Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-99.1 - EXHIBIT 99.1 - Aevi Genomic Medicine, Inc. | v419974_ex99-1.htm |
| 8-K - 8-K - Aevi Genomic Medicine, Inc. | v419974_8k.htm |
Exhibit 99.2

NFC - 1: Phase 2 Ready CNS Asset September 9 , 2015

Forward Looking Statement This presentation includes certain estimates and other forward - looking statements within the meaning of Section 21 E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 , as amended, including statements with respect to anticipated operating and financial performance, clinical results, potential partnerships, licensing opportunities and other statements of expectation . Words such as “ expects, ” “ anticipates, ” “ intends, ” “ plans, ” “ believes, ” “ assumes, ” “ seeks, ” “ estimates, ” “ should ” and variations of these words and similar expressions, are intended to identify these forward - looking statements . While we believe these statements are accurate, forward - looking statements are inherently uncertain and we cannot assure you that these expectations will occur and our actual results may be significantly different . These statements by the Company and its management are based on estimates, projections, beliefs and assumptions of management and are not guarantees of future performance . Important factors that could cause actual results to differ from those in the forward - looking statements include the factors described in the Company ’ s filings with the U . S . Securities and Exchange Commission . The Company disclaims any obligation to update or revise any forward - looking statement based on the occurrence of future events, the receipt of new information, or otherwise . CONFIDENTIAL

Sections • Executive Summary • MDGN/CHOP Collaboration • neuroFix / NFC - 1 Acquisition • NFC - 1 Phase 1b Clinical Trial in ADHD • 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome • Summary 3

Executive Summary 4 • Medgenics will acquire neuroFix – Provides access to a Phase 2 - ready program, NFC - 1 – P rivate company f ounded by Dr. Hakonarson, Director, Center for Applied Genomics (CAG ) at The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) – Breakthrough discovery: mGluR mutations cause ~20% of ADHD • NFC - 1 – Strong efficacy signal in Phase 1 b study of mGluR + ADHD – MDGN will progress NFC - 1 to Phase 2 in: • mGluR+ pediatric ADHD • 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome (large mGluR+ orphan population) • Additional mGluR+ neuropsychiatric disorders • Deal Terms – Low cash up - front payment ($2 million) – Success - based Development and Sales Milestones – Single digit royalties

Medgenics/CHOP Collaboration 5 • C ollaboration allows MDGN option to discoveries made by CAG: – Rare and Orphan diseases – Unique, druggable targets in high - need patients • Distinct, genetically identified participants allow for rapid clinical development including: – Comparatively small trials – Rapid proof - of - concept – Increased response rates and probability of success • NFC - 1 represents the first program of the collaboration

CAG/CHOP Capabilities 6 Datasets (Genomics EMR) ▪ Over 60K pediatric and 150K related adult patients GWAS genotyped with associated longitudinal EMR since 2006 Data Analytics ▪ End to end internal Next - Gen sequencing capabilities ▪ Integrated bioinformatics ▪ Rapid identification of novel genetic biomarkers Biobank (BB) ▪ Fully automated robotic biorepository Consented Patients • 85 % of the BB patients are consented for longitudinal follow up and are eligible for call back for future studies ▪ ~1.2M patient visits/year ▪ 10% of all R/O disease patients in N. America are treated at CHOP CAG’s pediatric biobank contains a high percentage of rare genetic variants ▪ Population is unique in that it represents the most severe forms of common diseases ▪ Global reach in many therapy areas In the last 8 years CAG has had over 400 peer reviewed publications focused on novel genetic discoveries H ighly scalable infrastructure to support translational research

Business Model Evolution: Gene Therapy to Genomic Medicine 7 Diverse Limited Medgenics capabilities Ex vivo Gene Therapy • TARGT EPO • TARGT GLP - 2 Time Genomic Medicine • C ommercial capabilities • Further pipeline diversification Genomic Drug Development • World - class biobank and analytics • G enetically defined pediatric biosamples MDGN growth and diversification enhanced by CAG collaboration TM

