EXHIBIT 99

2013 SUSTAINABILITY HIGHLIGHTS
| • |
|
We reduced our absolute greenhouse gas emissions by 3.1 million metric tons, or 7%. |
| • |
|
We had zero employee and contractor fatalities, and we reduced our days away, restricted, and transfer (DART) rate by 30% to 0.35.
|
| • |
|
We introduced Alcoa 951 bonding technology, which is “aluminizing” the automotive and truck industries. |
| • |
|
We rated 78% of our key suppliers as either leading or active in regards to their sustainability programs. |
| • |
|
Alcoa and Alcoa Foundation invested US$40.9 million in community programs, and a record 62% of our employees volunteered in their communities during
our Worldwide Month of Service. |
| • |
|
We were included in the Dow Jones Sustainability Indexes for the twelfth consecutive year and again recognized as the global sustainability leader for
the aluminum industry. |
|
|
|
|

Klaus Kleinfeld
Alcoa Chairman and Chief Executive Officer |
|
“For more than 125 years, Alcoa has delivered the sustainable solutions the world needs, with innovations that set us apart
as a true leader. We are growing in the areas the world needs most, meeting ever-increasing demands for lightweighting in automotive, commercial transportation, and aerospace, and for energy-efficient buildings.”

|
MATERIAL ASPECTS
Material aspects are a company’s most significant economic, environmental, and social impacts.
Using stakeholder input in accordance with the Global Reporting Initiative’s G4 guidelines, we identified our material aspects as greenhouse gas emissions, energy, health and safety, economic
performance, environmental footprint (emissions & waste), local communities, and biodiversity.
ALCOA PRODUCTS AND MATERIALS ARE
ESSENTIAL FOR THE INDUSTRIAL ECOSYSTEM
| • |
|
We were the first aluminum company to receive the Cradle to Cradle CertifiedCM designation, which is a multi-attribute eco-label that assesses a product’s safety to humans and potential impact
on the natural environment. |
| • |
|
For the next generation of short-range aircraft, we have developed new alloys and technologies that can lower the weight of the plane by up to 10%
versus composite-intensive planes. |
| • |
|
Automakers are incorporating more aluminum to deliver lighter weight vehicles and improve fuel economy while meeting durability, safety, and
performance requirements. |
| • |
|
Our new 18-kilogram (40-pound) Ultra ONE™ heavy duty truck wheel is 47% lighter than steel wheels of the same size. |
| • |
|
With a 76% global recycling rate, the aluminum can is the most recycled beverage container in the world and one of the most sustainable solutions for
eliminating packaging waste. |
| • |
|
We are the world’s leading producer of blades and vanes made of advanced nickel-based superalloys for the high-temperature environments in jet
engines and industrial gas turbines. |
| • |
|
We manufacture a wide array of aluminum doors, framing systems, curtain walls, and windows that help make buildings greener.
|

Through their light weight, high strength, durability, and recyclability, our products are inherently
sustainable and improve the sustainability of our customers’ products.
PRODUCT DESIGN & LIFE CYCLE
We were the first aluminum company to receive the Cradle to
|
|
|

|
|
Cradle CertifiedCM designation. We currently hold Silver certification for our primary metal, forged aluminum truck wheels, lithographic sheet, can sheet, aluminum bottle stock, and four product lines from our Kawneer
architectural systems business. |
TRANSPORTATION
Aluminum is the ideal material for transportation applications, helping reduce the overall weight of an aircraft, automobile, or commercial vehicle to improve fuel economy and significantly reduce
emissions during the vehicle use phase.
In response to growing consumer demand for more fuel-efficient cars, increasing fuel prices, and
stricter government
emission regulations, automakers are incorporating more aluminum to deliver lighter weight vehicles while
meeting durability, safety, and performance requirements. The mass production of aluminum-intensive vehicles is significantly enabled by Alcoa 951 bonding technology, which we introduced commercially in 2013.
|
|
|
| The commercial transportation industry is also facing stricter government regulations for vehicle fuel efficiency and emissions. Our portfolio of aluminum sheet, extrusions, and
wheel products can be used to replace heavier metals for many truck components. |
|

