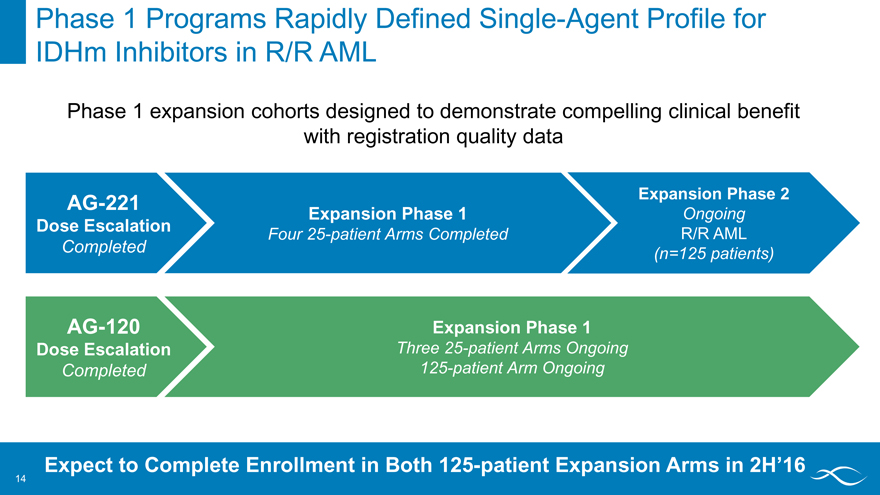
Phase 1 Programs Rapidly Defined Single-Agent Profile for IDHm Inhibitors in R/R AML
Phase 1 expansion cohorts designed to demonstrate compelling clinical benefit with registration quality data
AG-221 Expansion Phase 2
Expansion Phase 1 Ongoing Dose Escalation
Four 25-patient Arms Completed R/R AML Completed (n=125 patients)
AG-120 Expansion Phase 1
Dose Escalation Three 25-patient Arms Ongoing Completed 125-patient Arm Ongoing
Expect to Complete Enrollment in Both 125-patient Expansion Arms in 2H’16
14
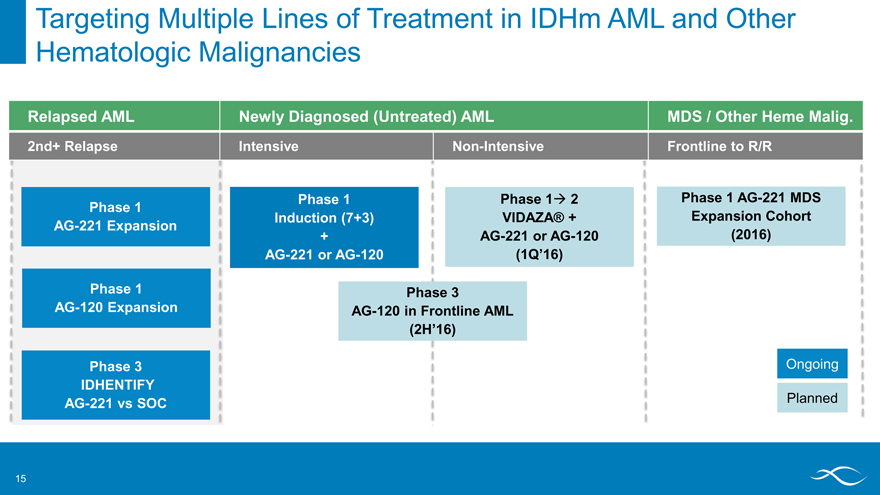
Targeting Multiple Lines of Treatment in IDHm AML and Other Hematologic Malignancies
Relapsed AML Newly Diagnosed (Untreated) AML MDS / Other Heme Malig.
