Attached files
Use these links to rapidly review the document
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PART IV
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| (Mark One) | ||
ý |
ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014 |
||
OR |
||
o |
TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
|
For the transition period from to |
||
Commission File Number: 001-35890
OVASCIENCE, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
45-1472564 (I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
|
215 First Street, Suite 240 Cambridge, Massachusetts (Address of Principal Executive Offices) |
02142 (Zip Code) |
Registrant's telephone number, including area code: (617) 500-2802
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class | Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered | |
|---|---|---|
| Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share | The NASDAQ Stock Market LLC |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act. Yes o No ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports) and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ý No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein and will not be contained, to the best of registrant's knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ý
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of "large accelerated filer," "accelerated filer" and "smaller reporting company" in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer o | Accelerated filer ý | Non-accelerated filer o (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Smaller reporting company o |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes o No ý
Aggregate market value of voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of June 30, 2014 (the last day of the registrant's second fiscal quarter of 2014) was: $140.9 million.
As of February 28, 2015, there were 26,955,670 shares of the registrant's Common Stock, par value $0.001 per share, outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the information required by Part III of Form 10-K will appear in the registrant's definitive proxy statement on Schedule 14A for the 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders and are hereby incorporated by reference into this report.
2
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K and the information incorporated by reference in this Annual Report contain forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or Securities Act, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, or Exchange Act, regarding our strategy, future, operations, future financial position, future revenues, projected costs, prospects, plans and objectives of management. You can identify these forward-looking statements by their use of words such as "anticipate," "believe," "estimate," "expect," "intend," "may," "plan," "project," "target," "potential," "shall," "will," "would," "could," "should," "continue," and similar expressions. You also can identify them by the fact that they do not relate strictly to historical or current facts. There are a number of important risks and uncertainties that could cause our actual results to differ materially from those indicated by forward-looking statements. For a description of these risks and uncertainties, please refer to the section entitled "Risk Factors" in this Annual Report and any other risk factors set forth in any information incorporated by reference in this Annual Report. While we may elect to update forward-looking statements wherever they appear in this Annual Report or in the documents incorporated by reference in this Annual Report, we do not assume, and specifically disclaim, any obligation to do so, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise.
3
Overview
OvaScience is a global fertility company focused on the discovery, development, and commercialization of new fertility treatments. The current standard of treatment for infertility is in vitro fertilization, or IVF, but according to certain studies, the success rate of IVF also decreases with age and fails approximately 70% of the time. The discovery of Egg precursor, or EggPCSM cells countered a long-held medical belief that women are born with a set number of eggs, thereby enabling new fertility treatment options. Our patented technology is based on these newly discovered EggPC cells and represents a new fertility treatment option.
These EggPC cells are immature egg cells found in the protective outer layer of a woman's own ovaries. These immature egg cells have the ability to grow into fresh, young healthy eggs. Our portfolio of fertility treatment options uses our patented technology including proprietary methods to identify and isolate EggPC cells from a patient's own ovarian tissue. By applying our EggPC technology platform in unique ways, we are developing and commercializing new fertility treatment options that are designed to improve egg health and revolutionize IVF.
More women around the world are waiting to start families and in need of new fertility treatment options. Fertility decreases with age. The main cause of age related infertility is poor egg health, which is linked to a reduction in the number of functioning mitochondria. Other causes of poor egg health relating to mitochondrial deficiency include Type 2 diabetes. Accordingly, women throughout the world are increasingly seeking new treatment options for infertility.
Our first treatment, the AUGMENTSM treatment, has been launched in select IVF clinics outside of the United States, and we anticipate that we will expand into new international regions in 2015. The AUGMENT treatment is not available in the United States. This treatment is specifically designed to improve egg health by supplementing a mitochondrial deficiency which may in turn offer the potential for enhanced IVF. With the AUGMENT treatment, energy-producing mitochondria from a patient's own EggPC cells are added to the patient's mature eggs during the IVF process to supplement the existing mitochondria. We expect 1,000 AUGMENT treatment cycles will be in process by the end of 2015. We have set this target to ensure that we are building a high quality and scalable operating process to support our future fertility treatment portfolio.
The OvaPrimeSM treatment is a potential fertility treatment that could enable a woman to increase her egg reserve. Approximately 25% of women who start an IVF cycle fail to produce a sufficient number of eggs (or the eggs are too immature). The OvaPrime treatment is designed to replenish a woman's egg reserve by transferring a patient's EggPC cells from the protective ovarian lining back into the patient's own ovaries where they may mature into fertilizable eggs during the IVF process. We reported large-animal proof-of-concept studies in 2014 and plan to optimize the process and introduce the OvaPrime treatment to patients in at least one international region outside of the United States by the end of 2015.
The OvaTureSM treatment is a potential next-generation IVF that could help a woman produce healthy, young, fertilizable eggs without the need for hormone injections. The OvaTure treatment seeks to mature a woman's own EggPC cells into eggs outside her body. This potential treatment may be an option for women with compromised eggs, who are unable to make eggs, or who may be unwilling or unable to undergo hormone hyperstimulation, such as women diagnosed with cancer. We established human preclinical proof-of-concept in 2014, and we plan to optimize the process and define the development pathway for the OvaTure treatment in 2015.
4
We believe our EggPC technology has the potential to make significant advances in the field of fertility because it is designed to address poor egg health and embryo quality due to age and other causes. We believe our EggPC technology could improve IVF by:
Increasing live birth rates and reducing the number of IVF cycles. By improving egg health, we believe we may increase the percentage of live births and reduce the number of IVF cycles required.
Reducing the incidence of multiple births. By generating higher quality eggs, we believe our EggPC technology may allow for the transfer of fewer embryos per IVF cycle and, as a result, lower the incidence of multiple births and the associated complications.
Lowering the overall cost of the IVF process. If we reduce the number of IVF cycles required for a live birth and the incidence of multiple births, we believe our fertility treatment options may also lower the overall costs associated with the IVF process.
Replenishing the ovary for women who make too few, or no, eggs. Our OvaPrime treatment is designed to replenish a woman's egg reserve by transferring a patient's EggPC cells from the protective ovarian lining back into the patient's own ovaries where they may mature into fertilizable eggs during the IVF process.
Reducing the need for hormonal hyperstimulation. We are designing our OvaTure treatment to mature EggPC cells into fertilizable eggs in vitro, or outside the body. If successful, the OvaTure treatment could reduce, or possibly eliminate, the need for hormonal hyperstimulation for the maturation of multiple oocytes prior to egg retrieval in the IVF process.
Preventing inherited diseases. OvaXonSM is a joint venture with Intrexon Corporation, or Intrexon, which is focused on developing new applications to prevent the transmission of inherited diseases by gene correcting EggPC cells for applications in human and animal health.
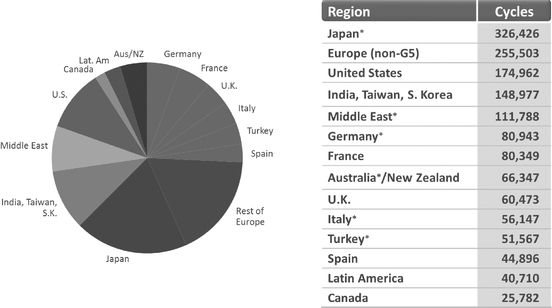
Global Fertility Market
In 2013, the European Society for Human Reproduction (ESHRE), the mission of which is to promote the understanding of reproductive biology and medicine, reported that the worldwide prevalence of infertility among women aged 20 to 44 was approximately 9%. There are 1.5 million IVF cycles performed each year globally, and the number of women seeking treatment for infertility is growing rapidly in regions like Japan, the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Latin America (Figure 1). ESHRE estimates that 1 in 6 couples worldwide experience some form of infertility. Female infertility
5
contributes to 45-75% of all cases. According to a 2014 report from Allied Market Research, the global IVF market in 2012 was valued at $9.3 billion, and projected to grow to $21.6 billion by 2020.
|
||
| Figure 1. Global fertility market | ||
* Donor egg restrictions in these regions Middle East includes: Bahrain, Egypt, Jordan, Lebanon, Libya, Saudi Arabia, Syria, Tunisia, UAE, Israel |
||
|
||
IVF Treatment and Success
IVF is one of the most common procedures in use today to address infertility.
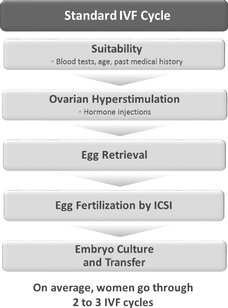
Figure 2. IVF cycle
6
An IVF procedure (Figure 2) typically begins with hyperstimulation of the woman's ovaries by a combination of fertility hormones. Then one or more eggs are taken from the woman's ovarian follicles and fertilized in vitro with either standard insemination, or a technique called intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), in which a single sperm is injected by needle into the egg. If the egg is healthy and has enough energy, it will start to divide, and the resulting embryo can be transferred into the woman's uterus 3-5 days after ICSI. These steps typically occur over several months.
Fertility decreases with age because of a decline in both egg health and embryo quality. A key factor for egg health and embryo quality is the energy level in the egg. Figure 3 demonstrates that IVF success declines with age if a woman is using her own egg. The IVF procedure also may be performed using eggs donated from another woman (donor egg). When a woman chooses to use a younger woman's donor egg, studies show that success rates are similar to a younger woman's.
Despite relatively low success rates, risks and other shortcomings, the use of IVF treatments has become increasingly common, especially for women faced with declining fertility due to their age.
It is estimated that the international markets account for 90% of global IVF. Examples of other countries in which a large number of IVF cycles are performed include Japan and Australia. In addition, countries like Brazil, Latin America, Russia, Turkey and UAE are estimated to be growing at a rate of 30-40%. In many markets globally, IVF is paid for out-of-pocket, particularly in high growth areas outside the European Union and the United States. Many third party payors, including national health services or government funded insurance programs, as well as private payors, place significant restrictions on coverage and reimbursement for IVF and other assisted reproductive technology, or ART, procedures. These restrictions include limits on the types of procedures covered, limits on the number of procedures covered and overall annual or lifetime dollar limits on reimbursement for IVF and other ART procedures. Our preliminary market research indicates that this is primarily due to the fact that many women seeking IVF treatments are of advanced maternal age and are concerned that fertility and IVF success rates will continue to decline over time. As a result, women and couples will frequently pay out of pocket for fertility treatments, such as IVF, rather than avail themselves of other step-based approaches to fertility treatment, such as oral fertility drugs to stimulate ovulation or intrauterine insemination procedures ("IUI"), that may be required by insurance programs.
As shown in the table below, according to a 2010 CDC report, IVF pregnancy success rates for women over age 35 remain relatively flat, regardless of the woman's age, when using donor eggs.
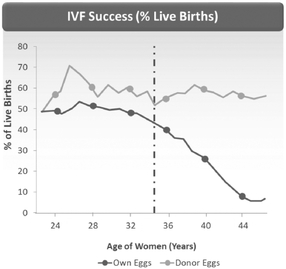
Figure 3. IVF success rates
7
The Role of Mitochondria in Egg Health
Fertility decreases with age, and the energy levels in the egg are believed to play a major role in this decline (Figure 3). After fertilization, the early stage embryo requires energy for cell division. Inadequate energy results in a failure of the newly formed embryo to develop. We believe that the energy level in a woman's eggs may be supplemented, and the success of embryo development improved, by the injection of mitochondria from the woman's own EggPC cells into her egg at the time of fertilization.
Studies published in peer reviewed medical journals, including Human Cell (2004), Electronic Journal of Biology (2005), Reproduction Research (2006) and Reproductive Biomedicine (2011), provided additional evidence of the effects of mitochondria on egg health. In these studies, which involved a number of species, including bovine, porcine, rabbit and murine, third-party scientists demonstrated that the addition of mitochondria to eggs with mitochondrial deficiencies increased cellular energy levels, egg health and the likelihood of fertilization and healthy live births.
In humans, clinical case reports published in the peer-reviewed medical journals Molecular Human Reproduction (1998) and Human Reproduction (2001), researchers transferred cytoplasm from the eggs of younger women donors into the eggs of older women who failed multiple IVF cycles. The cytoplasm is the liquid portion of a human cell that surrounds the nucleus and contains the egg's mitochondria. Each of these reports showed increased rates of fertilization, embryo development, implantation and pregnancy for the older women whose eggs were transfused. In one of these published reports, approximately 30 women who had previously failed two to five IVF cycles, achieved 13 pregnancies and delivered 16 healthy offspring. Additional published reports showed similar success rates ranging from 25%-44% for women who had previously failed multiple cycles and had not achieved a pregnancy.
These clinical case reports served as the basis for the scientific hypothesis that the addition of healthy donor mitochondria might be used to improve the quality of eggs with mitochondrial deficiencies. However, following publication of these initial clinical reports, many scientists and clinicians questioned the long-term safety of the use of third party donor mitochondria in humans because mitochondria contain DNA. Mitochondria produce energy in all cells of the body. Unlike nuclear DNA, contained in the nucleus, which is inherited from two different people, half from the biological mother and half from the biological father, mitochondrial DNA is inherited solely from the mother. As a result, while the process appeared to be safe with respect to the fertilized egg and the patient, scientists and clinicians questioned whether the presence of mitochondria, and therefore mitochondrial DNA, from two different women might adversely impact a child's health later in life. In response to these concerns, the United States Food and Drug Administration, or FDA, stated that the use of cells in therapy involving the transfer of third party genetic materials, including mitochondrial DNA, requires submission of an Investigational New Drug application, or IND.
The approach we are using with the AUGMENT treatment builds on these reports but uses a woman's own mitochondria from her own EggPC cells to improve her fertility instead of third-party donor mitochondria. While all cells contain mitochondria, we believe the mitochondria from cells involved in reproduction, known as germline cells, as opposed to other cells in the body, known as somatic cells, are the ideal source of mitochondria for transfer to improve egg health. This is because somatic cells are exposed to environmental toxins and cell waste products that may cause mutations or deletions in mitochondrial DNA that can be passed on during cell division. These mutations and deletions can decrease the quality of the mitochondria and the ability to produce energy. In contrast, the mitochondrial DNA from germline cells contain minimal mutations and deletions. Because the mitochondria within an egg are the template for all subsequent cell reproduction in the offspring, we believe that it is necessary to use high-quality mitochondria to improve egg health.
Based on the above reports, the approach we are using with the AUGMENT treatment is to use germline mitochondria from the patient's own EggPC cells to improve the quality of the patient's eggs.
8
By using mitochondria from the woman's own EggPC cells, instead of from a third party donor, the AUGMENT treatment does not involve the transfer of third-party genetic material.
The Discovery of Egg Precursor Cells
In 2004, one of our scientific founders, Jonathan Tilly, Ph.D. (who at that point in time was the co-founder and Director of the Vincent Center for Reproductive Biology at Harvard Medical School and the Massachusetts General Hospital, or MGH and is currently the Chair of Northeastern Department of Biology), discovered the existence of EggPC cells within the ovaries of adult mice. Subsequent research by Dr. Tilly demonstrated that these EggPC cells also exist in human ovaries and have the potential to mature into eggs and, therefore, to replenish a woman's egg supply. This research demonstrated that these EggPC cells might provide a source of fresh cellular components, such as mitochondria, that could potentially be used to enhance the health of existing eggs.
Dr. Tilly discovered the existence of mouse EggPC cell by staining the outer cell layer of the ovary using an antibody that binds specifically to a protein found on EggPC cells called mouse VASA homologue. Following publication of this discovery in Nature Medicine in 2004, Dr. Tilly performed additional research, beginning in 2005, which demonstrated the existence of human EggPC cells in adult human ovaries. In this research, Dr. Tilly replicated the results obtained with mouse tissue using human ovarian tissue. Dr. Tilly was able to isolate precursor cells in the ovaries of reproductive age women using an antibody that binds to the human VASA analogue protein, which is found on human EggPC cells. Dr. Tilly also conducted an experiment in which human EggPC cells were isolated in vitro and then grafted into female mouse hosts and matured in vivo into eggs that exhibited a genetic signature indicating the eggs could be fertilized. Dr. Tilly's research findings with respect to human EggPC cells were published in the March 2012 issue of Nature Medicine. These findings have been corroborated by multiple independent laboratories.
In 2014, we conducted additional preclinical proof-of-concept studies for the OvaPrime treatment that demonstrated the ability to mature an EggPC cell into a mature egg in the ovary (in vivo), and we achieved human preclinical proof-of-concept with the OvaTure treatment by demonstrating that human EggPC cells can be matured into eggs outside of the body.
We hold an exclusive license from MGH to multiple issued patents as well as various patent applications directed to methods of identifying and isolating EggPC cells, compositions comprising EggPC cells and methods of using EggPC cells to treat infertility and related disorders.
The AUGMENT Treatment
We have launched the AUGMENT treatment in select international IVF clinics outside of the United States and anticipate that we will continue to introduce the AUGMENT treatment into new international regions in 2015. The AUGMENT treatment is not available in the United States. We expect 1,000 AUGMENT treatment cycles will be in process by the end of 2015. The AUGMENT treatment cycle begins upon our receipt of the patient's tissue. We expect to receive payment before processing the patient's tissue and defer revenue until we deliver the mitochondria to the clinic. Based on our experiences to date, the period from receipt of the patient's tissue to when we expect to record revenue is expected to range between 30 and 120 days, the typical timeframe required to perform an IVF cycle. We do not expect to have significant AUGMENT revenue or deferred revenue until the second half of 2015, and we expect that a majority of this revenue and deferred revenue will be recorded in the fourth quarter.
We continue to target major international regions that combine elements of the following key criteria:
- •
- Key opinion leaders
9
- •
- High volume IVF clinics
- •
- High quality IVF labs
- •
- Out-of-pocket pay and high average cost per cycle
- •
- Donor egg restrictions
As part of the AUGMENT treatment, a woman's eggs may be revitalized by injecting mitochondria from her own EggPC cells into her egg during IVF. This has the potential to improve egg health. Improved egg health may offer the potential for enhanced IVF.
The AUGMENT treatment complements the existing standard of practice for an IVF cycle. Prior to hormone hyperstimulation, a small ovarian tissue biopsy is taken by the patient's doctor. Our proprietary process identifies and isolates the patient's own EggPC cells, and then the patient's own mitochondria from these EggPC cells are isolated. The patient's own mitochondria are then injected into her egg at the time of intracytoplasmic sperm injection, or ICSI.
The development of ART has a long history of innovation based on techniques and tools developed around the world. In fact, all of the major innovations in fertility treatment have been developed in countries outside of the United States, including IVF and ICSI, and more recently, time-lapse imaging, oocyte vitrification and in vitro maturation of oocytes. We believe that this is a main reason why the IVF market is predominantly located outside of the United States and why 90% of the 1.5 million annual IVF cycles are performed outside of the United States. Given the market size, as well as the innovative history and acceptance of new fertility methods and technologies internationally, we have consistently maintained a strategy to make our fertility treatments available to patients worldwide. We launched the AUGMENT treatment through our AUGMENT Centers of Excellence, or ACE, access program by partnering with select international IVF clinics and we are preparing to introduce a second fertility treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, in at least one international region, using this approach by the end of 2015. Our plans to continue and expand the launch of the AUGMENT treatment outside of the United States depend upon the treatment meeting the requirements of a class of products or a type of treatment exempt from pre-market review and approval in such regions. If applicable regulatory bodies disagree with our determination that the treatment meets these requirements, we may no longer make the AUGMENT treatment available in that region or suffer significant delay or expense in seeking necessary approvals. In September 2013, we received an "untitled" letter from the FDA advising us to file an IND application for the AUGMENT treatment. Following the receipt of the FDA letter, we chose to suspend the availability of the AUGMENT treatment in the United States.
AUGMENT Treatment Steps
We designed the AUGMENT treatment to use mitochondria from a woman's own EggPC cells in IVF procedures to improve the energy and health of the woman's eggs. The following is a summary of the process that we are using for our ACE program to prepare the patient's own mitochondria for injection into one of her own mature eggs during IVF:
- •
- Obtain Ovarian Tissue: Ovarian surface tissue is
obtained by the IVF clinic prior to the AUGMENT treatment.
- •
- Identify and Isolate EggPC Cells: We receive the ovarian tissue and perform all AUGMENT related proprietary procedures needed to isolate the EggPC cells. Ovarian tissue is washed, digested with enzymes, and mechanically dissociated to form a solution containing single cells. EggPC cells will be separated from the other cells in the single cell solution by a process known as fluorescence activated cell sorting, or FACS. EggPC cells can then be processed for isolation
10
- •
- Prepare Mitochondria from EggPC Cells: We perform all
AUGMENT related proprietary procedures needed to isolate the mitochondria from EggPC cells. EggPC cells will be disrupted mechanically and mitochondria isolated by differential centrifugation.
- •
- Inject EggPC Cell Mitochondria into Egg: An ACE clinic embryologist, trained by OvaScience, receives the preparation of mitochondria and injects it into the egg, in a single injection alongside the sperm, during the ICSI (intracytoplasmic injection) step of the IVF process.
of mitochondria (described below) or frozen and stored in vials until the day of egg fertilization in the IVF process.
Each of the steps described above follows routine clinical laboratory processes and procedures, and none of these steps requires new methods, equipment or technologies to execute. Specifically, the process of isolating the EggPC cells is performed using commercially available separation techniques. However, we have developed a proprietary monoclonal antibody to identify these cells, as the commercially available antibodies have been shown to be far less than optimal. The proprietary antibody has enabled us to establish a reliable and consistent method to readily identify and isolate the EggPC cells. Because the EggPC technology serves as the basis for all of our fertility treatments, including those on the market and in development, our proprietary monoclonal antibody and proprietary process by which EggPC cells are identified and isolated, together with a number of issued and pending patents, provides a strong intellectual property foundation.
We have established cGTP-compliant facilities and currently perform the steps in the process ourselves in our laboratories either within or contiguous to the IVF clinics in which the AUGMENT treatment is offered.
Additional Fertility Options under Development
We have additional fertility treatments under development, all based on the same EggPC technology as the AUGMENT treatment. Collectively, it is our goal to offer multiple options so physicians can help patients select the optimal treatment, which could include new solutions for age-related egg health issues, diminished ovarian reserve, premature ovarian failure, polycystic ovary syndrome, or other conditions affecting fertility.
The OvaPrime Treatment
The OvaPrime treatment is a potential new fertility treatment designed to replenish a woman's ovary by increasing her egg reserve using her own EggPC cells. Approximately 25% of women who start an IVF cycle fail to produce a sufficient number of eggs (or the eggs are too immature). Similar to the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment may be integrated into the IVF cycle starting with a small tissue biopsy of the outer layer of the ovary, where the EggPC cells reside. Our proprietary process aims to isolate a patient's own EggPC cells, which would then be delivered back into her own ovaries, where we believe they can mature into fertilizable eggs during the IVF process. We plan to optimize this process and introduce the OvaPrime treatment to patients in at least one international region outside of the United States by the end of 2015.
The OvaTure Treatment
The OvaTure treatment is a potential fertility treatment that seeks to create mature fertilizable eggs in vitro from a woman's own EggPC cells without the need for hormone hyperstimulation. The OvaTure treatment may provide a new option for women with compromised eggs who are unable to make eggs or who may be unwilling or unable to undergo hormone hyperstimulation, such as women diagnosed with cancer. To accelerate development, in December 2013, we entered into a collaboration agreement with Intrexon Corporation to access their industrialized synthetic biology platform. The
11
collaboration provides that Intrexon will deliver laboratory and animal data for the OvaTure treatment. We own exclusive human commercial rights for the OvaTure treatment in humans.
Research and Development Spending
During the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 we spent approximately $21.8 million, $15.8 million and $6.3 million, respectively, on our research and development activities.
Manufacturing
We have established cGTP-compliant facilities and currently perform the steps in the process ourselves in our laboratories either within or contiguous to the international IVF clinics in which the AUGMENT treatment is offered.
In addition, we have contracted with global third-party suppliers to perform the identification and isolation of EggPC cells and the preparation of mitochondria steps in the AUGMENT process in case in the future we decide to do offsite manufacturing. Our supplier has significant experience in tissue and cell therapy manufacturing. In the future, we may use our existing global cGTP-compliant manufacturer, contract with in-country manufacturers or continue to manufacture on-site in clinics using our own equipment and our own employees. In the future, we may contract with an additional global supplier and may build our own cGTP-compliant facility to carry out these steps in the AUGMENT process and certain steps in our potential fertility treatments. In some regions outside of the United States, we may contract with third parties, through partnerships, out-licenses or other arrangements, to process and manufacture our potential fertility treatments.
Marketing and Sales
We are in the process of expanding our global sales and marketing team, which is initially focused on supporting the international commercial launch of the AUGMENT treatment. The global IVF market, where we have begun to introduce the AUGMENT treatment, is concentrated and we believe would not require a large sales and marketing team to readily target these regions. We anticipate recruiting additional employees to support our international commercial efforts as we continue to increase the availability of the AUGMENT treatment and plan the introduction of the OvaPrime treatment in at least one international region outside of the United States by the end of 2015. We expect to offer the OvaPrime treatment, when available, to ACE clinics that also offer the AUGMENT treatment, and therefore expect to leverage the same sales and marketing infrastructure for both treatments.
UK Headquarters and Foreign Subsidiaries
We are establishing international headquarters in the United Kingdom to coordinate our international commercial efforts. We have also established, or are in the process of establishing, subsidiaries in certain key regions where we will offer our treatments. These subsidiaries are part of an international legal entity structure through which we plan to (and have, in some cases) license the ex-US commercial rights to the AUGMENT treatment, as well as the OvaPrime treatment, OvaTure treatment and any other potential future products or treatments. This arrangement would allow any potential value enhancement and future profits for the assets to be shared between us and the subsidiaries.
Intellectual Property
We believe we have a strong and growing intellectual property portfolio. We aggressively strive to protect the proprietary technology that we believe is important to our business, including seeking and maintaining patents intended to cover our treatments and compositions, their methods of use and
12
processes for their manufacture, as well as any other inventions that are commercially important to the development of our business. We seek to obtain domestic and international patent protection, and endeavor to promptly file patent applications for new commercially valuable inventions. We also rely on trade secrets to protect aspects of our business that are not amenable to, or that we do not consider appropriate for, patent protection.
Our success will depend on our ability to obtain and maintain patent and other proprietary protection for commercially important technology, inventions and know-how related to our business, defend and enforce our patents, preserve the confidentiality of our trade secrets and operate without infringing the valid and enforceable patents and proprietary rights of third parties. We will also rely on continuing technological innovation and in-licensing opportunities to develop and maintain our proprietary position.
Patents and Patent Applications
We have exclusively licensed a portfolio of patent applications owned or co-owned by The General Hospital Corporation, the corporate entity of MGH, pursuant to an agreement that is summarized below. As of March 2, 2015, we held an exclusive license under this agreement to four issued U.S. patents owned by MGH, four pending U.S. non-provisional patent applications owned by MGH, three patents issued by patent and trademark offices outside of the U.S. which are owned by MGH, sixty applications pending with patent and trademark offices outside of the U.S. which are owned by MGH, two pending U.S. non-provisional application co-owned by MGH and The President and Fellows of Harvard College, or Harvard, and sixteen applications pending in patent and trademark offices outside of the U.S. which are co-owned by MGH and Harvard.
One family of patents and applications that we have licensed from MGH is directed to compositions comprising, and methods of isolating, female germline stem cells, and various uses for such female germline stem cells, including methods for IVF, methods for egg production, methods to treat infertility and methods to restore ovarian function. This family includes two issued U.S. patents, both of which will expire in May 2025, and which include claims directed to the composition and processing methods for obtaining isolated non-embryonic stem cells that express the protein markers characteristic of female germline stem cells. We believe that these patents provide protection for therapeutic compositions comprising EggPC cells, which are referred to in the patents as female germline stem cells, as well as elements of the manufacturing process for obtaining such therapeutic compositions.
A second family of patent applications that we have licensed from MGH is directed to methods and compositions for producing female germline cells from stem cells derived from either bone marrow or peripheral blood. This family includes two pending U.S. non-provisional applications and one Canadian application, which, if issued as patent(s), also would expire in May 2025. We believe that patents issuing from this family may provide protection for an alternative method of obtaining EggPC cells.
A third family of patent applications that we have licensed from MGH is directed to methods and compositions for autologous germline mitochondrial energy transfer. This family includes two issued U.S. patents, one pending U.S. non-provisional patent application, one issued patent in each of Australia, Mongolia and Singapore, and an additional fifty-six counterpart applications that are pending with patent and trademark offices outside of the U.S. The issued patents, and any patents claiming priority to the underlying provisional application, generally will expire in April 2032. We believe that these patents, and any patents issuing from this family, provide protection for the AUGMENT treatment and several important aspects thereof.
13
A fourth family of patent applications that we have licensed from MGH and Harvard is directed to methods and compositions for enhancing the bioenergetic status in female germline cells. This family includes two pending U.S. non-provisional patent application, and sixteen counterpart applications that are pending with patent and trademark offices outside of the U.S. Any patents claiming priority to the underlying provisional application would expire in April 2032. We believe that patents issuing from this family may provide protection for aspects of the AUGMENT procedure, as well as culture media that we may develop in the future.
In addition to the patent portfolio that we have exclusively licensed from MGH, we have one issued U.S. patent and one pending U.S. non-provisional patent application, with all issued patents expiring in June 2026. We believe that patents issuing from this family may provide protection for an alternative method of producing healthy eggs.
Trade Secrets
In addition to patents, we expect to rely on trade secrets and know-how to develop and maintain our competitive positions. For example, significant aspects of the AUGMENT treatment are based on unpatented trade secrets and know-how. Trade secrets and know-how can be difficult to protect. We seek to protect our proprietary technology and processes, in part, by confidentiality agreements with our employees, consultants, scientific advisors and contractors. We also seek to preserve the integrity and confidentiality of our data and trade secrets by maintaining physical security of our premises and physical and electronic security of our information technology systems. While we have confidence in these individuals, organizations and systems, agreements or security measures may be breached and we may not have adequate remedies for any breach. In addition, our trade secrets and know-how may otherwise become known or may be independently discovered by competitors. To the extent that our consultants, contractors or collaborators use intellectual property owned by others in their work for us, disputes may arise as to the rights in related or resulting know-how and inventions.
Exclusive License Agreement with Massachusetts General Hospital
In June 2011, we entered into an exclusive license agreement with MGH under which we acquired an exclusive, worldwide license to specified patent rights owned by MGH and a non-exclusive license under specified know-how disclosed to us under the agreement by MGH which relates to the licensed patent rights. In September 2011, we amended this agreement to include additional patent rights owned by Harvard for which MGH has the right to grant us a license and we have subsequently amended it to broaden our license field. Under the agreement, as amended, we acquired an exclusive, royalty-bearing, worldwide license under the licensed patent rights to make, use and sell products covered by the licensed patent rights or which employ or are based on the licensed know-how and to develop and perform services covered by the licensed patent rights or which employ or are based on the licensed know-how. The license under MGH-owned patent rights and know-how is for human female fertility, the treatment or prevention of inherited (including mitochondrial) diseases or defects in all animals, including humans, assisted and/or artificial reproductive technology in all non-human animals, and the artificial creation of food, research animals and/or animal products; and the license under the MGH and Harvard co-owned patent right is for ex-vivo human female fertility treatments.
Under the agreement, as amended, we agreed to pay MGH upfront license fees and reimbursed patent related fees and costs incurred by MGH and Harvard totaling approximately $0.4 million in the aggregate. We also agreed to pay MGH annual license fees, annual maintenance fees, milestone payments, royalties as a percentage of net sales and a percentage of sublicense income that we receive. Annual license fees are creditable against royalties. Annual maintenance fees are due beginning in the third year of the agreement and are not creditable against royalties. Milestone payments of up to an aggregate of approximately $10.7 million are triggered upon the achievement of specified developmental and commercialization milestones and are not creditable against royalties. Additionally,
14
we paid $0.5 million in connection with our March 2014 public offering and $0.5 million will be due in March 2015. The royalty rate is in the low single digits as a percentage of net sales. Net sales do not include amounts billed to patients by clinics and medical practices that use licensed products or perform licensed services for such patients, but do include the amounts paid to us by such clinics and medical practices.
If we are required to pay royalties to a third party in consideration of a license or similar right in order to avoid potential infringement of third party patent rights, and the royalty payable to such third party is greater than one percent of net sales, then we may deduct up to 50% of the amounts paid to such third party that are in excess of one percent of net sales, subject to specified limitations, from the payments that we owe to MGH for such licensed product or licensed service; provided, however that the stacking provision does not apply to assisted and/or artificial reproductive technology in all non-human animals.
We are required to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop and commercialize licensed products and licensed services under the agreement. In particular, we are required to achieve specified development and commercialization milestones by specified dates.
MGH and Harvard retain the right to, and may grant licenses to other academic, government and non-profit institutions for the right to practice the licensed patent rights within the licensed fields for research and educational purposes only.
We have the right to terminate the agreement for any reason upon at least 90 days' prior written notice. MGH has the right to terminate the agreement if we fail, subject to a specified cure period, to pay any amounts due and payable under the agreement to MGH, we otherwise materially breach the agreement and fail to cure such breach within a specified cure period, we fail to maintain insurance coverage as required under the agreement, we enter bankruptcy proceedings or make an assignment for the benefit of our creditors, or we or a sublicensee challenges the licensed patent rights in a legal or administrative proceeding. The agreement otherwise terminates upon the expiration or abandonment of all licensed patents and patent applications.
Collaboration with Intrexon to Accelerate Development of OvaTure
In December 2013, we entered into a collaboration agreement (the "OvaTure Collaboration") with Intrexon governing the use of Intrexon's synthetic biology technology platform for the accelerated development of our OvaTure platform. The OvaTure Collaboration provides that Intrexon will deliver laboratory and animal data to support OvaTure development. Upon the delivery of laboratory and animal data, we will incur an obligation to pay Intrexon a mid-single digit royalty on net sales of any OvaTure fertility treatments in the future, and the exact royalty will depend upon whether Intrexon completes the milestone by the targeted deadline of two years after technology transfer.
As a technology access fee, we (1) issued Intrexon 273,224 shares of our common stock worth approximately $2.5 million on the date of issuance upon the execution of the OvaTure Collaboration in December 2013, and (2) paid Intrexon $2.5 million cash in December 2014. We also agreed to a commercial milestone payment three months after the first commercial sale of OvaTure. The shares issued to Intrexon are subject to "piggy-back" registration rights that entitle Intrexon, unless waived, to have the shares included in any new registration statement filed in connection with an underwritten public offering, subject to underwriter cutback.
We may terminate the OvaTure Collaboration after ninety (90) days prior written notice, and either party may terminate after a material breach by the other party that is not cured within sixty (60) days. We may assign the OvaTure Collaboration in the event of a change of control transaction. In the event that we pursue the OvaTure program on its own after terminating the OvaTure Collaboration, the royalty will apply if Intrexon intellectual property is utilized.
