Attached files
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-Q
| x | Quarterly report pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2012. |
OR
| ¨ | Transition report pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 for the transition period from to . |
Commission File Number: 001-33096
United States Natural Gas Fund, LP
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 20-5576760 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
1999 Harrison Street, Suite 1530
Oakland, California 94612
(Address of principal executive offices) (Zip code)
(510) 522-9600
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
1320 Harbor Bay Parkway, Suite 145
Alameda, California 94502
(Former name, former address and former fiscal year, if changed since last report)
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. x Yes ¨ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). x Yes ¨ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
| Large accelerated filer |
x |
Accelerated filer |
¨ | |||
| Non-accelerated filer |
¨ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) |
Smaller reporting company |
¨ | |||
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). ¨ Yes x No
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES NATURAL GAS FUND, LP
Table of Contents
| Item 1. | Condensed Financial Statements. |
Index to Condensed Financial Statements
1
Table of Contents
United States Natural Gas Fund, LP
Condensed Statements of Financial Condition
At June 30, 2012 (Unaudited) and December 31, 2011
| June 30, 2012 | December 31, 2011 | |||||||
| Assets |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents (Note 5) |
$ | 833,085,151 | $ | 938,678,961 | ||||
| Equity in UBS Securities LLC trading accounts: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
149,970,574 | 206,627,904 | ||||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on open commodity futures and cleared swap contracts |
95,315,512 | (48,992,305 | ) | |||||
| Unrealized gain (loss) on open swap contracts |
10,537,264 | (12,805,692 | ) | |||||
| Receivable for units sold |
85,186,733 | — | ||||||
| Dividend receivable |
9,722 | 8,866 | ||||||
| Interest receivable |
— | 174 | ||||||
| Other assets |
40,682 | 17,216 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total assets |
$ | 1,174,145,638 | $ | 1,083,535,124 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Liabilities and Partners’ Capital |
||||||||
| Investment payable |
$ | — | $ | 772 | ||||
| Payable for units redeemed |
11,145,018 | 8,523,736 | ||||||
| Professional fees payable |
990,543 | 2,064,537 | ||||||
| General Partner management fees payable (Note 3) |
474,028 | 599,523 | ||||||
| Brokerage commissions payable |
150,250 | 166,250 | ||||||
| Interest payable |
153 | 153 | ||||||
| Other liabilities |
37,778 | 83,980 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities |
12,797,770 | 11,438,951 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Commitments and Contingencies (Notes 3, 4, and 5) |
||||||||
| Partners’ Capital |
||||||||
| General Partner |
— | — | ||||||
| Limited Partners |
1,161,347,868 | 1,072,096,173 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Partners’ Capital |
1,161,347,868 | 1,172,096,173 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total liabilities and partners’ capital |
$ | 1,174,145,638 | $ | 1,083,535,124 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Limited Partners’ units outstanding |
60,266,476 | 41,399,457 | * | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net asset value per unit |
$ | 19.27 | $ | 25.88 | * | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Market value per unit |
$ | 19.29 | $ | 25.84 | * | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| * | On February 21, 2012, there was a 4-for-1 reverse unit split. Historical units outstanding, net asset value per unit and market value per unit have been adjusted to reflect the 4-for-1 reverse unit split on a retroactive basis. |
See accompanying notes to condensed financial statements.
