Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - 8-K - PINNACLE WEST CAPITAL CORP | a14-20853_18k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1
|
|
DELIVERING SUPERIOR SHAREHOLDER VALUE Investor Conferences | September 16 and 17, 2014 |
|
|
FORWARD LOOKING STATEMENTS This presentation contains forward-looking statements based on current expectations, including statements regarding our earnings guidance and financial outlook and goals. These forward-looking statements are often identified by words such as “estimate,” “predict,” “may,” “believe,” “plan,” “expect,” “require,” “intend,” “assume” and similar words. Because actual results may differ materially from expectations, we caution you not to place undue reliance on these statements. A number of factors could cause future results to differ materially from historical results, or from outcomes currently expected or sought by Pinnacle West or APS. These factors include, but are not limited to: our ability to manage capital expenditures and operations and maintenance costs while maintaining reliability and customer service levels; variations in demand for electricity, including those due to weather, the general economy, customer and sales growth (or decline), and the effects of energy conservation measures and distributed generation; power plant and transmission system performance and outages; competition in retail and wholesale power markets; regulatory and judicial decisions, developments and proceedings; new legislation or regulation, including those relating to environmental requirements, nuclear plant operations and potential deregulation of retail electric markets; fuel and water supply availability; our ability to achieve timely and adequate rate recovery of our costs, including returns on debt and equity capital; our ability to meet renewable energy and energy efficiency mandates and recover related costs; risks inherent in the operation of nuclear facilities, including spent fuel disposal uncertainty; current and future economic conditions in Arizona, particularly in real estate markets; the cost of debt and equity capital and the ability to access capital markets when required; environmental and other concerns surrounding coal-fired generation; volatile fuel and purchased power costs; the investment performance of the assets of our nuclear decommissioning trust, pension, and other postretirement benefit plans and the resulting impact on future funding requirements; the liquidity of wholesale power markets and the use of derivative contracts in our business; potential shortfalls in insurance coverage; new accounting requirements or new interpretations of existing requirements; generation, transmission and distribution facility and system conditions and operating costs; the ability to meet the anticipated future need for additional baseload generation and associated transmission facilities in our region; the willingness or ability of our counterparties, power plant participants and power plant land owners to meet contractual or other obligations or extend the rights for continued power plant operations; technological developments affecting the electric industry; and restrictions on dividends or other provisions in our credit agreements and ACC orders. These and other factors are discussed in Risk Factors described in Part I, Item 1A of the Pinnacle West/APS Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2013 and in Part II, Item 1A for the Pinnacle West/APS Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the quarter ended June 30, 2014, which you should review carefully before placing any reliance on our financial statements, disclosures or earnings outlook. Neither Pinnacle West nor APS assumes any obligation to update these statements, even if our internal estimates change, except as required by law. |