15
OvaXon Joint Venture with Intrexon
In December 2013, we also entered into a joint venture with Intrexon to leverage Intrexon's synthetic biology technology platform and our technology relating to EggPC cells to pursue the development of potential fertility treatments within fields-of-use defined under the joint venture, which include prevention of genetic disease and animal health. The joint venture anticipates initially targeting the animal health market, which is estimated to grow to $19 billion by 2018 according to consensus estimates for animal divisions of Elanco, Merck, Sanofi, and Zoetis.
We and Intrexon formed OvaXon, LLC ("OvaXon") to conduct the joint venture. Each party contributed $1.5 million to OvaXon and each has a 50% equity interest, with research and development costs and profits to be split accordingly. OvaXon is governed by a board of managers, which initially will have equal representation by OvaScience and Intrexon. Pursuant to an Intellectual Property License between OvaScience and OvaXon, we licensed our technology in the field of the joint venture to OvaXon, and OvaXon entered into a collaboration agreement with Intrexon to develop our technology in the field utilizing Intrexon's synthetic biology platform.
We recorded our $1.5 million investment in OvaXon as an equity method investment in December 2013. During the year ended December 31, 2014, we recorded $1.6 million of losses from our share of OvaXon's losses during the period.
Competition
The biotechnology and pharmaceutical industries are highly competitive and subject to rapid technological change. There are a number of pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies, universities and research organizations actively engaged in research and development of potential fertility treatments. Some of these treatments, similar to our current and future fertility treatments, are designed to address the shortcomings of IVF.
In particular, we are aware of a number of companies and laboratories that are currently developing potential fertility treatments intended to identify high quality embryos for use in IVF and a university study of the transfer of granulosa cell mitochondria into eggs. We are also aware of a university study of induced pluripotent stem cells, or iPS, showing that iPS cells can be generated from somatic cells and programmed to become differentiated cells, which can include germline cells such as oocytes. However, we believe it is unlikely this approach would have clinical applications because these are non-germline, pluripotent cells. Novocellus Ltd. is developing an embryo viability test, using culture media, to aid in the selection of embryos used in IVF. We believe that culture media is complementary to our fertility treatment options. FertiliTech and Auxogyn, Inc. are developing hardware and software that analyzes embryo development against cell division timing parameters to help identify the highest quality embryo within a group of embryos. If successfully developed, these products could improve outcomes and alleviate some of the other shortcomings of traditional IVF, thereby decreasing the need for our potential fertility treatments. Fertility Focus, along with strategic partner Norgenix, are developing a fertiloscope for the early diagnosis of, and immediate corrective surgery for, the physical causes of infertility. Molecular diagnostic companies like Reprogenetics are developing novel preimplantation genetic diagnosis and screening methods to detect chromosomal and genetic disorders of embryos prior to transfer back to the women. Testing embryos in this manner may increase the likelihood of pregnancy, reduce the chances of pregnancy loss, and improve the odds of delivery.
At this time, we cannot evaluate how our potential fertility treatments, if successfully developed and commercialized, would compare technologically, clinically or commercially to any other potential products being developed or to be marketed by competitors. There can be no assurance that we will be able to compete effectively. Our competitors may develop and commercialize new technologies before we do, allowing them to offer products, services or solutions that are superior to those that we may offer or that establish market positions before the time, if any, at which we are able to bring potential
16
fertility treatments to the market. Many of our competitors, either alone or with their strategic partners, have substantially greater financial, technical and human resources than we do and significantly greater experience in the discovery and development of product candidates, obtaining FDA and other regulatory approvals of products and the commercialization of those products. Accordingly, our competitors may be more successful than we may be in developing, commercializing and achieving widespread market acceptance. Our competitors' products may be more effective, or more effectively marketed and sold, than any treatment we may commercialize and may render our potential fertility treatments obsolete or non-competitive before we can recover the expenses of developing and commercializing any of our potential fertility treatments. We anticipate that we will face intense and increasing competition as new treatments enter the market and advanced technologies become available.
For the AUGMENT treatment and OvaPrime treatment, our ability to gain market acceptance will depend on, among other things, our ability to demonstrate improved IVF success rates, thereby reducing the number of cycles required to produce a live birth, and our ability to reduce multiple births. Our ability to gain market acceptance for the OvaTure treatment, if and when introduced, will depend on our ability to demonstrate increased pregnancy and live birth rates as compared to traditional IVF and other infertility treatments, reduced multiple births and a reduction in the need for hormonal hyperstimulation for egg retrieval. We anticipate that price also will be an important competitive factor for all our fertility treatment options. At this time, we cannot evaluate how our potential fertility treatments, if successfully developed and commercialized, would compare technologically, clinically or commercially to any other potential products being developed or to be marketed by competitors.
Government Regulation
Government authorities around the world regulate, among other things, the development, testing, manufacture, quality, approval, distribution, labeling, packaging, storage, record keeping, sale, marketing, import, export and promotion of drugs, biologics and medical devices, as well as other types of medical products and procedures. Most countries also have both rules relating to procurement and use of human tissues or cells, and rules relating to assisted human reproduction. Although the specific rules vary country by country, in general different levels of regulation are applicable depending on the nature of the treatment, the level of risk involved, and/or its intended uses. Some classes of products (e.g., treatments regulated as drugs or biologics in the U.S., or treatments regulated as "medicinal products" in the EU) require extensive preclinical testing, clearance to conduct clinical trials, successful completion of clinical trials, and submission and approval of an application for marketing authorization before the therapy can be commercially marketed. Such products also are subject to significant post-marketing requirements.
In many countries various classes of therapies are exempt from pre-market review and approval requirements. In these jurisdictions, the development and marketing of such therapies generally does not require the conduct of clinical trials or pre-review and approval of a marketing application by the relevant regulatory body. In addition, although many such therapies are still subject to post-marketing requirements, these requirements typically are substantially reduced as compared to the requirements for drugs, biologics, medical devices, or "medicinal products."
We are focusing our commercialization efforts for the AUGMENT treatment and, when we have completed development of the OvaPrime treatment, will focus our efforts to introduce the OvaPrime treatment, in countries in which we believe our fertility treatments do not require pre-review and approval of applications for marketing authorization by the relevant regulatory authorities. Therefore, we have initially elected to launch the AUGMENT treatment commercially in several countries outside of the United States. In each of these countries, we have done so based on our determination that the AUGMENT treatment meets the requirements of a class of products exempt from pre-market review
17
and approval under applicable laws and regulations. As a result, we have not completed clinical trials of the AUGMENT treatment, nor have we submitted applications for marketing authorization, in those countries. Consistent with this strategy, we currently intend to expand the launch of the AUGMENT treatment into additional countries outside of the United States that we also believe do not require pre-marketing review and approval. We also plan to introduce the OvaPrime treatment, when we have completed its development, in countries outside of the United States based on the same determination. We are still developing the OvaTure treatment, and have not yet made a judgment on the proper development pathway for that treatment.
There can be no assurance that regulatory authorities in countries where we have introduced, or will introduce, the AUGMENT treatment or the OvaPrime treatment will agree with our determinations that these fertility treatments are exempt from pre-market review and approval. If the regulatory authorities in a given country disagrees with our determination, then we likely will be required to cease commercial marketing of that fertility treatments in that country, and may not be able to resume commercial marketing without first demonstrating safety and efficacy through clinical trials, submitting an application for marketing authorization, and receiving approval from the relevant regulatory authorities. In these circumstances, we are likely to be significantly delayed in our ability to commercialize our treatments in such country, or we may elect to cease our commercialization activities in that country altogether. From time to time, we engage in discussions regarding the AUGMENT treatment and our potential fertility treatments with regulatory authorities in certain of the countries in which we have launched or plan to introduce our treatments. We expect to have ongoing dialogue with these regulatory authorities.
With regard to the United States, we commenced a clinical study of the AUGMENT treatment in the United States in 2012. We did so without an IND on the basis of our determination that the AUGMENT treatment was exempt from pre-market review and approval in the U.S., and did not require an IND to conduct clinical testing. In 2013, however, we received an "untitled" letter from the FDA questioning our determination of exempt status and advising us to file an IND for the potential fertility treatment. We have since discontinued our clinical study and are focused on commercializing our fertility treatments outside of the United States. We expect to re-examine our strategy with the United States after we have gained more experience with our fertility treatments.
European Union Requirements
In the European Union, we believe that neither the AUGMENT treatment nor, when introduced and available, the OvaPrime treatment is subject to regulation as a medical product or a medical device, and instead is subject to the less rigorous regulations that apply to use of human cells and tissues that are intended for human applications, as more fully described below. While we are proceeding with the introduction of the AUGMENT treatment into certain countries within the EU on this basis, there is a risk that European or national regulatory authorities may reach a different conclusion.
Regulation of Medicinal Products
If European regulatory authorities were to determine that any of our potential treatments are subject to regulation as medicinal products, including as advanced therapy medicinal products, they would be subject to extensive pre- and post-market regulation by regulatory authorities at both the EU and national levels. Advanced therapy medicinal products include tissue engineered products, which are cells or tissues that have undergone substantial manipulation and that are administered to human beings in order to regenerate, repair or replace a human tissue.
Clinical Trials. Clinical trials of medicinal products in the EU must be conducted in accordance with EU and national regulations and the International Conference on Harmonization, or ICH,
18
guidelines on Good Clinical Practices, or GCP. Prior to commencing a clinical trial, the sponsor must obtain a clinical trial authorization from the competent authority, and a positive opinion from an independent ethics committee. Currently, clinical trial authorization applications must be submitted to the competent authority in each EU member state in which the trial will be conducted. Under the new Regulation on Clinical Trials, which will take effect in May 2016 at the earliest, there will be a centralized application procedure where one national authority takes the lead in reviewing the application and the other national authorities have only a limited involvement. Any substantial changes to the trial protocol or other information submitted with the clinical trial applications must be notified to or approved by the relevant competent authorities and ethics committees.
During the development of a medicinal product, the European Medicines Agency, or EMA, and national medicines regulators within the EU provide the opportunity for dialogue and guidance on the development program. At the EMA level, this is usually done in the form of scientific advice, which is given by the Scientific Advice Working Party of the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use, or CHMP. A fee is incurred with each scientific advice procedure. Advice from the EMA is typically provided based on questions concerning, for example, quality (chemistry, manufacturing and controls testing), nonclinical testing and clinical studies, and pharmacovigilance plans and risk-management programs. Advice is not legally binding with regard to any future marketing authorization application of the product concerned. To date, we have not initiated any scientific advice procedures or other discussions with the EMA or any national regulatory authorities in the EU.
Marketing Authorizations. After completion of the required clinical testing, we must obtain a marketing authorization before we may place a medicinal product on the market in the EU. There are various application procedures available, depending on the type of product involved. All application procedures require an application in the common technical document, or CTD, format, which includes the submission of detailed information about the manufacturing and quality of the product, and non-clinical and clinical trial information. There is an increasing trend in the EU towards greater transparency and, while the manufacturing or quality information is currently generally protected as confidential information, the EMA and national regulatory authorities are now liable to disclose much of the non-clinical and clinical information in marketing authorization dossiers, including the full clinical study reports, in response to freedom of information requests after the marketing authorization has been granted. Clinical study reports will also be posted on the EMA's website following the grant, denial or withdrawal of a marketing authorization application, subject to procedures for limited redactions and protection against unfair commercial use.
The centralized procedure gives rise to marketing authorizations that are valid throughout the EU and, by extension (after national implementing decisions), in Norway, Iceland and Liechtenstein, which, together with the EU member states, comprise the European Economic Area, or EEA. Applicants file marketing authorization applications with the EMA, but the marketing authorization itself is granted by the European Commission. The centralized procedure is compulsory for medicinal products that (1) are derived from biotechnology processes, (2) contain a new active substance (approved after November 20, 2005) indicated for the treatment of certain diseases, (3) are orphan medicinal products or (4) are advanced therapy medicinal products, such as cell therapy medicines. For medicines that do not fall within these categories, an applicant may voluntarily submit an application for a centralized marketing authorization to the EMA, as long as the CHMP agrees that (i) the medicine concerned contains a new active substance (approved after November 20, 2005), (ii) the medicine is a significant therapeutic, scientific, or technical innovation, or (iii) if its authorization under the centralized procedure would be in the interest of public health.
For those medicinal products for which the centralized procedure is not available, the applicant must submit marketing authorization applications to the national medicines regulators through one of three procedures: (1) a national procedure, which results in a marketing authorization in a single EU member state; (2) the decentralized procedure, in which applications are submitted simultaneously in
19
two or more EU member states; and (3) the mutual recognition procedure, which must be used if the product has already been authorized in at least one other EU member state, and in which the EU member states are required to grant an authorization recognizing the existing authorization in the other EU member state, unless they identify a serious risk to public health.
The EU medicines rules expressly permit the member states to adopt national legislation prohibiting or restricting the sale, supply or use of any medicinal product containing, consisting of or derived from a specific type of human or animal cell, such as embryonic stem cells. Thus, it is possible that the national laws in certain EU member states may prohibit or restrict us from commercializing our fertility treatments, even if they have been granted an EU marketing authorization.
Data Exclusivity. Marketing authorization applications for generic medicinal products do not need to include the results of pre-clinical and clinical trials, but instead can refer to the data included in the marketing authorization of a reference product for which regulatory data exclusivity has expired. If a marketing authorization is granted for a medicinal product containing a new active substance, that product benefits from eight years of data exclusivity, during which generic marketing authorization applications referring to the data of that product may not be accepted by the regulatory authorities, and a further two years of market exclusivity, during which such generic products may not be placed on the market. The two-year period may be extended to three years if during the first eight years a new therapeutic indication with significant clinical benefit over existing therapies is approved.
There is a special regime for biosimilars, or biological medicinal products that are similar to a reference medicinal product but that do not meet the definition of a generic medicinal product, for example, because of differences in raw materials or manufacturing processes. For such products, the results of appropriate pre-clinical or clinical trials must be provided, and guidelines from the EMA detail the type of quantity of supplementary data to be provided for different types of biological product. There are no such guidelines for complex biological products, such as gene or cell therapy medicinal products, and so it is unlikely that biosimilars of those products will currently be approved in the EU. However, guidance from the EMA states that they will be considered in the future in light of the scientific knowledge and regulatory experience gained at the time.
Post-Approval Controls. The holder of a marketing authorization must establish and maintain a pharmacovigilance system and appoint an individual qualified person for pharmacovigilance, or QPPV, who is responsible for oversight of that system. Key obligations include expedited reporting of suspected serious adverse reactions and submission of periodic safety update reports, or PSURs.
All new marketing authorization applications must include a risk management plan, or RMP, describing the risk management system that the company will put in place and documenting measures to prevent or minimize the risks associated with the product. The regulatory authorities may also impose specific obligations as a condition of the marketing authorization. Such risk-minimization measures or post-authorization obligations may include additional safety monitoring, more frequent submission of PSURs, or the conduct of additional clinical trials or post-authorization safety studies. Risk management plans and PSURs are routinely available to third parties requesting access, subject to limited redactions.
All advertising and promotional activities for the product must be consistent with the approved summary of product characteristics, and therefore all off-label promotion is prohibited. Direct-to-consumer advertising of prescription medicines is also prohibited in the EU. Although general requirements for advertising and promotion of medicinal products are established under EU directives, the details are governed by regulations in each member state and can differ from one country to another.
20
Medicinal products may only be manufactured in the EU, or imported into the EU from another country, by the holder of a manufacturing authorization from the competent national authority. The manufacturer or importer must have a qualified person, or QP, who is responsible for certifying that each batch of product has been manufactured in accordance with EU standards of good manufacturing practice, or GMP, before releasing the product for commercial distribution in the EU or for use in a clinical trial. Manufacturing facilities are subject to periodic inspections by the competent authorities for compliance with GMP.
Regulation of Medical Devices
If European regulatory authorities were to determine that any of our potential treatments are subject to regulation as a medical device, the following requirements would apply. A medical device may be placed on the market within the EEA if it conforms to certain "essential requirements". These are general in nature and broad in scope. The most fundamental essential requirement, for example, is that a device must be designed and manufactured in such a way that it will not compromise the clinical condition or safety of patients, or the safety and health of users or other persons. Other essential requirements include that the device must achieve the performances intended by the manufacturer and be designed, manufactured and packaged in a suitable manner, and any undesirable side effect must constitute an acceptable risk when weighed against the performances intended.
The manufacturer is obliged to demonstrate that the device conforms to the relevant essential requirements through a conformity assessment procedure. The nature of the assessment depends upon the classification of the device. The classification rules are mainly based on three criteria: the length of time the device is in contact with the body, the degree of invasiveness, and the extent to which the device affects the anatomy. Class I (low risk) devices are those that do not enter or interact with the body. Class IIa and IIb (medium risk) devices are invasive or implantable or interact with the body. Class III (high risk) devices are those that affect the vital organs.
Conformity assessment procedures for all but the lowest risk classification of device involve a notified body. Notified bodies are entities licensed to provide independent certification of certain classes of medical device. Most notified bodies are private commercial entities, but some are state bodies and others are structured as private non-profit organizations.
EU regulatory bodies are not involved in the pre-market approval of medical devices, with only very limited exceptions (such as medical devices that incorporate a medicinal product as an ancillary substance). The onus of ensuring a device is safe enough to be placed on the market is ultimately the responsibility of the manufacturer and the notified body.
As part of the conformity assessment procedure, the manufacturer will need to conduct a clinical evaluation of the device. This clinical evaluation may consist of an analysis of the scientific literature relating to similar devices, new clinical investigations of the device, or a combination of the two. For class III devices, the conduct of clinical investigations is mandatory. Such studies must adhere to the Declaration of Helsinki, which requires appropriate ethics committee approval of the study.
Once the appropriate conformity assessment procedure for a medical device has been completed, the manufacturer must draw up a written declaration of conformity and affix the CE mark to the device. The device can then be marketed throughout the EEA.
Manufacturers must put in place a device vigilance system that allows them to review relevant post-marketing experience and take corrective actions where necessary. As part of that system, manufacturers must report to the competent regulatory authorities any adverse incident related to a medical device that leads or might lead, directly or indirectly, to the death of a patient, user or other person or to a serious deterioration in their state of health. They must also report any recalls or other field safety corrective actions.
21
Human Cells and Tissues
Human cells and tissues that are intended for human applications but that do not fall within the scope of rules governing medicinal products or medical devices are not subject to pre-market review and approval, nor do they require extensive preclinical and clinical testing. However, there are EU rules governing the donation, procurement, testing and storage of human cells and tissues intended for human application, whether or not they are advanced therapy medicinal products. These rules also cover the processing, preservation and distribution of human cell and tissues that are not advanced therapy medicinal products. Establishments that conduct such activities must be licensed and are subject to inspection by regulatory authorities. Such establishments must implement appropriate quality systems and maintain appropriate records to ensure that cells and tissues can be traced from the donor to the recipient and vice versa. There are also requirements to report serious adverse events and reactions linked to the quality and safety of cells and tissues. More detailed rules may exist at the national level.
IVF Treatment
While the procurement, processing and distribution of gametes and embryos for use in IVF and other assisted reproduction treatments falls within the scope of the EU rules governing human cells and tissues, there are no harmonized EU requirements for the performance of IVF and other medical treatments. Instead, the practice of medicine is regulated entirely at the national level in the individual member states. Such national regulations may permit only certain techniques to be used in IVF treatment, or may proscribe specific activities. For example, such national regulations may restrict the extent to which the eggs used in IVF treatments may be manipulated.
United States Requirements
Although we are not currently seeking to introduce any of our current or potential fertility treatments into the United States, we could elect to do so in the future. The United States Food and Drug Administration ("FDA") regulates human cell, tissue, or cellular or tissue-based products ("HCT/Ps") according to a tiered, risk-based approach. Higher risk HCT/Ps are generally regulated as biological products under the Public Health Service Act, or PHSA, the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act, or FDCA, and implementing regulations. Section 351 of the PHSA prohibits the introduction of a biological product into interstate commerce without an FDA-approved application for marketing authorization under that section. For pioneer products, the typical application under section 351 of the PHSA is the biologics license application, or BLA.
Biological products that are subject to section 351 of the PHSA are subject to significant pre and post-market regulation. Before such products may be marketed in the United States, the manufacturer must conduct extensive preclinical testing, submit an investigational new drug ("IND") application to FDA before clinical testing can begin, conduct extensive clinical testing, and submit and receive FDA approval of a BLA. After approval, these products are subject to significant requirements relating to, among other things, manufacturing, adverse event reporting, advertising and promotion, distribution, packaging, labeling, import/export, and recordkeeping.
Lower risk HCT/Ps, however, are regulated solely under section 361 of the PHSA, which gives FDA authority to promulgate regulations to prevent the spread of communicable diseases. Such products are referred to as "361 HCT/Ps." The FDA will regulate an HCT/P as a 361 HCT/P if it meets all of the following criteria:
- (1)
- the
HCT/P is minimally manipulated,
- (2)
- the HCT/P is intended for homologous use only, as reflected by the labeling, advertising, or other indications of the manufacturer's objective intent,
22
- (3)
- the
manufacture of the HCT/P does not involve the combination of the cells or tissues with another article, with a few exceptions, and
- (4)
- either:
- •
- the HCT/P does not have a systemic effect and is not dependent upon the metabolic activity of living cells for its
primary function, or
- •
- the HCT/P has a systemic effect or is dependent upon the metabolic activity of living cells for its primary function and
- (a)
- is
for autologous use,
- (b)
- is
for allogeneic use in a first or second degree blood relative, or
- (c)
- is for reproductive use.
HCT/Ps that meet all of these requirements are deemed 361 HCT/Ps and are regulated exclusively under section 361 of the PHSA and the FDA's implementing regulations at 21 C.F.R. Part 1271. These regulations impose requirements for registration and listing, donor screening and testing, and good tissue practices, among other things. They do not, however, impose the IND requirements or the pre-market review and approval requirements described above for biologics regulated under section 351 of the PHSA.
Other HCT/Ps are regulated neither as 351 biologics, nor 361 HCT/Ps. For example, certain HCT/Ps that are removed from a donor and returned to the same donor during a single surgical procedure are exempted from both the 351 biologics requirements and the 361 HCT/P requirements. Other procedures may involve human cellular or tissue based products but may be considered to fall into the category of "practice of medicine" and therefore are not regulated by FDA.
It is not certain how FDA would regulate any of our current or potential fertility treatments were we to seek to introduce them into the United States. As discussed above, in 2012 we commenced a clinical study of the AUGMENT treatment in the United States, but subsequently received from the FDA an "untitled" letter questioning the status of the AUGMENT treatment as a 361 HCT/P, and advising us to file an IND for the potential fertility treatment, following which we suspended our commercialization efforts in the United States. We continue to believe that the AUGMENT treatment meets the criteria for regulation as a 361 HCT/P and plan to engage the agency in further discussions after we have gained more extensive experience with the AUGMENT treatment through use outside of the United States. There is no guarantee, however, that FDA will ultimately agree with our classification of the AUGMENT treatment or any of our potential fertility treatments.
Other Healthcare Laws and Compliance Regulations
Both in and outside of the United States, our activities may be subject to regulation by various federal, state and local authorities in addition to the FDA or EMA. In the United States, this likely includes the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services, or CMS, other divisions of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, such as the Office of Inspector General, and the U.S. Department of Justice and individual U.S. Attorney offices within the Department of Justice, as well as state and local governments, and ex-US equivalents. Our operations in the relevant jurisdictions must comply with all of these applicable requirements or we may be unable to conduct our business or may face civil or criminal sanctions.
We are also subject to varying anti-corruption laws that exist both in the United States, where we are based, and the various countries in which we operate or otherwise offer our fertility treatments. For example, the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, or FCPA, prohibits any U.S. individual or business from paying, offering, or authorizing payment or offering of anything of value, directly or indirectly, to any
23
foreign official, political party or candidate for the purpose of influencing any act or decision of the foreign entity in order to assist the individual or business in obtaining or retaining business. The FCPA also obligates companies whose securities are listed in the United States to comply with certain accounting provisions requiring the company to maintain books and records that accurately and fairly reflect all transactions of the corporation, including international subsidiaries, and to devise and maintain an adequate system of internal accounting controls for international operations. The anti-bribery provisions of the FCPA are enforced primarily by the U.S. Department of Justice. The SEC is involved with enforcement of the books and records provisions of the FCPA. Failure to comply with the FCPA or similar laws in other countries where we operate could subject us to significant penalties that could have a material impact on our business.
Pharmaceutical Coverage, Pricing and Reimbursement
We believe that very few third party payors, either in the EU, the United States or other countries, including national health services and government funded insurance programs as well as private payors, will agree to cover and reimburse for the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or other potential fertility treatments we may attempt to commercialize. Thus, it is likely that IVF clinics and physicians will be able to use the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment and our other potential fertility treatments only if the patient can afford and is willing to pay for our treatment out of pocket. The cost of the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment, and our other potential fertility treatments may be beyond the means of many patients.
Third party payors include government health administrative authorities, managed care providers, private health insurers and other organizations. The process for determining whether a payor will provide coverage for a treatment or procedure may be separate from the process for setting the price or reimbursement rate that the payor will pay for the treatment or procedure. Even if third party payors were to provide some minimal level of coverage and reimbursement for the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or our other potential fertility treatments, such third party payors are increasingly challenging the price and examining the medical necessity and cost-effectiveness, in addition to the safety and efficacy, of medical products and procedures.
In the EU and elsewhere, governments influence the price of medical products and procedures through their pricing and reimbursement rules and control of national healthcare systems that fund a large part of consumers' medical costs. Some jurisdictions operate positive and negative list systems under which treatments or procedures may be marketed only after a reimbursement price has been agreed upon. To obtain reimbursement or pricing approval, some of these countries may require the completion of clinical trials that compare the cost-effectiveness of our particular treatments or procedures to currently available therapies. Other countries allow medical companies to fix their own prices, but monitor and control company profits. The downward pressure on healthcare costs has become very intense. As a result, increasingly high barriers are being erected to the entry of new treatments and procedures.
Employees
As of December 31, 2014, we had 52 full-time employees, including a total of 27 employees with advanced degrees. None of our employees are represented by a labor union or covered by a collective bargaining agreement. We consider our relationship with our employees to be good.
Our Corporate Information
We were incorporated under the laws of the State of Delaware in April 2011 under the name Ovastem, Inc. and changed our name to OvaScience, Inc. in May 2011. Our principal executive offices
24
are located at 215 First Street, Suite 240, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142, as well as 245 First Street, Cambridge, Massachusetts 02142, and our telephone number is (617) 500-2802. Our website address is www.ovascience.com. The information contained on, or that can be accessed through, our website is not a part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We have included our website address in this Annual Report solely as an inactive textual reference.
Available Information
You may obtain free copies of our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q and Current Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports, as soon as reasonably practicable after they are electronically filed or furnished to the United States Securities and Exchange Commission, or the SEC, on the Investors section of our website at www.ovascience.com or by contacting our Corporate Communications department at (617) 500-2802. The contents of our website are not incorporated by reference into this report and you should not consider information provided on our website to be part of this report.
25
RISK FACTORS
Our business is subject to numerous risks. We caution you that the following important factors, among others, could cause our actual results to differ materially from those expressed in forward-looking statements made by us or on our behalf in filings with the SEC, press releases, communications with investors and oral statements. Any or all of our forward-looking statements in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and in any other public statements we make may turn out to be wrong. They can be affected by inaccurate assumptions we might make or by known or unknown risks and uncertainties. Many factors mentioned in the discussion below will be important in determining future results. Consequently, no forward-looking statement can be guaranteed. Actual future results may differ materially from those anticipated in forward-looking statements. We undertake no obligation to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise. You are advised, however, to consult any further disclosure we make in our reports filed with the SEC.
Risks Related to Our Financial Position and Need for Additional Capital
Our short operating history may make it difficult for you to evaluate the success of our business to date and to assess our future viability.
We commenced active operations in April 2011. Our operations to date have been limited to organizing and staffing our company, business planning, raising capital, acquiring and developing our technology, identifying potential fertility treatments, developing the AUGMENT treatment, launching the AUGMENT treatment in select international IVF clinics, researching and developing the OvaPrime treatment and the OvaTure treatment, and determining the regulatory and development path for our fertility treatments. Any predictions you make about our future success or viability may not be as accurate as they could be if we had a longer operating history.
In addition, as a young business with a short operating history, we may encounter unforeseen expenses, difficulties, complications, delays and other known and unknown challenges. We are in the process of transitioning from a company focused on in-licensing and research to a company capable of developing multiple potential fertility treatments and supporting commercial activities, and specifically, we are transitioning from the initial international launch of the AUGMENT treatment in select clinics outside the United States towards a broad-based commercial build-out in multiple international regions. We may not be successful in such a transition.
We have incurred significant losses since our inception. We expect to incur losses for the foreseeable future and may never achieve or maintain profitability.
Since our inception, we have incurred significant operating losses. Our net loss was $49.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 and $94.7 million for the period from April 5, 2011 (inception) to December 31, 2014. To date in 2015, we have recorded limited revenues and have financed our operations primarily through equity financings. We have devoted significant efforts to acquiring our technology and developing, launching and commercializing the AUGMENT treatment.
We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and increasing operating losses for the foreseeable future. The net losses we incur may fluctuate significantly from quarter to quarter. We anticipate that our expenses will increase if and as we:
- •
- introduce the AUGMENT treatment through our ACE access program to additional international IVF clinics in new regions;
- •
- continue to transition ACE clinics to commercial centers;
- •
- educate physicians and embryologists regarding the use of the AUGMENT treatment;
26
- •
- incur costs associated with foreign expansion;
- •
- establish a domestic and international sales, marketing, manufacturing and distribution infrastructure, including the formation of an
international headquarters in the United Kingdom and additional international subsidiaries, to commercialize the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment and any other potential fertility treatments
we successfully develop;
- •
- continue optimization of and prepare to introduce the OvaPrime treatment;
- •
- continue development of the OvaTure treatment, both internally and in collaboration with Intrexon, and other potential fertility
treatments, and ultimately introduce the OvaTure treatment;
- •
- initiate any clinical trials of our potential fertility treatments;
- •
- collaborate with Intrexon through the OvaXon joint venture to create new applications to prevent inherited diseases for human and
animal health;
- •
- seek any required approvals from the FDA or similar regulatory agencies outside of the United States, which we refer to as Foreign
Regulatory Authorities, for our potential fertility treatments that require such approval;
- •
- maintain, expand and protect our intellectual property portfolio;
- •
- hire additional scientific, clinical, quality control and management personnel to support our potential fertility treatment
development and commercialization efforts in the United States and abroad;
- •
- add operational and financial personnel to support our international expansion plans;
- •
- seek to identify additional potential fertility treatments; and
- •
- develop, acquire or in-license other potential fertility treatments and technologies.
To become and remain profitable, we must significantly expand our commercial launch of the AUGMENT treatment in international markets, and we may also need to develop and eventually commercialize our potential fertility treatments with significant market potential, including the OvaPrime treatment and the OvaTure treatment. This will require us to be successful in a range of challenging activities, including successfully introducing the ACE access program into additional international IVF clinics, marketing and selling the AUGMENT treatment, developing and introducing the OvaPrime treatment into international IVF clinics, completing development of the OvaTure treatment, obtaining any required marketing approvals, manufacturing, marketing and selling those potential fertility treatments that we successfully develop, and addressing the challenges of foreign operations. We may never succeed in these activities and, even if we do, may never generate revenues that are significant or large enough to achieve profitability. We are currently optimizing the OvaTure treatment and plan to define a development pathway, both internally and in collaboration with Intrexon, and we are collaborating with Intrexon on the OvaXon joint venture. If we do achieve profitability, we may not be able to sustain or increase profitability on a quarterly or annual basis. Our failure to become and remain profitable would decrease the value of our company and could impair our ability to raise capital, maintain our research and development efforts, expand our business or continue our operations.
We will need substantial additional funding. If we are unable to raise capital when needed, we would be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate our fertility treatment development programs or commercialization efforts.
We launched the AUGMENT treatment in select international IVF clinics in 2014 through our ACE access program, and we anticipate expanding to new ACE clinics in other major regions of the
27
world in 2015, and we plan to significantly increase our international infrastructure as part of our commercial build-out. We also plan to continue to optimize the process and introduce the OvaPrime treatment in at least one international region by the end of 2015. In addition, we expect to incur significant expenses with respect to our optimization and development of the OvaTure treatment and other potential fertility treatments. Any clinical trials that we are required to conduct for these potential fertility treatments will be costly. Furthermore, we expect to incur additional costs associated with operating as a public company. Accordingly, we will need to obtain substantial additional funding in connection with our continuing operations. If we are unable to raise capital when needed or on attractive terms, we would be forced to delay, reduce or eliminate some or all of our research and development programs or commercialization efforts.
We believe that our cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments of approximately $60.2 million at December 31, 2014, together with the approximately $124.1 million of net proceeds received from our January 2015 secondary public offering, will be sufficient to fund our current operating plan for at least the next 12 months. There can be no assurances, however, that the current operating plan will be achieved or that additional funding, if needed, will be available on terms acceptable to us, or at all.
Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
- •
- our success in expanding to new ACE clinics in other major regions of the world, transitioning ACE clinics to commercial centers and
significantly increasing the number of patients receiving the AUGMENT treatment;
- •
- our success in optimizing, introducing, and the subsequent adoption of the OvaPrime treatment to international IVF clinics;
- •
- the costs associated with the expansion of foreign operations and building out our international commercial infrastructure, including
establishing and staffing an international headquarters and other international subsidiaries;
- •
- the costs associated with establishing a domestic and international sales, marketing, manufacturing and distribution infrastructure to
commercialize the AUGMENT treatment and any potential fertility treatment we successfully develop;
- •
- the pricing of the AUGMENT treatment and resulting revenues, as well as any future revenues we receive from our potential fertility
treatments;
- •
- the costs of continuing the optimization of the OvaTure treatment and our success in defining the development pathway;
- •
- the costs of any clinical trials of our potential fertility treatments;
- •
- the costs involved in collaborating with Intrexon through the OvaXon joint venture to create new applications to prevent inherited
diseases for human and animal health;
- •
- following any applicable regulatory process in the United States and abroad, including the premarketing and marketing approval
requirements, to which any of our potential fertility treatments may be subject;
- •
- following any regulatory or institutional review board review of our potential fertility treatments that are subject to such review;
- •
- preparing, filing and prosecuting patent applications, maintaining and enforcing our intellectual property rights and defending
intellectual property-related claims;
- •
- establishing collaborations and partnerships on favorable terms, if at all; and
28
- •
- developing, acquiring or in-licensing other potential fertility treatments and technologies.
