Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - bluebird bio, Inc. | d742372d8k.htm |
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - bluebird bio, Inc. | d742372dex991.htm |
 Making Hope A
Reality Nasdaq : BLUE
June 16, 2014
Exhibit 99.2 |
 Forward Looking
Statement 2
These slides and the accompanying oral presentation contain forward-looking statements and
information. The use of words such as “may,” “might,”
“will,” “should,” “expect,” “plan,”
“anticipate,” “believe,” “estimate,” “project,”
“intend,” “future,” “potential,” or “continue,” and
other similar expressions are intended to identify forward looking statements. For
example, all statements we make regarding the initiation, timing, progress and results
of our preclinical and clinical studies and our research and development programs, our
ability to advance product candidates into, and successfully complete, clinical
studies, and the timing or likelihood of regulatory filings and approvals are forward
looking. The data for LentiGlobin are preliminary in nature and the HGB-205 trial
is not completed. These data may not continue for these subjects or be repeated or
observed in ongoing or future studies involving our LentiGlobin product candidate,
including the HGB-205 Study, the Northstar Study or the HB-206 Study in sickle
cell disease. All forward-looking statements are based on estimates and assumptions by
our management that, although we believe to be reasonable, are inherently uncertain. All
forward-looking statements are subject to risks and uncertainties that may cause
actual results to differ materially from those that we expected. These statements are
also subject to a number of material risks and uncertainties that are described in the
our most recent quarterly report on Form 10-Q, as well as our subsequent fillings
with the Securities and Exchange Commission. Any forward-looking statement
speaks only as of the date on which it was made. We undertake no obligation to
publicly update or revise any forward-looking statement, whether as a result of new
information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law. |
 Summary
- Key Messages
Potential for
one-time transformative treatments for severe
genetic and orphan diseases
Encouraging
clinical
data
in
beta-thalassemia
major
patients
Promising
proof
of
concept
data
in
CCALD
patients
Industrialized
platform
across
people,
production,
development and deployment
Disruptive
product
platform
with
broad
product
and
deal
potential
Industry
leading
team
and
culture
funded
for
success
3 |
 bluebird
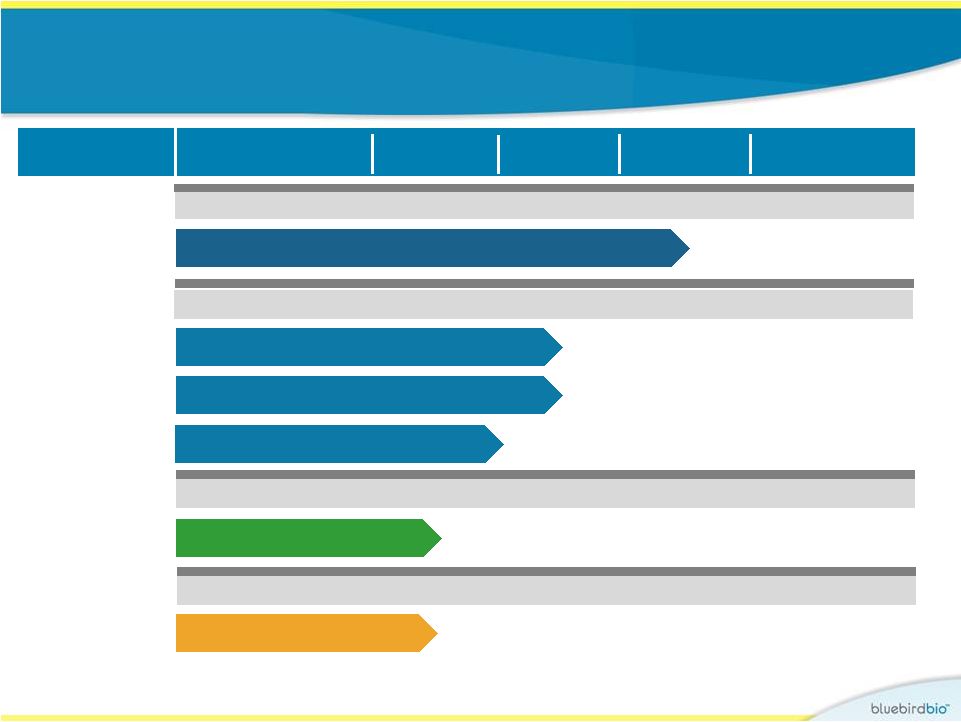
Pipeline CNS Diseases
Hematologic/Solid Tumors
Lenti-D
LentiGlobin™
CAR-T Cells
Undisclosed
Worldwide
Oncology
Hematologic Diseases
Products
Early Pipeline
Research
Worldwide
Worldwide
Global Celgene
Collaboration
4
Program Area
Preclinical
Phase I/II
Phase II/III
Rights
b-thalassemia/SCD (France) –
HGB-205 Study**
b-thalassemia (U.S.) –
Northstar Study**
Sickle Cell Disease (U.S.) –
HGB-206 Study
* The Phase II/III Starbeam Study is our first clinical study of our current Lenti-D
viral vector and product candidate. ** The Phase I/II HGB-205 and Northstar Studies are our first clinical studies of our
current LentiGlobin viral vector and product candidate.