2nd+ Relapse Intensive Non-Intensive Frontline to R/R
Phase 1 AG-221 Expansion
Phase 1 AG-120 Expansion
Phase 3 IDHENTIFY
AG-221 vs SOC
Phase 1 Induction (7+3) + AG-221 or AG-120
Phase 1? 2 VIDAZA® + AG-221 or AG-120
(1Q’16)
Phase 1 AG-221 MDS Expansion Cohort (2016)
Phase 3
AG-120 in Frontline AML
(2H’16)
Ongoing
Planned
15
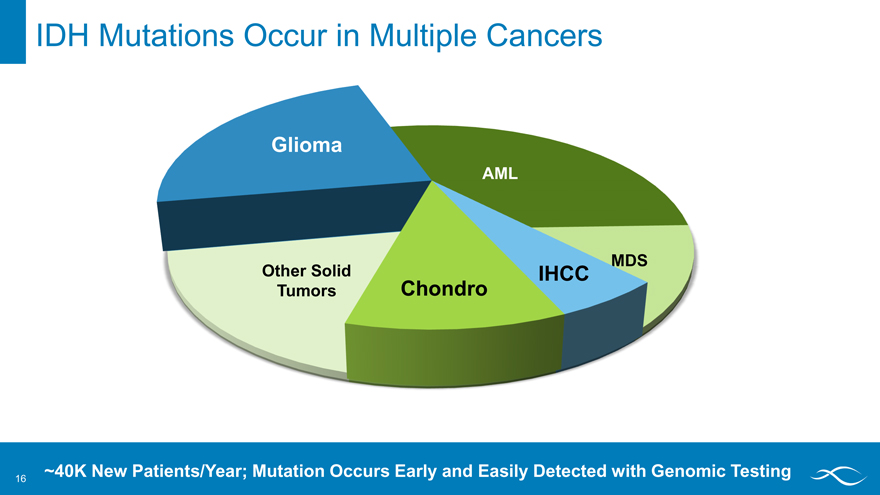
IDH Mutations Occur in Multiple Cancers Glioma IHCC Chondro Aml mds other solid tumors ~40K New Patients/Year; Mutation Occurs Early and Easily Detected with Genomic Testing 16
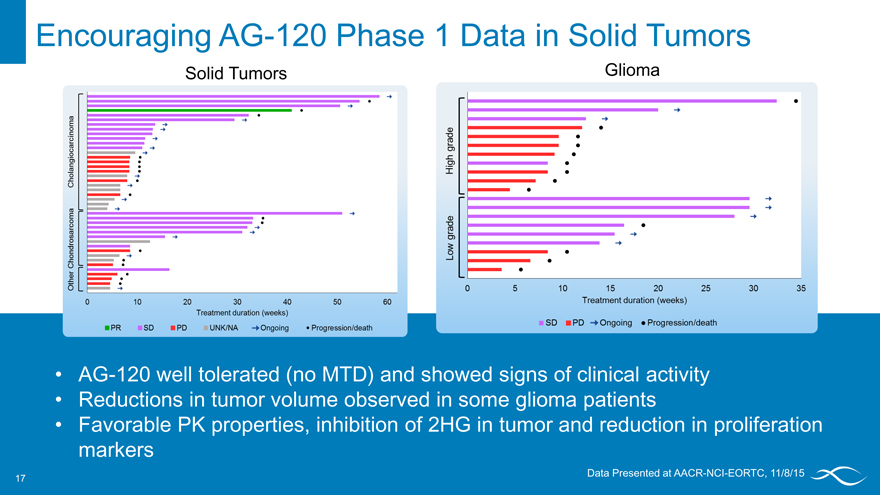
Encouraging AG-120 Phase 1 Data in Solid Tumors
Solid Tumors Glioma
Other chondrosarcoma cholangiocarcinoma treatment duration (weeks) pr sd pd unk/na ongoing progression/death
AG-120 well tolerated (no MTD) and showed signs of clinical activity Reductions in tumor volume observed in some glioma patients
Favorable PK properties, inhibition of 2HG in tumor and reduction in proliferation markers
Data Presented at AACR-NCI-EORTC, 11/8/15
17
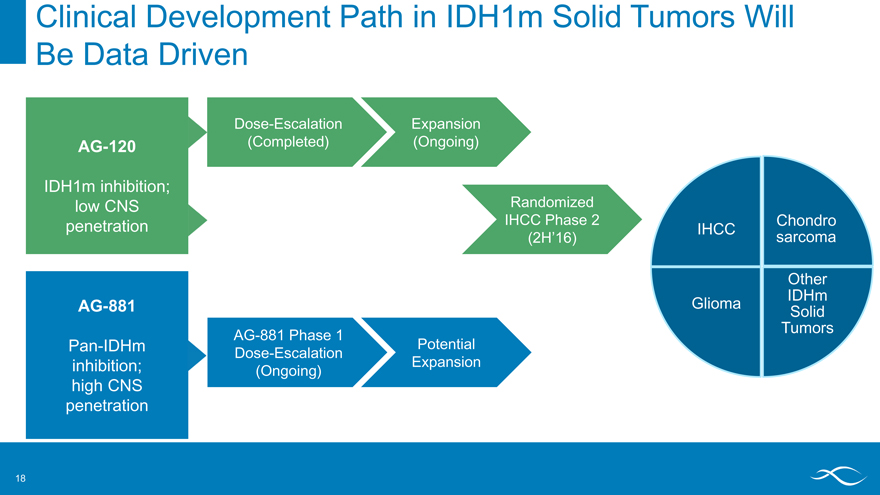
Clinical Development Path in IDH1m Solid Tumors Will
Be Data Driven
AG-120
IDH1m inhibition; low CNS penetration
