Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - LIFETIME BRANDS, INC | Financial_Report.xls |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - LIFETIME BRANDS, INC | d867597dex231.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - LIFETIME BRANDS, INC | d867597dex321.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - LIFETIME BRANDS, INC | d867597dex311.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - LIFETIME BRANDS, INC | d867597dex312.htm |
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - LIFETIME BRANDS, INC | d867597dex991.htm |
| EX-23.2 - EX-23.2 - LIFETIME BRANDS, INC | d867597dex232.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EX-21.1 - LIFETIME BRANDS, INC | d867597dex211.htm |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 or 15 (d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended: December 31, 2014
or
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 or 15 (d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission file number: 0-19254
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 11-2682486 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
1000 Stewart Avenue, Garden City, New York 11530
(Address of principal executive offices, including Zip Code)
(516) 683-6000
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Common Stock, $.01 par value | The NASDAQ Global Select Market | |
| (Title of each class) | (Name of each exchange on which registered) |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§ 232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§ 229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act:
| Large accelerated filer | ¨ | Accelerated filer | x | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ¨ (do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ¨ | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of 10,731,291 shares of the voting common equity held by non-affiliates of the registrant as of June 30, 2014 was approximately $167,944,704. Directors, executive officers, and trusts controlled by said individuals are considered affiliates for the purpose of this calculation and may not necessarily be considered affiliates for any other purpose.
The number of shares of common stock, par value $.01 per share, outstanding as of February 28, 2015 was 13,712,081.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Parts of the registrant’s definitive proxy statement for the 2014 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 are incorporated by reference in Part III of this Annual Report.
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
FORM 10-K
1
Table of Contents
DISCLOSURE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K of Lifetime Brands, Inc. (the “Company” and, unless the context otherwise requires, references to the “Company” shall include its consolidated subsidiaries) contains “forward-looking statements” as defined by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These forward-looking statements include information concerning the Company’s and its subsidiaries’ plans, objectives, goals, strategies, future events, future revenues, performance, capital expenditures, financing needs and other information that is not historical information. Many of these statements appear, in particular, under the headings Business and Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations included in Item 1 of Part I and Item 7 of Part II, respectively. When used in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, the words “estimates,” “expects,” “anticipates,” “projects,” “plans,” “intends,” “believes,” “may,” “should,” “seeks,” “potential” and variations of such words or similar expressions are intended to identify forward-looking statements. All forward-looking statements, including, without limitation, the Company’s examination of historical operating trends, are based upon the Company’s current expectations and various assumptions. The Company believes there is a reasonable basis for its expectations and assumptions, but there can be no assurance that the Company will realize its expectations or that the Company’s assumptions will prove correct.
There are a number of risks and uncertainties that could cause the Company’s actual results to differ materially from the forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report. Important factors that could cause the Company’s actual results to differ materially from those expressed as forward-looking statements are set forth in this Annual Report, including the risk factors discussed in Part I, Item 1A under the heading Risk Factors.
Except as may be required by law, the Company undertakes no obligation to publicly update or revise forward-looking statements which may be made to reflect events or circumstances after the date made or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated events.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND OTHER INFORMATION
The Company is required to file its annual reports on Forms 10-K and quarterly reports on Forms 10-Q, and other reports and documents as required from time to time with the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). The Company also maintains a website at http://www.lifetimebrands.com. Information contained on this website is not a part of or incorporated by reference into this annual report. The Company makes available on its website the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to these reports as soon as reasonably practicable after these reports are filed with or furnished to the SEC. Users can access these reports free of charge on the Company’s website. The public may read and copy any materials that the Company files with the SEC at the SEC’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, NE, Washington, DC 20549. Information may be obtained with respect to the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC also maintains an Internet site that contains reports, proxy and information statements, and other information regarding the Company’s electronic filings with the SEC at http://www.sec.gov.
2
Table of Contents
| Item 1. | Business |
OVERVIEW
The Company designs, sources and sells branded kitchenware, tableware and other products used in the home and markets its products under a number of widely-recognized brand names and trademarks, which are either owned or licensed by the Company, or through retailers’ private labels and their licensed brands. The Company’s products, which are targeted primarily towards consumer purchases of moderately priced kitchenware, tableware and housewares, are sold through virtually every major level of trade. The Company generally markets several lines within each of its product categories under more than one brand. The Company sells its products directly to retailers (including through their Internet websites) and, to a lesser extent, to distributors. The Company also sells a limited selection of its products directly to consumers through its own Internet websites. At the heart of the Company is a culture of innovation. The Company brought over 4,000 new or redesigned products to market in 2014 and expects to introduce approximately 4,000 new or redesigned products in 2015.
The Company’s product categories include two categories of products used to prepare, serve and consume foods, Kitchenware (kitchen tools and gadgets, cutlery, cutting boards, shears, cookware and bakeware) and Tableware (dinnerware, stemware, flatware and giftware); and one category, Home Solutions, which comprises other products used in the home (pantryware, spice racks, thermal beverageware, food storage, neoprene travel products and home décor).
The Company has expanded its presence in international markets through investments in various companies that operate outside of the United States. In 2007, the Company acquired a 30% equity interest in Grupo Vasconia, S.A.B. (“Vasconia”), an aluminum manufacturer and housewares company based in Mexico. In January 2008, the Company entered into a strategic alliance to distribute products in Canada. In November 2011, the Company acquired 100% of the share capital of each of Creative Tops Holdings Limited and Creative Tops Far East Limited (collectively, “Creative Tops”). Creative Tops is a UK-based supplier of private label and branded tableware and kitchenware products. In December 2011, the Company acquired a 40% equity interest in GS Internacional S/A (“GSI”). GSI is a wholesale distributor of branded housewares products in Brazil. GSI markets dinnerware, glassware, home décor, kitchenware and barware to customers, including major department stores, housewares retailers and independent shops throughout Brazil. In January 2011, the Company, together with Vasconia and unaffiliated partners, formed a joint venture based in Hong Kong that supplies imported kitchenware products to retailers in North, Central and South American. The Company sold its investment in this joint venture to an unaffiliated partner in October 2014. The Company also has a joint venture, since February 2012 with a Chinese corporation, to distribute Mikasa® products in China.
During the first half of 2014, the Company continued its expansion into international markets with the acquisitions of the share capital of Thomas Plant (Birmingham) Limited (“Thomas Plant” or “Kitchen Craft”), a leading supplier of kitchenware products and accessories in the United Kingdom with sales in over 70 countries, and La Cafetière, a supplier of coffee presses and accessories marketed primarily in the United Kingdom and Continental Europe under the La Cafetière and Randwyck brands. The Kitchen Craft acquisition, which was completed in January 2014, strengthened the Company’s global presence by adding to the Company’s existing products a broad range of kitchenware products with strong brand recognition and complements the Company’s Creative Tops’ division with strength in the tableware category. The acquisition of La Cafetière in March 2014 further strengthened the international footprint in tableware.
The Company continually evaluates opportunities to expand the reach of its brands and to invest in other companies that operate principally outside the United States and that own or license complementary brands. These opportunities involve risks as the industry and foreign markets may not evolve as anticipated and the Company’s objectives may not be achieved.
In addition to seeking opportunities to expand the Company’s international footprint, the Company regularly evaluates potential acquisitions of businesses or product lines to grow its product offerings and distribution in the United States market. In December 2012, the Company acquired Fred® & Friends, a business which designs and markets novelty housewares and other products under the Fred® brand. The acquisition resulted in an expansion of the Company’s
3
Table of Contents
Kitchenware product category to include novelty kitchen tools, tableware accessories, party goods, personal accessories and other products. In 2014, the Company acquired certain assets of Built NY, a designer and distributor of brightly colored, uniquely patterned neoprene travel products, including bags, totes, cases and sleeves, and acquired the business and assets of Empire Silver Company, a manufacturer of sterling silver and pewter giftware products.
The Company is a Delaware corporation, incorporated on December 22, 1983.
The Company’s top brands and their respective product categories are:
| Brand |
Licensed/Owned |
Product Category | ||
| Farberware® | Licensed* | Kitchenware | ||
| KitchenAid® | Licensed | Kitchenware | ||
| Mikasa® | Owned | Tableware and Home Solutions | ||
| KitchenCraft® | Owned | Kitchenware | ||
| Pfaltzgraff® | Owned | Tableware and Home Solutions | ||
| Fred® | Owned | Kitchenware | ||
| Sabatier® | Licensed | Kitchenware | ||
| masterclass® | Owned | Kitchenware | ||
| Kamenstein® | Owned | Home Solutions | ||
| Towle® | Owned | Tableware | ||
| Built® | Owned | Home Solutions |
| * | The Company has a royalty free license to utilize the Farberware® brand for kitchenware and tableware products for a term that expires in 2195, subject to earlier termination under certain circumstances. |
With the exception of the Company’s sterling silver products, the Company sources almost all of its products from suppliers located outside the United States, primarily in the People’s Republic of China. The Company manufactures its sterling silver products at a leased facility in San Germán, Puerto Rico and fills containers with spices and assembles spice racks at its owned Winchendon, Massachusetts distribution facility.
BUSINESS SEGMENTS
During the second quarter of 2014, the Company realigned its reportable segments into three categories, U.S. Wholesale, International and Retail Direct. The U.S. Wholesale segment, formerly the Wholesale segment, includes the domestic operations of the Company’s primary business that designs, markets and distributes its products to retailers and distributors. Due to the acquisition of Kitchen Craft, certain business operations conducted outside the U.S., previously included in the Wholesale segment, were moved to the International segment. The Retail Direct segment is that in which the Company markets and sells a limited selection of its products through its Pfaltzgraff®, Mikasa®, Built NY®, Fred® & Friends and Lifetime Sterling® internet websites remained unchanged. The Company has segmented its operations to reflect the manner in which management reviews and evaluates the results of its operations.
Additional information regarding the Company’s reportable segments is included in Note J of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 15.
CUSTOMERS
The Company’s wholesale customers include mass merchants, specialty stores, national chains, department stores, warehouse clubs, supermarkets, off-price retailers and Internet retailers.
4
Table of Contents
The Company’s products are sold globally to a diverse customer base including mass merchants (such as Wal-Mart and Target), specialty stores (such as Bed Bath & Beyond and Dunelm), national chains (such as Kohl’s and JCPenney), department stores (such as Macy’s and Bon-Ton), warehouse clubs (such as Costco and Sam’s Club), supermarkets (such as Stop & Shop, Meijer, Winn-Dixie, Tesco and Sainsbury’s), off-price retailers (such as TJX Companies, Ross Stores and Big Lots), home and garden centers (such as TrueValue, ACE Hardware Stores and Wyevale) and Internet retailers (such as Amazon). The Company also does business with independent retailers, including through business-to-business Internet sites aimed at independent retailers.
The Company also operates its own consumer Internet sites that provide information about the Company’s products and offer consumers the opportunity to purchase a limited selection of the Company’s products directly from the Company.
During the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, Wal-Mart Stores, Inc., including Sam’s Club and Asda Superstore (“Walmart”), accounted for 16%, 15% and 16% of consolidated net sales, respectively. No other customer accounted for 10% or more of the Company’s net sales during these periods.
DISTRIBUTION
The Company sells its products directly to retailers and, to a lesser extent, to distributors. The Company also sells a limited quantity of the Company’s products to individual consumers and smaller retailers through its own Internet sites. The Company operates distribution centers at the following locations:
| Location |
Size (square feet) |
|||
| Fontana, California |
753,000 | |||
| Robbinsville, New Jersey |
700,000 | |||
| Birmingham, England |
277,000 | |||
| Winchendon, Massachusetts |
175,000 | |||
| Corby, England |
116,000 | |||
| Medford, Massachusetts |
5,590 | |||
SALES AND MARKETING
The Company’s sales and marketing staff coordinates directly with its wholesale customers to devise marketing strategies and merchandising concepts and to furnish advice on advertising and product promotion. The Company has developed many promotional programs for use in the ordinary course of business to promote sales throughout the year.
The Company’s sales and marketing efforts are supported from its principal offices and showroom in Garden City, New York; as well as showrooms in New York, New York; Medford, Massachusetts; Atlanta, Georgia; Bentonville, Arkansas; Carlisle, Pennsylvania; Menomonee Falls, Wisconsin; Birmingham, England; Corby, England and Hong Kong.
The Company generally collaborates with its largest wholesale customers and in many instances produces specific versions of the Company’s product lines with exclusive designs and/or packaging for their stores.
DESIGN AND INNOVATION
At the heart of the Company is a culture of innovation and new product development. The Company’s in-house design and development teams currently consist of 105 professional designers, artists and engineers. Utilizing the latest available design tools, technology and materials, these teams create new products, redesign existing products and create packaging and merchandising concepts.
5
Table of Contents
SOURCES OF SUPPLY
The Company sources its products from hundreds of suppliers. Most of the Company’s suppliers are located in the People’s Republic of China. The Company also sources products from suppliers in Hong Kong, the United States, Vietnam, Malaysia, Indonesia, Slovakia, Taiwan, United Kingdom, Japan, India, Italy, American Samoa, Slovenia, Korea, Poland, Thailand, the Czech Republic, France, Portugal, Sweden, Netherlands, Turkey, Denmark, Tunisia, Germany and Israel. The Company orders products substantially in advance of the anticipated time of their sale by the Company. The Company does not have any formal long-term arrangements with any of its suppliers and its arrangements with most manufacturers allow for flexibility in modifying the quantity, composition and delivery dates of orders.
MANUFACTURING
The Company manufactures its sterling silver products at its leased manufacturing facility in San Germán, Puerto Rico and fills containers with spices and assembles spice racks at the Company’s owned Winchendon, Massachusetts distribution facility. The Company does not manufacture any of its other products.
COMPETITION
The markets for kitchenware, tableware and other products used in the home including home décor products are highly competitive and include numerous domestic and foreign competitors, some of which are larger than the Company. The primary competitive factors in selling such products to retailers are innovative products, brand, quality, aesthetic appeal to consumers, packaging, breadth of product line, distribution capability, prompt delivery and selling price.
PATENTS
The Company owns approximately 348 design and utility patents. The Company believes that the expiration of any of its patents would not have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business.
BACKLOG
Backlog is not material to the Company’s business, because actual confirmed orders from the Company’s customers are typically received within close proximity to the required shipment dates.
EMPLOYEES
At December 31, 2014, the Company had a total of 1,425 full-time employees, of whom 218 were located in Asia and 309 in Europe. In addition, the Company employed 41 people on a part-time basis, predominately in Corporate Marketing/Sales Support. The Company also hires seasonal workers at its distribution centers through temporary staffing agencies. None of the Company’s employees are represented by a labor union or subject to collective bargaining agreements, except as required by local law. The Company considers its employee relations to be good.
REGULATORY MATTERS
The Company and its affiliates are subject to significant regulation by various governmental, regulatory and other administrative authorities.
As a manufacturer and distributor of consumer products, the Company is subject to the Consumer Products Safety Act in the United States and the Consumer Protection Act in the United Kingdom. Additionally, laws regulating certain consumer products exist in some cities and states, as well as in other countries in which the Company or its subsidiaries and affiliates sell products.
The Company’s spice container filling operation is regulated by the Food and Drug Administration.
6
Table of Contents
The Company’s operations also are subject to national, state and local environmental and health and safety laws and regulations, including those that impose workplace standards and regulate the discharge of pollutants into the environment and establish standards for the handling, generation, emission, release, discharge, treatment, storage and disposal of materials and substances including solid and hazardous wastes.
The Company is subject to risks and uncertainties associated with economic and political conditions in foreign countries, including but not limited to, foreign government regulations, taxes including value-added taxes, import and export duties and quotas, anti-dumping regulations and related tariffs associated with certain types of products, incidents and fears involving security, terrorism and wars, political unrest and other restrictions on trade and travel.
SEASONALITY
The Company’s business and working capital needs are highly seasonal, with a majority of sales occurring in the third and fourth quarters. In 2014, net sales in the third and fourth quarters accounted for 60% of total annual net sales. In anticipation of the pre-holiday shipping season, inventory levels increase primarily in the June through October time period.
GEOGRAPHIC INFORMATION
Geographic information concerning the Company’s revenues and long-lived assets is contained in Note J of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 15 of this annual report.
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors |
The Company’s businesses, operations, liquidity and financial condition are subject to various risks. The Company’s business, financial condition or results of operation could be significantly affected by the risks below or additional risks not presently known to the Company or by risks that the Company presently deems immaterial such as changes in the economy, disruptions due to terrorist activity or manmade or natural disasters, or changes in law or accounting standards. The risks and uncertainties described below are those that the Company considers material.
The Company has substantial indebtedness and the Company’s business is highly seasonal.
The Company has a substantial amount of indebtedness and is dependent on the availability of its bank loan facilities to finance its liquidity needs. The Company’s Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement with JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A, as Administrative Agent and Co-Collateral Agent, and HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as Syndication Agent and Co-Collateral Agent (as amended, the “Credit Agreement”) provides for, among other things, a Revolving Credit Facility commitment totaling $175.0 million (the “Revolving Credit Facility”) and a term loan facility of $50.0 million (“Term Loan”). As of December 31, 2014, the Company had approximately $138.4 million of consolidated debt, including $137.7 million under the Credit Agreement, representing approximately 33% of total capital (net indebtedness plus stockholders’ equity) as of that date. The Company may borrow under its Revolving Credit Facility, subject to the limitations of a borrowing base. Because the borrowing capacity under the Revolving Credit Facility depends on levels of eligible inventory, accounts receivable and the appraised value of certain intellectual property that fluctuate from time to time, the full commitment amount may not represent actual borrowing capacity. The financial covenants governing the Company’s Term Loan agreement limit its ability to incur senior indebtedness. The Company may be unable to generate cash sufficient to pay when due the principal of, interest on, or other amounts due with respect to, its indebtedness. In addition, the Company’s business is seasonal with a significant amount of its revenue being realized during the latter portion of the year, therefore, the Company’s working capital and borrowing needs fluctuate.
7
Table of Contents
The Company’s leverage and the effects of seasonal fluctuations in its cash flow, borrowing requirements and ability to borrow could have significant negative consequences on the Company’s financial condition and results of operations, including:
| • | impairing the Company’s ability to meet one or more of the financial ratio covenants contained in its debt agreements or to generate cash sufficient to pay interest or principal due under those agreements, which could result in an acceleration of some or all of the Company’s outstanding debt; |
| • | increasing the Company’s vulnerability to general adverse economic and industry conditions; |
| • | limiting the Company’s ability to obtain additional debt or equity financing; |
| • | increasing the Company’s borrowing costs if the Company’s current debt ratings decline; |
| • | requiring the dedication of a substantial portion of the Company’s cash flow from operations to service the Company’s debt, thereby reducing the amount of cash flow available for other purposes, including capital expenditures or acquisitions; |
| • | requiring the Company to sell debt or equity securities or to sell some of the Company’s core assets, possibly on unfavorable terms, to meet payment obligations; |
| • | limiting the Company’s flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in its business and the markets in which the Company competes; |
| • | limiting the Company’s ability to declare and pay dividends to its stockholders and engage in share repurchase programs; and |
| • | placing the Company at a possible competitive disadvantage to less leveraged competitors and competitors that may have better access to capital resources. |
The Company’s failure to meet certain covenants or other requirements of its Credit Agreement may materially and adversely affect the Company’s assets, financial position and cash flows.
The Credit Agreement, under certain circumstances, requires the Company to maintain a certain fixed charge coverage ratio. In addition, at any time the Company’s Term Loan is outstanding, the Company’s credit agreement requires the Company to maintain its Senior Leverage Ratio within defined parameters. As a result of these requirements within the Credit Agreement, the Company is limited in its ability to incur additional debt, make investments or undertake certain other business activities. These requirements could limit the Company’s ability to obtain future financing and may prevent the Company from taking advantage of attractive business opportunities. The Company’s ability to meet the covenants or requirements in its Credit Agreement may be affected by events beyond the Company’s control, and the Company cannot assure you that it will satisfy such covenants and requirements. A breach of these covenants or the Company’s inability to comply with the restrictions could result in an event of default under the Credit Agreement, which in turn could result in an event of default under the terms the Company’s other indebtedness. Upon the occurrence of an event of default under the Company’s Credit Agreement, after the expiration of any grace periods, the Company’s lenders could elect to declare all amounts outstanding under the Company’s debt arrangements, together with accrued interest, to be immediately due and payable. If this happens, the Company cannot assure that its assets would be sufficient to repay in full the payments due under the Credit Agreement or the Company’s other indebtedness.
The Company’s borrowings are subject to interest rate fluctuations and an increase in interest rates could adversely affect the Company’s financial results.
The Company’s borrowings bear interest at floating rates. An increase in interest rates would adversely affect the Company’s profitability. The Company has entered into interest rate swap agreements to manage interest rate exposure in connection with a portion of its variable interest rate borrowings. To the extent that the Company’s access to credit may be restricted because of its own performance, its bank lenders’ performances or conditions in the capital markets generally, the Company would not be able to operate normally.
8
Table of Contents
The Company’s business may be materially adversely affected by market conditions and by global and economic conditions and other factors beyond its control.
The Company’s performance is affected by general economic factors, the strength of retail economies and political conditions that are beyond its control. Retail economies are impacted by factors such as consumer demand and the condition of the retail industry, which in turn, are affected by general economic factors. These general economic factors include, among other factors:
| • | recession, inflation, deflation, unemployment and other factors adversely affecting consumer spending patterns generally; |
| • | conditions affecting the retail environment for the home and other matters that influence consumer spending in the home retail industry specifically; |
| • | conditions affecting the housing markets; |
| • | consumer credit availability and consumer debt levels; |
| • | material input costs, including fuel and energy costs and labor cost inflation; |
| • | foreign currency translation; |
| • | interest rates and the ability to hedge interest rate risks; |
| • | government policies including tax policies relating to value-added taxes, import and export duties and quotas, anti-dumping regulations and related tariffs, import and export controls and social compliance standards; |
| • | the impact of natural disasters, conflicts and terrorist activities; |
| • | unfavorable economic conditions in the United States, the United Kingdom, Continental Europe, Asia and elsewhere; and |
| • | unstable economic and political conditions, lack of legal regulation enforcement, civil unrest and political activism, particularly in Asia. |
The Company faces intense competition from other companies worldwide.
The markets for the Company’s products are intensely competitive with the principal competitive factors being product innovation, brand name, product quality, aesthetic appeal to customers, packaging, breadth of product offerings, distribution capability, delivery time and price. Advantages or disadvantages in any of these competitive factors may be sufficient to cause the customer to consider changing providers of the kinds of products that the Company sells. The Company competes with many other suppliers, some of which are larger than the Company, have greater financial and other resources or employ brands that are more established, have greater consumer recognition or are more favorably perceived by consumers or retailers than the Company’s brands. Some competitors may be willing to reduce prices and accept lower profit margins to compete with the Company. As a result of this competition, the Company could lose market share and sales, or be forced to reduce its prices to meet competition. If the Company’s product offerings are unable to compete successfully, the Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition could be materially and adversely affected.
9
Table of Contents
Changes in the Company’s customer purchasing practices could materially adversely affect the Company’s operating results.
The Company’s wholesale customers include mass merchants, specialty stores, national chains, department stores, warehouse clubs, supermarkets, off-price retailers and Internet retailers. Unanticipated changes in purchasing and other practices by the Company’s customers, including a customer’s pricing and payment terms, inventory destocking, limitations on shelf space, more extensive packaging requirements, changes in order quantities, use of private label brands and other practices, could materially and adversely affect the Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition. In addition, as a result of the desire of retailers to more closely manage inventory levels, there is a growing trend among retailers to make purchases on a “just-in-time” basis. This requires the Company to shorten its lead time for production in certain cases and more closely anticipate demand, which could in the future require the Company to carry additional inventories. The Company’s annual earnings and cash flows also depend to a great extent on the results of operations in the latter half of the year due to the seasonality of its sales. The Company’s success and sales growth is also dependent on its evaluation of consumer preferences and changing trends.
Many of the Company’s wholesale customers are significantly larger than the Company, have greater financial and other resources and also purchase goods directly from vendors in Asia and elsewhere. Decisions by large customers to increase their purchases directly from overseas vendors could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition. Significant changes or financial difficulties, including consolidations of ownership, restructurings, bankruptcies, liquidations or other events that affect retailers, could result in fewer retailers selling the Company’s products, reliance on a smaller group of customers, an increase in the risk of extending credit to these customers or limitations on the Company’s ability to collect amounts due from these customers. Although the Company has long-established relationships with many of its customers, the Company does not have any long-term supply or binding contracts or guarantees of minimum purchases. Purchases by the Company’s customers are generally made using individual purchase orders. Customers may cancel their orders, change purchase quantities from forecast volumes, delay purchases for a number of reasons beyond the Company’s control or change other terms of their business relationship with the Company. Significant or numerous cancellations, reductions, delays in purchases or changes in business practices by customers could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
Retailers place great emphasis on timely delivery of products for specific selling seasons, especially during the third fiscal quarter, and on the fulfillment of consumer demand throughout the year. The Company cannot control all of the various factors that might affect product delivery to retailers. Failure to deliver products to the Company’s retailers in a timely and effective manner, often under special vendor requirements to use specific carriers and delivery schedules, could damage the Company’s reputation and brands and result in loss of customers or reduced orders.
Changes at the Company’s large customers, or actions taken by them, and consolidation in the retail industry could materially adversely affect the Company’s operating results.
In 2014, Wal-Mart Stores, Inc., including Sam’s Club and Asda Superstore (“Walmart”), accounted for 16% of the Company’s net sales. The Company’s top ten customers accounted for approximately 52% of the Company’s net sales in 2014. A material reduction in purchases by any of such customers could have a significant adverse effect on the Company’s business and operating results. In addition, pressures by such customers that would cause the Company to materially reduce the price of the Company’s products could result in reductions of the Company’s operating margin. Any significant changes or financial difficulties that affect these customers, such as reduced sales by such customers (whether for reasons that affect a particular customer or the retail industry in general) may also result in reduced demand for the Company’s products. The Company would also be subject to increased credit risk with respect to such customers. In particular, the concentration of the Company’s business with Walmart extends to its international business, including in China, as well as through Vasconia in Mexico, GSI in Brazil and the Company’s strategic alliance in Canada, due to the market presence of Walmart in these foreign countries. Further, with the continuing trend of consolidation in the retail industry, the ability of the Company’s largest customers to continue to purchase from the Company is always subject to risk. Any changes in purchasing practices or decline in the financial condition, of Walmart or other large customers may have a material adverse impact on the business, results of operations and financial condition of the Company.
The Company’s large customers also have significant purchasing leverage. They may demand lower pricing, special packaging, shorter lead times for the delivery of products or impose other requirements on product suppliers like the Company. These business demands may relate to inventory practices, logistics or other aspects of the customer-supplier relationship. If the Company does not effectively respond to the demands of its customers, they could decrease or
10
Table of Contents
eliminate their purchases from the Company. These risks could be exacerbated if such large customers consolidate, or if the Company’s smaller customers consolidate to become larger customers, which would increase their purchasing leverage. A reduction in the purchases of the Company’s products by its wholesale customers or the costs of complying with customer business demands could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
The Company’s customers could carry products that directly compete with the Company’s products for retail space and consumer purchases. There is a risk that these customers could give higher priority to products of, or form alliances with, our competitors. Failure of customers to provide the Company’s products with similar levels of promotional support and retail space could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
The loss of certain licenses or material changes in royalty rates could materially adversely affect the Company’s operating margin and cash flow.
Significant portions of the Company’s business are dependent on trade names, trademarks and patents, some of which are licensed from third parties. In 2014, sales of licensed brands accounted for approximately 40% of the Company’s gross sales. The Company’s licenses for many of these brands require it to pay royalties based on sales. Many of these license agreements are subject to termination by the licensor, if, for example, the Company fails to satisfy certain minimum sales obligations or breaches the terms of the license. The loss of significant licenses or a material increase in the royalty rates the Company pays or other new terms negotiated upon renewal of such licenses could result in a reduction of the Company’s operating margins and cash flow from operations or otherwise adversely affect its business. In particular, the Company’s license to use the KitchenAid brand, which represents a material portion of its sales, is subject to a license agreement that has a three-year term that will expire in December 2015. The Company originally entered into a licensing arrangement for use of the KitchenAid brand in 2000, and has renewed the license, typically for three-year periods, since that time. Although it expects to be able to renew its current KitchenAid license prior to its expiration, there is no assurance that the Company will be able to do so on reasonable terms, or at all, and any failure to do so could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
The Company also holds certain rights to use the Farberware brand for kitchen tools and gadgets, cutlery, cutting boards, shears and certain other products which together represent a material portion of its sales, through a fully-paid, royalty-free license for a term that expires in 2195, subject to earlier termination under certain circumstances. The licensor is a joint venture of which the Company is a 50% owner. The other 50% owner of the joint venture has the right to terminate the Company’s license if the Company materially breaches any of the material terms of the license and fails to cure the material breach within 180 days of notice of the breach, if it is determined in an arbitration proceeding that money damages alone would not be sufficient compensation to the licensor and that the breach is so egregious as to warrant termination of the license and forfeiture of the Company’s rights to use the brand under that license agreement. If the Company were to lose the Farberware license for kitchen tools and gadgets, cutlery, cutting boards and shears products through termination as a result of an uncured breach, its business, results of operations and financial condition would be materially adversely affected.
