Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - Aevi Genomic Medicine, Inc. | v392952_8-k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1

November 2014

Forward Looking Statement This presentation includes certain estimates and other forward - looking statements within the meaning of Section 21 E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 , as amended, including statements with respect to anticipated operating and financial performance, clinical results, potential partnerships, licensing opportunities and other statements of expectation . Words such as “ expects, ” “ anticipates, ” “ intends, ” “ plans, ” “ believes, ” “ assumes, ” “ seeks, ” “ estimates, ” “ should ” and variations of these words and similar expressions, are intended to identify these forward - looking statements . While we believe these statements are accurate, forward - looking statements are inherently uncertain and we cannot assure you that these expectations will occur and our actual results may be significantly different . These statements by the Company and its management are based on estimates, projections, beliefs and assumptions of management and are not guarantees of future performance . Important factors that could cause actual results to differ from those in the forward - looking statements include the factors described in the Company ’ s filings with the U . S . Securities and Exchange Commission . The Company disclaims any obligation to update or revise any forward - looking statement based on the occurrence of future events, the receipt of new information, or otherwise . 2
Investment Highlights • Rare and Orphan disease focused company • Proof of concept established with TARGT e x vivo gene therapy platform as evidenced by the positive initial data of ongoing TARGT EPO clinical trial • Multiple commercially attractive orphan indications for TARGT EPO identified; data from proof of concept studies expected in H 2 2015 • P latform expanded to include therapeutic peptides, as demonstrated by pre - clinical proof of concept with GLP - 2 , with potential utility in short bowel syndrome • Experienced management team 3

Management Team - Proven Track Record • President, Shire Specialty Pharmaceuticals - Responsible for all aspects of the $2.5 billion business e.g., commercial, R&D, manufacturing, etc. • President, Life Sciences, Safeguard Scientifics – Lead Life Sciences PE team, responsible for both investment and management of portfolio companies • Multiple senior operational leadership positions at Astra Merck/AstraZeneca Garry A Neil, MD Global Head of R&D • Group President, J&J Pharmaceutical R&D; Corporate VP, Science and Technology, J&J • Multiple senior R&D leadership positions at Astra Merck , Astra , Astra Zeneca and Merck KGaA • Industry R&D Thought Leader : Founder of Transcelerate ; Former Chair of PhRMA Science & Regulatory Committee; BOD of Reagan - Udall Foundation for FDA; BOD of Foundation for NIH • Directly contributed to >20 FDA approvals in multiple therapy areas • Vice - President Commercial Assessment for Shire Specialty Pharmaceuticals - Responsible for both corporate and business unit M&A and white space strategies • Principal, Devon Park Bioventures - Responsible for all aspects of venture investing e.g., negotiation, board governance, financing for $ 125 M Life Sciences VC fund • Associate Principal, McKinsey & Company – Worked on strategic issues for multiple Top 25 pharmaceutical companies; specialized in BD/M&A, and payer/reimbursement issues Mike Cola CEO John H. Leaman, MD CFO 4

Medgenics Vision 5 Driven by our commitment to patients we strive to create the premier rare and orphan disease company by: x Developing first - to - market or best - in - class therapies that are transformative to patients suffering from life - altering rare genetic diseases x Having unparalleled understanding of the underlying science of rare diseases from phenotype to genotype x Pushing the boundaries of medicine and technology to develop unique and better therapies x Working with patient s, families and advocacy groups to increase awareness and commitment to research and improve access to therapies

Medgenics Pipeline Product Program Area Preclinical Phase 1/2 Phase 2/3 Status TARGT EPO MDGN - 201 Chronic Renal Diseases and Hematological Disorders Renal Anemia - ESRD Ongoing Hypo - Responders to ESA Initiate Q1 15 Anemic CKD Transplant Initiate H1 15 Peritoneal Dialysis Initiate H1 15 Beta Thalassemia Intermedia Initiate H1 15 Myelodysplastic Syndrome Initiate H2 15 TARGT Peptides MDGN - 205 GLP - 2 for Short Bowel Syndrome IND H2 2015 Early Pipeline MDGN - 204 Orphan Metabolic Disease MDGN - 206 Orphan Enzyme Replacement 6
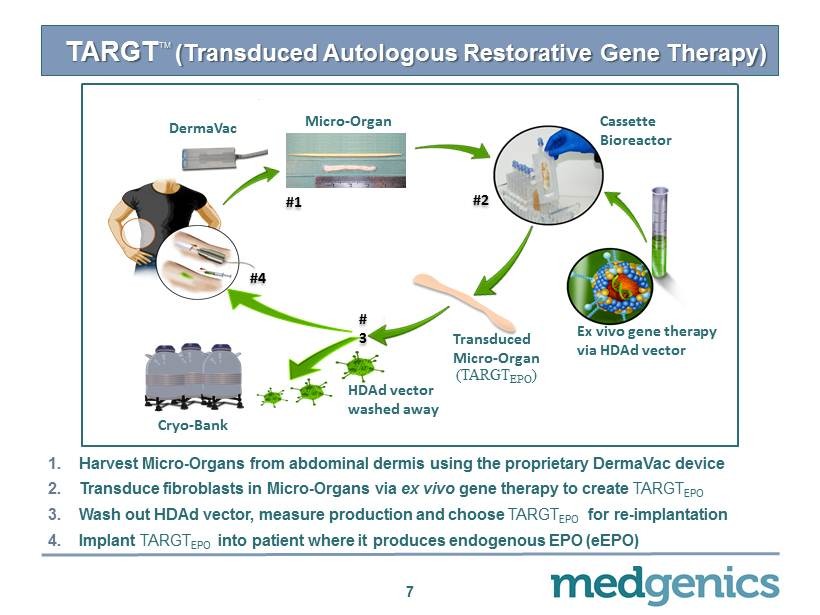
TARGT TM (Transduced Autologous Restorative Gene Therapy) 1. H arvest Micro - Organs from abdominal dermis using the proprietary DermaVac device 2. Transduce fibroblasts in Micro - Organs via ex vivo gene therapy to create TARGT EPO 3. Wash out HDAd vector, measure production and choose TARGT EPO for re - implantation 4. Implant TARGT EPO into patient where it produces endogenous EPO ( eEPO ) 7 Micro - Organ (TARGT EPO ) Cryo - Bank Ex vivo gene therapy via HDAd vector # 1 # 2 # 4 DermaVac # 3 Cassette Bioreactor HDAd vector washed away Transduced Micro - Organ
Significant Improvements to Technology Platform 8 • Vector optimization • Culture conditions • Re - implantation technique • Engraftment The entire system was re - engineered to increase and stabilize secretion levels in vivo
TARGT Platform Mimics the Natural System • Autologous proteins and peptides • Continuous secretion • Physiologic levels – Avoids supratherapeutic spikes • Precise, individualized dosing • Safe – Simple, well - tolerated procedure – Avoids exposure to viral antigen – Avoids viral DNA integration – Interruptible therapy through excision/ablation 9

