Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - CORETEC GROUP INC. | v404927_ex32-1.htm |
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - CORETEC GROUP INC. | Financial_Report.xls |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - CORETEC GROUP INC. | v404927_ex32-2.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - CORETEC GROUP INC. | v404927_ex31-2.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - CORETEC GROUP INC. | v404927_ex31-1.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
x ANNUAL REPORT UNDER SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
FOR THE FISCAL YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2014
¨ TRANSITION REPORT UNDER SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
FOR THE TRANSITION PERIOD FROM __________ TO __________
COMMISSION FILE NUMBER 000-54697
3DICON CORPORATION
(Name of small business issuer in its charter)
| OKLAHOMA | 73-1479206 |
| (State or other jurisdiction of | (I.R.S. Employer |
| incorporation or organization) | Identification No.) |
6804 South Canton Avenue, Suite 150, Tulsa, OK 74136
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip Code)
Issuer's telephone Number: (918) 494-0505
Securities registered under Section 12(b) of the Exchange Act: None.
Securities registered under Section 12(g) of the Exchange Act: None
Indicate by check mark is the issuer is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act.
Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check if the issuer is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act.
Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the issuer (1) filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act during the past 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check if disclosure of delinquent filers in response to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer", "accelerated filer", and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer ¨ | Accelerated filer ¨ |
| Non-accelerated filer ¨ | Smaller reporting company x |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act).
Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of the voting and non-voting common equity held by non-affiliates, computed by reference to the average bid and asked price of such common equity as of June 30, 2014 was $3,438,716.
As of March 27, 2015, the issuer had 612,664,741 outstanding shares of Common Stock.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE: NONE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
| 2 |
PART I
Organizational History
3DIcon Corporation was incorporated on August 11, 1995, under the laws of the State of Oklahoma as First Keating Corporation. Our articles of incorporation were amended August 1, 2003 to change the name to 3DIcon Corporation. The initial focus of First Keating Corporation was to market and distribute books written by its founder, Martin Keating. During 2001, First Keating Corporation began to focus on the development of 360-degree holographic technology. The effective date of this transition was January 1, 2001. We accounted for this transition as reorganization and accordingly, restated its capital accounts as of January 1, 2001. At the inception on January 1, 2001, our primary activity was the raising of capital in order to pursue its goal of becoming a significant participant in the formation and commercialization of interactive, optical holography for the communications and entertainment industries.
In April 2004, we engaged the University of Oklahoma (the “University” or “OU”) to conduct a pilot study to determine the opportunity and feasibility for the creation of volumetric three dimensional display systems.
On July 15, 2005, we entered into a Sponsored Research Agreement (“SRA”) with the University, which expired on January 14, 2007. Under this agreement, the University conducted a research project entitled "Investigation of 3-Dimensional Display Technologies".
On February 23, 2007, we entered into an SRA with the University, which expired on March 31, 2010. Under this agreement, the University conducted a research project entitled "3-Dimensional Display Development".
In the fourth quarter of 2007 we announced the release of our first product, "Pixel Precision". On
February 12, 2009, version 2.0 of Pixel Precision was released to expand capabilities and provide new compatibility with Texas Instrument's newly released DLP® Discovery 4000 kits. This is a companion software application to the DMD Discovery line of products manufactured by Texas Instruments®.
In July 2013, the Company won first place in the Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science and Technology’s Oklahoma Applied Research Support competition, securing $300,000 in grant funding over two years. This matching grant had a start date of September 1, 2013. We successfully completed year 1 and are part way through year 2. The grant will be completed by December 2015. The Company is using the funds provided by the grant to support the development of its First Product Platform, which will be the basis of a family of products leveraging the Company’s CSpace® volumetric 3D display technology.
Overview of Business
3DIcon is a small public company that is further developing a patented volumetric 3D display technology that was developed by and with the University under an SRA. The development to date has resulted in multiple new technologies, two working laboratory prototypes (Lab Proto 1 and Lab Proto 2), and eight provisional patents; five of the eight provisional patents have been combined and converted to five utility patents. Under the SRA, the Company has obtained the exclusive worldwide marketing rights to these 3D display technologies.

Figure 1 - Lab Proto 1 Image
| 3 |
On May 26, 2009, the United States Patent and Trademark Office ("USPTO") approved the patent called "Volumetric Liquid Crystal Display" for rendering a three-dimensional image and converted it to US patent No. 7,537,345. On December 28, 2010, USPTO approved the patent called “Light Surface Display for Rendering a Three-Dimensional Image,” and issued the United States Patent No. 7,858,913. On August 21, 2012, the USPTO approved a continuation patent called “3D Volumetric Display” and issued the US Patent No. 8,247,755. These patents describe the foundation of what we are calling our CSpace® technology (“CSpace”).
Volumetric
The Company plans to commercialize the CSpace volumetric 3D technology through a combination of government funded research and development contracts, joint development agreements with industry partners and technology licensing agreements with companies like Raytheon, Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Siemens, and General Electric for high value applications in military planning, cyber data analysis, battlespace visualization, oil and gas exploration and medical imaging. Although we do not have any definitive agreements in place that provides for such funding, we believe that the Federal Government would be interested in entering into funded arrangements based on past and existing discussions our management have had with Federal Government Program Managers. Likewise, we believe that Industry would be interested in entering into joint development agreements that could ultimately lead to licensing agreements. For example, Raytheon, Boeing and Schott Defense have provided letters of support for government grants that we have applied for, indicating their interest in working with us on the specific project if the grant were to be awarded. We have no formal agreements or commitments from Boeing or Raytheon beyond these initial discussions. We have had similar interactions with a number of companies, such as Lockheed, Honeywell, General Electric, Florida Institute of Human and Machine Cognition (IHMC), Cleveland Clinic, ShuffleMaster, etc. regarding our CSpace technology.
The above commercialization plan depends on our ability to convince potential customers (Government and Industry) that products based on our technology will meet their requirements and that the technical risk in developing products based on our technology will be acceptable to these potential customers. We are targeting high value applications that typically require products to be customized to the customer’s application. Since we understand the capabilities and limitations of CSpace better than potential customers, it is not unusual for this type of customer to ask the technology developer (in this case 3DIcon) to do most or part of the product development for or with the customer in exchange for funding by the customer. In 2015, we plan to continue to solicit the Federal Government and Industry to enter into customer-funded development contracts to develop our technology for or with those customers. Our goal is to generate sufficient funding from such arrangements that would meet or exceed the incremental costs of developing product prototypes for or with customers. If we are successful in completing the initial product prototypes on a timely basis, it is possible that the Company could generate licensing revenues from our CSpace technology beginning in the fourth quarter of 2017. The Company believes that it has an experienced display industry and management team with a proven track record of successfully commercializing multiple display technologies to move our CSpace technology strategy forward.
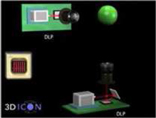
Figure 2 - CSpace Architecture
In March of 2012, the Company implemented a new evolutionary, step-by-step commercialization strategy for the CSpace volumetric display technology. Under this strategy we are developing multiple staged prototypes (laboratory and trade show) with successively higher performance (brightness, resolution, and image size). Lab Proto 2 is a working prototype with significant improvements over Lab Proto 1 and was completed in October 2012. Our technical team increased the image size of Lab Proto 2 by a factor of eight (8x) and the brightness of the image by a factor of five (5x). Taken together with the 50 times higher brightness already achieved, Lab Proto 2 is 250 times (250x) brighter than Lab Proto 1. Because of the larger image size and the much higher brightness, we achieved much higher effective resolution as well. Lab Proto 3, while not complete, is already 80 times brighter than Lab Proto 2 and more than 2,000 times brighter than Lab Proto 1. Most of the engineering work (optics, electronics and software) is complete, and the focus is now on the image space materials.
| 4 |
The $300,000 grant awarded by the Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science and Technology (“OCAST”) to the Company in July 2013 is providing funding for the development of the software and electronics necessary for a larger image space, including the completion of software necessary to enable animation and movement through the volume.
The goals for Lab Proto 3 are to develop a lower cost and more scalable image chamber material (specialty glass), to enhance imagine brightness by ten (10x) by utilizing a new scanning system, and to use that new material to construct an even larger image chamber than was demonstrated for Lab Proto 2. Part of our Joint Development Agreement (“JDA”) with Schott Defense (“Schott”) and our efforts to secure federal funding are aimed at accelerating the process of securing a scalable material for CSpace’s image space. Prototype 3 was originally scheduled for completion in fourth quarter 2013; however, delays were incurred to continue to seek the best possible solution to the material required for the image space. Our federal funding strategy and JDA with Schott are specifically targeted at securing this material.
We believe that Lab Proto 3 will enable the Company to credibly engage with potential customers and secure customer funded development contracts to develop even larger and higher resolution product prototypes. If we are successful in securing customer funded development contracts, we anticipate the development of various product prototypes, the first of which we have been calling the Trade Show Prototype. It is likely that in exchange for funding of the Trade Show Prototype, our initial customer will require an exclusive license to the technology in a particular field of use (e.g. medical imaging). The Company believes that any such exclusive license will be based on a set period of time during product and/or market development and based on performance thereafter. Failure by the customer to meet agreed upon performance criteria would most likely result in the license becoming non-exclusive. Any such exclusive license agreement would preclude the Company from working with other customers in that field of use during the period of the exclusive license. The Company does not believe that this strategy for funding the Tradeshow Prototype will significantly impact the revenue potential of the technology given the number of potential applications (fields of use). If successfully developed, the Trade Show Prototype, which is illustrated as an artist concept in Figure 3 below, will be fully packaged and portable so that it can be used for trade shows and on-site customer demonstrations. We believe that the Trade Show Prototype will enable the Company to market and secure licensing agreements with large government contractors and large medical or industrial products companies.

Figure 3 - Artist Concept of CSpace Trade Show Prototype
Federal Funding Strategy
As funding has increased for the 3D field, the Company has implemented a federal funding strategy to augment its other capital raising efforts. In December 2013, the Company secured the services of Doug Freitag, an expert in identifying and obtaining government grants of the type we are seeking. The initial targets for this strategy included: the Obama Administration’s multi-agency priorities of advanced manufacturing and information technology (e.g., Big Data Research and Development Initiative with over $200 million annually); the Department of Defense’s priorities to reduce the cost of developing, testing, and manufacturing new weapon systems, enhance training and operation of autonomous systems and accelerate data-to-decisions; and Federal Aviation Administration’s on-going priority to enhance air traffic control systems. As a result of feedback from various Federal Government Program Managers, the strategy has changed and now places increased emphasis on a growing need for new technologies to visualize cyber data, military planning, medical imaging data, data collected when screening for contraband and validation of 3D engineering designs prior to manufacturing by 3D printing. The strategy also places greater emphasis on Small Business Innovation Research Grants where funding continues to grow, competition is limited to other small businesses, 3DIcon can more easily be the project leader, and the cycle for awards from the date of submission can be much faster. Larger contracts will still be considered but include other partners and may require one of more partners to lead the projects if awarded. A pre-proposal titled “Glasses-Free 3D Volumetric Display for to Enhance Mission Analysis” was submitted to the Defense Intelligence Agency on November 26, 2014 and is under review. A proposal titled “3D Volumetric Display of Neurological Data Provided by MRI Imaging” was submitted to the National institute of Health on December 5, 2014 and is under review. A proposal titled “Transforming Cyber Data into Human-Centered 3D Visualizations” was submitted to the Air Force on February 25, 2015 and is under review. A pre-proposal titled “Glasses-Free 3D Volumetric Visualization of Critical Data to Enhance Decision Making” was submitted to the DOD Combating Terrorism Technical Support Office on March 20, 2015 and is under review. These submissions, if awarded, approach an aggregate of $3.75 million of multi-year funding. Additional submissions are planned over the next few months, approaching an aggregate of $5 million of multi-year funding requests.
| 5 |
Joint Development Agreement with Schott Defense
As part of our federal funding strategy we intend to effectively compete by forming interdisciplinary teams with potential strategic partners (large and small), academic and commercial laboratories, and systems integrators providing integrated data visualization solutions. The first of these partnerships was reached in March 2014 when the Company signed a JDA with Schott, a federally focused subsidiary of Schott North America. Schott is a world-class multi-billion dollar company with significant experience and success in partnering with federal agencies for development projects. In addition, Schott is one of the world’s leaders in developing specialty glass for many applications, including display technology. This partnership, coupled with the expertise of Doug Freitag, should facilitate the Company’s federal funding strategy and our ability to create the unique materials required to advance the CSpace technology.
Commercialization Strategy & Target Applications
The Company plans to commercialize the CSpace volumetric 3D technology through customer funded research and development contracts and technology licensing agreements with companies like Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Siemens, and General Electric for high value applications like air traffic control, design visualization, and medical imaging. The Company plans to develop products for contract engineering and with joint development customers. At this time the Company does not have any commercialized products and does not plan to develop its own products based on the CSpace technology due to the high value / low volume nature of the best-fit initial applications for this technology. These applications include but are not limited to the following:
| n | Healthcare (diagnostics, surgical planning, training, telemedicine, biosurveillance) |
| n | Cyber Security Data Visualization |
| n | Military (operational planning, training, modeling and simulation, battlespace awareness, damage assessment, autonomous piloting) |
| n | Physical Security (passenger, luggage & cargo screening) |
| n | Mining, Oil & Gas Exploration |
| n | Meteorological and Oceanographic data visualization |
In order to simplify internal development efforts on CSpace, software to control the initial laboratory prototype was created and later productized as "Pixel Precision" in 2007. The product has been made commercially available through a sales and distribution arrangement with Digital Light Innovations (“DLI”) that was signed March 6, 2008. The Company entered into a new licensing and distribution agreement with DLI for the Pixel Precision software in 2014. This product is a result of our research efforts involving the use of the Texas Instruments Digital Micro-Mirror Device (“DMD”). The product is targeted at the application development market involving the use of DMDs, specifically the DMD-Discovery line from Texas Instruments.
| 6 |
Competition
Based on our market research and competitive analysis to date, we have concluded that the CSpace volumetric technology is unique and advantaged versus other 3D technologies in that it can deliver both 1) a true 360 degree viewing experience for multiple simultaneous users, and 2) high image quality, high reliability and large image size. Rear projection 3D displays such as those from Zecotek, Setred, and EuroLCDs (formerly LC Tech LightSpace) do not provide a 360 degree viewing experience and are typically limited to one or two users. While rotating displays (also called swept volume) such as Perspecta from Optics For Hire (formerly Actuality, now licensed), Xigen (research only), Ray Modeler from Sony (research only), Felix 3D (research only), and the USC light field display (research only) do provide a true 360 degree viewing experience, they cannot deliver a large image, high image quality and reliability because the entire display is rotating at high speed. Early proof of concept work done on infrared active phosphor displays by 3D Display Laboratories proved to not be scalable due to limited phosphor persistence and vector scanning limitations. While holographic and light field displays show promise, they do not deliver a true 360 degree viewing experience and cost effective multiple user systems do not appear feasible due to current and expected pixel density, data bandwidth and compute power limitations.
Flat Screen 3D Strategy
Since March of 2012, the Company has been evaluating a number of second-generation, glasses-free flat screen 3D display technologies and the companies that are developing these technologies with the possibility of an acquisition of such a company in mind. Our goal was to identify a new technology that could deliver significantly better performance (3D impact and image quality) than current large area multiple-viewer glasses-free 3D flat screen displays without compromising resolution and brightness, as do current displays. The ideal company would also have a great technical team, a broad patent portfolio, and a credible technology roadmap to ensure that these competitive advantages are sustainable into the future. As a result of the above evaluation process, the Company previously entered into a non-binding Letter of Intent to acquire Dimension Technologies, Inc. (DTI) www.dti3d.com located in Rochester, NY. However, that Letter of Intent has since expired. Notwithstanding the expiration of the Letter of Intent, the Company’s interest in a potential acquisition of a small 3D flat screen display company remains.
There can be no assurance that the Company will successfully raise adequate funds for such a transaction in the future.
Currently, we do not have any agreements in place that would allow entry into the flat screen segment of the glasses-free 3D display industry or digital signage industry and no assurances can be made that such an agreement will ever be consummated. The Company is not actively seeking such acquisitions in the glasses-free 3D flat screen display segment at this time.
History of 3D Technology Research and Development at the University of Oklahoma
Beginning in 2007 the University, under an SRA with 3DIcon, undertook the development of the following three high potential 3D display technologies. The results of each project are summarized below.
| • | I - Swept Volume Displays - We have successfully achieved the initial demonstration and proof of technology for this approach. |
| • | II - Static Volumetric Displays - This technology was ranked by the University as the best for further development. |
| • | III - Stacked Volume Displays - We also have investigated the technologies for developing innovative Stacked Volumetric Displays. |
The Swept Volume Display is designed to be a 3D display system showing a volumetric image generated from an electronic medium. A proof-of-concept demonstration was achieved by the researchers around September 2007. The Swept Volume Display R&D entered into the subsequent second stage of improvement and development in 2008. Additional work on this particular approach has been deferred indefinitely because of the success and initial superiority of the CSpace technology.
| 7 |
Our implementation of a Static Volume Display (CSpace®) employs one or more Digital Micro-Mirror Devices (DMDs) and infra-red lasers to produce 3D images in advanced transparent nanotechnology materials, thereby enabling the creation, transmission and display of high resolution 3D images within a volume space, surrounded by glass or transparent screen. The initial investigation for the Static Volume system commenced in 2007. In September 2008, we built a laboratory prototype Static Volume Display using the CSpace technology and demonstrated the creation of true 3D images within a specified image space. New developments for eliminating the distortion occurred by the divergence of the constructed 3D image were presented at the SPIE Europe Security & Defense conference in Berlin, Germany in August 2009. Improvements for the optical systems utilized by CSpace with the latest achieved resolution were published in October 2009 in IEEE/OSA Journal of Display Technology titled "Static Volumetric Three-Dimensional Display" and can be found for a moderate fee at http://www.opticsinfobase.org. On February 15, 2010, at the SPIE Medical Imaging conference, we presented the latest software developments that allow reading Digital Imaging and Communication In Medicine ("DICOM") formats whether scanned by ultrasound devices, magnetic resonance imaging ("MRI"), or computed tomography ("CT") scanners. With this new software architecture, Static Volume 3D displays based on the CSpace technology would have the capability of displaying medical images.
On April 14, 2010, at the OSA Digital Holography and Three-Dimensional Imaging conference in Miami, FL, we presented an increase in brightness of the constructed 3D images. On September 23, 2010, at the SPIE Europe Security & Defense conference in Toulouse, France, we presented new implementations to reduce flicker of the 3D Images constructed by CSpace display. In November 2010, we published a new method of rendering 3D Images using a rotational-slicing technique at the Journal of the Society for Information Display and can be found for a moderate fee at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1889/JSID18.11.873/abstract. In December 2010, we published the utilization of new materials for CSpace image space at the Journal of the Society for Information Display and can be found for a moderate fee at http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1889/JSID18.12.1065/abstract. In April 2011, New Developments That Allow CSpace To Perfectly Fit Applications Such As Air Traffic Control was published in the IEEE/OSA Journal of Display Technology and can be found for a moderate fee at http://www.opticsinfobase.org/jdt/abstract.cfm?uri=jdt-7-4-186. On April 25, 2011, we presented a new paper called “Multi-layer overlay display,” at the SPIE Defense & Security Conference in Orlando, FL. On May 17, 2013, we presented a new paper called ”CSpace High-Resolution Volumetric 3D Display,” at the SPIE Defense & Security in Baltimore, Maryland. On September 26, 2014 we were interviewed for an article on medical imaging by Medical Device Daily and can be found at http://www.medicaldevicedaily.com/servlet/com.accumedia.web.Dispatcher?next=mdd_currentIssue&issueId=23719&prodID=4&month=09&year=2014. On December 18, 2014, we co-authored a new publication called “Scalable Upconversion Medium for Static Volumetric Display” in the Journal of Display Technology and can be found for a moderate fee at http://ieeexplore.ieee.org/xpl/articleDetails.jsp?reload=true&arnumber=6987226. On March 1, 2015 we published an overview on the applications for 3D Volumetric Displays in NASA Tech Briefs and can be found at http://www.techbriefs.com/component/content/article/27-ntb/features/application-briefs/21710. On February 27, 2015 we were interviewed for a Q/A article on 3D imaging by Medical Design Technology that can be found at http://www.mdtmag.com/blogs/2015/02/true-3d-imagesglasses-free. On March 24, 2015 we made a presentation called “Glasses-Free 3D Volumetric Display for Enhanced Decision Making” at the 2015 National Defense Industry Association Science & Engineering Technology Division Conference.
Regarding our continued efforts to improve the performance of the CSpace technology, we completed our second-generation prototype (Lab Proto 2) in October 2012. Our goals for Lab Proto 2 were to first improve image brightness, and then to improve resolution (increase the number of voxels or 3D pixels), and lastly to increase the size of the image. The image generated by Lab Proto 2 is approximately 250 times (250x) brighter than our first generation prototype and can now be viewed in normal room lighting. As a result of the increased brightness, resolution has also been improved. The estimated resolution of the second-generation prototype is approximately five times (5x) greater than the first generation prototype. The image size of Lab Proto 2 is approximately 8 times (8x) larger than our first generation prototype. We continue to develop a third-generation prototype (Lab Proto 3) with a larger image space, which we believe will enable the Company to credibly engage with potential customers and secure customer funded development contracts to develop even larger and higher resolution product prototypes, eventually leading to a trade show prototype that will be portable and package for display at trade shows or on-site customer demonstrations.
| 8 |
University of Oklahoma - Sponsored Research Agreement History
On December 1, 2010, the Company entered into an agreement (the "Agreement") with the University pursuant to which the University agreed to convert all sums due to it from the Company in connection with its SRA with the Company, which as of December 1, 2010 amounted to approximately $485,000, into an aggregate of 1,685,714 shares of the Company's common stock (the "Shares"). As a result of the debt conversion, the University became the holder of approximately 8% of the outstanding common stock of the Company. Pursuant to the Agreement, the Shares were subject to a put option allowing the University to require the Company to purchase certain of the Shares upon the occurrence of certain events. In addition, the Shares were subject to a call option allowing the Company to require the University to sell to the Company the Shares then held by the University in accordance with the terms of the Agreement. The put options and the call options expired on November 30, 2014 and the Shares are no longer subject to such options.
The Agreement also amended the existing agreements between the Company and the University such that all intellectual property, including all inventions and or discoveries, patentable or un-patentable, developed before July 28, 2008 by the University under the SRA is owned by the University. All intellectual property, including all inventions and/or discoveries, patentable or un-patentable, developed jointly by the Company and the University at any time is jointly owned by the Company and the University. Finally, all intellectual property developed by the Company after July 28, 2008, including all inventions and or discoveries, patentable or un-patentable, is owned by the Company.
Intellectual Property History, Status & Rights
On May 26, 2009, the United States Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”) approved the pending patent called "Volumetric Liquid Crystal Display" for rendering a three-dimensional image and converted it to US patent No. 7,537,345. On July 16, 2013, USPTO approved the pending patent called “Computer System with Digital Micromirror Device,” and issued US patent No. 8,487,865.