|
|
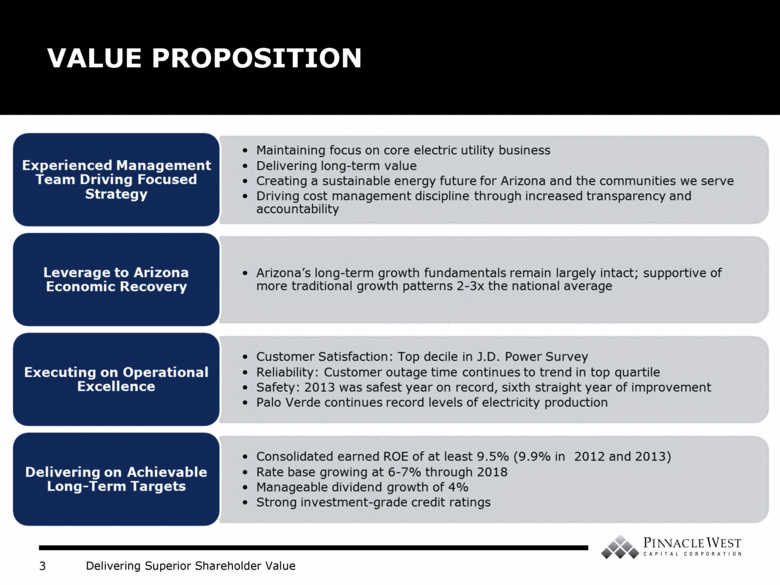
VALUE PROPOSITION Experienced Management Team Driving Focused Strategy • Maintaining focus on core electric utility business • Delivering long-term value • Creating a sustainable energy future for Arizona and the communities we serve • Driving cost management discipline through increased transparency and accountability Leverage to Arizona Economic Recovery • Arizona’s long-term growth fundamentals remain largely intact; supportive of more traditional growth patterns 2-3x the national average Executing on Operational Excellence • Customer Satisfaction: Top decile in J.D. Power Survey • Reliability: Customer outage time continues to trend in top quartile • Safety: 2013 was safest year on record, sixth straight year of improvement • Palo Verde continues record levels of electricity production Delivering on Achievable Long-Term Targets • Consolidated earned ROE of at least 9.5% (9.9% in 2012 and 2013) • Rate base growing at 6-7% through 2018 • Manageable dividend growth of 4% • Strong investment-grade credit ratings |
|
|
PINNACLE WEST: WHO WE ARE We are a vertically integrated, regulated electric utility in the growing southwest U.S. NYSE Ticker PNW Market Cap* $6.3 Billion Enterprise Value* $9.9 Billion Dividend Yield* 4% Consolidated Assets $13.7 Billion Principal Subsidiary Arizona’s largest and longest-serving electric utility Regulated utility provides stable, regulated earnings and cash flow base for Pinnacle West Service Territory 1.2 million customer accounts (89% residential) 34,646 square miles Peak Demand – ~7,000 MW (All time of 7,236 MW in July 2006) Nearly 6,400 MW of owned or leased capacity (~9,400 MW with long-term contracts); including 29.1% interest in Palo Verde Nuclear Generating Station, the largest in the United States 2013 Retail Sales: 28,088 GWh Operating Revenues: $3.2 Billion Residential 47% 52% Commercial 44% 42% Industrial 8% 6% Other < 1% < 1% * As of August 31, 2014 |
|
|
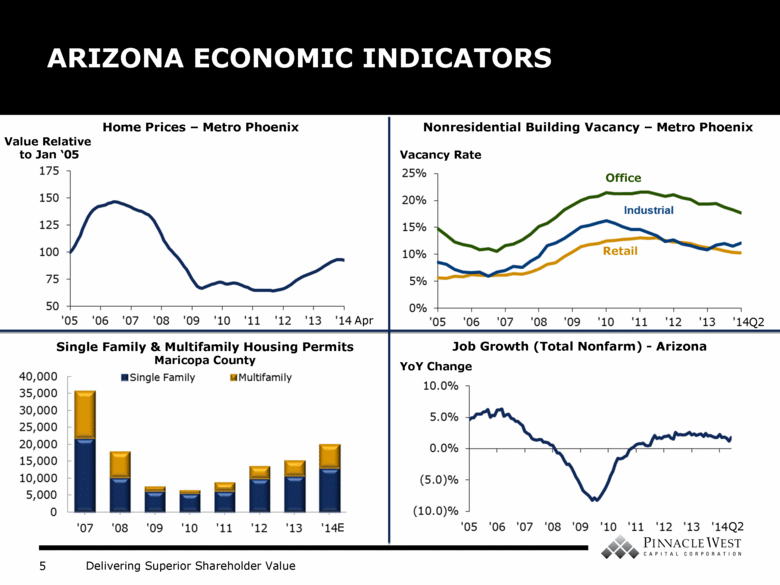
ARIZONA ECONOMIC INDICATORS Nonresidential Building Vacancy – Metro Phoenix Single Family & Multifamily Housing Permits Maricopa County Home Prices – Metro Phoenix Value Relative to Jan ‘05 Vacancy Rate Office Retail Job Growth (Total Nonfarm) - Arizona YoY Change E Q2 Q2 Apr |
|
|
ARIZONA ECONOMY – HOMEBUILDERS AGREE PHOENIX HAS SOLID LONG-TERM OUTLOOK “I am bullish on Phoenix over the long termI believe that going into 2015 we're going to experience a more normal market in Arizona after things get more in balance.” “We remain confident in the long-term growth of the opportunities in Arizona.” “Phoenix is a great place to live, and we're going to see growth there going forward.” “Overall, we remain positive on the Phoenix market and continue to believe it possesses strong market fundamentals.” |
|
|
RETAIL SALES GROWTH (WEATHER-NORMALIZED) YoY Retail Sales Before Customer Programs Energy Efficiency & Customer Conservation Distributed Generation Weather-normalized retail sales growth about 1% for 2014-2016 after impacts of energy efficiency, customer conservation and distributed renewable generation initiatives (excluding Lost Fixed Cost Recovery) Distributed Generation (DG) Impact DG makes up 0.5% (or less) of the negative impact to retail sales growth as shown in the chart; equates to approximately 60 GWh out of our total retail sales of over 28,000 GWh Average residential rooftop solar system produces 10,000 – 12,000 KWh per year (average metro-Phoenix customer’s usage is nearly 15,000 KWh) |
|
|
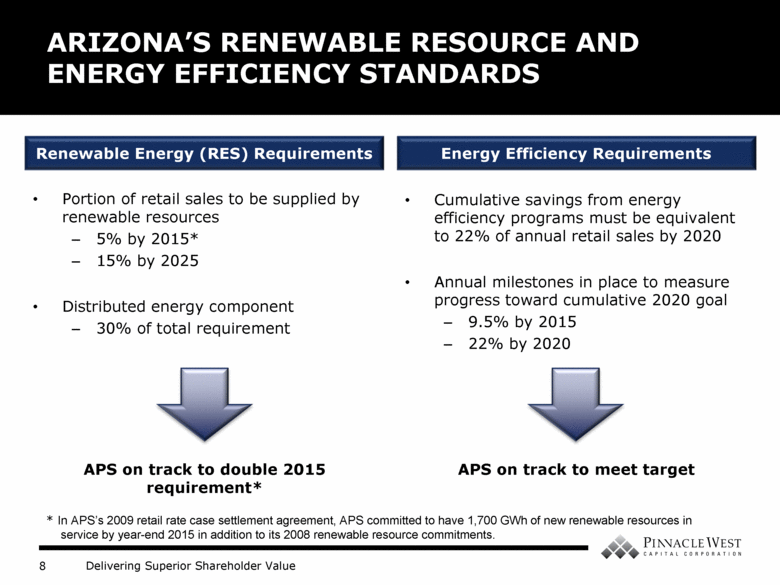
