Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - Sorrento Therapeutics, Inc. | d656994d8k.htm |
 March 2014
Next-Generation
Cancer Therapeutics
Sorrento Therapeutics
Exhibit 99.1 |
| 2
This presentation contains "forward-looking statements" as that term is
defined under the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 (PSLRA),
including statements regarding expectations, beliefs or intentions regarding
our business, technologies and products strategies or prospects. Actual
results may differ from those projected due to a number of risks and
uncertainties, including, but not limited to, the possibility that some or all of
the pending matters and transactions being considered by the Company may not
proceed as contemplated, and by
all other matters specified in Company's filings with the Securities and Exchange
Commission, as well as risks inherent in funding, developing and obtaining
regulatory approvals of new, commercially-viable and competitive
products and product candidates. Sufficiency of the data for approval with
respect to Cynviloq™ will be a review issue after NDA filing.
These statements are made based upon current expectations that are subject
to risk and uncertainty and information available to the Company as of the
date of this presentation. The Company does not undertake to update
forward-looking statements in this presentation to reflect actual
results, changes in assumptions or changes in other factors affecting such
forward-looking information. Assumptions and other information that
could cause results to differ from those set forth in the
forward-looking information can be found in the Company's filings with the
Securities and Exchange Commission, including its most recent periodic report. We
intend that all forward-looking statements be subject to the
safe-harbor provisions of the PSLRA. Safe Harbor Statement
NASDAQ: SRNE |
 Management Team
Board
of
Directors
William S. Marth -
Chairman
Albany Molecular
(President and CEO)
Teva –
Americas
(former President and CEO)
Mark Durand
Watson,
Teva
–
Americas
(former
CFO)
Cam Gallagher
Nerveda, LLC (Managing Director)
Kim D. Janda, Ph.D.
The Scripps Research Institute (Prof.)
Henry Ji, Ph.D.
Sorrento (CEO)
Daniel Levitt, M.D., Ph.D.
CytRx (EVP & CMO)
Jaisim Shah
PDL (former CBO)
Vuong Trieu, Ph.D.
Sorrento (CSO)
Richard Vincent
Sorrento (CFO)
Henry Ji, Ph.D.
President, CEO &
Director
Inventor
of
G-MAB
®
Technology
President & CEO of Stratagene Genomics
VP of CombiMatrix and Stratagene
Vuong
Trieu, Ph.D.
CSO & Director
Founder and CEO of IgDraSol
Co-inventor
of
IP
covering
Abraxane
®
Instrumental in the approval of Abraxane
Celgene acquired Abaxis Biosciences for > $3B
Amar
Singh
EVP & CBO
Closed major business transactions on oncology products
Led
Novacea
global
transaction
(Arsenal
®
)
with
Schering-
Plough valued at >$500M
Led major deals, including in-licensing of belinostat at
Spectrum Pharmaceuticals
Responsible for building Abraxis commercial organization
George Uy
CCO
CCO of IgDraSol
Directed
the
launches
of
Abraxane,
Xeloda
®
&
Fusilev
®
Built commercial infrastructures and organizations in startup
companies
David Miao, Ph.D.
