Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - CVENT INC | Financial_Report.xls |
| EX-10.9 - EXHIBIT 10.9 - CVENT INC | d831399dex109.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - CVENT INC | d831399dex321.htm |
| EX-10.8 - EXHIBIT 10.8 - CVENT INC | d831399dex108.htm |
| EX-21.1 - EXHIBIT 21.1 - CVENT INC | d831399dex211.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - CVENT INC | d831399dex312.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - CVENT INC | d831399dex231.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - CVENT INC | d831399dex322.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - CVENT INC | d831399dex311.htm |
| EX-10.10 - EXHIBIT 10.10 - CVENT INC | d831399dex1010.htm |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D. C. 20549
Form 10-K
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the Fiscal Year Ended: December 31, 2014
or
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File Number: 001-36043
Cvent, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 54-1954458 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| 1765 Greensboro Station Place, 7th Floor Tysons Corner, VA |
22102 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
(703) 226-3500
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities Registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Each Class |
Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered | |
| Common Stock, $0.001 par value per share | The New York Stock Exchange |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act: Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the Registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act: Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the Registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of Registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K, or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer | ¨ | Accelerated filer | x | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | ¨ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ¨ | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of Cvent common shares held by non-affiliates as of June 30, 2014 was $402,768,998 based on the last reported sale price on the New York Stock Exchange on June 30, 2014.
The number of shares outstanding of the Registrant’s Common Stock as of March 12, 2015 was 41,384,672 shares.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the Registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement for the 2015 Annual Stockholders’ Meeting, which the registrant expects to file with the Securities and Exchange Commission within 120 days of December 31, 2014, are incorporated by reference into Part III (Items 10, 11,12, 13 and 14) of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Table of Contents
CVENT, INC.
ANNUAL REPORT ON FORM 10-K
FOR THE PERIOD ENDED DECEMBER 31, 2014
| Page No. |
||||||
| PART I | ||||||
| Item 1. |
1 | |||||
| Item 1A. |
11 | |||||
| Item 1B. |
35 | |||||
| Item 2. |
35 | |||||
| Item 3. |
35 | |||||
| Item 4. |
35 | |||||
| PART II | ||||||
| Item 5. |
36 | |||||
| Item 6. |
39 | |||||
| Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
41 | ||||
| Item 7A. |
61 | |||||
| Item 8. |
63 | |||||
| Item 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
94 | ||||
| Item 9A. |
94 | |||||
| Item 9B. |
96 | |||||
| PART III | ||||||
| Item 10. |
97 | |||||
| Item 11. |
97 | |||||
| Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
97 | ||||
| Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
97 | ||||
| Item 14. |
97 | |||||
| PART IV | ||||||
| Item 15. |
98 | |||||
| 99 | ||||||
Table of Contents
CAUTIONARY NOTE REGARDING FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS
This Annual Report on Form 10-K, including the sections entitled “Business,” “Risk Factors,” and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” contains forward-looking statements. These statements may relate to, but are not limited to, expectations of future operating results or financial performance, macroeconomic trends that we expect may influence our business, plans for capital expenditures, expectations regarding the introduction of new products, regulatory compliance and changes in the regulatory landscape affecting our business, impact of litigation, plans for growth and future operations, effects of acquisitions, as well as assumptions relating to the foregoing. Forward-looking statements are inherently subject to risks and uncertainties, some of which cannot be predicted or quantified. These risks and other factors include, but are not limited to, those listed under the section entitled “Risk Factors” in Item 1A of Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terminology such as “may,” “will,” “should,” “could,” “expect,” “plan,” “anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “predict,” “intend,” “potential,” “continue,” “seek” or the negative of these terms or other comparable terminology. These statements are only predictions. Actual events and/or results may differ materially.
We believe that it is important to communicate our future expectations. However, there may be events in the future that we are not able to accurately predict or control and that may cause our actual results to differ materially from the expectations we describe in our forward-looking statements. Except as required by applicable law, including the securities laws of the United States and the rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission, we do not plan to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of any new information, future events or otherwise, other than through the filing of periodic reports in accordance with the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”). You should not place undue reliance on our forward-looking statements. You should be aware that the occurrence of any of the events described in the “Risk Factors” section and elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K could harm our business, prospects, operating results and financial condition. Although we believe that the expectations reflected in the forward-looking statements are reasonable, we cannot guarantee future results, levels of activity, performance or achievements.
| Item 1. | Business |
Overview
We are a leading cloud-based enterprise event management platform. We provide solutions for both sides of the events and meetings value chain: (i) event and meeting planners, and (ii) hotels and venues. Our integrated, cloud-based solution addresses the entire event lifecycle by allowing event and meeting planners to organize, market and manage their meetings, conferences, tradeshows and other events. Our hospitality cloud provides hotels and venues with a complete solution suite to generate, manage and measure their demand for group meetings The combination of these solutions creates an integrated platform that allows us to generate revenue from both sides of the events and meetings value chain.
For the event and meeting planner side of the value chain, which includes corporations, associations, not-for-profits, government agencies and universities, events and meetings are an integral way to build and strengthen relationships with customers, prospects, employees and partners. Enterprise events and meetings include external events, such as conferences, tradeshows, and customer summits, as well as internal functions, such as sales meetings, training seminars and team-building events. Planning and running an event can be a highly complex, inefficient and time-consuming task when managed using traditional manual processes and disparate solutions. We address these challenges by providing planners an integrated platform with solutions that unify the full lifecycle of an event. Meeting planners use our solutions to identify the appropriate venue, secure a competitive proposal from the hotel or venue, manage budgets, market the event, send invitations, utilize pre-event surveys, establish a social media presence for the event, process registrations, manage fee collections, build an event-specific mobile app, manage event logistics such as travel and lodging, survey and engage attendees,
1
Table of Contents
and analyze event results and survey feedback following the event. Our platform helps planners decrease costs and increase attendance for their events.
For the hotel and venue side of the value chain, group events and meetings are a vital source of revenue and profit. At certain types of hotels, group events and meetings can constitute approximately one-third of total revenue. Group meeting business is often a large hotel’s most profitable segment as these groups typically contract not only for significant sleeping room blocks, but also for meeting space, catering and audio visual equipment. Meeting attendees are often a captive audience at the hotel that can generate substantial incremental on property revenue.
The Cvent Hospitality Cloud was created to provide a full spectrum of cloud-based solutions across the hotel group sales lifecycle. The Hospitality Cloud consists of marketing solutions and software-as-a-service (SaaS) software enabling hotels, convention and visitor bureaus (CVBs), and other event venue owners to more effectively generate qualified demand for meetings and events, manage that demand more efficiently, and measure group business performance. An integral component of our Hospitality Cloud is the Cvent Supplier Network (CSN), our online marketplace, which connects tens of thousands of event and meeting planners seeking the best venue for their event with approximately 235,000 venues featured in our proprietary CSN database. We believe that CSN contains the world’s largest, most accurate database of detailed venue information with listings of hotels and venues in 175 countries that can be searched and filtered based on approximately 200 characteristics and data fields. CSN has become a leading solution for event and meeting planners who are researching potential locations and venues for their events, as well as for hotels and venues that are seeking to increase their group business revenue.
The number of event requests for proposal, or RFPs, submitted through our marketplace has increased from approximately 12,000 in 2008, the year CSN was initiated, to approximately 1.6 million in 2014. As a result of this substantial growth, we believe we have achieved critical mass and are benefiting from substantial network effects as increased adoption of our marketplace by planners attracts hoteliers to leverage our growing event planner user base to expand their group business activity.
Our dual role as a solution provider to both event planners and venues allows us to generate revenue from both sides of the value chain. Event and meeting planners enter into annual and multi-year subscription contracts to utilize our cloud-based event and meeting management software solutions. As of December 31, 2014, we had more than 7,700 event and meeting planner customers. Hotels and venues enter into annual and multi-year contracts with us for marketing solutions that increase the prominence of their properties in CSN. As of December 31, 2014, approximately 6,300 hotels and venues have purchased marketing solutions from us.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, our revenue was $142.2 million, a 28% increase over 2013. For the year ended December 31, 2013, our revenue was $111.1 million, representing year-over-year revenue growth from 2012 of 33%, as we had revenue of $83.5 million for the year ended December 31, 2012. Our enterprise-focused, cloud-based platform for event and meeting planners has historically constituted the majority of our revenue and represented approximately 70% of our total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. Our marketing solutions have represented approximately 30% of our revenue for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. For the year ended December 31, 2014, we generated a net income of $1.8 million, representing a margin of 1.3%. For the year ended December 31, 2013, we generated a net loss of $3.2 million, representing a net margin of (2.9)%. For the year ended December 31, 2012, we generated net income of $4.3 million, representing a margin of 5.2%. We had total assets of $302.0 million, $235.8 million and $90.0 million as of the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Industry Background
The hospitality and travel industry serves three types of customers: individual business travelers, leisure travelers, and group events and meetings. In the 1990s, American Express began offering travel services and
2
Table of Contents
subsequently transformed the way business travelers book hotel rooms and air travel. In the 2000s, online travel agencies revolutionized the industry for leisure travelers. We believe that we are driving a similar revolution today in the way group events and meetings are planned, booked and managed, both by the event planners and the hotels and venues that host these events.
Our Platform
We offer planners a robust platform that addresses the entire lifecycle of events and meetings, including budgeting, planning, venue sourcing, marketing, management and measurement of meetings. We offer six major product categories: (i) event management software, (ii) enterprise solutions software, (iii) mobile event apps, (iv) pre- and post-event feedback management software, (v) ticketing software and (vi) the Hospitality Cloud, which includes CSN, a marketplace that connects approximately 235,000 venues with high-quality, ready-to-transact event and meeting planners, and other group marketing solutions, group demand management and group business intelligence for hotels and venues.
Event Management
Cvent modernizes the traditional processes associated with event and meeting management. We provide planners with a complete solution to increase attendance and decrease the cost of managing events by streamlining the entire planning process. By automating and simplifying these processes, Cvent enables planners to focus their valuable time and resources on more strategic event aspects—and even other events—rather than on repetitive, time-consuming tasks.
Our comprehensive solution includes the following key functionalities:
| • | Event Planning. Our online event planning software gives users the ability to manage events quickly and affordably, from webinars to conferences. The streamlined interface is designed to make planning and building an event with speed and precision easy, and, for complex events, the necessary features are never more than a click away. Features include agenda and session management, online and mobile event registration, promotion codes/discounts, secure payment processing, housing and travel management, and event cloning (for recurring events). |
| • | Event Marketing. Our solution provides e-marketing tools that allow planners to increase meeting attendance. Marketing features include event websites (templates and custom), email marketing (templates and custom; initial and follow-up), mail merge data tags, contact management, event calendars, and social media integration. |
| • | Event Administration. We also facilitate all the processes and details of bringing an event to life. Administration features include budget management, seating management, name badge and certificate creation, resource and space allocation, speaker management, appointment scheduling, membership management, and continuing education credit tracking. |
| • | Onsite Event Management. Our solution also provides onsite solutions to help events run smoothly and engage attendees. Onsite features include onsite registration and session check-in functionality, badge printing, payment processing, and mobile app integration. |
| • | Software Integrations. Our platform integrates with commonly-used, mission critical software such as Salesforce.com, and can be integrated with other existing enterprise or accounting systems. |
Measurement and Reporting. Our platform measures all aspects of the event management process. Users can generate standard or custom reports, view event dashboards and schedule live reports to be sent to key stakeholders across departments. This enables efficient evaluation of return on investment and an enhanced ability to closely audit meeting-related activities to ensure regulatory compliance and control expenses.
In addition to the foregoing functionalities of our Event Management platform, all of our event and meeting planner users that are licensed pursuant to subscriptions to our Event Management platform have the ability to access our CSN product for free, which is further described in “Hospitality Cloud.”
3
Table of Contents
Enterprise
Our Enterprise solutions consist of Strategic Meetings Management (SMM) for internal meetings, and Enterprise Event Marketing (EEM) for external customer and prospect facing events. We offer our Enterprise solution for large enterprise customers who hold hundreds or thousands of events and meetings annually, many of which are hosted at off-site locations such as hotels and other venues. In addition to all of the services offered to our event management customers, our Enterprise platform also helps corporations manage their meetings and event programs more efficiently and manage previously untracked meeting expenditures.
With our platform, enterprises gain control over the entire meeting and event planning process by managing logistics, budgeting, sourcing, registration, housing, travel and reporting in a single application. As organizations strive to optimize spend across the enterprise, these consolidated processes help corporate travel, meeting and procurement managers gain more visibility into meeting expenditures and have historically enabled cost savings of 15% or more, as compared to companies that host events without an enterprise solution. Through our Enterprise solution, corporate travel, procurement and finance departments have the ability to review the meetings process to ensure compliance with established meeting and expense policies, while still granting creative control over the event to their planners.
Mobile Event Apps
With the proliferation of smartphones and tablets, we believe mobile applications, or apps, will be used more often at events. We offer planners the ability to generate and customize native apps for both business and consumer events on multiple operating systems, including Android, iOS and the web. Our apps are often used by planners and attendees to: provide schedule and location information; create personalized schedules and access them within the app; facilitate interaction among attendees, speakers and exhibitors; participate during sessions with live polling and surveys; conduct real-time messaging to build relationships and disseminate information; access rich media content such as video, pictures and internet radio; connect with integrated social media tools such as Facebook, Twitter and LinkedIn; and deliver advertising and targeted messaging.
Feedback Solutions
Our feedback solutions enable our customers to streamline the way they collect information both pre- and post-event. Additionally, more than 1,200 enterprises and over 13,000 active users utilize our software to solicit feedback from employees, measure customer satisfaction, capture sales leads and test new product ideas. We consider a user to be “active” if such user accessed their account within the 12 months preceding the date of measurement. Event management customers can also collect attendee feedback using our survey capabilities, which provides powerful analytics and insights useful for future events.
Audience Management Platform
We offer a ticketing, customer engagement and venue management platform that helps venues, promoters and artists improve the efficiency of their operations, increase ticket sales and better engage with their customers. Our easy-to-use platform includes customer websites and tools to generate website ticket sales, branded emails, print-at-home tickets, and box office and ticket scanning capabilities. We also offer a mobile solution that enhances events and drives attendee engagement. Our solutions integrate with social media platforms, enabling social buying, sharing, rewarding, tracking, auto-tweeting and auto-publishing, and also include analytical tools to track and measure results.
Hospitality Cloud
The Cvent Hospitality Cloud was branded to provide a full spectrum of cloud-based solutions across the hotel group sales lifecycle. The Hospitality Cloud consists of marketing solutions and SaaS software enabling
4
Table of Contents
hotels, CVBs, and other event venue owners to more effectively generate qualified demand for meetings and events, manage that demand more efficiently, and measure group business performance. Our Hospitality Cloud solutions are separated into three pillars:
| • | Group Marketing Solutions. Our Group Marketing Solutions consist of three online marketplaces—The Cvent Supplier Network, EliteMeetings.com, and SpeedRFP.com—that allow suppliers to directly connect and establish relationships with the hundreds of thousands of planners who use these tools to research destinations, find venues, and source group business. These three domains are designed to support the sourcing needs of a variety of meeting planners. |
The Cvent Supplier Network, or CSN, connects tens of thousands of professional meeting planners with approximately 235,000 venues featured in our proprietary database. We believe that CSN contains the world’s largest, most accurate database of detailed venue information with approximately 1.6 million requests for proposals (RFP) submitted through our system during 2014 and listings of hotels and venues in 175 countries that can be searched and filtered based on approximately 200 characteristics and data fields. CSN has become a leading solution for event and meeting planners who are researching potential locations and venues for their events, as well as for hotels and venues that are seeking to increase their group business revenue through online marketing.
EliteMeetings.com serves as a commission-free RFP-generating tool and a comprehensive vehicle for sourcing luxury and upscale properties. SpeedRFP™ (www.SpeedRFP.com), is another commission-free sourcing website, with a strong focus on ease-of-use, and is thus focused on planners in the SMERF—Social, Military, Education, Religious and Fraternal—market.
Our group marketing solutions allow hotels and venues to:
| • | Increase Revenue from Group Events and Meetings Solutions. Our products are an effective solution to help hotels increase the number of in-bound sales leads and amount of revenue from enterprise event and meeting planners. |
| • | More Accurately Target Meeting Planners through Online Marketing. Through our online marketing solutions, hotels and venues are able to target ready-to-transact event and meeting planners in a more cost efficient manner than many other marketing channels. Our solutions also make it easier for hotels and venues to market to hard-to-identify relevant planner personnel within organizations, which results in an increase in the number of sales leads and converted group bookings. |
We estimate that in 2014 planners sought to source approximately $8.0 billion of business to hotels and venues through the Hospitality Cloud as compared to $6.5 billion in 2013, $4.7 billion in 2012, $3.2 billion in 2011, $2.4 billion in 2010 and $0.6 billion in 2009 through CSN.
This estimate is based on the number of participant days and room days requested and (i) the average daily hotel room rate of all awarded proposals to RFPs transmitted through our marketplace for such year and (ii) a multi-year average daily food and beverage rate where applicable. This food and beverage average assumes any RFPs with meeting space consist of a morning break, afternoon break, and lunch in CSN and a snack and lunch for any RFPs from EliteMeetings.com and SpeedRFP.com. This estimate is premised on RFPs transmitted by planners in each year including those that were never responded to, and may not reflect the actual transactions that ultimately took place, which we generally expect are lower in total dollar value than the estimate above. While we do not earn material revenue from our role in facilitating the introduction of the parties to these transactions through the transmission of the RFPs, we believe that the total estimated value of unique RFPs provides an indication of the growing scale and importance of our marketplace.
In addition to the aforementioned online Group Marketing Solutions, Cvent also provides several offline, print and in-person marketing programs for hoteliers including the Elite Meetings Magazine, Cvent Connect, and the Elite Meetings Alliance.
5
Table of Contents
The Elite Meetings Magazine is published twice per year with a subscriber base encompassing both meeting planners as well as hospitality professionals. Cvent Connect is the company’s flagship event for customers and prospects, providing educational workshops, technology demonstrations, and networking opportunities to Cvent’s current and prospective customers. The Elite Meetings Alliance combines educational sessions with 1:1 networking opportunities for meeting planners and hoteliers focused on the luxury segment.
| • | Group Demand Management. Cvent’s solutions for Group Demand Management provide hotel sales personnel with the tools they need to efficiently manage, prioritize, and track a high volume of group business leads. Cvent’s solutions for Group Demand Management are comprised of the following components: |
| • | Lead Scoring. Prioritizing group leads is a constant dilemma for hotel sales staff as a number of factors that include lead type, dates, sleeping room availability, meeting space availability, meeting space to guest room ratio, food & beverage and audio-visual requirements need to be considered simultaneously. Cvent’s Lead Scoring software allows hoteliers to configure a scoring strategy based on the individual needs of their hotel. Leads are then scored and prioritized based on lead size, profitability and best fit/date patterns in the context of future inventory and demand. By scoring and prioritizing each lead, hoteliers are able to focus on, manage, and convert leads that maximize margins. Our Lead Scoring technology is currently in Beta. Based on feedback we have received, we anticipate making the software generally available in the second half of 2015. |
| • | Routing and Escalation Rules. Rapid responses to group leads is critical when competing for the best group-business opportunities. A defined workflow can dramatically enhance a hotelier’s ability to respond in a timely fashion. Routing and Escalation Rules ensure that the correct users are automatically assigned to leads based on a variety of configurable factors including geographies, lead dates, lead size, organization type and a number of other factors. Additional hotel constituents can also be notified of leads that are not responded to within a defined time period to ensure established corporate policies and workflows are met. |
| • | SpeedRFP Widget. The SpeedRFP Widget provides white-label technology that powers group business sourcing on hundreds of hotel websites and enables those clients to easily manage all of their electronic leads through one central interface. The most important and relevant information required by hoteliers to respond is captured through the Widget, ensuring a more efficient process for hoteliers and planners alike. In addition, planners that have previously created a profile do not need to rekey important personal and event information, allowing for a quicker, easier and more enjoyable user experience. |
| • | Group Business Intelligence. Cvent provides packaged analytics to hotels, enabling sales and marketing leaders on property to easily track and analyze their own group business performance and to compare that performance with their competitive set. Our analytic solutions equip on-site hotel sales professionals to make more-informed business decisions and better predict the highs and lows of their calendar for smart group planning and management. Specifically, our analytics help hotels understand their customers, local and national market, competitors, and business opportunities. |
Our comp set reports gauge a hotel’s group pace and future lead opportunities against its biggest competitors on a local, national, and international level. Our scorecards compare a hotel’s advertising performance against the market by going beyond click-through rates and impressions, and evaluates RFP traffic and group booking windows. This provides a more granular insight into what happens throughout the meeting planner buying cycle, including measuring the value of business received through our Hospitality Cloud. Finally, we provide our hotel customers best practices regarding how to improve their RFP responses and thus RFP success rate.
6
Table of Contents
Our Event and Meeting Planner Customers
As of December 31, 2014, we had more than 7,700 event and meeting planner customers. We also had approximately 90,000 active user event and meeting planners that freely access CSN, some of which also have a paid subscription to our other event and meeting planner solutions. We consider an event planner user to be “active” if such user accessed their account within 12 months preceding the date of measurement. Their industry profile spans across clients in the retail, consumer products, travel and leisure, technology, telecommunications, financial services, healthcare and automotive verticals, as well as trade associations, government agencies and universities. In 2014, 2013 and 2012, no single event and meeting planner customer represented more than 1% of our total revenue for that year.
Our Hotel and Venue Customers
As of December 31, 2014, approximately 6,300 hotels and venues purchased annual or multi-year marketing solutions from us. Some hotel companies and management companies purchase marketing solutions on behalf of multiple properties. In 2014, 2013 and 2012, no single hotel property or venue customer represented more than 1% of our total revenue for that year. Our ten largest event and meeting management customers and our ten largest hotel and venue advertising customers during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 represented 4%, 5% and 7%, respectively, of our total revenue during those periods.
In addition to the paid marketing relationships with hotels and venues, over 15,000 individual hotel properties, including two major U.S. hotel chains, have integrated our software into their back-end IT systems.
Sales and Marketing
We sell subscriptions to our platform primarily through our direct sales team. The sales and marketing department is our largest department by head count. We also work with affinity and channel partners that typically endorse our services worldwide, including leading global travel management, event planning associations and industry publications.
We have been refining our approach to sales and marketing for more than a decade, with a focus on generating high quality sales leads to secure new business. For example, in 2014, we conducted more than 260,000 aggregate prospect interactions, including more than 1,200 large group luncheons and in-person events to meet and educate prospects about our products, as well as more than 2,200 online group demonstrations for potential and existing customers.
We also employ a variety of other sales and marketing initiatives, including sponsoring and participating in user conferences, trade shows and industry events; online advertising; managing our own blogs relevant to the industry; hosting webinars; public relations efforts; and social networking. While we believe all of these methods are effective for generating sales leads and attracting new business, we continue to explore other ways to reach customers and prospects, including video marketing, creative social media initiatives and content marketing.
Partnerships and Industry Associations
We have established partnerships with a number of major travel solutions providers, conference and event managers, and expense management companies. Through these partnerships, we refer their products to our existing customers and receive referrals of their existing customers.
We also partner with many leading associations in both the meetings and hospitality industries including Meeting Professionals International (MPI), Association of Corporate Travel Executives (ACTE) and Destination Marketing Association International (DMAI). Along with our industry partnerships, we work directly with many key industry publications—such as Successful Meetings and Meetings and Convention Magazine—whose reach is our direct target market.
7
Table of Contents
We have built and maintained strong relationships with these organizations and work closely with them to co-market to meeting planners and hoteliers through a variety of initiatives, including attending and speaking at industry events and hosting educational forums and thought leadership sessions for their members. In most cases, these, and other industry partners, including hundreds of organizations, are our customers and use our solutions, giving us strong market and brand credibility.
Our Technology
We deliver our solutions using a cloud-based software-as-a-service model that we developed. This affords our clients quick, easy and near global reach of our solutions. Our cloud-based delivery model also limits involvement from our clients’ technical teams, and reduces implementation time and costs. We have developed a multi-tenant architecture and a secure, scalable and highly available technology platform that provides a high degree of customization to allow each customer to configure the business process workflow, branding and user interface to best meet their individual needs.
The architecture, design, deployment and management of our cloud-based platform are focused on the following:
Multi-Tenant Architecture. Our multi-tenant architecture enables all customers to be on the same version of our solutions. When we improve existing functionality, all customers receive the benefit of the new version at the same time.
Secure, Scalable and Highly Available Technology Platform. Our clients often rely on our solutions for their most important and largest events and meetings. To meet their demanding expectations, we designed a technology platform that is secure, scalable and highly available. We regularly review the key facets of our platform, making regular improvements and enhancements to keep pace with growth and technology evolution.
We maintain a comprehensive security program designed to protect our systems and our clients’ data. We also select service providers who adhere to best practices and industry standards, such as Statement on Standards for Attestation Engagements No. 16, or SSAE 16, whenever possible. Writing secure code is an integral part of our software development methodology, as well. We augment this practice with regular application and network security testing and periodic manual, third-party application and network penetration testing.
We designed our software and systems to handle substantial growth in users and data without requiring significant re-engineering. For example, our Event Management system processed over four times as many registrations in 2014 as compared to 2007, and it managed the additional scale without having to significantly alter our investment as a percentage of revenue.
We primarily host our solutions from a third-party data center in Ashburn, Virginia. Within the data center, our network, server and storage infrastructure is highly redundant and fault-tolerant, and is continuously monitored by both automated systems, as well as a dedicated operations team. A few weeks ago, this web hosting service provider declared bankruptcy, which raises a heightened risk of interruption in their service and a possibility of system failure. We also have a standby data center that is available in case the primary data center is not functioning for any reason.
Our mobile, ticketing, lead scoring and non-CSN components of our Hospitality Cloud are hosted on leading infrastructure-as-a-service platforms. These third-party services allow us to rapidly scale computing resources up or down as demanded. This flexibility is advantageous due to the highly variable usage of some of these products, allowing us to minimize capital expenditures.
Integrated Real-Time Analytics Capabilities. Our platform’s analytics and reporting capabilities allow clients to derive powerful, real-time insights. Hundreds of standard reports along with a robust, proprietary custom reporting engine allow clients to more easily recognize shifts in attendee sentiment, identify potential
8
Table of Contents
issues and make well-informed decisions. This insight enables better event organization and enhances future event return on investment. Our integrated analytics and reporting capabilities also allow our clients to more efficiently and accurately audit their event and meeting spending. By providing these features, we enable our customers to better control their budgets and ensure their compliance with regulations in their respective industries.
Mobile and Audience Management Platform Offerings
Our mobile and ticketing products are hosted on leading infrastructure-as-a-service platforms. These third-party services allow us to rapidly scale computing resources up or down as demanded. This flexibility is advantageous due to the highly variable usage of mobile event applications and online ticket sales, allowing us to minimize capital expenditures.
With respect to mobile offerings, we generally focus on native mobile event apps, primarily for iOS and Android devices. This strategy allows us to create apps for clients that function effectively, even in environments with weak, saturated or non-existent Internet connectivity. We designed our mobile application platform to facilitate rapid creation of mobile event apps, while still allowing clients to have a variety of design options.
Product Development
Our research and development effort is focused both on developing new software and on improving our existing products. Our engineering team works closely with customers and event attendees to identify their current and future needs. We believe that innovation and timely development of new features and products is essential to meeting the needs of our end-customer and improving our competitive position. We supplement our own research and development effort with technologies and products that we license from third parties. We test our products thoroughly to certify and ensure interoperability with third-party hardware and software products. Our U.S. and India personnel develop our products on a nearly continual basis, five days a week.
Our research and development expenses totaled $14.0 million, $11.2 million, and $7.6 million, representing 10%, 10%, and 9% of our revenue, for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, respectively. We plan to continue to significantly invest resources for our research and development efforts.
Competition
We operate in an intensely competitive market that is characterized by constant change and innovation. Our competition includes:
| • | existing manual, paper and spreadsheet-based systems that corporate personnel employ to organize events by themselves in a fragmented manner. For example, a significant number of planners process registrations by asking attendees to fill out PDF forms and aggregate that information manually using various office tools. They also frequently lack the ability to process registration payments online. Venue searches and bookings are often processed either by phone or email, while tracking of budget and expense is done on an ad-hoc basis through spreadsheets; |
| • | event, meeting management and hospitality solution firms such as Lanyon; |
| • | online event registration vendors focused primarily on consumer ticketing such as Eventbrite; and |
| • | small and large companies that offer point solutions that compete with some of the features present in our platform, such as registration management, travel management, venue bookings, web survey providers, email and search marketers, business intelligence solutions, and mobile app developers. |
We believe that we generally compete favorably with our competitors because of the features and performance of our various offerings, the ease of integration of our solutions with the technological infrastructures of both event planners as well as the venues and the incremental return on investment that our platform offers to our customers.
9
Table of Contents
Customer Support
Our customer support organization is available to our event management subscription customers 24 hours per day, 7 days per week and can be contacted via telephone, online chat and web form during the subscription period. We also provide support for CSN, mobile, ticketing and feedback solutions customers from 12 hours per day up to 24 hours per day, 5 days per week depending on the line of business. As of December 31, 2014, we had 310 employees dedicated to customer support, client success management, professional services and customer training in our locations in the United States, UK and India. “Professional services” include web site creation, graphics design, and mobile application creation for our customers. We also maintain an online knowledge database and offer extensive, on-demand video training available to our customers during the subscription period.
Intellectual Property
Our ability to protect our intellectual property, including our technology, is and will be an important factor in the success and continued growth of our business. We primarily protect our intellectual property through trade secrets, copyrights, trademarks and contracts.
Some of our technology relies upon third-party licensed intellectual property incorporated into our software solutions. We are not materially dependent upon these third-party providers.
We own U.S. registered trademarks for CVENT, CVENT.COM, REACH THE RESPONSE, CROWDCOMPASS, CROWDCOMPASS.COM, AND CROWDTORCH. We have registered trademarks for CROWDCOMPASS in Australia, Canada, and the European Union, for CVENT in Australia, Germany and the European Union, and for CROWDTORCH in Australia and the European Union. We have pending trademark applications for ONARRIVAL, COMPASS, ENTERPRISE EVENT MARKETING and SUPPLIER NETWORK in the United States, and for CVENT in China. In addition, TicketMob LLC, our subsidiary, owns U.S. registered trademarks for TICKETMOB, LAUGHSTUB, TUNESTUB and ELECTROSTUB. Elite Meetings International, LLC, our subsidiary, owns U.S. registered trademarks for SPEEDRFP and ATTENDEEHUB. We also have two patent applications pending in the United States.
We have also established business procedures designed to maintain the confidentiality of our proprietary information, including the use of confidentiality agreements and assignment-of-inventions agreements with employees, independent contractors, consultants and companies with which we conduct business.
For important additional information related to our intellectual property position, please review the information set forth in “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business and Industry—Legal and Regulatory Risks.”
Regulation
Although we do not believe that significant existing laws or government regulations adversely impact us, our business could be affected by different interpretations or applications of existing laws or regulations, future laws or regulations or actions by domestic or foreign regulatory agencies. Failure to comply with these and other laws and regulations may result in, among other consequences, administrative enforcement actions and fines, class action lawsuits and civil and criminal liability.
Many jurisdictions impose an obligation on any entity that holds personally identifiable information, personal health information, or payment card information to adopt appropriate security to protect such data against unauthorized access, misuse, destruction, or modification. Many jurisdictions have enacted laws requiring holders of such information to take certain actions in response to data breach incidents, such as providing prompt notification of the breach to affected individuals and government authorities. We have implemented and maintain physical, technical and administrative safeguards intended to protect all personal data and have processes in place to assist us in complying with applicable laws and regulations regarding the protection of this data and properly responding to any security incidents. We have adopted a system security plan and security breach incident response plans to address our compliance with these laws.
10
Table of Contents
For important information related to government regulation of our business and the risks related to our compliance with such laws, please review the information set forth in “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business and Industry—Legal and Regulatory Risks.”
Geographic Areas
For information with respect to our geographic markets, see note 13 to our consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this report. For important information related to our foreign operations, please review the information set forth in “Risk Factors—Risks Related to Our Business and Industry—Operational Risks.”
Employees
As of December 31, 2014, we had approximately 1,740 full-time employees. Of that total, 840 were based in Gurgaon, India; 645 were based in McLean, Virginia; and the remaining were either remote or located in our various offices in Texas, California, Oregon, Georgia, Canada and the United Kingdom. By department, 748 were in sales and marketing (of which 214 were dedicated to development of our proprietary databases), 390 in product development, 313 in client services, 102 in technology operations, and 185 in general and administrative. None of our employees is represented by a labor organization or is a party to any collective bargaining arrangement. We have never had a work stoppage, and we consider our relationship with our employees to be good.