Cumulative savings from energy efficiency programs must be equivalent to 22% of annual retail sales by 2020 Annual milestones in place to measure progress toward cumulative 2020 goal 9.5% by 2015 22% by 2020 ARIZONA’S RENEWABLE RESOURCE AND ENERGY EFFICIENCY STANDARDS Portion of retail sales to be supplied by renewable resources 5% by 2015* 15% by 2025 Distributed energy component 30% of total requirement Energy Efficiency Requirements Renewable Energy (RES) Requirements APS on track to double 2015 requirement* APS on track to meet target * In APS’s 2009 retail rate case settlement agreement, APS committed to have 1,700 GWh of new renewable resources in service by year-end 2015 in addition to its 2008 renewable resource commitments. |
|
|
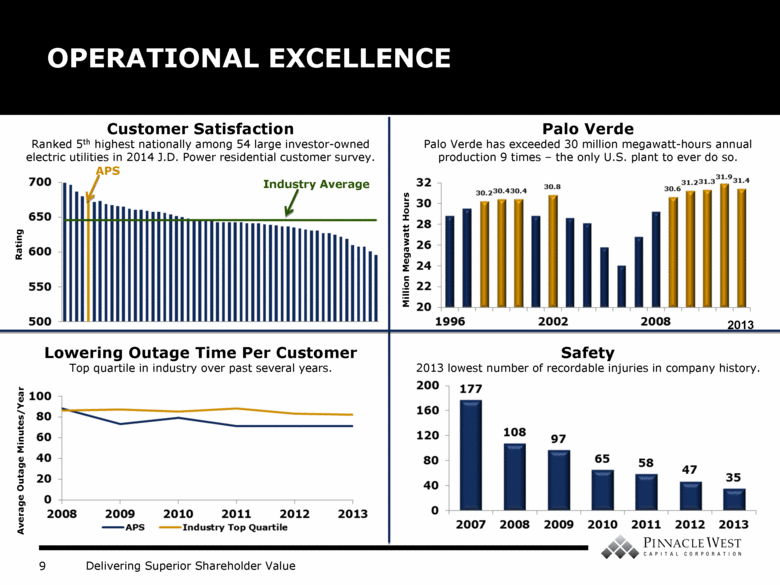
OPERATIONAL EXCELLENCE Palo Verde Palo Verde has exceeded 30 million megawatt-hours annual production 9 times – the only U.S. plant to ever do so. Safety 2013 lowest number of recordable injuries in company history. Customer Satisfaction Ranked 5th highest nationally among 54 large investor-owned electric utilities in 2014 J.D. Power residential customer survey. Lowering Outage Time Per Customer Top quartile in industry over past several years. Average Outage Minutes/Year Million Megawatt Hours Rating Industry Average APS 2013 |
|
|
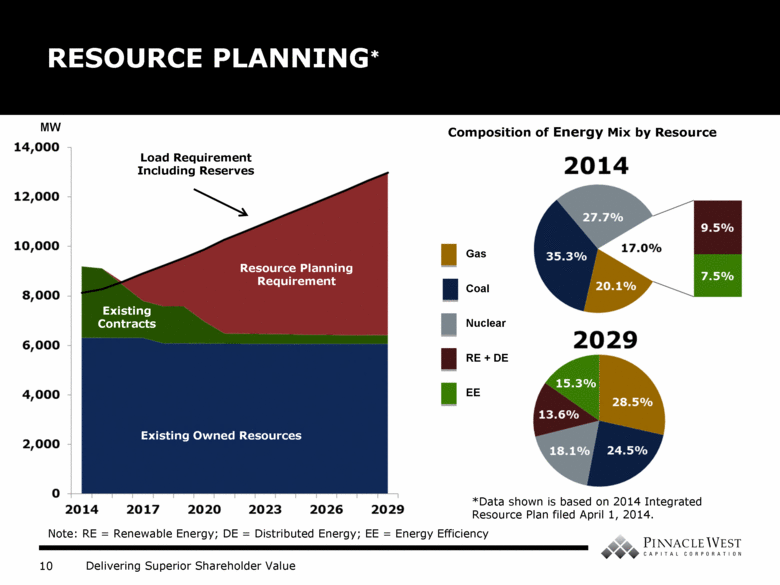
RESOURCE PLANNING* Existing Owned Resources Existing Contracts Resource Planning Requirement Load Requirement Including Reserves MW Coal Nuclear RE + DE EE Composition of Energy Mix by Resource Note: RE = Renewable Energy; DE = Distributed Energy; EE = Energy Efficiency *Data shown is based on 2014 Integrated Resource Plan filed April 1, 2014. |
|
|
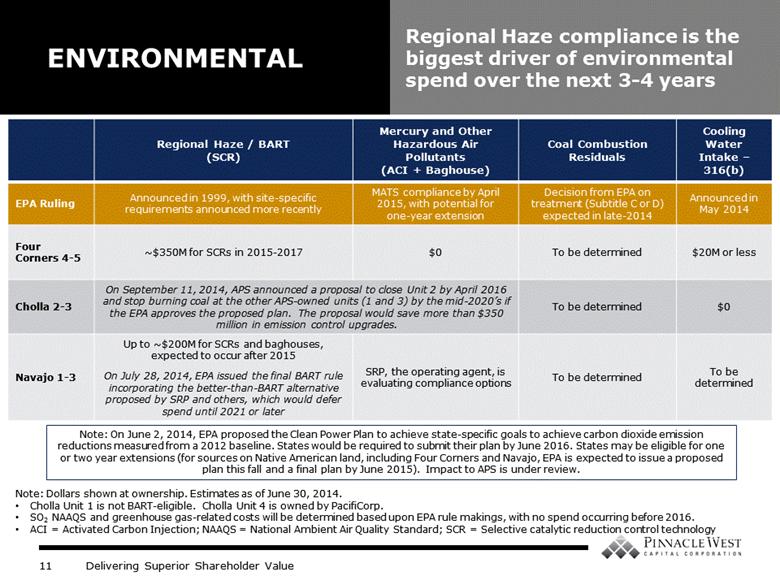
Regional Haze / BART (SCR) Mercury and Other Hazardous Air Pollutants (ACI + Baghouse) Coal Combustion Residuals Cooling Water Intake – 316(b) EPA Ruling Announced in 1999, with site-specific requirements announced more recently MATS compliance by April 2015, with potential for one-year extension Decision from EPA on treatment (Subtitle C or D) expected in late-2014 Announced in May 2014 Four Corners 4-5 ~$350M for SCRs in 2015-2017 $0 To be determined $20M or less Cholla 2-3 On September 11, 2014, APS announced a proposal to close Unit 2 by April 2016 and stop burning coal at the other APS-owned units (1 and 3) by the mid-2020’s if the EPA approves the proposed plan. The proposal would save more than $350 million in emission control upgrades. To be determined $0 Navajo 1-3 Up to ~$200M for SCRs and baghouses, expected to occur after 2015 On July 28, 2014, EPA issued the final BART rule incorporating the better-than-BART alternative proposed by SRP and others, which would defer spend until 2021 or later SRP, the operating agent, is evaluating compliance options To be determined To be determined Note: Dollars shown at ownership. Estimates as of June 30, 2014. Cholla Unit 1 is not BART-eligible. Cholla Unit 4 is owned by PacifiCorp. SO2 NAAQS and greenhouse gas-related costs will be determined based upon EPA rule makings, with no spend occurring before 2016. ACI = Activated Carbon Injection; NAAQS = National Ambient Air Quality Standard; SCR = Selective catalytic reduction control technology ENVIRONMENTAL Regional Haze compliance is the biggest driver of environmental spend over the next 3-4 years Note: On June 2, 2014, EPA proposed the Clean Power Plan to achieve state-specific goals to achieve carbon dioxide emission reductions measured from a 2012 baseline. States would be required to submit their plan by June 2016. States may be eligible for one or two year extensions (for sources on Native American land, including Four Corners and Navajo, EPA is expected to issue a proposed plan this fall and a final plan by June 2015). Impact to APS is under review. |
|
|
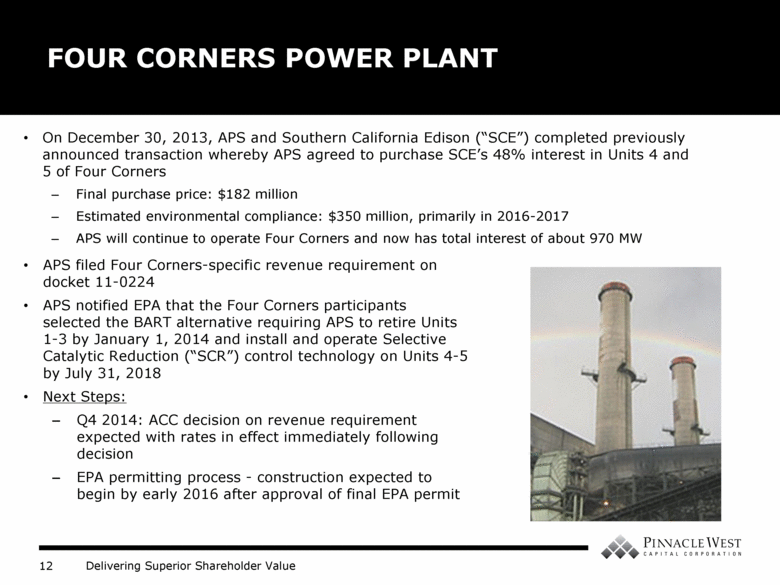