CSpace Patents are as follow: On December 28, 2010, USPTO approved the pending patent called “Light Surface Display for Rendering a Three-Dimensional Image,” and issued the United States Patent No. 7,858,913. On August 21, 2012, the USPTO approved a continuation patent called “3D Volumetric Display” and issued the US Patent No. 8,247,755. On December 13, 2011, USPTO approved a continuation patent called “3D Light Surface Display,” and issued the US Patent No. 8,075,139. On July 31, 2013, 3DIcon filed provisional patent called “Ultra High-Resolution Volumetric Three-Dimensional Display,” (US patent application serial No. 61859145).
Through a SRA with the University, we have obtained the exclusive worldwide marketing rights to certain 3D display technologies under development by the University. The development to date has resulted in the University filing eight provisional patents; five of the eight provisional patents have been combined and converted to five utility US patents, one pending European patent and one pending Japanese patent.
Key Patents Exclusively Licensed to 3DIcon from OU:
Patents Granted
| · | “3D Volumetric Display” – 8,247,755, August 21, 2012 |
| · | “3DLight Surface Display” – 8,075,139, December 13, 2011 |
| · | “Light Surface Display for Rendering a Three-Dimensional Image” – 7,858,913, December 28, 2010 |
| · | “Volumetric Liquid Crystal Display” – 7,537,345, May 26, 2009 |
| · | “Computer System with Digital Micromirror Device” – 8,487,865, July 16, 2013 |
International Patents Granted
| · | Granted – Japan |
| o | “Light Surface Display for Rendering a Three-Dimensional Image” – Japanese Patent Number 5,594,718, August 15, 2014 |
International Patents Pending
| · | Pending |
| o | “Light Surface Display for Rendering a Three-Dimensional Image” – European Application Number EP07755984, Filed April 25, 2007 |
| · | Pending – Europe |
| o | “Ultra High Resolution Three-Dimensional Display” – July 26, 2013 |
| o | “Holoform Projection Display” – March 12, 2013 |
| 9 |
Employees
We had four employees as of March 27, 2015, Mr. Victor Keen, Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Ronald Robinson, Chief Financial Officer, Dr. Hakki Refai, Chief Technology Officer, and Ms. Judith Keating, Company Secretary and Director of Investor Relations. None of our employees are covered by a collective bargaining agreement. We consider relations with our employees to be good.
Risks Relating to Our Business
We have a limited operating history, as well as a history of operating losses.
We have a limited operating history. We cannot assure you that we can achieve revenue or sustain revenue growth or profitability in the future. We have a cumulative net loss of $21,258,575 for the period from inception (January 1, 2001) to December 31, 2014. Our operations are subject to the risks and competition inherent in the establishment of a business enterprise. Unanticipated problems, expenses, and delays are frequently encountered in establishing a new business and marketing and developing products. These include, but are not limited to, competition, the need to develop customers and market expertise, market conditions, sales, marketing and governmental regulation. Our failure to meet any of these conditions would have a materially adverse effect upon us and may force us to reduce or curtail our operations. Revenues and profits, if any, will depend upon various factors. We may not achieve our business objectives and the failure to achieve such goals would have an adverse impact on our business.
We may not be able to achieve the target specifications for the second and third generation CSpace laboratory prototypes.
The process of developing new highly technical products and solutions is inherently complex and uncertain. It requires accurate anticipation of customer's changing needs and emerging technological trends. We must make long-term investments and commit significant resources before knowing whether these investments will eventually result in products that achieve customer acceptance and generate the revenues required to provide desired returns. If we fail to achieve and meet our target specifications in the development of the second and third generation CSpace laboratory prototypes, we could lose market position and customers to our competitors and that could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
We may not be able to secure the customer funding necessary to develop the CSpace Trade Show Prototype.
An important part of our business strategy moving forward is the development of our Lab Proto 3. While we believe this prototype will enable us to secure customer funded development contracts whereby our customer would provide part or all of the funding necessary to develop products for or with the customer and to secure technology licensing agreements, there can be no assurances that this will occur. If we are unable to secure customer funded development contracts we will likely not be able to develop our CSpace Trade Show Prototype. Without the CSpace Trade Show Prototype we will not be able to successfully implement our business strategy for our volumetric 3D Display products, which could cause harm to our competitive position and financial condition.
| 10 |
We may not be able to successfully license the CSpace technology to customers.
A significant portion of our expected future revenues will be generated through licensing our CSpace technology to third parties such as Boeing, Lockheed Martin, Siemens, and General Electric. However, there is no guarantee we will be able to successfully license our CSpace technology to such companies or to other third parties. If we fail to successfully license our CSpace technology it could negatively impact our revenue stream and financial condition.
We may not be able to compete successfully.
Although the volumetric 3D display technology that we are attempting to develop is new, and although at present we are aware of only a limited number of companies that have publicly disclosed their attempts to develop similar technology, we anticipate a number of companies are or will attempt to develop technologies/products that compete or will compete with our technologies. Further, even if we are the first to market with a technology of this type, and even if the technology is protected by patents or otherwise, because of the vast market and communications potential of such a product, we anticipate the market will be flooded by a variety of competitors (including traditional display companies), many of which will offer a range of products in areas other than those in which we compete, which may make such competitors more attractive to prospective customers. In addition, many if not all of our competitors and potential competitors will initially be larger and have greater financial resources than we do. Some of the companies with which we may now be in competition, or with which we may compete in the future, have or may have more extensive research, marketing and manufacturing capabilities and significantly greater technical and personnel resources than we do, even given our relationship to the University, and may be better positioned to continue to improve their technology in order to compete in an evolving industry. Further, technology in this industry may evolve rapidly once an initially successful product is introduced, making timely product innovations and use of new technologies essential to our success in the marketplace. The introduction by our competitors of products with improved technologies or features may render any product we initially market obsolete and unmarketable. If we or our partners are not able to deliver to market products that respond to industry changes in a timely manner, or if our products do not perform well, our business and financial condition will be adversely affected.
The technologies being developed may not gain market acceptance.
The products that we are currently developing utilize new technologies. As with any new technologies, in order for us to be successful, these technologies must gain market acceptance. Since the technologies that we anticipate introducing to the marketplace will exploit or encroach upon markets that presently utilize or are serviced by products from competing technologies, meaningful commercial markets may not develop for our technologies.
In addition, the development efforts of 3DIcon and the University on the 3D technology are subject to unanticipated delays, expenses or technical or other problems, as well as the possible insufficiency of funding to complete development. Our success will depend upon the ultimate products and technologies meeting acceptable cost and performance criteria, and upon their timely introduction into the marketplace. The proposed products and technologies may never be successfully developed, and even if developed, they may not satisfactorily perform the functions for which they are designed. Additionally, these may not meet applicable price or performance objectives. Unanticipated technical or other problems may occur which would result in increased costs or material delays in their development or commercialization.
If we are unable to successfully retain existing management and recruit qualified personnel having experience in our business, we may not be able to continue our operations.
Our success depends to a significant extent upon the continued services of our Board of Directors, management officers and our Chief Technology Officer. Our success also depends on our ability to attract and retain other key executive officers.
Our auditors have expressed substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. If we do not continue as a going concern, investors will lose their entire investment.
| 11 |
In their report dated March 31, 2015, our auditors have expressed substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern. These concerns arise from the fact that we are a development stage organization with insufficient revenues to fund development and operating expenses. If we are unable to continue as a going concern, you could lose your entire investment in us.
We will need significant additional capital, which we may be unable to obtain.
Our capital requirements in connection with our development activities and transition to commercial operations have been and will continue to be significant. We will require between $1.2 and $1.5 million additional funds through December 2015 to continue research, development and testing of our technologies, to obtain intellectual property protection relating to our technologies when appropriate, and to improve and market our technologies. There can be no assurance that financing will be available in amounts or on terms acceptable to us, if at all.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
If we fail to establish, maintain and enforce intellectual property rights with respect to our technology and/or licensed technology, our financial condition, results of operations and business could be negatively impacted.
Our ability to establish, maintain and enforce intellectual property rights with respect to our technology and the University’s ability to establish, maintain and enforce intellectual property rights with respect to our exclusively licensed technology, once successfully developed into 3D display technology that we intend to market, will be a significant factor in determining our future financial and operating performance. We seek to protect our intellectual property rights by relying on a combination of patent, trade secret and copyright laws. We also use confidentiality and other provisions in our agreements that restrict access to and disclosure of its confidential know-how and trade secrets.
Outside of our pending patent applications, we seek to protect our technology as trade secrets and technical know-how. However, trade secrets and technical know-how are difficult to maintain and do not provide the same legal protections provided by patents. In particular, only patents will allow us to prohibit others from using independently developed technologies that are similar. If competitors develop knowledge substantially equivalent or superior to our trade secrets and technical know-how, or gain access to our knowledge through other means such as observation of our technology that embodies trade secrets at customer sites that we do not control, the value of our trade secrets and technical know-how would be diminished.
While we strive to maintain systems and procedures to protect the confidentiality and security of our trade secrets and technical know-how, these systems and procedures may fail to provide an adequate degree of protection. For example, although we generally enter into agreements with our employees, consultants, advisors, and strategic partners restricting the disclosure and use of trade secrets, technical know-how and confidential information, we cannot provide any assurance that these agreements will be sufficient to prevent unauthorized use or disclosure. In addition, some of the technology deployed at customer sites in the future, which we do not control, may be readily observable by third parties who are not under contractual obligations of non-disclosure, which may limit or compromise our ability to continue to protect such technology as a trade secret.
While we are not currently aware of any infringement or other violation of our intellectual property rights, monitoring and policing unauthorized use and disclosure of intellectual property is difficult. If we learned that a third party was in fact infringing or otherwise violating our intellectual property, we may need to enforce our intellectual property rights through litigation. Litigation relating to our intellectual property may not prove successful and might result in substantial costs and diversion of resources and management attention.
If our technology is licensed to customers at some point in the future, the strength of the intellectual property under which we would grant licenses can be a critical determinant of the value of such potential licenses. If we are unable to secure, protect and enforce our intellectual property now and in the future, it may become more difficult for us to attract such customers. Any such development could have a material adverse effect on our business, prospects, financial condition and results of operations.
| 12 |
We may face claims that we are violating the intellectual property rights of others.
Although we are not aware of any potential violations of others’ intellectual property rights, we may face claims, including from direct competitors, other companies, scientists or research universities, asserting that our technology or the commercial use of such technology infringes or otherwise violates the intellectual property rights of others. We cannot be certain that our technologies and processes do not violate the intellectual property rights of others. If we are successful in developing technologies that allow us to earn revenues and our market profile grows we could become increasingly subject to such claims.
We may also face infringement claims from the employees, consultants, agents and outside organizations we have engaged to develop our technology. While we have sought to protect ourselves against such claims through contractual means, we cannot provide any assurance that such contractual provisions are adequate, and any of these parties might claim full or partial ownership of the intellectual property in the technology that they were engaged to develop.
If we were found to be infringing or otherwise violating the intellectual property rights of others, we could face significant costs to implement work-around methods, and we cannot provide any assurance that any such work-around would be available or technically equivalent to our potential technology. In such cases, we might need to license a third party’s intellectual property, although any required license might not be available on acceptable terms, or at all. If we are unable to work around such infringement or obtain a license on acceptable terms, we might face substantial monetary judgments against us or an injunction against continuing to use or license such technology, which might cause us to cease operations.
In addition, even if we are not infringing or otherwise violating the intellectual property rights of others, we could nonetheless incur substantial costs in defending ourselves in suits brought against us for alleged infringement. Also, if we are to enter into a license agreement in the future and it provides that we will defend and indemnify our customer licensees for claims against them relating to any alleged infringement of the intellectual property rights of third parties in connection with such customer licensees’ use of such technologies, we may incur substantial costs defending and indemnifying any customer licensees to the extent they are subject to these types of claims. Such suits, even if without merit, would likely require our management team to dedicate substantial time to addressing the issues presented. Any party bringing claims might have greater resources than we do, which could potentially lead to us settling claims against which we might otherwise prevail on the merits.
Any claims brought against us or any customer licensees alleging that we have violated the intellectual property of others could have negative consequences for our financial condition, results of operations and business, each of which could be materially adversely affected as a result.
At this time, we do not own any intellectual property in Volumetric Liquid Crystal Display or Light Surface Display for Rendering Three-Dimensional Images, and, apart from the SRA with the University and the exclusive worldwide marketing rights thereto, we have no contracts or agreements pending to acquire the intellectual property.
Although we have obtained exclusive worldwide marketing rights to “Volumetric Liquid Crystal Display” and “Light Surface Display for Rendering Three-Dimensional Images”, two technologies vital to our business and growth strategy, we do not own any intellectual property in these technologies. Although our exclusive worldwide marketing rights to these technologies stand alone and are independent of the SRA, outside of our SRA with the University, we have no pending agreements to obtain or purchase ownership over such intellectual property. Should the University lose their rights in such technologies or we are otherwise unable to utilize the rights obtained in such agreements it would be difficult to successfully implement our business strategy going forward and our stock value would likely decrease.
Risks Relating to Our Current Financing Arrangements:
There are a large number of shares underlying our convertible debentures, and warrants that may be available for future sale and the sale of these shares may depress the market price of our common stock.
| 13 |
As of March 27, 2015, we had 612,664,741 shares of common stock issued and outstanding and convertible debentures outstanding that may be converted into estimated 3,253,119,789 shares of common stock at current market prices, although the Company currently would not have enough authorized shares to issue such estimated conversion shares. The number of shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of the outstanding convertible debentures may increase if the market price of our stock declines. We also have outstanding warrants issued to Golden State Equity Investors, Inc. f/k/a Golden Gate Investors ("Golden State") to purchase 18,595 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $381.50. Additionally, there are 19,250,000 warrants to purchase common shares at an exercise price of $0.0055, which warrants were issued to investors that also purchased 385,000 shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock, which shares are convertible into an aggregate of 38,500,000 shares of common stock. The sale of the shares underlying the convertible debentures, the Series A Convertible Preferred Stock and warrants may adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
Our obligation to issue shares upon conversion of our convertible debentures is essentially limitless.
The conversion price of our convertible debentures is continuously adjustable, which could require us to issue a substantially greater number of shares, which will cause dilution to our existing stockholders.
The following is an example of the amount of shares of our common stock that are issuable, upon conversion of our 4.75% $100,000 convertible debenture (excluding accrued interest) issued to Golden State on November 3, 2006, based on the remaining principal balance of $65,095 and market prices 25%, 50% and 75% below the market price as of March 27, 2015 of $0.002.
| Effective | Number | % of | ||||||||||||||||
| % Below | Price Per | Conversion | of Shares | Outstanding | ||||||||||||||
| Market | Share | Price | Issuable(1) | Stock | ||||||||||||||
| 25 | % | $ | 0.0015 | $ | 0.0012 | 4,114,528,076 | 1,163 | % | ||||||||||
| 50 | % | $ | 0.0010 | $ | 0.0008 | 6,172,117,588 | 1,745 | % | ||||||||||
| 75 | % | $ | 0.0005 | $ | 0.0004 | 12,344,886,122 | 3,490 | % | ||||||||||
(1) Shares issuable exclude 18,595 shares underlying the remaining warrants exercisable at $381.50 per share.
As illustrated, the number of shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of our convertible debentures will increase if the market price of our stock declines, which will cause dilution to our existing stockholders.
The continuously adjustable conversion price feature of our convertible debentures may encourage investors to make short sales in our common stock, which could have a depressive effect on the price of our common stock.
So long as the market price of our stock is below $4.00, the issuance of shares in connection with the conversion of the $100,000 convertible debenture results in the issuance of shares at an effective 20% discount to the trading price of the common stock prior to the conversion. The significant downward pressure on the price of the common stock as the selling stockholders convert and sell material amounts of common stock could encourage short sales by investors. This could place further downward pressure on the price of the common stock. The selling stockholders could sell common stock into the market in anticipation of covering the short sale by converting their securities, which could cause the further downward pressure on the stock price. In addition, not only the sale of shares issued upon conversion or exercise of debentures and warrants, but also the mere perception that these sales could occur, may adversely affect the market price of the common stock.
The issuance of shares upon conversion of the convertible debentures and exercise of outstanding warrants may cause immediate and substantial dilution to our existing stockholders.
The issuance of shares upon conversion of our convertible debentures and exercise of warrants may result in substantial dilution to the interests of other stockholders since the selling stockholders may ultimately convert and sell the full amount issuable on conversion. Although Golden State may not convert its convertible debenture and/or exercise their warrants if such conversion or exercise would cause it to own more than 9.9% of our outstanding common stock, this restriction does not prevent the selling stockholders from converting and selling some of their holdings and then converting the rest of their holdings. In this way, assuming the market price remains at a level acceptable to the selling stockholders, the selling stockholders could continue on a "conversion-sell-conversion" trend while never holding more than 9.9% of our common stock. Further, under the convertible debenture there is theoretically no upper limit on the number of shares that may be issued, which will have the effect of further diluting the proportionate equity interest and voting power of holders of our common stock.
| 14 |
If we are unable to issue shares of common stock upon conversion of the convertible debenture as a result of our inability to increase our authorized shares of common stock or as a result of any other reason, we are required to pay penalties to Golden State, redeem the convertible debenture at 130% and/or compensate Golden State for any buy-in that it is required to make.
If we are unable to issue shares of common stock upon conversion of the convertible debenture as a result of our inability to increase our authorized shares of common stock or as a result of any other reason, we are required to:
| · | Pay late payments to Golden State for late issuance of common stock upon conversion of the convertible debenture, in the amount of $100 per business day after the delivery date for each $10,000 of convertible debenture principal amount being converted or redeemed; |
| · | In the event we are prohibited from issuing common stock, or fail to timely deliver common stock on a delivery date, or upon the occurrence of an event of default, then at the election of Golden State, we must pay to Golden State a sum of money determined by multiplying up to the outstanding principal amount of the convertible debenture designated by Golden State by 130%, together with accrued but unpaid interest thereon; and |
| · | If ten days after the date we are required to deliver common stock to Golden State pursuant to a conversion, Golden State purchases (in an open market transaction or otherwise) shares of common stock to deliver in satisfaction of a sale by Golden State of the common stock which it anticipated receiving upon such conversion (a "Buy-In"), then we are required to pay in cash to Golden State the amount by which its total purchase price (including brokerage commissions, if any) for the shares of common stock so purchased exceeds the aggregate principal and/or interest amount of the convertible debenture for which such conversion was not timely honored, together with interest thereon at a rate of 15% per annum, accruing until such amount and any accrued interest thereon is paid in full. |
In the event that we are required to pay penalties to Golden State or redeem the convertible debentures held by Golden State, we may be required to curtail or cease our operations.
Risks Relating to Our Common Stock:
The price of our common stock is volatile and fluctuations in our operating results and announcements and developments concerning our business affect our stock price, which may cause investment losses for our stockholders.
The market for our common stock is highly volatile and the trading price of our stock on the OTC Pink Marketplace is subject to wide fluctuations in response to, among other things, operating results, the number of stockholders desiring to sell their shares, changes in general economic conditions and the financial markets, the execution of new contracts and the completion of existing agreements and other developments affecting us. In addition, statements or changes in opinions, ratings, or earnings estimates made by brokerage firms or industry analysts relating to our market or relating to us could result in an immediate and adverse effect on the market price of our common stock. The highly volatile nature of our stock price may cause investment losses for our shareholders. In the past, securities class action litigation has often been brought against companies following periods of volatility in the market price of their securities. If securities class action litigation is brought against us, such litigation could result in substantial costs while diverting management’s attention and resources.
Our common stock is subject to the "Penny Stock" rules of the SEC and the trading market in our securities is limited, which makes transactions in our stock cumbersome and may reduce the value of an investment in our stock.
| 15 |
The Securities and Exchange Commission has adopted Rule 15g-9 which establishes the definition of a "penny stock," for the purposes relevant to us, as any equity security that has a market price of less than $5.00 per share or with an exercise price of less than $5.00 per share, subject to certain exceptions. For any transaction involving a penny stock, unless exempt, the rules require:
| · | That a broker or dealer approve a person's account for transactions in penny stocks; and |
| · | The broker or dealer receives from the investor a written agreement to the transaction, setting forth the identity and quantity of the penny stock to be purchased. |
In order to approve a person's account for transactions in penny stocks, the broker or dealer must:
| · | Obtain financial information and investment experience objectives of the person; and |
| · | Make a reasonable determination that the transactions in penny stocks are suitable for that person and the person has sufficient knowledge and experience in financial matters to be capable of evaluating the risks of transactions in penny stocks. |
The broker or dealer must also deliver, prior to any transaction in a penny stock, a disclosure schedule prescribed by the Commission relating to the penny stock market, which, in highlight form:
| · | Sets forth the basis on which the broker or dealer made the suitability determination; and |
| · | That the broker or dealer received a signed, written agreement from the investor prior to the transaction. |
Generally, brokers may be less willing to execute transactions in securities subject to the "penny stock" rules. This may make it more difficult for investors to dispose of our common stock and cause a decline in the market value of our stock.
Disclosure also has to be made about the risks of investing in penny stocks in both public offerings and in secondary trading and about the commissions payable to both the broker-dealer and the registered representative, current quotations for the securities and the rights and remedies available to an investor in cases of fraud in penny stock transactions. Finally, monthly statements have to be sent disclosing recent price information for the penny stock held in the account and information on the limited market in penny stocks.
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. (“FINRA”) sales practice requirements may limit a shareholder’s ability to buy and sell our common stock.
In addition to the “penny stock” rules described above, FINRA has adopted rules that require that in recommending an investment to a customer, a broker-dealer must have reasonable grounds for believing that the investment is suitable for that customer. Prior to recommending speculative low priced securities to their non-institutional customers, broker-dealers must make reasonable efforts to obtain information about the customer’s financial status, tax status, investment objectives and other information. Under interpretations of these rules, FINRA believes that there is a high probability that speculative low priced securities will not be suitable for at least some customers. FINRA requirements make it more difficult for broker-dealers to recommend that their customers buy our common stock, which may limit your ability to buy and sell our stock and have an adverse effect on the market for our shares.
Our stock is thinly traded, so you may be unable to sell your shares at or near the quoted bid prices if you need to sell a significant number of your shares.
The shares of our common stock are thinly-traded on the OTC Pink Marketplace, meaning that the number of persons interested in purchasing our common stock at or near bid prices at any given time may be relatively small or non-existent. As a consequence, there may be periods of several days or more when trading activity in our shares is minimal or non-existent, as compared to a seasoned issuer which has a large and steady volume of trading activity that will generally support continuous sales without an adverse effect on share price. We cannot give you any assurance that a broader or more active public trading market for our common stock will develop or be sustained, or that current trading levels will be sustained. Due to these conditions, we can give you no assurance that you will be able to sell your shares at or near bid prices or at all if you need money or otherwise desire to liquidate your shares.
| 16 |
Shares eligible for future sale may adversely affect the market.