Phase 1/2 trial in ESRD Patients with Renal Anemia 10
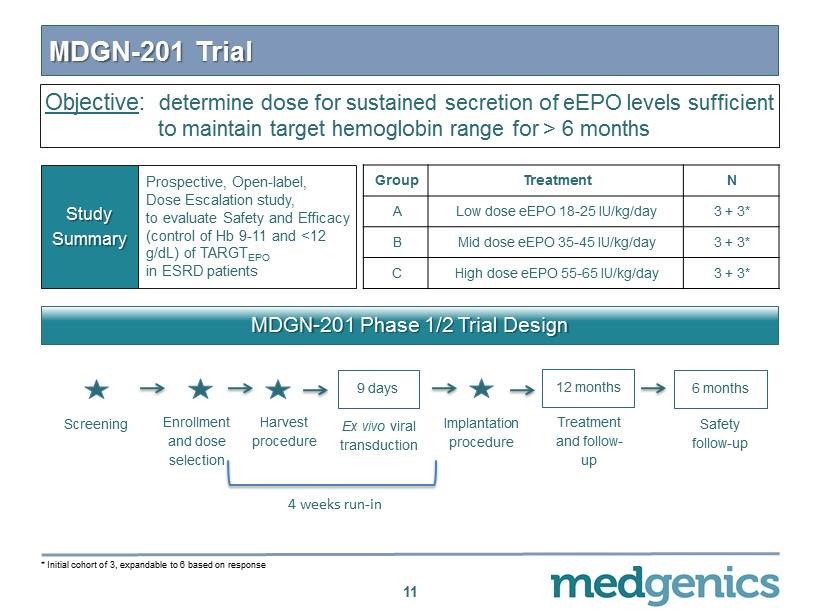
MDGN - 201 Trial 11 Prospective, Open - label, Dose Escalation study, to evaluate Safety and Efficacy (control of Hb 9 - 11 and < 12 g/ d L ) of TARGT EPO in ESRD patients Study Summary Group Treatment N A Low dose eEPO 18 - 25 IU/kg/day 3 + 3 * B Mid dose eEPO 35 - 45 IU/kg/day 3 + 3 * C High dose eEPO 55 - 65 IU/kg/day 3 + 3 * MDGN - 201 Phase 1/2 Trial Design Enrollment and dose selection Screening Harvest procedure Ex vivo viral transduction 9 days Treatment and follow - up 12 months Safety follow - up 6 months Implantation procedure 4 weeks run - in * Initial cohort of 3 , expandable to 6 based on response Objective : determine dose for sustained secretion of eEPO levels sufficient to maintain target hemoglobin range for > 6 months