Dose-Escalation Expansion
(Completed) (Ongoing)
Randomized IHCC Phase 2
(2H’16)
IHCC
Chondro sarcoma
Glioma
Other IDHm Solid Tumors
AG-881
Pan-IDHm inhibition; high CNS penetration
AG-881 Phase 1 Dose-Escalation (Ongoing)
Potential Expansion
18

Rare Genetic Metabolic Disorders: PKR
Transforming a metabolic disorder with a small molecule
agios
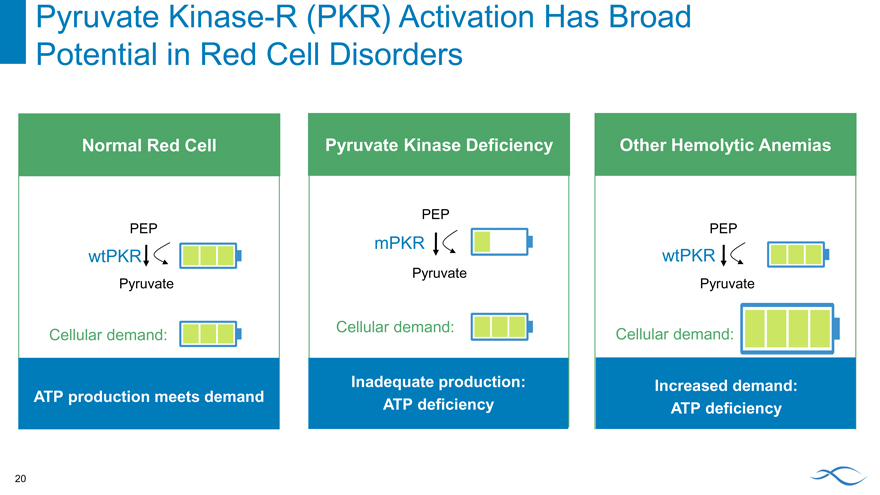
Pyruvate Kinase-R (PKR) Activation Has Broad Potential in Red Cell Disorders Normal Red Cell PEP wtPKR Pyruvate Cellular demand: ATP production meets demand Pyruvate Kinase Deficiency PEP mPKR Pyruvate Cellular demand: Inadequate production: ATP deficiency Other Hemolytic Anemias PEP wtPKR Pyruvate Cellular demand: Increased demand: ATP deficiency 20
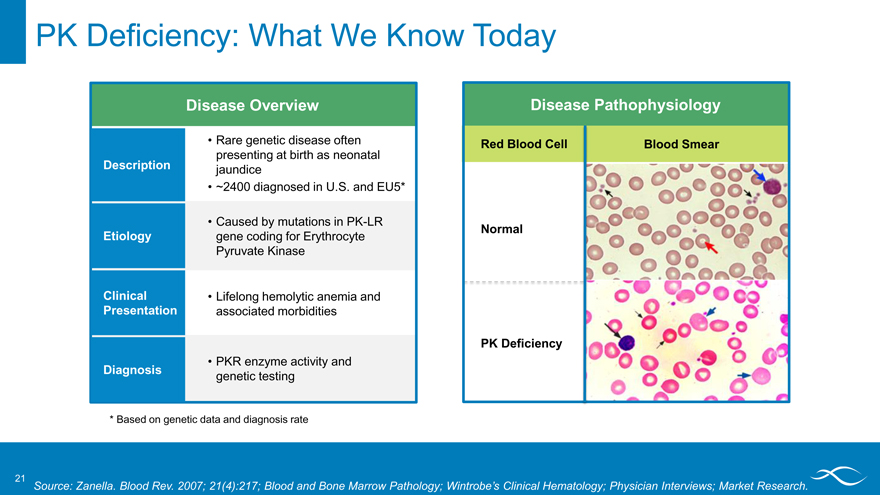
PK Deficiency: What We Know Today
Disease Overview Rare genetic disease often
presenting at birth as neonatal
Description jaundice
~2400 diagnosed in U.S. and EU5*
Caused by mutations in PK-LR
Etiology gene coding for Erythrocyte
Pyruvate Kinase
Clinical Lifelong hemolytic anemia and
Presentation associated morbidities
PKR enzyme activity and
Diagnosis genetic testing