Childhood Cerebral ALD – Starbeam Study*
|
 5
IMPROVING GENE THERAPY FOR
-THALASSEMIA
MAJOR: INITIAL RESULTS FROM STUDY HGB-205
M. Cavazzana, JA Ribeil*, E. Payen*, F. Suarez, O. Negre, Y. Beuzard, F. Touzot, R.
Cavallesco, F. Lefrere, S. Chretien, P. Bourget, F. Monpoux, C. Pondarre, B. Neven, F.
Bushman, M. Schmidt, C. von Kalle, L. Sandler, S. Soni, B. Ryu, R. Kutner, G. Veres,
M. Finer, S. Blanche, O. Hermine, S. Hacein-Bey-Abina, P. Leboulch
*these authors contributed equally |
 Epidemiology of
hemoglobin disorders 6
The hemoglobinopathies are the most prevalent monogenetic disorders in the world –
7% of global population carry an abnormal hemoglobin gene
Between 300,000 –
400,00 babies are born each year with a serious hemoglobin
disorder
•
>40,000 with -thalassemia major/HbE
-thalassemia •
>200,000 with sickle cell disease
Adapted from Williams and Weatherall 2012 and March of Dimes, 2006
b
b |
 -thalassemia
major is a serious disease potentially amenable to gene therapy
7
Only curative approach is allogeneic HSCT, but complicated by:
difficulty in finding well-matched donors
graft versus host disease
prolonged immunosuppression
At EHA we report data from two clinical trials of ex-vivo
gene
therapy in subjects with
b-thalassemia major
Study
Lentiviral vector
Current status
1 (LG001)
HPV569
Study closed, update presented today
2 (HGB-205)
BB305
Enrolling, initial results on first 2
subjects presented today |
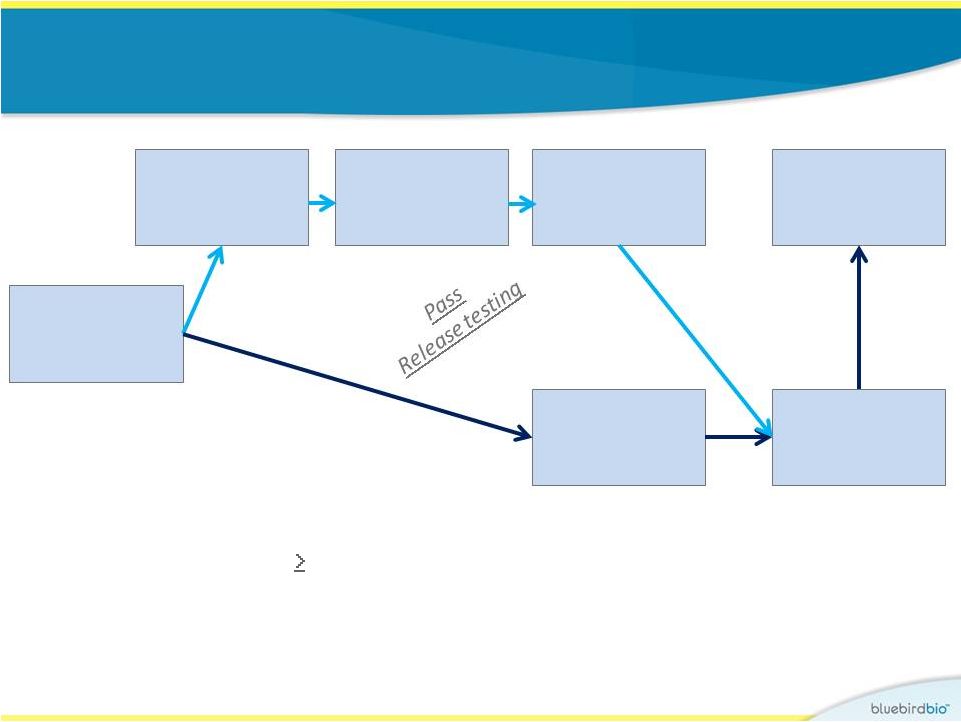 Identical study
design for both gene therapy trials •
Key eligibility:
