Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-23.3 - EX-23.3 - ProShares Trust II | d887368dex233.htm |
Table of Contents
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on March 30, 2015
Registration No. 333-202724
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
PRE-EFFECTIVE AMENDMENT NO. 1
TO
FORM S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
UNDER
THE SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
PROSHARES TRUST II
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 6221 | 87-6284802 | ||
| (State of Organization) | (Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
Michael L. Sapir
c/o ProShare Capital Management LLC
7501 Wisconsin Avenue
Suite 1000
Bethesda, Maryland 20814
(240) 497-6400
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Copies to:
Amy Doberman, Esq.
c/o ProShare Capital Management LLC
7501 Wisconsin Avenue
Suite 1000
Bethesda, MD 20814
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public: As promptly as practicable after the effective date of this Registration Statement.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933, check the following box. x
If this form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this form is a post–effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this form is a post–effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one.)
| Large accelerated filer | x | Accelerated filer | ¨ | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ¨ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ¨ | |||
CALCULATION OF REGISTRATION FEE
|
| ||||
| Title of Securities to be Registered | Proposed Aggregate |
Amount of Registration Fee1 | ||
| ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$619,302,925 | $71,963 | ||
| ProShares Managed Futures Strategy Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$509,027,538 | $59,149 | ||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$129,604,130 | $15,060 | ||
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$172,839,931 | $20,084 | ||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$540,275,387 | $62,780 | ||
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$412,030,981 | $47,878 | ||
| ProShares UltraShort Silver Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$2,083,528,399 | $242,106 | ||
| ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$193,296,041 | $22,461 | ||
| ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$172,771,084 | $20,076 | ||
| ProShares Ultra Euro Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$126,652,323 | $14,717 | ||
| ProShares Short Euro Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$174,672,977 | $20,297 | ||
| ProShares Ultra Yen Common Units of Beneficial Interest |
$138,726,333 | $16,120 | ||
| TOTAL |
$5,272,728,049 | $612,6912 | ||
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
| (1) | The amounts of the registration fees for the indicated securities have been calculated in reliance upon Rule 457(o) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “1933 Act”). |
| (2) | $162,680 is being paid contemporaneously with the filing of this Registration Statement. In addition, the following offsets in the aggregate amount of $450,011 are being applied for registered and unissued common units of beneficial interest: a) $71,963 for ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF, $54,560 of which was paid for with Registrant’s Form S-1 filing filed on April 29, 2013 (File No. 333-188215) and $17,403 of which was carried forward with Registrant’s Form S-1/A filed on June 11, 2012 (File No. 333-176878); b) $24,289 for ProShares Managed Futures Strategy, all of which was carried forward with Registrant’s Form S-1 filing filed on August 15, 2014 (File No. 333-198189); c) $10,412 for ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity, all of which was carried forward with Registrant’s Form S-1/A filed on June 11, 2012 (File No. 333-176878); d)$13,112 for ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity, all of which was carried forward with Registrant’s Form S-1/A filed on June 11, 2012 (File No. 333-176878); e) $45,350, for ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas, $23,240 of which was paid for with Registrant’s Form S-1 filing filed on October 28, 2014 (File No. 333-199642) and $22,110 of which was paid for with Registrant’s Form S-1 filing filed on April 29, 2013 (File No. 333-188215); f) $42,068 for ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas, $11,620 of which was paid for with Registrant’s S-1 filing filed on October 28, 2014 (File No. 333-199642), $9,548 of which was paid for with Registrant’s S-1 filing filed on April 29, 2013 (File No. 333-188215) and $20,900 of which was carried forward with Registrant’s Form S-1/A filed on June 11, 2012 (File No. 333-176878); g) $149,146 for ProShares UltraShort Silver, $81,340 of which was paid for with Registrant’s Form S-1 filing filed on October 28, 2014 (File No. 333-199642), $40,920 of which was paid for with Registrant’s Form S-3 filing filed on April 9, 2013 (File No. 333-187820), $22,920 of which was paid for with Registrant’s Form S-3 filing filed on August 31, 2012 (File No. 333-183674) and $3,966 of which was carried forward with Registrant’s POSAM filing filed on June 11, 2012 (File No. 333-163511) in agreement with the Commission; h) $22,461 for ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar, all of which was paid for with Registrant’s Form S-1/A filing filed on May 11, 2012 (File No. 333-178707); i) $20,076 for ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar, all of which was paid for with Registrant’s Form S-1/A filing filed on May 11, 2012 (File No. 333-178707); j) $14,717 for ProShares Ultra Euro, all of which was carried forward with Registrant’s Form S-1/A filing filed on June 11, 2012 (File No. 333-176878); k) $20,297 for ProShares Short Euro, all of which was paid for with Registrant’s Form S-1/A filing filed on May 11, 2012 (File No. 333-178707); and l) $16,120 for ProShares Ultra Yen, all of which was carried forward with Registrant’s Form S-1/A filing filed on June 11, 2012 (File No. 333-176878). |
This Registration Statement contains a combined prospectus under Rule 429 promulgated under the 1933 Act, which relates to File No. 333-199642. Accordingly, upon effectiveness, this Registration Statement shall act as Post-Effective Amendment No. 1 to File No. 333-199642.
The registrant hereby amends this Registration Statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this Registration Statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 or until this Registration Statement shall become effective on such date as the Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
Table of Contents
EXPLANATORY NOTE
This Registration Statement on Form S-1 (this “Registration Statement”) of ProShares Trust II (the “Registrant”) is being filed to update the Registration Statement by, among other things, incorporating by reference the Registrant’s updated financial statements, updating pool performance information and registering additional shares.
Table of Contents

PROSHARES TRUST II
Common Units of Beneficial Interest
| Title of Securities to be Registered |
Benchmark |
Proposed Maximum Aggregate Offering Price Per Fund |
||||
| ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF (VIXM) |
S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index | $ | 619,302,925 | |||
| ProShares Managed Futures Strategy (FUTS) |
S&P Strategic Futures Index | $ | 509,027,538 | |||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity (UCD) |
Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM | $ | 129,604,130 | |||
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity (CMD) |
Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM | $ | 172,839,931 | |||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas (BOIL) |
Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM | $ | 540,275,387 | |||
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas (KOLD) |
Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM | $ | 412,030,981 | |||
| ProShares UltraShort Silver (ZSL) |
The daily performance of silver bullion as measured by the London Silver Price | $ | 2,083,528,399 | |||
| ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar (GDAY) |
The U.S. dollar price of the Australian dollar | $ | 193,296,041 | |||
| ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar (CROC) |
The U.S. dollar price of the Australian dollar | $ | 172,771,084 | |||
| ProShares Ultra Euro (ULE) |
The U.S. dollar price of the euro | $ | 126,652,323 | |||
| ProShares Short Euro (EUFX) |
The U.S. dollar price of the euro | $ | 174,672,977 | |||
| ProShares Ultra Yen (YCL) |
The U.S. dollar price of the Japanese yen | $ | 138,726,333 | |||
ProShares Trust II (the “Trust”) is a Delaware statutory trust organized into separate series. The Trust may from time to time offer to sell common units of beneficial interest (“Shares”) of any or all of the twelve series of the Trust listed above (each, a “Fund” and collectively, the “Funds”) or other series of the Trust, which represent units of fractional undivided beneficial interest in and ownership of a series of the Trust. Please note that the Trust has series other than the Funds. Each Fund’s Shares will be offered on a continuous basis from time to time.
The Shares of ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF (the “VIX Fund”), ProShares Managed Futures Strategy (the “Managed Futures Fund”), ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas (each, a “Natural Gas Fund” and collectively, the “Natural Gas Funds”), ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Silver, ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar, ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar, ProShares Ultra Euro, ProShares Short Euro and ProShares Ultra Yen are listed on NYSE Arca Equities, Inc. (the “Exchange”) under the ticker symbols shown above.
Each of the Funds, other than the VIX Fund and the Managed Futures Fund, is “geared” (each, a “Geared Fund” and collectively, the “Geared Funds”) in the sense that each has an investment objective to correspond (before fees and expenses) to a multiple (i.e., 2x), the inverse (i.e., -1x) or an inverse multiple (i.e., -2x) of the performance of a benchmark for a single day, not for any other period. Each of the VIX Fund and the Managed Futures Fund has an investment objective to correspond (before fees and expenses) to the performance of a benchmark both over a single day and over time. A “single day” is measured from the time a Fund calculates its respective net asset value (“NAV”) to the time of the Fund’s next NAV calculation. The NAV calculation times for the Funds typically range from 7:00 a.m. to 4:15 p.m. (Eastern Time); please see the section entitled “Summary-Creation and Redemption Transactions” on page 4 for additional details on the NAV calculation times for the Funds.
The Funds do not currently intend to invest directly in spot volatility, any commodities or currencies. Rather, the Funds will attempt to gain exposure to the applicable benchmark through investments in Financial Instruments (i.e., instruments whose value is derived from the value of an underlying asset, rate or benchmark, including futures contracts, swap agreements, forward contracts and other instruments).
Table of Contents
INVESTING IN THE SHARES INVOLVES SIGNIFICANT RISKS. PLEASE REFER TO “RISK FACTORS” BEGINNING ON PAGE 6.
Each Fund will distribute to shareholders a Schedule K-1 that will contain information regarding the income and expenses of the Fund.
The Geared Funds are not appropriate for all investors and present different risks than other funds. The Geared Funds that use leverage are riskier than similarly benchmarked exchange-traded funds that do not use leverage. An investor should only consider an investment in a Geared Fund if he or she understands the consequences of seeking daily leveraged, daily inverse or daily inverse leveraged investment results.
Each Geared Fund seeks to return (before fees and expenses) a multiple (2x), the inverse (-1x) or an inverse multiple (-2x) times the performance of its benchmark daily, not for any other period. The return of a Geared Fund for a period longer than a single day is the result of its return for each day compounded over the period and usually will differ from the Geared Fund’s multiple times the return of the Geared Fund’s benchmark for the period. Daily compounding of a Geared Fund’s investment returns can dramatically and adversely affect its longer-term performance during periods of high volatility. Volatility may be at least as important to a Geared Fund’s return for a period as the return of the Geared Fund’s underlying benchmark. Each Ultra or UltraShort Fund uses leverage and should produce daily returns that are more volatile than that of its benchmark. For example, the daily return of an Ultra Fund with a 2x multiple should be approximately two times as volatile on a daily basis as the return of a fund with an objective of matching the same benchmark. The daily return of a Short or UltraShort Fund is designed to return the inverse (-1x) or two times the inverse (-2x), respectively, of the return that would be expected of a fund with an objective of matching the same benchmark. Shareholders who invest in the Geared Funds should actively manage and monitor their investments, as frequently as daily.
Each Fund continuously offers and redeems Shares in blocks of 50,000 Shares (25,000 Shares with respect to the VIX Fund only) (each such block, a “Creation Unit”). Only Authorized Participants may purchase and redeem Shares from a Fund and then only in Creation Units. An Authorized Participant is an entity that has entered into an Authorized Participant Agreement with the Trust and ProShare Capital Management LLC (the “Sponsor”). Shares of the Funds are offered to Authorized Participants in Creation Units at each Fund’s respective NAV. Authorized Participants may then offer to the public, from time to time, Shares from any Creation Unit they create at a per-Share market price. The form of Authorized Participant Agreement and the related Authorized Participant Handbook set forth the terms and conditions under which an Authorized Participant may purchase or redeem a Creation Unit. Authorized Participants will not receive from any Fund, the Sponsor, or any of their affiliates, any fee or other compensation in connection with their sale of Shares to the public. An Authorized Participant may receive commissions or fees from investors who purchase Shares through their commission or fee-based brokerage accounts.
These securities have not been approved or disapproved by the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) or any state securities commission nor has the SEC or any state securities commission passed upon the accuracy or adequacy of this Prospectus. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
NEITHER THE TRUST NOR ANY FUND IS A MUTUAL FUND OR ANY OTHER TYPE OF INVESTMENT COMPANY AS DEFINED IN THE INVESTMENT COMPANY ACT OF 1940, AS AMENDED (THE “1940 ACT”), AND NEITHER IS SUBJECT TO REGULATION THEREUNDER.
THE COMMODITY FUTURES TRADING COMMISSION HAS NOT PASSED UPON THE MERITS OF PARTICIPATING IN THIS POOL NOR HAS THE COMMISSION PASSED ON THE ADEQUACY OR ACCURACY OF THIS DISCLOSURE DOCUMENT.
April [ ], 2015
Table of Contents
The Shares are neither interests in nor obligations of the Sponsor, Wilmington Trust Company (the “Trustee”), or any of their respective affiliates. The Shares are not insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other governmental agency.
This Prospectus has two parts: the offered series disclosure and the general pool disclosure. These parts are bound together and are incomplete if not distributed together to prospective participants.
COMMODITY FUTURES TRADING COMMISSION
RISK DISCLOSURE STATEMENT
YOU SHOULD CAREFULLY CONSIDER WHETHER YOUR FINANCIAL CONDITION PERMITS YOU TO PARTICIPATE IN A COMMODITY POOL. IN SO DOING, YOU SHOULD BE AWARE THAT COMMODITY INTEREST TRADING CAN QUICKLY LEAD TO LARGE LOSSES AS WELL AS GAINS. SUCH TRADING LOSSES CAN SHARPLY REDUCE THE NET ASSET VALUE OF THE POOL AND CONSEQUENTLY THE VALUE OF YOUR INTEREST IN THE POOL. IN ADDITION, RESTRICTIONS ON REDEMPTIONS MAY AFFECT YOUR ABILITY TO WITHDRAW YOUR PARTICIPATION IN THE POOL.
FURTHER, COMMODITY POOLS MAY BE SUBJECT TO SUBSTANTIAL CHARGES FOR MANAGEMENT, AND ADVISORY AND BROKERAGE FEES. IT MAY BE NECESSARY FOR THOSE POOLS THAT ARE SUBJECT TO THESE CHARGES TO MAKE SUBSTANTIAL TRADING PROFITS TO AVOID DEPLETION OR EXHAUSTION OF THEIR ASSETS. THIS DISCLOSURE DOCUMENT CONTAINS A COMPLETE DESCRIPTION OF EACH EXPENSE TO BE CHARGED TO THIS POOL, AT PAGES 74 THROUGH 77, AND A STATEMENT OF THE PERCENTAGE RETURN NECESSARY TO BREAK EVEN, THAT IS, TO RECOVER THE AMOUNT OF YOUR INITIAL INVESTMENT, AT PAGES 73 THROUGH 76.
THIS BRIEF STATEMENT CANNOT DISCLOSE ALL THE RISKS AND OTHER FACTORS NECESSARY TO EVALUATE YOUR PARTICIPATION IN THIS COMMODITY POOL. THEREFORE, BEFORE YOU DECIDE TO PARTICIPATE IN THIS COMMODITY POOL, YOU SHOULD CAREFULLY STUDY THIS DISCLOSURE DOCUMENT, INCLUDING A DESCRIPTION OF THE PRINCIPAL RISK FACTORS OF THIS INVESTMENT, AT PAGES 6 THROUGH 33.
YOU SHOULD ALSO BE AWARE THAT THIS COMMODITY POOL MAY TRADE FOREIGN FUTURES OR OPTIONS CONTRACTS. TRANSACTIONS ON MARKETS LOCATED OUTSIDE THE UNITED STATES, INCLUDING MARKETS FORMALLY LINKED TO A UNITED STATES MARKET, MAY BE SUBJECT TO REGULATIONS WHICH OFFER DIFFERENT OR DIMINISHED PROTECTION TO THE POOL AND ITS PARTICIPANTS. FURTHER, UNITED STATES REGULATORY AUTHORITIES MAY BE UNABLE TO COMPEL THE ENFORCEMENT OF THE RULES OF REGULATORY AUTHORITIES OR MARKETS IN NON-UNITED STATES JURISDICTIONS WHERE TRANSACTIONS FOR THE POOL MAY BE EFFECTED.
SWAPS TRANSACTIONS, LIKE OTHER FINANCIAL TRANSACTIONS, INVOLVE A VARIETY OF SIGNIFICANT RISKS. THE SPECIFIC RISKS PRESENTED BY A PARTICULAR SWAP TRANSACTION NECESSARILY DEPEND UPON THE TERMS OF THE TRANSACTION AND YOUR CIRCUMSTANCES. IN GENERAL, HOWEVER, ALL SWAPS TRANSACTIONS INVOLVE SOME COMBINATION OF MARKET RISK, CREDIT RISK, COUNTERPARTY CREDIT RISK, FUNDING RISK, LIQUIDITY RISK, AND OPERATIONAL RISK.
HIGHLY CUSTOMIZED SWAPS TRANSACTIONS IN PARTICULAR MAY INCREASE LIQUIDITY RISK, WHICH MAY RESULT IN A SUSPENSION OF REDEMPTIONS. HIGHLY
- i -
Table of Contents
LEVERAGED TRANSACTIONS MAY EXPERIENCE SUBSTANTIAL GAINS OR LOSSES IN VALUE AS A RESULT OF RELATIVELY SMALL CHANGES IN THE VALUE OR LEVEL OF AN UNDERLYING OR RELATED MARKET FACTOR. IN EVALUATING THE RISKS AND CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS ASSOCIATED WITH A PARTICULAR SWAP TRANSACTION, IT IS IMPORTANT TO CONSIDER THAT A SWAP TRANSACTION MAY, IN CERTAIN INSTANCES, BE MODIFIED OR TERMINATED ONLY BY MUTUAL CONSENT OF THE ORIGINAL PARTIES AND SUBJECT TO AGREEMENT ON INDIVIDUALLY NEGOTIATED TERMS. THEREFORE, IT MAY NOT BE POSSIBLE FOR THE COMMODITY POOL OPERATOR TO MODIFY, TERMINATE, OR OFFSET THE POOL’S OBLIGATIONS OR THE POOL’S EXPOSURE TO THE RISKS ASSOCIATED WITH A TRANSACTION PRIOR TO ITS SCHEDULED TERMINATION DATE.
THIS PROSPECTUS DOES NOT INCLUDE ALL OF THE INFORMATION OR EXHIBITS IN THE REGISTRATION STATEMENT OF THE TRUST. INVESTORS CAN READ AND COPY THE ENTIRE REGISTRATION STATEMENT AT THE PUBLIC REFERENCE FACILITIES MAINTAINED BY THE SEC IN WASHINGTON, D.C.
THE BOOKS AND RECORDS OF THE FUNDS ARE MAINTAINED AS FOLLOWS:
| • | All marketing materials are maintained at the offices of: |
SEI Investments Distribution Co. (“SEI” or the “Distributor”)
1 Freedom Valley Drive
Oaks, Pennsylvania 19456
| • | Creation Unit creation and redemption books and records, accounting and certain other financial books and records (including Fund accounting records, ledgers with respect to assets, liabilities, capital, income and expenses, the register, transfer journals and related details) and certain trading and related documents received from Futures Commission Merchants (“FCMs”) are maintained at the offices of: |
Brown Brothers Harriman & Co. (“BBH&Co.” or the “Custodian”)
50 Post Office Square
Boston, Massachusetts 02110
| • | All other books and records of the Funds (including minute books and other general corporate records, trading records and related reports) are maintained at the Funds’ principal office, c/o ProShare Capital Management LLC, 7501 Wisconsin Avenue, Suite 1000, Bethesda, Maryland 20814. The main business telephone number of each of the Funds and the Sponsor is (240) 497-6400. |
SHAREHOLDERS HAVE THE RIGHT, DURING NORMAL BUSINESS HOURS, TO HAVE ACCESS TO AND COPY (UPON PAYMENT OF REASONABLE REPRODUCTION COSTS) SUCH BOOKS AND RECORDS IN PERSON OR BY THEIR AUTHORIZED ATTORNEY OR AGENT. MONTHLY ACCOUNT STATEMENTS CONFORMING TO THE COMMODITY FUTURES TRADING COMMISSION (“CFTC”) AND THE NATIONAL FUTURES ASSOCIATION (THE “NFA”) REQUIREMENTS ARE POSTED ON THE SPONSOR’S WEBSITE AT WWW.PROSHARES.COM. ADDITIONAL REPORTS MAY BE POSTED ON THE SPONSOR’S WEBSITE AT THE DISCRETION OF THE SPONSOR OR AS REQUIRED BY REGULATORY AUTHORITIES. THERE WILL SIMILARLY BE DISTRIBUTED TO SHAREHOLDERS, NOT MORE THAN 90 DAYS AFTER THE CLOSE OF THE FUNDS’ FISCAL YEAR, CERTIFIED AUDITED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS. THE
- ii -
Table of Contents
TAX INFORMATION RELATING TO SHARES OF EACH FUND NECESSARY FOR THE PREPARATION OF SHAREHOLDERS’ ANNUAL FEDERAL INCOME TAX RETURNS WILL ALSO BE DISTRIBUTED.
THE TRUST WILL FILE QUARTERLY AND ANNUAL REPORTS WITH THE SEC. INVESTORS CAN READ AND COPY THESE REPORTS AT THE SEC PUBLIC REFERENCE FACILITIES IN WASHINGTON, D.C. PLEASE CALL THE SEC AT 1–800–SEC–0330 FOR FURTHER INFORMATION.
THE FILINGS OF THE TRUST ARE POSTED AT THE SEC WEBSITE AT WWW.SEC.GOV.
REGULATORY NOTICES
NO DEALER, SALESMAN OR ANY OTHER PERSON HAS BEEN AUTHORIZED TO GIVE ANY INFORMATION OR TO MAKE ANY REPRESENTATION NOT CONTAINED IN THIS PROSPECTUS, AND, IF GIVEN OR MADE, SUCH OTHER INFORMATION OR REPRESENTATION MUST NOT BE RELIED UPON AS HAVING BEEN AUTHORIZED BY THE TRUST, ANY OF THE FUNDS, THE SPONSOR, THE AUTHORIZED PARTICIPANTS OR ANY OTHER PERSON.
THIS PROSPECTUS DOES NOT CONSTITUTE AN OFFER OR SOLICITATION TO SELL OR A SOLICITATION OF AN OFFER TO BUY, NOR SHALL THERE BE ANY OFFER, SOLICITATION, OR SALE OF THE SHARES IN ANY JURISDICTION IN WHICH SUCH OFFER, SOLICITATION, OR SALE IS NOT AUTHORIZED OR TO ANY PERSON TO WHOM IT IS UNLAWFUL TO MAKE ANY SUCH OFFER, SOLICITATION, OR SALE.
AUTHORIZED PARTICIPANTS MAY BE REQUIRED TO DELIVER A PROSPECTUS WHEN TRANSACTING IN SHARES. SEE “PLAN OF DISTRIBUTION” IN PART TWO OF THIS PROSPECTUS.
- iii -
Table of Contents
PROSHARES TRUST II
| Page | ||||
| PART ONE OFFERED SERIES DISCLOSURE |
||||
| 1 | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 3 | ||||
| 4 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| 5 | ||||
| 6 | ||||
| 34 | ||||
| 35 | ||||
| 35 | ||||
| 37 | ||||
| 39 | ||||
| 40 | ||||
| 40 | ||||
| Determining the Long/Short Positioning of each SFI Futures Contract |
41 | |||
| 42 | ||||
| DESCRIPTION OF THE BLOOMBERG COMMODITY INDEXSM AND SUBINDEXES |
43 | |||
| 43 | ||||
| 45 | ||||
| 45 | ||||
| 47 | ||||
| 47 | ||||
| 48 | ||||
| 48 | ||||
| 48 | ||||
| 49 | ||||
| 50 | ||||
| 50 | ||||
| 53 | ||||
| PERFORMANCE OF THE OFFERED COMMODITY POOLS OPERATED BY THE COMMODITY POOL OPERATOR |
63 | |||
| MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS |
73 | |||
| 74 | ||||
| 74 | ||||
- iv -
Table of Contents
| Page | ||||
| 76 | ||||
| 76 | ||||
| 78 | ||||
| 78 | ||||
| 93 | ||||
| 95 | ||||
| 96 | ||||
| 97 | ||||
| PART TWO GENERAL POOL DISCLOSURE |
||||
| PERFORMANCE OF THE OTHER COMMODITY POOLS OPERATED BY THE COMMODITY POOL OPERATOR |
108 | |||
| 116 | ||||
| 116 | ||||
| 117 | ||||
| 118 | ||||
| 119 | ||||
| 121 | ||||
| 121 | ||||
| 122 | ||||
| DESCRIPTION OF THE SHARES; THE FUNDS; CERTAIN MATERIAL TERMS OF THE TRUST AGREEMENT |
123 | |||
| 123 | ||||
| 123 | ||||
| 123 | ||||
| 124 | ||||
| 124 | ||||
| 128 | ||||
| 129 | ||||
| 129 | ||||
| 129 | ||||
| Possible Repayment of Distributions Received by Shareholders |
129 | |||
| 129 | ||||
| 130 | ||||
| 130 | ||||
| 131 | ||||
| 132 | ||||
| 132 | ||||
| 132 | ||||
| 132 | ||||
| 133 | ||||
| 133 | ||||
| 133 | ||||
| 133 | ||||
| THE SECURITIES DEPOSITORY; BOOK-ENTRY ONLY SYSTEM; GLOBAL SECURITY |
134 | |||
| 135 | ||||
- v -
Table of Contents
| Page | ||||
| 135 | ||||
| 136 | ||||
| 136 | ||||
| 136 | ||||
| 137 | ||||
| 137 | ||||
| 138 | ||||
| 138 | ||||
| 138 | ||||
| 139 | ||||
| 140 | ||||
| 140 | ||||
| 140 | ||||
| 140 | ||||
| 141 | ||||
| 142 | ||||
| 142 | ||||
| 142 | ||||
| 142 | ||||
| 144 | ||||
| 144 | ||||
| 144 | ||||
| 144 | ||||
| 144 | ||||
| 144 | ||||
| 146 | ||||
- vi -
Table of Contents
PART ONE:
OFFERED SERIES DISCLOSURE
Investors should read the following summary together with the more detailed information, including under the caption “Risk Factors,” and all exhibits to this Prospectus and the information specifically incorporated by reference in this Prospectus, including the financial statements and the notes to those financial statements in the Trust’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014, before deciding to invest in any Shares. Please see the section entitled “Incorporation by Reference of Certain Documents” in Part Two of this Prospectus. For ease of reference, any references throughout this Prospectus to various actions taken by each of the Funds are actually actions that the Trust has taken on behalf of such Funds.
Definitions used in this Prospectus can be found in the Glossary in Appendix A.
Important Information About the Geared Funds
The Geared Funds are not appropriate for all investors and present different risks than other funds. The Geared Funds that use leverage are riskier than similarly benchmarked exchange-traded funds that do not use leverage. An investor should only consider an investment in a Fund if he or she understands the consequences of seeking daily leveraged, daily inverse or daily inverse leveraged investment results.
Each Geared Fund seeks to return (before fees and expenses) a multiple (2x), the inverse (-1x) or an inverse multiple (-2x) times the performance of its benchmark daily, not for any other period. The return of a Geared Fund for a period longer than a single day is the result of its return for each day compounded over the period and usually will differ from the Geared Fund’s multiple times the return of the Geared Fund’s benchmark for the period. Daily compounding of a Geared Fund’s investment returns can dramatically and adversely affect its longer-term performance during periods of high volatility. Volatility may be at least as important to a Geared Fund’s return for a period as the return of the Geared Fund’s underlying benchmark. Each Ultra or UltraShort Fund uses leverage and should produce daily returns that are more volatile than that of its benchmark. For example, the daily return of an Ultra Fund with a 2x multiple should be approximately two times as volatile on a daily basis as the return of a fund with an objective of matching the same benchmark. The daily return of a Short or UltraShort Fund is designed to return the inverse (-1x) or two times the inverse (-2x), respectively, of the return that would be expected of a fund with an objective of matching the same benchmark. Shareholders who invest in the Geared Funds should actively manage and monitor their investments, as frequently as daily.
The Matching Funds
The VIX Fund and the Managed Futures Fund offer investors the opportunity to obtain “matching” (i.e., not leveraged, inverse or inverse leveraged) exposure to their respective benchmarks, as described herein.
The Geared Funds
The Geared Funds offer investors the opportunity to obtain leveraged, inverse or inverse leveraged exposure to a particular benchmark. The Geared Funds currently include funds linked to futures-based commodity indexes (the “Commodity Index Funds”) or individual currency exchange rates (the “Currency Funds”). Each Geared Fund targets a multiple, the inverse or an inverse multiple of the daily return of such benchmarks, rather than targeting a multiple, the inverse or an inverse multiple of the benchmark returns over any other period. The
1
Table of Contents
“Short Fund” seeks, on a daily basis, results that correspond (before fees and expenses) to the inverse (-1x) of its corresponding benchmark. Each “Ultra Fund” and “UltraShort Fund” seeks, on a daily basis, results that correspond (before fees and expenses) to two times (2x) or two times the inverse (-2x), respectively, of the performance of its corresponding benchmark. The Geared Funds do not seek to achieve their stated objective over a period greater than a single day. A “single day” is measured from the time the Fund calculates its net asset value (NAV) to the time of the Fund’s next NAV calculation.
Each Geared Fund seeks to engage in daily rebalancing to position its portfolio so that its exposure to its benchmark is consistent with such Geared Fund’s daily investment objective. The impact of the benchmark’s movements during the day will affect whether a particular Geared Fund’s portfolio needs to be repositioned. For example, if the Short or an UltraShort Fund’s benchmark has risen on a given day, net assets of such Fund should fall. As a result, inverse exposure will need to be decreased. Conversely, if the Short or an UltraShort Fund’s benchmark has fallen on a given day, net assets of such Fund should rise. As a result, inverse exposure will need to be increased. For Ultra Funds, the Fund’s long exposure will need to be increased on days when such Fund’s benchmark rises and decreased on days when such Fund’s benchmark falls. Daily rebalancing and the compounding of each day’s return over time means that the return of each Geared Fund for a period longer than a single day will be the result of each day’s returns compounded over the period, which will very likely differ from a multiple (2x), the inverse (-1x) or an inverse multiple (-2x) of the return of the Geared Fund’s benchmark for the period. A Geared Fund will lose money if its benchmark’s performance is flat over time, and it is possible for a Geared Fund to lose money over time regardless of the performance of an underlying benchmark, as a result of daily rebalancing, the benchmark’s volatility and compounding.
All Funds
Each of the Funds generally invests in Financial Instruments (i.e., instruments whose value is derived from the value of an underlying asset, rate or benchmark (such asset, rate or benchmark, a “Reference Asset”)), including futures contracts, swap agreements, forward contracts and other instruments, in order to gain exposure to its applicable benchmark. Financial Instruments also are used to produce economically “leveraged,” “inverse” or “inverse leveraged” investment results for the Geared Funds.
In seeking to achieve the Funds’ investment objectives, the Sponsor uses a mathematical approach to investing. Using this approach, the Sponsor determines the type, quantity and mix of investment positions that the Sponsor believes, in combination, should produce daily returns consistent with the Funds’ objectives. The Sponsor relies upon a pre-determined model to generate orders that result in repositioning the Funds’ investments in accordance with their respective investment objective. The mathematical model is engineered during the product development phase prior to a Fund’s launch and is adjusted, when necessary, in order to help the Funds achieve their investment objective. Changes to the mathematical model may occur at any time without notice to shareholders.
The Sponsor does not invest the assets of the Funds based on its view of the investment merit of a particular investment, other than for cash management purposes, nor does it conduct conventional commodity, currency or volatility research or analysis, or forecast market movement or trends in managing the assets of the Funds. Each Fund generally seeks to remain fully invested at all times in Financial Instruments and money market instruments that, in combination, provide exposure to its underlying benchmark consistent with its investment objective without regard to market conditions, trends or direction.
ProShare Capital Management LLC, a Maryland limited liability company, serves as the Trust’s Sponsor and commodity pool operator. The principal office of the Sponsor and the Funds is located at 7501 Wisconsin Avenue, Suite 1000, Bethesda, Maryland 20814. The telephone number of the Sponsor and each of the Funds is (240) 497-6400.
2
Table of Contents
Each Fund is listed below along with its corresponding benchmark:
| Fund Name |
Benchmark | |
| ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF | S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index (the “Mid-Term VIX Index”) |
| * | The VIX Fund is benchmarked to an index comprised of VIX futures contracts and not to the VIX (as defined herein), which is calculated based on the prices of put and call options on the S&P 500. As such, the VIX Fund can be expected to perform very differently from the VIX. |
| Fund Name |
Benchmark | |
| ProShares Managed Futures Strategy | S&P Strategic Futures Index (the “SFI”) |
| Fund Name |
Benchmark | |
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity | Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM | |
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity | ||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas | Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM | |
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas |
| Fund Name |
Benchmark | |
| ProShares UltraShort Silver | The daily performance of silver bullion as measured by the London Silver Price |
| Fund Name |
Benchmark | |
| ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar | The U.S. dollar price of the Australian dollar | |
| ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar | ||
| ProShares Ultra Euro | The U.S. dollar price of the euro | |
| ProShares Short Euro | ||
| ProShares Ultra Yen | The U.S. dollar price of the Japanese yen |
Purchases and Sales in the Secondary Market on NYSE Arca
The Shares of each Fund are listed on NYSE Arca (the Exchange) under the ticker symbols shown on the front cover of this Prospectus. Secondary market purchases and sales of Shares are subject to ordinary brokerage commissions and charges.
3
Table of Contents
Creation and Redemption Transactions
Only an Authorized Participant may purchase (i.e., create) or redeem Creation Units in the Funds. Creation Units in a Fund are expected to be created when there is sufficient demand for Shares in such Fund that the market price per Share is at a premium to the NAV per Share. Authorized Participants will likely sell such Shares to the public at prices that are expected to reflect, among other factors, the trading price of the Shares of such Fund and the supply of and demand for the Shares at the time of sale and are expected to fall between the NAV and the trading price of the Shares at the time of sale. Similarly, it is expected that Creation Units in a Fund will be redeemed when the market price per Share of such Fund is at a discount to the NAV per Share. The Sponsor expects that the exploitation of such arbitrage opportunities by Authorized Participants and their clients and customers will tend to cause the public trading price of the Shares to track the NAV per Share of a Fund closely over time. Retail investors seeking to purchase or sell Shares on any day are expected to effect such transactions in the secondary market at the market price per Share, rather than in connection with the creation or redemption of Creation Units.
A creation transaction, which is subject to acceptance by SEI, generally takes place when an Authorized Participant deposits a specified amount of cash (unless as provided otherwise in this Prospectus) in exchange for a specified number of Creation Units. Similarly, Shares can be redeemed only in Creation Units, generally for cash (unless as provided otherwise in this Prospectus). Except when aggregated in Creation Units, Shares are not redeemable. The prices at which creations and redemptions occur are based on the next calculation of the NAV after an order is received in a form described in the Authorized Participant Agreement and the related Authorized Participant Handbook. The manner by which Creation Units are purchased and redeemed is dictated by the terms of the Authorized Participant Agreement and Authorized Participant Handbook. By placing a purchase order, an Authorized Participant agrees to deposit cash (unless as provided otherwise in this Prospectus) with BBH&Co., the custodian of the Funds.
Creation and redemption transactions must be placed each day with SEI by the create/redeem cut-off time (stated below), or earlier if the Exchange or other exchange material to the valuation or operation of such Fund closes before such cut-off time, to receive that day’s NAV. Because the primary trading session for the commodities and/or futures contracts underlying certain of the Funds have different closing (or fixing) times than U.S. Equity markets, the NAV calculation times typically range from 7:00 a.m. to 4:15 p.m. Eastern Time.
| Underlying Benchmark |
Create/Redeem Cut-off | NAV Calculation Time | ||||||
| S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index |
2:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | 4:15 p.m. (Eastern Time) | ||||||
| S&P Strategic Futures Index |
10:45 a.m. (Eastern Time) | 3:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | ||||||
| Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM |
10:45 a.m. (Eastern Time) | 2:30 p.m. (Eastern Time) | ||||||
| Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM |
2:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | 2:30 p.m. (Eastern Time) | ||||||
| Silver |
6:30 a.m. (Eastern Time) | 7:00 a.m. (Eastern Time) | ||||||
| Australian dollar |
3:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | ||||||
| Euro |
3:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | ||||||
| Yen |
3:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | ||||||
4
Table of Contents
A Fund will be profitable only if returns from the Fund’s investments exceed its “breakeven amount.” Estimated breakeven amounts are set forth in the table below. The estimated breakeven amounts represent the estimated amount of trading income that each Fund would need to achieve during one year to offset the Fund’s estimated fees, costs and expenses, net of any interest income earned by the Fund on its investments. It is not possible to predict whether a Fund will break even at the end of the first twelve months of an investment or any other period. See “Charges—Breakeven Table,” beginning on page 74, for more detailed tables showing Breakeven Amounts.
| Fund Name |
Breakeven Amount (% Per Annum of Average Daily NAV)* |
Assumed Selling Price Per Share* |
Breakeven Amount ($ for the Assumed Selling Price Per Share)* |
|||||||||
| ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF |
0.85 | $ | 80.00 | 0.68 | ||||||||
| ProShares Managed Futures Strategy |
0.75 | $ | 20.00 | 0.15 | ||||||||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity |
1.55 | $ | 25.00 | 0.39 | ||||||||
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity |
1.56 | $ | 25.00 | 0.39 | ||||||||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas |
1.01 | $ | 40.00 | 0.40 | ||||||||
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas |
1.10 | $ | 40.00 | 0.44 | ||||||||
| ProShares UltraShort Silver |
1.54 | $ | 25.00 | 0.39 | ||||||||
| ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar |
1.01 | $ | 40.00 | 0.40 | ||||||||
| ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar |
1.04 | $ | 40.00 | 0.42 | ||||||||
| ProShares Ultra Euro |
0.93 | $ | 25.00 | 0.23 | ||||||||
| ProShares Short Euro |
0.95 | $ | 40.00 | 0.38 | ||||||||
| ProShares Ultra Yen |
0.93 | $ | 25.00 | 0.23 | ||||||||
| * | The breakeven analysis set forth in this table assumes that the Shares have a constant month-end NAV, and assumes that the selling price per Share will equal the NAV. The analysis is based on an assumed NAV per Share of each Fund as listed in the table above under Assumed Selling Price Per Share. The actual NAV of each Fund differs and is likely to change on a daily basis. The numbers in this chart have been rounded to the nearest 0.01. |
Please note that each Fund will distribute to shareholders a Schedule K-1 that will contain information regarding the income and expense items of the Fund. The Schedule K-1 is a complex form and shareholders may find that preparing tax returns may require additional time or may require the assistance of an accountant or other tax preparer, at an additional expense to the shareholder.
5
Table of Contents
Before investors invest in the Shares, they should be aware that there are various risks. Investors should consider carefully the risks described below together with all of the other information included in this Prospectus, as well as information found in documents incorporated by reference in this Prospectus, before they decide to purchase any Shares. These risk factors may be amended, supplemented or superseded from time to time by risk factors contained in any periodic report, prospectus supplement or post-effective amendment filed with the SEC in the future.
Key Risks Related to the Geared Funds
Due to the compounding of daily returns, the Geared Funds’ returns over periods longer than a single day will likely differ in amount and possibly even direction from the Geared Fund multiple times the benchmark return for the period.
Each of the Geared Funds is “geared” in the sense that each has an investment objective to correspond (before fees and expenses) to a multiple (i.e., 2x), the inverse (i.e., -1x) or an inverse multiple (i.e., -2x) of the performance of a benchmark on a given day. Each Geared Fund seeks investment results for a single day only, as measured from NAV calculation time to NAV calculation time, and not for any other period (see “Summary—Creation and Redemption Transactions” for the typical NAV calculation time of each Fund). The return of a Geared Fund for a period longer than a single day is the result of its return for each day compounded over the period and usually will differ from a multiple (2x), the inverse (-1x) or an inverse multiple (-2x) of the return of the Geared Fund’s benchmark for the period. A Geared Fund will lose money if its benchmark’s performance is flat over time, and it is possible for a Geared Fund to lose money over time regardless of the performance of an underlying benchmark, as a result of daily rebalancing, the benchmark’s volatility and compounding. Longer holding periods, higher benchmark volatility, inverse exposure and greater leverage each affect the impact of compounding on a Geared Fund’s returns. Daily compounding of a Geared Fund’s investment returns can dramatically and adversely affect its longer-term performance during periods of high volatility. Volatility may be at least as important to a Geared Fund’s return for a period as the return of the Geared Fund’s underlying benchmark.
Each Ultra or UltraShort Fund uses leverage and should produce daily returns that are more volatile than that of its benchmark. For example, the daily return of an Ultra Fund with a 2x multiple should be approximately two times as volatile on a daily basis as the return of a fund with an objective of matching the same benchmark. The daily return of a Short or UltraShort Fund is designed to return the inverse (-1x) or two times the inverse (-2x), respectively, of the return that would be expected of a fund with an objective of matching the same benchmark. The Geared Funds are not appropriate for all investors and present different risks than other funds. The Geared Funds that use leverage are riskier than similarly benchmarked exchange-traded funds that do not use leverage. An investor should only consider an investment in a Geared Fund if he or she understands the consequences of seeking daily leveraged, daily inverse or daily inverse leveraged investment results. Daily objective geared funds, if used properly and in conjunction with the investor’s view on the future direction and volatility of the markets, can be useful tools for investors who want to manage their exposure to various markets and market segments and who are willing to monitor and/or periodically rebalance their portfolios. Shareholders who invest in the Geared Funds should actively manage and monitor their investments, as frequently as daily.
6
Table of Contents
The hypothetical examples below illustrate how daily geared fund returns can behave for periods longer than a single day. Each involves a hypothetical fund XYZ that seeks to double the daily performance of benchmark XYZ. On each day, fund XYZ performs in line with its objective (two times (2x) the benchmark’s daily performance before fees and expenses). Notice that, in the first example (showing an overall benchmark loss for the period), over the entire seven-day period, the fund’s total return is more than two times the loss of the period return of the benchmark. For the seven-day period, benchmark XYZ lost 3.26% while fund XYZ lost 7.01% (versus -6.52% (or 2 x -3.26%)).
| Benchmark XYZ | Fund XYZ | |||||||||||||||
| Level | Daily Performance |
Daily Performance |
Net Asset Value |
|||||||||||||
| Start |
100.00 | $ | 100.00 | |||||||||||||
| Day 1 |
97.00 | -3.00 | % | -6.00 | % | $ | 94.00 | |||||||||
| Day 2 |
99.91 | 3.00 | % | 6.00 | % | $ | 99.64 | |||||||||
| Day 3 |
96.91 | -3.00 | % | -6.00 | % | $ | 93.66 | |||||||||
| Day 4 |
99.82 | 3.00 | % | 6.00 | % | $ | 99.28 | |||||||||
| Day 5 |
96.83 | -3.00 | % | -6.00 | % | $ | 93.32 | |||||||||
| Day 6 |
99.73 | 3.00 | % | 6.00 | % | $ | 98.92 | |||||||||
| Day 7 |
96.74 | -3.00 | % | -6.00 | % | $ | 92.99 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Return |
-3.26 | % | -7.01 | % | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Similarly, in another example (showing an overall benchmark gain for the period), over the entire seven-day period, the fund’s total return is considerably less than double that of the period return of the benchmark. For the seven-day period, benchmark XYZ gained 2.72% while fund XYZ gained 4.86% (versus 5.44% (or 2 x 2.72%)).
| Benchmark XYZ | Fund XYZ | |||||||||||||||
| Level | Daily Performance |
Daily Performance |
Net Asset Value |
|||||||||||||
| Start |
100.00 | $ | 100.00 | |||||||||||||
| Day 1 |
103.00 | 3.00 | % | 6.00 | % | $ | 106.00 | |||||||||
| Day 2 |
99.91 | -3.00 | % | -6.00 | % | $ | 99.64 | |||||||||
| Day 3 |
102.91 | 3.00 | % | 6.00 | % | $ | 105.62 | |||||||||
| Day 4 |
99.82 | -3.00 | % | -6.00 | % | $ | 99.28 | |||||||||
| Day 5 |
102.81 | 3.00 | % | 6.00 | % | $ | 105.24 | |||||||||
| Day 6 |
99.73 | -3.00 | % | -6.00 | % | $ | 98.92 | |||||||||
| Day 7 |
102.72 | 3.00 | % | 6.00 | % | $ | 104.86 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total Return |
2.72 | % | 4.86 | % | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
These effects are caused by compounding, which exists in all investments, but has a more significant impact in geared funds. In general, during periods of higher benchmark volatility, compounding will cause an Ultra Fund’s results for periods longer than a single day to be less than two times (2x) the return of the benchmark (or less than the inverse (-1x) or two times the inverse (-2x) times the return of the benchmark for the Short and UltraShort Funds, respectively). This effect becomes more pronounced as volatility increases. Conversely, in periods of lower benchmark volatility (particularly when combined with higher benchmark returns), an Ultra Fund’s returns over longer periods can be higher than two times (2x) the return of the benchmark. Actual results for a particular period, before fees and expenses, are also dependent on the magnitude of the benchmark return in addition to the benchmark volatility. Similar effects exist for the Short and UltraShort Funds, and the significance of these effects may be even greater with such inverse or inverse leveraged funds.
The graphs that follow illustrate this point. Each of the graphs shows a simulated hypothetical one-year performance of a benchmark compared with the performance of a geared fund that perfectly achieves its geared
7
Table of Contents
daily investment objective. The graphs demonstrate that, for periods greater than a single day, a geared fund is likely to underperform or overperform (but not match) the benchmark performance (or the inverse of the benchmark performance) times the multiple stated as the daily fund objective. Investors should understand the consequences of holding daily rebalanced funds for periods longer than a single day and should actively manage and monitor their investments, as frequently as daily. A one-year period is used solely for illustrative purposes. Deviations from the benchmark return (or the inverse of the benchmark return) times the fund multiple can occur over periods as short as two days (each day as measured from NAV to NAV) and may also occur in periods shorter than a single day (when measured intraday as opposed to NAV to NAV). See “—Intraday Price/Performance Risk” below for additional details. To isolate the impact of daily leveraged, inverse or inverse leveraged exposure, these graphs assume: a) no fund expenses or transaction costs; b) borrowing/lending rates (to obtain required leveraged, inverse or inverse leveraged exposure) and cash reinvestment rates of zero percent; and c) the fund consistently maintaining perfect exposure (2x, -1x or -2x) as of the fund’s NAV time each day. If these assumptions were different, the fund’s performance would be different than that shown. If fund expenses, transaction costs and financing expenses greater than zero percent were included, the fund’s performance would also be different than shown. Each of the graphs also assumes a volatility rate of 39% which is an approximate average of the five-year historical volatility rate of the most volatile benchmark referenced herein (the Bloomberg Natural Gas Sub-IndexSM). A benchmark’s volatility rate is a statistical measure of the magnitude of fluctuations in its returns.
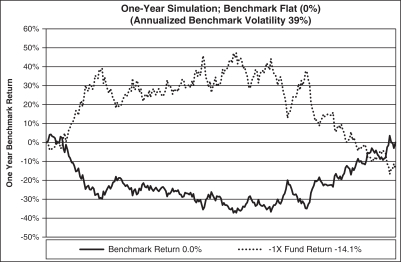
The graph above shows a scenario where the benchmark, which exhibits day-to-day volatility, is flat or trendless over the year (i.e., provides a return of 0% over the course of the year), but the Short Fund (-1x) is down.
8
Table of Contents
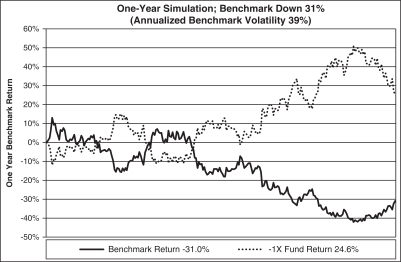
The graph above shows a scenario where the benchmark, which exhibits day-to-day volatility, is down over the year, but the Short Fund (-1x) is up less than the inverse of the benchmark.
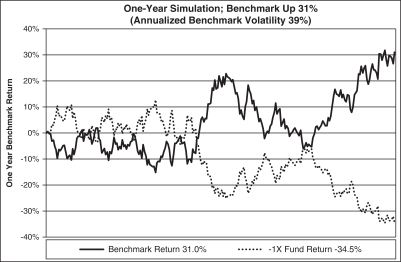
The graph above shows a scenario where the benchmark, which exhibits day-to-day volatility, is up over the year, but the Short Fund (-1x) is down more than the inverse of the benchmark.
9
Table of Contents
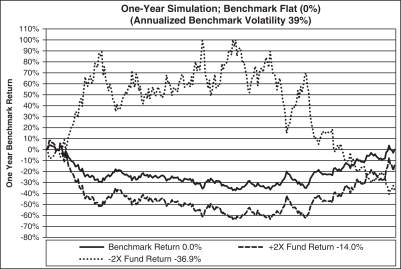
The graph above shows a scenario where the benchmark, which exhibits day-to-day volatility, is flat or trendless over the year (i.e., provides a return of 0% over the course of the year), but the Ultra Fund (2x) and the UltraShort Fund (-2x) are both down.
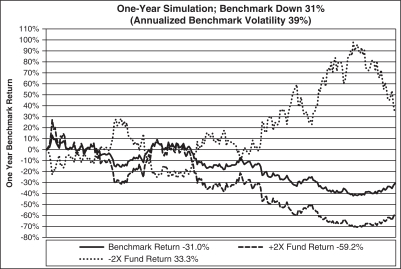
The graph above shows a scenario where the benchmark, which exhibits day-to-day volatility, is down over the year, but the Ultra Fund (2x) is down less than two times the benchmark and the UltraShort Fund (-2x) is up less than two times the inverse of the benchmark.
10
Table of Contents
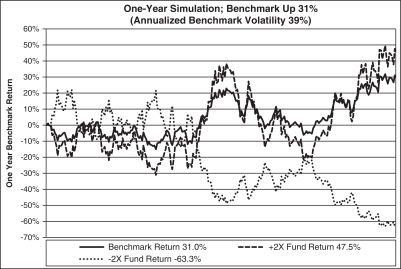
The graph above shows a scenario where the benchmark, which exhibits day-to-day volatility, is up over the year, but the Ultra Fund (2x) is up less than two times the benchmark and the UltraShort Fund (-2x) is down more than two times the inverse of the benchmark.
The historical five-year average volatility of the benchmarks utilized by the Funds ranges from 9.36% to 38.69%, as set forth in the table below.
| Benchmark |
Historical Five-Year Average Volatility Rate as of January 30, 2015 |
|||
| S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index |
31.92 | % | ||
| S&P Strategic Futures Index |
NA | * | ||
| Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM |
14.23 | % | ||
| Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM |
38.69 | % | ||
| The daily performance of silver bullion as measured by the London Silver Price |
37.69 | % | ||
| The U.S. dollar price of the Australian dollar |
11.46 | % | ||
| The U.S. dollar price of the euro |
9.36 | % | ||
| The U.S. dollar price of the Japanese yen |
9.42 | % | ||
| * | The S&P Strategic Futures Index launched on August 14, 2014. Accordingly, the Index has not been in existence for five years. |
The tables below illustrate the impact of two factors that affect a geared fund’s performance: benchmark volatility and benchmark return. Benchmark volatility is a statistical measure of the magnitude of fluctuations in the returns of a benchmark and is calculated as the standard deviation of the natural logarithms of one plus the benchmark return (calculated daily), multiplied by the square root of the number of trading days per year (assumed to be 252). The tables show estimated fund returns for a number of combinations of benchmark volatility and benchmark return over a one-year period. To isolate the impact of daily leveraged, inverse or inverse leveraged exposure, these graphs assume: a) no fund expenses or transaction costs; b) borrowing/lending rates of zero percent (to obtain required leveraged, inverse or inverse leveraged exposure) and cash reinvestment rates of zero percent; and c) the fund consistently maintaining perfect exposure (2x, -1x or -2x) as of the fund’s NAV time each day. If these assumptions were different, the fund’s performance would be different than that shown. If fund expenses, transaction costs and financing expenses were included, the fund’s performance would be different than shown. The first table below shows an example in which a geared fund has an investment objective to correspond (before fees and expenses) to two times (2x) the daily performance of a benchmark. The
11
Table of Contents
geared fund could incorrectly be expected to achieve a 20% return on a yearly basis if the benchmark return was 10%, absent the effects of compounding. However, as the table shows, with a benchmark volatility of 40%, such a fund would return 3.1%. In the charts below, shaded areas represent those scenarios where a geared fund with the investment objective described will outperform (i.e., return more than) the benchmark performance times the stated multiple in the fund’s investment objective; conversely areas not shaded represent those scenarios where the fund will underperform (i.e., return less than) the benchmark performance times the multiple stated as the daily fund objective.