NFC - 1, a first - in - class Metabotopic Glutamate Receptor ( mGluR ) Neuromodulator 8

Elia, Glessner et al. Nature Genetic s, 2012 CAG Breakthrough Discovery 9 Research by Dr. Hakonarson indicated approximately 20% of ADHD patients have an underlying mGluR network mutations • 10 fold increased frequency of copy number variations (CNV ) in the mGluR gene network detected in ADHD population vs. normal controls • Dr. Hakonarson found these mutations in several related neuropsychiatric diseases

NFC - 1, first - in - class mGluR Neuromodulator 10 • Small molecule, non - stimulant agonist of multiple mGluRs : • 1, 3, 5, 7, 8 • Up - regulates GABA B receptors • Positive effects seen in animal models • Ameliorate cognitive impairment • Reduce hyperactivity • Enhance memory • Antipsychotic activity Dr . Hakonarson identified NFC - 1 as a drug with potential to address mGluR network disruptions caused by genetic mutations

NFC - 1, An Excellent Candidate for R epositioning 11 • Failed on efficacy measure • Excellent safety profile in >1,000 patients • No addiction potential • Excellent oral bioavailability and predictable PK – Twice - daily dosing NFC - 1 tested in a large scale clinical trial in Vascular Dementia patients not enriched for mGluR mutations

NFC - 1 GREAT Study: mGluR mutation positive adolescents with ADHD symptoms 12

NFC - 1 GREAT Study: Design and Execution • Part 1: Single Ascending Dose(SAD)/Pharmacokinetics(PK) – SAD 24 hour PK 50 - 800mg • Part 2 : Ascending Dose Trial – 1 week of placebo followed by 4 weeks active therapy – Dose escalated: 50mg BID* - 400mg BID* weekly (x4) – Efficacy endpoints CGI, Vanderbilt, exploratory – Single - blinded (to patients/families) To be presented at American Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry (AACAP). October 26 - 31, San Antonio. 13 Two - part Phase 1B trial, n=30 Trial was completed Q3 2015 *Twice a day

GREAT Study Enrolled Complex, Severe Patients Inclusion Criteria • ADHD patients age 12 – 17 • mGluR network mutation positive ( mGluR +) Severe ADHD symptoms and high comorbidity • 73% had severe ADHD (CGI - S >5 at baseline) • 67% had co - morbid psychiatric conditions – Anxiety, ODD, Insomnia • 30% on antipsychotics and/or antidepressants • 70% had previous treatment with ADHD drugs 14

15 Strong Efficacy Signal in Key Endpoints – CGI - I 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% 1 2 3 4 5 CGI - I: Proportion of Responders at E ach Week for All Subjects W eek W eek W eek W eek W eek Treatment effect appeared more robust over time and at higher doses CGI - I, Clinical Global Impression of Symptom Improvement Responder – Global rating of much or very much improved

16 0% 10% 20% 30% 40% 50% 60% 70% 80% 90% Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Vanderbilt Scores: Proportion of Patients Improved from Pre - study Baseline for All Patients Improvement defined as 25% improvement in hyperactivity/inattention domains Strong Efficacy Signal in Key Endpoints – Vanderbilt Parent Rating Treatment effect appeared more robust over time and at higher doses