2
Table of Contents
United States Natural Gas Fund, LP
Condensed Schedule of Investments (Unaudited)
At June 30, 2012
| Number of Contracts |
Unrealized Gain on Open Commodity Contracts |
% of Partners’ Capital |
||||||||||
| Open Cleared Swap Contracts - Long |
||||||||||||
| Foreign Contracts |
||||||||||||
| ICE Natural Gas Cleared Swap ICE LOT August 2012 contracts, expiring August 2012 |
31,178 | $ | 23,762,812 | 2.05 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Open Futures Contracts - Long |
||||||||||||
| United States Contracts |
||||||||||||
| NYMEX Natural Gas Futures NG August 2012 contracts, expiring July 2012 |
22,244 | 54,662,960 | 4.71 | |||||||||
| NYMEX Natural Gas Futures NN August 2012 contracts, expiring July 2012 |
17,952 | 16,889,740 | 1.45 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 40,196 | 71,552,700 | 6.16 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total Open Cleared Swap and Futures Contracts |
71,374 | $ | 95,315,512 | 8.21 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Principal Amount |
Market Value |
|||||||||||
| Cash Equivalents |
||||||||||||
| United States Treasury Obligation |
||||||||||||
| U.S. Treasury Bill, 0.09%, 10/11/2012* |
$ | 250,020,000 | $ | 249,956,583 | 21.52 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| United States - Money Market Funds |
||||||||||||
| Fidelity Institutional Government Portfolio - Class I |
101,603,169 | 101,603,169 | 8.75 | |||||||||
| Goldman Sachs Financial Square Funds - Government Fund - Class SL |
150,484,587 | 150,484,587 | 12.96 | |||||||||
| Morgan Stanley Institutional Liquidity Fund - Government Portfolio |
150,454,215 | 150,454,215 | 12.95 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total Money Market Funds |
402,541,971 | 34.66 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total Cash Equivalents |
$ | 652,498,554 | 56.18 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
Open Over-the-Counter Total Return Swap Contracts
| Notional Amount** |
Market Value |
Unrealized Gain |
Termination Dates |
|||||||||||||
| Swap agreement to receive return on the Custom |
||||||||||||||||
| Natural Gas Index (UNG) - Excess Return |
$ | 104,219,616 | $ | 964,369 | $ | 964,369 | 10/24/2012 | |||||||||
| Swap agreement to receive return on the |
||||||||||||||||
| NYMEX Henry Hub Natural Gas Futures |
||||||||||||||||
| Contract |
71,572,422 | 9,572,895 | 9,572,895 | 8/31/2012 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| Total unrealized gain on open swap contracts |
$ | 10,537,264 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||
| * | Security or partial security segregated as collateral for open over-the-counter total return swap contracts. |
| ** | The aggregate notional amount of USNG’s over-the-counter swap transactions represented 14.97% of USNG’s total assets as of June 30, 2012. |
See accompanying notes to condensed financial statements.
3
Table of Contents
United States Natural Gas Fund, LP
Condensed Statements of Operations (Unaudited)
For the three and six months ended June 30, 2012 and 2011
| Three months ended June 30, 2012 |
Three months ended June 30, 2011 |
Six months ended June 30, 2012 |
Six months ended June 30, 2011 |
|||||||||||||
| Income |
||||||||||||||||
| Gain (loss) on trading of commodity contracts: |
||||||||||||||||
| Realized gain (loss) on closed futures contracts |
$ | (21,525,095 | ) | $ | 56,484,270 | $ | (320,916,173 | ) | $ | 59,088,085 | ||||||
| Realized gain (loss) on closed swap contracts |
5,092,756 | 3,898,665 | (86,284,041 | ) | (25,001,019 | ) | ||||||||||
| Change in unrealized gain (loss) on open futures contracts |
178,004,797 | (84,138,356 | ) | 144,307,817 | (111,622,973 | ) | ||||||||||
| Change in unrealized gain (loss) on open swap contracts |
26,708,280 | (26,685,181 | ) | 23,342,956 | (31,297,867 | ) | ||||||||||
| Dividend income |
28,497 | 33,816 | 52,798 | 148,738 | ||||||||||||
| Interest income |
34,732 | 59,864 | 64,870 | 157,859 | ||||||||||||
| Other income |
64,000 | 39,000 | 106,000 | 97,000 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total income (loss) |
188,407,967 | (50,307,922 | ) | (239,325,773 | ) | (108,430,177 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Expenses |
||||||||||||||||
| General Partner management fees (Note 3) |
1,335,505 | 2,744,152 | 2,715,198 | 5,928,503 | ||||||||||||
| Brokerage commissions |
929,220 | 1,164,253 | 1,950,611 | 2,561,036 | ||||||||||||
| Professional fees |
318,278 | 649,239 | 614,919 | 1,347,478 | ||||||||||||
| Other expenses |
72,810 | 216,489 | 133,852 | 500,203 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Total expenses |
2,655,813 | 4,774,133 | 5,414,580 | 10,337,220 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 185,752,154 | $ | (55,082,055 | ) | $ | (244,740,353 | ) | $ | (118,767,397 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net income (loss) per limited partnership unit |
$ | 3.26 | $ | (1.92 | )* | $ | (6.61 | ) $ | (3.92 | )* | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Net income (loss) per weighted average limited partnership unit |
$ | 3.48 | $ | (1.24 | )* | $ | (5.02 | ) $ | (2.44 | )* | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Weighted average limited partnership units outstanding |
53,337,905 | 44,421,435 | * | 48,714,755 | 48,531,522 | * | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| * | On February 21, 2012, there was a 4-for-1 reverse unit split. The Condensed Statements of Operations (Unaudited) have been adjusted for the period shown to reflect the 4-for-1 reverse unit split on a retroactive basis. |
See accompanying notes to condensed financial statements.