Ultra ONE wheels |
| For example, our new 18-kilogram (40-pound) Ultra ONE™ heavy duty truck wheel is 47% lighter than steel wheels of the same size. |
Aluminum Applications on
Automobiles
|
|
|
|
|
|
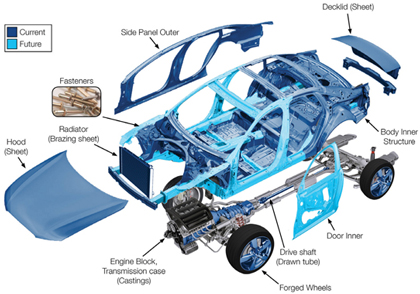
|
|
PACKAGING
We produce aluminum rigid container sheet for the packaging products market. Our customers use our sheet to manufacture beverage and food cans for the
beer, soft drink, juice, isotonic beverage, energy drink, packaged water, food, and pet food industries. We operate the largest can reclamation facility in the world in Alcoa, Tennessee, USA. This facility re-melts enough used beverage |
| |
containers to make billions of new aluminum cans each year. |
|

|

This LEED silver certified building at Washington State University Spokane in the United States, which uses Alcoa
aluminum architectural products, will be 48% more energy efficient than existing buildings.
BUILDING & CONSTRUCTION
We manufacture a wide array of aluminum doors, framing systems, curtain walls, and windows that help make buildings greener. We also have developed state-of-the-art framing and wall systems that are
hurricane- and blast-resistant.
Aluminum’s highly reflective surface allows for efficient light management and lower energy consumption,
and its light weight reduces transportation costs, vehicle fuel consumption, and related carbon dioxide emissions when being delivered to the construction site. In addition, architectural aluminum systems that use advanced thermal technologies can
provide superior thermal performance without compromising structural performance.
INDUSTRIAL & ENGINEERED
We are the world’s leading producer of blades and vanes made of advanced nickel-based superalloys for the high-temperature environments in jet
engines and industrial gas turbines. Our innovative products allow these engines and turbines to run at hotter temperatures. This improves overall energy efficiency and reduces noise, emissions, and the overall carbon footprint.
Fasteners
We are also a leading manufacturer of fastener systems made of aluminum, corrosion-resistant steels,
titanium, and super alloys for the aerospace, automotive, commercial transportation, and industrial markets.
RECYCLING
Almost 75% of all the primary aluminum ever produced is still in productive use.
In 2013, the advanced recycling system at our Barberton, Ohio, USA, wheels plant was operating at full capacity. The first of its kind in North America, the Barberton process uses innovative technology to
produce billet for new wheels from re-melted scrap aluminum wheels, many of which can be returned through scrap buy-back programs with our customers.
|
|
|
| We announced a closed-loop recycling program with Boeing in 2013
to significantly increase the recycling of internal aluminum aerospace alloys used during the production of Boeing airplanes.
We continue to educate the public about the sustainability and recyclability of aluminum. Globally, Alcoa and Alcoa Foundation invested approximately
US$6.3 million between 2007 and 2013 in education and community-based recycling programs. |
|

Alcoa Foundation funded a pilot project that placed 30 solar- powered waste
and recycling stations in New York City’s Times Square in 2013. |
|
|
|
| Visit www.alcoa.com/sustainability for more in-depth information and performance data. |
|
3 |

