Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - Auspex Pharmaceuticals, Inc. | d912489d8k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1


| • | Huntington disease (HD) is a hereditary, progressive, neurodegenerative disorder characterized by chorea, behavioral disturbance, cognitive dysfunction and psychiatric disease |
| • | Chorea affects up to 90% of patients with HD and can interfere with daily functioning and cause injury1 |
| • | Deutetrabenazine (SD-809) is a novel molecule which contains six deuterium atoms instead of six hydrogen atoms in specific positions in the tetrabenazine (TBZ) molecule |
| • | TBZ, a vesicular monoamine transporter type 2 (VMAT-2) inhibitor, is approved for the treatment of chorea of HD and is also used to treat tardive dyskinesia and tics2 |
| • | Deuterium forms a stronger bond with carbon than does hydrogen and requires more energy for cleavage, thus leading to attenuated metabolism enabling a differentiated pharmacokinetic profile3,4 |
Study Design:
| • | Randomized (1:1), double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group study |
| • | 8 week titration period followed by 4 week maintenance period and a 1 week washout period |
| • | Study drug was titrated weekly in increments of 6 mg to adequate chorea control (optimal dose) without knowledge of CYP2D6 genotype |
Key Inclusion Criteria:
| • | CAGn ³37 |
| • | Unified Huntington Disease Rating Scale (UHDRS) Total Maximal Chorea (TMC) score ³8 |
| • | UHDRS Total Functional Capacity (TFC) score ³5 |
Key Exclusion Criteria:
| • | Serious, untreated or undertreated psychiatric illness; stable antidepressant therapy was permitted |
| • | Significant swallowing or speech impairment |
| • | Recent use of TBZ (6 months), dopamine (DA) receptor antagonists, DA agonists, levodopa, reserpine, NMDA receptor antagonists, or MAO inhibitors |
Efficacy Endpoints:
| • | Primary: Change in Total Maximal Chorea (TMC) score from baseline to maintenance therapy (average of Weeks 9 and 12) |
| • | Secondary endpoints, assessed as the change from baseline to Week 12, were tested in a hierarchical manner as follows: |
| 1. | Patient Global Impression of Change (PGIC) |
| 2. | Clinical Global Impression of Change (CGIC) |
| 3. | SF-36 physical functioning score |
| 4. | Berg Balance Test |
| • | Additional prespecified efficacy endpoints: |
| • | UHDRS Total Motor Score (TMS) |
| • | Percentage change in TMC from baseline to maintenance therapy |
Safety Parameters:
| • | Adverse events (AEs), clinical laboratory tests, vital signs, ECG |
| • | Changes in Safety Scales: Epworth Sleepiness Scale, Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale, Swallowing Disturbance Questionnaire (SDQ), UPDRS dysarthria item, Barnes Akathisia Rating Scale, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale, Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA©) |