Estimated Fund Return Over One Year When the Fund Objective is to Seek Daily Investment Results, Before Fees and Expenses, that Correspond to Two Times (2x) the Daily Performance of a Benchmark.
| One Year Benchmark Performance |
Two Times (2x) One Year Benchmark Performance |
Benchmark Volatility | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 25% | 30% | 35% | 40% | 45% | 50% | 55% | 60% | 65% | 70% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -60% | -120 | % | -84.0 | % | -84.0 | % | -84.2 | % | -84.4 | % | -84.6 | % | -85.0 | % | -85.4 | % | -85.8 | % | -86.4 | % | -86.9 | % | -87.5 | % | -88.2 | % | -88.8 | % | -89.5 | % | -90.2% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -55% | -110 | % | -79.8 | % | -79.8 | % | -80.0 | % | -80.2 | % | -80.5 | % | -81.0 | % | -81.5 | % | -82.1 | % | -82.7 | % | -83.5 | % | -84.2 | % | -85.0 | % | -85.9 | % | -86.7 | % | -87.6% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -50% | -100 | % | -75.0 | % | -75.1 | % | -75.2 | % | -75.6 | % | -76.0 | % | -76.5 | % | -77.2 | % | -77.9 | % | -78.7 | % | -79.6 | % | -80.5 | % | -81.5 | % | -82.6 | % | -83.6 | % | -84.7% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -45% | -90 | % | -69.8 | % | -69.8 | % | -70.1 | % | -70.4 | % | -70.9 | % | -71.6 | % | -72.4 | % | -73.2 | % | -74.2 | % | -75.3 | % | -76.4 | % | -77.6 | % | -78.9 | % | -80.2 | % | -81.5% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -40% | -80 | % | -64.0 | % | -64.1 | % | -64.4 | % | -64.8 | % | -65.4 | % | -66.2 | % | -67.1 | % | -68.2 | % | -69.3 | % | -70.6 | % | -72.0 | % | -73.4 | % | -74.9 | % | -76.4 | % | -77.9% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -35% | -70 | % | -57.8 | % | -57.9 | % | -58.2 | % | -58.7 | % | -59.4 | % | -60.3 | % | -61.4 | % | -62.6 | % | -64.0 | % | -65.5 | % | -67.1 | % | -68.8 | % | -70.5 | % | -72.3 | % | -74.1% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -30% | -60 | % | -51.0 | % | -51.1 | % | -51.5 | % | -52.1 | % | -52.9 | % | -54.0 | % | -55.2 | % | -56.6 | % | -58.2 | % | -60.0 | % | -61.8 | % | -63.8 | % | -65.8 | % | -67.9 | % | -70.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -25% | -50 | % | -43.8 | % | -43.9 | % | -44.3 | % | -45.0 | % | -46.0 | % | -47.2 | % | -48.6 | % | -50.2 | % | -52.1 | % | -54.1 | % | -56.2 | % | -58.4 | % | -60.8 | % | -63.1 | % | -65.5% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -20% | -40 | % | -36.0 | % | -36.2 | % | -36.6 | % | -37.4 | % | -38.5 | % | -39.9 | % | -41.5 | % | -43.4 | % | -45.5 | % | -47.7 | % | -50.2 | % | -52.7 | % | -55.3 | % | -58.1 | % | -60.8% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -15% | -30 | % | -27.8 | % | -27.9 | % | -28.5 | % | -29.4 | % | -30.6 | % | -32.1 | % | -34.0 | % | -36.1 | % | -38.4 | % | -41.0 | % | -43.7 | % | -46.6 | % | -49.6 | % | -52.6 | % | -55.7% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -10% | -20 | % | -19.0 | % | -19.2 | % | -19.8 | % | -20.8 | % | -22.2 | % | -23.9 | % | -26.0 | % | -28.3 | % | -31.0 | % | -33.8 | % | -36.9 | % | -40.1 | % | -43.5 | % | -46.9 | % | -50.4% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -5% | -10 | % | -9.8 | % | -10.0 | % | -10.6 | % | -11.8 | % | -13.3 | % | -15.2 | % | -17.5 | % | -20.2 | % | -23.1 | % | -26.3 | % | -29.7 | % | -33.3 | % | -37.0 | % | -40.8 | % | -44.7% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0% | 0 | % | 0.0 | % | -0.2 | % | -1.0 | % | -2.2 | % | -3.9 | % | -6.1 | % | -8.6 | % | -11.5 | % | -14.8 | % | -18.3 | % | -22.1 | % | -26.1 | % | -30.2 | % | -34.5 | % | -38.7% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5% | 10 | % | 10.3 | % | 10.0 | % | 9.2 | % | 7.8 | % | 5.9 | % | 3.6 | % | 0.8 | % | -2.5 | % | -6.1 | % | -10.0 | % | -14.1 | % | -18.5 | % | -23.1 | % | -27.7 | % | -32.5% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10% | 20 | % | 21.0 | % | 20.7 | % | 19.8 | % | 18.3 | % | 16.3 | % | 13.7 | % | 10.6 | % | 7.0 | % | 3.1 | % | -1.2 | % | -5.8 | % | -10.6 | % | -15.6 | % | -20.7 | % | -25.9% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15% | 30 | % | 32.3 | % | 31.9 | % | 30.9 | % | 29.3 | % | 27.1 | % | 24.2 | % | 20.9 | % | 17.0 | % | 12.7 | % | 8.0 | % | 3.0 | % | -2.3 | % | -7.7 | % | -13.3 | % | -19.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20% | 40 | % | 44.0 | % | 43.6 | % | 42.6 | % | 40.8 | % | 38.4 | % | 35.3 | % | 31.6 | % | 27.4 | % | 22.7 | % | 17.6 | % | 12.1 | % | 6.4 | % | 0.5 | % | -5.6 | % | -11.8% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25% | 50 | % | 56.3 | % | 55.9 | % | 54.7 | % | 52.8 | % | 50.1 | % | 46.8 | % | 42.8 | % | 38.2 | % | 33.1 | % | 27.6 | % | 21.7 | % | 15.5 | % | 9.0 | % | 2.4 | % | -4.3% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30% | 60 | % | 69.0 | % | 68.6 | % | 67.3 | % | 65.2 | % | 62.4 | % | 58.8 | % | 54.5 | % | 49.5 | % | 44.0 | % | 38.0 | % | 31.6 | % | 24.9 | % | 17.9 | % | 10.8 | % | 3.5% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 35% | 70 | % | 82.3 | % | 81.8 | % | 80.4 | % | 78.2 | % | 75.1 | % | 71.2 | % | 66.6 | % | 61.2 | % | 55.3 | % | 48.8 | % | 41.9 | % | 34.7 | % | 27.2 | % | 19.4 | % | 11.7% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40% | 80 | % | 96.0 | % | 95.5 | % | 94.0 | % | 91.6 | % | 88.3 | % | 84.1 | % | 79.1 | % | 73.4 | % | 67.0 | % | 60.1 | % | 52.6 | % | 44.8 | % | 36.7 | % | 28.5 | % | 20.1% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 45% | 90 | % | 110.3 | % | 109.7 | % | 108.2 | % | 105.6 | % | 102.0 | % | 97.5 | % | 92.2 | % | 86.0 | % | 79.2 | % | 71.7 | % | 63.7 | % | 55.4 | % | 46.7 | % | 37.8 | % | 28.8% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50% | 100 | % | 125.0 | % | 124.4 | % | 122.8 | % | 120.0 | % | 116.2 | % | 111.4 | % | 105.6 | % | 99.1 | % | 91.7 | % | 83.8 | % | 75.2 | % | 66.3 | % | 57.0 | % | 47.5 | % | 37.8% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 55% | 110 | % | 140.3 | % | 139.7 | % | 137.9 | % | 134.9 | % | 130.8 | % | 125.7 | % | 119.6 | % | 112.6 | % | 104.7 | % | 96.2 | % | 87.1 | % | 77.5 | % | 67.6 | % | 57.5 | % | 47.2% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60% | 120 | % | 156.0 | % | 155.4 | % | 153.5 | % | 150.3 | % | 146.0 | % | 140.5 | % | 134.0 | % | 126.5 | % | 118.1 | % | 109.1 | % | 99.4 | % | 89.2 | % | 78.6 | % | 67.8 | % | 56.8% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
12
Table of Contents
Estimated Fund Return Over One Year When the Fund Objective is to Seek Daily Investment Results, Before Fees and Expenses, that Correspond to the Inverse (-1x) of the Daily Performance of a Benchmark.
| One Year Benchmark Performance |
Inverse of One Year Benchmark Performance |
Benchmark Volatility | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 25% | 30% | 35% | 40% | 45% | 50% | 55% | 60% | 65% | 70% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -60% | 60 | % | 150.0 | % | 149.4 | % | 147.5 | % | 144.4 | % | 140.2 | % | 134.9 | % | 128.5 | % | 121.2 | % | 113.0 | % | 104.2 | % | 94.7 | % | 84.7 | % | 74.4 | % | 63.9 | % | 53.2 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -55% | 55 | % | 122.2 | % | 121.7 | % | 120.0 | % | 117.3 | % | 113.5 | % | 108.8 | % | 103.1 | % | 96.6 | % | 89.4 | % | 81.5 | % | 73.1 | % | 64.2 | % | 55.0 | % | 45.6 | % | 36.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -50% | 50 | % | 100.0 | % | 99.5 | % | 98.0 | % | 95.6 | % | 92.2 | % | 87.9 | % | 82.8 | % | 76.9 | % | 70.4 | % | 63.3 | % | 55.8 | % | 47.8 | % | 39.5 | % | 31.1 | % | 22.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -45% | 45 | % | 81.8 | % | 81.4 | % | 80.0 | % | 77.8 | % | 74.7 | % | 70.8 | % | 66.2 | % | 60.9 | % | 54.9 | % | 48.5 | % | 41.6 | % | 34.4 | % | 26.9 | % | 19.2 | % | 11.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -40% | 40 | % | 66.7 | % | 66.3 | % | 65.0 | % | 63.0 | % | 60.1 | % | 56.6 | % | 52.3 | % | 47.5 | % | 42.0 | % | 36.1 | % | 29.8 | % | 23.2 | % | 16.3 | % | 9.2 | % | 2.1 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -35% | 35 | % | 53.8 | % | 53.5 | % | 52.3 | % | 50.4 | % | 47.8 | % | 44.5 | % | 40.6 | % | 36.1 | % | 31.1 | % | 25.6 | % | 19.8 | % | 13.7 | % | 7.3 | % | 0.8 | % | -5.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -30% | 30 | % | 42.9 | % | 42.5 | % | 41.4 | % | 39.7 | % | 37.3 | % | 34.2 | % | 30.6 | % | 26.4 | % | 21.7 | % | 16.7 | % | 11.3 | % | 5.6 | % | -0.3 | % | -6.4 | % | -12.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -25% | 25 | % | 33.3 | % | 33.0 | % | 32.0 | % | 30.4 | % | 28.1 | % | 25.3 | % | 21.9 | % | 18.0 | % | 13.6 | % | 8.9 | % | 3.8 | % | -1.5 | % | -7.0 | % | -12.6 | % | -18.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -20% | 20 | % | 25.0 | % | 24.7 | % | 23.8 | % | 22.2 | % | 20.1 | % | 17.4 | % | 14.2 | % | 10.6 | % | 6.5 | % | 2.1 | % | -2.6 | % | -7.6 | % | -12.8 | % | -18.1 | % | -23.4 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -15% | 15 | % | 17.6 | % | 17.4 | % | 16.5 | % | 15.0 | % | 13.0 | % | 10.5 | % | 7.5 | % | 4.1 | % | 0.3 | % | -3.9 | % | -8.4 | % | -13.1 | % | -17.9 | % | -22.9 | % | -27.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -10% | 10 | % | 11.1 | % | 10.8 | % | 10.0 | % | 8.6 | % | 6.8 | % | 4.4 | % | 1.5 | % | -1.7 | % | -5.3 | % | -9.3 | % | -13.5 | % | -17.9 | % | -22.5 | % | -27.2 | % | -31.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -5% | 5 | % | 5.3 | % | 5.0 | % | 4.2 | % | 2.9 | % | 1.1 | % | -1.1 | % | -3.8 | % | -6.9 | % | -10.3 | % | -14.0 | % | -18.0 | % | -22.2 | % | -26.6 | % | -31.0 | % | -35.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0% | 0 | % | 0.0 | % | -0.2 | % | -1.0 | % | -2.2 | % | -3.9 | % | -6.1 | % | -8.6 | % | -11.5 | % | -14.8 | % | -18.3 | % | -22.1 | % | -26.1 | % | -30.2 | % | -34.5 | % | -38.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5% | -5 | % | -4.8 | % | -5.0 | % | -5.7 | % | -6.9 | % | -8.5 | % | -10.5 | % | -13.0 | % | -15.7 | % | -18.8 | % | -22.2 | % | -25.8 | % | -29.6 | % | -33.6 | % | -37.6 | % | -41.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10% | -10 | % | -9.1 | % | -9.3 | % | -10.0 | % | -11.1 | % | -12.7 | % | -14.6 | % | -16.9 | % | -19.6 | % | -22.5 | % | -25.8 | % | -29.2 | % | -32.8 | % | -36.6 | % | -40.4 | % | -44.3 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15% | -15 | % | -13.0 | % | -13.3 | % | -13.9 | % | -15.0 | % | -16.5 | % | -18.3 | % | -20.5 | % | -23.1 | % | -25.9 | % | -29.0 | % | -32.3 | % | -35.7 | % | -39.3 | % | -43.0 | % | -46.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20% | -20 | % | -16.7 | % | -16.9 | % | -17.5 | % | -18.5 | % | -19.9 | % | -21.7 | % | -23.8 | % | -26.3 | % | -29.0 | % | -31.9 | % | -35.1 | % | -38.4 | % | -41.9 | % | -45.4 | % | -48.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25% | -25 | % | -20.0 | % | -20.2 | % | -20.8 | % | -21.8 | % | -23.1 | % | -24.8 | % | -26.9 | % | -29.2 | % | -31.8 | % | -34.7 | % | -37.7 | % | -40.9 | % | -44.2 | % | -47.6 | % | -51.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30% | -30 | % | -23.1 | % | -23.3 | % | -23.8 | % | -24.8 | % | -26.1 | % | -27.7 | % | -29.7 | % | -31.9 | % | -34.5 | % | -37.2 | % | -40.1 | % | -43.2 | % | -46.3 | % | -49.6 | % | -52.9 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 35% | -35 | % | -25.9 | % | -26.1 | % | -26.7 | % | -27.6 | % | -28.8 | % | -30.4 | % | -32.3 | % | -34.5 | % | -36.9 | % | -39.5 | % | -42.3 | % | -45.3 | % | -48.3 | % | -51.5 | % | -54.6 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40% | -40 | % | -28.6 | % | -28.7 | % | -29.3 | % | -30.2 | % | -31.4 | % | -32.9 | % | -34.7 | % | -36.8 | % | -39.1 | % | -41.7 | % | -44.4 | % | -47.2 | % | -50.2 | % | -53.2 | % | -56.2 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 45% | -45 | % | -31.0 | % | -31.2 | % | -31.7 | % | -32.6 | % | -33.7 | % | -35.2 | % | -37.0 | % | -39.0 | % | -41.2 | % | -43.7 | % | -46.3 | % | -49.0 | % | -51.9 | % | -54.8 | % | -57.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50% | -50 | % | -33.3 | % | -33.5 | % | -34.0 | % | -34.8 | % | -35.9 | % | -37.4 | % | -39.1 | % | -41.0 | % | -43.2 | % | -45.6 | % | -48.1 | % | -50.7 | % | -53.5 | % | -56.3 | % | -59.2 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 55% | -55 | % | -35.5 | % | -35.6 | % | -36.1 | % | -36.9 | % | -38.0 | % | -39.4 | % | -41.0 | % | -42.9 | % | -45.0 | % | -47.3 | % | -49.8 | % | -52.3 | % | -55.0 | % | -57.7 | % | -60.5 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60% | -60 | % | -37.5 | % | -37.7 | % | -38.1 | % | -38.9 | % | -40.0 | % | -41.3 | % | -42.9 | % | -44.7 | % | -46.7 | % | -49.0 | % | -51.3 | % | -53.8 | % | -56.4 | % | -59.0 | % | -61.7 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Estimated Fund Return Over One Year When the Fund Objective is to Seek Daily Investment Results, Before Fees and Expenses, that Correspond to Two Times the Inverse (-2x) of the Daily Performance of a Benchmark.
| One Year Benchmark Performance |
Two
Times Inverse (-2x) of One Year Benchmark Performance |
Benchmark Volatility | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0% | 5% | 10% | 15% | 20% | 25% | 30% | 35% | 40% | 45% | 50% | 55% | 60% | 65% | 70% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -60% | 120 | % | 525.0 | % | 520.3 | % | 506.5 | % | 484.2 | % | 454.3 | % | 418.1 | % | 377.1 | % | 332.8 | % | 286.7 | % | 240.4 | % | 195.2 | % | 152.2 | % | 112.2 | % | 76.0 | % | 43.7% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -55% | 110 | % | 393.8 | % | 390.1 | % | 379.2 | % | 361.6 | % | 338.0 | % | 309.4 | % | 277.0 | % | 242.0 | % | 205.6 | % | 169.0 | % | 133.3 | % | 99.3 | % | 67.7 | % | 39.0 | % | 13.5% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -50% | 100 | % | 300.0 | % | 297.0 | % | 288.2 | % | 273.9 | % | 254.8 | % | 231.6 | % | 205.4 | % | 177.0 | % | 147.5 | % | 117.9 | % | 88.9 | % | 61.4 | % | 35.8 | % | 12.6 | % | -8.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -45% | 90 | % | 230.6 | % | 228.1 | % | 220.8 | % | 209.0 | % | 193.2 | % | 174.1 | % | 152.4 | % | 128.9 | % | 104.6 | % | 80.1 | % | 56.2 | % | 33.4 | % | 12.3 | % | -6.9 | % | -24.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -40% | 80 | % | 177.8 | % | 175.7 | % | 169.6 | % | 159.6 | % | 146.4 | % | 130.3 | % | 112.0 | % | 92.4 | % | 71.9 | % | 51.3 | % | 31.2 | % | 12.1 | % | -5.7 | % | -21.8 | % | -36.1% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -35% | 70 | % | 136.7 | % | 134.9 | % | 129.7 | % | 121.2 | % | 109.9 | % | 96.2 | % | 80.7 | % | 63.9 | % | 46.5 | % | 28.9 | % | 11.8 | % | -4.5 | % | -19.6 | % | -33.4 | % | -45.6% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -30% | 60 | % | 104.1 | % | 102.6 | % | 98.1 | % | 90.8 | % | 81.0 | % | 69.2 | % | 55.8 | % | 41.3 | % | 26.3 | % | 11.2 | % | -3.6 | % | -17.6 | % | -30.7 | % | -42.5 | % | -53.1% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -25% | 50 | % | 77.8 | % | 76.4 | % | 72.5 | % | 66.2 | % | 57.7 | % | 47.4 | % | 35.7 | % | 23.1 | % | 10.0 | % | -3.2 | % | -16.0 | % | -28.3 | % | -39.6 | % | -49.9 | % | -59.1% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -20% | 40 | % | 56.3 | % | 55.1 | % | 51.6 | % | 46.1 | % | 38.6 | % | 29.5 | % | 19.3 | % | 8.2 | % | -3.3 | % | -14.9 | % | -26.2 | % | -36.9 | % | -46.9 | % | -56.0 | % | -64.1% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -15% | 30 | % | 38.4 | % | 37.4 | % | 34.3 | % | 29.4 | % | 22.8 | % | 14.7 | % | 5.7 | % | -4.2 | % | -14.4 | % | -24.6 | % | -34.6 | % | -44.1 | % | -53.0 | % | -61.0 | % | -68.2% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -10% | 20 | % | 23.5 | % | 22.5 | % | 19.8 | % | 15.4 | % | 9.5 | % | 2.3 | % | -5.8 | % | -14.5 | % | -23.6 | % | -32.8 | % | -41.7 | % | -50.2 | % | -58.1 | % | -65.2 | % | -71.6% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| -5% | 10 | % | 10.8 | % | 10.0 | % | 7.5 | % | 3.6 | % | -1.7 | % | -8.1 | % | -15.4 | % | -23.3 | % | -31.4 | % | -39.6 | % | -47.7 | % | -55.3 | % | -62.4 | % | -68.8 | % | -74.5% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 0% | 0 | % | 0.0 | % | -0.7 | % | -3.0 | % | -6.5 | % | -11.3 | % | -17.1 | % | -23.7 | % | -30.8 | % | -38.1 | % | -45.5 | % | -52.8 | % | -59.6 | % | -66.0 | % | -71.8 | % | -77.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 5% | -10 | % | -9.3 | % | -10.0 | % | -12.0 | % | -15.2 | % | -19.6 | % | -24.8 | % | -30.8 | % | -37.2 | % | -43.9 | % | -50.6 | % | -57.2 | % | -63.4 | % | -69.2 | % | -74.5 | % | -79.1% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 10% | -20 | % | -17.4 | % | -18.0 | % | -19.8 | % | -22.7 | % | -26.7 | % | -31.5 | % | -36.9 | % | -42.8 | % | -48.9 | % | -55.0 | % | -61.0 | % | -66.7 | % | -71.9 | % | -76.7 | % | -81.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 15% | -30 | % | -24.4 | % | -25.0 | % | -26.6 | % | -29.3 | % | -32.9 | % | -37.3 | % | -42.3 | % | -47.6 | % | -53.2 | % | -58.8 | % | -64.3 | % | -69.5 | % | -74.3 | % | -78.7 | % | -82.6% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 20% | -40 | % | -30.6 | % | -31.1 | % | -32.6 | % | -35.1 | % | -38.4 | % | -42.4 | % | -47.0 | % | -51.9 | % | -57.0 | % | -62.2 | % | -67.2 | % | -72.0 | % | -76.4 | % | -80.4 | % | -84.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 25% | -50 | % | -36.0 | % | -36.5 | % | -37.9 | % | -40.2 | % | -43.2 | % | -46.9 | % | -51.1 | % | -55.7 | % | -60.4 | % | -65.1 | % | -69.8 | % | -74.2 | % | -78.3 | % | -82.0 | % | -85.3% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 30% | -60 | % | -40.8 | % | -41.3 | % | -42.6 | % | -44.7 | % | -47.5 | % | -50.9 | % | -54.8 | % | -59.0 | % | -63.4 | % | -67.8 | % | -72.0 | % | -76.1 | % | -79.9 | % | -83.3 | % | -86.4% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 35% | -70 | % | -45.1 | % | -45.5 | % | -46.8 | % | -48.7 | % | -51.3 | % | -54.5 | % | -58.1 | % | -62.0 | % | -66.0 | % | -70.1 | % | -74.1 | % | -77.9 | % | -81.4 | % | -84.6 | % | -87.4% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 40% | -80 | % | -49.0 | % | -49.4 | % | -50.5 | % | -52.3 | % | -54.7 | % | -57.7 | % | -61.1 | % | -64.7 | % | -68.4 | % | -72.2 | % | -75.9 | % | -79.4 | % | -82.7 | % | -85.6 | % | -88.3% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 45% | -90 | % | -52.4 | % | -52.8 | % | -53.8 | % | -55.5 | % | -57.8 | % | -60.6 | % | -63.7 | % | -67.1 | % | -70.6 | % | -74.1 | % | -77.5 | % | -80.8 | % | -83.8 | % | -86.6 | % | -89.1% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 50% | -100 | % | -55.6 | % | -55.9 | % | -56.9 | % | -58.5 | % | -60.6 | % | -63.2 | % | -66.1 | % | -69.2 | % | -72.5 | % | -75.8 | % | -79.0 | % | -82.1 | % | -84.9 | % | -87.5 | % | -89.8% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 55% | -110 | % | -58.4 | % | -58.7 | % | -59.6 | % | -61.1 | % | -63.1 | % | -65.5 | % | -68.2 | % | -71.2 | % | -74.2 | % | -77.3 | % | -80.3 | % | -83.2 | % | -85.9 | % | -88.3 | % | -90.4% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 60% | -120 | % | -60.9 | % | -61.2 | % | -62.1 | % | -63.5 | % | -65.4 | % | -67.6 | % | -70.2 | % | -73.0 | % | -75.8 | % | -78.7 | % | -81.5 | % | -84.2 | % | -86.7 | % | -89.0 | % | -91.0% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
13
Table of Contents
The foregoing tables are intended to isolate the effect of benchmark volatility and benchmark performance on the return of leveraged, inverse or inverse leveraged funds. The Funds’ actual returns may be significantly greater or less than the returns shown above as a result of any of the factors discussed above or under the below risk factor describing correlation risks.
Correlation Risks Specific to the Geared Funds.
In order to achieve a high degree of correlation with their applicable underlying benchmarks, the Geared Funds seek to rebalance their portfolios daily to keep exposure consistent with their investment objectives. Being materially under- or overexposed to the benchmarks may prevent such Geared Funds from achieving a high degree of correlation with their applicable underlying benchmarks. Market disruptions or closures, large movements of assets into or out of the Geared Funds, regulatory restrictions or extreme market volatility will adversely affect such Geared Funds’ ability to adjust exposure to requisite levels. The target amount of portfolio exposure is impacted dynamically by the benchmarks’ movements during each day. Because of this, it is unlikely that the Geared Funds will be perfectly exposed (i.e., 2x, -1x or -2x, as applicable) at the end of each day, and the likelihood of being materially under- or overexposed is higher on days when the benchmark levels are volatile near the close of the trading day.
In addition, unlike other funds that do not rebalance their portfolios as frequently, each Geared Fund may be subject to increased trading costs associated with daily portfolio rebalancings in order to maintain appropriate exposure to the underlying benchmarks. Such costs include commissions paid to the FCMs, and may vary by FCM. The effects of these trading costs have been estimated and included in the Breakeven Table. See “Charges—Breakeven Table” below.
For general correlation risks of all Funds, please see “Correlation Risks for all Funds.” below.
Intraday Price/Performance Risk.
Each Geared Fund is typically rebalanced at or about the time of its NAV calculation time (which may be other than at the close of the U.S. equity markets). As such, the intraday position of the Geared Fund will generally be different from the Geared Fund’s stated daily investment objective (i.e., 2x, -1x or -2x). When Shares are bought intraday, the performance of a Geared Fund’s Shares until the Fund’s next NAV calculation will generally be greater than or less than the Fund’s stated daily multiple, inverse or inverse multiple.
The use of leveraged, inverse and/or inverse leveraged positions could result in the total loss of an investor’s investment.
Each of the Ultra and UltraShort Funds utilize leverage in seeking to achieve their respective investment objectives and will lose more money in market environments adverse to their respective daily investment objectives than funds that do not employ leverage. The use of leveraged and/or inverse leveraged positions could result in the total loss of an investor’s investment.
For example, because the Ultra and UltraShort Funds offered hereby include a two times (2x) or a two times the inverse (-2x) multiplier, a single-day movement in the relevant benchmark approaching 50% at any point in the day could result in the total loss or almost total loss of an investor’s investment if that movement is contrary to the investment objective of the Fund in which an investor has invested, even if such Fund’s benchmark subsequently moves in an opposite direction, eliminating all or a portion of the movement. This would be the case with downward single-day or intraday movements in the underlying benchmark of an Ultra Fund or upward single day or intraday movements in the benchmark of an UltraShort Fund, even if the underlying benchmark maintains a level greater than zero at all times.
Inverse positions can also result in the total loss of an investor’s investment. For the Short Fund, a single-day or intraday increase in the level of the Fund’s benchmark approaching 100% could result in the total loss or almost total loss of an investor’s investment, even if such Fund’s benchmark subsequently moves lower.
14
Table of Contents
Key Risks Related to All Funds
Correlation Risks for all Funds.
While the Funds seek to meet their investment objectives, there is no guarantee they will do so. Factors that may affect a Fund’s ability to meet its investment objective include: (1) the Sponsor’s ability to purchase and sell Financial Instruments in a manner that correlates to a Fund’s objective; (2) an imperfect correlation between the performance of the Financial Instruments held by a Fund and the performance of the applicable benchmark; (3) bid-ask spreads on such Financial Instruments; (4) fees, expenses, transaction costs, financing costs associated with the use of Financial Instruments and commission costs; (5) holding Financial Instruments traded in a market that has become illiquid or disrupted; (6) a Fund’s Share prices being rounded to the nearest cent and/or valuation methodologies; (7) changes to a benchmark that are not disseminated in advance; (8) the need to conform a Fund’s portfolio holdings to comply with investment restrictions or policies or regulatory or tax law requirements; (9) early and unanticipated closings of the markets on which the holdings of a Fund trade, resulting in the inability of the Fund to execute intended portfolio transactions; (10) accounting standards; and (11) differences caused by a Fund obtaining exposure to only a representative sample of the components of a benchmark, overweighting or underweighting certain components of a benchmark or obtaining exposure to assets that are not included in a benchmark.
Being materially under- or overexposed to its benchmark may prevent such Funds from achieving a high degree of correlation with their applicable underlying benchmark. Market disruptions or closures, large movements of assets into or out of a Fund, regulatory restrictions or extreme market volatility will adversely affect such Fund’s ability to maintain a high degree of correlation. The number of components included in the applicable benchmark index across which a Fund needs to allocate, and the frequency at which it rebalances its portfolio (and related costs), may also impact correlation.
Each Fund seeks to provide investment results that correspond (before fees and expenses) to the performance of, or a multiple, the inverse or an inverse multiple of the daily performance of a benchmark at all times, even during periods when the applicable benchmark is flat as well as when the benchmark is moving in a manner which causes the Fund’s NAV to decline, thereby causing losses to such Fund.
Other than for cash management purposes, the Funds are not actively managed by traditional methods (e.g., by effecting changes in the composition of a portfolio on the basis of judgments relating to economic, financial and market considerations with a view toward obtaining positive results under all market conditions). Rather, the Sponsor seeks to cause the NAV to track the daily performance of a benchmark in accordance with each Fund’s investment objective, even during periods in which the benchmark is flat or moving in a manner which causes the NAV of a Fund to decline. It is possible to lose money over time regardless of the performance of an underlying benchmark, due to the effects of daily rebalancing, volatility and compounding, as applicable (see the risk factors above for additional details).
The assets that the Funds invest in can be highly volatile and the Funds may experience large losses when buying, selling or holding such instruments.
Investments linked to volatility, commodity, currency or fixed income markets can be highly volatile compared to investments in traditional securities and the Funds may experience large losses. The value of these investments may be affected by changes in overall market movements, commodity or currency benchmarks (as the case may be), volatility, changes in interest rates or factors affecting a particular industry, commodity or currency. For example, commodity futures contracts (as may be held by the Managed Futures Fund or the Commodity Index Funds) may be affected by numerous factors, including drought, floods, fires, weather, livestock diseases, pipeline ruptures or spills, embargoes, tariffs and international, economic, political or regulatory developments. In particular, trading in VIX futures contracts and trading in natural gas futures contracts (or other Financial Instruments linked to natural gas) have been very volatile and can be expected to be very volatile in the future. High volatility may have an adverse impact on the Funds beyond the impact of any performance-based losses of the underlying benchmark.
15
Table of Contents
The number of underlying components included in a Fund’s benchmark may impact volatility, which could adversely affect an investment in the Shares.
The number of underlying components in a Fund’s benchmark may also impact volatility, which could adversely affect an investment in the Shares. For example, certain of the benchmarks are concentrated in terms of the number and type of commodities represented, and some of the subindexes are solely concentrated in a single commodity futures contract. Investors should be aware that other benchmarks are more diversified in terms of both the number and variety of investments included. Concentration in fewer underlying components may result in a greater degree of volatility in a benchmark and the NAV of the Fund which corresponds to that benchmark under specific market conditions and over time.
Potential negative impact from rolling futures positions.
The VIX Fund, the Managed Futures Fund, the Commodity Index Funds and the Commodity Fund invest in or have exposure to futures contracts and are subject to risks related to rolling. The contractual obligations of a buyer or seller holding a futures contract to expiration may be satisfied by settling in cash as designated in the contract specifications. Alternatively, futures contracts may be closed out prior to expiration by making an offsetting sale or purchase of an identical futures contract on the same or linked exchange before the designated date of settlement. Once this date is reached, the futures contract “expires.” As the futures contracts held by these Funds near expiration, they are generally closed out and replaced by contracts with a later expiration. This process is referred to as “rolling.” Such Funds do not intend to hold futures contracts through expiration, but instead to “roll” their respective positions.
When the market for these contracts is such that the prices are higher in the more distant delivery months than in the nearer delivery months, the sale during the course of the “rolling process” of the more nearby contract would take place at a price that is lower than the price of the more distant contract. This pattern of higher futures prices for longer expiration futures contracts is often referred to as “contango.” Alternatively, when the market for these contracts is such that the prices are higher in the nearer months than in the more distant months, the sale during the course of the “rolling process” of the more nearby contract would take place at a price that is higher than the price of the more distant contract. This pattern of higher futures prices for shorter expiration futures contracts is referred to as “backwardation.” The presence of contango in certain futures contracts at the time of rolling would be expected to adversely affect the relevant Funds with long positions, and positively affect the Funds with short positions. Similarly, the presence of backwardation in certain futures contracts at the time of rolling such contracts would be expected to adversely affect the Funds with short positions and positively affect the Funds with long positions.
There have been extended periods in which contango or backwardation has existed in the futures contract markets for various types of futures contracts, and such periods can be expected to occur in the future. These extended periods have in the past and can in the future cause significant losses for the Funds, and these periods can have as much or more impact over time than movements in the level of a Fund’s benchmark.
Credit and liquidity risks associated with collateralized repurchase agreements.
A portion of each Fund’s assets may be held in cash and/or U.S. Treasury securities, agency securities, or other high credit quality, short-term fixed-income or similar securities (such as shares of money market funds and collateralized repurchase agreements). These securities may be used for direct investment or serve as collateral for such Fund’s trading in Financial Instruments, as applicable, and may include collateralized repurchase agreements. Collateralized repurchase agreements involve an agreement to purchase a security and to sell that security back to the original seller at an agreed-upon price. The resale price reflects the purchase price plus an agreed-upon incremental amount which is unrelated to the coupon rate or maturity of the purchased security. As protection against the risk that the original seller will not fulfill its obligation, the buyer receives collateral marked-to-market daily, and maintained at a value at least equal to the sale price plus the accrued incremental amount. Although the collateralized repurchase agreements that the Funds enter into require that
16
Table of Contents
counterparties (which act as original sellers) overcollateralize the amount owed to a Fund with U.S. Treasury securities and/or agency securities, there is a risk that such collateral could decline in price at the same time that the counterparty defaults on its obligation to repurchase the security. If this occurs, a Fund may incur losses or delays in receiving proceeds. To minimize these risks, the Funds typically enter into transactions only with major, global financial institutions.
Possible illiquid markets may exacerbate losses.
Financial Instruments cannot always be liquidated at the desired price. It is difficult to execute a trade at a specific price when there is a relatively small volume of buy and sell orders in a market. A market disruption can also make it difficult to liquidate a position or find a swap or forward contract counterparty at a reasonable cost.
Market illiquidity may cause losses for the Funds. The large size of the positions which the Funds may acquire increases the risk of illiquidity by both making their positions more difficult to liquidate and increasing the losses incurred while trying to do so. Any type of disruption or illiquidity will potentially be exacerbated due to the fact that the Funds will typically invest in Financial Instruments related to one benchmark, which in many cases is highly concentrated.
It may not be possible to gain exposure to the benchmarks using exchange-traded Financial Instruments in the future.
The Funds may utilize exchange-traded Financial Instruments. It may not be possible to gain exposure to the benchmarks with these Financial Instruments in the future. If these Financial Instruments cease to be traded on regulated exchanges, they may be replaced with Financial Instruments traded on trading facilities that are subject to lesser degrees of regulation or, in some cases, no substantive regulation. As a result, trading in such Financial Instruments, and the manner in which prices and volumes are reported by the relevant trading facilities, may not be subject to the provisions of, and the protections afforded by, the Commodity Exchange Act, as amended (the “CEA”), or other applicable statutes and related regulations, that govern trading on regulated U.S. futures exchanges, or similar statutes and regulations that govern trading on regulated U.K. futures exchanges. In addition, many electronic trading facilities have only recently initiated trading and do not have significant trading histories. As a result, the trading of contracts on such facilities, and the inclusion of such contracts in a benchmark, may be subject to certain risks not presented by U.S. or U.K. exchange-traded futures contracts, including risks related to the liquidity and price histories of the relevant contracts.
Fees are charged regardless of a Fund’s returns and may result in depletion of assets.
The Funds are subject to the fees and expenses described herein which are payable irrespective of a Fund’s returns, as well as the effects of commissions, trading spreads, and embedded financing, borrowing costs and fees associated with swaps, forwards, futures contracts, and costs relating to the purchase of U.S. Treasury securities or similar high credit quality, short-term fixed-income or similar securities. Additional charges may include other fees as applicable.
For the Funds linked to an index, changes implemented by an index provider or the CBOE that affect the composition and valuation of the index could adversely affect the value of an investment in a Fund’s Shares.
The VIX Fund, the Managed Futures Fund and the Commodity Index Funds are linked to indexes maintained by an index provider, either Standard & Poor’s (“S&P”) or Bloomberg, as applicable, each of which is unaffiliated with the Funds or the Sponsor. The policies implemented by each index provider concerning the calculation of the level of an index or the composition of an index could affect the level of an index and, therefore, the value of the corresponding Fund’s Shares. An index provider may change the composition of the indexes, or make other methodological changes that could change the level of an index. Additionally, an index provider may alter, discontinue or suspend calculation or dissemination of an index. Any of these actions could
17
Table of Contents
adversely affect the value of Shares of a Fund using that index as a benchmark. An index provider has no obligation to consider Fund shareholder interests in calculating or revising an index. In addition, for the VIX Fund, the CBOE can make methodological changes to the calculation of the VIX that could affect the value of VIX futures contracts and, consequently, the value of the VIX Fund’s Shares. There can be no assurance that the CBOE will not change the VIX calculation methodology in a way which may affect the value of the VIX Fund’s Shares. The CBOE may also alter, discontinue or suspend calculation or dissemination of the VIX and/or exercise settlement value. Any of these actions could adversely affect the value of such Fund’s Shares.
Calculation of an index may not be possible or feasible under certain events or circumstances that are beyond the reasonable control of the Sponsor, which in turn may adversely impact both the index and/or the Shares, as applicable. Additionally, index calculations may be disrupted by rollover disruptions, rebalancing disruptions and/or market emergencies, which may have an adverse effect on the value of the Shares.
The Funds may be subject to counterparty risks.
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Silver, ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Ultra Yen will use swap agreements and/or forward contracts as a means to achieve their respective investment objectives. Such Funds will primarily use either swap agreements and/or forward contracts referencing their respective benchmarks or in other swap agreements or forward contracts if such instruments tend to exhibit trading prices or returns that correlate with its benchmark or a component of the benchmark and will further the investment objective of the Fund. Each of the other Funds may invest in swap agreements (for the VIX Fund, the Managed Futures Fund and the Natural Gas Funds) or forward contracts (for the other Currency Funds: ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar, ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar and ProShares Short Euro) if position accountability rules or position limits are reached with respect to specific futures contracts or the market for a specific futures contract experiences emergencies (e.g., natural disaster, terrorist attack or an act of God) or disruptions (e.g., a trading halt or a flash crash) that prevent such Fund from obtaining the appropriate amount of investment exposure to the affected futures contract or certain other futures contracts. Although unlikely, the Funds, under these circumstances, could have 100% exposure to swap agreements or forward contracts, as applicable.
Swap agreements and forward contracts are generally traded in over-the-counter (“OTC”) markets and have only recently become subject to regulation by the CFTC. CFTC rules, however, do not cover all types of swap agreements and forward contracts. Investors, therefore, may not receive the protection of CFTC regulation or the statutory scheme of the CEA in connection with each Fund’s swap agreements or forward contracts. The lack of regulation in these markets could expose investors to significant losses under certain circumstances, including in the event of trading abuses or financial failure by participants.
The Funds will be subject to credit risk with respect to the counterparties to the derivatives contracts (whether a clearing corporation in the case of cleared instruments or another third party in the case of OTC uncleared instruments). Unlike in futures contracts, the counterparty to uncleared swap agreements or forward contracts is generally a single bank or other financial institution, rather than a clearing organization backed by a group of financial institutions. As a result, a Fund is subject to increased credit risk with respect to the amount it expects to receive from counterparties to uncleared swaps and forward contracts entered into as part of that Fund’s principal investment strategy. If a counterparty becomes bankrupt or otherwise fails to perform its obligations due to financial difficulties, a Fund could suffer significant losses on these contracts and the value of an investor’s investment in a Fund may decline.
The Funds have sought to mitigate these risks by generally requiring that the counterparties for each Fund agree to post collateral for the benefit of the Fund, marked to market daily, subject to certain minimum thresholds; however there are no limitations on the percentage of its assets each Fund may invest in swap agreements or forward contracts with a particular counterparty. To the extent any such collateral is insufficient or there are delays in accessing the collateral, the Funds will be exposed to counterparty risk as described above,
18
Table of Contents
including possible delays in recovering amounts as a result of bankruptcy proceedings. The Funds typically enter into transactions only with major, global financial institutions.
OTC swaps and forward contracts of the type that may be utilized by the Funds are less liquid than futures contracts because they are not traded on an exchange, do not have uniform terms and conditions, and are generally entered into based upon the creditworthiness of the parties and the availability of credit support, such as collateral, and in general, are not transferable without the consent of the counterparty. These agreements contain various conditions, events of default, termination events, covenants and representations. The triggering of certain events or the default on certain terms of the agreement could allow a party to terminate a transaction under the agreement and request immediate payment in an amount equal to the net positions owed the party under the agreement. For example, if the level of the Fund’s benchmark has a dramatic intraday move that would cause a material decline in the Fund’s NAV, the terms of the swap may permit the counterparty to immediately close out the transaction with the Fund. In that event, it may not be possible for the Fund to enter into another swap agreement or to invest in other Financial Instruments necessary to achieve the desired exposure consistent with the Fund’s objective. This, in turn, may prevent the Fund from achieving its investment objective, particularly if the level of the Fund’s benchmark reverses all or part of its intraday move by the end of the day. In addition, cleared derivatives transactions benefit from daily marking-to-market and settlement, and segregation and minimum capital requirements applicable to intermediaries. Transactions entered into directly between two counterparties generally do not benefit from such protections. This exposes the Funds to the risk that a counterparty will not settle a transaction in accordance with its terms and conditions because of a dispute over the terms of the contract (whether or not bona fide) or because of a credit or liquidity problem, thus causing the Funds to suffer a loss.
As of the date of this Prospectus, the Funds’ approved counterparties for OTC swap agreements and forward contracts are: Deutsche Bank AG, UBS AG, Goldman Sachs International and Société Générale. The Sponsor regularly reviews the performance of its counterparties for, among other things, creditworthiness and execution quality. In addition, the Sponsor periodically considers the addition of new counterparties. Thus, the list of counterparties noted above may change at any time. See pages 56 through 57 for more information about the Funds’ swap agreements and forward contracts. Each day, the Funds disclose their portfolio holdings as of the prior Business Day (as such term is defined in “Creation and Redemption of Shares—Creation Procedures” below). Each Fund’s portfolio holdings identifies its counterparties, as applicable. This portfolio holdings information may be accessed through the web on the Sponsor’s website at www.ProShares.com.
More information about Deutsche Bank AG, including its current financial statements, may be found on the SEC’s EDGAR website under Central Index Key No (“CIK No.”) 0001159508 (for Deutsche Bank AG). More information about UBS AG, including its current financial statements, may also be found on the SEC’s EDGAR website under CIK No. 0001114446 (for UBS AG). More information about Goldman Sachs International, a U.K. broker-dealer and subsidiary of The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc., may also be found on the SEC’s EDGAR website under CIK No. 0000886982 (for The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc.). The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. consolidates the financial statements of each of its subsidiaries, including Goldman Sachs International, with its own. More information about Société Générale, a French public limited company, including its current financial statements as filed with the AMF (the French securities regulator), may be found on Société Générale’s website. Please note that the references to third-party websites have been provided solely for informational purposes. Neither the Funds nor the Sponsor endorses or is responsible for the content or information contained on any third-party website, including with respect to any financial statements. In addition, neither the Funds nor the Sponsor makes any warranty, express or implied or assumes any legal liability or responsibility for the accuracy, completeness or usefulness of any such information.
Each counterparty and/or any of its affiliates may be an Authorized Participant or shareholder of a Fund, subject to applicable law.
The counterparty risk for cleared derivatives transactions is generally lower than for uncleared OTC derivatives since generally a clearing organization becomes substituted for each counterparty to a cleared
19
Table of Contents
derivatives contract and, in effect, guarantees the parties’ performance under the contract as each party to a trade looks only to the clearing house for performance of financial obligations. However, there can be no assurance that the clearing house, or its members, will satisfy its obligations to the Fund.
Historical correlation trends between Fund benchmarks and other asset classes may not continue or may reverse, limiting or eliminating any potential diversification or other benefit from owning a Fund.
To the extent that an investor purchases a Fund seeking diversification benefits based on the historic correlation (whether positive or negative) between the returns of that Fund or its underlying benchmark and other asset classes, such historic correlation may not continue or may reverse itself. In this circumstance, the diversification or other benefits sought may be limited or non-existent.
Risks Specific to the VIX Fund
The VIX Fund is benchmarked to the S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index (the Mid-Term VIX Index). It is not benchmarked to the VIX or actual realized volatility of the S&P 500.
The level of the Mid-Term VIX Index is based on the value of the relevant futures contracts (the VIX futures contracts) based on the Chicago Board Options Exchange, Incorporated (“CBOE”) Volatility Index (the “VIX”) that comprise the Mid-Term VIX Index. The VIX Fund is benchmarked to the Mid-Term VIX Index. The VIX Fund is not linked to the VIX (which is a measure of implied volatility of the S&P 500 over the next 30 days derived from option prices), to the realized volatility of the S&P 500 or to the options that underlie the VIX calculation. The VIX Fund should be expected to perform very differently from the VIX over all periods of time. In many cases, the Mid-Term VIX Index will significantly underperform the VIX.
VIX futures contracts are not directly based on a tradable underlying asset.
The VIX is not directly investable. The settlement price at maturity of VIX futures contracts are based on the calculation that determines the level of the VIX. As a result, the behavior of the VIX futures contracts may be different from traditional futures contracts whose settlement price is based on a specific tradable asset.
The level of the VIX has historically reverted to a long-term mean level and any increase or decrease in the level of the VIX will likely continue to be constrained.
In the past, the level of the VIX has typically reverted over the longer term to a historical mean, and its absolute level has been constrained within a band. As such, the potential upside of long or short exposure to VIX futures contracts may be limited, and any gains may be subject to sharp reversals during such reversions to the mean.
When economic uncertainty increases and there is an associated increase in expected volatility, the value of VIX futures contracts will likely also increase. Similarly, when economic uncertainty recedes and there is an associated decrease in expected volatility, the value of VIX futures contracts will likely also decrease.
The value of the Shares of the VIX Fund relates directly to the value of, and realized profit or loss from, the Financial Instruments and other assets held by that Fund. Fluctuations in the price of these Financial Instruments or assets could materially adversely affect an investment in such Fund’s Shares.
Several factors may affect the price and/or liquidity of VIX futures contracts and other assets, if any, owned by the VIX Fund, including, but not limited to:
| • | Prevailing market prices and forward volatility levels of the U.S. stock markets, the S&P 500, the equity securities included in the S&P 500 and prevailing market prices of options on the S&P 500, the |
20
Table of Contents
| VIX, options on the VIX, the relevant VIX futures contracts, or any other financial instruments related to the S&P 500 and the VIX or VIX futures contracts; |
| • | Interest rates; |
| • | Economic, financial, political, regulatory, geographical, biological or judicial events that affect the level of the Mid-Term VIX Index or the market price or forward volatility of the U.S. stock markets, the equity securities included in the S&P 500, the S&P 500, the VIX or the relevant futures or option contracts on the VIX; |
| • | Supply and demand as well as hedging activities in the listed and OTC equity derivatives markets; |
| • | Disruptions in trading of the S&P 500, futures contracts on the S&P 500 or options on the S&P 500; and |
| • | The level of contango or backwardation in the VIX futures contract market. |
These factors interrelate in complex ways, and the effect of one factor on the market value of the VIX Fund may offset or enhance the effect of another factor.
Risks Specific to the Managed Futures Fund
Risks Associated with Concentrated Ownership of the Managed Futures Fund
As of the date of this Prospectus, more than half of the outstanding Shares of the Managed Futures Fund were owned by ProShares Morningstar Alternatives Solution ETF (“ALTS”), an affiliated exchange-traded fund. A sudden and significant sale of these shares by any significant shareholder, such as ALTS, would immediately increase the Managed Futures Fund’s brokerage fees and commissions due to the increased trading costs associated with the corresponding sale of a large part of the Managed Futures Fund’s portfolio. Remaining shareholders would bear these costs. In addition, if the number of the Managed Futures Fund’s outstanding Shares were to decrease significantly, the spread between the NAV of the Shares and the price of the Shares on the secondary market could increase due to a less active market. Furthermore, any significant reduction in the number of outstanding Shares could cause increased tracking error between the level of the Managed Futures Fund’s index (the SFI) and the performance of the Managed Futures Fund because the Managed Futures Fund’s ability to obtain exposure to the SFI through SFI Futures Contracts with relatively high minimum investment amounts would be limited.
The level of the SFI, and the returns attributable to the underlying SFI index components (the “SFI Futures Contracts”) depend on whether a particular SFI Futures Contract is positioned long or short.
The impact of changes in the prices of the SFI Futures Contracts will affect the Managed Futures Fund differently depending upon whether such SFI Futures Contract is positioned long or short. Increases in the price of an underlying SFI Futures Contract will negatively impact the Managed Futures Fund’s performance when the SFI Futures Contract is positioned short and decreases in the price of an underlying SFI Futures Contract will negatively impact the Managed Futures Fund’s performance when the SFI Futures Contract is positioned long.
Short positions should be considered to be speculative and could result in the total loss of an investor’s investment.
The Managed Futures Fund may take short positions in the SFI Futures Contracts. Because the holder of a short position is exposed to losses upon any increase in price, and a price increase is potentially unlimited, short positions will expose the Managed Futures Fund to potentially unlimited losses, which could result in a total loss of investment.
21
Table of Contents
Monthly repositioning may expose the Managed Futures Fund to increased losses in volatile markets.
The SFI is designed to potentially capture the economic benefit derived from both rising and declining trends in futures prices. In order to accomplish this, the SFI positions are rebalanced and repositioned, either long or short, on a monthly basis. As further described in “Description of the Managed Futures Fund’s Index—Determining the Long/Short Positioning of the Index Components,” long positions or short positions in each SFI Futures Contract are determined based on price movements over the past seven months. In volatile markets, this may result in the SFI Futures Contracts frequently being repositioned from long to short and vice versa. If the price movements that caused a particular SFI Futures Contract to be repositioned subsequently reverse themselves, the Managed Futures Fund’s index will be negatively impacted. For example, if Gold is positioned long for the month of March, and the underlying SFI Futures Contracts decline in price, the SFI will experience losses. Depending on the magnitude of the price decline, Gold may reposition itself to short at month end. If, in April, the market reverses and appreciates in price, Gold will again experience losses, even if the price of Gold futures contracts measured across both months is flat from a performance perspective. Such activity can cause the Managed Futures Fund to lose more, and possibly significantly more, than an investment focused only on long or short positions in the same futures contracts.
The Managed Futures Fund has a limited operating history, and, as a result, investors have a limited performance history to serve as a factor for evaluating an investment in the Managed Futures Fund.
The Managed Futures Fund has a limited performance history upon which to evaluate an investor’s investment in the Managed Futures Fund. Although past performance is not necessarily indicative of future results, if the Managed Futures Fund had a longer performance history, such performance history might (or might not) provide investors with more information on which to evaluate an investment in the Managed Futures Fund. Likewise, the SFI has a limited history which might (or might not) provide investors with more information on which to evaluate an investment in the Managed Futures Fund.
Risks Specific to the Managed Futures Fund, the Commodity Index Funds, the Commodity Fund and the Currency Funds.
Risks Specific to the Commodity, Currency and Fixed Income Markets.
With regard to the Managed Futures Fund, the Commodity Index Funds and the Commodity Fund, several factors may affect the price of commodities and, in turn, the Financial Instruments and other assets, if any, owned by such a Fund, including, but not limited to:
| • | Significant increases or decreases in the available supply of a physical commodity due to natural or technological factors. Natural factors would include depletion of known cost-effective sources for a commodity or the impact of severe weather on the ability to produce or distribute the commodity. Technological factors, such as increases in availability created by new or improved extraction, refining and processing equipment and methods or decreases caused by failure or unavailability of major refining and processing equipment (for example, shutting down or constructing oil refineries), also materially influence the supply of commodities. |
| • | Significant increases or decreases in the demand for a physical commodity due to natural or technological factors. Natural factors would include such events as unusual climatological conditions impacting the demand for commodities. Technological factors may include such developments as substitutes for particular commodities. |
| • | A significant change in the attitude of speculators and investors towards a commodity. Should the speculative community take a negative or positive view towards any given commodity, it could cause a change in world prices of any given commodity and the price of Shares based upon a benchmark related to that commodity will be affected. |
| • | Large purchases or sales of physical commodities by the official sector. Governments and large institutions have large commodities holdings or may establish major commodities positions. For |
22
Table of Contents
| example, a significant portion of the aggregate world gold holdings is owned by governments, central banks and related institutions. Similarly, nations with centralized or nationalized oil production and organizations such as the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries control large physical quantities of crude oil. If one or more of these institutions decides to buy or sell any commodity in amounts large enough to cause a change in world prices, the price of Shares based upon a benchmark related to that commodity will be affected. |
| • | Other political factors. In addition to the organized political and institutional trading-related activities described above, peaceful political activity such as imposition of regulations or entry into trade treaties, as well as political disruptions caused by societal breakdown, insurrection and/or war may greatly influence commodities prices. |
| • | A significant increase or decrease in commodity hedging activity by commodity producers. Should there be an increase or decrease in the level of hedge activity of commodity producing companies, countries and/or organizations, it could cause a change in world prices of any given commodity, causing the price of Shares based upon a benchmark related to that commodity to be affected. |
| • | The recent proliferation of commodity-linked products and their unknown effect on the commodity markets. |
With regard to the Managed Futures Fund and the Currency Funds, several factors may affect the value of foreign currencies or the U.S. dollar and, in turn, Financial Instruments and other assets, if any, owned by a Fund, including, but not limited to:
| • | Debt level and trade deficit of the relevant foreign countries; |
| • | Inflation rates of the United States and the relevant foreign countries and investors’ expectations concerning inflation rates; |
| • | Interest rates of the United States and the relevant foreign countries and investors’ expectations concerning interest rates; |
| • | Investment and trading activities of mutual funds, hedge funds and currency funds; |
| • | Global or regional political, economic or financial events and situations; |
| • | Sovereign action to set or restrict currency conversion; and |
| • | Monetary policies and other related activities of central banks within the U.S. and other relevant foreign markets. |
With regard to the Managed Futures Fund, several factors may affect the value of U.S. Treasury securities and, in turn, certain Financial Instruments and related assets, if any, owned by the Managed Futures Fund, including, but not limited to:
| • | Perception of risk, or the lack thereof, in assets other than U.S. Treasury securities; |
| • | Debt level and trade deficit of the United States; |
| • | Inflation rates of the United States and the relevant foreign countries and investors’ expectations concerning inflation rates; |
| • | Interest rates of the United States and the relevant foreign countries and investors’ expectations concerning interest rates; |
| • | Fluctuations in the value of the U.S. dollar relative to other currencies; and |
| • | Fluctuations in the supply of, and demand for, the underlying U.S. Treasury securities. |
These factors interrelate in complex ways, and the effect of one factor on the market value of a Fund may offset or enhance the effect of another factor. In addition, the impact of changes in the level of a commodity
23
Table of Contents
index or the value of a commodity or currency will affect investors differently depending upon the Managed Futures Fund, the Commodity Index Fund, the Commodity Fund or the Currency Fund in which an investor invests. Daily increases in the level of a commodity index or the value of a commodity or currency will negatively impact the daily performance of Shares of the Short and UltraShort Commodity Index, Commodity or Currency Funds.
The Managed Futures Fund and the Commodity Index Funds are linked to indexes comprised of commodity futures contracts and/or financial futures contracts, and are not directly linked to the “spot” prices of the underlying physical commodities or financial assets. Futures contracts may perform very differently from the spot price of the underlying physical commodities or financial assets.
The Managed Futures Fund and each Commodity Index Fund are designed to correspond (before fees and expenses) to the performance of, or a multiple or an inverse multiple of, the daily performance of its applicable benchmark, which is intended to reflect the performance of the prices of futures contracts on certain physical commodities and/or financial assets. The Managed Futures Fund and the Commodity Index Funds are not directly linked to the “spot” price of the physical commodities. While prices of swaps, futures contracts and other derivatives contracts are, as a rule, related to the prices of an underlying cash market, they are not perfectly correlated and often can perform very differently. It is possible that during certain time periods, the performance of different derivatives contracts may be substantially lower or higher than cash market prices for the underlying commodity or financial asset due to differences in derivatives contract terms or as supply, demand or other economic or regulatory factors become more pronounced in either the cash or derivatives markets.
For example, during the one-year period from January 1, 2013 to December 31, 2013, the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM underperformed the spot price of natural gas by 21.82% (the level of the Subindex increased 4.95%, while the spot price of natural gas increased by 26.77%). During a similar one-year period from January 1, 2003 to December 31, 2003, the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM outperformed the spot price of natural gas by 0.64% (the level of the Subindex increased 26.15%, while the spot price of natural gas increased by 25.51%).
Depending upon the direction and level of the benchmark changes, the Funds may underperform or outperform a portfolio of cash market commodities or financial assets.
The Commodity Fund does not invest in bullion itself as certain other exchange-traded products do. Rather, the Commodity Fund uses Financial Instruments to gain exposure to these precious metals. Not investing directly in bullion may introduce additional tracking error and the Commodity Fund is subject to the effects of contango and backwardation as described above.
Using Financial Instruments such as forwards and futures in an effort to replicate the inverse performance of silver bullion may introduce additional tracking error to the performance of the Commodity Fund. While prices of Financial Instruments are, as a rule, related to the prices of an underlying cash market, they are not perfectly correlated. In addition, the use of Financial Instruments causes the need to roll futures or forward contracts as described above and the resulting possibility that contango or backwardation can occur. Silver historically exhibits contango markets during most periods. The existence of backwardated markets, however, would be expected to adversely impact the Commodity Fund.
Risks specific to ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Short Euro.
The European financial markets and the value of the euro have experienced significant volatility, in part related to unemployment, budget deficits and economic downturns. In addition, several member countries of the Economic and Monetary Union of the European Union (the “EU”) have experienced credit rating downgrades, rising government debt levels and, for certain EU member countries (including Greece, Spain, Portugal, Ireland and Italy), weaknesses in sovereign debt. These events, along with decreasing imports or exports, changes in
24
Table of Contents
governmental or EU regulations on trade, the default or threat of default by an EU member country on its sovereign debt and/or an economic recession in an EU member country may continue to cause prolonged volatility in euro-related investments.
In addition, given recent events, it is possible that the euro could be abandoned in the future by countries that have already adopted its use. If this were to occur, the value of the euro could fluctuate or decline drastically, causing losses to ProShares Ultra Euro. Increased volatility related to the euro could exacerbate the effects of daily compounding on the performance of each of ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Short Euro over periods longer than a single day. If the euro is abandoned by all countries that have adopted its use, the Funds may be forced to switch benchmarks or liquidate.
ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar has received a potential delisting letter from NYSE Regulation, Inc. If the Fund is delisted, investors may not have an active trading market for the Fund’s Shares, and the Fund would likely be forced to liquidate.
On September 9, 2014, NYSE Regulation, Inc. (the “NYSE Regulation”) sent a letter informing the Sponsor that ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar failed to comply with continued NYSE Arca Equities, Inc. listing standards regarding its number of record or beneficial holders. The Sponsor sent a written plan (the “Plan”) to the NYSE Regulation designed to increase and sustain a higher number of record or beneficial holders. Upon review and consideration of the Plan, the NYSE Regulation Staff has granted an extension allowing the continued listing of ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar through at least June 23, 2015. There is no guarantee that the Fund will be able to meet the continued listing standards and avoid a delisting action after that date. If the Fund is delisted, there will not be an active trading market for the Fund’s Shares. If investors need to sell their Fund Shares at a time when no active market for them exists, the price investors receive for the Fund’s Shares, assuming that investors are able to sell them, likely will be lower than the price that investors would receive if an active market did exist. In addition, if the Fund is delisted, the Fund would likely be forced to liquidate.
Risks Related to All Funds
Investors cannot be assured of the Sponsor’s continued services, the discontinuance of which may be detrimental to the Funds.
Investors cannot be assured that the Sponsor will be able to continue to service the Funds for any length of time. If the Sponsor discontinues its activities on behalf of the Funds, the Funds may be adversely affected, as there may be no entity servicing the Funds for a period of time. If the Sponsor’s registrations with the CFTC or memberships in the NFA were revoked or suspended, the Sponsor would no longer be able to provide services and/or to render advice to the Funds. If the Sponsor were unable to provide services and/or advice to the Funds, the Funds would be unable to pursue their investment objectives unless and until the Sponsor’s ability to provide services and advice to the Funds was reinstated or a replacement for the Sponsor as commodity pool operator could be found. Such an event could result in termination of the Funds.
The lack of active trading markets for the Shares of the Funds may result in losses on investors’ investments at the time of disposition of Shares.