•
b-Thalassemia major ( 100 mls pRBCs/kg/year)
•
Subjects with severe sickle cell disease are also eligible; none
treated to date
•
No HLA-matched sibling donor
HSC
mobilization
then apheresis
Myeloablation
with IV
busulfan
Infusion
Follow-up
CD34+ cells
selection
Cryopreserve
Lentiviral
vector
transduction
8 |
 HPV569 lentiviral
vector used in Study 1 9
Globin production is under transcriptional control of an
erythroid-specific promoter and
enhancer R
U5
HIV U3
RRE
cPPT
pA
gag
3’enh/pA
Globin LCR
U3
R
A-T87Q
-globin allows
for monitoring of protein levels produced using HPLC
Human
-globin
gene
A-T87Q
cHS4 insulators |
 Study 1
– characteristics of included subjects
•
No AEs related to drug product, including no RCL nor malignancy
10
Subject
Outcome
1
Not treated
2
Low number of stem cells infused, no engraftment,
received rescue cells
3
Engrafted, 6 years follow-up
4
Engrafted, 2 years follow-up
Subject 3
Subject 4
Age
18
22
Genotype
b
0
/
b
0
/
CD34
+
VCN
0.6
0.3
CD34
+
cell dose (x 10
6
/kg)
4.9*
4.3
*Subject 3 source of CD34+ cells was bone marrow
E
E
b
b |
 Study 1 :
hemoglobin concentrations 11
•
Subject
3:
stable
levels
of
b
A-T87Q
–globin
beginning
at
Month
18,
transfusion
independent
by
Month
12.
Producing
2.7
g/dL
of
b
A-T87Q
-globin
at
6
years.
•
Subject
4:
minimal
levels
of
b
A-T87Q
-globin
post-treatment,
transfusion
dependent.
Producing
0.4
g/dL
of
b
A-T87Q
-globin
at
2
years.
Months post treatment
9.8
8.6
10.5
8.0
8.0
8.9
8.9
9.2
8.7
8.3
8.2
8.1
7.8
9.0
8.8
7.9
8.1
7.3
8.4
8.6
7.1
7.1 |