CTO
President and CSO of Concortis BioSystems
Co-inventor of IP covering ADC technologies
Head of Chemistry at Ambrx
Richard Vincent
EVP, CFO & Director
$430M sale of Elevation to Sunovion-Dainippon
Meritage Pharma option agreement with ViroPharma ($90M
upfront + milestones)
$310M sale of Versus asthma program to AstraZeneca
Elan: various acquisitions and divestitures with aggregate
values more than $300M
3 |
 Next-Generation Cancer Therapeutics
TUMOR
Cynviloq
Bioequivalence regulatory pathway
Efficacy demonstrated
US and EU rights
G-MAB
High-diversity human Ab library
Lead mAb programs include
PD-L1, PD-1, and CCR2
4
G-MAB targets toxin to cancer cell
Proprietary toxins and linkers
C-Lock and K-Lock conjugation chemistries |
 5
Multiple Commercialization & Partnership Opportunities
* Abraxane orphan drug status (FDA approval, September 2013)
INDICATION > TARGET
Cynviloq
G-MAB
ADC
RTX
Oncology > PD-L1 Oncology/Inflammation >
CCR2, CXCR3 Oncology > VEGFR2, c-Met, CXCR5 Oncology > PD-1
Intractable Cancer Pain
INDICATION
Metastatic Breast Cancer
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Bladder Cancer (sNDA)
Ovarian Cancer (sNDA)
505(b)(2) Bioequivalence
}
Pancreatic Cancer (BE* or sNDA)
PHASE 3
PHASE 2
PHASE 1
PRECLINICAL |
 6
Lead Oncology Product Opportunity
Cynviloq
Registration
Trial |
 Cynviloq: Next Generation Paclitaxel Therapy
Mean size
~25 nm
Cynviloq
paclitaxel
polymeric micelle
Chemical
polymer:
Poly-lactide and
polyethylene glycol
diblock copolymer
3
rd
>300
mg/m
(up
to
435
mg/m
2
)
Mean size
130 nm
Biological
polymer:
Donor-derived human
serum albumin (HSA)
2
nd
260
mg/m
Taxol
®
paclitaxel
Cremophor EL
excipient:
Polyoxyethylated
castor oil
Formulation
Generation
1
st
175
mg/m
Maximum
Tolerated Dose
Peak
Product Sales
~ $1.6B (WW in 2000)
Est. >$1.7B* (US)
($430M in 2012)
Conversion of
Abraxane sales +
new indications
*Analyst projection; in MBC + NSCLC + PC
7
2
2
2
Abraxane
nab-
paclitaxel |
| 8
Clinical Efficacy & Safety Summary
Total number of patients across all trials: 1,260
Phase 1:
>300 mg/m
2
(q3w) vs. 175 mg/m
2
(Taxol; weekly) and 275 mg/m
2
(Abraxane; q3w)
Phase 2:
Data suggestive of efficacy comparable to historic data for Abraxane and superior to
historic Taxol data or Standard-of-Care
Phase 3:
PM-Safety:
Phase 2b (IIS):
Phase 2 (IIS):
Possible Phase 3 sNDA programs in these tumor types
Ongoing trial for MBC in S. Korea (total n=209; Cynviloq n=105)
GPMBC301. An Open-label, Randomized, Parallel, Phase 3 Trial to Evaluate the
Efficacy and Safety of Cynviloq compared to Genexol
®
(Paclitaxel with Cremophor EL) in Subjects with Recurrent or Metastatic Breast
Cancer)
Interim analysis suggests ORR superior to Taxol and comparable to historic Abraxane
efficacy Efficacy and safety data supportive of 505(b)(2) BE submission
Completed for MBC and NSCLC (total n=502)
Efficacy and safety data supportive of 505(b)(2) BE submission
Chemo-naïve Stage IIIb/IV NSCLC vs Taxol in S. Korea (total n=276; Cynviloq
n=140) 230 mg/m
2
+ cis (q3w) vs. Taxol 175 mg/m
2
+ cis; non-inferiority established
1
st
line treatment of OC vs Taxol in S. Korea (total n=100; Cynviloq n=50)
260 mg/m
2
+ carbo (q3w) vs. Taxol 175 mg/m
2
+ carbo; non-inferiority established
Trials established higher MTD in US - Dana Farber Cancer Inst, Russia, & S. Korea
(total n=80)
Completed trials in MBC, NSCLC, PC, OC, BC; in US - Yale Cancer Center, Russia, S.