TARGT EPO Patient Profile • End Stage Renal Disease (ESRD) patients – CKD patients with renal failure and low baseline eEPO secretion – Hemodialysis patients with inability to regulate body fluid levels • rHuEPO dependent – Require 2 - 3 injections on a weekly basis to maintain hemoglobin in target range ( 9 - 11 and < 12 g/ dL ) and supplemental iron • Ongoing blood loss – Combination of disease state and hemodialysis ( 3 x weekly) significantly shortens red blood cell (RBC) lifespan and results in RBC loss – Frequent blood testing also results in significant RBC loss • Concomitant disease common – Diabetes – Hypertension 12
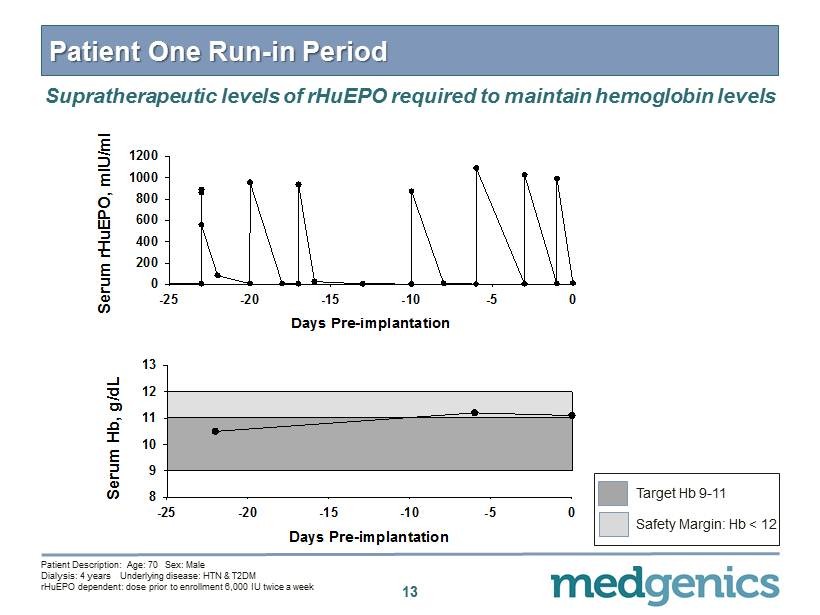
13 Patient One Run - in Period Supratherapeutic levels of rHuEPO required to maintain hemoglobin levels Days Pre-implantation -25 -20 -15 -10 -5 0 Serum rHuEPO, mIU/ml 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 Days Pre-implantation -25 -20 -15 -10 -5 0 Serum Hb, g/dL 8 9 10 11 12 13 Patient Description: Age: 70 Sex: Male Dialysis: 4 years Underlying disease: HTN & T 2 DM rHuEPO dependent: dose prior to enrollment 6 , 000 IU twice a week Target Hb 9 - 11 Safety Margin: Hb < 12
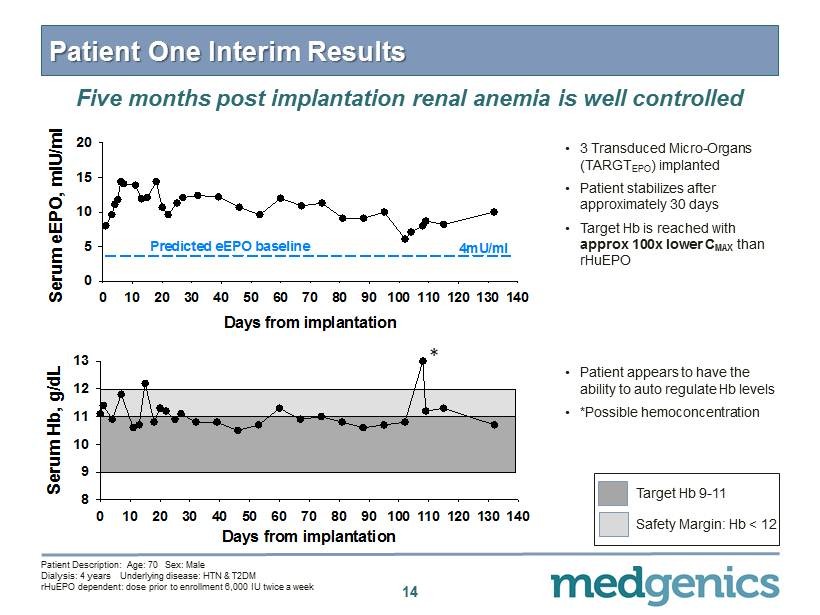
14 Patient One Interim Results • 3 Transduced Micro - Organs (TARG T EPO ) implanted • Patient stabilizes after approximately 30 days • Target Hb is reached with approx 100 x lower C MAX than rHuEPO • Patient appears to have the ability to auto regulate Hb levels • *Possible hemoconcentration Five months post implantation renal anemia is well controlled Days from implantation 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 Serum Hb, g/dL 8 9 10 11 12 13 Patient Description: Age: 70 Sex: Male Dialysis: 4 years Underlying disease: HTN & T 2 DM rHuEPO dependent: dose prior to enrollment 6 , 000 IU twice a week Days from implantation 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 Serum eEPO, mIU/ml 0 5 10 15 20 Predicted eEPO baseline 4mU/ml Target Hb 9 - 11 Safety Margin: Hb < 12 *