4
Table of Contents
United States Natural Gas Fund, LP
Condensed Statement of Changes in Partners’ Capital (Unaudited)
For the six months ended June 30, 2012
| General Partner | Limited Partners | Total | ||||||||||
| Balances, at December 31, 2011 |
$ | — | $ | 1,072,096,173 | $ | 1,072,096,173 | ||||||
| Addition of 96,000,000 partnership units |
— | 1,202,813,181 | 1,202,813,181 | |||||||||
| Redemption of 201,331,352 partnership units |
— | (868,821,133 | ) | (868,821,133 | ) | |||||||
| Net loss |
— | (244,740,353 | ) | (244,740,353 | ) | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Balances, at June 30, 2012 |
$ | — | $ | 1,161,347,868 | $ | 1,161,347,868 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net Asset Value Per Unit: |
||||||||||||
| At December 31, 2011 |
$ | 25.88 | * | |||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| At June 30, 2012 |
$ | 19.27 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| * | On February 21, 2012, there was a 4-for-1 reverse unit split. The Condensed Statement of Changes in Partners’ Capital (Unaudited) have been adjusted for the period shown to reflect the 4-for-1 reverse unit split on a retroactive basis. |
See accompanying notes to condensed financial statements.
5
Table of Contents
United States Natural Gas Fund, LP
Condensed Statements of Cash Flows (Unaudited)
For the six months ended June 30, 2012 and 2011
| Six months ended June 30, 2012 |
Six months ended June 30, 2011 |
|||||||
| Cash Flows from Operating Activities: |
||||||||
| Net loss |
$ | (244,740,353 | ) | $ | (118,767,397 | ) | ||
| Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash provided by (used in) operating activities: |
||||||||
| Decrease in commodity futures trading account - cash and cash equivalents |
56,657,330 | 98,208,951 | ||||||
| Unrealized (gain) loss on futures contracts |
(144,307,817 | ) | 111,622,973 | |||||
| Unrealized (gain) loss on open swap contracts |
(23,342,956 | ) | 31,297,867 | |||||
| Decrease in investment receivable |
— | 16,538,472 | ||||||
| (Increase) decrease in dividend receivable |
(856 | ) | 45,093 | |||||
| Decrease in interest receivable |
174 | — | ||||||
| (Increase) decrease in other assets |
(23,466 | ) | 61,432 | |||||
| Increase (decrease) in investment payable |
(772 | ) | 29,146,529 | |||||
| Decrease in professional fees payable |
(1,073,994 | ) | (731,163 | ) | ||||
| Decrease in General Partner management fees payable |
(125,495 | ) | (377,252 | ) | ||||
| Decrease in brokerage commissions payable |
(16,000 | ) | (40,000 | ) | ||||
| Decrease in other liabilities |
(46,202 | ) | (40,115 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
(357,020,407 | ) | 166,965,390 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash Flows from Financing Activities: |
||||||||
| Addition of partnership units |
1,117,626,448 | 822,486,194 | ||||||
| Redemption of partnership units |
(866,199,851 | ) | (1,604,866,410 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) financing activities |
251,426,597 | (782,380,216 | ) | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net Decrease in Cash and Cash Equivalents |
(105,593,810 | ) | (615,414,826 | ) | ||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents, beginning of period |
938,678,961 | 2,320,745,778 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents, end of period |
$ | 833,085,151 | $ | 1,705,330,952 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
See accompanying notes to condensed financial statements.