Although the Shares of the Funds are publicly listed and traded on the Exchange, there can be no guarantee that an active trading market for the Shares of the Funds will develop or be maintained. If investors need to sell their Shares at a time when no active market for them exists, the price investors receive for their Shares, assuming that investors are able to sell them, likely will be lower than the price that investors would receive if an active market did exist.
25
Table of Contents
Investors may be adversely affected by redemption or creation orders that are subject to postponement, suspension or rejection under certain circumstances.
A Fund may, in its discretion, suspend the right of creation or redemption or may postpone the redemption or purchase settlement date, for (1) any period during which the Exchange or any other exchange, marketplace or trading center, deemed to affect the normal operations of the Funds, is closed, or when trading is restricted or suspended or restricted on such exchanges in any of the Funds’ futures contracts, (2) any period during which an emergency exists as a result of which the fulfillment of a purchase order or the redemption distribution is not reasonably practicable, or (3) such other period as the Sponsor determines to be necessary for the protection of the shareholders of the Funds. In addition, a Fund will reject a redemption order if the order is not in proper form as described in the Authorized Participant Agreement or if the fulfillment of the order might be unlawful. Any such postponement, suspension or rejection could adversely affect a redeeming Authorized Participant. For example, the resulting delay may adversely affect the value of the Authorized Participant’s redemption proceeds if the NAV of a Fund declines during the period of delay. The Funds disclaim any liability for any loss or damage that may result from any such suspension or postponement. Suspension of creation privileges may adversely impact how the Shares are traded and arbitraged on the secondary market, which could cause them to trade at levels materially different (premiums and discounts) from the fair value of their underlying holdings.
The NAV may not always correspond to market price and, as a result, investors may be adversely affected by the creation or redemption of Creation Units at a value that differs from the market price of the Shares.
The NAV per Share of a Fund changes as fluctuations occur in the market value of a Fund’s portfolio. Investors should be aware that the public trading price per Share of a Fund may be different from the NAV per Share of the Fund (i.e., the secondary market price may trade at a premium or discount to NAV). Consequently, an Authorized Participant may be able to create or redeem a Creation Unit of a Fund at a discount or a premium to the public trading price per Share of that Fund.
Authorized Participants or their clients or customers may have an opportunity to realize a profit if they can purchase a Creation Unit at a discount to the public trading price of the Shares of a Fund or can redeem a Creation Unit at a premium over the public trading price of the Shares of a Fund. The Sponsor expects that the exploitation of such arbitrage opportunities by Authorized Participants and their clients and customers will tend to cause the public trading price to track the NAV per Share of the Funds closely over time.
The value of a Share may be influenced by non-concurrent trading hours between the Exchange and the market in which the Financial Instruments (or related Reference Assets) held by a Fund are traded. The Shares of each Fund trade on the Exchange, from 9:30 a.m. to 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time). The Financial Instruments (and/or the related Reference Assets) held by a particular Fund, however, may have different fixing or settlement times. Consequently, liquidity in the Financial Instruments (and/or the Reference Assets) may be reduced after such fixing or settlement time. As a result, during the time when the Exchange is open but after the applicable fixing or settlement time of an underlying component, trading spreads and the resulting premium or discount on the Shares of a Fund may widen, and, therefore, may increase the difference between the price of the Shares of a Fund and the NAV of such Shares. Furthermore, the NAVs for the Managed Futures Fund and the Commodity Index Funds are determined prior to the close of the Exchange, and the NAV for the VIX Fund is determined at 4:15 p.m. (Eastern Time) after the close of the Exchange. Consequently, for these Funds, the closing market price per Share may differ from the NAV per Share at the end of each day. Also, during the time when the Exchange is open but the Fund’s NAV has already been determined (or, in the case of the VIX Fund, closed but before the determination of its NAV), there could be market developments or other events that cause or exacerbate the difference between the price of the Shares of such Funds and the NAV of such Shares.
Trading on exchanges outside the United States is generally not subject to U.S. regulation and may result in different or diminished investor protections.
Some of the Funds’ trading may be conducted on exchanges outside the United States. Trading on such exchanges is generally not regulated by any U.S. governmental agency and may involve certain risks not
26
Table of Contents
applicable to trading on U.S. exchanges, including different or diminished investor protections. In trading contracts denominated in currencies other than U.S. dollars, the Shares are subject to the risk of adverse exchange rate movements between the dollar and the functional currencies of such contracts. Investors could incur substantial losses from trading on foreign exchanges which such investors would not have otherwise been subject had the Funds’ trading been limited to U.S. markets.
Competing claims of intellectual property rights may adversely affect the Funds and an investment in the Shares.
Although the Sponsor does not anticipate that such claims will adversely impact the Funds, it is impossible to provide definite assurances that no such negative impact will occur. The Sponsor believes that it has properly licensed or obtained the appropriate consent of all necessary parties with respect to intellectual property rights. However, other third parties could allege ownership as to such rights and may bring an action in asserting their claims. To the extent any action is brought by a third party asserting such rights, the expenses in litigating, negotiating, cross-licensing or otherwise settling such claims may adversely affect the Funds.
Investors may be adversely affected by an overstatement or understatement of the NAV calculation of the Funds due to the valuation method employed on the date of the NAV calculation.
Calculating the NAV of the Funds includes, in part, any unrealized profits or losses on open Financial Instrument positions. Under normal circumstances, the NAV of a Fund reflects the value of the Financial Instruments held by a Fund, as of the time the NAV is calculated. However, if any of the Financial Instruments held by a Fund could not be purchased or sold on a day when a Fund is accepting creation and redemption orders (due to the operation of daily limits or other rules of an exchange or otherwise), a Fund may be improperly exposed which could cause it to fail to meet its stated investment objective. Alternatively, a Fund may attempt to calculate the fair value of such Financial Instruments. In such a situation, there is a risk that the calculation of the relevant benchmark, and therefore, the NAV of the applicable Fund on such day, may not accurately reflect the realizable market value of the Financial Instruments underlying such benchmark.
The liquidity of the Shares may also be affected by the withdrawal from participation of Authorized Participants, which could adversely affect the market price of the Shares.
In the event that one or more Authorized Participants which have substantial interests in the Shares withdraw from participation, the liquidity of the Shares will likely decrease, which could adversely affect the market price of the Shares and result in investors incurring a loss on their investment.
Shareholders that are not Authorized Participants may only purchase or sell their Shares in secondary trading markets, and the conditions associated with trading in secondary markets may adversely affect investors’ investment in the Shares.
Only Authorized Participants may create or redeem Creation Units. All other investors that desire to purchase or sell Shares must do so through the Exchange or in other markets, if any, in which the Shares may be traded. Shares may trade at a premium or discount to NAV per Share.
The Exchange may halt trading in the Shares of a Fund which would adversely impact investors’ ability to sell Shares.
Trading in Shares of a Fund may be halted due to market conditions or, in light of the Exchange rules and procedures, for reasons that, in the view of the Exchange, make trading in Shares of a Fund inadvisable. In addition, trading is subject to trading halts caused by extraordinary market volatility pursuant to “circuit breaker” rules that require trading to be halted for a specified period based on a specified decline or rise in a market index (e.g., the Dow Jones Industrial Average) or in the price of a Fund’s Shares. Additionally, the ability to short sell a
27
Table of Contents
Fund’s Shares may be restricted when there is a 10% or greater change from the previous day’s official closing price. There can be no assurance that the requirements necessary to maintain the listing of the Shares of a Fund will continue to be met or will remain unchanged.
Shareholders do not have the protections associated with ownership of shares in an investment company registered under the 1940 Act.
None of the Funds are subject to registration or regulation under the 1940 Act. Consequently, shareholders do not have the regulatory protections provided to investors in investment companies.
Shareholders do not have the rights enjoyed by investors in certain other vehicles and may be adversely affected by a lack of statutory rights and by limited voting and distribution rights.
The Shares have limited voting and distribution rights. For example, shareholders do not have the right to elect directors, the Funds may enact splits or reverse splits without shareholder approval and the Funds are not required to pay regular distributions, although the Funds may pay distributions at the discretion of the Sponsor.
The value of the Shares will be adversely affected if the Funds are required to indemnify the Trustee.
Under the Amended and Restated Trust Agreement of the Trust, as may be further amended and restated from time to time (the “Trust Agreement”), the Trustee has the right to be indemnified for any liability or expense incurred without gross negligence or willful misconduct. That means the Sponsor may require the assets of a Fund to be sold in order to cover losses or liability suffered by it or by the Trustee. Any sale of that kind would reduce the NAV of one or more of the Funds.
Although the Shares of the Funds are limited liability investments, certain circumstances such as bankruptcy of a Fund will increase a shareholder’s liability.
The Shares of the Funds are limited liability investments; investors may not lose more than the amount that they invest plus any profits recognized on their investment. However, shareholders could be required, as a matter of bankruptcy law, to return to the estate of a Fund any distribution they received at a time when such Fund was in fact insolvent or in violation of the Trust Agreement.
Failure of the FCMs to segregate assets may increase losses in the Funds.
The CEA requires a clearing broker to segregate all funds received from customers from such broker’s proprietary assets. There is a risk that assets deposited by the Sponsor on behalf of the Funds as margin with the FCMs may, in certain circumstances, be used to satisfy losses of other clients of the FCMs. If an FCM fails to segregate the funds received from the Sponsor, the assets of the Funds might not be fully protected in the event of the FCM’s bankruptcy. Furthermore, in the event of an FCM’s bankruptcy, Fund Shares could be limited to recovering only a pro rata share of all available funds segregated on behalf of the FCM’s combined customer accounts, even though certain property specifically traceable to a particular Fund was held by the FCM. Each FCM may, from time to time, be the subject of certain regulatory and private causes of action.
Similarly, the CEA requires a clearing organization approved by the CFTC as a derivatives clearing organization to segregate all funds and other property received from a clearing member’s clients in connection with domestic futures and options contracts from any funds held at the clearing organization to support the clearing member’s proprietary trading. Nevertheless, customer funds held at a clearing organization in connection with any futures or options contracts may be held in a commingled omnibus account, which may not identify the name of the clearing member’s individual customers. With respect to futures and options contracts, a clearing organization may use assets of a non-defaulting customer held in an omnibus account at the clearing organization to satisfy payment obligations of a defaulting customer of the clearing member to the clearing
28
Table of Contents
organization. As a result, in the event of a default of the clearing FCM’s other clients or the clearing FCM’s failure to extend its own funds in connection with any such default, a Fund may not be able to recover the full amount of assets deposited by the clearing FCM on behalf of the Fund with the clearing organization.
In the event of a bankruptcy or insolvency of any exchange or a clearing house, a Fund could experience a loss of the funds deposited through its FCM as margin with the exchange or clearing house, a loss of any profits on its open positions on the exchange, and the loss of unrealized profits on its closed positions on the exchange.
A court could potentially conclude that the assets and liabilities of one Fund are not segregated from those of another series of the Trust and may thereby potentially expose assets in a Fund to the liabilities of another series of the Trust.
Each series of the Trust is a separate series of a Delaware statutory trust and not itself a separate legal entity. Section 3804(a) of the Delaware Statutory Trust Act, as amended (the “DSTA”), provides that if certain provisions are in the formation and governing documents of a statutory trust organized in series, and if separate and distinct records are maintained for any series and the assets associated with that series are held in separate and distinct records (directly or indirectly, including through a nominee or otherwise) and accounted for in such separate and distinct records separately from the other assets of the statutory trust, or any series thereof, then the debts, liabilities, obligations and expenses incurred, contracted for or otherwise existing with respect to a particular series are enforceable against the assets of such series only, and not against the assets of the statutory trust generally or any other series thereof, and none of the debts, liabilities, obligations and expenses incurred, contracted for or otherwise existing with respect to the statutory trust generally or any other series thereof shall be enforceable against the assets of such series. The Sponsor is not aware of any court case that has interpreted Section 3804(a) of the DSTA or provided any guidance as to what is required for compliance. The Sponsor maintains separate and distinct records for each series and accounts for them separately, but it is possible a court could conclude that the methods used did not satisfy Section 3804(a) of the DSTA and thus potentially expose assets of a Fund to the liabilities of another series of the Trust.
There may be circumstances that could prevent a Fund from being operated in a manner consistent with its investment objective and principal investment strategies.
There may be circumstances outside the control of the Sponsor and/or a Fund that make it, for all practical purposes, impossible to re-position such Fund and/or to process a purchase or redemption order. Examples of such circumstances include: natural disasters; public service disruptions or utility problems such as those caused by fires, floods, extreme weather conditions, and power outages resulting in telephone, telecopy, and computer failures; market conditions or activities causing trading halts; systems failures involving computer or other information systems affecting the aforementioned parties, as well as the Depository Trust Company (“DTC”), the National Securities Clearing Corporation (“NSCC”), or any other participant in the purchase process; and similar extraordinary events. Accordingly, while the Sponsor has implemented and tested a business continuity plan that transfers functions of any disrupted facility to another location and has effected a disaster recovery plan, circumstances, such as those above, may prevent a Fund from being operated in a manner consistent with its investment objective and/or principal investment strategies.
Due to the increased use of technologies, intentional and unintentional cyber attacks pose operational and information security risks.
With the increased use of technologies such as the Internet and the dependence on computer systems to perform necessary business functions, the Funds are susceptible to operational and information security risks. In general, cyber incidents can result from deliberate attacks or unintentional events. Cyber attacks include, but are not limited to gaining unauthorized access to digital systems for purposes of misappropriating assets or sensitive information, corrupting data, or causing operational disruption. Cyber attacks may also be carried out in a manner that does not require gaining unauthorized access, such as causing denial-of-service attacks on websites. Cyber security failures or breaches of a Fund’s third party service provider (including, but not limited to, index
29
Table of Contents
providers, the administrator and transfer agent) or the issuers of securities in which the Funds invest, have the ability to cause disruptions and impact business operations, potentially resulting in financial losses, the inability of Fund shareholders to transact business, violations of applicable privacy and other laws, regulatory fines, penalties, reputational damage, reimbursement or other compensation costs, and/or additional compliance costs. In addition, substantial costs may be incurred in order to prevent any cyber incidents in the future. The Funds and their shareholders could be negatively impacted as a result. While the Funds have established business continuity plans and systems to prevent such cyber attacks, there are inherent limitations in such plans and systems including the possibility that certain risks have not been identified. Furthermore, the Funds cannot control the cyber security plans and systems put in place by issuers in which the Funds invest.
Shareholders’ tax liability will exceed cash distributions on the Shares.
Shareholders of each Fund are subject to U.S. federal income taxation and, in some cases, state, local, or foreign income taxation on their share of the Fund’s taxable income, whether or not they receive cash distributions from the Fund. Each Fund does not currently expect to make distributions with respect to capital gains or ordinary income. Accordingly, shareholders of a Fund will not receive cash distributions equal to their share of the Fund’s taxable income or the tax liability that results from such income. A Fund’s income, gains, losses and deductions are allocated to shareholders on a monthly basis. If you own Shares in a Fund at the beginning of a month and sell them during the month, you are generally still considered a shareholder through the end of that month.
The U.S. Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) could adjust or reallocate items of income, gain, deduction, loss and credit with respect to the Shares if the IRS does not accept the assumptions or conventions utilized by the Fund.
U.S. federal income tax rules applicable to partnerships, which each Fund is anticipated to be treated as under the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended (the “Code”), are complex and their application is not always clear. Moreover, the rules generally were not written for, and in some respects are difficult to apply to, publicly traded interests in partnerships. The Funds apply certain assumptions and conventions intended to comply with the intent of the rules and to report income, gain, deduction, loss and credit to shareholders in a manner that reflects the shareholders’ economic gains and losses, but these assumptions and conventions may not comply with all aspects of the applicable Regulations (as defined below). It is possible therefore that the IRS will successfully assert that these assumptions or conventions do not satisfy the technical requirements of the Code or the Treasury regulations promulgated thereunder (the “Regulations”) and will require that items of income, gain, deduction, loss and credit be adjusted or reallocated in a manner that could be adverse to investors.
Shareholders will receive partner information tax returns on Schedule K-1, which could increase the complexity of tax returns.
The partner information tax returns on Schedule K-1, which the Funds will distribute to shareholders, will contain information regarding the income items and expense items of the Funds. If you have not received Schedule K-1s from other investments, you may find that preparing your tax return may require additional time, or it may be necessary for you to retain an accountant or other tax preparer, at an additional expense to you, to assist you in the preparation of your return.
Investors could be adversely affected if the current treatment of long-term capital gains under current U.S. federal income tax law is changed or repealed in the future.
Under current law, long-term capital gains are taxed to non-corporate investors at a maximum U.S. federal income tax rate of 20%. This tax treatment may be adversely affected, changed or repealed by future changes in tax laws at any time.
30
Table of Contents
Shareholders of each Fund may recognize significant amounts of ordinary income and short-term capital gain.
Due to the investment strategy of the Funds, the Funds may realize and pass-through to shareholders significant amounts of ordinary income and short-term capital gains as opposed to long-term capital gains, which generally are taxed at a preferential rate. A Fund’s income, gains, losses and deductions are allocated to shareholders on a monthly basis. If you own Shares in a Fund at the beginning of a month and sell them during the month, you are generally still considered a shareholder through the end of that month.
PROSPECTIVE INVESTORS ARE STRONGLY URGED TO CONSULT THEIR OWN TAX ADVISERS AND COUNSEL WITH RESPECT TO THE POSSIBLE TAX CONSEQUENCES TO THEM OF AN INVESTMENT IN THE SHARES OF A FUND; SUCH TAX CONSEQUENCES MAY DIFFER IN RESPECT OF DIFFERENT INVESTORS.
Regulatory changes or actions, including the implementation of new legislation, may alter the operations and profitability of the Funds.
The U.S. derivatives markets and market participants have been subject to comprehensive regulation, not only by the CFTC but also by self-regulatory organizations, including the NFA and the exchanges on which the derivatives contracts are traded and/or cleared. As with any regulated activity, changes in regulations may have unexpected results. For example, changes in the amount or quality of the collateral that traders in derivatives contracts are required to provide to secure their open positions, or in the limits on number or size of positions that a trader may have open at a given time, may adversely affect the ability of the Funds to enter into certain transactions that could otherwise present lucrative opportunities. Considerable regulatory attention has been focused on non-traditional investment pools which are publicly distributed in the United States. There is a possibility of future regulatory changes altering, perhaps to a material extent, the nature of an investment in the Funds or the ability of the Funds to continue to implement their investment strategies.
In addition, the SEC, CFTC and the exchanges are authorized to take extraordinary actions in the event of a market emergency, including, for example, the retroactive implementation of speculative position limits or higher margin requirements, the establishment of daily price limits and the suspension of trading. The regulation of swaps, forwards and futures transactions in the United States is a rapidly changing area of law and is subject to modification by government and judicial action. The effect of any future regulatory change on the Funds is impossible to predict, but could be substantial and adverse.
In particular, the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”) was signed into law on July 21, 2010. The Dodd-Frank Act has made and will continue to make sweeping changes to the way in which the U.S. financial system is supervised and regulated. Title VII of the Dodd-Frank Act sets forth a new legislative framework for OTC derivatives, including certain Financial Instruments, such as swaps, in which certain of the Funds may invest. Title VII of the Dodd-Frank Act makes broad changes to the OTC derivatives market, grants significant new authority to the SEC and the CFTC to regulate OTC derivatives and market participants, and will require clearing and exchange trading of many OTC derivatives transactions.
Provisions in the Dodd-Frank Act include the requirement that position limits on commodity futures contracts be established; new registration, recordkeeping, capital and margin requirements for “swap dealers” and “major swap participants” as determined by the Dodd-Frank Act and applicable regulations; and the mandatory use of clearinghouse mechanisms for many OTC derivatives transactions.
The CFTC, the SEC and other federal regulators have been tasked with developing the rules and regulations enacting the provisions of the Dodd-Frank Act. While certain regulations have been promulgated and are already in effect, the full impact of the Dodd-Frank Act on any of the Funds remains uncertain. The legislation and the related regulations that have been and may be promulgated in the future may negatively impact a Fund’s ability to meet its investment objective either through limits on its investments or requirements imposed on it or any of its counterparties. In particular, new requirements, including capital requirements and mandatory clearing of
31
Table of Contents
OTC derivatives transactions, which may increase derivative counterparties’ costs and are expected to generally be passed through to other market participants in the form of higher upfront and mark-to-market margin, less favorable trade pricing, and the imposition of new or increased fees, including clearinghouse account maintenance fees, may increase the cost of a Fund’s investments and the cost of doing business, which could adversely affect investors.
Regulatory and exchange accountability levels may restrict the creation of Creation Units and the operation of the Trust.
Many U.S. commodities exchanges and boards of trade limit the amount of fluctuation permitted in futures contract prices during a single trading day by regulations referred to as “daily price fluctuation limits” or “daily limits.” Once the daily limit has been reached in a particular contract, no trades may be made that day at a price beyond that limit or trading may be suspended for specified periods during the trading day. In addition, the CFTC, U.S. futures exchanges and certain non-U.S. exchanges have established limits referred to as “speculative position limits” or “accountability levels” on the maximum net long or short futures positions that any person may hold or control in derivatives traded on such exchanges.
In connection with these limits, the Dodd-Frank Act has required the CFTC to adopt regulations establishing speculative position limits applicable to regulated futures and OTC derivatives and impose aggregate speculative position limits across regulated U.S. futures, OTC positions and certain futures contracts traded on non-U.S. exchanges. On November 5, 2013, the CFTC proposed regulations on position limits with respect to the 28 physical delivery commodity futures and options contracts, as well as to swaps that are economically equivalent to such contracts. The proposed position limits would apply with respect to contracts traded on all U.S. and certain foreign exchanges on an aggregate basis. In addition, the CFTC proposed amendments to the requirement of U.S. commodities exchanges to establish corresponding speculative position limits. Under the proposed CFTC regulations, all accounts owned or managed by an entity that is responsible for such accounts’ trading decisions, their principals and their affiliates would be combined for position limit purposes. Although it is unclear what future position limit rules will be, the Sponsor is subject to current position and accountability limits established by the CFTC and exchanges. Accordingly, it may be required to reduce the size of outstanding positions or not enter into new positions that would otherwise be taken for the Funds or not trade certain markets on behalf of the Funds in order to comply with those limits or any future limits established by the CFTC and the relevant exchanges. Derivatives contract prices could move to a limit for several consecutive trading days with little or no trading, thereby preventing prompt liquidation of derivatives positions and potentially subjecting the Funds to substantial losses or periods in which such Funds do not create additional Creation Units. Modification of trades made by the Trust, if required, could adversely affect the Trust’s operations and profitability and significantly limit the Trust’s ability to reinvest income in additional contracts, create additional Creation Units, or add to existing positions in the desired amount.
In addition, the Sponsor may be required to liquidate certain open positions in order to ensure compliance with the speculative position limits at unfavorable prices, which may result in substantial losses for the relevant Funds. There also can be no assurance that the Sponsor will liquidate positions held on behalf of all the Sponsor’s accounts, including any proprietary accounts, in a proportionate manner. In the event the Sponsor chooses to liquidate a disproportionate number of positions held on behalf of any of the Funds at unfavorable prices, such Funds may incur substantial losses and the value of the Shares may be adversely affected.
Further, in October 2012, a new CFTC rule became effective, which requires each registered FCM to establish risk-based limits on position and order size. As a result, the Trust’s FCMs may be required to reduce their internal limits on the size of the positions they will execute or clear for the Funds, and the Trust may seek to use additional FCMs, which may increase the costs for the Funds and adversely affect the value of the Shares.
The Trust may apply to the CFTC or to the relevant exchanges for relief from certain position limits. If the Trust is unable to obtain such relief, a Fund’s ability to issue new Creation Units, or the Fund’s ability to reinvest income in additional futures contracts, may be limited to the extent these activities cause the Trust to exceed
32
Table of Contents
applicable position limits. Limiting the size of a Fund may affect the correlation between the price of the Shares, as traded on an exchange, and the net asset value of the Fund. Accordingly, the inability to create additional Creation Units or add to existing positions in the desired amount could result in Shares trading at a premium or discount to NAV.
Margin for Non-cleared and Forward Swap Transactions
In 2014, the CFTC and various federal bank regulators proposed new mandatory margin requirements for non-cleared swap and forward transactions and new requirements for the holding of collateral by derivatives dealers. These requirements, which are still pending final adoption, may increase the amount of collateral a Fund is required to provide derivatives dealers for non-cleared swaps and forwards.
33
Table of Contents
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference in this Prospectus contain forward-looking statements that are subject to risks and uncertainties. Investors can identify these forward-looking statements by the use of expressions such as “may,” “will,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “intend,” “plan,” “project,” “should,” “estimate” or any negative or other variations on such expression. These forward-looking statements are based on information currently available to the Sponsor and are subject to a number of risks, uncertainties and other factors, both known, such as those described in “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Prospectus and the documents incorporated by reference in this Prospectus, and unknown, that could cause the actual results, performance, prospects or opportunities of the Funds to differ materially from those expressed in, or implied by, these forward-looking statements.
Except as expressly required by federal securities laws, the Trust assumes no obligation to update publicly any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. Investors should not place undue reliance on any forward-looking statements.
34
Table of Contents
DESCRIPTION OF THE MID-TERM VIX INDEX
The S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index
ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF (the VIX Fund) is designed to correspond (before fees and expenses) to the performance of the S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index (the Mid-Term VIX Index) both over a single day and over time. The VIX Fund seeks to offer exposure to forward equity market volatility by obtaining exposure to the Mid-Term VIX Index, which is based on publicly traded VIX futures contracts. The Mid-Term VIX Index is intended to reflect the returns that are potentially available through an unleveraged investment in the VIX futures contracts comprising the Mid-Term VIX Index. The VIX, which is not the index underlying the VIX Fund, is calculated based on the prices of put and call options on the S&P 500. The VIX Fund can be expected to perform very differently from the VIX.
The Mid-Term VIX Index employs rules for selecting its VIX futures contracts comprising the Mid-Term VIX Index and a formula to calculate a level for that Index from the prices of these VIX futures contracts. Specifically, the VIX futures contracts comprising the Mid-Term VIX Index represent the prices for four contract months of VIX futures contracts, representing a rolling long position in the fourth, fifth, six and seventh month VIX futures contracts. The Mid-Term VIX Index rolls continuously throughout each month while maintaining positions in the fifth and sixth month contracts. This results in a constant weighted average maturity of five months.
The level of the Mid-Term VIX Index is calculated in accordance with the method described in “—Composition and Calculation of the Mid-Term VIX Index—Composition of the Mid-Term VIX Index” below. The level of the Mid-Term VIX Index will be published by Bloomberg in real time and at the close of trading on each Mid-Term VIX Index business day under the Bloomberg ticker symbol below:
| Index |
Bloomberg Ticker Symbol | |||
| S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index |
SPVXMPID | |||
The performance of the Mid-Term VIX Index is influenced by the S&P 500 (and options thereon) and the VIX. A description of VIX futures contracts, the VIX and S&P 500 follows.
VIX Futures Contracts
The Mid-Term VIX Index is comprised of VIX futures contracts. VIX futures contracts were first launched for trading by the CBOE in 2004. VIX futures contracts have expirations ranging from the front month consecutively out to the tenth month. VIX futures contracts allow investors the ability to invest based on their view of forward implied market volatility. Investors that believe the forward implied market volatility of the S&P 500, as represented by VIX futures contracts, will increase may buy VIX futures contracts. Conversely, investors that believe that the forward implied market volatility of the S&P 500, as represented by VIX futures contracts, will decline may sell VIX futures contracts. VIX futures contracts are reported by Bloomberg under the ticker symbol “VX.”
While the VIX represents a measure of the current expected volatility of the S&P 500 over the next 30 days, the prices of VIX futures contracts are based on the current expectation of what the expected 30-day volatility will be at a particular time in the future (on the expiration date). The VIX and VIX futures contracts generally behave quite differently. To illustrate, on January 30, 2015, the VIX was 20.97 and the price of the February 2015 VIX futures contracts expiring on February 18, 2015 was 21.025. In this example, the price of the VIX represented the 30-day implied, or “spot,” volatility (the volatility expected for the period from January 30, 2015 to March 1, 2015) of the S&P 500 and the February VIX futures contracts represented forward implied volatility (the volatility expected for the period from February 18, 2015 to March 20, 2015) of the S&P 500. The spot/forward relationship between the VIX and VIX futures contracts has two noteworthy consequences: (1) the price of a VIX futures contract can be lower, equal to or higher than the VIX, depending on whether the market
35
Table of Contents
expects volatility to be lower, equal to or higher in the 30-day forward period covered by the VIX futures contract than in the 30-day spot period covered by the VIX; and (2) you cannot create a position equivalent to one in VIX futures contracts by buying the VIX and holding the position to the futures expiration date while financing the transaction.
The VIX
The VIX Fund is not linked to the VIX and can be expected to perform very differently from the VIX. The VIX is an index designed to measure the implied volatility of the S&P 500 over 30 days in the future, and is calculated based on the prices of certain put and call options on the S&P 500. The VIX is reflective of the premium paid by investors for certain options linked to the level of the S&P 500. During periods of rising investor uncertainty, including periods of market instability, the implied level of volatility of the S&P 500 typically increases and, consequently, the prices of options linked to the S&P 500 typically increase (assuming all other relevant factors remain constant or have negligible changes). This, in turn, causes the level of the VIX to increase. The VIX has historically had a negative correlation to the S&P 500. The VIX was developed by the CBOE and is calculated, maintained and published by the CBOE. The CBOE has no obligation to continue to publish, and may discontinue the publication of, the VIX. The VIX is reported by Bloomberg under the ticker symbol “VIX.”
The calculation of the VIX involves a formula that uses the prices of a weighted series of out-of-the-money put and call options on the level of the S&P 500 (“SPX Options”) with two adjacent expiry terms to derive a constant 30-day forward measure of market volatility. The VIX is calculated independent of any particular option pricing model and in doing so seeks to eliminate any biases which may otherwise be included in using options pricing methodology based on certain assumptions. Although the VIX measures the 30-day forward volatility of the S&P 500 as implied by the SPX Options, 30-day options are only available once a month. To arrive at the VIX level, a broad range of out-of-the-money SPX Options expiring on the two closest nearby months (“near term options” and “next term options,” respectively) are selected in order to bracket a 30-day calendar period. SPX Options having a maturity of less than eight days are excluded at the outset and, when the near term options have eight days or less left to expiration, the VIX rolls to the second and third contract months in order to minimize pricing anomalies that occur close to expiration. The model-free implied volatility using prices of the near term options and next term options are then calculated on a strike price weighted average basis in order to arrive at a single average implied volatility value for each month. The results of each of the two months are then interpolated to arrive at a single value with a constant maturity of 30 days to expiration.
The S&P 500
The S&P 500 is an index that measures large-cap U.S. stock market performance. It is a float-adjusted, market capitalization-weighted index of 500 U.S. operating companies and real estate investment trusts selected by the S&P U.S. Index Committee through a non-mechanical process that factors in criteria such as liquidity, price, market capitalization and financial viability. Reconstitution occurs both on a quarterly and ongoing basis. S&P publishes the S&P 500. The daily calculation of the current value of the S&P 500 is based on the relative value of the aggregate market value of the common stocks of 500 companies as of a particular time compared to the aggregate average initial market value of the common stocks of 500 similar companies at the time of the inception of the S&P 500. The 500 companies are not the 500 largest publicly traded companies and not all 500 companies are listed on NYSE. S&P chooses companies for inclusion in the S&P 500 with the objective of achieving a distribution by broad industry groupings that approximates the distribution of these groupings in the common stock population of the U.S. equity market. S&P may from time to time, in its sole discretion, add companies to, or delete companies from, the S&P 500 to achieve the objectives stated above. Relevant criteria employed by S&P include the viability of the particular company, the extent to which that company represents the industry group to which it is assigned, the extent to which the company’s common stock is widely held and the market value and trading activity of the common stock of that company.
36
Table of Contents
Composition and Calculation of the Mid-Term VIX Index
Composition of the Mid-Term VIX Index
The Mid-Term VIX Index represents an unleveraged, rolling long position in the fourth, fifth, sixth and seventh month VIX futures contracts. The Mid-Term VIX Index rolls continuously throughout each month from the fourth month contract into the seventh month contract while maintaining positions in the fifth month and sixth month contracts.
The Mid-Term VIX Index rolls a portion of its positions on a daily basis. One of the effects of daily rolling is to maintain a constant weighted average maturity for the underlying futures contracts. Certain futures contracts, like those on the VIX, specify a date for settlement in cash based on the price of the underlying asset or index. Once this date is reached, the futures contract “expires.” As described in more detail below, the Mid-Term VIX Index operates by, on a daily basis, selling VIX futures contracts with a nearby settlement date and purchasing VIX futures contracts which settle on a later date. The roll for each contract occurs on each Mid-Term VIX Index business day according to a pre-determined schedule that has the effect of keeping constant the weighted average maturity of the relevant futures contracts. The constant weighted average maturity for the futures underlying the Mid-Term VIX Index is five months. Rolling futures contracts may have certain adverse consequences as described in the section entitled “Risk Factors- Potential negative impact from rolling futures positions” on page 16.
Calculation of the Mid-Term VIX Index
On any business day, t, the Mid-Term VIX Index is calculated as follows:
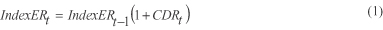
where:
| IndexERt-1 = | The Index Excess Return on the preceding business day, defined as any date on which the index is calculated. |
CDRt = Contract Daily Return, as determined by the following formula:

where:
t-1 = the preceding business day.
| TDWOt | = Total Dollar Weight Obtained on t, as determined by the following formula for the Mid-Term VIX Index: |
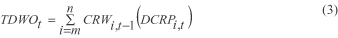
| TDWIt-1 | = Total Dollar Weight Invested on t-1, as determined by the following formula for the Mid-Term VIX Index: |
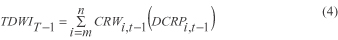
where:
| CRWi,t = Contract Roll Weight of the ith VIX futures contract on date t. |
| DCRPi,t = Daily Contract Reference Price of the ith VIX futures contract on date t. |
37
Table of Contents
| m = For the S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index m = 4. |
| n = For the S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index n = 7. |
Contract Rebalancing
The roll period starts on the Tuesday prior to the monthly VIX futures settlement date (the Wednesday falling 30 calendar days before the S&P 500 option expiration for the following month), and runs through the Tuesday prior to the subsequent month’s VIX futures settlement date. Thus, the Mid-Term VIX Index is rolling on a continual basis. On the business date after the current roll period ends, the following roll period will begin.
In calculating the Excess Return of the Mid-Term VIX Index, the Contract Roll Weights (CRWi,t) of each of the contracts in the Mid-Term VIX Index, on a given day, t, are determined as follows:
S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index
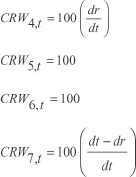
where:
| CRWi,t | = Contract Roll Weight of the ith VIX futures contract on date t. |
| dt = | The total number of business days in the current roll period beginning with, and including, the starting VIX futures settlement date and ending with, but excluding, the following VIX futures settlement date. The number of business days stays constant in cases of a new holiday introduced intra-month or an unscheduled market closure. |
| dr = | The total number of business days within a roll period beginning with, and including, the following business day and ending with, but excluding, the following VIX futures settlement date. The number of business days includes a new holiday introduced intra-month up to the business day preceding such a holiday. |
At the close on the Tuesday corresponding to the start of the roll period, an equal weight is allocated to the fourth, fifth and sixth month contracts. Then, on each subsequent business day a fraction of the fourth month VIX futures holding is sold and an equal notional amount of the seventh month VIX futures is bought. The fraction, or quantity, is proportional to the number of fourth month VIX futures contracts as of the previous index roll day, and inversely proportional to the length of the current roll period. In this way, the initial position in the fourth month contract is progressively moved to the seventh month contract over the course of the month, until the following roll period starts when the old fifth month VIX futures contract becomes the new fourth month VIX futures contract and gets sold every day afterwards as the process begins again.
In addition to the transactions described above, the weight of each VIX futures contract comprising the Mid-Term VIX Index is also adjusted every day to ensure that the change in total dollar exposure for the Mid-Term VIX Index is only due to the price change of each contract and not due to using a different weight for a contract trading at a higher price.
38
Table of Contents
Information about the Index Licensor
PROSHARES VIX MID-TERM FUTURES ETF (THE VIX FUND) IS NOT SPONSORED, ENDORSED, SOLD OR PROMOTED BY S&P AND ITS AFFILIATES OR CBOE. S&P AND CBOE MAKE NO REPRESENTATION, CONDITION OR WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, TO THE OWNERS OF THE VIX FUND OR ANY MEMBER OF THE PUBLIC REGARDING THE ADVISABILITY OF INVESTING IN SECURITIES GENERALLY OR IN THE VIX FUND PARTICULARLY OR THE ABILITY OF THE S&P 500 VIX MID-TERM FUTURES INDEX (THE MID-TERM VIX INDEX) TO TRACK MARKET PERFORMANCE AND/OR OF GROUPS OF ASSETS OR ASSET CLASSES AND/OR TO ACHIEVE ITS STATED OBJECTIVE AND/OR TO FORM THE BASIS OF A SUCCESSFUL INVESTMENT STRATEGY, AS APPLICABLE. S&P’S AND CBOE’S ONLY RELATIONSHIP TO PROSHARES TRUST II ON BEHALF OF ITS APPLICABLE SERIES AND PROSHARE CAPITAL MANAGEMENT LLC IS THE LICENSING OF CERTAIN TRADEMARKS AND TRADE NAMES AND OF THE MID-TERM VIX INDEX WHICH IS DETERMINED, COMPOSED AND CALCULATED BY S&P WITHOUT REGARD TO PROSHARES TRUST II ON BEHALF OF ITS APPLICABLE SERIES AND PROSHARE CAPITAL MANAGEMENT LLC OR THE VIX FUND. S&P HAS NO OBLIGATION TO TAKE THE NEEDS OF PROSHARES TRUST II ON BEHALF OF ITS APPLICABLE SERIES AND PROSHARE CAPITAL MANAGEMENT LLC OR THE OWNERS OF THE VIX FUND INTO CONSIDERATION IN DETERMINING, COMPOSING OR CALCULATING THE MID-TERM VIX INDEX. S&P AND CBOE ARE NOT ADVISORS TO THE VIX FUND AND ARE NOT RESPONSIBLE FOR AND HAVE NOT PARTICIPATED IN THE DETERMINATION OF THE PRICES AND AMOUNT OF THE VIX FUND OR THE TIMING OF THE ISSUANCE OR SALE OF THE VIX FUND OR IN THE DETERMINATION OR CALCULATION OF THE EQUATION BY WHICH THE VIX FUND SHARES ARE TO BE CONVERTED INTO CASH. S&P AND CBOE HAVE NO OBLIGATION OR LIABILITY IN CONNECTION WITH THE ADMINISTRATION, MARKETING, OR TRADING OF THE VIX FUND.
NEITHER S&P, ITS AFFILIATES NOR THIRD PARTY LICENSORS, INCLUDING CBOE, GUARANTEES THE ACCURACY AND/OR THE COMPLETENESS OF THE MID-TERM VIX INDEX OR ANY DATA INCLUDED THEREIN AND S&P, ITS AFFILIATES AND THEIR THIRD PARTY LICENSORS, INCLUDING CBOE, SHALL HAVE NO LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS, OMISSIONS, OR INTERRUPTIONS THEREIN. S&P AND CBOE MAKE NO WARRANTY, CONDITION OR REPRESENTATION, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, AS TO RESULTS TO BE OBTAINED BY PROSHARES TRUST II ON BEHALF OF ITS APPLICABLE SERIES AND PROSHARE CAPITAL MANAGEMENT LLC, OWNERS OF THE VIX FUND, OR ANY OTHER PERSON OR ENTITY FROM THE USE OF THE MID-TERM VIX INDEX OR ANY DATA INCLUDED THEREIN. S&P AND CBOE MAKE NO EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, REPRESENTATIONS OR CONDITIONS, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR USE AND ANY OTHER EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTY OR CONDITION WITH RESPECT TO THE MID-TERM VIX INDEX OR ANY DATA INCLUDED THEREIN. WITHOUT LIMITING ANY OF THE FOREGOING, IN NO EVENT SHALL S&P, ITS AFFILIATES OR THEIR THIRD PARTY LICENSORS, INCLUDING CBOE, HAVE ANY LIABILITY FOR ANY SPECIAL, PUNITIVE, INDIRECT, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING LOST PROFITS) RESULTING FROM THE USE OF THE MID-TERM VIX INDEX OR ANY DATA INCLUDED THEREIN, EVEN IF NOTIFIED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
39
Table of Contents
DESCRIPTION OF THE MANAGED FUTURES FUND’S INDEX
Developed by S&P and launched on August 14, 2014, the SFI is a long/short rules-based investable index that seeks to capture the economic benefit derived from both rising and declining trends in futures prices. The SFI is currently composed of 24 underlying futures contracts (each, a SFI Futures Contract, collectively, the SFI Futures Contracts), representing unleveraged long or short positions in futures contracts in the commodity and financial markets. The SFI includes both commodity futures contracts (the “Commodity Futures Contracts”) as well as currency and U.S. Treasury futures contracts (the “Financial Futures Contracts”) that were deemed to have sufficient liquidity.
The weight assigned to each SFI Futures Contract is determined on a monthly basis, and implemented as of each monthly repositioning. Weights are determined using a proprietary risk-weighting methodology that measures the risk exposure of the SFI Futures Contracts and then weights each SFI Futures Contract so that it contributes the same level of risk to the SFI.
The SFI’s exposure to the SFI Futures Contracts are not long-only, but will be either long or short based on a comparison of the current price input of each SFI Futures Contract with its own seven-month weighted moving average of its price input.
The following chart reflects the January 30, 2015 weight (rounded to the nearest one-hundredth) for each SFI Futures Contract of the SFI. The weights will be determined each month and implemented as of the next monthly rebalancing.
| SFI |
||||
| SFI Futures Contracts |
Base Weight (Rounded to the Nearest 0.01) |
|||
| Light Crude |
1.54 | % | ||
| Heating Oil |
2.14 | % | ||
| RBOB Gas |
1.78 | % | ||
| Natural Gas |
1.78 | % | ||
| Copper |
3.96 | % | ||
| Gold |
2.47 | % | ||
| Silver |
1.41 | % | ||
| Lean Hogs |
2.98 | % | ||
| Live Cattle |
4.56 | % | ||
| Corn |
2.24 | % | ||
| Soybeans |
2.59 | % | ||
| Wheat |
2.60 | % | ||
| Coffee |
1.25 | % | ||
| Cocoa |
5.85 | % | ||
| Sugar |
2.20 | % | ||
| Cotton |
3.25 | % | ||
| Australian dollar |
4.61 | % | ||
| British pound |
8.10 | % | ||
| Canadian dollar |
4.82 | % | ||
| Euro |
6.82 | % | ||
| Japanese yen |
5.30 | % | ||
| Swiss franc |
3.38 | % | ||
| U.S. Treasury Notes |
14.24 | % | ||
| U.S. Treasury Bonds |
10.11 | % | ||
|
|
|
|||
| 100 | % | |||
|
|
|
|||
40
Table of Contents
Determining the Long/Short Positioning of each SFI Futures Contract
Each month, S&P will determine whether an SFI Futures Contract should be either a long or short position by comparing the price change of the most recent month (the “First Month Price Change”) of the SFI Futures Contract to the seven-month exponential weighted moving average price change (the “Seven Month Price Change”). Long positions are tracked when an SFI Futures Contract’s First Month Price Change is greater than or equal to the Seven Month Price Change. Short positions are tracked when an SFI Futures Contract’s First Month Price Change is less than the Seven Month Price Change. The First Month Price Change of each SFI Futures Contract is calculated by calculating the percentage difference of each SFI Futures Contract’s price on the last PDD (as defined below) relative to the current PDD.
When calculating the Seven Month Price Change, each month’s price input is represented as the monthly percentage change of an SFI Futures Contract’s price which is calculated in the same manner as the First Month Price Change. Monthly positions are determined on the second to last SFI business day of the month (defined as the position determination date, or “PDD”) when the monthly percentage change of an SFI Future Contract’s price is compared to past monthly price changes, exponentially weighted to give greatest weight to the most recent return and least weight to the return seven months prior. The weighted sum of the percentage changes of all SFI Futures Contract prices equals the daily movement of the SFI. To create an exponential average for comparison, price inputs (percentage change from current and previous PDDs) are weighted per the schedule below. Due to this weighting methodology, current price movements are more important than those of the more distant past.
| Number of Months |
Weight (Rounded to the Nearest 0.01) |
|||
| 7 |
2.32 | % | ||
| 6 |
3.71 | % | ||
| 5 |
5.94 | % | ||
| 4 |
9.51 | % | ||
| 3 |
15.22 | % | ||
| 2 |
24.34 | % | ||
| 1 |
38.95 | % | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
100 | % | ||
|
|
|
|||
Rolling
During this monthly rebalancing, the SFI will also “roll” certain of its positions from the current contract to a contract further from settlement. In order to maintain consistent exposure to the SFI Futures Contracts that compose the SFI, each SFI Futures Contract must be sold prior to its expiration date and replaced by a contract maturing at a specified date in the future. This process is known as “rolling.” SFI Futures Contracts are rolled periodically. The rolls are implemented pursuant to a roll schedule over a five-day period from the first (1st) through the fifth (5th) index business days of the month. An index business day is any day on which the majority of the SFI Futures Contracts are open for official trading and official settlement prices are provided, excluding holidays and weekends.
In order to mitigate the potential negative impact of contango on long commodity positions, certain Commodity Futures Contracts will be rolled according to an “enhanced” rolling methodology. This methodology seeks to modify the normal roll methodology for futures contracts in the energy sector when such long position would be materially and negatively impacted by contango. In addition, the methodology identifies seasonal factors applicable to both the energy and agricultural futures markets and implements a modified roll to mitigate potential costs of such seasonal impacts.
41
Table of Contents
Information about the Index Licensor
The “S&P Strategic Futures” is a product of S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC or its affiliates (“SPDJI”) and has been licensed for use by ProShares. Standard & Poor’s® and S&P® are registered trademarks of Standard & Poor’s Financial Services LLC (“S&P”) and Dow Jones® is a registered trademark of Dow Jones Trademark Holdings LLC (“Dow Jones”). The trademarks have been licensed to SPDJI and have been sublicensed for use for certain purposes by ProShares. ProShares Managed Futures Strategy is not sponsored, endorsed, sold or promoted by SPDJI, Dow Jones, S&P, any of their respective affiliates (collectively, “S&P Dow Jones Indices”). S&P Dow Jones Indices does not make any representation or warranty, express or implied, to the owners of the ProShares Managed Futures Strategy or any member of the public regarding the advisability of investing in securities generally or in ProShares Managed Futures Strategy particularly or the ability of the S&P Strategic Futures Index to track general market performance. S&P Dow Jones Indices’ only relationship to ProShares with respect to the S&P Strategic Futures Index is the licensing of the Index and certain trademarks, service marks and/or trade names of S&P Dow Jones Indices and/or its licensors. The S&P Strategic Futures Index is determined, composed and calculated by S&P Dow Jones Indices without regard to ProShares or ProShares Managed Futures Strategy. S&P Dow Jones Indices has no obligation to take the needs of ProShares or the owners of ProShares Managed Futures Strategy into consideration in determining, composing or calculating the S&P Strategic Futures Index. S&P Dow Jones Indices is not responsible for and has not participated in the determination of the prices, and amount of ProShares Managed Futures Strategy or the timing of the issuance or sale of ProShares Managed Futures Strategy or in the determination or calculation of the equation by which ProShares Managed Futures Strategy is to be converted into cash, surrendered or redeemed, as the case may be. S&P Dow Jones Indices has no obligation or liability in connection with the administration, marketing or trading of ProShares Managed Futures Strategy. There is no assurance that investment products based on the S&P Strategic Futures Index will accurately track index performance or provide positive investment returns. S&P Dow Jones Indices LLC is not an investment advisor. Inclusion of a security within an index is not a recommendation by S&P Dow Jones Indices to buy, sell, or hold such security, nor is it considered to be investment advice.
NEITHER S&P DOW JONES INDICES NOR THIRD PARTY LICENSOR GUARANTEES THE ADEQUACY, ACCURACY, TIMELINESS AND/OR THE COMPLETENESS OF THE S&P STRATEGIC FUTURES INDEX OR ANY DATA RELATED THERETO OR ANY COMMUNICATION, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, ORAL OR WRITTEN COMMUNICATION (INCLUDING ELECTRONIC COMMUNICATIONS) WITH RESPECT THERETO. S&P DOW JONES INDICES SHALL NOT BE SUBJECT TO ANY DAMAGES OR LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS, OMISSIONS, OR DELAYS THEREIN. S&P DOW JONES INDICES MAKES NO EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR USE OR AS TO RESULTS TO BE OBTAINED BY PROSHARES, OWNERS OF PROSHARES MANAGED FUTURES STRATEGY, OR ANY OTHER PERSON OR ENTITY FROM THE USE OF THE S&P STRATEGIC FUTURES INDEX OR WITH RESPECT TO ANY DATA RELATED THERETO. WITHOUT LIMITING ANY OF THE FOREGOING, IN NO EVENT WHATSOEVER SHALL S&P DOW JONES INDICES BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO, LOSS OF PROFITS, TRADING LOSSES, LOST TIME OR GOODWILL, EVEN IF THEY HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBLITY OF SUCH DAMAGES, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, TORT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR OTHERWISE. THERE ARE NO THIRD PARTY BENEFICIARIES OF ANY AGREEMENTS OR ARRANGEMENTS BETWEEN S&P DOW JONES INDICES AND PROSHARES, OTHER THAN THE LICENSORS OF S&P DOW JONES INDICES.
42
Table of Contents
DESCRIPTION OF THE BLOOMBERG COMMODITY INDEXSM AND SUBINDEXES
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity are designed to correspond (before fees and expenses) to two times (2x) or two times the inverse (-2x), respectively, of the daily performance of the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM. The Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM (the “Bloomberg Commodity Index”) is designed to be a highly liquid and diversified benchmark for the commodity futures market. It is intended to reflect the overall commodity sector by measuring the performance of commodity futures contracts. The performance of the commodity futures market is often very different than the performance of the physical, or “spot,” commodities market. See “Risk Factors—The Managed Futures Fund and the Commodity Index Funds are linked to indexes comprised of commodity futures contracts and/or financial futures contracts, and are not directly linked to the ‘spot’ prices of the underlying physical commodities or financial assets. Futures contracts may perform very differently from the spot price of the underlying physical commodities or financial assets.” Unlike equities, which entitle the holder to a continuing stake in a corporation, commodity futures contracts specify a delivery date for the underlying physical commodity or its cash equivalent. The Bloomberg Commodity Index is a “rolling index,” which means that the Bloomberg Commodity Index does not take actual physical possession of any commodities; rather, it tracks a rolling futures position. An investor with a rolling futures position is able to avoid delivering (or taking delivery of) underlying physical commodities while maintaining exposure to those commodities. The roll for each Index component occurs over a period of five Bloomberg Commodity Index business days in certain months according to a pre-determined schedule, generally beginning on the fifth business day of the month and ending on the ninth business day. Each day, approximately 20% of each rolling futures position that is included in the month’s roll is rolled, increasing from 0% to 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and finally 100%. The Bloomberg Commodity Index is calculated by applying the weighting adjustments at the close of each day, with the adjusted weights used for the next day’s calculation. Not all contracts are rolled every month; generally, the futures that underlie the indexes within the Bloomberg Commodity Index family roll approximately every other month. The exact roll methodology differs between certain commodities. The index will reflect the performance of its underlying commodities, including the impact of rolling, without regard to income earned on cash positions. For more information about the risks associated with rolling futures positions, see “Risk Factors—Potential negative impact from rolling futures positions.”
The Bloomberg Commodity Index is comprised of five different commodity sectors: energy, livestock, industrial metals, precious metals and agriculture. These five sectors track futures contracts prices of 22 specific commodities: natural gas, WTI crude oil, brent crude, unleaded gasoline, heating oil, live cattle, lean hogs, wheat, Hard Red Winter Wheat (KBWT), corn, soybeans, soybean oil, soybean meal, aluminum, copper, zinc, nickel, gold, silver, sugar, cotton and coffee. The Bloomberg Commodity Index is designed to minimize concentration in any one commodity or sector. No single commodity can constitute more than 15% of the Bloomberg Commodity Index and no related group of commodities (e.g., energy, precious metals, livestock or grains) may constitute more than 33% of the index as of the annual reweighting of the components. The Bloomberg Commodity Index family of indexes also includes ten sub-indexes that group commodities based on type, as well as single commodity subindexes representing each of the commodities that are currently tracked by the Bloomberg Commodity Index. As discussed below, the Natural Gas Funds are designed to track one of these sub-indexes, the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM.
To determine its component weightings, the Bloomberg Commodity Index relies primarily on liquidity data, or the relative amount of trading activity of a particular commodity. Liquidity is an important indicator of the value placed on a commodity by financial and physical market participants. The index also relies to a lesser extent on dollar-adjusted production data. The index thus relies on data that is endogenous to the futures markets (liquidity) and exogenous to the futures markets (production) in determining relative weightings. All data used in both the liquidity and production calculations is averaged over a five-year period.
In consultation with the Bloomberg Commodity Index Advisory Committee, the Bloomberg Commodity Index Supervisory Committee meets annually to determine the composition of the index in accordance with the
43
Table of Contents
rules established in the Bloomberg Handbook. The Supervisory Committee consists of employees of Bloomberg. Bloomberg Commodity Index Advisory Committee members are drawn from the academic, financial and legal communities. The Bloomberg Commodity Index is re-weighted and rebalanced each year in January on a price-percentage basis. The annual weightings for the Index are determined each year in June or July by Bloomberg under the supervision of the Bloomberg Commodity Index Oversight Committee, announced after approval by the Committee and implemented the following January.
The Bloomberg Commodity Index is composed of commodities traded on U.S. exchanges, with the exception of aluminum, nickel and zinc, which trade on the London Metal Exchange. Trading hours for the U.S. commodity exchanges are between 8:00 a.m. and 3:00 p.m. (Eastern Time). The Bloomberg Commodity Index contract trades exclusively on the Chicago Board of Trade’s (“CBOT”) electronic trading platform. A daily settlement price for the Bloomberg Commodity Index is published at approximately 5:00 p.m. (Eastern Time).
The Bloomberg Commodity Index is designed to provide:
| • | Weightings that reflect economic significance |
| • | Diversification |
| • | Annual reweighting and rebalancing |
| • | Liquidity |
The Bloomberg Commodity Index is a proprietary index that Bloomberg calculates. The methodology for determining the composition and weighting of the Bloomberg Commodity Index and for calculating its level is subject to modification at any time. Bloomberg disseminates the Index level at least every 15 seconds from 8:00 a.m. to 3:00 p.m. (Eastern Time), and publishes a daily Index level at approximately 5:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) each business day.
As of January 2015, the target weightings of all Bloomberg Commodity Index components were as follows:
| Commodity |
Weight (%) | |||
| Natural Gas |
8.41 | % | ||
| WTI Crude Oil |
7.90 | % | ||
| Brent Crude |
7.73 | % | ||
| Unleaded Gasoline |
4.06 | % | ||
| Heating Oil |
3.91 | % | ||
| Live Cattle |
3.13 | % | ||
| Lean Hogs |
1.81 | % | ||
| Wheat |
2.96 | % | ||
| KCBT Wheat |
1.04 | % | ||
| Corn |
6.93 | % | ||
| Soybeans |
5.29 | % | ||
| Soybean Oil |
2.61 | % | ||
| Soy Meal |
2.62 | % | ||
| Aluminum |
4.90 | % | ||
| Copper |
6.98 | % | ||
| Zinc |
2.45 | % | ||
| Nickel |
2.12 | % | ||
| Gold |
12.88 | % | ||
| Silver |
4.56 | % | ||
| Sugar |
4.10 | % | ||
| Cotton |
1.52 | % | ||
| Coffee |
2.10 | % | ||
44
Table of Contents
Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas are designed to correspond (before fees and expenses) to two times (2x) or two times the inverse (-2x), respectively, of the daily performance of the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM. The Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM is intended to reflect the performance of a rolling position in natural gas futures contracts traded on the NYMEX without regard to income earned on cash positions. An investment in natural gas futures contracts may often perform very differently than the price of physical natural gas (e.g., the wellhead or end-user price of natural gas). See “Risk Factors—The Managed Futures Fund and the Commodity Index Funds are linked to indexes comprised of commodity futures contracts and/or financial futures contracts, and are not directly linked to the ‘spot’ prices of the underlying physical commodities or financial assets. Futures contracts may perform very differently from the spot price of the underlying physical commodities or financial assets.”
The Subindex is based on the Natural Gas component of the Bloomberg Commodity Index, which is described above under “Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM,” and tracks what is known as a rolling futures position. The roll occurs over a period of five Bloomberg Commodity Index business days in certain months according to a pre-determined schedule, generally beginning on the fifth business day of the month and ending on the ninth business day. Each day, approximately 20% of each rolling futures position that is included in the month’s roll is rolled, increasing from 0% to 20%, 40%, 60%, 80% and finally 100%. The exact roll methodology differs between certain commodities. The Index will reflect the performance of its underlying natural gas contracts, including the impact of rolling, without regard to income earned on cash positions. For more information about the risks associated with rolling futures positions, see “Risk Factors—Potential negative impact from rolling futures positions.”