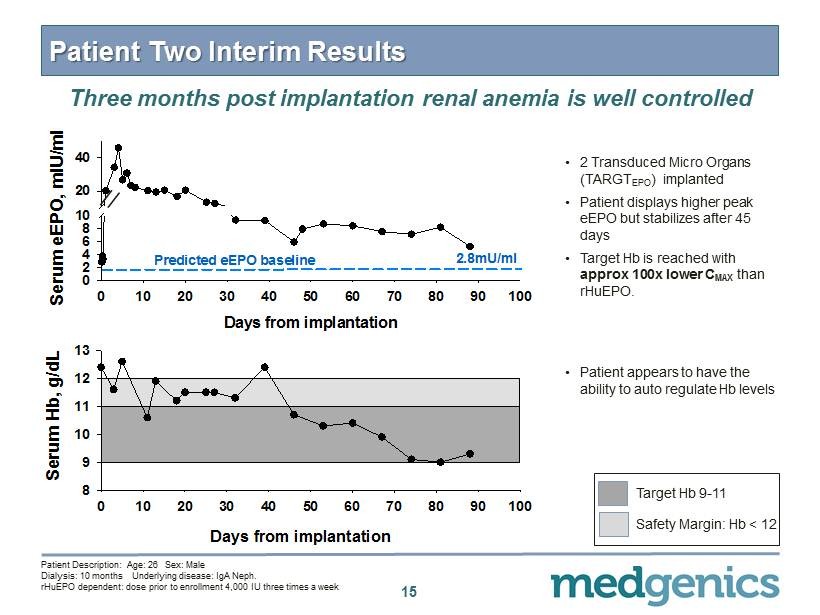
15 Patient Two Interim Results • 2 Transduced Micro Organs (TARGT EPO ) implanted • Patient displays higher peak eEPO but stabilizes after 45 days • Target Hb is reached with approx 100x lower C MAX than rHuEPO . Three months post implantation renal anemia is well controlled • Patient appears to have the ability to auto regulate Hb levels Days from implantation 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Serum eEPO, mIU/ml 0 2 4 6 8 10 20 40 Predicted eEPO baseline 2.8mU/ml Days from implantation 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Serum Hb, g/dL 8 9 10 11 12 13 Patient Description: Age: 26 Sex: Male Dialysis: 10 months Underlying disease: IgA Neph . rHuEPO dependent: dose prior to enrollment 4 , 000 IU three times a week Target Hb 9 - 11 Safety Margin: Hb < 12
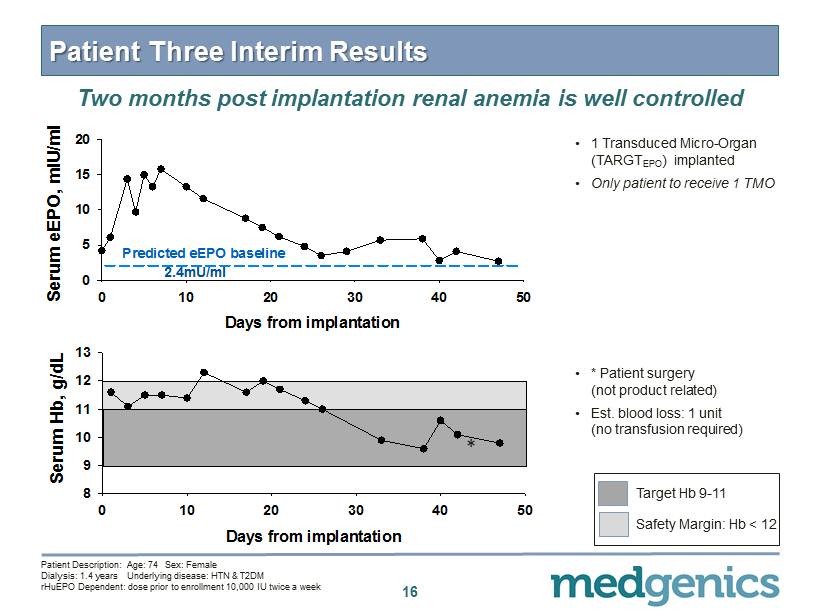
Patient Three Interim Results Two months post implantation renal anemia is well controlled • 1 Transduced Micro - Organ (TARGT EPO ) implanted • O nly patient to receive 1 TMO 16 Days from implantation 0 10 20 30 40 50 Serum eEPO, mIU/ml 0 5 10 15 20 Predicted eEPO baseline 2.4mU/ml Days from implantation 0 10 20 30 40 50 Serum Hb, g/dL 8 9 10 11 12 13 • * Patient surgery (not product related) • Est. blood loss: 1 unit (no transfusion required) Patient Description: Age: 74 Sex: Female Dialysis: 1.4 years Underlying disease: HTN & T 2 DM rHuEPO Dependent : dose prior to enrollment 10 , 000 IU twice a week * Target Hb 9 - 11 Safety Margin: Hb < 12