Company Information
We were incorporated in 1999 as a Delaware corporation. As of December 31, 2014, we had approximately 1,740 employees at our operations in the United States, India, Canada and the United Kingdom. Our headquarters are located at 1765 Greensboro Station Place, 7th Floor, Tysons Corner, VA 22102, and our telephone number is (703) 226-3500. You can access our website at www.cvent.com. In addition, we maintain a Facebook page at www.facebook.com/cvent, a LinkedIn page at www.linkedin.com/company/cvent and a Twitter feed at www.twitter.com/cvent. Information contained on, or that can be accessed through, our website, Facebook page, LinkedIn page or Twitter feed or other social media sources does not constitute part of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
Copies of annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to these reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a) and 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”) are available, free of charge, on our website as soon as reasonably practicable after we file such material electronically with or furnish it to the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”). The SEC also maintains a website that contains our SEC filings. The address of the site is www.sec.gov.
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors |
Our financial and operational results are subject to various risks and uncertainties including those described below. The risks and uncertainties described below are not the only ones we face. Additional risks and uncertainties, including general economic and business risks, that we are unaware of, or that we currently believe are not material, also may become important factors that affect us. If any of the following risks or others not specified below materialize, our business, financial condition and results of operations could be materially adversely affected. In that case, the trading price of our common stock could decline.
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
Operational Risks
We are substantially dependent upon the addition of new customers and the continued growth of the market for our cloud-based event and meeting management platform.
We derive, and expect to continue to derive, a substantial portion of our revenue from the sale of our cloud-based event and meeting management platform. During the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012,
11
Table of Contents
70% of our total revenue was derived from our cloud-based event and meeting management platform. The market for event and meeting management software is still evolving, and competitive dynamics may cause pricing levels to change as the market matures and as existing and new market participants introduce new types of solutions and different approaches to enable event and meeting planners and hotels to address their respective needs. As a result, we may be forced to reduce the prices we charge for our solutions and may be unable to renew existing customer agreements or enter into new customer agreements at the same prices and upon the same terms that we have historically.
Widespread acceptance and use of the cloud-based business model for delivery of our event and meeting management platform is critical to our future growth and success. Under the perpetual or periodic license model for software procurement, users of the software would typically install and operate the applications on their hardware. Because many companies were historically predisposed to maintaining control of their information technology, or IT, systems and infrastructure, there may be resistance to the concept of accessing a cloud-based service provided by a third party. If the market for cloud-based event and meeting management software fails to grow, grows more slowly than we currently anticipate or evolves and forces us to reduce the prices we charge for our solutions, our operating results and financial condition could be materially adversely affected.
A significant portion of our revenue is derived from event and meeting planners. As such, our business is dependent upon identifying new event planners and converting them to new customers.
Revenue from our solutions for event and meeting planners has historically constituted the majority of our revenue and represented 70% of our total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. Event and meeting planners can be found in a range of corporate departments, which makes it difficult to identify prospective planner customers. Since our formation, we have proactively and systematically worked to identify potential event planner customers. However, we cannot guarantee that we will be able to continue to identify new event planner customers, and the effort to identify new event planner customers will be more costly and time-consuming than seeking marketing contracts with new and existing venue customers.
Our business depends on maintaining and expanding our relationships with hotels and venues.
An important component of our business success depends on our ability to maintain and expand relationships with hotels and venues. A substantial portion of our revenue is derived from compensation negotiated with hotels and venues for marketing solutions, particularly through the Cvent Supplier Network. During the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012, 30% of our total revenue was derived from our marketing solutions.
If we are unable to continue to successfully sell marketing solutions to individual hotels and venues, our financial results may suffer. Furthermore, although individual hotel properties typically make separate decisions as to their advertising spending, the influence of the corporate offices of major hotel chains may affect the decisions of their individual properties. For example, if the corporate parent discontinues its relationship with us in favor of another solution, our relationship with the properties under that brand may suffer even though, in nearly all cases, we negotiate with each property individually. This may lead to considerable lost revenue or result in additional costs to complete sales of our advertising, any of which would adversely affect our operating results.
Finally, our strong network relationships with hotels and venues are a key differentiator for our event management solutions. This risk is heightened by the concentrated nature of the hospitality industry, which is dominated by a relatively small number of major hotel chains. If we are unable to maintain and grow our network of hotels and venues, we may be unable to satisfy our customers’ needs, lose market share or incur additional costs to support our customers, all of which may adversely affect our business, results of operations or financial condition. Further, if we are unable to successfully develop and sell additional products to hotels and venues, including but not limited to group demand management and group business intelligence, we may not achieve our anticipated revenue from these customers, which would adversely affect our business, results of operations or financial condition.
12
Table of Contents
If the security of our customers’ confidential information stored in our systems is breached or otherwise subjected to unauthorized access, our reputation may be severely harmed and we may be exposed to liability.
Our system stores personally identifiable information, proprietary email distribution lists, credit card information and other critical or private data for our customers and our customers’ event participants. We believe that we take reasonable steps to protect the security, integrity and confidentiality of the information we collect and store, but there is no guarantee that inadvertent (e.g., software bugs or other technical malfunctions, employee error or malfeasance, or other factors) or unauthorized disclosure will not occur or that third parties will not gain unauthorized access to this information despite our efforts. We have in the past and we may again in the future experience successful attempts by third-parties to obtain unauthorized access to our data despite our security measures. Since techniques used to obtain unauthorized access change frequently, we and our third-party hosting facilities may be unable to anticipate these techniques or to implement adequate preventative measures. Any willful or accidental security breaches or other unauthorized access could expose us to liability for the loss of such information, adverse regulatory action by federal and state governments, time-consuming and expensive investigation and litigation, extensive downtime of our systems and other possible liabilities.
If our security measures are breached because of third-party action, employee error, malfeasance or otherwise, or if design flaws in our software are exposed and exploited, and, as a result, a third party obtains unauthorized access to any of our customers’ data, our relationships with our customers will be severely damaged, and we could incur significant liability. In addition, many jurisdictions have enacted laws requiring companies to notify individuals of data security breaches involving certain types of personal data, and our agreements with certain partners require us to notify them in the event of a security incident. These mandatory disclosures regarding a security breach often lead to widespread negative publicity and may cause our customers to lose confidence in the effectiveness of our data security measures. Any security breach, whether actual or perceived, would harm our reputation, and we could lose customers or fail to acquire new customers.
If we experience compromises to our information technology as a result of security lapses, technical difficulties or otherwise that result in performance or availability problems of our cloud-based solutions, the complete shutdown of our cloud-based solutions, or the loss or unauthorized disclosure of confidential information, our partners or customers may be harmed or lose trust and confidence in us, and decrease the use of our solution or stop using our solution in its entirety, and we would suffer reputational and financial harm. Our third-party vendors may also suspend or discontinue their relationships with us. Additionally, in the future, we could be subject to regulatory investigations and litigation in connection with a security breach or related issue, and we could also face regulatory fines and be liable to third parties for these types of breaches. For example, we work with third-party vendors to process credit card payments by our customers and are subject to payment card association operating rules. If our security measures fail to protect this information adequately or we fail to comply with the applicable operating rules, we could be liable to both our customers for their losses, as well as the vendors under our agreements with them, we could be subject to fines and higher transaction fees, we could face regulatory action, and our customers and vendors could end their relationships with us, any of which could harm our business, results of operations or financial condition.
We have experienced rapid growth and significant organizational change in recent periods and expect continued future growth, both organically and by acquisitions. If we fail to manage our growth effectively, we may be unable to execute our business plan, maintain high levels of service or address competitive challenges adequately.
Our head count and operations have grown, both domestically and internationally, since our inception. In particular, during the year ended December 31, 2014, we have added over 280 full-time positions. This growth has placed, and will continue to place, a significant strain on our management, administrative, operational and financial infrastructure. We anticipate further growth will be required to address increases in our platform offerings and continued expansion. Our success will depend in part upon the ability of our management team to manage this growth effectively. To do so, we must continue to recruit, hire, train, manage and integrate a significant number of qualified managers, technical personnel and employees in specialized roles within our
13
Table of Contents
company, including in technology, sales and marketing. If our new employees perform poorly, or if we are unsuccessful in recruiting, hiring, training, managing and integrating these new employees, or retaining these or our existing employees, our business may suffer.
In addition, to manage the expected continued growth of our head count, operations and geographic expansion, we will need to continue to improve our information technology infrastructure, operational, financial and management systems and procedures. Our anticipated additional head count and capital investments will increase our costs, which will make it more difficult for us to address any future revenue shortfalls by reducing expenses in the short term. If we fail to successfully manage our growth, we will be unable to successfully execute our business plan, which could have a negative impact on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
Our long-term success depends, in part, on our ability to operate offices located outside of the United States including India.
We currently maintain offices and have sales personnel in the United States, India, the United Kingdom, and Canada, and we are exploring opening additional international offices. In addition, we have contracted with independent sales personnel in Australia, Germany, Mexico, Spain and Sweden. Any international expansion efforts that we may undertake may not be successful. Further, conducting more extensive international operations subjects us to new risks that we have not generally faced in the United States. These risks include:
| • | unexpected costs and errors in the localization of our solutions, including translation into foreign languages and adaptation for local practices and regulatory requirements; |
| • | challenges posed by different pricing environments and different forms of competition; |
| • | lack of familiarity and burdens of complying with foreign laws, legal standards, regulatory requirements (including privacy and data security requirements), tariffs, and other barriers; |
| • | changes in regulatory requirements, taxes, trade laws, tariffs, export quotas, custom duties or other trade restrictions; |
| • | difficulties in managing technology partners and differing technology standards; |
| • | difficulties in collecting accounts receivable; |
| • | difficulties in managing and staffing international operations; |
| • | varying expectations as to employee standards; |
| • | fluctuations in exchange rates that may increase the volatility of our foreign based revenue and costs; |
| • | potentially adverse tax consequences, including those arising from the complexities of foreign value added tax (or other tax, including transfer pricing) systems, and restrictions on the repatriation of earnings; |
| • | uncertain political and economic climates; |
| • | reduced or varied protection for intellectual property rights in some countries. |
These factors and other related issues may cause our costs of doing business in new geographies to exceed the existing costs of our comparable operations in the United States and India. Operating in new international markets also requires significant management attention and financial resources. Any negative impact from our international business efforts could negatively impact our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We have significant operations in India. As of December 31, 2014, 840 of our approximately 1,740 employees were based in India. Operating in India requires substantial resources and management attention and subjects us to economic, political and operational risks that are different from those in the United States. For example, there have been armed conflicts between India and neighboring Pakistan. Also, extremist groups within India and neighboring Pakistan have from time to time targeted Western interests. Other risks specific to our operations in India include, but are not limited to, difficulty with responding to changes in economic conditions
14
Table of Contents
that may include inflation and fluctuations in exchange rates and interest rates; problems that impair our business infrastructure, such as telephone system failure or an international disruption of our information technology systems by a third party; failure to act in accordance with labor, environmental, health and safety standards and regulations; and the need to increase the levels of our employee compensation more rapidly than in the past to retain talent. If any of these risks materialize, our business, results of operations and financial condition may be materially adversely affected.
We face significant competition from established and new companies offering event and meeting management software.
The market for event and meeting management software is evolving, highly competitive and significantly fragmented, and we expect competition to continue to increase in the future. With the increased demands for event and meeting management solutions as well as the potential influx of new entrants to the market, we expect competition to intensify in the future, which could harm our ability to increase sales and maintain our prices.
Our competitors vary with each challenge that our event and meeting management solutions address, and include providers of point solutions for email marketing, event registration, ecommerce payments, budgeting, web surveys, web content management, scheduling, room and table assignments, name badging, mobile app development, social media, and business intelligence for the hospitality industry. If individual point solutions become less expensive, we may face general pricing pressure or pressure to adjust our pricing model. For example, if mobile app development increases significantly and as a result developers reduce their fees, we may be forced to reduce the fees that we charge for our mobile event apps to remain competitive.
We expect to face additional competition with the continued development and expansion of the event management software market. We expect that new competitors, such as software vendors that have traditionally focused on other applications, may enter the event and meeting management market or hospitality business intelligence market with competing products, which could have an adverse effect on our business, operating results and financial condition. Additionally, competitors may develop a comprehensive event and meeting management platform that is similar to our own.
Our current and potential competitors may have significantly more financial, technical, marketing and other resources than we have; be able to devote greater resources to the development, promotion, sale and support of their products and services; have more extensive customer bases and broader customer relationships; and have longer operating histories and greater name recognition.
As a result, these competitors may be better able to respond quickly to new technologies and to undertake more extensive marketing campaigns. In some cases, these vendors may also be able to offer event and meeting management solutions at little or no additional cost by bundling them with their existing applications. If we are unable to compete with such companies, the demand for our solutions could substantially decline. To the extent any of our competitors have existing relationships with potential customers, those customers may be unwilling to purchase our solutions because of those existing relationships with that competitor. To the extent that we consider acquiring one of our competitors, this heightened competition could increase the cost of an acquisition within our industry.
Moreover, current and future competitors may also make strategic acquisitions or establish cooperative relationships among themselves or with others. By doing so, these competitors may increase their ability to meet the needs of our customers or potential customers. In addition, our current or prospective indirect strategic partners may establish cooperative relationships with our current or future competitors. These developments could limit our ability to obtain revenues from existing and new customers. If we are unable to compete successfully against current and future competitors, our business, results of operations and financial condition would be harmed.
15
Table of Contents
In the past we have completed acquisitions and may acquire or invest in other companies or technologies in the future, which could divert management’s attention, fail to meet our expectations, result in additional dilution to our stockholders, increase expenses, disrupt our operations and harm our operating results.
We have acquired businesses, products or technologies that we believe could complement or expand our platform, enhance our technical capabilities or otherwise offer growth opportunities. We cannot assure you that we will realize the anticipated benefits of these or any future acquisitions. The potential pursuit of additional acquisitions may divert the attention of management and cause us to incur various expenses related to identifying, investigating and pursuing suitable acquisitions, whether or not they are completed.
If we acquire additional businesses, we may be unable to assimilate or integrate the acquired personnel, operations or technologies successfully, effectively manage the combined business following the acquisition and our management may be distracted from operating our existing business. We also may not achieve the anticipated benefits from the acquired business due to a number of factors, including, but not limited to the following:
| • | unanticipated costs or liabilities associated with the acquisition; |
| • | incurrence of acquisition-related costs, which would be recognized as a current period expense; |
| • | inability to generate sufficient revenue to offset acquisition or investment costs, or failure to generate the revenue we had anticipated from the acquired business; |
| • | the inability to maintain and renew relationships with customers and partners of the acquired business; |
| • | the difficulty of incorporating acquired technology and rights into our platform and of maintaining quality and security standards consistent with our brand; |
| • | delays in customer purchases due to uncertainty related to any acquisition; |
| • | the need to integrate or implement additional controls, procedures and policies; |
| • | challenges caused by distance, language and cultural differences; |
| • | harm to our existing business relationships with business partners and customers as a result of the acquisition; |
| • | the potential loss of key employees; |
| • | use of resources that are needed in other parts of our business and diversion of management and employee resources; |
| • | the inability to recognize acquired revenue in accordance with our revenue recognition policies and the loss of acquired deferred revenue; |
| • | the use of substantial portions of our available cash or the incurrence of debt to consummate the acquisition; |
| • | delays or errors in integrating back-end systems and departments, including but not limited to accounting and CRM systems. |
Acquisitions may also increase the risk of unforeseen legal liability, including for potential violations of applicable law or industry rules and regulations, arising from prior or ongoing acts or omissions by the acquired businesses which are not discovered by due diligence during the acquisition process. If an acquired business fails to meet our expectations, our operating results, business and financial condition may suffer. Acquisitions could also result in dilutive issuances of equity securities or the incurrence of debt, which could adversely affect our business, results of operations or financial condition.
Many of these risks are heightened by the fact that the companies we have acquired have been small and technologically early in their development. It is common for such companies to lack mature systems and processes. This has created challenges, including with respect to financial integration and accounting for acquired companies, and will create future challenges to the extent we acquire similar companies in the future. In addition,
16
Table of Contents
a significant portion of the purchase price of companies we acquire may be allocated to goodwill and other intangible assets, which must be assessed for impairment at least annually. Also, contingent consideration related to acquisitions will be remeasured to fair value at each reporting period, with any changes in the value recorded as income or expense. Our recent acquisitions all contained a contingent consideration element and/or other compensatory arrangements based on continued employment of certain key employees. If our acquisitions do not ultimately yield expected returns, we may be required to take charges to our operating results based on our impairment assessment process, which could harm our results of operations.
Any significant disruption in service on our websites, mobile applications or in our computer systems—whether caused by a third party, by a failure to scale and adapt our infrastructure, or by other causes—could damage our reputation and result in fees to customers or a loss of users, which would harm our business and operating results.
Our websites, mobile applications and computer systems, the majority of which are hosted by third-party providers, are a critical component of our business. We have experienced limited interruptions in these systems in the past, including server failures that temporarily slowed down the performance of our websites and mobile applications, and we may experience more significant interruptions in the future. Regardless of cause, any interruptions in these systems could affect the security or availability of our services on our websites and mobile applications and prevent or inhibit the ability of our customers and event and meeting registrants to access our services. Problems with the reliability or security of our systems could also harm our reputation or result in substantial costs to remedy these problems, any of which could negatively affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We have entered into agreements with many of our customers and business partners that obligate us to compensate them should an interruption affect their use of our services. While some of the communications, network and computer hardware used to provide our services, including our websites and mobile applications, are located at our headquarters in Tysons Corner, Virginia, a significant amount of this hardware is located in a facility in Ashburn, Virginia which we do not own or control. Also, businesses we have acquired rely heavily on third-party service providers to host their software applications, web services, data storage, credit card processing and other computing infrastructure, thereby increasing our dependence on these third party providers. Problems faced by our third-party information technology providers could adversely affect the experience of our customers. Our third-party information technology providers could decide to close their facilities without adequate notice. Any financial difficulties, such as bankruptcy reorganization, faced by our third-party web-hosting providers or any of the service providers with whom they contract may have negative effects on our business, the nature and extent of which are difficult to predict. For example, our web hosting service provider has recently declared bankruptcy, which suggests a heightened risk of interruptions in their service and a possibility of system failure. Any errors, defects, disruptions or other performance problems with any of our third-party information technology providers could directly affect our ability to provide services to our customers, which may result in liabilities to us and our customers, harm our reputation and negatively affect our business, operating results and financial condition.
Further, we may have difficulty scaling and adapting our existing infrastructure to accommodate increased traffic and storage demands, technology advances or customer requirements, which could cause delays or service disruptions and adversely affect our reputation and operating and financial results. In the future, advances in technology, increases in traffic and storage demands and new customer requirements may require us to change our infrastructure, expand our infrastructure or replace our infrastructure entirely. Scaling and adapting our infrastructure is likely to be complex and require additional technical expertise. If we are required to make any changes to our infrastructure, we may incur substantial costs and experience delays or disruptions in our service. These delays or disruptions may cause customers and partners to become dissatisfied with our service and move to competing providers of event and meeting management solutions. Our failure to accommodate increased traffic and storage demands, increased costs, inefficiencies or failures to adapt to new technologies or customer requirements and the associated adjustments to our infrastructure could harm our business, results of operations and financial condition.
17
Table of Contents
We are also dependent on the maintenance and expansion of the infrastructure of the internet, over which we have no control. Any failure of the internet infrastructure we rely on, even for a short period of time, could harm our business, operating results and financial condition. In addition, our systems and operations are vulnerable to damage, interruption or complete failure from fire, flood, power loss, telecommunications failure, terrorist attacks, acts of war, electronic and physical break-ins, computer viruses, earthquakes and similar events. Our systems are not completely redundant, so a failure of our system at one site could result in reduced functionality for our customers, and a total failure of our systems at both sites could cause our platform to be completely unavailable for all customers. In particular, because our primary and back-up sites are both located in Virginia, a broad failure of the power grid could cause both sites to lose power, which could cause our platform to be completely unavailable to all customers.
Our business is susceptible to declines or disruptions in the demand for events and meetings, including those due to economic downturns or natural disasters.
Our business and financial performance are affected by the health of the worldwide events and meetings industry. Events and meetings are sensitive to business-related discretionary spending levels and tend to grow more slowly or even decline during economic downturns. Decreased expenditures by meeting planners and participants could also result in decreased demand for our event management solutions, thereby causing a reduction in our sales. In addition, sales of our marketing solutions to hotels and venues may suffer if fewer event and meeting planners use our solutions. Although we are optimistic about the capabilities of our solutions to assist event and meeting planners in maximizing return on investment when funds available to spend on events are limited, further economic weakness and uncertainty may nonetheless result in significantly decreased spending on our event and meeting management solutions, which may adversely affect our business, operating results and financial condition.
External factors beyond our control may adversely affect the events and meetings industry, with a corresponding negative impact on our business and operating results. Economic downturns, natural disasters, such as hurricanes, tsunamis, earthquakes or volcanic eruptions, and other phenomena, such as pandemics and epidemics, have previously disrupted normal travel patterns and levels, which has correspondingly disrupted the events and meetings industry. The events and meetings industry is also sensitive to other events beyond our control, such as political instability, regional hostilities, increases in fuel prices, the emergence and widespread adoption of more-effective teleconference and virtual meeting technologies, imposition of taxes or surcharges by regulatory authorities, travel related accidents and terrorist attacks, any of which could have an impact on our business and results of operations. For example, the September 2001 terrorist attacks in the U.S. had a dramatic and sustained impact on the travel industry generally, which had a corresponding negative impact on the events and meetings industry thereafter. Any future terrorist attack, whether on a small or large scale, could have a material and negative impact on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
We are dependent in part upon our relationships with our strategic partners to sustain the flow of business through the Cvent Supplier Network.
Our access to certain customers is facilitated in some cases by strategic partner relationships with certain companies. If these strategic partners terminate or do not renew their relationships with us, it could have a negative effect on revenue for sales of our event management software solutions. Approximately 56% of the RFPs transmitted to hotels and venues through CSN during the year ended December 31, 2014 originated from event planners introduced to us through these partnerships. As such, the loss of several of these partnerships would greatly diminish the value of the CSN.
Our business depends substantially on renewing agreements with existing customers and selling additional solutions to them. Any decline in our customer renewals or expansions would likely harm our future operating
18
Table of Contents
results, especially if we are unable to recognize sufficient revenue to offset related customer acquisition costs prior to such termination or cancellation of our customer agreements.
We offer our event and meeting management solutions primarily through annual and multi-year subscription agreements and our hotel and venue marketing solutions primarily through a mix of single-year and multi-year arrangements. In order for us to improve our operating results, it is important that our event and meeting management customers renew their existing subscription agreements and our hotel and venue advertisers renew their advertising agreements with us when the initial term expires, as well as purchase additional solutions and advertising from us.
In some cases, our customers have no renewal obligation after their initial term expires, and we cannot be assured that we will be able to renew agreements with any of our customers at the same or higher contract value. Some agreements also contain a termination right for the customer in the event of customer dissatisfaction with our services because of substantial nonperformance that remains uncured by us.
In addition, some of our customer contracts allow for a termination for convenience. If our customers do not renew their agreements, renew on less favorable terms to us or fail to purchase additional solutions or advertising, our revenue may decline, and our operating results would likely be harmed.
We typically bill customers for no longer than the upcoming contract year with payment due upfront regardless of the full length of the contract, although we incur most of our customer acquisition costs at the time of sale. These costs can be significant. If a customer does not renew or cancels its agreement with us, we may not recognize sufficient revenue from that customer prior to the termination or cancellation to offset the acquisition costs associated with that customer.
Growth of our business will depend on a strong brand, and any failure to maintain, protect, and enhance our brand would hurt our ability to retain or expand our base of users, or our ability to maintain or increase their level of engagement with us.
We believe that a strong brand is necessary to continue to attract and retain event and meeting planners and, in turn, the hotels and venues who choose to advertise on the Cvent Supplier Network. We need to maintain, protect, and enhance our brand to expand our base of customers and users and increase their engagement with our solutions. This will depend largely on our ability to continue to provide high-value, differentiated solutions, and we may not be able to do so effectively.
While we may choose to engage in a broader marketing campaign to further promote our brand, this effort may not be successful. Furthermore, negative publicity about our company, including our content, technology, sales practices, personnel or customer service could diminish confidence in, and the use of, our solutions, any of which could harm our operating results. If we are unable to maintain or enhance customer awareness of our brand cost-effectively, our business, operating results and financial condition could be harmed.
Event and meeting planners may not widely adopt our applications to manage the important aspects of their events and meetings, which would limit our ability to grow our business.
Our ability to grow our business and increase revenue depends on our success in educating event and meeting planners about the potential benefits of our cloud-based platform. Cloud applications for organizing and managing important aspects of events and meetings have not previously been widely adopted by event and meeting planners. Concerns about cost, fraud, privacy, security, reliability and other issues may cause event and meeting planners not to adopt our applications. Moreover, event and meeting planners who have already invested substantial resources in other registration and management systems or methods may be reluctant to adopt a new approach like ours to supplement or replace existing systems or methods. If event and meeting planners do not widely adopt applications such as ours, our ability to grow our business will be limited.
19
Table of Contents
We rely on third-party mobile application platforms such as the Apple App Store and the Google Play Store to distribute our mobile applications. If we are unable to maintain a good relationship with such platform providers, if their terms and conditions or pricing change to our detriment, if we violate, or if a platform provider believes that we have violated, the terms and conditions of its platform, or if any of these platforms are unavailable for a prolonged period of time, our business will suffer.
We distribute our mobile event applications through third-party platforms, such as the Apple App and Google Play stores. We are subject to these platforms’ standard terms and conditions for application developers, which govern the promotion, distribution and operation of applications on their platforms. If we violate, or if a platform provider believes that we have violated, these terms and conditions, the particular platform provider may discontinue or limit our access to that platform, which could prevent us from satisfying our contractual obligations to our mobile customers. Our business could also be harmed if a platform provider modifies its current terms of service or other policies, including fees, in a manner adverse to us.
We also rely on the continued operation of these third-party platforms. In the past, some of these platforms have been unavailable for short periods of time. If this recurs on a prolonged or frequent basis, or other similar issues arise that impact users’ ability to download or use our mobile event applications, we may owe our customers rebates, which would increase our expenses and lower our gross margins. Our revenue, operating results or brand could also suffer harm. Furthermore, any material change or deterioration in our relationship with these platform providers could harm our business.
We have experienced losses in the past and we may not sustain profitability in the future.
We have incurred a significant accumulated deficit in prior periods, in large part due to accretion of redemption features on previously outstanding preferred stock in those periods. We experienced net income of $1.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 and a net loss of $3.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2013, and have an accumulated deficit as of December 31, 2014 of $21.2 million.
We anticipate that our operating expenses will increase substantially in the foreseeable future as we continue to invest to grow our business and acquire clients, develop our platform, develop new solutions and comply with the requirements of being a public company. These efforts may prove to be more expensive than we currently anticipate, and we may not succeed in increasing our revenue sufficiently to offset these higher expenses. Many of our efforts to generate revenue from our business, particularly with respect to our marketing solutions are unproven, and any failure to increase our revenue or generate revenue from new solutions could prevent us from attaining or increasing profitability. Furthermore, to the extent we are successful in increasing our customer base, we could also incur increased losses because costs associated with entering into customer agreements are generally incurred up front, while revenue is generally recognized ratably over the term of the agreement. If we are unable to effectively manage these risks and difficulties as we encounter them, our business, financial condition and results of operations may suffer.
Seasonality may cause fluctuations in our revenue and operating results.
We generally experience seasonality in our marketing solutions sales due to the seasonality of the underlying marketing budgets of hotels and venues. Hotels and venues advertising on the Cvent Supplier Network have historically made more purchasing decisions in the fourth quarter of the calendar year.
If we do not continue to innovate and provide solutions that are useful to our customers and event registrants and attendees, we may not remain competitive, and our revenue and operating results could suffer.
Our success depends on continued innovation to provide features and services that make our solutions, websites and mobile apps useful for event and meeting planners, hotels and venues and event registrants and attendees. Our competitors are frequently developing innovations in services and features. Additionally, the rapid pace at which technology evolves generally requires us to find new ways to deliver our solutions to end users with better performance and functionality. As a result, we must continue to invest significant resources in research and development in order to continually improve the speed, accuracy and comprehensiveness of our
20
Table of Contents
solutions. We may introduce significant changes to our existing solutions or develop and introduce new and unproven solutions, including using technologies with which we have little or no prior development or operating experience. If we are unable to continue offering innovative solutions or if new or enhanced solutions fail to engage event and meeting planners, hotels and venues or event registrants and attendees, we may be unable to attract additional customers or event registrants or retain our current customers or event registrants and attendees, which may adversely affect our business, operating results and financial condition.
Defects or disruptions in our ability to deliver new products and product enhancements could diminish demand for our service, adversely affect our reputation and subject us to substantial liability.
Like many internet-based cloud companies, we provide frequent incremental releases of product updates and functional enhancements. Such new versions frequently contain undetected errors when first introduced or released. We have, from time to time, found defects in our service, and new errors in our existing service may be detected in the future. In addition, our customers may use our service in unanticipated ways that may cause a disruption in service for other customers or for event registrants. Since our customers use our service for important aspects of their business, any errors, defects, disruptions in service or other performance problems with our service could hurt our reputation and may damage our customers’ businesses. If that occurs, our customers may delay or withhold payment to us, elect not to renew, make service credit claims, warranty claims or other claims against us, and we could lose future sales. The occurrence of any of these events could result in an increase in our bad debt expense, an increase in collection cycles for accounts receivable, require us to increase our warranty provisions or incur the expense or risk of litigation. Further, if we are unable to meet the stated service level commitments we have guaranteed to our customers or suffer extended periods of unavailability for our service, we may be contractually obligated to provide these customers with credits for future service, and there would be a negative impact on our reputation.
Our sales cycle can be lengthy and unpredictable, which may cause our operating results to vary significantly.
Our sales cycle, which is the time between initial contact with a potential customer and the ultimate sale to that customer, is often lengthy and unpredictable. Potential customers typically spend significant time and resources evaluating event management and venue marketing solutions, which require us to expend substantial time, effort, and money educating them about the value of our offerings. Accordingly, it is difficult for us to forecast when or if a sale will close or the size of any specific sales. In addition, customers may delay their purchases from one quarter to another as they (i) wait for us to develop new features, (ii) assess their budget constraints or (iii) forecast future business activity. Any delay in closing, or failure to close, sales in a particular quarter or year could significantly harm our projected growth rates and could cause our operating results to vary significantly.
We are increasingly targeting our sales efforts at large enterprise customers. For large enterprises, the customer’s decision to use our solution may be an enterprise-wide decision and require us to provide more education about the use and benefits of our software, as well as education regarding privacy and data protection laws and regulations to prospective customers with international operations. In addition, larger customers may demand more complicated client set-up, integration services, and features. Further, these opportunities may require us to devote greater sales support and professional services resources to targeted customers. Accordingly, selling to enterprise customers will necessarily increase our costs of sales, lengthen our sales cycles, and decrease our capability to predict our ability to close the sale. The increased costs may also decrease our gross margins. If a customer is not satisfied with the quality of work performed by us or with the type of services or solutions delivered, we could incur additional costs to address the situation, the profitability of that work might be impaired, and the customer’s dissatisfaction with our services could damage our ability to obtain additional work from that customer. In addition, negative publicity related to our customer relationships, regardless of its accuracy, could harm our professional reputation and operating results.
21
Table of Contents
We rely on the performance of highly skilled personnel, including senior management and our sales and technology professionals; if we are unable to retain or motivate key personnel or hire, retain and motivate qualified personnel, our business would be harmed.
We believe our success has depended, and continues to depend, on the efforts and talents of our senior management and our highly skilled team members, including our sales personnel and software engineers. Competition for well-qualified employees in all aspects of our business, including sales personnel and software engineers, is intense. Our continued ability to compete effectively depends on our ability to attract new employees and to retain and motivate existing employees. If we do not succeed in attracting well-qualified employees or retaining and motivating existing employees, our business would be adversely affected. The loss of any of our senior management or key employees could adversely affect our ability to build on the efforts they have undertaken and to execute our business plan, and we may not be able to find adequate replacements. We cannot ensure that we will be able to retain the services of any members of our senior management or other key employees.
If we fail to offer high quality customer support, our business and reputation would suffer.
Our customers rely on our customer support services. High-quality education and customer support is important for the successful marketing and sale of our solutions and for the renewal of our agreements with existing customers. The importance of high quality customer support will increase as we expand our business and pursue new customers. If we do not help our customers quickly resolve issues and provide effective ongoing support, our ability to sell new services to existing and new customers would suffer and our reputation with existing or potential customers would be harmed.
Our growth rate over the past few years may not be sustainable. If we fail to maintain an adequate growth rate, our business will be adversely affected and we may not achieve or maintain profitability.