| • | 34 sites in the United States and Canada |
| • | 90 subjects (45:45) enrolled (Table 1); 87 completed; two placebo and one SD-809 subject discontinued prematurely |
| • | Mean daily dose SD-809 at Week 12 was ~40 mg |
Table 1. Baseline Characteristics
|
SD-809 (N = 45)
|
Placebo (N = 45)
|
All (N = 90)
| ||||
| Age, years, mean (SD) |
55.4 (10.3) | 52.1 (13.4) | 53.7 (12.0) | |||
| Male Gender, n (%) |
22 (49%) | 28 (62%) | 50 (56%) | |||
| Weight, kg, mean (SD) |
74.1 (13.6) | 74.1 (15.1) | 74.1 (14.3) | |||
| CAGn, mean (SD) |
43.4 (2.7) | 44.3 (4.4) | 43.9 (3.7) | |||
| UHDRS TFC, mean (SD) |
9.8 (2.3) | 9.2 (2.0) | 9.5 (2.1) | |||
| UHDRS TMC, mean (SD) |
12.1 (2.7) | 13.2 (3.5) | 12.7 (3.2) |
Efficacy:
| • | Primary endpoint: Total maximal chorea (TMC) score improved by 4.4 points for SD-809 vs.1.9 points for placebo, with a treatment effect of 2.5 points (21 percentage points) from baseline to maintenance therapy (p<0.0001) (Figure 1) |
| • | Total motor score (TMS) improved by 7.4 [6.3] for SD-809 vs. 3.4 [5.5] for placebo, for a treatment effect of 4.0 (p=0.0023) |
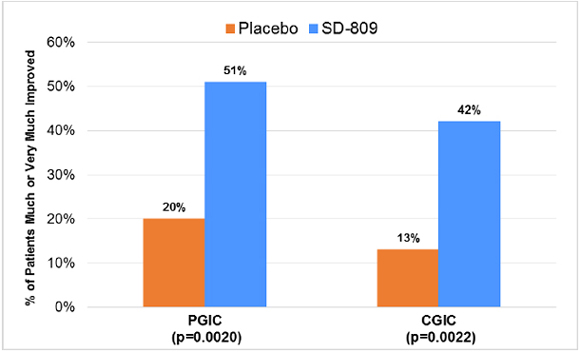
| • | Significantly improved secondary endpoints included PGIC and CGIC (each p=0.002) and SF-36 physical functioning scale (p=0.03) (Table 2 and Figure 2) |
Figure 1. Total Maximal Chorea Score
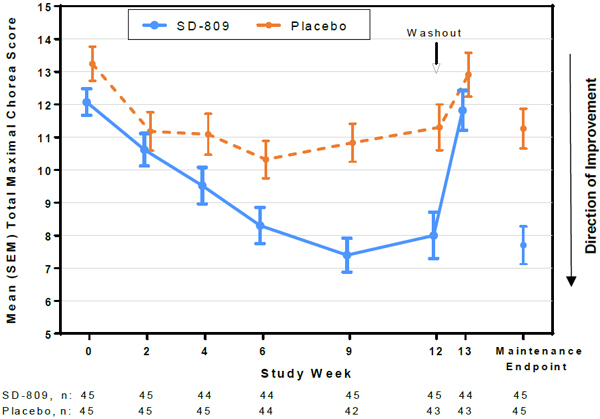
Table 2. Secondary Efficacy Parameters (Change from Baseline to Week 12)
|
Change from Baseline to Wk 12
|
Treatment Effect
|
Favors
|
P-Value
| |||
| SF-36 Physical Functioning |
4.34 | SD-809 | 0.0308 | |||
| Berg Balance Test |
1.0 | SD-809 | 0.14 | |||
|
Values shown above are LS Mean (SD) | ||||||