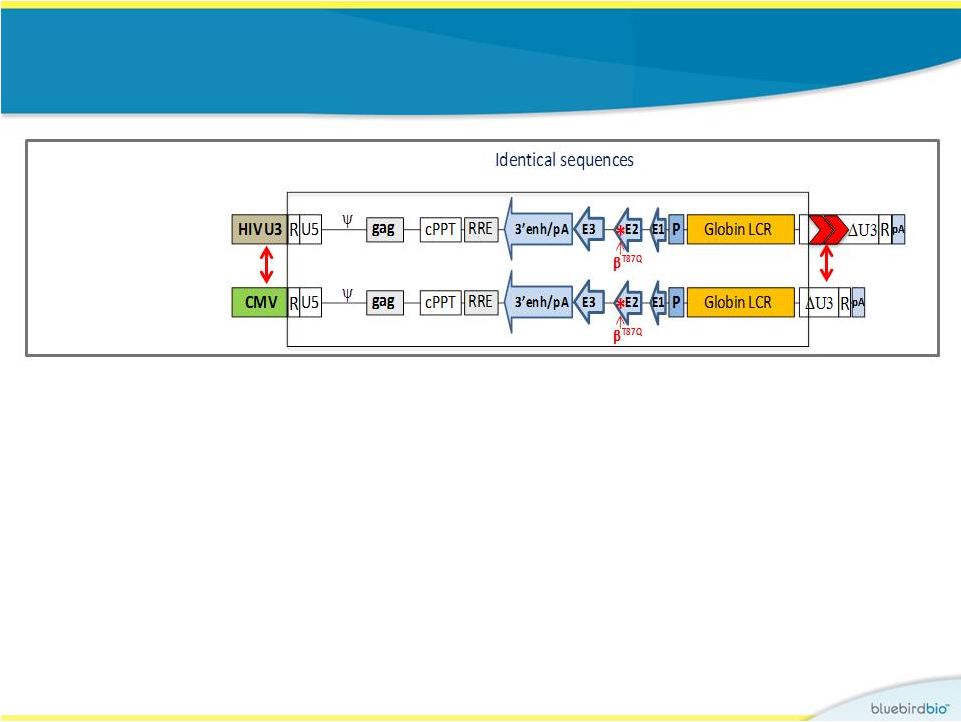 BB305 lentiviral
vector used in Study 2 12
•
Improvements made in vector design, vector
manufacturing process, and drug product manufacturing,
including:
Study 2:
Study 1:
•
CMV promoter to drive vector production (aim to increase
vector
titer)
•
cHS4 insulator elements were removed (aim to increase vector
titer, potency, and stability) |
 Improvements in
BB305 vector design and manufacturing process increase transduction efficiency in
vitro 13
•
Mean VCN was 2-
to 3-fold higher in transduced human CD34
+
cells
•
b
A-T87Q
–globin was produced at a 2-fold higher level in differentiated
erythroid lineage cells |
 Study 2 :
characteristics of included subjects (to date) 14
Subject 1
Subject 2
Age at Enrollment
18
16
Genotype
b
0
/b
E
b
0
/b
E
CD34
+
VCN
1.5
2.1
CD34
+
cell dose (x 10
6
/kg)
8.9
13.6 |
 Study 2 :
Safety 15
Subject 1
Subject 2
Follow up period
4.5 months
2 months
Day of neutrophil engraftment
ANC > 500/µL
Day 13
Day 15
Day of platelet engraftment
Unsupported platelet count > 20,000/µL
Day 17
Day 24
Non-laboratory Grade 3 AEs
Mucositis
1
Mucositis
SAEs occurring Day 0
None
None
Insertion site analysis
At 3 Months: highly
polyclonal (>1000), no
clonal dominance
Not yet available
1
Subject 1201 had an asymptomatic Grade 3 AST, ALT and GGT elevation from Days 23-90
•
No AEs related to drug product, including no RCL nor malignancy |
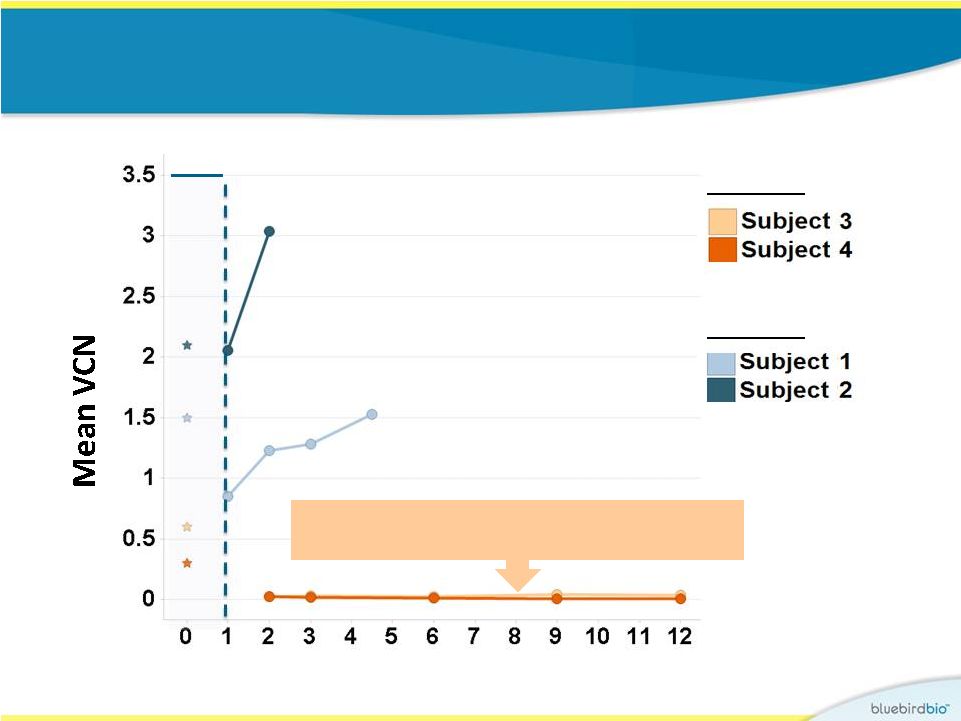    Study 2 vs. Study
1: VCN in peripheral blood leucocytes 16
Months post infusion
CD34+
VCN
Study 1
Study 2