Korea (total n=259) |
 9
IV bolus at 30 mg/kg; n = 3
Equivalent PK in Mice
Data on file
Cynviloq
Abraxane
Drug
HL (h)
T max (h)
AUCinf
(h*ng/mL)
Vz
(mL/kg)
Cl
(mL/h/kg)
Abraxane
2.99
0.08
61561.33
2103.71
487.32
Cynviloq
2.83
0.08
58151.31
2103.58
515.90 |
 10
Abraxane data from: Nuhad K. Ibrahim, Phase I and Pharmacokinetic Study of
ABI-007, a Cremophor-free, Protein-stabilized, Nanoparticle Formulation of
Paclitaxel. Clinical Cancer Research 2002;8:1038-44
Data from 2 separate studies
(3
h
infusion,
135
mg/m
2
dose,
n=3)
Comparable PK in Humans |
 11
Bioequivalence = Efficient Pathway to Market
BE registration study in breast cancer patients (2014)
-
Duration = 12 months (including patient recruitment)
-
Direct trial cost ~$5M
Abraxane
(n = 50)
Cynviloq
(n = 50)
Cynviloq
Abraxane
Cycle 1
Cycle 2
*
Based on FDA “Draft Guidance on Paclitaxel”
–
September 2012
Endpoints: AUC and
Cmax (90% CI)
Duration: 3 weeks +
crossover for 3 weeks
Infusion time: 30 min
Dose:
260
mg/m
2
Key Parameters*: |
 Potential Cynviloq Advantages
Cynviloq
Abraxane
Taxol
Cynviloq
Advantage
Maximum Tolerated Dose
(mg/m
2
)
>300
260
175
Potential for
higher efficacy
Rapid reconstitution:
no foaming concerns
Convenience for busy
practices and pharmacies
No donor-derived human
serum albumin (HSA)
No viral / prion concerns
Convenient storage
conditions
No requirement for
controlled temp storage
No microbial growth
Chemical polymer
Cremophor-free
Reduced side effects
Dosing
q3w
q3w* &
weekly**
q3w & weekly
Exploits PK advantage
@ higher dose
* = MBC; ** = NSCLC & PC
12 |
 13
Next Steps for Cynviloq
BE study initiation: 1Q 2014
NDA filing: 2015
Product launch (MBC and NSCLC): 2016
sNDA planning for label expansion into pancreatic, bladder, and
ovarian cancers
2016
2016
2014
2015
NDA
Filing
FDA
Approval
BE
Study
LAUNCH |
 Clinical Stage Pain Management Asset
RTX
Intractable
Cancer
Pain
14 |
 15
Two Injection Sites = Two Products for Human Use
Intrathecal
(injection into the
cerebrospinal fluid
space)
(injection into or
nerve the ganglion)
Intraganglionic |
 RTX
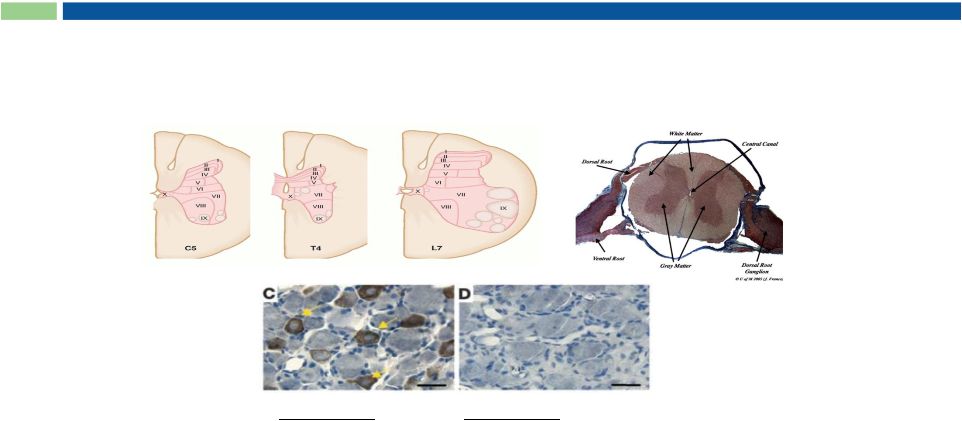
Ablates TRPV1-positive Neurons after Intrathecal Injection
TRPV1
TRPV1
TRPV1
Fore limb
TRPV1 positive
Hind limb
TRPV1 negative
Adapted from Karai et al. 2004
16 |
 17
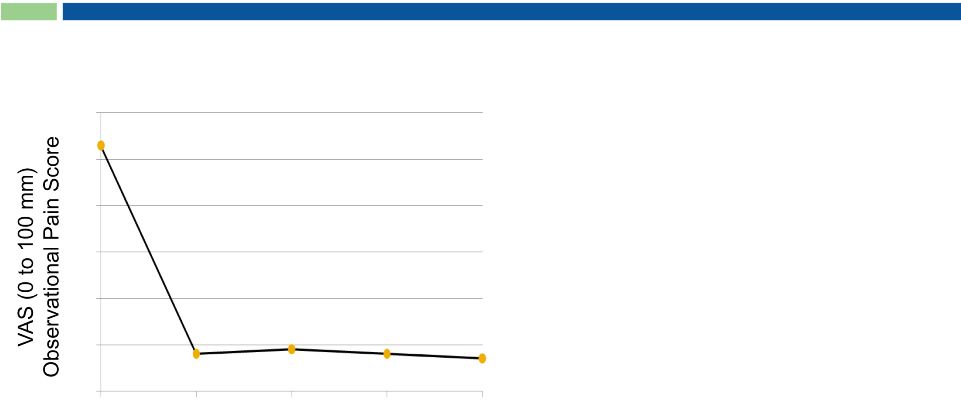
Brown et al, 2005
n=18
n=18
n=8
n=5
n=4
Weeks
(p < 0.0001 for all time points)
100% response rate with single
intrathecal injection
12 dogs reduced or discontinued
analgesics
Dogs passed away due to