6
Table of Contents
United States Natural Gas Fund, LP
Notes to Condensed Financial Statements
For the period ended June 30, 2012 (Unaudited)
NOTE 1 — ORGANIZATION AND BUSINESS
The United States Natural Gas Fund, LP (“USNG”) was organized as a limited partnership under the laws of the state of Delaware on September 11, 2006. USNG is a commodity pool that issues limited partnership units (“units”) that may be purchased and sold on the NYSE Arca, Inc. (the “NYSE Arca”). Prior to November 25, 2008, USNG’s units traded on the American Stock Exchange (the “AMEX”). USNG will continue in perpetuity, unless terminated sooner upon the occurrence of one or more events as described in its Third Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership dated as of December 31, 2010 (the “LP Agreement”). The investment objective of USNG is for the daily changes in percentage terms of its units’ per unit net asset value (“NAV”) to reflect the daily changes in percentage terms of the spot price of natural gas delivered at the Henry Hub, Louisiana as measured by the daily changes in the price of the futures contract on natural gas as traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange (the “NYMEX”), that is the near month contract to expire, except when the near month contract is within two weeks of expiration, in which case the futures contract will be the next month contract to expire (the “Benchmark Futures Contract”), less USNG’s expenses. It is not the intent of USNG to be operated in a fashion such that the per unit NAV will equal, in dollar terms, the spot price of natural gas or any particular futures contract based on natural gas. It is not the intent of USNG to be operated in a fashion such that its per unit NAV will reflect the percentage change of the price of any particular futures contract as measured over a time period greater than one day. United States Commodity Funds LLC (“USCF”), the general partner of USNG, believes that it is not practical to manage the portfolio to achieve such an investment goal when investing in Futures Contracts (as defined below) and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments (as defined below). USNG accomplishes its objective through investments in futures contracts for natural gas, crude oil, heating oil, gasoline and other petroleum-based fuels that are traded on the NYMEX, ICE Futures or other U.S. and foreign exchanges (collectively, “Futures Contracts”) and other natural gas-related investments such as cash-settled options on Futures Contracts, forward contracts for natural gas, cleared swap contracts and over-the-counter transactions that are based on the price of natural gas, crude oil and other petroleum-based fuels, Futures Contracts and indices based on the foregoing (collectively, “Other Natural Gas-Related Investments”). As of June 30, 2012, USNG held 22,244 NG Futures August 2012 Contracts and 17,952 NN Financially Settled Futures August 2012 Contracts traded on the NYMEX, 31,178 cleared swap contracts traded on the ICE Futures, and over-the-counter swap transactions with two counterparties, JPMorgan Chase Bank, NA (“JPMorgan”) and Deutsche Bank AG (“Deutsche Bank”).