Disease Pathophysiology
Red Blood Cell Blood Smear Normal PK Deficiency
* Based on genetic data and diagnosis rate
21
Source: Zanella. Blood Rev. 2007; 21(4):217; Blood and Bone Marrow Pathology; Wintrobe’s Clinical Hematology; Physician Interviews; Market Research.
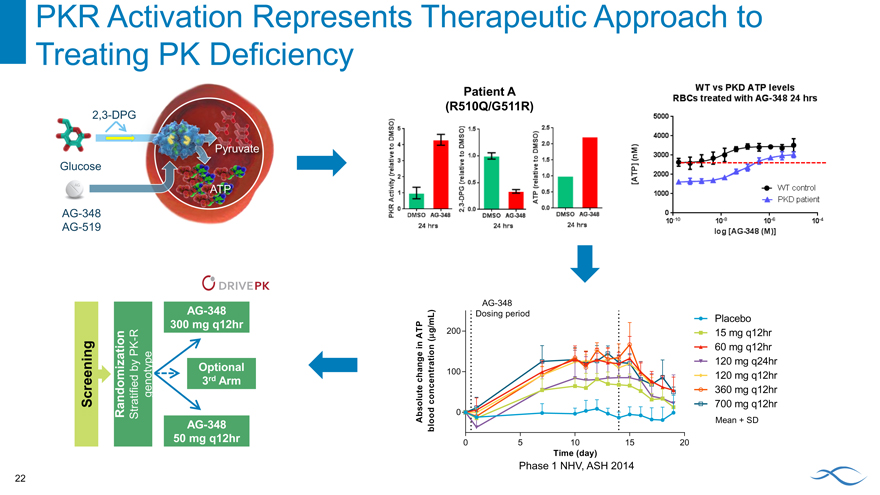
PKR Activation Represents Therapeutic Approach to
Treating PK Deficiency
2,3-DPG
pyruvate Glucose atp
AG-348 AG-519
Patient A (R510Q/G511R)
Pkr activity (relative to dmso) 2-3 dpg (relative to dmso) atp (relative to dmso) 24 hrs
Wt vs pkd atp levels rbcs treated with ag-348 24hrs wt control pkd patient log [ag-348 (m)]
AG-348 300 mg q12hr
R
-
PK by Optional
Screening RandomizationStratified genotype 3rd Arm
AG-348 50 mg q12hr
AG-348
L) Dosing period
m Placebo g/ 200 15 mg q12hr
ATP m ( n
i tion 60 mg q12hr a 120 mg q24hr hange 100 120 mg q12hr
c entr e c
lu t con 360 mg q12hr s o 700 mg q12hr
b od 0
A lo Mean + SD b
0 5 10 15 20
Time (day)
Phase 1 NHV, ASH 2014
22
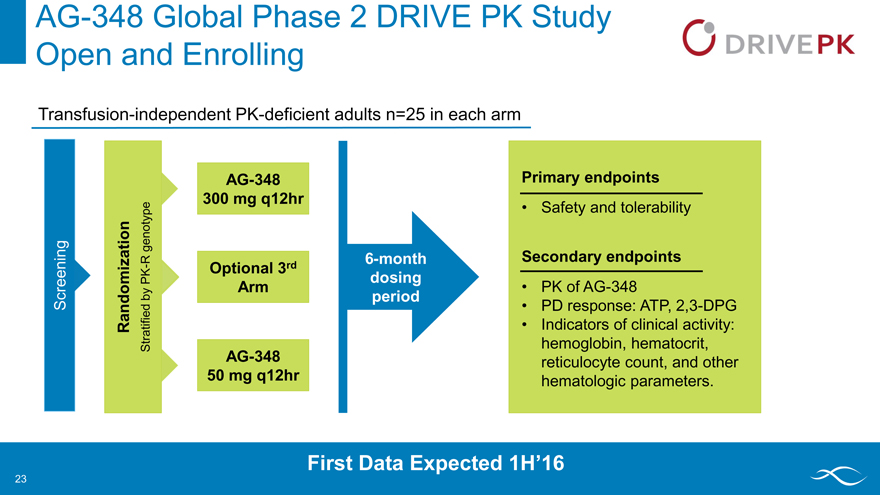
AG-348 Global Phase 2 DRIVE PK Study
Open and Enrolling
Transfusion-independent PK-deficient adults n=25 in each arm
Screening
Randomization