Potential Paradigm Shift in Treatment of Renal Anemia • Duration: – patients are meeting target secretion profile of continuously producing physiologic levels of endogenous EPO sufficient to maintain target Hb • Hemoglobin: – all patients are meeting endpoint of hemoglobin ( 9 - 11 and < 12 g/ dL ) due to RBC production stimulated by eEPO • Sustainability: – appears to mimic the restoration of the natural erythropoietic function of the kidneys that has been lost to CKD; no patient has required rHuEPO or transfusion post implantation • Safety: – consistent with the 23 patients treated with first generation system there have been no treatment related safety issues 17 These data presented herein are initial observations from an ongoing, non - randomized open - label trial. As such, no conclusions can be made about the safety and efficacy of TARGT EPO from these observations or the proposed hypotheses in this presentation.
Next Steps for MDGN - 201 Trial • Q 4 2014 – Complete enrollment in the low dose arm of trial ( 3 additional patients) • Q 1 2015 – Enroll 6 - patient cohort comparing single dose Depo - Medrol to multi - dose Depo - Medrol 18

TARGT EPO in Renal Anemia 19
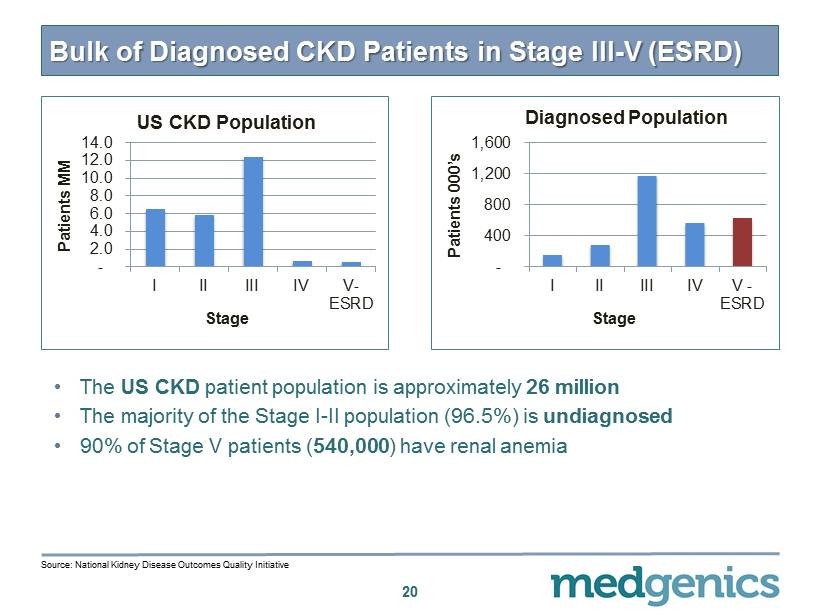
Bulk of Diagnosed CKD Patients in Stage III - V (ESRD) - 2.0 4.0 6.0 8.0 10.0 12.0 14.0 I II III IV V- ESRD Patients MM Stage US CKD Population 20 - 400 800 1,200 1,600 I II III IV V - ESRD Patients 000’s Stage Diagnosed Population • The US CKD patient population is approximately 26 million • The majority of the Stage I - II population ( 96.5 %) is undiagnosed • 90 % of Stage V patients ( 540 , 000 ) have renal anemia Source: National Kidney Disease Outcomes Quality Initiative
TARGT EPO in Patients Hypo - Responsive to rHuEPO 21 • Clinical Rationale: – Continuous physiologic levels of eEPO will stimulate bone marrow more effectively and safely than intermittent IV dosing 1 • Commercial Rationale: – Identified orphan population of high unmet need – Reduction of overall patient costs ( rHuEPO , iron management and transfusion) 2 – Rapid route to market ▪ Ability to do a small signal finding study ( 10 – 15 patients ), significantly de - risking the program; interim results H 2 2015 ▪ Relatively small, single pivotal trial similar to other orphan development programs for registration 1. Source: Besarab , A. Semin Nephrol . 2000;20(4):364 2. Source : USRDS data analysis and primary company research
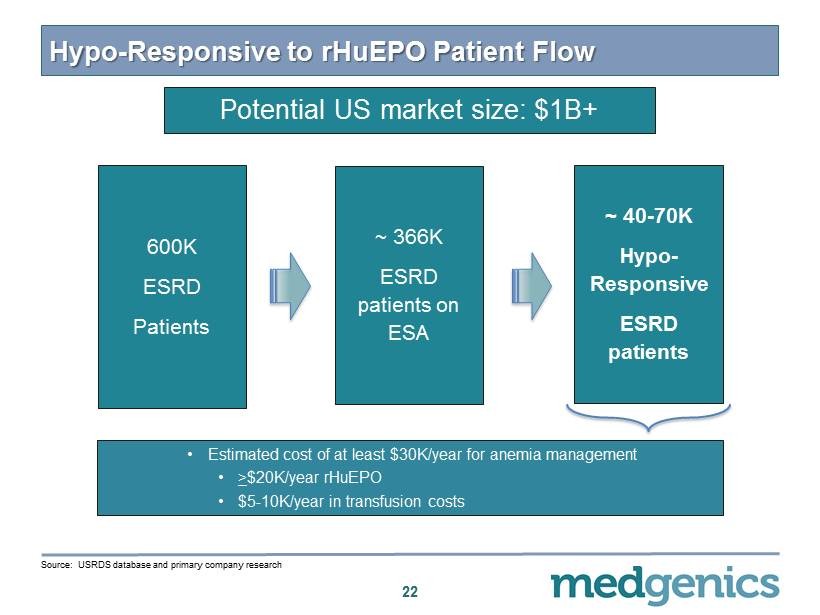
Hypo - Responsive to rHuEPO Patient Flow 22 600 K ESRD Patients ~ 40 - 70 K Hypo - Responsive ESRD patients ~ 366 K ESRD patients on ESA • Estimated cost of at least $ 30 K/year for anemia management • > $ 20 K/year rHuEPO • $ 5 - 10 K/year in transfusion costs Source: USRDS database and primary company research Potential US market size: $1B+
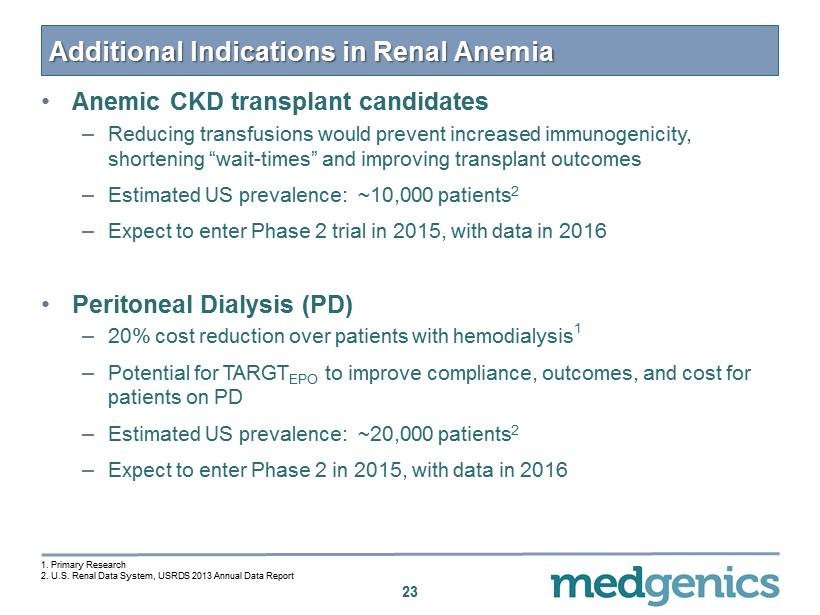
Additional Indications in Renal Anemia • Anemic CKD transplant candidates – Reducing transfusions would prevent increased immunogenicity, shortening “wait - times” and improving transplant outcomes – Estimated US prevalence: ~10,000 patients 2 – Expect to enter Phase 2 trial in 2015, with data in 2016 • Peritoneal Dialysis (PD ) – 20% cost reduction over patients with hemodialysis 1 – Potential for TARGT EPO to improve compliance, outcomes, and cost for patients on PD – Estimated US prevalence: ~20,000 patients 2 – Expect to enter Phase 2 in 2015, with data in 2016 23 1 . Primary Research 2 . U.S . Renal Data System, USRDS 2013 Annual Data Report