The Company’s international operations present special challenges that the Company may not be able to meet, and this could materially and adversely affect the Company’s financial results.
The Company conducts business outside of the United States through subsidiaries, affiliates and joint ventures. These entities have operations and assets in the United Kingdom, Mexico, Canada, Brazil, China and Hong Kong. Therefore, the Company is subject to increases and decreases in its investments in these entities resulting from the impact of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. These entities also bear risks similar to those risks faced by the Company. However, there are specific additional risks related to these organizations, such as the failure of the Company’s partners or other investors to meet their obligations and higher credit and liquidity risks related to thinly capitalized entities. Failure of these entities or the Company’s vendors to adhere to required regulatory or other standards, including social compliance standards, could materially and adversely impact the Company’s reputation and business.
11
Table of Contents
In addition, the Company sells its products in foreign countries and seeks to increase its level of international business activity. Accordingly, the Company is subject to various risks, including:
| • | U.S.-imposed embargoes of sales to specific countries; |
| • | foreign import controls (which may be arbitrarily imposed or enforced); |
| • | import regulations and duties; |
| • | export regulations (which require the Company to comply with stringent licensing regimes); |
| • | anti-dumping regulations; |
| • | price and currency controls; |
| • | exchange rate fluctuations; |
| • | dividend remittance restrictions; |
| • | expropriation of assets; |
| • | war, civil uprisings and riots; |
| • | government instability; |
| • | the necessity of obtaining governmental approval for new and continuing products and operations; |
| • | legal systems or decrees, laws, taxes, regulations, interpretations and court decisions that are not always fully developed and that may be retroactively or arbitrarily applied; |
| • | unanticipated income taxes, excise duties, import taxes, export taxes or other governmental assessments; and |
| • | difficulties in managing a global enterprise. |
Any significant violations of these regulations could result in civil or criminal sanctions or the loss of export or other licenses, which could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition. In addition, the Company’s organizational structure may limit its ability to transfer funds between countries, particularly into and out of the United States, without incurring adverse tax consequences. Any of these events could result in a loss of business or other unexpected costs that could reduce sales or profits and have a material adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
International suppliers subject the Company to regional regulatory, political, economic and foreign currency exchange risk that could materially and adversely affect the Company’s operating results.
The Company sources its products from suppliers located principally in Asia, Europe and the United States. The Company’s vendors in Asia, from whom a substantial majority of the Company’s products are sourced, are located primarily in the People’s Republic of China, which subjects the Company to various risks within the region including regulatory, political, economic and foreign currency changes. The Company’s ability to select and retain reliable vendors and suppliers who provide timely deliveries of quality parts and products efficiently will impact its success in meeting customer demand for timely delivery of quality products. The Company’s sourcing operations and its vendors are impacted by labor costs in China, where labor historically has been readily available at low cost relative to labor costs in North America. However, as China is experiencing rapid social, political and economic changes, labor costs have risen in some regions and labor in China may not continue to be available to the Company at costs consistent with historical levels. Changes in labor or other laws may be enacted which would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s operations in China, or those of the Company’s suppliers. Although China currently enjoys “most favored nation” trading status with the U.S., the U.S. government has in the past proposed to revoke such status and to impose higher tariffs on products imported from China.
12
Table of Contents
Changes in currency exchange rates might negatively affect the Company and its overseas vendors’ profitability and business prospects. The Company does not have access to its vendors’ financial information and the Company is unable to assess its vendors’ financial condition, including their liquidity. Interruption of supplies from any of the Company’s vendors, or the loss of one or more key vendors, could have a negative effect on the Company’s business and operating results.
Foreign exchange variability could materially adversely affect the Company’s operating results.
The Company’s functional currency is the U.S. Dollar. Changes in the relation of foreign currencies to the U.S. Dollar will affect the Company’s sales and profitability and can result in exchange losses because the Company has operations and assets located outside the United States. The Company transacts a portion of its business in currencies other than the U.S. Dollar, primarily British Pounds, and to a lesser degree, Chinese Renminbi, Euros and Canadian Dollars. Such transactions include sales, certain inventory purchases and operating expenses. As a result, portions of the Company’s cash, trade accounts receivable and trade accounts payable are denominated in foreign currencies. Accordingly, foreign operations expose the Company to foreign currency fluctuations, both for purposes of actual conversion and financial reporting purposes. The Company’s strategic alliances in Mexico, Canada and Brazil also subject the Company to increases and decreases in its investments resulting from the impact of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. The vast majority of products are purchased from China in U.S. Dollars. However, if the Chinese Renminbi should appreciate against the U.S. Dollar, the costs of the Company’s products will likely rise over time because of the impact the fluctuations will have on the Company’s suppliers, and the Company may not be able to pass on these price increases to its customers. The Company is also subject to the risks of currency controls and devaluations. Currency controls may limit the Company’s ability to convert currencies into U.S. Dollars or other currencies, as needed, or to pay dividends or make other payments from funds held by subsidiaries in the countries imposing such controls, which could adversely affect the Company’s liquidity.
The impact of future exchange rate fluctuations on the Company’s results of operations cannot be accurately predicted.
The Company’s international trade subjects it to transportation risks.
The Company imports its products for delivery to its distribution centers, as well as arranges for its customers to import goods to which title has passed overseas or at port of entry. For purchases that are to be delivered to its distribution centers, the Company arranges for transportation, primarily by sea, from ports in Asia and Europe to ports in the United States, principally New York/Newark/Elizabeth and Los Angeles/Long Beach, and in the United Kingdom, principally Felixstowe. Accordingly, the Company is subject to risks incidental to such transportation. These risks include, but are not limited to, increases in fuel costs, fuel shortages, the availability of ships, increased security restrictions, work stoppages, weather disruptions and carriers’ ability to provide delivery services to meet the Company’s shipping needs. Transportation disruptions and increased transportation costs could materially adversely affect the Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
The Company delivers its products to its customers or makes such products available for customer pickup from its distribution centers. During the third and fourth quarter of 2014, the Company’s distribution process was impacted by the longshoremen’s work slowdown and the threat of a strike on the west coast. The impact of this slowdown on the Company’s operations was not significant; however, prolonged domestic transportation disruptions, as well as workforce or systems issues related to the Company’s distribution centers, could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s ability to deliver goods to its customers.
The Company may not be able to adequately establish or protect its intellectual property rights, and the infringement or loss of the Company’s intellectual property rights could harm its business.
To establish and protect the Company’s intellectual property rights, the Company relies upon a combination of U.S., foreign and multi-national patent, trademark, copyright and trade secret laws, together with licenses, confidentiality agreements and other contractual arrangements. The measures that the Company takes to protect its intellectual property rights may prove inadequate to prevent third parties from infringing or misappropriating the Company’s intellectual property, or from breaching their contractual obligations to the Company.
13
Table of Contents
The Company has obtained and applied for numerous U.S. and foreign trademark, service mark and patent registrations, and will continue to evaluate the registration of additional marks, patents or other intellectual property, as appropriate. The Company cannot guarantee that any of its pending applications will be approved by the applicable governmental authorities. Moreover, even if such applications are approved, third parties may seek to oppose, declare invalid or otherwise challenge these registrations. Failure to obtain registrations for the Company’s intellectual property in the United States and other countries could limit the Company’s ability to protect its intellectual property rights and impede the Company’s marketing efforts and operations in those jurisdictions.
The Company may need to resort to litigation to enforce or defend its intellectual property rights. If a competitor or collaborator files a patent application claiming technology also claimed by the Company, or a trademark application claiming a trademark, service mark or trade dress also used by the Company, in order to protect the Company’s rights, the Company may have to participate in opposition or interference proceedings before the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office or a similar foreign agency. The Company cannot guarantee that the operation of its business does not infringe or otherwise violate the intellectual property rights of third parties, and the Company’s intellectual property rights may be challenged by third parties or invalidated through administrative process or litigation. The costs associated with protecting intellectual property rights, including litigation costs associated with litigation or administrative proceedings, may be material and there can be no assurance that any such litigation or administrative proceedings will be successful. Any such matters or proceedings could be burdensome, divert the time and resources of the Company’s personnel and the Company may not prevail. Furthermore, even if the Company’s intellectual property rights are not directly challenged, disputes among third parties could lead to the weakening or invalidation of the Company’s intellectual property rights, or other parties such as the Company’s competitors may independently develop technologies that are substantially equivalent or superior to the Company’s technology.
The laws of certain foreign countries in which the Company operates or may operate in the future do not protect, and the governments of certain foreign countries do not enforce, intellectual property rights to the same extent as do the laws and government of the U.S., which may negate the Company’s competitive or technological advantages in such markets. Moreover, any repeal or weakening of intellectual property laws or enforcement of those laws in the United States or foreign jurisdictions could make it more difficult for the Company to adequately protect its intellectual property rights, negatively impacting their value and increasing the cost of enforcing the Company’s rights. If the Company is unable to establish or adequately protect its intellectual property rights, the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially and adversely affected.
If the Company is unable to protect the confidentiality of its proprietary information and know-how, the value of the Company’s technology, products and services could be harmed significantly.
In addition to registered intellectual property, the Company relies on know-how and other proprietary information in operating its business. If this information is not adequately protected, then it may be disclosed or used in an unauthorized manner. To the extent that consultants, vendors, key employees or other third parties apply technology independently developed by them or by others to the Company’s proposed products in the absence of a valid license or suitable non-disclosure or assignment of inventions provisions, disputes may arise as to the ownership of or rights to use such technology, which may not be resolved in the Company’s favor. The risk that other parties may breach confidentiality or other agreements could harm the Company by enabling the Company’s competitors and other entities, who may have greater experience and financial resources, to copy or use the Company’s proprietary information in the advancement of their products, methods or technologies.
The Company sells consumer products which involve an inherent risk of product liability claims.
The marketing of certain of the Company’s consumer products involve an inherent risk of product liability claims or recalls or other regulatory or enforcement actions initiated by the U.S. Consumer Product Safety Commission, by the Office of Fair Trading in the U.K., by other regulatory authorities or through private causes of action and the Company has had in the past, and may have in the future, recalls (both voluntary and involuntary) of its products. Any defects in products the Company markets could harm the Company’s reputation, adversely affect its relationship with its customers and decrease market acceptance of the Company’s products and the strength of the brand names under which the Company markets such products. Potential product liability claims may exceed the amount of the Company’s insurance coverage and could materially damage the Company’s business and its financial condition. Additionally, the Company’s product standards could be impacted by new or revised environmental rules and regulations or other social initiatives.
14
Table of Contents
The Company operates in a regulated environment that imposes significant compliance requirements. Non-compliance with these requirements could subject the Company to sanctions and materially adversely affect the Company’s business.
The Company is subject in the ordinary course of its business, in the United States and elsewhere, to many statutes, ordinances, rules and regulations that, if violated by the Company or its affiliates, partners or vendors, could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business. The Company is required to comply with the United States Foreign Corrupt Practices Act (“FCPA”), the U.K. Bribery Act and similar anti-bribery, anti-corruption and anti-kickback laws adopted in many of the countries in which the Company does business which prohibit the Company from engaging in bribery or making other prohibited payments to foreign officials for the purpose of obtaining or retaining business and also require maintenance of adequate record-keeping and internal accounting practices to accurately reflect transactions. Under the FCPA, companies operating in the United States may be held liable for actions taken by their strategic or local partners or representatives. The U.K. Bribery Act is broader in scope than the FCPA in that it directly addresses commercial bribery in addition to bribery of government officials and it does not recognize certain exceptions, notably facilitation payments that are permitted by the FCPA. Civil and criminal penalties may be imposed for violations of these laws. In many of the countries in which the Company operates, particularly those with developing economies, it is or has been common for government officials and businesses to engage in business practices that are prohibited by these laws. If the Company does not properly implement and maintain practices and controls with respect to compliance with applicable anti-corruption, anti-bribery and anti-kickback laws, or if the Company fails to enforce those practices and controls properly, the Company may be subject to regulatory sanctions, including administrative costs related to governmental and internal investigations, civil and criminal penalties, injunctions and restrictions on the Company’s business and capital raising activities, any of which could materially and adversely affect the Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition. The Company’s employees, distributors, dealers and other agents could engage in conduct that is not in compliance with such laws for which the Company might be held responsible. If the Company’s employees, distributors, dealers or other agents are found to have engaged in illegal practices, the Company could suffer substantial penalties and the reputation, business, results of operations and financial condition of the Company could be materially adversely affected.
The Company is additionally subject to general business laws and regulations, as well as regulations and laws specifically governing the Internet and e-commerce. Such existing and future laws and regulations may impede the growth of Internet or other online services and thereby adversely impact the Company’s sales. These laws and regulations may cover taxation, user privacy, data security, pricing, content, proprietary rights, advertising, distribution, electronic contracts and other communications, consumer protection, the provision of online payment services, broadband residential Internet access and the characteristics and quality of products and services. It is not clear in certain cases how existing laws and regulations governing issues such as property ownership, sales and other taxes and personal privacy apply to the Internet and e-commerce. Unfavorable resolutions of these issues would harm the Company’s business, diminish the demand for the Company’s products on the Internet and increase the Company’s cost of doing business.
Demand for new products and the inability to develop and introduce new competitive products at favorable profit margins could adversely affect the Company’s performance and prospects for future growth.
New product introductions and product innovation are significant contributors to the Company’s growth strategy and the Company’s long-term success in the competitive retail environment depends in part on the Company’s ability to develop and market a continuing stream of innovative new products that meet changing consumer preferences. The uncertainties associated with developing and introducing new products, such as the market demands and the costs of development and production may impede the successful development and introduction of new products. Acceptance of the new products may not meet sales expectations due to several factors, such as the Company’s failure to accurately predict market demand or its inability to resolve technical issues in a timely and cost-effective manner. Additionally, the inability to develop new products on a timely basis could result in the loss of business to competitors.
15
Table of Contents
The Company’s brands are subject to reputational risks.
The Company’s brands and its reputation are among its most important assets. The Company’s ability to attract and retain customers depends, in part, upon the external perceptions of the Company, the quality of its products and its corporate and management integrity. The consumer goods industry is by its nature more prone to reputational risks than other industries. This has been compounded in recent years by the free flow of unverified information on the Internet and, in particular, on social media. Damage to the Company’s brands or reputation or negative publicity or perceptions about the Company could adversely affect its business. Additionally, with the exception of the Company’s silver products, manufactured in San Germán, Puerto Rico, and the filling and assembly of spice racks at its Winchendon, Massachusetts distribution facility, the Company’s products are manufactured by third parties. The Company does not control the third party manufacturers, and the majority of the Company’s manufacturers are located outside the United States, which further restricts the Company’s ability to monitor and control their manufacture of the Company’s goods. Although the Company has agreements with third party manufacturers regarding quality standards and regularly audits the facilities of its manufacturers, there can be no assurance that the third party manufacturers will continue to meet the Company’s quality standards or social standards regarding its workforce that is expected in the United States. Failure to meet any such standards would adversely affect the Company’s reputation.
A failure in the Company’s operating systems or infrastructure or those of third parties could disrupt the Company’s business and cause losses.
The Company relies on many information technology systems for the operation of its principal business functions, including the Company’s enterprise resource planning, warehouse management, inventory forecast and re-ordering and call center systems. In the case of the Company’s inventory forecast and re-ordering system, most of the Company’s orders are received directly through electronic connections with the Company’s largest customers. Additionally, the success of certain product categories in a competitive marketplace is dependent upon the creation and launch of new, innovative products. Accordingly, to keep pace within a competitive retail environment, the Company uses and will continue to evaluate new technologies to improve the efficiency of designing new innovative products. The failure of any of these systems or technologies could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business and results of operations.
The Company is subject to cyber security risks and may incur increasing costs in an effort to minimize those risks.
The Company employs information technology systems and Internet systems, including websites, which allow for the secure storage and transmission of proprietary or confidential information regarding the Company’s customers, employees and others, including credit card information and personal identification information. The Company has made significant efforts to secure its computer network to mitigate the risk of possible cyber-attacks. However, the regulatory environment governing information, security and privacy laws, as well as the requirements imposed on the Company by the credit card industry, is increasingly demanding and continues to evolve. The security of the Company’s computer networks could be compromised which could impact operations and confidential information could be misappropriated, which could lead to negative publicity, loss of sales and profits or cause the Company to incur significant costs to reimburse third-parties for damages which could adversely impact profits. Furthermore, maintaining compliance with applicable security and privacy regulations and standards may increase the Company’s operating costs and/or adversely impact the Company’s ability to market its products or process payment information.
If the Company is unable to attract and maintain its highly skilled personnel the Company’s business could be adversely affected.
The Company’s success depends on its ability to identify, hire and retain skilled personnel. The Company’s industry is characterized by a high level of employee mobility and aggressive recruiting among competitors for personnel with successful track records. The Company may not be able to attract and retain skilled personnel or may incur significant costs in order to do so.
Increases in the cost of employee benefits could materially adversely impact the Company’s financial results and cash flows.
The Company self-insures a substantial portion of the costs of employee healthcare and workers compensation. This could result in higher volatility in the Company’s earnings and exposes the Company to higher financial risks. The Patient
16
Table of Contents
Protection and Affordable Care Act, commonly referred to as the Affordable Care Act, which came into effect in 2013, contains provisions which could materially adversely impact the Company’s future healthcare costs. Changes in the law, including the imposition of a penalty on individuals who do not obtain healthcare coverage, may result in employees who are currently eligible but elect not to participate in the Company’s healthcare plans now finding it more advantageous to do so, which may increase the Company’s healthcare costs. Implementing the requirements of the Affordable Care Act is also likely to impose some additional administrative costs on the Company. It is also possible that making changes or failing to make changes in the healthcare plans the Company offers will make the Company less attractive to its current or potential employees.
The Company’s product costs are subject to a high degree of price fluctuation.
Various commodities comprise the raw materials used to manufacture of the Company’s products. The prices of these commodities have historically fluctuated on a cyclical basis and have often depended on a variety of factors over which the Company has no control. Additionally, labor costs represent a significant component of the Company’s supplier’s manufacturing costs and the Company’s suppliers may increase the prices they charge the Company if they experience rising labor costs. The cost of producing and distributing the Company’s products is also sensitive to energy costs, duties and tariffs. The selling prices of the Company’s products have not always increased in response to raw material, labor or other cost increases, and the Company is unable to determine to what extent, if any, it will be able to pass future cost increases through to its customers. The Company’s inability to come to favorable agreements with its suppliers or to pass increased costs through to the Company’s customers could materially and adversely affect its financial condition or results of operations.
The Company’s business is highly seasonal.
The Company’s business and working capital needs are highly seasonal, with a majority of sales occurring in the third and fourth quarters. In 2014, net sales for the third and fourth quarters accounted for 60% of total annual net sales. If the Company has poor operating results during the third and fourth quarters it would have a disproportionately adverse effect on the Company’s financial condition or results of operations. In addition, with a significant amount of its revenue being realized during the latter portion of the year, the Company’s working capital and borrowing needs fluctuate, which could result in higher borrowings and lower availability under the Credit Agreement during these quarters.
If the Company’s goodwill or other long-term assets become impaired, the Company will be required to record impairment charges, which may be significant.
A portion of the Company’s long-term assets consists of goodwill recorded as a result of the Company’s acquisitions. At December 31, 2014, goodwill totaled $18.1 million. The Company does not amortize goodwill but rather reviews it for impairment on an annual basis or more frequently whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that its carrying value may not be recoverable. If future operating performance of one or more of the Company’s operating segments does not meet expectations, the Company may be required to record a significant charge during the period in which any impairment of the Company’s goodwill or other long-term assets is determined. For the year ended December 31, 2012, the Company recorded an impairment charge of $1.1 million in the consolidated statement of operations which reduced the book value of the Elements home décor trade name. In the third quarter of 2014, the Company recorded another impairment charge of $3.4 million which further reduced the book value of Elements, as well as reduced the book value of Melannco, home decor trade names. In addition, during 2014, the Company recorded an impairment charge of $6.0 million related to its investment in GSI. The recognition of an impairment of the Company’s goodwill or any of the Company’s assets would negatively affect the results of operations and total capitalization, the effect of which could be material.
Interruptions in the Company’s operations caused by outside forces could cause material losses.
The Company’s worldwide operations could be subject to natural and man-made disasters, telecommunications failures, water shortages, tsunamis, floods, hurricanes, typhoons, fires, extreme weather conditions, conflicts, acts of terrorism, health epidemics and other business interruptions. The occurrence of any of these business disruptions could seriously harm the Company’s business, revenue and financial condition and increase the Company’s costs and expenses. If the Company’s or
17
Table of Contents
its manufacturers’ warehousing facilities or transportation facilities are damaged or destroyed, the Company would be unable to distribute products on a timely basis, which could harm the Company’s business. The Company’s back-up operations may be inadequate, and the Company’s business interruption insurance may not be sufficient to compensate for any losses that may occur.
The Company’s projections of product demand, sales and net income are highly subjective in nature and the Company’s future sales and net income could vary in a material amount from the Company’s projections.
From time to time, the Company may provide projections to its stockholders, lenders, the investment community, and other stakeholders of the Company’s future sales and net income. Since the Company does not have long-term purchase commitments from customers and the customer order and shipment process is very short, it is difficult for the Company to accurately predict the demand for many of its products, or the amount and timing of the Company’s future sales and related net income. The Company’s projections are based on management’s best estimate of sales using historical sales data and other information deemed relevant. These projections are highly subjective since sales can fluctuate substantially based on the demands of retail customers and due to other risks described in this Annual Report. Additionally, changes in retailer inventory management strategies could make the Company’s inventory management more difficult. Because the Company’s ability to forecast product demand and the timing of related sales includes significant subjective input, future sales and net income could vary materially from the Company’s projections.
The Company’s business requires it to maintain a large fixed-cost base that can affect its profitability.
The Company’s business requires it to maintain large distribution facilities in its key markets, which represent a high fixed rental costs relating to its leased facilities. In addition, significant portions of the Company’s selling, general and administrative expenses, including leased showrooms, are fixed, they neither increase nor decrease proportionally with sales. Furthermore, the Company’s gross margins depends, in part, on its ability to spread certain other costs, of which a significant portion are fixed, over its products sold. Decreased demand or the need to reduce inventories can lower the Company’s ability to absorb fixed costs and adversely affect its results of operations. This is exacerbated by the high degree of seasonality impacting the Company, which results in lower demand during the first two quarters of the year, while many of the operating costs remain fixed, which further affects profitability.
The Company may not be able to adequately address the additional review and disclosure required in respect of “Conflict Minerals.”
The Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act contains regulations concerning the supply of conflict minerals originating from the Democratic Republic of Congo and adjoining countries. As a result, the SEC adopted annual disclosure and reporting requirements for those companies that use such conflict minerals in the products they manufacture or contract to manufacture. These requirements require ongoing due diligence efforts and there are costs associated with complying with these disclosure requirements, including the costs of investigations to determine the sources of raw materials used in the Company’s products and the costs of any changes to products, processes or sources of supply as a consequence of the results of such investigations. These rules could adversely affect the sourcing, supply and pricing of materials used in the Company’s products. As there may be only a limited number of suppliers offering these conflict minerals from “conflict free” sources, the Company cannot ensure that it will be able to obtain necessary materials from such suppliers in sufficient quantities or at competitive prices. Also, the Company may face reputational challenges if it determines that certain of its products contain conflict minerals not determined to be “conflict free” or if it is unable to sufficiently verify the origins for all conflict minerals used in its products through the procedures the Company has implemented and may implement in the future.
The Company may incur material costs due to environmental liabilities.
The Company is subject to a broad range of federal, state, local, foreign and multi-national laws and regulations relating to the environment. These include laws and regulations that govern:
| • | discharges to the air, water and land; |
18
Table of Contents
| • | the handling and disposal of solid and hazardous substances and wastes; and |
| • | remediation of contamination associated with release of hazardous substances at the Company’s facilities and at off-site disposal locations. |
The Company may incur material costs to comply with increasingly stringent environmental laws and enforcement policies. Moreover, there are proposed international accords and treaties, as well as federal, state and local laws and regulations, which would attempt to control or limit the causes of climate change, including the effect of greenhouse gas emissions on the environment. In the event that the U.S. government or foreign governments enact new climate change laws or regulations or make changes to existing laws or regulations, compliance with applicable laws or regulations may result in increased manufacturing costs for the Company’s products, such as by requiring investment in new pollution control equipment or changing the ways in which certain of the Company’s products are made. The Company may incur some of these costs directly and others may be passed on to the Company from its third-party suppliers. Although the Company believes that it is substantially in compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations at its facilities, the Company may not always be in compliance with such laws and regulations or any new laws and regulations in the future, which could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
A wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company operates a leased manufacturing facility in San Germán, Puerto Rico. The United States Environmental Protection Agency (the “EPA”) announced that the San Germán Ground Water Contamination site in Puerto Rico had been added to the Superfund National Priorities List due to contamination present in the local drinking water supply. The EPA has been granted access to the site and further EPA investigation is pending. The Company is not able to estimate the extent of any possible liability, but any such liability could have a material adverse effect on the business, financial condition and results of operations of the Company. If previously unknown contamination of property underlying or in the vicinity of the Company’s manufacturing facility or other properties that are currently or have formerly been owned, operated or used by the Company is discovered, the Company could be required to incur material unforeseen expenses. If this occurs, it may have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
The Company’s growth has, to a material extent, depended upon acquisitions and its strategy is likely to continue to involve acquisitions. The Company may not be able to identify or complete future acquisitions or strategic alliances.
The Company has achieved growth through acquisitions, investments and joint ventures and the Company’s future growth will depend in part on the successful acquisition and integration of businesses into the Company’s existing operations. While the Company is focused on adding strategic pieces to its operations, primarily in international markets, by acquiring companies, product lines and manufacturing and distribution assets that complement the Company’s existing businesses, the Company may not be able to identify and successfully negotiate suitable acquisitions, obtain financing for future acquisitions on satisfactory terms, obtain regulatory approval or otherwise complete acquisitions in the future.
Additionally, the Company makes certain assumptions based on the information provided by potential acquisition candidates and also conducts due diligence to ensure the information provided is accurate and based on reasonable assumptions. However, the Company may be unable to realize the anticipated benefits from an acquisition or predict accurately how an acquisition will ultimately affect the business, financial condition or results of operations of the Company. The failure of any of these businesses to achieve expected results, the diversion of the Company’s management’s attention, the incurrence of unforeseen contingencies and the failure to retain key personnel at these businesses could have a material adverse effect on the Company’s business, results of operations and financial condition.
The Company may not be able to effectively integrate acquired businesses into its operations and if the Company is unable to manage its acquisitions effectively, its business may be materially harmed.
The Company has completed approximately 15 acquisitions and strategic investments since 2006, including four acquisitions completed in the first quarter of 2014. The Company seeks acquisition opportunities that complement and expand its operations, some of which are based outside the United States. The Company may not continue to be able to successfully integrate these businesses or identify and integrate future acquisitions into its existing business without
19
Table of Contents
substantial costs, delays or other operational or financial difficulties. The Company could face significant challenges in consolidating functions and integrating procedures and processes, internal controls, information technology and other systems, personnel, product lines and operations in a timely and efficient manner. The Company may encounter difficulties in training its sales forces to work with new products and customers. Many, if not all, of the entities the Company acquires may not be reporting companies under the Exchange Act and therefore may not have the internal controls and procedures that the Company, as a reporting company, is required to have under the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. Instituting and implementing such internal controls and procedures at the acquired businesses within the time period required by the Sarbanes Oxley Act may require significant time, costs and efforts. Additionally, disclosures the Company makes regarding past operating results of acquired businesses, projections and pro forma results are based on financial information provided to the Company by the management of the acquired business, which has not been reviewed by the Company’s auditors or subject to the Company’s internal controls and the combined company may be unable to achieve the projections and pro forma results reported.
The integration process is complex and time-consuming, may be disruptive to the Company’s businesses, and may cause an interruption of, or a loss of momentum in, the business as a result of a number of obstacles, such as:
| • | the loss of significant customers; |
| • | the need to retrain skilled design, sales and other personnel resulting from the loss of key employees; |
| • | the failure to maintain the quality of customer service that each business has historically provided; |
| • | the need to coordinate geographically diverse organizations; |
| • | the presence of unforeseen contingencies; |
| • | retooling and reprogramming of equipment and information technology systems; and |
| • | the resulting diversion of management’s attention from the day-to-day business and the need to hire additional management personnel to address integration obstacles. |
If the Company is not successful in integrating its recent and future acquisitions into its operations, if the integration takes longer than anticipated, if the companies or assets the Company acquires do not perform as anticipated, or if the integrated product offerings fail to achieve market acceptance, the business, financial position, results of operations and cash flows of the Company could be materially adversely affected.