underlying osteosarcoma,
not RTX treatment
Permanent analgesic effect
Personality intact
Gait and mood visibly improved
Lack of serious adverse events
No opioid-like side effects
Animal health market represents
separate licensing opportunity
Open-Label Study in Companion Dogs
Intractable pain due to osteosarcoma
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
0
2
6
10
14 |
 18
Unilateral Effect Following Trigeminal Injection
Adapted from Tender et al. 2005
Left eye (blue) vs
Right eye (red)
Nociceptive neuron-
mediated neurogenic
inflammation (Evans blue) |
 Next
Steps for RTX Development ~3 years for clinical
development
19
Filing for MUMS designation for osteosarcoma in dogs
Intractable cancer pain clinical Phase 1/2 trial (intrathecal injection);
n~40 patients Under Sorrento IND
Phase 1/2 trial for osteosarcoma (intraganglionic injection); n~15
patients Intractable cancer pain clinical Phase 1/2 trial (intrathecal
injection); n~13 patients Under NIH CRADA |
 Immunotherapy Programs
G-MAB
& ADC
20
Antibodies
+
Proprietary
Toxins |
 G-MAB: Library of Therapeutic Antibodies
High Value Oncology Targets:
Immune modulation:
PD1 and PD-L1
Antibody Drug Conjugates:
VEGFR2 and c-Met
Size of Target Antigen
Proprietary technology:
RNA amplification used for
library generation
Freedom-To-Operate
Very high library diversity:
2.1 x 10
16
distinct antibodies
Fully human antibodies
High successful screening hit rate
Difficult Targets:
Small Peptides
Most Difficult Targets:
G Protein-Coupled Receptors
(GPCRs)
21
No stacking royalties |
 Competitor mAb
Sorrento mAb
Anti-PD-L1 mAbs Exhibit Potent Activity
Immune Modulation*
Tumor Mouse Model**
* mAbs @ 0.05 mg/mL
** xenograft model using H1975 human NSCLC cells; % inhibition relative to control
mAb treatment *** p<0.05, mean tumor volumes are significantly reduced in
STI-A1010 group versus control groups as determined by Mann-Whitney u-test
22
Day |
 Days After Disease Induction
Sorrento mAb
Untreated
Potent Antibody against Difficult GPCR Target*
mAb
Cell Binding
(EC
50
–
nM)
Sorrento
0.17
Competitor
21
* Sorrento mAb against C-C Chemokine Receptor 2 (CCR2)
** Experimental Auto-immune Encephalomyelitis (EAE) = murine model of Multiple
Sclerosis 23 |
 Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs)
24
Key Components:
Drug released in CANCER CELL
Target-specific internalizing
antibody
Potent cytotoxic prodrugs
Linker and conjugation
chemistries
1.
2.
3. |
 Proprietary High Potency
Duostatin Toxins Duostatins vs. DM1