From time to time, certain of our stockholders may be eligible to sell all or some of their shares of common stock by means of ordinary brokerage transactions in the open market pursuant to Rule 144 promulgated under the Securities Act, subject to certain limitations. In general, pursuant to amended Rule 144, non-affiliate stockholders may sell freely after six months subject only to the current public information requirement. Affiliates may sell after six months subject to the Rule 144 volume, manner of sale (for equity securities), current public information and notice requirements. Any substantial sales of our common stock pursuant to Rule 144 may have a material adverse effect on the market price of our common stock.
We could issue additional common stock, which might dilute the book value of our common stock.
Our Board of Directors has authority, without action or vote of our shareholders, to issue all or a part of our authorized but unissued shares. Such stock issuances could be made at a price that reflects a discount or a premium from the then-current trading price of our common stock. In addition, in order to raise capital, we may need to issue securities that are convertible into or exchangeable for a significant amount of our common stock. These issuances would dilute the percentage ownership interest, which would have the effect of reducing your influence on matters on which our shareholders vote, and might dilute the book value of our common stock. You may incur additional dilution if holders of stock options, whether currently outstanding or subsequently granted, exercise their options, or if warrant holders exercise their warrants to purchase shares of our common stock.
Our common stock could be further diluted as the result of the issuance of convertible securities, warrants or options.
In the past, we have issued convertible securities (such as convertible debentures and notes), warrants and options in order to raise money or as compensation for services and incentive compensation for our employees and directors. We have shares of common stock reserved for issuance upon the exercise of certain of these securities and may increase the shares reserved for these purposes in the future. Our issuance of these convertible securities, options and warrants could affect the rights of our stockholders, could reduce the market price of our common stock or could result in adjustments to exercise prices of outstanding warrants (resulting in these securities becoming exercisable for, as the case may be, a greater number of shares of our common stock), or could obligate us to issue additional shares of common stock to certain of our stockholders.
We do not intend to pay dividends.
We do not anticipate paying cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. We may not have sufficient funds to legally pay dividends. Even if funds are legally available to pay dividends, we may nevertheless decide in our sole discretion not to pay dividends. The declaration, payment and amount of any future dividends will be made at the discretion of our board of directors, and will depend upon, among other things, the results of our operations, cash flows and financial condition, operating and capital requirements, and other factors our board of directors may consider relevant. There is no assurance that we will pay any dividends in the future, and, if dividends are paid, there is no assurance with respect to the amount of any such dividend.
If we fail to maintain effective internal controls over financial reporting, the price of our common stock may be adversely affected.
Our internal control over financial reporting may have weaknesses and conditions that could require correction or remediation, the disclosure of which may have an adverse impact on the price of our common stock. We are required to establish and maintain appropriate internal controls over financial reporting. Failure to establish those controls, or any failure of those controls once established, could adversely affect our public disclosures regarding our business, prospects, financial condition or results of operations. In addition, management’s assessment of internal controls over financial reporting may identify weaknesses and conditions that need to be addressed in our internal controls over financial reporting or other matters that may raise concerns for investors. Any actual or perceived weaknesses and conditions that need to be addressed in our internal control over financial reporting or disclosure of management’s assessment of our internal controls over financial reporting may have an adverse impact on the price of our common stock.
| 17 |
We are required to comply with certain provisions of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and if we fail to comply in a timely manner, our business could be harmed and our stock price could decline.
Rules adopted by the SEC pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 require an annual assessment of internal controls over financial reporting, and for certain issuers an attestation of this assessment by the issuer’s independent registered public accounting firm. The standards that must be met for management to assess the internal controls over financial reporting as effective are evolving and complex, and require significant documentation, testing, and possible remediation to meet the detailed standards. We expect to incur significant expenses and to devote resources to Section 404 compliance on an ongoing basis. It is difficult for us to predict how long it will take or how costly it will be to complete the assessment of the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting for each year and to remediate any deficiencies in our internal control over financial reporting. As a result, we may not be able to complete the assessment and remediation process on a timely basis. In addition, although attestation requirements by our independent registered public accounting firm are not presently applicable to us we could become subject to these requirements in the future and we may encounter problems or delays in completing the implementation of any resulting changes to internal controls over financial reporting. In the event that our Chief Executive Officer or Chief Financial Officer determine that our internal control over financial reporting is not effective as defined under Section 404, we cannot predict how regulators will react or how the market prices of our shares will be affected; however, we believe that there is a risk that investor confidence and share value may be negatively affected.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS
N/A
Our executive offices are located at 6804 South Canton Avenue, Suite 150, Tulsa, Oklahoma 74136. The Company signed an Office Lease Agreement (the “Lease Agreement”) on April 24, 2008. The Lease Agreement commenced on June 1, 2008 and expired June 1, 2011. On March 8, 2011 the Lease Agreement was amended (amendment 1) to extend the expiration date to May 31, 2012. On July 24, 2012 the Lease Agreement was amended (amendment 2) to extend the expiration date to July 31, 2015.
We are not a party to any pending legal proceeding, nor is our property the subject of a pending legal proceeding, that is not in the ordinary course of business or otherwise material to the financial condition of our business. None of our directors, officers or affiliates is involved in a proceeding adverse to our business or has a material interest adverse to our business.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES
N/A
PART II
ITEM 5. MARKET FOR COMMON EQUITY AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER PURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES
Our common stock is quoted on the OTC Pink marketplace under the symbol “TDCP”.
For the periods indicated, the following table sets forth the high and low bid prices per share of common stock. These prices represent inter-dealer quotations without retail markup, markdown, or commission and may not necessarily represent actual transactions. Where applicable, the prices set forth below give retroactive effect to our one-for-thirty-five reverse stock split which became effective on April 27, 2012.
| 18 |
2015 Fiscal Year
| High | Low | |||||||
| First Quarter ended March 31, 2015* | $ | 0.0036 | $ | 0.0012 | ||||
| * through March 27, 2015 | ||||||||
2014 Fiscal Year
| High | Low | |||||||
| First Quarter ended March 31, 2014 | $ | 0.039 | $ | 0.0031 | ||||
| Second Quarter ended June 30, 2014 | $ | 0.019 | $ | 0.0063 | ||||
| Third Quarter ended September 30, 2014 | $ | 0.012 | $ | 0.0031 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter ended December 31, 2014 | $ | 0.005 | $ | 0.0020 | ||||
2013 Fiscal Year
| High | Low | |||||||
| First Quarter ended March 31, 2013 | $ | 0.070 | $ | 0.032 | ||||
| Second Quarter ended June 30, 2013 | $ | 0.044 | $ | 0.016 | ||||
| Third Quarter ended September 30, 2013 | $ | 0.025 | $ | 0.003 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter ended December 31, 2013 | $ | 0.012 | $ | 0.003 | ||||
The market price of our common stock, like that of other technology companies, is highly volatile and is subject to fluctuations in response to variations in operating results, announcements of technological innovations or new products, or other events or factors. Our stock price may also be affected by broader market trends unrelated to our performance.
Holders
As of March 27, 2015 we had approximately 410 active holders of our common stock. The number of active record holders was determined from the records of our transfer agent and does not include beneficial owners of common stock whose shares are held in the names of various security brokers, dealers, and registered clearing agencies. Our transfer agent is Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company, 17 Battery Place, New York, NY 10004.
Dividend Policy
We have not declared any dividends to date. We have no present intention of paying any cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future, as we intend to use earnings, if any, to generate growth. The payment of dividends, if any, in the future, rests within the discretion of our Board of Directors and will depend, among other things, upon our earnings, capital requirements and our financial condition, as well as other relevant factors. There are no restrictions in our Certificate of Incorporation or By-laws that restrict us from declaring dividends.
Equity Compensation Plan Information
We have two stock-based compensation plans, the 2014 Equity Incentive Plan and the 2015 Equity Incentive Plan, together referred to herein as the “Stock Plans.” As of March 27, 2015, 23,030,274 options to purchase our common stock were issued and outstanding under the Stock Plans with a weighted-average price of $0.08 and 62,526,419 shares of our common stock were reserved for future issuance under the Stock Plans.
The following table sets forth the information indicated with respect to our compensation plans under which our common stock is authorized for issuance.
| 19 |
| Number of | Number of securities | |||||||||||
| securities to be | remaining available | |||||||||||
| issued upon | for future issuance | |||||||||||
| exercise of | under equity | |||||||||||
| outstanding | Weighted average | compensation plans | ||||||||||
| options, | exercise price of | (excluding securities | ||||||||||
| warrants and | outstanding options, | reflected in | ||||||||||
| Plan category | rights | warrants and rights | column (a) | |||||||||
| (a) | (b) | (c) | ||||||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders | - | - | - | |||||||||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders: | ||||||||||||
| 2014 Plan | 50,000,000 | $ | 0.08 | 750,103 | ||||||||
| 2015 Plan | 85,000,000 | 0.08 | 61,776,316 | |||||||||
| Total | 135,000,000 | $ | 0.08 | 62,526,419 | ||||||||
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
Shares of our common stock in this Item 5 refer to the number of shares of common stock after giving effect to the April 27, 2012 Reverse Split.
On August 24, 2012, August 28, 2012 and September 10, 2012, the Company issued and sold to accredited investors Convertible Bridge Notes in the aggregate principal amount of $438,000. The note sold on September 10, 2012 was purchased by Victor Keen, a director of the Company. The Notes included a $73,000 original issue discount. Accordingly, the Company received $365,000 gross proceeds from which the Company paid legal fees of $25,000 and placement agent fees of $27,675. The Bridge Notes matured in 90 days from their date of issuance and, other than the original issue discount, the Bridge Notes do not carry interest. However, in the event the Bridge Notes are not paid on maturity, all past due amounts will accrue interest at 15% per annum. Upon maturity of the Bridge Notes, the holders of the Bridge Notes may elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the Bridge Notes into (i) securities sold pursuant to an effective registration statement at the applicable offering price; or (ii) shares of Common Stock at a conversion price equal to the lesser of 100% of the Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP), as reported for the 5 trading days prior to (a) the date of issuance of the Bridge Notes, (b) the maturity date of the Bridge Notes, or (c) the first closing date of the securities sold pursuant an effective registration statement.
On December 21, 2012, the Company entered into an amendment agreement (the “GCASIF Amendment”) with GCA Strategic Investment Fund Limited, a Bermuda corporation ("GCASIF"), the holder of that certain Convertible Bridge Note (the “GCA Bridge Note”) in the principal amount of $300,000 issued by the Company on August 24, 2012.
The GCA Bridge Note matured on or about November 22, 2012, on which date all past due amounts of the GCA Bridge Note began accruing interest at 15% per annum. Furthermore, on November 22, 2012, because the shares of the Company’s common stock into which the GCA Bridge Note is convertible were not registered under an effective registration statement (the “Registration Statement”), GCASIF was entitled to liquidated damages equal to 2% of the outstanding principal for each 30 day period after the November 22, 2012 the Registration Statement is not declared effective (the “Liquidated Damages”).
Pursuant to the GCASIF Amendment, GCASIF agreed to extend the maturity of the GCA Bridge Note from November 22, 2012 to March 21, 2013 and the Company agreed to (i) increase the principal amount of the GCA Bridge Note from $300,000 to $325,000; (ii) amend the conversion price of the Bridge Note to the lesser of $0.04, or 100% of the Volume Weighted Average Price, as reported by Bloomberg, L.P., for the 5 trading days prior to the effective date of the Registration Statement; and (iii) grant additional registration rights to GCASIF from 5,172,414 shares to 8,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock into which the GCA Bridge Note may be convertible. Furthermore, GCASIF agreed to waive any and all defaults, default interest and the Liquidated Damages due to GCASIF. In connection with the GCASIF Amendment, the Company agreed to pay GCASIF a fee of $20,000. During 2013, GCASIF converted $204,480 of the note into 48,811,800 shares of common stock at an average of $0.0042 per share based on the formula in the note. The $120,520 remaining balance on the note was paid in cash in December 2013.
| 20 |
For the year ended December 31, 2013, shares of common stock totaling 25,892,479 were issued for consulting services for which the Company charged operations $295,350.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, Golden State converted $3,860 of a 4.75% convertible debenture into 37,651,544 shares of common stock and exercised warrants to purchase 1,103 shares of common stock at $381.50 per share.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, Golden State converted $4,710 of the $100,000 debenture into 98,093,643 shares of common stock and exercised warrants to purchase 1,347 shares of common stock at $381.50 per share.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, JMJ converted $203,700 of convertible promissory notes into 32,054,924 shares of common stock at $0.0064 under the terms of the securities purchase agreements.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, JMJ converted $148,680 of convertible promissory notes into 47,848,529 shares of common stock at $0.0031 under the terms of the securities purchase agreements.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, IBC converted $78,789 of outstanding settlement obligations into 53,720,000 shares of common stock at $0.0015 under the terms of the Settlement Agreement.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, IBC converted $3,162 of outstanding settlement obligations into 15,810,800 shares of common stock at $0.0002 under the terms of the Settlement Agreement.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, CPUS converted $204,480 of convertible promissory notes into 49,811,800 shares of common stock at $0.0041 under the terms of the securities purchase agreement.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, holders of the Senior Convertible Note dated October 1, 2013 converted $78,000 of such note into 2,025,974 shares of common stock at $0.0385.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, Golden State converted $400 of the 4.75% convertible debenture into 18,727,884 shares of common stock at $0.00002 per share and exercised 114 warrants at $381.50 per share for $43,545 and advanced $10,900 for future exercise of warrants under the terms of the securities purchase agreements.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, JMJ converted $17,500 of the convertible promissory note into 10,000,000 shares of common stock at $0.002 under the terms of the securities purchase agreements.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, the holder of the 10% Convertible Promissory Note converted $25,000 of the convertible promissory note into 14,245,014 shares of common stock at $0.002 under the terms of the securities purchase agreements.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, shares of common stock totaling 15,000,000 were issued for legal services for which the Company recognized $22,500 of expense.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, shares of common stock totaling 15,017,162 were issued for 2014 consulting services for which the Company reduced accounts payable by $25,000.
| 21 |
JMJ March 2015 5% Note
In March 2015, the Company issued and sold a convertible note (the “March 2015 5% Note") in aggregate Principal Sum of $250,000 to JMJ Financial (“JMJ”). The 5% Note includes a $25,000 original issue discount (the “OID”) that will be prorated based on the advances actually paid (the “Principal Sum”) to the Company. During 2015, JMJ advanced $30,000 on the 5% Note and earned $3,000 OID. In addition to the OID, the March 2015 5% Note provides for a one-time interest charge of 5% to be applied to the Principal Sum. If the Company repays the 5% Note on or before ninety days from the date of the principal amount advanced, the interest rate will be zero percent. If the Company does not repay the March 2015 5% Note on or before ninety days from the date of the advance, a one-time interest charge of 5% shall be applied to the Principal Sum. Pursuant to the terms of March 2015 5% Note, JMJ may, at its election, convert all or a part of the $250,000 note into shares of the Company's common stock at a conversion rate 70% of the lowest trade price during the twenty-five trading days prior to JMJ’s election to convert. The principal of the March 2015 5% Note is due two years from the date of each of the principal amounts advanced.
Typenex Co-Investment, LLC
In March 2015, the Company issued and sold a convertible note (the “5% Promissory Note") in aggregate Principal Sum of $87,500 to Typenex Co-Investment, LLC, (“Typenex”). The 5% Promissory Note includes a $7,500 original issue discount (the “OID”) that will be prorated based on the advances actually paid to the Company. Accordingly during 2015, the Company received $80,000 gross proceeds from which the Company paid legal and documentation fees of $20,000 and placement agent fees of $6,750. In addition to the OID, the 5% Promissory Note provides for a one-time interest charge of 5% to be applied to the principal of the 5% Promissory Note. If the Company repays the 5% Promissory Note on or before ninety days from the date of the principal amount advanced, the interest rate will be zero percent. If the Company does not repay the 5% Promissory Note on or before ninety days from the date of the advance, a one-time interest charge of 5% shall be applied to the Principal Sum. Pursuant to the terms of 5% Promissory Note, Typenex may, at its election, convert all or a part of the $87,500 principal and interest thereon of the 5% Promissory Note into shares of the Company's common stock at a conversion rate 70% of the lowest trade price during the twenty-five trading days prior to the election to convert. The principal of the 5% Promissory Note is due one year from the March 2015 effective date.
In connection with the securities issuances reported in this Item, the Company relied upon the exemption from securities registration afforded by Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”). No advertising or general solicitation was employed in offering any securities.
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
N/A
ITEM 7. MANAGEMENT'S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATION
The following discussion and analysis should be read together with our financial statements and the related notes appearing elsewhere in this Report. This discussion contains forward-looking statements reflecting our current expectations that involve risks and uncertainties. See “Forward-Looking Statements” for a discussion of the uncertainties, risks and assumptions associated with these statements. Actual results and the timing of events could differ materially from those discussed in our forward-looking statements as a result of many factors, including those set forth under “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Report.
Overview of Business
We are a development stage company. Our mission is to pursue, develop and market full-color volumetric 3D technology. Through a SRA with the University of Oklahoma, we have obtained the exclusive worldwide marketing rights to certain 3D display technologies under development by the University. The developments to date have resulted in the University filing seven provisional patents; six of the seven provisional patents have been combined and converted to four utility patents. On May 26, 2009, the United States Patent and Trademark Office (“USPTO”) approved the pending patent called "Volumetric Liquid Crystal Display" for rendering a three-dimensional image and converted it to US patent No. 7,537,345. On December 28, 2010, USPTO approved the pending patent called “Light Surface Display for Rendering a Three-Dimensional Image,” and issued the United States Patent No. 7,858,913. On December 13, 2011, USPTO approved a continuation patent called “3D Light Surface Display,” and issued the US Patent No. 8,075,139. On August 21, 2012, the USPTO approved a continuation patent called “3D Volumetric Display” and issued the US Patent No. 8,247,755. These patents describe what we are calling our CSpace technology. At this time, we do not own any intellectual property rights in these technologies, and, apart from the SRA with the University, have no contracts or agreements pending to acquire such rights or any other interest in such rights. We plan to market the technology and the intellectual property developed by the University and our staff by targeting various industries, such as retail, manufacturing, entertainment, medical, healthcare, transportation, homeland security and the military. On April 6, 2009, we filed a provisional patent on an emissive two-dimensional screen that is controlled and driven by a standard digital light projector or other optical input source. This provisional patent is called "Flexible/Inflexible Front/Back Projection screen or display" and owned solely by 3DIcon Corporation. Through the current agreement with the University of Oklahoma, the University filed a continuation patent application on November 19, 2010, called “3D Light Surface Display”. This application provides additional protections of our CSpace technology.
| 22 |
Since March of 2012, the Company has been evaluating a number of second-generation, glasses-free flat screen 3D display technologies and the companies that are developing these technologies with the possibility of an acquisition of such a company in mind. Our goal was to identify a new technology that could deliver significantly better performance (3D impact and image quality) than current large area multiple-viewer glasses-free 3D flat screen displays without compromising resolution and brightness, as do current displays. The ideal company would also have a great technical team, a broad patent portfolio, and a credible technology roadmap to ensure that these competitive advantages are sustainable into the future. As a result of the above evaluation process, the Company previously entered into a non-binding Letter of Intent to acquire Dimension Technologies, Inc. (DTI) www.dti3d.com located in Rochester, NY. However, that Letter of Intent has since expired. Notwithstanding the expiration of the Letter of Intent, the Company’s interest in a potential acquisition of a small 3D flat screen display company remains. Currently, we do not have any agreements in place that would allow entry into the flat screen segment of the glasses-free 3D display industry or digital signage industry and no assurances can be made that such an agreement will ever be consummated. The Company is not actively seeking such acquisitions in the glasses-free 3D flat screen display segment at this time.
Reverse Stock Split
On April 27, 2012, the Company filed an Amended Certificate of Incorporation to effect a 1-for-35 reverse split of the Company’s common stock. The reverse stock split was announced by Financial Industry Regulatory Authority on April 26, 2012 and became effective on April 27, 2012. As previously reported on the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K, filed on October 20, 2011, this action followed a stockholder vote at the Company’s annual meeting of the stockholders of the Company, which vote authorized the Company’s Board of Directors to effect a reverse stock split of the Company’s authorized, issued and outstanding common stock.
On April 27, 2012, the effective date, every 35 shares of the Company’s issued and outstanding common stock were combined into one share of common stock. The Company did not issue any fractional shares in connection with the reverse stock split. Stockholders of record who otherwise would have been entitled to receive fractional shares will be entitled, upon surrender to our transfer agent of certificates representing such shares, cash in lieu thereof.
Throughout this report, each instance which refers to a number of shares of our common stock refers to the number of shares of common stock after giving effect to the April 27, 2012 Reverse Split, unless otherwise indicated. References to a number of shares of common stock in our historical financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 are reported on a post-Reverse Split basis.
Critical Accounting Policies
The Securities and Exchange Commission ("SEC") defines "critical accounting policies" as those that require application of management's most difficult, subjective or complex judgments, often as a result of the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain and may change in subsequent periods. Not all of the accounting policies require management to make difficult, subjective or complex judgments or estimates. However, the following policies could be deemed to be critical within the SEC definition.
| 23 |
Research and Development Costs
The Company expenses all research and development costs as incurred. Until we have developed a commercial product, all costs incurred in connection with the SRA with the University, as well as all other research and development costs incurred, will be expensed as incurred. After a commercial product has been developed, we will report costs incurred in producing products for sale as assets, but we will continue to expense costs incurred for further product research and development activities.
Stock-Based Compensation
Since its inception 3DIcon has used its common stock or warrants to purchase its common stock as a means of compensating our employees and consultants. Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") guidance on accounting for share based payments requires us to estimate the value of securities used for compensation and to charge such amounts to expense over the periods benefited.
The estimated fair value at date of grant of options for our common stock is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, as follows:
The expected dividend yield is based on the average annual dividend yield as of the grant date. Expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of our stock. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rates as of the grant date. The expected life of the option is based on historical exercise behavior and expected future experience.
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenue when services are performed, and at the time of shipment of products, provided that evidence of an arrangement exists, title and risk of loss have passed to the customer, fees are fixed or determinable, and collection of the related receivable is reasonably assured.
We recognize grant revenue in the month earned in accordance with the terms of the grant agreement.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the accompanying financial statements. Significant estimates made in preparing these financial statements include the estimate of useful lives of property and equipment, the deferred tax valuation allowance, and the fair value of stock options. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The following methods and assumptions were used to estimate the fair value of each class of financial instrument held by the Company:
Current assets and current liabilities - The carrying value approximates fair value due to the short maturity of these items.
Debentures payable - The fair value of the Company's debentures payable has been estimated by the Company based upon the liability's characteristics, including interest rate. The carrying value approximates fair value.
| 24 |
Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
See the Recently Issued Accounting Standards section of Note 3 to our Financial Statements included in Part II, Item 8 of this report for further details of recent accounting pronouncements.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS FOR THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2014 COMPARED TO THE YEAR ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2013
Revenue
The Company received $70,748 and $43,896 from the OCAST grant for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
In January 2008 we launched our first software product Pixel Precision. We appointed Digital Light Innovations for the sales and distribution of this product in March 2008. We have earned income of $15,000 and $4,500 before commissions and costs from the sales of Pixel Precision for the years ended December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, respectively.