In first 12 months, VCN in PBLs for Study 1
subjects were between 0.02 and 0.04 |
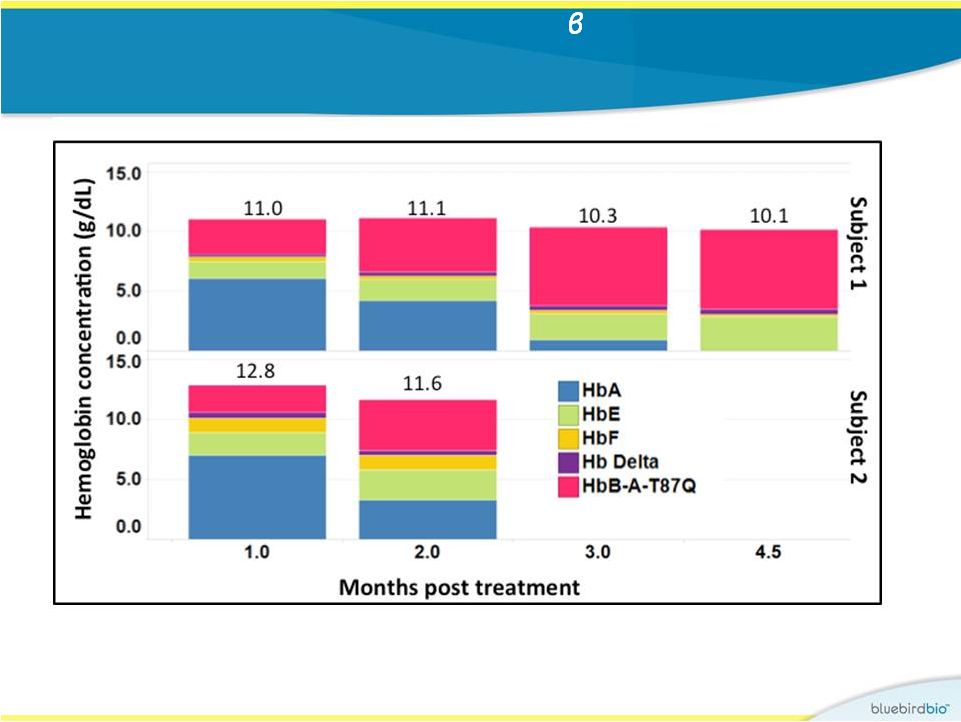 In
study
2,
early
and
high
production
of
A-T87Q
-globin
resulting
in
rapid transfusion-independence at near normal Hb levels in both
patients
17
•
Subject 1: producing 6.6 g/dL of b
A-T87Q
-globin at 4.5 months
•
Subject 2: producing 4.2 g/dL of b
A-T87Q
-globin at 2 months |
 Kinetics
of A-T87Q
expression and transfusion
independence
18
Study 2
Study 1
•
In Study 2, rapid production of therapeutic globin (weeks as opposed to one
year)
•
Both subjects in Study 2 have near-normal hemoglobin levels without
transfusion support (neither subject has required a transfusion post-
engraftment)
RBC transfusion Independence
Subject 3
Subject 1
Subject 2
Study
1
LG001
2
HGB-205
2
HGB-205
Vector
HPV569
BB305
BB305
Day of last
transfusion
Month 12
Day 10
Day 12
Duration since last
transfusion
>5 years
>125 days
>48 days
Months post treatment |
 Conclusions
19
•
BB305 lentiviral vector and improved manufacturing process produce superior
transduction efficiency as compared with HPV569
•
With BB305 lentiviral vector in Study 2, neither subject has received a transfusion since
the second week post transplantation
•
Production of b
A-T87Q
-globin has been rapid and clinically significant resulting in near-
normal hemoglobin levels
•
Initial safety profile is consistent with autologous transplantation, without gene-therapy
related adverse events, and with polyclonal reconstitution in the first subject
•