Efficient use of resources, such as water and energy, and effective control of emissions, waste, and land
use have positioned us as an industry leader in minimizing our environmental footprint.
|
|
|
| CLIMATE PROTECTION |
|
MATERIAL ASPECT |
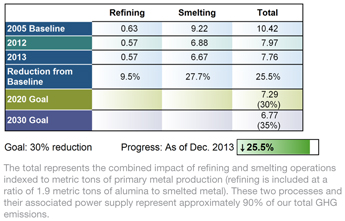
Our goal is to reduce 2005 levels of total carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2e) intensity in our Global Primary Products
business (refining and smelting) by 30% by 2020 and 35% by 2030. Carbon dioxide is our largest component of greenhouse gases (GHGs).
Between
2005 and 2013, we reduced the GHG emission intensity of our Global Primary Products business by 25.5%. We reduced our absolute GHG emissions by 3.1 million metric tons from 2012 to 2013, and our total 2013 GHG emissions (CO2 equivalents)
equaled 43.4 million metric tons.
Global Primary Products
Greenhouse Gas Emission Intensity
Metric tons of CO2 equivalents per ton of production
We are committed to reducing the energy requirements for all of our operations and have set the following long-term
strategic targets:
| • |
|
From a 2005 baseline, a 10% reduction in the energy intensity of Global Primary Products (GPP) by 2020; 15% by 2030; and |
| • |
|
A 20% reduction in the energy intensity of all other businesses—Global Rolled Products (GRP) and Engineered Products and Solutions (EPS)—by
2020 from their base-lines of 2005 and 2010, respectively; 30% by 2030.
|
In 2013, GPP reduced its energy intensity by 0.6% compared to 2012 and 3.1% compared to the 2005 baseline.
GRP had a 0.6% reduction compared to 2012 and 15% decrease compared to the 2005 baseline. EPS reduced its energy intensity by 2.4% compared to 2012 and 10.3% compared to the 2010 baseline.
Energy Intensity—Global Primary Products
Gigajoules per metric ton of aluminum
produced
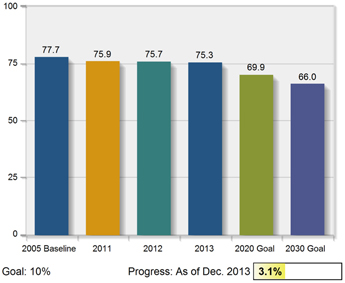
|
|
|
| EMISSIONS & WASTE |
|
MATERIAL ASPECT |
Bauxite residue and landfilled waste are two of our key strategic sustainability targets.
Bauxite Residue
A byproduct of the
alumina refining industry, bauxite residue is stored in impoundments that are capped and re-vegetated when full. Our long-term strategic targets for the material, and our progress against them through 2013, are:
| • |
|
From a 2005 baseline, 15% reduction in bauxite residue land requirements per unit of alumina produced by 2020; 30% by 2030. Achieved 15%.
|
| • |
|
Rehabilitate 30% of total residue storage area by 2020; 40% by 2030. Achieved 15%. |
|
|
|
| • Recycle or reuse 15% of residue generated by 2020; 30% by 2030.
Achieved 0%. We have a comprehensive and ongoing research program aimed at
continually improving residue storage practices to reduce potential |
|