We expect sales of Pixel Precision to the installed and active user base of the earlier D1100 and D3000 systems in the near term and as companion product sales to D4000 systems. We expect that the revenue from this product to offset operating expenses (general and administrative, research and development, interest) but do not expect the revenue generated in 2015 to cover the operating expenses.
Research and Development Expenses
The research and development expenses were $198,550 for the year ended December 31, 2014 as compared to $372,984 for the year ended December 31, 2013. The decrease was a result of the termination of agreements with outside research and development consultants of approximately $116,000, a decrease in lab supplies and equipment of approximately $45,000 a decrease in patent cost of approximately $8,000 and a decrease in the costs incurred for travel, meals, lodging and conference fees of $29,000, and an increase of $22,000 for the value of shares issued for the Technical Advisory Board.
General and Administrative Expenses
Our general and administrative expenses were $1,065,167 for the year ended December 31, 2014 as compared to $1,077,106 for the year ended December 31, 2013. The net decrease is due to a decrease in legal fees of $156,000 primarily due to the Depositary Trust Company (“DTC”) inquiry in 2013, a decrease of $44,000 in travel and related expense, a decrease in filing fees of $14,000 due to fewer filing in 2014 and a decrease in accounting fees of $4,000. These decreases were offset by an increase of financing fees of $78,000 primarily due to the 3a 10 settlement agreement, an increase of $63,000 in consultant fees, an increase of $56,000 in marketing and public relation consultant fees, an increase of $6,000 for the shareholders’ briefing, and an increase of $3,000 in insurance.
Interest Expense
Interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2014 was $75,735 as compared to $80,355 for the year ended December 31, 2013. The decrease in interest expense resulted from the decrease of $15,000 extension fee incurred in 2013 and an increase in interest paid on our outstanding debentures and bridge notes.
Financial Condition, Liquidity and Capital Resources
Management remains focused on controlling cash expenses. We recognize our limited cash resources and plan our expenses accordingly. We intend to leverage stock-for-services wherever possible. The operating budget consists of the following expenses:
| · | Research and development expenses pursuant to our development of an initial demonstrable prototype and a second prototype for static volume technology. |
| · | Acceleration of research and development through increased research personnel as well as other research agencies. |
| 25 |
| · | General and administrative expenses: salaries, insurance, investor related expenses, rent, travel, website, etc. |
| · | Hiring executive officers for technology, operations and finance. |
| · | Development, support and operational costs related to Pixel Precision software. |
| · | Professional fees for accounting and audit; legal services for securities and financing; patent research and protection. |
Our independent registered public accountants, in their audit report accompanying our financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2014, expressed substantial doubt about our ability to continue as a going concern due to our status as a development stage organization with insufficient revenues to fund development and operating expenses.
We had net cash of $34,485 at December 31, 2014.
We had negative working capital of $949,826 at December 31, 2014.
During the year ended December 31, 2014, we used $650,414 of cash for operating activities, a decrease of $412,525 or 39% compared to the year ended December 31, 2013. The decrease in the use of cash for operating activities was a result of the decrease in the net loss of approximately $228,000 and the decrease in stock and options issued for service of approximately $187,000 and the change in accounts payable and accrued liabilities in 2014 of approximately $363,000.
Cash used in investing activities during the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 was $-0-.
Cash provided by financing activities during the year ended December 31, 2014 was $614,130, a decrease of $518,228 or 46% compared to the year ended December 31, 2013. The decrease was the result of a decrease in funding under the terms of the convertible debentures from Golden State and bridge notes issued in 2013 of approximately $498,000 less the cash payment of $140,680 on the Global Capital/CPUS debenture.
We expect to fund the ongoing operations through the existing financing in place (see below); through raising additional funds as permitted by the terms of Golden State financing as well as reducing our monthly expenses.
Our ability to fund the operations of the Company is highly dependent on the underlying stock price of the Company.
On November 3, 2006, the Company issued to Golden State a 4.75% convertible debenture in a principal amount of $100,000, due December 2015 as a result of a maturity extension agreement received by the Company in March 2015, and warrants to buy25,571 shares of the common stock at an exercise price of $381.50 per share. In connection with each conversion, Golden State is expected to simultaneously exercise a percentage of warrants equal to the percentage of the principal being converted. During 2013, Golden State converted $3,860 of the $100,000 debenture into 37,651,544 shares of common stock, exercised warrants to purchase 1,103 shares of common stock at $381.50 per share based on the formula in the convertible debenture. Additionally Golden State advanced $671,810 against future exercises of warrants of which $420,740 was applied to the exercise of warrants leaving $185,671 of unapplied advances at December 31, 2013. During 2014, Golden State converted $4,710 of the $100,000 debenture into 98,093,643 shares of common stock, exercised warrants to purchase 1,347 shares of common stock at $381.50 per share based on the formula in the convertible debenture. Additionally Golden State advanced $349,310 against future exercises of warrants of which $513,390 was applied to the exercise of warrants leaving $21,591 of unapplied advances at December 31, 2014.
In September 2013, the Company was awarded a grant from Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science and Technology (“OCAST”). This matching grant is for $300,000 and had a start date of January 1, 2014. The Company earned $70,748 and $43,896 from the grant during the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 respectively. The money is being used to support the development of the Company’s first Product Platform, which will be the basis for a family of products based on the Company’s CSpace® volumetric 3D display technology.
| 26 |
On December 1, 2010 the Company entered into an agreement with the University pursuant to which the University agreed to convert all sums due to it from the Company in connection with its SRA with the Company, which as of December 1, 2010 amounted to approximately $485,000, into an aggregate of 1,685,714 shares of the Company's common stock. As a result of the debt conversion, the University became the holder of approximately 8% of the outstanding common stock of the Company. Pursuant to the agreement, the shares are subject to a put option allowing the University to require the Company to purchase certain of the shares upon the occurrence of certain events. In addition, the shares are subject to a call option allowing the Company to require the University to sell to the Company the shares then held by the University in accordance with the terms of the agreement. The put options and the call options expired on November 30, 2014 and the Shares are no longer subject to such options.
Director Debenture
On June 24, 2013, the Company issued to Victor Keen and Martin Keating, Directors of the Company, (“Directors”) 10% convertible debentures in a principal amount of $15,000 each, due June 26, 2014 and subsequently extended to December 26, 2014 and again extended to June 30, 2015. The Directors may elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the debentures at an exercise price of $0.01 per share. Provided that the debentures are paid in full on or before the maturity date, no interest shall accrue on the unpaid balance of the principal amount. In the event that the debentures are not paid in full on or before the maturity date, interest shall accrue on the unpaid outstanding balance of the principal amount of the debentures from June 26, 2013, until paid, at the fixed rate of ten percent (10%) per annum.
Newton, O'Connor, Turner & Ketchum 10% Convertible Debenture
On December 20, 2012, the Company issued to Newton, O'Connor, Turner & Ketchum (“NOTK”) a 10% convertible debenture in a principal amount of $29,007, initially due September 30, 2013 and extended to December 31, 2014 and subsequently extended to June 30, 2015. NOTK may elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the debenture at an exercise price of $0.02534 per share. The Company was indebted to NOTK for legal services performed for the Company and reimbursement of expenses in rendition of those services for the period ended December 31, 2012. The debenture was issued in settlement of the indebtedness.
5% Convertible Bridge Notes
On June 6, 2012 and August 1, 2012, the Company issued and sold convertible promissory notes (the “5% Notes") in aggregate principal amount of $415,000 to JMJ Financial (“JMJ”). The 5% Notes includes a $40,000 original issue discount (the “OID”) that will be prorated based on the advances actually paid to the Company. During 2012, JMJ advanced $150,000 on the 5% Notes and earned $14,000 OID. During 2013, JMJ advanced an additional $120,000 on the 5% Notes and earned $32,205 OID and accrued interest. During 2013, JMJ converted $203,700 of the 5% Notes into 31,854,924 shares of common stock at an average of $0.00639 per share based on the formula in the 5% Notes. During 2014, JMJ advanced an additional $75,000 on the 5% Notes and earned $5,975 OID and accrued interest. During 2014, JMJ converted $148,680 of the 5% Notes into 47,848,529 shares of common stock at an average of $0.003 per share based on the formula in the 5% Notes. In addition to the OID, the 5% Notes provides for a one-time interest charge of 5% to be applied to the principal sum advanced. Pursuant to the terms of 5% Notes, JMJ may, at its election, convert all or a part of the $275,000 note and the $140,000 note into shares of the Company's common stock at a conversion rate equal to the lesser of (i) $0.15 and $0.35, respectively or (ii) 70% of the lowest trade price during the twenty-five trading days prior to JMJ’s election to convert. If the Company repays the 5% Notes on or before ninety days from the date it was issued, the interest rate will be zero percent. If the Company does not repay the 5% Notes on or before ninety days from the date it was issued, a one-time interest charge of 5% shall be applied to the principal. The Company did not repay the 5% Notes within the ninety day period. The principal of the 5% Notes is due one year from the date of each of the principal amounts advanced.
The 5% Notes were subject to a Mandatory Registration Agreement (the “Registration Agreement”) whereby no later than August 31, 2012, the Company agreed to file, at its own expense, an amendment (the “Amendment”) to the S-1 Registration Statement (the “Registration Statement”) the Company filed with the SEC on July 3, 2012, to include in such Amendment 4,750,000 shares of common stock issuable under the 5% Notes. The Company agreed, thereafter, to use its best efforts to cause such Registration Statement to become effective as soon as possible after such filing but in no event later than one hundred and twenty (120) days from the date of the Registration Agreement. Since the Company failed to get the Registration Statement declared effective within the 120 days of the date of the Registration Agreement, a penalty/liquidated damages of $25,000 was added to the balance of the 5% Notes.
| 27 |
10% Convertible Bridge Note to Director
On September 11, 2012, the Company issued and sold to Victor F. Keen, a Director and an accredited investor a Convertible Bridge Note (the “Keen Bridge Note”) in the principal amount of $60,000. The sale of the Keen Bridge Notes in the principal of $60,000 included a $10,000 OID. Accordingly, the Company received $50,000 gross proceeds. The Keen Bridge Note matured 90 days from the date of issuance and, other than the OID, the Keen Bridge Note does not carry interest. However, in the event the Keen Bridge Note is not paid on maturity, all past due amounts will accrue interest at 15% per annum. Upon maturity of the Keen Bridge Note, the holders of the Keen Bridge Note may elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the Keen Bridge Note into (i) securities sold pursuant to an effective registration statement at the applicable offering price; or (ii) shares of common stock at a conversion price equal to the lesser of 100% of the Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP), as reported for the 5 trading days prior to (a) the date of issuance of the Keen Bridge Note, (b) the maturity date of the Keen Bridge Note, or (c) the first closing date of the securities sold pursuant an effective registration statement.
On January 26, 2013, the Company entered into an amendment agreement (the “Keen Amendment”) with Mr. Keen. The Pursuant to the Keen Amendment, Mr. Keen agreed to extend the maturity date of the Keen Bridge Note from December 10, 2012 to April 30, 2013 and to waive any and all defaults, default interest and Liquidated Damages then due to Mr. Keen.
On July 30, 2013, the Company entered into a second amendment agreement (the “Second Keen Amendment”) with Mr. Keen to amend the Keen Bridge Note.
Pursuant to the Second Keen Amendment, Mr. Keen agreed to extend the maturity of the Keen Bridge Note from April 30, 2013 to August 31, 2013 (the “New Maturity Date”) and to waive, if any, existing or prior defaults under the Keen Bridge Note or the Keen SPA and the Company agreed to (i) amend the conversion provision to allow for conversions based on a conversion price calculated on the Amendment Date or the New Maturity Date; and (ii) to include an interest rate equal to 10% per annum, payable on the New Maturity Date, as amended, which accrual shall commence on December 10, 2012.
On September 30, 2013, the Company entered into a third amendment agreement (the “Third Keen Amendment”) with Mr. Keen. Pursuant to the Third Keen Amendment, Mr. Keen agreed to extend the maturity of the Keen Bridge Note from August 31, 2013 to December 31, 2013 and to waive, if any, existing or prior defaults under the Keen Bridge Note or the Keen SPA.
On January 27, 2014, the Company entered into a fourth amendment agreement (the “Fourth Keen Amendment”) with Mr. Keen. Pursuant to the Fourth Keen Amendment, Mr. Keen agreed to extend the maturity of the Keen Bridge Note from December 31, 2013 to December 31, 2014 and to waive, if any, existing or prior defaults under the Keen Bridge Note or the Keen SPA.
On March 16, 2015 (the “Amendment Date”), the Company entered into a fifth amendment agreement (the “Fifth Keen Amendment”) with Keen to amend the Keen Bridge note. Pursuant to the Fifth Keen Amendment, Keen agreed to extend the maturity of the Note from December 31, 2014 to June 30, 2015 (the “New Maturity Date”) and to waive, if any, existing or prior defaults under the Keen Bridge Note or the Keen SPA.
15% Senior Convertible Bridge Notes due 2014
On October 1, 2013 (the “Date of Issuance”), the Company issued and sold to an accredited investor a Senior Convertible Note (the “Senior Note”) in the principal amount of $205,000 and a warrant to purchase 300,000 shares of the Company’s common stock at an exercise price equal to 110% of the closing bid price on September 30, 2013 (the “October 2013 Warrant”). The Senior Note included a $30,750 OID. Accordingly, the Company received $174,250 gross proceeds from which the Company paid legal and documentation fees of $22,500 and placement agent fees of $15,682.
| 28 |
The Senior Note matured on July 1, 2014 and did not carry interest. However, in the event the Senior Note was not paid on maturity, all past due amounts would accrue interest at 15% per annum. The Senior Note was paid on maturity and interest was not incurred. At any time subsequent to six months following the Date of Issuance, the Senior Note holder may elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the Senior Note into shares of Common Stock at a conversion price equal to the lesser of 100% of the VWAP, as reported for the 5 trading days prior to the Date of Issuance or 80% of the average VWAP during the 5 days prior to the date the holder delivers a conversion notice to the Company. During 2014, the holder of the $205,000 note converted $180,000 of the note into 83,705,721 common shares at an average price of $0.0021 per share under the terms of the debenture agreement. The remaining $25,000 balance of the note was paid in cash to retire the note.
The estimated fair value of the warrants for common stock issued of $2,130 was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The expected dividend yield of zero is based on the average annual dividend yield as of the issue date. Expected volatility of 173.64% is based on the historical volatility of our stock. The risk-free interest rate of 1.39% is based on the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rate for five years as of the issue date. The expected life of five years of the warrant is based on historical exercise behavior and expected future experience.
The October 2013 Warrant is exercisable at any time on or after March 31, 2014 and on or prior to the close of business on March 31, 2019. At the election of the October 2013 Warrant holder, the October 2013 Warrant may be exercised using a cashless exercise method.
Effective August 15, 2014, the Company entered into a Securities Settlement Agreement (the “SSA”) with an accredited investor (the “Investor”) to whom the $205,000 Senior Convertible Note was assigned. Pursuant to the SSA, the Investor agreed to extend the maturity of the $205,000 principal owed (the “Debt”) under the Senior Note until August 15, 2015 and the Company agreed, among other things, to (i) pay 10% interest on the Debt; (ii) pay 125% of principal in the event the Company elects to prepay any portion of the Debt; (iii) allow the Investor to convert the Debt, in whole or in part, into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price equal to 58% percent of the lowest traded VWAP, determined on the then current trading market for the Company’s common stock, for the 15 trading days prior to conversion.
Settlement Agreement
On July 26, 2013, the Circuit Court in the 12th Judicial Circuit in and for Sarasota County, Florida (the “Court”), entered an Order Granting Approval of Settlement Agreement (the “Order”) approving, among other things, the fairness of the terms and conditions of an exchange pursuant to Section 3(a)(10) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, in accordance with a Settlement Agreement (the “Settlement Agreement”) between the Company and IBC Funds, LLC, a Nevada limited liability company (“IBC”), in the matter entitled IBC Funds, LLC v. 3DIcon Corporation, Case No. 2013 CA 5705 NC (the “Action”). IBC commenced the Action against the Company on July 19, 2013 to recover an aggregate of $197,631 of past-due accounts payable of the Company, which IBC had purchased from certain vendors of the Company pursuant to the terms of separate claim purchase agreements between IBC and each of such vendors (the “Assigned Accounts”), plus fees and costs (the “Claim”). The Assigned Accounts relate to certain research, technical, development, accounting and legal services. The Order provides for the full and final settlement of the Claim and the Action. The Settlement Agreement became effective and binding upon the Company and IBC upon execution of the Order by the Court on July 26, 2013.
Pursuant to the terms of the Settlement Agreement approved by the Order, on July 26, 2013, the Company issued 650,000 shares of Common Stock as a settlement fee and agreed to issue, in one or more tranches as necessary, that number of shares equal to $197,631 upon conversion to Common Stock at a conversion rate equal to 65% of the lowest closing bid price of the Common Stock during the ten trading days prior to the date the conversion is requested by IBC minus $0.002. During 2013, IBC converted $78,789 of the note into 53,720,000 shares of common stock at an average of $0.0015 per share based on the formula in the note.
On January 22, 2014 the Company entered into a Mutual Release (the “Release”) with IBC pursuant to which each party would release the other party from any and all obligations pursuant to the Settlement Agreement. In consideration for the Release, IBC accepted and the Company remitted to IBC: (i) a cash payment of $190,000, (ii) an issuance of 9,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock, pursuant to the terms of the Settlement Agreement under the December 18, 2013 Conversion Notice, and (iii) an issuance of 6,810,811 shares of the Company’s common stock, pursuant to the terms of the Settlement Agreement under the January 17, 2014 Conversion Notice (together, the “Consideration”). Pursuant to the Release, IBC agreed that the Consideration was accepted as satisfaction in full of the payments due pursuant to the Settlement Agreement.
| 29 |
On January 23, 2014, the Company and IBC filed a Stipulation of Dismissal with Prejudice with the Circuit Court in the 12th Judicial Circuit in and for Sarasota County, Florida.
10% Convertible Debenture due August 2015
On August 15, 2014, the Company issued and sold to an accredited investor a Convertible Debenture (the “10% Debenture”) in the principal amount of $150,000. The 10% Debenture included a 3% OID. Accordingly, the Company received $145,500 gross proceeds, from which the Company paid legal and fees of $5,000. The 10% Debenture has a maturity date of August 15, 2015 and carries a 10% interest rate. Subject to a 4.99% beneficial ownership limitation, the holder of the 10% Debenture may, at any time, elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the 10% Debenture into shares of Common Stock at a conversion price equal Sixty Five Percent (65%) of the lowest traded VWAP, determined on the then current trading market for the Company’s common stock, for 15 trading days prior to conversion.
Series A Convertible Preferred Stock
January 23, 2014, the Company sold to Victor Keen, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and a member of the Company’s Board of Directors, 190,000 Units for a purchase price of $190,000, as part of the Private Placement (as defined therein) disclosed in the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 13, 2013. Pursuant to such Private Placement, the Company has now received aggregate proceeds equal to $385,000. Such Private Placement is now closed.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
The Company does not engage in any off balance sheet arrangements that are reasonably likely to have a current or future effect on our financial condition, revenues, and results of operations, liquidity or capital expenditures.
Significant Accounting Policies
Research and Development Costs
The Company expenses all research and development costs as incurred. Until we have developed a commercial product, all costs incurred in connection with the SRA with the University, as well as all other research and development costs incurred, will be expensed as incurred. After a commercial product has been developed, we will report costs incurred in producing products for sale as assets, but we will continue to expense costs incurred for further product research and development activities.
Stock-Based Compensation
Since its inception 3DIcon has used its common stock or warrants to purchase its common stock as a means of compensating our employees and consultants. Financial Accounting Standards Board ("FASB") guidance on accounting for share based payments requires us to estimate the value of securities used for compensation and to charge such amounts to expense over the periods benefited.
The estimated fair value at date of grant of options for our common stock is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model, as follows:
| 30 |
The expected dividend yield is based on the average annual dividend yield as of the grant date. Expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of our stock. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rates as of the grant date. The expected life of the option is based on historical exercise behavior and expected future experience.
Subsequent Events
Common stock issued for services and liabilities
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, Golden State converted $400 of the 4.75% convertible debenture into 18,727,884 shares of common stock at $0.00002 per share and exercised 114 warrants at $381.50 per share for $43,545 and advanced $10,900 for future exercise of warrants under the terms of the securities purchase agreements.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, JMJ converted $17,500 of the convertible promissory note into 10,000,000 shares of common stock at $0.002 under the terms of the securities purchase agreements.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, the holder of the 10% Convertible Promissory Note converted $25,000 of the convertible promissory note into 14,245,014 shares of common stock at $0.002 under the terms of the securities purchase agreements.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, shares of common stock totaling 15,000,000 were issued for legal services for which the Company recognized $22,500 of expense.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, shares of common stock totaling 15,017,162 were issued for 2014 consulting services for which the Company reduced accounts payable by $25,000.
Keen Bridge Note
On March 16, 2015 (the “Amendment Date”), the Company entered into a fifth amendment agreement (the “Fifth Keen Amendment”) with Victor Keen, a Director on the Board of Directors of the Company, to amend the Keen Bridge note. Pursuant to the Fifth Keen Amendment, Mr. Keen agreed to extend the maturity of the Note from December 31, 2014 to June 30, 2015 (the “New Maturity Date”) and to waive, if any, existing or prior defaults under the Keen Bridge Note or the Keen SPA.
2014 Equity Incentive Plan
Shares totaling 6,793,478 were issued from the 2014 EIP during 2015 for services rendered. There are 750,103 shares available for issuance under the 2014 EIP.
2015 Equity Incentive Plan
In February 2015, the Company established the 3DIcon Corporation 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (the "2015 EIP"). The total number of shares of stock which may be purchased or granted directly by options, stock awards or restricted stock purchase offers, or purchased indirectly through exercise of options granted under the 2015 EIP shall not exceed eighty-five million (85,000,000) shares. The shares are included in a registration statement filed February 2015. Shares totaling 23,223,684 were issued from the 2015 EIP during 2015 for legal and consulting services rendered. There are 61,776,316 shares available for issuance under the 2015 EIP.
JMJ March 2015 5% Note
In March 2015, the Company issued and sold a convertible note (the “March 2015 5% Note") in aggregate Principal Sum of $250,000 to JMJ Financial
(“JMJ”). The 5% Note includes a $25,000 original issue discount (the “OID”) that will be prorated based on the advances actually paid (the “Principal Sum”) to
the Company. During 2015, JMJ advanced $30,000 on the 5% Note and earned $3,000 OID. In addition to the OID, the March 2015 5% Note provides for a
one-time interest charge of 5% to be applied to the Principal Sum. If the Company repays the 5% Note on or before ninety days from the date of the principal
amount advanced, the interest rate will be zero percent. If the Company does not repay the March 2015 5% Note on or before ninety days from the date of the
advance, a one-time interest charge of 5% shall be applied to the Principal Sum. Pursuant to the terms of March 2015 5% Note, JMJ may, at its election, convert
all or a part of the $250,000 note into shares of the Company's common stock at a conversion rate 70% of the lowest trade price during the twenty-five trading
days prior to JMJ’s election to convert. The principal of the March 2015 5% Note is due two years from the date of each of the principal amounts advanced.