Information About the Index Licensor
“BLOOMBERG®” AND “BLOOMBERG WTI CRUDE OIL SUBINDEXSM” ARE SERVICE MARKS OF BLOOMBERG FINANCE L.P. AND ITS AFFILIATES (COLLECTIVELY, “BLOOMBERG”) AND HAVE BEEN LICENSED FOR USE FOR CERTAIN PURPOSES BY PROSHARES TRUST II (“LICENSEE”).
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity; ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas (collectively, the “Products”) are not sponsored, endorsed, sold or promoted by Bloomberg, UBS AG, UBS Securities LLC (“UBS Securities”) or any of their subsidiaries or affiliates. None of Bloomberg, UBS AG, UBS Securities or any of their subsidiaries or affiliates makes any representation or warranty, express or implied, to the owners of or counterparties to the Products or any member of the public regarding the advisability of investing in securities or commodities generally or in the Products particularly. The only relationship of Bloomberg, UBS AG, UBS Securities or any of their subsidiaries or affiliates to the Licensee is the licensing of certain trademarks, trade names and service marks and of the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM and Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM which are determined, composed and calculated by Bloomberg in conjunction with UBS Securities without regard to the Licensee or the Products. Bloomberg and UBS Securities have no obligation to take the needs of the Licensee or the owners of the Products into consideration in determining, composing or calculating the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM or the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM. None of Bloomberg, UBS AG, UBS Securities or any of their respective subsidiaries or affiliates is responsible for or has participated in the determination of the timing of, prices at, or quantities of the Products to be issued or in the determination or calculation of the equation by which the Products are to be converted into cash. None of Bloomberg, UBS AG, UBS Securities or any of their subsidiaries or affiliates shall have any obligation or liability, including, without limitation, to Products’ customers, in connection with the administration, marketing or trading of the Products. Notwithstanding the foregoing, UBS AG, UBS Securities and their respective subsidiaries and affiliates may independently issue and/or sponsor financial products unrelated to the Products currently being issued by Licensee, but which may be similar to and competitive with the Products. In addition, UBS AG, UBS Securities and their subsidiaries and affiliates actively
45
Table of Contents
trade commodities, commodity indexes and commodity futures (including the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM and the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM), as well as swaps, options and derivatives which are linked to the performance of such commodities, commodity indexes and commodity futures. It is possible that this trading activity will affect the value of the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM, the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM and Products.
The Prospectus relates only to the Products and does not relate to the exchange-traded physical commodities underlying any of the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM or Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM components. Purchasers of the Products should not conclude that the inclusion of a futures contract in the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM or the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM is any form of investment recommendation of the futures contract or the underlying exchange-traded physical commodity by Bloomberg, UBS AG, UBS Securities or any of their subsidiaries or affiliates. The information in the Prospectus regarding the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM or the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM components has been derived solely from publicly available documents. None of Bloomberg, UBS AG, UBS Securities or any of their subsidiaries or affiliates has made any due diligence inquiries with respect to the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM or the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM components in connection with the Products. None of Bloomberg, UBS AG, UBS Securities or any of their subsidiaries or affiliates makes any representation that these publicly available documents or any other publicly available information regarding the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM or the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM components, including without limitation a description of factors that affect the prices of such components, are accurate or complete.
NONE OF BLOOMBERG, UBS AG, UBS SECURITIES OR ANY OF THEIR SUBSIDIARIES OR AFFILIATES GUARANTEES THE ACCURACY AND/OR THE COMPLETENESS OF THE BLOOMBERG COMMODITY INDEXSM, THE BLOOMBERG NATURAL GAS SUBINDEXSM OR ANY DATA RELATED THERETO AND NONE OF BLOOMBERG, UBS AG, UBS SECURITIES OR ANY OF THEIR SUBSIDIARIES OR AFFILIATES SHALL HAVE ANY LIABILITY FOR ANY ERRORS, OMISSIONS OR INTERRUPTIONS THEREIN. NONE OF BLOOMBERG, UBS AG, UBS SECURITIES OR ANY OF THEIR SUBSIDIARIES OR AFFILIATES MAKES ANY WARRANTY, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, AS TO RESULTS TO BE OBTAINED BY THE LICENSEE, OWNERS OF THE PRODUCTS OR ANY OTHER PERSON OR ENTITY FROM THE USE OF THE BLOOMBERG COMMODITY INDEXSM, THE BLOOMBERG NATURAL GAS SUBINDEXSM OR ANY DATA RELATED THERETO. NONE OF BLOOMBERG, UBS AG, UBS SECURITIES OR ANY OF THEIR SUBSIDIARIES OR AFFILIATES MAKES ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES AND EXPRESSLY DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE OR USE WITH RESPECT TO THE BLOOMBERG COMMODITY INDEXSM, THE BLOOMBERG NATURAL GAS SUBINDEXSM OR ANY DATA RELATED THERETO. WITHOUT LIMITING ANY OF THE FOREGOING, TO THE MAXIMUM EXTENT ALLOWED BY LAW, BLOOMBERG, ITS LICENSORS (INCLUDING UBS), AND ITS AND THEIR RESPECTIVE EMPLOYEES, CONTRACTORS, AGENTS, SUPPLIERS, AND VENDORS SHALL HAVE NO LIABILITY OR RESPONSIBILITY WHATSOEVER FOR ANY INJURY OR DAMAGES WHETHER DIRECT, INDIRECT, CONSEQUENTIAL, INCIDENTAL, PUNITIVE OR OTHERWISE ARISING IN CONNECTION WITH THE PRODUCTS OR THE BLOOMBERG COMMODITY INDEXSM, THE BLOOMBERG NATURAL GAS SUBINDEXSM OR ANY DATA OR VALUES RELATING THERETO WHETHER ARISING FROM THEIR NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE, EVEN IF NOTIFIED OF THE POSSIBILITY THEREOF. THERE ARE NO THIRD PARTY BENEFICIARIES OF ANY AGREEMENTS OR ARRANGEMENTS AMONG BLOOMBERG, UBS SECURITIES AND THE LICENSEE, OTHER THAN UBS AG.
46
Table of Contents
DESCRIPTION OF THE COMMODITY BENCHMARK
ProShares UltraShort Silver is designed to correspond (before fees and expenses) to two times the inverse (-2x) of the daily performance of silver bullion as measured by the London Silver Price, which serves as the Fund’s benchmark. The Fund does not directly or physically hold the underlying silver to pursue its investment objective, but instead, seeks exposure to silver through the use of Financial Instruments whose value is based on the underlying London Silver Price.
On August 14, 2014, the company that ran the London silver fixing ceased running the process. The LBMA selected the CME Group and Thomson Reuters to calculate the price, which was renamed the London Silver Price, based on an electronic, auction-based methodology effective August 15, 2014. Like gold, the silver market is a global marketplace consisting of both OTC transactions and exchange-traded products. The OTC market generally consists of transactions in spot, forwards, options and other derivatives, while exchange-traded transactions consist of futures and options.
The London Silver Price is determined each trading day at 12:00 p.m. London time, providing a reference silver price for that day’s trading. Many long-term contracts are priced on the basis of the London Silver Price and market participants will usually refer to the London Silver Price when looking for a basis for valuation.
47
Table of Contents
DESCRIPTION OF THE CURRENCY BENCHMARKS
ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar, ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar, ProShares Ultra Euro, ProShares Short Euro, and ProShares Ultra Yen are designed to correspond (before fees and expenses) to a multiple (2x), the inverse (-1x) or an inverse multiple (-2x) of the daily performance of the spot price of the applicable currency versus the U.S. dollar. The spot price of each currency is measured by the 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) spot prices as provided by Bloomberg, expressed in terms of U.S. dollars per unit of foreign currency. The Currency Funds do not necessarily directly or physically hold the underlying currency and will instead seek exposure through the use of certain Financial Instruments whose value is based on the price of the underlying currency to pursue its investment objective.
ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar and ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar are designed to correspond (before fees and expenses) to two times (2x) or two times the inverse (-2x), respectively, of the daily performance of the Australian dollar spot price versus the U.S. dollar. These Funds use the 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) Australian dollar/U.S. dollar exchange rate as provided by Bloomberg, expressed in terms of U.S. dollars per unit of foreign currency, as the basis for the underlying benchmark.
The Australian dollar is the national currency of Australia and the currency of the accounts of the Reserve Bank of Australia, the Australian central bank. The official currency code for the Australian dollar is “AUD.” The Australian dollar is referred to in Australia as “dollar.” As with U.S. currency, 100 Australian cents are equal to one Australian dollar. In Australia, unlike most other countries, cash transactions are rounded to the nearest five cents. The most commonly used symbol used to represent the Australian dollar is “A$.”
In 1913, the Commonwealth Bank of Australia issued the first Australian currency notes. In 1915, the Commonwealth Bank of Australia became the exclusive issuer of currency in Australia. From 1930 through the 1960s, the Australian banking system underwent substantial transformation. In 1960, the Reserve Bank of Australia was established. In 1966, a new decimalized currency was introduced. At various times throughout the 1900s, the value of Australian currency was based on a fixed quantity of gold; at other times, the Australian dollar was pegged to foreign currencies, including the U.S. dollar. Beginning in 1983, the Australian dollar’s value was allowed to float, with the result that its value now depends almost entirely on market forces. The foregoing information is compiled from the Reserve Bank of Australia’s website (www.rba.gov.au).
ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Short Euro are designed to correspond (before fees and expenses) to two times (2x) or the inverse (-1x) of the daily performance of the euro spot price versus the U.S. dollar, respectively. These Funds use the 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) euro/U.S. dollar exchange rate as provided by Bloomberg, expressed in terms of U.S. dollars per unit of foreign currency, as the basis for the underlying benchmark.
In 1998, the European Central Bank in Frankfurt was organized by Austria, Belgium, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Italy, Luxembourg, the Netherlands, Portugal and Spain in order to establish a common currency-the euro. Unlike the U.S. Federal Reserve System, the Bank of Japan and other comparable central banks, the European Central Bank is a central authority that conducts monetary policy for an economic area consisting of many otherwise largely autonomous states.
At its inception on January 1, 1999, the euro was launched as an electronic currency used by banks, foreign exchange dealers and stock markets. In 2002, the euro became cash currency for approximately 300 million citizens of 12 European countries (the eleven countries mentioned above, in addition to Greece). Today, 23 countries use the euro, including Andorra, Cyprus, Finland, Kosovo, Malta, Monaco, Montenegro, San Marino, Slovakia, Slovenia and the Vatican City.
48
Table of Contents
Although the European countries that have adopted the euro are members of the European Union, the United Kingdom, Denmark and Sweden are European Union members that have not adopted the euro as their national currency.
ProShares Ultra Yen is designed to correspond (before fees and expenses) to two times (2x) of the daily performance of the Japanese yen spot price versus the U.S. dollar. This Fund uses the 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) Japanese yen/U.S. dollar exchange rate as provided by Bloomberg, expressed in terms of U.S. dollars per unit of foreign currency, as the basis for the underlying benchmark.
The Japanese yen has been the official currency of Japan since 1871. The Bank of Japan has been operating as the central bank of Japan since 1882.
49
Table of Contents
INVESTMENT OBJECTIVES AND PRINCIPAL INVESTMENT STRATEGIES
Each Fund seeks, on a daily basis, to provide investment results that correspond (before fees and expenses) to the performance of (1x) or two times (2x) the performance of, the inverse (-1x) or two times the inverse (-2x) of the performance of a benchmark. The Geared Funds do not seek to achieve their stated objective over a period greater than a single day. Because the Geared Funds seek investment results for a single day only (as measured from the time a Fund calculates its NAV to the time of the Fund’s next NAV calculation) and on a leveraged, inverse or inverse leveraged basis, each Geared Fund is different from most exchange-traded funds.
Investment Objective of the Matching Funds (the VIX Fund and the Managed Futures Fund):
The VIX Fund seeks results that, both over a single day and over time, match (before fees and expenses) the performance of its index. If the VIX Fund is successful in meeting its objective, its value (before fees and expenses) should gain approximately as much on a percentage basis as the level of the Mid-Term VIX Index when the index rises. Conversely, its value (before fees and expenses) should lose approximately as much on a percentage basis as the level of the Mid-Term VIX Index when the index declines. The VIX Fund seeks to obtain investment exposure to its benchmark through the relevant futures contracts.
The Managed Futures Fund seeks results that, both over a single day and over time, match (before fees and expenses) the performance of its index. If the Managed Futures Fund is successful in meeting its objective, its value (before fees and expenses) should gain approximately as much on a percentage basis as the level of the S&P Strategic Futures Index when the index rises. Conversely, its value (before fees and expenses) should lose approximately as much on a percentage basis as the level of the S&P Strategic Futures Index when the index declines. The Managed Futures Fund attempts to profit in both rising and falling markets by obtaining investment exposure to its benchmark through the relevant futures contracts.
Investment Objective of the “Ultra Funds”:
The “Ultra” Funds seek daily results that match (before fees and expenses) two times (2x) the daily performance of a benchmark. The Ultra Funds do not seek to achieve their stated objective over a period greater than a single day. A “single day” is measured from the time the Ultra Fund calculates its NAV to the time of the Ultra Fund’s next NAV calculation. If an Ultra Fund is successful in meeting its objective, its value on a given day (before fees and expenses) should gain approximately two times as much on a percentage basis as the level of its corresponding benchmark when the benchmark rises. Conversely, its value on a given day (before fees and expenses) should lose approximately two times as much on a percentage basis as the level of its corresponding benchmark when the benchmark declines. Each Ultra Fund acquires long exposure through any one of or combinations of Financial Instruments, including Financial Instruments with respect to the applicable Ultra Fund’s benchmark, such that each Ultra Fund has exposure intended to approximate two times (2x) its corresponding benchmark at the time of its NAV calculation.
Investment Objective of the “Short Fund”:
The “Short” Fund seeks daily results that match (before fees and expenses) the inverse (-1x) of the daily performance of a benchmark. The Short Fund does not seek to achieve its stated objective over a period greater than a single day. A “single day” is measured from the time the Short Fund calculates its NAV to the time of the Short Fund’s next NAV calculation. If the Short Fund is successful in meeting its objective, its value on a given day (before fees and expenses) should gain approximately as much on a percentage basis as the level of its corresponding benchmark when the benchmark declines. Conversely, its value on a given day (before fees and expenses) should lose approximately as much on a percentage basis as the level of its corresponding benchmark when the benchmark rises. The Short Fund acquires inverse exposure through futures contracts, and under certain circumstances, forward contracts , such that the Short Fund has exposure intended to approximate the inverse (-1x) of its corresponding benchmark at the time of its NAV calculation.
50
Table of Contents
Investment Objective of the “UltraShort Funds”:
The “UltraShort” Funds seek daily results that match (before fees and expenses) two times the inverse (-2x) of the daily performance of a benchmark. The UltraShort Funds do not seek to achieve their stated objectives over a period greater than a single day. A “single day” is measured from the time the UltraShort Fund calculates its NAV to the time of the UltraShort Fund’s next NAV calculation. If an UltraShort Fund is successful in meeting its objective, its value on a given day (before fees and expenses) should gain approximately two times as much on a percentage basis as the level of its corresponding benchmark when the benchmark declines. Conversely, its value on a given day (before fees and expenses) should lose approximately two times as much on a percentage basis as the level of its corresponding benchmark when the benchmark rises. Each UltraShort Fund acquires inverse exposure through any one of or combinations of Financial Instruments, including Financial Instruments with respect to the applicable UltraShort Fund’s benchmark, such that each UltraShort Fund has exposure intended to approximate two times the inverse (-2x) of its corresponding benchmark at the time of its NAV calculation.
There can be no assurance that any Fund will achieve its investment objective or avoid substantial losses. The Geared Funds do not seek to achieve their stated investment objective over a period of time greater than a single day because mathematical compounding prevents the Geared Funds from achieving such results. Results for the Geared Funds over periods of time greater than a single day should not be expected to be a simple multiple (2x), inverse (-1x) or inverse multiple (-2x) of the period return of the corresponding benchmark and will likely differ significantly from such. A Geared Fund will lose money if its benchmark’s performance is flat over time, and it is possible for a Geared Fund to lose money over time regardless of the performance of an underlying benchmark, as a result of daily rebalancing, the benchmark’s volatility and compounding. Daily compounding of a Geared Fund’s investment returns can dramatically and adversely affect its longer-term performance during periods of high volatility. Volatility may be at least as important to a Geared Fund’s return for a period as the return of the Geared Fund’s underlying benchmark. The VIX Fund and the Managed Futures Fund seek to achieve their stated investment objectives both over a single day and over time.
The corresponding benchmark for each Fund is listed below:
The VIX Fund:*
ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF: the S&P 500 VIX Mid-Term Futures Index (the Mid-Term VIX Index) (Bloomberg Ticker: SPVXMID). The Mid-Term VIX Index seeks to offer exposure to market volatility through publicly traded futures markets and is designed to measure the return from a rolling long position in the fourth, fifth, sixth and seventh month VIX futures contracts.
The Managed Futures Fund:
ProShares Managed Futures Strategy: the S&P Strategic Futures Index (the SFI) (Bloomberg Ticker SPSFIT). The SFI is a long/short rules-based investable index that seeks to potentially capture the economic benefit derived from both rising and declining trends in futures prices.
The Commodity Index Funds:
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity: the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM (the Bloomberg Commodity Index) (Bloomberg Ticker: BCOMTR). The Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM is designed to track commodity futures prices.
| * | The VIX Fund is benchmarked to an index comprised of VIX futures contracts and not to the VIX, which is calculated based on the prices of put and call options on the S&P 500. As such, the VIX Fund can be expected to perform very differently from the VIX. |
51
Table of Contents
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas: the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM (the “Natural Gas Index”) (Bloomberg Ticker: BCOMNGTR). The Natural Gas Index is designed to track the price of natural gas futures contracts traded on the NYMEX.
The Commodity Fund:
ProShares UltraShort Silver: the daily performance of silver bullion as measured by the London Silver Price (Bloomberg Ticker: SLVRLND).
The Currency Funds:
ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar and ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar: the 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) spot price of the Australian dollar versus the U.S. dollar using the Australian dollar exchange rate, expressed in terms of U.S. dollars per unit of foreign currency (Bloomberg Ticker: AUDUSD).
ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Short Euro: the 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) spot price of the euro versus the U.S. dollar using the euro/U.S. dollar exchange rate, expressed in terms of U.S. dollars per unit of foreign currency (Bloomberg Ticker: EURUSD).
ProShares Ultra Yen: the 4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) spot price of the Japanese yen versus the U.S. dollar using the Japanese yen/U.S. dollar exchange rate, expressed in terms of U.S. dollars per unit of foreign currency (Bloomberg Ticker: JPYUSD).
The following charts illustrate exchange rates for the Australian dollar, the euro, and the Japanese yen, respectively, as measured against the U.S. dollar from January 31, 2012 to January 31, 2015:
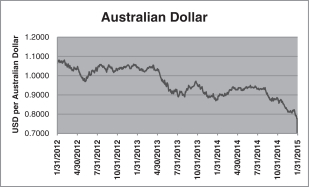
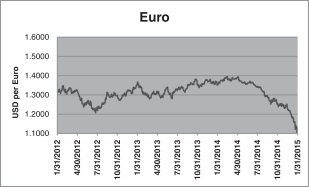
52
Table of Contents
Principal Investment Strategies
In seeking to achieve the Funds’ investment objectives, the Sponsor uses a mathematical approach to investing. Using this approach, the Sponsor determines the type, quantity and mix of investment positions that the Sponsor believes, in combination, should produce daily returns consistent with the Funds’ objectives. The Sponsor relies upon a pre-determined model to generate orders that result in repositioning the Funds’ investments in accordance with their respective investment objective.
Investment Strategies of ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF:
The VIX Fund intends to meet its investment objective by taking long or short positions in VIX futures contracts. In the event position accountability rules or position limits are reached with respect to VIX futures contracts, the Sponsor may, in its commercially reasonable judgment, cause the VIX Fund to obtain exposure to its index through swaps referencing the Mid-Term VIX Index or particular VIX futures contracts comprising the Mid-Term VIX Index, or invest in other futures contracts or swaps not based on the particular VIX futures contracts comprising the Mid-Term VIX Index if such instruments tend to exhibit trading prices or returns that correlate with the Mid-Term VIX Index or any VIX futures contract and will further the investment objective of the VIX Fund. The VIX Fund may also invest in swaps if the market for a specific futures contract experiences emergencies (e.g., natural disaster, terrorist attack or an act of God) or disruptions (e.g., a trading halt or a flash crash) to prevent the VIX Fund from obtaining the appropriate amount of investment exposure to the affected VIX futures contracts directly or other futures contracts. The VIX Fund will also hold cash or cash equivalents such as U.S. Treasury securities or other high credit quality, short-term fixed-income or similar securities (such as shares of money market funds and collateralized repurchase agreements) for direct investment or as collateral for Financial Instruments. The VIX Fund may invest up to 100% of its assets in any of these types of cash or cash equivalent securities.
Investment Strategies of ProShares Managed Futures Strategy:
The Managed Futures Fund intends to meet its investment objective by investing primarily in Commodity Futures Contracts or Financial Futures Contracts. In the event position accountability rules or position limits are reached with respect to those futures contracts, the Sponsor may, in its commercially reasonable judgment, cause such Fund to obtain exposure to the SFI through swaps whose value is derived from the level of the SFI, one or more SFI Futures Contracts or, in the case of currency-based Financial Futures Contracts, the exchange rates underlying such Financial Futures Contracts, or invest in other futures contracts or swaps if such instruments tend to exhibit trading prices or returns that correlate with the SFI or any SFI Futures Contract and will further the investment objective of the Managed Futures Fund. The Managed Futures Fund may also invest in swaps if the market for a specific futures contract experiences emergencies (e.g., natural disaster, terrorist attack or an act of God) or disruptions (e.g., a trading halt or a flash crash) that prevent the Fund from obtaining the appropriate amount of investment exposure to the affected Commodity Futures Contracts or Financial Futures Contracts directly or other futures contracts. The Managed Futures Fund will also hold cash or cash equivalents such as
53
Table of Contents
U.S. Treasury securities or other high credit quality, short-term fixed-income or similar securities (such as shares of money market funds and collateralized repurchase agreements) for direct investment or as collateral for Financial Instruments. The Managed Futures Fund may also invest up to 100% of its assets in any of these types of cash or cash equivalent instruments
Investment Strategies of ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Silver, ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Ultra Yen:
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Silver, ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Ultra Yen invest principally in any one of or combinations of Financial Instruments, including swap agreements, futures contracts or forward contracts with respect to the applicable Fund’s benchmark to the extent determined appropriate by the Sponsor. The types of commodity or currency interests in which these Funds invest may vary daily. The Funds do not currently intend to invest directly in any commodity or currency. The Funds will also hold cash or cash equivalents such as U.S. Treasury securities or other high credit quality, short-term fixed-income or similar securities (such as shares of money market funds and collateralized repurchase agreements) for direct investment or as collateral for Financial Instruments. Each of these Funds may invest up to 100% of its assets in any of these types of cash or cash equivalent securities.
Investment Strategies of ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas:
Each Natural Gas Fund intends to meet its investment objective by taking long or short positions in natural gas futures contracts. In the event position accountability rules or position limits are reached with respect to natural gas futures contracts, the Sponsor may, in its commercially reasonable judgment, cause the Natural Gas Funds to obtain exposure to the Natural Gas Index through swaps referencing the Natural Gas Index or particular natural gas futures contracts comprising the Natural Gas Index, or invest in other futures contracts or swaps not based on the particular natural gas futures contracts comprising the Natural Gas Index if such instruments tend to exhibit trading prices or returns that correlate with the Natural Gas Index or any natural gas futures contract and will further the investment objective of the applicable Natural Gas Fund. The Natural Gas Funds may also invest in swaps if the market for a specific futures contract experiences emergencies (e.g., natural disaster, terrorist attack or an act of God) or disruptions (e.g., a trading halt or a flash crash) that prevent the Natural Gas Fund from obtaining the appropriate amount of investment exposure to the affected natural gas futures contracts directly or other futures contracts. The Natural Gas Funds will also hold cash or cash equivalents such as U.S. Treasury securities or other high credit quality, short-term fixed-income or similar securities (such as shares of money market funds and collateralized repurchase agreements) for direct investment or as collateral for Financial Instruments. Each Natural Gas Fund may also invest up to 100% of its assets in any of these types of cash or cash equivalent securities.
Investment Strategies of ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar, ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar and ProShares Short Euro:
Each of ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar, ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar and ProShares Short Euro intends to meet its investment objective by obtaining long or short exposures to its benchmark through futures contracts on its underlying currency. In the event position accountability rules or position limits are reached with respect to futures contracts, the Sponsor may in its commercially reasonable judgment, cause such Fund to obtain exposure to its benchmark through forward contracts referencing the benchmark, or invest in other forward contracts if such instruments tend to exhibit trading prices or returns that correlate with the benchmark or a component of the benchmark and will further the investment objective of the Fund. The Funds may also invest in forward contracts if the market for a specific futures contract experiences emergencies (e.g., natural disaster, terrorist attack or an act of God) or disruptions (e.g., a trading halt or a flash crash) that prevent the Funds from obtaining the appropriate amount of investment exposure to the affected futures contracts directly. Each Fund will also hold cash or cash equivalents such as U.S. Treasury securities or other high credit quality,
54
Table of Contents
short-term fixed-income or similar securities (such as shares of money market funds and collateralized repurchase agreements) for direct investment or as collateral for Financial Instruments. Each Fund may invest up to 100% of its assets in any of these types of cash or cash equivalent securities.
The Sponsor does not invest the assets of the Funds based on its view of the investment merit of a particular investment, other than for cash management purposes, nor does it conduct conventional volatility, commodity or currency research or analysis, or forecast market movement or trends, in managing the assets of the Funds. Each Fund seeks to remain fully invested at all times in Financial Instruments and money market instruments that, in combination, provide exposure to its underlying benchmark consistent with its investment objective without regard to market conditions, trends or direction.
Certain of the Funds may obtain exposure through Financial Instruments to a representative sample of the components in its underlying index, which have aggregate characteristics similar to those of the underlying index. This “sampling” process typically involves selecting a representative sample of components in an index principally to enhance liquidity and reduce transaction costs while seeking to maintain high correlation with, and similar aggregate characteristics (e.g., underlying commodities and valuations) to, the underlying index. In addition, the Funds may obtain exposure to components not included in its underlying index, invest in assets that are not included in its underlying index or may overweight or underweight certain components contained in the underlying index.
As of the NAV calculation time each trading day, each Geared Fund will seek to position its portfolio so that its exposure to its benchmark is consistent with its investment objective. The impact of a benchmark’s movements during the day will affect whether the Geared Fund’s portfolio needs to be rebalanced. For example, if an UltraShort Fund’s benchmark has risen on a given day, net assets of such Fund should fall. As a result, inverse exposure will need to be decreased. Conversely, if a Short or UltraShort Fund’s benchmark has fallen on a given day, net assets of such Fund should rise. As a result, inverse exposure will need to be increased. For Ultra Funds, the Fund’s long exposure will need to be increased on days when such Fund’s benchmark rises and decreased on days when such Fund’s benchmark falls. Daily rebalancing and the compounding of each day’s return over time means that the return of each Geared Fund for a period longer than a single day will be the result of each day’s returns compounded over the period, which will very likely differ from two times (2x), the inverse (-1x) or two times the inverse (-2x) of the return of the Geared Fund’s benchmark for the period. A Geared Fund will lose money if its benchmark’s performance is flat over time, and it is possible for a Geared Fund to lose money over time regardless of the performance of an underlying benchmark, as a result of daily rebalancing, the benchmark’s volatility and compounding.
The amount of exposure each Fund has to Financial Instruments differs with each particular Fund and may be changed without shareholder approval at any given time. Currently, the Funds anticipate that, in the normal course of business and absent any unforeseen circumstances, they will be exposed to the specific Financial Instruments below as follows:
| Swaps | Forwards | Futures | ||||||||||
| ProShares VIX Mid Term Futures ETF |
0 | % | 0 | % | 100 | % | ||||||
| ProShares Managed Futures Strategy |
0 | % | 0 | % | 100 | % | ||||||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity |
200 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||||||
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity |
-200 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||||||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas |
0 | % | 0 | % | 200 | % | ||||||
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas |
0 | % | 0 | % | -200 | % | ||||||
| ProShares UltraShort Silver |
0 | % | -190 to -200 | % | 0 to -10 | % | ||||||
| ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar |
0 | % | 0 | % | 200 | % | ||||||
| ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar |
0 | % | 0 | % | -200 | % | ||||||
| ProShares Ultra Euro |
0 | % | 200 | % | 0 | % | ||||||
| ProShares Short Euro |
0 | % | 0 | % | -100 | % | ||||||
| ProShares Ultra Yen |
0 | % | 200 | % | 0 | % | ||||||
55
Table of Contents
Swap Agreements
Swap agreements are two-party contracts that have traditionally been entered into primarily by institutional investors in OTC markets for a specified period ranging from a day to more than a year. However, the Dodd-Frank Act provides for significant reforms of the OTC derivatives markets, including a requirement to execute certain swap transactions on a CFTC regulated market and/or to clear such transactions through a CFTC-regulated central clearing organization. In a standard swap transaction, the parties agree to exchange the returns on a particular predetermined investment, instrument or index for a fixed or floating rate of return (the “interest rate leg,” which will also include the cost of borrowing for short swaps) in respect of a predetermined notional amount. The notional amount of the agreement reflects the extent of a Fund’s total investment exposure under the swap agreement. In the case of futures contracts-based indexes, such as those used by the VIX Fund, the Managed Futures Fund and the Commodity Index Funds, the reference interest rate is zero, although a financing spread or fee is normally still applied. Transaction or commission costs are reflected in the benchmark level at which the transaction is entered into. The gross returns to be exchanged are calculated with respect to the notional amount and the benchmark returns to which the swap is linked. Swaps are usually closed out on a net basis, i.e., the two payment streams are netted out in a cash settlement on the payment date specified in the agreement, with the parties receiving or paying, as the case may be, only the net amount of the two payments. Thus, while the notional amount reflects a Fund’s total investment exposure under the swap agreement (i.e., the entire face amount or principal of a swap agreement), the net amount is a Fund’s current obligations (or rights) under the swap agreement, which is the net amount to be paid or received under the agreement based on the relative values of the positions held by each party to the agreement on any given termination date.
Swap agreements involve, to varying degrees, elements of market risk and exposure to loss in excess of the amount which would be reflected on the Statement of Financial Condition. The primary risks associated with the use of swap agreements arise from the inability of counterparties to perform. Each Fund that invests in swaps bears the risk of loss of the net amount, if any, expected to be received under a swap agreement in the event of the default or bankruptcy of a swap counterparty. Each such Fund enters or intends to enter into swap agreements only with major, global financial institutions; however, there are no limitations on the percentage of its assets each Fund may invest in swap agreements with a particular counterparty. Each Fund that invests in swaps may use various techniques to minimize credit risk.
Each Fund that invests in swaps generally collateralizes the swap agreements with cash and/or certain securities. Collateral posted in connection with uncleared derivatives transactions is generally held for the benefit of the counterparty in a segregated tri-party account at the Custodian to protect the counterparty against non-payment by the Fund. The counterparty also may collateralize the uncleared swap agreements with cash and/or certain securities, which collateral is typically held for the benefit of the Fund in a segregated tri-party account at the Custodian. In the event of a default by the counterparty, and the Fund is owed money in the uncleared swap transaction, such Fund will seek withdrawal of this collateral from the segregated account and may incur certain costs exercising its right with respect to the collateral. These Funds remain subject to credit risk with respect to the amount it expects to receive from counterparties.
The Funds have sought to mitigate these risks in connection with the uncleared OTC swaps by generally requiring that the counterparties for each Fund agree to post collateral for the benefit of the Fund, marked to market daily, subject to certain minimum thresholds; however there are no limitations on the percentage of its assets each Fund may invest in swap agreements with a particular counterparty. To the extent any such collateral is insufficient or there are delays in accessing the collateral, the Funds will be exposed to counterparty risk as described above, including possible delays in recovering amounts as a result of bankruptcy proceedings.
The counterparty risk for cleared derivatives transactions is generally lower than for uncleared OTC derivatives since generally a clearing organization becomes substituted for each counterparty to a cleared derivatives contract and, in effect, guarantees the parties’ performance under the contract as each party to a trade looks only to the clearing house for performance of financial obligations. In addition, cleared derivatives transactions benefit from daily marking-to-market and settlement, and segregation and minimum capital requirements applicable to intermediaries.
56
Table of Contents
Forward Contracts
A forward contract is a contractual obligation to purchase or sell a specified quantity of a particular underlying asset at or before a specified date in the future at a specified price and, therefore, is economically similar to a futures contract. Unlike futures contracts, however, forward contracts are typically traded in the OTC markets and are not standardized contracts. Forward contracts for a given commodity or currency are generally available for various amounts and maturities and are subject to individual negotiation between the parties involved. Moreover, there is generally no direct means of offsetting or closing out a forward contract by taking an offsetting position as one would a futures contract on a U.S. exchange. If a trader desires to close out a forward contract position, he generally will establish an opposite position in the contract but will settle and recognize the profit or loss on both positions simultaneously on the delivery date. Thus, unlike in the futures contract market where a trader who has offset positions will recognize profit or loss immediately, in the forward market a trader with a position that has been offset at a profit will generally not receive such profit until the delivery date, and likewise a trader with a position that has been offset at a loss will generally not have to pay money until the delivery date. In recent years, however, the terms of forward contracts have become more standardized, and in some instances such contracts now provide a right of offset or cash settlement as an alternative to making or taking delivery of the underlying commodity or currency. The primary risks associated with the use of forward contracts arise from the inability of the counterparty to perform.
Each Fund that invests in forward contracts generally collateralizes the uncleared forward contracts with cash and/or certain securities. Such collateral is generally held for the benefit of the counterparty in a segregated tri-party account at the Custodian to protect the counterparty against non-payment by the Fund. The counterparty also may collateralize the uncleared forward contracts with cash and/or certain securities, which collateral is typically held for the benefit of the Fund in a segregated tri-party account at the Custodian. In the event of a default by the counterparty, and the Fund is owed money in the uncleared forward transaction, such Fund will seek withdrawal of this collateral from the segregated account and may incur certain costs exercising its right with respect to the collateral. These Funds remain subject to credit risk with respect to the amount it expects to receive from OTC counterparties.
The Funds have sought to mitigate these risks with respect to uncleared OTC forwards by generally requiring that the counterparties for each Fund agree to post collateral for the benefit of the Fund, marked to market daily, subject to certain minimum thresholds; however, there are no limitations on the percentage of its assets each Fund may invest in forward contracts with a particular counterparty. To the extent any such collateral is insufficient or there are delays in accessing the collateral, the Funds will be exposed to counterparty risk as described above, including possible delays in recovering amounts as a result of bankruptcy proceedings.
The forward markets provide what has typically been a highly liquid market for foreign exchange trading, and in certain cases the prices quoted for foreign exchange forward contracts may be more favorable than the prices for foreign exchange futures contracts traded on U.S. exchanges. Forward contracts have traditionally not been cleared or guaranteed by a third party. As a result of the Dodd-Frank Act, the CFTC now regulates non-deliverable forwards (including deliverable forwards where the parties do not take delivery). Certain non-deliverable forward contracts, such as non-deliverable foreign exchange forwards, may be subject to regulation as swap agreements, including mandatory clearing. Changes in the forward markets may entail increased costs and result in burdensome reporting requirements.
Commercial banks participating in trading OTC foreign exchange forward contracts often do not require margin deposits, but rely upon internal credit limitations and their judgments regarding the creditworthiness of their counterparties. In recent years, however, many OTC market participants in foreign exchange trading have begun to require that their counterparties post margin.
57
Table of Contents
Futures Contracts
A futures contract is a standardized contract traded on, or subject to the rules of, an exchange that calls for the future delivery of a specified quantity and type of a particular underlying asset at a specified time and place or alternatively may call for cash settlement. Futures contracts are traded on a wide variety of underlying assets, including bonds, interest rates, agricultural products, stock indexes, currencies, energy, metals, economic indicators and statistical measures. The notional size and calendar term futures contracts on a particular underlying asset are identical and are not subject to any negotiation, other than with respect to price and the number of contracts traded between the buyer and seller. Each Fund generally deposits cash with an FCM for its open positions in futures contracts, which may, in turn, transfer such deposits to the clearing house to protect the clearing house against non-payment by the Fund. The clearing house becomes substituted for each counterparty to a futures contract, and, in effect, guarantees performance. In addition, the FCM may require the Funds to deposit collateral in excess of the clearing house’s margin requirements for the FCM’s own protection.
Certain futures contracts, including VIX futures contracts, stock index contracts and certain commodity futures contracts settle in cash, reflecting the difference between the contract purchase/sale price and the contract settlement price. The cash settlement mechanism avoids the potential for either side to have to deliver the underlying asset. For other futures contracts, the contractual obligations of a buyer or seller may generally be satisfied by taking or making physical delivery of the underlying asset or by making an offsetting sale or purchase of an identical futures contract on the same or linked exchange before the designated date of delivery. The difference between the price at which the futures contract is purchased or sold and the price paid for the offsetting sale or purchase, after allowance for brokerage commissions, constitutes the profit or loss to the trader.
Futures contracts involve, to varying degrees, elements of market risk and exposure to loss in excess of the amounts of variation margin, which are the amounts of cash that the Funds agree to pay to or receive from FCMs equal to the daily fluctuation in the value of a futures contract. Additional risks associated with the use of futures contracts are imperfect correlation between movements in the price of the futures contracts and the level of the underlying benchmark and the possibility of an illiquid market for a futures contract. With futures contracts, there is minimal but some counterparty risk to the Funds since futures contracts are exchange traded and the exchange’s clearinghouse, as counterparty to all exchange-traded futures contracts, effectively guarantees futures contracts against default. Many futures exchanges and boards of trade limit the amount of fluctuation permitted in futures contract prices during a single trading day. Once the daily limit has been reached in a particular contract, no trades may be made that day at a price beyond that limit or trading may be suspended for specified times during the trading day. Futures contracts prices could move to the limit for several consecutive trading days with little or no trading, thereby preventing prompt liquidation of futures positions and potentially subjecting a Fund to substantial losses. If trading is not possible or if a Fund determines not to close a futures position in anticipation of adverse price movements, the Fund may be required to make daily cash payments of variation margin.
Money Market Instruments
Money market instruments are short-term debt instruments that have a remaining maturity of 397 days or less and exhibit high quality credit profiles. Money market instruments may include U.S. government securities, securities issued by governments of other developed countries and repurchase agreements.
U.S. Derivatives Exchanges
Derivatives exchanges , including swap execution facilities that are required under the Dodd-Frank Act, provide centralized market facilities for trading derivatives in which multiple persons have the ability to execute or trade contracts by accepting bids and offers from multiple participants. Members of, and trades executed on, a particular exchange are subject to the rules of that exchange. Among the principal exchanges in the United States are the CBOE (which includes the CFE), the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (“CME”) (which includes, among others, the CBOT and the NYMEX) and the Intercontinental Exchange (“ICE”)).
58
Table of Contents
Each derivatives exchange in the United States has an associated “clearing house.” Clearing houses provide services designed to transfer credit risk and ensure the integrity of trades. Once trades between members of an exchange have been confirmed and/or cleared, the clearing house becomes substituted for each buyer and each seller of contracts traded on the exchange and, in effect, becomes the other party to each trader’s open position in the market. Thereafter, each party to a trade looks only to the clearing house for performance. The clearing house generally establishes some sort of security or guarantee fund to which all clearing members of the exchange must contribute. This fund acts as an emergency buffer which is intended to enable the clearing house to meet its obligations with regard to the other side of an insolvent clearing member’s contracts. Furthermore, clearing houses require margin deposits and continuously mark positions to market to provide some assurance that their members will be able to fulfill their contractual obligations. Thus, members effecting derivatives transactions on an organized exchange or clearing an OTC derivatives transaction through a clearing house do not bear the risk of the insolvency of the party on the opposite side of the trade; their credit risk is limited to the respective solvencies of their commodity broker and the clearing house. The clearing house “guarantee” of performance on open positions does not run to customers. If a member firm goes bankrupt, customers could lose money.
If a Fund decides to execute derivatives transactions through such derivatives exchanges—and especially if it decides to become a direct member of one or more exchanges or swap execution facilities—a Fund would be subject to the rules of the exchange or swap executive facility, which would bring additional risks and liabilities, and potential additional regulatory requirements.
Regulations
Derivatives exchanges in the United States are subject to regulation under the CEA, by the CFTC, the governmental agency having responsibility for regulation of derivatives exchanges and trading on those exchanges. Following the adoption of the Dodd-Frank Act, the CFTC also has authority to regulate OTC derivatives markets, including certain OTC foreign exchange markets.
The CFTC has exclusive authority to designate exchanges for the trading of specific futures contracts and options on futures contracts and to prescribe rules and regulations of the marketing of each. The CFTC also regulates the activities of “commodity pool operators” and the CFTC has adopted regulations with respect to certain of such persons’ activities. Pursuant to its authority, the CFTC requires a commodity pool operator, such as the Sponsor, to keep accurate, current and orderly records with respect to each pool it operates. The CFTC may suspend, modify or terminate the registration of any registrant for failure to comply with CFTC rules or regulations. Suspension, restriction or termination of the Sponsor’s registration as a commodity pool operator would prevent it, until such time (if any) as such registration were to be reinstated, from managing, and might result in the termination of, the Funds. If the Sponsor were unable to provide services and/or advice to the Funds, the Funds would be unable to pursue their investment objectives unless and until the Sponsor’s ability to provide services and advice to the Funds was reinstated or a replacement for the Sponsor as commodity pool operator could be found. Such an event could result in termination of the Funds.
The CEA requires all FCMs to meet and maintain specified fitness and financial requirements, segregate customer funds from proprietary funds and account separately for all customers’ funds and positions, and to maintain specified books and records open to inspection by the staff of the CFTC. See “Risk Factors—Failure of the FCMs to segregate assets may increase losses in the Funds.”
The CEA also gives the states certain powers to enforce its provisions and the regulations of the CFTC.
Under certain circumstances, the CEA grants shareholders the right to institute a reparations proceeding before the CFTC against the Sponsor (as a registered commodity pool operator), an FCM, as well as those of their respective employees who are required to be registered under the CEA. Shareholders may also be able to maintain a private right of action for certain violations of the CEA.
59
Table of Contents
Pursuant to authority in the CEA, the NFA has been formed and registered with the CFTC as a registered futures association. At the present time, the NFA is the only self-regulatory organization for commodities professionals other than exchanges. As such, the NFA promulgates rules governing the conduct of commodity professionals and disciplines those professionals that do not comply with such standards. The CFTC has delegated to the NFA responsibility for the registration of commodity pool operators, FCMs, swap dealers, commodity trading advisors, introducing brokers and their respective associated persons and floor brokers. The Sponsor is a member of the NFA (the Funds themselves are not required to become members of the NFA). As an NFA member, the Sponsor is subject to NFA standards relating to fair trade practices, financial condition, and consumer protection. The CFTC is prohibited by statute from regulating trading on foreign commodity exchanges and markets.
The CEA and CFTC regulations prohibit market abuse and generally require that all futures exchange-based trading be conducted in compliance with rules designed to ensure the integrity of market prices and without any intent to manipulate prices. CFTC regulations and futures exchange rules also impose limits on the size of the positions that a person may hold or control as well as standards for aggregating certain positions. The rules of the CFTC and the futures exchanges also authorize special emergency actions to halt, suspend or limit trading overall or to restrict, halt, suspend or limit the trading of an individual trader or to otherwise impose special reporting or margin requirements.
Non-U.S. Derivatives Exchanges
Foreign derivatives exchanges differ in certain respects from their U.S. counterparts. Non-U.S. derivatives exchanges are generally not subject to regulation by the CFTC. In contrast to U.S. exchanges, certain foreign exchanges are “principals’ markets,” where trades remain the liability of the traders involved, and the exchange or an affiliated clearing house, if any, does not become substituted for any party. Therefore, participants in such markets must often satisfy themselves as to the creditworthiness of their counterparty. Additionally, in the event of the insolvency or bankruptcy of a non-U.S. market or broker, the rights of market participants are likely to be more limited than the rights afforded by the U.S. derivatives exchanges. The Sponsor does not anticipate that the Funds will hold futures traded on foreign exchanges.
Daily Limits
Most U.S. futures exchanges (but generally not foreign exchanges or banks or dealers in the cases of forward contracts, swap agreements and options on forward contracts) limit the amount of fluctuation in some futures contract or options on futures contract prices during a single day by regulations. These regulations specify what are referred to as “daily price fluctuation limits” or more commonly “daily limits.” Once the daily limit has been reached in a particular futures contract, no trades may be made at a price beyond that limit.
As of January 30, 2015, there were no daily price fluctuation limits in place for the futures contracts held by the VIX Fund.
The following futures contracts that are part of the SFI, the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM and/or the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM have the following price limits:
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for NY Harbor ULSD Heating Oil futures for each contract month were $0.25 per gallon above or below the previous day’s settlement price for such contract month. If a market for any of the first three (3) contract months is bid or offered at the upper or lower price fluctuation limit, as applicable, on CME Globex it will be considered a triggering event which will halt trading for a five (5) minute period in all contract months of the Heating Oil futures contract, as well as all contract months in all products cited in the Associated Products Appendix of NYMEX Rulebook Rule 150.07.
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for RBOB Gasoline futures for each contract month were $0.25 per gallon above or below the previous day’s settlement price for such contract
60
Table of Contents
month. If a market for any of the first three (3) contract months is bid or offered at the upper or lower price fluctuation limit, as applicable, on CME Globex it will be considered a triggering event which will halt trading for a five (5) minute period in all contract months of the RB futures contract, as well as all contract months in all products cited in the Associated Products Appendix of NYMEX Rulebook Rule 191.07.
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for CBOT Corn futures contracts was $0.25 per bushel expandable to $0.40 when the market closes at limit bid or limit offer. There shall be no price limits on the current month contract on or after the second business day preceding the first day of the delivery month.
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for ICE Cotton No. 2® futures contracts was subject to a daily price limit that can range from $0.03 to $0.07 cents per pound, with details set forth in ICE Futures U.S.®, Inc. Cotton No. 2 Rule 10.09.
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for CME Live Cattle futures contracts was $0.03 per pound above or below the previous day’s settlement price.
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for CME Lean Hogs futures contracts was $0.03 per pound above or below previous day’s settlement price; none for expiring contracts in the last two trading days.
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for CBOT Soybeans futures contracts was $0.70 per bushel expandable to $1.05 when the market closes at limit bid or limit offer. There shall be no price limits on the current month contract on or after the second business day preceding the first day of the delivery month.
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for CBOT Soybean Oil futures contracts was $0.025 cents per pound expandable to $0.04 cents per pound when the market closes at limit bid or limit offer. There shall be no price limits on the current month contract on or after the second business day preceding the first day of the delivery month.
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for CBOT Wheat futures contracts was $0.35 per bushel expandable to $0.90 when the market closes at limit bid or limit offer. There shall be no price limits on the current month contract on or after the second business day preceding the first day of the delivery month.
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for crude oil futures contracts was $10.00 per barrel above or below the previous day’s settlement price for such contract month. If a market for any of the first three (3) contract months is bid or offered at the upper or lower price fluctuation limit, as applicable, on Globex it will be considered a Triggering Event which will halt trading for a five (5) minute period in all contract months of the CL futures contract, as well as all contract months in all products cited in the Associated Products Appendix of NYMEX Rulebook Rule 200.06. Trading in any option related to these contracts or in an option contract related to any products cited in the Associated Products Appendix which may be available for trading on either Globex or on the Trading Floor shall additionally be subject to a coordinated trading halt.
As of January 30, 2015, the maximum daily price fluctuation limit for natural gas futures contracts was $1.50 per MMBtu above or below the previous day’s settlement price for such contract month. If a market for any of the first three (3) contract months is bid or offered at the upper or lower price fluctuation limit, as applicable, on Globex it will be considered a Triggering Event which will halt trading for a five (5) minute period in all contract months of the NG futures contract, as well as all contract months in all products cited in the Associated Product Appendix of NYMEX Rulebook Rule 220.08. Trading in any option related to these
61
Table of Contents
contracts or in an option contract related to any products cited in the Associated Product Appendix which may be available for trading on either Globex or on the Trading Floor shall additionally be subject to a coordinated trading halt.
As of January 30, 2015, there were no daily price fluctuation limits in place for the futures contracts held by the Currency Funds.
Margin
“Initial” or “original” margin is the minimum amount of funds that a counterparty to a cleared derivatives contract must deposit with his commodity broker in order to establish an open position. Maintenance margin is the amount (generally less than initial margin) to which a trader’s account may decline before he must deliver additional margin so as to maintain open positions. A margin deposit is like a cash performance bond. It helps assure the futures trader’s performance of the futures contracts he purchases or sells. The minimum amount of margin required in connection with a particular futures contract is set by the exchange on which such contract is traded and is subject to change at any time during the term of the contract. Futures contracts are customarily bought and sold on margins that represent a very small percentage (ranging upward from less than 2%) of the aggregate purchase or sales price of the contract. Because of such low margins, price fluctuations occurring in the futures markets may create profits and losses that are greater, in relation to the amount invested, than are customary in other forms of investments.
Brokerage firms carrying accounts for traders in futures contracts may not accept lower, and may require higher, amounts of margin as a matter of policy in order to afford further protection for themselves.
Margin requirements are computed each day by a commodity broker and the relevant exchange. At the close of each trading day, each open futures contract is marked to market, that is, the gain or loss on the position is calculated from the prior day’s close. When the market value of a particular open futures contract position changes to a point where the margin on deposit does not satisfy maintenance margin requirements, a margin call is made by the commodity broker. If the margin call is not met within a reasonable time, the broker may close out the customer’s position.
62
Table of Contents
PERFORMANCE OF THE OFFERED COMMODITY POOLS OPERATED BY
THE COMMODITY POOL OPERATOR
The following performance information is presented in accordance with CFTC regulations. The performance of each Fund, which is presented herein, will differ materially from the performance of the other series of the Trust (the “Other Funds”), which is included in the section entitled “Performance of the Other Commodity Pools Operated by the Commodity Pool Operator” in Part Two of this Prospectus.
The performance information presented below reflects our preliminary estimated financial results based upon information available to us as of the date of this Prospectus for which financial statements are not yet available. Our independent registered public accounting firm, PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, has not audited, reviewed, compiled or performed any procedures on this preliminary financial data, and accordingly, does not express an opinion or provide any other form of assurance with respect thereto. There can be no assurance that our final results of operations for such periods will not differ from these estimates. Any such changes could be material.
All summary performance information is as of January 30, 2015. Performance information is set forth, in accordance with CFTC regulations, since each fund’s inception of trading.