|
environmental impacts. We also have investigated ways to modify the residue to further lessen its potential environmental impact while enhancing its prospects of reuse.
Landfilled Waste
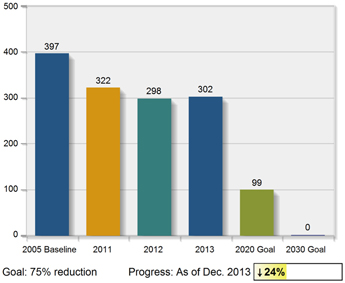
Our current strategic
target is a 75% reduction in landfilled waste by 2020 and 100% by 2030 from a 2005 baseline.
In 2013, we achieved a 24% reduction in
landfilled waste from the baseline. We again saw an increase in waste volumes from certain facilities that we permanently decommissioned in recent years.
Landfilled Waste
Thousands of metric tons
|
|
|
| BIODIVERSITY |
|
MATERIAL ASPECT |
We have a strategic sustainability target for all of our locations with substantive biodiversity values and land holdings
to develop biodiversity action plans by 2015.
In 2012, our global biodiversity team surveyed 40 select Alcoa locations around the world to
acquire information on their ecological values. We identified 14 locations as having potentially substantive biodiversity values, five of which worked on developing their biodiversity action plans in 2013.
MINE REHABILITATION
During 2013, we
continued to make progress in monitoring and reducing our collective mining footprint to the minimum required for efficient resource recovery.
Our strategic sustainability targets, initially developed in 2009, have been key drivers toward the minimum footprint:
| • |
|
By 2020, achieve a rolling five-year company-wide ratio of 0.75:1 for new active mining disturbance to rehabilitation; and
|
| • |
|
By 2030, maintain a ratio of 1:1 to ensure no net expansion in new disturbance (i.e., achieve a footprint-neutral condition).
|
|
|
|
| We disturbed 1,463 hectares (3,615 acres) of mine lands during 2013, and we rehabilitated 1,140 hectares (2,817 acres). Our five-year rolling average for new active mining
disturbance to rehabilitation is currently projected at 1.08:1. |
|

|
WATER
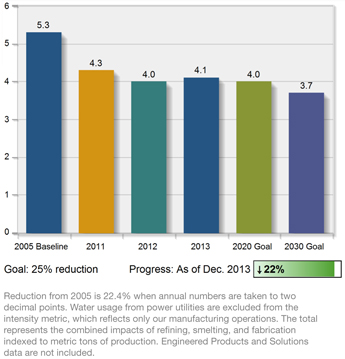
Water is an important raw material for Alcoa, with our refining and ingot-casting processes requiring significant water resources.
Our total overall use of freshwater was essentially flat in 2013 versus 2012. However, our freshwater-use intensity (consumption per unit of production)
increased by 3% in 2013 compared to 2012 because some production capacity was taken offline. We have reduced this intensity by 22% versus 2005 levels, approaching our 2020 goal of 25%.
Freshwater-Use Intensity
Cubic meters of water per metric ton of production
|
|
|
| Visit www.alcoa.com/sustainability for more in-depth information and performance data. |
|
5 |