Typenex Co-Investment, LLC
In March 2015, the Company issued and sold a convertible note (the “5% Promissory Note") in aggregate Principal Sum of $87,500 to Typenex Co-
Investment, LLC, (“Typenex”). The 5% Promissory Note includes a $7,500 original issue discount (the “OID”) that will be prorated based on the advances
actually paid to the Company. Accordingly during 2015, the Company received $80,000 gross proceeds from which the Company paid legal and documentation
fees of $20,000 and placement agent fees of $6,750. In addition to the OID, the 5% Promissory Note provides for a one-time interest charge of 5% to be applied
to the principal of the 5% Promissory Note. If the Company repays the 5% Promissory Note on or before ninety days from the date of the principal amount
advanced, the interest rate will be zero percent. If the Company does not repay the 5% Promissory Note on or before ninety days from the date of the advance, a
one-time interest charge of 5% shall be applied to the Principal Sum. Pursuant to the terms of 5% Promissory Note, Typenex may, at its election, convert all or a
part of the $87,500 principal and interest thereon of the 5% Promissory Note into shares of the Company's common stock at a conversion rate 70% of the lowest
trade price during the twenty-five trading days prior to the election to convert. The principal of the 5% Promissory Note is due one year from the March 2015
effective date.
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
N/A
ITEM 8. FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
All financial information required by this Item is attached hereto at the end of this report beginning on page F-1 and is hereby incorporated by reference.
| 31 |
ITEM 9. CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE
N/A
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES
Management's Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures. Under the supervision and with the participation of our management, including our President, Chief Financial Officer and Secretary, we evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rule 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the "Exchange Act")) as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based upon that evaluation, our President, Chief Financial Officer and Secretary concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this report were effective such that the information required to be disclosed by us in reports filed under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 is (i) recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms and (ii) accumulated and communicated to our management to allow timely decisions regarding disclosure. A controls system cannot provide absolute assurance, however, that the objectives of the controls system are met, and no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, within a company have been detected.
Management's Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting (as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) under the Exchange Act). Our internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes of accounting principles generally accepted in the United States.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their control objectives.
Our management evaluated the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. In making this assessment, our management used the 2013 Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission ("COSO") framework, an integrated framework for the evaluation of internal controls issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on this evaluation, our management concluded that, as of December 31, 2014, our internal control over financial reporting was effective.
This annual report does not include an attestation report of our registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management's report was not subject to attestation by our registered public accounting firm pursuant to rules of the SEC that permit the Company to provide only management's report in this annual report.
Changes. During the most recent quarter ended December 31, 2014, there has been no change in our internal control over financial reporting(as defined in Rule 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act) that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
None.
| 32 |
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS, PROMOTERS AND CONTROL PERSONS; COMPLIANCE WITH SECTION 16(A) OF THE EXCHANGE ACT
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS, DIRECTORS AND KEY EMPLOYEES
The following table sets forth the names and ages of the members of our Board of Directors and our executive officers and the positions held by each. There are no family relationships among any of our Directors and Executive Officers.
| Name | Age | Position | ||
| Victor F. Keen | 73 | Chief Executive Officer and Director | ||
| Ronald Robinson | 69 | Chief Financial Officer | ||
| John O'Connor | 59 | Chairman of the Board | ||
| Martin Keating | 73 | Director |
Victor F. Keen - Chief Executive Officer and Director
Victor F. Keen, the largest shareholder of 3DIcon, joined the board in November 2007 and became CEO November 1, 2013. Mr. Keen is a graduate of Harvard Law School and Trinity College. Until recently he was the chair of the Tax Practice Group at the international law firm, Duane Morris, LLP. Mr. Keen has become Of Counsel to the firm and devotes the majority of his time to his board memberships as well as real estate investments in New York City. For more than ten years Mr. Keen has served on the board of Research Frontiers (NASDAQ: REFR), a developer of “Smart Glass” through licensees around the world. For the past five years he has also served as the head of the Compensation Committee for Research Frontiers. Recently, Mr. Keen assumed the position of Board Observer for Egenix, Inc., a bioresearch firm focused on developing treatments for several specific cancers. Mr. Keen has been an active investor in a number of companies, both start up and later stage, including: Lending Tree, acquired by IAC Interactive Corp. (NASDAQ:IACI), a company controlled by Barry Diller; Circle Lending, Inc., now part of Richard Branson’s Virgin empire; and Rollover Systems, Inc., a privately held company involved in the matching of individual IRA/pension accounts with appropriate managers.
Ronald Robinson - Chief Financial Officer
Ronald Robinson was appointed Chief Financial Officer on January 28, 2013. He was a partner in three large local CPA firms spanning the last forty years, the latest of which was Sutton Robinson Freeman & Co., PC, from 1999 through 2010, of which he was the managing partner and performed SEC/PCOAB audits for several clients, including 3DIcon Corporation. He has been an SEC compliance and accounting consultant for 3DIcon Corporation since 2010. He is licensed to practice by the Oklahoma Board of Accountancy and is a member of the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants and the Oklahoma Society of Certified Public Accountants. Mr. Robinson, CPA is a graduate of East Central University Ada, Oklahoma with a BS in Accounting.
John O' Connor - Chairman of the Board of Directors
John O'Connor has been a director of the Company since October 2006. Mr. O’Connor is Chairman of the Board of the Tulsa law firm of Newton, O'Connor, Turner & Ketchum. He has practiced law in Tulsa since 1981, concentrating in the areas of corporate and commercial law. Mr. O’Connor has served two terms on the board of the Oklahoma Bar Association-Young Lawyers Division, and he has served on several committees of the Tulsa County Bar Association. He is a former member of the Oklahoma Academy of Mediators and Arbitrators, and has served as a Barrister in The Council Oak American Inn of Court.
Mr. O'Connor is a regular presenter at continuing legal education seminars sponsored by the Oklahoma Bar Association and the University Of Tulsa College Of Law. Mr. O'Connor is a member of the American Bar Association, the Oklahoma Bar Association, and the Tulsa County Bar Association. He is admitted to practice before the U.S. District Court of the Northern District of Oklahoma and state courts in Oklahoma and the U.S. Tax Court. He is a member of the Cherokee Nation Bar Association. Mr. O’Connor received his law degree from the University Of Tulsa College Of Law and his BA in political science from Oklahoma State University. He studied international law at the Friedreich Wilhelm RheinischeUniverstat in Bonn, Germany.
| 33 |
Martin Keating - Director
Martin Keating was Chief Executive Officer until August 8, 2011 and has been a director of the Company since 1998. As the founder, chairman, and CEO of 3DIcon Corporation, Mr. Keating has applied his vision and efforts to the creation and development of breakthrough 3D technology. Prior to founding the company, Mr. Keating structured and managed numerous investment vehicles including the capitalization and NASDAQ listing of CIS Technologies, where he served as general counsel. He also completed financing of the Academy Award-winning motion picture, “The Buddy Holly Story”. Mr. Keating has been a guest lecturer at several colleges and universities across the country. He has been featured on national television and radio programs including CNN, CNBC, HARD COPY, etc. In 1996, Mr. Keating published “The Final Jihad," a terrorist suspense novel which was excerpted four times by King Features Syndicate for more than 1,500 newspapers. Mr. Keating is an attorney licensed to practice law in Oklahoma and Texas.
Audit Committee
On February 25, 2008, the Board of Directors created an Audit Committee comprising of Mr. Victor Keen.
Compensation Committee
On February 25, 2008, the Board of Directors created a Compensation Committee comprising of Mr. Victor Keen.
Nomination and Corporate Governance Committee
On February 25, 2008, the Board of Directors created Nominations and Corporate Governance Committee comprising of Mr. Victor Keen.
Director or Officer Involvement in Certain Legal Proceedings
Our directors and executive officers were not involved in any legal proceedings as described in Item 401(f) of Regulation S-K in the past ten years.
Board Leadership Structure and Role in Risk Oversight
Although we have not adopted a formal policy on whether the Chairman and Chief Executive Officer positions should be separate or combined, in the past we determined that it was in the best interests of the Company and its shareholders to combine these roles. From the inception of the Company through June 13, 2011, Martin Keating served as our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer. Due to the small size and early stage of the Company, we believe it was most effective to have the Chairman and Chief Executive Officer positions combined. Since June 13, 2011, the role of the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and the Chairman, or any member, of the Board of Directors was separated.
Our Board of Directors receives and reviews periodic reports from management, auditors, legal counsel, and others, as considered appropriate regarding our Company's assessment of risks. Our Board of Directors focuses on the most significant risks facing our Company and our Company's general risk management strategy, and also ensure that risks undertaken by us are consistent with the Board's appetite for risk. While the Board oversees our Company's risk management, management is responsible for day-to-day risk management processes. We believe this division of responsibilities is the most effective approach for addressing the risks facing our company and that our board leadership structure and role in risk oversight is effective.
Code of Ethics
We have not adopted a Code of Ethics and Business Conduct for Officers, Directors and Employees that applies to all of our officers, directors and employees.
| 34 |
Employment Agreement
Employment Agreement - On March 19, 2012 the Company announced that Sidney Aroesty would resign as CEO and join the Board of Directors. Effective April 15, 2013, Mr. Aroesty resigned as a member of the Board of Directors.
Employment Agreement - On March 13, 2012, the Company entered into a one (1) year Agreement for At-Will Employment with Assignment of Inventions (“Employment Agreement”) with Mark Willner, pursuant to which Mr. Willner began serving as the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, effective immediately. Under the terms of the Employment Agreement, Mr. Willner is entitled to an annual base salary of $180,000, and, at the discretion of the Company’s Board of Directors, performance-based bonuses and/or salary increases. Pursuant to the Employment Agreement, the Company granted Mr. Willner five-year stock options to purchase 57,143 shares at a price equal to the average price of the five day period prior to March 19, 2012 which was $0.35 (the “Strike Price”). Furthermore, since Mr. Willner remained employed by the Company at the end of each quarter ending June 30, 2012, September 30, 2012 and December 31, 2012, he received additional stock options to purchase 28,571.5 shares at the Strike Price. In addition, since the Company achieved certain quarterly business objectives, Mr. Willner received, at the end of each such quarterly period, a further grant of stock options to purchase 28,571.5 shares at the Strike Price. The estimated fair value of each of the 57,143 block of options, valued at $18,840, was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model and was charged to operations in March 2012, June 2012, September 2012 and December 2012. The expected dividend yield of $-0- is based on the average annual dividend yield as of the grant date. Expected volatility of 163% is based on the historical volatility of the stock since July 25, 2007, the day the Company began trading on the Over-The-Counter Bulletin Board. The risk-free interest rate of 1.87% is based on the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rates as of the grant date. The expected life of the option of five years is based on historical exercise behavior and expected future experience.
On November 1, 2013, Mark Willner resigned as Chief Executive Officer of 3DIcon Corporation in order to allow Victor F. Keen to take over in his place as the Company’s Chief Executive Officer.
Mr. Willner’s resignation was not a result of any dispute with the Company. Furthermore, Mr. Willner assumed a strategic consulting role with the Company, focusing his efforts on the commercialization of and business development of the Company’s patented 3D display technology, CSpace®.
Mr. Keen, formerly Co-Chairman of the Company’s Board of Directors, remained a member of the Board while John M. O’Connor, also a former Co-Chairman, was elected as the sole Chairman of the Board. Mr. Keen has been a member of the Board since November 2007.
Employment Agreement - On March 16, 2012, the Company entered into a one (1) year Agreement for At-Will Employment with Assignment of Inventions (“Employment Agreement”) with George Melnik, pursuant to which Dr. Melnik began serving as the Company’s Senior Technical Advisor, effective immediately. Under the terms of the Employment Agreement, Dr. Melnik is entitled to an annual base salary of $144,000, and, at the discretion of the Company’s Board of Directors, performance-based bonuses and/or salary increases. Pursuant to the Employment Agreement, the Company granted Dr. Melnik five-year stock options to purchase 28,571 shares at a price equal to the average price of the five day period prior to March 16, 2012 which was $0.35 (the “Strike Price”). Furthermore, since Dr. Melnik remained employed by the Company at the end of each quarter ending June 30, 2012, September 30, 2012 and December 31, 2012, he received additional stock options to purchase 28,571 shares at the Strike Price. In addition, since the Company achieved certain quarterly business objectives, Dr. Melnik received, at the end of each such quarterly period, a further grant of stock options to purchase 28,571 shares at the Strike Price. The estimated fair value of each of the 28,571 block of options, valued at $9,420, was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model and was charged to operations in March 2012, June 2012, September 2012 and December 2012. The expected dividend yield of $-0- is based on the average annual dividend yield as of the grant date. Expected volatility of 163% is based on the historical volatility of the stock since July 25, 2007, the day the Company began trading on the Over-The-Counter Bulletin Board. The risk-free interest rate of 1.87% is based on the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rates as of the grant date. The expected life of the option of five years is based on historical exercise behavior and expected future experience.
The Employment Agreement may be terminated with or without reason by either the Company or Dr. Melnik and at any time, upon sixty (60) days written notice. The terms of the Employment Agreement will remain effective for one (1) year and will automatically renew, subject to the same termination rights. Upon termination, the Company will pay any base pay, bonus and benefits that have been earned and are due as of the date of the termination.
| 35 |
Employment Agreement - On January 28, 2013, the Board of Directors of the Company appointed Ronald Robinson to serve as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer. Accordingly, the Company decided not to renew its agreement with Christopher T. Dunstan pursuant to which Mr. Dunstan served as the Company’s Interim Chief Financial Officer. The Company’s appointment of Mr. Robinson and decision not to renew its agreement with Mr. Dunstan was not as a result of any disagreement between the Company and Mr. Dunstan.
Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act requires our directors and executive officers and persons who own more than 10% of the issued and outstanding shares of our common stock to file reports of initial ownership of common stock and other equity securities and subsequent changes in that ownership with the SEC. Officers, directors and greater than ten percent stockholders are required by SEC regulation to furnish us with copies of all Section 16(a) forms they file. Except as described below, to our knowledge, during the year ended December 31, 2014, all Section 16(a) filing requirements applicable to our officers, directors and greater than 10% beneficial owners were complied with.
On January 23, 2014, the Company sold to Victor Keen, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and a member of the Company’s Board of Directors, for a purchase price of $190,000, 190,000 units consisting of: (i) one share of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock and (ii) Warrants to purchase fifty (50) shares of Common Stock. Although Mr. Keen’s purchase of units was disclosed in the Company’s Form 8-K filed on January 28, 2014, the filing of a corresponding Form 4 was inadvertently overlooked. Subsequent to the year end, a Form 5 was filed reporting the transaction.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION
The following table sets forth all compensation earned in respect of our Chief Executive Officer and those individuals who received compensation in excess of $100,000 per year, collectively referred to as the named executive officers, for our last three completed fiscal years.
SUMMARY COMPENSATION TABLE
The following information is furnished for the years ended December 31, 2014, December 31, 2013 and December 31, 2012 for our principal executive officer and the two most highly compensated officers other than our principal executive officer who was serving as such at the end of our last completed fiscal year:
| Name &
Principal Position | Year | Salary
($) | Bonus
($) | Stock
Awards ($) | Option
Awards ($) | Non-Equity
Incentive Plan Compensation ($) | Change in
Pension Value and Non-Qualified Deferred Compensation Earnings ($) | All Other
Compensation ($) | Total
($) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Victor | 2014 | $ | 150,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 150,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Keen | 2013 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| CEO* | 2012 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 50,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 50,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Mark | 2014 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Willner | 2013 | $ | 162,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 162,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Former CEO ** | 2012 | $ | 173,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 75,360 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 248,300 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Sidney | 2014 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Aroesty | 2013 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Former CEO *** | 2012 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 50,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 50,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Ronald | 2014 | $ | 72,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 72,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Robinson | 2013 | $ | 66,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 66,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| CFO ***** | 2012 | $ | 46,444 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 46,444 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Chris | 2014 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Dunstan | 2013 | $ | 5,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 5,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Former CFO **** | 2012 | $ | 58,500 | $ | - | $ | 2,500 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 61,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Martin Keating | 2014 | $ | - | $ | 5,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 5,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Director & | 2013 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | |||||||||||||||||||
| Former CEO | 2012 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 50,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 50,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Hakki Refai | 2014 | $ | 144,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 144,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | $ | 144,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 144,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2012 | $ | 172,000 | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | - | $ | 172,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| * | Victor Keen was appointed CEO November 1, 2013 and waived any compensation for 2013. |
| ** | Mark Willner was the Company’s Chief Executive Officer from March 19, 2012 to November 1, 2013. See the “Employment Agreement” section for a discussion of Mr. Willner’s compensation arrangement. |
| *** | Sidney Aroesty was Chief Executive Officer from June 13, 2011 to March 19, 2012. |
| **** | On January 28, 2013, the Company decided not to renew its agreement with Christopher T. Dunstan pursuant to which Mr. Dunstan served as the Company’s Interim Chief Financial Officer. |
| ***** | Ronald Robinson was appointed CFO of the Company effective January 28, 2013. Accordingly, Mr. Robinson’s above listed compensation was received in his capacity as a consultant in 2012. |
| 36 |
OUTSTANDING EQUITY AWARDS AT FISCAL YEAR END
The following table sets forth with respect to grants of options to purchase our common stock to the executive officers as of December 31, 2014:
| Name | Number of
Securities Underlying Unexercised Options # Exercisable | Number of
Securities Underlying Unexercised Options # Un-exercisable | Equity
Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Unearned Options # | Option
Exercise Price $ | Option
Expiration Date | Number
of Shares or Units of Stock That Have Not Vested # | Market
Value of Shares or Units of Stock That have not vested $ | Equity
Incentive Plan Awards: Number of Unearned Shares Units or Other Rights That Have Not Vested # | Equity
Incentive Plan Awards Market or Payout Value of Unearned Shares Units or Other Rights That have not Vested $ | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Victor Keen, CEO | 11,078,538 | - | $ | 0.01 to 0.234 | 2018-2022 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mark Willner, former CEO | 228,572 | - | - | $ | 0.35 | 2017 | - | - | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Director Compensation 2014
| Name | Fees
Earned or Paid in Cash ($) | Stock
Awards ($) | Option
Awards ($) | Non-Equity
Incentive Plan Compensation ($) | Change in
Pension Value and Nonqualified Deferred Compensation Earnings ($) | All Other
Compensation ($) | Total ($) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Victor Keen | $ | - | - | $ | - | - | - | - | $ | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Martin Keating | $ | - | - | $ | - | - | - | - | $ | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| John O'Connor | $ | - | - | $ | - | - | - | - | $ | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Sidney Aroesty | $ | - | - | $ | - | - | - | - | $ | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| 37 |
ITEM 12. SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT
The following table provides information about shares of common stock beneficially owned as of March 27, 2015 by:
| · | each director; |
| · | each officer named in the summary compensation table; |
| · | each person owning of record or known by us, based on information provided to us by the persons named below, to own beneficially at least 5% of our common stock; and |
| · | all directors and executive officers as a group. |
| Number of Shares Beneficially | Percentage | |||||||||
| Name of Beneficial Owner (1) | Owned | Class of Stock | Outstanding (2) | |||||||
| Victor F. Keen, CEO, Director(3) | 54,598,690 | Common | 8.22 | % | ||||||
| Ronald Robinson , CFO(4) | 400,792 | Common | * % | |||||||
| Martin Keating , Director(5) | 2,635,524 | Common | * % | |||||||
| John O'Connor, Director (6) | 2,968,888 | Common | * % | |||||||
| All directors and executive officers as a group (4 persons) | 60,603,894 | Common | 9.09 | % | ||||||
| Golden State Investors, Inc. | 6,492,071 | Common | 1.06 | % | ||||||
| * | Less than 1% |
| (1) | Unless otherwise indicated, the address of each beneficial owner listed below is c/o 3DIcon Corporation, 6804 South Canton Avenue, Suite 150, Tulsa, Oklahoma 74136. |
| (2) | Applicable percentage ownership is based on 612,664,741 shares of common stock outstanding as of March 27, 2015. Beneficial ownership is determined in accordance with the rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission and generally includes voting or investment power with respect to securities. Options to acquire shares of common stock that are currently exercisable or exercisable within 60 days of March 27, 2015 are deemed to be beneficially owned by the person holding such securities for the purpose of computing the percentage of ownership of such person, but are not treated as outstanding for the purpose of computing the percentage. |
| (3) | Represents 3,020,152 shares owned by Mr. Keen and (i) 11,078,538 shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of vested options to purchase 11,078,538 shares of common stock at a weighted average of $0.09 per share; (ii) 1,500,000 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of a $15,000 Convertible Note; (iii) 19,000,000 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of a 265,000 shares of Series A convertible Preferred stock; and (iv) 20,000,000 common stock issuable upon conversion of a $60,000 convertible Note assuming a $0.003 conversion price. Does not include shares of common stock issuable upon exercise of warrants to purchase 13,250,000 shares of common stock, which warrant contains a 4.99% conversion limitation and which warrant was issued in connection with Mr. Keen’s purchase of 265,000 shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock. Victor Keen is our Chief Executive Officer and Director. |
| (4) | Represents 356,732 shares owned jointly with Mr. Robinson’s wife, Gayle A. Robinson, 999 shares in Mr. Robinson’s IRA, and 43,061 shares owned by Robinson, Freeman, PC, a corporation of which Mr. Robinson owns a 50% interest. Ronald Robinson is our Chief Financial Officer. |
| (5) | Represents (i) 1,942,499 shares of common stock owned by Mr. Keating, (ii) 286,453 options and (iii) 406,572 shares of common stock owned by Mr. Keating's wife, Judy Keating. |
| (6) | Represents (i) 3,143 shares of common stock owned by Mr. O'Connor and (ii) 2,857 shares of common stock owned by the John M. and Lucia D. O'Connor Revocable Living Trust over which Mr. O'Connor has voting and investment control and, (iii) 619,205 shares owned by Newton O’Connor & Ketchum (“NOTK”), a corporation of which Mr. O’Conner is partial owner; (iv) 1,144,710 shares of common stock issuable upon conversion of a $29,007 Convertible Note owned by NOTK; and (v) 1,198,973 options and warrants owned by Mr. O'Connor or NOTK. |
| 38 |
ITEM 13. CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE
Other than as set forth below, during the last two fiscal years there have not been any relationships, transactions, or proposed transactions to which 3DIcon was or is to be a party, in which any of the directors, officers, or 5% or greater stockholders (or any immediate family thereof) had or is to have a direct or indirect material interest.