TARGT EPO in Hematological Disorders 24

Beta Thalassemia 25 • Beta Thalassemia is the most common genetic disease worldwide – Yet, it represents an Orphan disorder with significant unmet need • Characteristics in symptomatic patients include 1 : – Severe anemia – Iron overload – Splenomegaly • Patients generally require transfusions and/or bone marrow transplant to alleviate anemia ( Hb < 7 gms/dl) 1. Weatherall , D.J. and Clegg, J.B. Bulletin of the World Health Organization , 2001, 79: 704 – 712.
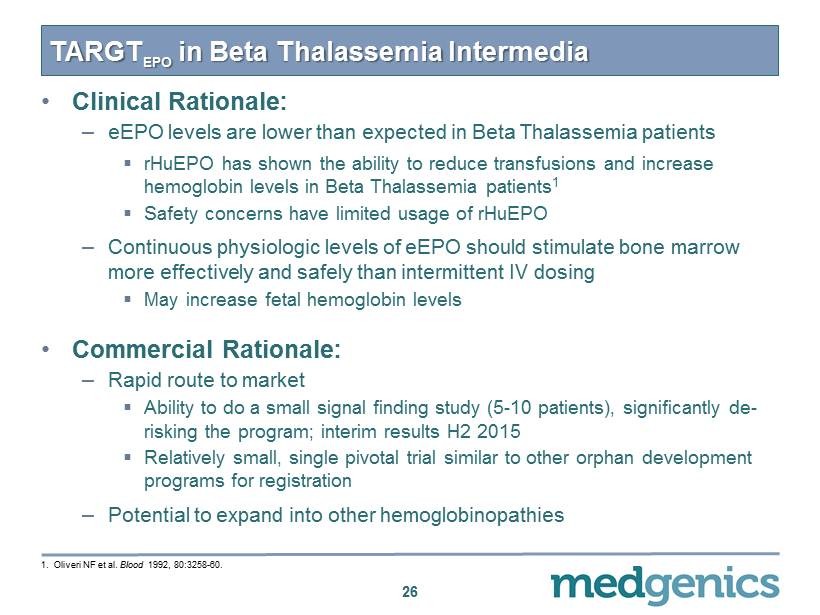
TARGT EPO in Beta Thalassemia Intermedia 26 • Clinical Rationale: – eEPO levels are lower than expected in Beta Thalassemia patients ▪ rHuEPO has shown the ability to reduce transfusions and increase hemoglobin levels in Beta Thalassemia patients 1 ▪ Safety concerns have limited usage of rHuEPO – Continuous physiologic levels of eEPO should stimulate bone marrow more effectively and safely than intermittent IV dosing ▪ May increase fetal hemoglobin levels • Commercial Rationale: – Rapid route to market ▪ Ability to do a small signal finding study ( 5 - 10 patients), significantly de - risking the program; interim results H 2 2015 ▪ Relatively small, single pivotal trial similar to other orphan development programs for registration – Potential to expand into other hemoglobinopathies 1 . Oliveri NF et al. Blood 1992 , 80 : 3258 - 60 .
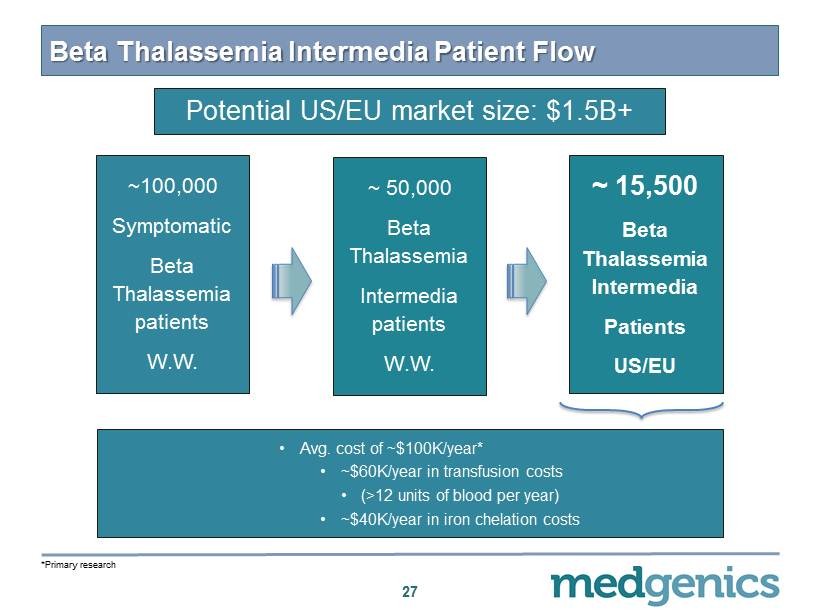
Beta Thalassemia Intermedia Patient Flow 27 ~ 100 , 000 Symptomatic Beta Thalassemia patients W.W. ~ 50,000 Beta Thalassemia Intermedia patients W.W. ~ 15 , 500 Beta Thalassemia Intermedia Patients US/EU • Avg. cost of ~$ 100 K/year* • ~$ 60 K/year in transfusion costs • (> 12 units of blood per year) • ~$ 40 K/year in iron chelation costs *Primary research Potential US/EU market size: $ 1.5 B+
Additional Indication in Hematology • Myelodysplastic Syndrome (MDS) – 20 - 55% of MDS patients respond to rHuEPO but use is limited due to safety concerns 1 – Reducing transfusions would limit iron overload – Target population: mild to intermediate patients, EPO levels < 150 – Estimated US prevalence: ~60,000 patients 2 – Expect to file IND in H2 2015 28 1. Giraldo , P. et al Cancer : 107 - 2807 - 14 2. Am Journal Med. 2012, Jul:125(7 Suppl ):S2 - 5