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
January 3, 2011 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$449,861,863 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$147,682,888 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$29,761,464 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$68.04 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-18.65% | |
| (January 2013) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-83.20% | |
| (September 2011—August 2014) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| January |
-10.88 | % | -9.76 | % | -18.65 | % | 3.08 | % | 6.98 | % | ||||||||||
| February |
-3.79 | % | 1.25 | % | -3.13 | % | -4.27 | % | ||||||||||||
| March |
-1.77 | % | -17.42 | % | -3.31 | % | -2.89 | % | ||||||||||||
| April |
-6.98 | % | -0.83 | % | -6.78 | % | -3.29 | % | ||||||||||||
| May |
-2.60 | % | 13.10 | % | 5.89 | % | -4.07 | % | ||||||||||||
| June |
1.15 | % | -12.30 | % | 8.41 | % | -9.99 | % | ||||||||||||
| July |
-3.41 | % | -5.77 | % | -16.71 | % | 1.32 | % | ||||||||||||
| August |
28.73 | % | -2.59 | % | 6.44 | % | -3.83 | % | ||||||||||||
| September |
16.65 | % | -17.84 | % | -7.58 | % | 6.37 | % | ||||||||||||
| October |
-16.01 | % | -5.90 | % | -4.36 | % | -2.28 | % | ||||||||||||
| November |
7.47 | % | -10.69 | % | -5.42 | % | -2.64 | % | ||||||||||||
| December |
-8.29 | % | -0.53 | % | -7.95 | % | 4.43 | % | ||||||||||||
| Annual |
-7.31 | % | -53.21 | % | -44.38 | % | -17.61 | % | ||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 6.98 | % | ||||||||||||||
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
63
Table of Contents
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Managed Futures Strategy | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
October 1, 2014 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$10,336,288 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$8,296,727 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$8,713,076 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$21.78 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
N/A | |
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
N/A |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
3.06 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| February |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| March |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| April |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| May |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| June |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| July |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| August |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| September |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| October* |
0.58 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| November |
3.16 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| December |
1.85 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Annual |
5.68 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3.06 | % | |||||||||||||||||
| * | Represents rate of return from inception to October 31, 2014, as the inception of trading date for the pool was after October 1, 2014. |
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
November 24, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$42,846,432 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$2,141,195 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$2,427,198 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$12.14 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-27.91% | |
| (September 2011) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-71.02% | |
| (April 2011—January 2015) |
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
64
Table of Contents
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
-14.51 | % | 1.63 | % | 4.65 | % | 4.64 | % | 0.37 | % | -6.90 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
6.89 | % | 2.58 | % | 5.24 | % | -8.17 | % | 12.63 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
-2.89 | % | 4.06 | % | -8.43 | % | 0.76 | % | 0.63 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
3.56 | % | 6.11 | % | -1.16 | % | -5.52 | % | 4.74 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
-13.83 | % | -10.53 | % | -17.71 | % | -4.66 | % | -5.82 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
0.16 | % | -10.87 | % | 10.78 | % | -9.44 | % | 1.03 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
13.55 | % | 6.50 | % | 12.77 | % | 2.51 | % | -9.88 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
-5.36 | % | 1.52 | % | 2.35 | % | 6.68 | % | -2.24 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
14.71 | % | -27.91 | % | 3.16 | % | -5.25 | % | -12.27 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
9.65 | % | 13.16 | % | -7.85 | % | -3.12 | % | -1.84 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
-1.44 | % | -4.74 | % | -0.16 | % | -1.77 | % | -8.30 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
22.04 | % | -7.73 | % | -5.34 | % | 2.31 | % | -14.97 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
28.95 | % | -28.84 | % | -5.78 | % | -20.32 | % | -32.92 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | -6.90 | % | |||||||||||||||||
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
November 24, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$95,173,240 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$8,650,362 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$5,592,550 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$93.21 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-19.03% | |
| (December 2010) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-74.41% | |
| (February 2009—April 2011) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
15.02 | % | -2.66 | % | -5.44 | % | -4.91 | % | -0.99 | % | 6.23 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
-8.21 | % | -3.16 | % | -5.47 | % | 8.48 | % | -11.70 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
1.86 | % | -5.66 | % | 8.11 | % | -1.25 | % | -1.10 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
-4.33 | % | -6.50 | % | 0.31 | % | 4.61 | % | -4.94 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
14.14 | % | 9.15 | % | 20.41 | % | 4.27 | % | 5.77 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
-1.55 | % | 11.01 | % | -11.11 | % | 9.63 | % | -1.42 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
-12.92 | % | -6.96 | % | -12.82 | % | -3.05 | % | 10.50 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
4.72 | % | -2.99 | % | -3.00 | % | -6.86 | % | 1.90 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
-13.42 | % | 35.06 | % | -3.84 | % | 4.94 | % | 13.23 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
-10.27 | % | -13.06 | % | 7.73 | % | 2.71 | % | 1.17 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
-1.01 | % | 3.77 | % | -0.57 | % | 1.38 | % | 7.82 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
-19.03 | % | 7.04 | % | 5.15 | % | -2.66 | % | 16.32 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
-34.35 | % | 18.60 | % | -4.97 | % | 17.00 | % | 38.64 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 6.23 | % | |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
65
Table of Contents
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
October 4, 2011 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$514,269,899 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$94,661,908 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$75,126,655 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$12.80 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-51.14% | |
| (December 2014) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-93.60% | |
| (Inception—January 2015) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| January |
-33.79 | % | -2.67 | % | 33.18 | % | -16.96 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
-7.98 | % | 2.40 | % | -4.60 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
-39.34 | % | 29.13 | % | -8.53 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
-0.48 | % | 13.20 | % | 19.28 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
-0.06 | % | -18.86 | % | -12.75 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
21.89 | % | -21.95 | % | -4.13 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
25.46 | % | -7.13 | % | -25.71 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
-28.03 | % | 3.79 | % | 8.98 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
23.97 | % | -7.10 | % | -0.68 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
-3.23 | % | 3.06 | % | -8.12 | % | -16.26 | % | ||||||||||||
| November |
-24.05 | % | -14.18 | % | 16.00 | % | 4.01 | % | ||||||||||||
| December |
-30.62 | % | -13.68 | % | 12.97 | % | -51.14 | % | ||||||||||||
| Annual |
-49.01 | % | -61.71 | % | -0.54 | % | -60.32 | % | ||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | -16.96 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
October 4, 2011 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$203,328,744 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$2,178,501 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$15,173,355 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$86.73 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-37.18% | |
| (January 2014) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-81.64% | |
| (March 2012—April 2014) |
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
66
Table of Contents
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| January |
30.13 | % | -1.67 | % | -37.18 | % | 3.30 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
0.98 | % | -5.48 | % | -5.47 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
56.44 | % | -24.30 | % | 5.67 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
-4.32 | % | -15.15 | % | -18.15 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
-8.88 | % | 17.55 | % | 11.26 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
-28.95 | % | 23.56 | % | 1.43 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
-27.12 | % | 3.81 | % | 31.07 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
30.80 | % | -5.64 | % | -10.42 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
-23.39 | % | 5.64 | % | -2.73 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
0.57 | % | -6.83 | % | 5.95 | % | 15.73 | % | ||||||||||||
| November |
27.35 | % | 11.11 | % | -15.20 | % | -13.02 | % | ||||||||||||
| December |
39.41 | % | 11.43 | % | -15.04 | % | 80.09 | % | ||||||||||||
| Annual |
78.55 | % | 7.26 | % | -31.50 | % | 20.00 | % | ||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3.30 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares UltraShort Silver | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
December 1, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$2,218,897,951 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$271,651,883 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$55,862,083 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$100.02 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-42.41% | |
| (April 2011) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-99.20% | |
| (Inception—November 2012) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
6.25 | % | 17.54 | % | -32.75 | % | -14.21 | % | 1.13 | % | -13.48 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
-1.65 | % | -33.03 | % | -20.18 | % | 21.21 | % | -18.74 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
-17.28 | % | -26.55 | % | 27.37 | % | 1.17 | % | 12.13 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
-13.65 | % | -42.41 | % | 6.34 | % | 28.38 | % | 6.27 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
-3.39 | % | 20.59 | % | 20.84 | % | 14.53 | % | 2.02 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
-5.63 | % | 16.50 | % | 3.78 | % | 39.17 | % | -17.87 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
10.64 | % | -26.91 | % | -9.59 | % | -11.88 | % | 1.26 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
-14.05 | % | -13.79 | % | -15.77 | % | -31.22 | % | 12.03 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
-28.05 | % | 38.68 | % | -25.12 | % | 14.19 | % | 28.17 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
-18.10 | % | -28.46 | % | 14.03 | % | -7.05 | % | 9.83 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
-26.17 | % | 15.21 | % | -12.57 | % | 23.06 | % | 0.22 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
-24.65 | % | 14.07 | % | 29.28 | % | 2.51 | % | -1.95 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
-78.79 | % | -61.57 | % | -32.99 | % | 74.69 | % | 28.77 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | -13.48 | % | |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
67
Table of Contents
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
July 17, 2012 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$4,000,200 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$4,000,200 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$2,498,460 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$24.98 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-14.54% | |
| (May 2013) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-40.68% | |
| (March 2013—January 2015) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| January |
0.94 | % | -3.72 | % | -8.78 | % | ||||||||||||||
| February |
-3.77 | % | 4.21 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| March |
4.28 | % | 8.27 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| April |
-0.56 | % | 0.71 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| May |
-14.54 | % | 0.68 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| June |
-8.63 | % | 2.93 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| July* |
4.03 | % | -3.08 | % | -2.53 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
-2.91 | % | -1.69 | % | 1.30 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
1.27 | % | 10.07 | % | -11.93 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
0.59 | % | 2.97 | % | 1.32 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
1.50 | % | -7.09 | % | -6.37 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
-0.42 | % | -3.42 | % | -7.59 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
3.98 | % | -23.77 | % | -13.58 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | -8.78 | % | ||||||||||||||
| * | Represents rate of return from inception to July 31, 2012, as the inception of trading date for the pool was after July 1, 2012. |
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
July 17, 2012 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$24,808,605 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$18,038,178 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$25,214,760 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$56.03 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-9.75% | |
| (September 2013) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-16.66% | |
| (August 2013—June 2014) |
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
68
Table of Contents
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| January |
-1.26 | % | 3.36 | % | 9.00 | % | ||||||||||||||
| February |
3.60 | % | -4.43 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| March |
-4.35 | % | -8.03 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| April |
0.10 | % | -0.98 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| May |
16.30 | % | -0.94 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| June |
8.41 | % | -3.11 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| July* |
-4.17 | % | 2.33 | % | 2.29 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
2.68 | % | 1.28 | % | -1.48 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
-1.71 | % | -9.75 | % | 12.91 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
-0.91 | % | -3.2 | % | -1.89 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
-1.76 | % | 7.19 | % | 6.17 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
0.15 | % | 3.06 | % | 7.76 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
-5.70 | % | 23.53 | % | 10.27 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 9.00 | % | ||||||||||||||
| * | Represents rate of return from inception to July 31, 2012, as the inception of trading date for the pool was after July 1, 2012. |
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Ultra Euro | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
November 24, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$34,779,985 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$3,926,264 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$3,458,554 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$17.29 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-15.18% | |
| (May 2010) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-47.90% | |
| (November 2009—January 2015) |
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
69
Table of Contents
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
-6.28 | % | 4.70 | % | 1.94 | % | 5.71 | % | -4.00 | % | -13.00 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
-3.74 | % | 1.57 | % | 3.62 | % | -7.71 | % | 4.65 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
-1.78 | % | 5.42 | % | 0.05 | % | -3.75 | % | -0.48 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
-2.97 | % | 9.16 | % | -1.62 | % | 5.39 | % | 1.35 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
-15.18 | % | -5.62 | % | -12.87 | % | -2.75 | % | -3.52 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
-0.90 | % | 1.50 | % | 4.59 | % | 0.17 | % | 0.84 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
13.32 | % | -1.85 | % | -5.68 | % | 4.27 | % | -4.48 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
-5.63 | % | -0.09 | % | 4.30 | % | -1.42 | % | -3.81 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
15.54 | % | -13.16 | % | 4.23 | % | 4.64 | % | -7.74 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
4.08 | % | 6.42 | % | 1.53 | % | 0.61 | % | -1.76 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
-13.15 | % | -5.83 | % | 0.53 | % | 0.01 | % | -1.66 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
5.95 | % | -7.32 | % | 2.79 | % | 2.46 | % | -5.45 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
-14.48 | % | -7.28 | % | 1.93 | % | 6.91 | % | -23.66 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | -13.00 | % | |||||||||||||||||
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Short Euro | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
June 26, 2012 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$18,468,997 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$12,776,384 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$15,000,408 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$42.86 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-2.88% | |
| (January 2013) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-13.09% | |
| (July 2012—April 2014) |
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
70
Table of Contents
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||
| January |
-2.88 | % | 1.91 | % | 6.92 | % | ||||||||||
| February |
3.91 | % | -2.39 | % | ||||||||||||
| March |
1.70 | % | 0.10 | % | ||||||||||||
| April |
-2.76 | % | -0.78 | % | ||||||||||||
| May |
1.24 | % | 1.69 | % | ||||||||||||
| June* |
-1.32 | % | -0.24 | % | -0.57 | % | ||||||||||
| July |
2.68 | % | -2.33 | % | 2.19 | % | ||||||||||
| August |
-2.27 | % | 0.58 | % | 1.82 | % | ||||||||||
| September |
-2.23 | % | -2.40 | % | 3.94 | % | ||||||||||
| October |
-0.93 | % | -0.46 | % | 0.67 | % | ||||||||||
| November |
-0.40 | % | -0.15 | % | 0.67 | % | ||||||||||
| December |
-1.51 | % | -1.37 | % | 2.61 | % | ||||||||||
| Annual |
-5.90 | % | -5.26 | % | 12.33 | % | ||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | 6.92 | % | |||||||||||
| * | Represents rate of return from inception to June 29, 2012, as the inception of trading date for the pool was after June 1, 2012. |
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Ultra Yen | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
November 24, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$12,038,697 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$3,670,102 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$2,198,492 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$14.66 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-12.23% | |
| (February 2012) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-62.02% | |
| (August 2011—December 2014) |
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
71
Table of Contents
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
6.21 | % | -2.25 | % | 1.83 | % | -10.24 | % | 6.04 | % | 3.80 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
2.89 | % | 0.55 | % | -12.23 | % | -2.89 | % | 0.65 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
-9.78 | % | -3.51 | % | -3.77 | % | -3.21 | % | -2.91 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
-1.08 | % | 4.97 | % | 7.33 | % | -7.13 | % | 1.82 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
6.40 | % | -1.08 | % | 3.66 | % | -6.03 | % | 0.72 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
5.51 | % | 2.38 | % | -4.03 | % | 2.26 | % | 0.86 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
4.39 | % | 9.24 | % | 4.50 | % | 2.39 | % | -3.14 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
5.59 | % | 0.78 | % | -0.57 | % | -0.77 | % | -2.34 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
0.99 | % | -1.62 | % | 0.57 | % | -0.41 | % | -10.17 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
7.47 | % | -2.89 | % | -4.61 | % | -0.20 | % | -4.92 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
-7.64 | % | 1.40 | % | -6.36 | % | -8.02 | % | -10.60 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
5.91 | % | 1.29 | % | -9.85 | % | -5.48 | % | -2.11 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
28.13 | % | 8.90 | % | -22.73 | % | -33.90 | % | -24.21 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 3.80 | % | |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
Footnotes to Performance Information
| 1. | “Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions” is the aggregate of all amounts ever contributed to the pool, including those of investors who subsequently redeemed their investments. |
| 2. | “Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions” is the aggregate of all amounts ever contributed to the pool, excluding those of investors who subsequently redeemed their investments. |
| 3. | “Net Asset Value per Share” is the net asset value, based on the pricing policies of the Trust and determined in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, of the pool divided by the total number of Shares outstanding as of January 30, 2015. Please see “Description of the Shares; The Funds; Certain Material Terms of the Trust Agreement—Net Asset Value (NAV)” for additional information regarding the pricing policies of the Trust. |
| 4. | “Worst Monthly Loss” is the largest single month loss sustained during the most recent five calendar years and year-to-date (or since inception of the Fund, if the Fund has had less than five calendar years of performance), expressed as a percentage. “Loss” as used in this section of the Prospectus means losses experienced by the relevant pool over the specified period and is calculated on a rate of return basis, i.e., dividing net performance by beginning equity. Loss is measured on the basis of monthly returns only, and does not reflect intra-month figures. |
| 5. | “Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss” is the largest percentage decline in Net Asset Value per Share over the most recent five calendar years and year-to-date (or since inception of the Fund, if the Fund has had less than five calendar years of performance). This need not be a continuous decline, but can be a series of positive and negative returns where the negative returns are larger than the positive returns. Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss represents the greatest percentage decline from any month-end Net Asset Value per Share that occurs without such month-end Net Asset Value per Share being equaled or exceeded as of a subsequent month-end during such period. A Peak-to-Valley loss that begins prior to the beginning of the most recent five calendar years and ends within the most recent five calendar year period is deemed to have occurred during such five calendar year period. |
| 6. | Based on the latest calculated net asset value, as applicable to creations and redemptions of Creation Units, with respect to each period. |
72
Table of Contents
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF
FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Investors should consider Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations with respect to the Funds, which section is incorporated by reference to our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014.
73
Table of Contents
The projected twelve-month breakeven analysis for the Funds is set forth in the Breakeven Table below. For purposes of calculating the amounts in the Breakeven Table for the Funds (other than ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF, ProShares Managed Futures Strategy, ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Silver, ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Ultra Yen) the analysis assumes that the average daily NAV per Fund is $40.00. For purposes of calculating the amounts in the Breakeven Table for ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF, the analysis assumes that the average daily NAV is $80.00. For purposes of calculating the amounts in the Breakeven Table for ProShares Managed Futures Strategy, the analysis assumes that the average daily NAV is $20.00. For purposes of calculating the amounts in the Breakeven Table for ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Silver, ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Ultra Yen, the analysis assumes that the average daily NAV per Fund is $25.00.
| Dollar Amount and Percentage of Expenses per Fund | ||||||||||||||||
| Expenses(1) |
ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF |
ProShares Managed Futures Strategy |
||||||||||||||
| $ | % | $ | % | |||||||||||||
| Selling price per share |
80.00 | 20.00 | ||||||||||||||
| Management fee(2) |
0.68 | 0.85 | % | 0.12 | 0.59 | % | ||||||||||
| Initial Offering Costs |
N/A | N/A | 0.03 | (3) | 0.16 | %(3) | ||||||||||
| Brokerage commissions and fees |
0.10 | (4) | 0.12 | %(4) | 0.00 | 0.02 | % | |||||||||
| Variable create/redeem fees(5) |
(0.08 | )(4) | (0.10 | )%(4) | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | |||||||||
| Other expenses |
0.00 | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | ||||||||||
| Total fees and expenses |
0.70 | 0.87 | % | 0.15 | 0.77 | % | ||||||||||
| Interest income(6) |
(0.02 | ) | (0.02 | )% | 0.00 | (0.02 | )% | |||||||||
| Amount of trading income required for the NAV at the end of one year to equal the initial selling price per share (12-Month breakeven)(7) |
0.68 | 0.85 | % | 0.15 | 0.75 | % | ||||||||||
| Dollar Amount and Percentage of Expenses per Fund | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expenses(1) |
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity |
ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity |
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | % | $ | % | $ | % | |||||||||||||||||||
| Selling price per share |
25.00 | 25.00 | 40.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Management fee(2) |
0.24 | 0.95 | % | 0.24 | 0.95 | % | 0.38 | 0.95 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Brokerage commissions and fees |
0.16 | 0.63 | % | 0.16 | 0.63 | % | 0.06 | 0.14 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Variable create/redeem fees(5) |
0.00 | (0.01 | )% | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | (0.02 | ) | (0.06 | )% | ||||||||||||||
| Other expenses |
0.00 | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total fees and expenses |
0.40 | 1.57 | % | 0.40 | 1.58 | % | 0.41 | 1.03 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Interest income(6) |
(0.01 | ) | (0.02 | )% | (0.01 | ) | (0.02 | )% | (0.01 | ) | (0.02 | )% | ||||||||||||
| Amount of trading income required for the NAV at the end of one year to equal the initial selling price per share (12-Month breakeven)(7) |
0.39 | 1.55 | % | 0.39 | 1.56 | % | 0.40 | 1.01 | % | |||||||||||||||
74
Table of Contents
| Dollar Amount and Percentage of Expenses per Fund | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expenses(1) |
ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas |
ProShares UltraShort Silver |
ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | % | $ | % | $ | % | |||||||||||||||||||
| Selling price per share |
40.00 | 25.00 | 40.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Management fee(2) |
0.38 | 0.95 | % | 0.24 | 0.95 | % | 0.38 | 0.95 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Brokerage commissions and fees |
0.09 | 0.23 | % | 0.19 | 0.74 | % | 0.03 | 0.08 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Variable create/redeem fees(5) |
(0.02 | ) | (0.06 | )% | (0.03 | ) | (0.13 | )% | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | |||||||||||||
| Other expenses |
0.00 | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total fees and expenses |
0.45 | 1.12 | % | 0.39 | 1.56 | % | 0.41 | 1.03 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Interest income(6) |
(0.01 | ) | (0.02 | )% | (0.01 | ) | (0.02 | )% | (0.01 | ) | (0.02 | )% | ||||||||||||
| Amount of trading income required for the NAV at the end of one year to equal the initial selling price per share (12-Month breakeven)(7) |
0.44 | 1.10 | % | 0.39 | 1.54 | % | 0.40 | 1.01 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Dollar Amount and Percentage of Expenses per Fund | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Expenses(1) |
ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar |
ProShares Ultra Euro |
ProShares Short Euro |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| $ | % | $ | % | $ | % | |||||||||||||||||||
| Selling price per share |
40.00 | 25.00 | 40.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Management fee(2) |
0.38 | 0.95 | % | 0.24 | 0.95 | % | 0.38 | 0.95 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Brokerage commissions and fees |
0.04 | 0.11 | % | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | 0.01 | 0.02 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Variable create/redeem fees(5) |
0.00 | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Other expenses |
0.00 | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | 0.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total fees and expenses |
0.42 | 1.06 | % | 0.24 | 0.95 | % | 0.39 | 0.97 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Interest income(6) |
(0.01 | ) | (0.02 | )% | (0.01 | ) | (0.02 | )% | (0.01 | ) | (0.02 | )% | ||||||||||||
| Amount of trading income required for the NAV at the end of one year to equal the initial selling price per share (12-Month breakeven)(7) |
0.42 | 1.04 | % | 0.23 | 0.93 | % | 0.38 | 0.95 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Dollar Amount and Percentage of Expenses per Fund | ||||||||||||||||
| Expenses(1) |
ProShares Ultra Yen |
|
| |||||||||||||
| $ | % | |||||||||||||||
| Selling price per share |
25.00 | |||||||||||||||
| Management fee(2) |
0.24 | 0.95 | % | |||||||||||||
| Brokerage commissions and fees |
0.00 | 0.00 | % | |||||||||||||
| Variable create/redeem fees(5) |
0.00 | 0.00 | % | |||||||||||||
| Other expenses |
0.00 | 0.00 | % | |||||||||||||
| Total fees and expenses |
0.24 | 0.95 | % | |||||||||||||
| Interest income(6) |
(0.01 | ) | (0.02 | )% | ||||||||||||
| Amount of trading income required for the NAV at the end of one year to equal the initial selling price per share (12-Month breakeven)(7) |
0.23 | 0.93 | % | |||||||||||||
| (1) | The breakeven analysis set forth in this table assumes that the Shares have a constant month-end NAV and is based on: $40.00 as the NAV per Share of each of the Funds, other than ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF, ProShares Managed Futures Strategy, ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Silver, ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Ultra Yen; $80.00 as the NAV per Shares of ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF; $20.00 as the NAV per Share of ProShares Managed Futures Strategy; and $25.00 as the NAV per Share of each of ProShares Ultra |
75
Table of Contents
| Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares UltraShort Silver, ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Ultra Yen. The actual NAV of each Fund differs and is likely to change on a daily basis. The numbers provided in this chart have been rounded to the nearest 0.01. The breakeven analysis reflects all fees and expenses, including estimated rebalancing expenses, that are anticipated to be incurred by each Fund during the first year of an investor’s investment. |
| (2) | From the Management Fee, though not contractually required, the Sponsor is responsible for paying the fees and expenses of the Administrator, Custodian, Distributor, ProFunds Distributors, Inc. (“PDI”), Transfer Agent and all routine operational, administrative and other ordinary expenses of each Fund, including fees payable to index providers and, for the VIX Fund only, brokerage commissions on its VIX futures contracts that exceed variable create/redeem fees collected by more than 0.02% of the VIX Fund’s average net assets annually. Please note that the fees and expenses paid by the Sponsor are not included in the above Breakeven Table. |
| (3) | Expenses incurred in connection with the initial offering of the Managed Futures Fund’s Shares will be paid by the Managed Futures Fund, and the Sponsor will not charge the Management fee in the first year of operations of the Managed Futures Fund in an amount equal to the offering costs. The Sponsor will reimburse the Managed Futures Fund to the extent that its initial offering costs exceed 0.75% of the Managed Futures Fund’s average daily net assets for the first year of operations. Expenses incurred in connection with the continuous offering of Shares of the Managed Futures Fund after the commencement of its trading operations will be paid by the Sponsor. |
| (4) | The Sponsor will pay for any VIX Fund brokerage commissions on VIX futures contracts that exceed the VIX Fund’s variable create/redeem fees collected by more than 0.02% of the VIX Fund’s average net assets annually. |
| (5) | Authorized Participants are generally required to pay variable create and redeem fees of up to 0.10% of the value of each order they place with the Funds. These variable transaction fees offset brokerage commissions incurred by the Funds. Please see “Creation and Redemption of Shares—Creation and Redemption Transaction Fee.” |
| (6) | Based on U.S. Treasury securities yields and anticipated investment levels in the various Funds, the breakeven analysis assumes an interest rate of 0.02% for the Funds. |
| (7) | Investors may pay customary brokerage commissions in connection with purchases of the Shares. Because such brokerage commission rates will vary from investor to investor, such brokerage commissions have not been included in the Breakeven Table. Investors are encouraged to review the terms of their brokerage accounts for applicable charges. The breakeven amount reflected in the Breakeven Table reflects the breakeven amount for investors in the secondary market. The breakeven amount for each Authorized Participant is equal to the sum of the breakeven amount for each applicable Fund plus the amount of transaction fees paid by each Authorized Participant for each applicable Fund. |
Initial Offering Costs
Initial offering costs will be amortized by the Managed Futures Fund over a twelve-month period on a straight line basis. The Sponsor will not charge the Management Fee, as defined below, in the first year of operations of the Managed Futures Fund in an amount equal to the initial offering costs incurred by the Managed Futures Fund. The Sponsor will reimburse the Managed Futures Fund to the extent that its initial offering costs exceed 0.75% of its average daily net assets for the first year of operations. Normal and expected expenses incurred in connection with the continuous offering of Shares of the Managed Futures Fund after the commencement of its trading operations will be paid by the Sponsor.
Management Fee
The VIX Fund pays the Sponsor a management fee (the “Management Fee”), monthly in arrears, in an amount equal to 0.85% per annum of its average daily net assets. The Managed Futures Fund pays the Sponsor a
76
Table of Contents
Management Fee, monthly in arrears, in an amount equal to 0.75% per annum of its average daily net assets. Each other Fund pays the Sponsor a Management Fee, monthly in arrears, in an amount equal to 0.95% per annum of its average daily net assets.
No other Management Fee is paid by the Funds. The Management Fee is paid in consideration of the Sponsor’s trading advisory services and the other services provided to the Funds that the Sponsor pays directly.
Licensing Fee
The Sponsor pays S&P a licensing fee for use of the Mid-Term VIX Index as the benchmark for the VIX Fund and a licensing fee for the S&P Strategic Futures Index as the benchmark for the Managed Futures Fund. The Sponsor pays Bloomberg a licensing fee for the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM, which serves as the benchmark for the ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity Funds, as well as for the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM, which serves as the benchmark for each Natural Gas Fund.
Routine Operational, Administrative and Other Ordinary Expenses
The Sponsor pays all of the routine operational, administrative and other ordinary expenses of each Fund, generally, as determined by the Sponsor, including, but not limited to, fees and expenses of the Administrator, Custodian, Distributor, PDI and Transfer Agent, licensors, accounting and audit fees and expenses, tax preparation expenses, legal fees not in excess of $100,000 per annum, ongoing SEC registration fees not exceeding 0.021% per annum of the net assets of the Funds, individual Schedule K-1 preparation and mailing fees not exceeding 0.10% per annum of the net assets of the Funds, and report preparation and mailing expenses.
Non-Recurring Fees and Expenses
The Funds pay all of their non-recurring and unusual fees and expenses, if any, as determined by the Sponsor. Non-recurring and unusual fees and expenses are fees and expenses which are unexpected or unusual in nature, such as legal claims and liabilities and litigation costs or indemnification or other unanticipated expenses. Extraordinary fees and expenses also include material expenses which are not currently anticipated obligations of the Funds. Routine operational, administrative and other ordinary expenses are not deemed extraordinary expenses.
Selling Commission
Retail investors may purchase and sell Shares through traditional brokerage accounts. Investors are expected to be charged a customary commission by their brokers in connection with purchases of Shares that will vary from investor to investor. Investors are encouraged to review the terms of their brokerage accounts for applicable charges. The price at which an Authorized Participant sells a Share may be higher or lower than the price paid by such Authorized Participant in connection with the creation of such Share in a Creation Unit.
Brokerage Commissions and Fees
Each of the Managed Futures Fund and the Geared Funds pays all of its respective brokerage commissions, including applicable exchange fees, NFA fees and give-up fees, pit brokerage fees and other transaction related fees and expenses charged in connection with trading activities for each Fund’s investments in CFTC regulated investments. The Sponsor is currently paying brokerage commissions on VIX futures contracts for the VIX Fund in amounts that exceed variable create/redeem fees collected by more than 0.02% of the VIX Fund’s average net assets annually.
Other Transaction Costs
The Funds bear other transaction costs including the effects of trading spreads and financing costs/fees, if any, associated with the use of Financial Instruments, and costs relating to the purchase of U.S. Treasury securities or similar high credit quality, short-term fixed-income or similar securities (such as shares of money market funds and collateralized repurchase agreements).
77
Table of Contents
Each of Goldman, Sachs & Co. (“Goldman Sachs”) and RBC Capital Markets, LLC (“RBC”) (formerly RBC Capital Markets Corporation), in its capacity as a registered FCM, serves as the Funds’ clearing broker and as such arranges for the execution and clearing of the Funds’ futures transactions. Each of Goldman Sachs and RBC acts as clearing broker for many other funds and individuals. A variety of executing brokers may execute futures transactions on behalf of the Funds. The executing brokers will give up all such transactions to Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable.
Investors should be advised that neither Goldman Sachs nor RBC is affiliated with or acts as a supervisor of the Funds or the Funds’ commodity pool operators, commodity trading advisors, investment managers, trustees, general partners, administrators, transfer agents, registrars or organizers, as applicable. Additionally, neither Goldman Sachs nor RBC, in its capacity as FCM, is acting as an underwriter or sponsor of the offering of any Shares or interests in the Funds or has passed upon the merits of participating in this offering.
Neither Goldman Sachs nor RBC has passed upon the adequacy of this Prospectus or on the accuracy of the information contained herein. Additionally, neither Goldman Sachs nor RBC provides any commodity trading advice regarding the Funds’ trading activities. Investors should not rely upon Goldman Sachs or RBC in deciding whether to invest in the Funds or retain their interests in the Funds. Investors should also note that the Funds may select additional clearing brokers or replace Goldman Sachs and/or RBC as the Funds’ clearing broker.
Litigation and Regulatory Disclosure Relating to FCMs
Goldman Sachs & Co. (Goldman Sachs)
Goldman Sachs, in addition to being a registered futures commission merchant, is a registered broker-dealer. From time to time, Goldman Sachs and its affiliates are involved in judicial, regulatory and arbitration concerning matters arising in connection with the conduct of its business. Goldman Sachs’ management believes, based on currently available information, that the results of such proceedings, in the aggregate, will not have a material adverse effect on Goldman Sachs’ financial condition, but may be material to Goldman Sachs’ operating results for any particular period, depending, in part, upon the results for such period. For further information, please refer to the periodic public filings by The Goldman Sachs Group, Inc. (“GS Group”) as periodically filed with the SEC and to Goldman Sachs’ Form BD as periodically filed with FINRA.
IPO Process Matters
Goldman Sachs is among numerous financial services companies that have been named as defendants in a variety of lawsuits alleging improprieties in the process by which those companies participated in the underwriting of public offerings in recent years.
Goldman Sachs has been named as a defendant in a number of related lawsuits filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York alleging, among other things, that the prospectuses for the offerings violated the federal securities laws by failing to disclose the existence of alleged arrangements tying allocations in certain offerings to higher customer brokerage commission rates as well as purchase orders in the aftermarket, and that the alleged arrangements resulted in market manipulation. On October 5, 2009, the district court approved a settlement agreement entered into by the parties. Goldman Sachs has paid into a settlement fund the full amount that Goldman Sachs would contribute in the settlement. Certain objectors appealed certain aspects of the settlement’s approval, but all such appeals have been withdrawn or finally dismissed, thereby concluding the matter.
Goldman Sachs was among numerous underwriting firms named as defendants in a number of complaints filed commencing October 3, 2007, in the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Washington alleging
78
Table of Contents
violations of Section 16 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “1934 Act”) in connection with offerings of securities for 15 issuers during 1999 and 2000. The complaints generally asserted that the underwriters, together with each issuer’s directors, officers and principal shareholders, entered into purported agreements to tie allocations in the offerings to increased brokerage commissions and aftermarket purchase orders. The complaints further alleged that, based upon these and other purported agreements, the underwriters violated the reporting provisions of, and are subject to short-swing profit recovery under, Section 16 of the 1934 Act. The district court granted defendants’ motions to dismiss on the grounds that the plaintiff’s demands were inadequate with respect to certain actions and that the remaining actions were time-barred. On December 2, 2010, the appellate court affirmed in part and reversed in part, upholding the dismissal of seven of the actions in which Goldman Sachs is a defendant that were dismissed based on the deficient demands but remanding the remaining eight actions in which Goldman Sachs is a defendant that were dismissed as time-barred for consideration of other bases for dismissal. On March 26, 2012, the U.S. Supreme Court vacated the appellate court’s determination that the actions were timely and remanded the actions to determine if the claims were subject to equitable tolling in further proceedings consistent with the Supreme Court’s opinion. On July 8, 2012, pursuant to the plaintiff’s notices of voluntary dismissal, all of the actions were dismissed with prejudice as to the deficiency of the demand letters and without prejudice as to all other issues, bringing this matter to conclusion.
Goldman Sachs has been named as a defendant in an action commenced on May 15, 2002 in New York Supreme Court, New York County, by an official committee of unsecured creditors on behalf of eToys, Inc., alleging that Goldman Sachs intentionally underpriced eToys, Inc.’s initial public offering. The action seeks, among other things, unspecified compensatory damages resulting from the alleged lower amount of offering proceeds. On appeal from rulings on Goldman Sachs’ motion to dismiss, the New York Court of Appeals dismissed claims for breach of contract, professional malpractice and unjust enrichment, but permitted claims for breach of fiduciary duty and fraud to continue. On remand, the lower court granted Goldman Sachs’ motion for summary judgment and, on December 8, 2011, the appellate court affirmed the lower court’s decision. On September 6, 2012, the New York Court of Appeals granted the creditors’ motion for leave to appeal.
Research Matters
Goldman Sachs is subject to a number of investigations and reviews by various governmental and regulatory bodies and self-regulatory organizations relating to research practices, including, among other things, research analysts’ methods for obtaining receipt and distribution of information and communications among research analysts, sales and trading personnel and clients. On June 9, 2011, pursuant to a settlement, a consent order was entered by the Massachusetts Securities Division pursuant to which Goldman Sachs paid a $10 million civil penalty and agreed to various undertakings regarding certain of its research practices. On April 12, 2012, the SEC and FINRA issued orders in connection with Goldman Sachs’ settlement of charges relating to matters similar to those involved in the Massachusetts settlement. Pursuant to these settlements, Goldman Sachs paid $11 million to each of the SEC and FINRA and agreed to various undertakings with regard to its policies and procedures.
Adelphia Communications Fraudulent Conveyance Litigation
Goldman Sachs is named a defendant in two adversary proceedings commenced in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York, one on July 6, 2003 by a creditors committee, and the second on or about July 31, 2003 by an equity committee of Adelphia Communications, Inc. Those proceedings were consolidated in a single amended complaint filed by the Adelphia Recovery Trust on October 31, 2007. The complaint seeks, among other things, to recover, as fraudulent conveyances, approximately $62.9 million allegedly paid to Goldman Sachs by Adelphia Communications, Inc. and its affiliates in respect of margin calls made in the ordinary course of business on accounts owned by members of the family that formerly controlled Adelphia Communications, Inc. The district court assumed jurisdiction over the action and on April 8, 2011 granted Goldman Sachs’ motion for summary judgment. The plaintiff appealed on May 6, 2011.
79
Table of Contents
Treasury Matters
Goldman Sachs was named as a defendant in a purported class action filed on March 10, 2004 in the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Illinois on behalf of holders of short positions in 30-year U.S. Treasury futures and options on the morning of October 31, 2001. The complaint alleged that Goldman Sachs purchased 30-year bonds and futures prior to a forthcoming U.S. Treasury refunding announcement that morning based on non-public information about that announcement, and that such purchases increased the costs of covering such short positions. The complaint also named as defendants the Washington, D.C.-based political consultant who allegedly was the source of the information, a former Goldman Sachs economist who allegedly received the information, and another company and one of its employees who also allegedly received and traded on the information prior to its public announcement. The complaint alleged violations of the federal commodities and antitrust laws, as well as Illinois statutory and common law, and seeks, among other things, unspecified damages including treble damages under the antitrust laws. The district court dismissed the antitrust and Illinois state law claims but permitted the federal commodities law claims to proceed. Plaintiff’s motion for class certification was denied. Goldman Sachs moved for summary judgment, and the district court granted the motion but only insofar as the claim relates to the trading of treasury bonds. On October 13, 2009, the parties filed an offer of judgment and notice of acceptance with respect to plaintiff’s individual claim. The plaintiff attempted to pursue an appeal of the denial of class certification, as did another individual trader who had previously litigated and lost an individual claim and unsuccessfully sought to intervene in the purported class action. On August 5, 2011, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Seventh Circuit affirmed the lower court’s rulings that neither the plaintiff nor the proposed intervenor could pursue the class issues on appeal, but remanded for further consideration as to the amount of pre-judgment interest on the plaintiff’s individual claim. The appellants’ petition for reconsideration en banc was denied on October 19, 2011. On remand, the district court entered a final stipulation and order on December 7, 2011 regarding calculation of pre-judgment interest, which concluded the matter.
Fannie Mae Litigation
Goldman Sachs was added as a defendant in an amended complaint filed on August 14, 2006 in a purported class action pending in the U.S. District Court for the District of Columbia. The complaint asserts violations of the federal securities laws generally arising from allegations concerning Fannie Mae’s accounting practices in connection with certain Fannie Mae-sponsored REMIC transactions that were allegedly arranged by Goldman Sachs. The complaint does not specify a dollar amount of damages. The other defendants include Fannie Mae, certain of its past and present officers and directors, and accountants. By a decision dated May 8, 2007, the district court granted Goldman Sachs’ motion to dismiss the claim against it, and the remaining parties agreed to a settlement in April 2013, subject to court approval, which would resolve the action in its entirety and would not involve any contribution by Goldman Sachs.
Mortgage-Related Matters
On April 16, 2010, the SEC brought an action (the “SEC Action”) under the U.S. federal securities laws in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York against Goldman Sachs and Fabrice Tourre, a former employee, in connection with a CDO offering made in early 2007 (ABACUS 2007-AC1 transaction), alleging that the defendants made materially false and misleading statements to investors and seeking, among other things, unspecified monetary penalties. Investigations of Goldman Sachs by FINRA and of GSI by the FSA were subsequently initiated and resolved, and GS Group and certain of its affiliates have received subpoenas and requests for information from other regulators, regarding CDO offerings, including the ABACUS 2007-AC1 transaction, and related matters. On July 14, 2010, Goldman Sachs entered into a consent agreement with the SEC, settling all claims made against Goldman Sachs in the SEC Action, pursuant to which Goldman Sachs paid $550 million of disgorgement and civil penalties, and which was approved by the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York on July 20, 2010.
On January 6, 2011, ACA Financial Guaranty Corp. filed an action against Goldman Sachs in respect of the ABACUS 2007-AC1 transaction in New York Supreme Court, New York County. The complaint includes
80
Table of Contents
allegations of fraudulent inducement, fraudulent concealment and unjust enrichment and seeks at least $30 million in compensatory damages, at least $90 million in punitive damages and unspecified disgorgement. On April 25, 2011, the plaintiff filed an amended complaint and, on June 3, 2011, Goldman Sachs moved to dismiss the amended complaint. By a decision dated April 23, 2012, the court granted the motion to dismiss as to the unjust enrichment claim and denied the motion as to the other claims, and on May 29, 2012, Goldman Sachs appealed the decision to the extent that its motion was denied and filed counterclaims for breach of contract and fraudulent inducement, and third-party claims against ACA Management, LLC for breach of contract, unjust enrichment and indemnification. ACA Financial Guaranty Corp. and ACA Management, LLC moved to dismiss Goldman Sachs’ counterclaims and third-party claims on August 31, 2012. On January 31, 2013, ACA filed an amended complaint naming a third party to the ABACUS 2007-AC1 transaction as an additional defendant.
Beginning April 22, 2010, a number of putative shareholder derivative actions were filed in New York Supreme Court, New York County, and the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York against GS Group, its board (the “Board”) and certain officers and employees of GS Group and its affiliates in connection with mortgage-related matters between 2004 and 2007, including the ABACUS 2007-AC1 transaction and other CDO offerings. These derivative complaints generally included allegations of breach of fiduciary duty, corporate waste, abuse of control, mismanagement, unjust enrichment, misappropriation of information, securities fraud and insider trading, and challenge the accuracy and adequacy of GS Group’s disclosure. These derivative complaints seek, among other things, declaratory relief, unspecified compensatory damages, restitution and certain corporate governance reforms. In addition, the plaintiffs in the compensation-related Delaware Court of Chancery actions twice amended their complaint, including to assert allegations similar to those in the derivative claims referred to above, the Delaware court granted the defendants’ motion to dismiss the second amended complaint and the Delaware Supreme Court affirmed the dismissal on May 3, 2012. The federal court cases were consolidated, plaintiffs filed a consolidated amended complaint on August 1, 2011, and, on October 6, 2011, the defendants moved to dismiss the action. On June 25, 2012, in light of the decision of the Delaware Supreme Court, the parties in the New York state action stipulated to a voluntary dismissal, which the court has entered.
Beginning in April 2010, a number of purported securities law class actions were filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York challenging the adequacy of GS Group’s public disclosure of, among other things, Goldman Sachs’ activities in the CDO market, the firm’s conflict of interest management, and the SEC investigation that led to Goldman Sachs entering into a consent agreement with the SEC, settling all claims made against Goldman Sachs by the SEC in connection with the ABACUS 2007-AC1 transaction, pursuant to which Goldman Sachs paid $550 million of disgorgement and civil penalties. The consolidated amended complaint filed on July 25, 2011, which names as defendants GS Group and certain officers and employees of GS Group and its affiliates, generally alleges violations of Sections 10(b) and 20(a) of the Exchange Act and seeks unspecified damages. On June 21, 2012, the district court dismissed the claims based on GS Group’s not disclosing that it had received a “Wells” notice from the staff of the SEC related to the ABACUS 2007-AC1 transaction, but permitted the plaintiffs’ other claims to proceed.
Since April 23, 2010, the Board has received letters from shareholders demanding that the Board take action to address alleged misconduct by Goldman Sachs, the Board and certain officers and employees of GS Group and its affiliates. These demands, which the Board has refused, generally alleged misconduct in connection with Goldman Sachs’ securitization practices, including the ABACUS 2007-AC1 transaction, the alleged failure by GS Group to adequately disclose the SEC investigation, and GS Group’s 2009 compensation practices.
In addition, the Board has received other books and records demands from several shareholders for materials relating to, among other subjects, Goldman Sachs’ mortgage servicing and foreclosure activities, participation in federal programs providing assistance to financial institutions and homeowners, loan sales to Fannie Mae and Freddie Mac, mortgage-related activities and conflicts management.
Goldman Sachs is a defendant in a putative class action commenced on December 11, 2008 in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York brought on behalf of purchasers of various mortgage
81
Table of Contents
pass-through certificates and asset-backed certificates issued by various securitization trusts established by Goldman Sachs and underwritten by Goldman Sachs in 2007. The complaint generally alleges that the registration statement and prospectus supplements for the certificates violated the federal securities laws, and seeks unspecified compensatory damages and rescission or rescissionary damages. By a decision dated September 6, 2012, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit affirmed the district court’s dismissal of plaintiff’s claims with respect to 10 of the 17 offerings included in plaintiff’s original complaint but vacated the dismissal and remanded the case to the district court with instructions to reinstate the plaintiff’s claims with respect to the other seven offerings. On October 31, 2012, the plaintiff served an amended complaint relating to those seven offerings, plus seven additional offerings (“additional offerings”). On July 10, 2014, the court granted the defendants’ motion to dismiss as to the additional offerings. On June 3, 2010, another investor filed a separate putative class action asserting substantively similar allegations relating to one of the additional offerings and thereafter moved to further amend its amended complaint to add claims with respect to two of the additional offerings. On March 27, 2014, the district court largely denied defendants’ motion to dismiss as to the original offering, but denied the separate plaintiff’s motion to add the two additional offerings through an amendment. The securitization trusts issued, and Goldman Sachs underwrote, approximately $11 billion principal amount of certificates to all purchasers in the offerings at issue in the complaints.
Goldman Sachs is among the defendants in a separate putative class action commenced on February 6, 2009 in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York brought on behalf of purchasers of various mortgage pass-through certificates and asset-backed certificates issued by various securitization trusts established by Goldman Sachs and underwritten by Goldman Sachs in 2006. The other original defendants include three current or former GS Group employees and various rating agencies. The second amended complaint generally alleges that the registration statement and prospectus supplements for the certificates violated the federal securities laws, and seeks unspecified compensatory and rescissionary damages. Defendants moved to dismiss the second amended complaint. On January 12, 2011, the district court granted the motion to dismiss with respect to offerings in which plaintiff had not purchased securities as well as all claims against the rating agencies, but denied the motion to dismiss with respect to a single offering in which the plaintiff allegedly purchased securities. These trusts issued, and Goldman Sachs underwrote, approximately $698 million principal amount of certificates to all purchasers in the offerings at issue in the complaint (excluding those offerings for which the claims have been dismissed). On February 2, 2012, the district court granted the plaintiff’s motion for class certification and on June 13, 2012, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit granted defendants’ petition to review that ruling. On July 31, 2012, the parties reached a settlement, subject to court approval. The firm has paid the full amount of the proposed settlement in an escrow account.
On September 30, 2010, a class action was filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York against Goldman Sachs, GS Group and two former Goldman Sachs employees on behalf of investors in $823 million of notes issued in 2006 and 2007 by two synthetic CDOs (Hudson Mezzanine 2006-1 and 2006-2). The amended complaint asserts federal securities law and common law claims, and seeks unspecified compensatory, punitive and other damages. The defendants’ motion to dismiss was granted as to plaintiff’s claim of market manipulation and denied as to the remainder of plaintiff’s claims by a decision dated March 21, 2012. On May 21, 2012, the defendants counterclaimed for breach of contract and fraud. On June 27, 2014, the appellate court denied defendants’ petition for leave to appeal from the district court’s January 22, 2014 order granting class certification. On January 30, 2015, defendants moved for summary judgment.
Goldman Sachs, GSMC and GSMSC are among the defendants in a lawsuit filed in August 2011 by CIFG Assurance of North America, Inc. (“CIFG”) in New York Supreme Court, New York County. The complaint alleges that CIFG was fraudulently induced to provide credit enhancement for a 2007 securitization sponsored by GSMC, and seeks, among other things, the repurchase of $24.7 million in aggregate principal amount of mortgages that CIFG had previously stated to be non-conforming, an accounting for any proceeds associated with mortgages discharged from the securitization and unspecified compensatory damages. On October 11, 2011, the Goldman Sachs defendants moved to dismiss. By a decision dated May 1, 2012, the court dismissed the fraud and accounting claims but denied the motion as to certain breach of contract claims that were also alleged. On
82
Table of Contents
June 6, 2012, the Goldman Sachs defendants filed counterclaims for breach of contract. In addition, the parties have each appealed the court’s May 1, 2012 decision to the extent adverse. By an order dated May 7, 2013, the appellate court reversed the dismissal of the fraud claim but otherwise affirmed the trial court’s May 1, 2012 decision.
In addition, on January 15, 2013, CIFG filed a complaint against Goldman Sachs in New York Supreme Court, New York County, alleging that Goldman Sachs falsely represented that a third party would independently select the collateral for a 2006 CDO. CIFG seeks unspecified compensatory and punitive damages, including claims for approximately $10 million in connection with its purchase of notes, which CIFG has agreed to refer to arbitration with FINRA, and claims for over $30 million for payments to discharge alleged liabilities arising from its issuance of a financial guaranty insurance policy guaranteeing payment on a credit default swap referencing the CDO, which CIFG has agreed to stay until the arbitration of the notes-related claims has concluded.
Various alleged purchasers of, and counterparties and providers of credit enhancement involved in transactions relating to, mortgage pass-through certificates, CDOs and other mortgage-related products (including Aozora Bank, Ltd., Basis Yield Alpha Fund (Master), the Charles Schwab Corporation, CIFG Assurance of North America, Inc., CMFG Life Insurance Company and related parties, Deutsche Zentral-Genossenschaftbank, the FDIC (as receiver for Guaranty Bank), the Federal Home Loan Banks of Chicago and Seattle, IKB Deutsche Industriebank AG, John Hancock and related parties, Massachusetts Mutual Life Insurance Company, National Australia Bank, the National Credit Union Administration (as conservator or liquidating agent for several failed credit unions), Phoenix Light SF Limited and related parties, Royal Park Investments SA/NV, The Union Central Life Insurance Company, Ameritas Life Insurance Corp., Acacia Life Insurance Company, Watertown Savings Bank, Commerzbank, Texas County & District Retirement System and the Commonwealth of Virginia (on behalf of the Virginia Retirement System)) have filed complaints or summonses with notice in state and federal court or initiated arbitration proceedings against firm affiliates, generally alleging that the offering documents for the securities that they purchased contained untrue statements of material fact and material omissions and generally seeking rescission and/or damages. Certain of these complaints allege fraud and seek punitive damages. Certain of these complaints also name other firms as defendants.
A number of other entities (including John Hancock and related parties, Norges Bank Investment Management, Selective Insurance Company and the State of Illinois (on behalf of Illinois state retirement systems)) have threatened to assert claims of various types against Goldman Sachs in connection with the sale of mortgage-related securities, and Goldman Sachs has entered into agreements with a number of these entities to toll the relevant statute of limitations.
As of February 23, 2015, the aggregate amount of mortgage-related securities sold to plaintiffs in active and threatened cases described in the preceding two paragraphs where those plaintiffs are seeking rescission of such securities was approximately $6.6 billion (which does not reflect adjustment for any subsequent paydowns or distributions or any residual value of such securities, statutory interest or any other adjustments that may be claimed). This amount does not include the potential claims by these or other purchasers in the same or other mortgage-related offerings that have not been described above, or claims that have been dismissed.
Goldman Sachs has entered into agreements with Deutsche Bank National Trust Company and U.S. Bank National Association to toll the relevant statute of limitations with respect to claims for repurchase of residential mortgage loans based on alleged breaches of representations related to $11.4 billion original notional face amount of securitizations issued by trusts for which they act as trustees.
Goldman Sachs is among the numerous financial services firms named as defendants in a qui tam action originally filed by a realtor on April 7, 2010 purportedly on behalf of the City of Chicago and State of Illinois in Cook County, Illinois Circuit Court asserting claims under the Illinois Whistleblower Reward and Protection Act and Chicago False Claims Act, based on allegations that defendants had falsely certified compliance with various
83
Table of Contents
Illinois laws, which were purportedly violated in connection with mortgage origination and servicing activities. The complaint, which was originally filed under seal, seeks treble damages and civil penalties. Plaintiff filed an amended complaint on December 28, 2011, naming Goldman Sachs, among others, as an additional defendant and a second amended complaint on February 8, 2012. On March 12, 2012, the action was removed to the U.S. District Court for the Northern District of Illinois, and on September 17, 2012, the district court granted plaintiff’s motion to remand the action to state court. On November 16, 2012, the defendants moved to dismiss, and discovery has been stayed pending a ruling on the motion to dismiss.
Goldman Sachs has also received, and continues to receive, requests for information and/or subpoenas as part of inquiries or investigations by the U.S. Department of Justice, other members of the RMBS Working Group and other federal, state and local regulators and law enforcement authorities relating to the mortgage-related securitization process, subprime mortgages, CDOs, synthetic mortgage-related products, sales communications and particular transactions involving these products, and servicing and foreclosure activities, which may subject the firm to actions, including litigation, penalties and fines. In December 2014, as part of the RMBS Working Group investigation, the firm received a letter from the U.S. Attorney for the Eastern District of California stating in connection with potentially bringing a civil action that it had preliminarily concluded that the firm had violated federal law in connection with its underwriting, securitization and sale of residential mortgage-backed securities and offering the firm an opportunity to respond. The firm is cooperating with these regulators and other authorities, including in some cases agreeing to the tolling of the relevant statute of limitations. See also “Regulatory Investigations and Reviews and Related Litigation” below.
The firm expects to be the subject of additional putative shareholder derivative actions, purported class actions, rescission and “put back” claims and other litigation, additional investor and shareholder demands, and additional regulatory and other investigations and actions with respect to mortgage-related offerings, loan sales, CDOs, and servicing and foreclosure activities.
On February 24, 2012, Goldman Sachs received a “Wells” notice from the staff of the SEC with respect to the disclosures contained in the offering documents used in connection with a late 2006 offering of approximately $1.3 billion of subprime residential mortgage-backed securities underwritten by Goldman Sachs. On August 6, 2012, Goldman Sachs was notified by the SEC staff that the investigation into this offering has been completed as to Goldman Sachs and that the staff does not intend to recommend any enforcement action by the SEC against Goldman Sachs with respect to this offering.
Washington Mutual Securities Litigation
Goldman Sachs is among numerous underwriters named as defendants in a putative securities class action amended complaint filed on August 5, 2008 in the U.S. District Court for the Western District of Washington. As to the underwriters, plaintiffs allege that the offering documents in connection with various securities offerings by Washington Mutual, Inc. failed to describe accurately the company’s exposure to mortgage-related activities in violation of the disclosure requirements of the federal securities laws. The defendants include past and present directors and officers of Washington Mutual, the company’s former outside auditors, and numerous underwriters. On June 30, 2011, the underwriter defendants and plaintiffs entered into a definitive settlement agreement, pursuant to which Goldman Sachs would contribute to a settlement fund. On November 4, 2011, the court approved the settlement, and the time to appeal has run, thereby concluding the matter. Goldman Sachs has paid the full amount of Goldman Sachs’ contribution to the settlement fund.
IndyMac Pass-Through Certificates Litigation
Goldman Sachs is among numerous underwriters named as defendants in a putative securities class action filed on May 14, 2009 in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. As to the underwriters, plaintiffs allege that the offering documents in connection with various securitizations of mortgage-related assets violated the disclosure requirements of the federal securities laws. The defendants include IndyMac-related
84
Table of Contents
entities formed in connection with the securitizations, the underwriters of the offerings, certain ratings agencies which evaluated the credit quality of the securities, and certain former officers and directors of IndyMac affiliates. On November 2, 2009, the underwriters moved to dismiss the complaint. The motion was granted in part on February 17, 2010 to the extent of dismissing claims based on offerings in which no plaintiff purchased, and the court reserved judgment as to the other aspects of the motion. By a decision dated June 21, 2010, the district court formally dismissed all claims relating to offerings in which no named plaintiff purchased certificates (including all offerings underwritten by Goldman Sachs), and both granted and denied the defendants’ motions to dismiss in various other respects. On November 16, 2012, the district court denied the plaintiffs’ motion seeking reinstatement of claims relating to 42 offerings previously dismissed for lack of standing (one of which was co-underwritten by Goldman Sachs) without prejudice to renewal depending on the outcome of the now-denied petition for a writ of certiorari to the U.S. Supreme Court with respect to the Second Circuit’s decision described under “Mortgage-Related Matters” above. By an order dated March 26, 2013, the district court stayed the action for 60 days and directed the parties to mediate. On May 17, 2010, four additional investors filed a motion seeking to intervene in order to assert claims based on additional offerings (including two underwritten by Goldman Sachs). The defendants opposed the motion on the ground that the putative intervenors’ claims were time-barred and, on June 21, 2011, the court denied the motion to intervene with respect to, among others, the claims based on the offerings underwritten by Goldman Sachs. Certain of the putative intervenors (including those seeking to assert claims based on two offerings underwritten by Goldman Sachs) have appealed. Goldman Sachs underwrote approximately $751 million principal amount of securities to all purchasers in the offerings at issue in the May 2010 motion to intervene. On July 11, 2008, IndyMac Bank was placed under an FDIC receivership, and on July 31, 2008, IndyMac Bancorp, Inc. filed for Chapter 7 bankruptcy in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court in Los Angeles, California.
RALI Pass-Through Certificates Litigation
Goldman Sachs is among numerous underwriters named as defendants in a securities class action initially filed in September 2008 in New York Supreme Court, and subsequently removed to the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. As to the underwriters, plaintiffs allege that the offering documents in connection with various offerings of mortgage-backed pass-through certificates violated the disclosure requirements of the federal securities laws. In addition to the underwriters, the defendants include Residential Capital, LLC (“ResCap”), Residential Accredit Loans, Inc. (“RALI”), Residential Funding Corporation (“RFC”), Residential Funding Securities Corporation (“RFSC”), and certain of their officers and directors. On January 3, 2013, the district court certified a class in connection with one offering underwritten by Goldman Sachs, which includes only initial purchasers who bought the securities directly from the underwriters or their agents no later than ten trading days after the offering date. On April 30, 2013, the district court granted in part plaintiffs’ request to reinstate a number of the previously dismissed claims relating to an additional nine offerings underwritten by Goldman Sachs. On May 10, 2013, the plaintiffs filed an amended complaint incorporating those nine additional offerings. On December 27, 2013, the court granted the plaintiffs’ motion for class certification as to the nine additional offerings but denied the plaintiffs’ motion to expand the time period and scope covered by the previous class definition. On October 17, 2014, the plaintiffs and defendants moved for summary judgment. On February 11, 2015, Goldman Sachs and the other underwriter defendants agreed to a settlement with the plaintiffs, subject to court approval. The firm has reserved the full amount of its proposed contribution to the settlement.
Goldman Sachs underwrote approximately $5.57 billion principal amount of securities to all purchasers in the offerings included in the amended complaint. On May 14, 2012, ResCap, RALI and RFC filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court for the Southern District of New York. On June 28, 2013, the district court entered a final order and judgment approving a settlement between plaintiffs and ResCap, RALI, RFC, RFSC and their officers and directors named as defendants in the action.
85
Table of Contents
MF Global Securities Litigation
Goldman Sachs is among numerous underwriters named as defendants in class action complaints and an individual action filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York commencing November 18, 2011. These complaints generally allege that the offering materials for two offerings of MF Global Holdings Ltd. (“MF Global”) convertible notes (aggregating approximately $575 million in principal amount) in February 2011 and July 2011, among other things, failed to describe adequately the nature, scope and risks of MF Global’s exposure to European sovereign debt, in violation of the disclosure requirements of the federal securities laws. On December 12, 2014, the court preliminarily approved a settlement resolving the class action, and on January 5, 2015, the court entered an order effectuating the settlement of all claims against Goldman Sachs in the individual action. Goldman Sachs has paid the full amount of its contribution to the settlements.
Goldman Sachs has also received inquiries from various governmental and regulatory bodies and self-regulatory organizations concerning certain transactions with MF Global prior to its bankruptcy filing. GS Group is cooperating with all such inquiries.
GT Advanced Technologies Securities Litigation
Goldman Sachs is among the underwriters named as defendants in several putative securities class actions filed in October 2014 in the U.S. District Court for the District of New Hampshire. In addition to the underwriters, the defendants include certain directors and officers of GT Advanced Technologies Inc. (“GT Advanced Technologies”). As to the underwriters, the complaints generally allege misstatements and omissions in connection with the December 2013 offerings by GT Advanced Technologies of approximately $86 million of common stock and $214 million principal amount of convertible senior notes, assert claims under the federal securities laws, and seek compensatory damages in an unspecified amount and rescission. Goldman Sachs underwrote 3,479,769 shares of common stock and $75 million principal amount of notes for an aggregate offering price of approximately $105 million. On October 6, 2014, GT Advanced Technologies filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy.
FireEye Securities Litigation
Goldman Sachs is among the underwriters named as defendants in several putative securities class actions, filed beginning in June 2014 in the California Superior Court, County of Santa Clara. In addition to the underwriters, the defendants include FireEye, Inc. (“FireEye”) and certain of its directors and officers. The complaints generally allege misstatements and omissions in connection with the offering materials for the March 2014 offering of approximately $1.15 billion of FireEye common stock, assert claims under the federal securities laws, and seek compensatory damages in an unspecified amount and rescission. Goldman Sachs underwrote 2,100,000 shares for a total offering price of approximately $172 million.
Millennial Media Securities Litigation
Goldman Sachs is among the underwriters named as defendants in a putative securities class action filed on September 30, 2014 in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. In addition to the underwriters, the defendants include Millennial Media, Inc. (“Millennial Media”) and certain of its directors, officers and shareholders. As to the underwriters, the complaint generally alleges misstatements and omissions in connection with Millennial Media’s $152 million March 2012 initial public offering and the October 2012 offering of approximately $163 million of Millennial Media’s common stock, asserts claims under the federal securities laws, and seeks compensatory damages in an unspecified amount and rescission. Goldman Sachs underwrote 3,519,000 and 3,450,000 shares of common stock in the March and October 2012 offerings, respectively, for an aggregate offering price of approximately $95 million.
86
Table of Contents
Zynga Securities Litigation
Goldman Sachs was among the underwriters named as defendants in a putative securities class action filed on August 1, 2012 in the California Superior Court, County of San Francisco. In addition to the underwriters, the defendants included Zynga Inc. (“Zynga”) and certain of its directors and officers. The consolidated amended complaint, filed on April 29, 2013, generally alleged that the offering materials for the March 2012 $516 million secondary offering of Zynga common stock by certain of Zynga’s shareholders violated the disclosure requirements of the federal securities laws, and sought compensatory damages in an unspecified amount and rescission. On February 11, 2015, the court dismissed the action.