3DIcon has engaged the law firm of Newton, O'Connor, Turner & Ketchum as its outside corporate counsel from 2005 through 2008 and certain legal services subsequent to 2008. John O'Connor, a director of 3DIcon, is the Chairman of Newton, O'Connor, Turner & Ketchum.
Director Independence
Of the members of the Company's Board of Directors, none of the members are considered to be independent under the listing standards of the Rules of NASDAQ set forth in the NASDAQ Manual.
ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL ACCOUNTANT FEES AND SERVICES
Audit Fees
The aggregate fees billed by our principal accountant for the audit of our annual financial statements, review of financial statements included in the quarterly reports and other fees that are normally provided by the accountant in connection with statutory and regulatory filings or engagements for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 were $68,700 and $66,262, respectively.
Audit-Related Fees
The aggregate fees billed by our principal accountant for assurance and advisory services that were related to the performance of the audit or review of our financial statements for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 were $0 and $0, respectively.
Tax Fees
The aggregate fees billed for professional services rendered by our principal accountant for tax compliance, tax advice and tax planning for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 were $0 and $0, respectively.
All Other Fees
The aggregate fees billed for products and services provided by our principal accountant for the fiscal years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 were $0 and $0, respectively.
Policy on Audit Committee Pre-Approval of Audit and Permissible Non-Audit Services of Independent Auditors
The Audit Committee's policy is to pre-approve all audit and permissible non-audit services provided by the independent auditors. These services may include audit services, audit-related services, tax services and other services. Pre-approval is generally provided for up to one year and any pre-approval is detailed as to the particular service or category of services and is generally subject to a specific budget. The independent auditors and management are required to periodically report to our Board of Directors regarding the extent of services provided by the independent auditors in accordance with this pre-approval, and the fees for the services performed to date. The Board of Directors may also pre-approve particular services on a case-by-case basis.
| 39 |
PART IV
| 3.1 | Certificate of Incorporation (1) |
| 3.2 | Bylaws (1) |
| 3.3 | Amended Certificate of Incorporation (1) |
| 3.4 | Amended Certificate of Incorporation (1) |
| 3.5 | Amended Certificate of Incorporation (1) |
| 3.6 | Amended Certificate of Incorporation (3) |
| 3.7 | Amended Certificate of Incorporation (6) |
| 3.8 | Amendment to the Bylaws as of April 4, 2013 (14) |
| 3.9 | Certificate of Designation of Preferences, Rights and Limitation of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock (20) |
| 4.1 | Convertible Promissory Note dated August 1, 2012 issued to JMJ Financial (7) |
| 4.2 | Form of Convertible Bridge Note (8) |
| 4.3 | Form of Convertible Debenture dated June 25, 2013 (18) |
| 4.4 | Senior Convertible Note dated October 1, 2013 (19) |
| 10.1 | Securities Purchase Agreement (1) |
| 10.2 | Amendment No. 1 to Securities Purchase Agreement and Debenture (1) |
| 10.3 | Registration Rights Agreement dated November 3, 2006(1) |
| 10.4 | $100,000 convertible debenture (1) |
| 10.5 | $1.25 million convertible debenture dated November 3, 2006 (1) |
| 10.6 | Common Stock Purchase Warrant (1) |
| 10.7 | Sponsored Research Agreement by and between 3DIcon Corporation and the Board of Regents of the University of Oklahoma (1) |
| 10.8 | Sponsored Research Agreement Modification No. 1 by and between 3DIcon Corporation and the Board of Regents of the University of Oklahoma (1) |
| 10.9 | Sponsored Research Agreement Modification No. 2 by and between 3DIcon Corporation and the Board of Regents of the University of Oklahoma (1) |
| 10.10 | Amendment No. 2 to Securities Purchase Agreement, Debentures, and Registration Rights Agreement (2) |
| 10.11 | Securities Purchase Agreement dated June 11, 2007 (2) |
| 40 |
| 10.12 | $700,000 Convertible Debenture (2) |
| 10.13 | $1.25 million convertible debenture dated November 21, 2007 (4) |
| 10.14 | Registration Rights Agreement dated November 21, 2007 (4) |
| 10.15 | Agreement to Convert Debt to Stock dated November 30, 2010 (5) |
| 10.16 | Agreement for At-Will Employment with Assignment of Inventions, dated June 13, 2011 (9) |
| 10.17 | Agreement for At-Will Employment with Assignment of Inventions, dated March 19, 2012 (10) |
| 10.18 | Registration Rights Agreement dated August 1, 2012 (11) |
| 10.19 | Form of Securities Purchase Agreement (8) |
| 10.20 | Amendment Agreement dated December 21, 2012 (12) |
| 10.21 | Form Amendment Agreement dated January 26, 2013 (13) |
| 10.22 | Third Amendment to Securities Purchase Agreement and Convertible Note, dated July 22, 2013 (15) |
| 10.23 | Settlement Agreement, dated July 17, 2013 (16) |
| 10.24 | Order Granting Approval of Settlement Agreement, dated July 26, 2013 (16) |
| 10.25 | Second Amendment to Securities Purchase Agreement and Convertible Note, dated July 30, 2013 (17) |
| 10.26 | Securities Purchase Agreement, dated October 1, 2013 (19) |
| 10.27 | Common Stock Purchase Warrant, dated October 1, 2013 (19) |
| 10.28 | Form of Common Stock Purchase Warrant (20) |
| 10.29 | Form of Securities Purchase Agreement (20) |
| 10.30 | Mutual Release, dated January 17, 2014 (21) |
| 10.31 | Stipulation of Dismissal with Prejudice, dated January 22, 2014 (21) |
| 31.1 | Certification by Chief Executive Officer, required by Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Exchange Act |
| 31.2 | Certification by Chief Financial Officer, required by Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Exchange Act |
| 32.1 | Certification by Chief Executive Officer, required by Rule 13a-14(b) or Rule 15d-14(b) of the Exchange Act and Section 1350 of Chapter 63 of Title 18 of the United States Code |
| 32.2 | Certification by Chief Financial Officer, required by Rule 13a-14(b) or Rule 15d-14(b) of the Exchange Act and Section 1350 of Chapter 63 of Title 18 of the United States Code |
| 41 |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation |
| (1) | Incorporated by reference to Form SB-2 as filed on December 15, 2006 (File No. 333-139420) and subsequently withdrawn on February 5, 2007 |
| (2) | Incorporated by reference to Form SB-2 as filed on June 14, 2007 (File No. 333-143761) |
| (3) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on December 7, 2010 (File No. 333-143761) |
| (4) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on November 26, 2007 (File No. 333-143761) |
| (5) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on December 23, 2010 (File No. 333-143761) |
| (6) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on May 2, 2012 (File No. 333-143761) |
| (7) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on August 7, 2012 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (8) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on August 31, 2012 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (9) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on June 14, 2011 (File No. 333-143761) |
| (10) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on March 21, 2012 (File No. 333-143761) |
| (11) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on August 7, 2012 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (12) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on December 31, 2012 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (13) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on January 31, 2013 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (14) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on April 5, 2013 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (15) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on July 26, 2013 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (16) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on July 31, 2013 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (17) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on August 5, 2013 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (18) | Incorporated by reference to Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q as filed on August 14, 2013 (File No. 000-54697) |
| 42 |
| (19) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on October 7, 2013 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (20) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on December 13, 2013 (File No. 000-54697) |
| (21) | Incorporated by reference to Current Report on Form 8-K as filed on January 28, 2014 (File No. 000-54697) |
SIGNATURES
In accordance with Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act, the registrant caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| 3DICON CORPORATION | ||
| Date: March 31, 2015 | /s/ Victor F. Keen | |
| Name: | Victor F. Keen | |
| Title: | Chief Executive Officer | |
| (Principal Executive Officer) | ||
| /s/ Ronald Robinson | ||
| Name: | Ronald W. Robinson | |
| Title: | Chief Financial Officer | |
| (Principal Financial Officer) | ||
In accordance with the Exchange Act, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| SIGNATURE | TITLE | DATE | |||
| By: | /s/ Martin Keating | Director | March 31, 2015 | ||
| Martin Keating | |||||
| By: | /s/ John O'Connor | Director | March 31, 2015 | ||
| John O'Connor | |||||
| By: | /s/ Victor F. Keen | Director | March 31, 2015 | ||
| Victor F. Keen | |||||
| 43 |
3DIcon CORPORATION
December 31, 2014 and 2013
CONTENTS
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
3DIcon Corporation
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of 3DIcon Corporation (the Company) as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related statements of operations, stockholders' deficiency, and cash flows for the years then ended. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of 3DIcon Corporation as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the results of its operations and its cash flows for the years then ended, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared assuming that the Company will continue as a going concern. As discussed in Note 1 to the financial statements, the Company is a development stage company having insufficient revenues and capital commitments to fund the development of its planned products. This raises substantial doubt about the Company's ability to continue as a going concern. Management's plan in regard to these matters is also described in Note 1. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might result from the outcome of this uncertainty.
/s/ HOGANTAYLOR LLP
Tulsa, Oklahoma
March 31, 2015
| F-1 |
3DIcon CORPORATION
BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Assets | ||||||||
| Current assets: | ||||||||
| Cash | $ | 34,485 | $ | 70,769 | ||||
| Prepaid expenses | 17,149 | 13,919 | ||||||
| Total current assets | 51,634 | 84,688 | ||||||
| Deferred debt costs, net | 3,125 | 25,455 | ||||||
| Deposits-other | 2,315 | 2,315 | ||||||
| Total Assets | $ | 57,074 | $ | 112,458 | ||||
| Liabilities and Stockholders' Deficiency | ||||||||
| Current liabilities: | ||||||||
| Current maturities of convertible notes and debentures payable | $ | 405,791 | $ | 612,744 | ||||
| Warrant exercise advances | 21,591 | 185,671 | ||||||
| Accounts payable | 384,639 | 140,410 | ||||||
| Accrued salaries | 158,102 | 1,713 | ||||||
| Accrued interest on debentures | 36,777 | 22,751 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities | 1,006,900 | 963,289 | ||||||
| Total Liabilities | 1,006,900 | 963,289 | ||||||
| Common stock subject to put rights and call right, 1,685,714 shares | - | 485,649 | ||||||
| Stockholders' deficiency: | ||||||||
| Preferred stock, Series A convertible, $0.0002 par value, 500,000 shares authorized; 355,000 and 195,000 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, respectively | 71 | 39 | ||||||
| Common stock $0.0002 par, 1,500,000,000 shares authorized; 539,674,567 and 248,191,444 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, respectively | 107,935 | 49,638 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital | 20,200,743 | 18,618,714 | ||||||
| Accumulated deficit | (21,258,575 | ) | (20,004,871 | ) | ||||
| Total Stockholders' Deficiency | (949,826 | ) | (1,336,480 | ) | ||||
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Deficiency | $ | 57,074 | $ | 112,458 | ||||
See notes to financial statements
| F-2 |
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
Years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Income: | ||||||||
| Sales | $ | 15,000 | $ | 4,500 | ||||
| Grant income | 70,748 | 43,896 | ||||||
| Total income | 85,748 | 48,396 | ||||||
| Expenses: | ||||||||
| Research and development | 198,550 | 372,984 | ||||||
| General and administrative | 1,065,167 | 1,077,106 | ||||||
| Interest | 75,735 | 80,355 | ||||||
| Total expenses | 1,339,452 | 1,530,445 | ||||||
| Net loss | $ | (1,253,704 | ) | $ | (1,482,049 | ) | ||
| Loss per share: | ||||||||
| Basic and diluted | $ | (0.003 | ) | $ | (0.014 | ) | ||
| Weighted average shares outstanding, Basic and diluted | 394,420,243 | 105,435,660 | ||||||
See notes to financial statements
| F-3 |
STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS' DEFICIENCY
Years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013
| Preferred Stock | Common Stock | Additional | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Par | Par | Paid-In | Accumulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Value | Shares | Value | Capital | Deficit | Total | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, December 31, 2012 | - | - | 45,934,839 | 9,187 | 17,044,786 | (18,522,822 | ) | (1,468,849 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Warrants and options exercised | - | - | 1,103 | 1 | 420,739 | - | 420,740 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Debentures converted | - | - | 175,264,242 | 35,053 | 533,775 | - | 568,828 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock issued for services | - | - | 25,892,479 | 5,178 | 290,172 | - | 295,350 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock issued for liabilities | - | - | 1,098,751 | 219 | 31,281 | - | 31,500 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred stock and options issued for cash | 195,000 | 39 | - | - | 267,961 | - | 268,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Warrants issued to purchase common stock | - | - | - | - | 30,000 | - | 30,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss for the year | - | - | - | - | - | (1,482,049 | ) | (1,482,049 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance December 31, 2013 | 195,000 | 39 | 248,191,414 | 49,638 | 18,618,714 | (20,004,871 | ) | (1,336,480 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Warrants and options exercised | - | - | 1,347 | 1 | 513,389 | - | 513,390 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Debentures converted | - | - | 245,458,693 | 49,092 | 287,460 | - | 336,552 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock issued for services | - | - | 28,205,571 | 5,641 | 102,859 | - | 108,500 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock issued for liabilities | - | - | 13,131,828 | 2,626 | 3,641 | - | 6,267 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred stock and options issued for cash | 190,000 | 38 | - | - | 155,036 | - | 155,074 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred stock converted to common shares | (30,000 | ) | (6 | ) | 3,000,000 | 600 | (594 | ) | - | - | ||||||||||||||||||
| Warrants issued to purchase common stock | - | - | - | - | 34,926 | - | 34,926 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares subject to expired put calls restored | - | - | 1,685,714 | 337 | 485,312 | - | 485,649 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss for the year | - | - | - | - | - | (1,253,704 | ) | (1,253,704 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
| Balance December 31, 2014 | 355,000 | $ | 71 | 539,674,567 | $ | 107,935 | $ | 20,200,743 | $ | (21,258,575 | ) | $ | (949,826 | ) | ||||||||||||||
See notes to financial statements
| F-4 |
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities | ||||||||
| Net loss | $ | (1,253,704 | ) | $ | (1,482,049 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: | ||||||||
| Stock issued for services | 108,500 | 295,350 | ||||||
| Amortization of debt issuance costs | 77,109 | 61,434 | ||||||
| Depreciation | - | 4,280 | ||||||
| Change in: | ||||||||
| Accounts receivable | - | 13,028 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets | (3,230 | ) | (1,309 | ) | ||||
| Accounts payable and accrued liabilities | 420,911 | 46,327 | ||||||
| Net cash used in operating activities | (650,414 | ) | (1,062,939 | ) | ||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities | ||||||||
| Proceeds from stock and warrant sales, exercise of warrants and warrant exercise advances | 539,310 | 969,810 | ||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of debentures, notes and options | 215,500 | 283,068 | ||||||
| Cash paid on debentures | (140,680 | ) | (120,520 | ) | ||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities | 614,130 | 1,132,358 | ||||||
| Net change in cash | (36,284 | ) | 69,419 | |||||
| Cash, beginning of period | 70,769 | 1,350 | ||||||
| Cash, end of period | $ | 34,485 | $ | 70,769 | ||||
| Supplemental Disclosures | ||||||||
| Non-Cash Investing and Financing Activities | ||||||||
| Conversion of debentures to common stock (net) | $ | 336,552 | $ | 568,828 | ||||
| Cash paid for interest | $ | 11,928 | $ | 21,145 | ||||
| Stock issued to satisfy payables | $ | 6,267 | $ | 31,500 | ||||
| Debenture issued to satisfy payable | $ | - | $ | 197,631 | ||||
See notes to financial statements
| F-5 |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Note 1 – Organization and Operations
Organization
3DIcon Corporation (the "Company") was incorporated on August 11, 1995, under the laws of the State of Oklahoma as First Keating Corporation. The articles of incorporation were amended August 1, 2003 to change the name to 3DIcon Corporation. The initial focus of First Keating Corporation was to market and distribute books written by its founder, Martin Keating. During 2001, First Keating Corporation began to focus on the development of 360-degree holographic technology. The effective date of this transition is January 1, 2001, and the financial information presented is from that date through the current period. The Company accounted for this transition as reorganization and accordingly, restated its capital accounts as of January 1, 2001. From January 1, 2001, the Company's primary activity has been the raising of capital in order to pursue its goal of becoming a significant participant in the development, commercialization and marketing of next generation 3D display technologies.
The mission of the Company is to develop (or acquire), commercialize, and market next generation 3D display technologies including auto-stereoscopic (glasses-free) volumetric 360-degree full-color 3D displays and possibly auto-stereoscopic (glasses-free) flat screen 3D displays. The Company’s initial market focus is on business, industrial, and government applications of the technologies. At this time the Company owns no intellectual property in 3D displays but does own the exclusive worldwide rights to commercial and government usage of the 3D display intellectual property developed by the University of Oklahoma.
Uncertainties
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared on a going concern basis. The Company is in the development stage and has insufficient revenue and capital commitments to fund the development of its planned product and to pay operating expenses.
The Company has realized a cumulative net loss of $21,258,575 for the period from inception (January 1, 2001) to December 31, 2014, and a net loss of $1,253,704 and $1,482,049 for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
The ability of the Company to continue as a going concern during the next year depends on the successful completion of the Company's capital raising efforts to fund the development of its planned technologies. The financial statements do not include any adjustments that might be necessary if the Company is unable to continue as a going concern.
Management plans to fund the future operations of the Company with existing cash of $34,485, grants and investor funding. Under the terms of the Golden State 4.75% Convertible Debenture due on December 31, 2015 as a result of a maturity extension agreement received by the Company in March 2015, beginning in November 2007, Golden State is obligated to submit conversion notices in an amount such that Golden State receives 1% of the outstanding shares of the Company every calendar quarter for a period of one year. In connection with each conversion, Golden State is expected to simultaneously exercise a percentage of warrants equal to the percentage of the principal being converted. The warrants are exercisable at $381.50 per share. The number of warrants exercisable is subject to certain beneficial ownership limitations contained in the 4.75% Convertible Debenture (“the Beneficial Ownership Limitations”). The Beneficial Ownership Limitations prevent Golden State from converting on the 4.75% Convertible Debenture or exercising warrants if such conversion or exercise would cause Golden State’s holdings to exceed 9.99% of the Company’s issued and outstanding common stock. Subject to the Beneficial Ownership Limitations and provided that Golden State is able to sell the shares under Rule 144, Golden State is required to convert $85.71 of the 4.75% Convertible Debenture and exercise 857 warrants per month. Based upon the current stock price, the issued and outstanding shares as of December 31, 2014 and ignoring the impact of the Beneficial Ownership Limitations, the Company may receive up to $327,000 per month in funding from Golden State as a result of warrant exercises. Due to the Beneficial Ownership Limitations, the Company received $349,310 in advances from Golden State during the year ended December 31, 2014. Such advances are recorded within warrant exercise advances on the balance sheet when received.
| F-6 |
On July 2, 2013, the Company was awarded a $300,000 grant in the 2013 Oklahoma Applied Research Support competition sponsored by the Oklahoma Center for the Advancement of Science and Technology (“OCAST”). The money is being used to support the development of the Company’s first Product Platform, which will be the basis for a family of products based on the Company’s CSpace® volumetric 3D display technology. (see Note 5)
As part of the Company’s federal funding strategy the Company intends to effectively compete by forming interdisciplinary teams with potential strategic partners (large and small), academic and commercial laboratories, and systems integrators providing integrated data visualization solutions. The first of these partnerships was reached in March 2014 when the Company signed a Joint Development Agreement with Schott Defense, a federally focused subsidiary of Schott North America.
Additionally, the Company is continuing to pursue financing through private offering of debt or common stock.
Note 2 – Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Research and development
Research and development costs, including payments made to the University pursuant to the SRA, are expensed as incurred (see Note 4).
Stock-based compensation
The Company accounts for stock-based compensation arrangements for employees in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") No. 718, Compensation-Stock Compensation. The Company recognizes expenses for employee services received in exchange for stock based compensation based on the grant-date fair value of the shares awarded. The Company accounts for stock issued to non-employees in accordance with the provisions of ASC No. 718.
Income taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes in accordance with ASC No. 740, Income Taxes. This standard requires the recognition of deferred tax assets and liabilities for the estimated future tax consequences attributable to temporary differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases. In addition, this standard requires the recognition of future tax benefits, such as net operating loss carry forwards, to the extent that realization of such benefits is more likely than not. The amount of deferred tax liabilities or assets is calculated using tax rates in effect for the year in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rate is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. Valuation allowances are established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the amounts more likely than not to be realized.
Net loss per common share
The Company computes net loss per share in accordance with ASC No. 260, Earnings Per Share. Under the provisions of this standard, basic net loss per common share is based on the weighted-average outstanding common shares. Diluted net loss per common share is based on the weighted-average outstanding shares adjusted for the dilutive effect of warrants to purchase common stock and convertible debentures. Due to the Company's losses, such potentially dilutive securities are anti-dilutive for all periods presented. The weighted average number of potentially dilutive shares is 42,819,990 and 33,321,337 for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
| F-7 |
Use of estimates
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U. S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues, expenses and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. Actual results could differ from the estimates and assumptions used.
Debt issue costs
The Company defers and amortizes the legal and filing fees associated with long-term debt that is issued. These costs are primarily related to the convertible debentures, the majority of which have a one year term. The amortization is charged to operations over the one year term and then adjusted quarterly for debenture conversions to common stock.
Fair value of financial instruments
The following methods and assumptions were used to estimate the fair value of each class of financial instrument held by the Company:
Current assets and current liabilities – The carrying value approximates fair value due to the short maturity of these items.
Debentures payable – The fair value of the Company's debentures payable has been estimated by the Company based upon the liability's characteristics, including interest rate. The carrying value approximates fair value.
Note 3 – Recent Accounting Pronouncements
The following is a summary of recent accounting pronouncements that are relevant to the Company:
In June 2014, the FASB issued “Development Stage Entities – Elimination of Certain Financial Reporting Requirements, Including an Amendment to Variable Interest Entities Guidance in Topic 810, Consolidation” (“ASU 2014-10”). ASU 2014-10 eliminates the concept of a development stage entity, thereby eliminating the financial reporting distinction between development stage entities and other reporting entities. As a result of the elimination, certain financial reporting disclosures have been eliminated as well, including the presentation of inception-to-date information and the labeling of financial statements as those of a development stage entity. ASU 2014-10 is effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years, beginning after December 15, 2014. Early adoption of this standard is permitted, and we adopted the standard as of July 1, 2014. Subsequent to the adoption of ASU 2014-10, the Company no longer presents inception-to-date information in the statements of operations, cash flows, and stockholders’ equity.
The FASB has issued ASU No. 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. This ASU supersedes the revenue recognition requirements in FASB ASC 605 - Revenue Recognition and most industry-specific guidance throughout the Codification. The standard requires that an entity recognizes revenue to depict the transfer of promised goods or services to customers in an amount that reflects the consideration to which the company expects to be entitled in exchange for those goods or services. This ASU is effective on January 1, 2017 and should be applied retrospectively to each prior reporting period presented or retrospectively with the cumulative effect of initially applying the ASU recognized at the date of initial application. The adoption of this standard is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s financial position and results of operations.