Statistically Significant Improvement in Key Endpoints 17 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Mean 29.1 26.4 24.0 23.3 22.5 Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 Mean 3.79 3.13 2.79 2.79 2.21 P < 0.001 P < 0.001 Average Vanderbilt score at each week – all patients Average CGI - I score at the end of each week – all patients Repeated Measures Analysis: mean scores by week CGI - I Scale: 1 - 7 Vanderbilt Scale (Questions 1 - 18): 0 - 54 Improvement magnitude comparable to best in class drugs in complex, severe patients
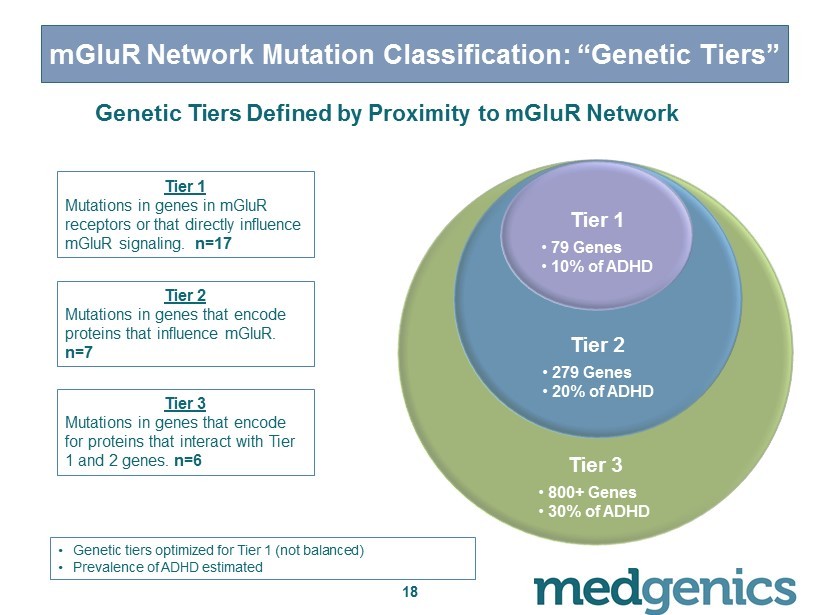
18 mGluR Network Mutation Classification: “Genetic Tiers” Tier 3 • 800+ Genes • 30% of ADHD Tier 2 • 279 Genes • 20% of ADHD Tier 1 • 79 Genes • 10% of ADHD Tier 1 Mutations in genes in mGluR receptors or that directly influence mGluR signaling. n=17 Tier 2 Mutations in genes that encode proteins that influence mGluR . n=7 Tier 3 Mutations in genes that encode for proteins that interact with Tier 1 and 2 genes. n=6 • G enetic tiers optimized for Tier 1 (not balanced) • Prevalence of ADHD estimated Genetic Tiers Defined by Proximity to mGluR Network

Core Mutations (Tier1/2) Predict Higher Response 19 0.00 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 3 CGI - I Proportion of Responders at Week 5 by Genetic Tier ( with 95% confidence intervals) Proportion of Responders (CGI - I) Note: genetic tiers were not balanced Note: Data is for the subset of patients who titrated to the highest dose (N=18)

20 Proportion of Responders (Vanderbilt) Note: genetic tiers were not balanced Note: Data is for the subset of patients who titrated to the highest dose (N=18) 0.00 0.20 0.40 0.60 0.80 1.00 Tier 1 Tier 2 Tier 3 Vanderbilt - Proportion of Responders at Week 5 by Genetic Tier ( with 95% confidence intervals) Core Mutations (Tier1/2) Predict Higher Response
NFC - 1 GREAT Study Summary • Strong efficacy signal detected in several validated ADHD scales • Improvement in multiple symptoms noted by caregivers – I nattention, hyperactivity, anxiety, mood disorders • Treatment effect more robust over time & higher doses • Genetic biomarker predictive of response to NFC - 1 (Tier 1 & 2) • Confirmation of PK profile – C omparable to previous PK study; BID dosing • W ell tolerated, no treatment related serious adverse events • 20 of the 30 patients chose to continue in a long - term safety trial – Study began August 2015 21

Efficacy & Safety Profile De - risk Pivotal Trials Phase 2/3 trial in Tier 1/2 mGluR + ADHD • Objective: Identify optimal dose and confirm enhanced response in mGluR network mutation positive patients – Primary endpoints: ADHD RS, CGI - I – Powered to serve as pivotal trial – Top - line data anticipated H216 • Additional study for approval: – Confirmatory Phase 3 trial in target population (ages 6 – 19) 22