Identifying, developing and commercializing potential fertility treatments is a time consuming, expensive and uncertain process that takes years to complete. We may fail to achieve sufficient revenues from the AUGMENT treatment and or potential fertility treatments to achieve profitability on our expected timelines or at all. We will need to continue to rely on additional financing to achieve our business objectives. Adequate additional financing may not be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
Raising additional capital may cause dilution to our stockholders, restrict our operations or require us to relinquish rights to our technologies or potential fertility treatments.
Until the time, if ever, that we can generate sufficient revenues from the AUGMENT treatment or our potential fertility treatments to become profitable, we plan to finance our cash needs through some combination of equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances and licensing arrangements. We do not have any committed external source of funds. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership interest of our existing stockholders will be diluted, and the terms of these new securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect the rights of our existing stockholders. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends.
If we raise additional funds through collaborations, strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, research programs or potential fertility treatments or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us.
We have limited experience in marketing and selling our fertility treatments, and if we are unable to successfully commercialize our fertility treatments, our business and operating results will be adversely affected.
We have limited experience marketing and selling our fertility treatments. We commercially launched the AUGMENT treatment in select international IVF clinics in 2014 through our ACE access program and we anticipate expanding to new ACE clinics in other major regions of the world in 2015. Our ability to generate revenue in the near term, however, will depend on the number of commercial AUGMENT treatment cycles our ACE clinics perform and the treatment prices charged. We expect that the commercial ramp up of the AUGMENT treatment during 2015 will depend upon the efficient and successful transition of ACE clinics to commercial operations, the addition of new ACE clinics and the results from ACE clinic experience as they become available. Because we have limited commercialization experience, our ability to forecast how long this commercial ramp up will take is unproven. If we are not able to successfully transition the ACE clinics to commercial operations, we may not be able to obtain significant revenue or deferred revenue from the AUGMENT treatment on the timelines we project, or at all.
Risks Related to Research, Development and Commercialization of Our Potential Fertility Treatments
The science underlying the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment and the OvaTure treatment is based on recent discoveries, and the OvaPrime treatment and the OvaTure treatment have not been used in humans. We may not be able to successfully commercialize the AUGMENT treatment on a large scale or develop and commercialize the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or other potential fertility treatments.
The AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment and the OvaTure treatment are based on recent scientific discoveries relating to egg precursor cells. We have limited patient experience with the
29
AUGMENT treatment and our experience with the AUGMENT treatment to date may not be representative of what women will experience in the future. Further, the OvaPrime treatment and the OvaTure treatment have not been used in humans, and the preclinical data we have generated for these treatments under development may not be replicated in humans. We may not be able to successfully develop the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or other potential fertility treatments.
In 2014, we launched the AUGMENT treatment in select international IVF clinics through our ACE access program and we began transitioning some of these IVF clinics to commercial centers. In 2015, we plan to expand the commercial launch of the AUGMENT treatment in major regions of the world outside of the United States. The data collected from the IVF clinics, including whether, and by how much, the use of the AUGMENT treatment improves egg health and embryo quality, increases the pregnancy and live birth rates of IVF and the safety of this potential fertility treatment will impact our ability to further commercialize and generate significant revenues from sales of the AUGMENT treatment. If the results that we receive from any of these IVF clinics are unfavorable, the AUGMENT treatment may not be viable or significant additional time and expense could be required before we are able to further commercialize this fertility treatment. If we experience delays or difficulties in introducing our ACE program into additional international IVF clinics, our ability to further commercialize the AUGMENT treatment could be delayed or prevented.
We plan to optimize the OvaPrime treatment in 2015 in anticipation of a planned introduction into a select IVF clinic or clinic group outside of the United States by the end of 2015. The data collected from the IVF clinics, including whether and by how much the OvaPrime treatment boosts egg reserves, will impact our ability to introduce and generate revenues from sales of the OvaPrime treatment. If the results are unfavorable, the OvaPrime treatment may not be viable or significant additional time and expense could be required before we are able to commercialize this potential fertility treatment.
In 2014, we achieved human preclinical proof-of-concept with the OvaTure treatment by demonstrating that human EggPC cells can be matured into eggs outside of the body. We expect to optimize the process and define a development pathway for the OvaTure treatment in 2015. Our plans to define a development pathway for the OvaTure treatment will depend upon the development pathway and the regulatory pathway applicable in regions of the world that we target. There are significant aspects of the OvaTure treatment that will require additional innovation for us to continue its development. The recent nature of the scientific discoveries underlying the OvaTure treatment, the need for additional innovation and the absence of information from human clinical trials all increase the risks associated with this potential fertility treatment. In any event, we believe that it will be costly and time consuming to develop and successfully commercialize the OvaTure treatment.
We may be required to conduct clinical studies of our fertility treatments in certain regions of the world. Any such clinical studies would be expensive, difficult to design and implement and uncertain as to outcome. Regulatory authorities and institutional review boards ("IRB") regulate clinical trials and can suspend or terminate them for many reasons. Success in animal and preclinical studies does not ensure that studies in humans will be successful, and interim or preliminary findings do not necessarily predict final results. In addition, the timing of results from and completion of the studies will depend, in part, on our ability to enroll the studies on the timeline expected. Enrollment in any studies could be delayed for a number of reasons, including the unwillingness of patients to undergo, or physicians to prescribe, an additional surgical procedure in connection with IVF.
Patient enrollment is affected by other factors including:
- •
- timing and capacity of GTP processing facilities / third party manufacturers;
- •
- novelty of the potential fertility treatments being tested;
- •
- form of infertility or severity of the condition being treated;
30
- •
- eligibility criteria for the study in question;
- •
- perceived risks and benefits of the potential fertility treatments under study;
- •
- known side effects of the potential fertility treatments under study, if any;
- •
- efforts of IVF clinics to facilitate enrollment in clinical trials;
- •
- patient referral practices of physicians;
- •
- ability to monitor patients adequately during and after treatment; and
- •
- proximity and availability of clinical trial sites for prospective patients.
Our inability to enroll a sufficient number of patients for any necessary clinical trials for the OvaTure treatment and other potential fertility treatments would result in significant delays or may require us to abandon one or more clinical trials altogether. Enrollment delays in our clinical trials may result in increased development costs for our potential fertility treatments, which would cause the value of our company to decline and limit our ability to obtain additional financing.
OvaXon, our joint venture with Intrexon, is seeking to create new applications to prevent inherited disease for human and animal health that are based on a novel gene editing based technology, which makes it difficult to predict the time and cost of development and subsequently obtaining regulatory approval.
OvaXon, our joint venture with Intrexon, is developing new gene editing based applications to prevent inherited disease for human and animal health by leveraging Intrexon's synthetic biology technology platform and our technology relating to EggPC cells. OvaXon may experience difficulties in the future related to its gene editing platform, which could cause significant delays or unanticipated costs, and which OvaXon may not be able to solve. OvaXon may also experience delays in developing a sustainable, reproducible and scalable manufacturing process or transferring those processes to commercial partners, which may prevent OvaXon from completing studies or commercializing potential fertility treatments on a timely or profitable basis, if at all.
The clinical study requirements of the FDA, the EMA and other regulatory agencies and the criteria these regulators use to determine the safety and efficacy of a product candidate vary substantially according to the type, complexity, novelty and intended use and market of the potential product candidate. The regulatory approval process for novel gene based fertility treatments such as those that OvaXon will pursue likely will be more expensive and take longer than for other, better known or extensively studied product candidates.
The FDA has never approved any gene therapy or gene editing technology for use in humans or other animals. Only one gene therapy product, UniQure's Glybera, which received an EU marketing authorization in 2012, has been approved in the Western world, which makes it difficult to determine how long it will take or how much it will cost to obtain regulatory approvals for OvaXon's potential treatments.
OvaXon's technologies involve the use of synthetic biologically engineered products or synthetic biological technologies. Public perception about the safety and environmental hazards of, and ethical concerns over, genetically engineered products and processes could influence public acceptance of OvaXon's technologies, potential products and processes. If OvaXon is not able to overcome the ethical, legal and social concerns relating to synthetic biological engineering, any potential treatments it develops may not be accepted. These concerns could result in increased expenses or abandonment of any potential fertility treatments OvaXon develops.
Regulatory requirements governing gene and cell therapy products have evolved and may continue to change in the future. Further, most of the laws and regulations concerning synthetic biology relate to the end products produced using synthetic biology, but that may change. For example, the Presidential
31
Commission for the Study of Bioethical Issues in December 2010 recommended that the federal government oversee, but not regulate, synthetic biology research. The Presidential Commission also recommended that the government lead an ongoing review of developments in the synthetic biology field and that the government conduct a reasonable risk assessment before the field release of synthetic organisms. Synthetic biology may become subject to additional government regulations as a result of the recommendations, which could require OvaXon to incur significant additional expenses in complying with these laws and regulations.
Regulatory review agencies, committees and advisory groups and any new requirements and guidelines they promulgate may lengthen the regulatory review process, require OvaXon to perform additional studies, increase OvaXon's development costs, which we share with Intrexon, lead to changes in regulatory positions and interpretations, delay or prevent approval and commercialization of these treatment candidates or lead to significant post-approval limitations or restrictions. As OvaXon advances its potential new treatments in human and animal health, it will be required to consult with these regulatory and advisory groups and comply with applicable requirements and guidelines. If OvaXon fails to do so, we may be required to delay or discontinue development of its potential fertility treatments. Delay or failure to obtain, or unexpected costs in obtaining, the regulatory approval necessary to bring a potential fertility treatment to market could decrease our ability to generate sufficient revenue to maintain our business.
Development of our potential fertility treatments may not be successful. If we are unable to commercialize our potential fertility treatments or experience significant delays in doing so, our business will be materially harmed.
We intend to invest a significant portion of our efforts and financial resources in the identification, development and commercialization of potential fertility treatments. Our ability to generate revenues will depend heavily on the successful development and eventual commercialization of our potential fertility treatments. Our plans to define a development pathway for the OvaTure treatment in 2015 will depend upon the development pathways and the regulatory pathways applicable to our fertility treatments in regions of the world that we target. Regulatory authorities may conclude that our fertility treatments qualify for a class of products exempt from pre-market review and approval under applicable laws and regulations. We have launched the AUGMENT treatment in various foreign countries based on our own assessment that the AUGMENT treatment qualifies for such class of products in these countries. However, some or even all regulatory authorities may determine to classify the AUGMENT treatment or our potential fertility treatments as drugs, biologics or medical devices. Any such regulation would mean, among other things, that we would have to conduct extensive clinical trials and would not be able to market such potential fertility treatments until we have received approval from the applicable regulatory authority. We have not received approval to market any potential fertility treatments from regulatory authorities in any jurisdiction. We have only limited experience in conducting preclinical testing and clinical trials and filing and supporting the applications necessary to gain marketing approvals and expect to rely on third parties, including contract research organizations, to assist us in this process.
If we are required to conduct clinical trials in any of the countries where we seek to commercialize our potential fertility treatments, we would be subject to significant additional risk. Prior to initiating any necessary clinical trials of our potential fertility treatments that may be required in particular regions, we may need to submit clinical trial applications (such as an IND or foreign equivalent) to regulatory authorities, based on preclinical, animal and other tests. Upon submitting such an application, the regulatory authorities might determine that the risks involved in our potential fertility treatments are too great to justify proceeding with a clinical study and impose a partial or full clinical hold. They may require us to do significant and costly additional preclinical work before commencing our clinical trials or may not allow us to proceed with clinical trials at all. In addition, an ethics
32
committee or IRB must review and approve any clinical trial before we can commence that trial. The ethics committee or IRB responsible for reviewing any of our clinical trials may decline to grant approval for a variety of reasons, including that they do not believe that patient rights would adequately be protected. Our potential fertility treatments rely on new and complex technology that impacts human reproductive systems. Therefore, regulatory authorities and ethics committees may be especially cautious in reviewing and approving our clinical protocols for such potential fertility treatments.
Clinical testing is expensive, difficult to design and implement, can take many years to complete, and is uncertain as to outcome. A failure of one or more clinical trials can occur at any stage of testing. The outcome of preclinical testing and early clinical trials may not predict the success of later clinical trials, and interim results of a clinical trial do not necessarily predict final results. Moreover, preclinical and clinical data are often susceptible to varying interpretations and analyses, and many companies that have believed their product candidates performed satisfactorily in preclinical studies and clinical trials have nonetheless failed to obtain marketing approval of their products. The FDA, equivalent Foreign Regulatory Authorities or an IRB or ethics committee can suspend or terminate any clinical development programs at any time, for a number of reasons, including that further study presents unreasonable risk to human subjects or that the rights of those subjects are not protected.
We may experience numerous unforeseen events during, or as a result of, any clinical trials if we are required to conduct them, which could delay or prevent our ability to receive marketing approval or commercialize our potential fertility treatments, including:
- •
- regulators, ethics committees, or IRBs may not authorize us or our investigators to commence a clinical trial or conduct a clinical
trial at a prospective trial site;
- •
- we may have delays in reaching, or fail to reach agreement on, acceptable clinical trial contracts or clinical trial protocols with
prospective trial sites;
- •
- clinical trials of our potential fertility treatments may produce negative or inconclusive results, or results subject to varying
interpretations, and we may decide, or regulators may require us, to conduct additional clinical trials or abandon potential fertility treatment development programs;
- •
- the number of patients required for clinical trials, and/or the necessary duration of clinical trials of our potential fertility
treatments may be larger than we anticipate, enrollment in our clinical trials may be slower than we anticipate or participants may drop out of our clinical trials at a higher rate than we anticipate;
- •
- we or our third party contractors may fail to comply with regulatory requirements, such as conducting trials in accordance with
current good clinical practices, and our contractors may fail to meet their contractual obligations to us in a timely manner or at all;
- •
- we may have to suspend or terminate clinical trials of our potential fertility treatments for various reasons, including discovery
that the participants are being exposed to unacceptable health risks;
- •
- the cost of clinical trials of our potential fertility treatments may be greater than we anticipate; and
- •
- the supply or quality of our potential fertility treatments or other materials necessary to conduct clinical trials of our potential fertility treatments may be insufficient or inadequate.
If we are unable to successfully complete any required clinical trials or other testing of our potential fertility treatments, if the results of these trials or tests are not positive or are only insufficient
33
to demonstrate safety or efficacy to applicable regulators, or if there are any safety concerns regarding our potential fertility treatments, we may:
- •
- be delayed in obtaining marketing approval for our potential fertility treatments;
- •
- not obtain marketing approval at all and therefore be unable to commercialize our fertility treatments;
- •
- obtain approval for indications or patient populations that are not as broad as we intend or desire;
- •
- obtain approval with labeling that includes significant restrictions on distribution or safety warnings, including boxed warnings;
- •
- be subject to additional post-marketing testing requirements; or
- •
- have the treatment removed from the market after obtaining marketing approval.
If serious adverse side effects are identified during the development or commercialization of the AUGMENT treatment or our other potential fertility treatments or with any procedures with which these fertility treatments are used, we may need to abandon or limit our development of those fertility treatments, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
Neither the AUGMENT treatment nor any of our potential fertility treatments has been proven effective and safe in humans through clinical trials. We have limited patient experience with the AUGMENT treatment and our experience with the AUGMENT treatment to date may not be representative of what women will experience in the future. It is impossible to predict when or if any of our potential fertility treatments will prove effective or safe in humans or, to the extent required, will receive marketing approval. If the AUGMENT treatment or our potential fertility treatments are associated with undesirable side effects or have characteristics that are unexpected with respect to the mother or the child conceived using the AUGMENT treatment or our potential fertility treatments, we may need to abandon their development or limit development to certain uses or subpopulations in which the undesirable side effects or other characteristics are less prevalent, less severe or more acceptable from a risk-benefit perspective. In addition, if any of the procedures with which our potential fertility treatments are used is determined to be unsafe, we may be required to delay or abandon our fertility treatment development or commercialization. For example, we expect the AUGMENT treatment will be administered as part of the ICSI process and the OvaPrime treatment will be administered as part of the IVF process. To the extent physicians limit or abandon the use of ICSI, IVF or other procedures with which the AUGMENT treatment or the OvaPrime treatment is used, we may need to delay or abandon our development or commercialization of these treatments.
Even if we are able to expand the commercialization of the AUGMENT treatment or commercialize any of our potential fertility treatments, they may fail to achieve the degree of market acceptance by physicians, patients and others in the medical community necessary for commercial success.
Even if we are able to expand the commercialization of the AUGMENT treatment or commercialize any of our potential fertility treatments, they may nonetheless fail to gain sufficient market acceptance by physicians, patients and others in the medical community. For example, doctors may continue to rely on current treatments, including fertility drugs and traditional IVF, which are well established in the medical community. In addition, the novel nature of the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment and the OvaTure treatment may affect market acceptance by physicians and patients. We have limited patient experience with the AUGMENT treatment and our experience with the AUGMENT treatment to date may not be representative of what women will experience in the future. Our ability to gain market acceptance of the AUGMENT treatment will depend on the experience women have with this treatment option over time. If our potential fertility treatments do not
34
achieve an adequate level of acceptance, we may not generate significant treatment revenues and we may not become profitable. The degree of market acceptance of the AUGMENT treatment and our potential fertility treatments, after receipt of any necessary approvals for commercial sale, will depend on a number of factors, including:
- •
- efficacy and potential advantages as compared to traditional IVF or other alternative treatments;
- •
- ability to reduce the number of IVF cycles required to achieve a live birth;
- •
- ability to reduce the cost of traditional IVF;
- •
- ability to reduce the incidence of multiple births;
- •
- the willingness of the target population to undergo, and of physicians to prescribe, an additional surgical procedure in connection
with IVF;
- •
- convenience compared to alternative treatments;
- •
- adverse effects on mothers or children conceived using our potential fertility treatments;
- •
- ability to improve the side effect profile of infertility treatment;
- •
- the willingness of the target population and of physicians to try new therapies based on recent scientific discoveries;
- •
- limitations on the existing infrastructure to support the AUGMENT treatment or our potential fertility treatments, including
adequately trained embryologists and the willingness of IVF clinics to incorporate the process into their current treatment regimen;
- •
- the willingness and ability of patients to pay out of pocket for our potential fertility treatments, which, in the case of the AUGMENT
treatment and the OvaPrime treatment, will be in addition to the price of a standard IVF procedure;
- •
- any negative publicity or political action related to our or similar potential fertility treatments or IVF; and
- •
- the strength of marketing and distribution support.
In addition, our ability to successfully commercialize our potential fertility treatments will depend on the continued use and acceptance of IVF, ICSI and fertility treatments generally. To the extent that the medical community or patient population determines that these procedures are unsafe or are otherwise not generally accepted, the market for our potential fertility treatments and, therefore, our business would be negatively affected.
If we are unable to establish sales and marketing capabilities or enter into additional agreements with third parties to sell and market our potential fertility treatments, we may not be successful in commercializing them.
We anticipate expanding to new ACE clinics in other major regions of the world in 2015 and we continue to expand our global sales and marketing team. To achieve commercial success for any potential fertility treatment, we must either develop a sales and marketing team or outsource these functions to third parties. We have retained appropriate sales and marketing assistance in the markets in which we have initially launched the AUGMENT treatment and plan to recruit appropriate sales and marketing resources for countries in which we determine to launch the AUGMENT treatment or the OvaPrime treatment on our own. In the future, we plan to expand the sales force for the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment or other potential fertility treatments.
There are risks involved both with establishing our own sales and marketing capabilities and entering into arrangements with third parties to perform these services. For example, recruiting and training a sales force is expensive and time consuming and could delay any fertility treatment launch. If
35
the commercial expansion of the AUGMENT treatment and/or the commercial introduction of the OvaPrime treatment or our other potential fertility treatments for which we recruit a sales force and establish marketing capabilities is delayed or does not occur for any reason, we would have prematurely or unnecessarily incurred these commercialization expenses. This may be costly, and our investment would be lost if we cannot retain or reposition our sales and marketing personnel.
If we enter into arrangements with third parties to perform sales, marketing and distribution services, our treatment revenues or the profitability of these treatment revenues to us are likely to be lower than if we were to market and sell any potential fertility treatment ourselves. In addition, we may not be successful in entering into arrangements with third parties to sell and market our potential fertility treatments or may be unable to do so on terms that are favorable to us. We likely will have limited control over such third parties, and any of them may fail to devote the necessary resources and attention to sell and market our potential fertility treatments effectively and in compliance with applicable laws.
We may not be successful in our efforts to identify or discover additional potential fertility treatments. If we do identify additional potential fertility treatments, we may expend our limited resources to pursue a particular potential fertility treatment and fail to capitalize on potential fertility treatments that may be more profitable or for which there is a greater likelihood of success.
An important element of our strategy is to identify and develop additional potential fertility treatments based on our EggPC cells technology. We may be unable to identify any such potential fertility treatments. If we do identify additional candidates, we may not advance such candidates into clinical development for a number of reasons, including:
- •
- there may be evidence that such candidates may have harmful side effects;
- •
- preclinical studies may put into question the efficacy of such candidates;
- •
- we may determine that such candidates are unlikely to achieve marketing approval or market acceptance; or
- •
- such candidates may be too costly to manufacture or market.
Because we have limited financial and managerial resources, we focus on research programs and potential fertility treatments based on which candidates we believe have the highest likelihood of success and commercial value. As a result, we may forego or delay pursuit of opportunities with other potential fertility treatments that later prove to have greater commercial potential. Our resource allocation decisions may cause us to fail to capitalize on viable commercial treatments or profitable market opportunities. Our spending on current and future research and development programs and potential fertility treatments may not yield any commercially viable treatments. For example, the programs we are considering relating to culture media and EggPC cells banking may not reach commercialization or, if commercialized, may not be successful. If we do not accurately evaluate the commercial potential or target market for a particular potential fertility treatment, we may relinquish valuable rights to potential fertility treatments through collaboration, licensing or other royalty arrangements when it would have been more advantageous for us to retain sole development and commercialization rights to such potential fertility treatment.
We may not be successful in obtaining necessary rights to additional technologies or potential fertility treatments, including from our scientific founders, for our development pipeline through acquisitions and in-licenses.
We may be unable to acquire or in-license additional technologies or potential fertility treatments from third parties, including our scientific founders, in order to grow our business. A number of more established companies may also pursue strategies to license or acquire potential fertility treatments that
36
we may consider attractive. These established companies may have a competitive advantage over us due to their size, cash resources and greater clinical development and commercialization capabilities.
For example, we continue to work collaboratively with our scientific founders. These scientists continue to be active in the field of infertility and may develop new potential fertility treatments or intellectual property based on their continued research relating to infertility. The rights to new inventions by our scientific founders generally belong to the hospitals and academic institutions at which they are employed and are not subject to license or other rights in our favor. In the event that our scientific founders, or other third party scientists or entities, develop potential fertility treatments or intellectual property that we wish to acquire or in-license, we may be unable to negotiate such acquisition or in-license. Our failure to reach an agreement for any applicable potential fertility treatment or intellectual property could result in a third party acquiring the related rights and thereby harm our business.
In addition, companies that perceive us to be a competitor may be unwilling to assign or license rights to us. We also may be unable to license or acquire relevant potential fertility treatments on terms that would allow us to make an appropriate return on our investment.
We expect competition for acquiring and in-licensing potential fertility treatments that are attractive to us may increase in the future, which may mean fewer suitable opportunities for us as well as higher acquisition or licensing costs. If we are unable to successfully obtain rights to suitable potential fertility treatments on reasonable terms, or at all, our business, financial condition and prospects for growth could suffer.
We face substantial competition, including from more established infertility treatments, such as traditional IVF, as well as advances in new artificial reproductive technologies, which may result in others discovering, developing or commercializing potential fertility treatments before or more successfully than we do.
There are a number of fertility treatments that are generally accepted in the medical and patient communities, including fertility drugs, IUI and IVF. Competition in the infertility market is largely based on pregnancy and live birth rates and side effects of treatment on patients. Accordingly, our success is highly dependent on our ability to develop potential fertility treatments that improve pregnancy and live birth rates and reduce risks and side effects, as compared to existing treatments. The ability of any potential fertility treatment that we successfully develop to reduce the overall costs associated with IVF also will be an important competitive factor.
Competitors may develop new infertility drugs, assisted reproductive technology, or ART, therapies, devices and techniques that could render obsolete our potential fertility treatments. There are a number of pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies, universities and research organizations actively engaged in research and development of potential fertility treatments. Like the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment and the OvaTure treatment, some of these potential fertility treatments are designed to address the shortcomings of IVF. In particular, we are aware of a number of companies and laboratories that are currently developing potential fertility treatments intended to identify high quality embryos for use in IVF, a university study of the transfer of granulosa cell mitochondria into eggs and a university study of induced pluriopotent stem cells, or iPS, shows that iPS cells can be generated from somatic cells and programmed to become differentiated cells, which can include germ line cells such as oocytes. Novocellus Ltd. is developing an embryo viability test, using culture media, to aid in the selection of embryos used in IVF. FertiliTech and Auxogyn, Inc. are developing hardware and software that analyzes embryo development against cell division timing parameters to help identify the highest quality embryo within a group of embryos. If successfully developed, these potential fertility treatments could improve outcomes and alleviate some of the other shortcomings of traditional IVF, thereby decreasing the need for our potential fertility treatments. Fertility Focus, along with its strategic partner Norgenix, are developing a fertiloscope for the early
37
diagnosis of, and immediate corrective surgery for, the physical causes of infertility. Molecular diagnostic companies like Reprogenetics are developing novel preimplantation genetic diagnosis and screening methods to detect chromosomal and genetic disorders of embryos prior to transfer back to the women. Testing embryos in this manner may increase the likelihood of pregnancy, reduce the chances of pregnancy loss, and improve the odds of delivery. At this time, we cannot evaluate how our potential fertility treatments, if successfully developed and commercialized, would compare technologically, clinically or commercially to any other potential fertility treatments being developed or to be marketed by competitors. There can be no assurance that we will be able to compete effectively. OvaXon, our joint venture with Intrexon, is engaged in gene editing, which is a rapidly evolving field. OvaXon could potentially have competitors in both in the United States and internationally, including major multinational pharmaceutical companies, biotechnology companies and universities and other research institutions. Some of the pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies we expect OvaXon to compete with include GlaxoSmithKline plc, Sangamo BioSciences Inc., HemaQuest Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Merck & Co., Inc., and Novartis AG.
Our competitors may develop and commercialize new technologies before we do, allowing them to offer potential fertility treatments, services or solutions that are superior to those that we may offer or which establish market positions before the time, if any, at which we are able to bring potential fertility treatments to the market. Many of our competitors, either alone or with their strategic partners, have substantially greater financial, technical and human resources than we do and significantly greater experience in the discovery and development of potential fertility treatments, obtaining FDA and other regulatory approvals of potential fertility treatments and the commercialization of those treatments. Accordingly, our competitors may be more successful than we may be in developing, commercializing and achieving widespread market acceptance. Our competitors' potential fertility treatments may be safer, more effective or more effectively marketed and sold than any treatment we may commercialize and may render our potential fertility treatments obsolete or non-competitive before we can recover the expenses of developing and commercializing any of our potential fertility treatments. We anticipate that we will face intense and increasing competition as new treatments enter the market and advanced technologies become available.
We could be subject to negative publicity, political action and additional regulation because of the nature of our potential fertility treatments. These factors could increase our development and commercialization costs.
Our potential fertility treatments are based on innovative science regarding eggs, embryos and fertilization, and in the case of our OvaXon joint venture, gene editing. These can be controversial subjects and, as a result, we could be subject to adverse publicity, political reaction and regulation, as well as changes to the laws and regulations affecting our potential fertility treatments. This may result in our incurring costs beyond what we anticipate in order to develop and commercialize our potential fertility treatments or may make it impossible to develop our potential fertility treatments at all. In addition, some states are considering adopting legislation defining when personhood begins. To the extent adopted, this legislation could limit, restrict or prohibit the use of IVF, which would have a negative effect on our ability to develop and sell our potential fertility treatments and, as a result, on our business.
Product liability lawsuits against us could cause us to incur substantial liabilities and to limit commercialization of any potential fertility treatments that we may develop.
We face an inherent risk of product liability exposure related to the use of our fertility treatments in humans and will face an even greater risk as we expand the commercialization of the AUGMENT treatment, or if we successfully introduce the OvaPrime treatment or any other potential fertility treatment that we may develop, including potential fertility treatments developed by OvaXon. Product liability claims involving our activities may be made for significant amounts because our potential
38
fertility treatments involve mothers and children. For example, it is possible that we will be subject to product liability claims that assert that our potential fertility treatments have caused birth defects in children or that such defects are inheritable. In light of the nature of our planned activities, these claims could be made many years into the future based on effects that were not observed or observable at the time of birth. If we cannot successfully defend ourselves against claims that our potential fertility treatments caused injuries, we will incur substantial liabilities. Regardless of merit or eventual outcome, liability claims may result in:
- •
- decreased demand for any potential fertility treatment that we may develop;
- •
- injury to our reputation and significant negative media attention;
- •
- withdrawal of clinical trial participants;
- •
- significant costs to defend the related litigation;
- •
- substantial monetary awards or payments to trial participants or patients;
- •
- loss of revenue;
- •
- the diversion of management's resources; and
- •
- the inability to commercialize any potential fertility treatments that we may develop.
We obtained product liability insurance coverage when we initiated our AUGMENT treatment study in the United States and introduced the AUGMENT treatment through our ACE access program in select IVF centers outside of the United States. We will need to maintain product liability insurance coverage as we further commercialize the AUGMENT treatment outside of the United States and expand to new ACE clinics in other regions of the world and additional international IVF clinics, introduce the OvaPrime treatment, and/or conduct clinical trials for our current or potential fertility treatments. Such insurance is increasingly expensive and difficult to procure. In the future, such insurance may not be available to us at all or may only be available at a very high cost and, if available, may not be adequate to cover all liabilities that we may incur. In addition, we may need to increase our insurance coverage in connection with the commercialization of our current or potential fertility treatments. If we are not able to obtain and maintain insurance coverage at a reasonable cost or in an amount adequate to satisfy any liability that may arise, our business could be harmed, possibly materially.
Procedures such as IVF, as well as companies that manufacture and store cells and tissues, are the subject of standards and recommendations by national non-governmental bodies. Failure to comply with these standards could harm our commercial prospects or subject us to negative media attention or government sanctions.
Various countries where we are seeking or may seek to introduce our fertility treatments have standards set by regulatory authorities and/or non-governmental bodies that govern IVF procedures and the procurement, storage and processing of gametes and embryos for use in IVF procedures. In the UK, for example, the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority (HFEA) has adopted a Code of Practice with which licensed IVF clinics are obliged to comply, as well as supplementary guidance documents. Similarly, the UK's Association of Clinical Embryologists has adopted a series of best practice guidelines for its members. Even where these standards are voluntary, if we, or third parties that we work with, including IVF clinics, fail to comply with these standards, our commercial prospects could be harmed because patients may prefer to use the services and potential fertility treatments of companies that meet these standards. Similarly, physicians or IVF clinics may be less likely to endorse or use procedures or potential fertility treatments that fail to comply with such standards. In addition, failure to meet the standards could subject us to negative media attention.
39
Risks Related to Regulatory Approval of Our Potential Fertility Treatments and Other Regulatory Matters
Our plans to continue and expand the commercial launch of the AUGMENT treatment outside of the United States and introduce the OvaPrime treatment in selected regions outside of the United States depend upon the AUGMENT treatment and the OvaPrime treatment meeting the requirements of a class of products or a type of practice or treatment exempt from pre-market review and approval in such regions. Determinations by regulators in the markets we target that the AUGMENT treatment and the OvaPrime treatment do not meet the requirements for a class of products exempt from pre-market review and approval could significantly delay or prevent commercialization of those products. Failure to obtain marketing approval in international regions, to the extent required, would prevent our potential fertility treatments from being marketed in such regions. Additionally, our plans to define a development pathway for the OvaTure treatment will depend upon the development pathway and the regulatory pathway applicable in regions of the world that we target.
Our plans to continue and expand the launch of the AUGMENT treatment outside of the United States and introduce the OvaPrime treatment in select regions outside of the United States depend upon the treatments meeting the requirements of a class of products or a type of practice or treatment exempt from pre-market review and approval in such regions. There can be no assurance that this will be the case in any particular jurisdiction, or that applicable Foreign Regulatory Authorities will agree with our determinations that the AUGMENT treatment and the OvaPrime treatment meet these requirements. If the Foreign Regulatory Authorities in a given country disagree with our determination that the AUGMENT treatment or the OvaPrime treatment is exempt from pre-market review and approval, then we likely will be required to cease commercial marketing of that fertility treatment in that country, and may not be able to resume commercial marketing without first demonstrating safety and efficacy through clinical trials, submitting an application for marketing authorization, and receiving approval from the relevant regulatory authorities. In these circumstances, we are likely to be significantly delayed in our ability to commercialize our treatments in such country, or we may elect to cease our commercialization activities in that country altogether. For example, in 2012, we commenced a clinical study of the AUGMENT treatment in the United States relying on our conclusion that the AUGMENT treatment met the requirements for a 361 HCT/P, and therefore did not require an IND. In September 2013, however, we received an "untitled" letter from the FDA questioning the status of the AUGMENT treatment as a 361 HCT/P and advising us to file an IND for the AUGMENT treatment. As a result, we chose to suspend enrollment in our AUGMENT study in the United States. Additionally, our plans to define a development pathway for the OvaTure treatment will depend upon the development pathway and the regulatory pathway applicable in regions of the world that we target. From time to time, we engage in discussions regarding the AUGMENT treatment and our potential fertility treatments with Foreign Regulatory Authorities in certain of the countries in which we have launched or plan to introduce the AUGMENT treatment. We expect to have ongoing dialogue with these regulatory authorities. If the AUGMENT treatment or any of our potential fertility treatments are subject to pre-market approval in a particular region, failure to obtain such required marketing approval in international regions would prevent us from marketing the AUGMENT treatment or our potential fertility treatments in such regions, which could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
Further, if Foreign Regulatory Authorities in a particular region determine that our fertility treatments do not meet the requirements of a class of products that is exempt from pre-market approval, then in order to market and sell our potential fertility treatments in that region, we or our third party collaborators may need to obtain separate marketing approvals and will need to comply with numerous and varying regulatory requirements, as described above. The approval process varies among countries and can involve additional testing. The time required to obtain approval in foreign regions can be lengthy, and may differ substantially from region to region. The regulatory approval process outside the United States generally is subject to risks like those associated with obtaining FDA
40
approval. In addition, in many countries, a treatment must be approved for reimbursement before the treatment can be approved for sale in that country. Furthermore, some countries have restrictions particular to IVF, which may impose additional regulatory barriers for market entry for our potential fertility treatments. If required, we may not obtain approvals from regulatory authorities outside the United States on a timely basis, if at all. Approval by the FDA for marketing in the United States does not ensure approval by regulatory authorities in other countries or jurisdictions, and approval by one regulatory authority outside the United States does not ensure approval by regulatory authorities in other countries or jurisdictions or by the FDA.