Our revenue has grown rapidly over the past few years. We may not be able to sustain this level of growth in future periods, and you should not rely on the revenue growth of any prior quarterly or annual period as an indication of our future performance. Further, a portion of our revenue growth in the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 resulted from acquisitions and not organic growth. We may not complete acquisitions in the future that increase our revenue at the same rate as in prior periods. The identification of suitable acquisition candidates can be difficult, time-consuming and costly, and we may not be able to successfully complete the acquisitions we do identify as worth pursuing. If we are unable to maintain an adequate rate of growth, our business will be adversely affected and we may not maintain profitability.
Failure to adequately expand our direct sales force will impede our growth.
We will need to continue to expand and optimize our sales infrastructure in order to grow our customer base and our business. We plan to continue to expand our direct sales force, both domestically and internationally. Identifying and recruiting qualified personnel and training them requires significant time, expense and attention. It can take several months before our sales representatives are fully trained and productive. Our business may be adversely affected if our efforts to expand and train our direct sales force do not generate a corresponding increase in revenue. In particular, if we are unable to hire, develop and retain talented sales personnel, or if new direct sales personnel are unable to achieve desired productivity levels in a reasonable period of time, we may not be able to realize the expected benefits of this investment or increase our revenue.
If we cannot maintain our corporate culture as we grow, we could lose the innovation, teamwork, passion and focus on execution that we believe contribute to our success, and our business may be harmed.
We believe that a critical component to our success has been our corporate culture. We have invested substantial time and resources in building our team. As we grow and develop the infrastructure of a public company, we may find it difficult to maintain these important aspects of our corporate culture. Any failure to
22
Table of Contents
preserve our culture could negatively affect our future success, including our ability to retain and recruit personnel and to effectively focus on and pursue our corporate objectives.
If we do not or cannot maintain the compatibility of our solutions with third-party applications that our customers use in their businesses, demand for our solutions could decline.
The functionality of our cloud-based platform depends, in part, on our ability to integrate it with third-party applications and data management systems that our customers use and from which they obtain data. In addition, we rely on access to third-party application programming interfaces, or APIs, to provide our social media channel offerings through social media platforms. Third-party providers of these applications, data management systems and APIs may terminate their relationships with us, change the features of their applications and platforms, restrict our access to their applications and platforms or alter the terms governing use of their applications, data management systems and APIs and access to those applications and platforms in an adverse manner. Such changes could functionally limit or terminate our ability to use these third-party applications and platforms with our cloud-based platform, which could negatively impact our offerings and harm our business. Further, if we fail to integrate our platform with new third-party applications and platforms that our customers use, or to adapt to the data transfer requirements of such third-party applications and platforms, we may not be able to offer the functionality that our customers need, which would negatively impact our offerings and, as a result, could negatively affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
If the estimates and assumptions we use to determine the size of our target market, customer groups or the verticals within customer groups are inaccurate, our future growth rate may be limited and our business would be harmed.
We calculate the size of our target market, customer groups and verticals within customer groups, based on data published by third parties and on internally generated data and assumptions. We have not independently verified any third-party information and cannot assure you of its accuracy or completeness. While we believe our market size information is generally reliable, such information is inherently imprecise. In addition, our projections, assumptions and estimates of future opportunities within our target market are necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk due to a variety of factors, including those described in this report. If third-party or internally generated data prove to be inaccurate or we make errors in our assumptions based on that data, our future growth rate may be limited. In addition, these inaccuracies or errors may cause us to misallocate capital and other business resources, which would harm our business.
If Internet search engines’ methodologies are modified or our search result page rankings decline for other reasons, participant engagement in our websites and online communities could decline.
We depend in part on various Internet search engines to direct a significant amount of traffic to our websites. Our ability to maintain the number of potential participants directed to our websites is not entirely within our control. Our competitors’ search engine optimization, or SEO, efforts may result in their websites receiving a higher search result page ranking than ours, or Internet search engines could revise their methodologies in an attempt to improve search results, which could adversely affect placement of our search result page rankings. If search engine companies revise their search algorithms in ways that are detrimental to new participant growth on our websites or in ways that make it more difficult for organizers or participants to use our websites, or if competitors’ SEO efforts are more successful than ours, the overall growth in the numbers of organizers and participants using our websites could slow, participant engagement could decrease and we could lose existing participants and become less attractive to existing and prospective organizer customers. Our websites have experienced fluctuations in search result rankings in the past, and we anticipate similar fluctuations in the future. Any reduction in the number of participants directed to our website would harm our business and operating results.
23
Table of Contents
Legal and Regulatory Risks
We are subject to U.S. and foreign data privacy and protection laws and regulations as well as contractual privacy obligations, and our failure to comply could subject us to fines and damages and would harm our reputation and business.
We are subject to the data privacy and protection laws and regulations adopted by federal, state and foreign legislatures and governmental agencies. Data privacy and protection is highly regulated, and may become the subject of additional regulation in the future. Privacy laws restrict our storage, use, processing, disclosure, transfer and protection of non-public personal information, including credit card data, provided to us by our event and meeting planners and registrants. We strive to comply with all applicable laws, regulations, policies and legal obligations relating to privacy and data protection. However, it is possible that these requirements may be interpreted and applied in a manner that is inconsistent from one jurisdiction to another and may conflict with other rules or our practices. Any failure, or perceived failure, by us to comply with federal, state, or international laws, including laws and regulations regulating privacy, payment card information, personal health information, data or consumer protection, could result in proceedings or actions against us by governmental entities or others.
The regulatory framework for privacy and data protection issues worldwide is evolving, and various government and consumer agencies and public advocacy groups have called for new regulation and changes in industry practices, including some directed at providers of mobile and online resources in particular. Our obligations with respect to privacy and data protection may become broader or more stringent. If we are required to change our business activities or revise or eliminate services, or to implement costly compliance measures, our business and results of operations could be harmed.
In addition, as we expand our operations globally, compliance with regulations that differ from country to country may also impose substantial burdens on our business. In particular, the European Union, or E.U., has traditionally taken a broader view as to what is considered personal information and has imposed greater obligations under data privacy regulations. In addition, individual E.U. member countries have had discretion with respect to their interpretation and implementation of the regulations, which has resulted in variation of privacy standards from country to country. Complying with any additional or new regulatory requirements could force us to incur substantial costs or require us to change our business practices in a manner that could compromise our ability to effectively pursue our growth strategy. Further, because we do not maintain a data center in the E.U., E.U. regulators could determine that we transfer data from the E.U. to the U.S., which could subject us to regulatory obligations or liability.
We are also subject to the privacy and data protection-related obligations in our contracts with our customers and other third parties, including voluntary third-party trade associations and industry self-regulatory groups that promulgate best practices or codes of conduct such as the Direct Marketing Association. We could be adversely affected by changes to these contracts, guidelines or codes in ways that are inconsistent with our practices or in conflict with the laws and regulations of the United States, foreign or international regulatory authorities. We may also be contractually liable to indemnify and hold harmless our clients from the costs or consequences of inadvertent or unauthorized disclosure of data that we store or handle as part of providing our services. Finally, we are also subject to contractual obligations and other legal restrictions with respect to our collection and use of data, and we may be liable to third parties in the event we are deemed to have wrongfully used or gathered data.
Any failure by us or a third-party contractor providing services to us to comply with applicable privacy and data protection laws, regulations, self-regulatory requirements or industry guidelines, our contractual privacy obligations or our own privacy policies, may result in fines, statutory or contractual damages, litigation or governmental enforcement actions. These proceedings or violations could force us to spend significant amounts in defense or settlement of these proceedings, result in the imposition of monetary liability, distract our management, increase our costs of doing business, and adversely affect our reputation and the demand for our solutions.
24
Table of Contents
Federal, state and foreign laws impose certain obligations on the senders of commercial emails, which could minimize the effectiveness of our event management email solutions, limit our ability to market to prospective customers and impose financial penalties for noncompliance.
The U.S.’s CAN-SPAM Act establishes certain requirements for commercial email messages and specifies penalties for the transmission of commercial email messages that are intended to deceive the recipient as to source or content. The CAN-SPAM Act, among other things, obligates the sender of commercial emails to provide recipients with the ability to opt out of receiving future emails from the sender. In addition, some states and foreign jurisdictions, including Canada, have passed laws regulating commercial email practices, some of which are significantly more punitive and difficult to comply with than the CAN-SPAM Act. The ability of recipients of emails from our customers using our event management software to opt out of receiving commercial emails may minimize the effectiveness of our solutions for our customers. Also, the ability of event planners to opt out of receiving future emails from us may minimize our ability to expand our event planner network. In addition, noncompliance with the CAN-SPAM Act carries significant litigation, regulatory investigation and related risks. If we were found to be in violation of the CAN-SPAM Act or similar state, foreign or international laws regulating the distribution of commercial email, whether as a result of violations by our customers or if we were deemed to be directly subject to and in violation of these requirements, we could incur penalties, and significant litigation and investigation-related expenses, and any inquiries might impact the deliverability of our commercial email regardless of outcome. This would adversely affect our operating results and financial condition and significantly harm our business, and our reputation would suffer. We also may be required to change one or more aspects of the way we operate our business, which could impair our ability to attract and retain customers or could increase our operating costs.
There can be no assurance that the limitations of liability in our contracts would be enforceable or adequate or would otherwise protect us from any such liabilities or damages with respect to any particular claim. We also cannot provide assurances that our existing general liability insurance coverage and coverage for errors and omissions will continue to be available on acceptable terms or will be available in sufficient amounts to cover one or more large claims or that the insurer will not deny coverage as to any future claim. The successful assertion of one or more large claims against us that exceeds available insurance coverage, or the occurrence of changes in our insurance policies, including premium increases or the imposition of large deductible or co-insurance requirements, could have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
We are subject to the rules and regulations adopted by the payment card networks, such as Visa, MasterCard and American Express, and if we fail to adhere to their rules and regulations, we would be in breach of our contractual obligations to payment processors and merchant banks, which could subject us to damages and liability and could eventually prevent us from processing or accepting credit card payments.
The payment card networks, such as Visa, MasterCard and American Express, have adopted rules and regulations that apply to all merchants who process and accept credit cards for payment of goods and services. We are obligated to comply with these rules and regulations as part of the contracts we enter into with payment processors and merchant banks. The rules and regulations adopted by the payment card networks include the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards, or the PCI DSS. Under the PCI DSS, we are required to adopt and implement internal controls over the use, storage and security of payment card data to help prevent fraud. We assess our compliance with the PCI DSS on a periodic basis, and make necessary improvements to our internal controls. If we fail to comply with the rules and regulations adopted by the payment card networks, including the PCI DSS, we would be in breach of our contractual obligations to payment processors and merchant banks. Such failure to comply may subject us to fines, penalties, damages and civil liability, and could eventually prevent us from processing or accepting debit and credit cards or could lead to a loss of payment processor partners. Further, there is no guarantee that even if we comply with the rules and regulations adopted by the payment card networks, we will be able to maintain our compliance. For example, we have acquired businesses in the past that were not immediately compliant with PCI DSS at the time of our acquisition. Until those businesses are fully integrated with our own systems we may be unable to comply with PCI DSS standards for those acquired businesses without substantial additional costs. We also cannot guarantee that such compliance will prevent illegal or improper use of
25
Table of Contents
our payments systems or the theft, loss or misuse of the debit or credit card data of customers or participants or regulatory or criminal investigations. Any such event would harm our reputation and may result in a loss of service for our customers, which would adversely affect our business, operating results and financial condition.
Our failure to protect our intellectual property, in the United States and abroad, could harm our business and operating results.
Our business depends on proprietary technology and content, including software, databases, confidential information and know-how, the protection of which is crucial to the success of our business. We rely on a combination of trademark, domain name, trade secret, and copyright law and contractual restrictions to protect our proprietary technology and content. We have begun to seek patent protection for certain of our technologies and currently have two U.S. patent applications on file, although there can be no assurance that a patent will ultimately be issued in either case. We are also pursuing the registration of our domain names, trademarks and service marks in the United States and in certain locations outside the United States.
Effective trademark, trade secret, patent, copyright and domain name protection is expensive to develop and maintain, and the costs of defending our rights may be significant. The intellectual property rights we obtain may not be sufficient to provide us with a competitive advantage, and may be successfully challenged, invalidated, circumvented, infringed or misappropriated. For example, in the past, competitors in both the United States and foreign jurisdictions have infringed our trademark rights and infringed our copyright rights and we have incurred varying levels of costs to respond to such infringement. Over time, we may increase our investment in protecting our intellectual property through additional trademark, patent and other intellectual property filings that could be expensive and time-consuming. Some aspects of our business and services also rely on technologies, software and content developed by or licensed from third parties, and we may not be able to maintain our relationships with such third parties or enter into similar relationships in the future on reasonable terms or at all.
We may also be required to protect our proprietary technology and content in an increasing number of jurisdictions, a process that is potentially expensive and may not be successful, or which we may not pursue in every location. In addition, effective intellectual property protection may not be available to us in every country, and the laws of some foreign countries may not be as protective of intellectual property rights as those in the United States. Additional uncertainty may result from changes to intellectual property legislation enacted in the United States and elsewhere, and from interpretations of intellectual property laws by applicable courts and agencies. Accordingly, despite our efforts, we may be unable to obtain and maintain the intellectual property rights necessary to provide us with a competitive advantage.
We attempt to further protect our proprietary technology and content by requiring our employees and consultants to enter into confidentiality and assignment of inventions agreements and third parties to enter into nondisclosure agreements. These agreements may not effectively prevent unauthorized use or disclosure of our confidential information, intellectual property or technology and may not provide an adequate remedy in the event of unauthorized use or disclosure of our confidential information, intellectual property or technology. Despite our efforts to protect our proprietary rights, unauthorized parties may attempt to copy aspects of our website features, software and functionality or obtain and use information that we consider confidential or proprietary.
Litigation or proceedings before the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office or other governmental authorities and administrative bodies in the United States and abroad may be necessary in the future to: Enforce our intellectual property rights; to protect our trademarks, trade secrets, patents, copyrights and domain names; and to determine the validity and scope of the proprietary rights of others. We may also be involved in disputes relating to the rights to, and ownership of, the intellectual property developed by our employees, consultants and others. Our efforts to enforce or protect our proprietary rights may be ineffective and could result in substantial costs and diversion of resources, as well as the invalidation or narrowing of the scope of our intellectual property, any of which could harm our business and operating results. Attempting to enforce our intellectual property rights against third parties could also expose us to counterclaims from such third parties.
26
Table of Contents
Claims by third parties that we infringe upon their intellectual property rights could result in significant costs and have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results or financial condition.
Our success depends, in part, upon our noninfringement of intellectual property rights owned by others and being able to resolve claims of intellectual property infringement without major financial expenditures or adverse consequences. The software industry generally is characterized by extensive intellectual property litigation. Although we were an early pioneer of event management software, a field which continues to rapidly evolve, many participants that own, or claim to own, intellectual property related to elements of our business historically have aggressively asserted their rights. From time to time, we may be subject to legal proceedings and claims that we, our customers, licensees or parties indemnified by us are infringing, misappropriating or otherwise violating the intellectual property rights of others, and the risk of such proceedings and claims may increase as we expand the complexity, scope and public profile of our business. For example, we may be subject to claims that we are infringing the patent, trademark or copyright rights of third parties, or that our employees have misappropriated or divulged their former employers’ trade secrets or confidential information.
It may therefore be necessary to defend against future claims by, for example, determining the scope, enforceability and validity of third-party proprietary rights or asserting and defining our proprietary rights. Some claimants may have substantially greater resources than we do and may be able to sustain the costs of complex intellectual property litigation to a greater degree and for longer periods of time than we could. In addition, patent holding companies that focus solely on extracting royalties and settlements by enforcing patent rights may target us. Regardless of whether they have any merit, these claims are time-consuming and costly to evaluate and defend and could:
| • | adversely affect our relationships with our current or future customers; |
| • | cause delays or stoppages in providing our software solutions; |
| • | divert management’s attention and resources; |
| • | require technology changes to our platform that would cause us to incur substantial cost; |
| • | subject us to significant liabilities; |
| • | necessitate incurring significant legal fees; and |
| • | require us to cease some or all of our activities. |
In addition to liability for monetary damages against us, which may be tripled and may include attorneys’ fees, or, in some circumstances, damages against our customers, we may be prohibited from developing, commercializing or continuing to provide some or all of our event and meeting management solutions unless we obtain licenses from, and pay royalties to, the holders of the patents or other intellectual property rights, which may not be available on commercially favorable terms, or at all.
Some of our applications utilize open source software, and any failure to comply with the terms of one or more of these open source licenses could negatively affect our business.
Some of our applications include software covered by open source licenses, which may include, by way of example, GNU General Public License and the Apache License. The terms of various open source licenses have not been interpreted by courts, and there is a risk that such licenses could be construed in a manner that imposes unanticipated conditions or restrictions on our ability to market our applications. By the terms of certain open source licenses, we could be required to release the source code of our applications and to make our applications available under open source licenses, if we combine or distribute our applications with open source software in a certain manner. In the event that portions of our applications are determined to be subject to an open source license, we could be required to publicly release the affected portions of our source code, re-engineer all, or a portion of, those applications or otherwise be limited in the licensing of our applications, each of which could reduce or eliminate the value of our technologies and services. In addition to risks related to license requirements, usage of open source software can lead to greater risks than use of third party commercial software, as open source licensors generally do not provide warranties or controls on the origin of the software.
27
Table of Contents
Many of the risks associated with usage of open source software cannot be eliminated, and could negatively affect our business, results of operations and financial condition.
Our business may be adversely affected by third-party claims, including by governmental bodies, regarding the content and advertising distributed by our customers through our service.
We rely on our customers to secure the rights to redistribute content over the internet or through mobile event apps, and we do not screen the content that they distribute using our solutions. There is no assurance that our customers have licensed all rights necessary for distribution, including internet or mobile app distribution. Other parties may claim certain rights in the content of our customers. In the event that our customers do not have the necessary distribution rights related to content, we may be required to cease distributing such content, or we may be subject to lawsuits and claims of damages for infringement of such rights. If these claims arise with frequency, the likelihood of our business being adversely affected would rise significantly.
We are a multinational organization faced with increasingly complex tax issues in many jurisdictions, including in the United States, and we could be obligated to pay additional taxes in various jurisdictions.
As a multinational organization that operates in numerous jurisdictions in the United States and around the world, we may be subject to taxation in several jurisdictions with increasingly complex tax laws, the application of which can be uncertain. The authorities in these jurisdictions, including state and local taxing authorities in the United States, could successfully assert that we are obligated to pay additional taxes, interest and penalties. In addition, the amount of taxes we pay could increase substantially as a result of changes in the applicable tax principles, including increased tax rates, new tax laws or revised interpretations of existing tax laws and precedents, which could have a material adverse effect on our liquidity and operating results. The authorities could also claim that various withholding requirements apply to us or our subsidiaries or assert that benefits of tax treaties are not available to us or our subsidiaries, any of which could have a material impact on us and the results of our operations.
As Internet commerce develops, federal, state and foreign governments may propose and implement new taxes and new laws to regulate Internet commerce, which could increase our operating costs and negatively affect our business.
As Internet commerce continues to evolve, increasing regulation by federal, state or foreign governments becomes more likely. Our business could be negatively impacted by the interpretation and enforcement of existing laws and regulations or the enactment of new laws applicable to interactive marketing. The cost to comply with such laws or regulations could be significant and would increase our operating expenses, and we may be unable to pass along those costs to our customers in the form of increased fees. Legislation has been introduced in Congress in the past and may be reintroduced in the future that, if enacted into law, would authorize states to require out-of-state retailers to collect and remit sales taxes on goods sold online. In addition, federal, state and foreign governmental or regulatory agencies may decide to impose taxes on services provided over the Internet or via email. Such taxes could discourage the use of the Internet and email as a means of commercial marketing, which would adversely affect the viability of our software.
Risks Relating to Finance and Financial Reporting
We have identified material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting, and if we are unable to achieve and maintain effective internal control over financial reporting or effective disclosure controls, this could have a material adverse effect on our business.
In connection with the preparation of our consolidated financial statements for the year ended December 31, 2014, and as discussed in Item 9A “Controls and Procedures”, we concluded there were material weaknesses in the design and operating effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as defined in SEC Regulation S-X. A material weakness is defined as a deficiency, or a combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of a company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis by the
28
Table of Contents
company’s internal controls. As of December 31, 2014, the primary factors contributing to the material weaknesses, which relates to our control environment and financial statement close process, were:
| • | We did not have adequate policies and procedures in place to ensure the effective design and operation of general IT controls over our financial reporting systems. Specifically, we identified significant deficiencies in internal controls related to access to programs and data, and program development and changes, which we consider in the aggregate to be a material weakness, due to the inability to rely on certain system generated reports and application controls. |
| • | We had ineffective entity and process level controls impacting the preparation and review of our consolidated financial statements and ineffective process level controls related to the review of manually prepared analyses and supporting information used to prepare our consolidated financial statements. Specifically, we identified significant deficiencies in internal controls related to inappropriately designed and ineffective controls over financial integration of and accounting for acquired companies, cut off procedures and review of account reconciliations. We also determined we had ineffective controls related to the preparation and review of our financial statements; all of which in the aggregate, were determined to be a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. |
As a result of various factors including, in part, the identified material weaknesses in the design and operation of our internal controls over financial reporting, our management concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures as of December 31, 2014 were ineffective. Furthermore, our management may be unable to conclude in future periods that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective due to the effects of various factors, which may, in part, include unremediated material weakness in internal controls over financial reporting. The term “disclosure controls and procedures,” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the rules and forms of the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the company’s management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Because we are an emerging growth company, our independent registered public accounting firm did not perform an audit of our internal control over financial reporting for the fiscal year ending December 31, 2014. Had our independent registered public accounting firm performed an audit of our internal control over financial reporting, material weaknesses and/or significant deficiencies, in addition to those discussed above, may have been identified. Our qualification as an emerging growth company may last for up to five years following our IPO on August 8, 2013, during which time our independent registered public accounting firm will not perform any audits of our internal control over financial reporting. On the other hand, our qualification as an emerging growth company may expire as early as December 31, 2015. If our qualification as an emerging growth company expires before we have remediated our material weaknesses, our independent registered public accounting firm may not be able to attest to the effectiveness of our internal controls over financial reporting.
We cannot assure you that we will be able to remediate our existing material weaknesses in a timely manner, if at all, or that in the future additional material weaknesses will not exist, reoccur or otherwise be discovered, a risk that is significantly increased in light of the complexity of our business. If our efforts to remediate these material weaknesses are not successful or if other deficiencies occur, our ability to accurately and timely report our financial position, results of operations, cash flows or key operating metrics could be impaired, which could result in late filings of our annual and quarterly reports under the Exchange Act, restatements of our consolidated financial statements or other corrective disclosures. Additional impacts could include a decline in our stock price, suspension of trading or delisting of our common stock by the New York Stock Exchange, or other material adverse effects on our business, reputation, results of operations, financial condition or liquidity. Furthermore, if we continue to have these existing material weaknesses, other material weaknesses or significant deficiencies in the future, it could
29
Table of Contents
create a perception that our financial results do not fairly state our financial condition or results of operations. Any of the foregoing could have an adverse effect on the value of our stock.
Because we generally recognize revenue from subscriptions ratably over the term of the agreement, near term changes in sales may not be reflected immediately in our operating results.
We offer our event and meeting management solutions primarily through a mix of single-year and multi-year subscription agreements and generally recognize revenue ratably over the related subscription period. We offer our hotel and venue marketing solutions primarily through a mix of single-year and multi-year arrangements and generally recognize revenue ratably over the related advertising period. As a result, much of the revenue we report in each quarter is derived from the recognition of previously billed and unbilled contract value relating to agreements entered into during prior quarters or years. In addition, as we generally invoice for no more than the next fiscal year for most customer contracts, including those for multiple years, we do not record deferred revenue beyond amounts invoiced as a liability on our balance sheet. A decline in new or renewed subscriptions or marketing solutions agreements in any one quarter is not likely to be reflected immediately in our revenue results for that quarter. Such declines, however, would negatively affect our revenue and deferred revenue balances in future periods, and the effect of significant downturns in sales and market acceptance of our solutions, and potential changes in our rate of renewals, may not be fully reflected in our results of operations until future periods. Our subscription and advertising model also makes it difficult for us to rapidly increase our total revenue and deferred revenue balance through additional sales in any period, as revenue from new customers must be recognized over the applicable subscription or advertising term.
Changes in financial accounting standards or practices, or our application of those standards or practices may cause adverse, unexpected financial reporting fluctuations and affect our reported results of operations.
Generally accepted accounting principles in the United States are subject to interpretation by the Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants, the Securities and Exchange Commission and various bodies formed to promulgate and interpret appropriate accounting principles. A change in accounting standards or practices can have a significant effect on our reported results and may even affect our reporting of transactions completed before the change is effective. New accounting pronouncements and varying interpretations of accounting pronouncements have occurred and may occur in the future. In addition, we may have flexibility to choose among multiple accounting methods that are generally accepted. Changes to existing rules, our application of those rules or the questioning of current practices may adversely affect our reported financial results or the way we conduct our business.
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) issued joint guidance to improve and converge the financial reporting requirements for revenue from contracts with customers. ASU 2014-9, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, prescribes a five-step model for revenue recognition that will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance under U.S. GAAP. The new standard supersedes nearly all existing revenue recognition guidance under U.S. GAAP, and requires companies to recognize revenue when it transfers goods or services to a customer in an amount that reflects the consideration to which a company expects to be entitled for those goods or services. This update also requires additional disclosure about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from customer contracts, including significant judgments and changes in judgments, and assets recognized from costs incurred to obtain or fulfill a contract. ASU 2014-09 allows for either full retrospective or modified retrospective adoption and will become effective for the Company in the first quarter of 2017. Early adoption is prohibited. Management is currently evaluating which adoption method it will use and assessing the effect the adoption of this standard will have on the consolidated financial statements. Our adoption of this standard may adversely affect our reported revenue and results of operations.
We may not be able to utilize a significant portion of our net operating loss carryforwards, which could adversely affect our profitability.
As of December 31, 2014, we had federal and state net operating loss carryforwards due to prior period losses, which, if not utilized, will begin to expire in 2021 for both federal and state purposes. These net operating
30
Table of Contents
loss carryforwards could expire unused and be unavailable to offset future income tax liabilities, which could adversely affect our profitability. In addition, under Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, our ability to utilize net operating loss carryforwards or other tax attributes, such as research tax credits, in any taxable year may be further limited if we experience an “ownership change”. A Section 382 “ownership change” generally occurs if one or more stockholders or groups of stockholders who own at least 5% of our stock increase their ownership by more than 50 percentage points over their lowest ownership percentage within a rolling three-year period. Similar rules may apply under state tax laws. For example, we had an “ownership change” under Section 382 in 2001. Future issuances of our stock could cause an “ownership change.” It is possible that an ownership change in connection with any future ownership change, could have a material effect on the use of our net operating loss carryforwards or other tax attributes, which could adversely affect our profitability.
We are exposed to fluctuations in currency exchange rates.
We face exposure to movements in currency exchange rates, which may cause our revenue and operating results to differ materially from expectations. Our operating results could be negatively affected depending on the amount of expense denominated in foreign currencies, primarily the Indian rupee. As exchange rates vary, revenue, cost of revenue, operating expenses and other operating results, when remeasured, may differ materially from expectations. In addition, our operating results are subject to fluctuation if our mix of U.S. and foreign currency denominated transactions and expenses changes in the future. Although we may apply certain strategies to mitigate foreign currency risk, these strategies might not eliminate our exposure to foreign exchange rate fluctuations and would involve costs and risks of their own, such as ongoing management time and expertise, external costs to implement the strategies and potential accounting implications. Additionally, as we anticipate growing our business further outside of the U.S., the effects of movements in currency exchange rates will increase as our transaction volume outside of the U.S. increases.
We may not be able to secure additional financing on favorable terms, or at all, to meet our future capital needs.
We have funded our operations since inception primarily through equity financings, lease arrangements, and cash from operations. In the future, we may require additional capital to respond to business opportunities, challenges, acquisitions, a decline in the level of operating cash flows or unforeseen circumstances. We may determine to engage in equity or debt financings or enter into credit facilities for other reasons, and we may not be able to secure additional debt or equity financing in a timely manner on favorable terms, or at all. We do not currently have access to a credit arrangement, and we currently fund our operations using cash generated from operations. Any debt financing obtained by us in the future could involve restrictive covenants relating to our capital raising activities and other financial and operational matters, which may make it more difficult for us to obtain additional capital and to pursue business opportunities, including potential acquisitions. If we raise additional funds through further issuances of equity, convertible debt securities or other securities convertible into equity, our existing stockholders could suffer significant dilution in their ownership of our company, and any new equity securities we issue could have rights, preferences and privileges senior to those of holders of our common stock. If we are unable to obtain adequate financing or financing on terms satisfactory to us, when we require it, our ability to continue to grow or support our business and to respond to business challenges could be significantly limited.
Risks Related to this Securities Market and Ownership of Our Common Stock
Our quarterly results may fluctuate significantly and may not fully reflect the underlying performance of our business.
Our quarterly results of operations, including the level of our revenue, profitability, cash flow and deferred revenue, may vary significantly in the future and period-to-period comparisons of our operating results may not be meaningful. Accordingly, the results of any one quarter should not be relied upon as an indication of future performance. Our quarterly financial results may fluctuate as a result of a variety of factors, many of which are
31
Table of Contents
outside of our control, and as a result, may not fully reflect the underlying performance of our business. Fluctuation in quarterly results may negatively impact the value of our common stock. Factors that may cause fluctuations in our quarterly financial results include, without limitation, those listed below:
| • | our ability to attract new customers; |
| • | the addition or loss of existing customers, including through acquisitions or consolidations; |
| • | the timing of recognition of revenue; |
| • | the amount and timing of operating expenses related to the maintenance and expansion of our business, operations and infrastructure; |
| • | network outages or security breaches; |
| • | general economic, industry and market conditions; |
| • | customer renewal rates; |
| • | increases or decreases in the number of features and functionality of our services or pricing changes upon any renewals of customer agreements; |
| • | changes in estimates used in the calculation of our income tax provision; |
| • | changes in our pricing policies or those of our competitors; and |
| • | seasonal variations in sales of our solutions, which have historically been highest in the fourth quarter of a calendar year. |
If securities or industry analysts do not publish or cease publishing research or reports about us, our business or our market, or if they change their recommendations regarding our stock adversely, or if our actual results differ significantly from our guidance, our stock price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common stock will be influenced by the research and reports that industry or securities analysts may publish about us, our business, our market or our competitors. If any of the analysts who may cover us change their recommendation regarding our stock adversely, or provide more favorable relative recommendations about our competitors, our stock price would likely decline. If any analyst who may cover us were to cease coverage of our company or fail to regularly publish reports on us, we could lose visibility in the financial markets, which in turn could cause our stock price or trading volume to decline.
In addition, from time to time, we may release earnings guidance or other forward-looking statements in our earnings releases, earnings conference calls or otherwise regarding our future performance that represent our management’s estimates as of the date of release. Some or all of the assumptions of any future guidance that we furnish may not materialize or may vary significantly from actual future results. Any failure to meet guidance or analysts’ expectations could have a material adverse effect on the trading price or volume of our stock.
An active, liquid and orderly trading market for our common stock may not develop, the price of our stock may be volatile, and you could lose all or part of your investment.
Prior to our initial listing of our common stock on the New York Stock Exchange on August 9, 2013 in connection with our IPO, there was no public market for shares of our common stock. We cannot assure you that an active trading market for our shares will continue to develop or be sustained. If an active market for our common stock does not continue to develop or is not sustained, it may be difficult to sell shares without depressing the market price for the shares or to sell your shares at all.
In addition, the stock market in general, and the market for technology companies in particular, has experienced extreme price and volume fluctuations that have often been unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of those companies. Broad market and industry factors may seriously affect the market price of companies’ stock, including ours, regardless of actual operating performance. In addition, in the past, following periods of volatility in the overall market and the market price of a particular company’s securities,
32
Table of Contents
securities class action litigation has often been instituted against these companies. This litigation, if instituted against us, could result in substantial costs and a diversion of our management’s attention and resources.
We do not expect to declare any dividends in the foreseeable future.
We do not anticipate declaring any cash dividends to holders of our common stock in the foreseeable future. We anticipate that we will retain all of our future earnings for use in the development of our business and for general corporate purposes. Any determination to pay dividends in the future will be at the discretion of our Board of Directors. Consequently, investors may need to rely on sales of their common stock after price appreciation, which may never occur, as the only way to realize any future monetary benefit on their investment. Investors seeking cash dividends should not purchase our common stock.
A significant portion of our total outstanding shares are restricted from immediate resale but may be sold into the market in the near future. This could cause the market price of our common stock to drop significantly, even if our business is doing well.