The Company may not be able to realize the anticipated cost savings, synergies or revenue enhancements from acquisitions, and the Company may incur significant costs to achieve these savings.
Even if the Company is able to integrate successfully its operations and the operations of recent and any future acquisitions, the Company may not be able to realize the cost savings, synergies or revenue enhancements that were anticipated from these acquisitions, either as to amount or in the time frame that the Company expects. The Company’s ability to realize anticipated cost savings, synergies and revenue enhancements may be materially adversely affected by a number of factors, including the following:
| • | the ability to effectively eliminate duplicative administrative overhead and overlapping sales personnel, synchronize information technology and other systems, consolidate warehousing and distribution facilities and shift production to more economical vendors; |
| • | the incurrence of significant cash and non-cash integration and implementation costs or charges in order to achieve those cost savings, which could offset any such savings and other synergies resulting from recent or future acquisitions; and |
| • | the ability to avoid labor disruption in connection with integration efforts. |
20
Table of Contents
The Company’s growth to date has placed, and future acquisitions could continue to place, significant demands on the Company’s administrative, operational and financial resources. Acquisitions may also result in the assumption of unexpected liabilities and may divert management’s attention from the operation of the Company’s legacy business. Additionally, strategic investments and partnerships with other companies expose the Company to the risk that it may not be able to control the operations of the investee or partnership, which could decrease the amount of benefits the Company realizes from a particular relationship. The Company is also exposed to the risk that its partners in strategic investments may encounter financial difficulties which could lead to disruption of investee or partnership activities, or impairment of assets acquired, which could materially adversely affect future reported results of operations and financial condition.
There are inherent limitations on the effectiveness of the Company’s controls.
The Company does not expect that its disclosure controls or the Company’s internal controls over financial reporting will prevent or detect all errors and all fraud. A control system, no matter how well-designed and operated, can provide only reasonable, not absolute, assurance that the control system’s objectives will be met. The design of a control system must reflect the fact that resource constraints exist, and the benefits of controls must be considered relative to their costs. Further, because of the inherent limitations in all control systems, no evaluation of controls can provide absolute assurance that misstatements due to error or fraud will not occur or that all control issues and instances of fraud, if any, have been detected. The design of any system of controls is based in part on certain assumptions about the likelihood of future events, and there can be no assurance that any design will succeed in achieving its stated goals under all potential future conditions. Projections of any evaluation of the effectiveness of controls to future periods are subject to risks. Over time, controls may become inadequate due to changes in conditions or deterioration in the degree of compliance with policies or procedures. If the Company’s controls become inadequate, it could fail to meet its financial reporting obligations, its reputation may be adversely affected, its business and operating results could be harmed, and the market price of its stock could decline.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish or cease publishing research or reports about the Company, its business or its market, or if they change their recommendations regarding the Company’s common stock adversely, the price and trading volume of the Company’s common stock could decline.
The trading market for the Company’s common stock will be influenced by the research and reports that industry or securities analysts may publish about the Company, its business, its market, or its competitors. If any of the analysts who may cover the Company change their recommendation regarding our stock adversely or provide more favorable relative recommendations about the Company’s competitors, the price of the Company’s common stock would likely decline. If any analyst who may cover the Company were to cease coverage of the Company or fail to regularly publish reports on it, the Company could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause its stock price or trading volume to decline.
21
Table of Contents
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
None
| Item 2. | Properties |
The following table lists the principal properties at which the Company operates its business at December 31, 2014:
| Location |
Description |
Size (square feet) |
Owned/ Leased | |||||
| Fontana, California (1) | Principal West Coast warehouse and distribution facility | 753,000 | Leased | |||||
| Robbinsville, New Jersey(1) | Principal East Coast warehouse and distribution facility | 700,000 | Leased | |||||
| Birmingham, England (2) | Offices, showroom, warehouse and distribution facilities | 277,000 | Leased | |||||
| Winchendon, Massachusetts(1) | Warehouse and distribution facility, and spice packing line | 175,000 | Owned | |||||
| Garden City, New York(3) | Corporate headquarters/main showroom | 159,000 | Leased | |||||
| Corby, England (2) | Offices, showroom, warehouse and distribution facility | 147,000 | Leased | |||||
| Medford, Massachusetts(1) | Offices, showroom, warehouse and distribution facility | 69,000 | Leased | |||||
| San Germán, Puerto Rico(1) | Sterling silver manufacturing facility | 55,000 | Leased | |||||
| Cumberland, Rhode Island(1) | Offices | 34,000 | Leased | |||||
| Shanghai, China(3) | Offices | 22,000 | Leased | |||||
| Kowloon, Hong Kong(3) | Offices and showrooms | 19,000 | Leased | |||||
| Guangzhou, China(3) | Offices | 18,000 | Leased | |||||
| New York, New York (1) | Showrooms | 17,000 | Leased | |||||
| York, Pennsylvania(1) | Offices | 14,000 | Leased | |||||
| Atlanta, Georgia(1) | Showrooms | 11,000 | Leased | |||||
| Bentonville, Arkansas(1) | Offices and showroom | 7,000 | Leased | |||||
| Menomonee Falls, Wisconsin(1) | Showroom | 4,000 | Leased | |||||
| Carlisle, Pennsylvania(1) | Showroom | 2,300 | Leased | |||||
| (1) | Location used by the U.S. Wholesale segment. |
| (2) | Location used by the International segment. |
| (3) | Location used by all segments. |
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings |
Wallace Silversmiths de Puerto Rico, Ltd. (“Wallace de Puerto Rico”), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, operates a manufacturing facility in San Germán, Puerto Rico that is leased from the Puerto Rico Industrial Development Company (“PRIDCO”). In March 2008, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (the “EPA”) announced that the San Germán Ground Water Contamination site in Puerto Rico (the “Site”) had been added to the Superfund National Priorities List due to contamination present in the local drinking water supply.
22
Table of Contents
In May 2008, Wallace de Puerto Rico received from the EPA a Notice of Potential Liability and Request for Information Pursuant to 42 U.S.C. Sections 9607(a) and 9604(e) of the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, Liability Act. The Company responded to the EPA’s Request for Information on behalf of Wallace de Puerto Rico. In July 2011, Wallace de Puerto Rico received a letter from the EPA requesting access to the property that it leases from PRIDCO, and the Company granted such access. In February 2013, the EPA requested access to conduct further environmental investigation at the property. The Company granted such access.
The Company is not aware of any determination by the EPA that any remedial action is required for the Site and, accordingly, is not able to estimate the extent of any possible liability.
The Company is, from time to time, involved in other legal proceedings. The Company believes that such other current litigation is routine in nature and incidental to the conduct of the Company’s business and that none of this litigation, individually or collectively, would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosure |
Not applicable.
Item 5. Market For Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities
The Company’s common stock is traded under the symbol “LCUT” on the NASDAQ Global Select Market (“NASDAQ”).
The following table sets forth the quarterly high and low sales prices for the common stock of the Company for the fiscal periods indicated as reported by NASDAQ.
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||
| High | Low | High | Low | |||||||||||||
| First quarter |
$ | 18.84 | $ | 14.03 | $ | 13.00 | $ | 10.28 | ||||||||
| Second quarter |
19.95 | 14.47 | 13.75 | 11.11 | ||||||||||||
| Third quarter |
18.06 | 15.03 | 16.35 | 13.50 | ||||||||||||
| Fourth quarter |
18.15 | 14.74 | 16.35 | 13.80 | ||||||||||||
At December 31, 2014, the Company estimates that there were approximately 2,500 record holders of the Company’s common stock.
The Company is authorized to issue 100 shares of Series A Preferred stock and 2,000,000 shares of Series B Preferred stock, none of which were issued or outstanding at December 31, 2014.
In the last two fiscal years, the Board of Directors declared a dividend of $0.025 per share payable on February 15, 2013, a dividend of $0.03125 per share payable on May 15, 2013, August 15, 2013 and November 15, 2013 and a dividend of $0.0375 per share payable on February 14, 2014, May 15, 2014, August 15, 2014, November 14, 2014 and February 13, 2015. The Board of Directors currently intends to continue paying cash dividends for the foreseeable future, although the Board of Directors may in its discretion determine to modify or eliminate such dividends at any time. On March 4, 2015, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.0375 per share payable on May 15, 2015 to shareholders of record on May 1, 2015. The Company’s Credit Agreement, however, may restrict its ability to declare and pay dividends, establishing conditions that are to be met prior to making any dividend payment as well as restrictions in the amount of any dividend payment.
There were no purchases made by or on behalf of the Company or any “affiliated purchaser” of the Company’s common stock during the quarter ended December 31, 2014.
23
Table of Contents
The following table summarizes the Company’s equity compensation plan as of December 31, 2014:
| Plan category |
Number of shares of common stock to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options |
Weighted- average exercise price of outstanding options |
Number of shares of common stock remaining available for future issuance |
|||||||||
| Equity compensation plan approved by security holders |
2,326,627 | $ | 14.19 | 296,362 | ||||||||
| Equity compensation plan not approved by security holders |
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
2,326,627 | $ | 14.19 | 296,362 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
PERFORMANCE GRAPH
The following chart compares the cumulative total return on the Company’s common stock with the NASDAQ Market Index and the Hemscott Group Index for Housewares & Accessories. The comparisons in this chart are required by the SEC and are not intended to forecast or be indicative of the possible future performance of the Company’s common stock.
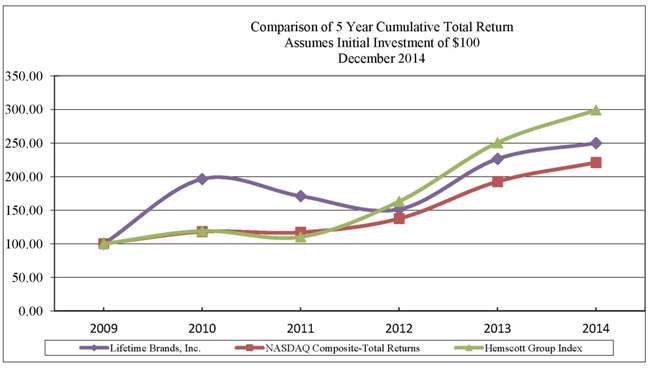
24
Table of Contents
| Date |
Lifetime Brands, Inc. |
Hemscott Group Index |
NASDAQ Market Index |
|||||||||
| 12/31/2009 |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 100.00 | $ | 100.00 | ||||||
| 12/31/2010 |
196.36 | 119.05 | 118.02 | |||||||||
| 12/31/2011 |
171.01 | 110.14 | 117.04 | |||||||||
| 12/31/2012 |
151.35 | 162.93 | 137.47 | |||||||||
| 12/31/2013 |
226.41 | 250.47 | 192.62 | |||||||||
| 12/31/2014 |
249.90 | 299.01 | 221.02 | |||||||||
Note:
| (1) | The graph assumes $100 was invested as of the open of trading on January 1, 2010 and dividends were reinvested. Measurement points are at the last trading day of each of the fiscal years ended December 31, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014. The material in this chart is not soliciting material, is not deemed filed with the SEC and is not incorporated by reference in any filing of the Company under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, whether or not the chart is prepared before or after the date of this Annual Report on Form 10-K and irrespective of any general incorporation language in such filing. A list of the companies included in the Hemscott Group Index will be furnished by the Company to any stockholder upon written request to the Chief Financial Officer of the Company. |
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
The selected consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 has been derived from the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. The selected consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2011 and 2010 and the selected consolidated balance sheet data at December 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 have been derived from the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements included in the Company’s Annual Reports on Form 10-K for those respective years, which are not included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
This information should be read together with the discussion in Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations and the Company’s consolidated financial statements and notes to those statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
25
Table of Contents
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010(2) | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| STATEMENT OF OPERATIONS DATA(1) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 586,010 | $ | 502,721 | $ | 486,842 | $ | 444,418 | $ | 443,171 | ||||||||||
| Cost of sales |
373,129 | 315,459 | 310,054 | 282,058 | 273,774 | |||||||||||||||
| Distribution expenses |
54,202 | 44,364 | 44,046 | 43,882 | 44,570 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses (3) |
133,786 | 114,345 | 104,338 | 93,894 | 95,044 | |||||||||||||||
| Intangible asset impairment |
3,384 | — | 1,069 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Restructuring expenses |
125 | 367 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Income from operations |
21,384 | 28,186 | 27,335 | 24,584 | 29,783 | |||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(6,418 | ) | (4,847 | ) | (5,898 | ) | (7,758 | ) | (9,351 | ) | ||||||||||
| Financing expense |
(758 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Loss on early retirement of debt |
(346 | ) | (102 | ) | (1,363 | ) | — | (764 | ) | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Income before income taxes, equity in earnings and extraordinary item |
13,862 | 23,237 | 20,074 | 16,826 | 19,668 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision |
(5,825 | ) | (9,175 | ) | (5,208 | ) | (6,122 | ) | (4,602 | ) | ||||||||||
| Equity in (losses) earnings, net of taxes (4) |
(6,493 | ) | (4,781 | ) | 6,081 | 3,362 | 2,718 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Income before extraordinary item |
1,544 | 9,281 | 20,947 | 14,066 | 17,784 | |||||||||||||||
| Extraordinary item, net of taxes |
— | — | — | — | 2,477 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 1,544 | $ | 9,281 | $ | 20,947 | $ | 14,066 | $ | 20,261 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Basic income per common share before extraordinary item |
$ | 0.11 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 1.67 | $ | 1.16 | $ | 1.48 | ||||||||||
| Basic income per common share of extraordinary item |
— | — | — | — | 0.20 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Basic income per common share |
$ | 0.11 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 1.67 | $ | 1.16 | $ | 1.68 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Weighted-average shares outstanding – basic |
13,519 | 12,757 | 12,511 | 12,128 | 12,036 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Diluted income per common share before extraordinary item |
$ | 0.11 | $ | 0.71 | $ | 1.64 | $ | 1.12 | $ | 1.44 | ||||||||||
| Diluted income per common share of extraordinary item |
— | — | — | — | 0.20 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Diluted income per common share |
$ | 0.11 | $ | 0.71 | $ | 1.64 | $ | 1.12 | $ | 1.64 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Weighted-average shares outstanding – diluted |
13,974 | 13,043 | 12,810 | 12,529 | 12,376 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Cash dividends declared per common share |
$ | 0.15 | $ | 0.13125 | $ | 0.125 | $ | 0.075 | $ | — | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCE SHEET DATA(1) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Current assets |
$ | 258,117 | $ | 214,676 | $ | 212,759 | $ | 198,797 | $ | 182,253 | ||||||||||
| Current liabilities |
83,869 | 69,494 | 66,899 | 69,962 | 60,512 | |||||||||||||||
| Working capital |
174,248 | 145,182 | 145,860 | 128,835 | 121,741 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
421,402 | 336,739 | 348,797 | 318,745 | 277,586 | |||||||||||||||
| Short-term borrowings |
10,765 | 3,937 | 11,375 | 15,000 | 4,100 | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
127,655 | 65,919 | 84,593 | 82,625 | 50,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Convertible senior notes |
— | — | — | — | 23,557 | |||||||||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity |
188,233 | 180,905 | 172,230 | 146,175 | 127,606 | |||||||||||||||
Notes:
| (1) | Investments and acquisitions of the following, in the respective years noted, affect the comparability of the periods: the acquisition of Creative Tops in November 2011, a 40% equity investment in GS Internacional S/A (“GSI”) in December 2011, the acquisition of Fred® & Friends in December 2012 and the acquisition of Kitchen Craft in January 2014. |
| (2) | In 2010, the Company recorded an extraordinary gain of $2.5 million as a result of the elimination of the negative goodwill recorded in conjunction with the purchase of the business and certain assets of Mikasa®, Inc. |
| (3) | In 2014, the Company recorded a credit of $4.2 million related to an adjustment to the fair value of certain contingent consideration. |
| (4) | In 2012, the Company recorded a gain of $4.1 million related to Vasconia’s purchase of Almexa and in 2013, the Company recorded a charge of $5.0 million, net of tax for a reduction of the fair value of the Company’s investment in Vasconia. In 2014, the Company recorded a charge of $6.0 million, net of tax, for a reduction of the fair value of the Company’s investment in GSI. |
26
Table of Contents
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements for the Company and notes thereto set forth in Item 15. This discussion contains forward-looking statements relating to future events and the future performance of the Company based on the Company’s current expectations, assumptions, estimates and projections about it and the Company’s industry. These forward-looking statements involve risks and uncertainties. The Company’s actual results and timing of various events could differ materially from those anticipated in such forward-looking statements as a result of a variety of factors, as more fully described in this section and elsewhere in this Annual Report including those discussed on pages 2-3 of this Annual Report under “Disclosures regarding Forward-Looking Statements” and under Item 1A “Risk Factors” and Item 7A “Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures Regarding Market Risk.” The Company undertakes no obligation to update publicly any forward-looking statements for any reason, even if new information becomes available or other events occur in the future.
ABOUT THE COMPANY
The Company designs, sources and sells branded kitchenware, tableware and other products used in the home. The Company’s product categories include two categories of products that people use to prepare, serve and consume foods: Kitchenware (kitchen tools and gadgets, cutlery, cutting boards, cookware and bakeware) and Tableware (dinnerware, stemware, flatware and giftware); and one category, Home Solutions, which comprises other products used in the home (pantryware, spice racks, thermal beverageware, food storage and home décor). In 2014, Kitchenware products and Tableware products accounted for approximately 88% of the Company’s U.S. Wholesale net sales and 87% of the Company’s consolidated net sales, as compared with 88% and 86%, respectively, in 2013.
The Company markets several product lines within each of its product categories and under most of the Company’s brands, primarily targeting moderate price points through virtually every major level of trade. The Company believes it possesses certain competitive advantages based on its brands, its emphasis on innovation and new product development and its sourcing capabilities. The Company owns or licenses a number of leading brands in its industry including Farberware®, KitchenAid®, Mikasa®, KitchenCraft®, Pfaltzgraff®, Fred®, Sabatier®, masterclass®, Kamenstein®, Towle® and Built NY®. Historically, the Company’s sales growth has come from expanding product offerings within its product categories, by developing existing brands, acquiring new brands and establishing new product categories. Key factors in the Company’s growth strategy have been the selective use and management of the Company’s brands and the Company’s ability to provide a stream of new products and designs. A significant element of this strategy is the Company’s in-house design and development teams that create new products, packaging and merchandising concepts. More recently, the Company has significantly expanded its international footprint through acquisitions of businesses which own or license complementary brands in markets outside the United States.
BUSINESS SEGMENTS
During the second quarter of 2014, the Company realigned its reportable segments into three categories: U.S. Wholesale, International and Retail Direct. The U.S. Wholesale segment, formerly the Wholesale segment, is the Company’s primary domestic business that designs, markets and distributes its products to retailers and distributors. The International segment consists of certain business operations conducted outside the U.S. which were previously included in the Wholesale segment. The Retail Direct segment is that in which the Company markets and sells a limited selection of its products to consumers through its Pfaltzgraff®, Mikasa®, Fred® and Friends, Built NY® and Lifetime Sterling® Internet websites. The Company has segmented its operations to reflect the manner in which management reviews and evaluates its results of operations. To facilitate year over year comparison, previous periods presented have been recast to conform with the current period presentation.
27
Table of Contents
EQUITY INVESTMENTS
The Company owns approximately 30% of the outstanding capital stock of Grupo Vasconia, S.A.B. (“Vasconia”), an integrated manufacturer of aluminum products and one of Mexico’s largest housewares companies.
The Company accounts for its investment in Vasconia using the equity method of accounting and has recorded its proportionate share of Vasconia’s net income, net of taxes, as equity in earnings in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations. Pursuant to a Shares Subscription Agreement (the “Agreement”), the Company may designate four persons to be nominated as members of Vasconia’s Board of Directors. Shares of Vasconia’s capital stock are traded on the Bolsa Mexicana de Valores, the Mexican Stock Exchange. The Quotation Key is VASCONI.
The Company recorded equity in earnings (losses) of Vasconia, net of taxes, of $230,000, $(4.0) million and $6.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. In 2013, as a result of a decline in the quoted stock price and the 2013 quarterly decline in the operating results of Vasconia, the carrying amount of the Company’s investment in Vasconia exceeded its fair value and, therefore, the Company reduced its investment value by $5.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2013, net of tax, to its fair value. Equity in earnings of Vasconia in 2012 includes $4.1 million related to the Company’s portion of a bargain purchase gain recognized by Vasconia on its purchase of Almexa, an aluminum mill and manufacturer of aluminum foil, a $1.1 million tax benefit realized in the period and a reduction of the Company’s investment to fair value of $1.3 million, net of tax.
In December 2011, the Company acquired a 40% equity interest in GS Internacional S/A (“GSI”). GSI is a wholesale distributor of branded housewares products in Brazil. GSI markets dinnerware, glassware, home décor, kitchenware and barware to customers throughout Brazil including major department stores, housewares retailers and independent shops. The Company accounts for its investment in GSI using the equity method of accounting and has recorded its proportionate share of GSI’s net income, net of taxes, as equity in earnings in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations. Pursuant to a Shareholders’ Agreement, the Company has the right to designate three persons (including one independent person, as defined) to be nominated as members of GSI’s Board of Directors.
As a result of the decline in operating results of GSI and the business environment in Brazil, in September 2014, the Company evaluated the carrying value of its investment for other-than-temporary impairment under the equity-method of accounting and recorded an impairment charge of $5.2 million, net of tax, during the third quarter of 2014. During the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company purchased 40% of newly issued common stock of GSI for R$2.0 million ($764,000). The Company assessed the valuation of its fourth quarter investment in GSI and determined there were no significant changes to the assumptions that were used in the valuation of GSI performed during the third quarter and as a result, the new investment also was impaired.
In February 2012, the Company acquired a 50% stake in Grand Venture Holdings Limited (“Grand Venture”), a joint venture with Manweal Development Limited (“Manweal”), a Chinese corporation, to distribute Mikasa® products in China, which included an initial investment by the Company of $500,000. The Company and Manweal each own 50% of Grand Venture and have rights and obligations proportionate to their ownership percentages. The Company accounts for its investment in Grand Venture using the equity method of accounting and has recorded its proportionate share of Grand Venture’s net loss in equity in earnings in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations.
In January 2011, the Company, together with Vasconia and unaffiliated partners, formed a joint venture based in Hong Kong that supplies imported kitchenware products to retailers in North, Central and South American. The Company sold its investment in this joint venture to an unaffiliated partner in October 2014.
SEASONALITY
The Company’s business and working capital needs are highly seasonal, with a majority of sales occurring in the third and fourth quarters. In 2014, 2013 and 2012, net sales for the third and fourth quarters accounted for 60%, 61% and 58%, of total annual net sales, respectively. In anticipation of the pre-holiday shipping season, inventory levels increase primarily in the June through October time period.
28
Table of Contents
IMPACT OF INFLATION
Inflation rates in the United States and in major foreign countries where the Company operates have not had a significant impact on its results of operations or financial position during 2014, 2013, or 2012. The Company will continue its practice of monitoring costs and adjusting prices, accordingly.
EFFECT OF ADOPTION OF ACCOUNTING PRINCIPLES
In July 2012, the FASB issued ASU No. 2012-02, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Testing Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets for Impairment, which permits an entity to first assess qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount as a basis for determining whether it is necessary to perform the quantitative impairment test described in ASC Topic No. 350, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other. The amendments in this update are effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after September 15, 2012. The Company’s adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Effective January 2013, the Company adopted ASU No. 2013-02, Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reporting of Amounts Reclassified Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income, which requires an entity to provide information about the amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by component. In addition, an entity is required to present, either on the face of the statement where net income is presented or in the notes, significant amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by the respective line items of net income but only if the amount reclassified is required under U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) to be reclassified to net income in its entirety in the same reporting period. For other amounts that are not required under GAAP to be reclassified in their entirety to net income (e.g., net periodic pension benefit cost), an entity is required to cross-reference to other disclosures required under GAAP that provide additional detail about those amounts. In connection with the adoption of this standard, the Company added additional disclosure about the Company’s accumulated other comprehensive income to Note M of its financial statements.
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, to clarify the principles of recognizing revenue and create common revenue recognition guidance under U.S. GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards. This ASU is effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those years beginning after December 15, 2016 and can be adopted either retrospectively to each reporting period presented or as a cumulative effect adjustment as of the date of the adoption, with early application not permitted. The Company is currently determining its implementation approach and assessing the impact, if any, on the consolidated financial statements.
29
Table of Contents
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following table sets forth statement of operations data of the Company as a percentage of net sales for the periods indicated below.
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Net sales |
100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||
| Cost of sales |
63.7 | 62.8 | 63.7 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross margin |
36.3 | 37.2 | 36.3 | |||||||||
| Distribution expenses |
9.2 | 8.8 | 9.0 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
22.8 | 22.7 | 21.4 | |||||||||
| Intangible asset impairment |
0.6 | — | 0.2 | |||||||||
| Restructuring |
— | 0.1 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income from operations |
3.7 | 5.6 | 5.7 | |||||||||
| Interest expense |
(1.1 | ) | (1.0 | ) | (1.2 | ) | ||||||
| Financing expense |
(0.1 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Loss on early retirement of debt |
(0.1 | ) | — | (0.3 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income before income taxes and equity in earnings |
2.4 | 4.6 | 4.2 | |||||||||
| Income tax provision |
(1.0 | ) | (1.8 | ) | (1.1 | ) | ||||||
| Equity in (losses) earnings, net of taxes |
(1.1 | ) | (1.0 | ) | 1.2 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income |
0.3 | % | 1.8 | % | 4.3 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
30
Table of Contents
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
2014 COMPARED TO 2013
As a result of the Company’s realignment of its reportable segments into three categories: U.S. Wholesale, International and Retail Direct in the second quarter of 2014, previous periods presented have been recast to conform with the current period presentation.
Net Sales
Net sales for the year 2014 were $586.0 million, an increase of 16.6%, compared to net sales of $502.7 million in 2013.
Net sales for the U.S. Wholesale segment in 2014 were $441.3 million, a decrease of $2.9 million, or 0.7%, compared to net sales of $444.2 million in 2013.
Net sales for the Company’s Kitchenware product category in 2014 were $269.3 million, a decrease of $11.9 million, or 4.2%, compared to net sales of $281.2 million in 2013. The decrease in the U.S. Wholesale’s Kitchenware product category sales was in part, due to a decrease in cutlery programs and decreased sales volume in both cookware and novelty kitchenware.
Net sales for the Company’s Tableware product category in 2014 were $117.5 million, an increase of $7.4 million, or 6.7%, compared to net sales of $110.1 million for 2013. The Tableware product category sales increase reflects higher sales volumes of luxury tableware and stainless flatware. The increased sales volume was primarily attributable to an increase in successful warehouse club programs year over year.
Net sales for the Company’s Home Solutions products category in 2014 were $54.5 million, an increase of $1.6 million, or 3.0%, compared to net sales of $52.9 million in 2013. The increase in the Home Solutions product category reflects the inclusion of Built NY®, acquired in the first quarter of 2014, partially offset by a decrease in pantryware warehouse club programs and lower volume for the home décor product line from a reduction in retail space allocated to this category.
Net sales for the International segment in 2014 were $125.2 million, an increase of $86.3 million, compared to net sales of $38.9 million for 2013. Of the increase, $71.9 million represents sales from Kitchen Craft and La Cafetière, which were acquired during the first quarter of 2014. The balance of the increase was due to higher sales of tableware products as the impact of higher duties on ceramic products imposed by the European Union in 2013 has subsided and to a lesser degree the strength of the British Pound.
Net sales for the Retail Direct segment in 2014 were $19.5 million, a decrease of $1.2 million, or 5.8%, compared to $20.7 million for 2013. The decrease was primarily attributable to reduced activity on the Company’s Pfaltzgraff® and Mikasa® internet websites in 2014 compared to 2013. The decrease in activity on the Pfaltzgraff® and Mikasa® internet websites was partially offset by the launch of the Built NY® and Fred® & Friends internet websites in 2014.
Gross margin
Gross margin for 2014 was $212.9 million, or 36.3%, compared to $187.3 million, or 37.2%, for the corresponding period in 2013.