By way of example, regulators could determine that the AUGMENT treatment and/or our potential fertility treatments do not meet the requirements for a class of products exempt from pre-market review and approval under applicable laws and regulations. In that case, they could be regulated as advanced therapy medicinal products, as medical devices or as human tissues and cells intended for human applications. For example, products regulated as advanced therapy medicinal products may only be placed on the market in the EU once they have been granted a marketing authorization by the European Commission. Securing a marketing authorization from the European Commission requires the submission of extensive preclinical and clinical data and supporting information, including information about the manufacturing process, to the EMA to establish the potential fertility treatment's safety, efficacy and quality. Following review of the marketing authorization application the EMA will issue an opinion, which the European Commission will take into account when deciding whether or not to grant a marketing authorization. If we are required to follow this regulatory pathway for the AUGMENT treatment or our potential fertility treatments, this may significantly delay or preclude commercialization of these treatments. Similar determinations in other markets outside of the United States could have the same impact.
Even if regulators in regions outside of the United States, such as the EU, deem the AUGMENT treatment and any of our potential fertility treatments to be exempt from pre-market review and approval, medical treatments and processes, such as IVF, may be regulated at the national level, which is the case in the EU. Such national regulations may restrict the extent to which the eggs used in IVF treatments may be manipulated and so may prevent us from commercializing the AUGMENT treatment or the OvaPrime treatment in that country. In addition, certain other countries outside the EU and United States may have regulations that require us to obtain permission prior to commercializing the AUGMENT treatment or the OvaPrime treatment.
It is unclear what regulatory pathway FDA will ultimately require for the AUGMENT treatment or our potential fertility treatments.
We are focusing our commercial efforts outside of the United States and we are not currently seeking to commercialize any of our fertility treatments inside of the United States. We believe that the AUGMENT treatment meets the regulatory definition of a 361 HCT/P or as a type of practice of medicine that is exempt from pre-market approval. The AUGMENT treatment involves mere isolation of mitochondria from egg precursor cells, and injection of those mitochondria into the same woman's egg, which we believe constitutes minimal manipulation of both the mitochondria and the egg. The AUGMENT treatment involves only homologous use, is not combined with any other article, and has a systemic effect, but is for reproductive use. We therefore believe that the AUGMENT treatment meets all four of the criteria for a 361 HCT/P set forth in FDA's regulation. If FDA ultimately agrees with our conclusions, the AUGMENT treatment will not be required to conduct clinical trials pursuant to an IND, nor will it be required to seek FDA pre-market review and approval through an NDA or BLA. However, both the AUGMENT treatment and our potential fertility treatments constitute new technologies, the proper regulatory characterization of which likely constitute matters of first impression for FDA. Particularly because the AUGMENT treatment and our potential fertility treatments are potential fertility treatments that are intended to result in the creation of human life,
41
there can be no assurance that FDA will agree with our views as to the proper regulatory characterization of the AUGMENT treatment or any of our potential fertility treatments. FDA may conclude that the AUGMENT treatment and/or potential fertility treatments constitute drugs, biologics, or medical devices. If FDA makes such a determination for any of our potential fertility treatments, we may be required to conduct clinical trials under an IND (or IDE for a medical device) and seek FDA pre-market review and approval pursuant to an NDA or BLA (or PMA for a medical device). In that event, we may abandon pursuing that potential fertility treatment in the United States, or suffer significant delays and expense seeking to approve any necessary approval.
In 2012, we commenced a clinical study of the AUGMENT treatment in the United States. We did so without an IND on the basis of our conclusion that FDA would regulate the AUGMENT treatment as a 361 HCT/P. On September 6, 2013, however, we received an "untitled" letter from the FDA questioning the status of the AUGMENT treatment as a 361 HCT/P and advising us to file an IND for the potential fertility treatment. We have since discontinued our clinical trial and are now focused on commercializing our fertility treatments outside of the United States.
Even if the FDA regulates the AUGMENT treatment as a 361 HCT/P, we must still generate adequate substantiation for any claims made in our marketing of the AUGMENT treatment before we commercialize it in the United States. Failure to establish such adequate substantiation in the opinion of federal or state authorities or equivalent Foreign Regulatory Authorities could substantially impair our ability to generate revenue.
If we ultimately do not need to submit the AUGMENT treatment to the FDA for preapproval due to the FDA regulating the treatment as a 361 HCT/P, we still must generate adequate substantiation for claims we make in our marketing materials. Both the FTC and the states retain jurisdiction over the marketing of products in commerce and require a reasonable basis for claims made in marketing materials. Many countries outside of the U.S. have similar regulatory authorities that regulate the marketing of products. We intend to generate such adequate substantiation for any claims we make about the AUGMENT treatment. If, however, after we commence marketing of the AUGMENT treatment in the United States, the FTC or one or more states or foreign authorities conclude that we lack adequate substantiation for our claims, we may be subject to significant penalties or may be forced to alter or cease our marketing of the AUGMENT treatment in one or more jurisdictions. Any of this could materially harm our business. In addition, if our promotion of the AUGMENT treatment suggests that the AUGMENT treatment is not a 361 HCT/P, the FDA or equivalent Foreign Regulatory Authorities might consider the potential fertility treatment to be a new drug or biologic. We will therefore be limited in the promotional claims that we could make about the AUGMENT treatment.
Numerous states place restrictions on the operation of facilities and laboratories that recover, test, process, manufacture, store or dispose of certain cells and tissues. If we do not comply with such state regulations, as well as potential local regulations, we could be subject to significant sanctions.
Various states, including New York, California, Florida, Illinois, Maryland, Texas, Massachusetts and others, impose requirements on facilities and laboratories that recover, test, process, manufacture, store or dispose of certain cells and tissues. These requirements can have significant geographic reach. In Maryland, for example, the permit requirements applicable to tissue banks, including reproductive tissue banks, apply not only to tissue banks located in Maryland, but also those tissue banks located outside of the state that are represented or serviced in Maryland. In some cases, the requirements imposed by states, such as record keeping and testing requirements, may be more stringent than those imposed by the FDA. If we begin commercialization of the AUGMENT treatment and/or our potential fertility treatments in the United States, we will have to comply with these state requirements. Failure to comply with these state requirements could subject us to significant sanctions.
42
We will not be able to sell any potential fertility treatment that is regulated as a medical device without obtaining and maintaining necessary regulatory clearances or approvals.
Some regions or countries may determine that certain of our potential fertility treatments, or certain aspects of such treatments, such as the innovative culture media solution that we are planning to develop, should be regulated as medical devices. In such cases, we will need to seek approval or clearance from the appropriate regulatory authorities in such countries.
In the EU, for example, we will need to complete a conformity assessment procedure, to demonstrate that our fertility treatments conform to the essential requirements set out in EU law, and only then may we apply the CE mark to the products, which would allow the products to be marketed throughout the EU. In other countries, such products may be subject to pre-market review and approval by regulatory authorities or some other form of regulatory clearance. We cannot guarantee that we will be able to complete the necessary conformity assessment procedures or obtain the necessary regulatory clearances of pre-market approvals of these medical devices. In addition, any modifications to medical devices that we successfully bring to market, if any, may require new conformity assessment procedures, regulatory clearances or pre-market approvals. Marketing a medical device without the necessary CE mark, clearance or approval could result in a warning letter, fines, injunctions, product seizures or other civil or criminal penalties. Delays in our receipt of CE marking, regulatory clearance or pre-market approval will cause delays in our ability to sell our potential fertility treatments, which will have a negative effect on our ability to generate and grow revenues.
In addition to the challenges associated with obtaining any necessary marketing approvals in international jurisdictions, economic, political and other risks associated with foreign operations could adversely affect our international sales.
We are currently subject to risks associated with doing business internationally as a result of our commercialization of the AUGMENT treatment outside of the United States. We expect 2015 to be a build-out year as we expand our international commercial infrastructure to support our planned expanded commercialization of the AUGMENT treatment outside of the United States and our planned introduction of the OvaPrime treatment in at least one international region by the end of 2015. If we succeed with our international commercialization strategy, then our business will be subject to additional risks associated with doing business internationally. For example, our future results of operations could be harmed by a variety of factors, including:
- •
- changes in foreign currency exchange rates;
- •
- changes in a country's or region's political or economic conditions, particularly in developing or emerging markets;
- •
- trade protection measures and import or export licensing requirements;
- •
- differing business practices associated with foreign operations;
- •
- difficulty in staffing and managing widespread operations, including compliance with labor laws and changes in those laws;
- •
- differing protection of intellectual property and changes in that protection; and
- •
- differing regulatory requirements and changes in those requirements.
We currently have a limited international infrastructure including, without limitation, sales, manufacturing and distribution capabilities and have just recently begun conducting foreign operations. Establishing and expanding commercial activities and complying with laws in foreign jurisdictions may be costly and could disrupt our operations.
43
Even if the AUGEMENT treatment and the OvaPrime treatment are not subject to pre-market review and approval, they may be subject to certain ongoing regulation in some regions. We could be subject to significant civil or criminal penalties if we fail to comply with these requirements, and we may be unable to commercialize our potential fertility treatments.
If regulatory authorities allow the AUGMENT treatment or any potential fertility treatment of ours to be offered to patients in any of the countries we seek to access, we will still be subject to numerous post-market requirements. Post-marketing requirements applicable to such products vary by region and by country. For example, in the United States, 361 HCT/Ps are subject to several post-market requirements, including those related to registration and listing, record keeping, labeling, current good tissue practices, or cGTPs, donor eligibility and other activities. HCT/Ps that do not meet the definition of a 361 HCT/P and, therefore, are approved via an NDA or BLA, are also subject to these and additional ongoing obligations as well as others. If we fail to comply with these requirements, or similar requirements in foreign jurisdictions, we could be subject to warning letters, product seizures, injunctions or civil and criminal penalties.
Moreover, even if the FDA or equivalent Foreign Regulatory Authorities allow the AUGMENT treatment or any potential fertility treatment to be marketed without pre-market approval, the regulatory authorities could still seek to withdraw the potential fertility treatment from the market for a variety of reasons, including if the agency develops concerns regarding the safety or efficacy of the potential fertility treatment or its manufacturing process.
Any fertility treatment for which we are required to obtain marketing approval, and for which we obtain such marketing approval, are subject to continuing regulation after approval. We may be subject to significant penalties if we fail to comply with these requirements.
Any potential fertility treatment, including any potential fertility treatment developed by our OvaXon joint venture, for which we obtain marketing approval or clearance, will be subject to continuing regulation by the FDA or equivalent Foreign Regulatory Authorities. Specific requirements will vary by country and/or region. In general, however, such requirements will include those relating to, among other things, submission of safety and other post-marketing information and reports, registration and listing, manufacturing, packaging, quality control, storage, distribution, quality assurance and corresponding maintenance of records and documents, labeling, advertising and promotional activities, distribution of samples to physicians and recordkeeping. Even if marketing approval or clearance of a potential fertility treatment is granted, the approval or clearance may be subject to limitations on the uses for which the potential fertility treatment may be marketed, be subject to restrictions on distribution or use, or contain requirements for costly post-marketing testing to further evaluate the safety or efficacy of the potential fertility treatment. The FDA and equivalent Foreign Regulation Authorities closely regulate the post-approval marketing and promotion of drugs, biologics and medical devices to ensure such products are marketed only for the approved indications or cleared uses and in accordance with the provisions of the approved labeling. The FDA and equivalent Foreign Regulation Authorities impose stringent restrictions on manufacturers' communications regarding off-label use and if we market our potential fertility treatments other than for their approved indications, we may be subject to enforcement action for off-label marketing.
In addition, later discovery of previously unknown problems with our potential fertility treatments, manufacturers or manufacturing processes, or failure to comply with regulatory requirements, may yield various results, including:
- •
- restrictions on the labeling or marketing of potential fertility treatments;
- •
- restrictions on distribution or use of potential fertility treatments;
- •
- requirements to conduct post-marketing clinical trials;
44
- •
- warning or untitled letters from the FDA or equivalent Foreign Regulatory Authorities;
- •
- withdrawal of potential fertility treatments from the market;
- •
- refusal to approve pending applications or supplements to approved applications;
- •
- recall of potential fertility treatments;
- •
- fines, restitution or disgorgement of profits or revenue;
- •
- suspension or withdrawal of marketing approvals;
- •
- refusal to permit the import or export of our potential fertility treatments;
- •
- product seizure;
- •
- injunctions; or
- •
- the imposition of civil or criminal penalties.
It is unlikely that third party payors will cover or reimburse for the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or other future potential fertility treatments and services, and many patients may be unable to afford them.
Many third party payors, both in the United States and foreign countries, including national health services or government funded insurance programs as well as private payors, place significant restrictions on coverage and reimbursement for IVF and other ART procedures. Those restrictions may include limits on the types of procedures covered, limits on the number of procedures covered and overall annual or lifetime dollar limits on reimbursement for IVF and other ART procedures. As a result, we believe very few third party payors, either in the United States or outside the United States, will reimburse for the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or other future potential fertility treatments and services. Thus, it is likely that IVF clinics and physicians will be able to use the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment and other future potential fertility treatments and services only if the patient can afford and is willing to pay out-of-pocket. The cost of the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment and other future potential fertility treatments and services may be beyond the means of many patients. This may limit the size of the market and prices charged for the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or other future potential fertility treatments and services and, thereby, limit our future revenues.
Even in those limited situations in which government or private payors may cover the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or other future potential fertility treatments and services, cost containment pressures may later cause these third party payors to adopt strategies designed to limit the amount of reimbursement paid to IVF clinics and physicians, including but not limited to the following:
- •
- reducing reimbursement rates;
- •
- challenging the prices charged for medical potential fertility treatments or services;
- •
- further limiting potential fertility treatments and services covered;
- •
- challenging whether potential fertility treatments or services are medically necessary;
- •
- taking measures to limit utilization of potential fertility treatments and services;
- •
- negotiating prospective or discounted contract pricing;
- •
- adopting capitation strategies; and
- •
- seeking competitive bids.
45
Additionally, in those limited situations where ART procedures such as IVF are available to disabled patients of childbearing age enrolled in federal healthcare programs, such as Medicare, the covered services and potential fertility treatments may be subject to changes in coverage and reimbursement rules and procedures, including retroactive rate adjustments. These contingencies could even further decrease the range of potential fertility treatments and services covered by such programs or the reimbursement rates paid directly or indirectly for such potential fertility treatments and services. Such changes could further limit our ability to sell our potential fertility treatments, which may have a material adverse effect on our revenues.
In March 2010, Congress enacted sweeping healthcare reform legislation known as the Affordable Care Act. The Affordable Care Act will substantially change the way that healthcare is financed by both governmental and private insurers and significantly affect the delivery and financing of healthcare in the United States. The Affordable Care Act contains provisions that, among other things, govern enrollment in federal healthcare programs, effect reimbursement changes, encourage use of comparative effectiveness research in healthcare decision making and enhance fraud and abuse requirements and enforcement. The Affordable Care Act imposes a significant annual fee on companies that manufacture or import branded prescription drug products, which could include potential fertility treatments such as, if the FDA regulates it as a biologic. The fee, which is not deductible for federal income tax purposes, is based on the manufacturer's market share of sales of branded drugs and biologics, excluding orphan drugs, to, or pursuant to coverage under, specified U.S. government programs. In addition, the law subjects most medical devices to a 2.3% excise tax, beginning on January 1, 2013. The implementation of the Affordable Care Act may have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and financial condition.
The reimbursement process for products and procedures outside the United States generally is subject to risks, like those associated with reimbursement in the United States, including the risk that it is unlikely that third party payors will cover or reimburse the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or other future potential fertility treatments and services. Many national health services and third party payors in the EU already place coverage and reimbursement limits on ART procedures, including IVF, and may impose even greater limits in the future. In many EU member states medicinal products and medical devices are subject to formal pricing and reimbursement approvals before they can be reimbursed by national health services or government-funded insurance schemes. Reimbursement may be conditional on the agreement by the seller not to sell the product above a fixed price in that country, or the national authority may unilaterally establish a reimbursement price in connection with the inclusion of the product on a list of reimbursable products.
The likelihood that many third party payors will refuse to cover and reimburse for the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment and other future potential fertility treatments and services and that many patients will be unable to afford to pay for them out of pocket may reduce the demand for, or the price of, the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment and other future potential fertility treatments and services, which would have a material adverse effect on our revenues. Additional legislation or regulation relating to the healthcare industry or third party coverage and reimbursement may be enacted in the future, and could adversely affect the revenues generated from the sale of our potential fertility treatments.
Several states and certain foreign countries have enacted legislation that may hamper the ability of IVF clinics and physicians to pass through the cost of our potential fertility treatments to patients or third party payors.
Several states, including California and New York, and certain foreign countries require direct billing of laboratory or pathology services, prohibit physicians from marking up the cost of laboratory or pathology services when they pass these costs on to patients or other payors or require that physicians disclose to patients what they actually paid to obtain laboratory or pathology services.
46
Additionally, the federal government has enacted regulations limiting the Medicare reimbursement available to physicians who contract out the technical component of certain laboratory and pathology procedures.
To the extent that the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or other future potential fertility treatments or services are treated as laboratory or pathology services for purposes of reimbursement, these laws may make it difficult for us to market those potential fertility treatments and services to IVF clinics and physicians in some states and may also require us to restructure our business model before we can expand into certain markets. To the extent that our IVF clinic and physician customer base anticipates seeking Medicare reimbursement, these laws may require a comprehensive restructuring of our business model, and therefore adversely impact our ability to market our potential fertility treatments. Any additional legislation or regulation in this area could also adversely affect our ability to market our potential fertility treatments.
Even though we anticipate very limited third party coverage and reimbursement for the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment and our future potential fertility treatments and services, our future arrangements with third party payors and IVF clinics and physicians may be subject to foreign, federal and state fraud and abuse laws and regulations, which could expose us to criminal sanctions, civil penalties, contractual damages, reputational harm and diminished profits and future earnings.
Even though we anticipate very limited third party coverage and reimbursement, including from federal healthcare programs, for the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment and other future potential fertility treatments and services, our future arrangements with third party payors and IVF clinics and physicians may expose us to broadly applicable fraud and abuse laws and regulations that may constrain the business or financial arrangements and relationships through which we market, sell and distribute the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment and other future potential fertility treatments and services for which we obtain marketing approval. Restrictions under federal and state fraud and abuse laws and regulations that may be applicable to our business include the following:
- •
- the federal Anti-Kickback Statute prohibits, among other things, persons from knowingly and willfully soliciting, offering, receiving
or providing remuneration, directly or indirectly, in cash or in kind, to induce or reward either the referral of an individual for, or the purchase, order or recommendation of, any good or service,
for which payment may be made under federal healthcare programs such as Medicare and Medicaid;
- •
- the federal Stark law prohibits physicians from referring patients to hospitals, laboratories, and other types of entities in which
they or their immediate family members have a financial interest, if the referral is for a select list of Medicare or Medicaid-covered services, including most clinical laboratory services, and also
prohibits entities that furnish the covered services subsequent to a prohibited referral from billing Medicare or Medicaid for the services provided and from receiving payment from a federal
healthcare program for those services;
- •
- the federal False Claims Act imposes civil penalties, often through civil whistleblower or qui tam actions, against individuals or
entities for knowingly presenting, or causing to be presented, to the federal government, claims for payment that are false or fraudulent or making a false statement to avoid, decrease or conceal an
obligation to pay money to the federal government;
- •
- HIPAA, as amended by the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health Act, imposes criminal and civil liability for failure to safeguard the privacy, security and transmission of individually identifiable health information and for executing a scheme to defraud any federal healthcare program;
47
- •
- the federal false statements statute prohibits knowingly and willfully falsifying, concealing or covering up a material fact or making
any materially false statement in any matter within the jurisdiction of the executive, legislative, or judicial branch of the U.S. government, including in connection with the delivery of or payment
for federally reimbursed healthcare benefits, items or services;
- •
- the federal transparency requirements under the "sunshine" provisions of the Affordable Care Act require manufacturers of drugs,
devices, biologics and medical supplies to report to the Department of Health and Human Services information related to physician payments and other transfers of value and physician ownership and
investment interests;
- •
- analogous state laws and regulations, such as state anti-kickback and false claims laws, may apply to sales or marketing arrangements
and claims involving healthcare items or services reimbursed by non-governmental third party payors, including private insurers, and some state laws require pharmaceutical companies to comply with the
pharmaceutical industry's voluntary compliance guidelines and the relevant compliance guidance promulgated by the federal government in addition to requiring drug manufacturers to report information
related to payments to physicians and other healthcare providers or marketing expenditures; and
- •
- analogous foreign laws and regulations, such as anti-bribery laws and laws governing the promotion of medicinal potential fertility treatments or medical devices, as well as the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, may apply to sales or marketing arrangements and interactions with physicians in countries outside the United States.
Efforts to ensure that our business arrangements with third parties will comply with applicable fraud and abuse laws and regulations will involve substantial costs. It is possible that governmental authorities may conclude that our business practices do not comply with current or future statutes, regulations or case law involving applicable fraud and abuse laws and regulations. If our operations are found to be in violation of any of these laws or any other governmental regulations that may apply to us, we may be subject to significant civil, criminal and administrative penalties, damages, fines, exclusion from government funded healthcare programs, such as Medicare and Medicaid, and the curtailment or restructuring of our operations. If any of the IVF clinics or physicians or other providers or entities with whom we expect to do business are found to be not in compliance with applicable laws, they may be subject to criminal, civil or administrative sanctions, including exclusions from government funded healthcare programs.
Even the assertion of a violation under any of these provisions could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations. Any such assertion would likely trigger an investigation of our business or executives that could cause us to incur substantial costs and result in significant liabilities or penalties, as well as damage to our reputation.
Laws and regulations governing international operations, including the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, may preclude us from developing, manufacturing and selling certain potential fertility treatments outside of the United States and require us to develop and implement costly compliance programs.
We have active operations outside of the United States, and we must comply with numerous laws and regulations relating to our business operations in each jurisdiction in which we plan to operate. The creation and implementation of international business practices compliance programs is costly and such programs are difficult to enforce, particularly where reliance on third parties is required.
The Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, or FCPA, prohibits any U.S. individual or business from paying, offering, or authorizing payment or offering of anything of value, directly or indirectly, to any foreign official, political party or candidate for the purpose of influencing any act or decision of the foreign entity in order to assist the individual or business in obtaining or retaining business. The FCPA
48
also obligates companies whose securities are listed in the United States to comply with certain accounting provisions requiring the company to maintain books and records that accurately and fairly reflect all transactions of the corporation, including international subsidiaries, and to devise and maintain an adequate system of internal accounting controls for international operations. The anti-bribery provisions of the FCPA are enforced primarily by the U.S. Department of Justice. The SEC is involved with enforcement of the books and records provisions of the FCPA.
Compliance with the FCPA is expensive and difficult, particularly in countries in which corruption is a recognized problem. In addition, the FCPA presents particular challenges in the biotechnology industry, because, in many countries, hospitals are operated by the government, and doctors and other hospital employees are considered foreign officials. Certain payments to hospitals in connection with clinical studies and other work have been deemed to be improper payments to government officials and have led to FCPA enforcement actions.
The failure to comply with laws governing international business practices may result in substantial penalties. Violation of the FCPA can result in significant civil and criminal penalties. The SEC also may suspend or bar issuers from trading securities on United States exchanges for violations of the FCPA's accounting provisions.
We may have obligations under our contracts with IVF clinics and physicians or other healthcare providers to protect the privacy of patient health information.
In the course of performing our business, we will obtain, from time to time, confidential patient health information. For example, we may learn patient names and be exposed to confidential patient health information when we provide training on the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment and other future potential fertility treatments and services to the staff at IVF clinics and physicians' offices. United States federal and state laws protect the confidentiality of certain patient health information, in particular individually identifiable information, and restrict the use and disclosure of that information. At the federal level, the Department of Health and Human Services promulgated health information and privacy and security rules under HIPAA. At this time, we are not a HIPAA covered entity. However, our current and future business associate or other confidentiality agreements with covered entities contain commitments to protect the privacy and security of patients' health information and, in some instances, may require us to indemnify the covered entity for any claim, liability, damage, cost or expense arising out of or in connection with a breach of the agreement by us. If we were to violate one of these agreements, we could lose customers and be exposed to liability or our reputation and business could be harmed. In addition, the Health Information Technology for Economic and Clinical Health (HITECH) Act, enacted in February 2009, expands the HIPAA privacy and security rules, including imposing many of the requirements of those rules directly on business associates and making business associates directly subject to HIPAA civil and criminal enforcement provisions and associated penalties. We may be required to make costly system modifications to comply with the HIPAA privacy and security requirements. Our failure to comply may result in criminal and civil liability.
Other federal and state laws apply to the use and disclosure of health information, as well as certain financial information, which could affect the manner in which we conduct our business. Such laws are not necessarily preempted by HIPAA, in particular those laws that afford greater protection to the individual than does HIPAA or cover different subject matter. Such state laws typically have their own penalty provisions, which could be applied in the event of an unlawful action affecting health information.
In the member states of the EU and many other countries, we will be subject to similar or more stringent data privacy laws, such as those implementing the European Data Protection Directive 95/46/EC, that require us to protect all individually identifiable information and restrict the
49
use, disclosure and onward transfer of that information. Such national laws typically have their own civil or criminal enforcement provisions and associated penalties. We may incur costs in complying with the applicable privacy and security requirements, which may include registration with the national data protection authorities.
If we fail to comply with environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, we could become subject to fines or penalties or incur costs that could have a material adverse effect on the success of our business.
We are subject to numerous environmental, health and safety laws and regulations, including those governing laboratory procedures and the handling, use, storage, treatment and disposal of hazardous materials and wastes. Our operations involve the use of hazardous and flammable materials, including chemicals and biological materials. Our operations also produce hazardous waste products. We generally contract with third parties for the disposal of these materials and wastes. We cannot eliminate the risk of contamination or injury from these materials. In the event of contamination or injury resulting from our use of hazardous materials, we could be held liable for any resulting damages, and any liability could exceed our resources. We also could incur significant costs associated with civil or criminal fines and penalties.
Although we maintain workers' compensation insurance to cover us for costs and expenses we may incur due to injuries to our employees resulting from the use of hazardous materials, this insurance may not provide adequate coverage against potential liabilities. We do not maintain insurance for environmental liability or toxic tort claims that may be asserted against us in connection with our storage or disposal of biological, hazardous or radioactive materials.
In addition, we may incur substantial costs in order to comply with current or future environmental, health and safety laws and regulations. These current or future laws and regulations may impair our research, development or production efforts. Failure to comply with these laws and regulations also may result in substantial fines, penalties or other sanctions.
Risks Related to the Manufacturing of Our Potential Fertility Treatments
We currently rely on on-site manufacturing at or next to the IVF clinics in which the AUGMENT treatment is offered. In case we decide to use centralized off-site manufacturing in the future, we have entered into an agreement with a third party for the manufacture of the AUGMENT treatment and expect to rely on third parties for the manufacture of our potential fertility treatments for development and commercialization to the extent that we do not rely on on-site manufacturing. This reliance on third parties increases the risk that we will not have sufficient quantities of our potential fertility treatments or such quantities at an acceptable cost, which could delay, prevent or impair our development or commercialization efforts because we have limited control of third parties' activities, including manufacturing capacity and costs and regulatory compliance.
In the international IVF clinics where we have launched the AUGMENT treatment, we currently manufacture on-site in such clinics, using our own equipment and employees. In case we decide in the future to utilize centralized off-site manufacturing, we entered into a master services agreement with global third party manufacturers to provide services for the manufacture of the AUGMENT treatment to perform the identification and isolation of EggPC cells and the preparation of mitochondria steps in the AUGMENT treatment process for our ACE access program and early commercial activities. Though we currently rely on on-site manufacturing, in the future we may decide use our existing global cGTP-compliant manufacturers, contract with in-country manufacturers, manufacture on-site in clinics using our own equipment and employees, or a combination of such methods. While we believe that our third party manufacturers have the capabilities to undertake the manufacture of the AUGMENT treatment in accordance with all applicable rules and regulations, there can be no assurance that they will be able to do so successfully. There can be no assurance that our global contract manufacturers, or any in-country manufacturer that we contract with, will maintain consistent quality standards with
50
respect to any in-house manufacturing we do at individual IVF clinics. While we will seek to maintain high standards by working with high quality clinics, providing our own manufacturing equipment and personnel, and conducting regular training and quality audits, there can be no assurance that such clinics will maintain consistent quality standards. We do not have internal capabilities to manufacture the AUGMENT treatment, or internal or external capabilities to manufacture the OvaPrime treatment, the OvaTure treatment or any other potential fertility treatment.
Reliance on third party manufacturers and laboratories entails additional risks, including:
- •
- reliance on the third party for regulatory compliance and quality assurance;
- •
- the possible breach of the manufacturing or service agreement by the third party; and
- •
- the possible termination or nonrenewal of the agreement by the third party at a time that is costly or inconvenient for us.
We expect to rely on third party manufacturers or third party collaborators for the manufacture of our other potential fertility treatments for preclinical testing, clinical trials and for commercial supply. We may be unable to establish any agreements with third party manufacturers or to do so on acceptable terms.
Third party manufacturers and laboratories may not be able to comply with cGTP or current good manufacturing practice, or cGMP, regulations or similar regulatory requirements outside the United States. Any performance failure on the part of our existing or future manufacturers and service providers could delay clinical development or marketing approval or adversely affect or impede commercial sales. Our failure, or the failure of our third party manufacturers and service providers, to comply with applicable regulations could also result in sanctions being imposed on us, including fines, injunctions, civil penalties, suspension or withdrawal of approvals, license revocation, seizures or recalls of products, operating restrictions and criminal prosecutions, any of which could significantly and adversely affect supplies of our potential fertility treatments and harm our business and results of operations.
We may compete with other companies for access to manufacturing facilities. There are a limited number of manufacturers that operate under cGTP and cGMP regulations and that might be capable of manufacturing for us. It is possible that some of these manufacturers have agreements with our competitors that limit or restrict their ability to contract with us, further narrowing the number of manufacturers that are available to us.
We do not currently have arrangements in place for redundant supply or a second manufacturing source for the AUGMENT treatment. Although we believe that there are other potential alternative manufacturers who could manufacture our potential fertility treatments, we may incur added costs and delays in identifying and qualifying any such replacement. We are pursuing a second manufacturing source for the AUGMENT treatment.
Our potential future dependence upon others for the manufacture of our potential fertility treatments, were we to cease relying on on-site manufacturing, may adversely affect our future profit margins and our ability to commercialize the AUGMENT treatment or any future potential fertility treatments that we seek to market on a timely and competitive basis.
We do not currently manufacture the AUGMENT treatment outside of the United States, other than on-site in ACE clinics. If our current third party manufacturer is unable to supply the AUGMENT treatment for certain countries outside the United States, and if we decide not to rely on on-site manufacturing, we will need to contract with third party manufacturers that comply with cGTP regulations to supply the AUGMENT treatment in other jurisdictions in which we decide to commercialize the AUGMENT treatment. Although we believe there are other manufacturers who could manufacture our potential fertility treatments outside the United States, we may incur added costs and delays in identifying and qualifying a non-United States manufacturer.
51
If we use separate manufacturing sites in the future, rather than relying on on-site manufacturing, providing the AUGMENT treatment to patients in regions outside the region where the manufacturing site is located will require coordination internally among our employees and externally with physicians, IVF clinics, regulatory authorities and third party manufacturers, suppliers and carriers. For example, a patient's physician or clinical site will need to coordinate with us to ship a patient's ovarian tissue biopsy to the cGTP-compliant facility responsible for the next steps in the AUGMENT treatment process, and we will need to coordinate with them to ship isolated cellular components from the patient's processed tissue back to them. Such coordination involves a number of risks that may lead to failures or delays in processing the AUGMENT treatment. If we are unable to coordinate appropriately, we may encounter delays, incur additional costs or adversely affect our ability to commercialize the AUGMENT treatment.
In the future, we may build and equip a cGTP-compliant facility for the processing of the AUGMENT treatment. Constructing and equipping such a facility in compliance with regulatory requirements will be time consuming and expensive.
In the future, we may lease, build and equip a cGTP-compliant facility for the processing of the AUGMENT treatment. We believe that such a facility may be important to our ability to meet demand for the AUGMENT treatment and to process the AUGMENT treatment on a cost-effective basis. The leasing, build-out and equipping of this facility will require substantial capital expenditures. In addition, it will be costly and time consuming to recruit necessary additional personnel for the operation of the facility. Furthermore, we do not have experience running a manufacturing facility. Nor do we currently have funding available for any of these purposes. If we are unable to successfully construct and equip a commercial manufacturing facility in compliance with regulatory requirements, or hire additional necessary personnel appropriately, our revenues from the AUGMENT treatment, and the profitability of such revenues, may be adversely affected.
Lack of coordination internally among our employees and externally with physicians, IVF clinics and third party suppliers and carriers could result in processing and manufacturing difficulties, regulatory enforcement actions, disruptions or delays and cause us to have insufficient resources to meet any of the AUGMENT treatment site's requirements or potential commercial requirements.
Providing the AUGMENT treatment to patients requires coordination internally among our employees and externally with physicians, IVF clinics and third party suppliers and carriers. For example, a patient's physician or clinical site will need to coordinate with us to ship a patient's ovarian tissue biopsy to the cGTP-compliant facility responsible for the next steps in the AUGMENT treatment process, such as the ACE clinic, and we will need to coordinate with them to ship the patient's egg precursor cells, or the patient's mitochondria from the egg precursor cells, to them if the manufacturing is not done on-site at the ACE clinic. Such coordination involves a number of risks that may lead to failures or delays in processing our AUGMENT treatment, including:
- •
- difficulties in the timely shipping of patient-specific materials to us or in the shipping of our potential fertility treatments to
the treating physicians due to errors by third party carriers, transportation restrictions or delays or other reasons;
- •
- destruction of, or damage to, patient-specific materials or our potential fertility treatments during the shipping process due to
improper handling by third party carriers, hospitals, physicians or us;
- •
- destruction of, or damage to, patient-specific materials during any of the tissue or cell processing steps required for egg precursor
cell isolation and selection of the patient-specific mitochondria;
- •
- destruction of, or damage to, patient-specific materials or our potential fertility treatments during storage at our facilities;
52
- •
- failure to maintain precise patient records sufficient to ensure the chain of custody procedures are followed;
- •
- destruction of, or damage to, patient-specific materials or our potential fertility treatments stored at clinical and future
commercial sites due to improper handling or holding by clinicians, hospitals or physicians;
- •
- failure to ensure adequate quality control and assurances in the AUGMENT treatment process as we increase production quantities; and
- •
- failure to establish or maintain sufficient manufacturing capacity, whether through third party manufacturers or internally.