On December 30, 2013, APS and Southern California Edison (“SCE”) completed previously announced transaction whereby APS agreed to purchase SCE’s 48% interest in Units 4 and 5 of Four Corners Final purchase price: $182 million Estimated environmental compliance: $350 million, primarily in 2016-2017 APS will continue to operate Four Corners and now has total interest of about 970 MW FOUR CORNERS POWER PLANT APS filed Four Corners-specific revenue requirement on docket 11-0224 APS notified EPA that the Four Corners participants selected the BART alternative requiring APS to retire Units 1-3 by January 1, 2014 and install and operate Selective Catalytic Reduction (“SCR”) control technology on Units 4-5 by July 31, 2018 Next Steps: Q4 2014: ACC decision on revenue requirement expected with rates in effect immediately following decision EPA permitting process - construction expected to begin by early 2016 after approval of final EPA permit |
|
|
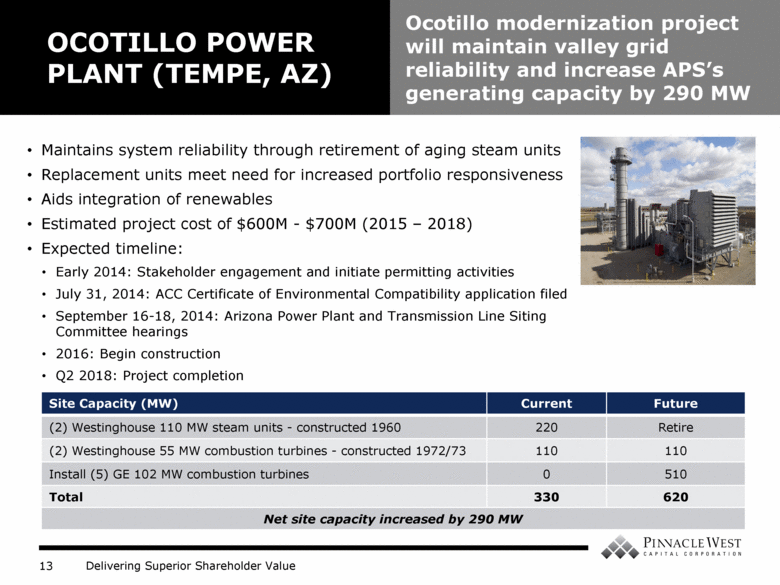
OCOTILLO POWER PLANT (TEMPE, AZ) Ocotillo modernization project will maintain valley grid reliability and increase APS’s generating capacity by 290 MW Maintains system reliability through retirement of aging steam units Replacement units meet need for increased portfolio responsiveness Aids integration of renewables Estimated project cost of $600M - $700M (2015 – 2018) Expected timeline: Early 2014: Stakeholder engagement and initiate permitting activities July 31, 2014: ACC Certificate of Environmental Compatibility application filed September 16-18, 2014: Arizona Power Plant and Transmission Line Siting Committee hearings 2016: Begin construction Q2 2018: Project completion Site Capacity (MW) Current Future (2) Westinghouse 110 MW steam units - constructed 1960 220 Retire (2) Westinghouse 55 MW combustion turbines - constructed 1972/73 110 110 Install (5) GE 102 MW combustion turbines 0 510 Total 330 620 Net site capacity increased by 290 MW |
|
|
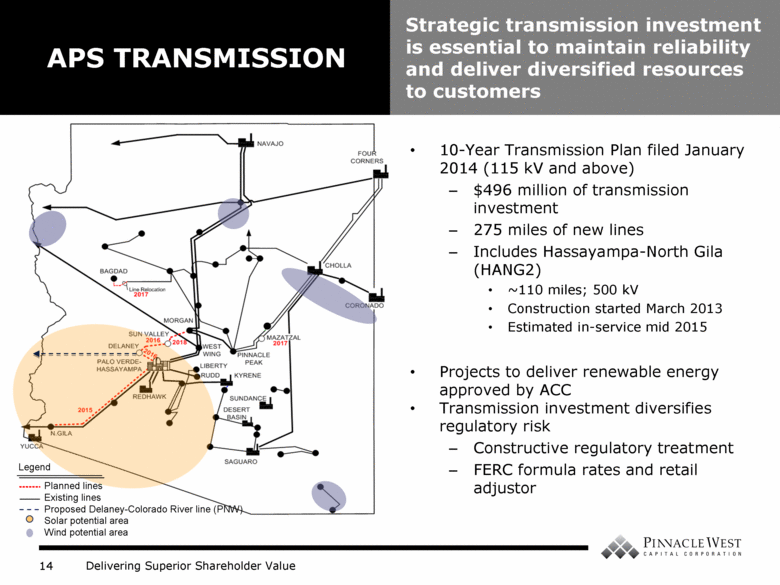
10-Year Transmission Plan filed January 2014 (115 kV and above) $496 million of transmission investment 275 miles of new lines Includes Hassayampa-North Gila (HANG2) ~110 miles; 500 kV Construction started March 2013 Estimated in-service mid 2015 Projects to deliver renewable energy approved by ACC Transmission investment diversifies regulatory risk Constructive regulatory treatment FERC formula rates and retail adjustor APS TRANSMISSION Strategic transmission investment is essential to maintain reliability and deliver diversified resources to customers Legend Planned lines Existing lines Proposed Delaney-Colorado River line (PNW) Solar potential area Wind potential area |
|
|
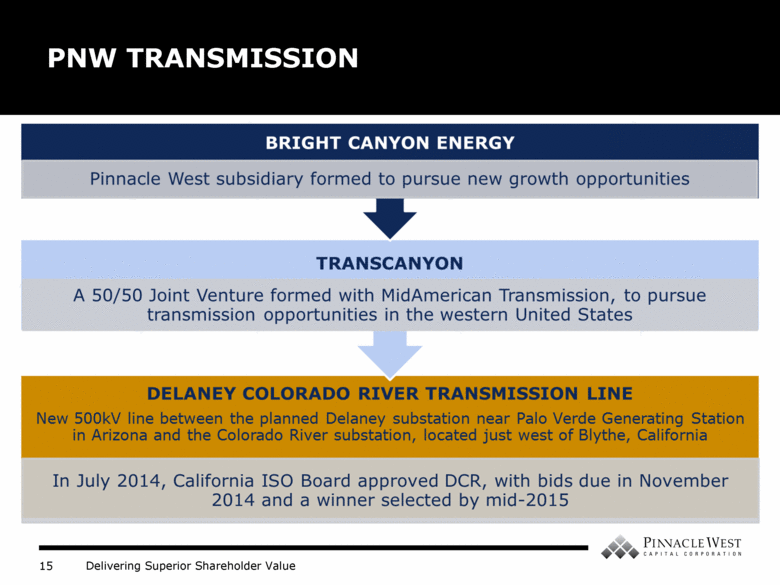
PNW TRANSMISSION Pinnacle West subsidiary formed to pursue new growth opportunities TRANSCANYON A 50/50 Joint Venture formed with MidAmerican Transmission, to pursue transmission opportunities in the western United States DELANEY COLORADO RIVER TRANSMISSION LINE New 500kV line between the planned Delaney substation near Palo Verde Generating Station in Arizona and the Colorado River substation, located just west of Blythe, California In July 2014, California ISO Board approved DCR, with bids due in November 2014 and a winner selected by mid-2015 |
|
|
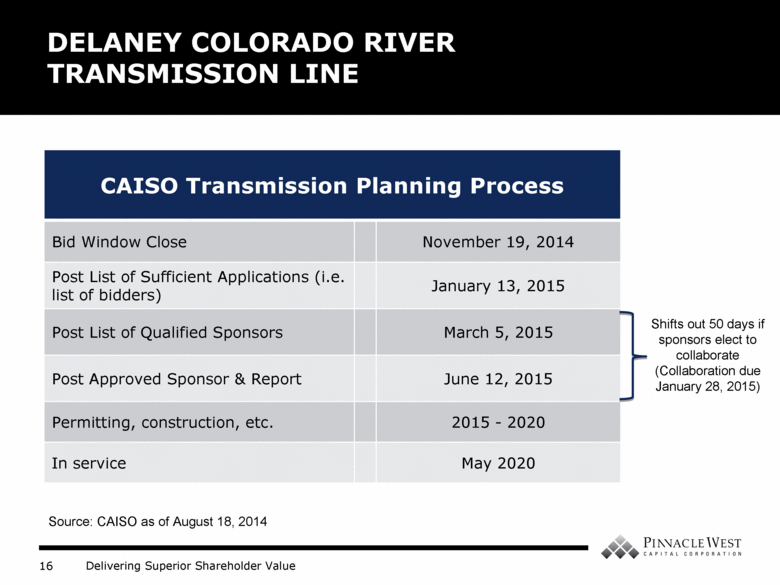
DELANEY COLORADO RIVER TRANSMISSION LINE CAISO Transmission Planning Process Bid Window Close November 19, 2014 Post List of Sufficient Applications (i.e. list of bidders) January 13, 2015 Post List of Qualified Sponsors March 5, 2015 Post Approved Sponsor & Report June 12, 2015 Permitting, construction, etc. 2015 - 2020 In service May 2020 Shifts out 50 days if sponsors elect to collaborate (Collaboration due January 28, 2015) Source: CAISO as of August 18, 2014 |
|
|
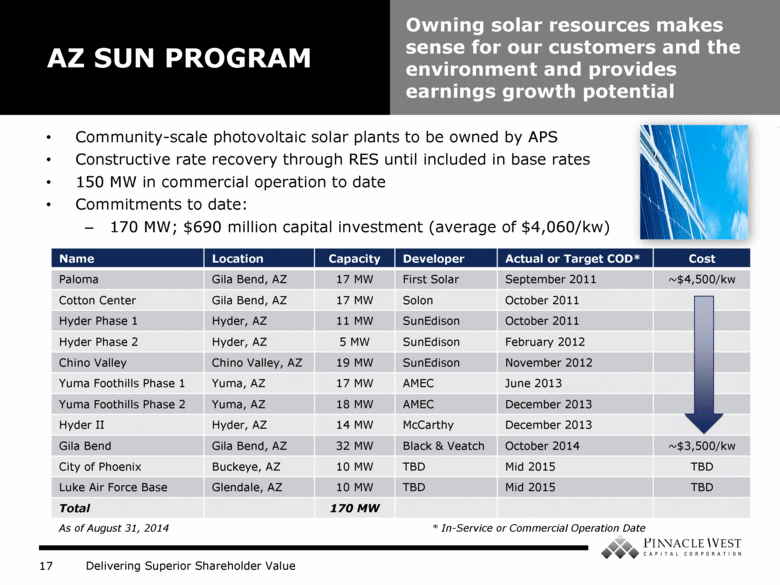