Gross margin for the U.S. Wholesale segment was $155.8 million, or 35.3%, for 2014 compared to $163.4 million, or 36.8%, for 2013. Gross margin may be expected to fluctuate from period to period based on a number of factors, including product and customer mix. The decrease in gross margin for the U.S. Wholesale segment reflects actions taken to create opportunities to expand the Company’s retail placement, an increase in the proportion of tableware product sales, which typically have lower gross margin than kitchenware products, and an increase in promotional activities to introduce new brands and products. The decreases in margin in the Kitchenware and Tableware product categories were partially offset by an increase in margin in the Home Solutions product category.
31
Table of Contents
Gross margin for the International segment was $43.8 million, or 35.0%, for 2014 compared to $10.7 million, or 27.6%, for 2013. The increase in gross margin in the International segment is due to the inclusion of Kitchen Craft, the products of which carry a higher margin than other product categories in the segment, and, to a lesser extent, a decrease in pricing promotions for tableware products.
Gross margin for the Retail Direct segment was $13.4 million, or 68.8%, for 2014 compared to $14.3 million, or 68.8%, for 2013.
Distribution expenses
Distribution expenses for 2014 were $54.2 million as compared to $44.4 million for 2013. Distribution expenses as a percentage of net sales were 9.2% in 2014 and 8.8% in 2013.
Distribution expenses as a percentage of sales shipped from the Company’s warehouses located in the United States for the U.S. Wholesale segment were 9.3% for 2014 as compared to 8.8% for 2013. The increase reflects higher expenses despite flat year over year shipments and the effect of labor costs on lower revenue per shipment.
Distribution expenses as a percentage of sales shipped from the Company’s warehouses for the International segment were 12.1% and 15.1% for the 2014 and 2013, respectively. The decrease in expenses as a percentage of sales shipped reflects the higher sales volume from the tableware warehouses and a more efficient use of freight lines.
Distribution expenses as a percentage of net sales for the Retail Direct segment were 29.7% for 2014 compared to 29.6% for 2013. The increase was due to declining sales relative to fixed expenses.
Selling, general and administrative expenses
Selling, general and administrative expenses (“SG&A”) for 2014 were $133.8 million, an increase of $19.5 million, or 17.1%, as compared to $114.3 million for 2013. The 2014 period includes a credit of $4.2 million for the reduction in the fair value of certain contingent consideration obligations.
SG&A expenses for 2014 for the U.S. Wholesale segment were $85.0 million (excluding the credit related to the contingent consideration), an increase of $3.2 million, or 3.9%, compared to $81.8 million in 2013. During 2014, the Company incurred certain expenses related to its growth and acquisition activities which were offset primarily by a reduction in short term incentive compensation expense. As a percentage of net sales, SG&A expenses were 19.3% for 2014 compared to 18.4% for 2013.
SG&A expenses for 2014 for the International segment were $28.0 million compared to $9.5 million for 2013. The increase was primarily due to the inclusion of Kitchen Craft. As a percentage of net sales, SG&A expenses decreased to 22.4% for 2014 compared to 24.4% for 2013.
SG&A expenses for 2014 for the Retail Direct segment were $8.7 million compared to $8.2 million for 2013. The increase is primarily due to an increase in costs related to the launch of two new websites in 2014.
Unallocated corporate expenses for 2014 were $16.2 million compared to $14.9 million for 2013. The increase is primarily due to an increase in professional fees and acquisition related expenses.
Intangible asset impairment
The Company’s home décor products category has experienced a decline in sales and profit in recent years. The Company believes the most significant factor resulting in the decline was the reduction in retail space allocated to the category which has also contributed to pricing pressure. The Company has been re-branding a portion of the home décor products under the Mikasa® and Pfaltzgraff® trade names and more recently under the Bombay® license. The Company is also taking advantage of promotional sale opportunities, such as flash sale websites and online retailers to offset the effect of a reduction in retail space for this product category and pricing pressures. As a result of these factors, the Company recorded an impairment charge of $3.4 million, related to these brands in its consolidated statement of operations for 2014.
32
Table of Contents
Restructuring expenses
The Company incurred one-time restructuring expenses of $0.1 million in 2014 and $0.4 million in 2013. The restructuring expenses in 2014 resulted from the consolidation of our customer service and call center functions which resulted in the elimination of certain employee positions. The expenses in 2013 resulted from the planned closure of the Fred® & Friends distribution center which included the elimination of certain employee positions in the third quarter of 2013.
Interest expense
Interest expense for 2014 was $6.4 million compared to $4.8 million for 2013. The increase in interest expense was attributable to higher average borrowings attributable to the recent acquisitions, which were partially offset by lower rates resulting from the debt refinancing in January 2014.
Financing expenses
In 2014 the Company wrote off $0.7 million of expenses related to the refinancing of indebtedness that was not completed. The Company did not incur financing expenses in 2013.
Loss on early retirement of debt
In January 2014, in connection with the refinancing of its senior debt, the Company repaid the senior secured term loan outstanding under its Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of October 28, 2011 with JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A. as Administrative Agent and a Co-Collateral Agent, which was replaced by the Credit Agreement (the “Senior Secured Term Loan”). In connection therewith, the Company wrote off the related debt issuance costs of $0.3 million. In December 2013, the Company repaid a portion of its senior secured credit agreement. In connection with the payoff, the Company wrote off debt issuance costs of $0.1 million.
Income tax provision
The income tax provision was $5.8 million in 2014 and $9.2 million in 2013. The Company’s effective tax rate for 2014 was 42.0%, compared to 39.5% for 2013. The effective tax rate in 2014 reflects non-deductable transaction costs in both the U.S. and the U.K., as well as a reduction in the deferred tax assets in Puerto Rico as a result of a rate change and an increase in uncertain state tax positions. The effective tax rate in 2013 reflects a reduced tax rate in the U.K. and an increased tax rate in Puerto Rico.
33
Table of Contents
Equity in earnings (losses)
The Company’s equity in earnings (losses) for 2014 and 2013 are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Equity in earnings (losses) of Grupo Vasconia: |
||||||||
| Equity earnings before reduction in investment to fair value, net of tax |
$ | 1,293 | $ | 1,000 | ||||
| Tax provision recorded in equity in earnings (1) |
(1,063 | ) | — | |||||
| Reduction in investment to fair value, net of tax |
— | (5,040 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Equity in earnings (losses) of Grupo Vasconia |
230 | (4,040 | ) | |||||
| Equity in losses of GSI: |
||||||||
| Equity in losses before reduction in investment to fair value, net of tax |
(692 | ) | (656 | ) | ||||
| Reduction in investment to fair value, net of tax |
(5,977 | ) | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Equity in losses of GSI |
(6,669 | ) | (656 | ) | ||||
| Equity in losses of other investments |
(54 | ) | (85 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | (6,493 | ) | $ | (4,781 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| (1) | Income tax provision related to the valuation allowance for deferred taxes associated with the cumulative foreign currency translation adjustment. |
Equity in earnings of Vasconia, net of taxes, was $230,000 in 2014, as compared to equity in losses, net of taxes, of $4.0 million for 2013. Equity in losses in 2013 includes a charge of $5.0 million, net of tax, for the reduction in Vasconia’s fair value. Vasconia reported income from operations for 2014 of $7.8 million, compared to $5.4 million for 2013 and net income of $5.3 million in 2014, compared to $4.3 million in 2013.
Equity in losses of GSI was $6.7 million (including a charge of $6.0 million, net of tax, for the reduction in the fair value of the Company’s investment in GSI) for 2014 and $0.7 million for 2013, respectively. As discussed under Equity Investments above, as a result of the decline in operating results of GSI and the business environment in Brazil, the Company recorded an aggregate impairment charge of $6.0 million, net of tax, during 2014.
34
Table of Contents
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
2013 COMPARED TO 2012
As a result of the Company’s realignment of its reportable segments into three categories: U.S. Wholesale, International and Retail Direct in the second quarter of 2014, previous periods presented have been recast to conform with the current period presentation.
Net Sales
Net sales for the year 2013 were $502.7 million, an increase of 3.3%, compared to net sales of $486.8 million in 2012. The increase was primarily the result of the inclusion of the net sales of Fred® & Friends, which was acquired in December 2012.
Net sales for the U.S. Wholesale segment in 2013 were $444.2 million, an increase of $22.0 million, or 5.2%, as compared to net sales of $422.2 million in 2012.
Net sales for the Company’s Kitchenware product category in 2013 were $281.2 million, an increase of $25.1 million, or 9.8%, as compared to net sales of $256.1 million in 2012. Net sales for the Company’s Kitchenware product category included $19.5 million of net sales for the year ended December 31, 2013 from Fred® & Friends as compared to $0.2 million from Fred® & Friends in 2012. The increase in the Company’s Kitchenware product category was primarily attributable to successful new cutlery programs and new kitchen tools and gadgets programs throughout the year.
Net sales for the Company’s Tableware product category in 2013 were $110.1 million, a decrease of $3.8 million, or 3.3%, as compared to net sales of $113.9 million for 2012. The Tableware product category sales decrease reflected a decline in luxury tableware sales.
Net sales for the Company’s Home Solutions products category in 2013 were $52.9 million, an increase of $0.7 million, or 1.3%, as compared to net sales of $52.2 million in 2012. The increase in sales for the Company’s Home Solutions product category was primarily due to new pantryware programs, larger seasonal programs related to wall décor and lighting products in the second half of 2013, which offset reduced sales in the first half of the year resulting from a decline in close out activity, and lower volume at a major warehouse club in the first quarter.
Net sales for the International segment in 2013 were $38.9 million, a decrease of $3.7 million, or 8.7%, as compared to net sales of $42.6 million for 2012. The decrease in International segment net sales was due to the impact of higher duties imposed by the European Union. Sales increased in the fourth quarter of 2013 as customers in the European Union adjusted to the increased pricing resulting from duty rates.
Net sales for the Retail Direct segment in 2013 were $20.7 million, a decrease of $1.3 million, or 5.9%, as compared to $22.0 million for 2013. The decrease was primarily attributable to a reduction in promotional activities in 2013.
In 2013, the Company recorded a non-operating adjustment of $1.1 million to reduce accounts receivable for previously issued credits within the Retail Direct business which related to 2010 and earlier periods.
Gross margin
Gross margin for 2013 was $187.3 million, or 37.2%, as compared to $176.8 million, or 36.3%, for the corresponding period in 2012.
Gross margin for the U.S. Wholesale segment was 36.8% for 2013 as compared to 35.1% for 2012. Gross margin may be expected to fluctuate from period to period based on a number of factors, including product mix and customer mix. The increase in gross margin was the result of the inclusion of Fred® & Friends which was acquired in December 2012.
35
Table of Contents
Gross margin for the International segment was 27.6% for 2013 as compared to 31.9% for 2012. The decrease in gross margin was a result of an increase in pricing promotions.
Gross margin for the Retail Direct segment was 68.8% for 2013 as compared to 68.6% for 2012. The increase in gross margin reflects reduced discounting of dinnerware in 2013 principally from the elimination of the use of multiple coupons for one transaction.
Distribution expenses
Distribution expenses for 2013 were $44.4 million as compared to $44.0 million for 2012. Distribution expenses as a percentage of net sales were 8.8% in 2013 and 9.0% in 2012.
Distribution expenses as a percentage of sales shipped from the Company’s warehouses located in the United States for the U.S. Wholesale segment were 8.8% for 2013 as compared to 8.9% for 2012. The decrease primarily reflects labor efficiencies and improved labor management which reduced headcount in the distribution facilities in 2013. Additionally, the closure of the Fred® & Friends distribution center reduced the related distribution expenses.
Distribution expenses as a percentage of sales shipped from the Company’s warehouses for the International segment were 15.1% and 17.8% for 2013 and 2012, respectively. The decrease primarily relates to an increase in sales.
Distribution expenses as a percentage of net sales for the Retail Direct segment were 29.6% for 2013 compared to 28.9% for 2012. The increase was due to declining sales relative to fixed expenses.
Selling, general and administrative expenses
SG&A expenses for 2013 were $114.3 million, an increase of $10.0 million, or 9.6%, as compared to $104.3 million for 2012.
SG&A expenses for 2013 for the U.S. Wholesale segment were $81.8 million, an increase of $9.1 million, or 12.5%, as compared to $72.7 million in 2012. As a percentage of net sales, SG&A expenses were 18.5% for 2013 compared to 17.2% for 2012. The increase was due to the inclusion of Fred® & Friends and an increase in selling expenses, such as trade show expenses and employee-related expenses.
SG&A expenses for 2013 for the International segment were $9.5 million compared to $9.7 million for 2012.
SG&A expenses for 2013 for the Retail Direct segment were $8.2 million compared to $8.3 million for 2012.
Unallocated corporate expenses for 2013 and 2012 were $14.9 and $13.6 million, respectively, the increase being due to an increase in professional fees.
Restructuring expenses
Restructuring expenses for 2013 were $0.4 million. The expenses resulted from the planned closure of the Fred® & Friends distribution center which included the elimination of certain employee positions in the third quarter of 2013.
Intangible asset impairment
During the year ended December 31, 2012, the Company’s home décor products category experienced a significant decline in sales. The Company believes the most significant factor was the reduction in retail space allocated to the category which has also contributed to pricing pressure. While the Company believed this market condition was not permanent, following a strategic review of the business, it decided to re-brand a portion of the home décor products under the Mikasa® and Pfaltzgraff® trade names. As a result of these factors, the Company recorded an impairment charge of $1.1 million in its statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2012, which reduced the book value of its Elements® trade name.
36
Table of Contents
Interest expense
Interest expense for 2013 was $4.8 million as compared to $5.9 million for 2012. The decrease in interest expense was attributable to lower average interest rates and lower average borrowings in 2013 as compared to 2012.
Loss on early retirement of debt
In December 2013, the Company repaid a portion of its senior secured credit agreement. In connection with the payoff, the Company wrote off debt issuance costs of $0.1 million. In June and July 2012, the Company repaid its second lien credit agreement. In connection with the payoff, the Company wrote off debt issuance costs of $1.4 million.
Income tax provision
The income tax provision was $9.2 million in 2013 and $5.2 million in 2012. The Company’s effective tax rate for 2013 was 39.5% as compared to 25.9% for 2012. The effective tax rate in 2013 reflects a reduced tax rate in the United Kingdom and an increased tax rate in Puerto Rico. The effective tax rate for 2012 reflects an income tax benefit for a non-cash adjustment to a deferred tax liability of $2.3 million related to an earlier period.
Equity in earnings
Equity in losses of Vasconia, net of taxes, was $4.0 million for 2013 as compared to equity in earnings of $6.9 million for 2012. Equity in losses in 2013 includes a charge of $5.0 million, net of tax, for the reduction in Vasconia’s fair value. Vasconia reported income from operations for 2013 of $5.4 million compared to $14.6 million for 2012 and net income of $4.3 million in 2013 compared to $34.2 million in 2012. The decrease in net income was due to a decline in kitchenware and aluminum sales and reduced margins on aluminum sales in 2013 and a $22.9 million bargain purchase gain recognized by Vasconia on its purchase of Almexa, an aluminum mill and manufacturer of aluminum foil in 2012.
Equity in earnings for 2013 also includes a loss of $0.7 million from the Company’s 40% equity interest in GSI and losses of $85,000 related to other investments. Equity in earnings for 2012 also includes a loss of $0.7 million from the Company’s 40% equity interest in GSI and losses of $0.1 million related to other investments.
37
Table of Contents
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES AND ESTIMATES
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations discusses the Company’s consolidated financial statements which have been prepared in accordance with GAAP and with the instructions to Form 10-K and Article 10 of Regulation S-X. The preparation of these financial statements requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. On an on-going basis, management evaluates its estimates and judgments based on historical experience and on various other factors that are believed to be reasonable under the circumstances, the results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. The Company evaluates these estimates including those related to revenue recognition, allowances for doubtful accounts, reserves for sales returns and allowances and customer chargebacks, inventory mark-down provisions, health insurance reserves, impairment of goodwill, tangible and intangible assets, stock option expense, accruals related to the Company’s tax positions and tax valuation allowances. Actual results may differ from these estimates using different assumptions and under different conditions. The Company’s significant accounting policies are more fully described in Note A of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 15. The Company believes that the following discussion addresses its most critical accounting policies, which are those that are most important to the portrayal of the Company’s consolidated financial condition and results of operations and require management’s most difficult, subjective and complex judgments.
Inventory
Inventory consists principally of finished goods sourced from third-party suppliers. Inventory also includes finished goods, work in process and raw materials related to the Company’s manufacture of sterling silver products. Inventory is priced using the lower of cost (first-in, first-out basis) or market method. The Company estimates the selling price of its inventory on a product by product basis based on the current selling environment. If the estimated selling price is lower than the inventory’s cost, the Company reduces the value of the inventory to its net realizable value.
Accounts Receivable
The Company periodically reviews the collectability of its accounts receivable and establishes allowances for estimated losses that could result from the inability of its customers to make required payments. A considerable amount of judgment is required to assess the ultimate realization of these receivables including assessing the initial and on-going creditworthiness of the Company’s customers. The Company also maintains an allowance for anticipated customer deductions. The allowances for deductions are primarily based on contracts with customers. However, in certain cases the Company does not have a formal contract and, therefore, customer deductions are non-contractual. To evaluate the reasonableness of non-contractual customer deductions, the Company analyzes currently available information and historical trends of deductions. If the financial conditions of the Company’s customers or general economic conditions were to deteriorate, resulting in an impairment of their ability to make payments or sell the Company’s products at reasonable sales prices, or the Company’s estimate of non-contractual deductions varied from actual deductions, revisions to allowances would be required, which could adversely affect the Company’s financial condition. Historically, the Company’s allowances have been appropriate and have not resulted in material unexpected charges.
Goodwill, intangible assets and long-lived assets
Goodwill and intangible assets deemed to have indefinite lives are not amortized but, instead, are subject to an annual impairment assessment. Additionally, if events or conditions were to indicate the carrying value of a reporting unit may not be recoverable, the Company would evaluate goodwill and other intangible assets for impairment at that time. As it relates to the goodwill assessment, the Company first assesses qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount as a basis for determining whether it is necessary to perform the two-step goodwill impairment testing described in ASU Topic No. 350, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other. If, after assessing qualitative factors, the Company determines that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, then performing the two-step impairment test is unnecessary and the
38
Table of Contents
Company’s goodwill is considered to be unimpaired. However, if based on the Company’s qualitative assessment it concludes that it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, or if the Company elects to bypass the qualitative assessment, the company will proceed with performing the two-step process. The first step in the two-step process compares the carrying value of each reporting unit that has goodwill with the estimated fair value of the respective reporting unit. Should the carrying value of a reporting unit be in excess of the estimated fair value of that reporting unit, the second step must be performed. The second step represents a hypothetical purchase price allocation as if the company had acquired the reporting unit on that date. The Company also evaluates qualitative factors to determine whether or not its indefinite lived intangibles have been impaired and then performs quantitative tests if required. These tests can include the royalty savings model or other valuation models.
Long-lived assets, including intangible assets deemed to have finite lives, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that such assets may have been impaired. Impairment indicators include, among other conditions, cash flow deficits, historic or anticipated declines in revenue or operating profit or material adverse changes in the business climate that indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may be impaired. When impairment indicators are present, the Company compares the carrying value of the assets to the estimated discounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the assets. If the assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the assets exceeds the fair value of the assets.
In 2014, the result of the impairment assessment of the Company’s indefinite-lived trade names indicated that the carrying values of the Elements® and Melannco® trade names exceeded their fair values as of October 1, 2014. The Company recorded an impairment charge of $3.4 million, related to these brands. The impairment was triggered by a period of decline in the sales and gross margin of the brands.
Revenue recognition
The Company sells products:
| • | Wholesale, to retailers and distributors, and |
| • | Retail, directly to consumers. |
Wholesale sales and retail sales are recognized when title passes to the customer, which is primarily at the shipping point for wholesale sales and upon delivery to the customer for retail sales. Shipping and handling fees that are billed to customers in sales transactions are included in net sales. Net sales exclude taxes that are collected from customers and remitted to the taxing authorities.
The Company offers various sales incentives and promotional programs to its customers from time to time in the normal course of business. These incentives and promotions typically include arrangements such as cooperative advertising, buydowns, volume rebates and discounts. These arrangements and an estimate of sales returns are reflected as reductions in net sales in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations.
Employee stock options
The Company accounts for its stock options through measurement of compensation expense for all share-based compensation granted to employees and non-employee directors at fair value on the date of grant and recognition of compensation expense over the related service period for awards expected to vest. The Company uses the Black-Scholes option valuation model to estimate the fair value of its stock options. The Black-Scholes option valuation model requires the input of highly subjective assumptions including the expected stock price volatility of the Company’s common stock and the risk-free interest rate. Changes in these subjective input assumptions can materially affect the fair value estimate of the Company’s stock options on the date of the option grant. The Company historically has not issued options which would be variable awards.
39
Table of Contents
Employee healthcare
The Company self-insures certain portions of its health insurance plan. The Company maintains an accrual for unpaid claims and estimated claims incurred but not yet reported (“IBNR”). Although management believes that it uses the best information available to estimate IBNR claims, actual claims may vary significantly from estimated claims.
Income taxes
The Company applies the required provisions for financial statement recognition, measurement and disclosure of uncertain tax positions recognized in the Company’s financial statements. Tax positions must meet a more-likely-than-not recognition threshold and measurement attribute for financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken. The valuation allowance is also calculated, established or maintained when it is “more likely than not” that all or a portion of deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Derivatives
The Company accounts for all derivative instruments on the balance sheet at fair value as either an asset or a liability. Changes in the fair value of derivatives that qualify as hedges and have been designated as part of a hedging relationship for accounting purposes have no net impact on earnings to the extent the derivative is considered highly effective in achieving offsetting changes in fair value or cash flows attributable to the risk being hedged, until the hedged item is recognized in earnings. If the derivative which is designated as part of a hedging relationship is considered ineffective in achieving offsetting changes in fair value or cash flows attributable to the risk being hedged, the changes in fair value are recorded in operations. For derivatives that do not qualify or are not designated as hedging instruments for accounting purposes, changes in fair value are recorded in operations.
40
Table of Contents
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
The Company’s principal sources of cash to fund liquidity needs are: (i) cash provided by operating activities and (ii) borrowings available under its Revolving Credit Facility under the Credit Agreement. The Company’s primary uses of funds consist of working capital requirements, capital expenditures, acquisitions and investments and payments of principal and interest on its debt.
At December 31, 2014, the Company had cash and cash equivalents of $5.1 million compared to $4.9 million at December 31, 2013, working capital of $174.2 million at December 31, 2014 compared to $145.2 million at December 31, 2013 and the current ratio (current assets to current liabilities) was 3.1 to 1 at December 31, 2014 compared to 3.09 to 1 at December 31, 2013.
Borrowings under the Company’s Revolving Credit Facility increased to $92.7 million at December 31, 2014 compared to $49.2 million at December 31, 2013. The increase in borrowings was primarily attributable to the financing of the Kitchen Craft acquisition in January 2014.
The Company believes that availability under its Revolving Credit Facility and cash flows from operations are sufficient to fund the Company’s operations for the next twelve months. However, if circumstances were to adversely change, the Company may seek alternative sources of liquidity including debt and/or equity financing. However, there can be no assurance that any such alternative sources would be available or sufficient. The Company closely monitors the creditworthiness of its customers. Based upon its evaluation of changes in customers’ creditworthiness, the Company may modify credit limits and/or terms of sale. However, notwithstanding the Company’s efforts to monitor its customers’ financial condition, the Company could be materially affected in the future.
Credit Facilities
In January 2014, the Company entered into the Credit Agreement. The Credit Agreement, which expires in January 2019, provides for, among other things, the Revolving Credit Facility commitment totaling $175.0 million ($40.0 million of which is available for multi-currency borrowings) and the Term Loan facility of $50.0 million.
Each borrowing under the Revolving Credit Facility bears interest, at the Company’s option, at one of the following rates: (i) the Alternate Base Rate, defined as the greater of the Prime Rate, Federal Funds Rate plus 0.5% or the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.0%, plus a margin of 0.75% to 1.25%, or (ii) the Eurodollar Rate, defined as the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus a margin of 1.75% to 2.25%. Interest rates on outstanding borrowings at December 31, 2014 ranged from 2.00% to 4.6875%. In addition, the Company pays a commitment fee of 0.375% on the unused portion of the Revolving Credit Facility.
Availability under the Credit Agreement depends on the valuation of certain current assets and trademark values and the Company’s ability to meet and maintain certain financial ratios, as discussed below. Due to the Company’s seasonality, this may mean that the Company will have greater borrowing availability during the third and fourth quarters of each year. At December 31, 2014, borrowings outstanding under the Revolving Credit Facility were $92.7 million and open letters of credit were $2.3 million. At December 31, 2014, availability under the Revolving Credit Facility was approximately $64.9 million. The borrowing capacity under the Revolving Credit Facility depends, in part, on eligible levels of accounts receivable and inventory that fluctuate regularly and certain trademark values based upon periodic appraisals. Consequently, the $175.0 million commitment may not represent actual borrowing capacity.
The Company classifies a portion of the Revolving Credit Facility as a current liability if the Company intends to and is able to repay the loan from cash flows from operations which are expected to occur within the year. Repayments and borrowings under the facility can vary significantly from planned levels based on cash flow needs and general economic conditions.
ABR Term Loans or Eurocurrency Term Loans, provided for under the Credit Agreement, bear interest based on the applicable Senior Leverage Ratio. As of December 31, 2014, the Company’s Senior Leverage Ratio was 3.3 to 1. The ABR Spread for Term Loans is 3.0% to 3.5% and the Eurocurrency Spread for Term Loans is 4.0% to 4.5%. As of December 31, 2014, $45.0 million was outstanding under the Term Loan.
41
Table of Contents
The Company’s payment obligations under the Revolving Credit Facility are unconditionally guaranteed by each of its existing and future U.S. subsidiaries. Certain payment obligations under the Revolving Credit Facility are also direct obligations of its foreign subsidiary borrowers designated as such under the Credit Agreement and, subject to limitations on such guaranty, are guaranteed by the foreign subsidiary borrowers, as well as by the Company. The obligations of the Company under the Revolving Credit Facility and any hedging arrangements and cash management services and the guarantees by its domestic subsidiaries in respect of those obligations are secured by substantially all of the assets and stock (but in the case of foreign subsidiaries, limited to 65% of the capital stock in first-tier foreign subsidiaries and not including stock of subsidiaries of such first-tier foreign subsidiaries) owned by the Company and the U.S. subsidiary guarantors, subject to certain exceptions. Such security interest consists of a first-priority lien, subject to certain permitted liens, with respect to the assets of the Company and its domestic subsidiaries pledged as collateral in favor of lenders under the Revolving Credit Facility.
The Credit Agreement provides for customary restrictions and events of default. Restrictions include limitations on the incurrence of additional indebtedness, acquisitions, investments and payment of dividends, among other things. Further, the Credit Agreement provides that at any time any Term Loan is outstanding or at any time no Term Loan is outstanding and availability under the Revolving Credit Facility is less than $17.5 million and continuing until availability of at least $20.0 million is maintained for three consecutive months, the Company is required to maintain a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio of 1.10 to 1.00 for each of four consecutive fiscal quarter periods. The Credit Agreement also provides that when the Term Loan is outstanding, the Company is required to maintain a Senior Leverage Ratio (the ratio of the aggregate principal amount of all of the Company’s indebtedness, other than certain subordinated indebtedness, to the Company’s EBITDA) within defined parameters not to exceed 4.00 to 1.00 at the fiscal quarter ending September 30, 2014; and, prior to its amendment in February 2015, the Company was required to maintain a Senior Leverage Ratio of 4.25 to 1.00 at the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2014; 3.50 to 1.00 at each fiscal quarter end in 2015; and 2.50 to 1.00 at each fiscal quarter end thereafter; provided that for any fiscal quarter ending on September 30 of any year, the maximum Senior Leverage Ratio specified above shall be increased by an additional 0.25:1.00.
Pursuant to the term loan agreement, as of December 31, 2014 the maximum additional permitted indebtedness other than certain subordinated indebtedness was $40.2 million. The Company was in compliance with the financial covenants of the Credit Agreement at December 31, 2014.
In February 2015, the Company entered into an amendment to its Credit Agreement (“Amendment No. 2”). Amendment No. 2, among other things, modified the Company’s maximum permitted Senior Leverage Ratio to provide for a more gradual reduction, beginning March 31, 2015, than was previously the case as described above. The Company is now required to maintain a Senior Leverage Ratio not to exceed 4.25 to 1.00 for the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2014; 4.00 to 1.00 for each fiscal quarter ending during 2015; and 3.25 to 1.00 for each fiscal quarter ending thereafter. Amendment No. 2 also amended the definition of EBITDA to exclude non-recurring one-time cash charges incurred during 2014 in connection with a permitted acquisition and the refinancing of certain indebtedness if not completed, as well clarifying language as to the exclusion from EBITDA of potential contingent consideration payments related to certain completed acquisitions.