These data demonstrate that early transfusion independence (within weeks of
transplantation) with near-normal levels of hemoglobin can be achieved with
ex-vivo gene therapy using BB305 lentiviral vector in subjects
with b 0
/b
E
-thalassemia major |
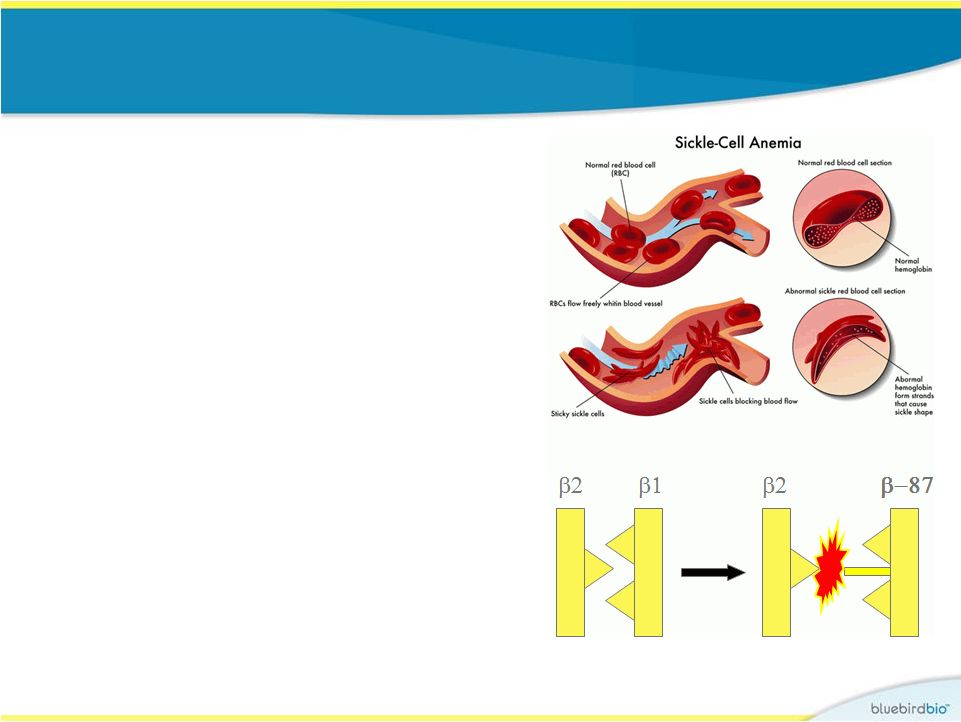 Evidence for why
BB305 globin may work for sickle cell disease
•
BB305 globin incorporates an anti-
sickling amino acid that is found in
fetal hemoglobin (glutamine at
position 87)
•
Anti-sickling activity of
b A-T87Q
-globin
has been demonstrated in a mouse
model of SCD (Science 2001)
•
Elevated fetal hemoglobin from
hereditary persistence of fetal
hemoglobin (HPFH) or treatment
with hydroxurea has shown clinical
benefit
F
L
T
V
F
L
Q
polymerization
destabilization
20
V |
 Ongoing Studies
using BB305 lentiviral vector 21
Study
Centers
Indication
Planned
subjects
Current Status
HGB-205
(trial reported
today)
1 in France
7
4 subjects enrolled
2 subjects treated to
date
Northstar Study
(HGB-204)
4 in US
1 in Australia
1 in Thailand
15
6 subjects enrolled
1 subject treated to
date
HGB-206
3-6 planned,
all in US
Severe sickle cell
disease
8
Open IND, pending
initiation
b-
thalassemia
major and severe
sickle cell disease
b-
thalassemia
major
|
 Recent and
Upcoming News Flow Enroll first SCD patient in
HGB-205 or HGB-206 (2014)
Preliminary Thal Northstar &
HGB-205 data (late 2014)
Various clinical publications
Signed global Oncology
collaboration with Celgene
Completed IPO
Initiated phase II/III Starbeam
Study
Initiated two phase I/II Thal
studies (Northstar & HGB-
205)