Community-scale photovoltaic solar plants to be owned by APS Constructive rate recovery through RES until included in base rates 150 MW in commercial operation to date Commitments to date: 170 MW; $690 million capital investment (average of $4,060/kw) AZ SUN PROGRAM Owning solar resources makes sense for our customers and the environment and provides earnings growth potential Name Location Capacity Developer Actual or Target COD* Cost Paloma Gila Bend, AZ 17 MW First Solar September 2011 ~$4,500/kw Cotton Center Gila Bend, AZ 17 MW Solon October 2011 Hyder Phase 1 Hyder, AZ 11 MW SunEdison October 2011 Hyder Phase 2 Hyder, AZ 5 MW SunEdison February 2012 Chino Valley Chino Valley, AZ 19 MW SunEdison November 2012 Yuma Foothills Phase 1 Yuma, AZ 17 MW AMEC June 2013 Yuma Foothills Phase 2 Yuma, AZ 18 MW AMEC December 2013 Hyder II Hyder, AZ 14 MW McCarthy December 2013 Gila Bend Gila Bend, AZ 32 MW Black & Veatch October 2014 ~$3,500/kw City of Phoenix Buckeye, AZ 10 MW TBD Mid 2015 TBD Luke Air Force Base Glendale, AZ 10 MW TBD Mid 2015 TBD Total 170 MW As of August 31, 2014 * In-Service or Commercial Operation Date |
|
|
APS-OWNED ROOFTOP SOLAR PROPOSAL APS proposed an option to the ACC to convert 20 MW of AZ Sun into APS-owned residential rooftop solar, equates to approximately 3,000 customers Estimated cost of $57-70 million Benefits: Provides an alternative for those who cannot afford solar or do not want a lease Participating customers receive monthly credit on their bill through the 20-year life Support and partner with Arizona solar installers TBD APS has track record through the Flagstaff Community Power Project Launched in 2010 1.5 MW of distributed energy from solar panels owned by APS, spread across: 125 residential rooftops Schools Neighborhood-scale solar power plant |
|
|
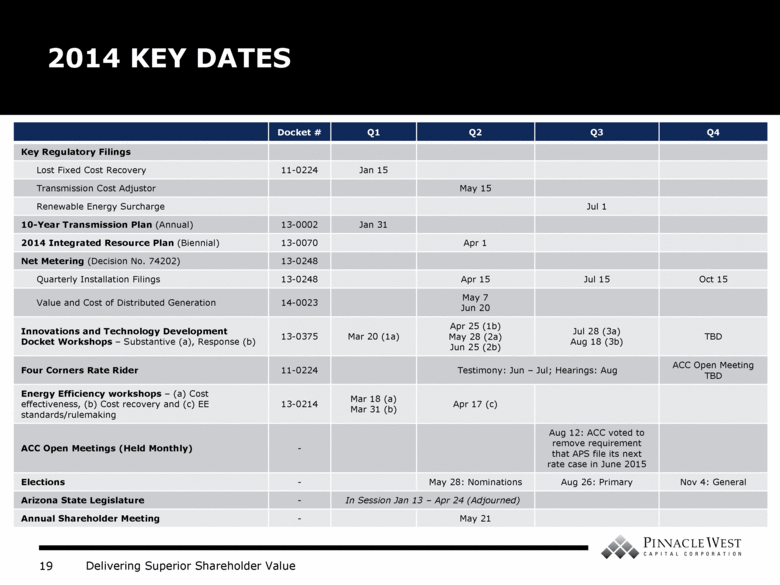
2014 KEY DATES Docket # Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Key Regulatory Filings Lost Fixed Cost Recovery 11-0224 Jan 15 Transmission Cost Adjustor May 15 Renewable Energy Surcharge Jul 1 10-Year Transmission Plan (Annual) 13-0002 Jan 31 2014 Integrated Resource Plan (Biennial) 13-0070 Apr 1 Net Metering (Decision No. 74202) 13-0248 Quarterly Installation Filings 13-0248 Apr 15 Jul 15 Oct 15 Value and Cost of Distributed Generation 14-0023 May 7 Jun 20 Innovations and Technology Development Docket Workshops – Substantive (a), Response (b) 13-0375 Mar 20 (1a) Apr 25 (1b) May 28 (2a) Jun 25 (2b) Jul 28 (3a) Aug 18 (3b) TBD Four Corners Rate Rider 11-0224 Testimony: Jun – Jul; Hearings: Aug ACC Open Meeting TBD Energy Efficiency workshops – (a) Cost effectiveness, (b) Cost recovery and (c) EE standards/rulemaking 13-0214 Mar 18 (a) Mar 31 (b) Apr 17 (c) ACC Open Meetings (Held Monthly) - Aug 12: ACC voted to remove requirement that APS file its next rate case in June 2015 Elections - May 28: Nominations Aug 26: Primary Nov 4: General Arizona State Legislature - In Session Jan 13 – Apr 24 (Adjourned) Annual Shareholder Meeting - May 21 |
|
|
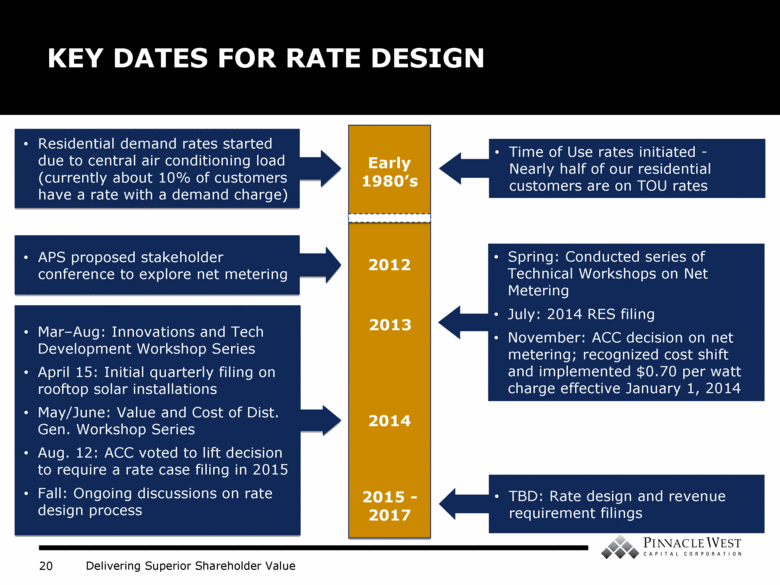
KEY DATES FOR RATE DESIGN 2012 2013 2014 2015 - 2017 APS proposed stakeholder conference to explore net metering Spring: Conducted series of Technical Workshops on Net Metering July: 2014 RES filing November: ACC decision on net metering; recognized cost shift and implemented $0.70 per watt charge effective January 1, 2014 Mar–Aug: Innovations and Tech Development Workshop Series April 15: Initial quarterly filing on rooftop solar installations May/June: Value and Cost of Dist. Gen. Workshop Series Aug. 12: ACC voted to lift decision to require a rate case filing in 2015 Fall: Ongoing discussions on rate design process Time of Use rates initiated - Nearly half of our residential customers are on TOU rates Residential demand rates started due to central air conditioning load (currently about 10% of customers have a rate with a demand charge) Early 1980’s TBD: Rate design and revenue requirement filings |
|
|