Figure 2. Secondary Efficacy Parameters (Week 12)
Safety:
| • | Rates of depression, irritability, insomnia were low with SD-809 and similar to or less than observed in placebo |
| • | No AEs of parkinsonism were reported |
| • | Low overall rates of AEs (Table 3), dose reduction (6.7%) or dose suspension (2.2%) for AEs in both the SD-809 and placebo groups |
| • | Safety scales showed no evidence of subclinical toxicity associated with SD-809 treatment. SDQ scores favored SD-809 over placebo (Figure 3) |
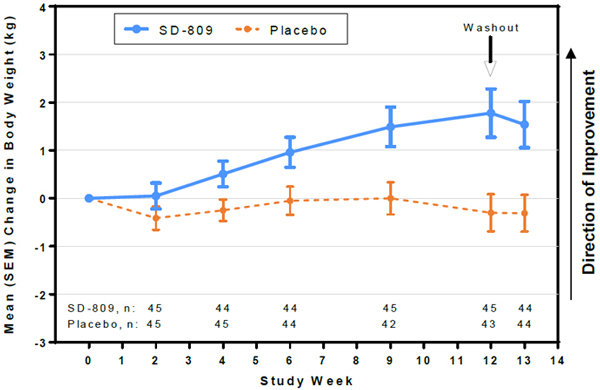
| • | At Week 12, SD-809 subjects had mean (SD) change in body weight of +1.8 (3.4) kg vs –0.30 (2.5) kg in placebo (treatment effect, +2.1 kg) (Fig 4) |
Table 3. Treatment-Emergent AEs Occurring in >5% of Patients in Either Group, n (%)
| Preferred Term |
SD-809 (N=45)
|
Placebo (N=45)
| ||
| Any Adverse Event |
27 (60) | 27 (60) | ||
| Somnolence |
5 (11.1) | 2 (4.4) | ||
| Dry mouth |
4 (8.9) | 3 (6.7) | ||
| Diarrhoea |
4 (8.9) | 0 (0.0) | ||
| Irritability |
3 (6.7) | 6 (13.3) | ||
| Insomnia |
3 (6.7) | 2 (4.4) | ||
| Fatigue |
3 (6.7) | 2 (4.4) | ||
| Dizziness |
2 (4.4) | 4 (8.9) | ||
| Fall |
2 (4.4) | 4 (8.9) | ||
| Depression |
2 (4.4) | 3 (6.7) | ||
| Sleep disorder |
0 (0.0) | 3 (6.7) | ||
| Headache |
0 (0.0) | 3 (6.7) | ||
| Vomiting |
0 (0.0) | 3 (6.7) |
Figure 3. Swallowing Disturbance Questionnaire Score
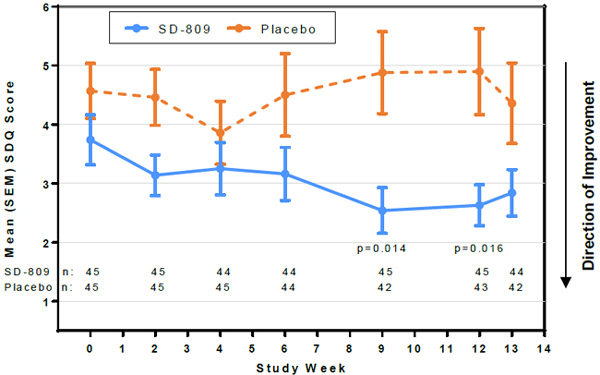



Figure 4. Mean Change in Weight

| • | Treatment with deutetrabenazine effectively reduced chorea in patients with HD and showed improvement in the Total Motor Score that was greater in magnitude than the effect on chorea, suggesting a benefit on other motor symptoms. |
| • | The clinical importance of improved motor function was indicated by patients and clinicians with significant improvements on the PGIC, CGIC and the SF-36 physical functioning scale. |
| • | Weight gain was observed in subjects who received deutetrabenazine. |
| • | Deutetrabenazine demonstrated a favorable safety and tolerability profile, with low rates of neurologic and psychiatric AEs, as well as low rates of dose reduction or suspension for AEs. |
| • | Deutetrabenazine was safely titrated without knowledge of CYP2D6 genotype. |

| 1 | Burgunder J, Guttman M, Perlman S, et al. An international survey-based algorithm for the pharmacological treatment of chorea in Huntington’s disease. PloS Currents Huntington’s Disease. 2011 Sept 2. Edition 1. Doi: 10.1371/currents.RRN1260. |
| 2 | Kenney C, Hunter C, Jankovic J. Long-term tolerability of tetrabenazine in the treatment of hyperkinetic movement disorders. Movement Disorders. 2007;22(2):193-197. |
| 3 | Guengerich FP. Kinetic deuterium isotope effects in cytochrome P450 oxidation reactions. J Labelled Comp Radiopharm. 2013;56(9-10):428-31. |
| 4 | Stamler D, Bradbury M, Brown F. The pharmacokinetics and safety of deuterated-tetrabenazine. Neurology. 2013;80(1):P07.210. |
Acknowledgments: 34 site investigators and coordinators, Samuel Frank (PI), Claudia Testa (co-PI), David Stamler (Chief Medical Officer, Auspex), Elise Kayson (Administrative PI), Clinical Trials Coordination Center University of Rochester, Huntington Study Group staff, University of Rochester Biostatistics
Disclosures: The Huntington Study Group Coordination and Biostatistics Center at the University of Rochester independently compiled and analyzed the data for this study. The study was funded by Auspex Pharmaceuticals.