The market price of shares of our common stock could decline as a result of (i) substantial sales of our common stock (particularly sales by our directors, executive officers, employees and significant stockholders), (ii) a large number of shares of our common stock becoming available for sale or (iii) the perception in the market that holders of a large number of shares intend to sell their shares.
We have 41,353,520 shares of common stock outstanding including early exercised shares, as of December 31, 2014. Of this amount, 27,336,065 shares are currently held by our executive officers, directors and current beneficial owners of 5% or more of our common stock and their respective affiliates and are eligible to be sold in the public market, subject to any vesting requirements and the provisions of Rule 144 or Rule 701.
Additionally, the holders of an aggregate of approximately 8,500,000 shares of our common stock will continue to have rights, subject to some conditions, to require us to file one or more registration statements covering their shares or to include their shares in registration statements that we may file for ourselves or other stockholders. If we were to register these shares for resale, they could be freely sold in the public market. If these additional shares are sold, or if it is perceived that they will be sold, in the public market, the trading price of our common stock could decline.
Concentration of ownership of our common stock among our existing executive officers, directors and principal stockholders may prevent new investors from influencing significant corporate decisions.
Our executive officers, directors and current beneficial owners of 5% or more of our common stock and their respective affiliates, in aggregate, beneficially own approximately 66% of our outstanding common stock. These persons, acting together, would be able to significantly influence all matters requiring stockholder approval, including the election and removal of directors and any merger or other significant corporate transactions. The interests of this group of stockholders may not coincide with our interests or the interests of other stockholders.
Anti-takeover provisions contained in our certificate of incorporation and bylaws, as well as provisions of Delaware law, could impair a takeover attempt.
Our certificate of incorporation, bylaws, and Delaware law contain provisions which could have the effect of rendering more difficult, delaying, or preventing an acquisition deemed undesirable by our board of directors. Our corporate governance documents include provisions: creating a classified board of directors whose members serve staggered three-year terms; authorizing “blank check” preferred stock, which could be issued by our board of directors without stockholder approval and may contain voting, liquidation, dividend and other rights superior to our common stock; limiting the liability of, and providing indemnification to, our directors and officers; limiting the ability of our stockholders to call and bring business before special meetings; requiring advance notice of stockholder proposals for business to be conducted at meetings of our stockholders and for nominations of candidates for election to our board of directors; and controlling the procedures for the conduct and scheduling
33
Table of Contents
of board of directors and stockholder meetings. These provisions, alone or together, could delay or prevent hostile takeovers and changes in control or changes in our management.
As a Delaware corporation, we are also subject to provisions of Delaware law, including Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation law, which prevents some stockholders holding more than 15% of our outstanding common stock from engaging in certain business combinations without approval of the holders of substantially all of our outstanding common stock.
Any provision of our certificate of incorporation, bylaws or Delaware law that has the effect of delaying or deterring a change in control could limit the opportunity for our stockholders to receive a premium for their shares of our common stock, and could also adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
We will continue to incur significantly increased costs and devote substantial management time as a result of operating as a public company.
As a public company, we incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company. For example, we are subject to the reporting requirements of the Exchange Act and will be required to comply with the applicable requirements of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010, as well as rules and regulations subsequently implemented by the Securities and Exchange Commission and the New York Stock Exchange, including the establishment and maintenance of effective disclosure and financial controls and changes in corporate governance practices. We expect that compliance with these requirements will increase our legal and financial compliance costs and will make some activities more time consuming and costly. In addition, our management and other personnel devote substantial time to our public company requirements, which diverts attention from operational and other business matters. In particular, we expect to incur significant expenses and devote substantial management effort toward ensuring compliance with the requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, which will increase when we are no longer an “emerging growth company,” as defined by the JOBS Act. We will need to continue to hire additional accounting and financial staff with appropriate public company experience and technical accounting knowledge and maintain an internal audit function. We cannot predict or estimate the amount of additional costs we may incur as a result of becoming a public company or the timing of such costs.
As a public company, it is more difficult and more expensive for us to obtain director and officer liability insurance on the terms that we would like as compared to prior periods when we were a privately-held company. As a result, it may be more difficult for us to attract and retain qualified people to serve on our board of directors, our board committees or as executive officers.
We are an “emerging growth company,” and any decision on our part to comply only with certain reduced reporting and disclosure requirements applicable to emerging growth companies could make our common stock less attractive to investors.
We are an “emerging growth company,” as defined in the JOBS Act, and, for as long as we continue to be an “emerging growth company,” we may choose to take advantage of exemptions from various reporting requirements applicable to other public companies but not to “emerging growth companies.” These examples include, but are limited to, not being required to have our independent registered public accounting firm audit our internal controls over financial reporting under Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, reduced disclosure obligations regarding executive compensation in our periodic reports and proxy statements, and exemptions from the requirements of holding a nonbinding advisory vote on executive compensation and stockholder approval of any golden parachute payments not previously approved. We could be an “emerging growth company” for up to five years following the completion of our initial public offering, although, if we have more than $1.0 billion in annual revenue, if the market value of our common stock that is held by non-affiliates exceeds $700 million as of June 30 of any year, or if we issue more than $1.0 billion of non-convertible debt over a three-year period before the end of that five-year period, we would cease to be an “emerging growth company” as of the following December 31, which could be as early as December 31, 2015. When our qualification as an emerging growth
34
Table of Contents
company expires, we will face some additional costs and different risks, as detailed above under the Risk Factors captioned “—We will continue to incur significantly increased costs and devote substantial management time as a result of operating as a public company” and “—We have identified material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting, and if we are unable to achieve and maintain effective internal control over financial reporting or effective disclosure controls, this could have a material adverse effect on our business.”
We cannot predict if investors will find our common stock less attractive if we choose to rely on the exemptions applicable to emerging growth companies. If some investors find our common stock less attractive as a result of any choices to reduce future disclosure, there may be a less active trading market for our common stock and our stock price may be more volatile.
We may invest or spend the proceeds from our initial and secondary public offerings in ways which may not yield a return.
Our management will have considerable discretion in the application of the net proceeds from our initial and secondary public offerings, and you will not have the opportunity, as a stockholder, to assess whether the proceeds are being used appropriately. The net proceeds may be invested with a view towards long-term benefits for our stockholders and this may not increase our operating results or market value. Until the net proceeds are used, they may be placed in investments that do not produce significant income or that may lose value.
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
None.
| Item 2. | Properties |
We currently lease approximately 129,000 square feet of space for our corporate headquarters in Tysons Corner, Virginia. The lease is for a fixed 11-year term with options for two additional renewal terms of five years each. We also lease approximately 70,000 square feet of space for our Gurgaon, India office under a lease agreement that expires in April 2018. Both of these offices are used for administrative, marketing, support and development operations. We also lease office space in Austin, Texas; Portland, Oregon; Los Angeles, California; Santa Barbara, California; Atlanta, Georgia; Fredericton, Canada; and London, England.
We believe that our current facilities and planned expansion space will be adequate for the foreseeable future; however, we will continue to seek additional space as needed, to satisfy our growth.
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings |
From time to time, we are subject to claims in legal proceedings arising in the normal course of our business. We do not believe that we are party to any pending legal action that could reasonably be expected to have a material adverse effect on our business or operating results. The information set forth under Legal Proceedings, Regulatory Matters and Other Contingencies in note 11 contained in the “Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements” is incorporated herein by reference.
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures |
Not applicable.
35
Table of Contents
PART II
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
Stock Price
Our common stock commenced trading on the New York Stock Exchange under the symbol “CVT” on August 9, 2013. The following table sets forth, for the periods indicated, the high and low reported sales prices of our common stock as reported on the New York Stock Exchange:
| High | Low | |||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2014 |
||||||||
| Fourth quarter |
$ | 28.82 | $ | 22.13 | ||||
| Third quarter |
$ | 29.83 | $ | 24.27 | ||||
| Second quarter |
$ | 36.46 | $ | 22.42 | ||||
| First quarter |
$ | 44.31 | $ | 33.61 | ||||
| Year ended December 31, 2013 |
||||||||
| Fourth quarter |
$ | 40.60 | $ | 30.49 | ||||
| Third quarter (from August 9, 2013) |
$ | 46.13 | $ | 30.01 | ||||
Holders
As of March 12, 2015, there were approximately 99 holders of record of our common stock, although we believe that there may be a significantly larger number of beneficial owners of our common stock. We derived the number of stockholders by reviewing the listing of outstanding common stock recorded by our transfer agent as of March 12, 2015.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock. We anticipate that we will retain any earnings for use in the development of our business and for general corporate purposes. Accordingly, we do not expect to pay cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. Any determination to pay dividends in the future will be at the discretion of our board of directors.
Use of Proceeds from Sale of Registered Equity Securities
August 2013 Initial Public Offering
On August 8, 2013, our Registration Statement on Form S-1, as amended (Reg. No. 333-189837) was declared effective in connection with the initial public offering of our common stock, pursuant to which we registered an aggregate of 6,440,000 shares of our common stock, all of which were sold by us, including the underwriters’ over-allotment, at a price to the public of $21.00 per share. The offering closed on August 14, 2013, and, as a result, we received net proceeds of approximately $122.1 million after underwriters’ discounts and commissions of approximately $9.5 million and additional offering-related costs of approximately $3.6 million). The managing underwriters of the offering were Morgan Stanley & Co. LLC and Goldman, Sachs & Co. No payments for such expenses were made directly or indirectly to (i) any of our officers or directors or their associates, (ii) any persons owning 10% or more of any class of our equity securities, or (iii) any of our affiliates. There has been no material change in the planned use of proceeds from our IPO as described in the final prospectus relating to that offering dated August 8, 2013. We invested the funds received in registered money market funds and to date have used a portion of the funds for acquisition costs.
January 2014 Follow-On Public Offering
On January 16, 2014, our Registration Statements on Form S-1, as amended (Reg. Nos. 333-193188 and 333-193400) were declared effective in connection with the follow-on public offering of our common stock,
36
Table of Contents
pursuant to which we and the selling stockholders in such transaction registered the sale of an aggregate of 6,072,000 shares of our common stock, 747,500 shares of which were sold by us and 5,324,500, including the underwriters’ over-allotment sold by the selling shareholders, at a price to the public of $35.50 per share. The offering closed on January 23, 2014, and, as a result, we received net proceeds of approximately $24.8 million after underwriters’ discounts and commissions of approximately $1.1 million and additional offering-related costs of approximately $650,000. We did not receive any proceeds from the sales of shares by the selling stockholders, other than $96,844 in disgorged profits remitted to the Company by two officers due to their sale of 7,500 shares of common stock under Section 16(b) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. The managing underwriters of the offering were Morgan Stanley & Co. LLC and Goldman, Sachs & Co.
We paid all of the expenses related to the registration and offering of the shares sold by the selling stockholders, other than underwriting discounts and commissions relating to those shares and the fees and expenses of counsel to the selling stockholders. Other than these expenses, we made no payments directly or indirectly to (i) any of our officers or directors or their associates, (ii) any persons owning 10% or more of any class of our equity securities, or (iii) any of our affiliates.
The principal purposes of the offering were to facilitate an orderly distribution of shares for the selling stockholders in the offering and increase our public float. We currently have no specific plans for the use of a significant portion of the net proceeds to us of the offering. As noted above, we used a portion of the net proceeds to us from the offering to pay certain expenses of the selling stockholders in that offering. Additional funds have been used for working capital and general corporate purposes, including further expansion of our operations, product development and acquisition expenses. We invested the remaining funds received in registered money market funds. There has been no material change in the planned use of proceeds from our initial public offering from that described in the final prospectus filed by us with the SEC pursuant to Rule 424(b) dated January 16, 2014.
Stock Performance Graph
This chart compares the cumulative total stockholder return on our common stock with that of the NYSE Composite index and the NASDAQ Computer index. The chart assumes $100 was invested at the close of the market on August 9, 2013 (the date our common stock first commenced trading on the New York Stock Exchange) in our common stock, the NYSE Composite index and the NASDAQ Computer index. The comparison assumes reinvestment of dividends. The comparisons shown in the graph below are based upon historical data. We caution that the stock price performance shown in the graph below is not necessarily indicative of, nor is it intended to forecast, the potential future performance of our common stock.
This performance graph shall not be deemed to be incorporated by reference into our SEC filings and shall not constitute soliciting material or otherwise be considered filed under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
37
Table of Contents
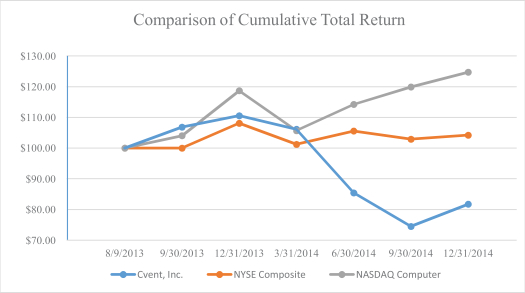
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities
Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities during the Year Ended December 31, 2014
None.
Use of Proceeds from Sale of Unregistered Equity Securities
Not applicable.
Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchasers
None.
38
Table of Contents
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
The following selected consolidated statement of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013, and 2012 and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements that are included elsewhere in this report. The following selected consolidated statement of operations data for the year ended December 31, 2011 and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2012 and 2011 are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements that are not included in this report. The following selected consolidated statement of operations data for the year ended December 31, 2010 and the selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2010 are derived from our unaudited consolidated financial statements that are not included in this report.
Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected in the future. The selected consolidated financial data should be read together with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements, related notes, and other financial information included elsewhere in this report. The selected data in this section is not intended to replace the consolidated financial statements.
Consolidated Statement of Operations Data
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | Unaudited 2010 |
||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 142,245 | $ | 111,136 | $ | 83,474 | $ | 60,854 | $ | 45,060 | ||||||||||
| Cost of revenue(1) |
42,421 | 32,262 | 20,573 | 16,660 | 10,122 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Gross profit |
99,824 | 78,874 | 62,901 | 44,194 | 34,938 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing(1) |
61,764 | 48,405 | 35,873 | 29,305 | 18,227 | |||||||||||||||
| Research and development(1) |
14,049 | 11,190 | 7,605 | 4,172 | 2,201 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative(1) |
24,242 | 21,218 | 11,523 | 8,422 | 6,946 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
100,055 | 80,813 | 55,001 | 41,899 | 27,374 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(231 | ) | (1,939 | ) | 7,900 | 2,295 | 7,564 | |||||||||||||
| Interest income |
1,595 | 1,015 | 811 | 270 | 111 | |||||||||||||||
| Other income |
(434 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations before income taxes |
930 | (924 | ) | 8,711 | 2,565 | 7,675 | ||||||||||||||
| Provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
(864 | ) | 2,315 | 4,406 | 2,749 | 2,932 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 1,794 | $ | (3,239 | ) | $ | 4,305 | $ | (184 | ) | $ | 4,743 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income (loss) per common share: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.04 | $ | (0.13 | ) | $ | 0.13 | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | 0.28 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.04 | $ | (0.13 | ) | $ | 0.12 | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | 0.14 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
40,970 | 25,290 | 33,167 | 16,758 | 17,194 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
43,173 | 25,290 | 34,791 | 16,758 | 33,914 | |||||||||||||||
| (1) | Stock-based compensation expense included in the above: |
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 820 | $ | 1,046 | $ | 762 | $ | 690 | $ | 33 | ||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
1,571 | 2,306 | 2,895 | 2,376 | 57 | |||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
1,002 | 609 | 539 | 373 | 9 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
978 | 772 | 1,010 | 512 | 12 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total stock-based compensation expense |
$ | 4,371 | $ | 4,733 | $ | 5,206 | $ | 3,951 | $ | 111 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
39
Table of Contents
Consolidated Balance Sheet Data
| Unaudited | ||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments, net of restricted cash |
$ | 167,583 | $ | 157,766 | $ | 26,170 | $ | 26,485 | $ | 19,315 | ||||||||||
| Total current assets |
229,849 | 202,583 | 61,320 | 48,764 | 36,806 | |||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
300,908 | 235,836 | 90,030 | 58,441 | 45,376 | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
82,030 | 65,203 | 51,554 | 37,293 | 29,362 | |||||||||||||||
| Total current liabilities |
105,621 | 89,068 | 68,747 | 45,189 | 34,022 | |||||||||||||||
| Total non-current liabilities |
21,453 | 4,730 | 2,553 | 1,086 | 992 | |||||||||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity |
173,834 | 142,038 | 18,730 | 12,166 | 10,362 | |||||||||||||||
40
Table of Contents
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
You should read the following discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations in conjunction with our consolidated financial statements and the related notes to those statements included elsewhere in this report. In addition to historical financial information, the following discussion and analysis contains forward-looking statements that involve risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Consolidated financial data referenced in this section for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 and as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 are derived from our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this report. Our actual results and timing of selected events may differ materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of many factors, including those discussed under “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this report. See “Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements.”
Overview
We are a leading cloud-based enterprise event management platform. We provide solutions for both sides of the events and meetings value chain: (i) event and meeting planners, and (ii) hotels and venues. Our integrated, cloud-based solution addresses the entire event lifecycle by allowing event and meeting planners to organize, market and manage their meetings, conferences, tradeshows and other events. Our online marketplace connects event planners and venues through our vertical search engine that accesses our proprietary database of detailed venue information. The combination of these solutions creates an integrated platform that allows us to generate revenue from both sides of the events and meetings value chain.
Our event and meeting planner customers include enterprises such as corporations, associations, not-for-profits, government agencies and universities. These customers enter into annual and multi-year subscription contracts to utilize part or all of our cloud-based software solutions to plan, manage and execute enterprise events and meetings including external events, such as conferences, tradeshows, and customer events, as well as internal events, such as sales meetings, training seminars and team-building events. As of December 31, 2014, we had over 7,700 event and meeting planner customers. Our event and meeting planner customers used our event management solutions to execute approximately 264,000 events and meetings and managed 10.9 million registrations during the year ended December 31, 2014. Revenue from our event and meeting planning platform subscription solutions were $99.7 million and $77.5 million during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, or 70% of our total revenue during those periods. We generally recognize revenue from these contracts ratably over the term of the contract.
On the other side of the event value chain, hotels and venues utilize our online marketing solutions to generate more visibility with ready-to-transact event and meeting planners. Our online marketplace, the Cvent Supplier Network, or CSN, connects tens of thousands of event and meeting planners seeking the best venue for their event with approximately 235,000 venues in our proprietary database. We believe that CSN contains the world’s largest, most accurate and searchable database of detailed meeting venue information with listings of hotels, conference centers, convention centers, resorts, restaurants, museums, country clubs, wineries, castles and other special event venues in 175 countries. Hotels and venues enter into annual and multi-year advertising contracts with us for marketing solutions that increase the prominence of their properties in CSN; we recognize the revenue from these marketing solutions over the term of the agreement based on the estimated selling prices of each solution. As of December 31, 2014, we had more than 70,000 active CSN event and meeting planner users compared to the approximately 60,000 active CSN event and meeting planner users as of December 31, 2013. The CSN is available with the same functionality to users of our paid subscription event and meeting platform solutions as well as to event and meeting planners that simply visit the CSN site and establish a free user account. All of these users have the ability to submit RFPs to hotels and venues free of charge using the CSN. We consider an event and meeting planner to be “active” if such user accessed their account within the 12 months preceding the date of measurement. As of December 31, 2014, we had approximately 6,300 hotel and venue customers paying for marketing solutions. Event planners transmitted approximately 1.6 million RFPs for events requiring approximately 27.4 million room nights during the year ended December 31, 2014. Revenue from our marketing solutions was $42.5 million and $33.7 million during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively, or 30% of our total revenue during those periods.
41
Table of Contents
We were established in 1999 as a provider of event registration software to event and meeting planners. During the steep economic downturn in the technology sector from 2000 to 2002, we faced initial macroeconomic setbacks to our business and endured substantial austerity. We believe our early struggles have resulted in a strong culture of teamwork and entrepreneurial spirit. We have also evolved during that period from an event registration and event marketing software provider to a comprehensive platform solution covering the entire event value chain starting from venue sourcing to collecting online feedback from attendees.
Our revenue has increased from $26.1 million (unaudited) for the year ended December 31, 2008 to $142.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2014. We first launched CSN in 2008, and revenue from advertising solutions has grown from an immaterial percentage of total revenue during the year ended December 31, 2008, the year CSN was initiated, to 30% of total revenue during each of the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013. Although we have experienced substantial growth in revenues in recent years, we are dependent on attracting new event and meeting planner customers and new marketing customers to sustain a similar level of growth in future periods.
Although we have historically grown our business organically, we acquired two complementary businesses during the year ended December 31, 2014 and three complementary businesses during the year ended December 31, 2012. No acquisitions were completed during the year ended December 31, 2013.
In September 2014, we acquired Decision Street, LLC to enhance group demand management, one of the three pillars of our Hospitality Cloud. In December 2014, we acquired Elite Meetings International, Inc. (EMI), which complemented our group marketing solutions pillar of the Hospitality Cloud by adding two additional RFP vehicles to power business sourcing.
In January 2012, we acquired Seed Labs, LLC, now branded, together with our ticketing business, as our CrowdTorch product, to develop our mobile app capabilities for consumer events. In June 2012, we acquired CrowdCompass, Inc. to develop our mobile app capabilities for business events. In December 2012, we acquired TicketMob LLC to develop our ticketing capabilities. We expect to maintain our focus on organic growth in the future and may pursue opportunistic acquisitions that add complementary technology or expand our geographic footprint. We have also seen an encouraging demand for mobile applications within our existing and new event planning customers.
We generate the majority of our revenue from North America. Revenue from outside North America accounted for 11%, 10% and 9% for years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. We believe our market opportunity is global, and we expect that international revenue will grow as a percentage of our total revenue in future periods as we place increasing emphasis on developing that element of our business. To support our international expansion and to increase global sales for all of our solutions, we opened our first European sales office in London in May 2013 and ultimately plan to expand our sales force in Europe. We also plan to introduce select European and Asian language planner interfaces in future periods to strengthen our penetration within European and Asian event and meeting planner markets.
We believe an important element of our past success has been the effective use of our India office. As of December 31, 2014, we employed approximately 840 personnel in India, representing every business function. Our India operations help us accomplish three business objectives: (i) near-continuous technical development and customer service, (ii) worldwide geographic reach for marketing efforts and (iii) building and maintaining our proprietary databases. Combining the resources of our U.S. and India operations, we are able to continue technical development and customer support throughout the normal business hours of each region. In addition, our India office houses the majority of our marketing personnel for the Asia-Pacific and Europe, Middle East and Africa regions. Finally, we leverage our Indian operations to build our large event planner contact database and to research and maintain approximately 235,000 venues on our CSN. We are able to benefit greatly from the labor and infrastructure cost advantages of the region and accomplish many critical business tasks in an efficient and cost effective manner.
42
Table of Contents
Since 1999, we have relied on private placements of capital stock, our initial public offering of common stock, our secondary offering of common stock, and cash from operating activities to fund our ongoing operations. In July 2011, three venture capital funds invested $135.9 million in our business. The net proceeds from this transaction were used to repurchase shares held by long-time early angel and venture capital investors as well as from certain members of our senior management. In August 2013, we closed our initial public offering, pursuant to which we received net proceeds of $122.1 million after underwriters’ discounts and commissions and offering-related costs. In January 2014, we closed our follow-on public offering resulting in net proceeds of approximately $24.8 million to us after offering expenses.
Our ability to grow our revenue and capitalize on the significant market opportunity we see for ourselves depends on our ability to get more event planners, hotels and venues to adopt our solutions, grow the number of our solutions being used per customer and expand our geographical presence. In the near-term, although we expect revenue growth, we expect that our cost of revenue and operating expenses will increase as a percentage of revenue. Marketing and sales expenses are also expected to increase as a percentage of revenue, as we continue to expand our direct sales teams, international operations and increase our marketing activities. We believe that we must invest in maintaining a high level of client service and support as we consider it critical for our continued success. As such, we expect to invest in research and development to continue to provide cutting edge solutions for our clients. Finally, we also expect to incur additional general and administrative expenses as a result of our growth.
Key Metrics
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands, except year over year percentage data) |
||||||||||||
| Financial metrics |
||||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 142,245 | $ | 111,136 | $ | 83,474 | ||||||
| Year-over-year percentage increase |
28 | % | 33 | % | 37 | % | ||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 1,794 | $ | (3,239 | ) | $ | 4,305 | |||||
| Cash flows provided by operating activities |
$ | 28,375 | $ | 22,064 | $ | 23,581 | ||||||
| Operating metrics |
||||||||||||
| Event registrations processed |
10,947 | 8,711 | 7,325 | |||||||||
| Events and meetings managed |
264 | 206 | 139 | |||||||||
| Room nights requested |
27,394 | 20,930 | 13,851 | |||||||||
| Number of RFPs transmitted |
1,574 | 1,239 | 1,108 | |||||||||
We monitor the key financial and operating metrics set forth in the preceding table to help us evaluate trends, establish budgets, measure the effectiveness and efficiency of our operations and gauge our cash generation. We discuss revenue and the components of net income (loss) in the sections titled “—Financial Operations Overview” and “—Results of Operations” and cash flows provided by operating activities in the section titled “—Liquidity and Capital Resources.” The other metrics presented are described in further detail as follows:
Event Registrations Processed. We measure event registrations processed as the total number of all attendee registrations executed through our platform in a given period. We believe that the number of event registrations processed and the year-on-year growth rate help us evaluate the scale of events being executed through our software platform. We do not generate revenue on the basis of a fixed percentage per registration. Our pricing model is based on a combination of (i) contracted fees for blocks of registrations with an additional fee being charged for every registration being processed over and above that contracted amount, (ii) annual maintenance fees and (iii) a fee per each additional module sold within our platform, among other considerations. Thus, increases in registrations are a leading indicator of future increases in our revenue. These registrations do not include any tickets/registrations sold on the CrowdTorch event ticketing platform.
43
Table of Contents
Events and Meetings Managed. We define events and meetings managed as the total number of all events and meetings managed through our platform in a given period. This amount includes all events and meetings using the date the event was created as listed in our system to determine which period the event was first actively managed by our platform. This also includes meetings being tracked on our platform by large enterprise clients for budgeting and management purposes, some of which may be historical meetings. This amount does not include events and meetings identified by the planner as not yet active or deleted or any ticketing events managed on the CrowdTorch event ticketing platform. We generally do not generate revenue on the basis of a rate per event or meeting. Our pricing model is based on a combination of (i) contracted fees for blocks of registrations with an additional fee being charged for every registration being processed over and above that contracted amount, (ii) annual maintenance fees and (iii) a fee per each additional module sold within our platform. Thus, the total number of events and meetings managed is a leading indicator of our revenue and helps us evaluate the scale being executed through our Event Management or Strategic Meetings Management solutions.
Room Nights Requested. We measure the number of room nights requested by event planners in a given period based on the total number of hotel guest room nights requested in connection with all unique RFPs transmitted through our Hospitality Cloud in such period less known cancelled RFPs. Although planners may submit a unique RFP created on our system to multiple venues, we consider each individual RFP created and transmitted on our system as an RFP representative of only one event. Event planners occasionally create more than one unique RFP for a particular event under certain circumstances, but we believe such behavior is infrequent. In addition, the actual number of room nights purchased in connection with an event from a particular venue may vary from the room nights requested. Nonetheless, we believe that room nights requested is a leading indicator of our online marketplace’s adoption by event planners and its significant network effects. As the number of room nights requested increases, more venues are incentivized to advertise and list in our Hospitality Cloud due to its value proposition for advertisers.
Number of RFPs Transmitted. We calculate the number of RFPs transmitted as the total count of all RFPs sent to all hotels and venues through our Hospitality Cloud during the period excluding events and meetings identified by the planner as cancelled. Most event planners request proposals from multiple venues for a particular event, and this metric reflects the gross level of activity by planners interacting with venues. We believe that the number of RFPs processed through our Hospitality Cloud is a leading indicator of our online marketplace’s adoption by event planners, as it shows the total level of activity on our network. As the number of RFPs transmitted increases, more venues are incentivized to advertise and list in our Hospitality Cloud due to the increased opportunity for venues to connect with planners.
44
Table of Contents
Financial Operations Overview
Revenue
We generate revenue by offering subscriptions to our Event Management platform and by providing marketing solutions on the Cvent Supplier Network. From 2012 through 2014, our revenue by product was as follows:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Revenue by product: |
||||||||||||
| Platform subscriptions |
$ | 99,707 | $ | 77,468 | $ | 58,733 | ||||||
| Marketing solutions |
42,538 | 33,668 | 24,741 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 142,245 | $ | 111,136 | $ | 83,474 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Percentage of revenue by product: |
||||||||||||
| Platform subscriptions |
70 | % | 70 | % | 70 | % | ||||||
| Marketing solutions |
30 | % | 30 | % | 30 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Platform Subscriptions. We generate the majority of our revenue through subscriptions for our event management solutions platform, pricing for which is based on the features and functionality selected. Our Enterprise solution is targeted towards the large enterprise market, and includes the full functionality of our platform. Our Event Management solution, which is targeted towards mid-market and smaller enterprises, has many of the same features as our Enterprise solution but does not include some of the advanced features and functionality required by larger organizations. The number of attendee registrations available to customers subscribing to the registration functionality is contractually fixed, and registrations above the contracted amount result in additional fees paid by the customer.
Our customer contracts are typically not cancellable without cause and typically range in length from one to four years. We generally recognize revenue from platform subscriptions ratably over the term of the agreement. Customers are typically invoiced in advance on an annual or quarterly basis. Amounts that have been contractually invoiced are initially recorded as deferred revenue and are recognized as revenue ratably over the subscription period. We refer to contractual amounts that have not been invoiced as unbilled contract value. Unbilled contract value is not reflected in our consolidated financial statements.
Platform subscription revenue also includes revenue from our mobile event apps, ticketing, and web survey products. Our mobile event apps and our Enterprise solutions are the fastest growing products within our business.
Marketing Solutions. As discussed above under Item 1. Business, towards the end of 2014, we branded the Hospitality Cloud to provide a full spectrum of cloud-based solutions across the hotel group sales lifecycle. Prior to this, we primarily concentrated on servicing the hospitality sector with marketing solutions through our CSN, which provided substantially all of the revenue for this product line in 2014 and before. Marketing solutions revenue is generated through the delivery of various forms of advertising sold through annual or multi-year contracts to marketers, principally hotels and venues. Such solutions include prominent display of a customer’s venue within the Cvent Supplier Network, the Cvent Destination Guide, the Elite Meetings magazine or in various electronic newsletters. Pricing for the advertisements is based on the term of the advertisement, targeted geography, number of advertisements and prominence of the ad placement.
We generally recognize the revenue from these marketing solutions over the period the advertisements are delivered. Customer contracts are typically not cancellable without cause and typically range in length from one to two years. We generally invoice our customers in advance in annual installments. Amounts that have been invoiced are initially recorded as deferred revenue and are recognized as revenue over the contract period.
45
Table of Contents
Contractual amounts that have not been invoiced, which we refer to as unbilled contract value, are not reflected in our consolidated financial statements.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of revenue primarily consists of employee-related expenses, including salaries, benefits, bonuses and stock-based compensation, related to providing support and hosting our applications, costs of data center capacity, software license fees and amortization expense associated with capitalized software development costs. In addition, we allocate a portion of overhead, such as rent, information technology costs, depreciation and amortization to cost of revenue based on head count.
We are invested in our customers’ success and as such, we will continue to invest in providing support and expanding our capacity to support our growth, which in the near-term will result in higher cost of revenue in absolute dollars and as a percentage of revenue.
Gross Profit and Gross Margin
Gross profit is total revenues less total cost of revenues. Gross margin is gross profit expressed as a percentage of total revenues. We expect that our gross margin may fluctuate from period to period as a result of an increase in depreciation and amortization run-rates in the short-term, and additional costs associated with our recent acquisitions. We also expect gross profit and gross margin to be affected by stock compensation expense due to grants of stock options as we continue to grow and incentivize our employees.
Operating Expenses
Sales and Marketing
Sales and marketing expenses primarily consist of personnel and related expenses for our sales and marketing staff, including salaries, benefits, bonuses, commissions and stock-based compensation. Commissions are expensed when the customer contract is signed. In addition to staff costs, our cost of marketing includes product marketing and other brand-building activities, such as trade shows, product seminars and online marketing.
We intend to continue to invest in sales and marketing and expect spending in these areas to increase in the near-term in absolute dollars and as a percentage of revenue as we continue to expand our business both domestically and internationally. We expect sales and marketing expenses to continue to be among the most significant components of our operating expenses.
Research and Development
Research and development expenses consist primarily of personnel and related expenses for our research and development staff, including salaries, benefits, bonuses and stock-based compensation and the cost of certain third-party contractors. Research and development costs, other than software development expenses qualifying for capitalization, are expensed as incurred.