We place great value on our employees and suppliers and hold each responsible for working in a manner that
adheres to the highest standards for human rights and is safe, responsible, ethical, and focused on sustainability.
HUMAN RIGHTS
Alcoa’s Human Rights Policy comprises policies related to children and young workers, freedom of engagement, equality of opportunity,
compensation, freedom of association, and relationships with indigenous people.
We endorse the United Nations Global Compact with respect to
human rights. The compact’s 10 principles provide that businesses should support and respect the protection of internationally proclaimed human rights and ensure that they are not complicit in human rights abuses.
We offer a human rights course to managers and professional employees to ensure they understand and adhere to our human rights principles. More than
5,800 employees have completed the course since its initial deployment in late 2010.
OUR PEOPLE
Our people are the foundation of our success throughout the world, and we foster a high-performance culture that attracts and develops talent and promotes
teamwork.
A major achievement in 2013 was women comprising 20.8% of our global leadership, exceeding our goal of 19% by year’s end. We
had a similar goal to increase U.S. minority representation in leadership roles to 16%, but we fell slightly short with 15.6% representation. For 2014, we raised the targets to 21.3% of women in global leadership roles and 16.1% of U.S. minorities
in leadership roles.
In 2013, we received the prestigious Catalyst Award, which honors innovative organizational approaches that address the
recruitment, development, and advancement of women in the workplace.
To ensure the integration of sustainability into our core business
strategies, up to 20% of our 2013 variable compensation was tied to achieving significant aspects of our sustainability targets. Across the entire workforce, the targets focused on safety and carbon dioxide emission reductions. Our management-level
employees had an additional target to improve the diversity of our workforce.
We continued to reaffirm our Values during 2013, launching a global Integrity Champion Network of
high-potential managers to further embed a values-based culture of integrity and compliance at all levels of the company.
Each year, the
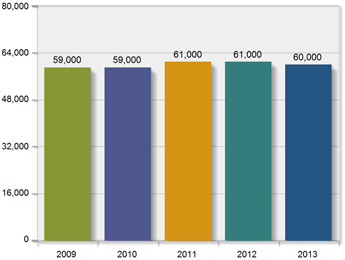
entire Alcoa workforce is invited to participate in our Global Voices Survey, which is administered by Kenexa and measures 11 dimensions of the employee experience. From 2010 to 2013, our employee engagement score increased from 60% to 74% and was
within 7% of the Kenexa best-in-class engagement level. We have seen year-over-year improvement in employee engagement since starting the survey in 2006.
Number of Employees
|
|
|
| HEALTH & SAFETY |
|
MATERIAL ASPECT |
We are committed to reducing work-related illnesses and injuries while improving the overall health of our workforce.
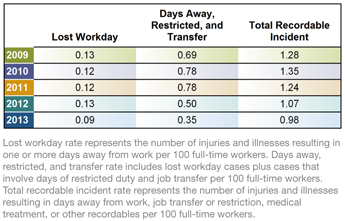
In 2013, we had zero employee and contractor fatalities. We also achieved year-over-year declines in all three of our major safety rates in
2013:
| • |
|
Lost workday (LWD) rate declined 31% to 0.09; |
| • |
|
DART rate reached 0.35, a 30% improvement; and |
| • |
|
Total recordable incident rate (TRIR) declined 8% to 0.98. |
At the end of 2013, 84.2% of our safety reporting units had worked 12 consecutive months without a lost workday, 49.5% without a DART incident, and 42.4% without a total recordable incident.
Incident Rates
In 2011, we established two critical health protocols—exposure assessment and hazardous materials management. Our
goal is 100% of our locations receiving a “Good” or better internal audit score for both protocols. By year-end 2013, 95% of our locations achieved the goal for exposure assessment and 98% for hazardous materials management. These
increased from 86% and 90%, respectively, in 2012.
We expanded the Alcoa Global Wellness Initiative to all of our global locations in 2013
following a successful U.S. launch in 2012. The initiative focuses on the most important issues for our employees—physical activity, nutrition, tobacco usage, and well-being.
The Global Corporate Challenge (GCC) was our first global activity challenge. More than 20,000 employees committed to a daily step challenge, taking a total of 28 billion steps. These results earned us
GCC’s designation of “World’s Most Active Company” out of the more than 1,200 companies participating in the challenge.

Employees at Alcoa’s Suralco operations in Suriname participated in the kickoff of the 2013 Global Corporate
Challenge.
Our 2013 Global Voices Survey gathered employee perceptions of our various wellness and culture of health activities. The
statement “The health and wellness activities at my location promote employee personal health” received an 82% favorable response rate from the respondents compared to 76% in 2012 and
72% in 2011. Our goal is 100% by 2020.
SUPPLY CHAIN
Sustainability within our procurement function means selecting materials and services that consider, among others, the environmental, social, and economic impact in evaluating total cost. It is building
relationships with suppliers who behave in a responsible and sustainable manner and ensuring that our interactions with suppliers are carried out with the highest standard of integrity and in compliance with all relevant laws and regulations.
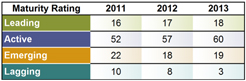
Our Global Supplier Sustainability Program focuses on our key suppliers and has four components—communicating expectations, assessing,
developing and educating, and monitoring. The assessments evaluate the maturity of our suppliers’ sustainability programs and determine where improvements are needed. Suppliers are provided with one of four possible ratings based on the results
of their assessments:
| • |
|
Leading—Program is in place with public reporting; |
| • |
|
Active—Program is in place; |
| • |
|
Emerging—Has the beginning of a program but no history; and |
| • |
|
Lagging—No formal program. |
For suppliers that attain leading or active ratings, we will conduct reassessments every three years to confirm their continued focus on sustainability. Suppliers that receive emerging or lagging ratings
are moved into the “develop and educate” and “monitor” phases of the program.
Of our key suppliers, we rated 78% as
either leading or active in regards to their sustainability programs in 2013.
Supplier Assessment Results
Percent of key suppliers
|
|
|
| Visit www.alcoa.com/sustainability for more in-depth information and performance data. |
|
7 |