KEY RATE DESIGN PRINCIPLES Smarter rates for smarter grid Arizona Public Service, Tucson Electric Power, Residential Utility Consumer Office and Arizona solar developers filed a joint letter with the ACC agreeing on the following rate design principles: Customer-focused Meaningful options Meet lifestyle needs Allow customers to choose among technologies Forward-thinking Maintain reliable service Enable technology innovation Put all technologies on a level playing field Affordable & Fair For all of our 1.2 million customers Transparent Accurately reflect services and products customers use Rate design changes needed to align fixed costs and revenue |
|
|
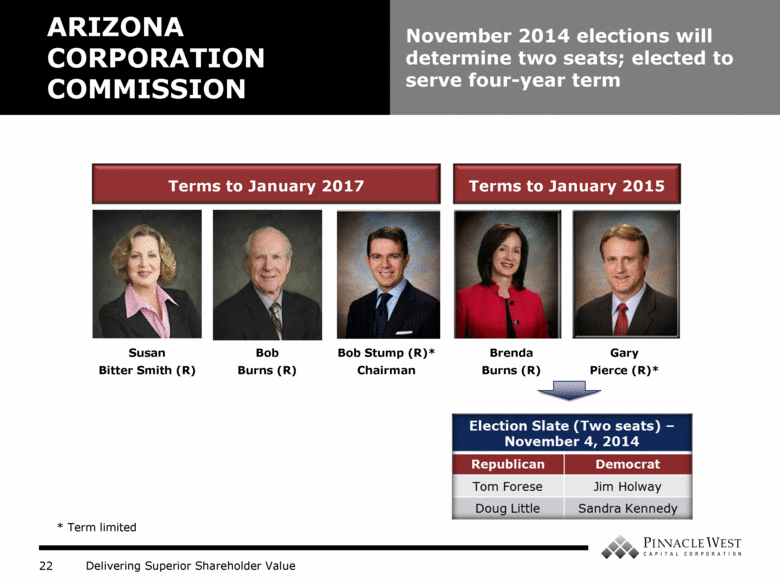
ARIZONA CORPORATION COMMISSION November 2014 elections will determine two seats; elected to serve four-year term Bob Stump (R)* Chairman Brenda Burns (R) Gary Pierce (R)* Terms to January 2015 Terms to January 2017 Susan Bitter Smith (R) Bob Burns (R) * Term limited |
|
|
APPENDIX |
|
|
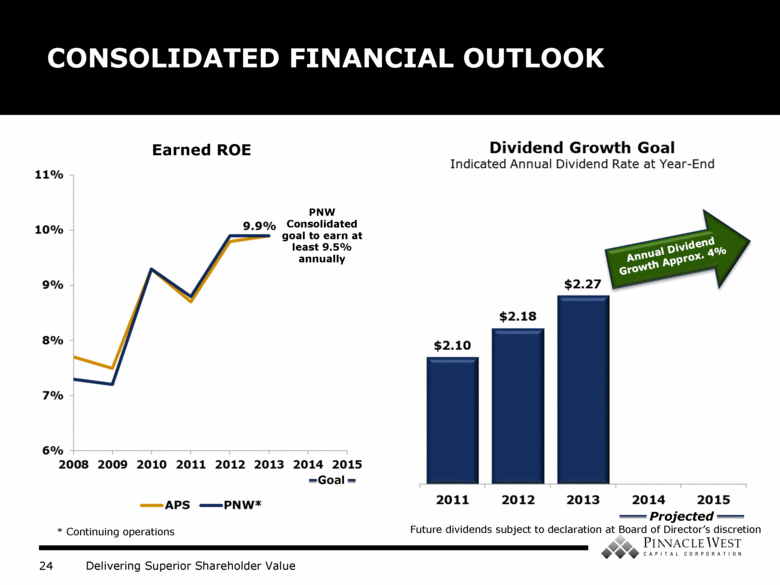
PNW Consolidated goal to earn at least 9.5% annually CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL OUTLOOK Earned ROE * Continuing operations Projected Future dividends subject to declaration at Board of Director’s discretion Annual Dividend Growth Approx. 4% Goal |
|
|
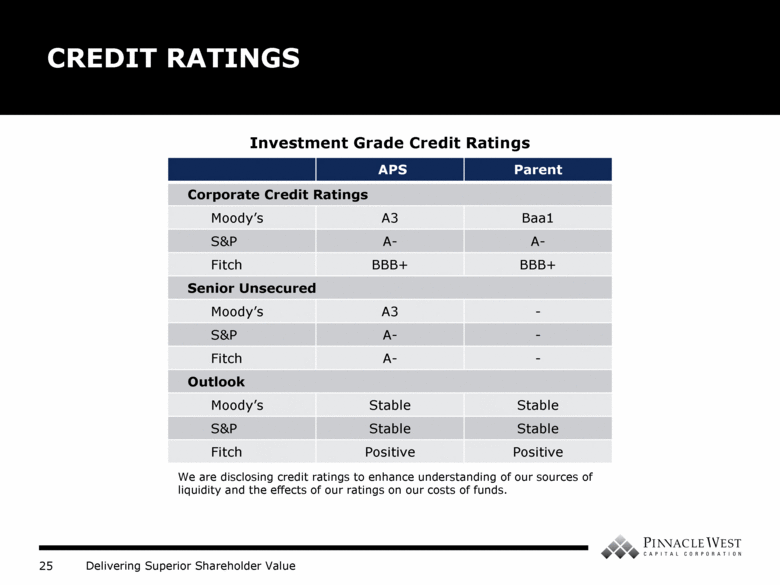
CREDIT RATINGS APS Parent Corporate Credit Ratings Moody’s A3 Baa1 S&P A- A- Fitch BBB+ BBB+ Senior Unsecured Moody’s A3 - S&P A- - Fitch A- - Outlook Moody’s Stable Stable S&P Stable Stable Fitch Positive Positive We are disclosing credit ratings to enhance understanding of our sources of liquidity and the effects of our ratings on our costs of funds. Investment Grade Credit Ratings |
|
|
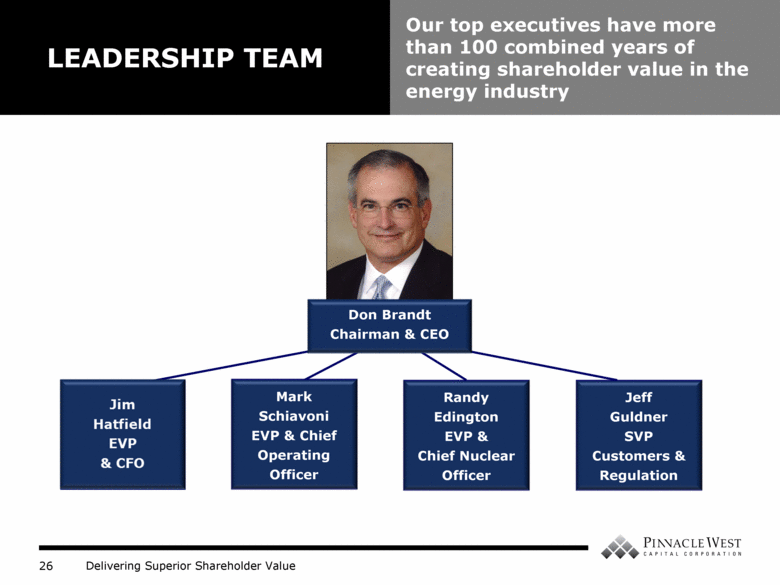
LEADERSHIP TEAM Our top executives have more than 100 combined years of creating shareholder value in the energy industry Don Brandt Chairman & CEO Mark Schiavoni EVP & Chief Operating Officer Jeff Guldner SVP Customers & Regulation Randy Edington EVP & Chief Nuclear Officer |
|
|
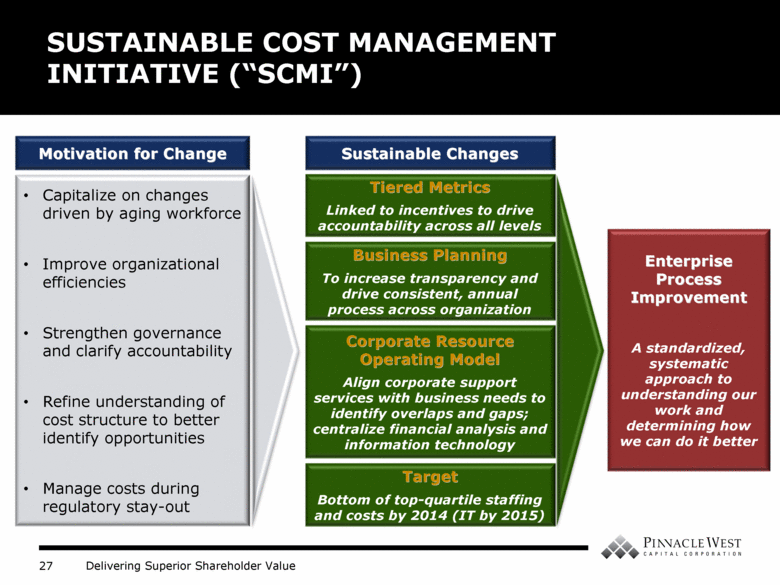
Motivation for Change SUSTAINABLE COST MANAGEMENT INITIATIVE (“SCMI”) Capitalize on changes driven by aging workforce Improve organizational efficiencies Strengthen governance and clarify accountability Refine understanding of cost structure to better identify opportunities Manage costs during regulatory stay-out Sustainable Changes Tiered Metrics Linked to incentives to drive accountability across all levels Business Planning To increase transparency and drive consistent, annual process across organization Corporate Resource Operating Model Align corporate support services with business needs to identify overlaps and gaps; centralize financial analysis and information technology Target Bottom of top-quartile staffing and costs by 2014 (IT by 2015) Enterprise Process Improvement A standardized, systematic approach to understanding our work and determining how we can do it better |
|
|
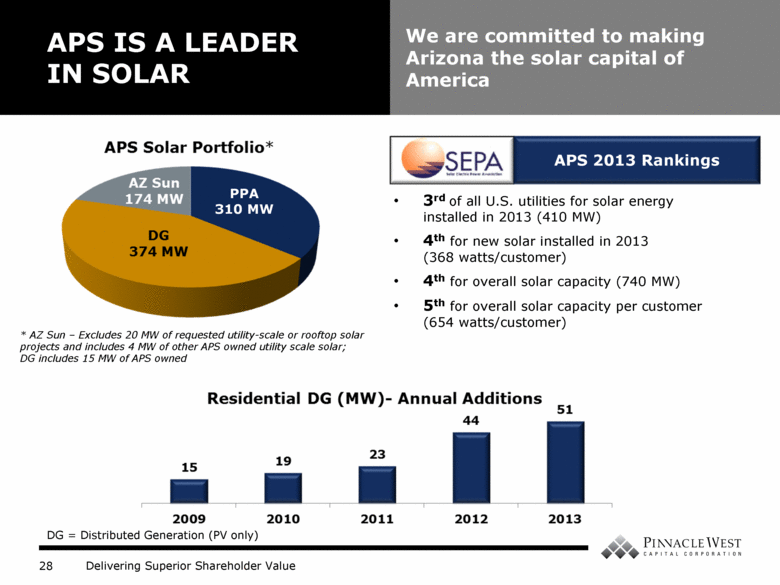
APS IS A LEADER IN SOLAR We are committed to making Arizona the solar capital of America 3rd of all U.S. utilities for solar energy installed in 2013 (410 MW) 4th for new solar installed in 2013 (368 watts/customer) 4th for overall solar capacity (740 MW) 5th for overall solar capacity per customer (654 watts/customer) APS 2013 Rankings * AZ Sun – Excludes 20 MW of requested utility-scale or rooftop solar projects and includes 4 MW of other APS owned utility scale solar; DG includes 15 MW of APS owned DG = Distributed Generation (PV only) PPA 310 MW |
|
|
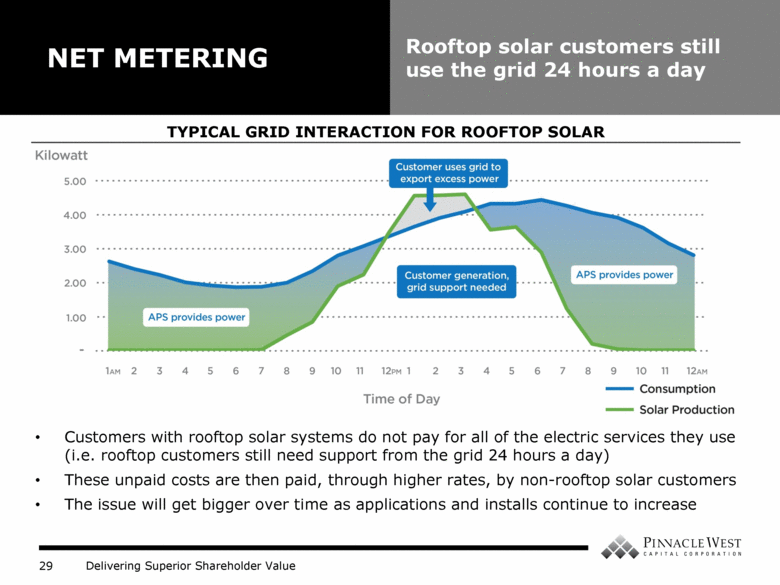