With the exception of software developed by companies we have acquired, we maintain a unified software code base for our entire platform, which we believe improves the efficiency of our research and development activities. We expect research and development expenses to increase in the near-term in absolute dollars and as a percentage of revenue as we invest in the integration and technological support associated with acquired businesses and technologies.
General and Administrative
General and administrative expenses consist primarily of personnel and related expenses for administrative, finance, legal and human resource staffs, including salaries, benefits, bonuses and stock-based compensation, as well as professional fees, insurance premiums, other corporate expenses, and overhead.
46
Table of Contents
We expect our general and administrative expenses to begin to stabilize as we have now transitioned to operating as a public company. Nevertheless, we expect these expenses to grow incrementally, albeit at a slower rate, to support the growth of the business. Specifically, we still expect to continue to expand our operations and hire additional personnel and will continue to incur expenses related to outside legal counsel, accounting and auditing activities, compliance with public company reporting and corporate governance requirements, insurance requirements and enhancing our internal control environment.
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth selected consolidated statement of operations data for each of the periods indicated.
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 142,245 | $ | 111,136 | $ | 83,474 | ||||||
| Costs of revenue |
42,421 | 32,262 | 20,573 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross profit |
99,824 | 78,874 | 62,901 | |||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
61,764 | 48,405 | 35,873 | |||||||||
| Research and development |
14,049 | 11,190 | 7,605 | |||||||||
| General and administrative |
24,242 | 21,218 | 11,523 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
100,055 | 80,813 | 55,001 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(231 | ) | (1,939 | ) | 7,900 | |||||||
| Interest income |
1,595 | 1,015 | 811 | |||||||||
| Other expense |
(434 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from operations before income taxes |
930 | (924 | ) | 8,711 | ||||||||
| Provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
(864 | ) | 2,315 | 4,406 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 1,794 | $ | (3,239 | ) | $ | 4,305 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The following table sets forth our consolidated statement of operations data as a percentage of revenue for each of the periods indicated.
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Revenue |
100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||||||
| Costs of revenue |
30 | 29 | 25 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross profit |
70 | 71 | 75 | |||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
43 | 44 | 43 | |||||||||
| Research and development |
10 | 10 | 9 | |||||||||
| General and administrative |
17 | 19 | 14 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
70 | 73 | 66 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
— | (2 | ) | 9 | ||||||||
| Interest income |
1 | 1 | 1 | |||||||||
| Other expense |
— | — | — | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from operations before income taxes |
1 | (1 | ) | 10 | ||||||||
| Provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
— | 2 | 5 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) |
1 | % | (3 | )% | 5 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
47
Table of Contents
Revenue
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2014 and 2013
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | Period-to-period change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage of revenue |
Amount | Percentage of revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue by product: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platform subscriptions |
$ | 99,707 | 70 | % | $ | 77,468 | 70 | % | $ | 22,239 | 29 | % | ||||||||||||
| Marketing solutions |
42,538 | 30 | 33,668 | 30 | % | 8,870 | 26 | |||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 142,245 | 100 | % | $ | 111,136 | 100 | % | $ | 31,109 | 28 | % | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Total revenue increased by $31.1 million during the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the prior year due to a $17.2 million increase in revenue from sales to new customers. Revenue from sales of additional features and functionality to existing customers contributed $25.0 million in revenue during the year ended December 31, 2014. These amounts were primarily offset by decreases in revenue due to customers lost during the year ended December 31, 2014.
Platform subscription revenue increased $22.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the prior year due to a $12.5 million increase in revenue from sales of event planning subscriptions to new customers in 2014. Revenue from sales of additional features and functionality to existing customers, increased registration usage and price increase contributed $17.6 million in platform subscription revenue during the year ended December 31, 2014. These amounts were primarily offset by decreases in revenue due to customers lost during the year ended December 31, 2014.
Marketing solutions revenue increased $8.9 million during the year ended December 31, 2014 compared to the prior year due to recognition of $4.7 million revenue from sales to new customers. Net revenue recognized from sales of additional marketing solutions and price increases contributed an additional $7.4 million during the year ended December 31, 2014. These amounts were primarily offset by decreases in revenue due to customers lost during the year.
The impact of acquisitions made in 2014 was not material.
We generate the majority of our revenue from North America with revenue from outside North America accounting for 11% and 10% of total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. As we invest in our UK office, we expect that the proportion of total revenue from outside of North America will grow in the future.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2013 and 2012
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | Period-to-period change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage of revenue |
Amount | Percentage of revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue by product: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Platform subscriptions |
$ | 77,468 | 70 | % | $ | 58,733 | 70 | % | $ | 18,735 | 32 | % | ||||||||||||
| Marketing solutions |
33,668 | 30 | % | 24,741 | 30 | % | 8,927 | 36 | % | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total revenue |
$ | 111,136 | 100 | % | $ | 83,474 | 100 | % | $ | 27,662 | 33 | % | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
48
Table of Contents
Total revenue increased by $27.7 million during the year ended December 31, 2013 compared to the prior year primarily driven by an $18.2 million increase in revenue from sales of products to new customers. Revenue from sales of additional products to existing customers and a full year of revenue for new 2012 customers contributed an additional $18.5 million increase in revenue in 2013. This was partially offset by customers lost during year.
Platform subscription revenue increased in 2013 compared to the prior year primarily due to a $13.6 million increase in revenue from sales of event planning subscriptions to new customers in 2013. Revenue from sales of additional products to existing customers, increased registration usage and a full year of revenue for new 2012 customers contributed $12.1 million in platform subscription revenue in 2013. These amounts were partially offset by customers lost during the year.
Marketing solutions revenue increased in 2013 compared to the prior year primarily due to recognition of revenue from additional marketing solutions, price increases and recognition of a full year of revenue for new 2012 customers of $6.4 million in 2013. Sales of marketing solutions to new 2013 customers contributed an additional $4.7 million in 2013. These amounts were partially offset by customers lost during the year.
We generate the majority of our revenue from North America with revenue from outside North America accounting for 10% and 9% of total revenue for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Cost of Revenue
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2014 and 2013
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | Period-to-period change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage of revenue |
Amount | Percentage of revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 42,421 | 30 | % | $ | 32,262 | 29 | % | $ | 10,159 | 31 | % | ||||||||||||
Cost of revenue increased primarily due to expansion of our customer service and technology divisions to support the growth of our business. Total headcount in our technology division increased by 38% and in our customer service division by 7% from December 31, 2013 to December 31, 2014. This contributed $9.3 million of additional expense in 2014 related to cost of revenue. Depreciation and amortization of capitalized software and acquired technology contributed an increase of $2.1 million. Increases in licenses and fees related to maintaining our data center of $1.7 million, overhead costs of $1.4 million, contracted services of $0.9 million and rent of $0.7 million further contributed to the increase. These increases were partially offset by an increase in capitalized software development cost of $6.1 million, due to increased employee expenses for product development, and a higher percentage of all employees’ time being spent on capitalized projects.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2013 and 2012
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | Period-to-period change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage of revenue |
Amount | Percentage of revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 32,262 | 29 | % | $ | 20,573 | 25 | % | $ | 11,689 | 57 | % | ||||||||||||
Cost of revenue increased primarily due to expansion of our customer service and technology divisions to support the growth of our business. Total headcount in our technology division increased by 44% and customer service division increased by 34% from December 31, 2012 to December 31, 2013, respectively. This contributed
49
Table of Contents
$7.3 million of additional expense in 2013 related to cost of revenue. Amortization of capitalized software and acquired technology contributed to an increase of $1.3 million. Credit card processing fees contributed approximately $0.9 million primarily because of fees paid to merchant A/C providers of our ticketing software. Increases in technology costs of $0.7 million and overhead cost of $0.9 million further contributed to the increase. Stock based compensation increased by $0.3 million due to greater head count and the increase in the grant date fair value of our common stock underlying options granted in the year ended December 31, 2013 as compared to the prior year. Depreciation allocated to cost of revenue increased by $0.3 million.
Operating Expenses
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2014 and 2013
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | Period-to-period change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage of revenue |
Amount | Percentage of revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
$ | 61,764 | 43 | % | $ | 48,405 | 44 | % | $ | 13,359 | 28 | % | ||||||||||||
| Research and development |
14,049 | 10 | % | 11,190 | 10 | % | 2,859 | 26 | % | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
24,242 | 17 | % | 21,218 | 19 | % | 3,024 | 14 | % | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
$ | 100,055 | 70 | % | $ | 80,813 | 73 | % | $ | 19,242 | 24 | % | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Sales and Marketing
Sales & marketing expenses increased by $13.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 over the previous year. The increase is primarily due to increased headcount and expansion of our marketing efforts both domestically and internationally. Total head count of our sales and marketing personnel increased by 11% during 2014 as compared to year-end 2013 to support revenue growth, new product lines and global expansion. This increase contributed $7.9 million of additional expenses in 2014. Increased costs related to our marketing efforts, such as increasing our digital marketing spend, increasing the size of our annual customer conference, increasing the number of partnerships, product seminars and tradeshows in which we participate, contributed an additional $5.4 million to the year-over-year difference.
Research and Development
Research and development expenses increased by $2.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 over the previous year. The increase is primarily due to increased head count within our software development group for technology support for the new functionality on the platform and expanded cloud-delivery infrastructure.
General and Administrative
General and administrative expenses increased by $3.0 million for the year ended December 31, 2014 over the previous year. The increase was primarily due to increased head count for administrative operations, particularly related to increased personnel necessary to operate as a public company following our August 2013 initial public offering. Total head count related to general and administrative operations increased by 28% from December 31, 2013 to December 31, 2014, which contributed $2.4 million of increased personnel and related expenses in the twelve months ended December 31, 2014. The remaining $0.6 million increase was driven by increases in rent, general and administrative expenses and depreciation, partially offset by decreases in transaction costs related to foreign currency rate fluctuations, stock-based compensation and earn out payments related to our acquisitions.
50
Table of Contents
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2013 and 2012
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | Period-to-period change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage of revenue |
Amount | Percentage of revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
$ | 48,405 | 44 | % | $ | 35,873 | 43 | % | $ | 12,532 | 35 | % | ||||||||||||
| Research and development |
11,190 | 10 | % | 7,605 | 9 | % | 3,585 | 47 | % | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
21,218 | 19 | % | 11,523 | 14 | % | 9,695 | 84 | % | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
$ | 80,813 | 73 | % | $ | 55,001 | 66 | % | $ | 25,812 | 47 | % | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
Sales & marketing expenses increased primarily due to increased headcount and expansion of our marketing efforts. Total head count of our sales and marketing personnel increased by 23% during 2013 as compared to year-end 2012 to support revenue growth, new product lines and global expansion. This increase contributed $8.6 million of additional expenses in 2013. Costs related to marketing efforts contributed an additional $2.7 million to the year-over-year difference.
Research and Development
Research and development expenses increased primarily due to increased head count within our software development group as we continue to expand support for product enhancements, add features and functionality to our platform and integrate new product lines. Total head count within research and development increased by 43% from December 31, 2012 to December 31, 2013, which increased personnel and related expenses in 2012 by $2.7 million. Research and development related licensing and fees and other expenses increased by approximately $0.9 million primarily due to spending on investment in recent acquisitions.
General and Administrative
General and administrative expenses increased primarily due to increased head count for administrative operations, particularly related to increased personnel necessary to operate as a public company following our August 2013 initial public offering. Total head count related to general and administrative operations increased by 47% from December 31, 2012 to December 31, 2013, which contributed $3.5 million of increased personnel and related expenses in the twelve months ended December 31, 2013. Additionally, expenses associated with general and administrative expenses contributed an additional $3.2 million. Earn out payments associated with our acquisitions increased $1.4 million. Depreciation and amortization increased by $2.3 million due to the completion of the build out of our new India office and other additions to capitalized software and property, plant and equipment.
Interest Income
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2014 and 2013
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | Period-to-period change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage of revenue |
Amount | Percentage of revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest income |
$ | 1,595 | 1 | % | $ | 1,015 | 1 | % | $ | 580 | 57 | % | ||||||||||||
Interest income increased for the year ended December 31, 2014 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013 due to higher interest rates, comparatively longer deposit periods, and the increased cash and cash equivalents balances from the secondary offering proceeds we held throughout the year ended December 31, 2014, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2013.
51
Table of Contents
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2013 and 2012
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | Period-to-period change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage of revenue |
Amount | Percentage of revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest income |
$ | 1,015 | 1 | % | $ | 811 | 1 | % | $ | 204 | 25 | % | ||||||||||||
Interest income increased for the year ended December 31, 2013 as compared to the year ended December 31, 2012 due to higher interest rates, comparatively longer deposit periods, and the increased cash and cash equivalents balances from IPO proceeds we held throughout the year ended December 31, 2013, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2012.
Provision for (Benefit from) Income Taxes
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2014 and 2013
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | Period-to-period change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage of revenue |
Amount | Percentage of revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
$ | (864 | ) | — | % | $ | 2,315 | 2 | % | $ | (3,179 | ) | (137 | )% | ||||||||||
Income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2014 decreased $3.1 million compared to the year ended December 31, 2013. The decrease principally resulted from an increase in deductions generated from disqualifying dispositions of incentive stock options, a decrease in non-deductible stock-based compensation expense as well as realization of income tax benefits resulting from our operations in a Special Economic Zone in India that were implemented in the fourth quarter of 2013. These decreases are partially offset by the period over period decrease in the loss from operations before income tax.
Comparison of Years Ended December 31, 2013 and 2012
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2013 | 2012 | Period-to-period change | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage of revenue |
Amount | Percentage of revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Percentage | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| (Dollars in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Provision for income taxes |
$ | 2,315 | 2 | % | $ | 4,406 | 5 | % | $ | (2,091 | ) | (47 | )% | |||||||||||
Income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2013 decreased $2.1 million compared to the year ended December 31, 2012. The decrease principally resulted from a decrease in pre-tax book income from 2012 to 2013, offset by a decrease in nondeductible expenses in 2013.
Quarterly Results of Operations
See “Unaudited Quarterly Results of Operations” included in note 15 of the consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K for the unaudited quarterly results of operations for each of the quarters in the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
52
Table of Contents
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Sources of Liquidity
Prior to our IPO, we financed our operations primarily through cash generated from operating activities and in earlier periods from private placements of capital stock. On August 14, 2013, we closed our IPO in which we sold and issued 6,440,000 shares of common stock resulting in net proceeds of approximately $122.1 million to us after offering expenses. On January 23, 2014, we closed our follow-on public offering in which we sold and issued 747,500 shares of common stock resulting in net proceeds of approximately $24.8 million to us after offering expenses. As of December 31, 2014, we had $144.5 million of cash and cash equivalents, excluding $0.4 million of restricted cash and $23.0 million of short-term investments.
We believe our current cash and cash equivalents, short-term investments and cash flow from operations will be sufficient to meet our working capital and capital expenditure requirements for at least the next twelve months. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including our revenue growth rate, our spending to support development efforts, the expansion of sales and marketing activities, the introduction of new and improved software solutions, and our planned investments, particularly in our product development efforts or acquisitions of complementary business and technologies.
Working Capital and Cash Flows
| For the year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in): |
||||||||||||
| Operating activities |
$ | 28,375 | $ | 22,064 | $ | 23,581 | ||||||
| Investing activities |
(55,644 | ) | (13,679 | ) | (22,019 | ) | ||||||
| Financing activities |
25,625 | 121,362 | (2,862 | ) | ||||||||
Our cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments at December 31, 2014 were held for working capital purposes. We do not enter into investments for trading or speculative purposes. Our policy is to invest any cash in excess of our immediate requirements in investments designed to preserve the principal balance and maintain liquidity. Accordingly, our cash and cash equivalents and short-term investments are invested primarily in demand deposit accounts, certificates of deposit and money market funds that are currently providing only a minimal return.
As of December 31, 2014, $1.2 million of our total cash and cash equivalents and $23.0 million of our short-term investments were held in India and $2.7 million of our total cash and cash equivalents were held in deposit accounts in the United Kingdom. These balances are available for general corporate purposes.
Operating Activities
Net cash provided by operating activities is significantly influenced by the amount of cash we invest in personnel and infrastructure to support the anticipated growth of our business, the increase in the number of customers, recurring dollar retention rates and the amount and timing of customer payments. Cash provided by operations in the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 is primarily attributable to net income (loss), which is driven by an increasing customer base and increased sales of our platform subscriptions and marketing services. Cash provided by operations is also attributable to the change in accounts receivable and deferred revenue, which is driven by the seasonality of our business and our strong collections process. Our cash flows from operating activities are generally reflective of our ability to invoice annual subscription fees upfront with net 30 payment terms. Our days sales outstanding, or DSO, is a primary indicator in cash flows from operating activities for a given period. We experience seasonality in our accounts receivable. The first and fourth quarters historically include a higher level of cash collections, which is a result of higher levels of invoicing in the fourth quarter. Additionally, we generally invoice our large hotel customers of the Hospitality Cloud in the fourth
53
Table of Contents
quarter, resulting in higher accounts receivable and deferred revenue balances at year-end and subsequently higher cash collections during the first quarter of the following year. We calculate our DSO on a twelve-month rolling basis using billings for the period divided by accounts receivable and adjusted for the number of days in the period.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $28.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2014, which was primarily driven by a net increase in deferred revenue, offset by an increase in accounts receivable, of $6.3 million during the period, which reflected the continued growth of our business and our practice of invoicing for subscriptions annually in advance. Additionally, an increase in our accounts payable, accrued and other liabilities contributed $8.6 million during the period, reflecting the growth of our business. This amount was partially offset by a $5.2 million increase in prepaids and other assets, which also grew largely due to the increased scale of our business. Net income, as adjusted for depreciation and amortization and stock-based compensation, contributed an additional $16.8 million to cash from operating activities. Our DSO as of December 31, 2014 was 46.
Net cash provided by operating activities was $22.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2013, which was primarily driven by a net increase in deferred revenue, offset by an increase in accounts receivable, of $8.6 million during the period, which reflected the continued growth of our business and our practice of invoicing for subscriptions annually at the beginning of the subscription period. Additionally, an increase in our accounts payable contributed $7.5 million during the period, reflecting the increase in activity due to the growth of our business. This amount was partially offset by a $5.0 million increase in accounts receivable during the period and the $4.8 million increase in prepaids and other assets, which also grew largely due to the increased scale of our business. Net loss, as adjusted for depreciation and amortization and stock-based compensation, contributed an additional $9.3 million to cash from operating activities. Our DSO as of December 31, 2013 was 42.
Investing Activities
Our investing activities have consisted primarily of purchases of equipment and costs related to software developed for internal use, short-term investments, business acquisitions in 2012 and 2014, and contingent consideration payments related to acquisitions. We expect our capital expenditures and our investment activity to continue to increase as our business grows.
For the year ended December 31, 2014, net cash used in investing activities was $55.7 million. This amount was the result of $18.8 million in investments in property and equipment to accommodate the growth of our business and the build out of our new McLean headquarters office and $13.7 million in capitalized software development. In addition, we also invested $11.7 million into acquisitions, including Decision Street and EMI, as well as contingent consideration payments of $2.3 million related to previous acquisitions. We also purchased $11.7 million, net, of short-term investments during the period.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, net cash used in investing activities was $13.7 million. This amount was the result of our $4.2 million in investments in property and equipment to accommodate the growth of our business and the build out of our new India office and $7.1 million in capitalized software development. We also purchased $2.0 million, net, of short-term investments during the period.
Financing Activities
For the year ended December 31, 2014, net cash provided by financing activities was $25.6 million. In January 2014, we completed a follow-on public offering, which resulted in net proceeds of $24.8 million to the Company. Additionally, we received $0.8 million from the exercise of stock options.
For the year ended December 31, 2013, net cash provided by financing activities was $121.4 million. In August 2013, we completed an initial public offering, which resulted in net proceeds to the Company of $122.1 million. We received $0.5 million from the exercise of stock options, offset by the repurchase of non-employee warrants in the amount of $1.3 million.
54
Table of Contents
Contractual Obligations
Set forth in the following table is information concerning our known contractual obligations as of December 31, 2014 that are fixed and determinable.
| Contractual Obligations |
Payment due by period | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Less than 1 Year |
1-3 years | 3-5 years | More than 5 years |
||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations(1) |
$ | 43,731 | $ | 3,412 | $ | 9,941 | $ | 8,473 | $ | 21,905 | ||||||||||
| Minimum purchase commitments(2) |
7,352 | 3,177 | 4,175 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 51,083 | $ | 6,589 | $ | 14,116 | $ | 8,473 | $ | 21,905 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | We lease our office facilities in Virginia, Texas, California, Georgia, Oregon, India, Canada and the United Kingdom under operating leases that are scheduled to expire at various times through 2025. |
| (2) | This includes guaranteed payments related to our acquisitions. |
In addition to the guaranteed payments due under our acquisition agreements noted in footnote 2 above, as of December 31, 2014, we had contingent payments that may become due to certain of Seed Lab, LLC’s, Crowd Compass, Inc.’s, TicketMob LLC’s sellers based upon the achievement of certain sales-based targets and continued employment. These contingent payments are described in further detail below under the section titled “Acquisitions.”
In April 2013, we signed two new office leases in India that replaced the expired leases.
In August 2014, we moved into a new office space for our corporate headquarters in Tysons Corner, Virginia. The operating lease is for a fixed 11-year term with options for two additional renewal terms of five years each.
In December 2014, we moved into a new office space for our Portland, Oregon office. The operating lease is for a fixed 5 year term.
Unbilled Contract Value
We have typically entered into annual and multiple-year subscription contracts for our software solutions and our marketing solutions. For multiple-year agreements, we typically invoice the amount for the first year of the contract at signing followed by subsequent annual invoices at the anniversary of each year. Since we bill most of our customers in advance, there can be amounts that we have not yet been contractually able to invoice. Until such time as these amounts are invoiced, they are not recorded in revenue, deferred revenue or elsewhere in our consolidated financial statements, and are considered by us to be unbilled contract value. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, our current deferred revenue was $82.0 million and $65.2 million, respectively, which amount does not include unbilled contract value for subscriptions and marketing solution contracts not yet billed of approximately $110.1 million and $88.6 million, respectively. We expect that the amount of unbilled contract value relative to the total value of our contracts will change from year to year for several reasons, including the amount of cash collected early in the contract term, the specific timing and duration of customer agreements, varying invoicing cycles of agreements, the specific timing of customer renewal, changes in customer financial circumstances and foreign currency fluctuations.
Customer Retention
We believe that our ability to retain our customers and expand their use of our platform over time is an indicator of the stability of our revenue base and the long-term value of our customer relationships. We assess our performance in this area using a metric we refer to as our recurring dollar retention rate. Our recurring dollar retention rate for our platform subscriptions was greater than 95% for 2014 and 2013. Our recurring dollar
55
Table of Contents
retention rate for our marketing solutions was greater than 100% for 2014 and 2013. We calculate our recurring dollar retention rate by dividing (a) Retained Revenue by (b) Retention Base Revenue. We define Retention Base Revenue as recurring revenue by product from all customers in the prior period; and Retained Revenue as recurring revenue by product from the same group of customers in the current period, including any additional sales to those customers during the current period. We do not include non-renewable revenue such as overage fees for registrations and other miscellaneous services in this calculation. Such non-renewable revenue represented 4% of our total revenue in each of the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2014.
Acquisitions
We made two acquisitions during the year ended December 31, 2014, which were neither individually or collectively significant to our financial position and result of operations as of and for the year ended December 31, 2014. We made no acquisitions during the year ended December 31, 2013. During the year ended December 31, 2012, we acquired three separate businesses, which were neither individually or collectively significant to our financial position and result of operations as of and for the year ended December 31, 2012.
In December 2014, we acquired 100% of the equity interests of Elite Meetings International, Inc. (“EMI”) for total consideration of $9.8 million. EMI is an event management and marketing solution company that offers two unique online marketplaces, allowing suppliers to directly connect and establish relationships with the hundreds of thousands of planners who use these types of tools to research destinations, find venues, and source group business. The purchase agreement provides for contingent payments, including deferred consideration, of $2,375, payable on December 18, 2017. Approximately $962 of the contingent payments is contingent upon the continued employment of one key employee and is considered a compensatory arrangement and will be recognized as expense over the requisite service period, as earned. The remaining $1,450 of the contingent payments is due to former shareholders of EMI, do not require the continued employment of the recipients and have been included in the purchase price as deferred consideration. This deferred consideration is subject to a performance condition and has been recorded at the probable amount expected to be paid. Any changes in assumptions related to the probability of achieving the performance condition will be recorded in the Company’s statements of operations when identified.
In September 2014, we acquired 100% of the equity interests of Decision Street, LLC (“Decision Street”) for $3.7 million in cash, net, at closing. Decision Street is a development stage company that is building RFP lead scoring and sales optimization technology. The agreement provides for a deferred consideration payment due November 30, 2015 of $0.2 million. In addition, the purchase agreement provides for additional contingent payments totaling $2.7 million, of which $0.9 million will become payable on November 30, 2015, and $1.8 million will become payable on October 31, 2017. These additional payments are contingent upon the continued employment of two key employees and are considered compensatory arrangements that are being recognized as expense over the requisite service period, as earned.
In December 2012, in order to expand our consumer-facing event ticketing and registration offerings, we acquired all of the outstanding unit interests in TicketMob LLC in exchange for $5.2 million in cash, net. In addition, the sellers are entitled to earn up to an additional $14.6 million in part based upon the achievement of certain revenue-based targets and the continued employment of certain key employees of TicketMob LLC, which will be recognized as compensation when earned. As of December 31, 2014, we have paid approximately $0.7 million of these additional payments. For financial reporting purposes, we allocated $5.9 million to the assets acquired, liabilities assumed and goodwill of TicketMob LLC.
In June 2012, in order to expand our mobile event applications offerings, we acquired all of the outstanding capital stock in CrowdCompass, Inc. in exchange for $5.8 million in cash, net. In addition, the sellers are entitled to earn up to an additional $3.8 million based upon the continued employment of certain key employees of CrowdCompass, Inc, which will be recognized as compensation expense when earned. As of December 31, 2014, we have paid approximately $2.6 million of these additional payments to certain key employees. For financial
56
Table of Contents
reporting purposes, we allocated $6.0 million to the assets acquired, liabilities assumed and goodwill of CrowdCompass, Inc.
In January 2012, in order to enter the mobile event application space, we acquired all of the outstanding unit interests in Seed Labs LLC in exchange for $1.5 million in cash, net, and 116,925 shares of our common stock valued at $0.9 million at the time of the acquisition. In addition, the sellers are entitled to earn up to an additional $2.1 million in part based upon the achievement of certain sales-based targets and the continued employment of certain key employees of Seed Labs LLC, which will be recognized as compensation expense when earned. As of December 31, 2014, we have paid approximately $0.5 million of these additional payments to certain key employees. For financial reporting purposes, we allocated $2.4 million to the assets acquired and goodwill of Seed Labs LLC. We subsequently rebranded Seed Labs as our CrowdTorch mobile application functionality.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
As of December 31, 2014, we did not have any off-balance sheet arrangements, as defined in Item 303(a)(4)(ii) of SEC Regulation S-K, such as the use of unconsolidated subsidiaries, structured finance, special purpose entities or variable interest entities.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Our financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this report are prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets, liabilities, revenue, cost of revenue, operating expenses, other income and expenses, provision for income taxes and related disclosures. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe to be reasonable under the circumstances. Changes in accounting estimates are reasonably likely to occur from period to period. Accordingly, actual results could differ significantly from our estimates. We evaluate our estimates and assumptions on an ongoing basis. To the extent that there are material differences between our estimates and our actual results, our future financial statement presentation, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows will be affected.
We believe that the assumptions and estimates associated with revenue recognition, business combinations, goodwill, capitalized software, stock-based compensation and income taxes have the greatest potential impact on our consolidated financial statements. Therefore, we consider these to be our critical accounting policies and estimates. Accordingly, we believe these are the most critical to fully understand and evaluate our financial condition and results of operations.
Revenue Recognition
We derive revenue from two primary sources: platform subscription-based solutions and marketing solutions. These services are generally provided under annual and multi-year contracts that are generally only cancellable for cause and revenue is generally recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the contract. We recognize revenue when all of the following conditions are met:
(i) persuasive evidence exists of an arrangement with the customer reflecting the terms and conditions under which the solutions or services will be provided;
(ii) delivery to customers has occurred or services have been rendered;
(iii) the fee is fixed or determinable; and
(iv) collection of the fees is reasonably assured.
57
Table of Contents
We consider a signed agreement or other similar documentation to be persuasive evidence of an arrangement. Collectability is assessed based on a number of factors, including transaction history and the creditworthiness of a customer. If it is determined that collection is not reasonably assured, revenue is not recognized until collection becomes reasonably assured, which is generally upon receipt of cash.
We apply the provisions of FASB ASU 2009-13, Revenue Recognition (Topic 605): Multiple-Deliverable Revenue Arrangements (EITF Issue No. 08-1, Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables) with respect to our multiple-element arrangements entered into or significantly modified on or after January 1, 2011.
Platform Subscription Revenue
Event Management
We generate the majority of our revenue through software-as-a-service (SaaS) subscriptions to the event management platform, pricing for which is subject to the features and functionality selected by the customer. No features or functionality within the subscription-based services have stand-alone value from one another and, therefore, the entire subscription fee is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the subscription arrangement.
SaaS subscriptions may include functionality that enables customers to manage the registration of participants attending the customer’s event or events. In some cases, the negotiated fee for the subscription is based on a maximum number of event registrations permitted over the subscription term. At any time during the subscription term, customers may elect to purchase blocks of additional registrations, which are referred to as subscription up-sells. The fees associated with the up-sells are added to the original subscription fee, and the revenue is recognized over the remaining subscription period. No portion of the subscription fee is refundable regardless of the actual number of registrations that occur, or to the extent to which other features and functionality are used.
Mobile Apps
Subscription-based solutions also include the sale of mobile event apps. The revenue for mobile event apps solutions is generally recognized on a straight-line basis over the life of the contract. A customer may use a singular mobile event app for any number of events. At any time during the subscription term, customers may elect to purchase additional mobile event apps, which are referred to as mobile up-sells. The fees associated with the mobile up-sells are treated as a piece of the original contract and the revenue is recognized over the appropriate subscription period designated in the up-sell agreement. No portion of the subscription fee is refundable.
Audience Management Platform
Revenue related to the Audience Management Platform is generated primarily through convenience and order processing fees charged to the end user purchasing tickets at the time a ticket for an event is sold and is recorded net of the face value of the ticket. Revenue for these ticket fees collected in advance of the event is recorded as deferred revenue until the event occurs at which time revenue is recognized. If an event is cancelled, the customer receives a full refund of the ticket price and fees paid.
Other subscription-based solutions include the sale of survey solutions, which are contracted though annual or multiyear arrangements.
Subscription agreements do not provide customers with the right to take possession of the underlying software at any time.
58
Table of Contents
Marketing Solutions Revenue
As discussed above under Item 1. Business, towards the end of 2014, we branded the Hospitality Cloud to provide a full spectrum of cloud-based solutions across the hotel group sales lifecycle. Prior to this, we primarily concentrated on servicing the hospitality sector with marketing solutions through our CSN, which provided substantially all of the revenue for this product line in 2014 and before. Marketing solutions revenue is generated through the delivery of various forms of advertising sold through annual or multi-year contracts to marketers, principally hotels and venues. Such solutions include prominent display of a customer’s venue within the Cvent Supplier Network, the Cvent Destination Guide, the Elite Meetings magazine or in various electronic newsletters. Pricing for the advertisements is based on the term of the advertisement, targeted geography, number of advertisements and prominence of the ad placement.
We enter into arrangements with multiple deliverables that generally include various marketing solutions that may be sold individually or bundled together and delivered over various periods of time. In such situations, we apply the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, Accounting Standards Codification, or ASC Subtopic 605-25, Revenue Recognition—Multiple Element Arrangements to account for the various elements within the marketing solution agreements delivered over the platform. Under such guidance, in order to treat deliverables in a multiple-deliverable arrangement as separate units of accounting, the deliverables must have standalone value upon delivery. If the deliverables have standalone value upon delivery, we account for each deliverable separately and revenue is recognized ratably over the contractual period that the related advertising deliverable is provided. Annual marketing solutions on the Cvent Supplier Network are often sold separately, and, as such, all have standalone value.
Certain one-time marketing solutions, which can run for a month, several months, or a year, are primarily sold in a package. In determining whether the marketing solutions sold in packages have standalone value, we consider the availability of the services from other vendors, the nature of the solutions, and the contractual dependence of the solutions to the rest of the package. Based on these considerations, we have determined the estimated selling price for each marketing solution sold in a package.