ADHD Market Opportunity Overall US Market • 2015 Sales in excess of $10B* (> 60M total prescriptions**) • Approximately 6M pediatric patients • Stimulants dominate market with 90+% of total prescriptions NFC - 1 Opportunity • Genetic Biomarker identifies eligible patients (20 % of all ADHD) and response • Superior clinical profile in mGluR + ADHD patients – Not scheduled – No cardiovascular risk – Potential to address broad range of symptoms ( eg . a nxiety, conduct, mood) – Should lead to broad reimbursement coverage and premium pricing – Great clinical profile for Europe 23 *IBIS World.com **IMS, 2014

22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome (DS) Overview 24

Orphan Opportunity - 22q11.2 DS • 90% of 22q11.2DS patients have at least one mGluR network related deletion (RANBP1) 25 Micro deletion occurs in chromosome 22 Hypothesis: neuropsychiatric symptoms in 22q11.2DS patients are causally related to mGluR CNV/mutations and will respond to NFC - 1

26 Orphan Opportunity - 22q11.2 DS Physical Symptoms • Heart defects • Cleft palate • Gastrointestinal problems • Poor wound healing • Skeletal abnormalities Surgical / medical therapies mortality <4% after CV surgery (excluding critically ill infants) No effective therapy Approx. 40% progress to schizophrenia Psychiatric Symptoms* Prevalence estimates range from 1/2,000 to 1/4,000 *Jonas et al Biol Pyschiatry 2014;75:351 - 360

22q11.2 Patient in GREAT Study 27 T wo 22q11.2 p atients in the trial; one deletion and one duplication • Parents reported significant symptom improvement in both • M arked improvement in CGI - I and Vanderbilt • Both families elected to enroll in long - term safety trial to maintain access to NFC - 1

Orphan Pathway - 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome • Phase 1/2 indication & dose finding study – File IND 4Q15 – Explore major neuropsychiatric disorders: ADHD, Anxiety, Mood – Initial data expected mid - 2016 – Transition to pivotal trial in one or more disorders – Rapid path to approval based on potential of Orphan Designation 28

Opportunity to work with the Leading 22q11.2 Center • “ 22q and You” Center at The Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) – World’s leading 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome (DS) Center – Caring for > 1,300 children with a 22q11.2 deletion – Draws families from around the world – Staffed by geneticists, genetic counselors and physicians 29

Summary 30

NFC - 1 Summary • First program from the collaboration – Phase 2 ready program via neuroFix acquisition • P rogram in mGluR + ADHD is highly de - risked – Extensive safety database – Compelling Phase 1b efficacy signal in mGluR+ ADHD • Potential rapid path to approval in 22q11.2 DS – Potentially large orphan indication – Compelling genetic hypothesis and positive signal in one patient – Potential for rapid development path with single pivotal trial • Opportunity in additional mGluR+ CNS/psych diseases 31

Regulatory & IP Summary • Regulatory Exclusivity (approximately 7 years) – NFC - 1 has not been registered in the US – S hould receive New Chemical Entity status – 5 years Hatch - Waxman exclusivity – Additional 30 - month stay upon challenge – Potential for Orphan Indication in 22q11.2DS • IP Position – Multiple “ Test and Treat” patent applications pending – S upported by companion diagnostic tied to the therapeutic – Could allow for IP protection for 20+ years – Patent estate will continue to build over time 32

NFC - 1 Near - term Milestones 33 PROGRAM TIMING mGluR + ADHD GREAT Study Data presented at AACAP Oct 15 Request type “C” meeting with the FDA Q4 15 Initiate Phase 2/3 dose finding pivotal trial Q1 16 Initial data readout H2 16 22q11.2 Deletion Syndrome Submit IND for 22q11.2 DS Q4 15 Initiate exploratory study of psychiatric symptoms Q1 16 Initial data readout Mid 16