If we are unable to coordinate appropriately, we may encounter delays or additional costs in achieving our clinical and commercialization objectives. We, or third parties, could face regulatory action as a result of the failure to comply with cGTPs or other applicable rules. Some or all of these risks may also be applicable to the OvaTure treatment and any other future potential fertility treatments.
Risks Related to Our Dependence on Third Parties
We currently rely and will in the future rely on selected international IVF clinics to continue to commercialize, gain experience and generate data on the AUGMENT treatment and to introduce the OvaPrime treatment if our preclinical studies and potential fertility treatment optimization efforts are successful. We will also rely on third parties to conduct any necessary clinical trials for other potential fertility treatments. Such third parties may not perform satisfactorily, including failing to meet volume expectations, quality standards or deadlines for the completion of such studies or trials.
Our reliance on these third parties for providing our potential fertility treatments and for clinical development activities will reduce our control over these activities.
We will remain responsible for ensuring that the AUGMENT treatment and the OvaPrime treatment, when and if the OvaPrime treatment is introduced to international IVF clinics, are introduced with consistent and high quality standards. Moreover, the FDA and equivalent Foreign Regulatory Authorities will require us to comply with GCPs with respect to any clinical trials for any of our potential fertility conducted in connection with a submission to the FDA or Foreign Regulatory Authorities, including an IND or equivalent application, and will require that we record and report clinical trial results to assure that data and reported results are credible and accurate and that the rights and safety are protected. We will also be required to register ongoing FDA-regulated clinical trials and post the results of completed clinical trials on a government-sponsored database, ClinicalTrials.gov, within certain timeframes. Failure to do so can result in fines, adverse publicity and civil and criminal sanctions.
Our reliance on these third parties for providing the AUGMENT treatment to IVF clinics and conducting clinical development activities will reduce our control over these activities. If these third parties do not successfully carry out their contractual duties, meet expected deadlines, provide our potential fertility treatments, conduct our clinical trials in accordance with regulatory requirements or our stated protocols or maintain consistent quality standards, in the case of contract manufacturing and clinics manufacturing our treatments on site, we will not be able to obtain, or may be delayed in obtaining, regulatory approvals for our potential fertility treatments and will not be able to, or may be delayed in our efforts to, successfully commercialize our potential fertility treatments. Furthermore, these third parties may also have relationships with other entities, some of which may be our competitors, and could devote more of their resources to such other entities at the expense of expending sufficient resources on our clinical development activities.
53
We expect to depend on collaborations with third parties, particularly Intrexon, for the development and commercialization of our potential fertility treatments. If those collaborations are not successful, we may not be able to capitalize on the market potential of these potential fertility treatments.
In December 2013, we established a collaboration with Intrexon to accelerate development of the OvaTure treatment, and entered into the OvaXon joint venture with Intrexon to create new applications to prevent inherited diseases for human and animal health. Further, we currently intend to commercialize the AUGMENT treatment and the OvaPrime treatment ourselves in some markets and to collaborate with third parties to commercialize the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment and any future potential fertility treatments in other markets. In addition, we may seek partners for further development and commercialization of our other potential fertility treatments. These collaborations could take the form of license, distribution, sales representative, joint venture, sponsored research, co-promotion or other arrangements with pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, other commercial entities and academic and other institutions.
In any such arrangements with third parties, we will likely have limited control over the amount and timing of resources that such collaborators dedicate to the development or commercialization of our potential fertility treatments. Collaboration agreements may not lead to development or commercialization of potential fertility treatments in the most efficient manner, or at all. Our ability to generate revenues from these arrangements will depend on, among other things, our collaborators' successful performance of the functions assigned to them in these arrangements.
Collaborations involving our potential fertility treatments would pose the following risks to us:
- •
- collaborators have significant discretion in determining the efforts and resources that they will apply to these collaborations and
could devote fewer resources to our potential fertility treatments than we expect them to;
- •
- a collaborator with marketing and distribution rights to one or more other potential fertility treatments may not commit sufficient
resources to the marketing and distribution of our potential fertility treatments;
- •
- collaborators may not pursue development and commercialization of our potential fertility treatments or may elect not to continue or
renew development or commercialization programs based on clinical trial results, changes in the collaborator's strategic focus or available funding, or external factors such as an acquisition that
diverts resources or creates competing priorities;
- •
- collaborators may delay clinical trials, provide insufficient funding for a clinical trial program, stop a clinical trial, abandon a
potential fertility treatment or repeat or conduct new clinical trials;
- •
- collaborators could independently develop, or develop with third parties, potential fertility treatments that compete directly or
indirectly with our potential fertility treatments;
- •
- collaborators may create intellectual property that we need to in-license, may not properly maintain or defend our intellectual
property rights or may use our proprietary information in such a way as to invite litigation that could jeopardize or invalidate our proprietary information;
- •
- disputes may arise between the collaborators and us that result in the delay or termination of the research, development or
commercialization of our potential fertility treatments or that result in costly litigation or arbitration that diverts management's attention and resources; and
- •
- collaborations may be terminated and, if terminated, may result in a need for additional capital to pursue further development or commercialization of the applicable potential fertility treatments.
54
If we are not able to establish collaborations, we may have to alter our development and commercialization plans.
Our potential fertility treatment development programs and the potential commercialization of such treatments will require substantial additional cash to fund expenses. We may collaborate with pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies for the development and potential commercialization of some of our potential fertility treatments. For example, we currently intend to seek to collaborate with third parties to commercialize the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment and other potential fertility treatments we successfully develop.
We face significant competition in seeking appropriate collaborators. Whether we reach a definitive agreement for a collaboration will depend, among other things, upon our assessment of the collaborator's resources and expertise, the terms and conditions of the proposed collaboration, and the proposed collaborator's evaluation of a number of factors. Those factors may include the design or results of our clinical trials, if any, the likelihood of approval by the FDA or similar regulatory authorities outside the United States or the availability of an exemption for the need or pre-marketing review or approval of our potential fertility treatment, the potential market for such potential fertility treatment, the costs and complexities of manufacturing and delivering the potential fertility treatment to patients, the potential and relative cost of competing fertility treatments, uncertainty with respect to our ownership of technology, which can exist if there is a challenge to such ownership without regard to the merits of the challenge, and industry and market conditions generally. The collaborator may also consider alternative potential fertility treatments or technologies for similar indications or conditions that may be available to collaborate on and whether such a collaboration could be more attractive than the one with us for our potential fertility treatment. We may also be restricted under existing license agreements from entering into agreements on certain terms with potential collaborators. In addition, there have been a significant number of business combinations among pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies that have resulted in a reduced number of potential future collaborators. Collaborations are complex and time consuming to negotiate, document and manage. We may not be able to negotiate collaborations on a timely basis, on acceptable terms, or at all.
If we are not able to obtain a collaborator for a particular program, we may have to curtail the development of such program or of one or more of our other development programs, delay the potential commercialization of such program, reduce the scope of any sales or marketing activities for the program or increase our expenditures and undertake development or commercialization activities for the program at our own expense. If we elect to increase our expenditures to fund development or commercialization activities on our own, we may need to obtain additional capital, which may not be available to us on acceptable terms or at all. If we do not have sufficient funds, we may not be able to further develop our potential fertility treatments or bring these potential fertility treatments to market and generate revenue.
Risks Related to Our Intellectual Property
If we fail to comply with our obligations under our intellectual property licenses, we could lose license rights that are important to our business.
We have an exclusive license from MGH with respect to the intellectual property that forms the basis of our business. The license under MGH-owned patent rights and know-how is for human female fertility, the treatment or prevention of inherited (including mitochondrial) diseases or defects in all animals, including humans, assisted and/or artificial reproductive technology in all non-human animals, and the artificial creation of food, research animals and/or animal products; and the license under the MGH and Harvard co-owned patent right is for ex-vivo human female fertility treatments. Our existing MGH license agreement and another agreement granting rights impose, and we expect that future license agreements will impose, various obligations on us, including diligence, milestone payments,
55
royalty payments, insurance and other obligations. For example, under our license agreement with MGH, we are required to use commercially reasonable efforts to develop and make available to the public licensed fertility treatments and to satisfy specified diligence milestones within specified timeframes. If we fail to comply with our obligations under this or other of our license agreements, our licensors may have the right to terminate our licenses, in which event we might not be able to market potential fertility treatments that are covered by these agreements, or to convert our licenses to non-exclusive licenses, which could materially adversely affect the value of the potential fertility treatments we developed under the license agreements. Termination of these license agreements or reduction or elimination of our licensed rights may result in our having to negotiate new or reinstated licenses with less favorable terms, or to cease commercialization of licensed technology and potential fertility treatments. This could materially adversely affect our business, particularly in the case of our license from MGH.
If we are unable to obtain and maintain patent protection for our technology and potential fertility treatments, or if our licensors are unable to obtain and maintain patent protection for the technology or potential fertility treatments that we license from them, our competitors could develop and commercialize technology and potential fertility treatments similar or identical to ours, and our ability to successfully commercialize our technology and potential fertility treatments may be adversely affected.
Our success depends in large part on our and our licensors' ability to obtain and maintain patent protection in the United States and other countries with respect to our proprietary technology and potential fertility treatments. We and our licensors have sought to protect our proprietary position by filing patent applications within the United States and abroad related to our novel technologies and potential fertility treatments that are important to our business. The process of obtaining patent protection is uncertain, and we and our licensors may not succeed in obtaining the patent protection for our novel technologies and potential fertility treatments that we seek. If we and our licensors are unable to obtain and maintain patent protection of sufficient scope for our technology and potential fertility treatments, our competitors could develop and commercialize technology and potential fertility treatments similar or identical to ours, and in that case our ability to successfully commercialize our technology and potential fertility treatments may be adversely affected. This risk is greater outside the United States where some aspects of our in-licensed intellectual property are not protected by patents. In addition, the laws of foreign countries may not protect our rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States.
Moreover, under our license agreement with MGH, we do not have the right to control the preparation, filing and prosecution of the licensed patent applications, to defend the validity and enforceability of the licensed patents against challenges by third parties, or to maintain the licensed patents covering our technology or potential fertility treatments. This could also be the case under any other license agreements we enter into in the future. Therefore, we rely on MGH, and may rely on other licensors in the future, to file, defend and maintain patents that are important to our business. The failure of MGH or other licensors to successfully prosecute, defend and maintain these patents and patent applications in a manner consistent with the best interests of our business could adversely affect our ability to successfully commercialize our technology and potential fertility treatments.
The patent position of biotechnology and pharmaceutical companies generally is highly uncertain, involves complex legal and factual questions and has in recent years been the subject of much litigation. As a result, the issuance, scope, validity, enforceability and commercial value of our and our licensors' patent rights are highly uncertain. Our and our licensors' pending and future patent applications may not result in patents being issued which protect our technology or potential fertility treatments or that effectively prevent others from commercializing competitive technologies and potential fertility treatments. Changes in either the patent laws or interpretation of the patent laws in the United States
56
and other countries may diminish the value of our patents or narrow the scope of our patent protection.
Publications of discoveries in the scientific literature often lag behind the actual discoveries, and patent applications in the United States and other jurisdictions are typically not published until 18 months after filing, or in some cases not at all. Therefore we cannot be certain that we or our licensors were the first to make the inventions claimed in our owned or licensed patents or pending patent applications, or that we or our licensors were the first to file for patent protection of such inventions.
Under the America Invents Act enacted in September 2011, the United States moved to a first inventor to file system in March 2013. Outside the United States, the first to file a patent application is generally entitled to the patent. We may become involved in patent litigation or reexamination, post-grant review, opposition, derivation or interference proceedings challenging our patent rights or the patent rights of others. An adverse determination in any such litigation or proceeding could reduce the scope of, or invalidate, our patent rights, allow third parties to commercialize our technology or potential fertility treatments and compete directly with us, without payment to us, or result in our inability to manufacture or commercialize potential fertility treatments without infringing third party patent rights.
If the scope of the patent protection we or our licensors obtain is not sufficiently broad, we may not be able to prevent others from developing and commercializing technology and potential fertility treatments similar or identical to ours.
Our owned and licensed patents and any owned or licensed patent applications that issue as patents may not provide us with any meaningful protection, prevent competitors from competing with us or otherwise provide us with any competitive advantage. Our competitors may be able to circumvent our owned or licensed patents by developing similar or alternative technologies or potential fertility treatments in a non-infringing manner. The issuance of a patent is not conclusive as to its scope, validity or enforceability, and our owned and licensed patents may be challenged in the courts or patent offices in the United States and abroad. Such challenges may result in patent claims being narrowed, invalidated or held unenforceable, which could limit our ability to use and commercialize, or to stop or prevent others from using or commercializing, similar or identical technology and potential fertility treatments, or limit the duration of the patent protection of our technology and potential fertility treatments. Given the amount of time required for the development, testing and regulatory review of new potential fertility treatments, patents protecting such candidates might expire before or shortly after such candidates are commercialized. For example, certain of the U.S. patents and patent applications that we exclusively license from MGH will expire in May 2025. As a result, our owned and licensed patent portfolio may not provide us with sufficient rights to exclude others from commercializing potential fertility treatments similar or identical to ours.
We may initiate lawsuits to protect or enforce our patents, which could be expensive, time consuming and unsuccessful.
Competitors may infringe our patents. To counter infringement or unauthorized use, we may be required to file infringement claims, which can be expensive and time consuming. In addition, in an infringement proceeding, a court may decide that a patent of ours is invalid or unenforceable, or may refuse to stop the other party from using the technology at issue on the grounds that our patents do not cover the technology in question. An adverse result in any litigation proceeding could put one or more of our patents at risk of being invalidated or interpreted narrowly. Furthermore, because of the substantial amount of discovery required in connection with intellectual property litigation, there is a risk that some of our confidential information could be compromised by disclosure during litigation.
57
Third parties may initiate legal proceedings alleging that we are infringing their intellectual property rights, the outcome of which would be uncertain and could have a material adverse effect on the success of our business.
Our commercial success depends upon our ability and the ability of our current and future collaborators to develop, manufacture, market and sell our potential fertility treatments and use our proprietary technologies without infringing the proprietary rights of third parties. We may become party to, or threatened with, future adversarial proceedings or litigation regarding intellectual property rights with respect to our potential fertility treatments and technology, including interference proceedings before the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office. Third parties may assert infringement claims against us based on existing patents or patents that may be granted in the future. If we are found to infringe a third party's intellectual property rights, we could be required to obtain a license from such third party to continue developing and marketing our potential fertility treatments and technology. However, we may not be able to obtain any required license on commercially reasonable terms or at all. Even if we were able to obtain a license, it could be non-exclusive, thereby giving our competitors access to the same technologies licensed to us. We could be forced, including by court order, to cease commercializing the infringing technology or treatment. In addition, we could be found liable for monetary damages. A finding of infringement could prevent us from commercializing our potential fertility treatments or force us to cease some of our business operations, which could materially harm our business. Claims that we have wrongfully appropriated the confidential information or trade secrets of third parties could have a similar negative impact on our business.
We may be subject to claims that our employees have wrongfully appropriated, used or disclosed intellectual property of their former employers.
Many of our employees were previously employed at universities or other biotechnology or pharmaceutical companies. Although we try to ensure that our employees do not appropriate or use the proprietary information or know-how of others in their work for us, we may be subject to claims that we or these employees have appropriated, used or disclosed intellectual property, including information forming the basis of patents and patent applications, trade secrets or other proprietary information, of any such employee's former employer. Litigation may be necessary to defend against these claims. If we fail in defending any such claims, in addition to paying monetary damages, we may lose valuable intellectual property rights or personnel and our reputation may be harmed.
Intellectual property litigation could cause us to spend substantial resources and distract our personnel from their normal responsibilities.
Even if resolved in our favor, litigation or other legal proceedings relating to intellectual property claims may cause us to incur significant expenses, and could distract our technical and management personnel from their normal responsibilities. In addition, there could be public announcements of the results of hearings, motions or other interim proceedings or developments and if securities analysts or investors perceive these results to be negative, such developments could have a substantial adverse effect on the price of our common stock. Such litigation or proceedings could substantially increase our operating losses, reduce the resources available for development activities and adversely affect our ability to raise additional funds. We may not have sufficient financial or other resources to adequately conduct such litigation or proceedings. Some of our competitors may be able to sustain the costs of such litigation or proceedings more effectively than we can because of their greater financial resources. Uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of patent litigation or other proceedings could have a material adverse effect on our ability to compete in the marketplace.
58
If we are unable to protect the confidentiality of our trade secrets, our business and competitive position would be harmed.
In addition to seeking patents for some of our technology and potential fertility treatments, we also rely on trade secrets, including unpatented know-how, technology and other proprietary information, to maintain our competitive position. The protection available for trade secrets is particularly important with respect to our process for manufacturing the AUGMENT treatment, to the OvaPrime treatment and to our other potential fertility treatments, which will involve significant unpatented know-how. Any appropriation of our know-how, by competing contract manufacturers, collaborators or otherwise, could harm our business and we could suffer financial loss. We seek to protect these trade secrets, in part, by entering into non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements with parties who have access to such trade secrets, such as our employees, corporate collaborators, outside scientific collaborators, sponsored researchers, contract manufacturers, consultants, advisors and other third parties. We also enter into confidentiality and invention or patent assignment agreements with our employees and consultants. Despite these efforts, any of these parties may breach the agreements and disclose our proprietary information, including our trade secrets, and we may not be able to obtain adequate remedies for such breaches. Enforcing a claim that a party illegally disclosed or misappropriated a trade secret is difficult, expensive and time consuming, and the outcome is unpredictable. In addition, some courts inside and outside the United States are less willing or unwilling to protect trade secrets. If any of our trade secrets were to be lawfully obtained or independently developed by a competitor, we would have no right to prevent such competitor from using that technology or information to compete with us. If any of our trade secrets were to be disclosed to or independently developed by a competitor, our competitive position would be harmed.
Risks Related to Employee Matters and Managing Growth
Our future success depends on our ability to retain our chief executive officer and other key executives and to attract, retain and motivate qualified personnel.
We are highly dependent on Dr. Dipp, our chief executive officer, Arthur Tzianabos, our president and chief scientific officer, David Harding, our chief commercial officer and Jeff Young, our chief financial officer, as well as the other principal members of our management and scientific teams. Although we have entered into employment arrangements with Dr. Dipp, Dr. Tzianabos, Mr. Harding and Mr. Young providing for certain benefits, including severance in the event of a termination without cause, these arrangements do not prevent them from terminating their employment with us at any time. We do not maintain "key person" insurance for any of our executives or other employees. The loss of the services of any of these persons could impede the achievement of our research, development and commercialization objectives.
In addition to her role as chief executive officer of our company, Dr. Dipp also serves as a general partner of Longwood Fund, LP, a venture capital investment fund. It is possible that Dr. Dipp may transition to an executive chairman role at our company at some point in the future, once we have meaningfully advanced our development efforts, grown our company overall and identified and hired a suitable successor. In such event, we will need to recruit and hire a new principal executive officer. Our inability to hire a suitable executive to assume this position in a timely fashion could delay the execution of our business plans or disrupt our operations.
Recruiting and retaining qualified scientific, clinical, manufacturing and sales and marketing personnel will also be critical to our success. We may not be able to attract and retain these personnel on acceptable terms given the competition among numerous pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies for similar personnel. We also experience competition for the hiring of scientific and clinical personnel from universities and research institutions. In addition, we rely on consultants and advisors, including scientific and clinical advisors, to assist us in formulating our research and development and
59
commercialization strategy. Our consultants and advisors, including our scientific co-founders, may be employed by employers other than us and may have commitments under consulting or advisory contracts with other entities that may limit their availability to us.
We expect to expand our research and development and future sales and marketing capabilities, and as a result, we may encounter difficulties in managing our growth, which could disrupt our operations.
We expect to experience growth in the number of our employees and the scope of our operations, particularly in the areas of research and development and sales and marketing. To manage our anticipated future growth, we must continue to implement and improve our managerial, operational and financial systems, expand our facilities and continue to recruit and train additional qualified personnel. Due to our limited financial resources and the limited experience of our management team in managing a company with such anticipated growth, we may not be able to effectively manage the expansion of our operations or recruit and train additional qualified personnel.
The physical expansion of our operations may also lead to significant costs and may divert our management and business development resources. Any inability to manage growth could delay the execution of our business plans or disrupt our operations.
A breakdown or breach of our information technology systems could subject us to liability or interrupt the operation of our business.
Many of our key business processes are facilitated by information technology systems. Information technology systems are potentially vulnerable to breakdown, malicious intrusion and random attack. Likewise, individuals authorized to access our information technology systems may pose a risk by exposing private or confidential data to unauthorized persons or to the public. While we believe that we have taken appropriate security measures to minimize these risks to our data and information technology systems, there can be no assurance that our efforts will prevent breakdowns or breaches in our systems that could adversely affect our business.
Risks Associated with Our Capital Stock
The market price of our common stock may be volatile and may fluctuate in a way that is disproportionate to our operating performance.
Even if an active trading market develops for our common stock, our stock price may experience substantial volatility as a result of a number of factors, including:
- •
- sales or potential sales of substantial amounts of our common stock;
- •
- the delay or failure to execute our plans for the AUGMENT treatment, the OvaPrime treatment or the OvaTure treatment;
- •
- results of preclinical testing or clinical trials of our potential fertility treatments, including the OvaTure treatment, or those of
our competitors;
- •
- the cost of our development programs;
- •
- the success of competitive potential fertility treatments or technologies;
- •
- the success of our OvaXon joint venture with Intrexon;
- •
- announcements about us or about our competitors, including clinical trial results, regulatory approvals, new potential fertility
treatment introductions and commercial results;
- •
- the recruitment or departure of key personnel;
- •
- developments concerning our licensors or manufacturers;
60
- •
- the results of our efforts to discover, acquire or in-license additional potential fertility treatments;
- •
- litigation and other developments relating to our issued patents or patent applications or other proprietary rights or those of our
competitors or other material litigation;
- •
- disagreement by the FDA or equivalent Foreign Regulatory Authorities regarding the regulatory pathway applicable to the AUGMENT
treatment, the OvaPrime treatment or the OvaTure treatment;
- •
- regulatory or legal developments in the United States or other countries, particularly with respect to IVF procedures;
- •
- conditions in the pharmaceutical or biotechnology industries;
- •
- changes in the structure of healthcare payment systems;
- •
- actual or anticipated changes in estimates as to financial results, development timelines or recommendations by securities analysts;
- •
- variations in our financial results or those of companies that are perceived to be similar to us; and
- •
- general economic, industry and market conditions.
Many of these factors are beyond our control. The stock markets in general, and the market for pharmaceutical and biotechnological companies in particular, have historically experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations. These fluctuations often have been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of these companies. Broad market and industry factors could reduce the market price of our common stock, regardless of our actual operating performance.
We have never paid and do not intend to pay cash dividends.
We have never paid cash dividends on any of our capital stock and we currently intend to retain future earnings, if any, to fund the development and growth of our business. As a result, capital appreciation, if any, of our common stock will be our common stockholders' sole source of gain for the foreseeable future.
Provisions in our certificate of incorporation and by-laws and under Delaware law could make an acquisition of us, which may be beneficial to our stockholders, more difficult and may prevent attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management.
Provisions in our certificate of incorporation and by-laws may discourage, delay or prevent a merger, acquisition or other change in control of us that stockholders may consider favorable, including transactions in which our common stockholders might otherwise receive a premium price for their shares. These provisions could also limit the price that investors might be willing to pay in the future for shares of our common stock, thereby depressing the market price of our common stock. In addition, because our board of directors is responsible for appointing the members of our management team, these provisions may frustrate or prevent any attempts by our stockholders to replace or remove our current management by making it more difficult for stockholders to replace members of our board of directors. Among other things, these provisions:
- •
- establish a classified board of directors such that not all members of the board are elected at one time;
- •
- allow the authorized number of our directors to be changed only by resolution of our board of directors;
61
- •
- limit the manner in which stockholders can remove directors from the board;
- •
- establish advance notice requirements for stockholder proposals that can be acted on at stockholder meetings and for nominations to
our board of directors;
- •
- limit who may call stockholder meetings;
- •
- prohibit actions by our stockholders by written consent;
- •
- require that stockholder actions be effected at a duly called stockholders meeting;
- •
- authorize our board of directors to issue preferred stock without stockholder approval, which could be used to institute a "poison
pill" that would work to dilute the stock ownership of a potential hostile acquirer, effectively preventing acquisitions that have not been approved by our board of directors; and
- •
- require the approval of the holders of at least 75% of the votes that all our stockholders would be entitled to cast to amend or repeal certain provisions of our certificate of incorporation or by-laws.
Moreover, because we are incorporated in Delaware, we are governed by the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law, which prohibits a person who owns 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock from merging or combining with us for a period of three years after the date of the transaction in which the person acquired 15% or more of our outstanding voting stock, unless the merger or combination is approved in a manner prescribed by the statute.
We are an "emerging growth company" and have elected to comply with certain reduced public company reporting requirements applicable to emerging growth companies, which could make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an "emerging growth company," as defined in the JOBS Act enacted in April 2012. We have chosen and may continue to choose to take advantage of exemptions from various public company reporting requirements for as long as we continue to be an emerging growth company.
These exemptions include, but are not limited to, (1) not being required to comply with the auditor attestation requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, (2) reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports, proxy statements and registration statements, and (3) exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. We could be an emerging growth company for up to five years after the first sale of our common equity securities pursuant to an effective registration statement under the Securities Act. However, if certain events occur prior to the end of such five year period, including if we become a "large accelerated filer," our annual gross revenues exceed $1 billion or we issue more than $1 billion of non-convertible debt in any three year period, we would cease to be an emerging growth company prior to the end of such five year period. We have taken advantage of certain of the reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in the filings we have made with the SEC and may elect to take advantage of other reduced burdens in future filings. As a result, the information that we provide to our stockholders may be different than you might receive from other public reporting companies in which you hold equity interests. We cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive as a result of our reliance on these exemptions. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result of any choice we make to reduce disclosure, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile.
62
We will continue to incur increased costs as a result of operating as a public company, particularly once we cease to be an emerging growth company, and our management will be required to devote substantial time to new compliance initiatives.
As a public reporting company, we have incurred significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company. In addition, the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and rules subsequently implemented by the SEC and NASDAQ have imposed various requirements on public companies, including establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls and corporate governance practices. Our management and other personnel have devoted a substantial amount of time to these compliance initiatives. Moreover, these rules and regulations will increase our legal and financial compliance costs and will make some activities more time consuming and costly. For example, we expect that these rules and regulations may make it more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance, and we may be required to accept reduced policy limits and coverage or incur substantial costs to maintain the same or similar coverage.
Pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, or Section 404, we are required to furnish a report by our management on our internal control over financial reporting, and, once we cease to be an emerging growth company, will be required to include an attestation report on internal control over financial reporting issued by our independent registered public accounting firm. To achieve compliance with Section 404 within the prescribed time period we have documented and evaluated our internal control over financial reporting, which may be costly. In this regard, we will need to continue to dedicate internal resources, potentially engage outside consultants and adopt a detailed work plan to assess and document the adequacy of internal control over financial reporting, continue steps to improve control processes as appropriate, validate through testing that controls are functioning as documented and implement a continuous reporting and improvement process for internal control over financial reporting.
We and certain of our executive officers are currently subject to securities class action litigation in connection with our announcement of receiving an "untitled" letter from the FDA, that could result in substantial costs and divert management's attention.
Following our announcement of an "untitled" letter from the FDA, a purported shareholder class action was filed against us and certain of our executive officers alleging violation of federal securities laws. We believe such claims are without merit, and will engage in a vigorous defense of such litigation. In connection with such litigation, we could incur substantial costs and such costs and any related settlements or judgments may not be covered by insurance. We could also suffer a significant adverse impact on our reputation and divert management's attention and resources, which could have a material adverse effect on our business.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments
None.
We currently occupy approximately 13,700 square feet of office and laboratory space in Cambridge, Massachusetts. 6,000 square feet are under a lease that expires in August 2017, 5,800 square feet are under a lease that expires in December 2015, and the remaining 1,900 square feet are under a sublease that expires in August 2015. We believe our facility is sufficient to meet our current needs and that suitable additional space will be available if and when needed.
63
On September 16, 2013, a purported shareholder class action, styled Meriam Ratner v. OvaScience, Inc., et al., was filed in the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts, naming us and certain of our officers as defendants. The lawsuit alleges that we made material misrepresentations and/or omissions of material fact relating to the qualification of AUGMENT as a 361 HCT/P in our public disclosures during the period from February 25, 2013 through September 10, 2013, in violation of Sections 10(b) and 20(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and Rule 10b-5 promulgated thereunder. On February 2, 2014, we and certain of our officers, as defendants, filed a motion to dismiss with the District Court. On February 3, 2014, plaintiff Meriam Ratner voluntarily dismissed the suit without prejudice.
On June 6, 2014, this purported shareholder class action was re-filed by the plaintiff in the United States District Court for the District of Massachusetts, naming us and certain of our officers as defendants. The lawsuit includes the same allegations as were included in the action filed on September 16, 2013. The plaintiff filed an amended complaint on October 31, 2014. As amended, the complaint seeks certification of a class of purchasers of our stock during the period February 25, 2013 through September 10, 2013. The plaintiff seeks unspecified monetary damages on behalf of the putative class and an award of costs and expenses, including attorney's fees. On December 16, 2014, we moved to dismiss the complaint. The court has not yet ruled on that motion. We believe that this action is without merit and intend to defend it vigorously. At this time, no assessment can be made as to the likely outcome of this lawsuit or whether the outcome will be material to us.
We are not party to any other litigation in any court and management is not aware of any contemplated proceeding by any governmental authority against the Company.
Item 4. Mine Safety Disclosures
Not Applicable.
64
Item 5. Market for Registrant's Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
Market Information
Our common stock began trading on the NASDAQ Global Market ("NASDAQ") on April 30, 2013 under the symbol "OVAS." Our common stock was first traded on the OTC Bulletin Board on November 9, 2012 under the symbol "OVSC." Prior to that date, there was no public market for our common stock.
The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the high and low sales prices and the high and low bid information of our common stock as reported by NASDAQ and the OTC Bulletin Board, as applicable, for the periods indicated:
Year Ended December 31, 2014
|
High | Low | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Fourth Quarter 2014 |
$ | 50.44 | $ | 13.25 | |||
Third Quarter 2014 |
$ | 16.90 | $ | 8.73 | |||
Second Quarter 2014 |
$ | 9.57 | $ | 5.51 | |||
First Quarter 2014 |
$ | 11.48 | $ | 8.37 | |||
Year Ended December 31, 2013
|
High | Low | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Fourth Quarter 2013 |
$ | 10.30 | $ | 8.14 | |||
Third Quarter 2013 |
$ | 15.75 | $ | 9.06 | |||
Second Quarter 2013 (beginning April 30, 2013) |
$ | 16.00 | $ | 10.50 | |||
| |
High Closing Price |
Low Closing Price |
High Bid Price |
Low Bid Price |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Second Quarter 2013 (through April 29, 2013) |
$ | 12.50 | $ | 9.00 | $ | 13.50 | $ | 9.00 | |||||
First Quarter 2013 |
$ | 14.00 | $ | 8.15 | $ | 15.00 | $ | 8.15 | |||||
The over-the-counter market quotations from January 1, 2013 to April 29, 2013 reflect inter-dealer prices, without retail mark-up, mark-down or commission. The high and low bid prices do not necessarily represent actual transactions.
On March 6, 2015, the closing price of a share of our common stock on NASDAQ was $42.00.
Holders
As of February 28, 2015, there were 26,955,670 shares of common stock outstanding, which were held by approximately 100 record holders.
Dividends
We have never paid cash dividends on any of our capital stock and we currently intend to retain our future earnings, if any, to fund the development and growth of our business. We do not intend to pay cash dividends to holders of our common stock in the foreseeable future.
Performance Graph
The graph below compares the cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock, the NASDAQ Composite Index and the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index assuming the investment of $100.00 on November 12, 2012, the day our stock began trading publically, with dividends being
65
reinvested. The stock price performance in the graph below is not necessarily indicative of future price performance.
Recent Sales of Unregistered Securities
As previously reported, on December 9, 2014, the Company issued an option grant to David P. Harding, Chief Commercial Officer, as a new hire inducement grant pursuant to NASDAQ Listing Rule 5635(c)(4) and Section 4(a)(2) of the Securities Act. The option grant is for the purchase of an aggregate of 343,000 shares of Common Stock at a price per share of $32.36 subject to his continued employment with the Company.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data
The selected financial data set forth below is derived from our audited consolidated financial statements and may not be indicative of future operating results. The following selected consolidated financial data should be read in conjunction with Item 7, "Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations" and the consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto included elsewhere in this report. The selected financial data in this section are not
66
intended to replace our consolidated financial statements and the related notes. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of our future results.
| |
Year Ended, December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
| |
(in thousands, except per share amounts) |
|||||||||
Consolidated Statements of Operations Data: |
||||||||||
Total operating expenses(1) |
$ | 47,933 | $ | 29,134 | $ | 13,529 | ||||
Loss from operations |
(47,933 | ) | (29,134 | ) | (13,529 | ) | ||||
Net loss |
$ | (49,520 | ) | $ | (29,044 | ) | $ | (13,510 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share applicable to common stockholders—basic and diluted |
$ | (2.19 | ) | $ | (1.80 | ) | $ | (2.33 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average number of common shares used in net loss per share applicable to common stockholders—basic and diluted |
22,647 | 16,160 | 5,810 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| |
As of December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
| |
(in thousands) |
|||||||||
Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||
Cash, cash equivalents, and short-term investments |
$ | 60,231 | $ | 44,427 | $ | 31,391 | ||||
Total assets |
65,572 | 47,545 | 32,814 | |||||||
Total current liabilities |
10,174 | 5,774 | 2,086 | |||||||
Total long-term liabilities |
73 | 70 | 7 | |||||||
- (1)
- In 2013 the loss from operations includes $4.7 million related to the technology access fee to Intrexon related to the OvaTure Collaboration.
Item 7. Management's Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with our financial statements and related notes appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The following discussion contains forward-looking statements. Actual results may differ significantly from those projected in the forward-looking statements. Factors that might cause future results to differ materially from those projected in the forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to, those discussed in "Risk Factors" and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. See also "Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements."
Overview
OvaScience is a global fertility company focused on the discovery, development, and commercialization of new fertility treatments. More women around the world are waiting to start families. However, fertility decreases with age. The main cause of age related infertility is poor egg health, which is linked to a reduction of in the number of functioning mitochondria. Other causes of poor egg health relating to mitochondrial deficiency include Type 2 diabetes. Accordingly, women throughout the world are increasingly seeking new treatment options for infertility. The current standard of treatment for infertility is in vitro fertilization, or IVF, but according to certain studies, the success rate of IVF also decreases with age and fails approximately 70% of the time.