Revenue arrangements with multiple deliverables are divided into separate units of accounting and the arrangement consideration is allocated to all deliverables based on the relative selling price method. In such circumstances, we use the selling price hierarchy of: (i) vendor specific objective evidence of fair value, or VSOE, if available, (ii) third-party evidence of selling price, or TPE, and (iii) best estimate of selling price. VSOE is limited to the price charged when the same element is sold separately by us. Due to the unique nature of some multiple deliverable revenue arrangements, we may not be able to establish selling prices based on historical stand-alone sales using VSOE or TPE; therefore we may use our best estimate to establish selling prices for these arrangements. We establish the best estimates within a range of selling prices considering multiple factors including, but not limited to, factors such as size of transaction, customer demand and price lists.
Business Combinations
We are required to allocate the purchase price of acquired companies to the identifiable tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the acquisition date based upon their estimated fair values.
Goodwill as of the acquisition date represents the excess of the purchase consideration of an acquired business over the fair value of the underlying net tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed. This allocation and valuation require management to make significant estimates and assumptions, especially with respect to long-lived and intangible assets.
Critical estimates in valuing intangible assets include but are not limited to estimates about: future expected cash flows from customer contracts, customer lists, distribution agreements, proprietary technology and non-competition agreements; the acquired company’s brand awareness and market position, assumptions about the period of time the brand will continue to be used in our product portfolio; as well as expected costs to develop in-
59
Table of Contents
process research and development into commercially viable products and estimated cash flows from the projects when completed, and discount rates. Our estimates of fair value are based upon assumptions we believe to be reasonable, but which are inherently uncertain and unpredictable. Assumptions may be incomplete or inaccurate, and unanticipated events and circumstances may occur.
In addition, uncertain tax positions and tax-related valuation allowances assumed in connection with a business combination are initially estimated as of the acquisition date. We continue to evaluate these items quarterly and record any adjustments to the preliminary estimates to goodwill provided that we are within the measurement period. Subsequent to the measurement period, changes to these uncertain tax positions and tax related valuation allowances will affect our provision for income taxes in the consolidated statements of operations.
Other estimates associated with the accounting for these acquisitions may change as additional information becomes available regarding the assets acquired and liabilities assumed.
Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of: (i) the aggregate of the fair value of consideration transferred in a business combination, over (ii) the fair value of assets acquired, net of liabilities assumed. Goodwill is not amortized, but is subject to annual impairment tests. The goodwill impairment test is a two-step test. Under the first step, the fair value of the reporting unit is compared with its carrying value, including goodwill. If the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an indication of goodwill impairment exists for the reporting unit and the entity must perform step two of the impairment test (measurement). Under step two, an impairment loss is recognized for any excess of the carrying amount of the reporting unit’s goodwill over the implied fair value of that goodwill. The implied fair value of goodwill is determined by allocating the fair value of the reporting unit in a manner similar to a purchase price allocation and the residual fair value after this allocation is the implied fair value of the reporting unit goodwill. Fair value of the reporting unit is estimated using a discounted cash flow analysis. If the fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, step two is not performed.
In September 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-08, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Testing Goodwill for Impairment. This ASU permits an entity to make a qualitative assessment of whether it is more likely than not that a reporting unit’s fair value is less than its carrying amount before applying the two-step goodwill impairment test. If an entity concludes it is not more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, it need not perform the two-step impairment test. The Company adopted the provisions of ASU 2011-08 as of January 1, 2012.
We perform our annual impairment review of goodwill on November 30 and when a triggering event occurs between annual impairment tests. During the 2014 and 2013 qualitative assessments of goodwill, management concluded that it was more likely than not that the estimated fair value of the Company exceeded its carrying value and the estimated fair value of the Company’s reporting unit was substantially in excess of its carrying value, resulting in no indication of impairment as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
Capitalized Software Development Costs
Costs to develop internal use software are capitalized and recorded as capitalized software development costs in accordance with the provisions of FASB ASC Subtopic 350-40, Intangibles-Goodwill and Other Subtopic 40 Internal-Use Software on the balance sheet. These costs are amortized on a project-by-project basis using the straight-line method over the estimated economic life of the application, which is generally three years, beginning when the asset is substantially ready for use. Costs incurred during the preliminary development stage, as well as maintenance and training costs are expensed as incurred.
60
Table of Contents
Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. To the extent that it is not considered to be more likely than not that a deferred tax asset will be realized, a valuation allowance is established. We apply the provisions of ASC Subtopic 740-10, Income Taxes—Overall, which provides guidance related to the accounting for uncertain tax positions. In accordance with FIN 48, we only recognize the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained on examination.
Stock-Based Compensation
We account for our employee stock-based compensation awards in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718, Compensation—Stock Compensation. ASC Topic 718 requires that all employee stock-based compensation is recognized as a cost in the financial statements and that for equity-classified awards, such cost is measured at the grant date fair value of the award. We estimate grant date fair value for stock options using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. We estimate grant date fair value for restricted stock units based on the closing price of the underlying shares on grant date.
Determining the fair value of stock-based compensation awards under this model requires judgment, including estimating the value per share of our common stock prior to our initial public offering in August 2013, estimated volatility, risk free rate, expected term and estimated dividend yield. The assumptions used in calculating the fair value of stock-based compensation awards represent our best estimates, based on management judgment. The estimate of the value per share of our common stock used in the option-pricing model prior to our IPO is based on the contemporaneous valuations performed with the assistance of an unrelated third-party valuation specialist and management’s analysis of market transactions in proximity to the valuation dates. The estimated dividend yield is zero since we have not issued dividends to date and do not anticipate issuing dividends. The risk-free interest rate is based on the implied yield currently available on U.S. Treasury zero coupon issues with an equivalent remaining term. Due to its limited trading history, we estimate volatility for option grants by evaluating the average historical volatility of a peer group of similar public companies. The expected term of our option plans represent the period that our stock-based awards are expected to be outstanding. For purposes of determining the expected term, we apply the simplified approach, in which the expected term of an award is presumed to be the mid-point between the vesting date and the expiration date of the award. Awards generally vest over a service period of four years, with a maximum contractual term of ten years.
Pursuant FASB ASC Subtopic 718-10-35, Stock Compensation, the initial determination of compensation cost is based on the number of stock options granted amortized over the vesting period. The value of the awards granted is discounted by the forfeiture rate equal to the value expected to vest. The forfeiture rate was derived by taking into consideration historical employee turnover rates as well as expectations for the future. Expense is recognized using the straight-line attribution method.
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures about Market Risk |
Market risk represents the risk of loss that may impact our financial position due to adverse changes in financial market prices and rates. Our market risk exposure is primarily a result of fluctuations in foreign currency rates, although we also have some exposure due to potential changes in inflation or interest rates. We do not hold financial instruments for trading purposes.
61
Table of Contents
Foreign Currency Risk
Foreign currency exchange rates are subject to fluctuation and may cause us to recognize transaction gains and losses in our statement of operations. A portion of our business is conducted through our subsidiary in India whose functional currency is the U.S. Dollar. To the extent that transactions by foreign subsidiaries are denominated in currencies other than the U.S. Dollar, we bear the risk that fluctuations in the exchange rates of the U.S. Dollar in relation to other currencies could increase our costs and expenses. Realized foreign currency transaction losses are included in net income (loss) and were $0.3 million and $0.7 million in the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
Certain of our revenues are earned in British pounds and euros. The revenue denominated in pounds and euros is immaterial for the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013.
An increase or decrease of 10% in the applicable foreign exchange rates would not have a material impact on our financial position.
As of December 31, 2014, we have not entered into any hedging transactions to reduce our exposure to foreign currency exchange risk. While we may decide to enter into hedging transactions in the future, the availability and effectiveness of these hedging transactions may be limited and we may not be able to successfully hedge our exposure.
Inflation Risk
Inflationary factors, such as increases in our operating expenses, may adversely affect our results of operations, as our customers typically purchase services from us on a subscription basis over a multi-year period. Although we do not believe that inflation has had a material impact on our financial position or results of operations to date, an increase in the rate of inflation in the future may have an adverse effect on our levels of operating expenses as a percentage of revenue if we are unable to increase the prices for our subscription-based solutions to keep pace with these increased expenses.
Interest Rate Risk
We are exposed to market risk related to changes in interest rates. Our cash equivalents primarily consist of money market funds backed by United States Treasury Bills and certificates of deposit. Our short-term investments primarily consist of bank certificates of deposit, all of which are held in India. As of December 31, 2014, we had $144.6 million of cash and cash equivalents, excluding $0.4 million of restricted cash and $23.0 million of short-term investments. The carrying amount of our cash equivalents and short-term investments reasonably approximates fair value, due to the short maturities of these instruments. The primary objectives of our investment activities are the preservation of capital, the fulfillment of liquidity needs and the fiduciary control of cash and investments. We do not enter into investments for trading or speculative purposes. Our investments are exposed to market risk due to a fluctuation in interest rates, which may affect our interest income and the fair market value of our investments. Due to the short-term nature of our investment portfolio and our tendency to hold investments to maturity, we do not believe an immediate increase or decrease in interest rates of as much as 3% would have a material effect on the fair market value of our portfolio. We therefore do not expect our operating results or cash flows to be materially affected by a sudden change in market interest rates.
We do not believe our cash equivalents or short-term investments have significant risk of default or illiquidity. While we believe our cash equivalents and short-term investments do not contain excessive risk, we cannot provide absolute assurance that in the future our investments will not be subject to adverse changes in market value. In addition, we maintain significant amounts of cash and cash equivalents at one or more financial institutions that are in excess of federally insured limits. We cannot be assured that we will not experience losses on these deposits.
62
Table of Contents
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
Cvent Inc.
Index to Consolidated Financial Statements
| Page No. | ||||
| 64 | ||||
| 65 | ||||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
66 | |||
| 67 | ||||
| 68 | ||||
| 69 | ||||
| 93 | ||||
63
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Stockholders
Cvent, Inc.:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Cvent, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the related consolidated statements of operations and comprehensive income (loss), changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2014. In connection with our audits of the consolidated financial statements, we have also audited financial statement schedule II. These consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements and financial statement schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Cvent, Inc. and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the years in the three-year period ended December 31, 2014, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also, in our opinion, the related financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic consolidated financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly, in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
/s/ KPMG LLP
McLean, Virginia
March 16, 2015
64
Table of Contents
CVENT, INC.
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Assets |
||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 144,544 | $ | 146,407 | ||||
| Restricted cash |
397 | 664 | ||||||
| Short-term investments |
23,039 | 11,359 | ||||||
| Accounts receivable, net of reserve of $339 and $731, respectively |
44,986 | 33,199 | ||||||
| Prepaid expense and other current assets |
13,107 | 7,894 | ||||||
| Deferred tax assets |
3,776 | 3,060 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
229,849 | 202,583 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
22,535 | 7,906 | ||||||
| Capitalized software development costs, net |
17,967 | 9,264 | ||||||
| Intangible assets, net |
9,442 | 3,123 | ||||||
| Goodwill |
20,802 | 12,703 | ||||||
| Other non-current assets |
313 | 257 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 300,908 | $ | 235,836 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Liabilities and Stockholders’ Equity |
||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 5,057 | $ | 5,388 | ||||
| Accrued and other current liabilities |
18,534 | 18,477 | ||||||
| Deferred revenue |
82,030 | 65,203 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
105,621 | 89,068 | ||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities, non-current |
7,086 | 3,323 | ||||||
| Deferred rent, non-current |
9,576 | 568 | ||||||
| Other liabilities, non-current |
4,791 | 839 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
127,074 | 93,798 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 11) |
||||||||
| Stockholders’ equity: |
||||||||
| Preferred stock, $0.001 par value, 100,000,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively; and zero issued and outstanding at December 31 2014 and 2013 |
— | — | ||||||
| Common stock, $0.001 par value; 1,000,000,000 shares authorized at December 31, 2014, 41,685,048 and 40,409,791 issued and 41,164,834 and 39,889,577 outstanding at December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively |
42 | 40 | ||||||
| Treasury stock |
(3,966 | ) | (3,966 | ) | ||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
199,169 | 168,949 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(220 | ) | — | |||||
| Accumulated deficit |
(21,191 | ) | (22,985 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
173,834 | 142,038 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and stockholders’ equity |
$ | 300,908 | $ | 235,836 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements
65
Table of Contents
CVENT, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 142,245 | $ | 111,136 | $ | 83,474 | ||||||
| Cost of revenue(1) |
42,421 | 32,262 | 20,573 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross profit |
99,824 | 78,874 | 62,901 | |||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing(1) |
61,764 | 48,405 | 35,873 | |||||||||
| Research and development(1) |
14,049 | 11,190 | 7,605 | |||||||||
| General and administrative(1) |
24,242 | 21,218 | 11,523 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total operating expenses |
100,055 | 80,813 | 55,001 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(231 | ) | (1,939 | ) | 7,900 | |||||||
| Interest income |
1,595 | 1,015 | 811 | |||||||||
| Other expense |
(434 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) from operations before income taxes |
930 | (924 | ) | 8,711 | ||||||||
| Provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
(864 | ) | 2,315 | 4,406 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 1,794 | $ | (3,239 | ) | $ | 4,305 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income (loss) per common share: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.04 | $ | (0.13 | ) | $ | 0.13 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.04 | $ | (0.13 | ) | $ | 0.12 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding—basic |
40,970,083 | 25,289,788 | 33,167,358 | |||||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding—diluted |
43,172,673 | 25,289,788 | 34,790,637 | |||||||||
| Other comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation loss |
$ | (220 | ) | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
$ | 1,574 | $ | (3,239 | ) | $ | 4,305 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (1) | Stock-based compensation expense included in the above: |
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 820 | $ | 1,046 | $ | 762 | ||||||
| Sales and marketing |
1,571 | 2,306 | 2,895 | |||||||||
| Research and development |
1,002 | 609 | 539 | |||||||||
| General and administrative |
978 | 772 | 1,010 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 4,371 | $ | 4,733 | $ | 5,206 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements
66
Table of Contents
CVENT, INC.
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CHANGES IN STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(in thousands except share data)
| Series A convertible preferred stock |
Common stock | Treasury stock | Additional paid-in capital |
Accumulated deficit |
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
Total stockholders’ equity |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2011 |
17,418,807 | $ | 17 | 15,665,416 | $ | 16 | (13,155 | ) | $ | (16 | ) | $ | 36,200 | $ | (24,051 | ) | — | $ | 12,166 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock issued for Seed Labs acquisition |
— | — | 116,925 | — | — | — | 935 | — | — | 935 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock |
— | — | — | — | (507,059 | ) | (3,950 | ) | — | — | — | (3,950 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options |
— | — | 118,842 | — | — | — | 68 | — | — | 68 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 5,206 | — | — | 5,206 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 4,305 | — | 4,305 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2012 |
17,418,807 | $ | 17 | 15,901,183 | $ | 16 | (520,214 | ) | $ | (3,966 | ) | $ | 42,409 | $ | (19,746 | ) | — | $ | 18,730 | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of early exercised shares |
— | — | 255,572 | — | — | — | 452 | — | — | 452 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of warrants |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (1,275 | ) | — | — | (1,275 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Preferred stock converted to common stock |
(17,418,807 | ) | (17 | ) | 17,418,807 | 17 | — | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from IPO, net of issuance costs |
— | — | 6,440,000 | 6 | — | — | 122,125 | — | — | 122,131 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options and warrants |
— | — | 394,229 | 1 | — | — | 505 | — | — | 506 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 4,733 | — | — | 4,733 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | (3,239 | ) | — | (3,239 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2013 |
$ | — | $ | — | 40,409,791 | $ | 40 | (520,214 | ) | $ | (3,966 | ) | $ | 168,949 | $ | (22,985 | ) | — | $ | 142,038 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of early exercised shares |
— | — | 129,494 | — | — | — | 226 | — | — | 226 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from follow on public offering, net of issuance costs |
— | — | 747,500 | 1 | — | — | 24,845 | — | — | 24,846 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of stock options and vesting of RSUs |
— | — | 398,263 | 1 | — | — | 778 | — | — | 779 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | — | — | 4,371 | — | — | 4,371 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 1,794 | — | 1,794 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation loss |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | — | (220 | ) | (220 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2014 |
— | — | 41,685,048 | 42 | (520,214 | ) | (3,966 | ) | 199,169 | (21,191 | ) | (220 | ) | 173,834 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
67
Table of Contents
CVENT, INC.
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(in thousands)
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 1,794 | $ | (3,239 | ) | $ | 4,305 | |||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
10,590 | 7,769 | 5,446 | |||||||||
| Bad debt expense, net |
317 | 392 | 344 | |||||||||
| Loss on asset disposal |
487 | — | — | |||||||||
| Foreign currency transaction loss |
8 | 190 | — | |||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
4,371 | 4,733 | 5,206 | |||||||||
| Change in deferred taxes |
1,097 | 788 | 434 | |||||||||
| Change in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
(11,005 | ) | (4,945 | ) | (9,618 | ) | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other assets |
(5,184 | ) | (4,766 | ) | (587 | ) | ||||||
| Accounts payable, accrued and other liabilities |
8,623 | 7,493 | 4,486 | |||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
17,277 | 13,649 | 13,565 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
28,375 | 22,064 | 23,581 | |||||||||
| Investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Purchase of property and equipment |
(18,838 | ) | (4,197 | ) | (4,455 | ) | ||||||
| Capitalized software development costs |
(13,720 | ) | (7,144 | ) | (3,663 | ) | ||||||
| Purchase of short-term investments, net |
(11,680 | ) | (2,039 | ) | (986 | ) | ||||||
| Acquisitions, net of cash acquired |
(11,673 | ) | (90 | ) | (12,460 | ) | ||||||
| Restricted cash |
267 | (209 | ) | (455 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(55,644 | ) | (13,679 | ) | (22,019 | ) | ||||||
| Financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Repurchase of common stock and warrants |
— | (1,275 | ) | (3,950 | ) | |||||||
| Proceeds from initial public offering, net of transaction costs |
— | 122,131 | — | |||||||||
| Proceeds from follow-on public offering, net of transaction costs |
24,846 | — | — | |||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock options and warrants |
779 | 506 | 1,088 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) in financing activities |
25,625 | 121,362 | (2,862 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents |
(219 | ) | (190 | ) | — | |||||||
| Increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
(1,863 | ) | 129,557 | (1,300 | ) | |||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, beginning of year |
146,407 | 16,850 | 18,150 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents, end of year |
$ | 144,544 | $ | 146,407 | 16,850 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental cash flow information: |
||||||||||||
| Income taxes paid |
$ | 1,662 | $ | 3,339 | $ | 3,207 | ||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of non-cash investing and financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Change in accounts payable for purchase of property and equipment |
$ | 973 | $ | 618 | $ | 102 | ||||||
| Issuance of common stock in acquisition |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 935 | ||||||
| Change in goodwill due to finalization of purchase accounting |
$ | 462 | $ | 198 | $ | — | ||||||
See accompanying notes to the consolidated financial statements
68
Table of Contents
CVENT, INC
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
(in thousands, except share and per share data)
December 31, 2013 and 2012
1. Description of Business
Cvent, Inc. (the “Company”) provides a cloud-based enterprise event management platform with solutions for both sides of the events and meetings value chain: (i) event and meeting planners and (ii) hotels and venues. The Company’s integrated, cloud-based solution addresses the entire event lifecycle by allowing event and meeting planners to organize, market and manage meetings, conferences, tradeshows and other events. The Company’s hospitality cloud provides hotels and venues with a full solution suite to generate, manage and measure demand for their group meetings. The combination of these solutions creates an integrated platform that allows the Company to generate revenue from both sides of the events and meetings value chain.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
(a) Basis of Presentation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All significant intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. These consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
(b) Use of Estimates
The preparation of the consolidated financial statements in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Significant estimates and assumptions made by management include estimated useful lives of property and equipment and capitalized software development costs, goodwill and intangibles, determination of estimated selling prices, allowances for doubtful accounts, valuation of deferred tax assets, valuation assumptions in purchase accounting, certain assumptions related to stock-based compensation, income taxes and legal and other contingencies. Actual results could differ from those estimates and assumptions.
(c) Cash and Cash Equivalents
Highly liquid financial instruments purchased with original maturities of 90 days or less at the date of purchase are reported as cash equivalents. Cash equivalents are recorded at cost, which approximates fair value.
Included in cash and cash equivalents are funds representing amounts reserved for the face value of registration fees or tickets sold on behalf of customers. While these cash accounts are not restricted as to their use, a liability for amounts due to customers under these arrangements has been recorded in accounts payable in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. The Company had amounts due to customers of $3,431 and $2,560 of these funds as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
(d) Restricted Cash
Restricted cash includes amounts required to be held for regulatory purposes in India. The Company held $397 and $664 of restricted cash in certificates of deposit as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively.
69
Table of Contents
(e) Short-term Investments
The Company’s short-term investments consist of highly liquid financial instruments with original maturities greater than 90 days but less than one year. These short-term investments are comprised of certificates-of-deposit.
(f) Accounts Receivable
Accounts receivable are recorded at the amount invoiced to customers and do not bear interest. The Company maintains an allowance for doubtful accounts for estimated losses inherent in its accounts receivable portfolio. In reviewing outstanding receivables, management considers historical write-off experience, the amount of receivables in dispute, the current receivables aging and current payment patterns. Past due balances over 90 days and over a specified amount are reviewed individually for collectability. Account balances are written off after all means of collection have been exhausted and the potential for recovery is considered remote.
Bad debt expense during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 was $317, $392 and $344, respectively. The allowance for bad debt is consistent with actual historical write-offs; however, higher than expected bad debts may result in the future if write-offs are greater than the Company’s estimates. The Company does not have any off-balance-sheet credit exposure related to its customers.
No single customer accounted for more than 10% of the total accounts receivable as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, and no single customer accounted for more than 10% of revenue during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
(g) Revenue Recognition
The Company derives revenue from two primary sources: platform subscription-based solutions and marketing solutions. These services are generally provided under annual and multi-year contracts that are generally only cancellable for cause. Revenue is generally recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the contract. The Company recognizes revenue when all of the following conditions are met:
(i) persuasive evidence exists of an arrangement with the customer reflecting the terms and conditions under which the solutions or services will be provided;
(ii) delivery to customers has occurred or services have been rendered;
(iii) the fee is fixed or determinable; and
(iv) collection of the fees is reasonably assured.
The Company considers a signed agreement or other similar documentation to be persuasive evidence of an arrangement. Collectability is assessed based on a number of factors, including transaction history and the creditworthiness of a customer. If it is determined that collection is not reasonably assured, revenue is not recognized until collection becomes reasonably assured, which is generally upon receipt of cash.
The Company applies the provisions of FASB ASU 2009-13, Revenue Recognition (Topic 605): Multiple-Deliverable Revenue Arrangements (EITF Issue No. 08-1, Revenue Arrangements with Multiple Deliverables) with respect to its multiple-element arrangements entered into or significantly modified on or after January 1, 2011.
Platform Subscription Revenue
Event Management
The Company generates the majority of its revenue through software-as-a-service (SaaS) subscriptions to the event management platform, pricing for which is subject to the features and functionality selected by the
70
Table of Contents
customer. No features or functionality within the subscription-based services have stand-alone value from one another and, therefore, the entire subscription fee is recognized on a straight-line basis over the term of the subscription arrangement.
SaaS subscriptions may include functionality that enables customers to manage the registration of participants attending the customer’s event or events. In some cases, the negotiated fee for the subscription is based on a maximum number of event registrations permitted over the subscription term. At any time during the subscription term, customers may elect to purchase blocks of additional registrations, which are referred to as subscription up-sells. The fees associated with the up-sells are added to the original subscription fee, and the revenue is recognized over the remaining subscription period. No portion of the subscription fee is refundable regardless of the actual number of registrations that occur, or the extent to which other features and functionality are used.
Mobile Apps
Subscription-based solutions also include the sale of mobile event apps. The revenue for mobile event apps solutions is generally recognized on a straight-line basis over the life of the contract. A customer may use a singular mobile event app for any number of events. At any time during the subscription term, customers may elect to purchase additional mobile event apps, which are referred to as mobile up-sells. The fees associated with the mobile up-sells are added to the original subscription fee, and the revenue is recognized over the remaining subscription period. No portion of the subscription fee is refundable.
Audience Management Platform
Revenue related to the Audience Management Platform is generated primarily through convenience and order processing fees charged to the end user purchasing tickets at the time a ticket for an event is sold and is recorded net of the face value of the ticket. Revenue for these ticket fees collected in advance of the event is recorded as deferred revenue until the event occurs. If an event is cancelled, the customer receives a full refund of the ticket price and fees paid.
Other subscription-based solutions include the sale of survey solutions, which are contracted though annual or multiyear arrangements.
Subscription agreements do not provide customers with the right to take possession of the underlying software at any time.
Marketing Solutions Revenue
Towards the end of 2014, the Hospitality Cloud was branded to provide a full spectrum of cloud-based solutions across the hotel group sales lifecycle. Prior to this, the Company primarily concentrated on servicing the hospitality sector with marketing solutions through CSN, which provided substantially all of the revenue for the product line in 2014 and before. Marketing solutions revenue is generated through the delivery of various forms of advertising sold through annual or multi-year contracts to marketers, principally hotels and venues. Such solutions include prominent display of a customer’s venue within the Cvent Supplier Network, the Cvent Destination Guide, the Elite Meetings magazine or in various electronic newsletters. Pricing for the advertisements is based on the term of the advertisement, targeted geography, number of advertisements and prominence of the ad placement.
The Company enters into arrangements with multiple deliverables that generally include various marketing solutions that may be sold individually or bundled together and delivered over various periods of time. In such situations, the Company applies the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board, or FASB, Accounting Standards Codification, or ASC Subtopic 605-25, Revenue Recognition—Multiple Element Arrangements to
71
Table of Contents
account for the various elements within the marketing solution agreements delivered over the platform. Under such guidance, in order to treat deliverables in a multiple-deliverable arrangement as separate units of accounting, the deliverables must have standalone value upon delivery. If the deliverables have standalone value upon delivery, the Company accounts for each deliverable separately and revenue is recognized ratably over the contractual period that the related advertising deliverable is provided. Annual marketing solutions on the Cvent Supplier Network are often sold separately, and, as such, all have standalone value.
Certain one-time marketing solutions, which can run for a month, several months, or a year, are primarily sold in a package. In determining whether the marketing solutions sold in packages have standalone value, the Company considers the availability of the services from other vendors, the nature of the solutions, and the contractual dependence of the solutions to the rest of the package. Based on these considerations, the Company has determined the estimated selling price for each marketing solution sold in a package.
Revenue arrangements with multiple deliverables are divided into separate units of accounting and the arrangement consideration is allocated to all deliverables based on the relative selling price method. In such circumstances, the Company uses the selling price hierarchy of: (i) vendor specific objective evidence of fair value, or VSOE, if available, (ii) third-party evidence of selling price, or TPE, and (iii) best estimate of selling price. VSOE is limited to the price charged when the same element is sold separately by the Company. Due to the unique nature of some multiple deliverable revenue arrangements, the Company may not be able to establish selling prices based on historical stand-alone sales using VSOE or TPE; therefore the Company may use its best estimate to establish selling prices for these arrangements. The Company establishes the best estimates within a range of selling prices considering multiple factors including, but not limited to, factors such as size of transaction, customer demand and price lists.
(h) Business Combinations
The Company is required to allocate the purchase price of acquired companies to the identifiable tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed at the acquisition date based upon their estimated fair values.
Goodwill as of the acquisition date represents the excess of the purchase consideration of an acquired business over the fair value of the underlying net tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities assumed. This allocation and valuation require management to make significant estimates and assumptions, especially with respect to long-lived and intangible assets.
Critical estimates in valuing intangible assets include but are not limited to estimates about: future expected cash flows from customer contracts, customer lists, distribution agreements, proprietary technology and non-competition agreements; the acquired company’s brand awareness and market position, assumptions about the period of time the brand will continue to be used in our product portfolio; as well as expected costs to develop in-process research and development into commercially viable products and estimated cash flows from the projects when completed, and discount rates. The Company’s estimates of fair value are based upon assumptions the Company believe to be reasonable, but which are inherently uncertain and unpredictable. Assumptions may be incomplete or inaccurate, and unanticipated events and circumstances may occur.
In addition, uncertain tax positions and tax-related valuation allowances assumed in connection with a business combination are initially estimated as of the acquisition date. The Company continues to evaluate these items quarterly and record any adjustments to the preliminary estimates to goodwill provided that the Company is within the measurement period. Subsequent to the measurement period, changes to these uncertain tax positions and tax related valuation allowances will affect the Company’s provision for income taxes in the consolidated statements of operations.
Other estimates associated with the accounting for these acquisitions may change as additional information becomes available regarding the assets acquired and liabilities assumed.
72
Table of Contents
(i) Deferred Revenue
Deferred revenue consists of contractual billings made or payments received in advance of revenue recognition from platform subscription services or marketing solutions that are subsequently recognized when the revenue recognition criteria are met. The Company generally invoices customers in annual or quarterly installments.
(j) Cost of Revenue
The Company’s cost of revenue consists of employee-related expenses, including salaries, benefits and stock-based compensation related to providing support and hosting applications, costs of data center capacity, software license fees and amortization expense associated with capitalized internal use software. In addition, the Company allocates a portion of overhead, such as rent, information technology costs and depreciation and amortization, to cost of revenue based on headcount.
(k) Property and Equipment
Property and equipment is stated at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Improvements and replacements of property and equipment are capitalized. Maintenance and repairs that do not improve or extend the lives of property and equipment are charged to expense as incurred. When assets are sold or retired, their cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and any gain or loss is reported in operating income (loss) in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Depreciation is computed using the straight line method over the estimated useful lives of the related assets. The estimated useful life of computer equipment and software is three years while the estimated useful lives of furniture and equipment is seven years. Leasehold improvements are amortized on a straight-line basis over the shorter of the lease term or estimated useful life of the asset.
(l) Capitalized Software Development Costs
Costs to develop internal use software are capitalized and recorded as capitalized software development costs in accordance with the provisions of FASB ASC Subtopic 350-40, Intangibles-Goodwill and Other Subtopic 40 Internal-Use Software on the balance sheet. These costs are amortized on a project-by-project basis using the straight-line method over the estimated economic life of the application, which is generally three years, beginning when the asset is substantially ready for use. Costs incurred during the preliminary development stage, as well as maintenance and training costs are expensed as incurred.
(m) Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company evaluates the recoverability of its long-lived assets in accordance with Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets Subsections of FASB ASC Subtopic 360-10, Property, Plant, and Equipment—Overall. Long-lived assets are reviewed for possible impairment whenever events or circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may not be recoverable. If such review indicates that the carrying amount of long-lived assets is not recoverable from future undiscounted cash flows, the carrying amount of such assets is reduced to the lower of the carrying value or fair value.
In addition to the recoverability assessment, the Company routinely reviews the remaining estimated lives of its long-lived assets. Any reduction in the useful life assumption will result in increased depreciation and amortization expense in the period when such determinations are made, as well as in subsequent periods. There was no impairment of long-lived assets during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
(n) Goodwill
Goodwill represents the excess of: (i) the aggregate of the fair value of consideration transferred in a business combination, over (ii) the fair value of assets acquired, net of liabilities assumed. Goodwill is not
73
Table of Contents
amortized, but is subject to annual impairment tests. The goodwill impairment test is a two-step test. Under the first step, the fair value of the reporting unit is compared with its carrying value, including goodwill. If the fair value of the reporting unit is less than its carrying value, an indication of goodwill impairment exists for the reporting unit and the entity must perform step two of the impairment test (measurement). Under step two, an impairment loss is recognized for any excess of the carrying amount of the reporting unit’s goodwill over the implied fair value of that goodwill. The implied fair value of goodwill is determined by allocating the fair value of the reporting unit in a manner similar to a purchase price allocation and the residual fair value after this allocation is the implied fair value of the reporting unit goodwill. Fair value of the reporting unit is estimated using a discounted cash flow analysis. If the fair value of the reporting unit exceeds its carrying value, step two is not performed.
In September 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-08, Intangibles—Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Testing Goodwill for Impairment. This ASU permits an entity to make a qualitative assessment of whether it is more likely than not that a reporting unit’s fair value is less than its carrying amount before applying the two-step goodwill impairment test. If an entity concludes it is not more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount, it need not perform the two-step impairment test. The Company adopted the provisions of ASU 2011-08 as of January 1, 2012.
The Company performs its annual impairment review of goodwill on November 30 and when a triggering event occurs between annual impairment tests. During the 2014 and 2013 qualitative assessments of goodwill, management concluded that it was more likely than not that the estimated fair value of the Company exceeded its carrying value and the estimated fair value of the Company’s reporting unit was substantially in excess of its carrying value, resulting in no indication of impairment as of December 31, 2014 and 2013.