Duostatins vs. MMAE
Duostatin toxin 1 (K-lock)
>15x higher
potency
Duostatin toxin 2 (K-lock)
DM1 (conventional; NHS)
Duostatin toxin 1 (K-lock)
Duostatin toxin 2 (K-lock)
MMAE (conventional; maleimide)
SKBR3
(Breast Cancer Cell Line)
25 |
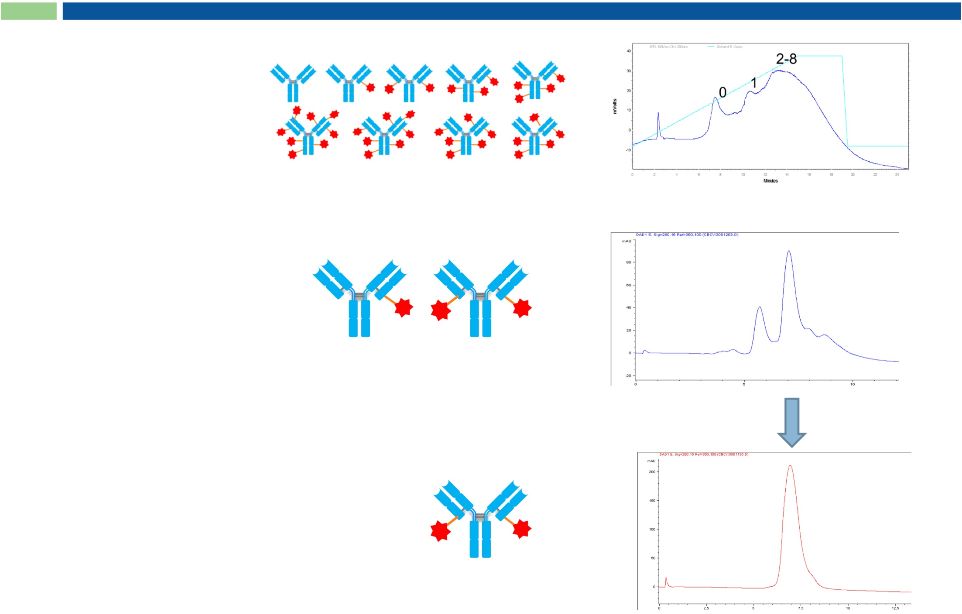 2
purified
K-Lock Conjugation Enables Homogeneous ADCs
0
1
2
3
Current industry
standard chemistry
Proprietary
K-Lock chemistry
Sorrento’s homogenous ADC
No need for:
non-natural amino acids
genetic re-engineering
enzymatic posttranslational modification
26 |
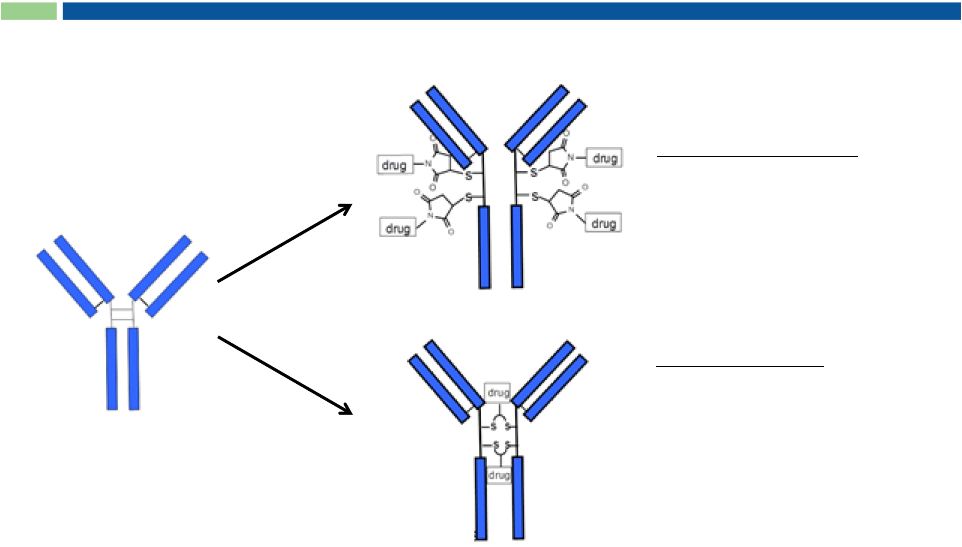 C-Lock Conjugation Stabilizes ADCs
C-lock conjugation
Enhances ADC stability
Prolongs PK profile
Reduced off-target effects
Current industry
standard
Maleimide conjugation
Destabilizes antibody structure
Reduced target specificity
Altered PK profile
Drug-antibody linkage not stable
Off-target drug effects
Sorrento’s
proprietary
C-Lock chemistry
27 |
 Proprietary ADC Screening and Optimization Panels
Fast track to IND
Identification of optimal combination of linker, conjugation chemistry and drug
payload essential for efficient and expedited development
28
from target to candidates |
| 29
Investment Highlights
Intractable Cancer Pain Treatment
Ongoing Phase 1/2 study
Orphan drug status received
Three potential drug products from same API
Targeted Cancer Immunotherapeutics
First therapeutic antibody candidate in clinic 1H 2015
Proprietary
linker/conjugation chemistry for homogenous ADC generation
First ADC in clinic 2H 2015
Late-Stage Cancer Drug
Product launch expected in 1H 2016
Addresses multi-billion dollar paclitaxel market
Abbreviated regulatory pathway (“bioequivalence”) for approval
Cynviloq
RTX
G-MAB
& ADC |
 30
Company Comparables
Company
Small Molecule
Oncology Drug
Antibody
Platform
Targeted
Drug Delivery
Mkt Cap*
Puma:
Pre-revenue
MBC (Phase 3)
~$3.7B
Clovis:
Pre-revenue
NSCLC, MBC (Phase 1)
~$2.9B
MorphoSys:
Pre-revenue
Antibody
Library
~$2.5B
CAT:
Pre-revenue
Antibody
Library
~$1.4B
Domantis:
Pre-revenue
Antibody
Library
~$450M
Seattle Genetics:
Product sales + royalty
ADC
~$6.6B
ImmunoGen:
Royalty only
ADC
~$1.4B
Sorrento: SRNE
NSCLC, MBC
(Ph3/Registration Trial)
Antibody
Library
ADC
~$330M
* based on publicly-available information (03/18/14)
PBYI
CLVS
MOR.DE
Acquired (2006)
Acquired (2007)
SGEN
IMGN |
 DEVELOPING THERAPEUTIC SOLUTIONS TO
HELP MAN'S LIFE COMPANIONS
31 |
 VET
Indications for Resiniferatoxin/Vaccine Programs Ark-001
(Canine Osteosarcoma)