We are committed to transparent and open engagement with stakeholders, as well as improving the quality of
life in the communities in which we operate.
STAKEHOLDER ENGAGEMENT
The principal way we manage engagement with stakeholders at the community level is through a tool we developed called the Alcoa Community Framework. In 2013, 97% of our manufacturing locations were using
the framework.
Examples of community and stakeholder issues that were raised during 2013 are highlighted below. A more complete listing is
available in our online reporting.
|
|
|
| ECONOMIC PERFORMANCE |
|
MATERIAL ASPECT |
We operate in many communities throughout the world. Our contributions to those communities, and to society at large, are
significant and bring social and economic benefit to regions wherever we operate.
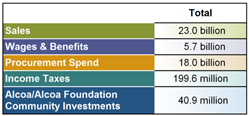
2013 Value Added
U.S. dollars
2013 Stakeholder Issues
|
|
|
|
|
| Location |
|
Issue |
|
Response |
| Anglesea, Australia |
|
The community raised concerns relating to the health risks associated with air emissions from the power station and coal mine. |
|
We contracted an independent company to update a voluntary air dispersion modeling study and a screening human health risk assessment for the Anglesea power station and coal mine.
The results from the study showed emission levels from both facilities were safe for residents, employees, and the broader Anglesea community. The report was peer-reviewed by two independent experts, and the results were made available to the
community during 2013. |
|
|
|
| Baie-Comeau, Canada |
|
In May 2013, we announced the permanent closure of the two remaining Söderberg potlines at our Baie-Comeau Smelter. |
|
Members of the Baie-Comeau Community Advisory Board and local media were informed of the decision, and a meeting was held with the city’s mayor. The shutdown was completed
successfully in September 2013. |
|
|
|
| Manchester, Jamaica |
|
The mining operations received complaints from nearby communities about dust and noise. |
|
Our Jamalco operations conducted a thorough investigation of the complaints. This included visiting the homes of those citizens who lodged a complaint and placing dust and noise
monitors to provide an objective assessment. In situations where levels were excessive, Jamalco took mitigation steps and provided compensation when appropriate. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Periodic meetings of the Mines/Community Complaints Review Committee ensure each complaint is quickly addressed and follow-up actions are taken. |
|
|
|
| Forward-Looking Statements: This report contains, in addition to historical information, statements concerning Alcoa’s expectations, goals, targets,
strategies, or future performance. These “forward-looking statements” include such words as “anticipates,” “estimates,” “should,” “will,” or other words of similar meaning and are subject to a number
of known and unknown risks and uncertainties. Some of the factors that may cause Alcoa’s actual results to differ materially from those expressed or implied in the forward-looking statements include changes in aluminum industry or global
economic conditions generally, factors affecting Alcoa’s operations, such as unavailability of energy, equipment outages, natural disasters, or other unexpected events, changes in the regulatory environment, the impact of reductions in
Alcoa’s capital expenditures, Alcoa’s inability to realize expected benefits from its productivity improvement, sustainability, restructuring, technology, and other initiatives, and the other risk factors summarized in Alcoa’s Form
10-K for the year ended December 31, 2013 and other SEC reports |
|

|

|
|
|
| Visit www.alcoa.com/sustainability for more in-depth information and performance data. |
|
8 |



