Additional Pipeline Opportunities 29
Novel Peptide Production Capability • TARGT system has demonstrated the unique ability to produce native peptides in vivo • Native peptides have been difficult to develop into drugs – Short half - life: poor metabolic stability and rapid clearance – Delicate: often require a complex manufacturing process – Frequently require structural modification and long - acting formulations, which can lead to off - target effects 30
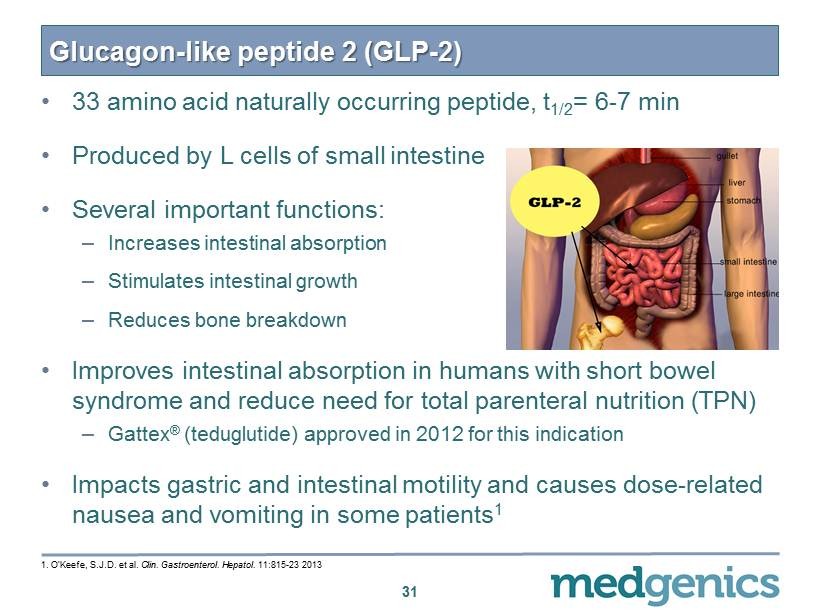
Glucagon - like peptide 2 (GLP - 2) • 33 amino acid naturally occurring peptide, t 1 / 2 = 6 - 7 min • Produced by L cells of small intestine • Several important functions: – Increases intestinal absorption – Stimulates intestinal growth – Reduces bone breakdown • Improves intestinal absorption in humans with short bowel syndrome and reduce need for total parenteral nutrition (TPN) – Gattex ® ( teduglutide ) approved in 2012 for this indication • Impacts gastric and intestinal motility and causes dose - related nausea and vomiting in some patients 1 31 1 . O’Keefe, S.J.D. et al. Clin . Gastroenterol . Hepatol . 11 : 815 - 23 2013
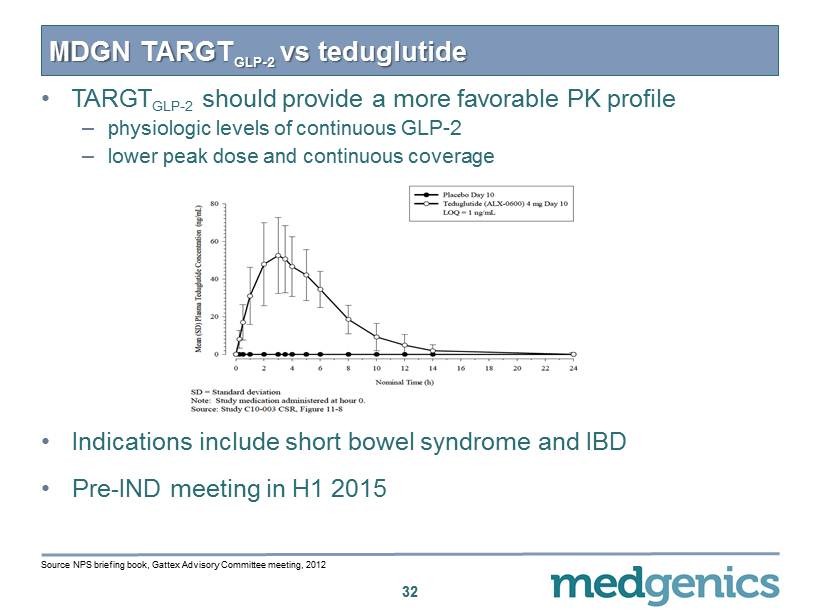
• TARGT GLP - 2 should provide a more favorable PK profile – physiologic levels of continuous GLP - 2 – lower peak dose and continuous coverage • Indications include short bowel syndrome and IBD • Pre - IND meeting in H 1 2015 MDGN TARGT GLP - 2 vs teduglutide 32 Source NPS briefing book, Gattex Advisory Committee meeting, 2012
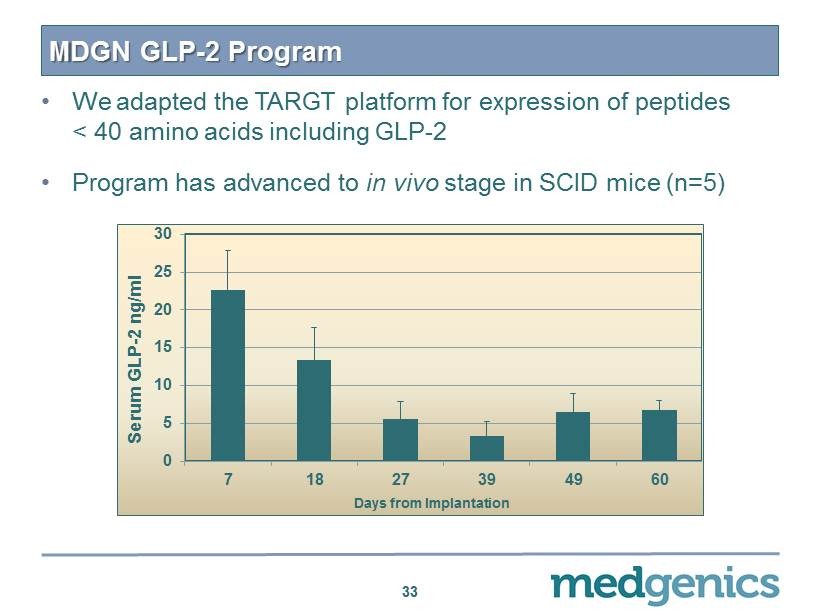
MDGN GLP - 2 Program • We adapted the TARGT platform for expression of peptides < 40 amino acids including GLP - 2 • Program has advanced to in vivo stage in SCID mice (n= 5 ) 33 0 5 10 15 20 25 30 7 18 27 39 49 60 Serum GLP - 2 ng/ml Days from Implantation
Conclusion • Proof of concept established with TARGT ex vivo gene therapy platform as evidenced by the positive initial data of ongoing TARGT EPO clinical trial • Multiple commercially attractive orphan indication s for TARGT EPO identified; data from proof of concept studies expected in H 2 2015 • Platform expanded to include therapeutic peptides, as demonstrated by pre - clinical proof of concept with GLP - 2 , with potential utility in short bowel syndrome 34
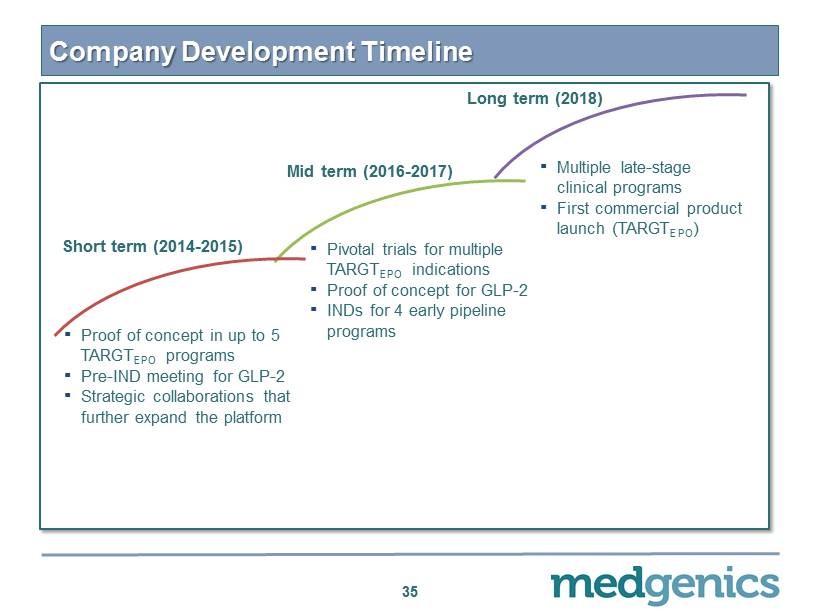
Company Development Timeline 35 Long term (2018) ▪ Multiple late - stage clinical programs ▪ First commercial product launch (TARGT EPO ) Mid term ( 2016 - 2017 ) ▪ P ivotal trials for multiple TARGT EPO indications ▪ Proof of concept for GLP - 2 ▪ INDs for 4 early pipeline programs Short term ( 2014 - 2015 ) ▪ Proof of concept in up to 5 TARGT EPO programs ▪ Pre - IND meeting for GLP - 2 ▪ Strategic collaborations that further expand the platform