The FASB has issued ASU No. 2014-12, Compensation - Stock Compensation (ASC Topic 718): Accounting for Share-Based Payments When the Terms of an Award Provide That a Performance Target Could Be Achieved after the Requisite Service Period. This ASU requires that a performance target that affects vesting, and that could be achieved after the requisite service period, be treated as a performance condition. As such, the performance target should not be reflected in estimating the grant date fair value of the award. This update further clarifies that compensation cost should be recognized in the period in which it becomes probable that the performance target will be achieved and should represent the compensation cost attributable to the period(s) for which the requisite service has already been rendered.. The amendments in this ASU are effective for annual periods and interim periods within those annual periods beginning after December 15, 2015. Earlier adoption is permitted. The adoption of this standard is not expected to have a material impact on the Company's financial position and results of operations.
Note 4 – Sponsored Research Agreement ("SRA") Common Stock Subject to Put Rights and Call Right
Since April 20, 2002, the Company has entered into a number of SRAs with the University of Oklahoma (“OU”) as follows:
Phase I: “Pilot Study to Investigate Digital Holography”, April 20, 2004. The Company paid the University $14,116.
Phase II: “Investigation of 3-Dimensional Display Technologies”, April 15, 2005, as amended. The Company paid the University $528,843.
Phase III: “3-Dimensional Display Development”. The Company made partial payment to the University by issuing 121,849 shares with a market price of $290,000 on October 14, 2008 and final payment on December 1, 2010 in the amount of $525,481 of which $40,481 was in cash and 1,685,714 shares of Company stock (the “Shares”). The Shares were subject to the University ‘put’ right and a 3Dicon ‘call’ right.
| F-8 |
The University “Put” Rights on the Shares
First “put” period: December 1, 2012 to November 30, 2013. If the Shares (held plus previously sold) are valued at less than $100,000 then the University can “put” one-tenth of the Shares for $50,000 plus accrued interest retro-active to December 1, 2012 less the value of sold shares. The University currently holds 1,807,563 shares with a market value of less than $100,000. Under the terms of put rights, the put rights could be exercised by the University and the Company would be obligated to pay the University $50,000.
Second “put” period: December 1, 2013 to November 30, 2014. If the Shares (held & previously sold) are valued at less than $970,000 than the University can “put” the remaining Shares for $485,000 plus accrued interest retro-active to December 1, 2012 less the value of shares previously sold or redeemed during the first “put”.
The “put” periods expired without the University taking any action. The shares have therefore been restored to the equity section of the Balance Sheet as of December 31, 2014 as the shares are no longer subject to the put and call options.
3DIcon “Call” rights on the Shares
Commencing December 1, 2012, the Company shall have the right to “call” the Shares for an amount equal to $970,000 less the amount (if any) of prior shares by the University including amounts “put” to 3DIcon.
The Company has presented the shares outside of deficit in the mezzanine section of the balance sheets through November 30, 2014 as the Agreement includes put rights, which are not solely within the control of the Company.
The Agreement also amended the existing agreements between the Company and the University such that all intellectual property, including all inventions and or discoveries, patentable or un-patentable, developed before July 28, 2008 by the University under the SRA is owned by OU. All intellectual property, including all inventions and/or discoveries, patentable or un-patentable, developed jointly by the Company and the University at any time is jointly owned by the Company and OU. Finally, all intellectual property developed by the Company after July 28, 2008, including all inventions and or discoveries, patentable or un-patentable, is owned by the Company.
Note 5 – OCAST Grant
In July 2013, the Company was awarded a two year grant from OCAST. This is the second $300,000 grant received from OCAST. The first grant was completed in August 2012. This matching grant is for a total of $300,000 and commenced September 1, 2013. The Company earned $70,748 and $43,896 from the grant during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The funds are being used to support the development of the Company’s first Product Platform, which will be the basis for a family of products based on the Company’s CSpace® volumetric 3D display technology.
Note 6 – Consulting Agreements
Concordia Financial Group
The Company entered into a one-year Independent Consulting Agreement with Concordia Financial Group (“Concordia”) effective November 1, 2007, and month-to-month thereafter. Under the terms of the agreement Concordia will serve as liaison to Golden State Investors, Inc. and provide business strategy services by assisting the Company by reviewing and evaluating the Company's plans, personnel, board composition, technology, development of business models, building financial models for projections, developing materials to describe the Company, developing capital sources and assisting and advising the Company in its financial negotiations with capital sources. Concordia also advises with respect to effective registration of offerings of Company securities, the management team, the Company's development of near and long-term budgets, marketing strategies and plans, and assists in presentations related to the above services. Concordia is paid a monthly fee of $15,750. Concordia, at its option, may take up to 100% of this monthly fee in registered stock at 50% discount to market; and the Company, at its option, may pay up to 50% of Concordia's monthly invoice in registered stock, at 50% discount to market, provided that the payment of stock is made within ten (10) days of receipt of invoice and further provided that the stock trades above $.30 per share at any time during the last business day of the month. Market is defined as the five day average of closing prices immediately preceding the last business day of the calendar month in which the invoiced services were rendered. The monthly fee was reduced to $15,000 monthly effective June 1, 2013 under the revised terms of the agreement. Effective March 1, 2014 the agreement was revised again to reduce the monthly fee to $12,500 monthly. The Company incurred consulting fees of $155,000 and $183,750, respectively for services from Concordia during each of the periods ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, under the terms of the agreement.
| F-9 |
Bayside Materials Technology
The Company entered into a Consulting Agreement with Bayside Material Technology (“Bayside”) effective November 1, 2013. Under the terms of the agreement Bayside will provide consulting services in the area of Federal Business Development. Bayside is paid an hourly fee of $176 for each hour of consulting time through the period ending November 11, 2014. The Company incurred consulting fees of $90,244 and -0- for the years ending December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 respectively.
Note 7 – Debentures and Notes Payable
Debentures payable consist of the following:
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Senior Convertible Debentures: | ||||||||
| 10% Convertible debentures to Directors due June 2015 | $ | 30,000 | $ | 30,000 | ||||
| 10% Convertible debenture due June 2015 | 29,007 | 29,007 | ||||||
| 4.75% Convertible debenture due December 2014 | 65,095 | 69,805 | ||||||
| 5.0% Convertible notes due 2014 (net of $498 and $19,115 OID) | 74,502 | 123,590 | ||||||
| 10% Convertible bridge notes due August 2015 (net of $2,813 OID) | 147,187 | - | ||||||
| 15% Convertible bridge notes due 2014 (net of $23,500 OID) | - | 181,500 | ||||||
| Settlement Agreement 3(a)(10) | - | 118,842 | ||||||
| 10% Convertible bridge note to Director due December 2014 | 60,000 | 60,000 | ||||||
| Total Debentures Payable | $ | 405,791 | $ | 612,744 | ||||
10% Convertible Debentures to Directors due December 31, 2014 and subsequently extended to June 30, 2015
On June 24, 2013, the Company issued to Victor Keen and Martin Keating, Directors of the Company, (“Directors”) 10% convertible debentures in a principal amount of $15,000 each, due June 26, 2014 and subsequently extended to June 30, 2015. The Directors may elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the debentures at an exercise price of $0.01 per share. Provided that the debentures are paid in full on or before the maturity date, no interest shall accrue on the unpaid balance of the principal amount. In the event that the debentures are not paid in full on or before the maturity date, interest shall accrue on the unpaid outstanding balance of the principal amount of the debentures from June 26, 2013, until paid, at the fixed rate of ten percent (10%) per annum.
10% Convertible Debenture due Newton, O'Connor, Turner & Ketchum, due December 31, 2014 and subsequently extended to June 30, 2015
On December 20, 2012, the Company issued to Newton, O'Connor, Turner & Ketchum (“NOTK”) a 10% convertible debenture in a principal amount of $29,007, initially due September 30, 2013 and extended to June 30, 2014 and subsequently extended to June 30, 2015. NOTK may elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the debenture at an exercise price of $0.02534 per share. The Company was indebted to NOTK for legal services performed for the Company and reimbursement of expenses in rendition of those services for the period ended December 31, 2012. The debenture was issued in settlement of the indebtedness.
| F-10 |
4.75% Convertible Debenture due December 31, 2014
On November 3, 2006, the Company issued to Golden State a 4.75% convertible debenture in a principal amount of $100,000, due in December 31, 2014, (see Note 12) and warrants to buy 28,571 shares of the common stock at an exercise price of $381.50 per share. In connection with each conversion, Golden State is expected to simultaneously exercise a percentage of warrants equal to the percentage of the principal being converted. During 2013, Golden State converted $3,860 of the $100,000 debenture into 37,651,544 shares of common stock, exercised warrants to purchase 1,103 shares of common stock at $381.50 per share based on the formula in the convertible debenture. Additionally Golden State advanced $671,810 against future exercises of warrants of which $420,740 was applied to the exercise of warrants leaving $185,671 of unapplied advances at December 31, 2013. During 2014, Golden State converted $4,710 of the $100,000 debenture into 98,093,643 shares of common stock, exercised warrants to purchase 1,347 shares of common stock at $381.50 per share based on the formula in the convertible debenture. Additionally Golden State advanced $349,310 against future exercises of warrants of which $513,390 was applied to the exercise of warrants leaving $21,591 of unapplied advances at December 31, 2014.
The conversion price for the 4.75% $100,000 convertible debenture is the lesser of (i)$140 or (ii) 80% of the average of the five lowest volume weighted average prices during the twenty (20) trading days prior to the conversion. If Golden State elects to convert a portion of the debenture and, on the day that the election is made, the volume weighted average pre-split price is below $0.70, the Company shall have the right to prepay that portion of the debenture that Golden State elected to convert, plus any accrued and unpaid interest, at 135% of such amount.
5% Convertible Bridge Notes
On June 6, 2012 and August 1, 2012, the Company issued and sold convertible promissory notes (the “5% Notes") in aggregate principal amount of $415,000 to JMJ Financial (“JMJ”). The 5% Notes includes a $40,000 original issue discount (the “OID”) that will be prorated based on the advances actually paid to the Company. During 2012, JMJ advanced $150,000 on the 5% Notes and earned $14,000 OID. During 2013, JMJ advanced an additional $120,000 on the 5% Notes and earned $32,205 OID and accrued interest. During 2013, JMJ converted $203,700 of the 5% Notes into 31,854,924 shares of common stock at an average of $0.00639 per share based on the formula in the 5% Notes. During 2014, JMJ advanced an additional $75,000 on the 5% Notes and earned $5,975 OID and accrued interest. During 2014, JMJ converted $148,680 of the 5% Notes into 47,848,529 shares of common stock at an average of $0.003 per share based on the formula in the 5% Notes. In addition to the OID, the 5% Notes provides for a one-time interest charge of 5% to be applied to the principal sum advanced. Pursuant to the terms of 5% Notes, JMJ may, at its election, convert all or a part of the $275,000 note and the $140,000 note into shares of the Company's common stock at a conversion rate equal to the lesser of (i) $0.15 and $0.35, respectively or (ii) 70% of the lowest trade price during the twenty-five trading days prior to JMJ’s election to convert. If the Company repays the 5% Notes on or before ninety days from the date it was issued, the interest rate will be zero percent. If the Company does not repay the 5% Notes on or before ninety days from the date it was issued, a one-time interest charge of 5% shall be applied to the principal. The Company did not repay the 5% Notes within the ninety day period. The principal of the 5% Notes is due one year from the date of each of the principal amounts advanced.
The 5% Notes were subject to a Mandatory Registration Agreement (the “Registration Agreement”) whereby no later than August 31, 2012, the Company agreed to file, at its own expense, an amendment (the “Amendment”) to the S-1 Registration Statement (the “Registration Statement”) the Company filed with the SEC on July 3, 2012, to include in such Amendment 4,750,000 shares of common stock issuable under the 5% Notes. The Company agreed, thereafter, to use its best efforts to cause such Registration Statement to become effective as soon as possible after such filing but in no event later than one hundred and twenty (120) days from the date of the Registration Agreement. Since the Company failed to get the Registration Statement declared effective within the 120 days of the date of the Registration Agreement, a penalty/liquidated damages of $25,000 was added to the balance of the 5% Notes.
10% Convertible Debenture due August 2015
On August 15, 2014, the Company issued and sold to an accredited investor a Convertible Debenture (the “10% Debenture”) in the principal amount of $150,000. The 10% Debenture included a 3% original issue discount. Accordingly, the Company received $145,500 gross proceeds, from which the Company paid legal and fees of $5,000. The 10% Debenture has a maturity date of August 15, 2015 and carries a 10% interest rate. Subject to a 4.99% beneficial ownership limitation, the holder of the 10% Debenture may, at any time, elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the 10% Debenture into shares of Common Stock at a conversion price equal Sixty Five Percent (65%) of the lowest traded VWAP, determined on the then current trading market for the Company’s common stock, for 15 trading days prior to conversion.
| F-11 |
10% Convertible Bridge Notes
On August 24, 2012, August 28, 2012 and September 11, 2012, the Company issued and sold to three accredited investors Convertible Bridge Notes (the “Bridge Notes”) in the aggregate principal amount of $438,000. The note sold on August 24, 2012, in principal amount of $300,000, was purchased by GCA Strategic Investment Fund Limited, a Bermuda corporation ("GCASIF"). The note sold August 28, 2012, in principal amount of $78,000, was purchased by George Widener. The note sold on September 11, 2012, in principal amount of $60,000, was purchased by Victor Keen, a director of the Company. The sale of the Bridge Notes in aggregate principal of $438,000 included a $73,000 original issue discount. Accordingly, the Company received $365,000 gross proceeds from which the Company paid legal fees of $25,000 and placement agent fees of $27,675. The Bridge Notes mature in 90 days from their date of issuance and, other than the original issue discount, the Bridge Notes do not carry interest. However, in the event the Bridge Notes are not paid on maturity, all past due amounts will accrue interest at 15% per annum. Upon maturity of the Bridge Notes, the holders of the Bridge Notes may elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the Bridge Notes into (i) securities sold pursuant to an effective registration statement at the applicable offering price; or (ii) shares of common stock at a conversion price equal to the lesser of 100% of the Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP), as reported for the 5 trading days prior to (a) the date of issuance of the Bridge Notes, (b) the maturity date of the Bridge Notes, or (c) the first closing date of the securities sold pursuant an effective registration statement. The GCA Bridge Note matured on or about November 22, 2012, on which date all past due amounts of the GCA Bridge Note began accruing interest at 15% per annum. Furthermore, on November 22, 2012, because the shares of the Company’s common stock into which the GCA Bridge Note is convertible were not registered under an effective registration statement (the “Registration Statement”), GCASIF was entitled to liquidated damages equal to 2% of the outstanding principal for each 30 day period after the November 22, 2012 the Registration Statement is not declared effective (the “Liquidated Damages”).
On December 21, 2012, the Company entered into an amendment agreement (the “GCASIF Amendment”) with GCASIF, the holder of that certain Convertible Bridge Note (the “GCA Bridge Note”) in the principal amount of $300,000. Pursuant to the GCASIF Amendment, GCASIF agreed to extend the maturity of the GCA Bridge Note from November 22, 2012 to March 21, 2013 and the Company agreed to (i) increase the principal amount of the GCA Bridge Note from $300,000 to $325,000; (ii) amend the conversion price of the GCA Bridge Note to the lesser of $0.04, or 100% of the VWAP, as reported by Bloomberg, L.P., for the 5 trading days prior to the effective date of the Registration Statement; and (iii) grant additional registration rights to GCASIF from 5,172,414 shares to 8,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock into which the GCA Bridge Note may be convertible. Furthermore, GCASIF agreed to waive any and all defaults, default interest and the Liquidated Damages due to GCASIF. In connection with the GCASIF Amendment, the Company agreed to pay GCASIF a fee of $20,000. GCASIF agreed to waive any defaults resulting from the non-payment of the GCA Bridge Note, so long as, GCASIF is paid in full by April 15, 2013 or GCASIF elects to convert the GCA Bridge Note into shares of the Company’s common stock on or before April 15, 2013. In April 2013, the GCA Bridge Note was assigned to a successor in interest and the Company executed an amendment to the GCA Bridge Note in order to extend the maturity until July 22, 2014 and reduce the conversion price to the greater of (x) the par value of the Common Stock, or (y) 60% of the lowest closing bid price, as reported by Bloomberg, L.P., for the 10 trading days prior to the date the conversion of all or part of its principal and interest are requested. During 2013, GCASIF converted $204,480 of the note into 48,811,800 shares of common stock at an average of $0.0042 per share based on the formula in the note. The $120,520 remaining balance on the note was paid in cash in December 2013.
On January 26, 2013, the Company entered into an amendment agreement (the “Widener Amendment”) with George Widener, the holder of that certain Convertible Bridge Note (the “Widener Bridge Note”) in the principal amount of $78,000 issued by the Company on August 30, 2012.
The Widener Bridge Note matured on or about November 26, 2012, on which date all past due amounts of the Widener Bridge Note began accruing interest at 15% per annum. Pursuant to the Widener Amendment, Mr. Widener agreed to extend the maturity date of the Widener Bridge Note from November 26, 2012 to April 30, 2013 and to waive any and all defaults, default interest and Liquidated Damages then due to Mr. Widener. On April 30, 2013, Mr. Widener converted the entire $78,000 balance of the Widener Bridge Note into 2,025,974 shares of common stock.
| F-12 |
On January 26, 2013, the Company entered into an amendment agreement (the “Keen Amendment”) with Victor F. Keen, the holder of that certain Convertible Bridge Note (the “Keen Bridge Note”) in the principal amount of $60,000 issued by the Company on September 10, 2012.
The Keen Bridge Note matured on or about December 10, 2012, on which date all past due amounts of the Keen Bridge Note began accruing interest at 15% per annum. Pursuant to the Keen Amendment, Mr. Keen agreed to extend the maturity date of the Keen Bridge Note from December 10, 2012 to April 30, 2013 and to waive any and all defaults, default interest and Liquidated Damages then due to Mr. Keen.
On July 30, 2013 (the “Amendment Date”), the Company entered into a second amendment agreement (the “Second Keen Amendment”) with Mr. Keen to amend the Keen Bridge note.
Pursuant to the Second Keen Amendment, Mr. Keen agreed to extend the maturity of the Note from May 15, 2013 to August 31, 2013 (the “New Maturity Date”) and to waive, if any, existing or prior defaults under the Keen Bridge Note or the Keen SPA and the Company agreed to (i) amend the conversion provision to allow for conversions based on a conversion price calculated on the Amendment Date or the New Maturity Date; and (ii) to include an interest rate equal to 10% per annum, payable on the New Maturity Date, as amended, which accrual shall commence on December 10, 2012.
On September 30, 2013 (the “Amendment Date”), the Company entered into a third amendment agreement (the “Third Keen Amendment”) with Victor Keen, a Director on the Board of Directors of the Company, to amend the Keen Bridge note. Pursuant to the Third Keen Amendment, Mr. Keen agreed to extend the maturity of the Note from August 31, 2013 to December 31, 2013 (the “New Maturity Date”) and to waive, if any, existing or prior defaults under the Keen Bridge Note or the Keen SPA.
On January 27, 2014, the Company entered into a fourth amendment agreement (the “Fourth Keen Amendment”) with Mr. Keen. Pursuant to the Fourth Keen Amendment, Mr. Keen agreed to extend the maturity of the Note from December 31, 2013 to December 31, 2014 and to waive, if any, existing or prior defaults under the Keen Bridge Note or the Keen SPA.
(see Note 12)
15% Convertible Bridge Notes due 2014
On October 1, 2013 (the “Date of Issuance”), 3DIcon Corporation issued and sold to an accredited investor a Senior Convertible Note (the “Senior Note”) in the principal amount of $205,000 and a warrant to purchase 300,000 shares of the Company’s common stock at an exercise price equal to 110% of the closing bid price on September 30, 2013 (the “October 2013 Warrant”). The Senior Note included a $30,750 original issue discount. Accordingly, the Company received $174,250 gross proceeds from which the Company paid legal and documentation fees of $22,500 and placement agent fees of $15,682.
The Senior Note matured on July 1, 2014 and does not carry interest. However, in the event the Senior Note is not paid on maturity, all past due amounts will accrue interest at 15% per annum. At any time subsequent to six months following the Date of Issuance, the Senior Note holder may elect to convert all or any portion of the outstanding principal amount of the Senior Note into shares of Common Stock at a conversion price equal to the lesser of 100% of the Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP), as reported for the 5 trading days prior to the Date of Issuance or 80% of the average VWAP during the 5 days prior to the date the holder delivers a conversion notice to the Company. During 2014, the holder of the $205,000 note converted $180,000 of the note into 83,705,721 common shares at an average price of $0.002 per share under the terms of the debenture agreement. The remaining $25,000 balance of the note was paid in cash to retire the note.
| F-13 |
The estimated fair value of the warrants for common stock issued of $2,130 was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The expected dividend yield of zero is based on the average annual dividend yield as of the issue date. Expected volatility of 173.64% is based on the historical volatility of our stock. The risk-free interest rate of 1.39% is based on the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rate for five years as of the issue date. The expected life of five years of the warrant is based on historical exercise behavior and expected future experience.
The October 2013 Warrant is exercisable at any time on or after March 31, 2014 and on or prior to the close of business on March 31, 2019. At the election of the October 2013 Warrant holder, the October 2013 Warrant may be exercised using a cashless exercise method.
The Senior Note and October 2013 Warrant were offered and sold to an accredited investor on October 1, 2013 in a private placement transaction made in reliance upon exemptions from registration pursuant to Section 4(2) under the Securities Act of 1933.
Effective August 15, 2014, the Company entered into a Securities Settlement Agreement (the “SSA”) with an accredited investor (the “Investor”) to whom the $205,000 Senior Convertible Note was assigned. Pursuant to the SSA, the Investor agreed to extend the maturity of the $205,000 principal owed (the “Debt”) under the Senior Note until August 15, 2015 and the Company agreed, among other things, to (i) pay 10% interest on the Debt; (ii) pay 125% of principal in the event the Company elects to prepay any portion of the Debt; (iii) allow the Investor to convert the Debt, in whole or in part, into shares of the Company’s common stock at a conversion price equal to 58% percent of the lowest traded VWAP, determined on the then current trading market for the Company’s common stock, for the 15 trading days prior to conversion.
Settlement Agreement
On July 26, 2013, the Circuit Court in the 12th Judicial Circuit in and for Sarasota County, Florida (the “Court”), entered an Order Granting Approval of Settlement Agreement (the “Order”) approving, among other things, the fairness of the terms and conditions of an exchange pursuant to Section 3(a)(10) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, in accordance with a Settlement Agreement (the “Settlement Agreement”) between the Company and IBC Funds, LLC, a Nevada limited liability company (“IBC”), in the matter entitled IBC Funds, LLC v. 3DIcon Corporation, Case No. 2013 CA 5705 NC (the “Action”). IBC commenced the Action against the Company on July 19, 2013 to recover an aggregate of $197,631 of past-due accounts payable of the Company, which IBC had purchased from certain vendors of the Company pursuant to the terms of separate claim purchase agreements between IBC and each of such vendors (the “Assigned Accounts”), plus fees and costs (the “Claim”). The Assigned Accounts relate to certain research, technical, development, accounting and legal services. The Order provides for the full and final settlement of the Claim and the Action. The Settlement Agreement became effective and binding upon the Company and IBC upon execution of the Order by the Court on July 26, 2013.