In January 2014, the Company repaid the previously outstanding Senior Secured Term Loan in connection with the execution and delivery of the Credit Agreement.
The Company expects that it will continue to borrow and repay funds, subject to availability, under the Credit Agreement based on working capital and other corporate needs.
42
Table of Contents
Covenant Calculations
Consolidated EBITDA, as provided below, is used in the calculation of covenants provided for in the Company’s Credit Agreement. The following is the Company’s Consolidated EBITDA for the last four fiscal quarters:
| Consolidated EBITDA for the four quarters ended | ||||
| December 31, 2014 |
||||
| (in thousands) | ||||
| Three months ended December 31, 2014 |
20,918 | |||
| Three months ended September 30, 2014 |
16,470 | |||
| Three months ended June 30, 2014 |
1,494 | |||
| Three months ended March 31, 2014 |
3,660 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total for the four quarters |
$ | 42,542 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Non-GAAP financial measure
Consolidated EBITDA is a non-GAAP financial measure within the meaning of Regulation G promulgated by the SEC. This measure is provided because management of the Company uses this financial measure in evaluating the Company’s on-going financial results and trends. Management also uses this non-GAAP information as an indicator of business performance. Consolidated EBITDA is also one of the measures used to calculate financial covenants required to be maintained under the Company’s Credit Agreement.
Investors should consider these non-GAAP financial measures in addition to, and not as a substitute for, the Company’s financial performance measures prepared in accordance with GAAP. Further, the Company’s non-GAAP information may be different from the non-GAAP information provided by other companies including other companies within the home retail industry.
The following is a reconciliation of net income as reported to Consolidated EBITDA for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 and each fiscal quarter of 2014 and 2013:
| Three Months Ended | Year Ended | |||||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2014 |
June 30, 2014 |
September 30, 2014 |
December 31, 2014 |
December 31, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income as reported |
(2,929 | ) | $ | (3,202 | ) | $ | (1,586 | ) | $ | 9,261 | $ | 1,544 | ||||||||
| Subtract out: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Undistributed equity (earnings) losses, net |
208 | (41 | ) | 5,193 | 1,364 | 6,724 | ||||||||||||||
| Add back: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision (benefit) |
(1,185 | ) | (1,586 | ) | 3,123 | 5,473 | 5,825 | |||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
1,390 | 1,672 | 1,698 | 1,658 | 6,418 | |||||||||||||||
| Financing expense |
— | — | — | 758 | 758 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
3,613 | 3,716 | 3,299 | 3,572 | 14,200 | |||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense |
726 | 713 | 694 | 2,360 | 4,493 | |||||||||||||||
| Loss on early retirement of debt (1) |
319 | — | — | 27 | 346 | |||||||||||||||
| Intangible asset impairment |
— | — | 3,384 | — | 3,384 | |||||||||||||||
| Contingent consideration accretion |
— | — | 665 | (4,115 | ) | (3,450 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Restructuring expenses (1) |
— | 125 | — | — | 125 | |||||||||||||||
| Permitted acquisition related expenses |
1,518 | 97 | — | 560 | 2,175 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Consolidated EBITDA |
$ | 3,660 | $ | 1,494 | $ | 16,470 | $ | 20,918 | $ | 42,542 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
43
Table of Contents
| Three Months Ended | Year Ended | |||||||||||||||||||
| March 31, 2013 |
June 30, 2013 |
September 30, 2013 |
December 31, 2013 |
December 31, 2013 |
||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income as reported |
(632 | ) | $ | (568 | ) | $ | 1,093 | $ | 9,388 | $ | 9,281 | |||||||||
| Subtract out: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Undistributed equity (earnings) losses, net |
(246 | ) | 480 | 5,452 | (332 | ) | 5,354 | |||||||||||||
| Add back: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision (benefit) |
(399 | ) | (477 | ) | 3,869 | 6,182 | 9,175 | |||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
1,162 | 1,149 | 1,280 | 1,256 | 4,847 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
2,523 | 2,667 | 2,517 | 2,708 | 10,415 | |||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense |
671 | 722 | 738 | 750 | 2,881 | |||||||||||||||
| Loss on early retirement of debt (1) |
— | — | — | 102 | 102 | |||||||||||||||
| Restructuring expenses (1) |
— | 288 | 79 | — | 367 | |||||||||||||||
| Permitted acquisition related expenses |
— | 60 | 39 | 957 | 1,056 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Consolidated EBITDA |
$ | 3,079 | $ | 4,321 | $ | 15,067 | $ | 21,011 | $ | 43,478 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | Loss on retirement of debt and restructuring expenses represent non-recurring charges incurred during such periods and are permitted exclusions from the Company’s Consolidated EBITDA, pursuant to the Company’s Credit Agreement. |
Other Credit Agreements
A subsidiary of the Company has a credit facility (“HSBC Facility” or “Short term loan”) with HSBC Bank (China) Company Limited, Shanghai Branch (“HSBC”) for up to 18.0 million Chinese Renminbi (“RMB”) ($2.9 million). The HSBC Facility is subject to annual renewal and may be used to fund general working capital needs of the subsidiary which is a trading company in the People’s Republic of China. Borrowings under the HSBC Facility are guaranteed by the Company and are granted at the sole discretion of HSBC. At December 31, 2014, RMB 4.8 million ($765,000) was outstanding and the interest rate was 6.44% under the HSBC Facility.
Capital expenditures
Capital expenditures for the year ended December 31, 2014 were $6.2 million.
Derivatives
The Company is a party to interest rate swap agreements with an aggregate notional amount of $25.4 million to manage interest rate exposure in connection with its variable interest rate borrowings. The hedge periods in these agreements commenced in March 2013 and will expire in September 2018, and the notional amounts amortize over this period.
The Company has also entered into certain foreign exchange contracts, primarily to offset the earnings impact related to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates associated with inventory purchases denominated in foreign currencies. None of these foreign exchange contracts were designated as hedges as required in order to apply hedge accounting. There were no open foreign exchange contracts at December 31, 2014.
Dividends
The Board of Directors declared a dividend of $0.025 per share payable on February 15, 2013, a dividend of $0.03125 per share payable on May 15, 2013, August 15, 2013 and November 15, 2013 and a dividend of $0.0375 payable on February 14, 2014, May 15, 2014, August 15, 2014, November 14, 2014 and February 13, 2015.
Operating activities
Net cash provided by operating activities was $4.6 million in 2014 compared to $35.8 million in 2013 and $22.7 million in 2012. The decrease was primarily attributable to an increase in accounts receivable and an increase in payments of accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities.
44
Table of Contents
Investing activities
Net cash used in investing activities was $72.2 million in 2014 compared to $3.8 million in 2013 and $22.2 million in 2012. In 2014 investing activities primarily related to the cash consideration paid in the 2014 acquisition of Kitchen Craft. In 2012 investing activities principally related to the cash consideration of $14.5 million paid in the acquisition of Fred® and Friends and the cash consideration of $2.6 million for the investment in GSI. No such investing activities occurred in 2013.
Financing activities
Net cash provided by financing activities was $67.8 million in 2014 compared to cash used in financing activities of $29.0 million in 2013 and $2.2 million in 2012. The Company had net borrowings of $43.9 million under its Revolving Credit Facility in 2014, compared to net repayments of $11.7 million in 2013 and net borrowings of $3.3 million in 2012. The proceeds from the 2014 borrowings were principally used to finance the 2014 acquisition of Kitchen Craft. The proceeds from the 2012 borrowings were principally used to finance a portion of the Fred® & Friends acquisition. Additionally, a portion of the Company’s 2013 borrowings were used to repurchased 245,575 shares under the 2013 stock repurchase program for a total cost of $3.2 million.
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS
As of December 31, 2014, the Company’s contractual obligations were as follows (in thousands):
| Payment due by period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Less than | 1-3 years | 3-5 years | More than | ||||||||||||||||
| 1 year | 5 years | |||||||||||||||||||
| Operating leases |
$ | 109,250 | $ | 15,976 | $ | 27,489 | $ | 15,201 | $ | 50,584 | ||||||||||
| Short-term debt |
10,765 | 10,765 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
130,203 | — | 78,552 | 51,651 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Interest on debt |
13,553 | 4,833 | 6,605 | 2,115 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Minimum royalty payments |
17,709 | 8,632 | 4,659 | 3,822 | 596 | |||||||||||||||
| Post retirement benefits |
6,230 | 376 | 912 | 1,327 | 3,615 | |||||||||||||||
| Contingent consideration (1) |
3,286 | — | 3,270 | 16 | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 290,996 | $ | 40,582 | $ | 121,487 | $ | 74,132 | $ | 54,795 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | Reported amounts reflect the present value of contingent payment obligations in connection with certain acquisition. |
45
Table of Contents
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk |
Market risk represents the risk of loss that may impact the consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows of the Company. The Company is exposed to market risk associated with changes in interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates. The Company believes it has moderate exposure to these risks. The Company assesses market risk based on changes in interest rates and foreign currency exchange rates utilizing a sensitivity analysis that measures the potential loss in earnings and cash flows based on a hypothetical 10% or 100 basis point change in these rates.
The Company’s functional currency is the U.S. Dollar. The Company has foreign operations through its acquisitions, investments and strategic alliances in the United Kingdom, Mexico, Canada, Brazil, Hong Kong and China; therefore, the Company is subject to increases and decreases in its investments resulting from the impact of fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates. Additional transactions exposing the company to exchange rate risk include sales, certain inventory purchases and operating expenses. Through its subsidiaries, including the January 2014 acquisition of Kitchen Craft as described in Note B of the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements included in Item 15 of this Annual Report, portions of the Company’s cash, trade accounts receivable and trade accounts payable are denominated in foreign currencies. For the year ended December 31, 2014, approximately 18% of the Company’s net sales revenue was in foreign currencies, compared to 10% for the year ended December 31, 2013. These sales were primarily denominated in British Pounds, Euro and Canadian Dollars. The increase in foreign currency sales revenue primarily relates to the acquisition of Kitchen Craft. The Company makes most of its inventory purchases from the Far East and uses the U.S. Dollar for such purchases. In the Company’s consolidated statements of operations, foreign exchange gains and losses are recognized in SG&A expense. A hypothetical 10% change in exchange rates, with U.S. Dollar as the functional and reporting currency, would result in an approximately $2.0 million increase in SG&A expense.
In 2014, the Company entered into certain foreign exchange contracts, primarily to offset the earnings impact related to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates associated with inventory purchases denominated in foreign currencies. Included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statement of operations is a gain of $0.7 million related to these foreign exchange derivative contracts. There were no open foreign exchange contracts at December 31, 2014.
The Company’s Revolving Credit Facility and Term Loan, provided for under the Credit Agreement bear interest at variable rates. The Credit Agreement provides for interest rates linked to one of Adjusted LIBO, Prime Rate or Federal Funds Rate; and, therefore, the Company is subject to increases and decreases in interest expense resulting from fluctuations in interest rates. The Company entered into an interest rate swap agreement in August 2012 to manage interest rate exposure in connection with its variable interest rate borrowings. As of December 31, 2014, approximately $113.0 million of the Company’s debt carries a variable rate of interest, as compared to $40.1 million at December 31, 2013. The increase of variable rate interest borrowings primarily arose out of the refinancing of the Company’s existing debt and entry into the Credit Agreement in January 2014. The remainder of the debt at December 31, 2014 (approximately $25.4 million) carries a fixed rate of interest either by the rate itself being fixed or through the use of interest rate swaps. A hypothetical and instantaneous 100 basis point increase in the Company’s variable interest rates would increase interest expense by approximately $1.5 million over a twelve month period.
The sensitivity analysis above assumes interest rate changes are instantaneous, parallel shifts in the yield curve.
The Company is a party to interest rate swap agreements with an aggregate notional amount of $25.4 million to manage interest rate exposure in connection with its variable interest rate borrowings. The hedge periods in these agreements commenced in March 2013 and will expire in September 2018.
Interest rate swaps expose the Company to counterparty credit risk for nonperformance. The Company manages its exposure to counterparty credit risk by dealing with counterparties who are international financial institutions with investment grade credit ratings. Although the Company’s credit risk is the replacement cost at the estimated fair value of these instruments, the Company believes that the risk of incurring credit risk losses as a result of counterparty nonperformance is remote.
The Company does not enter into derivative financial instruments for trading purposes.
46
Table of Contents
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
The Company’s Consolidated Financial Statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2014 in Item 15 commencing on page F-1 are incorporated herein by reference.
The following tables set forth certain unaudited consolidated quarterly statement of operations data for the eight quarters ended December 31, 2014. This information is unaudited, but in the opinion of management, it has been prepared substantially on the same basis as the audited consolidated financial statements appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K and all necessary adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, have been included in the amounts stated below to present fairly the unaudited consolidated quarterly results of operations. The consolidated quarterly data should be read in conjunction with the Company’s audited consolidated financial statements and the notes to such statements appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report. The results of operations for any quarter are not necessarily indicative of the results of operations for any future period:
| Year ended December 31, 2014 | ||||||||||||||||
| First quarter |
Second quarter |
Third quarter |
Fourth quarter |
|||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 118,411 | $ | 115,321 | $ | 162,244 | $ | 190,034 | ||||||||
| Gross margin |
44,332 | 40,852 | 57,923 | 69,774 | ||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(2,197 | ) | (3,157 | ) | 8,428 | 18,310 | ||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
(2,929 | ) | (3,202 | ) | (1,586 | ) | 9,261 | |||||||||
| Basic income (loss) per common share |
(0.22 | ) | (0.24 | ) | (0.12 | ) | 0.68 | |||||||||
| Diluted income (loss) per common share |
(0.22 | ) | (0.24 | ) | (0.12 | ) | 0.66 | |||||||||
|
Year ended December 31, 2013 |
||||||||||||||||
| First quarter |
Second quarter |
Third quarter |
Fourth quarter(1) |
|||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 98,657 | $ | 96,976 | $ | 142,229 | $ | 164,859 | ||||||||
| Gross margin |
36,312 | 36,356 | 51,277 | 63,317 | ||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(115 | ) | 12 | 11,693 | 16,596 | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
(632 | ) | (568 | ) | 1,093 | 9,388 | ||||||||||
| Basic income (loss) per common share |
(0.05 | ) | (0.04 | ) | 0.09 | 0.73 | ||||||||||
| Diluted income (loss) per common share |
(0.05 | ) | (0.04 | ) | 0.08 | 0.72 | ||||||||||
Note:
| (1) | The fourth quarter December 31, 2013 reflects a non-operating adjustment of $1,053 to reduce accounts receivable for previously issued credits with respect to the Retail Direct business which related to 2010 and earlier periods. |
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None
47
Table of Contents
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
The Chief Executive Officer and the Chief Financial Officer of the Company (its principal executive officer and principal financial officer, respectively) have concluded, based on their evaluation as of December 31, 2014, that the Company’s controls and procedures are effective to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the Company in the reports filed by it under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms, and include controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the Company in such reports is accumulated and communicated to the Company’s management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer of the Company, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Changes in Internal Controls
On January 15, 2014, the Company acquired 100% of the share capital of Kitchen Craft. The Company has begun to integrate policies, processes, people, technology and operations of Kitchen Craft with those of the Company and is evaluating and will continue to evaluate the impact of any changes to internal control over financial reporting. Except for any changes in internal controls related to the integration of Kitchen Craft into the post-acquisition combined company, during the quarter ended on December 31, 2014, there has been no change in the Company’s internal control over financial reporting that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management of the Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for performing an assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. Internal control over financial reporting is defined in Rule 13a-15(f) or 15d-15(f) promulgated under the Exchange Act as a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the Company’s principle executive and principal financial officers and effected by the Company’s Board of Directors, management and other personnel, to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that:
| • | Pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; |
| • | Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit the preparation of financial statements in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and |
| • | Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
All internal control systems, no matter how well designed, have inherent limitations. Because of the inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions or the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate. Accordingly, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation.
Management performed an assessment of the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014 using the criteria set forth in the Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework). Based on this assessment, management has determined that the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014 is effective.
Management’s assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of disclosure controls and procedures and internal controls over financial reporting did not include the internal controls related to the operations acquired in the 2014
48
Table of Contents
acquisition of Kitchen Craft which is included in the Company’s 2014 consolidated financial statements and constituted total and net assets of $38.1 million and $30.9 million, respectively as of December 31, 2014 and $67.6 million and $8.7 million, respectively, of net revenues and income from operations for the year then ended.
The effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014 has been audited by Ernst & Young LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, as stated in their report.
49
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Lifetime Brands, Inc.
We have audited Lifetime Brands, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework) (the COSO criteria). Lifetime Brands, Inc.’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
As indicated in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting, management’s assessment of and conclusion on the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting did not include the internal controls of Kitchen Craft, which is included in the 2014 consolidated financial statements of Lifetime Brands, Inc. and constituted $38.1 million and $30.9 million of total and net assets, respectively, as of December 31, 2014 and $67.6 million and $7.6 million of revenues and net income, respectively, for the year then ended. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting of Lifetime Brands, Inc. also did not include an evaluation of the internal control over financial reporting of Kitchen Craft.
In our opinion, Lifetime Brands, Inc. maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014 based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of Lifetime Brands, Inc. as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive (loss) income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014 of Lifetime Brands, Inc. and our report dated March 16, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ ERNST & YOUNG LLP
Jericho, New York
March 16, 2015
50
Table of Contents
| Item 9B. | Other Information |
Not applicable.
The information required under these items is contained in the Company’s 2015 Proxy Statement, which will be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the close of the Company’s fiscal year covered by this Annual Report on Form 10-K and is incorporated herein by reference.
51
Table of Contents
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
| (a) | See Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedule on page F-1. |
| (b) | Exhibits*: |
| Exhibit No. |
Description | |
| 3.1 | Second Restated Certificate of Incorporation of the Company (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.2 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2005) | |
| 3.2 | Amended and Restated By-Laws of the Company (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 3.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed on June 10, 2014) | |
| 4.1 | Indenture dated as of June 27, 2006, Lifetime Brands, Inc. as issuer, and HSBC Bank USA, National Association as trustee, $75,000,000 4.75% Convertible Senior Notes due 2011 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 4.2 to Amendment No. 1 to the Registrant’s registration statement No. 333-137575 on Form S-3) | |
| 10.1 | License Agreement dated December 14, 1989 between the Company and Farberware, Inc. (incorporated by reference to the Registrant’s registration statement No. 33-40154 on Form S-1) | |
| 10.2 | Evan Miller employment agreement dated July 1, 2003 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.41 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2003)* | |
| 10.3 | Evan Miller Amendment of Employment Agreement dated June 29, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 3, 2007)* | |
| 10.4 | Employment Agreement, dated March 4, 2011, by and between Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Jeffrey Siegel (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 8, 2011)* | |
| 10.5 | First Amendment to Employment Agreement, dated April 30, 2012, between Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Jeffrey Siegel (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed April 30, 2012)* | |
| 10.6 | Employment Agreement, dated March 12, 2014, by and between Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Jeffrey Siegel (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 18, 2014)* | |
| 10.7 | Lease Agreement dated as of May 10, 2006 between AG Metropolitan Endo, L.L.C and Lifetime Brands, Inc. for the property located at 1000 Stewart Avenue in Garden City, New York (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant’s Current Reports on Form 8-K filed May 15, 2006) | |
| 10.8 | First Amendment to the Lease Agreement dated as of May 10, 2006 between AG Metropolitan Endo, L.L.C and Lifetime Brands, Inc. for the property located at 1000 Stewart Avenue in Garden City, New York (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2006) | |
| 10.9 | Amended 2000 Long-Term Incentive Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 9, 2006)* | |
| 10.10 | Amendment to the Lifetime Brands, Inc. 2000 Long-Term Incentive Plan dated November 1, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 5, 2007)* | |
52
Table of Contents
| 10.11 | Amendment of the Lifetime Brands, Inc. 2000 Long-Term Incentive Plan dated June 11, 2009 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 12, 2009)* | |
| 10.12 | Amendment of the Lifetime Brands, Inc. 2000 Long-Term Incentive Plan dated June 13, 2012 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 15, 2012)* | |
| 10.13 | Amended 2000 Incentive Bonus Compensation Plan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 9, 2006)* | |
| 10.14 | Employment Agreement dated June 28, 2007 between Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Laurence Winoker (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 3, 2007)* | |
| 10.15 | Amendment to Employment Agreement, dated March 8, 2010, between Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Laurence Winoker (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 10, 2010)* | |
| 10.16 | Amendment of Employment Agreement, dated April 12, 2012, between Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Laurence Winoker (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed April 16, 2012)* | |
| 10.17 | Shares Subscription Agreement by and among Lifetime Brands, Inc., Ekco, S.A.B. and Mr. José Ramón Elizondo Anaya and Mr. Miguel Ángel Huerta Pando, dated as of June 8, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 11, 2007) | |
| 10.18 | Amendment No.1 dated September 5, 2007 to the Shares Subscription Agreement by and among Lifetime Brands, Inc., Ekco, S.A.B. and Mr. José Ramón Elizondo Anaya and Mr. Miguel Ángel Huerta Pando, dated as of June 8, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.17 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008) | |
| 10.19 | Amendment No. 2 dated September 25, 2008 to the Shares Subscription Agreement by and among Lifetime Brands, Inc., Ekco, S.A.B. and Mr. José Ramón Elizondo Anaya and Mr. Miguel Ángel Huerta Pando, dated as of June 8, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.21 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008) | |
| 10.20 | Lease Agreement between Granite Sierra Park LP and Lifetime Brands, Inc. dated June 29, 2007 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed July 6, 2007) | |
| 10.21 | Asset Purchase Agreement between Mikasa, Inc. and Lifetime Brands, Inc. dated June, 6 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant’s Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2008) | |
| 10.22 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement, dated August 10, 2009 by and between Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Ronald Shiftan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed August 12, 2009)* | |
| 10.23 | Amendment of Amended and Restated Employment Agreement, dated November 9, 2010, by and between Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Ronald Shiftan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.33 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010)* | |
| 10.24 | Second Amended and Restated Employment Agreement, dated as of December 20, 2012, by and between Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Ronald Shiftan (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 21, 2012)* | |
| 10.25 | Credit Agreement, dated as of June 9, 2010, among Lifetime Brands, Inc., JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as administrative agent and a co-collateral agent, and HSBC Business Credit (USA) Inc., as syndication agent and a co-collateral agent, with exhibits (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.3 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2013) | |
53
Table of Contents
| 10.26 | Second Lien Credit Agreement, dated as of June 9, 2010, among Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Citibank, N.A., as administrative agent and collateral agent, with exhibits (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 15, 2010) | |
| 10.27 | Amendment No. 1 to the Second Lien Credit Agreement, dated as of March 9, 2011, among Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Citibank, N.A., as administrative agent and collateral agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.34 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2010) | |
| 10.28 | Amendment No. 2 of the Second Lien Credit Agreement, dated as of October 28, 2011, by and among Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Citibank, N.A., as administrative agent and collateral agent, with exhibits (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 3, 2011) | |
| 10.29 | Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of October 28, 2011, by and among Lifetime Brands, Inc., the Foreign Subsidiary Borrowers parties thereto, the Other Loan Parties hereto, the Lenders party hereto, JP Morgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent and a Co-Collateral Agent, and HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as Syndication Agent and a Co-Collateral Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.4 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2013) | |
| 10.30 | Share Purchase Agreement, dated November 4, 2011, by and among Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Creative Tops Holding Limited and Creative Tops Far East Limited (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed November 8, 2011) | |
| 10.31 | Senior Secured Credit Agreement, dated as of July 27, 2012, among Lifetime Brands, Inc., the Subsidiary Guarantors, the Lenders and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent and Collateral Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.6 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September 30, 2013) | |
| 10.32 | Amendment No. 1 to the Senior Secured Credit Agreement, dated as of November 13, 2012, among Lifetime Brands, Inc., the Subsidiary Guarantors party thereto, the Swap Agreement Counterparty, the financial institutions party thereto and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.3 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 27, 2013) | |
| 10.33 | Amendment No. 2 to the Senior Secured Credit Agreement, dated as of June 21, 2013, among Lifetime Brands, Inc., the Subsidiary Guarantors party thereto, the financial institutions party thereto and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed June 27, 2013) | |
| 10.34 | Share Purchase Agreement, dated January 15, 2014, relating to Thomas Plant (Birmingham) Limited (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.2 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 17, 2014) | |
| 10.35 | Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of January 13, 2014, among Lifetime Brands, Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiary Guarantors Party Thereto, as Subsidiary Guarantors, the Lenders Party Thereto and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent and a Co-Collateral Agent, and HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as Syndication Agent and a Co-Collateral Agent, with exhibits. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.3 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed January 17, 2014) | |
| 10.36 | Amendment No. 1 to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of September 23, 2014 among Lifetime Brands, Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiary Guarantors Party Thereto, as Subsidiary Guarantors, the Lenders Party Thereto and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent and a Co-Collateral Agent, and HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as Syndication Agent and a Co-Collateral Agent. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed September 26, 2014) | |
54
Table of Contents
| 10.37 | Amendment No. 2 to the Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement, dated as of February 17, 2015 among Lifetime Brands, Inc., as Borrower, the Subsidiary Guarantors Party Thereto, as Subsidiary Guarantors, The Lenders Party Thereto and JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Administrative Agent and a Co-Collateral Agent, and HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as Syndication Agent and a Co-Collateral Agent. (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed February 23, 2015) | |
| 10.38 | Employment Agreement, dated November 28, 2014, by and between Lifetime Brands, Inc. and Daniel Siegel (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 10.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed December 3, 2014)* | |
| 14.1 | Code of Ethics dated February 28, 2013 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 14.1 to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K filed March 6, 2013) | |
| 18.1 | Letter from Ernst & Young LLP stating an acceptable change in accounting method for the impairment of goodwill dated October 28, 2008 (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 18 to the Registrant’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended September, 30 2008) | |
| 21.1 | Subsidiaries of the registrant | |
| 23.1 | Consent of Ernst & Young LLP | |
| 23.2 | Consent of KPMG Cardenas Dosal, S. C. (Mexico) | |
| 31.1 | Certification by Jeffrey Siegel, Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors, pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| 31.2 | Certification by Laurence Winoker, Senior Vice President – Finance, Treasurer and Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| 32.1 | Certification by Jeffrey Siegel, Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board of Directors, and Laurence Winoker, Senior Vice President – Finance, Treasurer and Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 | |
| 99.1 | Grupo Vasconia, S.A.B. (formerly Ekco, S.A.B.), Report of Independent Registered Accounting Firm | |
| 99.2 | Grupo Vasconia, S.A.B. (formerly Ekco, S.A.B.), separate financial statements and Report of Independent Registered Accounting Firm (incorporated by reference to Exhibit 99.1 to the Registrant’s Annual Report on Form 10-K/A for the year ended December 31, 2013) | |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document | |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema Document | |
| 101.DEF | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase Document | |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase Document | |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Labels Linkbase Document | |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase Document | |
Notes to exhibits:
The Company will furnish a copy of any of the exhibits listed above upon payment of $5.00 per exhibit to cover the cost of the Company furnishing the exhibit.
| * | Compensatory plans in which the directors and executive officers of the Company participate. |
| (c) | Financial Statement Schedules — the response to this portion of Item 15 is submitted as a separate section of this Annual Report. |
55
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| Lifetime Brands, Inc. |
| /s/ Jeffrey Siegel |
| Jeffrey Siegel |
| Chairman of the Board of Directors, |
| Chief Executive Officer and Director |
| Date: March 16, 2015 |
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature | Title | Date | ||
| /s/ Jeffrey Siegel Jeffrey Siegel |
Chairman of the Board of Directors, Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) |
March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Ronald Shiftan Ronald Shiftan |
Vice Chairman of the Board of Directors, Chief Operating Officer and Director |
March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Laurence Winoker Laurence Winoker |
Senior Vice President – Finance, Treasurer and Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ David Dangoor David Dangoor |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Michael Jeary Michael Jeary |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ John Koegel John Koegel |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Cherrie Nanninga Cherrie Nanninga |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Craig Phillips Craig Phillips |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Dennis Reaves Dennis Reaves |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Michael Regan Michael Regan |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ William Westerfield William Westerfield |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
56
Table of Contents
| Item 15 |
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
LIST OF FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULE
The following consolidated financial statements of Lifetime Brands, Inc. are filed as part of this Annual Report under Item 8 – Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
The following consolidated financial statement schedule of Lifetime Brands, Inc. required pursuant to Item 15(a) is submitted herewith:
| S-1 |
All other financial schedules are not required under the related instructions or are inapplicable, and therefore have been omitted.