First patient transplanted in
Starbeam Study
First patient transplanted in
Thal HGB-205 study
2013
2013
22
Complete enrollment of
Starbeam Study
Complete enrollment
Thal Northstar & HGB-
205
Preliminary SCD data
2015
2015
2014
2014
First patient transplanted in
Northstar Study
File IND for sickle cell disease
(SCD) study
Preliminary Thal HGB-205
data at EHA |
 Q&A
|
 Backups
|
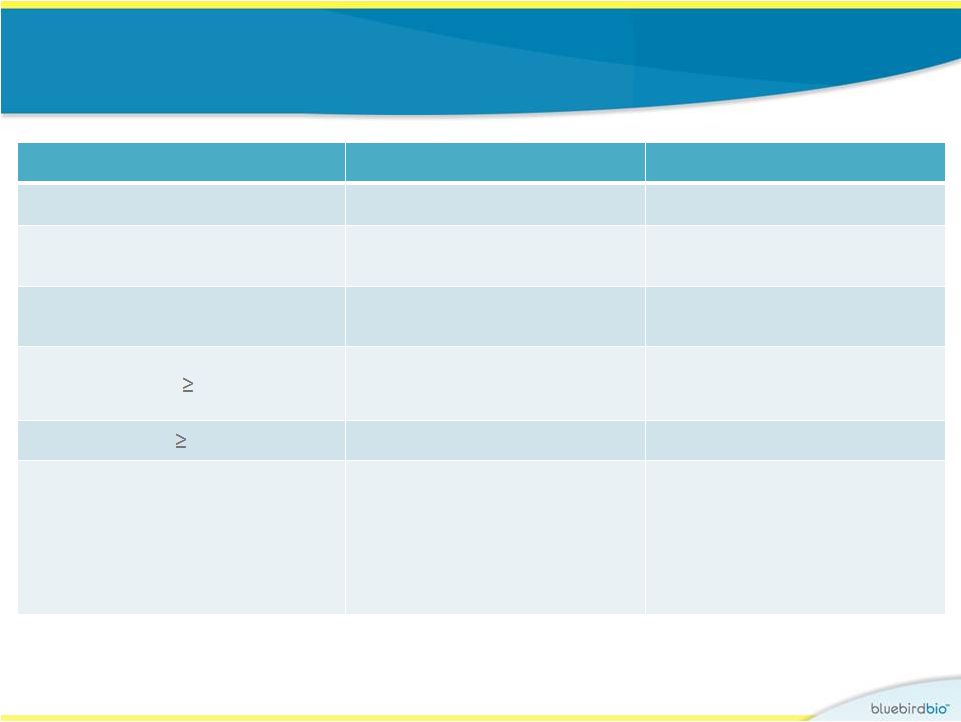 Study 1 (LG001)
: Safety •
No AEs related
to drug product, including no RCL nor malignancy
Subject 3
Subject 4
Follow-up period
6 years
2 years
Day of neutrophil engraftment
ANC > 500/µL
Day 27
Day 19
Day of platelet engraftment
Unsupported platelet count > 20,000/µL
Day 40
Day 130
Non-laboratory Grade 3 AEs
None
Mucositis, metrorrhagia,
epistaxis, mouth bleeding
SAEs occurring Day 0
None
Thrombocytopenia
Insertion site analysis
Multiple clones (25-50
detected at each timepoint),
including HMGA2, many
observed repeatedly over
the following 5 years
Polyclonal (90-200 clones
detected at each timepoint)
reconstitution without
clonal dominance at Year 1 |
 Subject 3
(LG001) : prominence of HMGA2 clone decreasing over time
•
By Year 5, SPATS2 and ZZEF1 have replaced HMGA2 as the most common clones
identified by LAM-PCR
•
In
spite
of
decrease
in
HMGA2
clone,
therapeutic
effect
has
been
maintained
•
No hematological or clinical effects of the HMGA2 clone have been noted in over
6 years of follow-up
Months
0
5
10
15
20
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
vector-modified
cells
HMGA2-
modified cells |