Cobalt International Energy Securities Litigation
Cobalt International Energy, Inc. (“Cobalt”), certain of its officers and directors (including employees of affiliates of GS Group who served as directors of Cobalt), shareholders of Cobalt (including certain funds affiliated with GS Group), affiliates of these shareholders (including GS Group) and underwriters (including Goldman Sachs) for certain offerings of Cobalt’s securities are defendants in a putative securities class action filed on November 30, 2014 in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of Texas. The complaint asserts claims under the federal securities laws, seeks compensatory and rescissory damages in unspecified amounts and alleges material misstatements and omissions concerning Cobalt in connection with a $1.67 billion February 2012 offering of Cobalt common stock, a $1.38 billion December 2012 offering of Cobalt’s convertible notes, a $1.00 billion January 2013 offering of Cobalt’s common stock, a $1.33 billion May 2013 offering of Cobalt’s common stock, and a $1.30 billion May 2014 offering of Cobalt’s convertible notes. The complaint alleges that GS Group, Goldman Sachs and the affiliated funds are liable as controlling persons with respect to all five offerings. The complaint also seeks damages (i) from Goldman Sachs in connection with its acting as an underwriter of 14,430,000 shares of common stock representing an aggregate offering price of approximately $465 million, $690 million principal amount of convertible notes, and approximately $508 million principal amount of convertible notes in the February 2012, December 2012 and May 2014 offerings, respectively, for an aggregate offering price of approximately $1.66 billion, and (ii) from GS Group and the affiliated funds in connection with their sales of 40,042,868 shares of common stock for aggregate gross proceeds of approximately $1.06 billion in the February 2012, January 2013 and May 2013 common stock offerings.
Employment-Related Matters
On May 27, 2010, a putative class action was filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York by several contingent technology workers who were employees of third-party vendors. The plaintiffs are seeking overtime pay for alleged hours worked in excess of 40 per work week. The complaint alleges that the plaintiffs were de facto employees of Goldman Sachs and that Goldman Sachs is responsible for the overtime pay under federal and state overtime laws. The complaint seeks class action status and unspecified damages. On March 21, 2011, the parties agreed to the terms of a settlement in principle and on February 10, 2012, the court approved the terms of the settlement. Goldman Sachs has reserved the full amount of the proposed settlement.
On September 15, 2010, a putative class action was filed in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York by three female former employees alleging that GS Group and Goldman Sachs have systematically discriminated against female employees in respect of compensation, promotion, assignments, mentoring and performance evaluations. The complaint alleges a class consisting of all female employees employed at specified levels in specified areas by GS Group and Goldman Sachs since July 2002, and asserts claims under federal and New York City discrimination laws. The complaint seeks class action status, injunctive relief and unspecified amounts of compensatory, punitive and other damages. On July 17, 2012, the district court issued a decision granting in part GS Group’s and Goldman Sachs’ motion to strike certain of plaintiffs’ class allegations on the ground that plaintiffs lacked standing to pursue certain equitable remedies and denying GS Group’s and Goldman Sachs’ motion to strike plaintiffs’ class allegations in their entirety as premature. On March 21, 2013, the U.S. Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit held that arbitration should be compelled with one of the named plaintiffs, who as a managing director was a party to an arbitration agreement with the firm. On May 19, 2014, plaintiffs moved for class certification.
87
Table of Contents
Hellenic Republic (Greece) Matters
GS Group and certain of its affiliates have been subject to a number of investigations and reviews by various governmental and regulatory bodies and self-regulatory organizations in connection with Goldman Sachs’ transactions with the Hellenic Republic (Greece), including financing and swap transactions, as well as trading and research activities with respect to Greek sovereign debt. GS Group has cooperated with the investigations and reviews.
Investment Management Services
GS Group and certain of its affiliates are parties to various civil litigation and arbitration proceedings and other disputes with clients relating to losses allegedly sustained as a result of Goldman Sachs’ investment management services. These claims generally seek, among other things, restitution or other compensatory damages and, in some cases, punitive damages.
Financial Advisory Services
GS Group and certain of its affiliates are from time to time parties to various civil litigation and arbitration proceedings and other disputes with clients and third parties relating to the firm’s financial advisory activities. These claims generally seek, among other things, compensatory damages and, in some cases, punitive damages, and in certain cases allege that the firm did not appropriately disclose or deal with conflicts of interest. In addition, GS Group and its affiliates are subject from time to time to investigations and reviews by various governmental and regulatory bodies and self-regulatory organizations in connection with conflicts of interest. GS Group is cooperating with all such investigations and reviews.
GS Group, Goldman Sachs and The Goldman, Sachs & Co. L.L.C. are defendants in an action brought by the founders and former majority shareholders of Dragon Systems, Inc. (Dragon) on November 18, 2008, alleging that the plaintiffs incurred losses due to Goldman Sachs’ financial advisory services provided in connection with the plaintiffs’ exchange of their purported $300 million interest in Dragon for stock of Lernout & Hauspie Speech Products, N.V. (L&H) in 2000. L&H filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy in the U.S. Bankruptcy Court in Wilmington, Delaware on November 29, 2000. The action is pending in the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts. The complaint sought unspecified compensatory, punitive and other damages, and alleged breach of fiduciary duty, violation of Massachusetts unfair trade practices laws, negligence, negligent and intentional misrepresentation, gross negligence, willful misconduct and bad faith. Former minority shareholders of Dragon brought a similar action against Goldman Sachs with respect to their purported $49 million interest in Dragon, and this action was consolidated with the action described above. By an order dated October 31, 2012, the court granted summary judgment with respect to certain counterclaims and an indemnification claim brought by the Goldman Sachs defendants against one of the shareholders, but denied summary judgment with respect to all other claims. On January 23, 2013, a jury found in favor of the Goldman Sachs defendants on the plaintiffs’ claims for negligence, negligent and intentional misrepresentation, gross negligence and breach of fiduciary duty. On June 11, 2013, a court also found in favor of the Goldman Sachs defendants on the remaining claims in the action. Plaintiffs have appealed.
Sales, Trading and Clearance Practices
GS Group and certain of its affiliates are subject to a number of investigations and reviews, certain of which are industry-wide, by various governmental and regulatory bodies and self-regulatory organizations relating to the sales, trading and clearance of corporate and government securities and other financial products, including compliance with the SEC’s short sale rule, algorithmic and quantitative trading, futures trading, transaction reporting, securities lending practices, trading and clearance of credit derivative instruments, commodities trading, private placement practices and compliance with the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act.
88
Table of Contents
Credit Derivatives Antitrust Matters
The European Commission announced in April 2011 that it was initiating proceedings to investigate further numerous financial services companies, including GS Group, in connection with the supply of data related to credit default swaps and in connection with profit sharing and fee arrangements for clearing of credit default swaps, including potential anti-competitive practices. On July 1, 2013, the European Commission issued to those financial services companies a Statement of Objections alleging that they colluded to limit competition in the trading of exchange-traded unfunded credit derivatives and exchange trading of credit default swaps more generally, and setting out its process for determining fines and other remedies. GS Group’s current understanding is that the proceedings related to profit sharing and fee arrangements for clearing of credit default swaps have been suspended indefinitely. Goldman Sachs has received civil investigative demands from the U.S. Department of Justice for information on similar matters.
Goldman Sachs is among the numerous defendants in putative antitrust class actions relating to credit derivatives, filed beginning in May 2013 and consolidated in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. The complaints generally allege that defendants violated federal antitrust laws by conspiring to forestall the development of alternatives to OTC trading of credit derivatives and maintain inflated bid-ask spreads for credit derivatives trading. The complaints seek declaratory and injunctive relief as well as treble damages in an unspecified amount. On September 4, 2014, the court granted in part and denied in part the defendants’ motion to dismiss, permitting the claim alleging an antitrust conspiracy to proceed but confining it to a period after the fall of 2008.
The CFTC has been investigating the role of Goldman Sachs Execution & Clearing, L.P. (“GSEC”), as the clearing broker for an SEC-registered broker-dealer client. The CFTC staff has orally advised GSEC that it intends to recommend that the CFTC bring aiding and abetting, civil fraud and supervision-related charges against GSEC arising from its provision of clearing services to this broker-dealer client based on allegations that GSEC knew or should have known that the client’s subaccounts maintained at GSEC were actually accounts belonging to customers of the broker-dealer client and not the client’s proprietary accounts. GSEC has been discussing a potential resolution. GS Group is cooperating with the investigations and reviews.
In December 2012, Goldman Sachs, without admitting or denying the findings, consented to a civil monetary penalty in the amount of $1.5 million and a cease and desist order from the CFTC in connection with CFTC findings that Goldman Sachs failed to ensure that certain aspects of its risk management, compliance and supervision programs comported with its obligations to supervise diligently the trading activities of an associated person (the “trader”), whose trading activities on seven days in mid-November and mid-December 2007 in the e-mini S&P 500 futures contract traded on the CME resulted in a substantial loss to Goldman Sachs. Specifically, in violation of CFTC Regulation 166.3, Goldman Sachs was alleged to have failed to have procedures reasonably designed to detect and prevent the manual entry of fabricated futures trades into its front office systems, which aggregated manually entered and electronically executed trades in the same product. As a result, the trader entered fabricated e-mini S&P 500 sell trades into its manual trading system, which artificially offset and camouflaged e-mini S&P buy trades the trader had executed in the market. In particular, the trader established an $8.3 billion e-mini S&P 500 position in a firm trading account causing Goldman Sachs a loss of over $118 million in unwinding the trader’s position. Separately, after the trader was discharged, Goldman Sachs withheld certain key information from the NFA and the CFTC until after the CFTC’s Division of Enforcement commenced its investigation. In addition to the civil monetary penalty, Goldman Sachs agreed to cease and desist from violating CFTC Regulation 166.3.
Municipal Securities Matters
GS Group and certain of its affiliates are subject to a number of investigations and reviews by various governmental and regulatory bodies and self-regulatory organizations relating to transactions involving municipal securities, including wall-cross procedures and conflict of interest disclosure with respect to state and
89
Table of Contents
municipal clients, the trading and structuring of municipal derivative instruments in connection with municipal offerings, political contribution rules, underwriting of Build America Bonds, municipal advisory services and the possible impact of credit default swap transactions on municipal issuers. GS Group is cooperating with the investigations and reviews.
On October 11, 2013, the Cook County, Illinois Circuit Court entered a final judgment dismissing all claims in a 2010 qui tam action filed against GS Group, Goldman Sachs and Goldman Sachs Mortgage Company in connection with municipal finance transactions.
Goldman Sachs (along with, in some cases, other financial services firms) is named as respondent in a number of FINRA arbitrations filed by municipalities, municipal owned entities, state-owned agencies or instrumentalities and non-profit entities, based on Goldman Sachs’ role as underwriter of the claimants’ issuances of an aggregate of approximately $2.0 billion of auction rate securities from 2003 through 2007 and as a broker-dealer with respect to auctions for those securities. The claimants generally allege that Goldman Sachs failed to disclose that it had a practice of placing cover bids in auctions, and/or failed to inform the claimants of the deterioration of the auction rate market beginning in the fall of 2007, and that, as a result, the claimants were forced to engage in a series of expensive refinancing and conversion transactions after the failure of the auction market in February 2008. Certain claimants also allege that Goldman Sachs advised them to enter into interest rate swaps in connection with their auction rate securities issuances, causing them to incur additional losses. The claims include breach of fiduciary duty, fraudulent concealment, negligent misrepresentation, breach of contract, violations of the 1934 Act and state securities laws, and breach of duties under the rules of the Municipal Securities Rulemaking Board and the NASD. One claimant has also filed a complaint against Goldman Sachs in federal court asserting the same claims as in the FINRA arbitration.
Goldman Sachs filed complaints and motions in federal court seeking to enjoin certain of the arbitrations to effectuation the exclusive forum selection clauses in the transaction documents. In one case, the district court denied the injunction but was reversed by the appellate court, and the U.S. Supreme Court denied the claimant’s petition for certiorari seeking review of the appellate court’s decision; in other cases, the district court granted the injunctions, which have been affirmed by the appellate court.
Goldman Sachs has also filed motions with the FINRA Panels to dismiss the arbitrations, one of which has been granted.
ISDAFIX-Related Litigation
Goldman Sachs is among the defendants named in several putative class actions relating to trading in interest rate derivatives, filed beginning in September 2014 in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. The complaints generally allege that the defendants violated federal antitrust laws and the Commodity Exchange Act in connection with an alleged conspiracy to manipulate the ISDAFIX benchmark and seek declaratory and injunctive relief as well as treble damages in an unspecified amount. On December 12, 2014, defendants moved to dismiss the consolidated amended complaint, and on February 12, 2015, the plaintiffs filed a second amended consolidated complaint.
Currencies-Related Litigation
Goldman Sachs and GS Group are among the defendants named in several putative antitrust class actions relating to trading in the foreign exchange markets, filed beginning in December 2013 in the U.S. District Court for the Southern District of New York. The complaints generally allege that defendants violated federal antitrust laws in connection with an alleged conspiracy to manipulate the foreign currency exchange markets and seek declaratory and injunctive relief as well as treble damages in an unspecified amount. On February 13, 2014, the cases were consolidated into one action. On February 28, 2014, GS Group was named in a separate putative class action on behalf of non-U.S. plaintiffs containing substantially similar allegations, which was not consolidated
90
Table of Contents
but was coordinated with the other proceedings for pre-trial purposes; that complaint was amended on April 30, 2014. On January 28, 2015, the court denied defendants’ motion to dismiss the consolidated action and granted defendants’ motion to dismiss the amended complaint on behalf of the non-U.S. plaintiffs.
Regulatory Investigations and Reviews and Related Litigation
GS Group and certain of its affiliates are subject to a number of other investigations and reviews by, and in some cases have received subpoenas and requests for documents and information from, various governmental and regulatory bodies and self-regulatory organizations and litigation relating to various matters relating to the firm’s businesses and operations, including:
| • | The 2008 financial crisis; |
| • | The public offering process; |
| • | The firm’s investment management services and financial advisory services; |
| • | Conflicts of interest; |
| • | Research practices, including research independence and interactions between research analysts and other firm personnel, including investment banking personnel, as well as third parties; |
| • | Transactions involving municipal securities, including wall-cross procedures and conflict of interest disclosure with respect to state and municipal clients, the trading and structuring of municipal derivative instruments in connection with municipal offerings, political contribution rules, underwriting of Build America Bonds, municipal advisory services and the possible impact of credit default swap transactions on municipal issuers; |
| • | The sales, trading and clearance of corporate and government securities, currencies, commodities and other financial products and related sales and other communications and activities, including compliance with the SEC’s short sale rule, algorithmic, high-frequency and quantitative trading, the firm’s U.S. alternative trading system, futures trading, options trading, transaction reporting, technology systems and controls, securities lending practices, trading and clearance of credit derivative instruments, commodities activities and metals storage, private placement practices, allocations of and trading in securities, and trading activities and communications in connection with the establishment of benchmark rates, such as currency rates and the ISDAFIX benchmark rates; |
| • | Compliance with the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, including with respect to the firm’s hiring practices; and |
| • | Insider trading, the potential misuse of material non-public information regarding private company and governmental developments and the effectiveness of the firm’s insider trading controls and information barriers. |
GS Group and Goldman Sachs are cooperating with all such regulatory investigations and reviews.
RBC Capital Markets LLC (RBC)
RBC is a large broker-dealer subject to many different complex legal and regulatory requirements. As a result, certain of RBC’s regulators may from time to time conduct investigations, initiate enforcement proceedings and/or enter into settlements with RBC with respect to issues raised in various investigations. RBC complies fully with its regulators in all investigations being conducted and in all settlements it reaches. In addition, RBC is and has been subject to a variety of civil legal claims in various jurisdictions, a variety of settlement agreements and a variety of orders, awards and judgments made against it by courts and tribunals, both in regard to such claims and investigations. RBC complies fully with all settlements it reaches and all orders, awards and judgments made against it.
91
Table of Contents
RBC has been named as a defendant in various legal actions, including arbitrations, class actions and other litigation including those described below, arising in connection with its activities as a broker-dealer. Certain of the actual or threatened legal actions include claims for substantial compensatory and/or punitive damages or claims for indeterminate amounts of damages. RBC is also involved, in other reviews, investigations and proceedings (both formal and informal) by governmental and self-regulatory agencies regarding RBC’s business, including among other matters, accounting and operational matters, certain of which may result in adverse judgments, settlements, fines, penalties, injunctions or other relief.
RBC contests liability and/or the amount of damages, as appropriate, in each pending matter. In view of the inherent difficulty of predicting the outcome of such matters, particularly in cases where claimants seek substantial or indeterminate damages or where investigations and proceedings are in the early stages, RBC cannot predict the loss or range of loss, if any, related to such matters; how or if such matters will be resolved; when they will ultimately be resolved; or what the eventual settlement, fine, penalty or other relief, if any, might be. Subject to the foregoing, RBC believes, based on current knowledge and after consultation with counsel, that the outcome of such pending matters will not have a material adverse effect on the consolidated financial condition of RBC.
On March 11, 2013, the New Jersey Bureau of Securities entered a consent order settling an administrative complaint against RBC, which alleged that RBC failed to follow its own procedures with respect to monthly account reviews and failed to maintain copies of the monthly account reviews with respect to certain accounts that James Hankins Jr. maintained at the firm in violation of N.J.S.A. 49:3-58(a)(2)(xi) and 49:3-59(b). Without admitting or denying the findings of fact and conclusions of law, RBC consented to a civil monetary penalty of $150,000 (of which $100,000 was suspended as a result of the firm’s cooperation) and to pay disgorgement of $300,000.
On June 12, 2012, the State of Illinois Secretary of State Securities Department consented to entry of a judgment enjoining the firm for violation of the Illinois Securities Law of 1953. RBC undertook to repurchase auction rate securities from certain customers before June 30, 2009. RBC also undertook to use best efforts to provide, by December 31, 2009, liquidity opportunities for customers ineligible for the buyback. RBC undertook to provide periodic reports to regulator. RBC paid a penalty of $1,400,139.82.
On May 10, 2012, FINRA commenced and settled an administrative proceeding against RBC for violations of FINRA Rules 1122 and 2010 and NASD Rules 2110 and 3010 for failing to establish, maintain and enforce written supervisory procedures reasonably designed to achieve compliance with applicable rules concerning short-term transactions in closed end funds. RBC paid a fine of $200,000.
On May 2, 2012, the Massachusetts Securities Division entered a consent order settling an administrative complaint against RBC, which alleged that RBC recommended unsuitable products to its brokerage and advisory clients and failed to supervise its registered representatives’ sales of inverse and leveraged ETFs in violation of Section 204(a)(2) of the Massachusetts Uniform Securities Act (“MUSA”). Without admitting or denying the allegations of fact, RBC consented to permanently cease and desist from violations of MUSA, pay restitution of $2.9 million to the investors who purchased the inverse and leveraged ETFs and pay a civil monetary penalty of $250,000.
On September 27, 2011, the SEC commenced and settled an administrative proceeding against RBC for willful violations of Sections 17(a)(2) and 17(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933 (the “1933 Act”) for negligently selling the collateralized debt obligations to five Wisconsin school districts despite concerns about the suitability of the product. The firm agreed to pay disgorgement of $6.6 million, prejudgment interest of $1.8 million, and a civil monetary penalty of $22 million.
Please see RBC’s Form BD for more details.
92
Table of Contents
Margin Levels Expected to be Held at the FCMs
The following is based on how the Funds have been managed as of the date of this Prospectus. While the portfolio composition may vary over time, it is not expected that, as of any daily rebalance, the Matching Funds and the Short Fund will ever have futures exposure greater than one times (1x) the Fund’s assets or that the Ultra Funds or UltraShort Funds will ever have futures exposure greater than two times (2x) the Fund’s assets. Thus, the maximum margin held at an FCM would not exceed the margin requirement for the Matching Fund or the Short Fund or two times the margin requirement for the Ultra Funds or UltraShort Funds. The margin levels described below are based upon current exchange requirements for non-hedger accounts. It is possible that the Funds’ FCMs will require margins greater than the levels set by the relevant exchange and it is also possible that the Funds may qualify for the lower margin levels available to hedge accounts. However, because there is no certainty as to these probabilities, the estimates are made with the assumption that the applicable margin levels for the Funds are the current exchange margin levels for non-hedger accounts. The expected amount is listed first and the maximum amount is listed second. These amounts are based on current margin requirements and current futures levels. They will fluctuate with changes to either factor.
As of January 30, 2015, ProShares VIX Mid Term Futures ETF had futures contracts with notional amounts equal to approximately 100% of Fund assets. As of January 30, 2015, the minimum margin requirement as a percentage of futures notional was approximately 13.2%. Thus, the minimum margin held at FCMs was approximately 13.2% of Fund assets for ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF.
ProShares Managed Futures Strategy expects to have futures contracts with notional amounts equal to approximately 100% of Fund assets. As of January 30, 2015, the minimum margin requirement as a percentage of futures notional was approximately 3.7%. Thus, the minimum margin held at FCMs was approximately 3.7% of Fund assets for ProShares Managed Futures Strategy.
As of January 30, 2015, ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity did not hold futures contracts. Each of ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity may hold futures contracts in the future.
As of January 30, 2015, ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas each had futures contracts with notional amounts equal to approximately 200% of Fund assets. As of January 30, 2015, the minimum margin requirement as a percentage of futures notional was approximately 14.9%. Thus, the minimum margin held at FCMs was approximately 29.8% of Fund assets for each of ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas and ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas.
As of January 30, 2015, ProShares UltraShort Silver had futures contracts with a notional amount equal to approximately 0.3% of Fund assets. The minimum margin requirement as a percentage of futures notional was approximately 8.5%. Thus, the minimum margin held at FCMs was approximately 0.0% of Fund assets for ProShares UltraShort Silver.
As of January 30, 2015, ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar and ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar each had futures contracts with notional amounts equal to approximately 200% of the Fund’s assets. As of January 30, 2015, the minimum margin requirement as a percentage of futures notional was approximately 3.1%. Thus, the minimum margin held at FCMs was approximately 6.2% of the Fund’s assets for each of ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar and ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar.
As of January 30, 2015, ProShares Ultra Euro did not hold futures contracts. ProShares Ultra Euro may hold futures contracts in the future.
As of January 30, 2015, ProShares Short Euro had futures contracts with notional amounts equal to approximately 100% of the Fund’s assets. As of January 30, 2015, the minimum margin requirement as a percentage of futures notional was approximately 2.4%. Thus, the minimum margin held at FCMs was approximately 2.4% of the Fund’s assets for ProShares Short Euro.
93
Table of Contents
As of January 30, 2015, ProShares Ultra Yen did not hold futures contracts. ProShares Ultra Yen may hold futures contracts in the future.
The Funds receive the income on any securities or other property of the Funds transferred to the FCMs to fulfill requirements for margin to be held by the FCMs in respect of commodity interests, and receive a negotiated portion of any income derived by the FCMs in respect of any cash transferred to the FCMs and held for this purpose.
94
Table of Contents
MATERIAL U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS
The following discussion describes the material U.S. federal (and certain state and local) income tax considerations associated with the purchase, ownership and disposition of Shares as of the date hereof by U.S. Shareholders (as defined below) and non-U.S. Shareholders (as defined below). Except where noted, this discussion deals only with Shares held as capital assets by shareholders who acquired Shares by purchase and does not address special situations, such as those of:
| • | dealers in securities or commodities; |
| • | financial institutions; |
| • | regulated investment companies; |
| • | real estate investment trusts; |
| • | partnerships and persons in their capacity as partners; |
| • | tax-exempt organizations; |
| • | insurance companies; |
| • | persons holding Shares as a part of a hedging, integrated or conversion transaction or a straddle; |
| • | traders in securities that elect to use a mark-to-market method of accounting for their securities holdings; or |
| • | persons liable for alternative minimum tax. |
Furthermore, the discussion below is based upon the provisions of the Code, the Regulations, and administrative and judicial interpretations thereof, all as of the date hereof, and such authorities may be repealed, revoked, modified or subject to differing interpretations, possibly on a retroactive basis, so as to result in U.S. federal income tax consequences different from those described below.
A “U.S. Shareholder” of Shares means a beneficial owner of Shares that is for U.S. federal income tax purposes:
| • | an individual that is a citizen or resident of the United States; |
| • | a corporation (or other entity taxable as a corporation) created or organized in or under the laws of the United States, any state thereof or the District of Columbia; |
| • | an estate the income of which is subject to U.S. federal income taxation regardless of its source; or |
| • | a trust if it (1) is subject to the primary supervision of a court within the United States and one or more U.S. persons have the authority to control all substantial decisions of such trust or (2) has a valid election in effect under applicable Regulations to be treated as a U.S. person. |
A “non-U.S. Shareholder” of Shares means a beneficial owner of Shares that is for U.S. federal income tax purposes:
| • | an individual that is a non-resident alien; |
| • | a foreign corporation; |
| • | a foreign estate; or |
| • | a foreign trust. |
If a partnership or other entity or arrangement treated as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes holds Shares, the tax treatment of a partner will generally depend upon the status of the partner and the activities of the partnership. If an investor is a partner of a partnership holding Shares, the Trust urges such investor to consult its own tax adviser.
95
Table of Contents
No statutory, administrative or judicial authority directly addresses the treatment of Shares or instruments similar to Shares for U.S. federal income tax purposes. As a result, the Trust cannot assure investors that the IRS or the courts will agree with the tax consequences described herein. A different treatment from that described below could adversely affect the amount, timing and character of income, gain or loss in respect of an investment in the Shares. If an investor is considering the purchase of Shares, the Trust urges investors to consult their own tax adviser concerning the particular U.S. federal income tax consequences to investors of the purchase, ownership and disposition of Shares, as well as any consequences to investors arising under the laws of any other taxing jurisdiction.
Under Section 7704 of the Code, unless certain exceptions apply, a publicly traded partnership is generally treated and taxed as a corporation, and not as a partnership, for U.S. federal income tax purposes. A partnership is a publicly traded partnership if (1) interests in the partnership are traded on an established securities market or (2) interests in the partnership are readily tradable on a secondary market or the substantial equivalent thereof. It is expected that initially or in the future each Fund may be treated as a publicly traded partnership. If 90% or more of the income of a publicly traded partnership during each taxable year consists of “qualifying income” and the partnership is not required to register under the Investment Company Act, it will be treated as a partnership, and not as an association or publicly traded partnership taxable as a corporation, for U.S. federal income tax purposes (the “qualifying income exception”). Qualifying income includes dividends, interest, capital gains from the sale or other disposition of stocks and debt instruments and, in the case of a partnership a principal activity of which is the buying and selling of commodities or certain positions with respect to commodities, income and gains derived from certain swap agreements or regulated futures or forward contracts with respect to commodities. Each Fund anticipates that at least 90% of its gross income for each taxable year will constitute qualifying income within the meaning of Section 7704(d) of the Code.
Sidley Austin LLP has acted as counsel to the Trust in connection with this offering. Under current law and assuming full compliance with the terms of the Trust Agreement (and other relevant documents) and based on factual representations made by each Fund, in the opinion of Sidley Austin LLP, each Fund will be classified as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes. The factual representations upon which Sidley Austin LLP has relied are: (1) the Funds have not elected and will not elect to be treated as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes; and (2) for each taxable year, 90% or more of a Fund’s gross income will be qualifying income. Shareholders should be aware that opinions of counsel are not binding on the IRS, and no assurance can be given that the IRS will not challenge the conclusions set forth in such opinion. The Sponsor will use its best efforts to operate each Fund in such manner as is necessary for a Fund to continue to meet the qualifying income exception.
While it is expected that each Fund will operate so that it will qualify to be treated for U.S. federal income tax purposes as a partnership, and not as an association or a publicly traded partnership taxable as a corporation, given the highly complex nature of the rules governing partnerships, the ongoing importance of factual determinations, the lack of direct guidance with respect to the application of tax laws to the activities the Funds are undertaking and the possibility of future changes in its circumstances, it is possible that a Fund will not so qualify for any particular year. Sidley Austin LLP has no obligation to advise a Fund or its shareholders of any subsequent change in the matters stated, represented or assumed, or of any subsequent change in the applicable law. A Fund’s taxation as a partnership will depend on such Fund’s ability to meet, on a continuing basis, through actual operating results, the qualifying income exception, the compliance of which will not be reviewed by Sidley Austin LLP. Accordingly, no assurance can be given that the actual results of a Fund’s operations for any taxable year will satisfy the qualifying income exception.
If, for any reason a Fund becomes taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, such Fund’s items of income and deduction would not pass through to the Fund’s shareholders and shareholders would be treated for U.S. federal income tax purposes as stockholders in a corporation. The Fund would be required to pay income tax at corporate rates on its net income. Distributions by the Fund to the shareholders
96
Table of Contents
would constitute dividend income taxable to such shareholders, to the extent of the Fund’s earnings and profits, and the payment of these distributions would not be deductible by the Fund. These consequences would have a material adverse effect on the Fund, the Fund’s shareholders and the value of the Shares.
If at the end of any taxable year a Fund fails to meet the qualifying income exception, the Fund may still qualify as a partnership if the Fund is entitled to relief under the Code for an inadvertent termination of partnership status. This relief will be available if (1) the failure is cured within a reasonable time after discovery, (2) the failure is determined by the IRS to be inadvertent, and (3) the Fund agrees to make such adjustments or to pay such amounts as are determined by the IRS. It is not possible to state whether a Fund would be entitled to this relief in any or all circumstances. It also is not clear under the Code whether this relief is available for the Fund’s first taxable year as a publicly traded partnership. If this relief provision is not applicable to a particular set of circumstances involving a Fund, it will not qualify as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes. Even if this relief provision applies and a Fund retains its partnership qualification, the Fund or its shareholders (during the failure period) will be required to pay such amounts as determined by the IRS.
The remainder of this discussion assumes that each Fund will qualify to be taxed as a partnership for U.S. federal income tax purposes.
Treatment of Fund Income
A partnership does not incur U.S. federal income tax liability. Instead, each partner of a partnership is required to take into account its share of items of income, gain, loss, deduction and other items of the partnership. Accordingly, each shareholder in a Fund is required to include in income its allocable share of a Fund’s income, gain, loss, deduction and other items for a Fund’s taxable year ending with or within its taxable year. In computing a partner’s U.S. federal income tax liability, such items must be included, regardless of whether cash distributions are made by the partnership. Thus, shareholders in a Fund may be required to take into account taxable income without a corresponding current receipt of cash if a Fund generates taxable income but does not make cash distributions in an amount equal to, or if the shareholder is not able to deduct, in whole or in part, such shareholder’s allocable share of a Fund’s expenses or capital losses. Each Fund’s taxable year ends on December 31 unless otherwise required by law. Each Fund uses the accrual method of accounting.
Shareholders must take into account their share of ordinary income realized by the respective Fund’s investments, including from accruals of interest on the U.S. Treasury securities or other cash and cash equivalents held in a Fund’s portfolio. Each Fund may hold U.S. Treasury securities or other debt instruments with “acquisition discount” or “original issue discount,” in which case shareholders in such Fund are required to include accrued amounts in taxable income on a current basis even though receipt of those amounts may occur in a subsequent year. Each Fund may also acquire U.S. Treasury securities with “market discount.” Upon disposition of such obligations, gain would generally be required to be treated as interest income to the extent of the market discount, and shareholders in such Fund would be required to include as ordinary income their share of such market discount that accrued during the period the obligations were held by such Fund. Income or loss from transactions involving certain derivative instruments, such as periodic and certain non-periodic payments in swap transactions, will also generally constitute ordinary income or loss and may result in recognition of taxable income to a U.S. Shareholder on a current basis even though receipt of those amounts may occur in a subsequent year.
The character and timing of income that a Fund earns from the positions in its investment strategy depends on the particular U.S. federal income tax treatment of each such position. The U.S. federal income tax treatment of certain positions is not always clear, and the IRS and Congress sometimes take steps which change the manner in which certain positions are taxed. For example, the IRS has issued guidance indicating that a position that certain taxpayers were previously accounting for as prepaid forward contracts for U.S. federal income tax purposes should, instead, be accounted for under the U.S. federal income tax rules for non-dollar denominated
97
Table of Contents
debt instruments. The IRS has also released a Notice seeking comments from practitioners about the application of U.S. federal income tax rules to certain derivative positions, including derivative positions in commodities. The Notice asks for comments about, among other questions, when investors in these positions should have income, the character of income and gain or loss from these positions and whether the U.S. federal “constructive ownership” rules should apply to these positions. It is not possible to predict what changes, if any, will be adopted or when any such changes would take effect. However, any such changes could affect the amount, timing and character of income, gain and loss in respect of a Fund’s investments, possibly with retroactive effect. As the Funds pass-through their items of income, gain and loss to Shareholders, any change in the manner in which a Fund accounts for these items could have an adverse impact on the shareholders of that Fund.
The Code generally applies a “mark-to-market” system of taxing unrealized gains and losses on, and otherwise provides for special rules of taxation with respect to, Section 1256 Contracts. A Section 1256 Contract includes certain regulated futures contracts, certain non-equity options and certain non-U.S. currency forward contracts. The Sponsor expects substantially all of its futures contracts and foreign currency forward contracts to qualify as Section 1256 Contracts. Swap agreements and non-currency forward contracts are generally not Section 1256 Contracts. Section 1256 Contracts held by the Funds at the end of a taxable year of the Funds will be treated for U.S. federal income tax purposes as if they were sold by the Funds at their fair market value on the last business day of the taxable year. The net gain or loss, if any, resulting from these deemed sales (known as “marking-to-market”), together with any gain or loss resulting from any actual sales of Section 1256 Contracts (or other termination of a Fund’s obligations under such contracts), must be taken into account by a Fund in computing its taxable income for the year. If a Section 1256 Contract held by a Fund at the end of a taxable year is sold in the following year, the amount of any gain or loss realized on the sale will be adjusted to reflect the gain or loss previously taken into account under the mark-to-market rules.
Capital gains and losses from Section 1256 Contracts generally are characterized as short-term capital gains or losses to the extent of 40% of the gains or losses and as long-term capital gains or losses to the extent of 60% of the gains or losses. Shareholders of a Fund will generally take into account their pro rata share of the long-term capital gains and losses and short-term capital gains and losses from Section 1256 Contracts held by a Fund. If a non-corporate taxpayer incurs a net capital loss for a year, the portion of the loss, if any, which consists of a net loss on Section 1256 Contracts may, at the election of the taxpayer, be carried back three years. A loss carried back to a year by a non-corporate taxpayer may be deducted only to the extent (1) the loss does not exceed the net gain on Section 1256 Contracts for the year and (2) the allowance of the carryback does not increase or produce a net operating loss for the year. Due to the Funds’ investment strategy, it is also likely that a significant portion of any capital gain or loss realized by the Funds with respect to non-Section 1256 Contracts will be short-term.
Allocation of the Funds’ Profits and Losses
For U.S. federal income tax purposes, a shareholder’s distributive share of a Fund’s income, gain, loss, deduction and other items are determined by the Trust Agreement, unless an allocation under the agreement does not have “substantial economic effect,” in which case the allocations will be determined in accordance with the “partners’ interests in the partnership.” Subject to the discussions below under “—Monthly Allocation and Revaluation Conventions” and “—Section 754 Election,” the allocations pursuant to the Trust Agreement should be considered to have substantial economic effect or deemed to be made in accordance with the partners’ interests in the partnership.
If the allocations provided by the Trust Agreement were successfully challenged by the IRS, the amount of income or loss allocated to shareholders for U.S. federal income tax purposes under the agreement could be increased or reduced, or the character of the income or loss could be modified.
As described in more detail below, the U.S. tax rules that apply to partnerships are complex and their application is not always clear. Additionally, the rules generally were not written for, and in some respects are
98
Table of Contents
difficult to apply to, publicly traded partnerships. Each Fund will apply certain assumptions and conventions intended to comply with the intent of the rules and to report income, gain, deduction, loss and credit to shareholders in a manner that reflects the economic gains and losses, but these assumptions and conventions may not comply with all aspects of the applicable Regulations. It is possible, therefore, that the IRS will successfully assert that assumptions made and/or conventions used do not satisfy the technical requirements of the Code or the Regulations and will require that tax items be adjusted or reallocated in a manner that could adversely impact an investor.
Monthly Allocation and Revaluation Conventions
In general, each Fund’s taxable income and losses are determined monthly and are apportioned among the shareholders of a Fund in proportion to the number of Shares treated as owned by each of them as of the close of the last trading day of the preceding month; provided, however, such items for the period beginning on the closing date and ending on the last day of the month in which the option closing date or the expiration of the over-allotment option occurs shall be allocated to the shareholders as of the opening of the Exchange on the first business day of the next succeeding month. By investing in Shares, a U.S. Shareholder agrees that, in the absence of an administrative determination or judicial ruling to the contrary, it will report income and loss under the monthly allocation and revaluation conventions described below, except for the period beginning on the closing date and ending on the last day of the month in which the option closing date or the expiration of the over-allotment option occurs, in which case the allocation shall take place as described above.
Under the monthly allocation convention, whoever is treated for U.S. federal income tax purposes as holding Shares as of the close of the last trading day of the preceding month will be treated as continuing to hold the Shares until immediately before the close of the last trading day of the following month. For the initial month during which a Fund becomes operational, the shareholders at the close of trading at month-end will also receive that month’s allocation. As a result, a holder who has disposed of Shares prior to the close of the last trading day of a month may be allocated income, gain, loss and deduction realized after the date of transfer.
The Code generally requires that items of partnership income and deductions be allocated between transferors and transferees of partnership interests on a daily basis. It is possible that transfers of Shares could be considered to occur for U.S. federal income tax purposes when the transfer is completed without regard to a Fund’s monthly convention for allocating income and deductions. If this were to occur, a Fund’s allocation method might be deemed to violate that requirement.
In addition, for any month in which a creation or redemption of Shares takes place, a Fund generally credits or debits, respectively, the “book” capital accounts of the holders of existing Shares with any unrealized gain or loss in that Fund’s assets. This results in the allocation of items of a Fund’s income, gain, loss, deduction and credit to existing holders of Shares to account for the difference between the tax basis and fair market value of property owned by such Fund at the time new Shares are issued or old Shares are redeemed, or the reverse section 704(c) allocations. The intended effect of these allocations is to allocate any built-in gain or loss in a Fund’s assets at the time of a creation or redemption of Shares to the investors that economically have earned such gain or loss.
As with the other allocations described above, each Fund generally will use a monthly convention for purposes of the reverse section 704(c) allocations. More specifically, each Fund generally credits or debits, respectively, the “book” capital accounts of the holders of existing Shares with any unrealized gain or loss in a Fund’s assets based on a calculation utilizing the creation/redemption price of a Fund’s Shares during the month in which the creation or redemption transaction takes place, rather than the fair market value of its assets at the time of such creation or redemption, or the “revaluation convention.” As a result, it is possible that, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, (1) a purchaser of newly issued Shares will be allocated some or all of the unrealized gain in a Fund’s assets at the time it acquires the Shares or (2) a purchase of newly issued Shares will not be allocated its entire share in the loss in a Fund’s assets accruing after the time of such acquisition.
99
Table of Contents
Furthermore, the applicable Regulations generally require that the “book” capital accounts will be adjusted based on the fair market value of partnership property on the date of adjustment and do not explicitly allow the adoption of a monthly revaluation convention. The Sponsor, in an attempt to eliminate book-tax disparities, allocates items of income, gain, or loss for U.S. federal income tax purposes among the Members under the principles of the remedial method of Section 1.704-3(d) of the Regulations.
The Code and applicable Regulations generally require that items of partnership income and deductions be allocated between transferors and transferees of partnership interests on a daily basis, and that adjustments to “book” capital accounts be made based on the fair market value of partnership property on the date of adjustment. The Code and Regulations do not contemplate monthly allocation or revaluation conventions.
If the IRS does not accept a Fund’s monthly allocation or revaluation convention, the IRS may contend that taxable income or losses of the Funds must be reallocated among the shareholders. If such a contention were sustained, the holders’ respective tax liabilities would be adjusted to the possible detriment of certain holders. The Sponsor is authorized to revise the Funds’ allocation and revaluation methods in order to comply with applicable law or to allocate items of partnership income and deductions in a manner that reflects more accurately the shareholders’ interests in the Funds.
Section 754 Election
Each Fund has made the election permitted by Section 754 of the Code. Such an election, once made, is irrevocable without the consent of the IRS. The making of such election by a Fund generally has the effect of requiring a purchaser of Shares in that Fund to adjust, utilizing the lowest closing price during the month, its proportionate share of the basis in that Fund’s assets, or the inside basis, pursuant to Section 743(b) of the Code to fair market value (as reflected in the purchase price for the purchaser’s Shares), as if it had acquired a direct interest in that Fund’s assets. The Section 743(b) adjustment is attributed solely to a purchaser of Shares and is not added to the basis of a Fund’s assets associated with all of the other shareholders. Depending on the relationship between a holder’s purchase price for Shares and its unadjusted share of a Fund’s inside basis at the time of the purchase, the Section 754 election may be either advantageous or disadvantageous to the holder as compared to the amount of gain or loss a holder would be allocated absent the Section 754 election.
The calculations under Section 754 of the Code are complex, and there is little legal authority concerning the mechanics of the calculations, particularly in the context of publicly traded partnerships. Therefore, in making the election under Section 754 of the Code, a Fund applies certain conventions in determining and allocating the Section 743 basis adjustments to help reduce the complexity of those calculations and the resulting administrative costs to a Fund. It is possible that the IRS will successfully assert that some or all of such conventions utilized by a Fund do not satisfy the technical requirements of the Code or the Regulations and, thus, will require different basis adjustments to be made.
In order to make the basis adjustments permitted by Section 754, each Fund is required to obtain information regarding each holder’s secondary market transactions in Shares, as well as creations and redemptions of Shares. Each Fund seeks such information from the record holders of Shares, and, by purchasing Shares, each beneficial owner of Shares will be deemed to have consented to the provision of such information by the record owner of such beneficial owner’s Shares. Notwithstanding the foregoing, however, there can be no guarantee that a Fund will be able to obtain such information from record owners or other sources, or that the basis adjustments that a Fund makes based on the information it is able to obtain will be effective in eliminating disparity between a holder’s outside basis in its share of the Fund interests and its share of inside basis.
Constructive Termination
A Fund will be considered to have terminated for tax purposes if there is a sale or exchange of 50% or more of the total Shares in that Fund within a twelve-month period. A constructive termination results in the closing of a Fund’s taxable year for all holders of Shares in that Fund. In the case of a holder of Shares reporting on a
100
Table of Contents
taxable year other than the taxable year used by a Fund (which is a fiscal year ending December 31), the early closing of a Fund’s taxable year may result in more than twelve months of its taxable income or loss being includable in such holder’s taxable income for the year of termination. A Fund would be required to make new tax elections after a termination, including a new election under Section 754. A termination could also result in penalties if a Fund were unable to determine that the termination had occurred.
Treatment of Distributions
Distributions of cash by a partnership are generally not taxable to the distributee to the extent the amount of cash does not exceed the distributee’s tax basis in its partnership interest. Thus, any cash distributions made by a Fund will be taxable to a shareholder only to the extent such distributions exceed the shareholder’s tax basis in the partnership interests it is treated as owning. (See “—U.S. Shareholders—Tax Basis in Shares” below.) Any cash distributions in excess of a shareholder’s tax basis generally will be considered to be gain from the sale or exchange of the Shares. See “—U.S. Shareholders—Disposition of Shares” below. The Funds do not currently expect to make any cash distributions.
Creation and Redemption of Creation Units
Shareholders, other than Authorized Participants (or holders for which an Authorized Participant is acting), generally will not recognize gain or loss as a result of an Authorized Participant’s creation or redemption of a Creation Unit. If a Fund disposes of assets in connection with the redemption of a Creation Unit, however, the disposition may give rise to gain or loss that will be allocated in part to investors. An Authorized Participant’s creation or redemption of a Creation Unit may also affect an investor’s share of a Fund’s tax basis in its assets, which could affect the amount of gain or loss allocated to an investor on the sale or disposition of portfolio assets by a Fund.
Disposition of Shares
If a U.S. Shareholder transfers Shares of a Fund, in a sale or other taxable disposition, the U.S. Shareholder will generally be required to recognize gain or loss measured by the difference between the amount realized on the sale and the U.S. Shareholder’s adjusted tax basis in the Shares. The amount realized will include the U.S. Shareholder’s share of a Fund’s liabilities, as well as any proceeds from the sale. The gain or loss recognized will generally be taxable as capital gain or loss.
Capital gain of non-corporate U.S. Shareholders is eligible to be taxed at reduced rates when the Shares are held for more than one year. The maximum rate is currently 20%. Capital gain of corporate U.S. Shareholders is taxed at the same rate as ordinary income. Any capital loss recognized by a U.S. Shareholder on a sale of Shares will generally be deductible only against capital gains, except that a non-corporate U.S. Shareholder may generally also offset up to $3,000 per year of ordinary income.
Medicare Tax on Investment Income
Certain U.S. shareholders that are individuals, estates or trusts must pay an additional 3.8% tax on their “net investment income.” U.S. Shareholders should consult their own tax advisors regarding the effect, if any, of this tax on their investment in the Funds.
Tax Basis in Shares
A U.S. Shareholder’s initial tax basis in the partnership interests it is treated as holding will equal the sum of (1) the amount of cash paid by such U.S. Shareholder for its Shares and (2) such U.S. Shareholder’s share of a
101
Table of Contents
Fund’s liabilities. A U.S. Shareholder’s tax basis in the Shares will be increased by (1) the U.S. Shareholder’s share of a Fund’s taxable income, including capital gain, (2) the U.S. Shareholder’s share of a Fund’s income, if any, that is exempt from tax and (3) any increase in the U.S. Shareholder’s share of a Fund’s liabilities. A U.S. Shareholder’s tax basis in Shares will be decreased (but not below zero) by (1) the amount of any cash distributed (or deemed distributed) to the U.S. Shareholder, (2) the U.S. Shareholder’s share of a Fund’s losses and deductions, (3) the U.S. Shareholder’s share of a Fund’s expenditures that is neither deductible nor properly chargeable to its capital account and (4) any decrease in the U.S. Shareholder’s share of a Fund’s liabilities.
Limitations on Deductibility of Certain Losses and Expenses
The deductibility for U.S. federal income tax purposes of a U.S. Shareholder’s share of losses and expenses of a Fund is subject to certain limitations, including, but not limited to, rules providing that: (1) a U.S. Shareholder may not deduct a Fund’s losses that are allocated to it in excess of its adjusted tax basis in its Shares; (2) individuals and personal holding companies may not deduct the losses allocable to a particular “activity” in excess of the amount that they are considered to have “at risk” with respect to the activity; (3) the ability of individuals to take certain itemized deductions may be limited by the “alternative minimum tax;” and (4) a non-corporate U.S. Shareholder may deduct its share of expenses of a Fund only to the extent that such share, together with such non-corporate U.S. Shareholder’s other miscellaneous itemized deductions, exceeds 2% of such non-corporate U.S. Shareholder’s adjusted gross income. In addition, in the case of individuals whose U.S. federal adjusted gross income exceeds a certain inflation-adjusted threshold, the aggregate itemized deductions allowable for the year will be reduced by the lesser of (i) 3% of the excess of U.S. federal adjusted gross income over the applicable threshold; or (ii) 80% of the aggregate itemized deductions otherwise allowable for the taxable year (determined after giving effect to the 2% limitation described above and any other applicable limitations). It is anticipated that Management Fees that each Fund will pay will constitute miscellaneous itemized deductions. To the extent that a loss or expense that cannot be deducted currently is allocated to a U.S. Shareholder, such U.S. Shareholder may be required to report taxable income in excess of its economic income or cash distributions on the Shares. Prospective shareholders are urged to consult their own tax advisors with regard to these and other limitations on the ability to deduct losses or expenses with respect to an investment in a Fund.
Under Section 709(b) of the Code, amounts paid or incurred to organize a partnership may, at the election of the partnership, be treated as deferred expenses, which are allowed as a deduction ratably over a period of not less than 180 months. Each Fund has elected, or is expected to elect, to treat such expenses as ratably deductable over 180 months, beginning with the month the Fund is considered to have started its investment activities for federal tax purposes. A non-corporate U.S. Shareholder’s allocable share of such organizational expenses would constitute miscellaneous itemized deductions. Expenditures in connection with the issuance and marketing of Shares (so-called “syndication fees”) are not eligible for the 180-month amortization provision and are not deductible.
Transferor/Transferee Allocations
In general, a Fund’s taxable income and losses are determined monthly and are apportioned among a Fund’s shareholders in proportion to the number of Shares owned by each of them as of the close of the last trading day of the preceding month; provided, however, such items for the period beginning on the closing date and ending on the last day of the month in which the option closing date or the expiration of the over-allotment option occurs shall be allocated to the shareholders as of the opening of the Exchange on the first business day of the next succeeding month. With respect to any Share that was not treated as outstanding as of the close of the last trading day of the preceding month, the first person that is treated as holding such Share (other than an underwriter or other person holding in a similar capacity and except with respect to the period beginning on the closing date and ending on the last day of the month in which the option closing date or the expiration of the over-allotment option occurs) for U.S. federal income tax purposes will be treated as holding such Share for this purpose as of the close of the last trading day of the preceding month. As a result, a shareholder transferring its Shares may be allocated income, gain, loss and deduction realized after the date of transfer.
102
Table of Contents
Section 706 of the Code generally requires that items of partnership income and deductions be allocated between transferors and transferees of partnership interests on a daily basis. It is possible that transfers of Shares could be considered to occur for U.S. federal income tax purposes when the transfer is completed without regard to a Fund’s convention for allocating income and deductions. In that event, a Fund’s allocation method might be considered a monthly convention that does not literally comply with that requirement.
If the IRS treats transfers of Shares as occurring throughout each month and a monthly convention is not allowed by the Regulations (or only applies to transfers of less than all of a shareholder’s Shares), or if the IRS otherwise does not accept a Fund’s convention, the IRS may contend that taxable income or losses of a Fund must be reallocated among the shareholders. If such a contention were sustained, the shareholders’ respective tax liabilities would be adjusted to the possible detriment of certain shareholders. Each Fund’s Sponsor is authorized to revise a Fund’s methods of allocation between transferors and transferees (as well as among shareholders whose interests otherwise vary during a taxable period).
Tax Reporting by each Fund
Information returns will be filed with the IRS as required with respect to income, gain, loss, deduction and other items derived from Shares of each Fund. Each Fund will file a partnership return with the IRS and a Schedule K-1 to the shareholders.
Treatment of Securities Lending Transactions Involving Shares
A shareholder whose Shares are loaned to a “short seller” to cover a short sale of Shares may be considered as having disposed of those Shares. If so, such shareholder would no longer be a beneficial owner of a pro rata portion of the partnership interests with respect to those Shares during the period of the loan and may recognize gain or loss from the disposition. As a result, during the period of the loan, (1) any of the relevant Fund’s income, gain, loss, deduction or other items with respect to those Shares would not be reported by the shareholder, and (2) any cash distributions received by the shareholder as to those Shares could be fully taxable, likely as ordinary income. Accordingly, shareholders who desire to avoid the risk of income recognition from a loan of their Shares to a short seller are urged to modify any applicable brokerage account agreements to prohibit their brokers from borrowing their Shares.
Audits and Adjustments to Tax Liability
Under the Code, adjustments in tax liability with respect to a Fund’s items generally will be made at the Fund level in a partnership proceeding rather than in separate proceedings with each shareholder. Pursuant to the Trust Agreement, the Sponsor will represent each Fund as such Fund’s “Tax Matters Partner” during any audit and in any dispute with the IRS. Each shareholder will be informed of the commencement of an audit of a Fund. In general, the Tax Matters Partner may enter into a settlement agreement with the IRS on behalf of, and that is binding upon, the shareholders.
Adjustments resulting from an IRS audit may require each shareholder to adjust a prior year’s liability, and possibly may result in an audit of its return. Any audit of a shareholder’s return could result in adjustments not related to a Fund’s returns as well as those related to the Fund’s returns.
The Tax Matters Partner can extend the statute of limitations for assessment of tax deficiencies against shareholders for items in a Fund’s returns. The Tax Matters Partner may bind a shareholder with less than a 1% profits interest in a Fund to a settlement with the IRS unless that shareholder elects, by filing a statement with the IRS, not to give that authority to the Tax Matters Partner. The Tax Matters Partner may seek judicial review, by which all the shareholders are bound, of a final partnership administrative adjustment and, if the Tax Matters Partner fails to seek judicial review, judicial review may be sought by any shareholder having at least a 1%
103
Table of Contents
interest in profits or by any group of shareholders having in the aggregate at least a 5% interest in profits. However, only one action for judicial review will go forward, and each shareholder with an interest in the outcome may participate.
Foreign Tax Credits
Subject to generally applicable limitations, U.S. Shareholders will be able to claim foreign tax credits with respect to certain foreign income taxes paid or incurred by a Fund, withheld on payments made to the Trust or paid by the Trust on behalf of Fund shareholders (if any of such foreign income taxes are so paid, incurred or withheld). U.S. Shareholders must include in their gross income, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, both their share of a Fund’s items of income and gain and also their share of the amount which is deemed to be the shareholder’s portion of foreign income taxes paid with respect to, or withheld from interest or other income derived by, a Fund. U.S. Shareholders may then subtract from their U.S. federal income tax the amount of such taxes withheld, or else treat such foreign taxes as deductions from gross income; however, as in the case of investors receiving income directly from foreign sources, the tax credit or deduction described above is subject to certain limitations. Even if the shareholder is unable to claim a credit, he or she must include all amounts described above in income. U.S. Shareholders are urged to consult their tax advisers regarding this election and its consequences to them.
Tax Shelter Disclosure Rules
There are circumstances under which certain transactions must be disclosed to the IRS in a disclosure statement attached to a taxpayer’s U.S. federal income tax return. (A copy of such statement must also be sent to the IRS Office of Tax Shelter Analysis.) In addition, the Code imposes a requirement on certain “material advisers” to maintain a list of persons participating in such transactions, which list must be furnished to the IRS upon written request. These provisions can apply to transactions not conventionally considered to involve abusive tax planning. Consequently, it is possible that such disclosure could be required by a Fund or the shareholders (1) if a shareholder incurs a loss (in each case, in excess of a threshold computed without regard to offsetting gains or other income or limitations) from the disposition (including by way of withdrawal) of Shares, or (2) possibly in other circumstances. Furthermore, a Fund’s material advisers could be required to maintain a list of persons investing in that Fund pursuant to the Code. While the tax shelter disclosure rules generally do not apply to a loss recognized on the disposition of an asset in which the taxpayer has a qualifying basis (generally a basis equal to the amount of cash paid by the taxpayer for such asset), such rules will apply to a taxpayer recognizing a loss with respect to interests in a pass-through entity (such as the Shares) even if its basis in such interests is equal to the amount of cash it paid. In addition, under recently enacted legislation, significant penalties may be imposed in connection with a failure to comply with these reporting requirements. U.S. Shareholders are urged to consult their tax advisers regarding the tax shelter disclosure rules and their possible application to them.
U.S. Shareholders should consult their own tax advisers regarding any tax reporting or filing obligations they may have as a result of their acquisition, ownership or disposition of Shares.
Non-U.S. Shareholders
Except as described below, each Fund anticipates that a non-U.S. Shareholder will not be subject to U.S. federal income tax on such shareholder’s distributive share of a Fund’s income, provided that such income is not considered to be income of the shareholder that is effectively connected with the conduct of a trade or business within the United States. In the case of an individual non-U.S. Shareholder, such shareholder will be subject to U.S. federal income tax on gains on the sale of Shares in a Fund’s or such shareholder’s distributive share of gains if such shareholder is present in the United States for 183 days or more during a taxable year and certain other conditions are met.
104
Table of Contents
If the income from a Fund is “effectively connected” with a U.S. trade or business carried on by a non-U.S. Shareholder (and, if certain income tax treaties apply, is attributable to a U.S. permanent establishment), then such shareholder’s share of any income and any gains realized upon the sale or exchange of Shares will be subject to U.S. federal income tax at the graduated rates applicable to U.S. citizens and residents and domestic corporations. Non-U.S. Shareholders that are corporations may also be subject to a 30% U.S. branch profits tax (or lower treaty rate, if applicable) on their effectively connected earnings and profits that are not timely reinvested in a U.S. trade or business.
To the extent any interest income allocated to a non-U.S. Shareholder is considered “portfolio interest,” generally neither the allocation of such interest income to the non-U.S. Shareholder nor a subsequent distribution of such interest income to the non-U.S. Shareholder will be subject to withholding, provided that the non-U.S. Shareholder is not otherwise engaged in a trade or business in the United States and provides the relevant Fund with a timely and properly completed and executed IRS Form W-8BEN, W-8BEN-E or other applicable form. In general, “portfolio interest” is interest paid on debt obligations issued in registered form, unless the “recipient” owns 10% or more of the voting power of the issuer.
Non-U.S. Shareholders that are individuals will be subject to U.S. federal estate tax on the value of U.S. situs property owned at the time of their death (unless a statutory exemption or tax treaty exemption applies). It is unclear whether partnership interests such as the Shares will be considered U.S. situs property. Accordingly, non-U.S. Shareholders may be subject to U.S. federal estate tax on all or part of the value of the Shares owned at the time of their death.
Non-U.S. Shareholders are advised to consult their own tax advisers with respect to the particular tax consequences to them of an investment in the Shares.
Foreign Account Tax Compliance
The Foreign Account Tax Compliance provisions of the Hiring Incentives to Restore Employment Act (“FATCA”) generally impose a new reporting and 30% withholding tax regime with respect to certain items of U.S. source income (including dividends and interest) and gross proceeds from the sale or other disposal of property that can produce U.S. source interest or dividends (“Withholdable Payments”). As a general matter, the new rules are designed to require U.S. persons’ direct and indirect ownership of non-U.S. accounts and non-U.S. entities to be reported to the IRS. The 30% withholding tax regime applies if there is a failure to provide required information regarding U.S. ownership. The new withholding rules generally apply to Withholdable Payments (other than gross proceeds of the type described above) and beginning January 1, 2017, payments of gross proceeds of the type described above with respect to a sale or disposition.