The unaudited supplementary data regarding quarterly results of operations are incorporated by reference to the information set forth in Item 8 – Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
F-1
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Lifetime Brands, Inc.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Lifetime Brands, Inc. (the “Company”) as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations, comprehensive (loss) income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the Index at Item 15(a). These financial statements and schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and schedule based on our audits. We did not audit the consolidated financial statements of Grupo Vasconia, S.A.B. and Subsidiaries, a corporation in which the Company has a 30% interest. In the consolidated financial statements, the Company’s investment in Grupo Vasconia, S.A.B. and Subsidiaries is stated at $27.8 million and $30.5 million at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, and the Company’s equity in the net income (loss) of Grupo Vasconia, S.A.B. and Subsidiaries is stated at $0.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, ($4.0) million for the year ended December 31, 2013 and $6.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2012. Those statements were audited by other auditors whose report has been furnished to us, and our opinion, insofar as it relates to the amounts included for Grupo Vasconia, S.A.B. and Subsidiaries, is based solely on the report of the other auditors.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits and the report of other auditors provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, based on our audits and the report of other auditors, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of Lifetime Brands, Inc. at December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the consolidated results of its operations and its cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also, in our opinion, the related financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly in all material respects the information set forth therein.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), Lifetime Brands, Inc.’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014, based on criteria established in Internal Control – Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (1992 framework) and our report dated March 16, 2015 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ ERNST & YOUNG LLP
Jericho, New York
March 16, 2015
F-2
Table of Contents
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(in thousands-except share data)
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| ASSETS |
||||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 5,068 | $ | 4,947 | ||||
| Accounts receivable, less allowances of $6,663 at December 31, 2014 and $5,209 at December 31, 2013 |
107,211 | 87,217 | ||||||
| Inventory (Note M) |
137,924 | 112,791 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
7,914 | 5,781 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes (Note I) |
— | 3,940 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| TOTAL CURRENT ASSETS |
258,117 | 214,676 | ||||||
| PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, net (Note M) |
26,801 | 27,698 | ||||||
| INVESTMENTS (Note C) |
28,155 | 36,948 | ||||||
| INTANGIBLE ASSETS, net (Note D) |
103,597 | 55,149 | ||||||
| OTHER ASSETS |
4,732 | 2,268 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| TOTAL ASSETS |
$ | 421,402 | $ | 336,739 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
||||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES |
||||||||
| Current maturity of Credit Agreement Term Loan (Note E) |
$ | 10,000 | $ | — | ||||
| Current maturity of Senior Secured Term Loan (Note E) |
— | 3,937 | ||||||
| Short term loan (Note E) |
765 | — | ||||||
| Accounts payable |
28,694 | 21,426 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses (Note M) |
36,961 | 41,095 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes (Note I) |
2,293 | — | ||||||
| Income taxes payable (Note I) |
5,156 | 3,036 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| TOTAL CURRENT LIABILITIES |
83,869 | 69,494 | ||||||
| DEFERRED RENT & OTHER LONG-TERM LIABILITIES (Note M) |
20,160 | 18,644 | ||||||
| DEFERRED INCOME TAXES (Note I) |
1,485 | 1,777 | ||||||
| REVOLVING CREDIT FACILITY (Note E) |
92,655 | 49,231 | ||||||
| CREDIT AGREEMENT TERM LOAN (Note E) |
35,000 | — | ||||||
| SENIOR SECURED TERM LOAN (Note E) |
— | 16,688 | ||||||
| STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
||||||||
| Preferred stock, $.01 par value, shares authorized: 100 shares of Series A and 2,000,000 shares of Series B; none issued and outstanding |
— | — | ||||||
| Common stock, $.01 par value, shares authorized: 25,000,000; shares issued and outstanding: 13,712,081 at December 31, 2014 and 12,777,407 at December 31, 2013 |
137 | 128 | ||||||
| Paid-in capital |
160,315 | 146,273 | ||||||
| Retained earnings |
37,703 | 38,224 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss (Note M) |
(9,922 | ) | (3,720 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| TOTAL STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
188,233 | 180,905 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
$ | 421,402 | $ | 336,739 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-3
Table of Contents
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
(in thousands – except per share data)
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 586,010 | $ | 502,721 | $ | 486,842 | ||||||
| Cost of sales |
373,129 | 315,459 | 310,054 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross margin |
212,881 | 187,262 | 176,788 | |||||||||
| Distribution expenses |
54,202 | 44,364 | 44,046 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
133,786 | 114,345 | 104,338 | |||||||||
| Intangible asset impairment (Note D) |
3,384 | — | 1,069 | |||||||||
| Restructuring expenses |
125 | 367 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income from operations |
21,384 | 28,186 | 27,335 | |||||||||
| Interest expense (Note E) |
(6,418 | ) | (4,847 | ) | (5,898 | ) | ||||||
| Financing expense |
(758 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Loss on early retirement of debt (Note E) |
(346 | ) | (102 | ) | (1,363 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income before income taxes and equity in earnings |
13,862 | 23,237 | 20,074 | |||||||||
| Income tax provision (Note I) |
(5,825 | ) | (9,175 | ) | (5,208 | ) | ||||||
| Equity in (losses) earnings, net of taxes (Note C) |
(6,493 | ) | (4,781 | ) | 6,081 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| NET INCOME |
$ | 1,544 | $ | 9,281 | $ | 20,947 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| BASIC INCOME PER COMMON SHARE (NOTE H) |
$ | 0.11 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 1.67 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| DILUTED INCOME PER COMMON SHARE (NOTE H) |
$ | 0.11 | $ | 0.71 | $ | 1.64 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-4
Table of Contents
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF COMPREHENSIVE (LOSS) INCOME
(in thousands)
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 1,544 | $ | 9,281 | $ | 20,947 | ||||||
| Other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax: |
||||||||||||
| Translation adjustment (Note M) |
(4,736 | ) | (140 | ) | 3,077 | |||||||
| Deferred gains (losses) on cash flow hedges (Notes F & M): |
||||||||||||
| Fair value adjustment, net of tax of $9 in 2014 and tax benefit of $160 in 2013 |
13 | 241 | (272 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total deferred gains (losses) on cash flow hedges |
13 | 241 | (272 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effect of retirement benefit obligations (Note M): |
||||||||||||
| Net (loss) income arising from retirement benefit obligations, net of tax of ($589) in 2014 and $241 in 2013 |
(1,507 | ) | 361 | (1,187 | ) | |||||||
| Less: amortization of loss included in net income, net of tax of $19 in 2014 and $36 in 2013 |
28 | 54 | 27 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total effects of retirement benefit obligations |
(1,479 | ) | 415 | (1,160 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Other comprehensive (loss) income, net of tax |
(6,202 | ) | 516 | 1,645 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Comprehensive (loss) income |
$ | (4,658 | ) | $ | 9,797 | $ | 22,592 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-5
Table of Contents
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(in thousands)
| Common stock | Paid-in | Retained | Accumulated other comprehensive |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | capital | earnings | loss | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2011 |
12,431 | 124 | 137,467 | 14,465 | (5,881 | ) | 146,175 | |||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | 20,947 | — | 20,947 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustment |
— | — | — | — | 3,077 | 3,077 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Derivative fair value adjustment (Note F) |
— | — | — | — | (272 | ) | (272 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Effect of retirement benefit obligations |
— | — | — | — | (1,160 | ) | (1,160 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income |
22,592 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued to directors (Note G) |
23 | — | 267 | — | — | 267 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense (Note G) |
— | — | 2,526 | — | — | 2,526 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of 143,568 shares of common stock for acquisition of Fred® & Friends (Note B) |
144 | 1 | 1,506 | — | — | 1,507 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit on exercise of stock options |
— | — | 150 | — | — | 150 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options |
156 | 3 | 573 | — | — | 576 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends (Note G) |
— | — | — | (1,563 | ) | — | (1,563 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2012 |
12,754 | 128 | 142,489 | 33,849 | (4,236 | ) | 172,230 | |||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | 9,281 | — | 9,281 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustment |
— | — | — | — | (140 | ) | (140 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Derivative fair value adjustment (Note F) |
— | — | — | — | 241 | 241 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Effect of retirement benefit obligations |
— | — | — | — | 415 | 415 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income |
9,797 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued to directors (Note G) |
21 | — | 277 | — | — | 277 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense (Note G) |
— | — | 2,604 | — | — | 2,604 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Reduction of tax benefit from stock options, net |
— | — | (310 | ) | — | — | (310 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options |
248 | 2 | 1,213 | — | — | 1,215 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury Stock Repurchase |
(246 | ) | (2 | ) | — | (3,227 | ) | — | (3,229 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Dividends (Note G) |
— | — | — | (1,679 | ) | — | (1,679 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2013 |
12,777 | $ | 128 | $ | 146,273 | $ | 38,224 | $ | (3,720 | ) | $ | 180,905 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | 1,544 | — | 1,544 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Translation adjustment |
— | — | — | — | (4,736 | ) | (4,736 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Derivative fair value adjustment (Note F) |
— | — | — | — | 13 | 13 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Effect of retirement benefit obligations |
— | — | — | — | (1,479 | ) | (1,479 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss |
(4,658 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued to directors (Note G) |
23 | — | 344 | — | — | 344 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued to employee (Note G) |
5 | — | 2 | — | — | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock compensation expense (Note G) |
— | — | 2,489 | — | — | 2,489 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of 581,432 shares of common stock for acquisition of Kitchen Craft (Note B) |
581 | 6 | 8,376 | — | — | 8,382 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Tax provision on exercise of stock options |
— | — | 343 | — | — | 343 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options |
326 | 3 | 2,488 | — | — | 2,491 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Dividends (Note G) |
— | — | — | (2,065 | ) | — | (2,065 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| BALANCE AT DECEMBER 31, 2014 |
13,712 | $ | 137 | $ | 160,315 | $ | 37,703 | $ | (9,922 | ) | $ | 188,233 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements.
F-6
Table of Contents
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(in thousands)
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 1,544 | $ | 9,281 | $ | 20,947 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Provision for doubtful accounts |
286 | 139 | 123 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
14,200 | 10,415 | 9,324 | |||||||||
| Amortization of financing costs |
617 | 528 | 649 | |||||||||
| Deferred rent |
(722 | ) | (962 | ) | (668 | ) | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
(3,757 | ) | (2,275 | ) | (3,011 | ) | ||||||
| Stock compensation expense |
4,493 | 2,881 | 2,793 | |||||||||
| Undistributed equity losses (earnings) |
6,724 | 5,354 | (5,665 | ) | ||||||||
| Intangible asset impairment (Note D) |
3,384 | — | 1,069 | |||||||||
| Loss on early retirement of debt (Note E) |
346 | 102 | 1,363 | |||||||||
| Contingent consideration fair value adjustment |
(4,203 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities (excluding the effects of business acquisitions) |
||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable |
(6,209 | ) | 10,099 | (14,741 | ) | |||||||
| Inventory |
(6,354 | ) | (8,207 | ) | 9,694 | |||||||
| Prepaid expenses, other current assets and other assets |
(2,063 | ) | (449 | ) | (529 | ) | ||||||
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities |
(950 | ) | 9,437 | (166 | ) | |||||||
| Income taxes payable |
(2,747 | ) | (579 | ) | 1,515 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| NET CASH PROVIDED BY OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
4,589 | 35,764 | 22,697 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
||||||||||||
| Purchases of property and equipment |
(6,171 | ) | (3,842 | ) | (4,955 | ) | ||||||
| Equity investments |
(764 | ) | — | (2,765 | ) | |||||||
| Kitchen Craft acquisition, net of cash acquired |
(59,977 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Other acquisitions, net of cash acquired |
(5,389 | ) | — | (14,500 | ) | |||||||
| Net proceeds from sale of property |
68 | 11 | 27 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| NET CASH USED IN INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
(72,233 | ) | (3,831 | ) | (22,193 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from Revolving Credit Facility (Note E) |
278,014 | 220,222 | 183,600 | |||||||||
| Repayments from Revolving Credit Facility (Note E) |
(234,067 | ) | (231,959 | ) | (180,257 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from Senior Secured Term Loan (Note E) |
— | — | 35,000 | |||||||||
| Repayments of Senior Secured Term Loan (Note E) |
(20,625 | ) | (14,375 | ) | — | |||||||
| Repayments of Term Loan (Note E) |
— | — | (40,000 | ) | ||||||||
| Proceeds from Credit Agreement Term Loan (Note E) |
50,000 | — | — | |||||||||
| Repayments of Credit Agreement Term Loan (Note E) |
(5,000 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Proceeds from Short Term Loan (Note E) |
1,645 | — | — | |||||||||
| Payments from Short Term Loan (Note E) |
(880 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Payments for stock repurchase |
— | (3,229 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Payment of financing costs |
(2,283 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Cash dividends paid (Note G) |
(2,031 | ) | (1,515 | ) | (1,249 | ) | ||||||
| Proceeds from the exercise of stock options |
2,488 | 1,215 | 577 | |||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from stock options |
553 | 613 | 150 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| NET CASH PROVIDED BY (USED IN) FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
67,814 | (29,028 | ) | (2,179 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effect of foreign exchange on cash |
(49 | ) | 171 | 574 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| INCREASE (DECREASE) IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
121 | 3,076 | (1,101 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
4,947 | 1,871 | 2,972 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS AT END OF YEAR |
$ | 5,068 | $ | 4,947 | $ | 1,871 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
See notes to consolidated financial statements
F-7
Table of Contents
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
NOTE A — SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Organization and business
Lifetime Brands, Inc. (the “Company”) designs, sources and sells branded kitchenware, tableware and other products used in the home and markets its products under a number of brand names and trademarks, which are either owned or licensed by the Company or through retailers’ private labels. The Company markets and sells its products principally on a wholesale basis to retailers. The Company also markets and sells a limited selection of its products directly to consumers through its Pfaltzgraff®, Mikasa®, Fred® and Friends, Built NY®, Lifetime Sterling® and The English Table Internet websites.
Basis of Presentation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (“U.S. GAAP”) for financial information and with the instructions to Form 10-K.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include estimates and assumptions relating to the reporting of assets and liabilities and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities to prepare these financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP. The most significant of these estimates and assumptions relate to revenue recognition, allowances for doubtful accounts, reserves for sales returns and allowances and customer chargebacks, inventory mark-down provisions, impairment of tangible and intangible assets, stock option expense, estimates for unpaid healthcare claims, derivative valuations, accruals related to the Company’s tax positions and tax valuation allowances. Although these and other estimates and assumptions are based on the best available information, actual results could be materially different from these estimates.
Principles of consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its subsidiaries. All intercompany accounts and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Foreign Currency
All foreign wholly-owned subsidiaries use the local currency of their respective countries as their functional currency. Assets and liabilities are translated into U.S. dollars at exchange rates prevailing at the balance sheet dates. Revenues, costs and expenses are translated into U.S. dollars at average exchange rates for the relevant period. Income and losses resulting from translation are recorded as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). Gains and losses from foreign currency transactions are recognized in selling, general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statements of operations. Foreign currency gain/loss included within selling, general and administrative expenses was a $1.4 million loss in 2014, a $258,000 loss in 2013 and a $415,000 loss in 2012.
Revenue recognition
The Company sells products wholesale, to retailers and distributors, and retail, directly to consumers. Wholesale sales and retail direct sales are recognized when title passes to the customer, which is primarily at the shipping point for wholesale sales and upon delivery to the customer for retail direct sales. Shipping and handling fees that are billed to customers in sales transactions are included in net sales and amounted to $1.4 million for each of the three years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012. Net sales exclude taxes that are collected from customers and remitted to the taxing authorities.
F-8
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
The Company offers various sales incentives and promotional programs to its customers from time to time in the normal course of business. These incentives and promotions typically include arrangements such as cooperative advertising, buydowns, volume rebates and discounts. These arrangements and an estimate of sales returns are reflected as reductions in net sales in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations.
Cost of sales
Cost of sales consist primarily of costs associated with the production and procurement of product, inbound freight costs, purchasing costs, royalties and other product procurement related charges.
Distribution expenses
Distribution expenses consist primarily of warehousing expenses and freight-out expenses. Freight-out expenses were $11.4 million, $9.0 million, and $8.5 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Handling costs of products sold are included in cost of sales.
Advertising expenses
Advertising expenses are expensed as incurred and are included in selling, general and administrative expenses. Advertising expenses were $1.6 million, $0.8 million, and $0.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively.
Accounts receivable
The Company periodically reviews the collectability of its accounts receivable and establishes allowances for estimated losses that could result from the inability of its customers to make required payments. A considerable amount of judgment is required to assess the ultimate realization of these receivables including assessing the initial and on-going creditworthiness of the Company’s customers. The Company also maintains an allowance for anticipated customer deductions. The allowances for deductions are primarily based on contracts with customers.
However, in certain cases the Company does not have a formal contract and, therefore, customer deductions are non-contractual. To evaluate the reasonableness of non-contractual customer deductions, the Company analyzes currently available information and historical trends of deductions.
Inventory
Inventory consists principally of finished goods sourced from third-party suppliers. Inventory also includes finished goods, work in process and raw materials related to the Company’s manufacture of sterling silver products. Inventory is priced using the lower of cost (first-in, first-out basis) or market method. The Company estimates the selling price of its inventory on a product by product basis based on the current selling environment. If the estimated selling price is lower than the inventory’s cost, the Company reduces the value of the inventory to its net realizable value.
Property and equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost. Property and equipment, other than leasehold improvements, is depreciated using the straight-line method over the estimated useful lives of the assets. Building and improvements are being depreciated over 30 years and machinery, furniture and equipment over periods ranging from 3 to 10 years. Leasehold improvements are amortized over the term of the lease or the estimated useful lives of the improvements, whichever is shorter. Advances paid towards the acquisition of property and equipment and the cost of property and equipment not ready for use before the end of the period are classified as construction in progress.
F-9
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Cash equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid instruments with a maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash equivalents.
Concentration of credit risk
The Company’s cash and cash equivalents are potentially subject to concentration of credit risk. The Company maintains cash with several financial institutions that, in some cases, is in excess of Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation insurance limits.
Concentrations of credit risk with respect to trade accounts receivable are limited due to the large number of entities comprising the Company’s customer base.
During the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. (including Sam’s Club and Asda Superstore, in the United Kingdom) accounted for 16%, 15%, and 16% of net sales, respectively. Sales to Wal-Mart Stores, Inc. are included in the Company’s U.S. Wholesale and International segments. No other customer accounted for 10% or more of the Company’s sales during these periods.
Fair value measurements
Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) Topic No. 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures, provides enhanced guidance for using fair value to measure assets and liabilities and establishes a common definition of fair value, provides a framework for measuring fair value under U.S. generally accepted accounting principles and expands disclosure requirements about fair value measurements. Fair value measurements included in the Company’s consolidated financial statements relate to the Company’s annual goodwill and other intangible asset impairment tests and derivatives, described in Notes D and F, respectively.
Fair value of financial instruments
The Company determined the carrying amounts of cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable are reasonable estimates of their fair values because of their short-term nature. The Company determined that the carrying amounts of borrowings outstanding under its Revolving Credit Facility and Term Loan approximate fair value since such borrowings bear interest at variable market rates.
Derivatives
The Company accounts for derivative instruments in accordance with ASC Topic No. 815, Derivatives and Hedging. ASC Topic No. 815 requires that all derivative instruments be recognized on the balance sheet at fair value as either an asset or liability. Changes in the fair value of derivatives that qualify as hedges and have been designated as part of a hedging relationship for accounting purposes have no net impact on earnings to the extent the derivative is considered highly effective in achieving offsetting changes in fair value or cash flows attributable to the risk being hedged, until the hedge item is recognized in earnings. If the derivative which is designated as part of a hedging relationship is considered ineffective in achieving offsetting changes in fair value or cash flows attributable to the risk being hedged, the changes in fair value are recorded in operations. For derivatives that do not qualify or are not designated as hedging instruments for accounting purposes, changes in fair value are recorded in operations.
F-10
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Goodwill, intangible assets and long-lived assets
Goodwill and intangible assets deemed to have indefinite lives are not amortized but, instead, are subject to an annual impairment assessment. Additionally, if events or conditions were to indicate the carrying value of a reporting unit may not be recoverable, the Company would evaluate goodwill and other intangible assets for impairment at that time. As it relates to the goodwill assessment, the Company first assesses qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount as a basis for determining whether it is necessary to perform the two-step goodwill impairment testing described in ASU Topic No. 350, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other. If, after assessing qualitative factors, the Company determines that it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, then performing the two-step impairment test is unnecessary and the Company’s goodwill is considered to be unimpaired. However, if based on the Company’s qualitative assessment it concludes that it is more likely than not that the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, or if the Company elects to bypass the qualitative assessment, the Company will proceed with performing the two-step process. The first step in the two-step process compares the carrying value of each reporting unit that has goodwill with the estimated fair value of the respective reporting unit. Should the carrying value of a reporting unit be in excess of the estimated fair value of that reporting unit, the second step must be performed. The second step represents a hypothetical purchase price allocation as if the Company had acquired the reporting unit on that date. The Company also evaluates qualitative factors to determine whether or not its indefinite lived intangibles have been impaired and then performs quantitative tests if required. These tests can include the royalty savings model or other valuation models.
Long-lived assets, including intangible assets deemed to have finite lives, are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that such amounts may have been impaired. Impairment indicators include, among other conditions, cash flow deficits, historic or anticipated declines in revenue or operating profit or material adverse changes in the business climate that indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may be impaired. When impairment indicators are present, the Company compares the carrying value of the asset to the estimated discounted future cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If the asset is considered to be impaired, the impairment to be recognized is measured by the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset.
Income taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes using the asset and liability method. Under this method, deferred tax assets and liabilities are determined based on differences between financial reporting and tax bases of assets and liabilities and are measured using the enacted tax rates and laws that are expected to be in effect when the differences are expected to reverse. The Company accounts for foreign income taxes based upon anticipated reinvestment of profits into respective foreign tax jurisdictions.
The Company applies the authoritative guidance for the financial statement recognition, measurement and disclosure of uncertain tax positions recognized in the Company’s financial statements. In accordance with this guidance, tax positions must meet a more-likely-than-not recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position. A valuation allowance is required to be established or maintained when it is “more likely than not” that all or a portion of deferred tax assets will not be realized.
Stock options
The Company measures compensation expense for all share-based compensation granted to employees and non-employee directors at fair value on the date of grant and recognizes compensation expense over the related service period for awards expected to vest. The Company uses the Black-Scholes option valuation model to estimate the fair value of its stock options. The Black-Scholes option valuation model requires the input of highly subjective assumptions including the expected stock price volatility of the Company’s common stock and the risk free interest rate.
F-11
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Employee Healthcare
The Company self-insures certain portions of its health insurance plan. The Company maintains an accrual for estimated unpaid claims and claims incurred but not yet reported (“IBNR”). Although management believes that it uses the best information available to estimate IBNR claims, actual claims may vary significantly from estimated claims.
Restructuring Expenses
Costs associated with restructuring activities are recorded at fair value when a liability has been incurred. A liability has been incurred at the point of closure for any remaining operating lease obligations and at the communication date for severance.
In May 2014, the Company commenced a plan to consolidate its customer service and call center functions and eliminated certain employee positions in connection with this consolidation. The Company recorded $125,000 of restructuring expenses during the year ended December 31, 2014 related to the execution of this plan.
In April 2013, the Company commenced a plan to close the Fred® & Friends distribution center and eliminate certain employee positions in conjunction with the closure. The Company recorded $367,000 of restructuring expenses during the year ended December 31, 2013 related to the execution of this plan. The Company does not anticipate that it will incur any further restructuring expenses related to this closure.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In July 2012, the FASB issued ASU No. 2012-02, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Testing Indefinite-Lived Intangible Assets for Impairment, which permits an entity to first assess qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount as a basis for determining whether it is necessary to perform the quantitative impairment test described in ASC Topic No. 350, Intangibles – Goodwill and Other. The amendments in this update are effective for annual and interim impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after September 15, 2012. The Company’s adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Effective January 2013, the Company adopted ASU No. 2013-02, Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Reporting of Amounts Reclassified Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income, which requires an entity to provide information about the amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by component. In addition, an entity is required to present, either on the face of the statement where net income is presented or in the notes, significant amounts reclassified out of accumulated other comprehensive income by the respective line items of net income but only if the amount reclassified is required under GAAP to be reclassified to net income in its entirety in the same reporting period. For other amounts that are not required under GAAP to be reclassified in their entirety to net income (e.g., net periodic pension benefit cost), an entity is required to cross-reference to other disclosures required under GAAP that provide additional detail about those amounts. In connection with the adoption of this standard, the Company added additional disclosure about the Company’s accumulated other comprehensive income to Note M of its financial statements.
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) 2014-09, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, to clarify the principles of recognizing revenue and create common revenue recognition guidance under U.S. GAAP and International Financial Reporting Standards. This ASU is effective for fiscal years and interim periods within those years beginning after December 15, 2016 and can be
F-12
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
adopted either retrospectively to each reporting period presented or as a cumulative effect adjustment as of the date of the adoption, with early application not permitted. The Company is currently determining its implementation approach and assessing the impact, if any, on the consolidated financial statements.
NOTE B —ACQUISITIONS
Kitchen Craft
On January 15, 2014, the Company acquired 100% of the share capital of Thomas Plant (Birmingham) Limited (“Kitchen Craft”) for cash in the amount of £37.4 million ($61.5 million) and 581,432 shares of common stock of the Company with an intrinsic value of £5.5 million ($9.0 million). The purchase price also includes contingent cash consideration of up to £5.5 million ($9.0 million) which will be payable in future years if Kitchen Craft achieves certain financial targets. Kitchen Craft is a leading supplier of kitchenware products and accessories in the United Kingdom. The assets, liabilities and operating results of Kitchen Craft are reflected in the Company’s consolidated financial statements in accordance with ASC Topic No. 805, Business Combinations, commencing from the acquisition date.
The purchase price has been determined to be as follows (in thousands):
| Cash |
$ | 61,302 | ||
| Share consideration issued(1) |
8,382 | |||
| Value of contingent consideration(2) |
2,488 | |||
| Working capital adjustment(3) |
374 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total purchase price |
$ | 72,546 | ||
|
|
|
| (1) | Share consideration issued is valued at the closing market price discounted to account for lack of marketability related to the lock up period as described in the share purchase agreement. |
| (2) | The value of contingent consideration represents the present value of the estimated payments related to the attainment of certain financial targets for the years 2014 through 2016. The maximum undiscounted contingent consideration to be paid on the agreement is £5.5 million ($9.0 million). |
| (3) | A working capital adjustment was made in May 2014 as provided for in the share purchase agreement. |
The purchase price was allocated based on the Company’s estimate of the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed, as follows (in thousands):
| Purchase Price Allocation |
||||
| Accounts Receivable (1) |
$ | 14,267 | ||
| Inventory |
17,912 | |||
| Other assets |
4,054 | |||
| Other liabilities |
(10,242 | ) | ||
| Deferred income tax |
(8,391 | ) | ||
| Goodwill and other intangibles |
54,946 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total allocated value |
$ | 72,546 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| (1) | The fair value of accounts receivable approximated the gross contractual amounts receivable. |
F-13
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Goodwill results from such factors as an assembled workforce. The total amount of goodwill is not expected to be deductible for tax purposes. All of the goodwill and other intangible assets are included in the International Segment. Customer relationships and trade names are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives (see Note D).
Kitchen Craft pension plan
Kitchen Craft is the sponsor of a defined benefit pension plan (the “Plan”) for which service costs accrual ceased prior to the acquisition. Pursuant to the share purchase agreement, the Company and the sellers agreed to take action to settle the Plan’s obligation through the purchase of a group annuity contract and terminate the Plan.
As of the acquisition closing date, the projected benefit obligation of the Plan was estimated to be £7.1 million ($11.7 million) and was fully funded pursuant to the share purchase agreement. The assumptions utilized in the measurement of the funded status at the acquisition date, including a discount rate of 3.3%, reflected Kitchen Craft’s intent to settle the Plan through the purchase of a group annuity contract.
On October 31, 2014, the Plan trustees secured, in full, all benefits payable or contingently payable under the Plan (subject to adjustment as determined by the UK pension authority in connection with its approval of the Plan’s termination) through the purchase of a group annuity contract from a major UK-based insurance company. The terms of the group annuity contract required Kitchen Craft to make an additional payment of approximately £1.5 million ($2.4 million). The share purchase agreement provides that any additional contribution required in connection with the settlement and termination of the Plan shall be offset by future amounts owed to the sellers or, if those amounts are insufficient, reimbursed by the sellers. Accordingly, there was no impact, nor is there any expected future impact, to the Company’s statement of operations in connection with the settlement and planned termination of the Plan, which is expected to occur in 2015.
The Company’s net periodic benefit cost for the year ended December 31, 2014 is described in Note L.
Unaudited pro forma results
The year ended December 31, 2014 includes the operations of Kitchen Craft for the period from January 15, 2014 to December 31, 2014. The consolidated statements of operations for the year ended December 31, 2014 includes $67.6 million of net sales and $4.1 million of income from operations contributed by Kitchen Craft.