(o) Research and Development
Research and development expenses consist primarily of personnel and related expenses for the Company’s research and development staff, including salaries, benefits, bonuses and stock-based compensation and the cost of certain third-party contractors. Research and development costs, other than software development expenses qualifying for capitalization, are expensed as incurred.
(p) Sales Commissions
Sales commissions are the costs directly associated with obtaining platform subscription and marketing solutions contracts with customers and consist of commissions paid to the Company’s direct sales force and other marketing partners. Sales commissions are expensed when incurred as a component of sales and marketing expense and are generally paid one month in arrears. Commissions incurred, but not paid, are included in accrued expenses in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Sales commissions paid are subject to a claw back provision in the event a customer contract is cancelled in proportion to the remaining contract period at the date of cancellation and are recorded net of estimated claw backs in sales and marketing expense. Amounts charged back have not been material to the Company’s results of operations.
(q) Deferred Tax Assets and Liabilities
Income taxes are accounted for under the asset and liability method. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are recognized for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax bases and operating loss and tax credit carryforwards. Deferred tax assets and liabilities are measured using enacted tax rates expected to apply to taxable income in the years in which those temporary differences are expected to be recovered or settled. The effect on deferred tax assets and liabilities of a change in tax rates is recognized in income in the period that includes the enactment date. To the extent that it is not considered to be more likely than not that a deferred tax asset will be realized, a valuation allowance is established. The Company applies the provisions of ASC Subtopic
74
Table of Contents
740-10, Income Taxes—Overall, which provides guidance related to the accounting for uncertain tax positions. In accordance with FIN 48, the Company only recognizes the tax benefit from an uncertain tax position if it is more likely than not that the tax position will be sustained on examination.
(r) Stock-Based Compensation
The Company accounts for its employee stock-based compensation awards in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718, Compensation—Stock Compensation. ASC Topic 718 requires that all employee stock-based compensation is recognized as a cost in the financial statements and that for equity-classified awards, such cost is measured at the grant date fair value of the award. The Company estimates grant date fair value for stock options using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The Company estimates grant date fair value for restricted stock units based on the closing price of the underlying shares on grant date.
Determining the fair value of stock options under the Black-Scholes model requires judgment, including estimating the value per share of the Company’s common stock prior to the Company’s initial public offering in August 2013 (see note 9), estimated volatility, risk free rate, expected term and estimated dividend yield. The assumptions used in calculating the fair value of stock-based compensation awards represent the Company’s best estimates, based on management judgment. The estimate of the value per share of the Company’s common stock used in the option-pricing model prior to the Company’s IPO was based on the contemporaneous valuations performed with the assistance of an unrelated third-party valuation specialist and management’s analysis of market transactions in proximity to the valuation dates. The estimated dividend yield is zero since the Company has not issued dividends to date and does not anticipate issuing dividends. The risk-free interest rate is based on the implied yield currently available on U.S. Treasury zero coupon issues with an equivalent remaining term. Due to its limited trading history, the Company estimates volatility for option grants by evaluating the average historical volatility of a peer group of similar public companies. The expected term of the Company’s option plans represent the period that its stock-based awards are expected to be outstanding. For purposes of determining the expected term, the Company applies the simplified approach, in which the expected term of an award is presumed to be the mid-point between the vesting date and the expiration date of the award. Awards generally vest over a service period of four years, with a maximum contractual term of ten years.
Pursuant FASB ASC Subtopic 718-10-35, Stock Compensation, the initial determination of compensation cost is based on the number of stock options granted amortized over the vesting period. The value of the awards granted is discounted by the forfeiture rate equal to the value expected to vest. The forfeiture rate was derived by taking into consideration historical employee turnover rates as well as expectations for the future. Expense is recognized using the straight-line attribution method. Compensation cost for restricted stock units is measured at the fair value of the underlying shares on grant date and recognized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period.
(s) Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Comprehensive income (loss) includes foreign currency translation losses of $220 for the year ended December 31, 2014. There was no comprehensive income (loss) for the years ended December 31, 2013 or 2012.
(t) Foreign Currency Transactions
The Company’s foreign subsidiary in India designates the U.S. dollar as the functional currency. For the subsidiary, assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currency are remeasured into U.S. dollars at current exchange rates for monetary assets and liabilities and historical exchange rates for nonmonetary assets and liabilities. Foreign currency gains and losses associated with remeasurement are included in general and administrative expense in the consolidated statements of operations.
Foreign currency losses associated with transactions and remeasurement were $1,109, $1,796 and $286 for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
75
Table of Contents
(u) Non-Monetary Transactions
The Company occasionally participates in non-monetary transactions with its customers in exchange for marketing and other services. The cost of the services received approximate the value of the services provided and as a result no gain or loss is generally recognized on the transaction. Non-monetary transactions totaled $1,718, $592 and $362 for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
(v) Fair Value Measurements
Fair value represents the exchange price that would be received for an asset or paid to transfer a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value must maximize the use of observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. The fair value hierarchy is based on the following three levels of inputs, of which the first two are considered observable and the last one is considered unobservable:
Level 1 Inputs: Unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities accessible to the reporting entity at the measurement date.
Level 2 Inputs: Other than quoted prices included in Level 1 inputs that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly, for substantially the full term of the asset or liability.
Level 3 Inputs: Unobservable inputs that require the Company to use present value and other valuation techniques in the determination of fair value.
The Company’s financial instruments include cash and cash equivalents, restricted cash, short-term investments, accounts receivable, accounts payable and accrued liabilities. The carrying value of these financial instruments on the consolidated balance sheets approximate their fair value based on their short-term nature.
The Company is also subject to certain contingent consideration arrangements associated with some of its recent acquisitions that are based on achieving specified operating targets and the passage of time. Assumptions including revenue forecasts, future market opportunities, complexity and size of addressable markets and the scalability of the product are developed to determine the fair value of such contingent consideration. In addition, the probability of achieving the specified targets is considered in determining the fair value of the contingent consideration included in the purchase price. Contingent consideration will be remeasured to fair value at each reporting date, and will recognize any changes to the fair value in earnings in the period.
(w) Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In May 2014, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) and the International Accounting Standards Board (IASB) issued joint guidance to improve and converge the financial reporting requirements for revenue from contracts with customers. ASU 2014-9, Revenue from Contracts with Customers, prescribes a five-step model for revenue recognition that will replace most existing revenue recognition guidance under U.S. GAAP. The new standard supersedes nearly all existing revenue recognition guidance under U.S. GAAP, and requires companies to recognize revenue when it transfers goods or services to a customer in an amount that reflects the consideration to which a company expects to be entitled for those goods or services. This update also requires additional disclosure about the nature, amount, timing and uncertainty of revenue and cash flows arising from customer contracts, including significant judgments and changes in judgments, and assets recognized from costs incurred to obtain or fulfill a contract. ASU 2014-09 allows for either full retrospective or modified retrospective adoption and will become effective for the Company in the first quarter of 2017. Early adoption is prohibited. Management is currently evaluating which adoption method it will use and assessing the effect the adoption of this standard will have on the consolidated financial statements.
76
Table of Contents
3. Net Income (Loss) Per Share
The Company calculates basic net income (loss) per share of common stock by dividing net income (loss) attributable to the common stockholders for the period by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock and participating convertible preferred stock outstanding during the period. The Company calculates diluted net income per share by dividing net income (loss) attributable to the Company for the period by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock and convertible preferred stock outstanding during the period, plus any dilutive effect from share-based equity awards and warrants during the period, using the treasury stock method. Prior to the Company’s IPO in August 2013, the Series A Convertible Preferred Stock did not participate in earnings differently than common stock, but was not obligated to participate in losses. Accordingly, the net income attributable to common and preferred stockholders would have been divided proportionately by the number of shares outstanding of each and there would have been no difference in the determination of basic and diluted net income per share calculated separately for common and preferred stock. Included in the diluted weighted average shares outstanding is the effect of non-vested, early option exercises of 188,875 shares, which are the remaining non-vested shares as of December 31, 2014 of the 573,941 shares subject to early option exercises on June 13, 2012. These shares are removed from the basic earnings per share calculation as the shares can be repurchased by the Company prior to the vesting date should employment of the early exercised option shareholders be terminated. The computation of basic and diluted net income (loss) per share is as follows:
| Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 1,794 | $ | (3,239 | ) | $ | 4,305 | |||||
| Weighted average number of shares outstanding: |
||||||||||||
| Weighted average common shares outstanding |
40,970,083 | 25,289,788 | 15,748,551 | |||||||||
| Effect of convertible preferred stock |
— | — | 17,418,807 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding for basic earnings per share |
40,970,083 | 25,289,788 | 33,167,358 | |||||||||
| Effect of share-based equity awards |
2,202,590 | — | 1,555,447 | |||||||||
| Effect of warrants |
— | — | 67,832 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding for diluted earnings per share |
43,172,673 | 25,289,788 | 34,790,637 | |||||||||
| Net income (loss) per share: |
||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.04 | $ | (0.13 | ) | $ | 0.13 | |||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.04 | $ | (0.13 | ) | $ | 0.12 | |||||
The weighted average number of shares outstanding used in the computation of basic and diluted loss per share for the year ended December 31, 2013 does not include the effect of 10,499,007 shares of convertible preferred stock, as these shares are not obligated to participate in losses. Additionally, the weighted average number of shares outstanding used in the computation of diluted loss per share for the year ended December 31, 2013 does not include the effect of 2,050,265 stock options, warrants, and restricted stock units as the effects of these potentially outstanding shares would have been anti-dilutive.
4. Acquisitions
The Company made no acquisitions during the year ended December 31, 2013. The Company made the following acquisitions during 2014 and 2012:
EMI
On December 16, 2014, the Company acquired 100% of the equity interests of Elite Meetings International, Inc. (“EMI”) for total consideration of $9,845, net of cash acquired. EMI is an event management and marketing solution company that offers two unique online marketplaces, allowing suppliers to directly connect and establish
77
Table of Contents
relationships with the hundreds of thousands of planners who use these tools to research destinations, find venues, and source group business. The acquisition was accounted for as a purchase business combination.
Total consideration is comprised of cash paid at closing of $7,429, net of cash acquired of $671, $1,450 of deferred consideration due December 18, 2017, and $966 of net liabilities assumed by the Company.
The purchase agreement provides for contingent payments, including deferred consideration, of $2,375, payable on December 18, 2017. Approximately $962 of the contingent payments is contingent upon the continued employment of one key employee and is considered a compensatory arrangement and will be recognized as expense over the requisite service period, as earned. The remaining $1,450 of the contingent payments is due to former shareholders of EMI, do not require the continued employment of the recipients and have been included in the purchase price as deferred consideration. This deferred consideration is subject to a performance condition and has been recorded at the probable amount expected to be paid. Any changes in assumptions related to the probability of achieving the performance condition will be recorded in the Company’s statements of operations when identified.
The table below represents the preliminary allocation of the purchase price for the acquired net assets of EMI based on their estimated fair values as of December 16, 2014. The allocation of the purchase price was based upon preliminary estimates of fair value of the corresponding assets and liabilities as follows:
| Tangible assets, net |
$ | 179 | ||
| Customer relationships |
4,320 | |||
| Software |
640 | |||
| Trademarks |
415 | |||
| Goodwill |
6,193 | |||
| Deferred tax liability |
(1,902 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Total consideration |
$ | 9,845 | ||
|
|
|
Customer relationships represent the fair values of the underlying relationships and agreements with EMI customers. Software represents the estimated fair value of EMI’s developed software. Trademarks represents the estimated fair value of EMI’s existing trademarks. The excess of purchase consideration over the fair value of the net tangible and identifiable intangible assets acquired of $6,193 was recorded as goodwill. Changes to amounts recorded as assets or liabilities may result in a corresponding adjustment to goodwill. The goodwill balance is attributed to the assembled workforce and expanded market opportunities when integrating Decision Street’s lead scoring technology into the Company’s technology. The goodwill balance is deductible for U.S. income tax purposes.
Acquisition-related costs, including transaction costs such as legal and accounting fees, were expensed as incurred. The Company incurred $142 of transaction costs for the year ended December 31, 2014, which have been included in general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statement of operations. The amount of revenue attributable to this acquisition was immaterial for the year ended December 31, 2014.
Decision Street
On September 15, 2014, the Company acquired 100% of the equity interests of Decision Street, LLC (“Decision Street”) for total consideration of $4,699, net of cash acquired. Decision Street is a development stage company that is building request for proposal (RFP) lead scoring and sales optimization technology. The acquisition was accounted for as a purchase business combination.
Total consideration is comprised of cash paid at closing of $3,705, net of cash acquired of $434, $192 of deferred consideration payment due November 30, 2015, and $802 of liabilities assumed by the Company. In addition, the purchase agreement provides for additional contingent payments totaling $2,700, of which $900 will
78
Table of Contents
become payable on November 30, 2015, and $1,800 will become payable on October 31, 2017. These additional payments are contingent upon the continued employment of two key employees and are considered compensatory arrangements that are being recognized as expense over the requisite service period, as earned.
The table below represents the preliminary allocation of the purchase price for the acquired net assets of Decision Street based on their estimated fair values as of September 15, 2014. The allocation of the purchase price was based upon preliminary estimates of fair value of the corresponding assets and liabilities as follows:
| Tangible assets, net |
$ | 689 | ||
| In-process research and development |
1,442 | |||
| Customer relationships |
200 | |||
| Goodwill |
2,368 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total consideration |
$ | 4,699 | ||
|
|
|
In-process research and development represents the estimated fair value of Decision Street’s development stage software. Customer relationships represent the fair values of the underlying relationships and agreements with Decision Street customers on existing contracts, expiring in January 2015. The excess of purchase consideration over the fair value of the net tangible and identifiable intangible assets acquired of $2,368 was recorded as goodwill. Changes to amounts recorded as assets or liabilities may result in a corresponding adjustment to goodwill. The goodwill balance is attributed to the assembled workforce and expected expanded market opportunities when Decision Street’s lead scoring technology is completed and integrated into the Company’s technology. The goodwill balance is deductible for U.S. income tax purposes.
Acquisition-related costs, including transaction costs such as legal and accounting fees, were expensed as incurred. The Company incurred $136 of transaction costs for the year ended December 31, 2014, which have been included in general and administrative expenses in the consolidated statement of operations. Revenue in the period post-acquisition was not significant.
TicketMob
In December 2012, in order to expand its consumer-facing event ticketing and registration offerings, Cvent acquired all of the outstanding unit interests in TicketMob LLC in exchange for total consideration of $5,918, consisting of $5,223 in cash, net, and $695 of deferred payments to be paid over periods ranging from 18 to 36 months. In addition, the acquisition agreement provides for additional contingent payments of up to an additional $14,555 based upon the achievement of certain revenue-based targets, the continued employment of certain key employees of TicketMob LLC, or both, which will be recognized as compensation when earned. As of December 31, 2014, the Company has paid approximately $742 of these additional payments. As of December 31, 2014, the Company has accrued $487 for future payments. For financial reporting purposes, total consideration was allocated to goodwill of $6,042, acquired intangible assets of $1,615 and acquired net liabilities of $1,739.
CrowdCompass
In June 2012, in order to expand its mobile event applications offerings, Cvent acquired all of the outstanding capital stock in CrowdCompass, Inc. in exchange for total consideration of $5,977, consisting of $5,831 in cash, net, and deferred consideration of $200 to be paid over three years. In addition, the purchase agreement provides for additional contingent payment of up to an additional $3,800 based upon the continued employment of certain key employees of CrowdCompass, Inc, which will be recognized as compensation expense when earned over periods ranging from one to three years. As of December 31, 2014, the Company has paid approximately $2,648 of these additional payments to certain key employees. As of December 31, 2014, the Company has accrued $729 for future payments. For financial reporting purposes, total consideration was allocated to goodwill of $4,752, acquired intangible assets of $2,130, and acquired net liabilities of $392 and net deferred tax liabilities of $513.
79
Table of Contents
Seed Labs
In January 2012, in order to enter the mobile event application space, Cvent acquired all of the outstanding unit interests in Seed Labs, LLC in exchange for total consideration of $2,398, consisting of $1,463 in cash, net, and 116,925 shares of our common stock valued at $935 at the time of the acquisition. In addition, the purchase agreement provides for additional contingent payments of up to $2,060 in part based upon the achievement of certain sales-based targets and the continued employment of certain key employees of Seed Labs, LLC, which will be recognized as compensation expense when earned over periods ranging from one to three years. As of December 31, 2014, the Company has paid approximately $513 of these additional payments to certain key employees. As of December 31, 2014, the Company has accrued $223 for future payments. For financial reporting purposes, total consideration was allocated to goodwill of $1,909, acquired intangible assets of $493 and acquired net liabilities of $4. Cvent subsequently rebranded Seed Labs as our CrowdTorch mobile application functionality.
5. Property and Equipment and Capitalized Software Development Costs
Property and equipment and capitalized software development costs are summarized as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | |||||||
| Computer equipment and purchased software |
$ | 10,979 | $ | 9,278 | ||||
| Furniture and equipment |
6,734 | 3,864 | ||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
14,807 | 6,293 | ||||||
| Work in Progress |
490 | 99 | ||||||
| Automobile |
67 | 67 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 33,077 | 19,601 | |||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation |
(10,542 | ) | (11,695 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total property and equipment, net |
$ | 22,535 | $ | 7,906 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Capitalized software development costs |
$ | 31,854 | $ | 18,134 | ||||
| Less accumulated amortization |
(13,887 | ) | (8,870 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total capitalized software development costs |
$ | 17,967 | $ | 9,264 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Depreciation expense on property and equipment was $4,707, $3,665 and $2,623 during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Amortization expense on capitalized software development costs was $5,017, $3,308 and $2,504 during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
6. Goodwill and Intangible Assets
The following table presents the change in carrying amount of goodwill due to the finalization of purchase accounting:
| Goodwill as of December 31, 2013 |
$ | 12,703 | ||
| Additions from acquisitions (note 4) |
8,561 | |||
| Other |
(462 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Goodwill as of December 31, 2014 |
$ | 20,802 | ||
|
|
|
80
Table of Contents
Intangible assets were acquired through acquisitions completed during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2012. Intangible assets are amortized on a straight line basis over their estimated useful lives between four and six years. The following table summarizes intangible assets as of December 31, 2014 and 2013:
| Net carrying amount December 31, 2013 |
Additions | Amortization | Net carrying amount December 31, 2014 |
Weighted average life as of December 31, 2014 |
||||||||||||||||
| Customer relationships |
1,358 | $ | 4,520 | $ | 334 | $ | 5,544 | 6 years | ||||||||||||
| Software technology and in-process research and development |
1,575 | 2,250 | 476 | 3,349 | 5 years | |||||||||||||||
| Trademarks/Tradenames |
190 | 415 | 56 | 549 | 5 years | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Total intangible assets |
3,123 | $ | 7,185 | $ | 866 | $ | 9,442 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
The total amount of amortization expense relating to acquired intangibles was $866 and $796 during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The intangible balance remaining as of December 31, 2014 will be amortized in future periods as follows:
| 2015 |
$ | 2,089 | ||
| 2016 |
2,072 | |||
| 2017 |
1,819 | |||
| 2018 |
1,518 | |||
| 2019 |
1,169 | |||
| 2020 |
690 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
$ | 9,357 | ||
|
|
|
7. Income Taxes
Income before income taxes is compromised of the following:
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Pretax income (loss): |
||||||||||||
| U.S. |
$ | (3,664 | ) | $ | (1,119 | ) | $ | 6,638 | ||||
| Foreign |
4,594 | 195 | 2,073 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
$ | 930 | $ | (924 | ) | $ | 8,711 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
81
Table of Contents
The provision for (benefit from) income taxes for 2014, 2013 and 2012 are as follows:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Current: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | (2,507 | ) | $ | 367 | $ | 3,132 | |||||
| State |
(411 | ) | 272 | 900 | ||||||||
| Foreign |
957 | 888 | 808 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total current tax expense (benefit) |
$ | (1,961 | ) | $ | 1,527 | $ | 4,840 | |||||
| Deferred: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | 873 | $ | 1,081 | $ | (304 | ) | |||||
| State |
7 | 196 | (81 | ) | ||||||||
| Foreign |
217 | (489 | ) | (49 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total deferred tax expense (benefit) |
1,097 | 788 | (434 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
$ | (864 | ) | $ | 2,315 | $ | 4,406 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
A reconciliation between the Company’s statutory tax rate and the effective tax rate is as follows:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| U.S. federal statutory rate |
34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||||
| Increase (reduction) resulting from: |
||||||||||||
| U.S. state income taxes, net of federal benefits |
(27.5 | ) | (26.3 | ) | 5.9 | |||||||
| Stock compensation adjustment |
(103.5 | ) | (144.8 | ) | 16.1 | |||||||
| Non-deductible/non-taxable items |
111.4 | (22.8 | ) | 2.3 | ||||||||
| Uncertain tax positions |
44.7 | (66.0 | ) | 1.2 | ||||||||
| Acquisition related expenses |
— | (56.7 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Benefit of credits |
(100.9 | ) | 97.3 | (9.1 | ) | |||||||
| Provision to return differences |
(5.9 | ) | (34.3 | ) | — | |||||||
| Foreign tax rate differential |
(16.1 | ) | (11.2 | ) | (0.6 | ) | ||||||
| Change in Valuation Allowance |
(20.9 | ) | (23.4 | ) | — | |||||||
| Foreign tax expense |
7.5 | (4.9 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Other |
(15.7 | ) | 8.5 | (0.5 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| (92.9 | )% | (250.6 | %) | 50.3 | % | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
82
Table of Contents
Significant components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and liabilities are as follows:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Deferred tax assets: |
||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 176 | $ | 279 | $ | 199 | ||||||
| Reserves |
806 | 1,110 | 823 | |||||||||
| Deferred rent |
4,242 | 427 | 488 | |||||||||
| Accrued expenses and other |
2,012 | 1,583 | 674 | |||||||||
| Foreign tax credit carryforward |
2,000 | 329 | 185 | |||||||||
| Stock compensation |
862 | 88 | 790 | |||||||||
| Net operating loss carryforwards |
1,057 | 945 | 970 | |||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
202 | — | — | |||||||||
| Valuation allowance |
— | (194 | ) | — | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total deferred tax assets, net |
$ | 11,357 | $ | 4,567 | $ | 4,129 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Basis difference in fixed assets |
$ | (4,531 | ) | $ | (408 | ) | $ | (914 | ) | |||
| Capitalized software development costs |
(7,253 | ) | (3,715 | ) | (2,147 | ) | ||||||
| Intangibles—acquisitions |
(2,578 | ) | (450 | ) | (614 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total deferred tax liabilities |
(14,362 | ) | (4,573 | ) | (3,675 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net deferred tax asset (liability) |
$ | (3,005 | ) | $ | (6 | ) | $ | 454 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
In assessing the Company’s ability to realize the future benefit associated with its deferred tax assets, management considers whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets may not be realized. The ultimate realization is dependent on the generation of taxable income within the periods that those temporary differences become deductible. The Company has not recorded a valuation allowance for its deferred tax assets in 2014 due to management’s assessment that it is more-likely-than-not that the Company will be able to realize these tax assets. In 2013, the Company recorded a valuation allowance on foreign net operating loss carryforwards; those losses were utilized during 2014.
The Company previously established new operations in India that management believes are eligible for tax benefits under the Special Economic Zones (“SEZ”) Act, 2005. The SEZ legislation introduced a 15-year tax holiday for operations established in designated “special economic zones” or SEZs. Under the SEZ legislation, qualifying operations are eligible for a deduction from taxable income equal to (i) 100% of their export profits derived for the first five years from the commencement of operations; (ii) 50% of such export profits for the next five years; and (iii) 50% of the export profits for a further five years, subject to satisfying certain capital investment requirements. The tax holiday for the Company will expire in 2028.
The percentage of the Company’s operations in India that is eligible for SEZ benefits is variable, and depends, among other factors, upon how much of our business can be conducted at the qualifying location and how much of that business can be considered to meet the restrictive conditions of the SEZ legislation. The benefit of the tax holiday under Indian Income Tax was $792 for the year ended December 31, 2014. The Company’s SEZ operations in India were implemented in the fourth quarter of 2013.
As the SEZ legislation benefits phase-out, the Company’s Indian tax expense may materially increase and its after-tax profitability may be materially reduced, unless the Company can obtain comparable benefits under new legislation or otherwise reduce the Company’s tax liability.
The Company had approximately $2,273, $1,972 and $2,488 of federal net operating loss carryforwards at December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The tax effected amounts of this carryforward is $796, $690
83
Table of Contents
and $871 at December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. Additionally the tax effected state net operating carryforwards are $261, $59 and $99 at the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012. The net operating loss carryforwards will expire, if unused, in varying amounts beginning in 2021. The realization of the benefits of the net operating loss carryforwards is dependent on sufficient taxable income in future years. Among other things, the lack of future earnings, or a change in ownership of the Company, could adversely affect the Company’s ability to utilize the net operating loss carryforward to reduce future current tax expense.
The Company had an ownership change in a prior year, as defined by Internal Revenue Code section 382, which triggered a limitation on the amount of net operating loss carryforward available to offset annual taxable income. The remaining net operating loss carryforward at December 31, 2014 and 2013 is subject to an annual limitation of approximately $246. Management has determined the Company will be able to utilize its net operating loss carryforwards subject to Section 382 limitations during the carryforward period.
In general, it is the practice and intention of the Company to reinvest the earnings of its non-U.S. subsidiaries in those operations. As of December 31, 2014, the Company has not made a provision for U.S. or additional foreign withholding taxes on approximately $4,799 of the excess of the amount for financial reporting purposes over the tax basis of investments in foreign subsidiaries that is indefinitely reinvested. Generally, such amounts become subject to U.S. taxation upon the remittance of dividends and under certain other circumstances. It is not practicable to estimate the amount of deferred tax liability related to investments in these foreign subsidiaries.
The Company applies the provisions of ASC 740-10 to uncertain tax positions. ASC 740-10 clarifies accounting for income taxes by prescribing a minimum probability threshold that a tax position must meet before a financial statement benefit is recognized. If the probability for sustaining a tax position is greater than 50%, then the tax position is warranted and recognition should be at the highest amount which would be expected to be realized upon ultimate settlement. The impact of the adoption of ASC 740-10 did not have a material effect on the consolidated financial statements of the Company.
The following table presents a reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits:
| December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits, opening balance |
$ | 1,168 | $ | 614 | $ | 508 | ||||||
| Gross increases—tax positions in prior period |
219 | 83 | — | |||||||||
| Gross decreases—tax positions in prior period |
(60 | ) | (72 | ) | 1 | |||||||
| Gross increases—current-period tax positions |
254 | 543 | 105 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Unrecognized tax benefits, ending balance |
$ | 1,581 | $ | 1,168 | $ | 614 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The Company’s tax reserves for uncertainties relate to federal, state and international tax positions. The Company does not believe it is reasonably possible that the composition of its unrecognized tax benefits would materially change in the next 12 months.
Included in the balance of unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, are $1,268, $840 and $435 respectively, of tax benefits that, if recognized, would impact the effective tax rate. Also included in the balance of unrecognized tax benefits as of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 are $313, $328 and $179 respectively, of tax benefits that, if recognized, would result in adjustments to other tax accounts, primarily deferred taxes.
The Company is subject to U.S. federal income tax and state and local income tax in multiple jurisdictions. With few exceptions, the Company is no longer subject to income tax examinations by the U.S. federal, state or
84
Table of Contents
local tax authorities for years before 2011. While the federal statute of limitations generally is three years, the IRS can re-determine items in tax years normally barred by the statute of limitations if a net operating loss utilized in an open year was carried over from a closed year.
The Company is currently under audit by several taxing jurisdictions in the United States. Some audits may conclude in the next 12 months and the unrecognized tax benefits that have been recorded in relation to the jurisdictions under audit may differ from actual settlement amounts. It is not practical to estimate the effect, if any, of any amount of such change during the next 12 months to previously recorded uncertain tax positions in connection with these audits. The Company does not anticipate that there will be a material increase or decrease in the total amount of unrecognized tax benefits in the next 12 months.
The Company’s practice is to recognize interest and penalties related to uncertain tax positions in income tax expense. The amount of interest and penalties included in income tax expense for the year ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 was approximately $219, $111 and $50, respectively.
8. Stock-Based Compensation
The Company’s equity incentive plan provides for equity based compensation awards to employees, service providers and directors for the purpose of providing an effective means for attracting, retaining and motivating directors, officers and key employees and service providers to provide them with incentives to enhance the Company’s growth and profitability. Prior to the Company’s IPO in August 2013, these awards were provided under the 1999 Plan. Subsequent to the Company’s IPO, the 1999 Plan was replaced by the 2013 Plan.
2013 Plan
On July 5, 2013, the Company’s board of directors adopted a 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (or the “2013 Plan”), which was approved by the Company’s stockholders on July 25, 2013. The 2013 Plan was effective upon the effective date of the Company’s IPO, August 8, 2013. The 2013 Plan provides for the grant of incentive stock options, within the meaning of Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code, to employees and any parent and subsidiary corporations’ employees, and for the grant of non-statutory stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock appreciation rights, performance units and performance shares to employees, directors and consultants of the Company and its subsidiaries. The 2013 Plan is administered by the Company’s board of directors or the compensation committee of the board of directors, including the ability to determine the terms of awards and the authority to amend existing awards. The 2013 Plan will automatically terminate in 2023, unless terminated sooner by the plan administrator.
The 2013 Plan generally includes the following provisions relative to the awards available for grant under the plan:
Stock Options. The exercise price of options granted under the 2013 Plan must at least be equal to the fair market value per share of the Company’s common stock on the date of grant. Upon separation from their service to the Company, an employee, director or service provider generally has either 30 days (under our current form of award) or three months (under our previous form of award) to exercise vested options, but in no event can an employee, director or service provider exercise an option after the term of the option, which is generally ten years from the grant date. Option awards have various terms and vest at various times from the date of grant, with most options vesting in tranches generally over four years.
Restricted Stock Units. Restricted stock units are bookkeeping entries representing an amount equal to the fair market value of one share of the Company’s common stock for each restricted stock unit. The administrator determines the terms and conditions of restricted stock units, including the form and timing of payment and vesting schedule, with most restricted stock units vesting in tranches over four years.
The 2013 Plan allows for the following additional types of awards, none of which have been issued as of December 31, 2014: restricted stock, stock appreciation rights, performance units and performance shares.
85
Table of Contents
Other Key Provisions. All non-employee directors are eligible to receive all types of awards (except for incentive stock options) under the 2013 Plan and generally, awards are not transferable. In the event of a merger or change in control, as defined under the 2013 Plan, if a successor corporation does not assume or substitute an equivalent award for any outstanding award under the 2013 Plan, then such outstanding award will fully vest, all restrictions on such award will lapse, all performance goals or other vesting criteria applicable to such award will be deemed achieved at 100% of target levels and such award will become fully exercisable, for a specified period.
As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, awards granted under the 2013 Plan consisted of only stock options and restricted stock units. There were no other grants of any other award types under the plan. As of December 31, 2014 and 2013, no awards have been granted to service providers under the 2013 Plan.
The shares to be reserved for issuance under the 2013 Plan also include shares returned to the 1999 Plan as the result of expiration or termination of awards up to a maximum of 4,600,000. The number of shares available for issuance under the 2013 Plan will also include an annual increase on the first day of each fiscal year beginning in 2014, equal to the least of:
| • | 4,000,000 shares; |
| • | 5% of the outstanding shares of our common stock as of the last day of our immediately preceding year; or |
| • | such other amount as our board of directors may determine. |
At December 31, 2014, there were 5,448,769 shares underlying all awards available for issuance under the 2013 Plan. On January 1, 2015, the shares underlying all awards available for issuance increased by 2,067,676 pursuant to the automatic share reserve increase provision under the 2013 Plan.
1999 Plan
The Company’s board of directors adopted a stock incentive plan (the “1999 Plan”). In August 1999, and the Company’s stockholders approved it in March 2000. The 1999 Plan was amended in July 2011.
Prior to the Company’s IPO, the 1999 Plan provided for the grant of incentive stock options, within the meaning of Section 422 of the Internal Revenue Code, to employees and any parent and subsidiary corporations’ employees, and for the grant of nonstatutory stock options and restricted stock and stock appreciation rights to employees, directors and consultants and any parent and subsidiary corporations’ employees and consultants. On August 8, 2013, the date of effectiveness of the registration statement for the Company’s IPO, the Company ceased using the 1999 Stock Plan to grant new equity awards, and began using the 2013 Equity Incentive Plan for grants of new equity awards. Accordingly, as of December 31, 2013, no shares were available for future grant under the 1999 Stock Plan. However, the 1999 Stock Plan will continue to govern the terms and conditions of any outstanding awards granted thereunder.