Stratified by PK-R genotype
AG-348
300 mg q12hr
Optional 3rd
Arm
AG-348
50 mg q12hr
6-month
dosing
PK
period
PD
Primary endpoints
Safety and tolerability
Secondary endpoints
PK of AG-348
PD response: ATP, 2,3-DPG
Indicators of clinical activity: hemoglobin, hematocrit, reticulocyte count, and other hematologic parameters.
First Data Expected 1H’16
23
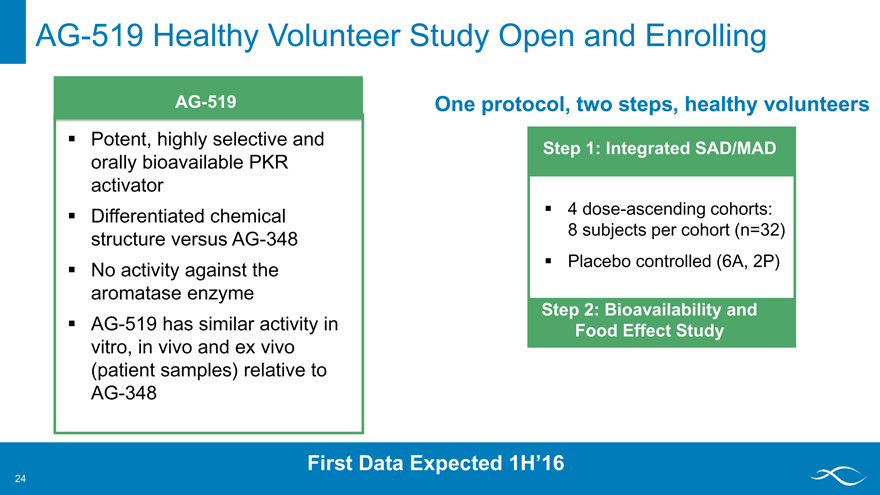
AG-519 Healthy Volunteer Study Open and Enrolling
AG-519
Potent, highly selective and orally bioavailable PKR activator Differentiated chemical structure versus AG-348 No activity against the aromatase enzyme AG-519 has similar activity in vitro, in vivo and ex vivo (patient samples) relative to AG-348
One protocol, two steps, healthy volunteers
Step 1: Integrated SAD/MAD
4 dose-ascending cohorts: 8 subjects per cohort (n=32) Placebo controlled (6A, 2P)
Step 2: Bioavailability and Food Effect Study
First Data Expected 1H’16
24
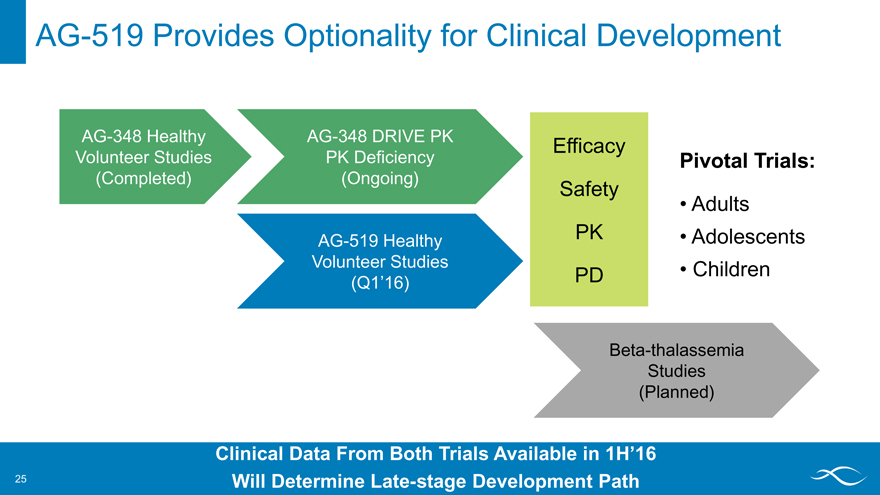
AG-519 Provides Optionality for Clinical Development
AG-348 Healthy Volunteer Studies (Completed)
AG-348 DRIVE PK PK Deficiency (Ongoing)
AG-519 Healthy Volunteer Studies
(Q1’16)
Efficacy Safety PK
PD
Pivotal Trials:
Adults
Adolescents
Children Beta-thalassemia Studies (Planned)
Clinical Data From Both Trials Available in 1H’16 Will Determine Late-stage Development Path
25

Research
Initiating the development of a new research program
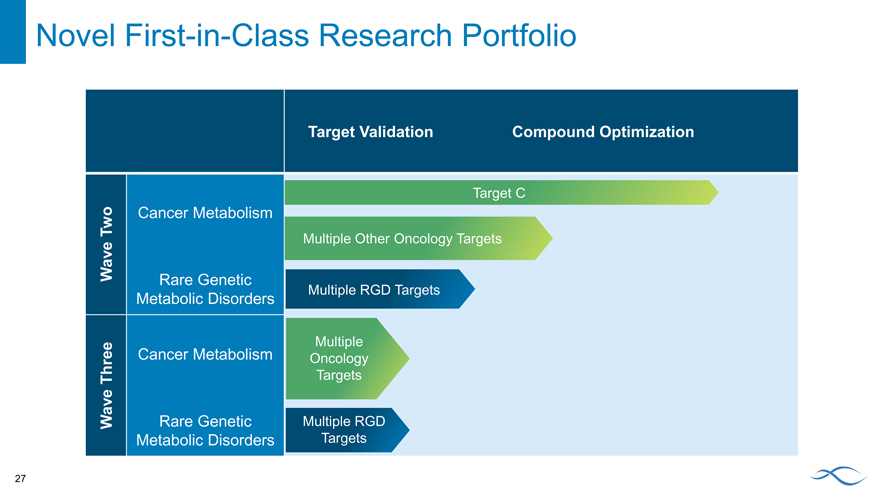
Novel First-in-Class Research Portfolio
Target Validation Compound Optimization
Target C
Two Cancer Metabolism
Multiple Other Oncology Targets
Wave
Rare Genetic
Multiple RGD Targets
Metabolic Disorders
Cancer Metabolism Multiple
Oncology Three Targets
Wave Rare Genetic Multiple RGD
Metabolic Disorders Targets
27
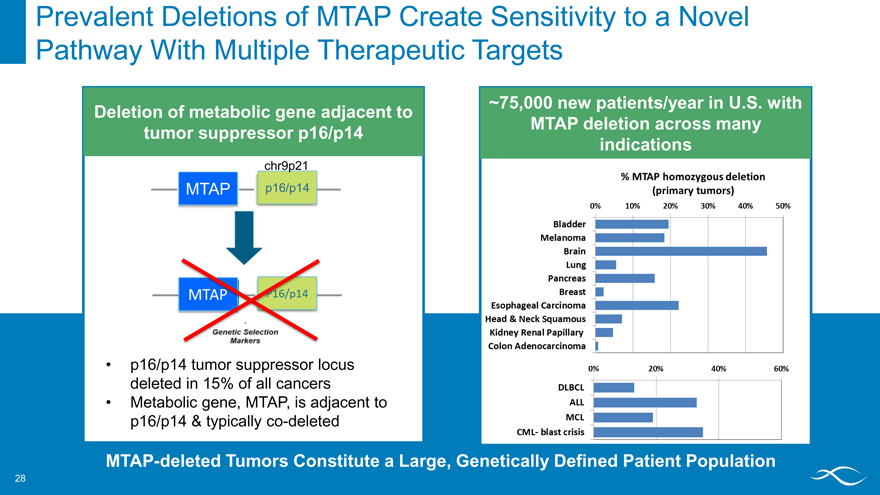
Prevalent Deletions of MTAP Create Sensitivity to a Novel Pathway With Multiple Therapeutic Targets
Deletion of metabolic gene adjacent to tumor suppressor p16/p14
chr9p21 MTAP p16/p14
genetic selection markers ~75,000 new patients/year in U.S. with MTAP deletion across many indications
% mtap homozygous deletion (primary tumors)
Bladder melanoma brain lung pancreas breast esophageal carcinoma head & neck squamous kidney renal papillary colon adenocarcinoma dlbcl all mcl cml- balst crisis
MTAP-deleted Tumors Constitute a Large, Genetically Defined Patient Population