The following table presents the Company’s pro forma consolidated net sales and income before income taxes and equity in earnings for the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. The unaudited pro forma results include the historical statements of operations information of the Company and of Kitchen Craft, giving effect to the Kitchen Craft acquisition and related financing as if they had occurred at the beginning of the period presented. As described below under “Other Acquisitions,” the Company consummated certain other acquisitions during the year ended December 31, 2014; however the Company has not included the results prior to their acquisition in these pro forma results as the impact would not have been material.
F-14
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
| Unaudited pro forma results | ||||||||
| Year ended | ||||||||
| December 31, 2014 | December 31, 2013 | |||||||
| (In thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 586,010 | $ | 567,218 | ||||
| Income before income taxes and equity in earnings |
15,760 | 26,491 | ||||||
| Net income |
2,702 | 12,031 | ||||||
| Basic earnings per common share |
0.20 | 0.90 | ||||||
| Diluted earnings per common share |
$ | 0.19 | $ | 0.88 | ||||
The pro forma results, prepared in accordance with U.S. GAAP, include the following pro forma adjustments related to the Kitchen Craft acquisition:
| (i) | the elimination of the charge in cost of sales related to the increase in fair value of acquired inventory of $0.9 million in the year ended December 31, 2014; |
| (ii) | an increase in amortization expense related to the fair value of the identifiable intangible assets of $3.4 million in the year ended December 31, 2013; |
| (iii) | the elimination of acquisition costs recorded in the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 of $1.0 million and $0.6 million, respectively; |
| (iv) | an increase in interest expense and amortization of debt issuance costs of $2.0 million, resulting from the refinancing of the Company’s debt to finance the acquisition, during the year ended December 31, 2013; and |
| (v) | an adjustment of $2.2 million in the year ended December 31, 2013 to conform compensation expense to the Company’s current compensation policies. |
The unaudited pro forma results do not include any revenue or cost reductions that may be achieved through the business combination, or the impact of non-recurring items directly related to the business combination.
The unaudited pro forma results are not necessarily indicative of the operating results that would have occurred if the Kitchen Craft acquisition had been completed as of the date for which the pro forma financial information is presented. In addition, the unaudited pro forma results do not purport to project the future consolidated operating results of the combined companies.
Other 2014 acquisitions
In February 2014, the Company acquired certain assets of Built NY, Inc. (“Built NY”), including inventory, trademarks and other intellectual property. Also in February 2014, the Company acquired certain assets of The Empire Silver Company, Inc. (“Empire Silver”), including trademarks and other intellectual property. In March 2014, the Company acquired the share capital of La Cafetière (UK) Limited, together with certain assets of other subsidiaries of The Greenfield Group Limited (collectively, “La Cafetière”). The La Cafetière acquisition included the purchase of certain trademarks and other intellectual property, and certain inventory and receivables.
In aggregate, the Company paid approximately $5.4 million of primarily cash consideration for the acquisitions of Built NY, Empire Silver and La Cafetière. The assets, liabilities and operating results of the acquisitions are reflected in the Company’s consolidated financial statements in accordance with ASC Topic No. 805, Business Combinations, commencing from the acquisition dates.
F-15
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Fred® & Friends
On December 20, 2012, the Company acquired the Fred® & Friends (“F&F”) business. F&F designs and distributes novelty housewares under the Fred® brand directly to retailers throughout the United States and Canada. The assets, liabilities and operating results of F&F have been reflected in the Company’s consolidated financial statements in accordance with ASC Topic No. 805, Business Combinations, commencing from the acquisition date and did not significantly impact the Company’s consolidated financial results for the year ended December 31, 2012.
The purchase price was comprised of the following (in thousands):
| Cash paid |
$ | 14,500 | ||
| Common stock issued |
1,507 | |||
| Value of contingent consideration |
5,370 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total purchase price |
$ | 21,377 | ||
|
|
|
The cash portion of the purchase price was funded by borrowings under the Company’s revolving credit facility. The value of contingent consideration represents the present value of estimated contingent payments of $4.0 million related to the attainment of certain gross contribution targets for the years 2013 through 2016 and the present value of the contractual holdback amount of $1.4 million, which serves as security for payments in satisfaction of any claim. The maximum undiscounted deferred and contingent consideration to be paid under the agreement is $7.7 million.
The Company assessed the fair value of the contingent consideration as of December 31, 2014 and based upon the projected attainment of certain gross contribution margin targets, a fair value adjustment to reduce the contingent consideration accrual by $4.2 million is included within Selling, general and administrative expenses for the year ended December 31, 2014.
The purchase price has been allocated based on management’s estimate of the fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed, as follows (in thousands):
| Purchase Price Allocation |
||||
| Accounts receivable(1) |
$ | 5,003 | ||
| Inventory |
3,941 | |||
| Other assets |
360 | |||
| Other liabilities |
(1,519 | ) | ||
| Goodwill and other intangibles |
13,592 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total allocated value |
$ | 21,377 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Note:
| (1) | The fair value of accounts receivable approximated the gross contractual amounts receivable. |
On the basis of estimated fair values, the excess of the purchase price over the net assets acquired of $13.6 million has been allocated as follows: $7.2 million for customer relationships, $3.9 million for trade names and $2.5 million for goodwill. The goodwill recognized results from such factors as an assembled workforce and the value of other
F-16
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
synergies expected from combining operations with the Company. The total amount of goodwill is expected to be deductible for tax purposes. All of the goodwill and other intangibles are included in the U.S. Wholesale segment. Customer relationships and trade names are amortized on a straight-line basis over their estimated useful lives (see Note D).
See Note M for amounts accrued as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 related to contingent consideration. The estimated fair value of the contingent consideration was calculated using Level 3 unobservable inputs.
NOTE C — EQUITY INVESTMENTS
The Company owns approximately 30% of the outstanding capital stock of Grupo Vasconia, S.A.B. (“Vasconia”) an integrated manufacturer of aluminum products and one of Mexico’s largest housewares companies. Shares of Vasconia’s capital stock are traded on the Bolsa Mexicana de Valores, the Mexican Stock Exchange. The Quotation Key is VASCONI. The Company accounts for its investment in Vasconia using the equity method of accounting and records its proportionate share of Vasconia’s net income in the Company’s statement of operations. Accordingly, the Company has recorded its proportionate share of Vasconia’s net income (reduced for amortization expense related to the customer relationships acquired) for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012 in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. The value of the Company’s investment balance has been translated from Mexican Pesos (“MXN”) to U.S. Dollars (“USD”) using the spot rate of MXN 14.74 and MXN 13.06 at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The Company’s proportionate share of Vasconia’s net income has been translated from MXN to USD using the average exchange rates of MXN 12.99 to 13.87, MXN 12.46 to 13.01, and MXN 12.94 to 13.51 during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. The effect of the translation of the Company’s investment resulted in a (decrease) increase of the investment of $(4.0) million, $(0.3) million, and $2.7 million during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. These translation effects are recorded in accumulated other comprehensive loss. The Company received cash dividends of $230,000, $571,000, and $416,000 from Vasconia during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Included in prepaid expenses and other current assets at December 31, 2014 is $33,000 due from Vasconia. Included within accrued expenses at December 31, 2013 is $152,000 due to Vasconia.
Summarized income statement information for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, as well as summarized balance sheet information as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, for Vasconia in USD and MXN is as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| USD | MXN | USD | MXN | USD | MXN | |||||||||||||||||||
| Income Statement |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Sales |
$ | 188,863 | $ | 2,514,294 | $ | 159,574 | $ | 2,038,200 | $ | 168,712 | $ | 2,224,256 | ||||||||||||
| Gross Profit |
35,592 | 474,482 | 28,775 | 367,944 | 38,134 | 497,413 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Income from operations |
7,790 | 103,658 | 5,438 | 70,430 | 14,614 | 192,182 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Net Income |
5,328 | 71,732 | 4,315 | 55,077 | 34,172 | 443,630 | ||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| USD | MXN | USD | MXN | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Current assets |
$ | 110,865 | $ | 1,634,154 | $ | 100,227 | $ | 1,309,210 | ||||||||||||||||
| Non-current assets |
86,888 | 1,280,723 | 75,659 | 988,289 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Current liabilities |
37,032 | 545,852 | 26,187 | 342,060 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-current liabilities |
58,753 | 866,022 | 39,033 | 509,868 | ||||||||||||||||||||
F-17
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
The Company recorded equity in (losses) earnings of Vasconia, net of taxes, of $0.2 million, $(4.0) million, and $6.9 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. Equity in losses in 2013 includes a charge of $5.0 million, net of tax, for the reduction in Vasconia’s fair value, as discussed in the following paragraph. Equity in earnings of Vasconia in 2012 includes $4.1 million related to the Company’s portion of a bargain purchase gain recognized by Vasconia on its purchase of Almexa, an aluminum mill and manufacturer of aluminum foil, a $1.1 million tax benefit realized in the period and the reduction of the Company’s investment to fair value of $1.3 million, net of tax.
As of December 31, 2014, the fair value (based upon the quoted stock price) of the Company’s investment in Vasconia was $30.8 million. The carrying value of the Company’s investment in Vasconia was $27.8 million.
In 2013, as a result of a decline in the quoted stock price and the 2013 quarterly decline in the operating results of Vasconia, the carrying amount of the Company’s investment in Vasconia exceeded its fair value and, therefore, the Company reduced its investment value by $5.0 million during the year ended December 31, 2013, net of tax, to its fair value.
In 2012, as a result of recording the bargain purchase gain and a corresponding increase in the investment, the Company determined it was necessary to perform an impairment test on its investment in Vasconia as of December 31, 2012. The test involved the assessment of the fair value of the Company’s investment in Vasconia based on Level 1 quoted prices in active markets. The result of the assessment of the Company’s investment in Vasconia indicated that the carrying amount of the investment exceeded its quoted fair value and, therefore, was required to be reduced by $1.3 million, net of tax.
The Company owns a 40% equity interest in GS Internacional S/A (“GSI”), a wholesale distributor of branded housewares products in Brazil, which the Company acquired in December 2011. As a result of the decline in operating results of GSI and the current business environment in Brazil, the Company evaluated its carrying value of the investment for other-than-temporary impairment under the equity-method of accounting. Management performed an evaluation of quantitative factors and concluded that the investment was other-than-temporarily impaired as of September 30, 2014. The estimate of fair value was based upon the median of the income-approach (discounted cash flow method) and market-approach valuation methodology using Level 3 unobservable inputs. During the fourth quarter of 2014, the Company purchased 40% of newly issued common stock of GSI for R$2.0 million ($764,000). The Company assessed the valuation of its fourth quarter investment in GSI and determined there were no significant changes to the assumptions used in the valuation of GSI performed during the third quarter. As a result, the new investment is also impaired. Accordingly, the Company recorded a total $6.0 million impairment charge, net of tax, in equity in earnings (losses), net of tax during the third and fourth quarters of 2014.
The Company, together with Vasconia and unaffiliated partners, formed Housewares Corporation of Asia Limited (“HCA”), a Hong Kong-based company, to supply direct import kitchenware products to retailers in North, Central and South America. The Company initially invested $105,000 for a 40% equity interest in this entity during 2011. The operating results of HCA were not significant through December 31, 2013. As of December 31, 2013, the carrying value of the Company’s investment in HCA was $144,000. In October 2014, the Company sold its investment in HCA to an unaffiliated partner. No significant gains or losses were recognized in connection with this sale.
In February 2012, the Company entered into Grand Venture Holdings Limited (“Grand Venture”), a joint venture with Manweal Development Limited (“Manweal”), a Chinese corporation, to distribute Mikasa® products in China, which included an initial investment of $500,000. The Company and Manweal each own 50% of Grand Venture and have rights and obligations proportionate to their ownership percentages. The Company accounts for its investment in Grand Venture using the equity method of accounting and has recorded its proportionate share of Grand Venture’s net loss as equity in earnings (losses) in the Company’s consolidated statements of operations. The Company recorded
F-18
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
equity in losses of the joint venture of $39,000, $83,000 and $125,000 for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, the carrying value of the Company’s investment in Grand Venture was $251,000 and $287,000, respectively.
The Company evaluated the disclosure requirements of ASC Topic No. 860, Transfers and Servicing, and determined that at December 31, 2014, the Company did not have a controlling voting interest or variable interest in any of its investments and therefore continued accounting for the investments using the equity method of accounting.
NOTE D — GOODWILL AND INTANGIBLE ASSETS
The Company’s intangible assets, all of which are included in the U.S. Wholesale and International segments, consist of the following (in thousands):
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross | Accumulated Amortization |
Net | Gross | Accumulated Amortization |
Net | |||||||||||||||||||
| Goodwill |
$ | 18,101 | $ | — | $ | 18,101 | $ | 5,085 | $ | — | $ | 5,085 | ||||||||||||
| Indefinite -lived intangible assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Trade names |
7,616 | — | 7,616 | 18,364 | — | 18,364 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Finite -lived intangible assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Licenses |
15,847 | (8,007 | ) | 7,840 | 15,847 | (7,551 | ) | 8,296 | ||||||||||||||||
| Trade names |
29,768 | (4,568 | ) | 25,200 | 10,056 | (2,677 | ) | 7,379 | ||||||||||||||||
| Customer relationships |
50,823 | (6,754 | ) | 44,069 | 18,406 | (2,736 | ) | 15,670 | ||||||||||||||||
| Other |
1,202 | (431 | ) | 771 | 584 | (229 | ) | 355 | ||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 123,357 | $ | (19,760 | ) | $ | 103,597 | $ | 68,342 | $ | (13,193 | ) | $ | 55,149 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
The Company performed its 2014 annual impairment test for its indefinite-lived trade names as of October 1, 2014. The test involved the assessment of the fair market values of the Company’s indefinite-lived trade names based on Level 3 unobservable inputs, using a relief from royalty approach, assuming a discount rate of 14.0%-15.5% and an average long term growth rate of 2.5%-3%. The result of the impairment assessment of the Company’s indefinite-lived trade names indicated that the carrying values of the Elements® and Melannco® trade names exceeded their fair values as of October 1, 2014.
The Company’s home décor products category has experienced a decline in sales and profit in recent years. The Company believes the most significant factor resulting in the decline was the reduction in retail space allocated to the category which has also contributed to pricing pressure. The Company has been re-branding a portion of the home décor products under the Mikasa® and Pfaltzgraff® trade names and more recently under the Bombay® license. The Company is also taking advantage of promotional sale opportunities, such as flash sale websites and online retailers to offset the effect of a reduction in retail space for this product category and pricing pressures. As a result of these factors, the Company recorded an impairment charge of $3.4 million, related to these brands, in its consolidated statement of operations for the year ended December 31, 2014.
In addition, as of October 1, 2014 and December 31, 2014, the Company assessed the carrying value of its goodwill and determined based on quantitative and qualitative factors that no impairment existed.
As part of the Company’s annual impairment analysis of indefinite-lived trade names it was determined that certain of the Company’s trade names, previously estimated to contribute to cash flows indefinitely, have definite lives.
F-19
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Accordingly, these trade names were reclassified from indefinite-lived or unamortizable intangible assets to finite lived or amortizable intangible assets as of October 1, 2014. The remaining useful lives of these trade names is 10 to 15 years.
A summary of the activities related to the Company’s intangible assets for the year ended December 31, 2014 consists of the following (in thousands):
| Intangible Assets |
Goodwill | Total Intangible Assets and Goodwill |
||||||||||
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets, December 31, 2011 |
$ | 44,264 | $ | 2,673 | $ | 46,937 | ||||||
| Acquisition of trade names |
3,940 | — | 3,940 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of customer relationships |
7,240 | — | 7,240 | |||||||||
| Goodwill from F&F acquisition |
— | 2,412 | 2,412 | |||||||||
| Impairment of Elements® trade name |
(1,069 | ) | — | (1,069 | ) | |||||||
| Amortization |
(1,618 | ) | — | (1,618 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets, December 31, 2012 |
52,757 | 5,085 | 57,842 | |||||||||
| Amortization |
(2,693 | ) | — | (2,693 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets, December 31, 2013 |
50,064 | 5,085 | 55,149 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Acquisition of trade names |
12,348 | — | 12,348 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of customer relationships |
32,417 | — | 32,417 | |||||||||
| Acquisition of other intangible assets |
618 | — | 618 | |||||||||
| Goodwill from Kitchen Craft acquisition |
— | 13,016 | 13,016 | |||||||||
| Impairment of trade names |
(3,384 | ) | — | (3,384 | ) | |||||||
| Amortization |
(6,567 | ) | — | (6,567 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Goodwill and Intangible Assets, December 31, 2014 |
$ | 85,496 | $ | 18,101 | $ | 103,597 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The weighted-average amortization periods for the Company’s finite-lived intangible assets as of December 31, 2014 are as follows:
| Years | ||||
| Trade names |
14 | |||
| Licenses |
33 | |||
| Customer relationships |
13 | |||
| Other |
11 | |||
Estimated amortization expense for each of the five succeeding fiscal years is as follows (in thousands):
| Year ending December 31, | ||||
| 2015 |
$ | 7,004 | ||
| 2016 |
6,996 | |||
| 2017 |
6,708 | |||
| 2018 |
6,708 | |||
| 2019 |
6,708 | |||
F-20
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Amortization expense for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012 was $6.6 million, $2.7 million, and $1.6 million, respectively.
NOTE E — DEBT
Credit Agreement
In January 2014, the Company entered into a Second Amended and Restated Credit Agreement with JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A, as Administrative Agent and Co-Collateral Agent, and HSBC Bank USA, National Association, as Syndication Agent and Co-Collateral Agent (as amended, the “Credit Agreement”) amending and restating the Company’s then existing Amended and Restated Credit Agreement. The Credit Agreement, which expires in January 2019, provides for, among other things, a Revolving Credit Facility commitment totaling $175.0 million ($40.0 million of which is available for multi-currency borrowings) and a new Term Loan facility of $50.0 million.
Each borrowing under the Revolving Credit Facility bears interest, at the Company’s option, at one of the following rates: (i) the Alternate Base Rate, defined as the greater of the Prime Rate, Federal Funds Rate plus 0.5% or the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus 1.0%, plus a margin of 0.75% to 1.25%, or (ii) the Eurodollar Rate, defined as the Adjusted LIBO Rate plus a margin of 1.75% to 2.25%. The respective margins are based upon availability which is a function of usage and the borrowing base. Interest rates on outstanding borrowings at December 31, 2014 ranged from 2.125% to 4.25%. In addition, the Company pays a commitment fee of 0.375% on the unused portion of the Revolving Credit Facility.
At December 31, 2014 and 2013, borrowings outstanding under the Revolving Credit Facility were $92.7 million and $49.2 million, respectively. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, open letters of credit were $2.3 million and $1.3 million, respectively. At December 31, 2014 and 2013, availability under the Revolving Credit Facility was approximately $64.9 million and $87.8 million, respectively. The borrowing capacity under the Revolving Credit Facility depends, in part, on eligible levels of accounts receivable and inventory that fluctuate regularly and certain trademark values based upon periodic appraisals and may be lower in the first two quarters when the Company’s inventory level is lower due to seasonality. Consequently, the $175.0 million commitment may not represent actual borrowing capacity.
The Company classifies a portion of the Revolving Credit Facility as a current liability if the Company’s intent and ability is to repay the loan from cash flows from operations which are expected to occur within the next 12 months. Repayments and borrowings under the facility can vary significantly from planned levels based on cash flow needs and general economic conditions. The Company expects that it will continue to borrow and repay funds, subject to availability, under the facility based on working capital and other corporate needs.
ABR Term Loans or Eurocurrency Term Loans, provided for under the Credit Agreement, bear interest based on the applicable Senior Leverage Ratio. The ABR Spread for Term Loans is 3.0% to 3.5% and the Eurocurrency Spread for Term Loans is 4.0% to 4.5%. As of December 31, 2014, $45.0 million was outstanding under the Term Loan.
The Company’s payment obligations under the Revolving Credit Facility are unconditionally guaranteed by each of its existing and future U.S. subsidiaries. Certain payment obligations under the Revolving Credit Facility are also direct obligations of its foreign subsidiary borrowers designated as such under the Credit Agreement and, subject to limitations on such guaranty, are guaranteed by the foreign subsidiary borrowers, as well as by the Company. The obligations of the Company under the Revolving Credit Facility and any hedging arrangements and cash management services and the guarantees by its domestic subsidiaries in respect of those obligations are secured by substantially all of the assets and stock (but in the case of foreign subsidiaries, limited to 65% of the capital stock in first-tier foreign subsidiaries and not including stock of subsidiaries of such first-tier foreign subsidiaries) owned by the Company and the U.S. subsidiary guarantors, subject to certain exceptions. Such security interest consists of a first-priority lien, subject to certain permitted liens, with respect to the assets of the Company and its domestic subsidiaries pledged as collateral in favor of lenders under the Revolving Credit Facility.
F-21
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
The Credit Agreement provides for customary restrictions and events of default. Restrictions include limitations on additional indebtedness, acquisitions, investments and payment of dividends, among other things. Further, the Credit Agreement provides that at any time any Term Loan is outstanding or at any time no Term Loan is outstanding and availability under the Revolving Credit Facility is less than $17.5 million and continuing until availability of at least $20.0 million is maintained for three consecutive months, the Company is required to maintain a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio of 1.10 to 1.00 for each of four consecutive fiscal quarter periods. The Credit Agreement also provides that when the Term Loan is outstanding, the Company is required to maintain a Senior Leverage Ratio within defined parameters not to exceed 4.00 to 1.00 at the fiscal quarter ending September 30, 2014; 4.25 to 1.00 at the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2014; 3.50 to 1.00 at each fiscal quarter end in 2015; and 2.50 to 1.00 at each fiscal quarter end thereafter; provided that for any fiscal quarter ending on September 30 of any year, the maximum Senior Leverage Ratio specified above shall be increased by an additional 0.25:1.00.
Pursuant to the term loan agreement, as of December 31, 2014 the maximum additional permitted indebtedness other than certain subordinated indebtedness was $40.2 million. The Company was in compliance with the financial covenants of the Credit Agreement at December 31, 2014.
In February 2015, the Company entered into an amendment to its Credit Agreement (“Amendment No. 2”). Amendment No. 2, among other things, modified the Company’s maximum permitted Senior Leverage Ratio to provide for a more gradual reduction, beginning March 31, 2015, than was previously the case. The Company is now required to maintain a Senior Leverage Ratio not to exceed 4.25 to 1.00 for the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2014; 4.00 to 1.00 for each fiscal quarter ending during 2015; and 3.25 to 1.00 for each fiscal quarter ending thereafter. Amendment No. 2 also amended the definition of EBITDA to exclude non-recurring one-time cash charges incurred during 2014 in connection with a permitted acquisition and the refinancing of certain indebtedness if not completed, as well clarifying language as to the exclusion from EBITDA of potential contingent consideration payments related to certain completed acquisitions.
In January 2014, the Company repaid the previously outstanding Senior Secured Term Loan in connection with the execution and delivery of the Credit Agreement.
Other Credit Agreements
A subsidiary of the Company has a credit facility (“HSBC Facility” or “Short term loan”) with HSBC Bank (China) Company Limited, Shanghai Branch (“HSBC”) for up to RMB 18.0 million ($2.9 million). The HSBC Facility is subject to annual renewal and may be used to fund general working capital needs of the subsidiary which is a trading company in the People’s Republic of China. Borrowings under the HSBC Facility are guaranteed by the Company and are granted at the sole discretion of HSBC. At December 31, 2014, RMB 4.8 million ($765,000) was outstanding and the interest rate was 6.44% under the HSBC Facility.
NOTE F — DERIVATIVES
The Company is a party to interest rate swap agreements with an aggregate notional amount of $25.4 million to manage interest rate exposure in connection with its variable interest rate borrowings. The hedge periods of these agreements commenced in March 2013 and expire in June 2018 and the notional amounts amortize over this period. The interest rate swap agreements were designated as cash flow hedges under ASC Topic No. 815. The effective portion of the fair value gain or loss on these agreements is recorded as a component of accumulated other comprehensive loss. The effect of recording these derivatives at fair value resulted in an unrealized gain of $13,000 and $241,000 and an unrealized loss of $272,000, net of taxes, for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. No amounts recorded in accumulated other comprehensive loss are expected to be reclassified to interest expense in the next twelve months.
F-22
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
The fair values of the derivatives have been obtained from the counterparties to the agreements and were based on Level 2 observable inputs using proprietary models and estimates about relevant future market conditions. The aggregate fair value of the Company’s interest derivative instruments was a liability of $32,000 and $54,000 at December 31, 2014 and December 31, 2013, respectively, and is included in accrued expenses and other long-term liabilities in the consolidated balance sheets.
During 2014, the Company also entered into certain foreign exchange contracts, primarily to offset the earnings impact related to fluctuations in foreign currency exchange rates associated with inventory purchases denominated in foreign currencies. These foreign exchange contracts were not designated as hedges as required in order to apply hedge accounting. The changes in the fair values of these contracts were recorded in earnings immediately. As of December 31, 2014, there were no open foreign exchange contracts. Included in selling, general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statement of operations is a gain of $0.7 million related to these foreign exchange derivative contracts.
NOTE G — CAPITAL STOCK
Long-term incentive plan
The Company’s 2000 Long-Term Incentive Plan, as amended (the “Plan”) provides for up to 4,200,000 shares available for grant. These shares of the Company’s common stock are available for grants to directors, officers, employees, consultants and service providers and affiliates in the form of stock options or other equity-based awards. The Plan authorizes the Board of Directors of the Company, or a duly appointed committee thereof, to issue incentive stock options, non-qualified options and other stock-based awards. Options that have been granted under the Plan expire over a range of five to ten years from the date of grant and vest over a range of up to five years from the date of grant. As of December 31, 2014, there were 296,362 shares available for the grant of awards.
Cash dividends
Dividends declared in 2014 and 2013 are as follows:
| Dividend per share |
Date declared |
Date of record |
Payment date | |||
| $0.03125 |
March 12, 2013 | May 1, 2013 | May 15, 2013 | |||
| $0.03125 |
June 13, 2013 | August 1, 2013 | August 15, 2013 | |||
| $0.03125 |
August 2, 2013 | November 1, 2013 | November 15, 2013 | |||
| $0.0375 |
October 31, 2013 | January 31, 2014 | February 14, 2014 | |||
| $0.0375 |
March 11, 2014 | May 1, 2014 | May 15, 2014 | |||
| $0.0375 |
June 19, 2014 | August 1, 2014 | August 15, 2014 | |||
| $0.0375 |
July 29, 2014 | October 31, 2014 | November 14, 2014 | |||
| $0.0375 |
November 5, 2014 | January 30, 2015 | February 13, 2015 |
On March 4, 2015, the Board of Directors declared a quarterly dividend of $0.0375 per share payable on May 15, 2015 to shareholders of record on May 1, 2015.
Stock repurchase program
On April 30, 2013, Lifetime’s Board of Directors authorized the repurchase of up to $10.0 million of the Company’s common stock. The repurchase authorization permits the Company to effect repurchases from time to time through open market purchases and privately negotiated transactions. During the year ended December 31, 2013, the Company repurchased 245,575 shares for a total cost of $3.2 million and thereafter retired the shares. No shares were repurchased during the year ended December 31, 2014.
F-23
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Preferred stock
The Company is authorized to issue 100 shares of Series A Preferred Stock and 2,000,000 shares of Series B Preferred Stock, none of which is issued or outstanding at December 31, 2014.
Restricted stock
In 2014, 2013, and 2012, the Company granted an aggregate of 21,511, 22,459, and 23,394 restricted shares, respectively, of the Company’s common stock to its non-employee directors representing payment of a portion of their annual retainer. In 2014, the Company also granted 5,000 restricted shares to an employee.
The total fair value of the restricted shares, based on the number of shares granted and the quoted market prices of the Company’s common stock on the dates of grant was $420,000 in 2014, $298,000 in 2013 and $270,000 in 2012. For restricted stock grants made to the Company’s non-employee directors, the restrictions lapse one year from the date of grant and the stock is expensed over the one year period. For the restricted stock granted to an employee in 2014, the restriction on one third of the shares lapses annually, over three years. Total unrecognized restricted stock compensation expense at December 31, 2014 was $232,000 and is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 0.9 years.