Stock-based Compensation Expense
The following table details the components of stock-based compensation expense recognized in earnings in each as follows:
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Stock options |
$ | 3,805 | $ | 2,552 | $ | 2,035 | ||||||
| Restricted stock units |
566 | 58 | — | |||||||||
| Common stock warrants |
— | 299 | 206 | |||||||||
| Common stock call option |
— | 1,824 | 2,965 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| $ | 4,371 | $ | 4,733 | $ | 5,206 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
86
Table of Contents
Stock Options
The grant-date fair value of each option award is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The weighted average assumptions for 2014, 2013 and 2012 grants are provided in the table below. Because the Company’s shares were not publicly traded prior to August 9, 2013 and its shares were rarely traded privately, and due to the limited trading history since August 9, 2013, expected volatility is estimated based on the average historical volatility of similar entities with publicly traded shares. The risk-free rate for the expected term of the option is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve at the date of grant. Expense is recognized using the straight-line attribution method.
The following is a summary of the assumptions used in the valuation of stock-based awards under the Black-Scholes model:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2014 | 2013 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Dividend yield |
0.00 | % | 0.00 | % | 0.00 | % | ||||||
| Volatility |
47.04 | % | 53.94 | % | 54.28 | % | ||||||
| Expected term (years) |
6.42 | 6.43 | 6.49 | |||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.81 | % | 1.38 | % | 0.97 | % | ||||||
Stock option activity during the periods indicated is as follows:
| Number of shares subject to option |
Weighted average exercise price |
Weighted average remaining contractual term (years) |
Aggregate intrinsic value |
|||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2012 |
3,290,039 | $ | 2.40 | 8.08 | $ | 23,030 | ||||||||||
| Granted |
1,114,801 | 13.52 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
(635,072 | ) | 1.47 | |||||||||||||
| Forfeited |
(129,609 | ) | 7.50 | |||||||||||||
| Expired |
(8,887 | ) | 1.18 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2013 |
3,631,272 | 5.78 | 7.85 | 111,150 | ||||||||||||
| Granted |
1,255,088 | 28.96 | ||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
(522,202 | ) | 1.92 | |||||||||||||
| Forfeited |
(197,574 | ) | 17.30 | |||||||||||||
| Expired |
(370 | ) | 2.34 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2014 |
4,166,214 | 12.70 | 7.56 | 63,186 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Exercisable at December 31, 2014 |
1,176,090 | $ | 2.21 | 6.23 | $ | 30,178 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
The weighted average grant date fair value of options granted during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, was $13.93 and $7.20, respectively. The total intrinsic value of options exercised during the years ended December 31, 2014 and 2013, was $15,423 and $13,823, respectively.
The Company recorded stock-based compensation expense related to options of $3,805; $2,552 and $2,035 as of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
At December 31, 2014, there was $15,823 of total unrecognized compensation cost related to unvested stock options granted under the Plan. That cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted average period of 2.76 years.
On June 13, 2012, 573,941 of shares subject to option were exercised prior to vesting pursuant to an early exercise feature. The proceeds from the transaction are recorded as a liability within accrued and other current
87
Table of Contents
liabilities and other liabilities, non-current until vested. There are 188,875 options remaining unvested and outstanding and a related $340 liability as of December 31, 2014. These options will be reclassified to common stock as the Company’s repurchase rights lapse.
Restricted Stock Units
During 2014 and 2013, the Company issued restricted stock units (RSUs) to employees and a non-employee director.
RSU activity during the periods indicated is as follows:
| Number of shares subject to restriction |
Weighted average share value |
Weighted average remaining contractual term (years) |
Aggregate intrinsic value |
|||||||||||||
| Balance at January 1, 2013 |
— | $ | — | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Granted |
7,555 | 34.27 | ||||||||||||||
| Vested |
— | — | ||||||||||||||
| Forfeited |
— | — | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2013 |
7,555 | 34.27 | 1.18 | 275 | ||||||||||||
| Granted |
426,263 | 28.37 | ||||||||||||||
| Vested |
5,555 | — | ||||||||||||||
| Forfeited |
6,000 | — | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2014 |
422,263 | 28.43 | 2.62 | 11,756 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
The related compensation expense for restricted stock units recognized during the year ended December 31, 2014 and 2013 was $566 and $58. At December 31, 2014, there was $11,572 of total unrecognized compensation cost related to unvested restricted stock units granted under the 2013 Plan.
Common Stock Warrants
In 2011, the Company issued warrants to a non-employee to purchase 125,000 shares of common stock, with which it had an existing commercial agreement. The warrants had an exercise price of $1.80, vesting annually over a four-year period, and expiring on December 31, 2017. Additionally in 2011, the Company issued warrants to certain other non-employee stockholders for 203,700 shares of common stock at the exercise price of $1.80 per share, vesting immediately and expiring in 2018.
Unvested warrants to non-employees are re-measured at fair value as of each balance sheet date. The following is a summary of the weighted average assumptions used in the valuation of warrants under the Black-Scholes model at each balance sheet date:
| Year ended December 31, |
||||
| 2013 | ||||
| Dividend yield |
0.00 | % | ||
| Volatility |
55.0 | % | ||
| Expected term (years) |
4.63 | |||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.09 | % | ||
88
Table of Contents
Common stock warrant activity during the periods indicated is as follows:
| Number of shares subject to warrants |
Weighted average exercise price |
Weighted average remaining contractual term (years) |
Aggregate intrinsic value |
|||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2012 |
139,729 | $ | 1.80 | 5.02 | $ | 1,006 | ||||||||||
| Exercised |
(14,729 | ) | 1.80 | |||||||||||||
| Repurchased |
(125,000 | ) | 1.80 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Balance at December 31, 2013 |
— | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
There were no warrants outstanding and no unrecognized expenses related to unvested warrants as of December 31, 2014 and 2013 because all warrants have been exercised or repurchased. The total intrinsic value of warrants exercised during the year ended December 31, 2013 was $150. The total intrinsic value of warrants repurchased during the year ended December 31, 2013 was $1,275. The related compensation expense for non-employee warrants recognized during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012 recorded in general and administrative expense, was zero, $299, and $206, respectively.
Common Stock Call Option
In conjunction with the recapitalization and issuance of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock in July 2011 (note 9), the Company entered into a stock repurchase agreement (the Agreement) with certain members of senior management. The Agreement included a contractual call option, providing the Company an option to repurchase up to 50% of the employee’s then outstanding shares of common stock for $7.80 per share in the event of resignation or termination by the employee. The call option was effective for the two-year period following the recapitalization transaction, expired on July 15, 2013, and represented a compensatory arrangement in that the key employees were required to continue employment for a period of two years to earn back the right to participate in any appreciation in the value of the underlying shares or be subject to repurchase under the Company’s call option. Pursuant to the terms of the Agreement, stock options that vest and are exercised by management during the two-year period of the Agreement become subject to the repurchase provisions.
The value of the effective stock options created upon execution of the Agreement was determined using a Black-Scholes pricing model, and the associated compensation expense is being recognized on a straight-line basis over the two-year period and is included in sales and marketing, research and development, and general and administrative expense in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Key assumptions used in the Black-Scholes pricing model were:
| Dividend yield |
0.00 | % | ||
| Volatility |
40.00 | % | ||
| Expected term (years) |
2.00 | |||
| Risk-free interest rate |
0.37 | % |
The Company recorded stock-based compensation expense related to the employee’s compensatory arrangement created by the Company’s call option of $1,824 and $2,965 for the years ended December 31, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The call option agreement expired on July 15, 2013.
The Company repurchased 504,559 shares of common stock in September 2012 at $7.80 per share for a total of $3,936 under this agreement resulting from the exercise of its call option in connection with the termination of the former chief financial officer. The repurchased shares are held in treasury stock at cost.
89
Table of Contents
Common Stock Valuations
Prior to the Company’s IPO in August 2013, the Company derived the value of its common stock using valuation models prepared by third parties. In addition, management and the Company’s Board of Directors also considered relevant market activity including the then anticipated IPO, and other events occurring in recent proximity to valuation dates, including the recapitalization transaction and issuance of New Series A Convertible Preferred Stock in July 2011 to determine an estimate of fair value per share for stock options granted prior to August 2013.
Subsequent to the Company’s IPO, the value of the Company’s common stock was determined based on the closing market price of the Company’s common stock traded on the New York Stock Exchange.
9. Stockholders’ Equity
Initial public offering
On August 14, 2013, the Company completed its Initial Public Offering (IPO) of common stock at a price to the public of $21.00 per share. In connection with the Company’s IPO, the Company’s Board of Directors and stockholders approved a 1-for-4 reverse stock split of its outstanding common stock and convertible preferred stock effective August 5, 2013. All share and per share amounts contained in the accompanying consolidated financial statements have been retroactively adjusted to reflect the reverse stock split. Upon completion of the Company’s IPO, (i) all outstanding shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock converted into an aggregate of 17,418,807 shares of common stock and (ii) the Company issued 6,440,000 shares of common stock resulting in net proceeds of $122,131 after deducting the underwriters discount and offering expenses.
Follow-On Public Offering
On January 16, 2014, the Company completed a follow-on public offering of 6,072,000 shares of its common stock. The Company sold 747,500 shares of its common stock, and the selling shareholders sold 5,324,500 shares in the offering, including the underwriters’ over-allotment, at a price to the public of $35.50 per share. The offering closed on January 23, 2014, and the Company received net proceeds of $24,846 after deducting the underwriters discount and offering expenses, which have been included in additional paid-in-capital in the accompanying consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2014.
Preferred Stock
Concurrent with the IPO, the Company amended and restated its certificate of incorporation (“Amended Articles”) to authorize 100,000,000 shares of $0.001 par value undesignated preferred stock, of which zero shares were issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2014 and 2013. Under the terms of the Amended Articles, the Company’s board is authorized to issue shares of preferred stock in one or more series without stockholder approval. The Company’s board of directors has the discretion to determine the rights, preferences, privileges and restrictions, including voting rights, dividend right, conversion rights, redemption privileges and liquidation preferences of each series of preferred stock issued.
Common Stock
Pursuant to the Amended Articles and concurrent with the Company’s IPO, the Company authorized 1,000,000,000 shares of $0.001 par value common stock, of which 41,164,834 and 39,889,577 shares were outstanding as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The holders of the common stock are entitled to dividends only when declared out of legally available funds by the Board of Directors and subject to any preferential rights of any outstanding preferred stock. Each share of common stock has one vote and there are no cumulative rights to holders of common stock. The holders of common stock have no preemptive or conversion rights and he rights, preferences and privileges of the holders of common stock are subject to the rights of the holders of any series of preferred shares which may be designated and issued in the future
90
Table of Contents
Treasury Stock
The Company repurchased 520,214 shares of common stock in 2012 and earlier periods for a total of $3,966, of which 504,559 shares and $3,936 related to the exercise of call options in connection with the termination of the former chief financial officer. The repurchased shares are held in treasury at cost.
Recapitalization and Series A Convertible Preferred Stock
In July 2011, all of the Company’s previously existing series of preferred stock were converted to common stock. The Company simultaneously issued and sold 17,418,807 shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock to new, unaffiliated investors at a price of $7.80 per share, generating proceeds of $135,023, net of transaction costs. Immediately thereafter, the Company repurchased 17,418,695 shares of common stock held by certain stockholders for an aggregate $135,525, net of $341 related to a cashless exercise. The repurchased shares were retired by the Company’s board of directors upon repurchase.
The Series A Convertible Preferred Stock was convertible at the option of the holder, at any time, on a one-to-one basis to common stock. The Series A Convertible Preferred Stock was not redeemable, had no preferences over the common stock with respect to dividends and voting rights, and had no liquidation preferences upon dissolution or winding up of the Company and was akin to common stock. The Series A Convertible Preferred Stock voted on an as-if converted to common stock basis. There were 17,418,807 shares of Series A Convertible Preferred Stock outstanding as of December 31, 2012.
In August 2013 and concurrent with the IPO, all of the shares of existing Series A Convertible Preferred Stock were converted into 17,418,807 shares of common stock at a one-to-one ratio.
10. Retirement Plans
a) U.S. 401(k) Plan
All employees are eligible to participate in the Company’s Profit Sharing 401(k) Plan (the “Plan”) according to certain age and period of service restrictions. The Plan provides for discretionary Company contributions. No Company contributions were made during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
b) India Gratuity Plan
In addition, under the India Payment of Gratuity Act of 1972, the Company maintains a gratuity defined-benefit plan for eligible employees of the Company’s India subsidiary. Upon termination of an employee for any reason, the Company must pay the equivalent of 15 days of the current salary to the employee for each year of service. The benefit begins to accrue after five years of service.
The funding liability under the plan is actuarially-determined, based on a rate of interest of 8.1% and 9.3% and a retirement age of 58 years, and was $892 and $851 as of December 31, 2014 and 2013, respectively. The liability is included in accrued and other current liabilities in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. Expense under the plan was $104, $402 and $145 for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively. The plan is currently unfunded.
11. Commitments and Contingencies
a) Legal Proceedings, Regulatory Matters and Other Contingencies
From time to time, the Company may become involved in legal proceedings, regulatory matters or other contingencies in the ordinary course of its business. The Company is not presently involved in any legal proceeding, regulatory matter or other contingency that, if determined adversely to it, would individually or in the aggregate have a material adverse effect on its business, operating results, financial condition or cash flows.
91
Table of Contents
b) Lease Agreements
The Company leases office facilities under non-cancelable operating leases with various expiration dates. The operating leases may include options that permit renewals for additional periods. Rent abatements and escalations are considered in the determination of straight-line rent expense for operating leases. Lease incentives are recorded as a deferred credit and recognized as a reduction to rent expense on a straight-line basis over the lease term.
Future minimum lease payments under non-cancelable operating leases as of December 31, 2014 are as follows:
| 2015 |
$ | 3,412 | ||
| 2016 |
5,040 | |||
| 2017 |
4,901 | |||
| 2018 |
4,484 | |||
| 2019 |
3,989 | |||
| Thereafter |
21,905 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total minimum lease payments |
$ | 43,731 | ||
|
|
|
Rent expense under the operating leases was $4,533, $2,815 and $2,080 for the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
In August 2014, the Company moved into a new office space for its corporate headquarters in Tysons Corner, Virginia. The lease is for a fixed 11-year term with options for two additional renewal terms of five years each. The lease covers approximately 129,000 square feet of office space. Total rent for the lease of headquarters’ space is $37,187 over the 11 year-term.
c) Acquisition Payouts
A summary of the changes in the recorded amount of accrued compensation and deferred consideration from acquisitions from December 31, 2013 to December 31, 2014 is as follows:
| Compensation | Deferred Consideration |
|||||||
| Liability as of December 31, 2012 |
$ | 903 | $ | 113 | ||||
| Payments |
(1,578 | ) | (90 | ) | ||||
| Additional accruals |
1,863 | 576 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Liability as of December 31, 2013 |
$ | 1,188 | $ | 599 | ||||
| Payments |
(2,256 | ) | (166 | ) | ||||
| Additional accruals |
2,306 | 1,642 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Liability as of December 31, 2014 |
$ | 1,238 | $ | 2,075 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The accrued compensation and consideration related to acquisition payouts is recorded within accrued and other current liabilities on the balance sheet.
12. Related-Party Transactions
The Company had no related party transactions during the years ended December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012.
13. Segment Information and Geographic Data
The Company is organized and operates as a single reportable segment. The Company’s chief operating decision maker is its chief executive officer, who reviews financial information presented on a consolidated basis for the purpose of making operating decisions and assessing financial performance.
92
Table of Contents
Platform subscription and marketing solutions revenue are principally derived from North America. Revenue from outside North American sources represented 11%, 10% and 9% of total revenue in 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively.
Property and equipment in non-North American geographic locations totaled $4,379, $3,766 and $1,753, which represented 19%, 48% and 26% of total property and equipment, net as of December 31, 2014, 2013 and 2012, respectively, and are located primarily in India.
14. Subsequent Events
The Company has evaluated subsequent events through March 16, 2015, the date the consolidated financial statements were available to be issued.
15. Unaudited Quarterly Results of Operations
| Dec. 31, 2014 |
Sept. 30, 2014 |
Jun. 30, 2014 |
Mar. 31, 2014 |
Dec. 31, 2013 |
Sept. 30, 2013 |
Jun. 30, 2013 |
Mar. 31, 2013 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenue |
$ | 39,325 | $ | 37,386 | $ | 34,133 | $ | 31,401 | $ | 30,696 | $ | 29,145 | $ | 26,935 | $ | 24,360 | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
12,966 | 11,208 | 9,039 | 9,208 | 10,675 | 8,412 | 7,172 | 6,003 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
26,359 | 26,178 | 25,094 | 22,193 | 20,021 | 20,733 | 19,763 | 18,357 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
17,549 | 14,571 | 15,977 | 13,667 | 13,203 | 11,552 | 12,131 | 11,519 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
3,701 | 3,875 | 3,284 | 3,189 | 3,086 | 2,813 | 2,789 | 2,502 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
8,146 | 6,446 | 4,953 | 4,697 | 4,325 | 6,092 | 6,154 | 4,647 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
29,396 | 24,892 | 24,214 | 21,553 | 20,614 | 20,457 | 21,074 | 18,668 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(3,037 | ) | 1,286 | 880 | 640 | (593 | ) | 276 | (1,311 | ) | (311 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest income |
504 | 450 | 362 | 279 | 338 | 295 | 123 | 259 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other expense |
(434 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations before income taxes |
(2,533 | ) | 1,302 | 1,242 | 919 | (255 | ) | 571 | (1,188 | ) | (52 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
(623 | ) | 231 | 250 | (722 | ) | 178 | 1,400 | 1,099 | (362 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | (1,910 | ) | $ | 1,071 | $ | 992 | $ | 1,641 | $ | (433 | ) | $ | (829 | ) | $ | (2,287 | ) | $ | 310 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) per share—basic |
$ | (0.05 | ) | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.02 | $ | 0.04 | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.15 | ) | $ | 0.01 | ||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) per share—diluted |
$ | (0.05 | ) | $ | 0.02 | $ | 0.02 | $ | 0.04 | $ | (0.01 | ) | $ | (0.03 | ) | $ | (0.15 | ) | $ | 0.01 | ||||||||||||
Schedule II—VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
| Description |
Balance at Beginning of Period |
Charged to Costs and Expenses |
Charged to Other Accounts |
Deductions | Balance at End of Period |
|||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2012: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 326 | $ | 344 | — | $ | 165 | $ | 505 | |||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2013: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
505 | 392 | — | 166 | 731 | |||||||||||||||
| Year ended December 31, 2014: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
731 | 317 | — | 709 | 339 | |||||||||||||||
93
Table of Contents
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
None.
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
(a) Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Under the supervision and with the participation of our principal executive officer and principal financial officer, our management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures. The term “disclosure controls and procedures,” as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, or the Exchange Act, means controls and other procedures of a company that are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the rules and forms of the Securities and Exchange Commission, or SEC. Disclosure controls and procedures include, without limitation, controls and procedures designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by a company in the reports that it files or submits under the Exchange Act is accumulated and communicated to the company’s management, including its principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
Based on this evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were not effective as of December 31, 2014, due to the material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting as discussed below. Furthermore, our management may be unable to conclude in future periods that our disclosure controls and procedures are effective due to the effects of various factors, which may, in part, include unremediated material weaknesses in internal controls over financial reporting.
(b) Management’s Annual Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
We produce our consolidated financial statements in accordance with the requirements of U.S. GAAP. Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining an adequate system of internal control over financial reporting of our company. Effective internal controls are necessary for us to provide reliable financial reports, to help mitigate the risk of fraud and to operate successfully as a publicly traded company. The design, monitoring and revision of the system of internal financial reporting controls involves, among other things, management’s judgments with respect to the relative cost and expected benefits of specific control measures. The effectiveness of the control system is supported by the selection, retention and training of qualified personnel and an organizational structure that provides an appropriate division of responsibility and formalized procedures. The system of internal accounting controls is periodically reviewed and modified in response to changing conditions. Designated company employees regularly monitor the adequacy and effectiveness of internal accounting controls.
Management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of the system of internal control over financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control—Integrated Framework (1992) issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and identified material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014 as defined in SEC Regulation S-X. A material weakness is a deficiency, or combination of deficiencies, in internal control over financial reporting, such that there is a reasonable possibility that a material misstatement of the Company’s annual or interim financial statements will not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Because of the material weaknesses described below, management concluded that our system of internal control over financial reporting was not effective as of December 31, 2014.
As of December 31, 2014, the primary factors contributing to the material weaknesses, which relates to our control environment and financial statement close process, were:
| • | We did not have adequate policies and procedures in place to ensure the effective design and operation of general IT controls over our financial reporting systems. Specifically, we identified significant deficiencies in internal controls related to access to programs and data, and program development and |
94
Table of Contents
| changes, which we consider in the aggregate to be a material weakness, due to the inability to rely on certain system generated reports and application controls. |
| • | We had ineffective entity and process level controls impacting the preparation and review of our consolidated financial statements and ineffective process level controls related to the review of manually prepared analyses and supporting information used to prepare our consolidated financial statements. Specifically, we identified significant deficiencies in internal controls related to inappropriately designed and ineffective controls over financial integration of and accounting for acquired companies, cut off procedures and reviews of account reconciliations. We also determined we had ineffective controls related to the preparation and review of financial statements, all of which in the aggregate, were determined to be a material weakness in internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. |
As long as we qualify as an “emerging growth company” as defined by the Jumpstart our Business Startups Act of 2012, we will not be required to obtain an auditor’s attestation report on our internal controls in future annual reports on Form 10-K as otherwise required by Section 404(b) of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. Accordingly, our independent registered public accounting firm did not perform an audit of our internal control over financial reporting for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2014. Had our independent registered public accounting firm performed an audit of our internal control over financial reporting, material weaknesses and/or significant deficiencies, in addition to those discussed above, may have been identified. Our qualification as an emerging growth company may last for up to five years following our IPO on August 8, 2013 or expire as early as December 31, 2015.
(c) Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Since December 31, 2013, with the oversight of senior management and our audit committee, we have implemented steps to take additional measures to remediate the underlying causes of the previously identified material weaknesses, primarily through the performance of a risk assessment process; the development and implementation of formal, documented policies and procedures, improved processes and control activities (including an assessment of the segregation of duties); as well as the hiring of additional finance personnel for specific roles such as financial reporting. During the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2014, we continued to make the following changes to our internal control over financial reporting:
| • | We have developed and implemented entity level and process level controls with respect to the preparation and review of our consolidated financial statements. We have developed monitoring and management oversight of the financial reporting control environment. We have developed, implemented and tested process level controls relating to the review of manually prepared analyses and supporting information used to prepare our consolidated financial statements and are in process of performing necessary remediation activities as a result of our testing procedures. At this time, we cannot state whether these controls will prove to be effective. |
| • | We have developed, implemented and tested policies and procedures around the design and operation of general IT controls over our financial reporting systems and in process of performing necessary remediation activities as a result of our testing procedures. At this time, we cannot state whether these controls will prove to be effective. |
We have completed the development, formal documentation and preliminary testing of our policies and procedures relating to our internal control over financial reporting. We have also completed the development and formal documentation of general IT controls over our financial reporting systems. While we have made significant progress with respect to cut off procedures, account reconciliations and account analyses, and with respect to the enhancement of controls related to the preparation and review of our financial statements, we will not consider the material weaknesses remediated until our internal control processes have been operational for a sufficient period of time and have been successfully tested. Accordingly, we have determined that we continue to have material weaknesses in our internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2014. We also cannot provide assurance that management will be able to report that our internal control over financial reporting will be effective as of December 31, 2015.
95
Table of Contents
We cannot assure you that we will be able to remediate our existing material weaknesses in a timely manner, if at all, or that in the future, additional material weaknesses will not exist, reoccur or otherwise be discovered, a risk that is significantly increased in light of the complexity of our business. If our efforts to remediate these material weaknesses are not successful or if other deficiencies occur, our ability to accurately and timely report our financial position, results of operations, cash flows or key operating metrics could be impaired, which could result in late filings of our annual and quarterly reports under the Exchange Act, restatements of our consolidated financial statements or other corrective disclosures. Additional impacts could include a decline in our stock price, suspension of trading or delisting of our common stock by the New York Stock Exchange, or other material adverse effects on our business, reputation, results of operations, financial condition or liquidity. Furthermore, if we continue to have these existing material weaknesses or other material weaknesses or significant deficiencies in the future, it could create a perception that our financial results do not fairly state our financial condition or results of operations. Any of the foregoing could have an adverse effect on the value of our stock.
| Item 9B. | Other Information |
None.
96
Table of Contents
PART III
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
Information responsive to this item is incorporated herein by reference to our definitive proxy statement with respect to our 2015 Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be filed with the SEC within 120 days after the end of the fiscal year covered by this annual report on Form 10-K, under the headings “Board of Directors,” “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” and “Governance of the Company.”
As part of our system of corporate governance, our board of directors has adopted a code of business conduct and ethics. The code applies to all of our employees, officers (including our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller, or persons performing similar functions), agents and representatives, including our independent directors and consultants, who are not employees of the Company, with regard to their Cvent-related activities. Our code of business conduct and ethics is available on our website at http://investors.cvent.com/governance/governance-documents.aspx . We will post on this section of our website any amendment to our code of business conduct and ethics, as well as any waivers of our code of business conduct and ethics, that are required to be disclosed by the rules of the SEC or the New York Stock Exchange.
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the section entitled “Compensation” in our 2015 Proxy Statement.
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the section entitled “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management,” and “Equity Compensation Plan Information” in our 2015 Proxy Statement.
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the section entitled “Governance of the Company” in our 2015 Proxy Statement.
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
The information required by this Item is incorporated herein by reference to the sections entitled “Audit and Non-Audit Fees” in our 2015 Proxy Statement. Our audit committee’s policy on pre-approval of audit and permissible non-audit services of our independent registered public accounting firm is incorporated by reference from the discussion under the heading “Policy on Audit Committee Pre-Approval of Audit and Permissible Non-Audit Services of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm.”
97
Table of Contents
PART IV
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
(a) Documents filed as part of this report are as follows:
| 1. | Consolidated Financial Statements: Our Consolidated Financial Statements are listed in the “Index to Consolidated Financial Statements” Under Part II, Item 8 of this report. |
| 2. | Financial Statement Schedules: Schedule II is included in Part II, Item 8 of this report. All other financial statement schedules have been omitted because they are not applicable or the required information is shown in the Consolidated Financial Statements or Notes thereto. |
| 3. | Exhibits: See the Exhibit Index immediately following the signature page of this report. |
98
Table of Contents
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the County of Fairfax, Commonwealth of Virginia, on the sixteenth day of March, 2015.
| Cvent, Inc. | ||
| By: | /s/ Rajeev K. Aggarwal | |
| Rajeev K. Aggarwal | ||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||
POWER OF ATTORNEY
KNOW ALL PERSONS BY THESE PRESENT, that each person whose signature appears below hereby constitutes and appoints Rajeev K. Aggarwal. and Peter L. Childs, and each of them acting individually, as his true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, with full power of each to act alone, with full powers of substitution and resubstitution, for him and in his name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments to this Annual Report on Form 10-K with all exhibits thereto and all documents in connection therewith, with the Securities and Exchange Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents, with full power of each to act alone, full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing requisite and necessary to be done in connection therewith, as fully for all intents and purposes as he might or could do in person, hereby ratifying and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents, or his or their substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this Annual Report on Form 10-K has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated:
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||
| /s/ Rajeev K. Aggarwal Rajeev K. Aggarwal |
Chairman of the Board of Directors and Chief (Principal Executive Officer) |
March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Peter L. Childs Peter L. Childs |
Chief Financial Officer (Principal Financial and Accounting Officer) |
March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Sanju K. Bansal Sanju K. Bansal |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Tony Florence Tony Florence |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Jeffrey Lieberman Jeffrey Lieberman |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
| /s/ Kevin T. Parker Kevin T. Parker |
Director | March 16, 2015 | ||
99
Table of Contents
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit |
Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date | |||||
| 2.1 |
Stock Purchase Agreement, dated June 12, 2012, by and among Registrant, CrowdCompass, Inc. and stockholders of CrowdCompass, Inc. | S-1 | 333-189837 | 2.1 | July 8, 2013 | |||||
| 3.1 |
Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation. | S-1/A | 333-189837 | 3.2 | August 5, 2013 | |||||
| 3.2 |
Amended and Restated Bylaws | S-1 | 333-189837 | 3.3 | July 8, 2013 | |||||
| 4.1 |
Second Amended and Restated Investors’ Rights Agreement, dated July 15, 2011, by and among Registrant and certain security holders of Registrant. | S-1 | 333-189837 | 4.1 | July 8, 2013 | |||||
| 10.1+ |
Form of Indemnification Agreement entered into between Registrant and its directors and executive officers. | S-1 | 333-189837 | 10.1 | July 8, 2013 | |||||
| 10.2+ |
1999 Stock Incentive Plan, as amended to date. | S-1 | 333-189837 | 10.4 | July 8, 2013 | |||||
| 10.3+ |
Form of Stock Option Agreement under 1999 Stock Incentive Plan. | S-1 | 333-189837 | 10.5 | July 8, 2013 | |||||
| 10.4+ |
2013 Equity Incentive Plan. | S-1/A | 333-189837 | 10.6 | July 29, 2013 | |||||
| 10.5+ |
Form of Stock Option Grant Notice and Stock Option Agreement under 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (for grants made before December 31, 2014). | S-1/A | 333-189837 | 10.7 | July 29, 2013 | |||||
| 10.6+ |
Form of Restricted Stock Unit Grant Notice and Restricted Stock Unit Agreement under 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (for grants made before December 31, 2014). | S-1/A | 333-189837 | 10.8 | July 29, 2013 | |||||
| 10.7+ |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement under 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (for grants made before December 31, 2014). | S-1/A | 333-189837 | 10.14 | July 29, 2013 | |||||
| 10.8+ |
Form of Stock Option Grant Notice and Stock Option Agreement under 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (for grants made on or after December 31, 2014). | |||||||||
| 10.9+ |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement for Employees under 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (for grants made on or after December 31, 2014). | |||||||||
| 10.10+ |
Form of Restricted Stock Agreement for Non-Employee Directors under 2013 Equity Incentive Plan (for grants made on or after December 31, 2014). | |||||||||
100
Table of Contents
| Exhibit |
Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date | |||||
| 10.11+ |
Offer Letter by and between the Registrant and Peter L. Childs, dated October 2, 2012. | S-1 | 333-189837 | 10.11 | July 8, 2013 | |||||
| 10.12+ |
Non-Employee Director Compensation Policy | S-1/A | 333-189837 | 10.13 | July 29, 2013 | |||||
| 10.13 |
Office Lease, dated as of May 17, 2006, as amended, by and between the Registrant and Greensboro Park Property Owner LLC. | S-1/A | 333-189837 | 10.2 | August 5, 2013 | |||||
| 10.14 |
Office Leases, dated as of January 13, 2010 and May 15, 2011, by and between Cvent India Private Limited and DLF Cyber City Developers Limited. | S-1 | 333-189837 | 10.3 | July 8, 2013 | |||||
| 10.15 |
Office Leases by and between Cvent India and DLF Assets Private Limited. | S-1/A | 333-189837 | 10.15 | August 5, 2013 | |||||
| 10.16 |
Office Leases by and among Registrant and TMG Solutions Plaza 1, L.L.C., TMG Solutions Plaza 2, L.L.C., and TMG Solutions Plaza 3, L.L.C. dated October 23, 2013. | 10-Q | 001-36043 | 10.1 | November 12, 2013 | |||||
| 10.17 |
Service Agreement, dated as of August 23, 2010, by and between the Registrant and JPS Holdings, Inc. | S-1 | 333-189837 | 10.12 | July 8, 2013 | |||||
| 10.18 |
Third Amended and Restated Stockholders’ Agreement, dated July 15, 2011, by and among Registrant and certain security holders of Registrant. | S-1 | 333-189837 | 10.9 | July 8, 2013 | |||||
| 21.1 |
Subsidiaries of Registrant. | |||||||||
| 23.1 |
Consent of KPMG LLP, independent registered public accounting firm. | |||||||||
| 24.1 |
Power of Attorney (included on signature page of this Annual Report on Form 10K) | |||||||||
| 31.1 |
Certification of the Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) and Rule 15d-14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |||||||||
| 31.2 |
Certification of the Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) and Rule 15d- 14(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |||||||||
| 32.1 |
Certification of Chief Executive Officer Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |||||||||
101
Table of Contents
| Exhibit |
Description |
Form |
File No. |
Exhibit |
Filing Date | |||||
| 32.2 |
Certification of Chief Financial Officer Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |||||||||
| 101.INS |
XBRL Instance Document. | |||||||||
| 101.SCH |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema. | |||||||||
| 101.CAL |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase. | |||||||||
| 101.LAB |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase. | |||||||||
| 101.PRE |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase. | |||||||||
| 101.DEF |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase. | |||||||||
| + | Indicates management contract or compensatory plan. |
102