Appendix 34

Glossary of Terms 35 TERM DEFINITION CGI - S Clinical Global Impression – Severity. Clinician - rated assessment used to measure treatment effect. Used in all FDA regulated ADHD trials. CGI - I Clinical Global Impression – Improvement. Clinician - rated assessment used to measure treatment effect. Used in all FDA regulated ADHD trials. Vanderbilt Parent - rated assessment based upon frequency of occurrence of 47 different symptoms. (GREAT study used 18 questions, making it comparable to the ADHD RS). BRIEF Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function. Parent and child - rated assessment. 86 - item questionnaire that measures behaviors related to 8 clinical domains of executive function. PERMP Permanent Product Measure of Performance Math Pre - Test and Test. 5 page test consisting of 80 math problems per page. Subjects asked to complete as many math problems as possible in 10 minutes. Scoring based on problems completed plus problems completed correctly. ADHD RS ADHD Rating Scale - IV. Obtains parent ratings regarding the frequency of each ADHD symptom based on DSM - IV criteria. mGluR Metabotropic glutamate receptor. mGluR’s perform a variety of functions in the central and peripheral nervous systems involving learning, memory, anxiety, etc.

mGluR : Important Components of Brain Signaling Network 36 • Widespread distribution and function makes mGluRs attractive drug targets for neuropsychiatric disease • K ey neuronal signaling functions regulated by mGluRs : • Cognition • Memory • Attention • Learning • Activity • Behavior • mGluR modulators have been studied as therapies for autism, mood disorders anxiety and schizophrenia Ohashi et al Z . Naturforsch ., C, J. Biosci . 57 (3 - 4): 348 – 55 Dunayievich et al Neuropsychopharmacology 33 (7): 1603 – 10.

NFC - 1 GREAT Study Efficacy Measures and Results Efficacy Measure Result Comments CGI - S Strong positive signal • Clinician was blinded to genetic tier CGI - I Strong positive signal • Clinician was blinded to genetic tier Vanderbilt (Parent) Strong positive signal • Only used the first 18 questions for the assessment making this assessment comparable to the ADHD RS BRIEF (Parent) Positive signal* • All three domains trended positively BRIEF (Self) Weak positive signal* • Subjects often do not see themselves as impaired PERMP Inconclusive* • Multiple protocol violators and poorly administered Quotient ADHD Test Weak positive signal* • Signal in tier - 1 subjects at high dose, poorly administered Actigraphy Weak positive signal* • Reduced medium/high burst of activities on highest dose *Qualitative assessment of results 37

NFC - 1 GREAT Study Phase 1b Trial Design: Active Treatment Phase 38 Part 2 5 - week Daily Dosing Weekly Dose - Escalation Notes: - S tudy was single blinded (to patient/family) - Animal tox initially limited the max exposure to 200 mg BID initially (per FDA) - 18/30 patients were titrated to the highest dose 50mg BID Week 1 Week 2 Week 3 Week 4 Week 5 100mg BID Placebo 2 00mg BID 400mg BID Active Treatment Phase; Weekly Measures of Drug Levels Weekly ADHD Scales and Measures

2015 TARGT EPO Milestones 39 PROGRAM TIMING RENAL ANEMIA Complete enrollment in low dose MDGN - 201 cohort ✓ Initiate enrollment in mid dose MDGN - 201 cohort ✓ Initiate Phase 2 study in Peritoneal Dialysis (PD), including: ✓ - Renal Anemia Transplant patients - ESA Hypo - responsive patients Oral presentation at ESGCT Sep 15 HEMATOLOGICAL DISORDERS Initiate Phase 2 study in Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) H2 15 Pre - IMPD meeting for Beta Thalassemia Intermedia ✓ PRECLINICAL Pre - IMPD meeting for GLP - 2 ✓ Lead program from CHOP collaboration ✓

Medgenics Vision 40 Driven by our commitment to patients we strive to create the premier rare and orphan disease company by : • Having unparalleled understanding of the underlying science of rare diseases from genotype to phenotype • Developing first - to - market or best - in - class therapies that are transformative to patients suffering from life - altering rare genetic diseases • Pushing the boundaries of medicine and technology to develop unique and better therapies • Working with patient s, families and advocacy groups to increase awareness and commitment to research and improve access to therapies