F-24
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Stock options
A summary of the Company’s stock option activity and related information for the three years ended December 31, 2014, is as follows:
| Options | Weighted- average exercise price |
Weighted- average remaining contractual life (years) |
Aggregate intrinsic value |
|||||||||||||
| Options outstanding at December 31, 2011 |
2,475,750 | $ | 12.62 | |||||||||||||
| Grants |
305,000 | 11.64 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercises |
(199,823 | ) | 5.47 | |||||||||||||
| Cancellations |
(52,750 | ) | 12.82 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Options outstanding at December 31, 2012 |
2,528,177 | 13.06 | ||||||||||||||
| Grants |
390,800 | 12.26 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercises |
(247,827 | ) | 4.91 | |||||||||||||
| Cancellations |
(68,000 | ) | 16.89 | |||||||||||||
| Expirations |
(231,500 | ) | 22.46 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Options outstanding at December 31, 2013 |
2,371,650 | 12.75 | ||||||||||||||
| Grants |
394,400 | 18.83 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercises |
(365,223 | ) | 8.63 | |||||||||||||
| Cancellations |
(32,200 | ) | 12.23 | |||||||||||||
| Expirations |
(42,000 | ) | 26.61 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Options outstanding at December 31, 2014 |
2,326,627 | 14.19 | 5.99 | $ | 10,670,919 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Options exercisable at December 31, 2014 |
1,533,785 | $ | 13.69 | 4.83 | $ | 8,425,516 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
The aggregate intrinsic value in the table above represents the total pre-tax intrinsic value that would have been received by the option holders had all option holders exercised their stock options on December 31, 2014. The intrinsic value is calculated for each in-the-money stock option as the difference between the closing price of the Company’s common stock on December 31, 2014 and the exercise price.
The total intrinsic values of stock options exercised for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012 were $3,103,000, $1,997,000, and $1,182,000, respectively. The intrinsic value of a stock option that is exercised is calculated at the date of exercise.
The Company recognized stock compensation expense of $4.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, of which $2.5 million represents stock option compensation expense, $0.3 million represents restricted share compensation expense and $1.7 million represents stock awards to be granted in 2015. The Company recognized stock compensation expense of $2.9 million and $2.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2013, and 2012, respectively. The stock compensation expense recognized each year is equal to the grant date fair values of stock options vested during the year. Total unrecognized compensation cost related to unvested stock options at December 31, 2014, before the effect of income taxes, was $5.0 million and is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.54 years.
The Company values stock options using the Black-Scholes option valuation model. The Black-Scholes option valuation model, as well as other available models, was developed for use in estimating the fair value of traded options, which have no vesting restrictions and are fully transferable. The Black-Scholes option valuation model requires the input of highly subjective assumptions including the expected stock price volatility and risk-free interest rate. Because the Company’s stock options have characteristics significantly different from those of traded options, changes in the subjective input assumptions can materially affect the fair value estimates of the Company’s stock options. The weighted-average per share grant date fair value of stock options granted during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012 was $9.73, $6.12, and $6.05, respectively.
F-25
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
The fair values for these stock options were estimated at the dates of grant using the following weighted-average assumptions:
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Historical volatility |
58 | % | 61 | % | 61 | % | ||||||
| Expected term (years) |
6.0 | 5.6 | 6.0 | |||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.95 | % | 0.88 | % | 1.10 | % | ||||||
| Expected dividend yield |
0.77 | % | 0.97 | % | 0.86 | % | ||||||
NOTE H — INCOME PER COMMON SHARE
Basic income per common share has been computed by dividing net income by the weighted-average number of shares of the Company’s common stock outstanding. Diluted income per common share adjusts net income and basic income per common share for the effect of all potentially dilutive shares of the Company’s common stock. The calculations of basic and diluted income per common share for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012 are as follows:
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands - except per share amounts) | ||||||||||||
| Net income – Basic and Diluted |
$ | 1,544 | $ | 9,281 | $ | 20,947 | ||||||
| Weighted-average shares outstanding – Basic |
13,519 | 12,757 | 12,511 | |||||||||
| Effect of dilutive securities: |
||||||||||||
| Stock options |
455 | 286 | 299 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted-average shares outstanding – Diluted |
13,974 | 13,043 | 12,810 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Basic income per common share |
$ | 0.11 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 1.67 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted income per common share |
$ | 0.11 | $ | 0.71 | $ | 1.64 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The computations of diluted income per common share for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 and excludes options to purchase 2,004,836, 1,417,145 and 1,450,200 shares of the Company’s common stock, respectively. The above shares were excluded due to their antidilutive effect.
NOTE I — INCOME TAXES
The components of income before income taxes, equity in earnings and extraordinary item are as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Domestic |
$ | 10,251 | $ | 26,470 | $ | 20,609 | ||||||
| Foreign |
3,611 | (3,233 | ) | (535 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total income before income taxes and equity in earnings |
$ | 13,862 | $ | 23,237 | $ | 20,074 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
F-26
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
The provision for income taxes (before equity in earnings) consists of:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Current: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | 4,709 | $ | 8,996 | $ | 6,691 | ||||||
| State and local |
1,284 | 1,707 | 761 | |||||||||
| Foreign |
1,691 | 747 | 503 | |||||||||
| Deferred |
(1,859 | ) | (2,275 | ) | (2,747 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income tax provision |
$ | 5,825 | $ | 9,175 | $ | 5,208 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes. Significant components of the Company’s deferred income tax assets are as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Deferred income tax assets: |
||||||||
| Deferred rent expense |
$ | 3,686 | $ | 3,694 | ||||
| Stock options |
3,348 | 3,237 | ||||||
| Inventory |
1,312 | 1,317 | ||||||
| Operating loss carry-forward |
2,073 | 2,140 | ||||||
| Accounts receivable allowances |
406 | 192 | ||||||
| Accrued compensation |
897 | 758 | ||||||
| Other |
2,911 | 1,831 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deferred income tax assets |
$ | 14,633 | $ | 13,169 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Significant components of the Company’s net deferred income tax (liability) asset are as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Deferred income tax liabilities: |
||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
$ | (3,461 | ) | $ | (3,826 | ) | ||
| Intangibles |
(12,549 | ) | (5,162 | ) | ||||
| Equity in earnings |
(504 | ) | (805 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deferred income tax liabilities |
(16,514 | ) | (9,793 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred income tax (liability) asset |
(1,881 | ) | 3,376 | |||||
| Valuation allowance |
(1,897 | ) | (1,213 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred income tax (liability) asset |
$ | (3,778 | ) | $ | 2,163 | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The Company has generated various state net operating loss carryforwards of which, $14.0 million remains at December 31, 2014 that begin to expire in 2015. The Company has net operating losses in foreign jurisdictions of $6.9 million at December 31, 2014 that begin to expire in 2020. The increase in the deferred tax liabilities is primarily
F-27
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
due to the 2014 acquisition of Kitchen Craft, which included approximately $8.8 million of deferred tax liabilities related to the intangible assets acquired. The valuation allowance which remains as of December 31, 2014 relates to certain state net operating losses.
The provision for income taxes (before equity in earnings) differs from the amounts computed by applying the applicable federal statutory rates as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Provision for federal income taxes at the statutory rate |
35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||||
| Increases (decreases): |
||||||||||||
| State and local income taxes, net of Federal income tax benefit |
4.9 | 5.5 | 3.2 | |||||||||
| Foreign rate differences |
(2.7 | ) | (1.1 | ) | (1.8 | ) | ||||||
| Non-deductible expenses |
6.4 | 2.8 | 1.2 | |||||||||
| Reduction of deferred tax liabilities related to the prior year |
— | — | (11.6 | ) | ||||||||
| Other |
(1.6 | ) | (2.7 | ) | (0.1 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Provision for income taxes |
42.0 | % | 39.5 | % | 25.9 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The estimated values of the Company’s gross uncertain tax positions at December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 are liabilities of $572,000, $351,000 and $301,000, respectively, and consist of the following:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1 |
$ | (351 | ) | $ | (301 | ) | $ | (134 | ) | |||
| Additions based on tax positions related to the current year |
— | (31 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Additions for tax positions of prior years |
(221 | ) | (164 | ) | (167 | ) | ||||||
| Settlements |
— | 145 | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance at December 31 |
$ | (572 | ) | $ | (351 | ) | $ | (301 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The Company had approximately $40,000 and $71,000, net of federal and state tax benefit, accrued at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, for the payment of interest. The Company’s policy for recording interest and penalties is to record such items as a component of income taxes.
If the Company’s tax positions are ultimately sustained, the Company’s liability, including interest, would be reduced by $530,000, all of which would impact the Company’s tax provision. On a quarterly basis, the Company evaluates its tax positions and revises its estimates accordingly. The Company believes that it is reasonably possible that $420,000 of its tax positions will be resolved within the next twelve months.
The Company is no longer subject to U.S. Federal income tax examinations for the years prior to 2011. The Company has identified the following jurisdictions as “major” tax jurisdictions: U.S. Federal, California, Massachusetts, Illinois, New York, New Jersey and the United Kingdom. At December 31, 2014, the periods subject to examination for the Company’s major state jurisdictions are the years ended 2010 through 2013.
F-28
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
NOTE J — BUSINESS SEGMENTS
Segment information
During the second quarter of 2014, the Company realigned its reportable segments into three categories, U.S. Wholesale, International and Retail Direct. The U.S. Wholesale segment, formerly the Wholesale segment, includes the Company’s primary domestic business that designs, markets and distributes its products to retailers and distributors. The International Segment consists of certain business operations conducted outside the U.S. which was previously included in the Wholesale segment. The Retail Direct segment is that in which the Company markets and sells a limited selection of its products to consumers through its Pfaltzgraff®, Mikasa®, Built NY®, Fred® & Friends and Lifetime Sterling® websites.
The Company has segmented its operations to reflect the manner in which management reviews and evaluates the results of its operations. While the three segments distribute similar products, the segments have been distinct due to the different methods the Company uses to sell, market and distribute the products. Management evaluates the performance of the U.S. Wholesale, International and Retail Direct segments based on net sales and income (loss) from operations. Such measures give recognition to specifically identifiable operating costs such as cost of sales, distribution expenses and selling, general and administrative expenses. Certain general and administrative expenses, such as senior executive salaries and benefits, stock compensation, director fees and accounting, legal and consulting fees, are not allocated to the specific segments and are reflected as unallocated corporate expenses.
As a result of the Company’s realignment of its reportable segments, previous periods presented have been recast to conform with the current period presentation
F-29
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Net sales: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Wholesale |
$ | 441,293 | $ | 444,187 | $ | 422,241 | ||||||
| International |
125,230 | 38,907 | 42,621 | |||||||||
| Retail Direct |
19,487 | 20,680 | 21,980 | |||||||||
| Non-operating adjustment(1) |
— | (1,053 | ) | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total net sales |
$ | 586,010 | $ | 502,721 | $ | 486,842 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income from operations: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Wholesale(2) |
$ | 34,874 | $ | 46,303 | $ | 40,227 | ||||||
| International |
3,759 | (2,151 | ) | 303 | ||||||||
| Retail Direct |
(1,034 | ) | (62 | ) | 463 | |||||||
| Non-operating adjustment(1) |
— | (1,053 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Unallocated corporate expenses |
(16,215 | ) | (14,851 | ) | (13,658 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total income from operations |
$ | 21,384 | $ | 28,186 | $ | 27,335 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Depreciation and amortization: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Wholesale |
$ | 8,618 | $ | 8,549 | $ | 7,637 | ||||||
| International |
5,379 | 1,601 | 1,437 | |||||||||
| Retail Direct |
203 | 265 | 250 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total depreciation and amortization |
$ | 14,200 | $ | 10,415 | $ | 9,324 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Note:
| (1) | In 2013, the Company recorded a non-operating adjustment to reduce accounts receivable for previously issued credits within the Retail Direct business which related to 2010 and earlier periods. |
| (2) | In 2014, income from operations for the U.S. Wholesale segment includes $3.4 million of intangible asset impairment and $4.2 million related to the reduction in certain contingent consideration accruals. In 2012, income from operations for the U.S. Wholesale segment includes $1.1 million of intangible asset impairment. |
F-30
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Assets: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Wholesale |
$ | 287,744 | $ | 291,757 | $ | 305,054 | ||||||
| International |
128,055 | 35,365 | 37,818 | |||||||||
| Retail Direct |
535 | 730 | 512 | |||||||||
| Unallocated/ corporate/ other |
5,068 | 8,887 | 5,413 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 421,402 | $ | 336,739 | $ | 348,797 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Capital expenditures: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Wholesale |
$ | 5,431 | $ | 3,375 | $ | 3,637 | ||||||
| International |
650 | 272 | 1,260 | |||||||||
| Retail Direct |
90 | 195 | 58 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total capital expenditures |
$ | 6,171 | $ | 3,842 | $ | 4,955 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Goodwill: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Wholesale |
||||||||||||
| Beginning balance |
$ | 2,412 | $ | 2,412 | $ | — | ||||||
| Acquisition activity |
— | — | 2,412 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Ending balance |
2,412 | 2,412 | 2,412 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| International |
||||||||||||
| Beginning balance |
2,673 | 2,673 | 2,673 | |||||||||
| Acquisition activity |
13,016 | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Ending balance |
15,689 | 2,673 | 2,673 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total goodwill (1) |
$ | 18,101 | $ | 5,085 | $ | 5,085 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Note:
| (1) | No goodwill is allocated to the Company’s Retail Direct reportable segment. |
F-31
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Geographical information
The following table sets forth net sales and long-lived assets by the major geographic locations (in thousands):
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Net sales: |
||||||||||||
| United States |
$ | 436,049 | $ | 439,129 | $ | 430,758 | ||||||
| United Kingdom |
93,432 | 29,012 | 30,709 | |||||||||
| Rest of World |
56,529 | 34,580 | 25,375 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 586,010 | $ | 502,721 | $ | 486,842 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||||||
| Long-lived assets, excluding intangible assets, at period-end: |
||||||||||||
| United States |
$ | 54,594 | $ | 65,043 | ||||||||
| United Kingdom |
3,927 | 1,321 | ||||||||||
| Rest of World |
1,167 | 550 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total |
$ | 59,688 | $ | 66,914 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Product category information – net sales
The following table sets forth net sales by major product categories included within the Company’s U.S. Wholesale operating segment:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Category: |
||||||||||||
| Kitchenware |
$ | 269,265 | $ | 281,211 | $ | 256,154 | ||||||
| Tableware (1) |
117,546 | 110,108 | 113,911 | |||||||||
| Home Solutions |
54,482 | 52,868 | 52,176 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 441,293 | $ | 444,187 | $ | 422,241 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (1) | The tableware product category previously included revenue from Creative Tops, which is included as part of the International segment. Revenue sources disclosed in 2013 have been reclassified to conform to the current year presentation for comparative purposes. |
The following table sets forth net sales by major product categories included within the Company’s International operating segment:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Category: |
||||||||||||
| Kitchenware |
$ | 67,604 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
| Tableware |
57,626 | 38,907 | 42,621 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 125,230 | $ | 38,907 | $ | 42,621 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
F-32
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
NOTE K — COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Operating leases
The Company has lease agreements for its corporate headquarters, distribution centers, showrooms and sales offices that expire through 2029. These leases generally provide for, among other things, annual base rent escalations and additional rent for real estate taxes and other costs.
Future minimum payments under non-cancelable operating leases are as follows (in thousands):
| Year Ending December 31, | ||||
| 2015 |
$ | 15,976 | ||
| 2016 |
15,417 | |||
| 2017 |
12,072 | |||
| 2018 |
8,394 | |||
| 2019 |
6,807 | |||
| Thereafter |
50,584 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
$ | 109,250 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Rent and related expenses under operating leases were $15.8 million, $14.3 million and $14.8 million for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. There was no sublease rental income in 2014, 2013 or 2012.
Royalties
The Company has license agreements that require the payment of royalties on sales of licensed products which expire through 2023. Future minimum royalties payable under these agreements are as follows (in thousands):
| Year ending December 31, | ||||
| 2015 |
$ | 8,632 | ||
| 2016 |
2,574 | |||
| 2017 |
2,085 | |||
| 2018 |
1,952 | |||
| 2019 |
1,870 | |||
| Thereafter |
596 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
$ | 17,709 | ||
|
|
|
|||
Legal proceedings
Wallace Silversmiths de Puerto Rico, Ltd. (“Wallace de Puerto Rico”), a wholly-owned subsidiary of the Company, operates a manufacturing facility in San Germán, Puerto Rico that is leased from the Puerto Rico Industrial Development Company (“PRIDCO”). In March 2008, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (the “EPA”) announced that the San Germán Ground Water Contamination site in Puerto Rico (the “Site”) had been added to the Superfund National Priorities List due to contamination present in the local drinking water supply.
F-33
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
In May 2008, Wallace de Puerto Rico received from the EPA a Notice of Potential Liability and Request for Information Pursuant to 42 U.S.C. Sections 9607(a) and 9604(e) of the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, Liability Act. The Company responded to the EPA’s Request for Information on behalf of Wallace de Puerto Rico. In July 2011, Wallace de Puerto Rico received a letter from the EPA requesting access to the property that it leases from PRIDCO, and the Company granted such access. In February 2013, the EPA requested access to conduct further environmental investigation at the property. The Company granted such access and further EPA investigation is pending.
The Company is not aware of any determination by the EPA that any remedial action is required for the Site, and, accordingly, is not able to estimate the extent of any possible liability.
The Company is, from time to time, involved in other legal proceedings. The Company believes that other current litigation is routine in nature and incidental to the conduct of the Company’s business and that none of this litigation, individually or collectively, would have a material adverse effect on the Company’s consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
NOTE L — RETIREMENT PLANS
401(k) plan
The Company maintains a defined contribution retirement plan for eligible employees under Section 401(k) of the Internal Revenue Code. Participants can make voluntary contributions up to the Internal Revenue Service limit of $17,500 ($23,000 for employees 50 years or over) for 2014. Effective January 1, 2009, the Company suspended its matching contribution as an expense savings measure. The Company’s U.K.-based subsidiaries also maintain defined contribution pension plans.
Retirement benefit obligations
The Company assumed retirement benefit obligations, which are paid to certain former executives of an acquired business in 2006. These obligations under these agreements are unfunded and amounted to $6.9 million at December 31, 2014 and $5.4 million at December 31, 2013.
The discount rate used to calculate the retirement benefit obligations was 3.65% at December 31, 2014 and 4.50% at December 31, 2013. The retirement benefit obligations are included in accrued expenses and deferred rent and other long-term liabilities.
The Company expects to recognize $132,000 of actuarial losses included in accumulated other comprehensive loss in net periodic benefit cost in 2015.
F-34
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Expected benefit payments for each of the next five fiscal years and in aggregate for the five fiscal years thereafter are as follows (in thousands):
| Year ending December 31, | ||||
| 2015 |
$ | 144 | ||
| 2016 |
137 | |||
| 2017 |
264 | |||
| 2018 |
388 | |||
| 2019 |
377 | |||
| 2020 through 2024 |
1,909 | |||
Kitchen Craft pension plan
Kitchen Craft is the sponsor of a defined benefit pension plan (the “Plan”) for which service costs accrual ceased prior to the acquisition in January 2014. In October 2014, the Plan trustees secured, in full, all benefits payable or contingently payable under the Plan (subject to adjustment as determined by the UK pension authority in connection with its approval of the Plan’s termination) through the purchase of a group annuity contract from a major UK-based insurance company. The share purchase agreement, pursuant to which the Company acquired Kitchen Craft, provides that any additional contributions required in connection with the settlement and termination of the Plan shall be offset by future amounts owed to the sellers or, if those amounts are insufficient, reimbursed to the Company by the sellers. Accordingly, there was no impact, nor is there any expected future impact, to the Company’s statement of operations in connection with the settlement and planned termination of the Plan, which is expected to occur in 2015.
The following table summarizes the changes in the projected benefit obligations and plan assets for the year ended December 31, 2014:
| December 31, 2014 |
||||
| (in thousands) | ||||
| Change in projected benefit obligations |
||||
| Projected benefit obligations, acquisition |
$ | 11,678 | ||
| Interest cost |
364 | |||
| Actuarial losses |
2,887 | |||
| Benefits paid |
(216 | ) | ||
| Currency adjustment |
(917 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Projected benefit obligations, end of year |
$ | 13,796 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Change in plan assets |
||||
| Fair value of plan assets, acquisition |
$ | 11,678 | ||
| Actual return on plan assets |
2,618 | |||
| Employer contributions |
2,471 | |||
| Benefits paid |
(216 | ) | ||
| Currency adjustment |
(1,018 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Fair value of plan assets, end of year |
$ | 15,533 | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Net Plan funding, end of year |
$ | 1,738 | ||
|
|
|
|||
F-35
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
The following table summarizes the components of net period pension costs:
| Year Ended December 31, 2014 |
||||
| (in thousands) | ||||
| Components of net periodic pension cost |
||||
| Expected return on plan assets |
$ | (390 | ) | |
| Interest cost on projected benefit obligations |
364 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Net periodic pension cost |
$ | (26 | ) | |
|
|
|
|||
The accumulated benefit obligations at December 31, 2014 are $13.8 million. The amount in accumulated Other comprehensive income at December 31, 2014 is $623,000.
The following are assumptions used to determine the actuarial present value of the projected benefit obligations and net periodic pension benefit cost as of and for the year ended December 31, 2014:
| December 31, 2014 |
||||
| Discount rate |
2.19 | % | ||
| Expected long-term rate of return on plan assets |
2.43 | % | ||
Expected Benefit Payments – Expected benefit payments for each of the next five fiscal years and in the aggregate for the five fiscal years thereafter are as follows (in thousands):
| Year ending December 31, | ||||
| 2015 |
$ | 232 | ||
| 2016 |
252 | |||
| 2017 |
258 | |||
| 2018 |
274 | |||
| 2019 |
288 | |||
| 2020 through 2024 |
1,706 | |||
Plan Assets- As described above, the Plan trustees invested the Plan assets in a deferred annuity contract in October 2014. As of December 31, 2014, the fair value of this insurance contract was $15.5 million. The fair value of the insurance contract was obtained using Level 3 unobservable inputs. Assets of the Plan also include less than $0.1 million of cash and cash equivalents with a Level 1 observable fair value. The net Plan assets are included within Other Assets on the Company’s Consolidated Balance Sheet.
F-36
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
NOTE M — OTHER
Inventory
The components of inventory are as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Finished goods |
$ | 134,564 | $ | 108,340 | ||||
| Work in process |
1,887 | 1,966 | ||||||
| Raw materials |
1,473 | 2,485 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 137,924 | $ | 112,791 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Property and equipment
Property and equipment consist of:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Machinery, furniture and equipment |
$ | 85,556 | $ | 79,132 | ||||
| Leasehold improvements |
28,056 | 26,959 | ||||||
| Building and improvements |
1,604 | 1,604 | ||||||
| Construction in progress |
1,108 | 104 | ||||||
| Land |
100 | 100 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 116,424 | 107,899 | |||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization |
(89,623 | ) | (80,201 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 26,801 | $ | 27,698 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Depreciation and amortization expense of property and equipment for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $7.7 million, $7.7 million, and $7.8 million, respectively.
Included in machinery, furniture and equipment at each of December 31, 2014 and 2013 is $2.1 million related to assets recorded under capital leases. Included in accumulated depreciation and amortization at each of December 31, 2014 and 2013 is $2.0 million and $1.9 million related to assets recorded under capital leases.
F-37
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Accrued expenses
Accrued expenses consist of:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Customer allowances and rebates |
$ | 12,314 | $ | 11,756 | ||||
| Compensation and benefits |
9,412 | 11,781 | ||||||
| Interest |
224 | 98 | ||||||
| Vendor invoices |
3,071 | 5,135 | ||||||
| Royalties |
2,266 | 2,567 | ||||||
| Commissions |
1,222 | 1,245 | ||||||
| Freight |
1,519 | 1,419 | ||||||
| Professional fees |
1,527 | 1,170 | ||||||
| VAT |
1,400 | 533 | ||||||
| Contingent consideration related to acquisitions |
— | 1,647 | ||||||
| Working capital excess related to F&F acquisition |
— | 254 | ||||||
| Other |
4,006 | 3,490 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 36,961 | $ | 41,095 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Deferred rent & other long-term liabilities
Deferred rent & other long-term liabilities consist of:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| Deferred rent liability |
$ | 9,530 | $ | 9,737 | ||||
| Retirement benefit obligations |
6,776 | 5,212 | ||||||
| Contingent consideration related to acquisitions |
3,286 | 3,647 | ||||||
| Compensation guarantees |
542 | — | ||||||
| Derivative liability |
26 | 48 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total |
$ | 20,160 | $ | 18,644 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Supplemental cash flow information
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information: |
||||||||||||
| Cash paid for interest |
$ | 5,035 | $ | 4,115 | $ | 5,498 | ||||||
| Cash paid for taxes |
4,912 | 10,862 | 6,067 | |||||||||
| Non-cash investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Translation adjustment |
$ | (4,736 | ) | $ | (140 | ) | $ | 3,077 | ||||
F-38
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Components of accumulated other comprehensive loss, net
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Accumulated translation adjustment: |
||||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of year |
$ | (2,944 | ) | $ | (2,804 | ) | $ | (5,881 | ) | |||
| Translation adjustment during period |
(4,736 | ) | (140 | ) | 3,077 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance at end of year |
$ | (7,680 | ) | $ | (2,944 | ) | $ | (2,804 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Accumulated effect of retirement benefit obligations: |
||||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of year |
$ | (745 | ) | $ | (1,160 | ) | $ | — | ||||
| Net gain (loss) arising from retirement benefit obligations, net of tax |
(1,507 | ) | 361 | (1,187 | ) | |||||||
| Amounts reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||||
| Amortization of loss, net of tax(1) |
28 | 54 | 27 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance at end of year |
$ | (2,224 | ) | $ | (745 | ) | $ | (1,160 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Accumulated deferred gains (losses) on cash flow hedges: |
||||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of year |
$ | (31 | ) | $ | (272 | ) | $ | — | ||||
| Derivative fair value adjustment, net of tax |
13 | 241 | (272 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balance at end of year (2) |
$ | (18 | ) | $ | (31 | ) | $ | (272 | ) | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Notes:
| (1) | Amount is recorded in selling, general and administrative expenses on the consolidated statements of operations. |
| (2) | No amounts were reclassified out of accummulared other comprehensive loss. Amounts reclassifed would be recorded in interest expense on the consolidated statements of operations. |
NOTE N — SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
Credit Agreement Amendment
In February 2015, the Company entered into an amendment to its Credit Agreement (“Amendment No. 2”). Amendment No. 2, among other things, modified the Company’s maximum permitted Senior Leverage Ratio to provide for a more gradual reduction, beginning March 31, 2015, than was previously the case. The Company is now required to maintain a Senior Leverage Ratio not to exceed 4.25 to 1.00 for the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2014; 4.00 to 1.00 for each fiscal quarter ending during 2015; and 3.25 to 1.00 for each fiscal quarter ending thereafter.
Amendment No. 2 also amended the definition of EBITDA to exclude non-recurring one-time cash charges incurred during 2014 in connection with a permitted acquisition and the refinancing of certain indebtedness if not completed, as well clarifying language as to the exclusion from EBITDA of potential contingent consideration payments related to certain completed acquisitions.
F-39
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
DECEMBER 31, 2014
Reed and Barton
In February 2015, the Company entered into an asset purchase agreement to acquire the operating asset and to assume certain liabilities of Reed and Barton Corporation, a designer and marketer of fine tableware and giftware products. The agreement provides that Lifetime will purchase the assets pursuant to Section 363 of the United States Bankruptcy Code. The transaction is subject to a number of conditions, including completion of an auction process and bankruptcy court approval.
F-40
Table of Contents
LIFETIME BRANDS, INC.
SCHEDULE II - VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
(in thousands)
| COL. A |
COL. B | COL. C | COL. D | COL. E | ||||||||||||||||
| Additions | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Description |
Balance at beginning of period |
Due to acquisitions |
Charged to costs and expenses |
Deductions | Balance at end of period |
|||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Deducted from asset accounts: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 473 | $ | 119 | $ | 401 | $ | (178 | )(a) | $ | 815 | |||||||||
| Reserve for sales returns and allowances |
4,736 | 350 | 10,996 | (c) | (10,234 | )(b) | 5,848 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| $ | 5,209 | $ | 469 | $ | 11,397 | $ | (10,412 | ) | $ | 6,663 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2013 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Deducted from asset accounts: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 361 | $ | — | $ | 260 | $ | (148 | )(a) | $ | 473 | |||||||||
| Reserve for sales returns and allowances |
3,635 | — | 6,004 | (c) | (4,903 | )(b) | 4,736 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| $ | 3,996 | $ | — | $ | 6,264 | $ | (5,051 | ) | $ | 5,209 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2012 |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Deducted from asset accounts: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 328 | $ | 67 | $ | 181 | $ | (215 | )(a) | $ | 361 | |||||||||
| Reserve for sales returns and allowances |
4,274 | 179 | 6,660 | (c) | (7,478 | )(b) | 3,635 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| $ | 4,602 | $ | 246 | $ | 6,841 | $ | (7,693 | ) | $ | 3,996 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (a) | Uncollectible accounts written off, net of recoveries. |
| (b) | Allowances granted. |
| (c) | Charged to net sales. |
S-1