Our patented technology is based on egg precursor, or EggPCSM cells, which are immature egg cells found in the protective outer layer of a woman's own ovaries. These immature egg cells have the ability to grow into fresh, young healthy eggs. The discovery of EggPC cells countered a long-held
67
medical belief that women are born with a set number of eggs, thereby enabling new fertility treatment options.
Our portfolio of fertility treatment options uses proprietary methods to identify and isolate EggPC cells from a patient's ovarian tissue. By applying our EggPC technology platform in unique ways, we are developing and commercializing new fertility treatment options that are designed to improve egg health and revolutionize IVF.
Our first treatment, the AUGMENTSM treatment has been launched in select IVF clinics outside of the United States, and we anticipate that we will introduce the AUGMENT treatment into new international regions in 2015. The AUGMENT treatment is not available in the United States. This treatment is specifically designed to improve egg health by supplementing a mitochondrial deficiency which mayin turn offer the potential for improved IVF. With the AUGMENT treatment, energy-producing mitochondria from a patient's own EggPC cells are added to the patient's mature eggs during the IVF process to supplement the existing mitochondria. We expect 1,000 AUGMENT treatment cycles will be in process by the end of 2015. We have set this target to ensure that we are building a high quality and scalable operating process to support our future fertility treatment portfolio.
The OvaPrimeSM treatment is a potential fertility treatment that could enable a woman to increase her egg reserve. The OvaPrime treatment is designed to replenish a woman's egg reserve by transferring a patient's EggPC cells from the protective ovarian lining back into the patient's own ovaries where they may mature into fertilizable eggs during the IVF process. We reported large animal proof-of-concept studies in 2014 and plan to optimize the process and introduce the OvaPrime treatment to patients in at least one international region outside of the United States by the end of 2015.
The OvaTureSM treatment is a potential next-generation IVF that could help a woman produce healthy, young, fertilizable eggs without the need for hormone injections. The OvaTure treatment seeks to mature a woman's own EggPC cells into eggs outside her body. This potential treatment may be an option for women with compromised eggs, who are unable to make eggs, or who may be unwilling or unable to undergo hormone hyperstimulation, such as women diagnosed with cancer. We established human preclinical proof-of-concept in 2014, and we plan to optimize the process and define the development pathway for the OvaTure treatment in 2015.
We believe our EggPC technology has the potential to make significant advances in the field of fertility because it is designed to address poor egg health and embryo quality due to age and other causes. We believe our EggPC technology could improve IVF by:
Increasing live birth rates and reducing the number of IVF cycles. By improving egg health, we believe we may increase the percentage of live births and reduce the number of IVF cycles required.
Reducing the incidence of multiple births. By generating higher quality eggs, we believe our EggPC technology may allow for the transfer of fewer embryos per IVF cycle and, as a result, lower the incidence of multiple births and the associated complications.
Lowering the overall cost of the IVF process. If we reduce the number of IVF cycles required for a live birth and the incidence of multiple births, we believe our fertility treatment options may also lower the overall costs associated with the IVF process.
Replenishing the ovary for women who make too few, or no, eggs. Our OvaPrime treatment is designed to replenish a woman's egg reserve by transferring a patient's EggPC cells from the protective ovarian lining back into the patient's own ovaries where they may mature into fertilizable eggs during the IVF process.
68
Reducing the need for hormonal hyperstimulation. We are designing our OvaTure treatment to mature EggPC cells into fertilizable eggs in vitro, or outside the body. If successful, the OvaTure treatment could reduce, or possibly eliminate, the need for hormonal hyperstimulation for the maturation of multiple oocytes prior to egg retrieval in the IVF process.
Preventing inherited diseases. OvaXonSM is a joint venture with Intrexon Corporation, or Intrexon, which is focused on developing new applications to prevent the transmission of inherited diseases by gene editing EggPC cells for applications in human and animal health.
The AUGMENT Treatment
We have launched the AUGMENT treatment in select international IVF clinics outside of the United States and anticipate that we will introduce the AUGMENT treatment into new international regions in 2015. The AUGMENT treatment is not available in the United States. We expect 1,000 AUGMENT treatment cycles will be in process by the end of 2015. The AUGMENT treatment cycle begins upon our receipt of the patient's tissue. We expect to receive payment before processing tissue and defer revenue until we deliver the mitochondria to the clinic. Based on our experiences to date, the period from receipt of the patient's tissue to recording revenue is expected to range between 30 and 120 days, the typical timeframe required to perform an IVF cycle. We do not expect to have significant revenue or deferred revenue until the second half of 2015, and we expect that a majority of this revenue and deferred revenue will be recorded in the fourth quarter.
We continue to target major international regions that combine elements of the following key criteria:
- •
- Key opinion leaders
- •
- High volume IVF clinics
- •
- High quality IVF labs
- •
- Out-of-pocket pay and high average cost per cycle
- •
- Donor egg restrictions
As part of the AUGMENT treatment, a woman's eggs may be revitalized by injecting mitochondria from her own EggPC cells into her egg during IVF. This has the potential to improve egg health. Improved egg health may offer the potential for improved IVF.
The AUGMENT treatment complements the existing standard of practice for an IVF cycle. Prior to hormone hyperstimulation, a small ovarian tissue biopsy is taken by the patient's doctor. Our proprietary process identifies and isolates the patient's own EggPC cells, and then the patient's own mitochondriafrom these EggPC cells are isolated. The patient's own mitochondria are then injected into her egg at the time of intracytoplasmic sperm injection, or ICSI.
Strategic Alliances
Strategic alliances are integral to our growth. These alliances provide access to breakthrough science, potential funding and innovative drug development programs, all intended to help us realize the full potential of our potential fertility treatment pipeline while at the same time allowing us to retain significant downstream value in our programs through commercialization rights.
69
Collaboration with Intrexon to Accelerate Development of OvaTure
Scope
In December 2013, we entered into a collaboration agreement (the "OvaTure Collaboration") with Intrexon governing the use of Intrexon's synthetic biology technology platform for the accelerated development of our OvaTure platform. The OvaTure Collaboration provides that Intrexon will deliver laboratory and animal data to support the successful filing of an IND for OvaTure.
We participate as an equal member on the Joint Steering Committee ("JSC") and Intellectual Property Committee ("IPC"). The JSC shall agree upon the services and the activities to be included in the work plan, and IPC has authority over intellectual property matters. We have the tie-breaking vote if there are any disputes with the JSC.
Technology Access Fee Payable to Intrexon
The technology access fee that we were required to pay to Intrexon was comprised of (1) the issuance of 273,224 shares, or $2.5 million of our newly issued common stock, to Intrexon upon the execution of the OvaTure Collaboration in December 2013, and (2) a $2.5 million cash payment that we made December 2014, which was payable solely upon the passage of time.
The technology access fee does not give us the right to any research and development services, and the technology access has no alternative future use to us. We therefore recorded $4.7 million in research and development expense in the year ended December 31, 2013 with $2.5 million recorded to additional paid-in capital and common stock and $2.2 million recorded in accrued liabilities, which represented the present value of the $2.5 million technology access fee due in December 2014. The accrual was accreted up to $2.5 million through interest expense during 2014 before being paid to Intrexon in December 2014.
The shares issued to Intrexon are subject to "piggy-back" registration rights, unless waived, that entitle Intrexon to have the shares included in any new registration statement filed in connection with an underwritten public offering, subject to underwriter cutback.
Research and Development Funding and Potential Commercial Milestone
The JSC will also approve a budget under the work plan. We will reimburse Intrexon for research and development services performed, subject to budget caps. If applicable, OvaScience will also make a commercial milestone payment three months after the first commercial sale of OvaTure.
Termination Rights
The collaboration has an indefinite term, with OvaScience having the right to terminate the collaboration after 90 days' prior written notice, and either OvaScience or Intrexon may terminate after a material breach by the other party that is not cured within 60 days. We may assign the collaboration in the event of a change of control transaction.
Royalties
Upon the delivery of laboratory and animal data necessary to support the successful filing of an IND application, we will incur an obligation to pay Intrexon a mid-single digit royalty on net sales of any OvaTure fertility treatments, and the exact royalty will depend upon whether Intrexon completes the milestone by the targeted deadline of two years after technology transfer.
70
Joint Venture
In December 2013, we also entered into a joint venture with Intrexon to leverage Intrexon's synthetic biology technology platform and OvaScience's technology relating to egg precursor cells to pursue the prevention of genetic disease and animal health. We and Intrexon formed OvaXon, LLC ("OvaXon") to conduct the joint venture. Each party contributed $1.5 million to OvaXon and each has a 50% equity interest, and research and development costs and profits will be split accordingly. Each party will also have 50% control over OvaXon with disputes resolved through arbitration, if necessary.
We recorded $1.5 million as an equity method investment in OvaXon LLC in December 2013. As of December 31, 2014 OvaXon has incurred expense in excess of the initial investment. The additional expense incurred is included within accrued expenses on our balance sheet, as we had the intent to fund the joint venture in the future. Each party contributed an additional $0.8 million in January 2015.
Financial Operations Overview
Revenue
As of December 31, 2014, we had not generated any revenue. To date in 2015, we have recorded limited revenue and deferred revenue as certain of our ACE clinics recently transitioned to commercial centers. Our ability to generate revenue in the near term will depend on the number of commercial AUGMENT treatment cycles our ACE clinics perform and the treatment prices charged. We expect that the commercial ramp up of the AUGMENT treatment during 2015 will depend upon the successful transition of ACE clinics to commercial operations, the addition of new ACE clinics and the results from ACE clinic experience as they become available.
The AUGMENT treatment cycle begins upon our receipt of the patient's tissue. We expect to receive payment before processing the tissue and defer revenue until we deliver the mitochondria to the clinic. Based on our experiences to date, the period from receipt of the patient's tissue to when we expect to record revenue is expected to range between 30 and 120 days, the typical timeframe required to perform an IVF cycle. Accordingly, we do not expect to have significant revenue or deferred revenue until the second half of 2015, and we expect that a majority of this revenue and deferred revenue will be recorded in the fourth quarter.
Our ability to generate revenue from sources other than the AUGMENT treatment, if ever, will depend upon the successful development and commercialization of the OvaPrime treatment, OvaTure treatment and any other future treatments.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses consist of costs associated with our research activities, discovery efforts and the development of our treatments. Our research and development expenses consist of:
- •
- employee-related expenses, including salaries, benefits, travel and stock-based compensation expense;
- •
- Fees for acquired technologies which have not yet reached technological feasibility and have no alternative use;
- •
- external research and development expenses incurred under arrangements with third parties, such as contract research organizations,
manufacturing organizations and consultants, including our scientific advisory board;
- •
- license fees; and
- •
- facilities, laboratory supplies and other allocated expenses.
71
We expense research and development cost to operations as incurred. We account for nonrefundable advance payments for goods and services that will be used in future research and development activities as expenses when the service has been performed or when the goods have been received, rather than when the payment is made.
We use our employee and infrastructure resources across multiple research and development projects. We do not maintain or evaluate, and therefore do not allocate, internal research and development costs on a project-by-project basis. We do not have actual external or total expenses by project for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
We continue to expect that our research and development expenses will increase if our programs successfully advance towards commercialization. We do not believe that our historical costs are indicative of the future costs associated with these programs nor represent what any other future treatment program we initiate may cost. Due to the variability in the length of time and scope of activities necessary to develop a treatment and uncertainties related to cost estimates and our ability to commercialize and/or obtain marketing approval for our treatments, accurate and meaningful estimates of the total costs required to bring our treatments to market are not available.
Because of the risks inherent in drug discovery and development, we cannot reasonably estimate or know:
- •
- the nature, timing and estimated costs of the efforts necessary to complete the development of our programs;
- •
- the anticipated completion dates of our programs; or
- •
- the period in which material net cash inflows are expected to commence, if at all, from our current programs and any potential future treatments.
There is significant uncertainty regarding our ability to successfully develop potential fertility treatments. These risks include the uncertainty of:
- •
- whether we are able to expand to new ACE clinics in other major regions of the world outside of the United States and transition ACE
clinics to commercial centers and significantly increase the number of patients receiving the AUGMENT treatment;
- •
- our expectation that the AUGMENT treatment and OvaPrime treatment meet the requirements of a class of products exempt from pre-market
review and approval under applicable regulations in those countries where we plan to introduce the AUGMENT treatment and OvaPrime treatment;
- •
- the scope and rate of progress of our preclinical studies and other research and development activities from the OvaPrime treatment,
the OvaTure treatment and any other potential fertility treatments;
- •
- our ability to optimize and introduce the OvaPrime treatment into international IVF clinics;
- •
- our ability to define a development pathway for the OvaTure treatment;
- •
- the scope, rate of progress and cost of any clinical trials that we may commence in the future;
- •
- the cost of filing, prosecuting, defending and enforcing any patent claims and other intellectual property rights relating to our
programs under development;
- •
- the terms and timing of any strategic alliance, licensing and other arrangements that we have or may establish in the future relating to our programs under development;
72
- •
- the cost and timing of any regulatory approvals;
- •
- the cost of establishing clinical supplies of any treatments; and
- •
- the effect of competing technological and market developments.
A change in the outcome of any of these variables with respect to the development of a treatment could mean a significant change in the costs and timing associated with the development of that potential fertility treatment.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses consist primarily of salaries and related costs for personnel, including stock-based compensation expense, in our executive, finance, accounting, legal, corporate communications, corporate development, human resources and commercial functions. Other costs include facilities costs not otherwise included in research and development expense, and professional fees for legal and accounting services. General and administrative costs also consist of the costs of maintaining our intellectual property portfolio.
Interest Income
Interest income typically consists of interest earned on cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
Our management's discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations is based on our financial statements, which we have prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities and expenses and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities in our financial statements. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our estimates and judgments, including those related to accrued expenses and stock-based compensation described in greater detail below. We base our estimates on our limited historical experience, known trends and events and various other factors that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Our significant accounting policies are described in more detail in the notes to our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report. However, we believe that the following accounting policies are the most critical to aid you in fully understanding and evaluating our financial condition and results of operations.
Accrued Research and Development Expenses
As part of the process of preparing our financial statements, we are required to estimate our accrued expenses. This process involves reviewing quotations and contracts, identifying services that have been performed on our behalf and estimating the level of service performed and the associated cost incurred for the service when we have not yet been invoiced or otherwise notified of the actual cost. The majority of our service providers invoice us monthly in arrears for services performed or when contractual milestones are met. We make estimates of our accrued expenses as of each balance sheet date in our financial statements based on facts and circumstances known to us at that time. We periodically confirm the accuracy of our estimates with the service providers and make adjustments if necessary. The significant estimates in our accrued research and development expenses include fees
73
paid to contract research organizations in connection with research and development activities for which we have not yet been invoiced.
We base our expenses related to contract research organizations on our estimates of the services received and efforts expended pursuant to quotes and contracts with the contract research organizations that conduct research and development on our behalf. The financial terms of these agreements are subject to negotiation, vary from contract to contract and may result in uneven payment flows. There may be instances in which payments made to our vendors will exceed the level of services provided and result in a prepayment of the research and development expense. In accruing service fees, we estimate the time period over which services will be performed and the level of effort to be expended in each period. If the actual timing of the performance of services or the level of effort varies from our estimate, we adjust the accrual or prepayment accordingly. Although we do not expect our estimates to be materially different from amounts actually incurred, our understanding of the status and timing of services performed relative to the actual status and timing of services performed may vary and could result in us reporting amounts that are too high or too low in any particular period.
Stock-Based Compensation
As we continue to grow, we expect to make additional stock option and restricted stock grants, which will result in additional stock-based compensation expense. Accordingly, we describe below the methodology we have employed to date in measuring such expenses.
Since our inception in April 2011, we have applied the fair value recognition provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board Accounting Standards Codification ("ASC") Topic 718, Compensation—Stock Compensation, which we refer to as ASC 718. Determining the amount of stock-based compensation to be recorded requires us to develop estimates of the fair value of stock options as of their grant date. Stock-based compensation expense is recognized ratably over the requisite service period, which in most cases is the vesting period of the award. For awards with performance conditions, we estimate the likelihood of satisfaction of the performance criteria, which affects the awards expected to vest and the period over which the expense is recognized, and recognize the expense using the accelerated attribution model to the extent the condition is deemed probable. Calculating the fair value of stock-based awards requires that we make highly subjective assumptions. We used the Black-Scholes option pricing model to value our stock option awards.
The valuation assumptions were determined as follows:
- •
- Risk-free interest rate: The yield on zero-coupon U.S.
Treasury securities for a period that is commensurate with the expected term of the awards.
- •
- Expected annual dividend yield: The estimate for annual
dividends is zero, because we have not historically paid a dividend and do not intend to do so in the foreseeable future.
- •
- Expected stock price volatility: We determine the
expected volatility by using a blend of our historical experience and a weighted average of selected peer companies.
- •
- Expected term of options: We have used the simplified method to calculate the expected term as we do not have sufficient historical exercise and post-vest termination data to provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate the expected term for the options granted to employees. The contractual term will be used for option awards granted to non-employees. Historical data will be incorporated into our assumption as it becomes available.
Under ASC 718, we are required to estimate the level of forfeitures expected to occur and record compensation expense only for those awards that we ultimately expect will vest. We evaluate our estimated forfeiture rate at the end of each reporting period. We estimate forfeitures based upon historical data, adjusted for known trends and anticipated future actual results, and we will adjust the
74
estimate of forfeitures if actual forfeitures differ or are expected to differ from such estimates. Subsequent changes in estimated forfeitures are recognized through a cumulative adjustment in the period of change and will also impact the amount of stock-based compensation expense in future periods.
We began trading on the NASDAQ Global Market on April 30, 2013.
Between November 14, 2012 and April 30, 2013, we granted stock options at exercise prices not less than the fair market value of our common stock as determined by our board of directors, with input from management. Our board of directors had historically determined the estimated fair value of our common stock on the date of grant based on a number of objective and subjective factors, including external market conditions affecting the biotechnology industry sector and the prices at which we sold shares of our preferred stock, the superior rights and preferences of securities senior to our common stock at the time of each grant and the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event such as an IPO, the listing of our common stock on a securities exchange, which we refer to as public trading, or sale of our company.
At the time of each of these stock option grants made prior to November 14, 2012, the exercise price was determined by our board of directors, with input from management, based on the various objective and subjective factors noted below. As of November 14, 2012, the date our common stock first became publicly traded, the fair value at the grant date was determined using the closing price of a share of our common stock, as listed on the OTC Bulletin Board on the grant date. As there was no public market for our common stock prior to November 14, 2012, our board of directors determined the estimated fair value of our common stock on the grant dates, taking into consideration various objective and subjective factors, including:
- •
- external market conditions affecting the biopharmaceutical industry;
- •
- prices at which we sold shares of preferred stock to third party investors;
- •
- the superior rights and preferences of securities senior to our common stock at the time of each grant;
- •
- our historical operating and financial performance;
- •
- the timing of hiring key members of our management team including the nature and timing of regulatory requirements for our potential
fertility treatments;
- •
- the status of our research and development efforts;
- •
- the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event, such as an IPO, public trading or sale of our company; and
- •
- estimates, contemporaneous valuations and analysis provided by management.
There were significant judgments and estimates inherent in the determination of these valuations.
75
Results of Operations
The following table summarizes our results of operations for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012 (dollars in thousands).
| |
|
|
|
2014 / 2013 Comparison |
2013 / 2012 Comparison |
|||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
Year Ended, December 31, | Increase / (Decrease) |
Increase / (Decrease) |
|||||||||||||||||||
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||||||||||||||
| |
$ | % | $ | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Research and development |
$ | 21,784 | $ | 15,802 | $ | 6,323 | $ | 5,982 | 38 | % | $ | 9,479 | 150 | % | ||||||||
Selling, general and administrative |
26,149 | 13,332 | 7,206 | 12,817 | 96 | % | 6,126 | 85 | % | |||||||||||||
Interest expense (income), net |
126 | (90 | ) | (19 | ) | 216 | –240 | % | (71 | ) | 374 | % | ||||||||||
Other (income), net |
(122 | ) | — | — | (122 | ) | 100 | % | — | 0 | % | |||||||||||
Loss from equity method investment |
1,583 | — | — | 1,583 | 100 | % | — | 0 | % | |||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net Loss |
$ | 49,520 | $ | 29,044 | $ | 13,510 | $ | 20,476 | 70 | % | $ | 15,534 | 115 | % | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Revenue
As of December 31, 2014, we had not generated any revenue. Our ability to generate revenue in the near term will depend on the number of commercial AUGMENT treatment cycles our ACE clinics perform and the treatment prices charged.
Our ability to generate revenue from sources other than the AUGMENT treatment, if ever, will depend upon the successful development and commercialization of the OvaPrime treatment, OvaTure treatment and any other future treatments.
Research and Development Expenses
The increase in research and development expense for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013 was primarily attributable to:
- •
- a $5.2 million increase in stock-based compensation for employees and non-employees including $3.7 million of additional
expense for nonemployee awards that are marked-to-market each period end, and $1.4 million of additional expense related to existing and additional employee awards;
- •
- a $1.4 million increase in salaries, bonus, payroll taxes and benefits, which were driven primarily by the timing of new
research and development personnel hired;
- •
- a $0.8 million increase in lab expenses and travel as we continue to grow our team and develop our future treatments;
- •
- a $1.0 million license milestone fee due as a result of our initial public offering in March of 2014;
- •
- a $4.7 million decrease resulting from the one-time technology access fee in 2013 that did not recur in 2014; and
- •
- a $0.4 million increase of facilities charges as we increased headcount and expanded internationally offset by a $0.4 million decrease resulting from the impairment of laboratory equipment in 2013 that did not recur in 2014.
76
The increase in research and development expense for the year ended December 31, 2013 compared to the year ended December 31, 2012 was primarily attributable to:
- •
- a $4.7 million increase for a one-time technology access fee in connection with a collaboration agreement with
Intrexon, Inc. for our OvaTure program;
- •
- a $1.9 million increase in stock-based compensation for employees and non-employees (including a modification of options that
resulted in incremental stock-based compensation expense of $0.4 million) and salaries, bonus, payroll taxes and benefits, which were driven primarily by the hiring of new research and
development personnel;
- •
- a $1.6 million increase in contract research organization expenses and consulting fees primarily related to AUGMENT; and
- •
- a $0.4 million increase resulting from the impairment of laboratory equipment;
We continue to expect that our research and development expenses will increase if our programs successfully advance toward commercialization. We do not believe that our historical costs are indicative of the future costs associated with these programs nor represent what any other future treatment program we initiate may cost. Due to the variability in the length of time and scope of activities necessary to develop a treatment and uncertainties related to cost estimates and our ability to commercialize and/or obtain marketing approval for our treatments, accurate and meaningful estimates of the total costs required to bring our treatments to market are not available.
Because of the risks inherent in drug discovery and development, we cannot reasonably estimate or know:
- •
- the nature, timing and estimated costs of the efforts necessary to complete the development of our programs;
- •
- the anticipated completion dates of our programs; or
- •
- the period in which material net cash inflows are expected to commence, if at all, from our current programs and any potential future treatments.
There is significant uncertainty regarding our ability to successfully develop any potential fertility treatments. These risks include the uncertainty of:
- •
- whether we are able to expand to new ACE clinics in other major regions of the world outside of the United States and transition ACE
clinics to commercial centers and significantly increase the number of patients receiving the AUGMENT treatment;
- •
- our expectation that the AUGMENT treatment and OvaPrime treatment meet the requirements of a class of products exempt from pre-market
review and approval under applicable regulations in those countries where we plan to introduce the AUGMENT treatment and OvaPrime treatment;
- •
- the scope and rate of progress of our preclinical studies and other research and development activities from OvaPrime, OvaTure and any
other potential fertility treatments;
- •
- our ability to optimize and introduce the OvaPrime treatment into international IVF clinics;
- •
- our ability to define a development pathway for the OvaTure treatment;
- •
- the scope, rate of progress and cost of any clinical trials that we may commence in the future;
- •
- the cost of filing, prosecuting, defending and enforcing any patent claims and other intellectual property rights relating to our programs under development;
77
- •
- the terms and timing of any strategic alliance, licensing and other arrangements that we have or may establish in the future relating
to our programs under development;
- •
- the cost and timing of any regulatory approvals;
- •
- the cost of establishing clinical supplies of any treatments; and
- •
- the effect of competing technological and market developments.
Selling, General and Administrative Expenses
The increase in selling, general and administrative expense for the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the year ended December 31, 2013 was primarily attributable to:
- •
- a $3.9 million increase in costs related to our ACE AUGMENT launch including $0.6 million of sales and marketing travel
expenses.
- •
- a $3.5 million increase in salaries, bonus, payroll taxes and benefits, which were driven primarily by the hiring of new
selling, general and administrative personnel (a 129% headcount increase during the year);
- •
- a $2.9 million increase in consulting, marketing, legal and contract manufacturing expenses as we launched our first product
internationally and began to implement an international organizational structure; and
- •
- a $2.1 million increase in stock-based compensation for employees and non-employees including $2.4 million of additional expense for nonemployee awards that are marked-to-market each period; and $0.8 million of additional expense related to existing and additional employee awards offset by $1.0 million employee forfeitures during the year.
The increase in selling, general and administrative expense for the year ended December 31, 2013 compared to the year ended December 31, 2012 was primarily attributable to:
- •
- a $4.2 million increase in stock-based compensation and salaries, bonus, payroll taxes and benefits; and
- •
- a $1.2 million increase in consulting and commercial preparation expenses.
Stock-based compensation for the year ended December 31, 2013 included expense related to December 2012 restricted stock units and stock options granted to our Chief Executive Officer. Increases in salaries, bonus, payroll taxes and benefits were primarily driven by the hiring of new general and administrative personnel.
Interest (Expense) Income, net
Interest (expense) income for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 relates to interest earned on the average balances on our cash equivalents and short-term investments, offset in 2014 by $0.3 million of interest expense recorded to accrete the Intrexon technology access fee to fair value through December 2014.
78
Liquidity and Capital Resources
We have generated limited commercial sales to date since certain of our ACE clinics recently transitioned to commercial centers. We have instead relied on the proceeds from sales of equity securities to fund our operations. Our short-term investments primarily trade in liquid markets, and the average days to maturity of our portfolio as of December 31, 2014 are less than six months. We have only recently commenced the commercial launch of the AUGMENT treatment. Further, the OvaPrime and OvaTure treatments are in various stages of development and the outcome of these efforts in uncertain. Accordingly, we cannot estimate the actual amounts necessary to successfully complete the development and commercialization of the OvaPrime treatment or the OvaTure treatment, or whether or when we may achieve profitability.
In January 2015, we issued and sold in a public offering, or the January 2015 public offering, an aggregate of 2,645,000 shares of our common stock at $50.00 per share, which included 345,000 shares that represented the full exercise of an option to purchase additional shares granted to the underwriters in connection with the offering. The January 2015 public offering resulted in $124.1 million of net proceeds, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and other offering expenses payable by us.
Our significant capital resources are as follows (in thousands):
| |
December 31, 2014 |
December 31, 2013 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments |
$ | 60,231 | $ | 44,427 | |||
Working capital |
51,704 | 39,303 | |||||
| |
Year Ended, December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
Cash (used in) provided by: |
||||||||||
Operating activities |
$ | (30,588 | ) | $ | (18,094 | ) | $ | (11,156 | ) | |
Investing activities |
(32,788 | ) | (11,018 | ) | (17,640 | ) | ||||
Capital expenditures (included in investing activities above) |
(2,804 | ) | (719 | ) | (849 | ) | ||||
Financing activities |
51,712 | 32,414 | 39,031 | |||||||
Cash Flows
Cash used in operating activities in all of the periods presented was primarily attributed to the funding of our net loss. Cash flows from operations can vary significantly due to various factors, including changes in the net loss and the timing of disbursements made for accounts payable and accruals.
Cash used in investing activities for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 included the purchase of and proceeds from maturities of short-term investments, as well as purchases of property, plant and equipment. Capital expenditures for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 consisted primarily of laboratory equipment.
We will need substantial additional funds to support our planned operations. In the absence of additional funding, business development activities, and treatment sales, we expect our existing cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments of $60.2 million at December 31, 2014, together with the approximately $124.1 million of net proceeds from the January 2015 public offering, will enable us to fund our current operating plan for at least the next 12 months. We have based this estimate on assumptions that may prove to be wrong, and we could use our available capital resources sooner than we currently expect. Because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with the development and commercialization of our treatments, and the extent to which we may enter into collaborations with
79
third parties for development and commercialization of our treatments, we are unable to estimate the amounts of increased capital outlays and operating expenses associated with completing the development of our current treatments. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including:
- •
- our success in expanding to new ACE clinics in other major regions of the world, transitioning ACE clinics to commercial centers and
significantly increasing the number of patients receiving the AUGMENT treatment ;
- •
- our success in optimizing and introducing the OvaPrime treatment to international IVF clinics;
- •
- the costs associated with the expansion of foreign operations and building out our international commercial infrastructure, including
establishing and staffing an international headquarters and other international subsidiaries;
- •
- the costs associated with establishing a domestic and international sales, marketing, manufacturing and distribution infrastructure to
commercialize the AUGMENT treatment and any potential fertility treatment we successfully develop;
- •
- the pricing of the AUGMENT treatment and resulting revenues, as well as any future revenues we receive from our potential fertility
treatments;
- •
- the costs of continuing the optimization of the OvaTure treatment and our success in defining a development pathway;
- •
- the costs of any clinical trials of potential fertility treatments;
- •
- the costs involved in collaborating with Intrexon through the OvaXon joint venture to create new applications to prevent inherited
diseases for human and animal health;
- •
- following any applicable regulatory process in the United States and abroad, including the premarketing and marketing approval
requirements, to which any of our potential fertility treatments may be subject;
- •
- following any regulatory or institutional review board review of our potential fertility treatments that are subject to such review;
- •
- preparing, filing and prosecuting patent applications, maintaining and enforcing our intellectual property rights and defending
intellectual property-related claims;
- •
- establishing collaborations and partnerships on favorable terms, if at all; and
- •
- developing, acquiring or in-licensing other potential fertility treatments and technologies.
Until such time, if ever, as we can generate sufficient revenues from the AUGMENT treatment or our potential fertility treatments to become profitable, we expect to finance our cash needs through a combination of equity offerings, debt financings, collaborations, strategic alliances and licensing arrangements. We do not have any committed external source of funds. In addition, we may elect to raise additional funds even before we need them if the conditions for raising capital are favorable. To the extent that we raise additional capital through the sale of equity or convertible debt securities, the ownership interest of our stockholders will be diluted, and the terms of these securities may include liquidation or other preferences that adversely affect the rights of common stockholders. Debt financing, if available, may involve agreements that include covenants limiting or restricting our ability to take specific actions, such as incurring additional debt, making capital expenditures or declaring dividends. If we raise additional funds through collaborations, strategic alliances or licensing arrangements with third parties, we may have to relinquish valuable rights to our technologies, future revenue streams, research programs or treatments or grant licenses on terms that may not be favorable to us. If we are unable to raise additional funds through equity or debt financings when needed, we
80
may be required to delay, limit, reduce or terminate our fertility treatment development or future commercialization efforts or grant rights to develop and market treatments that we would otherwise prefer to develop and market ourselves.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We did not have during the periods presented, and we do not currently have, any off-balance sheet arrangements, as defined under SEC rules.
Contractual Obligations
| |
Payments Due by Period | |||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Contractual Obligations
|
Total | Less than 1 Year |
1 - 3 Years | 3 - 5 Years | More than 5 Years |
|||||||||||
License obligations(1) |
$ | 1,043 | $ | 595 | $ | 224 | $ | 224 | * | |||||||
Long-term liabilities(2) |
120 | 10 | 30 | 30 | 50 | |||||||||||
Operating leases |
1,111 | 646 | 465 | — | — | |||||||||||
Purchase obligations(3) |
97 | 97 | — | — | — | |||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
|
$ | 2,371 | $ | 1,348 | $ | 719 | $ | 254 | $ | 50 | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- Includes
$0.5 million related to our 2014 financing milestone which is included in accounts payable at December 31, 2014. Additionally, we
have agreed to pay license fees and maintenance fees totaling $0.1 million annually (*). The agreement is cancellable by us. As we are unable to reasonably predict the likelihood, timing or
amount of any milestone, royalty or sublicense income payments due under the arrangement, we have excluded them from the table above.
- (2)
- Long-term
liabilities include current maturities.
- (3)
- At December 31, 2014 we have non-cancellable payments that become due in January 2015 for research services and research grants of approximately $0.1 million.
Recently Adopted Accounting Standards
In August 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Accounting Standard Update (ASU) 2014-15, Presentation of Financial Statements—Going Concern. The new standard requires management of public and private companies to evaluate whether there is substantial doubt about the entity's ability to continue as a going concern and, if so, disclose that fact. We will also be required to evaluate and disclose whether our plans alleviate that doubt. This guidance is effective for annual periods ending after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016. We are evaluating this standard to determine if adoption will have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In June 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-10, which eliminates the concept of a development stage entity, or DSE, in its entirety from generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Under existing guidance, DSEs are required to report incremental information, including inception-to-date financial information, in their financial statements. A DSE is an entity devoting substantially all of its efforts to establishing a new business and for which either planned principal operations have not yet commenced or have commenced but there has been no significant revenues generated from that business. Entities classified as DSEs will no longer be subject to these incremental reporting requirements after adopting ASU No. 2014-10. ASU No. 2014-10 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2014, with early adoption permitted. Retrospective application is required for the elimination of incremental DSE disclosures. Prior to the issuance of ASU No. 2014-10, we had met the definition of a DSE since our inception. We have elected to adopt this ASU early, and therefore we
81
have eliminated the incremental disclosures previously required of DSEs, starting with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2014.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, which amends the guidance for accounting for revenue from contracts with customers. This ASU supersedes the revenue recognition requirements in Accounting Standards Codification Topic 605, Revenue Recognition, and creates a new Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. This guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, with early adoption not permitted. Two adoption methods are permitted: retrospectively to all prior reporting periods presented, with certain practical expedients permitted; or retrospectively with the cumulative effect of initially adopting the ASU recognized at the date of initial application. We have not yet determined which adoption method we will utilize or the effect that the adoption of this guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk
We are exposed to market risk related to changes in interest rates. We had cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments of $60.2 million as of December 31, 2014 and $44.4 million as of December 31, 2013. The cash and cash equivalents as of December 31, 2014 consist of cash in bank deposits, money market funds and corporate debt securities. Our primary exposure to market risk is interest rate sensitivity, which is affected by changes in the general level of U.S. interest rates, particularly because our investment strategy is primarily in short term securities. Our available for sale securities are subject to interest rate risk and will fall in value if market interest rates increase.