Pursuant to the terms of the Settlement Agreement approved by the Order, on July 26, 2013, the Company issued 650,000 shares of Common Stock as a settlement fee and agreed to issue, in one or more tranches as necessary, that number of shares equal to $197,631 upon conversion to Common Stock at a conversion rate equal to 65% of the lowest closing bid price of the Common Stock during the ten trading days prior to the date the conversion is requested by IBC minus $0.002. During 2013, IBC converted $78,789 of the note into 53,720,000 shares of common stock at an average of $0.002 per share based on the formula in the note.
On January 22, 2014 the Company entered into a Mutual Release (the “Release”) with IBC Funds, LLC pursuant to which each party would release the other party from any and all obligations pursuant to that certain court-approved Settlement Agreement dated as of July 26, 2013, as described in the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on July 31, 2013.
In consideration for the Release, IBC will accept and the Company will remit to IBC: (i) a cash payment of $190,000, (ii) an issuance of 9,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock, pursuant to the terms of the Settlement Agreement under the December 18, 2013 Conversion Notice, and (iii) an issuance of 6,810,811 shares of the Company’s common stock, pursuant to the terms of the Settlement Agreement under the January 17, 2014 Conversion Notice (together, the “Consideration”). Pursuant to the Release, IBC has agreed that the Consideration shall be accepted as satisfaction in full of the payments due pursuant to the Settlement Agreement.
| F-14 |
On January 23, 2014, the Company and IBC filed a Stipulation of Dismissal with Prejudice with the Circuit Court in the 12th Judicial Circuit in and for Sarasota County, Florida.
Note 8 – Common Stock and Paid-In Capital
Registration Statement on Form S-1
Pursuant to a Registration Statement on Form S-1 and the prospectus therein, filed on July 3, 2012, and amendment thereto, the Registration Statement was declared effective on February 13, 2013.
Downgraded from the OTCQB to the OTC Pink
On September 2, 2014, the Company received notification from OTC Markets that because the Company’s common stock, which trades under the symbol TDCP, has not had a minimum closing bid price of $.01 during the last thirty days, it has been downgraded from the OTCQB to the OTC Pink, effective September 3, 2014. On March 26, 2014, OTC Markets had announced a series of rule changes to take place between May 1, 2014 and April 1, 2015. These rules set forth new qualifications and fees for quotation of securities on the various tiers of OTC Markets. One of such changes requires that a company’s stock have a minimum closing bid price of $.01 for at least one day in any consecutive thirty day period to continue being quoted on the OTCQB.
The Company has the option of filing an application for reinstatement to have its common stock quoted on the OTCQB. The Company’s common stock could be reinstated to the OTCQB commencing at such time as it has had a minimum closing bid price of $.01 for any consecutive 30 day period. The downgrading of the Company’s common stock from the OTCQB to the OCT Pink will have no effect on the common stock’s ability to trade or its DWAC (method of electronic transfer of shares) eligibility.
Warrants issued
As of December 31, 2014, NOTK has warrants outstanding to purchase 125,098 shares of common stock at a price of $3.15 per share that expire on September 30, 2016 and, warrants to purchase 96,024 shares of common stock at a price of $3.15 per share that expire on June 1, 2015. Golden State has warrants outstanding to purchase 18,595 shares of common stock at a price of $381.50 per share which expired December 31, 2014 (See Note 12). Global Capital has warrants outstanding to purchase 300,000 shares of common stock at a price of $0.0032 per shares which expire on March 31, 2019. Additionally from the preferred stock issuance, there are 9,750,000 warrants outstanding to purchase common shares at $0.0055 per share which expire December 31, 2017 and 9,500,000 warrants outstanding that were issued to Victor Keen, the CEO and Director of the Company, which expire on January 17, 2018.
Common stock and options issued for services and liabilities
During the years ending December 31, 2014 and 2013, shares of common stock totaling 28,205,571 and 25,892,479, respectively were issued for consulting services for which the Company recognized $108,500 and $295,350 of expense, respectively. Additionally, during the years ending December 31, 2014 and 2013, shares totaling 13,131,828 and 1,098,751, respectively were issued to consultants for previous services provided to the Company for which the accounts payable liability was reduced by $6,267 and $31,500, respectively.
| F-15 |
Employment Agreement - On March 13, 2012, the Company entered into a one (1) year Agreement for At-Will Employment with Assignment of Inventions (“Employment Agreement”) with Mark Willner, pursuant to which Mr. Willner began serving as the Company’s Chief Executive Officer, effective immediately. Under the terms of the Employment Agreement, Mr. Willner was entitled to an annual base salary of $180,000, and, at the discretion of the Company’s Board of Directors, performance-based bonuses and/or salary increases. Pursuant to the Employment Agreement, the Company granted Mr. Willner five-year stock options to purchase 57,143 shares at a price equal to the average price of the five day period prior to March 19, 2012 which was $0.35 (the “Strike Price”). Furthermore, since Mr. Willner remained employed by the Company at the end of each quarter ending June 30, 2012, September 30, 2012 and December 31, 2012, he received additional stock options to purchase 28,571.5 shares at the Strike Price. In addition, since the Company achieved certain quarterly business objectives, Mr. Willner received, at the end of each such quarterly period, a further grant of stock options to purchase 28,571.5 shares at the Strike Price. The estimated fair value of each of the 57,143 block of options, valued at $18,840, was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model and was charged to operations in March 2012, June 2012, September 2012 and December 2012. The expected dividend yield of $-0- is based on the average annual dividend yield as of the grant date. Expected volatility of 163% is based on the historical volatility of the stock since July 25, 2007, the day the Company began trading on the Over-The-Counter Bulletin Board. The risk-free interest rate of 1.87% is based on the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rates as of the grant date. The expected life of the option of five years is based on historical exercise behavior and expected future experience. On November 1, 2013, Mark Willner resigned as Chief Executive Officer.
Employment Agreement - On March 16, 2012, the Company entered into a one (1) year Agreement for At-Will Employment with Assignment of Inventions (“Employment Agreement”) with George Melnik, pursuant to which Dr. Melnik began serving as the Company’s Senior Technical Advisor, effective immediately. Under the terms of the Employment Agreement, Dr. Melnik is entitled to an annual base salary of $144,000, and, at the discretion of the Company’s Board of Directors, performance-based bonuses and/or salary increases. Pursuant to the Employment Agreement, the Company granted Dr. Melnik five-year stock options to purchase 28,571 shares at a price equal to the average price of the five day period prior to March 16, 2012 which was $0.35 (the “Strike Price”). Furthermore, since Dr. Melnik remained employed by the Company at the end of each quarter ending June 30, 2012, September 30, 2012 and December 31, 2012, he received additional stock options to purchase 28,571 shares at the Strike Price. In addition, since the Company achieved certain quarterly business objectives, Dr. Melnik received, at the end of each such quarterly period, a further grant of stock options to purchase 28,571 shares at the Strike Price. The estimated fair value of each of the 28,571 block of options, valued at $9,420, was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model and was charged to operations in March 2012, June 2012, September 2012 and December 2012. The expected dividend yield of $-0- is based on the average annual dividend yield as of the grant date. Expected volatility of 163% is based on the historical volatility of the stock since July 25, 2007, the day the Company began trading on the Over-The-Counter Bulletin Board. The risk-free interest rate of 1.87% is based on the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rates as of the grant date. The expected life of the option of five years is based on historical exercise behavior and expected future experience.
The Employment Agreement may be terminated with or without reason by either the Company or Dr. Melnik and at any time, upon sixty (60) days written notice. The terms of the Employment Agreement will remain effective for one (1) year and will automatically renew, subject to the same termination rights. Upon termination, the Company will pay any base pay, bonus and benefits that have been earned and are due as of the date of the termination.
| F-16 |
Employment Agreement - On January 28, 2013, the Board of Directors of the Company appointed Ronald Robinson to serve as the Company’s Chief Financial Officer. Accordingly, the Company decided not to renew its agreement with Christopher T. Dunstan pursuant to which Mr. Dunstan served as the Company’s Interim Chief Financial Officer. The Company’s appointment of Mr. Robinson and decision not to renew its agreement with Mr. Dunstan was not as a result of any disagreement between the Company and Mr. Dunstan.
On April 11, 2013, the Company completed the sale of two options, each to purchase 10,000,000 shares of the Company’s common stock (the “Option Agreements”) to two accredited investors. One of the accredited investors was Victor Keen, a director on the Board of Directors of the Company. Each of the Option Agreements provide for the option to purchase up to 10,000,000 shares of restricted common stock at a purchase price of $0.01 per share. The holders of the Option Agreements may exercise the option to purchase common stock on a cashless basis for a period of five years. Furthermore, the holders of the Option Agreements were granted “piggyback” registration rights for the inclusion, on a subsequent registration statement, the shares of common stock underlying the Option Agreements. The gross proceeds to the Company for the sale of both Option Agreements were $100,000.
Private Placement
On December 9, 2013 and December 11, 2013 the Company closed on $195,000 in a private placement (the “Private Placement”) contemplated by a Securities Purchase Agreement (the “Securities Purchase Agreement”), dated December 9, 2013, pursuant to which the Company sold 195,000 Units (as defined below) to accredited investors (each, an “Investor” and collectively, the “Investors”), one of whom was Victor Keen, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and a member of the board of directors of the Company. Accordingly, at the closings, the Company issued (i) 195,000 shares of its newly designated Series A Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series A Preferred”), and (ii) warrants (“Warrants”) to purchase an aggregate of 9,750,000 shares of Common Stock for gross proceed of $195,000.
On January 23, 2014, the Company sold to Victor Keen, the Company’s Chief Executive Officer and a member of the Company’s Board of Directors, 190,000 Units for a purchase price of $190,000, as part of the Private Placement (as defined therein) disclosed in the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on December 13, 2013. Pursuant to such Private Placement, the Company has received aggregate proceeds equal to $385,000. Such Private Placement is now closed.
Under the terms of the Securities Purchase Agreement, the Company sold units (“Units”) consisting of: (i) one share of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock and (ii) Warrants to purchase fifty (50) shares of Common Stock. The purchase price of each Unit was $1.00. The total purchase price of the securities sold in the Private Placement was $195,000. The offer and sale of the foregoing securities under the Securities Purchase Agreement was not a “public offering” as referred to in Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”), and was intended meet the requirements to qualify for exemption under Rule 506(b) of Regulation D promulgated under the Securities Act.
The terms of the Series A Convertible Preferred Stock and Warrants are as follows:
Series A Convertible Preferred Stock
A total of 195,000 shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock (the “Series A Preferred Stock”) have been authorized for issuance under the Certificate of Designation of Preferences, Rights and Limitation of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock of 3DIcon Corporation (the “Certificate of Designation”), which Certificate of Designation was filed with the Secretary of State of the State of Oklahoma on December 11, 2013. The shares of Series A Preferred Stock have a par value of $0.0002 per share (the “Stated Value”), and shall receive a dividend of 6% of their Stated Value per annum. Under the Certificate of Designation, the holders of the Series A Preferred Stock have the following rights, preferences and privileges:
The Series A Preferred Stock may, at the option of the Investor, be converted at any time after the first anniversary of the issuance of the Series A Preferred Stock or from time to time thereafter into 50,000,000 shares of Common Stock that Such Investor is entitled to in proportion to the 500,000 shares of Series A Preferred so designated in the Certificate of Designation.
| F-17 |
The Series A Preferred Stock will automatically be converted into Common Stock anytime the 5 day average VWAP of the Company’s Common Stock prior to such conversion is equal to $0.05 or more. Such mandatory conversion would be converted by the same method described above for discretionary conversions.
Except as otherwise required by law, the holders of shares of Series A Preferred Stock shall not have voting rights or powers.
In the event of any (i) liquidation, dissolution or winding up of the Company, whether voluntary or involuntary, or ii) sale, merger, consolidation, reorganization or other transaction that results in a change of control of the Company, each holder of a share of Series A Preferred shall be entitled to receive, subject to prior preferences and other rights of any class or series of stock of the Company senior to the Series A Preferred, but prior and in preference to any distribution of any of the assets or surplus funds of the Company to holders of Common Stock, or any other class or series of stock of the Company junior to the Series A Preferred, an amount equal to the Stated Value plus accrued and unpaid dividends (as adjusted for any stock dividends, combinations or splits with respect to such shares) (the “Preference Amount”). After such payment has been made to the holders of Series A Preferred of the full Preference Amount to which such holders shall be entitled, the remaining net assets of the Company available for distribution, if any, shall be distributed pro rata among the holders of Common Stock. In the event the funds or assets legally available for distribution to the holders of Series A Preferred are insufficient to pay the Preference Amount, then all funds or assets available for distribution to the holders of capital stock shall be paid to the holders of Series A Preferred pro rata based on the full Preference Amount to which they are entitled.
The Company may not declare, pay or set aside any dividends on shares of any class or series of capital stock of the Company (other than dividends on shares of Common Stock payable in shares of Common Stock) unless the holders of the Series A Preferred Stock shall first receive, or simultaneously receive, a dividend on each outstanding share of Series A Preferred in an amount equal to the dividend per share that such holders would have received had they converted their shares of Series A Preferred into shares of Common Stock immediately prior to the record date for the declaration of the Common Stock dividend in an amount equal to the average VWAP during the 5 trading days prior to the date such dividend is due.
Warrants
Each Unit under the Securities Purchase Agreement consists of Warrants entitling the Investor to purchase fifty (50) shares of Common Stock for each share of Series A Preferred purchased by such Investor in the Private Placement, at an initial exercise price per share of $0.0055. The exercise price and number of shares of Common Stock issuable under the Warrants are subject to adjustments for stock dividends, splits, combinations and similar events. On or after the first anniversary of the issuance of the Warrants and prior to close of business on fourth anniversary of the issuance of the Warrants and may be exercised at any time upon the election of the holder, provided however, that an Investor may at any given time convert only up to that number of shares of Common Stock so that, upon conversion, the aggregate beneficial ownership of the Company’s Common Stock (calculated pursuant to Rule 13d-3 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended) of such Investor and all persons affiliated with such Investor, is not more than 4.99% of the Company’s Common Stock then outstanding (subject to adjustment up to 9.99% at the Investor’s discretion upon 61 days’ prior notice).
The $27,000 estimated fair value of warrants for common stock issued was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The expected dividend yield of $0 is based on the average annual dividend yield at the date issued. Expected volatility of 178% is based on the historical volatility of the stock. The risk-free interest rate of 1.38% is based on the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rates as of the issue date. The expected life of the warrants of five years is based on historical exercise behavior and expected future experience.
Transaction Documents Series A Convertible Preferred Stock
The Securities Purchase Agreement, the Warrants and Certificate of Designation contain ordinary and customary provisions for agreements of this nature, such as representations, warranties, covenants, and indemnification obligations, as applicable. The foregoing descriptions of the Securities Purchase Agreement and the Warrants do not purport to describe all of the terms and provisions thereof and are qualified in their entirety by reference. The Securities Purchase Agreement and the form of Warrant are filed as Exhibits 4.1 and 10.1, respectively, to the Current Report on Form 8-K filed on December 13, 2013 and are incorporated herein by reference.
| F-18 |
The following summary reflects warrant and option activity for the year ending December 31, 2014:
| Attached | Golden State | |||||||||||
| Warrants | Warrants | Options | ||||||||||
| Outstanding December 31, 2013 | 10,271,122 | 19,942 | 23,030,274 | |||||||||
| Granted/purchased | 9,500,000 | - | - | |||||||||
| Exercised | - | (1,347 | ) | - | ||||||||
| Cancelled | - | - | - | |||||||||
| Outstanding December 31, 2014 | 19,771,122 | 18,595 | 23,030,274 | |||||||||
Stock options are valued at the date of award, which does not precede the approval date, and compensation cost is recognized in the period the options are granted. Stock options generally become exercisable on the date of grant and expire based on the terms of each grant.
The estimated fair value of options for common stock granted was determined using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The expected dividend yield is based on the average annual dividend yield as of the grant date. Expected volatility is based on the historical volatility of our stock. The risk-free interest rate is based on the U.S. Treasury Constant Maturity rates as of the grant date. The expected life of the option is based on historical exercise behavior and expected future experience.
Note 9 – Incentive Stock Plan
In June 2013, the Company established the 3DIcon Corporation 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (the "2013 EIP"). The total number of shares of stock which may be purchased or granted directly by options, stock awards or restricted stock purchase offers, or purchased indirectly through exercise of options granted under the 2013 EIP shall not exceed twenty million (20,000,000) shares. The shares are included in a registration statement filed June 10, 2013. Shares totaling 20,000,000 were issued from the 2013 EIP during 2013 for services rendered. As of December 31, 2014 there are -0- shares available for issuance under the 2013 EIP.
In March 2014, the Company established the 3DIcon Corporation 2014 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2014 EIP”). The total number of shares of stock which may be purchased or granted directly by options, stock awards or restricted stock purchase offers, or purchased indirectly through exercise of options granted under the 2014 EIP shall not exceed fifty million (50,000,000) shares. The shares are included in a registration statement filed March 2014. Shares totaling 42,456,419 were issued from the 2014 EIP during 2014 for services rendered. As of December 31, 2014, there were 7,543,581 shares available for issuance under the 2014 EIP. (see Note 12)
Note 10 – Office Lease
The Company signed an Office Lease Agreement (the “Lease Agreement”) on April 24, 2008. The Lease Agreement commenced on June 1, 2008 and expired June 1, 2011. On March 8, 2011 the Lease Agreement was amended (amendment 1) to extend the expiration date to May 31, 2012. On July 24, 2012 the Lease Agreement was amended (amendment 2) to extend the expiration date to July 31, 2015. The minimum future lease payment to be paid under the remaining 2015 term is $13,000 under the three-year non-cancellable amended operating lease for office space.
Note 11 – Related Party Transaction
3DIcon has engaged the law firm of Newton, O’Connor, Turner & Ketchum as its outside corporate counsel since 2005. John O’Connor, a director of 3DIcon, is the Chairman of Newton, O’Connor, Turner & Ketchum. During the years ending December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, the Company incurred legal fees to Newton, O’Connor, Turner & Ketchum in the amount of $3,360 and $23,137, respectively.
| F-19 |
Note 12 – Subsequent Events
Common stock issued for services and liabilities
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, Golden State converted $400 of the 4.75% convertible debenture into 18,727,884 shares of common stock at $0.00002 per share and exercised 114 warrants at $381.50 per share for $43,545 and advanced $10,900 for future exercise of warrants under the terms of the securities purchase agreements. Additionally, Golden Gate extended the debenture due date to December 31, 2016.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, JMJ converted $17,500 of the convertible promissory note into 10,000,000 shares of common stock at $0.002 under the terms of the securities purchase agreements.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, the holder of the 10% Convertible Promissory Note converted $25,000 of the convertible promissory note into 14,245,014 shares of common stock at $0.002 under the terms of the securities purchase agreements.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, shares of common stock totaling 15,000,000 were issued for legal services for which the Company recognized $22,500 of expense.
Subsequent to December 31, 2014, shares of common stock totaling 15,017,162 were issued for 2014 consulting services for which the Company reduced accounts payable by $25,000.
Keen Bridge Note
On March 16, 2015 (the “Amendment Date”), the Company entered into a fifth amendment agreement (the “Fifth Keen Amendment”) with Victor Keen, a Director on the Board of Directors of the Company, to amend the Keen Bridge note. Pursuant to the Fifth Keen Amendment, Mr. Keen agreed to extend the maturity of the Note from December 31, 2014 to June 30, 2015 (the “New Maturity Date”) and to waive, if any, existing or prior defaults under the Keen Bridge Note or the Keen SPA.
Incentive Stock Plan
Shares totaling 6,793,478 were issued from the 2014 EIP during 2015 for prior services rendered for which the Company reduced accounts payable by $12,500. There are 750,103 shares available for issuance under the 2014 EIP.
In March 2015, the Company established the 3DIcon Corporation 2015 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2014 EIP”). The total number of shares of stock which may be purchased or granted directly by options, stock awards or restricted stock purchase offers, or purchased indirectly through exercise of options granted under the 2015 EIP shall not exceed eighty-five million (85,000,000) shares. The shares are included in a registration statement filed March, 2015. Shares totaling 23,223,684 were issued from the 2015 EIP during 2015 for $35,000 of legal and consulting services rendered. There are 61,776,316 shares available for issuance under the 2015 EIP.
JMJ March 2015 5% Note
In March 2015, the Company issued and sold a convertible note (the “March 2015 5% Note") in aggregate Principal Sum of $250,000 to JMJ Financial (“JMJ”). The 5% Note includes a $25,000 original issue discount (the “OID”) that will be prorated based on the advances actually paid (the “Principal Sum”) to the Company. During 2015, JMJ advanced $30,000 on the 5% Note and earned $3,000 OID. In addition to the OID, the March 2015 5% Note provides for a one-time interest charge of 5% to be applied to the Principal Sum. If the Company repays the 5% Note on or before ninety days from the date of the principal amount advanced, the interest rate will be zero percent. If the Company does not repay the March 2015 5% Note on or before ninety days from the date of the advance, a one-time interest charge of 5% shall be applied to the Principal Sum. Pursuant to the terms of March 2015 5% Note, JMJ may, at its election, convert all or a part of the $250,000 note into shares of the Company's common stock at a conversion rate 70% of the lowest trade price during the twenty-five trading days prior to JMJ’s election to convert. The principal of the March 2015 5% Note is due two years from the date of each of the principal amounts advanced.
Typenex Co-Investment, LLC
In March 2015, the Company issued and sold a convertible note (the “5% Promissory Note") in aggregate Principal Sum of $87,500 to Typenex Co-Investment, LLC, (“Typenex”). The 5% Promissory Note includes a $7,500 original issue discount (the “OID”) that will be prorated based on the advances actually paid to the Company. Accordingly during 2015, the Company received $80,000 gross proceeds from which the Company paid legal and documentation fees of $20,000 and placement agent fees of $6,750. In addition to the OID, the 5% Promissory Note provides for a one-time interest charge of 5% to be applied to the principal of the 5% Promissory Note. If the Company repays the 5% Promissory Note on or before ninety days from the date of the principal amount advanced, the interest rate will be zero percent. If the Company does not repay the 5% Promissory Note on or before ninety days from the date of the advance, a one-time interest charge of 5% shall be applied to the Principal Sum. Pursuant to the terms of 5% Promissory Note, Typenex may, at its election, convert all or a part of the $87,500 principal and interest thereon of the 5% Promissory Note into shares of the Company's common stock at a conversion rate 70% of the lowest trade price during the twenty-five trading days prior to the election to convert. The principal of the 5% Promissory Note is due one year from the March 2015 effective date.
| F-20 |