Customers with rooftop solar systems do not pay for all of the electric services they use (i.e. rooftop customers still need support from the grid 24 hours a day) These unpaid costs are then paid, through higher rates, by non-rooftop solar customers The issue will get bigger over time as applications and installs continue to increase NET METERING Rooftop solar customers still use the grid 24 hours a day TYPICAL GRID INTERACTION FOR ROOFTOP SOLAR |
|
|
As of August 31, 2014, over 27,500 residential grid-tied solar photovoltaic (PV) systems have been installed in APS’s service territory APS anticipates that it will be in compliance with the Renewable Energy Standard (RES) residential DG requirements through mid-2017 and with RES non-residential through 2021 *Note: www.arizonagoessolar.org logs total applications, but currently excludes canceled applications. Data also contains Commercial applications and other installation types, including Solar water heaters. RESIDENTIAL PV APPLICATIONS 2013 Applications* 2014 Applications* 2014 Canceled Apps 2013 Canceled Apps Jan Feb Mar Apr May Jun Jul Aug Sep Oct Nov Dec |
|
|
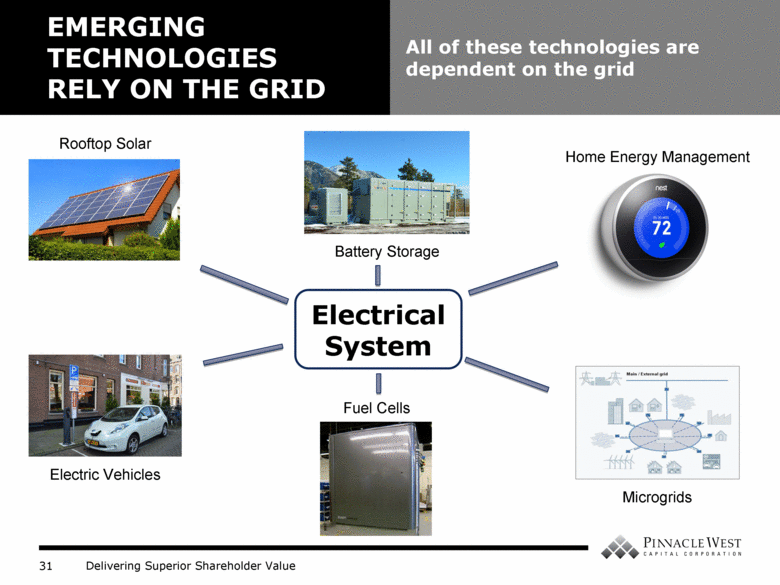
EMERGING TECHNOLOGIES RELY ON THE GRID All of these technologies are dependent on the grid Electric Vehicles Battery Storage Fuel Cells Home Energy Management Microgrids Rooftop Solar Electrical System |
|
|
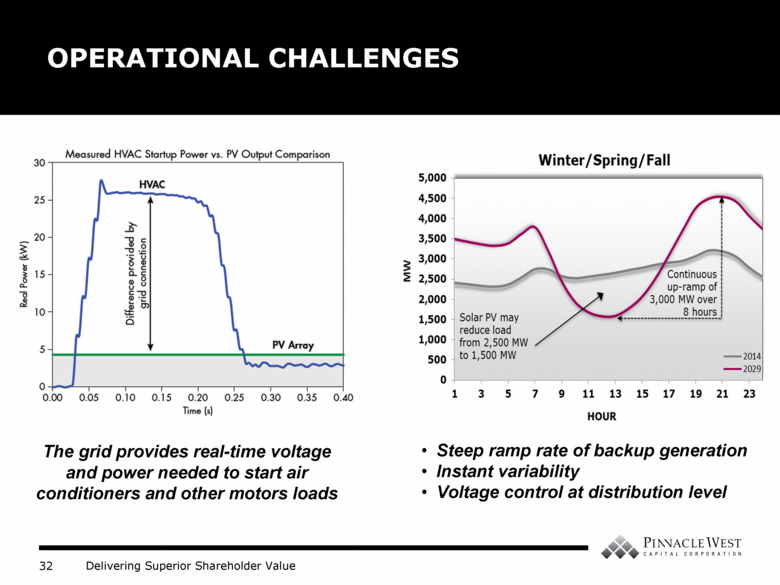
OPERATIONAL CHALLENGES The grid provides real-time voltage and power needed to start air conditioners and other motors loads Steep ramp rate of backup generation Instant variability Voltage control at distribution level |
|
|
RELIABILITY SERVICES REQUIRE TECHNOLOGY ADVANCEMENTS ON THE UTILITY SIDE Substation Health Monitoring Integrated Volt/VAR Control (IVVC) Communicating Fault Indicators (CFI) Synchrophasors (WISP) Supervisory Controlled Switches Advanced Distribution Management System Smart Meters Energy Management System (EMS) Upgrades Strategic Fiber 2013 Benefits include over 1,000,000 customer outage minutes avoided |
|
|
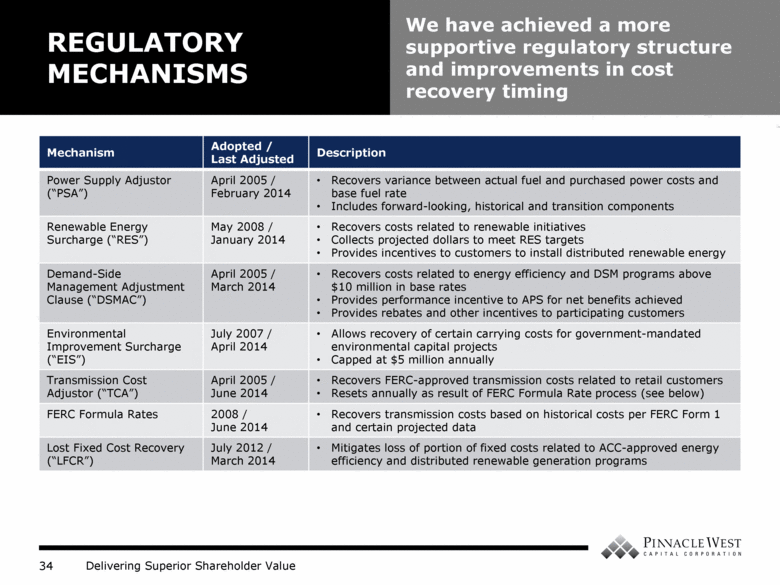
Mechanism Adopted / Last Adjusted Description Power Supply Adjustor (“PSA”) April 2005 / February 2014 Recovers variance between actual fuel and purchased power costs and base fuel rate Includes forward-looking, historical and transition components Renewable Energy Surcharge (“RES”) May 2008 / January 2014 Recovers costs related to renewable initiatives Collects projected dollars to meet RES targets Provides incentives to customers to install distributed renewable energy Demand-Side Management Adjustment Clause (“DSMAC”) April 2005 / March 2014 Recovers costs related to energy efficiency and DSM programs above $10 million in base rates Provides performance incentive to APS for net benefits achieved Provides rebates and other incentives to participating customers Environmental Improvement Surcharge (“EIS”) July 2007 / April 2014 Allows recovery of certain carrying costs for government-mandated environmental capital projects Capped at $5 million annually Transmission Cost Adjustor (“TCA”) April 2005 / June 2014 Recovers FERC-approved transmission costs related to retail customers Resets annually as result of FERC Formula Rate process (see below) FERC Formula Rates 2008 / June 2014 Recovers transmission costs based on historical costs per FERC Form 1 and certain projected data Lost Fixed Cost Recovery (“LFCR”) July 2012 / March 2014 Mitigates loss of portion of fixed costs related to ACC-approved energy efficiency and distributed renewable generation programs REGULATORY MECHANISMS We have achieved a more supportive regulatory structure and improvements in cost recovery timing |
|
|
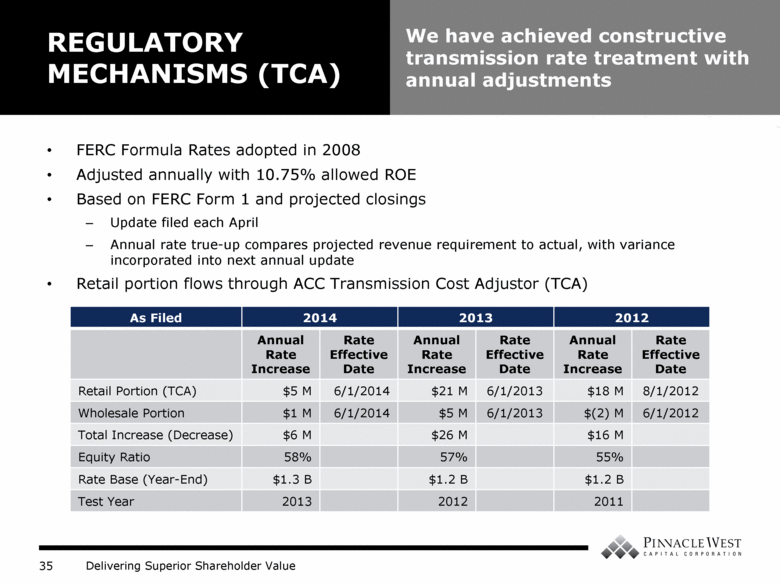