The new rules may subject a non-U.S. Shareholder’s share of Withholdable Payments received by a Fund to 30% withholding tax unless such shareholder provides information, representations and waivers of non-U.S. law as may be required to comply with the provisions of the new rules, including information regarding certain U.S. direct and indirect owners of such non-U.S. Shareholder. A non-U.S. Shareholder that is treated as a “foreign financial institution” will generally be subject to withholding unless it agrees to report certain information to the IRS regarding its U.S. accountholders and those of its affiliates.
Although the application of the new withholding rules to a sale or other disposal of an interest in a partnership is unclear, it is possible that the gross proceeds of the sale or other disposal of an interest in a Fund will be subject to tax under the new withholding rules if such proceeds are treated as an indirect disposal of the non-U.S. Shareholder’s interest in assets that can produce U.S. source interest or dividends, unless the selling non-U.S. Shareholder provides appropriate reporting information. Prospective shareholders should consult their own advisors regarding the requirements under FATCA with respect to their own situation.
105
Table of Contents
Regulated Investment Companies (RICs)
The treatment of a RIC’s investment in a Fund will depend, in part, on whether a Fund is classified as a qualified publicly traded partnership (“PTP”) for purposes of the RIC rules. RICs are only allowed to invest up to 25% of their assets in qualified PTPs and to treat gross income and gross gains derived from such investments as qualifying income for purposes of certain rules relevant to determining whether an entity qualifies as a RIC. Similarly, interests in a qualified PTP are treated as issued by such PTP and a RIC is not required to look through to the underlying partnership assets when testing compliance with certain asset diversification or gross income tests applicable to determining whether an entity qualified as a RIC. On the other hand, an investment by a RIC in a publicly traded partnership that is not a qualified PTP is not counted against the 25% limit on a RIC’s investments in qualified PTPs and the RIC is treated as owning its proportionate share of the partnership’s gross assets and earning its proportionate share of the partnership’s gross income and gross gains for purposes of the asset and income tests relevant to determining whether an entity qualifies as a RIC.
It is generally expected that the VIX Fund, the Commodity Index Funds and the Commodity Fund will be treated as qualified PTPs and that the Currency Funds will not. The Managed Futures Fund’s classification as a qualified PTP is uncertain and may vary by year based on the weighting and performance of its futures positions. Prospective RIC investors should consult a tax adviser regarding the treatment of an investment in a Fund under current tax rules and in light of their particular circumstances.
Tax-Exempt Organizations
An organization that is otherwise exempt from U.S. federal income tax is nonetheless subject to taxation with respect to its “unrelated business taxable income,” or UBTI, to the extent that its UBTI from all sources exceeds $1,000 in any taxable year. Except as noted below with respect to certain categories of exempt income, UBTI generally includes income or gain derived (either directly or through a partnership) from a trade or business, the conduct of which is substantially unrelated to the exercise or performance of the organization’s exempt purpose or function.
UBTI generally does not include passive investment income, such as dividends, interest and capital gains, whether realized by the organization directly or indirectly through a partnership (such as the Funds) in which it is a partner. This type of income is exempt, subject to the discussion of “unrelated debt-financed income” below, even if it is realized from securities-trading activity that constitutes a trade or business.
UBTI includes not only trade or business income or gain as described above, but also “unrelated debt-financed income.” This latter type of income generally consists of (1) income derived by an exempt organization (directly or through a partnership) from income producing property with respect to which there is “acquisition indebtedness” at any time during the taxable year and (2) gains derived by an exempt organization (directly or through a partnership) from the disposition of property with respect to which there is acquisition indebtedness at any time during the twelve-month period ending with the date of the disposition. Each Fund does not expect to incur a significant amount of acquisition indebtedness with respect to its assets.
To the extent a Fund recognizes gain from property with respect to which there is “acquisition indebtedness,” the portion of the gain that will be treated as UBTI will be equal to the amount of the gain multiplied by a fraction, the numerator of which is the highest amount of the “acquisition indebtedness” with respect to the property during the twelve-month period ending with the date of their disposition, and the denominator of which is the “average amount of the adjusted basis” of the property during the period that such property is held by a Fund during the taxable year. In determining the unrelated debt-financed income of a Fund, an allocable portion of deductions directly connected with a Fund’s debt-financed property will be taken into account. In making such a determination, for instance, a portion of losses from debt-financed securities (determined in the manner described above for evaluating the portion of any gain that would be treated as UBTI) would offset gains treated as UBTI. A charitable remainder trust is subject to a 100% federal excise tax on any UBTI that it earns; in view of the potential for UBTI, the Shares may not be a suitable investment for a charitable remainder trust.
106
Table of Contents
Certain State and Local Taxation Matters
Prospective shareholders should consider, in addition to the U.S. federal income tax consequences described above, the potential state and local tax consequences of investing in the Shares.
State and local laws often differ from U.S. federal income tax laws with respect to the treatment of specific items of income, gain, loss, deduction and credit. A shareholder’s distributive share of the taxable income or loss of a Fund generally will be required to be included in determining the shareholder’s reportable income for state and local tax purposes in the jurisdiction in which the shareholder is a resident. A Fund may conduct business in one or more jurisdictions that will subject a shareholder to tax (and require a shareholder to file an income tax return with the jurisdiction with respect to the shareholder’s share of the income derived from that business). A prospective shareholder should consult its tax adviser with respect to the availability of a credit for such tax in the jurisdiction in which the shareholder is resident.
Backup Withholding
In certain circumstances, shareholders may be subject to backup withholding on certain payments paid to them if they do not establish that they are exempt from the backup withholding rules or if they do not furnish their correct taxpayer identification number (in the case of individuals, their social security number) and certain certifications, or who are otherwise subject to backup withholding. Backup withholding is not an additional tax. Any amounts withheld from payments made to an investor may be refunded or credited against an investor’s U.S. federal income tax liability, if any, provided that the required information is furnished to the IRS.
Shareholders should be aware that certain aspects of the U.S. federal, state and local income tax treatment regarding the purchase, ownership and disposition of Shares are not clear under existing law. Thus, shareholders are urged to consult their own tax advisers to determine the tax consequences of ownership of the Shares in their particular circumstances, including the application of U.S. federal, state, local and foreign tax laws.
107
Table of Contents
PART TWO:
GENERAL POOL DISCLOSURE
This Prospectus has two parts: the offered series disclosure and the general pool disclosure. These parts are bound together and are incomplete if not distributed together to prospective participants.
PERFORMANCE OF THE OTHER COMMODITY POOLS OPERATED
BY THE COMMODITY POOL OPERATOR
The following performance information is presented in accordance with CFTC regulations. The performance of the Funds will differ materially in certain respects from the performance of the Other Funds which is included herein. The performance of the Other Funds which is summarized herein is materially different from the Funds and the past performance summaries of the Other Funds below are generally not representative of how the Funds might perform in the future.
The performance information presented below reflects our preliminary estimated financial results based upon information available to us as of the date of this Prospectus for which financial statements are not yet available. Our independent registered public accounting firm, PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, has not audited, reviewed, compiled or performed any procedures on this preliminary financial data, and accordingly, does not express an opinion or provide any other form of assurance with respect thereto. There can be no assurance that our final results of operations for such periods will not differ from these estimates. Any such changes could be material.
All summary performance information is as of January 30, 2015. Performance information is set forth, in accordance with CFTC regulations, since each fund’s inception of trading.
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Crude Oil | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
November 24, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$6,290,399,377 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$842,904,135 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$769,352,898 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$7.96 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-36.15% | |
| (December 2014) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-92.04% | |
| (Inception—January 2015) |
108
Table of Contents
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
-17.41 | % | -0.76 | % | -1.50 | % | 11.40 | % | -2.52 | % | -21.61 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
16.44 | % | -0.93 | % | 16.39 | % | -12.31 | % | 11.74 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
9.05 | % | 16.17 | % | -8.66 | % | 10.30 | % | -0.94 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
6.28 | % | 11.89 | % | 1.99 | % | -8.84 | % | -1.60 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
-30.86 | % | -21.14 | % | -32.85 | % | -4.07 | % | 7.17 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
-1.02 | % | -15.38 | % | -5.48 | % | 8.91 | % | 7.33 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
6.72 | % | -1.08 | % | 5.40 | % | 18.13 | % | -12.40 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
-16.13 | % | -16.65 | % | 18.59 | % | 7.04 | % | -4.12 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
17.69 | % | -22.33 | % | -9.61 | % | -9.00 | % | -8.50 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
1.00 | % | 35.20 | % | -13.83 | % | -10.16 | % | -20.49 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
4.12 | % | 15.54 | % | 4.23 | % | -8.24 | % | -33.62 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
17.17 | % | -4.15 | % | 4.52 | % | 12.14 | % | -36.15 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
-0.99 | % | -18.23 | % | -28.11 | % | 9.17 | % | -68.37 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | -21.61 | % | |||||||||||||||||
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Crude Oil | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
November 24, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$3,137,489,737 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
($23,404,711) | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$192,433,315 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$88.68 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-30.03% | |
| (October 2011) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-87.86% | |
| (February 2009—June 2014) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
19.06 | % | -1.93 | % | -0.18 | % | -10.82 | % | 1.19 | % | 13.70 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
-17.55 | % | -1.17 | % | -15.40 | % | 12.92 | % | -11.09 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
-9.94 | % | -16.39 | % | 7.52 | % | -10.12 | % | -0.21 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
-7.28 | % | -12.36 | % | -3.25 | % | 7.27 | % | 0.71 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
37.38 | % | 17.41 | % | 45.59 | % | 2.47 | % | -7.31 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
-2.10 | % | 13.87 | % | -0.84 | % | -9.37 | % | -7.36 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
-8.74 | % | -0.90 | % | -8.47 | % | -16.56 | % | 13.04 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
16.03 | % | 11.34 | % | -17.32 | % | -8.08 | % | 3.35 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
-16.55 | % | 21.29 | % | 8.99 | % | 8.57 | % | 6.99 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
-3.48 | % | -30.03 | % | 12.73 | % | 9.94 | % | 23.12 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
-6.34 | % | -15.40 | % | -6.95 | % | 7.90 | % | 41.23 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
-15.66 | % | 1.48 | % | -5.36 | % | -11.62 | % | 45.65 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
-25.70 | % | -23.66 | % | 3.84 | % | -21.28 | % | 145.78 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 13.70 | % | |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
109
Table of Contents
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Ultra Gold | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
December 1, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$538,201,858 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$99,733,137 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$108,793,321 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$43.52 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-27.55% | |
| (June 2013) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-66.09% | |
| (August 2011—October 2014) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
-2.22 | % | -11.26 | % | 28.64 | % | 0.48 | % | 7.49 | % | 8.78 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
4.96 | % | 12.66 | % | 2.55 | % | -9.22 | % | 12.19 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
0.81 | % | 3.57 | % | -12.33 | % | 1.03 | % | -5.49 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
11.30 | % | 13.40 | % | -1.83 | % | -16.74 | % | -0.77 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
4.29 | % | -0.32 | % | -11.53 | % | -10.49 | % | -6.04 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
5.47 | % | -4.33 | % | 4.62 | % | -27.55 | % | 10.33 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
-12.14 | % | 16.53 | % | 2.48 | % | 20.84 | % | -4.74 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
13.12 | % | 22.50 | % | 2.91 | % | 12.07 | % | -0.15 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
9.62 | % | -21.35 | % | 15.51 | % | -10.09 | % | -10.69 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
5.68 | % | 12.10 | % | -6.65 | % | -1.02 | % | -8.75 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
4.89 | % | 2.19 | % | 0.43 | % | -10.70 | % | 2.95 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
2.65 | % | -23.82 | % | -8.05 | % | -8.02 | % | 3.63 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
57.02 | % | 9.71 | % | 10.35 | % | -50.75 | % | -3.05 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 8.78 | % | |||||||||||||||||
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares UltraShort Gold | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
December 1, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$710,712,883 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$151,081,783 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$78,642,360 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$87.67 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-24.37% | |
| (January 2012) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-88.74% | |
| (Inception—September 2012) |
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
110
Table of Contents
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
0.61 | % | 11.62 | % | -24.37 | % | -1.47 | % | -8.02 | % | -9.28 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
-6.45 | % | -11.95 | % | -3.48 | % | 9.42 | % | -11.43 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
-2.01 | % | -4.43 | % | 12.18 | % | -1.44 | % | 4.69 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
-11.01 | % | -12.72 | % | 0.60 | % | 14.63 | % | 0.00 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
-5.46 | % | -0.84 | % | 11.02 | % | 9.24 | % | 5.61 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
-6.70 | % | 3.70 | % | -6.17 | % | 34.26 | % | -9.92 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
12.44 | % | -15.13 | % | -3.57 | % | -19.13 | % | 4.17 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
-12.50 | % | -21.72 | % | -3.63 | % | -12.23 | % | -0.49 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
-9.53 | % | 21.16 | % | -14.63 | % | 8.79 | % | 11.32 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
-6.43 | % | -12.90 | % | 6.40 | % | -1.16 | % | 8.36 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
-6.35 | % | -3.74 | % | -1.39 | % | 11.00 | % | -3.59 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
-4.06 | % | 28.00 | % | 8.09 | % | 7.09 | % | -4.56 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
-45.83 | % | -27.18 | % | -22.78 | % | 62.07 | % | -6.64 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | -9.28 | % | |||||||||||||||||
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Ultra Silver | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
December 1, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$2,672,634,279 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$1,198,992,983 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$318,688,403 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$43.68 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-50.93% | |
| (September 2011) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-94.67% | |
| (April 2011—December 2014) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
-9.19 | % | -19.29 | % | 39.92 | % | 13.30 | % | -2.45 | % | 10.95 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
-3.77 | % | 44.19 | % | 21.64 | % | -18.79 | % | 20.54 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
16.36 | % | 25.05 | % | -25.33 | % | -2.67 | % | -12.40 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
11.87 | % | 62.43 | % | -8.23 | % | -29.79 | % | -7.29 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
-2.78 | % | -43.56 | % | -19.70 | % | -15.45 | % | -3.41 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
0.64 | % | -19.37 | % | -8.46 | % | -31.08 | % | 20.02 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
-12.07 | % | 25.13 | % | 7.40 | % | 10.94 | % | -2.11 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
13.00 | % | 6.12 | % | 16.30 | % | 38.75 | % | -11.89 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
35.55 | % | -50.93 | % | 27.12 | % | -17.19 | % | -23.25 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
16.11 | % | 22.20 | % | -13.81 | % | 3.68 | % | -11.00 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
25.47 | % | -17.46 | % | 11.96 | % | -19.82 | % | -3.87 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
25.30 | % | -21.78 | % | -24.27 | % | -5.11 | % | -0.86 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
173.63 | % | -44.69 | % | -0.52 | % | -63.16 | % | -37.84 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 10.95 | % | |||||||||||||||||
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
111
Table of Contents
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares UltraShort Euro | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
November 24, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$2,266,810,557 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$391,647,990 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$572,245,808 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$24.67 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-14.03% | |
| (September 2010) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-36.77% | |
| (November 2008—April 2011) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
6.32 | % | -5.04 | % | -2.49 | % | -5.76 | % | 3.83 | % | 14.22 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
3.37 | % | -1.95 | % | -3.88 | % | 7.90 | % | -4.66 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
1.30 | % | -5.56 | % | -0.47 | % | 3.51 | % | 0.22 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
2.58 | % | -8.81 | % | 1.33 | % | -5.46 | % | -1.53 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
16.81 | % | 5.21 | % | 14.31 | % | 2.46 | % | 3.44 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
0.30 | % | -2.15 | % | -4.86 | % | -0.50 | % | -1.04 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
-12.37 | % | 1.32 | % | 5.50 | % | -4.58 | % | 4.48 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
5.33 | % | -0.58 | % | -4.52 | % | 1.15 | % | 3.75 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
-14.03 | % | 14.26 | % | -4.43 | % | -4.73 | % | 8.01 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
-4.60 | % | -6.97 | % | -1.83 | % | -0.92 | % | 1.29 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
14.26 | % | 5.48 | % | -0.81 | % | -0.29 | % | 1.32 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
-6.11 | % | 7.49 | % | -2.97 | % | -2.64 | % | 5.33 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
8.66 | % | 0.22 | % | -6.49 | % | -10.29 | % | 26.58 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 14.22 | % | |||||||||||||||||
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares UltraShort Yen | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
November 24, 2008 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$1,565,523,953 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$298,582,236 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$500,651,608 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$85.59 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-8.79% | |
| (July 2011) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-47.04% | |
| (March 2009—January 2012) |
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
112
Table of Contents
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||
| January |
-6.25 | % | 1.85 | % | -2.11 | % | 10.61 | % | -6.14 | % | -4.19 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
-3.39 | % | -0.87 | % | 13.43 | % | 2.19 | % | -0.93 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
10.27 | % | 2.79 | % | 3.44 | % | 2.86 | % | 2.61 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
0.74 | % | -5.14 | % | -7.26 | % | 6.29 | % | -2.09 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
-7.31 | % | 0.74 | % | -3.88 | % | 5.69 | % | -0.91 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
-5.58 | % | -2.64 | % | 3.81 | % | -3.30 | % | -1.07 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
-4.67 | % | -8.79 | % | -4.54 | % | -2.97 | % | 3.00 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
-5.79 | % | -1.49 | % | 0.25 | % | 0.08 | % | 2.18 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
-1.61 | % | 1.33 | % | -0.86 | % | -0.11 | % | 10.91 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
-7.23 | % | 2.26 | % | 4.51 | % | -0.16 | % | 4.36 | % | ||||||||||||||
| November |
7.93 | % | -1.62 | % | 6.38 | % | 8.32 | % | 11.44 | % | ||||||||||||||
| December |
-6.09 | % | -1.51 | % | 10.53 | % | 5.35 | % | 1.40 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Annual |
-26.84 | % | -12.90 | % | 23.92 | % | 39.61 | % | 26.07 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | -4.19 | % | |||||||||||||||||
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Ultra VIX Short-Term Futures ETF | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
October 3, 2011 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$5,355,994,576 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$1,286,486,388 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$357,560,236 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$31.17 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-57.41% | |
| (March 2012) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-99.98% | |
| (Inception—November 2014) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| January |
-44.29 | % | -42.22 | % | 33.26 | % | 24.24 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
-18.65 | % | -3.28 | % | -27.25 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
-57.41 | % | -32.67 | % | -7.29 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
-6.68 | % | -17.72 | % | -10.58 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
55.72 | % | 4.28 | % | -30.55 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
-53.69 | % | 10.79 | % | -29.08 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
-20.88 | % | -48.79 | % | 23.53 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
-30.01 | % | 25.79 | % | -24.12 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
-42.97 | % | -25.54 | % | 19.63 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
-55.10 | % | 8.79 | % | -27.85 | % | -14.78 | % | ||||||||||||
| November |
-4.14 | % | -41.80 | % | -22.65 | % | -18.82 | % | ||||||||||||
| December |
-28.30 | % | 4.64 | % | -12.99 | % | 21.81 | % | ||||||||||||
| Annual |
-69.14 | % | -97.28 | % | -91.67 | % | -62.59 | % | ||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 24.24 | % | ||||||||||||||
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
113
Table of Contents
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares VIX Short-Term Futures ETF | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
January 3, 2011 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$2,014,734,642 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$385,841,003 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$100,274,773 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$24.02 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-32.69% | |
| (March 2012) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-96.83% | |
| (September 2011—November 2014) |
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| January |
-12.84 | % | -24.92 | % | -22.82 | % | 17.09 | % | 14.74 | % | ||||||||||
| February |
-6.37 | % | -8.04 | % | 0.85 | % | -13.37 | % | ||||||||||||
| March |
-1.88 | % | -32.69 | % | -17.16 | % | -2.59 | % | ||||||||||||
| April |
-21.52 | % | -1.14 | % | -5.88 | % | -4.97 | % | ||||||||||||
| May |
-8.52 | % | 28.89 | % | 2.55 | % | -16.45 | % | ||||||||||||
| June |
-1.13 | % | -29.23 | % | 7.12 | % | -15.10 | % | ||||||||||||
| July |
11.10 | % | -9.26 | % | -28.01 | % | 12.63 | % | ||||||||||||
| August |
65.31 | % | -15.50 | % | 13.12 | % | -11.98 | % | ||||||||||||
| September |
38.45 | % | -22.58 | % | -13.20 | % | 10.50 | % | ||||||||||||
| October |
-24.39 | % | 5.59 | % | -12.96 | % | -2.57 | % | ||||||||||||
| November |
1.68 | % | -21.88 | % | -11.75 | % | -9.56 | % | ||||||||||||
| December |
-14.06 | % | 7.09 | % | -6.05 | % | 14.09 | % | ||||||||||||
| Annual |
-4.53 | % | -78.02 | % | -66.00 | % | -26.66 | % | ||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | 14.74 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Name of Pool: |
ProShares Short VIX Short-Term Futures ETF | |
| Type of Pool: |
Public, Exchange-listed Commodity Pool | |
| Date of Inception of Trading: |
October 3, 2011 | |
| Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions1 as of January 30, 2015: |
$2,247,842,906 | |
| Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions2 as of January 30, 2015: |
$398,639,553 | |
| Net Asset Value as of January 30, 2015: |
$461,401,076 | |
| Net Asset Value per Share3 as of January 30, 2015: |
$50.15 | |
| Worst Monthly Loss:4 |
-26.85% | |
| (May 2012) | ||
| Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss:5 |
-43.27% | |
| (June 2014—January 2015) |
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
114
Table of Contents
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS.
Rate of Return:6
| 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | ||||||||||||||||
| January |
31.19 | % | 25.87 | % | -17.67 | % | -18.32 | % | ||||||||||||
| February |
4.50 | % | -6.34 | % | 11.30 | % | ||||||||||||||
| March |
39.60 | % | 18.25 | % | 0.01 | % | ||||||||||||||
| April |
-3.41 | % | -2.00 | % | 3.83 | % | ||||||||||||||
| May |
-26.85 | % | -3.39 | % | 18.89 | % | ||||||||||||||
| June |
29.53 | % | -10.35 | % | 15.77 | % | ||||||||||||||
| July |
5.11 | % | 36.57 | % | -13.79 | % | ||||||||||||||
| August |
16.20 | % | -13.36 | % | 10.93 | % | ||||||||||||||
| September |
23.02 | % | 13.40 | % | -11.50 | % | ||||||||||||||
| October |
27.51 | % | -7.76 | % | 9.11 | % | -8.50 | % | ||||||||||||
| November |
-10.40 | % | 22.09 | % | 12.30 | % | 9.50 | % | ||||||||||||
| December |
13.17 | % | -13.67 | % | 4.91 | % | -18.10 | % | ||||||||||||
| Annual |
29.29 | % | 155.84 | % | 104.06 | % | -9.03 | % | ||||||||||||
| Year-to-Date |
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | -18.32 | % | ||||||||||||||
See accompanying Footnotes to Performance Information.
Footnotes to Performance Information
| 1. | “Aggregate Gross Capital Subscriptions” is the aggregate of all amounts ever contributed to the pool, including those of investors who subsequently redeemed their investments. |
| 2. | “Aggregate Net Capital Subscriptions” is the aggregate of all amounts ever contributed to the pool, excluding those of investors who subsequently redeemed their investments. |
| 3. | “Net Asset Value per Share” is the net asset value, based on the pricing policies of the Trust and determined in accordance with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles, of the pool divided by the total number of Shares outstanding as of January 30, 2015. Please see “Description of the Shares; The Funds; Certain Material Terms of the Trust Agreement—Net Asset Value (NAV)” for additional information regarding the pricing policies of the Trust. |
| 4. | “Worst Monthly Loss” is the largest single month loss sustained during the most recent five calendar years and year-to-date (or since inception of the Fund, if the Fund has had less than five calendar years of performance), expressed as a percentage. “Loss” as used in this section of the Prospectus means losses experienced by the relevant pool over the specified period and is calculated on a rate of return basis, i.e., dividing net performance by beginning equity. Loss is measured on the basis of monthly returns only, and does not reflect intra-month figures. |
| 5. | “Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss” is the largest percentage decline in Net Asset Value per Share over the most recent five calendar years and year-to-date (or since inception of the Fund, if the Fund has had less than five calendar years of performance). This need not be a continuous decline, but can be a series of positive and negative returns where the negative returns are larger than the positive returns. Worst Peak-to-Valley Loss represents the greatest percentage decline from any month-end Net Asset Value per Share that occurs without such month-end Net Asset Value per Share being equaled or exceeded as of a subsequent month-end during such period. A Peak-to-Valley loss that begins prior to the beginning of the most recent five calendar years and ends within the most recent five calendar year period is deemed to have occurred during such five calendar year period. |
| 6. | Based on the latest calculated net asset value, as applicable to creations and redemptions of Creation Units, with respect to each period. |
115
Table of Contents
Substantially all of the proceeds of the offering of the Shares of the Funds are used to enter into Financial Instruments in which a Fund invests, in combination with cash or cash equivalents and/or U.S. Treasury securities or other high credit quality, short-term fixed-income or similar securities (such as shares of money market funds and collateralized repurchase agreements) that may in part be used for direct investment or deposited with the FCMs as margin in connection with futures contracts or in segregated accounts at the Funds’ custodian bank as collateral for swap agreements or forward contracts, as applicable. To the extent that the Funds do not invest the proceeds of the offering of the Shares in the manner described above on the day such proceeds are received, such proceeds will be deposited with the Custodian in a non-interest bearing account.
To the extent that the Funds trade in futures contracts on U.S. exchanges, the assets deposited by the Funds with the FCMs (or another eligible financial institution, as applicable) as margin must be segregated pursuant to the regulations of the CFTC. Such segregated funds may be invested only in a limited range of instruments-principally U.S. government obligations to margin futures and forward contract positions.
The Sponsor has selected Goldman, Sachs & Co. (Goldman Sachs) and RBC Capital Markets, LLC (RBC) as its FCMs. Each of Goldman Sachs and RBC, in its capacity as a registered FCM, serves as a clearing broker to the Trust and the Funds and as such arranges for the execution and clearing of the Funds’ futures transactions. Each of Goldman Sachs and RBC acts as clearing broker for many other funds and individuals. A variety of executing brokers may execute futures transactions on behalf of the Funds. The executing brokers will give-up all such transactions to Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable. Each of Goldman Sachs and RBC is registered as an FCM with the CFTC and is a member of the NFA. Goldman Sachs and RBC are clearing members of the CBOT, CME, NYMEX, and all other major U.S. commodity exchanges. Neither Goldman Sachs nor RBC is affiliated with or acts as a supervisor of the Trust, the Funds, the Sponsor, the Trustee or BBH&Co. (the Administrator and the Custodian). Neither Goldman Sachs nor RBC, in its capacity as FCM, is acting as an underwriter or sponsor of the offering of the Shares, or has passed upon the merits of participating in this offering. Neither Goldman Sachs nor RBC has passed upon the adequacy of this Prospectus or on the accuracy of the information contained herein. Neither Goldman Sachs nor RBC provides any commodity trading advice regarding the Funds’ trading activities. Investors should not rely upon Goldman Sachs or RBC in deciding whether to invest in the Funds or retain their interests in the Funds. Prospective investors should also note that the Sponsor may select additional clearing brokers or replace Goldman Sachs and/or RBC as the Funds’ clearing broker.
To the extent, if any, that the Funds enter into trades in futures on markets other than regulated U.S. futures exchanges, funds deposited to margin positions held on such exchanges are invested in bank deposits or in instruments of a credit standing generally comparable to those authorized by the CFTC for investment of “customer segregated funds,” although applicable CFTC rules prohibit funds employed in trading on foreign exchanges from being deposited in “customer segregated fund accounts.”
The Sponsor, a registered commodity pool operator, is responsible for the cash management activities of the Funds, including investing in cash equivalents that may be used as margin for the Financial Instruments as described above.
Only Authorized Participants may create or redeem Creation Units. Each Authorized Participant must (1) be a registered broker-dealer or other securities market participant such as a bank or other financial institution which is not required to register as a broker-dealer to engage in securities transactions, (2) be a participant in DTC, and (3) have entered into an agreement with the Trust and the Sponsor (an Authorized Participant Agreement).
116
Table of Contents
CREATION AND REDEMPTION OF SHARES
Each Fund creates and redeems Shares from time to time, but only in one or more Creation Units. A Creation Unit is a block of 50,000 Shares (25,000 with respect to the VIX Fund). Except when aggregated in Creation Units, the Shares are not redeemable securities.
The manner by which Creation Units are purchased and redeemed is dictated by the terms of the Authorized Participant Agreement and Authorized Participant Handbook, and all such procedures are at the discretion of the Sponsor. By placing a purchase order, an Authorized Participant agrees to deposit cash with the Custodian of the Funds (unless as provided otherwise in this Prospectus).
If permitted by the Sponsor in its sole discretion with respect to a Fund, an Authorized Participant may also agree to enter into or arrange for an exchange of a futures contract for related position (“EFCRP”) or block trade with the relevant Fund whereby the Authorized Participant would also transfer to such Fund a number and type of exchange-traded futures contracts at or near the closing settlement price for such contracts on the purchase order date. Similarly, the Sponsor in its sole discretion may agree with an Authorized Participant to use an EFCRP to effect an order to redeem Creation Units.
An EFCRP is a technique permitted by the rules of certain futures exchanges that, as utilized by a Fund in the Sponsor’s discretion, would allow such Fund to take a position in a futures contract from an Authorized Participant, or give futures contracts to an Authorized Participant, in the case of a redemption, rather than to enter the futures exchange markets to obtain such a position. An EFCRP by itself will not change either party’s net risk position materially. Because the futures position that a Fund would otherwise need to take in order to meet its investment objective can be obtained without unnecessarily impacting the financial or futures markets or their pricing, EFCRPs can generally be viewed as transactions beneficial to a Fund. A block trade is a technique that permits certain Funds to obtain a futures position without going through the market auction system and can generally be viewed as a transaction beneficial to the Fund.
Authorized Participants pay a fixed transaction fee of up to $500 in connection with each order to create or redeem a Creation Unit in order to compensate BBH&Co., as the Administrator, the Custodian and the Transfer Agent of each Fund and its Shares, for services in processing the creation and redemption of Creation Units and to offset the costs of increasing or decreasing derivative positions. Authorized Participants also may pay a variable transaction fee to the Funds of up to 0.10% (and a variable transaction fee to the VIX Fund of 0.05%) of the value of the Creation Unit that is purchased or redeemed unless the transaction fee is waived or otherwise adjusted by the Sponsor. The Sponsor provides such Authorized Participant with prompt notice in advance of any such waiver or adjustment of the transaction fee. Authorized Participants may sell the Shares included in the Creation Units they purchase from the Funds to other investors. Further detail on the fees is set forth in the Authorized Participant Handbook.
The form of Authorized Participant Agreement and the related Authorized Participant Handbook set forth the procedures for the creation and redemption of Creation Units and for the payment of cash required for such creations and redemptions. The Sponsor may delegate its duties and obligations under the form of Authorized Participant Agreement to SEI or the Administrator without consent from any shareholder or Authorized Participant. The form of Authorized Participant Agreement and the related procedures attached thereto may be amended by the Sponsor without the consent of any shareholder or Authorized Participant. Authorized Participants who purchase Creation Units from the Funds receive no fees, commissions or other form of compensation or inducement of any kind from either the Sponsor or the Funds, and no such person has any obligation or responsibility to the Sponsor or the Fund to effect any sale or resale of Shares.
Authorized Participants are cautioned that some of their activities may result in their being deemed participants in a distribution in a manner which would render them statutory underwriters and subject them to the prospectus delivery and liability provisions of the 1933 Act, as described in “Plan of Distribution.”
117
Table of Contents
Each Authorized Participant must be registered as a broker-dealer under the 1934 Act and regulated by FINRA, or exempt from being, or otherwise not required to be, so regulated or registered, and must be qualified to act as a broker or dealer in the states or other jurisdictions where the nature of its business so requires. Certain Authorized Participants may be regulated under federal and state banking laws and regulations. Each Authorized Participant must have its own set of rules and procedures, internal controls and information barriers as it determines is appropriate in light of its own regulatory regime.
Authorized Participants may act for their own accounts or as agents for broker-dealers, custodians and other securities market participants that wish to create or redeem Creation Units.
Persons interested in purchasing Creation Units should contact the Sponsor or the Administrator to obtain the contact information for the Authorized Participants. Shareholders who are not Authorized Participants are only able to redeem their Shares through an Authorized Participant.
Pursuant to the Authorized Participant Agreement, the Sponsor agreed to indemnify the Authorized Participants against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the 1933 Act, and to contribute to the payments the Authorized Participants may be required to make in respect of those liabilities.
The following description of the procedures for the creation and redemption of Creation Units is only a summary and an investor should refer to the relevant provisions of the Trust Agreement and the form of Authorized Participant Agreement for more detail. The Trust Agreement and the form of Authorized Participant Agreement are filed as exhibits to the Registration Statement of which this Prospectus is a part.
On any Business Day, an Authorized Participant may place an order with the Distributor to create one or more Creation Units. For purposes of processing both purchase and redemption orders, a “Business Day” for each Fund means any day on which the NAV of such Fund is determined.
Purchase orders must be placed by the cut-off time shown on page 4, or earlier if the Exchange or other exchange material to the valuation or operation of such Fund closes before the cut-off time. If a purchase order is received prior to the applicable cut-off time, the day on which SEI receives a valid purchase order is the purchase order date. If the purchase order is received after the applicable cut-off time, the purchase order date will be the next day. Purchase orders are irrevocable. By placing a purchase order, and prior to delivery of such Creation Units, an Authorized Participant’s DTC account will be charged the non-refundable transaction fee due for the purchase order.
Determination of Required Payment
The total payment required to create each Creation Unit is the NAV of 25,000 Shares of the VIX Fund or 50,000 Shares of the applicable Managed Futures Fund or Geared Fund, on the purchase order date plus the applicable transaction fee. For each Fund, Authorized Participants have create/redeem cut-off times prior to the NAV calculation time, which may be different from the close of U.S. markets, as shown in the table on page 4.
Delivery of Cash
Cash required for settlement will typically be transferred to the Custodian through: (1) the Continuous Net Settlement (“CNS”) clearing process of NSCC, as such processes have been enhanced to effect creations and redemptions of Creation Units; or (2) the facilities of DTC on a Delivery Versus Payment (“DVP”) basis, which is the procedure in which the buyer’s payment for securities is due at the time of delivery. Security delivery and payment are simultaneous. If the Custodian does not receive the cash by the market close on the first Business Day following the purchase order date (T+1), such order may be charged interest for delayed settlement or cancelled. The Sponsor reserves the right to extend the deadline for the Custodian to receive the cash required for settlement up to the third Business Day following the purchase order date (T+3). In the event a purchase order is
118
Table of Contents
cancelled, the Authorized Participant will be responsible for reimbursing the Fund for all costs associated with cancelling the order including costs for repositioning the portfolio. At its sole discretion, the Sponsor may agree to a delivery date other than T+3. Additional fees may apply for special settlement. The Creation Unit will be delivered to the Authorized Participant upon the Custodian’s receipt of the purchase amount.
Delivery of Exchange of Futures Contract for Related Position (EFCRP) Futures Contracts or Block Trades
In the event that the Sponsor shall have determined to permit the Authorized Participant to transfer futures contracts pursuant to an EFCRP or to engage in a block trade purchase of futures contracts from the Authorized Participant with respect to a Fund, as well as to deliver cash, in the creation process, futures contracts required for settlement must be transferred directly to the Fund’s account at its FCM. If the cash is not received by the market close on the third Business Day following the purchase order date (T+3); such order may be charged interest for delayed settlements or cancelled. In the event a purchase order is cancelled, the Authorized Participant will be responsible for reimbursing a Fund for all costs associated with cancelling the order including costs for repositioning the portfolio. At its sole discretion, the Sponsor may agree to a delivery date other than T+3. The Creation Unit will be delivered to the Authorized Participant upon the Custodian’s receipt of the cash purchase amount and the futures contracts.
Suspension or Rejection of Purchase Orders
In respect of any Fund, the Sponsor may, in its discretion, suspend the right to purchase, or postpone the purchase settlement date: (1) for any period during which the Exchange, CBOE, CFE, CME (including CBOT and NYMEX) or ICE or other exchange material to the valuation or operation of the Fund is closed or when trading is suspended or restricted on such exchanges in any of the underlying Reference Assets; (2) for any period during which an emergency exists as a result of which the fulfillment of a purchase order is not reasonably practicable; or (3) for such other period as the Sponsor determines to be necessary for the protection of the shareholders. The Sponsor will not be liable to any person or in any way for any loss or damages that may result from any such suspension or postponement.
The Sponsor also may reject a purchase order if:
| • | it determines that the purchase order is not in proper form; |
| • | the Sponsor believes that the purchase order would have adverse tax consequences to a Fund or its shareholders; |
| • | the order would be illegal; or |
| • | circumstances outside the control of the Sponsor make it, for all practical purposes, not feasible to process creations of Creation Units. |
None of the Sponsor, the Administrator or the Custodian will be liable for the suspension or rejection of any purchase order.
The procedures by which an Authorized Participant can redeem one or more Creation Units mirror the procedures for the creation of Creation Units. On any Business Day, an Authorized Participant may place an order with the Distributor to redeem one or more Creation Units. If a redemption order is received prior to the applicable cut-off time, or earlier if the Exchange or other exchange material to the valuation or operation of such Fund closes before the cut-off time, the day on which SEI receives a valid redemption order is the redemption order date. If the redemption order is received after the applicable cut-off time, the redemption order date will be the next day. Redemption orders are irrevocable. The redemption procedures allow Authorized Participants to redeem Creation Units. Individual shareholders may not redeem directly from a Fund.
119
Table of Contents
By placing a redemption order, an Authorized Participant agrees to deliver the Creation Units to be redeemed through DTC’s book-entry system to the applicable Fund not later than noon (Eastern Time), on the first Business Day immediately following the redemption order date (T+1). The Sponsor reserves the right to extend the deadline for the Fund to receive the Creation Units required for settlement up to the third Business Day following the redemption order date (T+3). By placing a redemption order, and prior to receipt of the redemption proceeds, an Authorized Participant must wire to the Custodian the non-refundable transaction fee due for the redemption order or any proceeds due will be reduced by the amount of the fee payable. At its sole discretion, the Sponsor may agree to a delivery date other than T+3. Additional fees may apply for special settlement.
Upon request of an Authorized Participant made at the time of a redemption order, the Sponsor at its sole discretion may determine, in addition to delivering redemption proceeds, to transfer futures contracts to the Authorized Participant pursuant to an EFCRP or to a block trade sale of futures contracts to the Authorized Participant.
Determination of Redemption Proceeds
The redemption proceeds from a Fund consist of the cash redemption amount and, if permitted by the Sponsor in its sole discretion with respect to a Fund, an EFCRP or block trade with the relevant Fund as described in “Creation and Redemption of Shares” above. The cash redemption amount is equal to the NAV of the number of Creation Unit(s) of such Fund requested in the Authorized Participant’s redemption order as of the time of the calculation of such Fund’s NAV on the redemption order date, less transaction fees and any amounts attributable to any applicable EFCRP or block trade.
Delivery of Redemption Proceeds
The redemption proceeds due from a Fund are delivered to the Authorized Participant at noon (Eastern Time), on the third Business Day immediately following the redemption order date if, by such time on such Business Day immediately following the redemption order date, a Fund’s DTC account has been credited with the Creation Units to be redeemed. The Fund should be credited through: (1) the CNS clearing process of NSCC, as such processes have been enhanced to effect creations and redemptions of Creation Units; or (2) the facilities of DTC on a Delivery Versus Payment basis. If a Fund’s DTC account has not been credited with all of the Creation Units to be redeemed by such time, the redemption distribution is delivered to the extent whole Creation Units are received. Any remainder of the redemption distribution is delivered on the next Business Day to the extent any remaining whole Creation Units are received if: (1) the Sponsor receives the fee applicable to the extension of the redemption distribution date which the Sponsor may, from time to time, determine, and (2) the remaining Creation Units to be redeemed are credited to the Fund’s DTC account by noon (Eastern Time), on such next Business Day. Any further outstanding amount of the redemption order may be cancelled. The Authorized Participant will be responsible for reimbursing a Fund for all costs associated with cancelling the order including costs for repositioning the portfolio.
The Sponsor is also authorized to deliver the redemption distribution notwithstanding that the Creation Units to be redeemed are not credited to a Fund’s DTC account by noon (Eastern Time), on the third Business Day immediately following the redemption order date if the Authorized Participant has collateralized its obligation to deliver the Creation Units through DTC’s book-entry system on such terms as the Sponsor may determine from time to time.
In the event that the Authorized Participant shall have requested, and the Sponsor shall have determined to permit the Authorized Participant to receive futures contracts pursuant to an EFCRP, as well as the cash redemption proceeds, in the redemption process, futures contracts required for settlement shall be transferred directly from the Fund’s account at its FCM to the account of the Authorized Participant at its FCM.
120
Table of Contents
Suspension or Rejection of Redemption Orders
In respect of any Fund, the Sponsor may, in its discretion, suspend the right of redemption, or postpone the redemption settlement date: (1) for any period during which the Exchange, CBOE, CFE, CME (including CBOT and NYMEX) or ICE or other exchange material to the valuation or operation of the Fund is closed or when trading is suspended or restricted on such exchanges in any of the underlying Reference Assets; (2) for any period during which an emergency exists as a result of which the redemption distribution is not reasonably practicable; or (3) for such other period as the Sponsor determines to be necessary for the protection of the shareholders. The Sponsor will not be liable to any person or in any way for any loss or damages that may result from any such suspension or postponement.
The Sponsor will reject a redemption order if the order is not in proper form as described in the form of Authorized Participant Agreement or if the fulfillment of the order might be unlawful.
Creation and Redemption Transaction Fee
To compensate BBH&Co. for services in processing the creation and redemption of Creation Units and to offset some or all of the transaction costs, an Authorized Participant may be required to pay a fixed transaction fee to BBH&Co. of up to $500 per order to create or redeem Creation Units and may pay a variable transaction fee to a Fund of up to 0.10% (and a variable transaction fee to the VIX Fund of 0.05%) of the value of a Creation Unit. An order may include multiple Creation Units. The transaction fee(s) may be reduced, increased or otherwise changed by the Sponsor at its sole discretion.
The Sponsor may allow for early settlement of purchase or redemption orders. Such arrangements may result in additional charges to the Authorized Participant.
121
Table of Contents
As of the date of this Prospectus, there is no pending legal proceeding, other than ordinary routine litigation incidental to the business of the Trust and that which is described below, to which the Trust or a Fund is a claimant or defendant or to which any of their property is the subject.
As of the date of this Prospectus, there are no material administrative, civil or criminal actions, whether pending or concluded, within five years preceding the date of the Prospectus, against the Sponsor. Louis Mayberg and Michael Sapir, both principals of the Sponsor, were named as defendants in a purported class action lawsuit in the United States District Court for the Southern District of New York, styled In re ProShares Trust Securities Litigation, Civ. No. 09-cv-6935. The Trust was also a defendant in this action, along with several others. The action was initially brought by Steven Novick, on behalf of himself and all others similarly situated, in a complaint filed August 5, 2009, and was consolidated on April 28, 2011, with 33 related putative class actions. The second amended complaint alleged that the defendants violated Sections 11 and 15 of the 1933 Act by including untrue statements of material fact and omitting material facts in the Registration Statement for one or more of ProShares’ exchange-traded funds (“ETFs”) and allegedly failing to adequately disclose the funds’ investment objectives and risks. Claimants, all purchasers of shares of ETFs sold by the Trust or ProShares Trust, sought class certification, compensatory damages, punitive damages, litigation costs, expectation damages and declaratory judgment. The six other series of the Trust named in the complaint were ProShares Ultra Silver, ProShares Ultra Gold, ProShares UltraShort Gold, ProShares UltraShort DJ-UBS Crude Oil (n/k/a ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg DJ-UBS Crude Oil), ProShares Ultra DJ-UBS Crude Oil (n/k/a ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Crude Oil), and ProShares UltraShort Silver. On September 10, 2012, the District Court issued an Opinion and Order dismissing the class action lawsuit in its entirety. On July 22, 2013, the United States Court of Appeals for the Second Circuit issued an Opinion affirming the District Court’s decision and dismissing the class action lawsuit in its entirety.
Goldman Sachs and RBC are clearing members of the CBOT, CME, NYMEX, and all other major U.S. commodity exchanges. From time to time, each of Goldman Sachs and RBC (in its capacity as a commodities broker) and its respective principals may be involved in numerous legal actions, some of which individually and all of which in the aggregate, seek significant or indeterminate damages. However, except for the actions described in the section entitled “Futures Commission Merchants—Litigation and Regulatory Disclosure Relating to FCMs” beginning on page 78, each of Goldman Sachs and RBC has advised that during the five years preceding the date of this Prospectus there has been no material administrative, civil, or criminal action against it or any of its respective principals.
122
Table of Contents
DESCRIPTION OF THE SHARES; THE FUNDS; CERTAIN MATERIAL
TERMS OF THE TRUST AGREEMENT
The following summary describes in brief the Shares and certain aspects of the operation of the Trust, the Funds, and the respective responsibilities of the Trustee and the Sponsor concerning the Trust and the material terms of the Trust Agreement. Prospective investors should carefully review the Trust Agreement filed as an exhibit to the Registration Statement of which this Prospectus is a part and consult with their own advisers concerning the implications to such prospective investors of investing in a series of a Delaware statutory trust. Capitalized terms used in this section and not otherwise defined shall have such meanings assigned to them under the Trust Agreement.
Each Fund issues common units of beneficial interest, or Shares, which represent units of fractional undivided beneficial interest in and ownership of the Funds.
The Shares may be purchased from the Funds or redeemed on a continuous basis, but only by Authorized Participants and only in Creation Units. Individual Shares may not be purchased or redeemed from the Funds. Shareholders that are not Authorized Participants may not purchase or redeem any Shares or Creation Units from the Funds.
Principal Office; Location of Records; Fiscal Year
The Trust is organized as a statutory trust under the DSTA. The Trust is managed by the Sponsor, whose office is located at 7501 Wisconsin Avenue, Suite 1000, Bethesda, Maryland 20814.
The books and records of the Funds are maintained as follows: all marketing materials are maintained at the offices of SEI, One Freedom Valley Drive, Oaks, Pennsylvania 19456. Creation Unit creation and redemption books and records, certain financial books and records (including Fund accounting records, ledgers with respect to assets, liabilities, capital, income and expenses, the registrar, transfer journals and related details) and certain trading and related documents received from FCMs are maintained by BBH&Co., 50 Post Office Square, Boston, Massachusetts 02110.
All other books and records of the Funds (including minute books and other general corporate records, trading records and related reports) are maintained at the Funds’ principal office, c/o ProShare Capital Management LLC, 7501 Wisconsin Avenue, Suite 1000, Bethesda, Maryland 20814.
Trust books and records located at the foregoing addresses are available for inspection and copying (upon payment of reasonable reproduction costs) by Fund shareholders or their representatives for any purposes reasonably related to such shareholder’s interest as a beneficial owner during regular business hours as provided in the Trust Agreement. The Sponsor will maintain and preserve the Trust’s books and records for a period of not less than six years.
The fiscal year of each Fund ends on December 31 of each year.
The Trust is formed and operated in a manner such that each Fund is liable only for obligations attributable to such Fund and shareholders of a Fund are not subject to the losses or liabilities of any other series of the Trust. If any creditor or shareholder in a Fund asserted against a Fund a valid claim with respect to its indebtedness or Shares, the creditor or shareholder would only be able to recover money from that particular Fund and its assets. Accordingly, the debts, liabilities, obligations and expenses, or collectively, claims, incurred, contracted for or
123
Table of Contents
otherwise existing solely with respect to a particular Fund are enforceable only against the assets of that Fund, and not against any other series of the Trust or the Trust generally, or any of their respective assets. The assets of each Fund include only those funds and other assets that are paid to, held by or distributed to a Fund on account of and for the benefit of that Fund, including, without limitation, funds delivered to the Trust for the purchase of Shares or Creation Units in a Fund. This limitation on liability is referred to as the “Inter-Series Limitation on Liability.” The Inter-Series Limitation on Liability is expressly provided for under the DSTA, which provides that if certain conditions (as set forth in Section 3804(a)) are met, then the debts of any particular series will be enforceable only against the assets of such series and not against the assets of any other series of the Trust or the Trust generally.
Wilmington Trust Company, a Delaware trust company, is the sole Trustee of the Trust. The rights and duties of the Trustee and the Sponsor with respect to the offering of the Shares and Fund management and the shareholders are governed by the provisions of the DSTA and by the Trust Agreement. The Trustee will accept service of legal process on the Trust in the State of Delaware and will make certain filings under the DSTA. The Trustee does not owe any other duties to the Trust, the Sponsor or the shareholders of a Fund. The Trustee’s principal offices are located at 1100 North Market Street, Wilmington, Delaware 19890. The Trustee is unaffiliated with the Sponsor.
The Trustee is permitted to resign upon at least sixty (60) days’ notice to the Trust, provided, that any such resignation will not be effective until a successor Trustee is appointed by the Sponsor. The Trustee is compensated by the Funds, as appropriate, and is indemnified by the Funds, as appropriate, against any expenses it incurs relating to or arising out of the formation, operation or termination of such Fund, as appropriate, or the performance of its duties pursuant to the Trust Agreement, except to the extent that such expenses result from the gross negligence or willful misconduct of the Trustee. The Sponsor has the discretion to replace the Trustee.
Only the assets of the Trust and the Sponsor are subject to issuer liability under the federal securities laws for the information contained in this Prospectus and under federal securities laws with respect to the issuance and sale of the Shares. Under such laws, neither the Trustee, either in its capacity as Trustee or in its individual capacity, nor any director, officer or controlling person of the Trustee is, or has any liability as, the issuer or a director, officer or controlling person of the issuer of the Shares. The Trustee’s liability in connection with the issuance and sale of the Shares is limited solely to the express obligations of the Trustee set forth in the Trust Agreement.
Under the Trust Agreement, the Sponsor has exclusive management and control of all aspects of the Trust’s business. The Trustee has no duty or liability to supervise the performance of the Sponsor, nor will the Trustee have any liability for the acts or omissions of the Sponsor. The shareholders have no voice in the day-to-day management of the business and operations of the Funds and the Trust, other than certain limited voting rights as set forth in the Trust Agreement. In the course of its management of the business and affairs of the Funds and the Trust, the Sponsor may, in its sole and absolute discretion, appoint an affiliate or affiliates of the Sponsor as additional sponsors and retain such persons, including affiliates of the Sponsor, as it deems necessary to effectuate and carry out the purposes, business and objectives of the Trust.
Because the Trustee has no authority over the Trust’s operations, the Trustee itself is not registered in any capacity with the CFTC.
ProShare Capital Management LLC is the Sponsor of the Trust, the Funds and the other series of the Trust. As noted above, the Sponsor has exclusive management and control of all aspects of the business of the Funds. The Trustee has no duty or liability to supervise the performance of the Sponsor, nor will the Trustee have any liability for the acts or omissions of the Sponsor.
124
Table of Contents
The Sponsor serves as the Trust’s commodity pool operator.
Specifically, with respect to the Trust, the Sponsor:
| • | selects the Funds’ service providers; |
| • | negotiates various agreements and fees; |
| • | performs such other services as the Sponsor believes that the Trust may require from time to time; |
| • | selects the FCM and Financial Instrument counterparties, if any; |
| • | manages the Funds’ portfolio of other assets, including cash equivalents; and |
| • | manages the Funds with a view toward achieving the Funds’ investment objectives. |
The Shares are not deposits or other obligations of the Sponsor, the Trustee or any of their respective subsidiaries or affiliates or any other bank, are not guaranteed by the Sponsor, the Trustee or any of their respective subsidiaries or affiliates or any other bank and are not insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation or any other governmental agency. An investment in the Shares of the Funds offered hereby is speculative and involves a high degree of risk.
The principal office of the Sponsor is located at 7501 Wisconsin Avenue, Suite 1000, Bethesda, Maryland 20814. The telephone number of the Sponsor is (240) 497-6400.
Background and Principals
The Sponsor currently serves as the commodity pool operator of the Trust and the Funds, and previously also served as the commodity trading advisor to the Trust and the Funds. The Sponsor is registered as a commodity pool operator with the CFTC and is a member in good standing of the NFA. The Sponsor’s membership with the NFA was originally approved on June 11, 1999. It withdrew its membership with the NFA on August 31, 2000 but later re-applied and had its membership subsequently approved on January 8, 2001. Its membership with the NFA is currently effective. The Sponsor’s registration as a commodity trading advisor was approved on June 11, 1999. On February 17, 2013, the Sponsor’s commodity trading advisor registration was withdrawn. The Sponsor’s registration as a commodity pool operator was originally approved on June 11, 1999. It withdrew its registration as a commodity pool operator on August 30, 2000 but later re-applied and had its registration subsequently approved on November 28, 2007. Its registration as a commodity pool operator is currently effective. As a registered commodity pool operator, with respect to the Trust, the Sponsor must comply with various regulatory requirements under the CEA, and the rules and regulations of the CFTC and the NFA, including investor protection requirements, antifraud prohibitions, disclosure requirements, and reporting and recordkeeping requirements. The NFA approved the Sponsor as a Swaps Firm on January 4, 2013. The Sponsor is also subject to periodic inspections and audits by the CFTC and NFA. Its principal place of business is 7501 Wisconsin Avenue, Suite 1000, Bethesda, Maryland 20814 and its telephone number is (240) 497-6400. The registration of the Sponsor with the CFTC and its membership in the NFA must not be taken as an indication that either the CFTC or the NFA has recommended or approved the Sponsor, the Trust and the Funds.
In its capacity as a commodity pool operator, the Sponsor is an organization which operates or solicits funds for commodity pools; that is, an enterprise in which funds contributed by a number of persons are combined for the purpose of trading futures contracts. For past performance of commodity pools operated by the Sponsor, see the section entitled “Performance of the Offered Commodity Pools Operated by the Commodity Pool Operator” beginning on page 63 and the section entitled “Performance of the Other Commodity Pools Operated by the Commodity Pool Operator” beginning on page 107.
125
Table of Contents
Executive Officers of the Trust and Principals and Significant Employees of the Sponsor
| Name |
Position | |
| Michael L. Sapir |
Chief Executive Officer and Principal of the Sponsor | |
| Louis M. Mayberg |
Principal of the Sponsor | |
| William E. Seale |
Principal of the Sponsor | |
| Sapir Family Trust |
Principal of the Sponsor | |
| Northstar Trust |
Principal of the Sponsor | |
| Timothy N. Coakley |
Chief Financial Officer and Principal of the Sponsor | |
| Edward J. Karpowicz |
Principal Financial Officer of the Trust and Principal of the Sponsor | |
| Todd B. Johnson* |
Principal Executive Officer of the Trust and Chief Investment Officer and Principal of the Sponsor | |
| Hratch Najarian |
Director, Portfolio Management and Principal of the Sponsor | |
| Jeffrey Ploshnick |
Senior Portfolio Manager and Associated Person of the Sponsor | |
| Ryan Dofflemeyer |
Portfolio Manager and Associated Person of the Sponsor | |
| Lisa P. Johnson |
Principal of the Sponsor | |
| Victor M. Frye |
Principal of the Sponsor |
| * | Denotes principal of the Sponsor who supervises persons who participate in making trading decisions for the Funds. |
The following is a biographical summary of the business experience of the executive officers of the Trust and the principals and significant employees of the Sponsor.
ProFund Advisors LLC (“PFA”) and ProShare Advisors LLC (“PSA”) are investment advisers registered under the Investment Advisers Act of 1940 (the “Advisers Act”) and commodity pool operators registered under the CEA. PFA is also a commodity trading advisor registered under the CEA.
Michael L. Sapir, Co-Founder, Chief Executive Officer and a listed principal of the Sponsor since August 14, 2008; Co-Founder, Chief Executive Officer and a member of PFA since April 1997, and a listed principal of PFA since November 26, 2012; and Co-Founder, Chief Executive Officer and a member of PSA since January 2005 and a listed principal of PSA since January 14, 2014. As Chief Executive Officer of the Sponsor, PFA and PSA, Mr. Sapir’s responsibilities include oversight of all aspects of the Sponsor, PFA and PSA, respectively.
Louis M. Mayberg, a member and a listed principal of the Sponsor since June 9, 2008; a member of PFA since April 1997 and a listed principal of PFA since November 26, 2012; and a member of PSA since January 2005 and a listed principal of PSA since January 14, 2014. Mr. Mayberg served as Principal Executive Officer of the Trust from June 2008 to December 2013.
William E. Seale, Ph.D., a member of the Sponsor and a listed principal of the Sponsor since June 11, 1999; a member of PFA since April 1997 and a listed principal of PFA since November 8, 2013; and a member of PSA since April 2005 and a listed principal of PSA since January 14, 2014. He served as Chief Investment Officer of PFA from January 2003 to July 2005 and from October 2006 to June 2008 and as Director of Portfolio from January 1997 to January 2003. He served as Chief Investment Officer of PSA from October 2006 to June 2008. In these roles, Dr. Seale’s responsibilities included oversight of the investment management activities of the respective entities. Dr. Seale is a former commissioner of the CFTC.