A hypothetical 100 basis point increase in interest rates would result in an approximate $0.2 million decrease in the fair value of our investments as of December 31, 2014, as compared to an approximate $0.1 million decrease as of December 31, 2013. We have the ability to hold our fixed income investments until maturity and, therefore, we do not expect our operating results to be affected to any significant degree by the effect of a change in market interest rates on our investments.
We contract with third party research and development organizations and contract manufacturers globally. We may be subject to fluctuations in foreign currency rates in connection with any such agreements. Transactions denominated in currencies other than the functional currency are recorded based on exchange rates at the time such transactions arise. As of December 31, 2014, all of our liabilities were denominated in our functional currency.
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data
The information required by Item 8 is contained on pages F-1 through F-27 of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure
None.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures.
Our management, with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, evaluated the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2014. The term "disclosure controls and procedures," as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d- 15(e) under the Exchange Act, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the SEC's rules and forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and
82
procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to our management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure. Management recognizes that any controls and procedures, no matter how well designed and operated, can provide only reasonable assurance of achieving their objectives and management necessarily applies its judgment in evaluating the cost-benefit relationship of possible controls and procedures. Based on the evaluation of our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2014, our principal executive officer and principal financial officer concluded that, as of such date, our disclosure controls and procedures were effective at the reasonable assurance level.
Our management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting as defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and 15d-15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Our internal control system was designed to provide reasonable assurance to our management and board of directors regarding the preparation and fair presentation of published financial statements. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Our management assessed the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. In making this assessment, we used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission ("COSO") in Internal Control—Integrated Framework. Based on our assessment we believe that, as of December 31, 2014, our internal control over financial reporting is effective based on those criteria.
This annual report does not include an attestation report from our registered public accounting firm regarding internal control over financial reporting. Management's report was not subject to attestation by our registered public accounting firm pursuant to rules of the Securities and Exchange Commission that permit emerging growth companies, which we are, to provide only management's report in this annual report.
Changes in Internal Controls.
No change in our internal control over financial reporting, identified in connection with the evaluation of such internal control, that occurred during the fourth quarter ended December 31, 2014 has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Not applicable.
83
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance
The information required by Item 10 of Form 10-K may be found under the captions "Corporate Governance" and "Ownership of our Common Stock—Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance" in the definitive proxy statement to be delivered to stockholders in connection with our 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
We have adopted a written code of business conduct and ethics that applies to our directors, officers and employees, including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller, or persons performing similar functions. We make available our code of business conduct and ethics free of charge through our website which is located at www.ovascience.com. We intend to disclose any amendment to, or waiver from, our code of business conduct and ethics that is required to be publicly disclosed pursuant to SEC rules.
Item 11. Executive Compensation
The information required by Item 11 of Form 10-K may be found under the captions "Executive Compensation," "Director Compensation," "Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation" and "Compensation Committee Report" in the definitive proxy statement to be delivered to stockholders in connection with our 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters
The information required by Item 12 of Form 10-K may be found under the captions "Ownership of our Common Stock—Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management" and "Securities Authorized for Issuance Under our Equity Compensation Plans" in the definitive proxy statement to be delivered to stockholders in connection with our 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence
The information required by Item 13 of Form 10-K may be found under the captions "Certain Relationships and Related Transactions" and "Corporate Governance" in the definitive proxy statement to be delivered to stockholders in connection with our 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services
The information required by Item 14 of Form 10-K may be found under the caption "Audit-Related Matters" in the definitive proxy statement to be delivered to stockholders in connection with our 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders. Such information is incorporated herein by reference.
84
Item 15. Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules
- (a)
- (1) The following financial statements are filed as part of this report:
- (a)
- (2) Consolidated Financial Statement Schedules:
No schedules are submitted because they are not applicable, not required or because the information is included in the Consolidated Financial Statements or Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
- (a)
- (3) Exhibits.
The following is a list of exhibits filed as part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| Exhibit No. | Exhibit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 3.1 | Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Registrant (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on April 30, 2013) | ||
| 3.2 | Second Amended and Restated By-laws of the Registrant (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on April 30, 2013) | ||
| 4.1 | Specimen Stock Certificate evidencing the shares of Common Stock (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.1 to the Registration Statement on Form S-1 (File No. 333-183602) filed by the Registrant on August 29, 2012) | ||
| 4.2 | Amended and Restated Investors' Rights Agreement, dated March 29, 2012, by and among the Registrant and the other parties thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.4 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on April 11, 2012) | ||
| 4.3 | Registration Rights Agreement, dated August 13, 2012, by and among the Company and the persons party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on August 14, 2012) | ||
| 10.1 | # | 2011 Stock Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on April 11, 2012) | |
| 10.2 | # | Forms of Incentive Stock Option Agreement under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on May 17, 2012) | |
85
| Exhibit No. | Exhibit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.3 | # | Forms of Nonstatutory Stock Option Agreement under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on May 17, 2012) | |
| 10.4 | # | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement under the 2011 Stock Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on April 11, 2012) | |
| 10.5 | # | 2012 Stock Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.5 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the registrant on April 11, 2012) | |
| 10.6 | #* | Form of Incentive Stock Option Agreement under the 2012 Stock Incentive Plan | |
| 10.7 | #* | Form of Nonstatutory Stock Option Agreement under the 2012 Stock Incentive Plan | |
| 10.8 | # | Form of Amended and Restated Restricted Stock Agreement between the Registrant and each of Michelle Dipp and Christoph Westphal (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.8 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on April 11, 2012) | |
| 10.9 | # | Amended and Restated Restricted Stock Agreement between the Registrant, Richard Aldrich and the Richard H. Aldrich Irrevocable Trust of 2011, dated March 29, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.10 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on April 11, 2012) | |
| 10.10 | † | Exclusive License Agreement, dated June 27, 2011, between the Registrant and The General Hospital Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.11 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on April 11, 2012) | |
| 10.11 | † | Amendment No. 1 to the Exclusive License Agreement, dated September 7, 2011, between the Registrant and The General Hospital Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the registrant on April 11, 2012) | |
| 10.12 | † | Amendment No. 2 to the Exclusive License Agreement, dated July 30, 2013, between the Registrant and The General Hospital Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.12 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on February 27, 2014) | |
| 10.13 | Amendment No. 3 to the Exclusive License Agreement, dated September 9, 2013, between the Registrant and The General Hospital Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.13 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on February 27, 2014) | ||
| 10.14 | † | Amendment No. 4 to the Exclusive License Agreement, dated November 14, 2013, between the Registrant and The General Hospital Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.14 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on February 27, 2014) | |
| 10.15 | † | Amendment No. 5 to the Exclusive License Agreement, dated December 18, 2013, between the Registrant and The General Hospital Corporation (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on February 27, 2014) | |
86
| Exhibit No. | Exhibit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.16 | Amended and Restated Voting Agreement, dated March 29, 2012, between the Registrant and the other parties thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.15 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000- 54647) filed by the Registrant on April 11, 2012) | ||
| 10.17 | Form of Indemnification Agreement between the Registrant and each of Richard Aldrich and Michelle Dipp(incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on April 11, 2012) | ||
| 10.18 | Form of Indemnification Agreement between the Registrant and each of Jeffrey Capello, Mary Fisher, Marc Kozin, Thomas Malley and Harald Stock (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.22 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on April 11, 2012) | ||
| 10.19 | Lease Agreement, dated May 1, 2012, between the Registrant and ARE-MA Region No. 38, LLC, as amended (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.23 to Amendment No. 1 to the Registration Statement on Form 10 (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on May 17, 2012) | ||
| 10.20 | # | Letter Agreement, dated December 5, 2012, between the Registrant and Michelle Dipp (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.24 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on February 25, 2013) | |
| 10.21 | #* | Amended and Restated Letter Agreement, dated December 9, 2014, between the Registrant and Michelle Dipp | |
| 10.22 | #* | Time-Based Restricted Stock Unit Agreement, dated December 9, 2014, between the Registrant and Michelle Dipp | |
| 10.23 | #* | Performance-Based Restricted Stock Unit Agreement, dated December 9, 2014, between the Registrant and Michelle Dipp | |
| 10.24 | #* | Stock Option Agreement, dated December 9, 2014, between the Registrant and Michelle Dipp | |
| 10.25 | [Reserved.] | ||
| 10.26 | Securities Purchase Agreement, dated March 12, 2013, among the Registrant and the persons party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on March 14, 2013) | ||
| 10.27 | Registration Rights Agreement, dated March 12, 2013, among the Registrant and the persons party thereto (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 000-54647) filed by the Registrant on March 14, 2013) | ||
| 10.28 | # | Letter Agreement, dated July 15, 2013, between the Registrant and Arthur Tzianabos (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on November 13, 2013) | |
| 10.29 | # | Stock Option Agreement, dated September 10, 2013, between the Registrant and Arthur Tzianabos (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on November 13, 2013) | |
| 10.30 | # | Offer Letter, dated July 22, 2014, between the Registrant and Jeffrey E. Young (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Current Report on Form 8-K (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on September 18, 2014) | |
87
| Exhibit No. | Exhibit | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 10.31 | # | Stock Option Agreement, dated September 18, 2014, between the Registrant and Jeffrey E. Young (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on November 10, 2014) | |
| 10.32 | #* | Offer Letter, dated October 21, 2014, between the Registrant and David P. Harding | |
| 10.33 | #* | Stock Option Agreement, dated December 9, 2014, between the Registrant and David P. Harding | |
| 10.34 | #* | Amended and Restated Non-Employee Director Compensation Policy of the Registrant (effective March 3, 2015) | |
| 10.35 | † | Intellectual Property License Agreement, dated December 18, 2013, between the Registrant and OvaXon, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.34 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on February 27, 2014) | |
| 10.36 | † | Exclusive Channel Collaboration Agreement, dated December 18, 2013, between the Registrant and Intrexon Corporation and OvaXon, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.35 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on February 27, 2014) | |
| 10.37 | † | Exclusive Channel Collaboration Agreement, dated December 18, 2013, between Intrexon Corporation and OvaXon, LLC (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.36 to the Annual Report on Form 10-K (File No. 001-35890) filed by the Registrant on February 27, 2014) | |
| 21.1 | * | List of Subsidiaries of the Registrant | |
| 23.1 | * | Consent of Ernst & Young | |
| 31.1 | * | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| 31.2 | * | Certification of Principal Financial Officer pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| 32.1 | * | Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, by Chief Executive Officer | |
| 32.2 | * | Certification pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, by Principal Financial Officer | |
| 101.INS | * | XBRL Instance Document | |
| 101.SCH | * | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | |
| 101.CAL | * | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | |
| 101.DEF | * | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition | |
| 101.LAB | * | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase Document | |
| 101.PRE | * | XBRL Taxonomy Presentation Linkbase Document | |
- †
- Confidential
treatment requested as to portions of the exhibit. Confidential materials omitted and filed separately with the SEC.
- #
- Indicates
a management contract or compensatory plan.
- *
- Filed herewith.
88
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, hereunto duly authorized, on March 16, 2015.
| OVASCIENCE, INC. | ||||
By: |
/s/ MICHELLE DIPP Michelle Dipp, M.D., Ph.D. Chief Executive Officer |
|||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
Signature
|
Title
|
Date
|
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| /s/ MICHELLE DIPP Michelle Dipp, M.D., Ph.D. |
Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal executive officer) | March 16, 2015 | ||
/s/ JEFFREY YOUNG Jeffrey Young |
Chief Financial Officer (Principal financial and accounting officer) |
March 16, 2015 |
||
/s/ RICHARD ALDRICH Richard Aldrich |
Director |
March 16, 2015 |
||
/s/ JEFFREY D. CAPELLO Jeffrey D. Capello |
Director |
March 16, 2015 |
||
/s/ MARY FISHER Mary Fisher |
Director |
March 16, 2015 |
||
/s/ MARC KOZIN Marc Kozin |
Director |
March 16, 2015 |
||
/s/ THOMAS MALLEY Thomas Malley |
Director |
March 16, 2015 |
||
/s/ HARALD STOCK Harald Stock, Ph.D. |
Director |
March 16, 2015 |
89
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
The
Board of Directors and Stockholders of
OvaScience, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of OvaScience, Inc. as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive loss, consolidated statements of stockholders' equity (deficit) and consolidated statements of cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company's management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. We were not engaged to perform an audit of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company's internal control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of OvaScience, Inc. at December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
/s/ Ernst & Young LLP
Boston,
Massachusetts
March 16, 2015
F-1
OvaScience, Inc.
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In thousands, except share and per share data)
| |
As of December 31, | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||
Assets |
|||||||
Current assets: |
|||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 6,414 | $ | 18,078 | |||
Short-term investments |
53,817 | 26,349 | |||||
Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
1,647 | 650 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total current assets |
61,878 | 45,077 | |||||
Property and equipment, net |
3,367 | 880 | |||||
Investment in joint venture |
— | 1,500 | |||||
Restricted cash |
197 | 88 | |||||
Other long-term assets |
130 | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total assets |
$ | 65,572 | $ | 47,545 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
Liabilities and stockholders' equity |
|||||||
Current liabilities: |
|||||||
Accounts payable |
$ | 2,520 | $ | 1,654 | |||
Accrued expenses |
7,654 | 4,120 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total current liabilities |
10,174 | 5,774 | |||||
Other non-current liabilities |
73 | 70 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities |
10,247 | 5,844 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Commitments and contingencies (Note 11) |
|||||||
Stockholders' equity: |
|||||||
Preferred stock, $0.001 par value; 5,000,000 shares authorized, no shares issued and outstanding |
— | — | |||||
Common stock, $0.001 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; 24,413,666, and 18,528,215 shares issued at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively; 24,084,637 and 17,541,126 shares outstanding at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively |
24 | 18 | |||||
Additional paid-in capital |
150,025 | 86,851 | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive (loss) income |
(26 | ) | 10 | ||||
Accumulated deficit |
(94,698 | ) | (45,178 | ) | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Total stockholders' equity |
55,325 | 41,701 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities and stockholders' equity |
$ | 65,572 | $ | 47,545 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-2
OvaScience, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Loss
(In thousands, except per share data)
| |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
Operating expenses: |
||||||||||
Research and development |
$ | 21,784 | $ | 15,802 | $ | 6,323 | ||||
Selling, general and administrative |
26,149 | 13,332 | 7,206 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total operating expenses |
47,933 | 29,134 | 13,529 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Loss from operations |
(47,933 | ) | (29,134 | ) | (13,529 | ) | ||||
Interest (expense) income, net |
(126 | ) | 90 | 19 | ||||||
Other income (expense), net |
122 | — | — | |||||||
Loss from equity method investment |
(1,583 | ) | — | — | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss |
$ | (49,520 | ) | $ | (29,044 | ) | $ | (13,510 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share—basic and diluted |
$ | (2.19 | ) | $ | (1.80 | ) | $ | (2.33 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average number of shares used in net loss per share—basic and diluted |
22,647 | 16,160 | 5,810 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss |
$ | (49,520 | ) | $ | (29,044 | ) | $ | (13,510 | ) | |
Other comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||
Unrealized gains (losses) on available-for-sale securities |
(36 | ) | 16 | (6 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Comprehensive loss |
$ | (49,556 | ) | $ | (29,028 | ) | $ | (13,516 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Non-cash stock-based compensation expenses included in operating expenses are as follows: |
||||||||||
Research and development |
$ | 7,578 | $ | 2,361 | $ | 1,143 | ||||
Selling, general and administrative |
4,829 | 2,733 | 239 | |||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-3
OvaScience, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Stockholders' Equity (Deficit)
(In thousands, except share data)
| |
Series A convertible preferred stock | Series B convertible preferred stock |
|
Common stock | |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
|
Total stockholders' equity (deficit) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
|
Additional paid-in capital |
Accumulated deficit |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount |
|
Shares | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Balance at January 1, 2012 |
6,200,000 | $ | 6,200 | — | $ | — | 1,209,752 | $ | 1 | $ | 246 | $ | — | $ | (2,624 | ) | $ | (2,377 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Vesting of Founders Stock |
— | — | — | — | 674,505 | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of Series B convertible preferred stock, net of issuance costs of $2,246 |
— | — | 6,770,563 | 34,992 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of Series A convertible preferred stock to common stock on a one-for-2.023 basis |
(6,200,000 | ) | (6,200 | ) | — | — | 3,064,753 | 3 | 6,197 | — | — | 6,200 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Conversion of Series B convertible preferred stock to common stock on a one-for-one basis |
— | — | (6,770,563 | ) | (34,992 | ) | 6,770,563 | 7 | 34,985 | — | — | 34,992 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Common stock issued as part of the private placement, net of issuance costs of $898 |
— | — | — | — | 897,554 | 1 | 4,038 | — | — | 4,039 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options |
— | — | — | — | 5,792 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 1,382 | — | — | 1,382 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized Loss on Investments |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (6 | ) | — | (6 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (13,510 | ) | (13,510 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2012 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | — | 12,622,919 | $ | 13 | $ | 46,848 | $ | (6 | ) | $ | (16,134 | ) | $ | 30,721 | ||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Common stock issued as part of the private placement, net of issuance costs of $2,348 |
— | — | — | — | 3,888,880 | 4 | 32,652 | — | — | 32,656 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of shares to Intrexon |
— | — | — | — | 273,224 | — | 2,500 | — | — | 2,500 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Vesting of Founders Stock |
— | — | — | — | 658,060 | 1 | — | — | — | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options |
— | — | — | — | 42,799 | — | 42 | — | — | 42 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 5,094 | — | — | 5,094 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Vesting of restricted stock |
— | — | — | — | 55,244 | — | (285 | ) | — | — | (285 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized gain on Investments |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 16 | — | 16 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (29,044 | ) | (29,044 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2013 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | — | 17,541,126 | $ | 18 | $ | 86,851 | $ | 10 | $ | (45,178 | ) | $ | 41,701 | |||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Issuance of common stock under public offering, net of underwriters' discounts and issuance costs |
— | — | — | — | 5,518,630 | 5 | 51,728 | — | — | 51,733 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Vesting of Founders Stock |
— | — | — | — | 658,060 | 1 | 1 | — | — | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options |
— | — | — | — | 308,150 | — | 163 | — | — | 163 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 12,407 | — | — | 12,407 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Vesting of restricted stock |
— | — | — | — | 58,671 | — | (1,125 | ) | — | — | (1,125 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Unrealized Loss on Investments |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (36 | ) | — | (36 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (49,520 | ) | (49,520 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | — | 24,084,637 | $ | 24 | $ | 150,025 | $ | (26 | ) | $ | (94,698 | ) | $ | 55,325 | ||||||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-4
OvaScience, Inc.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In thousands)
| |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (49,520 | ) | $ | (29,044 | ) | $ | (13,510 | ) | |
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
450 | 231 | 93 | |||||||
Impairment of property and equipment |
— | 364 | — | |||||||
Amortization of premium on debt securities |
871 | 586 | 77 | |||||||
Stock-based compensation expense |
12,407 | 5,094 | 1,382 | |||||||
Issuance of common stock for technology access fee |
— | 2,500 | — | |||||||
Net loss on equity method investment |
1,583 | — | — | |||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||
Prepaid expenses and other assets |
(997 | ) | (76 | ) | (530 | ) | ||||
Accounts payable |
2,317 | (721 | ) | 599 | ||||||
Accrued expenses and other non-current liabilities |
2,301 | 2,972 | 733 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in operating activities |
(30,588 | ) | (18,094 | ) | (11,156 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||
Investment in joint venture |
(1,500 | ) | — | — | ||||||
Purchases of property, plant and equipment |
(2,804 | ) | (719 | ) | (849 | ) | ||||
Maturities of short-term investments |
20,797 | 5,670 | — | |||||||
Sales of short-term investments |
8,431 | — | — | |||||||
Purchases of short-term investments |
(57,603 | ) | (15,974 | ) | (16,698 | ) | ||||
(Increase) decrease in restricted cash |
(109 | ) | 5 | (93 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash used in investing activities |
(32,788 | ) | (11,018 | ) | (17,640 | ) | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||
Proceeds from issuance of preferred stock, net of issuance costs |
— | — | 34,992 | |||||||
Net proceeds from the issuance of common stock |
51,733 | 32,414 | 4,039 | |||||||
Issuances of common stock under benefit plans, net of withholding taxes paid |
(21 | ) | — | — | ||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net cash provided by financing activities |
51,712 | 32,414 | 39,031 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net (decrease) increase in cash and cash equivalents |
(11,664 | ) | 3,302 | 10,235 | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period |
18,078 | 14,776 | 4,541 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
$ | 6,414 | $ | 18,078 | $ | 14,776 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing activity |
||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Conversion of convertible preferred stock to common stock |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 41,192 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Investment in OvaXon |
$ | — | $ | 1,500 | $ | — | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Vesting of restricted stock, net of shares withheld for taxes |
$ | 939 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statement.
F-5
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
1. Organization
OvaScience, Inc., incorporated on April 5, 2011 as a Delaware corporation, is a life science company developing proprietary potential treatments for female infertility based on recent scientific discoveries about the existence of egg precursor cells. As used through these consolidated financial statements, the terms "OvaScience," "we," "us," and "our" refer to the business of OvaScience, Inc. and its wholly owned subsidiary. Our operations to date have been limited to organizing and staffing our company, business planning, raising capital, acquiring and developing our technology, identifying potential fertility treatments, developing the AUGMENT treatment, launching the AUGMENT treatment in select international IVF clinics, researching and developing the OvaPrime treatment and the OvaTure treatment, and determining the regulatory and development path for our fertility treatments. We have commenced our planned principal operations but have not generated any significant revenues to date.
We are subject to a number of risks similar to other life science companies in the development stage, including, but not limited to, the need to obtain adequate additional funding, possible failure to provide our treatments to IVF clinics to gain clinical experience in select countries outside of the United States, the need to obtain marketing approval for certain of our treatments, competitors developing new technological innovations, the need to successfully commercialize and gain market acceptance of our treatments and protection of proprietary technology. If we do not successfully commercialize any of our treatments, we will be unable to generate treatment revenue or achieve profitability. As of December 31, 2014 we had an accumulated deficit of approximately $94.7 million.
Unless otherwise indicated, all information in these financial statements gives retrospective effect to the one-for-2.023 reverse stock split of our common stock (the "Reverse Stock Split") that was effected on March 28, 2012 (see Note 7).
Liquidity
We have incurred annual net operating losses in each year since our inception. We have not generated any treatment revenues related to our primary business purpose and have financed our operations primarily through private placements of our preferred stock and common stock. We have not completed development of any treatment and have devoted substantially all of our financial resources and efforts to raising capital and research and development. We expect to continue to incur significant expenses and operating losses for at least the next several years.
We believe that our cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments of approximately $60.2 million at December 31, 2014, together with the approximately $124.1 million of net proceeds received from our January 2015 secondary public offering, will be sufficient to fund our current operating plan for at least the next 12 months. There can be no assurances, however, that the current operating plan will be achieved or that additional funding, if needed, will be available on terms acceptable to us, or at all.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Presentation
Our consolidated financial statements include the accounts of OvaScience and our wholly-owned subsidiaries. We have eliminated all significant intercompany accounts and transactions in consolidation.
The consolidated financial statements are prepared in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America ("GAAP"), which requires our management to make estimates and judgments that may affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenues and
F-6
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities. On an ongoing basis, we evaluate our estimates and judgments. We based our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that are believed to be reasonable, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Cash Equivalents and Short-Term Investments
Cash equivalents and short-term investments primarily consist of money market funds and corporate debt securities. Corporate debt securities include obligations issued by corporations in countries other than the United States, including some issues that have not been guaranteed by governments and government agencies. We consider all highly liquid investments with maturities of three months or less at the time of purchase to be cash equivalents. Cash equivalents, which consist of money market funds, are stated at fair value. They are also readily convertible to known amounts of cash and have such short-term maturities that each presents insignificant risk of change in value due to changes in interest rates.
The appropriate classification of short-term investments is determined at the time of purchase and reevaluated at each balance sheet date. We have classified all of our short-term investments at December 31, 2014 and 2013 as available-for-sale. We carry available-for-sale securities at fair value, with the unrealized gains and losses reported in accumulated other comprehensive income / (loss), which is a separate component of stockholders' equity.
The cost of available-for-sale debt securities is adjusted for amortization of premiums and accretion of discounts to maturity. Such amortization and accretion is included in interest income. The cost of securities sold or the amount reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income into earnings is based on the specific identification method. Interest and dividends on securities classified as available-for-sale are included in interest income.
We conduct periodic reviews to identify and evaluate each investment that is in an unrealized loss position in order to determine whether an other-than-temporary impairment exists. An unrealized loss exists when the current fair value of an individual security is less than its amortized cost basis. Unrealized losses on available-for-sale debt securities that are determined to be temporary, and not related to credit loss, are recorded, net of tax, in accumulated other comprehensive income / (loss). For available-for-sale debt securities in an unrealized loss position, we perform an analysis to assess whether we intend to sell or whether we would more likely than not be required to sell the security before the expected recovery of the amortized cost basis. Where we intend to sell a security, or may be required to do so, the security's decline in fair value is deemed to be other-than-temporary and the full amount of the unrealized loss is recorded within the statement of operations as an impairment loss.
Regardless of our intent to sell a security, we perform an additional analysis on all securities in an unrealized loss position to evaluate losses associated with the creditworthiness of the security. Credit losses are identified where we do not expect to receive cash flows sufficient to recover the amortized cost basis of a security and are recorded within earnings as an impairment loss.
Fair Value Measurements
We define fair value as the price that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. We determine
F-7
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
fair value based on the assumptions market participants use when pricing the asset or liability. We also use the fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the information used to develop these assumptions.
We value our short-term investments utilizing third party pricing services. The pricing services use observable market inputs to determine value, including benchmark yields, reportable trades, broker/dealer quotes, issuer spreads, two-sided markets, benchmark securities, bids, offers, reference data, new issue data, and monthly payment information. We validate the prices provided by our third party pricing services by understanding the models used, obtaining market values from other pricing sources, and confirming that those securities trade in active markets. We valued the balance of the technology access fee payable to Intrexon Inc. for $2.5 million in cash in December 2014 based on a discounted cash flow model. We used a 15% discount rate, which we believe approximates our one year unsecured borrowing rate. We paid the $2.5 million balance of the technology access fee in December 2014.
Restricted Cash
Restricted cash consists of balances held in deposit with major financial institutions to collateralize letters of credit in the names of our landlords pursuant to certain operating lease agreements. We disclose these amounts separately on our consolidated balance sheet as restricted cash.
Concentrations of Risk
We have no significant off-balance sheet risk.
Cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments are the only financial instruments we have that are subject to concentration of credit risk. Cash and cash equivalents are primarily maintained with two major financial institutions in the United States. Deposits at banks may exceed the insurance provided on such deposits. Generally, these deposits may be redeemed upon demand and, therefore, bear minimal risk. Short-term investments consistent of investment grade corporate debt securities. Our investment policy, which has been approved by our board of directors, limits the amount we may invest in any one issuer of investments, thereby reducing credit risk concentrations.
Segment Information
We make operating decisions based upon the performance of the enterprise as a whole and utilize our consolidated financial statements for decision making. We operate in one segment, which focuses on developing treatments dedicated to the treatment of female infertility.
Research and Development Costs
We expense research and development costs to operations as incurred. Research and development expenses consist of costs associated with research activities, including license payments paid to third parties for rights to intellectual property, the costs of development of treatments and advances in the field of infertility. We account for nonrefundable advance payments for goods and services that will be used in future research and development activities as expenses when the goods have been received or when the service has been performed rather than when the payment is made. We also include as research and development expense access fees for technologies which have not yet reached technological feasibility and have no alternative use. Research and development expenses consist of:
- •
- employee-related expenses, including salaries, benefits, travel and stock-based compensation expense;
F-8
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
- •
- external research and development expenses incurred under arrangements with third parties, such as contract research organizations,
contract manufacturing organizations and consultants;
- •
- license fees; and
- •
- facilities and other expenses, which include direct and allocated expenses for rent and maintenance of facilities and laboratory and other supplies.
We are a party to a collaboration agreement with Intrexon Corporation in which we will reimburse the collaborator for work it has performed. If the arrangement provides for us to reimburse the collaborator for research and development expenses or achieving a development milestone for which a payment is due, as is the case with Intrexon Corporation in future periods, we record the reimbursement or the achievement of the development milestone as research and development expense.
Stock-based Compensation
For stock options granted to employees and directors with only service-based vesting conditions, we measure stock-based compensation cost at the grant date based on the estimated fair value of the award, and recognize it as expense over the requisite service period on a straight-line basis. We record the expense of services rendered by non-employees based on the estimated fair value of the stock option as of the respective vesting date. Further, we expense the fair value of non-employee stock options that contain only service-based vesting conditions over the requisite service period of the underlying stock options. For awards with performance conditions, we estimate the likelihood of satisfaction of the performance criteria, which affects the awards expected to vest and the period over which the expense is recognized, and recognize the expense using the accelerated attribution model, to the extent achievement of the performance condition is deemed probable. We use the Black-Scholes valuation model in determining the fair value of equity awards.
Stock-based compensation expense is determined including estimated forfeitures, and is adjusted each period to reflect actual forfeitures and the outcomes of certain performance conditions.
Income Taxes
We account for income taxes under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on differences between financial reporting and income tax basis of assets and liabilities, as well as net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards, and are measured using the enacted tax rates and laws that will be in effect when the differences reverse. Deferred tax assets are reduced by a valuation allowance to reflect the uncertainty associated with their ultimate realization. The effect of a change in tax rate on deferred taxes is recognized in income or loss in the period that includes the enactment date.
We apply judgment in the determination of the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. We recognize any material interest and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax expense.
Due to the uncertainty surrounding the realization of the net deferred tax assets in future periods, we have recorded a full valuation allowance against our otherwise recognizable net deferred tax assets as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
F-9
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost. Depreciation is recorded using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the applicable assets. Upon sale or retirement, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are eliminated from the respective account and resulting gain or loss, if any, is included in current operations. Amortization of leasehold improvements is included in depreciation expense. Repairs and maintenance charges that do not increase the useful life of the assets are charged to operations as incurred. Property and equipment are depreciated over the following periods:
| Laboratory equipment | 3 - 5 years | |
| Furniture | 5 years | |
| Computer equipment | 3 years | |
| Leasehold improvements | Shorter of asset life or lease term |
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
We evaluate our long-lived assets for potential impairment. Potential impairment is assessed when there is evidence that events or changes in circumstances have occurred that indicate that the carrying amount of a long-lived asset may not be recovered. Recoverability of these assets is assessed based on undiscounted expected future cash flows from the assets, considering a number of factors, including past operating results, budgets and economic projections, market trends, and potential fertility treatment development cycles. Impairment in the carrying value of each asset is assessed when the undiscounted expected future cash flows, including its eventual residual value, derived from the asset are less than its carrying value. Impairments, if any, are recognized in earnings. An impairment loss would be recognized in an amount equal to the excess of the carrying amount over the undiscounted expected future cash flows. See Note 6 for discussion on impairment charges recognized during the periods presented.
Net Loss per Share
Basic and diluted net loss per common share is calculated by dividing net loss applicable to common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during the period, without consideration for common stock equivalents. Our potentially dilutive shares, which include outstanding stock options, restricted stock units and unvested Founders' shares, are considered to be common stock equivalents and are only included in the calculation of diluted net loss per share when their effect is dilutive.
Consolidation of Variable Interest Entities
We use a qualitative approach in assessing the consolidation requirement for variable interest entities. The approach focuses on identifying which enterprise has the power to direct the activities that most significantly impact the variable interest entity's economic performance and which enterprise has the obligation to absorb losses or the right to receive benefits from the variable interest entity. In the event that we are the primary beneficiary of a variable interest entity, the assets, liabilities, and results of operations of the variable interest entity are included in our consolidated financial statements.
New accounting pronouncements
In August 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) issued Accounting Standard Update (ASU) 2014-15, Presentation of Financial Statements—Going Concern. The new standard
F-10
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies (Continued)
requires management of public and private companies to evaluate whether there is substantial doubt about the entity's ability to continue as a going concern and, if so, disclose that fact. We will also be required to evaluate and disclose whether our plans alleviate that doubt. This guidance is effective for annual periods ending after December 15, 2016, and interim periods within annual periods beginning after December 15, 2016. We are evaluating this standard to determine if adoption will have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In June 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-10, which eliminates the concept of a development stage entity, or DSE, in its entirety from generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP). Under existing guidance, DSEs are required to report incremental information, including inception-to-date financial information, in their financial statements. A DSE is an entity devoting substantially all of its efforts to establishing a new business and for which either planned principal operations have not yet commenced or have commenced but there has been no significant revenues generated from that business. Entities classified as DSEs will no longer be subject to these incremental reporting requirements after adopting ASU No. 2014-10. ASU No. 2014-10 is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2014, with early adoption permitted. Retrospective application is required for the elimination of incremental DSE disclosures. Prior to the issuance of ASU No. 2014-10, we had met the definition of a DSE since our inception. We have elected to adopt this ASU early, and therefore we have eliminated the incremental disclosures previously required of DSEs, starting with our Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the period ended June 30, 2014.
In May 2014, the FASB issued ASU No. 2014-09, which amends the guidance for accounting for revenue from contracts with customers. This ASU supersedes the revenue recognition requirements in Accounting Standards Codification Topic 605, Revenue Recognition, and creates a new Topic 606, Revenue from Contracts with Customers. This guidance is effective for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2016, with early adoption not permitted. Two adoption methods are permitted: retrospectively to all prior reporting periods presented, with certain practical expedients permitted; or retrospectively with the cumulative effect of initially adopting the ASU recognized at the date of initial application. We have not yet determined which adoption method we will utilize or the effect that the adoption of this guidance will have on our consolidated financial statements.
3. Collaboration with Intrexon and OvaXon Joint Venture
Scope
On December 18, 2013, we entered into a collaboration agreement (the "OvaTure Collaboration") with Intrexon governing the use of Intrexon's synthetic biology technology platform for the accelerated development of our OvaTure platform. The OvaTure Collaboration provides that Intrexon will deliver laboratory and animal data to support the successful filing of an investigational new drug application ("IND") for OvaTure.
We will participate as an equal member on the Joint Steering Committee ("JSC") and Intellectual Property Committee ("IPC"). The JSC shall agree upon the services and the activities to be included in the work plan, and IPC has authority over intellectual property matters. We have the tie-breaking vote if there are any disputes with the JSC.
F-11
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
3. Collaboration with Intrexon and OvaXon Joint Venture (Continued)
Technology Access Fee Payable to Intrexon
The technology access fee paid to Intrexon was comprised of (1) the issuance of 273,224 shares, or $2.5 million of common stock issued to Intrexon, upon the execution of the OvaTure Collaboration in December 2013, and (2) a $2.5 million cash payment in December 2014.