Upcoming Catalysts 36 TIMING Complete enrollment in MDGN - 201 study Q4 14 Initiate Phase 2 study in Hypo - Responders Q1 15 Initiate Phase 2 study in Anemic CKD Transplant H1 15 Initiate Phase 2 study in Peritoneal Dialysis H1 15 Initiate Phase 2 study in Beta Thalassemia Intermedia H1 15 Initiate Phase 2 study in Myelodysplastic Syndrome H2 15 Pre - IND meeting for GLP - 2 H1 15
Financial Summary • NYSE - MKT: MDGN • Shares outstanding – 18.9 M • Warrants and options – 9 M warrants – 7 M options • Cash runway – $ 15 M at September 2014 – Cash burn of ~ $ 1 M per month 37

APPENDIX 38
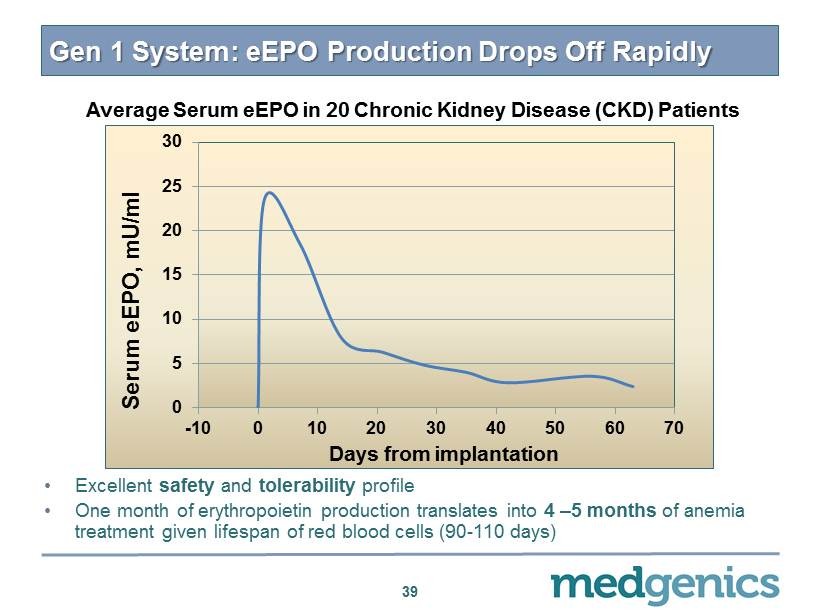
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 -10 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 Serum e EPO , mU /ml Days from implantation Gen 1 System: eEPO Production Drops O ff Rapidly • Excellent safety and tolerability profile • One month of erythropoietin production translates into 4 – 5 months of anemia treatment given lifespan of red blood cells ( 90 - 110 days) Average Serum eEPO in 20 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) Patients 39
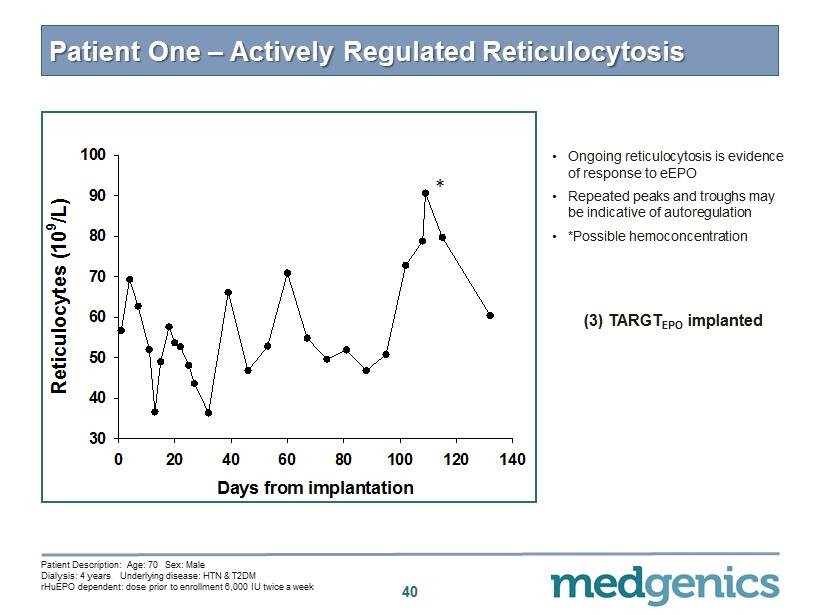
40 Patient One – Actively Regulated Reticulocytosis (3) TARGT EPO implanted • O ngoing reticulocytosis is evidence of response to eEPO • Repeated peaks and troughs may be indicative of autoregulation • *Possible hemoconcentration * Days from implantation 0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 Reticulocytes (10 9 /L) 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 * Patient Description: Age: 70 Sex: Male Dialysis: 4 years Underlying disease: HTN & T 2 DM rHuEPO dependent: dose prior to enrollment 6 , 000 IU twice a week
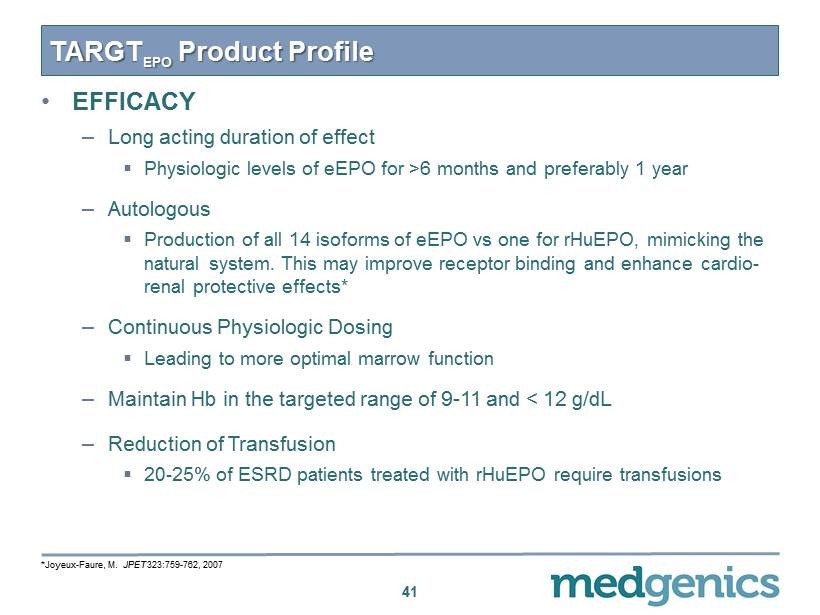
TARGT EPO Product Profile • EFFICACY – Long acting duration of effect ▪ Physiologic levels of eEPO for > 6 months and preferably 1 year – Autologous ▪ Production of all 14 isoforms of eEPO vs one for rHuEPO , mimicking the natural system. This may improve receptor binding and enhance cardio - renal protective effects* – Continuous Physiologic Dosing ▪ Leading to more optimal marrow function – Maintain Hb in the targeted range of 9 - 11 and < 12 g/ dL – Reduction of Transfusion ▪ 20 - 25 % of ESRD patients treated with rHuEPO require transfusions 41 * Joyeux - Faure, M. JPET 323:759 - 762, 2007

TARGT EPO Product Profile • SAFETY – Elimination of supratherapeutic peaks ▪ High Cmax has been associated with hypertension and serious thromboembolic events* – Reduction in blood pressure vs. injectable rHuEPO • ADMINISTRATION – Simple outpatient procedure – Increase compliance due to implantation should improve outcomes vs. injectable rHuEPO 42 *Berglund B, et al J Intern Med. 1991 Feb; 229 ( 2 ): 125 - 30 .

Q 3 2014 - Results of Operations 43 • Net R&D expenses for the 3 rd Quarter was $ 2.28 million decreased from $ 2.45 million for the same period in 2013 due to decrease in sub - contractor costs • G&A expenses for the 3 rd Quarter was $ 2.31 million decreasing from $ 2.56 million for the same period in 2013 due to a decrease in professional fees • Net R&D expenses for the nine months ended September 30 , 2014 were $ 4.48 M – Decrease from $ 5.23 M for the same period in 2013 – Primarily due to decrease in subcontractor costs and increase in participation by the Office of the Chief Scientist • G&A expenses for the nine months ended September 30 , 2014 were $ 8.26 M – Increase from $ 6.70 M for the same period in 2013 – Primarily due to increase in personnel and stock - based compensation expenses • Cash balance as of September 30 , 2014 was $ 14.7 million