28
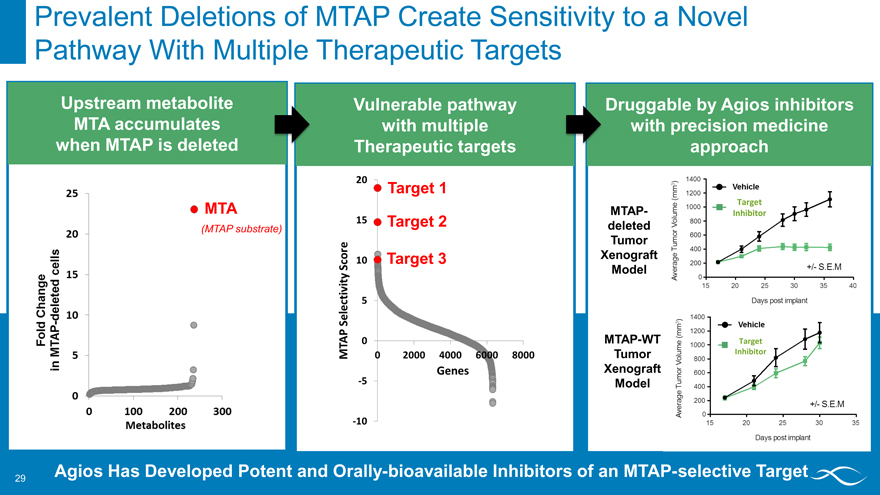
Prevalent Deletions of MTAP Create Sensitivity to a Novel Pathway With Multiple Therapeutic Targets
Upstream metabolite MTA accumulates when MTAP is deleted
MTA
(MTAP substrate)
Vulnerable pathway
with multiple
Therapeutic targets
Target 1
Target 2
Target 3
Druggable by Agios inhibitors with precision medicine approach
Target MTAP- Inhibitor
deleted Tumor Xenograft Model
MTAP-WT Target
Tumor Inhibitor
Xenograft Model
Agios Has Developed Potent and Orally-bioavailable Inhibitors of an MTAP-selective Target
Fold change in mtap-deleted cells metabolites mtap selectivity score mtap-deleted tumor xenograft model mtap-wt tumor xenograft model vechicle target inhibitor days post implant s.e.m
29

Key Takeaways
Focus on Strategic Priorities and Execution:
Continue rapid, broad late-stage clinical development for our
IDHm inhibitors
Demonstrate clinical activity of our wholly owned, PKR activators in patients
Advance research and initiate preclinical development of a new research program
Building a great sustainable biopharmaceutical company
Passionate in our vision to change patients’ lives
30