Sapir Family Trust, a listed principal of the Sponsor. The Sapir Family Trust has an ownership interest in the Sponsor and PSA. The Sapir Family Trust has a passive ownership interest in the Sponsor and exercises no management authority over the Funds.
126
Table of Contents
Northstar Trust, a listed principal of the Sponsor. Northstar Trust has an ownership interest in the Sponsor and PFA. Northstar Trust has a passive ownership interest in the Sponsor and exercises no management authority over the Funds.
Timothy N. Coakley, Chief Financial Officer and a listed principal of the Sponsor since March 7, 2014; Chief Financial Officer and a listed principal of PFA since March 11, 2014; and Chief Financial Officer and a listed principal of PSA since March 11, 2014. As Chief Financial Officer of the Sponsor, Mr. Coakley’s responsibilities include oversight of the financial matters of the Sponsor.
Edward J. Karpowicz, Principal Financial Officer of the Trust since July 2008 and a listed principal of the Sponsor since September 18, 2013. Mr. Karpowicz has been employed by PFA since July 2002 and PSA since its inception as Vice President of Financial Administration.
Todd B. Johnson, Principal Executive Officer of the Trust since January 2014; Chief Investment Officer of the Sponsor since February 27, 2009, a registered swap associated person of the Sponsor since January 4, 2013, a registered associated person of the Sponsor since January 29, 2010, and a listed principal of the Sponsor since January 16, 2009. As Principal Executive Officer of the Trust, Mr. Johnson’s responsibilities include oversight of the operations of the Trust. As Chief Investment Officer of the Sponsor, Mr. Johnson’s responsibilities include oversight of the investment management activities of the Sponsor. Mr. Johnson has served as Chief Investment Officer of PFA and PSA since December 2008 and has been registered as an associated person of PFA since December 5, 2012 and listed as a principal of PFA since November 26, 2012. In addition, Mr. Johnson has been listed as a principal and associated person of PSA since January 14, 2014. Mr. Johnson served from 2002 to December 2008 at World Asset Management (a financial services firm), working as President and Chief Investment Officer from January 2006 to December 2008, and as Managing Director and Chief Investment Officer of Quantitative Investments of Munder Capital Management, an asset management firm, from January 2002 to December 2005.
Hratch Najarian, Director, Portfolio Management of the Sponsor since August 2013 and a listed principal of the Sponsor since October 15, 2013. In these roles, Mr. Najarian’s responsibilities include oversight of the investment management activities of the Sponsor. Mr. Najarian also serves as Director, Portfolio Management of PFA and PSA since August 2013, and is listed as a principal of PFA since January 8, 2014 and a principal and associated person of PSA since January 14, 2014. Mr. Najarian served as Senior Portfolio Manager of PSA from December 2009 through September 2013. He also served as Senior Portfolio Manager of PFA from December 2009 through September 2013, as Portfolio Manager of PFA from May 2007 through November 2009, and as Associate Portfolio Manager of PFA from November 2004 through April 2007.
Jeffrey Ploshnick, Senior Portfolio Manager of the Sponsor since April 12, 2011, a registered associated person and an NFA associate member of the Sponsor since April 12, 2011. In these roles, Mr. Ploshnick’s responsibilities include day-to-day portfolio management of the Currency Funds and certain other series of the Trust. Mr. Ploshnick has been registered as an associated person of PFA since December 5, 2012. Mr. Ploshnick also serves as a Senior Portfolio Manager of PFA since May 2007 and has served as Portfolio Manager from February 2001 to April 2007. In addition, Mr. Ploshnick serves as a Senior Portfolio Manager of PSA since March 2011.
Ryan Dofflemeyer, Portfolio Manager of the Sponsor since January 3, 2011, a registered associated person and an NFA associate member of the Sponsor since October 26, 2010. In these roles, Mr. Dofflemeyer’s responsibilities include day-to-day portfolio management of the VIX Fund, the Managed Futures Fund, the Commodity Index Funds, the Commodity Fund and certain other series of the Trust. Mr. Dofflemeyer has been registered as an associated person of PFA since December 5, 2012. Mr. Dofflemeyer also serves as a Portfolio Manager of PFA since August 2007 and was a Portfolio Analyst between October 2003 and August 2007. In addition, Mr. Dofflemeyer also serves as Portfolio Manager for Horizon BetaPro Funds (investment funds) since
127
Table of Contents
May 2008 and served as a Portfolio Manager of PSA from March 2010 through September 2013. Mr. Dofflemeyer worked as a Research Assistant for the Investment Company Institute (investment funds trade organization) from September 2001 to August 2003.
Lisa Johnson, a listed principal of the Sponsor since November 11, 2008 and a listed principal of PFA since November 26, 2012, and a listed principal of PSA since January 14, 2014. Ms. Johnson’s responsibilities include the review and approval of advertising material of the Sponsor. Ms. Johnson has been employed with PDI since April 2008 as Head of Compliance. Prior to her employment with PDI, Ms. Johnson was the Senior Corporate Compliance Officer for ICMA Retirement Corporation (a financial services company) where she was employed from February 2005 to April 2008. She served as Senior Compliance Officer for Delaware Investments (a financial services firm) from January 2001 to February 2005. Ms. Johnson is FINRA registered and holds Series 7, 24 and 63 licenses. She also possesses a Certified Regulatory and Compliance Professional designation, from the NASD Institute at Wharton.
Victor Frye, a listed principal of the Sponsor since December 2, 2008, a listed principal of PFA since November 26, 2012, and a listed principal of PSA since January 14, 2014. Mr. Frye’s responsibilities include the review and approval of advertising material of the Sponsor. Mr. Frye has been employed as Chief Compliance Officer of PFA since October 2002 and of PSA since December 2004.
Fiduciary and Regulatory Duties of the Sponsor
The general fiduciary duties which would otherwise be imposed on the Sponsor (which would make its operation of the Trust as described herein impracticable due to the strict prohibition imposed by such duties on, for example, conflicts of interest on behalf of a fiduciary in its dealings with its beneficiaries), are replaced by the terms of the Trust Agreement (to which terms all shareholders, by subscribing to the Shares, are deemed to consent).
The Trust Agreement provides that the Sponsor and its affiliates shall have no liability to the Trust or to any shareholder for any loss suffered by the Trust arising out of any action or inaction of the Sponsor or its affiliates or their respective directors, officers, shareholders, partners, members, managers or employees (the “Sponsor Related Parties”), if the Sponsor Related Parties, in good faith, determined that such course of conduct was in the best interests of the Funds and such course of conduct did not constitute gross negligence or willful misconduct by the Sponsor Related Parties. The Trust has agreed to indemnify the Sponsor Related Parties against claims, losses or liabilities based on their conduct relating to the Trust, provided that the conduct resulting in the claims, losses or liabilities for which indemnity is sought did not constitute gross negligence or willful misconduct and was done in good faith and in a manner reasonably believed to be in the best interests of the Funds.
Under Delaware law, a beneficial owner of a statutory trust (such as a shareholder of a Fund) may, under certain circumstances, institute legal action on behalf of himself and all other similarly situated beneficial owners (a “class action”) to recover damages for violations of fiduciary duties, or on behalf of a statutory trust (a “derivative action”) to recover damages from a third party where there has been a failure or refusal to institute proceedings to recover such damages. In addition, beneficial owners may have the right, subject to certain legal requirements, to bring class actions in federal court to enforce their rights under the federal securities laws and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder by the SEC. Beneficial owners who have suffered losses in connection with the purchase or sale of their beneficial interests may be able to recover such losses from the Sponsor where the losses result from a violation by the Sponsor of the anti-fraud provisions of the federal securities laws.
Under certain circumstances, shareholders also have the right to institute a reparations proceeding before the CFTC against the Sponsor (a registered commodity pool operator), an FCM, as well as those of their respective employees who are required to be registered under the CEA, and the rules and regulations promulgated thereunder. Private rights of action are conferred by the CEA. Investors in futures and in commodity pools may, therefore, invoke the protections provided thereunder.
128
Table of Contents
The foregoing summary describing in general terms the remedies available to shareholders under federal law is based on statutes, rules and decisions as of the date of this Prospectus. As this is a rapidly developing and changing area of the law, shareholders who believe that they may have a legal cause of action against any of the foregoing parties should consult their own counsel as to their evaluation of the status of the applicable law at such time.
Ownership or Beneficial Interest in the Funds
As of the date of this Prospectus, the Sponsor owns (1) 14 Shares in each of ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity, ProShares Ultra Euro and ProShares Ultra Yen, (2) two Shares of ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity and ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas, (3) seven Shares of ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas, (4) five Shares in each of ProShares Ultra Australian dollar, ProShares UltraShort Australian dollar and ProShares Short Euro, (5) one Share of ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF and (6) ten Shares of ProShares Managed Futures Strategy. As of the date of this Prospectus, the Sponsor did not own any Shares of ProShares UltraShort Silver. As of the date of this Prospectus, PSA, an affiliate of the Sponsor, owns 100 Shares in ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity. As of the date of this Prospectus, none of the principals of the Sponsor has an ownership or beneficial interest in any Fund.
Although the Sponsor and its trading principals (i.e., those principals that are responsible for or oversee the Funds’ trading decisions) do not currently trade or hold commodity interests that could be held by the Funds for their own accounts as of the date of this Prospectus, the Sponsor and its principals reserve the right to trade commodity interests for their own accounts. Fund investors will not be permitted to inspect the records of such person’s trades or any written policies related to such trading.
Management; Voting by Shareholders
The shareholders of the Funds take no part in the management or control, and have no voice in the Trust’s operations or business.
The Sponsor has the right unilaterally to amend the Trust Agreement as it applies to the Funds provided that the shareholders have the right to vote only if expressly required under Delaware or federal law or rules or regulations of the Exchange, or if submitted to the shareholders by the Sponsor in its sole discretion. No amendment affecting the Trustee shall be binding upon or effective against the Trustee unless consented to by the Trustee in writing.
Recognition of the Trust and the Funds in Certain States
A number of states do not have “statutory trust” statutes such as that under which the Trust has been formed in the State of Delaware. It is possible, although unlikely, that a court in such a state could hold that, due to the absence of any statutory provision to the contrary in such jurisdiction, the shareholders, although entitled under Delaware law to the same limitation on personal liability as stockholders in a private corporation for profit organized under the laws of the State of Delaware, are not so entitled in such state.
Possible Repayment of Distributions Received by Shareholders
The Shares are limited liability investments; investors may not lose more than the amount that they invest plus any profits recognized on their investment. However, shareholders of the Funds could be required, as a matter of bankruptcy law, to return to the estate of a Fund any distribution they received at a time when such Fund was in fact insolvent or in violation of the Trust Agreement.
The Shares of each Fund trade on the Exchange and provide institutional and retail investors with direct access to each Fund. Each Fund’s Shares may be bought and sold on its Exchange like any other exchange-listed security.
129
Table of Contents
Individual certificates will not be issued for the Shares. Instead, global certificates are deposited by the Trust with DTC and registered in the name of Cede & Co., as nominee for DTC. The global certificates evidence all of the Shares outstanding at any time. Under the Trust Agreement, shareholders are limited to (1) participants in DTC such as banks, brokers, dealers and trust companies (“DTC Participants”), (2) those who maintain, either directly or indirectly, a custodial relationship with a DTC Participant (“Indirect Participants”), and (3) those banks, brokers, dealers, trust companies and others who hold interests in the Shares through DTC Participants or Indirect Participants. The Shares are only transferable through the book-entry system of DTC. Shareholders who are not DTC Participants may transfer their Shares through DTC by instructing the DTC Participant holding their Shares (or by instructing the Indirect Participant or other entity through which their Shares are held) to transfer the Shares. Transfers are made in accordance with standard securities industry practice.
The Sponsor will furnish an annual report of the Funds in the manner required by the rules and regulations of the SEC as well as any reports required by the CFTC and the NFA, including, but not limited to, annual audited financial statements of the Funds examined and certified by independent registered public accountants and any other reports required by any other governmental authority that has jurisdiction over the activities of the Funds. Monthly account statements conforming to CFTC and NFA requirements are posted on the Sponsor’s website at www.ProShares.com. Shareholders of record will also be provided with appropriate information to permit them to file U.S. federal and state income tax returns with respect to Shares held. Additional reports may be posted on the Sponsor’s website at the discretion of the Sponsor or as required by regulatory authorities.
The Sponsor will notify shareholders of any change in the fees paid by the Trust or of any material changes to the Funds by filing with the SEC a supplement to this Prospectus and a Form 8-K, as applicable, which will be publicly available at www.sec.gov and at the Sponsor’s website at www.ProShares.com. Any such notification will include a description of shareholders’ voting rights.
130
Table of Contents
The NAV in respect of a Fund means the total assets of that Fund including, but not limited to, all cash and cash equivalents or other debt securities less total liabilities of such Fund, consistently applied under the accrual method of accounting. In particular, the NAV includes any unrealized profit or loss on open Financial Instruments, and any other credit or debit accruing to a Fund but unpaid or not received by a Fund. The NAV per Share of a Fund is computed by dividing the value of the net assets of such Fund (i.e., the value of its total assets less total liabilities) by its total number of Shares outstanding. Expenses and fees are accrued daily and taken into account for purposes of determining the NAV. Each Fund’s NAV is calculated on each day other than a day when the Exchange is closed for regular trading. The Funds compute their NAVs at the times set forth below, or an earlier time as set forth on www.ProShares.com, if necessitated by the Exchange or other exchange material to the valuation or operation of such Fund closing early. Each Fund’s NAV is calculated only once each trading day.
| Fund |
NAV Calculation Time |
|||
| ProShares VIX Mid-Term Futures ETF |
4:15 p.m. (Eastern Time) | |||
| ProShares Managed Futures Strategy |
3:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | |||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Commodity |
2:30 p.m. (Eastern Time) | |||
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Commodity |
||||
| ProShares Ultra Bloomberg Natural Gas |
2:30 p.m. (Eastern Time) | |||
| ProShares UltraShort Bloomberg Natural Gas |
||||
| ProShares UltraShort Silver |
7:00 a.m. (Eastern Time) | |||
| ProShares Ultra Australian Dollar |
4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | |||
| ProShares UltraShort Australian Dollar |
||||
| ProShares Ultra Euro |
4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | |||
| ProShares Short Euro |
||||
| ProShares Ultra Yen |
4:00 p.m. (Eastern Time) | |||
In calculating the NAV of a Fund, the settlement value of the Fund’s non-exchange-traded Financial Instruments is determined by applying the then-current disseminated levels for the applicable benchmark to the terms of such Fund’s non-exchange-traded Financial Instruments. However, in the event that an underlying Reference Asset is not trading due to the operation of daily limits or otherwise, the Sponsor may, in its sole discretion, choose to fair value the index level in order to value the Fund’s non-exchange-traded Financial Instruments for purposes of the NAV calculation. Such fair value prices would generally be determined based on available inputs about the current value of the underlying Reference Assets and would be based on principles that the Sponsor deems fair and equitable so long as such principles are consistent with normal industry standards.
Futures contracts traded on a U.S. exchange are calculated at their then-current market value, which is based upon the settlement price (for the VIX Fund, the Managed Futures Fund and the Commodity Index Funds) or the last traded price before the NAV time (for the Currency Funds), for that particular futures contract traded on the applicable U.S. exchange on the date with respect to which the NAV is being determined. If a futures contract traded on a U.S. exchange could not be liquidated on such day, due to the operation of daily limits or other rules of the exchange upon which that position is traded or otherwise, the Sponsor may, in its sole discretion, choose to determine a fair value price as the basis for determining the market value of such position for such day. Such fair value prices would generally be determined based on available inputs about the current value of the underlying Reference Assets and would be based on principles that the Sponsor deems fair and equitable so long as such principles are consistent with normal industry standards.
131
Table of Contents
The Funds may use a variety of money market instruments to invest excess cash. Short-term debt instruments used in this capacity and expected to be held-to-maturity will be priced for NAV purposes at amortized cost.
Indicative Optimized Portfolio Value (“IOPV”)
The IOPV is an indicator of the value of a Fund’s net assets at the time the IOPV is disseminated. The IOPV is calculated and disseminated every 15 seconds throughout the trading day. The IOPV is generally calculated using the prior day’s closing net assets of a Fund as a base and updating throughout the trading day changes in the value of the Financial Instruments held by a Fund. The IOPV should not be viewed as an actual real time update of the NAV because NAV is calculated only once at the end of each trading day. The IOPV also should not be viewed as a precise value of the Shares. The IOPV for Funds based on the Bloomberg Natural Gas SubindexSM will not update following the determination of the 2:30 p.m. settlement price of the futures contracts underlying that index. The IOPVs for Funds based on the Bloomberg Commodity IndexSM will receive progressively more limited updates during a trading day as the settlement price for each individual component is determined, and such IOPVs will not update after all of the underlying components have determined settlement prices.
The Exchange disseminates the IOPV. In addition, the IOPV is published on the Exchange’s website and is available through on-line information services such as Bloomberg and/or Reuters.
The Trust, or, as the case may be, a Fund, may be dissolved at any time and for any reason by the Sponsor with written notice to the shareholders.
The Sponsor does not expect to make distributions. Depending on a Fund’s performance and an investor’s own tax situation, an investor’s income tax liability for his, her or its allocable share of such Fund’s net ordinary income or loss and capital gain or loss may exceed the capital gains an investor may realize from selling his, her or its Shares of such Fund in a taxable year.
The Sponsor and the Trust, on behalf of itself and on behalf of the Funds, have appointed BBH&Co. as the Administrator of the Funds and BBH&Co. has entered into an administrative agency agreement (the “Administrative Agency Agreement”) with the Trust (for itself and on behalf of the Funds) and the Sponsor in connection therewith. In addition, BBH&Co. serves as Transfer Agent of the Funds pursuant to the Administrative Agency Agreement. A copy of the Administrative Agency Agreement is available for inspection at BBH&Co.’s offices identified above.
The Administrator’s fees are paid on behalf of the Funds by the Sponsor.
Pursuant to the terms of the Administrative Agency Agreement and under the supervision and direction of the Sponsor, BBH&Co. prepares and files certain regulatory filings on behalf of the Funds. BBH&Co. may also perform other services for the Funds pursuant to the Administrative Agency Agreement as mutually agreed to from time to time.
132
Table of Contents
The Administrator and any of its affiliates may from time to time purchase or sell Shares for their own account, as agent for their customers and for accounts over which they exercise investment discretion.
The Sponsor, on behalf of the Funds, is expected to retain the services of one or more additional service providers to assist with certain tax reporting requirements of the Funds and their shareholders.
BBH&Co., a private bank founded in 1818, is not a publicly held company nor is it insured by the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation. BBH&Co. is authorized to conduct a commercial banking business in accordance with the provisions of Article IV of the New York State Banking Law, New York Banking Law §§ 160 – 181, and is subject to regulation, supervision, and examination by the New York State Banking Department. BBH&Co. is also licensed to conduct a commercial banking business by the Commonwealths of Massachusetts and Pennsylvania and is subject to supervision and examination by the banking supervisors of those states.
BBH&Co. serves as the Custodian of the Funds and has entered into a custodian agreement (the “Custodian Agreement”) with the Trust (for itself and on behalf of the Funds) in connection therewith. Pursuant to the terms of the Custodian Agreement, BBH&Co. is responsible for the holding and safekeeping of assets delivered to it by the Funds, and performing various administrative duties in accordance with instructions delivered to BBH&Co. by the Funds. The Custodian’s fees are paid on behalf of the Funds by the Sponsor.
BBH&Co. serves as the Transfer Agent of the Funds for Authorized Participants and has entered into the Administrative Agency Agreement referred to above in connection therewith. Pursuant to the terms of the Administrative Agency Agreement, BBH&Co. is responsible for processing purchase and redemption orders and maintaining records of the ownership of the Funds. The Transfer Agent fees are paid on behalf of the Funds by the Sponsor.
SEI serves as the Distributor of the Funds and assists the Sponsor and the Administrator with functions and duties relating to distribution and marketing, which include the following: taking creation and redemption orders, and consulting with the marketing staff of the Sponsor and its affiliates with respect to compliance matters in connection with marketing efforts.
SEI retains all marketing materials separately for the Funds, at the offices of SEI, One Freedom Valley Drive, Oaks, Pennsylvania 19456; and its telephone number is (610) 676-1000.
The Sponsor pays SEI for performing its duties on behalf of the Funds.
SEI is a wholly owned subsidiary of SEI Investments Company, which is a public company and a global provider of investment processing, fund processing, and investment management business outsourcing solutions.
133
Table of Contents
THE SECURITIES DEPOSITORY; BOOK-ENTRY ONLY SYSTEM; GLOBAL SECURITY
DTC acts as securities depository for the Shares. DTC is a limited purpose trust company organized under the laws of the State of New York, a member of the Federal Reserve System, a “clearing corporation” within the meaning of the New York Uniform Commercial Code, and a “clearing agency” registered pursuant to the provisions of section 17A of the 1934 Act. DTC was created to hold securities of DTC Participants and to facilitate the clearance and settlement of transactions in such securities among the DTC Participants through electronic book-entry changes. This eliminates the need for physical movement of securities certificates. DTC Participants include securities brokers and dealers, banks, trust companies, clearing corporations and certain other organizations, some of whom (and/or their representatives) own DTC. Access to the DTC system is also available to others such as banks, brokers, dealers and trust companies that clear through or maintain a custodial relationship with a DTC Participant, either directly or indirectly. DTC has agreed to administer its book-entry system in accordance with its rules and bylaws and the requirements of law.
Individual certificates will not be issued for the Shares. Instead, global certificates are signed by the Sponsor on behalf of the Funds, registered in the name of Cede & Co., as nominee for DTC, and deposited with the Trust on behalf of DTC. The global certificates evidence all of the Shares of the Funds outstanding at any time. The representations, undertakings and agreements made on the part of the Funds in the global certificates are made and intended for the purpose of binding only the Funds and not the Trustee or the Sponsor individually.
Upon the settlement date of any creation, transfer or redemption of Shares, DTC credits or debits, on its book-entry registration and transfer system, the amount of the Shares so created, transferred or redeemed to the accounts of the appropriate DTC Participants. The Sponsor and the Authorized Participants designate the accounts to be credited and charged in the case of creation or redemption of Shares.
Beneficial ownership of the Shares is limited to DTC Participants, Indirect Participants and persons holding interests through DTC Participants and Indirect Participants. Owners of beneficial interests in the Shares are shown on, and the transfer of ownership is effected only through, records maintained by DTC (with respect to DTC Participants), the records of DTC Participants (with respect to Indirect Participants) and the records of Indirect Participants (with respect to shareholders that are not DTC Participants or Indirect Participants). Shareholders are expected to receive from or through the DTC Participant maintaining the account through which the shareholder has purchased their Shares a written confirmation relating to such purchase.
Shareholders that are not DTC Participants may transfer the Shares through DTC by instructing the DTC Participant or Indirect Participant through which the shareholders hold their Shares to transfer the Shares. Shareholders that are DTC Participants may transfer the Shares by instructing DTC in accordance with the rules of DTC. Transfers are made in accordance with standard securities industry practice.
DTC may decide to discontinue providing its service with respect to Creation Units and/or the Shares of the Funds by giving notice to the Trust and the Sponsor. Under such circumstances, the Sponsor will either find a replacement for DTC to perform its functions at a comparable cost or, if a replacement is unavailable, terminate the Funds.
The rights of the shareholders generally must be exercised by DTC Participants acting on their behalf in accordance with the rules and procedures of DTC. Because the Shares can only be held in book-entry form through DTC and DTC Participants, investors must rely on DTC, DTC Participants and any other financial intermediary through which they hold the Shares to receive the benefits and exercise the rights described in this section. Investors should consult with their broker or financial institution to find out about procedures and requirements for securities held in book-entry form through DTC.
134
Table of Contents
SHARE SPLITS OR REVERSE SPLITS
If the Sponsor believes that the per Share price of a Fund in the secondary market has fallen outside a desirable trading price range, the Sponsor may direct the Trust to declare a split or reverse split in the number of Shares outstanding and, if necessary in the Sponsor’s opinion, to make a corresponding change in the number of Shares of a Fund constituting a Creation Unit.
The Sponsor has not established formal procedures to resolve all potential conflicts of interest. Consequently, investors may be dependent on the good faith of the respective parties subject to such conflicts to resolve them equitably. The Sponsor does not expect that material conflicts of interest will arise in the operation of the Funds, each of which operates independently of the others.
135
Table of Contents
Administrative Agency Agreement
BBH&Co. serves as the Funds’ Administrator pursuant to the terms of the Administrative Agency Agreement among the Trust, on behalf of itself and on behalf of the Funds, the Administrator and the Sponsor. The Administrator performs or supervises the performance of services necessary for the operation and administration of the Funds (other than making investment decisions or providing services provided by other service providers), including the NAV calculations, accounting and other fund administrative services.
BBH&Co. serves as the Funds’ Transfer Agent. Pursuant to the Administrative Agency Agreement among the Trust, on behalf of itself and on behalf of the Funds, the Transfer Agent and the Sponsor, the Transfer Agent serves as the Funds’ transfer agent and agent in connection with certain other activities as provided under the Administrative Agency Agreement. Under the Administrative Agency Agreement, the Transfer Agent’s services include, among other things, assisting the Funds with the issuance and redemption of Creation Units to and from Authorized Participants, recording the issuance of Creation Units and maintaining a record of the total number of Creation Units that are authorized, issued and outstanding based upon data provided to the Transfer Agent by the Funds or the Sponsor.
The Administrative Agency Agreement has an initial term of one year and, after the initial term, will continue in effect for successive one-year periods unless terminated on at least seventy-five (75) days’ prior written notice by any party to the other parties. Notwithstanding the foregoing, any party may terminate the Administrative Agency Agreement at any time upon thirty (30) days’ prior written notice to the other party if either party is adjudged bankrupt or insolvent, or there shall be commenced against such party a case under any applicable bankruptcy, insolvency or other similar law.
In its capacity as Administrator and Transfer Agent, BBH&Co. is both exculpated and indemnified under the Administrative Agency Agreement.
BBH&Co. serves as the Funds’ Custodian. Pursuant to the Custodian Agreement between the Trust, on its own behalf and on behalf of the Funds, and the Custodian, the Custodian serves as custodian of all securities and cash at any time delivered to the Custodian by the Funds during the term of the Custodian Agreement and has authorized the Custodian to hold its securities in its name or the names of its nominees. Pursuant to the terms of the Custodian Agreement, the Custodian may deposit and/or maintain the investment assets of the Funds in a securities depository and may appoint a subcustodian to hold investment assets of the Funds. The Custodian establishes and maintains one or more securities accounts and cash accounts for the Funds pursuant to the Custodian Agreement. The Custodian maintains separate and distinct books and records segregating the assets of the Funds.
The Custodian Agreement had an initial term of one year. After the initial term, the Custodian Agreement continued and will continue in effect for successive one-year periods unless the Trust, on behalf of the Funds, independently, or the Custodian terminates the Custodian Agreement by giving to the other party a notice in writing specifying the date of such termination, which will not be less than seventy-five (75) days after the date of such notice. In the event of the appointment of a successor custodian, the parties agree that the investment assets of the Funds held by the Custodian or any subcustodian shall be delivered to the successor custodian in accordance with reasonable instructions described in the Custodian Agreement. The parties further agree to cooperate in the execution of documents and performance of other actions necessary or desirable in order to facilitate the succession of the new custodian. If no successor custodian is appointed, the Custodian shall in like manner transfer the Funds’ investment assets in accordance with the instructions set forth in the Custodian Agreement. If no instructions are given as of the effective date of termination, the Custodian may, at any time on
136
Table of Contents
or after such termination date and upon ten (10) consecutive calendar days’ written notice to the Fund, either: (1) deliver the investment assets held under the Custodian Agreement to the Fund; or (2) deliver any investment assets held under the Custodian Agreement to a bank or trust company that meets the criteria set forth in the Custodian Agreement, with such delivery being at the risk of the Funds. In the event that investment assets or moneys of the Funds remain in the custody of the Custodian or its subcustodians after the date of termination of the Custodian Agreement due to the failure of the Fund to issue instructions with respect to its disposition or the fact that such disposition could not be accomplished in accordance with such instructions despite diligent efforts of the Custodian, the Custodian shall be entitled to compensation for its services with respect to such investments and moneys during such period as the Custodian or its subcustodians retain possession of such items, and the provisions of the Custody Agreement shall remain in full force and effect until the disposition of the investment assets.
The Custodian is both exculpated and indemnified under the Custodian Agreement.
Pursuant to a distribution agreement (the “Distribution Agreement”) between the Trust and SEI, SEI assists the Sponsor and the Administrator with certain functions and duties relating to distribution and marketing of Shares including reviewing and approving marketing materials.
The Distribution Agreement became effective on the date of the offering of the Shares of the Funds and the Distribution Agreement will continue until December 19, 2014, continuing automatically for successive periods of three years. The Distribution Agreement may be terminated by either party at the end of the initial term or the end of any renewal term on ninety (90) days’ prior written notice. Notwithstanding the foregoing, either party may terminate the Distribution Agreement in the event of a material breach of the agreement by the other party, upon forty-five (45) days’ prior written notice, if such breach is not cured. The Distribution Agreement will automatically terminate in the event of a liquidation of the Trust.
Each of Goldman Sachs and RBC, in its capacity as a registered FCM, serves as the Funds’ clearing broker and as such arranges for the execution and clearing of the Funds’ futures transactions. Pursuant to futures account agreements (each, a “Futures Account Agreement”) between Goldman Sachs and the Funds and RBC and the Funds, the Funds agree to indemnify and hold harmless each of Goldman Sachs and RBC, its directors, officers, employees, agents and affiliates from and against all claims, damages, losses and costs (including reasonable attorneys’ fees) incurred by Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable, in connection with: (1) any failure by the Funds to perform its obligations under the Futures Account Agreement and any exercise by Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable, of its rights and remedies thereunder; (2) any failure by the Funds to comply with the applicable law; (3) any action reasonably taken by Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable, or its affiliates or agents to comply with the applicable law; and (4) any reliance by Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable, on any instruction, notice or communication that Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable reasonably believes to originate from a person authorized to act on behalf of the Funds. Also, the Funds agree to remain liable for and pay to Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable, on demand the amount of any deficiency in the Funds’ Accounts, and the Funds shall reimburse, compensate and indemnify Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable, for any and all costs, losses, penalties, fines, taxes and damages that Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable may incur in collecting such deficiency or otherwise exercising its rights and remedies under the Futures Account Agreement.
The Futures Account Agreement may be terminated at any time by the Funds, or Goldman Sachs or RBC, as applicable, by written notice to the other.
137
Table of Contents
PURCHASES BY EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
The following section sets forth certain consequences under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974, as amended, or ERISA, and the Code, which a fiduciary of an “employee benefit plan” as defined in and subject to ERISA or of a “plan” as defined in and subject to Section 4975 of the Code who has investment discretion should consider before deciding to invest the plan’s assets in a Fund (such “employee benefit plans” and “plans” being referred to herein as “Plans,” and such fiduciaries with investment discretion being referred to herein as “Plan Fiduciaries”). The following summary is not intended to be complete, but only to address certain questions under ERISA and the Code which are likely to be raised by the Plan Fiduciary’s own counsel.
In general, the terms “employee benefit plan” as defined in and subject to Title I of ERISA and “plan” as defined in Section 4975 of the Code together refer to any plan or account of various types which provide retirement benefits or welfare benefits to an individual or to an employer’s employees and their beneficiaries. Such plans and accounts include, but are not limited to, corporate pension and profit-sharing plans, “simplified employee pension plans,” plans for self-employed individuals (including partners), individual retirement accounts described in Section 408 of the Code and medical plans.
Each Plan Fiduciary must give appropriate consideration to the facts and circumstances that are relevant to an investment in a Fund, which may include, among other things, the role that such an investment would play in the Plan’s overall investment portfolio. Each Plan Fiduciary, before deciding to invest in a Fund, must be satisfied that such investment is prudent for the Plan, that the investments of the Plan, including the investment in a Fund, are diversified so as to minimize the risk of large losses and that an investment in a Fund complies with the Plan documents and that the purchase will not result in any non-exempt prohibited transaction under ERISA or Section 4975 of the Code.
EACH PLAN FIDUCIARY CONSIDERING ACQUIRING SHARES ON BEHALF OF A PLAN MUST CONSULT WITH ITS OWN LEGAL AND TAX ADVISERS BEFORE DOING SO. AN INVESTMENT IN A FUND IS SPECULATIVE AND INVOLVES A HIGH DEGREE OF RISK. NONE OF THE FUNDS IS INTENDED AS A COMPLETE INVESTMENT PROGRAM.
ERISA and a regulation issued thereunder by the U.S. Department of Labor contain rules for determining when an investment by a Plan in an equity interest of an entity will result in the underlying assets of such entity being considered to constitute assets of the Plan for purposes of ERISA and Section 4975 of the Code (i.e., “plan assets”). Those rules provide that assets of an entity will not be considered assets of a Plan which purchases an equity interest in the entity if one or more exceptions apply, including (1) an exception applicable if the equity interest purchased is a “publicly offered security” (the “Publicly Offered Security Exception”), and (2) an exception applicable if equity interests purchased by a plan are not significant.
The Publicly Offered Security Exception applies if the equity interest is a security that is (1) “freely transferable,” (2) part of a class of securities that is “widely held” and (3) either (a) part of a class of securities registered under Section 12(b) or 12(g) of the 1934 Act, or (b) sold to the Plan as part of a public offering pursuant to an effective registration statement under the 1933 Act and the class of which such security is a part is registered under the 1934 Act within 120 days (or such later time as may be allowed by the SEC) after the end of the fiscal year of the issuer in which the offering of such security occurred.
The Trust expects that the Publicly Offered Security Exception should apply with respect to the Shares of each Fund.
138
Table of Contents
Among other considerations, Shares generally may not be purchased with the assets of a Plan if the Sponsor, the FCMs or any of their respective affiliates, any of their respective employees or any employees of their respective affiliates: (1) has investment discretion with respect to the investment of such plan assets; (2) has authority or responsibility to give or regularly gives investment advice with respect to such plan assets, for a fee, and pursuant to an agreement or understanding that such advice will serve as a primary basis for investment decisions with respect to such plan assets and that such advice will be based on the particular investment needs of the Plan; or (3) is an employer maintaining or contributing to such Plan. A party that is described in clause (1) or (2) of the preceding sentence would be a fiduciary under ERISA and the Code with respect to the Plan, and unless an exemption applies, any such purchase might result in a “prohibited transaction” under ERISA and the Code.
Except as otherwise set forth, the foregoing statements regarding the consequences under ERISA and the Code of an investment in Shares of the Funds are based on the provisions of the Code and ERISA as currently in effect, and the existing administrative and judicial interpretations thereunder. No assurance can be given that administrative, judicial or legislative changes will not occur that will not make the foregoing statements incorrect or incomplete.
THE PERSON WITH INVESTMENT DISCRETION SHOULD CONSULT WITH HIS OR HER ATTORNEY AND FINANCIAL ADVISERS AS TO THE PROPRIETY OF AN INVESTMENT IN SHARES IN LIGHT OF THE CIRCUMSTANCES OF THE PARTICULAR PLAN AND CURRENT TAX LAW.
139
Table of Contents
Most investors buy and sell Shares in secondary market transactions through brokers. Shares of the Funds trade on the Exchange under the ticker symbols listed in this Prospectus. Shares are bought and sold throughout the trading day like other publicly traded securities. When buying or selling Shares through a broker, most investors incur customary brokerage commissions and charges.
The Funds continuously offer Shares in Creation Units to Authorized Participants. Shares of the Funds are to be offered to Authorized Participants in Creation Units at each Fund’s respective NAV.
Authorized Participants may offer to the public, from time to time, Shares of a Fund from any Creation Units they create. Shares of a Fund offered to the public by Authorized Participants are offered at a per Share market price that varies depending on, among other factors, the trading price of the Shares of each Fund on its Exchange, the NAV per Share and the supply of and demand for the Shares at the time of the offer. Shares initially comprising the same Creation Unit but offered by Authorized Participants to the public at different times may have different offering prices. Additionally, the price at which an Authorized Participant sells a Share may be higher or lower than the price paid by such Authorized Participant in connection with the creation of such Share in a Creation Unit. Authorized Participants do not receive from any Fund, the Sponsor or any of their affiliates, any fee or other compensation in connection with their sale of Shares to the public, although investors are expected to be charged a customary commission by their brokers in connection with the purchase and sale of Shares that varies from investor to investor. Investors are encouraged to review the terms of their brokerage accounts for applicable charges.
As of the date of this Prospectus, ABN AMRO Clearing Chicago LLC, Banca IMI Securities Corp., Barclays Capital Inc., BNP Paribas Securities Corp., Citadel Securities LLC, Credit Suisse Securities (USA) LLC, Deutsche Bank Securities Inc., EWT, LLC, Goldman, Sachs & Co., Goldman Sachs Execution & Clearing, L.P., HRT Financial LLC, Jefferies LLC, J.P. Morgan Securities Inc., Knight Clearing Services LLC, Merrill Lynch Professional Clearing Corp., Mizuho Securities USA Inc., Newedge USA LLC, Nomura Securities International, Inc., RBC Capital Markets, LLC, SG Americas Securities, LLC, Timber Hill LLC, UBS Securities LLC, Virtu Financial BD LLC and Wedbush Morgan Securities, Inc. have each executed an Authorized Participant Agreement and are the only Authorized Participants.
Likelihood of Becoming a Statutory Underwriter
Each Fund issues Shares in Creation Units to Authorized Participants from time to time generally in exchange for cash. Because new Shares can be created and issued on an ongoing basis at any point during the life of each Fund, a “distribution,” as such term is used in the 1933 Act, will be occurring. An Authorized Participant, other broker-dealer firm or its client could be deemed a statutory underwriter, and thus would be subject to the prospectus delivery and liability provisions of the 1933 Act, if it purchased a Creation Unit from each Fund, broke the Creation Unit down into the constituent Shares and sold the Shares to its customers; or if it chose to couple the creation of a supply of new Shares with an active selling effort involving solicitation of secondary market demand for the Shares. A determination of whether one is an underwriter must take into account all the facts and circumstances pertaining to the activities of the broker-dealer or its client in the particular case, and the examples mentioned above should not be considered a complete description of all the activities that would lead to categorization as an underwriter. Authorized Participants, other broker-dealers and other persons are cautioned that some of their activities may result in their being deemed participants in a distribution in a manner which would render them statutory underwriters and subject them to the prospectus delivery and liability provisions of the 1933 Act.
140
Table of Contents
Dealers who are neither Authorized Participants nor “underwriters” but are participating in a distribution (as contrasted to ordinary secondary trading transactions), and thus dealing with Shares that are part of an “unsold allotment” within the meaning of section 4(3)(C) of the 1933 Act, would be unable to take advantage of the prospectus delivery exemption provided by section 4(3) of the 1933 Act.
Retail investors may purchase and sell Shares through traditional brokerage accounts. Investors who purchase Shares through a commission/fee based brokerage account may pay commissions/fees charged by the brokerage account. Investors are encouraged to review the terms of their brokerage accounts for applicable charges.
The offering of Creation Units is being made in compliance with FINRA Rule 2310. Accordingly, the Authorized Participants may not make any sales to any account over which they have discretionary authority without the prior written approval of a purchaser of Shares. In any event, the maximum amount of all items of value, including compensation paid from the offering proceeds and in the form of “trail commissions,” to be paid to FINRA members, including to SEI and PDI, in connection with the offering of the Shares by a Fund will not exceed 10% of gross offering proceeds.
141
Table of Contents
Sidley Austin LLP has advised the Sponsor in connection with the Shares being offered. Sidley Austin LLP also advises the Sponsor with respect to its responsibilities as sponsor of, and with respect to matters relating to, the Trust and the Funds. Sidley Austin LLP has prepared the sections “Material U.S. Federal Income Tax Considerations” with respect to U.S. federal income tax laws and “Purchases By Employee Benefit Plans” with respect to ERISA. Sidley Austin LLP has not represented, nor will it represent, the Trust, the Funds or the shareholders in matters relating to the Trust or the Funds and no other counsel has been engaged to act on their behalf.
Richards, Layton & Finger, P.A. has represented the Trust in connection with the legality of the Shares being offered hereby.
Certain opinions of counsel have been filed with the SEC as exhibits to the Registration Statement of which this Prospectus is a part.
The financial statements and management’s assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting (which is included in Management’s Report of Internal Control over Financial Reporting) incorporated in this Prospectus by reference to ProShares Trust II’s Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014, have been so incorporated in reliance on the report of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS
The following table sets forth information with respect to each person known to own beneficially more than 5% of the outstanding voting common units of beneficial interest of the Managed Futures Fund as of December 31, 2014:
| Title of Class |
Name and Address of |
Amount and Nature of |
Percent of Class | |||
| Common Units of Beneficial Interest | ProShares Morningstar Alternatives Solution ETF 7501 Wisconsin Avenue, Suite 1000E Bethesda, MD 20814 |
234,702 Common Units of Beneficial Interest | 78.2% |
WHERE INVESTORS CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
The Trust has filed a Registration Statement on Form S-1 with the SEC under the 1933 Act. This Prospectus constitutes part of the Registration Statement filed by the Trust for itself and on behalf of each Fund. Additionally, as further discussed under “Incorporation by Reference of Certain Documents,” we have incorporated by reference certain historical information. This Prospectus does not contain all of the information set forth in such Registration Statement, certain portions of which have been omitted pursuant to the rules and regulations of the SEC, including, without limitation, certain exhibits thereto (for example, the form of the Authorized Participant Agreement). The descriptions contained herein of agreements included as exhibits to the Registration Statement are necessarily summaries and may not be complete; the exhibits themselves may be
142
Table of Contents
inspected without charge at the Public Reference Room maintained by the SEC at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, DC 20549, and copies of all or part thereof may be obtained from the SEC upon payment of the prescribed fees. Investors may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains a website that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding registrants that file electronically with the SEC. The address of such site is www.sec.gov.
RECENT FINANCIAL INFORMATION AND ANNUAL REPORTS
You should read the financial statements and the notes to those financial statements in the Trust’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014, along with any amendments thereto, which have been incorporated by reference into this Prospectus. Please refer to the section entitled “Incorporation by Reference of Certain Documents” in this Prospectus. The Sponsor will furnish an annual report of the Funds in the manner required by the rules and regulations of the SEC as well as with those reports required by the CFTC and the NFA, including, but not limited to, annual audited financial statements of the Funds examined and certified by independent registered public accountants and any other reports required by any other governmental authority that has jurisdiction over the activities of the Funds. Monthly account statements conforming to CFTC and NFA requirements, as well as the current annual and quarterly reports and other filings made with the SEC, are posted on the Sponsor’s website at www.ProShares.com. Shareholders of record will also be provided with appropriate information to permit them to file U.S. federal and state income tax returns with respect to Shares held. Additional reports may be posted on the Sponsor’s website at the discretion of the Sponsor or as required by regulatory authorities.
143
Table of Contents
The Trust’s Commitment to Investors
The Sponsor and the Trust are committed to respecting the privacy of personal information investors entrust to the Trust in the course of doing business.
The Information the Trust Collects About Investors
The Sponsor, on behalf of the Trust, collects non-public personal information from various sources. For instance, forms may include names, addresses, and social security numbers. The Funds receive information from transactions in investors’ accounts, including account balances, and from correspondence between investors and the Funds or third parties, such as the Funds’ service providers. The Sponsor, on behalf of the Funds, uses such information provided by investors or their representative to process transactions, to respond to inquiries from investors, to deliver reports, products, and services, and to fulfill legal and regulatory requirements.
How the Trust Handles Investors’ Personal Information
The Sponsor does not disclose any non-public personal information about investors to anyone unless permitted by law or approved by the affected investor. The Sponsor may share information about investors with certain third parties who are not affiliated with the Trust to process or service a transaction that investors have requested or as permitted by law. For example, sharing information with non-affiliated third parties that maintain or service investors’ accounts for the Funds is essential.
The Sponsor may also share information with companies that perform administrative or marketing services for the Funds including research firms. When the Funds enter into such a relationship, such third parties’ use of customer’s information is restricted and they are prohibited from sharing it or using it for any purposes other than those for which they were hired. The Sponsor also requires service providers to maintain physical, electronic and procedural safeguards that comply with federal standards to guard investors’ non-public personal information.
How the Trust Safeguards Investors’ Personal Information
The Sponsor maintains physical, electronic, and procedural safeguards to protect investors’ personal information. Within the Funds, access to personal information is restricted to those employees who require access to that information in order to provide products or services to customers such as processing transactions and handling inquiries. Use of customer information is restricted and customer information is required to be held in strict confidence.
The Sponsor will adhere to the policies and practices described in this notice for both current and former customers of the Funds.
INCORPORATION BY REFERENCE OF CERTAIN DOCUMENTS
The SEC allows the Trust to “incorporate by reference” into this Prospectus certain information that the Trust files with the SEC, meaning it can disclose important information to an investor by referring to those documents on file with the SEC.
The information that the Trust incorporates by reference is an important part of this Prospectus. The Trust incorporates by reference in this Prospectus the documents listed below as filed with the SEC pursuant to Section 13(a), 13(c), 14 or 15(d) of the 1934 Act.
This filing incorporates by reference the following documents:
| • | Our Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2014. |
144
Table of Contents
Any statement contained in a document that is incorporated by reference will be modified or superseded for all purposes to the extent that a statement contained in this Prospectus modifies or is contrary to that previous statement. Any statement so modified or superseded will not be deemed a part of this Prospectus except as so modified or superseded.
The Trust will provide to you a copy of the filings that have been incorporated by reference in this Prospectus upon your request, at no cost. In addition, the Trust will also provide you with information regarding the other series of the Trust upon your request, at no cost. Any request may be made by writing or calling at the following address or telephone number:
ProShares Trust II
c/o ProShare Capital Management LLC
7501 Wisconsin Avenue
Suite 1000
Bethesda, Maryland 20814
Telephone: (240) 497-6400
These documents may also be accessed through the web at www.ProShares.com or as described under “Where Investors Can Find More Information.” The information and other content contained on or linked from the website are not incorporated by reference in this Prospectus and should not be considered a part of this Prospectus.
Annual, quarterly and current reports and other information are on file with the SEC. You may read and copy these materials at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, DC 20549. The public may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC maintains an internet site at www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding the Trust and the Funds.
145
Table of Contents
The Glossary below defines certain of the terms and meanings used throughout this Prospectus. Each term also is defined the first time it is used in this Prospectus.
| 1933 Act |
Securities Act of 1933, as amended | |
| 1934 Act |
Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended | |
| 1940 Act |
Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended | |
| Administrator |
Brown Brothers Harriman & Co., as administrator for the Funds | |
| Advisers Act |
The Investment Advisers Act of 1940 | |
| Authorized Participant |
Those who may purchase (i.e., create) or redeem Creation Units directly from the Funds | |
| BBH&Co. |
Brown Brothers Harriman & Co. | |
| Business Day |
Any day on which the NAV of a specified Fund is determined. | |
| CBOE |
Chicago Board Options Exchange | |
| CBOT |
Chicago Board of Trade | |
| CEA |
Commodity Exchange Act, as amended | |
| CFE |
CBOE Futures Exchange | |
| CFTC |
United States Commodity Futures Trading Commission | |
| CME |
Chicago Mercantile Exchange | |
| Creation Unit |
A block of 25,000 or 50,000 Shares, as applicable, that is created for sale by the Trust to Authorized Participants and/or submitted to the Trust for redemption by an Authorized Participant. | |
| Custodian |
Brown Brothers Harriman & Co., as custodian for the Funds | |
| Distributor |
SEI Investments Distribution Co., as distributor for the Funds | |
| DSTA |
Delaware Statutory Trust Act | |
| DTC |
Depository Trust Company | |
| Exchange |
The exchange on which a Fund is primarily listed and traded (i.e., NYSE Arca) | |
| FCM |
Futures Commission Merchant | |
| Financial Instrument |
Instruments whose value is derived from the value of an underlying asset, rate or benchmark, including futures contracts, swap agreements, forward contracts and other instruments. | |
| FINRA |
Financial Industry Regulatory Authority, Inc. | |
| Fund(s) |
One or more of the series of the Trust offered herein. | |
| Goldman Sachs |
Goldman, Sachs & Co. | |
| ICE |
Intercontinental Exchange | |
| IRS |
United States Internal Revenue Service | |
| LME |
London Metal Exchange | |
146
Table of Contents
| NAV |
Net Asset Value | |
| NFA |
National Futures Association | |
| NSCC |
National Securities Clearing Corporation | |
| NYMEX |
New York Mercantile Exchange | |
| NYSE |
New York Stock Exchange | |
| NYSE Arca |
NYSE Arca Equities, Inc. | |
| Other Fund |
A series of the Trust that is not being offered pursuant to this Prospectus. | |
| PDI |
ProFunds Distributors, Inc. | |
| PTP |
Publicly traded partnership | |
| RBC |
RBC Capital Markets, LLC | |
| Reference Asset |
The underlying asset that is used to determine the value of a Financial Instrument. | |
| S&P |
Standard & Poor’s | |
| SEC |
United States Securities & Exchange Commission | |
| SEI |
SEI Investments Distribution Co. | |
| Shares |
Common units of beneficial interest that represent units of fractional undivided beneficial interest in and ownership of the Funds. | |
| Sponsor |
ProShare Capital Management LLC | |
| Transfer Agent |
Brown Brothers Harriman & Co., as transfer agent for the Funds | |
| Trust |
ProShares Trust II | |
| Trustee |
Wilmington Trust Company | |
| U.S. |
United States of America | |
147
Table of Contents

S-1 (April 2015)
Table of Contents
PART II
Information Not Required in Prospectus
| Item 13. | Other Expenses of Issuance and Distribution. |
The following chart reflects estimated amounts required to prepare and file this Registration Statement and complete the offering of the Shares.
| Approximate Amount |
||||
| Securities and Exchange Commission Registration Fee |
$ | 612,691 | ||
| FINRA Filing Fee |
$ | 0 | ||
| Printing Expenses |
$ | 15,000 | ||
| Fees of Certified Public Accountants |
$ | 5,000 | ||
| Fees of Counsel |
$ | 15,000 | ||
| Miscellaneous Offering Costs |
$ | 0 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
$ | 647,691 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Item 14. | Indemnification of Directors and Officers. |
The amended and restated Trust Agreement of the Trust provides for, and as amended from time-to-time, will provide for, the indemnification of the Sponsor. The Sponsor (including Covered Persons as will be provided under each amended and restated Trust Agreement) shall be indemnified by the Trust (or any Fund separately to the extent the matter in question relates to a single Fund or is otherwise disproportionate), against any losses, judgments, liabilities, expenses and amounts paid in settlement of any claims sustained by it in connection with the defense or disposition of any action, suit or other proceeding, whether civil or criminal, before any court or administrative or legislative body, in which such Sponsor may be or may have been involved as a party or otherwise or with which such Sponsor may be or may have been threatened, while in office or thereafter, by reason of any alleged act or omission as the Sponsor or by reason of his or her being or having been the Sponsor except with respect to any matter as to which such Sponsor shall have been finally adjudicated in any such action, suit or other proceeding not to have acted in good faith in the reasonable belief that such Sponsor’s action was in the best interests of the Trust and except that the Sponsor shall not be indemnified against any liability to the Trust or its Shareholders by reason of willful misconduct or gross negligence of such Sponsor.
| Item 15. | Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities. |
None.
| Item 16. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules. |
The following documents (unless otherwise indicated) are filed herewith and made a part of this Registration Statement:
| (a) | Exhibits. The following exhibits are filed herewith: |
| Exhibit Number |
Description of Document | |
| 4.1 | Amended and Restated Trust Agreement of ProShares Trust II(1) | |
| 4.2 | Form of Authorized Participant Agreement(2) | |
| 5.1 | Opinion of Richards, Layton & Finger, P.A. as to legality(3) | |
| 8.1 | Opinion of Sidley Austin LLP as to income tax matters(3) | |
Table of Contents
| Exhibit Number |
Description of Document | |
| 10.1 | Form of Sponsor Agreement(4) | |
| 10.2 | Form of Administration and Transfer Agency Services Agreement(2) | |
| 10.3 | Form of Custodian Agreement(5) | |
| 10.4 | Form of Distribution Agreement(2) | |
| 10.5 | Form of Futures Account Agreement(2) | |
| 10.6 | Form of Institutional Master Futures Client Account Agreement(6) | |
| 23.1 | Consent of Richards, Layton & Finger, P.A. (included in Exhibit 5.1) | |
| 23.2 | Consent of Sidley Austin LLP (included in Exhibit 8.1) | |
| 23.3 | Consent of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP(7) | |
| (1) | Incorporated by reference to the Trust’s Registration Statement, filed on September 18, 2008. |
| (2) | Incorporated by reference to the Trust’s Registration Statement, filed on November 17, 2008. |
| (3) | Incorporated by reference to the Trust’s Registration Statement, filed on March 13, 2015. |
| (4) | Incorporated by reference to the Trust’s Registration Statement, filed on August 15, 2008. |
| (5) | Incorporated by reference to the Trust’s Registration Statement, filed on October 22, 2008. |
| (6) | Incorporated by reference to the Trust’s Registration Statement filed on September 16, 2011. |
| (7) | Filed herewith. |
| (b) | The following financial statements are included in the Prospectus: |
| None. |
| Item 17. | Undertakings. |
| (a) | The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes: |
| (1) | To file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a post-effective amendment to this registration statement; |
| (i) | To include any prospectus required by section 10(a)(3) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended; |
| (ii) | To reflect in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date of the registration statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change in the information set forth in the registration statement. |
| Notwithstanding the foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume of securities offered (if the total dollar value of securities offered would not exceed that which was registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the estimated maximum offering range may be reflected in the form of prospectus filed with the Commission pursuant to Rule 424(b) if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and price represent no more than a 20 per cent change in the maximum aggregate offering price set forth in the “Calculation of Registration Fee” table in the effective registration statement; |
| (iii) | To include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not previously disclosed in the registration statement or any material change to such information in the registration statement; |
Provided, however, that:
| (A) | Paragraphs (a)(1)(i) and (a)(1)(ii) of this section do not apply if the registration statement is on Form S–8, and the information required to be included in a post- |
Table of Contents
| effective amendment by those paragraphs is contained in reports filed with or furnished to the Commission by the registrant pursuant to section 13 or section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 that are incorporated by reference in the registration statement; and |
| (B) | Paragraphs (a)(1)(i), (a)(1)(ii) and (a)(1)(iii) of this section do not apply if the registration statement is on Form S–3 or Form F–3 and the information required to be included in a post-effective amendment by those paragraphs is contained in reports filed with or furnished to the Commission by the registrant pursuant to section 13 or section 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 that are incorporated by reference in the registration statement, or is contained in a form of prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) that is part of the registration statement. |
| (2) | That, for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the bona fide offering thereof. |
| (3) | To remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the offering. |
| (4) | That each prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a registration statement relating to this offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other than prospectuses filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in this registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such first use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such date of first use. |
| (5) | That, for the purpose of determining liability of the registrant under the Securities Act of 1933 to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities: |
| The undersigned registrant undertakes that in a primary offering of securities of the undersigned registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following communications, the undersigned registrant will be a seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such purchaser: |
| (i) | Any preliminary prospectus or prospectus of the undersigned registrant relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424; |
| (ii) | Any free writing prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned registrant; |
| (iii) | The portion of any other free writing prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the undersigned registrant or their securities provided by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant; and |
| (iv) | Any other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned registrant to the purchaser. |
| (b) | Insofar as indemnification for liabilities under the Securities Act of 1933 may be permitted to directors, officers or persons controlling the registrant pursuant to the provisions described in Item 14 above, or otherwise, the registrant has been informed that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Act and |
Table of Contents
| is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any such action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will, unless in the opinion of their respective counsel the matter has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue. |
| (i) | The undersigned registrant hereby undertakes that: |
| (1) | For purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this registration statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of this registration statement as of the time it was declared effective. |
| (2) | For the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at the time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof. |
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, the Registrant has duly caused this Registration Statement on Form S-1 to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the city of Bethesda, State of Maryland, on the 30th day of March, 2015.
| ProShares Trust II | ||
| By: | /s/ Todd B. Johnson | |
| Name: | Todd B. Johnson | |
| Title: | Principal Executive Officer | |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this Registration Statement on Form S-1 has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the date indicated.
| /s/ Todd B. Johnson Name: Todd B. Johnson |
Principal Executive Officer | March 30, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Edward Karpowicz Name: Edward Karpowicz |
Principal Financial Officer Principal Accounting Officer | March 30, 2015 | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this Registration Statement on Form S-1 has been signed by the following persons on behalf of the Sponsor in the capacities and on the date indicated.
| /s/ Louis M. Mayberg* Name: Louis M. Mayberg |
Member of the Sponsor (Director) |
March 30, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Michael L. Sapir* Name: Michael L. Sapir |
Member of the Sponsor (Director) |
March 30, 2015 | ||
| * | Signed by Amy R. Doberman pursuant to powers of attorney date July 18, 2012 and March 13, 2015. |