The technology access fee does not give OvaScience the right to any research and development services, and the technology has no alternative future use to OvaScience. We therefore recorded $4.7 million in research and development expense in the year ended December 31, 2013 with $2.5 million recorded to additional paid-in capital and common stock and $2.2 million recorded in accrued liabilities, which represented the present value of the remaining $2.5 million technology access fee due in December 2014. We accreted the liability up to $2.5 million through interest expense and ultimately paid the full amount in December 2014.
The shares issued to Intrexon are subject to "piggy-back" registration rights that entitle Intrexon, unless waived, to have the shares included in any new registration statement filed in connection with an underwritten public offering, subject to underwriter cutback.
Research and Development Funding and Potential Commercial Milestone
The JSC will also approve a budget for services to be performed under the work plan. We have reimbursed and will reimburse Intrexon for research and development services performed, as dictated by the approved budget. If applicable, OvaScience will also make a commercial milestone payment three months after the first commercial sale of OvaTure.
Termination Rights
The collaboration has an indefinite term, with OvaScience having the right to terminate the collaboration after 90 days' prior written notice, and either OvaScience or Intrexon may terminate after a material breach by the other party that is not cured within 60 days. We may assign the collaboration in the event of a change of control transaction.
Royalties
Upon the delivery of laboratory and animal data necessary to support the successful filing of an IND application, we will pay Intrexon a mid-single digit royalty on net sales of OvaTure potential fertility treatments, and the exact royalty will depend upon whether Intrexon completes this milestone within two years after technology transfer.
Joint Venture
On December 18, 2013, we also entered into a joint venture with Intrexon to leverage Intrexon's synthetic biology technology platform and OvaScience's technology relating to egg precursor cells to pursue the prevention of genetic disease and animal health. We and Intrexon formed OvaXon, LLC ("OvaXon") to conduct the joint venture. Each party contributed $1.5 million to OvaXon and each has a 50% equity interest, and research and development costs and profits will be split accordingly. Each party will also have 50% control over OvaXon with disputes resolved through arbitration, if necessary.
F-12
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
3. Collaboration with Intrexon and OvaXon Joint Venture (Continued)
We consider OvaXon a variable interest entity. OvaXon does not have a primary beneficiary as both OvaScience and Intrexon have equal ability to direct the activities of OvaXon through JSC and IPC membership and 50% voting rights. OvaXon has been accounted for under the equity method and is not consolidated. This analysis and conclusion will be updated annually to reflect any changes in ownership or power over OvaXon.
As of December 31, 2013, we recorded a $1.5 million investment in OvaXon, an equity method investment, with the offset recorded to Accounts Payable. This was paid in January 2014. As of December 31, 2014 OvaXon has incurred expense in excess of the initial investment. The additional expense incurred is included within accrued expenses on our balance sheet, as we had the intent to fund the joint venture in the future. Each party contributed an additional $0.8 million in January 2015.
4. Fair Value Measurements
The fair value of our financial assets and liabilities reflects our estimate of amounts that we would have received in connection with the sale of the assets or paid in connection with the transfer of the liabilities in an orderly transaction between market participants at the measurement date. In connection with measuring the fair value of our assets and liabilities, we seek to maximize the use of observable inputs (market data obtained from independent sources) and to minimize the use of unobservable inputs (our assumptions about how market participants would price assets and liabilities). The following fair value hierarchy is used to classify assets and liabilities based on the observable inputs and unobservable inputs used in order to value our assets and liabilities:
- •
- Level 1 — quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities.
- •
- Level 2 — quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets or inputs that are observable
for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly through market corroboration, for substantially the full term of the financial instrument.
- •
- Level 3 — unobservable inputs based on our assumptions used to measure assets and liabilities at fair value.
For fixed income securities, we reference pricing data supplied by our custodial agent and nationally known pricing vendors, using a variety of daily data sources, largely readily-available market data and broker quotes. The prices provided by third party pricing services are validated by reviewing their pricing methods and obtaining market values from other pricing sources. After completing these validation procedures, we did not adjust or override any fair value measurements provided by the pricing services as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013.
We review investments for other-than-temporary impairment whenever the fair value of an investment is less than the amortized cost and evidence indicates that an investment's carrying amount is not recoverable within a reasonable period of time. To determine whether an impairment is other-than-temporary, we consider the intent to sell, or whether it is more likely than not that we will be required to sell, the investment before recovery of the investment's amortized cost basis. Evidence considered in this assessment includes reasons for the impairment, compliance with our investment policy, the severity and the duration of the impairment and changes in value subsequent to year end. As of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, there were no investments with a fair value that was significantly lower than the amortized cost basis or any investments that had been in an unrealized loss position for a significant period.
F-13
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
4. Fair Value Measurements (Continued)
The following tables provide the Company's assets and liabilities that are measured at fair value on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 (in thousands).
Description
|
Balance as of December 31, 2014 |
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Assets: |
|||||||||||||
Cash and money market funds |
$ | 6,414 | $ | 6,414 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Corporate debt securities (including commercial paper) |
53,817 | — | 53,817 | — | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets |
$ | 60,231 | $ | 6,414 | $ | 53,817 | $ | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Description
|
Balance as of December 31, 2013 |
Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Assets: |
|||||||||||||
Cash and money market funds |
$ | 18,078 | $ | 18,078 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
Corporate debt securities (including commercial paper) |
26,349 | — | 26,349 | — | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total assets |
$ | 44,427 | $ | 18,078 | $ | 26,349 | $ | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Liabilities: |
|||||||||||||
Technology access fee due to Intrexon |
$ | 2,186 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 2,186 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total liabilities |
$ | 2,186 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 2,186 | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Changes in the fair value of the Level 3 technology access fee due to Intrexon for the years ended December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 were as follows:
| |
Technology access fee | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
(in thousands) |
|||
Balance at December 31, 2012 |
$ | — | ||
Collaboration with Intrexon |
2,174 | |||
Fair value adjustment(1) |
12 | |||
| | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2013 |
$ | 2,186 | ||
| | | | | |
Fair value adjustment(1) |
314 | |||
Payments(2) |
$ | (2,500 | ) | |
| | | | | |
Balance at December 31, 2014 |
$ | — | ||
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
- (1)
- Fair
value adjustments consist of interest recorded.
- (2)
- The full $2.5 million was paid in December 2014.
There have been no changes to the valuation methods during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. There were no transfers of assets or liabilities between Level 1 and Level 2 during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. We had no short-term investments that were classified as Level 3 during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
F-14
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
4. Fair Value Measurements (Continued)
Cash and cash equivalents, prepaid expenses, accounts payable and accrued expenses are carried at amounts that approximate fair value due to their short-term maturities.
5. Cash, Cash Equivalents and Short-term Investments
The following tables summarize the Company's cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments as of December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013 (in thousands):
December 31, 2014
|
Amortized Cost |
Gross Unrealized Gains |
Gross Unrealized Losses |
Fair Value |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cash and money market funds |
$ | 6,414 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,414 | |||||
Corporate debt securities: |
|||||||||||||
Due in one year or less |
53,843 | 2 | (28 | ) | 53,817 | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 60,257 | $ | 2 | $ | (28 | ) | $ | 60,231 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Reported as: |
|||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 6,414 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 6,414 | |||||
Short-term investments |
53,843 | 2 | (28 | ) | 53,817 | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 60,257 | $ | 2 | $ | (28 | ) | $ | 60,231 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
December 31, 2013
|
Amortized Cost |
Gross Unrealized Gains |
Gross Unrealized Losses |
Fair Value |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Cash and money market funds |
$ | 18,078 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 18,078 | |||||
Corporate debt securities: |
|||||||||||||
Due in one year or less |
22,631 | 11 | (2 | ) | 22,640 | ||||||||
Due in two years or less |
3,708 | 2 | (1 | ) | 3,709 | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 44,417 | $ | 13 | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 44,427 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Reported as: |
|||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 18,078 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 18,078 | |||||
Short-term investments |
26,339 | 13 | (3 | ) | 26,349 | ||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
$ | 44,417 | $ | 13 | $ | (3 | ) | $ | 44,427 | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
At December 31, 2014 and 2013 we held thirty two and eight debt securities that had been in an unrealized loss position for less than 12 months, respectively. We held no investments that have been in a continuous unrealized loss position for 12 months or longer. The aggregate fair value of these securities was $44.2 million and $9.5 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013 respectively. We evaluated our securities for other-than-temporary impairments based on quantitative and qualitative factors. We considered the decline in market value for the thirty two securities as of December 31, 2014 to be primarily attributable to current economic and market conditions. It is not more likely than not that we will be required to sell these securities. Based on our analysis, we do not consider these investments to be other-than-temporarily impaired as of December 31, 2014 or 2013.
F-15
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
5. Cash, Cash Equivalents and Short-term Investments (Continued)
As of December 31, 2014, we held $7.5 million in financial institution debt securities and other corporate debt securities located in Canada, the United Kingdom, and France. As of December 31, 2013, we held $11.7 million in financial institution debt securities and other corporate debt securities located in Canada, the United Kingdom, the Netherlands, Australia, and Norway. Based on our analysis, we do not consider these investments to be other-than-temporarily impaired as of December 31, 2014 or 2013.
We had no realized gains or losses or other-than-temporary impairments on our short-term investments for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012.
6. Property and Equipment
Property and equipment and related accumulated depreciation are as follows (in thousands):
| |
As of December 31, | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||
Laboratory equipment |
$ | 4,093 | $ | 1,377 | |||
Furniture |
207 | 106 | |||||
Computer equipment |
7 | 7 | |||||
Leasehold improvements |
198 | 78 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Total property and equipment, gross |
4,505 | 1,568 | |||||
Less: accumulated depreciation |
(1,138 | ) | (688 | ) | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Total property and equipment, net |
$ | 3,367 | $ | 880 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
We recorded depreciation and amortization expense of $0.5 million, $0.2 million and $0.1 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. In July 2013, we entered into a master services agreement with a new global third party manufacturer to provide services for the manufacture of AUGMENT to replace our existing contract manufacturer. As a consequence of the contract manufacturer transition, we determined that we would no longer use certain laboratory equipment, and as such, recorded an impairment loss of $0.4 million during the year ended December 31, 2013. The loss was included within research and development expense.
7. Convertible Preferred Stock
In July 2011, we sold 6,200,000 shares of Series A Preferred Stock at a price of $1.00 per share for gross proceeds of $6.2 million. We incurred approximately $0.1 million of issuance costs in connection with the sale of the Series A Preferred Stock, which were recorded to additional paid-in capital.
On March 29, 2012, we sold 6,770,563 shares of Series B Preferred Stock at a price of $5.50 per share for gross proceeds of approximately $37.2 million. We incurred approximately $2.2 million of issuance costs in connection with the sale of the Series B Preferred Stock, which were recorded as a reduction of the proceeds received.
On August 13, 2012, as a result of the completion of the private placement of our common stock (see Note 8), our Series A and Series B Preferred Stock automatically converted into shares of common stock. Each share of Series A Preferred Stock converted into common stock on a one-for- 2.023 basis, into a total of 3,064,753 shares of common stock, and each share of Series B Preferred
F-16
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
7. Convertible Preferred Stock (Continued)
Stock converted into common stock on a one-for-one basis, into a total of 6,770,563 shares of common stock.
8. Common Stock
On March 28, 2012, our board of directors and stockholders approved, and we filed, a restated certificate of incorporation effecting a Reverse Stock Split of the outstanding shares of our common stock at a ratio of one share for every 2.023 shares outstanding, so that every 2.023 outstanding shares of common stock (the "Reverse Stock Split") before the Reverse Stock Split represented one share of common stock after the Reverse Stock Split. Each stockholder's percentage ownership interest in the Company and proportional voting power remains unchanged after the Reverse Stock Split, except for minor changes and adjustments resulting from rounding of fractional interests. The rights and privileges of the holders of capital stock were unaffected by the Reverse Stock Split. All information in these financial statements has, unless otherwise indicated, been retroactively adjusted for all periods presented to give effect to the Reverse Stock Split.
On August 13, 2012, we issued and sold in a private placement an aggregate of 897,554 shares of common stock at a price per share of $5.50 resulting in net proceeds of $4.0 million. As a result of the completion of the private placement, on August 13, 2012, our Series A Preferred Stock and Series B Preferred Stock automatically converted into shares of common stock. Each share of Series A Preferred Stock converted into common stock on a one-for-2.023 basis, into a total of 3,064,753 shares of common stock, and each share of Series B Preferred Stock converted into common stock on a one-for-one basis, into a total of 6,770,563 shares of common stock.
In March 2013, we issued and sold in a private placement an aggregate of 3,888,880 shares of our common stock to investors at $9.00 per share. The private placement resulted in $32.7 million of net proceeds. We filed a registration statement covering the resale of all such shares.
In December 2013, we issued 273,224 shares of our common stock to Intrexon Corporation at $9.15 per share. The shares were issued in conjunction with a research and development agreement as the first installment of technology access fee (see Note 3).
In March 2014, we issued and sold in a public offering an aggregate of 5,518,630 shares of our common stock at $10.00 per share, which included 518,630 shares that represented the partial exercise of an overallotment option granted to the underwriters in connection with the offering. This public offering resulted in $51.7 million of net proceeds, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and other offering expenses payable by us.
We have reserved the following shares of common stock for the potential exercise of stock options and issuance of shares upon vesting of restricted stock units:
| |
December 31, 2014 |
December 31, 2013 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Outstanding stock options |
3,628,628 | 2,413,237 | |||||
Outstanding restricted stock units |
54,078 | 96,155 | |||||
F-17
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
9. Stock-Based Compensation
In March 2012, our board of directors and stockholders approved the 2012 Stock Incentive Plan (the "2012 Plan"). The 2012 Plan provides for the grant of incentive stock options, non-statutory stock options, stock appreciation rights, restricted stock units and other stock-based or cash awards to purchase shares of common stock to eligible employees, officers, directors and consultants. The number of shares of our common stock that are reserved for issuance under the 2012 Plan is equal to the sum of (1) 1,453,253 shares of common stock issuable under the 2012 Plan plus the number of shares of our common stock subject to outstanding awards under the 2011 Plan, described below, that expire, terminate or are otherwise surrendered, cancelled, forfeited or repurchased by us at their original issuance price pursuant to a contractual repurchase right (up to 679,622 shares) plus (2) an annual increase, to be added on the first day of each year beginning in 2013 and each subsequent anniversary until the expiration of the 2012 Plan, equal to the lowest of 975,000 shares of its common stock, 4.0% of the number of shares of our common stock outstanding on the first day of the year and an amount determined by our board of directors. We began making grants under the 2012 Plan following June 11, 2012, the effective date of our registration of securities on Form 10. Shares issued under the 2012 Plan are funded through the issuance of new shares. We ceased granting options under the 2011 Plan following the effective date of our registration of securities on Form 10.
Founders' stock
In April 2011, we issued 3,509,634 shares of common stock to founders at a purchase price of $0.002 per share, which was determined by the board of directors to be the fair value of the common stock on the date of issuance. The shares were issued under restricted stock purchase agreements and not pursuant to the 2011 Plan. These restricted stock purchase agreements allow us, at our discretion, to repurchase unvested shares if the founder's relationship with us is terminated. The shares issued to three of the co-founders vested with respect to 25% of the shares on the grant date and with respect to the remaining shares in approximately equal quarterly installments through the fourth anniversary of the grant date. The shares issued to the remaining two co- founders vest in approximately equal quarterly installments from and after the grant date. Additionally, 25% of the then-unvested shares issued to the remaining two co-founders vested in July 2011 in connection with the Series A Preferred Stock financing.
A summary of our Founders' stock activity and related information is as follows:
| |
Shares | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Unvested at December 31, 2012 |
1,645,141 | |||
Granted |
— | |||
Vested |
(658,060 | ) | ||
| | | | | |
Unvested at December 31, 2013 |
987,081 | |||
Granted |
— | |||
Vested |
(658,060 | ) | ||
| | | | | |
Unvested at December 31, 2014 |
329,021 | |||
We record stock-based compensation expense for the common stock subject to repurchase based on the grant date intrinsic value for employees and the vesting date intrinsic value for non-employees. All of the restricted shares were issued at fair value. We recognized total stock-based compensation
F-18
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
9. Stock-Based Compensation (Continued)
expense of $7.5 million, $1.4 million, and $0.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively for the Founders' stock.
Stock options
A summary of the Company's stock option activity and related information is as follows (in thousands, except share and per share data):
| |
Shares | Weighted average exercise price per share |
Weighted average remaining contractual term (years) |
Aggregate intrinsic value |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Outstanding at December 31, 2013 |
2,413,237 | $ | 9.26 | 9.05 | $ | 6,087 | |||||||
Granted |
2,464,138 | 19.12 | |||||||||||
Exercised |
(370,808 | ) | 3.81 | ||||||||||
Forfeited |
(852,564 | ) | 11.51 | ||||||||||
Cancelled |
(25,375 | ) | 5.48 | ||||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Outstanding at December 31, 2014 |
3,628,628 | 16.01 | 9.11 | 102,355 | |||||||||
Exercisable at December 31, 2014 |
688,562 | 8.43 | 8.07 | 24,641 | |||||||||
Vested and expected to vest at December 31, 2014 |
2,394,044 | 15.11 | 9.01 | 69,692 | |||||||||
The total intrinsic value (the amount by which the fair market value exceeded the exercise price) of stock options exercised was $4.2 million, $0.4 million, and $48 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, and 2012, respectively.
The fair value of each employee stock-based award is estimated on the grant date using the Black-Scholes option pricing model.
We have used the simplified method to calculate the expected term as we do not have sufficient historical exercise and post-vest termination data to provide a reasonable basis upon which to estimate the expected term for the options granted to employees. The remaining contractual term is used for option awards granted to non-employees. Historical data will be incorporated into our assumption as it becomes available.
The computation of expected volatility is based on a hybrid approach of blending the Company's historical volatility with the historical volatility of a representative group of companies with similar characteristics to ours, including stage of potential fertility treatment development and life science industry focus. The representative group of companies consisted of ANI Pharmaceuticals, Inc., Corcept Therapeutics Inc., Neogenomics Inc., Sangamo Biosciences, Inc., and Stem Cells Inc. As a result of being an early stage fertility company with no revenues, the representative group of companies has certain similar, but not all similar, characteristics to ours. We believe the group selected has sufficient similar economic and industry characteristics and includes companies that are most representative of ours.
F-19
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
9. Stock-Based Compensation (Continued)
The fair value of each stock option is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model using the following assumptions:
| |
December 31, | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||
Risk-free interest rate |
1.62% - 2.17% | 0.91% - 2.11% | 0.8% - 1.78% | |||
Dividend yield |
— | — | — | |||
Volatility |
76% - 84% | 83% - 91% | 79% - 89% | |||
Expected term (years) |
5.3 - 9.97 | 5.1 - 9.93 | 5.1 - 9.93 | |||
During the year ended December 31, 2014, we granted 2,434,138 options to purchase common stock to employees with a weighted average exercise price of $19.19 per share at a weighted average grant date fair value of $13.41. During the year ended December 31, 2013, we granted 1,537,172 options to purchase common stock to employees with a weighted average exercise price of $12.87 per share at a weighted average grant date fair value of $9.34.
We recognized total stock-based compensation expense for employee stock option grants of $3.3 million, $2.3 million, and $0.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
During 2014, we granted 30,000 options to purchase common stock with a weighted average exercise price of $13.26 per share to non-employees. There were no stock options granted to non-employees in 2013.
Stock-based awards including Founders' stock issued to non-employees are accounted for using the fair value method. These stock-based awards are revalued at each reporting date until vested. We recognized total stock-based compensation of $8.3 million, $2.2 million, and $1.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively for these non-employee awards.
At December 31, 2014 there was $27.3 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested stock options and restricted stock. We expect to recognize these costs over a remaining weighted average period of 2.9 years.
Restricted stock units
On December 5, 2012, we issued a total of 192,308 restricted stock units ("RSUs") to our Chief Executive Officer. This included a grant of 128,205 RSUs with service-based vesting as follows: 16,025 shares on March 31, 2013 and 16,025 shares each quarter thereafter until December 31, 2014. The fair value of the service-based RSUs is based on the closing price of our common stock on the award date, or $7.80 per share. The stock-based compensation expense for this grant will be recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period. We also granted 64,103 RSUs to our Chief Executive Officer that will vest only upon the achievement of performance conditions as determined by the Company's board of directors. On March 20, 2013 the board of directors established the 2013 performance criteria for the first tranche of the award and communicated the performance criteria to the Chief Executive Officer. The grant date stock price of these performance-based RSUs was $10.00 per share. In December 2013, 19,230 performance-based RSUs vested out of a total of 32,051 performance-based RSUs granted. The total fair value of RSUs vested during 2013 (measured on the
F-20
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
9. Stock-Based Compensation (Continued)
date of vesting) was $0.8 million. On February 7, 2014 the board of directors established the 2014 performance criteria for the second tranche of the award and communicated the performance criteria to the Chief Executive Officer. The closing price of our common stock on the grant date, the date the board established the 2014 performance criteria, of these performance-based RSUs was $8.75 per share. As of December 31, 2014, we determined that all of the 2014 performance conditions were achieved and has recognized the remaining expense for these awards. We recognized total stock-based compensation for the service-based awards and performance-based awards of $0.8 million, $0.7 million and $36 thousand for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively.
On December 9, 2014, we issued a total of 54,078 restricted stock units ("RSUs") to our Chief Executive Officer. This included a grant of 30,902 RSUs with service condition-based vesting as follows: 3,863 shares on March 31, 2015 and 3,863 shares each quarter thereafter until December 31, 2016. The fair value of the service condition-based RSUs is based on the closing price of our common stock on the award date, or $32.36 per share. The stock-based compensation expense for this grant will be recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period. We also granted 23,176 RSUs that will vest only upon the achievement of performance conditions in 2015 and 2016 as determined by the Company's board of directors. As of December 31, 2014, the Company recognized $30 thousand in expense related to the service based awards.
The performance conditions for the 2015 and 2016 tranches of the performance-based RSUs had not been established as of December 31, 2014. As a result, the measurement date and grant date have not occurred for accounting purposes and no expense has been taken related to these awards as of December 31, 2014.
As of December 31, 2014, there was $1.0 million of total unrecognized compensation cost related to non-vested service-based RSUs granted under the 2012 Plan. The expense is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 2.0 years.
10. Income Taxes
We had no income tax expense or benefit for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
Subject to the limitations described below at December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, we had net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $72.1 million, $33.0 million and approximately $14.1 million, respectively, to offset future federal taxable income, which expire beginning in 2031 continuing through 2034. The federal net operating loss carryforwards exclude approximately $5.5 million of deductions related to the exercise of stock options. This amount represents an excess tax benefit and has not been included in the gross deferred tax asset reflected for net operating losses. This amount will be recorded as an increase in additional paid in capital on the consolidated balance sheet once the excess benefits are "realized" in accordance with ASC 718. As of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, we had net operating loss carryforwards of approximately $71.5 million, $32.6 million and approximately $13.9 million, respectively, to offset future state taxable income, which expire beginning in 2031 continuing through 2034. The state net operating loss carryfowards include $5.5 million of deductions related to the exercise of stock options. We also had tax credit carryforwards of approximately $1.9 million, $0.9 million and $0.2 million as of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, to offset future federal and state income taxes, which expire beginning in 2027 continuing through 2034.
F-21
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
10. Income Taxes (Continued)
The NOL and tax credit carryforwards are subject to review and possible adjustment by the Internal Revenue Service and state tax authorities and may become subject to an annual limitation in the event of certain cumulative changes in the ownership interest of significant shareholders over a three year period in excess of 50%, as defined under Sections 382 and 383 of the Internal Revenue Code, as well as similar state provisions. This could limit the amount of tax attributes that can be utilized annually to offset future taxable income or tax liabilities. The amount of the annual limitation is determined based on our value immediately prior to the ownership change. Subsequent ownership changes may further affect the limitation in future years.
We have not, as yet, conducted a study of IRC Section 382. As a full valuation allowance has been provided against our NOL and tax credit carryforwads, and if an adjustment is required, this adjustment would be offset by an adjustment to the valuation allowance, there would be no impact to the consolidated balance sheet or consolidated statements of operations.
A reconciliation of income taxes computed using the U.S. federal statutory rate to that reflected in operations follows:
| |
Year Ended December 31, 2014 |
Year Ended December 31, 2013 |
Year Ended December 31, 2012 |
|||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Income tax benefit using U.S. federal statutory rate |
34.00 | % | 34.00 | % | 34.00 | % | ||||
State income taxes, net of federal benefit |
5.28 | % | 5.28 | % | 5.42 | % | ||||
Research and development tax credits |
1.75 | % | 2.31 | % | 0.00 | % | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Permanent items |
(0.55 | )% | (1.09 | )% | (2.78 | )% | ||||
Foreign differential |
(1.59 | )% | —% | —% | ||||||
Other adjustments (state) |
(0.03 | )% | —% | —% | ||||||
Change in the valuation allowance |
(38.86 | )% | (40.50 | )% | (36.64 | )% | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
|
— | % | — | % | — | % | ||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
The principal components of our deferred tax assets are as follows (in thousands):
| |
2014 | 2013 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Deferred Tax Assets: |
|||||||
Net operating loss carryforwards |
26,133 | 12,939 | |||||
Tax credit carryforwards |
1,689 | 823 | |||||
Accrued Expenses |
655 | 190 | |||||
Stock based compensation |
5,591 | 1,602 | |||||
Intangibles |
2,536 | 1,954 | |||||
Other |
305 | 160 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
Gross deferred tax assets |
36,909 | 17,668 | |||||
Valuation allowance |
(36,909 | ) | (17,668 | ) | |||
| | | | | | | | |
Net deferred tax assets |
— | — | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
We have evaluated the positive and negative evidence bearing upon the realizability of our deferred tax assets. We have considered our history of operating losses and concluded, in accordance
F-22
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
10. Income Taxes (Continued)
with the applicable accounting standards, that it is more likely than not that we may not realize the benefit of our deferred tax assets. Accordingly, our deferred tax assets have been fully reserved at December 31, 2014 and 2013. We reevaluate the positive and negative evidence on a quarterly basis.
The valuation allowance increased approximately $19.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2014, due primarily to the increase in net operating loss carryforwards and tax credits. The valuation allowance increased approximately $11.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2013, due primarily to the increase in the net operating loss carryforwards and tax credits.
We apply ASC 740, Income Taxes. ASC 740 provides guidance on the accounting for uncertainty in income taxes recognized in financial statements. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, we had no unrecognized tax benefits.
We will recognize interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions in income tax expense. As of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, we had no accrued interest or penalties related to uncertain tax positions and no amounts have been recognized in our consolidated statements of operations.
We file income tax returns in the U.S. Federal and Massachusetts jurisdictions. The statute of limitations for assessment by the Internal Revenue Service ("IRS") and state tax authorities is open for tax years ended December 31, 2013, 2012 and 2011. There are currently no federal or state income tax audits in progress.
We have not, as yet, conducted a study of research and development ("R&D") credit carryforwards. Such a study, once undertaken by us, may result in an adjustment to our R&D credit carryforwards; however, until a study is completed and any adjustment is known, no amounts are being presented as an uncertain tax position. A full valuation allowance has been provided against our R&D credits and, if an adjustment is required, this adjustment would be offset by an adjustment to the valuation allowance. Thus, there would be no impact to the balance sheet or statement of operations if an adjustment is required.
11. Commitments and Contingencies
On May 1, 2012, we entered into a commercial building lease agreement. The sixty month lease, which commenced on August 10, 2012, provides for the lease of approximately 6,000 square feet of space in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Base annual rent is initially set at approximately $22,000 per month with an annual increase of 3%. From April 2011 through April 2012, we leased office space from a significant stockholder. There was no formal lease arrangement with the stockholder. In May 2012 we entered into an additional commercial building sublease agreement. The 24 month sublease, which commenced on August 26, 2013, provides for the lease of 1,900 square feet of space also in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Base rent is approximately $4 thousand per month with an annual increase of 3%. In June 2014, we entered into a commercial building lease agreement. The seventeen and a half month lease, which commenced on July 15, 2014, provides for the lease of an additional approximately 5,800 square feet of space in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Base annual rent is initially $27,272 per month with an annual increase of approximately 1.8%.
F-23
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
11. Commitments and Contingencies (Continued)
Future minimum lease payments as of December 31, 2014 are as follows (in thousands):
Year
|
|
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
2015 |
$ | 646 | ||
2016 |
292 | |||
2017 |
173 | |||
2018 |
— | |||
2019 |
— | |||
| | | | | |
|
$ | 1,111 | ||
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
| | | | | |
Rent expense is recorded straight-line over the operating lease term, with deferred rent included on the balance sheet in other liabilities. Rent expense for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 amounted to $0.6 million, $0.4 million, and $0.2 million, respectively.
12. Accrued Expenses
Accrued expenses consist of the following (in thousands):
| |
December 31, 2014 |
December 31, 2013 |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Compensation and related benefits |
$ | 2,753 | $ | 719 | |||
Development, site costs, and contract manufacturing |
2,567 | 258 | |||||
Legal, audit and tax services |
829 | 605 | |||||
Consulting |
793 | 174 | |||||
Other expenses |
712 | 178 | |||||
Technology access fee payable to Intrexon (present value) |
— | 2,186 | |||||
| | | | | | | | |
|
$ | 7,654 | $ | 4,120 | |||
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | |
13. Net Loss Per Share
The following table sets forth the computation of basic and diluted loss per share applicable to common stockholders (in thousands, except per share data):
| |
Year Ended December 31, | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
Net loss applicable to common stockholders |
$ | (49,520 | ) | $ | (29,044 | ) | $ | (13,510 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average number of common shares used in net loss per share applicable to common stockholders—basic and diluted |
22,647 | 16,160 | 5,810 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share applicable to common stockholders—basic and diluted |
$ | (2.19 | ) | $ | (1.80 | ) | $ | (2.33 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
F-24
OvaScience, Inc.
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements (Continued)
13. Net Loss Per Share (Continued)
The amounts in the table below were excluded from the calculation of diluted net loss per share, prior to the use of the treasury stock method, due to their anti-dilutive effect (in thousands):
| |
Year Ended, December 31, |
|
||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (in thousands) |
2014 | 2013 | 2012 | |||||||
Outstanding stock options and restricted stock units |
3,683 | 2,509 | 1,410 | |||||||
Founders' stock |
329 | 987 | 1,645 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
Total |
4,012 | 3,496 | 3,055 | |||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | |
14. Related Party Transactions
Our chief executive officer, Michelle Dipp, M.D., Ph.D., has not historically received any cash compensation for her service as chief executive officer because of her service as a general partner of one of our principal stockholders. Pursuant to the terms of an employment agreement that we entered into with Dr. Dipp in December 2012, we granted Dr. Dipp an option to purchase 339,313 shares of our common stock and restricted stock units in the aggregate amount of 192,308 shares of our common stock (see Note 9). Pursuant to the term of stock option agreement that we entered into with Dr. Dipp in June 2014, we granted Dr. Dipp an option to purchase 500,000 shares of our common stock (Note 9). Pursuant to the terms of an employment agreement that we entered into with Dr. Dipp in December 2014, we granted Dr. Dipp an option to purchase 200,000 shares of our common stock and restricted stock units in the aggregate amount of 54,078 shares of our common stock (see Note 9). In addition, we may in the future determine to compensate Dr. Dipp with cash or other compensation.
As discussed in Note 11, during 2011 and a portion of 2012, we leased office space from one of our principal stockholders.
15. Employee Benefit Plan
In January 2012, we adopted a 401(k) retirement and savings plan (the "401(k) Plan") covering all employees. The 401(k) Plan allows employees to make pre-tax contributions up to the maximum allowable amount set by the Internal Revenue Service. Under the 401(k) Plan, we may make discretionary contributions as approved by our board of directors. During the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, we made contributions to the 401(k) Plan of $0.2 million, $0.1 million, and $0.1 million, respectively.
16. Subsequent Events
In January 2015, we issued and sold in a public offering an aggregate of 2,645,000 shares of our common stock at $50.00 per share, which included 345,000 shares that represented the full exercise of an option to purchase additional shares granted to the underwriters in connection with the offering. This public offering resulted in $124.1 million of net proceeds, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and other offering expenses payable by us. At December 31, 2014 we capitalized $0.1 million of costs related to expenses incurred in this public offering that will be recorded to APIC when the offering closes, which are included in other long-term assets.
F-25
SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION
(Unaudited)
The following sets forth certain unaudited consolidated quarterly statements of operations data for each of our last eight quarters. In our opinion, this quarterly information reflects all adjustments consistency only of normal recurring adjustments, necessary for a fair statement for the periods presented. Such quarterly results are not necessarily indicative of future results of operations and should be read in conjunction with audited consolidated financial statements and the notes thereto included elsewhere herein.
| |
Three months Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
March 31, 2014 |
June 30, 2014 |
September 30, 2014 |
December 31, 2014 |
|||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except per share amounts) |
||||||||||||
Total operating expenses(1)(2) |
$ | 7,650 | $ | 9,595 | $ | 12,399 | $ | 18,289 | |||||
Loss from operations |
(7,650 | ) | (9,595 | ) | (12,399 | ) | (18,289 | ) | |||||
Net loss |
(7,814 | ) | (9,893 | ) | (12,923 | ) | (18,890 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share—basic and diluted |
$ | (0.41 | ) | $ | (0.42 | ) | $ | (0.54 | ) | $ | (0.79 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average number of common shares used in net loss per share—basic and diluted |
19,214 | 23,546 | 23,766 | 23,998 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- During
the third quarter of 2014, we recorded stock-based compensation expense of $3.0 million primarily due to the increase in our stock price (see
Note 9).
- (2)
- During the fourth quarter of 2014, we recorded stock-based compensation expense of $6.4 million primarily due to the increase in our stock price (see Note 9).
| |
Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| |
March 31, 2013 |
June 30, 2013 |
September 30, 2013 |
December 31, 2013 |
|||||||||
| |
(in thousands, except per share amounts) |
||||||||||||
Total operating expenses(1)(2) |
$ | 5,175 | $ | 6,021 | $ | 6,925 | $ | 11,013 | |||||
Loss from operations |
(5,175 | ) | (6,021 | ) | (6,925 | ) | (11,013 | ) | |||||
Net loss |
(5,157 | ) | (5,996 | ) | (6,891 | ) | (11,000 | ) | |||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Net loss per share—basic and diluted |
$ | (0.39 | ) | $ | (0.36 | ) | $ | (0.40 | ) | $ | (0.64 | ) | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
Weighted average number of common shares used in net loss per share—basic and diluted |
13,345 | 16,869 | 17,048 | 17,270 | |||||||||
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
| | | | | | | | | | | | | | |
- (1)
- During
the third quarter of 2013, we recorded an impairment of certain laboratory equipment of approximately $0.4 million (see Note 6).
- (2)
- During the fourth quarter of 2013, we recorded research and development expense of approximately $4.7 million related to a technology access fee to Intrexon (see Note 3).
F-26