FERC Formula Rates adopted in 2008 Adjusted annually with 10.75% allowed ROE Based on FERC Form 1 and projected closings Update filed each April Annual rate true-up compares projected revenue requirement to actual, with variance incorporated into next annual update Retail portion flows through ACC Transmission Cost Adjustor (TCA) REGULATORY MECHANISMS (TCA) We have achieved constructive transmission rate treatment with annual adjustments As Filed 2014 2013 2012 Annual Rate Increase Rate Effective Date Annual Rate Increase Rate Effective Date Annual Rate Increase Rate Effective Date Retail Portion (TCA) $5 M 6/1/2014 $21 M 6/1/2013 $18 M 8/1/2012 Wholesale Portion $1 M 6/1/2014 $5 M 6/1/2013 $(2) M 6/1/2012 Total Increase (Decrease) $6 M $26 M $16 M Equity Ratio 58% 57% 55% Rate Base (Year-End) $1.3 B $1.2 B $1.2 B Test Year 2013 2012 2011 |
|
|
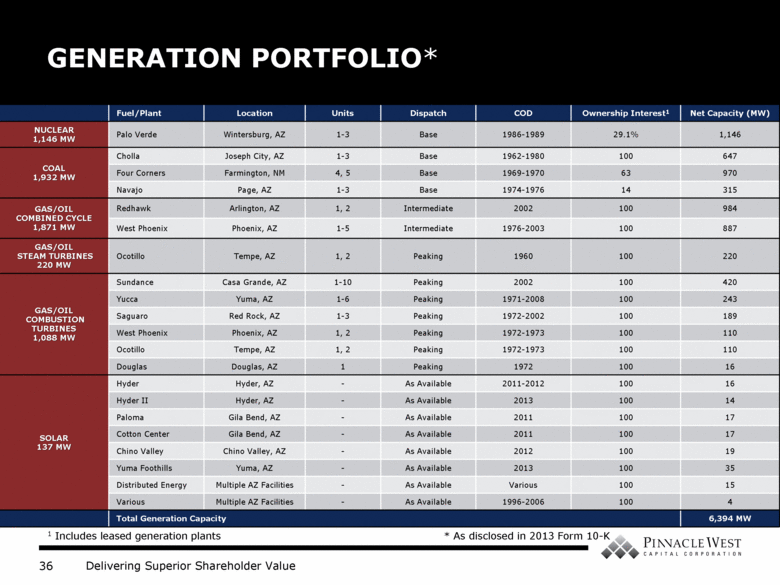
GENERATION PORTFOLIO* Fuel/Plant Location Units Dispatch COD Ownership Interest1 Net Capacity (MW) NUCLEAR 1,146 MW Palo Verde Wintersburg, AZ 1-3 Base 1986-1989 29.1% 1,146 COAL 1,932 MW Cholla Joseph City, AZ 1-3 Base 1962-1980 100 647 Four Corners Farmington, NM 4, 5 Base 1969-1970 63 970 Navajo Page, AZ 1-3 Base 1974-1976 14 315 GAS/OIL COMBINED CYCLE 1,871 MW Redhawk Arlington, AZ 1, 2 Intermediate 2002 100 984 West Phoenix Phoenix, AZ 1-5 Intermediate 1976-2003 100 887 GAS/OIL STEAM TURBINES 220 MW Ocotillo Tempe, AZ 1, 2 Peaking 1960 100 220 GAS/OIL COMBUSTION TURBINES 1,088 MW Sundance Casa Grande, AZ 1-10 Peaking 2002 100 420 Yucca Yuma, AZ 1-6 Peaking 1971-2008 100 243 Saguaro Red Rock, AZ 1-3 Peaking 1972-2002 100 189 West Phoenix Phoenix, AZ 1, 2 Peaking 1972-1973 100 110 Ocotillo Tempe, AZ 1, 2 Peaking 1972-1973 100 110 Douglas Douglas, AZ 1 Peaking 1972 100 16 SOLAR 137 MW Hyder Hyder, AZ - As Available 2011-2012 100 16 Hyder II Hyder, AZ - As Available 2013 100 14 Paloma Gila Bend, AZ - As Available 2011 100 17 Cotton Center Gila Bend, AZ - As Available 2011 100 17 Chino Valley Chino Valley, AZ - As Available 2012 100 19 Yuma Foothills Yuma, AZ - As Available 2013 100 35 Distributed Energy Multiple AZ Facilities - As Available Various 100 15 Various Multiple AZ Facilities - As Available 1996-2006 100 4 Total Generation Capacity 6,394 MW 1 Includes leased generation plants * As disclosed in 2013 Form 10-K |
|
|
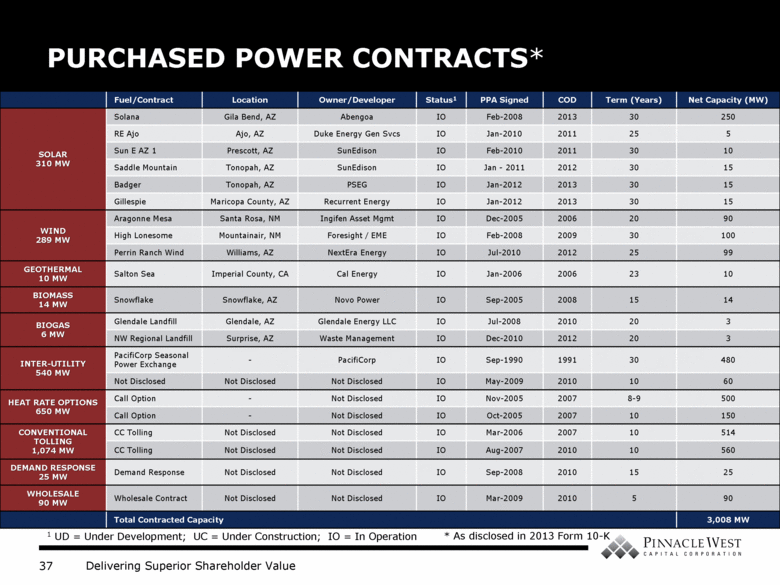
PURCHASED POWER CONTRACTS* Fuel/Contract Location Owner/Developer Status1 PPA Signed COD Term (Years) Net Capacity (MW) SOLAR 310 MW Solana Gila Bend, AZ Abengoa IO Feb-2008 2013 30 250 RE Ajo Ajo, AZ Duke Energy Gen Svcs IO Jan-2010 2011 25 5 Sun E AZ 1 Prescott, AZ SunEdison IO Feb-2010 2011 30 10 Saddle Mountain Tonopah, AZ SunEdison IO Jan - 2011 2012 30 15 Badger Tonopah, AZ PSEG IO Jan-2012 2013 30 15 Gillespie Maricopa County, AZ Recurrent Energy IO Jan-2012 2013 30 15 WIND 289 MW Aragonne Mesa Santa Rosa, NM Ingifen Asset Mgmt IO Dec-2005 2006 20 90 High Lonesome Mountainair, NM Foresight / EME IO Feb-2008 2009 30 100 Perrin Ranch Wind Williams, AZ NextEra Energy IO Jul-2010 2012 25 99 GEOTHERMAL 10 MW Salton Sea Imperial County, CA Cal Energy IO Jan-2006 2006 23 10 BIOMASS 14 MW Snowflake Snowflake, AZ Novo Power IO Sep-2005 2008 15 14 BIOGAS 6 MW Glendale Landfill Glendale, AZ Glendale Energy LLC IO Jul-2008 2010 20 3 NW Regional Landfill Surprise, AZ Waste Management IO Dec-2010 2012 20 3 INTER-UTILITY 540 MW PacifiCorp Seasonal Power Exchange - PacifiCorp IO Sep-1990 1991 30 480 Not Disclosed Not Disclosed Not Disclosed IO May-2009 2010 10 60 HEAT RATE OPTIONS 650 MW Call Option - Not Disclosed IO Nov-2005 2007 8-9 500 Call Option - Not Disclosed IO Oct-2005 2007 10 150 CONVENTIONAL TOLLING 1,074 MW CC Tolling Not Disclosed Not Disclosed IO Mar-2006 2007 10 514 CC Tolling Not Disclosed Not Disclosed IO Aug-2007 2010 10 560 DEMAND RESPONSE 25 MW Demand Response Not Disclosed Not Disclosed IO Sep-2008 2010 15 25 WHOLESALE 90 MW Wholesale Contract Not Disclosed Not Disclosed IO Mar-2009 2010 5 90 Total Contracted Capacity 3,008 MW 1 UD = Under Development; UC = Under Construction; IO = In Operation * As disclosed in 2013 Form 10-K |