Ark-002
(Canine Osteoarthritis)
Ark-004
(Idiopathic Cystitis in cats)
Ark-006
(Horse Ocular Pain)
Ark-007
(Horse Laminitis)
Ark-005
(Mastitis in cows)
32 |
 33
Disease-Specific Market Factors
Small Animals
*APPA 2012 and Canine Cancer.com
**Veterinary Medicine, Dec 1, 2012
Disease/Drug
Unmet Need
Competition
Prevalence
Level of
Differentiation
Ark-001 (Dogs)
Osteosarcoma/Pain
High
Opiates rare use
Amputation
Alternative
interventions
unsatisfactory
*83 M Pet dogs
1 in 3 have tumors
5% of all tumors=
Osteosarcoma
Approximately 1.35 M
Transformative
Ark-002 (Dogs)
Osteoarthritis/Pain
Moderate to High
NSAIDs
May result in hepatic
and GI toxicity
4 M dogs in active
NSAID treatment
Transformative
Intrathecal inj may
allow for coverage of
all joints
Ark-003 (Dogs)
Recurring
dermatitis/infections
Moderate to High
Antibiotics
Corticosteroids
**MRSA 1.5-2 % of
dogs in community
and Vet hospitals
Moderate to
significant
Ark-004 (Cats)
Interstitial Cystitis
High
Castration/Spaying
Anti-anxiety drugs
Pheromones
Unknown
TBD
May reduce bladder
hyperactivity |
 34
Disease/Drug
Unmet Need
Competition
Prevalence
Level of
Differentiation
Ark-005 (Cows)
Mastitis
High
Antibiotics
Mastitis prevention
programs
Approximately 9.2M
cows and 1/3
infected with mastitis
annually
TBD:
Vaccine delivery may
offer high
differentiation
potential
Ark-006 (Horses)
Ocular Pain/Ocular
abrasions
High
Eye drops
Antibacterial
opthalmic ointments
Lidocaine
High
No reliable estimates
Moderate to High:
Desensitization of
nerves may facilitate
abrasion healing
Ark-007 (Horses)
Laminitis
Moderate to High
Pain Killers including
NSAIDs
Peripheral
vasodilators
*9.2 M horses in US
** 15% will suffer
from laminitis in
lifetime
Potentially high
based on limited
results to date
* Making sense of laminitis; Michelle Andersen, Feb 1
2013 ** US Horse Industry
Statistics- The equestrian channel 2013
Disease-Specific Market Factors
Large Animals |
 Market Valuation of
Competitor Companies Products on
Market
Products in
development
Disease Area
Focus
Time to market
Market Valuation
ARATANA
(PETX)
None
>15
Pain
Appetite Stimulants
etc
Near Term
$513 M
KINDRED
(KIN)
None
10
Pain
Cancer
GI, Allergy
Inflammation
Autoimmune
Near Term
$405 M
ARK ANIMAL
THERAPEUTICS
None
>10
Pain
Osteoarthritis
Infections
Interstitial Cystitis
Mastitis
Ocular Pain
Laminitis
Near Term
IPO Mid year
35 |
 Sorrento Therapeutics
Next-Generation
Cancer Therapeutics
Contact:
Henry Ji
President and CEO
hji@sorrentotherapeutics.com
(858) 668-6923 |