USNG commenced investment operations on April 18, 2007 and has a fiscal year ending on December 31. USCF is responsible for the management of USNG. USCF is a member of the National Futures Association (the “NFA”) and became a commodity pool operator registered with the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (the “CFTC”) effective December 1, 2005. USCF is also the general partner of the United States Oil Fund, LP (“USOF”), the United States 12 Month Oil Fund, LP (“US12OF”), the United States Gasoline Fund, LP (“UGA”) and the United States Diesel-Heating Oil Fund, LP (formerly, the United States Heating Oil Fund, LP) (“USDHO”), which listed their limited partnership units on the AMEX under the ticker symbols “USO” on April 10, 2006, “USL” on December 6, 2007, “UGA” on February 26, 2008 and “UHN” on April 9, 2008, respectively. As a result of the acquisition of the AMEX by NYSE Euronext, each of USOF’s, US12OF’s, UGA’s and USDHO’s units commenced trading on the NYSE Arca on November 25, 2008. USCF is also the general partner of the United States Short Oil Fund, LP (“USSO”), the United States 12 Month Natural Gas Fund, LP (“US12NG”) and the United States Brent Oil Fund, LP (“USBO”), which listed their limited partnership units on the NYSE Arca under the ticker symbols “DNO” on September 24, 2009, “UNL” on November 18, 2009 and “BNO” on June 2, 2010, respectively. USCF is also the sponsor of the United States Commodity Index Fund (“USCI”), the United States Copper Index Fund (“CPER”), the United States Agriculture Index Fund (“USAG”) and the United States Metals Index Fund (“USMI”), each a series of the United States Commodity Index Funds Trust. USCI, CPER, USAG and USMI listed their units on the NYSE Arca under the ticker symbol “USCI” on August 10, 2010, “CPER” on November 15, 2011, “USAG” on April 13, 2012 and “USMI” on June 19, 2012, respectively. All funds listed previously are referred to collectively herein as the “Related Public Funds.” USCF has also filed registration statements to register units of the United States Sugar Fund (“USSF”), the United States Natural Gas Double Inverse Fund (“UNGD”), the United States Gasoil Fund (“USGO”) and the United States Asian Commodities Basket Fund (“UAC”), each a series of the United States Commodity Funds Trust I and the US Golden Currency Fund (“USGCF”), a series of the United States Currency Funds Trust.
7
Table of Contents
USNG issues units to certain authorized purchasers (“Authorized Purchasers”) by offering baskets consisting of 100,000 units (“Creation Baskets”) through ALPS Distributors, Inc., as the marketing agent (the “Marketing Agent”). The purchase price for a Creation Basket is based upon the NAV of a unit calculated shortly after the close of the core trading session on the NYSE Arca on the day the order to create the basket is properly received.
In addition, Authorized Purchasers pay USNG a $1,000 fee for each order placed to create one or more Creation Baskets or to redeem one or more baskets (“Redemption Baskets”), consisting of 100,000 units. Units may be purchased or sold on a nationally recognized securities exchange in smaller increments than a Creation Basket or Redemption Basket. Units purchased or sold on a nationally recognized securities exchange are not purchased or sold at the per unit NAV of USNG but rather at market prices quoted on such exchange.
In April 2007, USNG initially registered 30,000,000 units on Form S-1 with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). On April 18, 2007, USNG listed its units on the AMEX under the ticker symbol “UNG”. On that day, USNG established its initial per unit NAV by setting the price at $50.00 and issued 200,000 units in exchange for $10,001,000. USNG also commenced investment operations on April 18, 2007, by purchasing Futures Contracts traded on the NYMEX based on natural gas. As of June 30, 2012, USNG had registered a total of 1,480,000,000 units.
On March 8, 2011, after the close of trading on the NYSE Arca, USNG effected a 2-for-1 reverse unit split and post-split units of USNG began trading on March 9, 2011. As a result of the reverse unit split, every two pre-split units of USNG were automatically exchanged for one post-split unit. Immediately prior to the reverse split, there were 447,200,000 units of USNG issued and outstanding, representing a per unit NAV of $5.16. Immediately after the reverse unit split, the number of issued and outstanding units of USNG decreased to 223,600,000, not accounting for fractional units, and the per unit NAV increased to $10.31. In connection with the reverse split, the CUSIP number of USNG’s units changed to 912318110. USNG’s ticker symbol, “UNG,” remains the same.
On February 21, 2012, after the close of trading on the NYSE Arca, USNG effected a 4-for-1 reverse unit split and post-split units of USNG began trading on February 22, 2012. As a result of the reverse unit split, every four pre-split units of USNG were automatically exchanged for one post-split unit. Immediately prior to the reverse split, there were 174,297,828 units of USNG issued and outstanding, representing a per unit NAV of $5.51. Immediately after the reverse unit split, the number of issued and outstanding units of USNG decreased to 43,574,457, not accounting for fractional units, and the per unit NAV increased to $22.06. In connection with the reverse unit split, the CUSIP number of USNG’s units changed to 912318201. USNG’s ticker symbol, “UNG,” remains the same.
The accompanying unaudited condensed financial statements have been prepared in accordance with Rule 10-01 of Regulation S-X promulgated by the SEC and, therefore, do not include all information and footnote disclosure required under generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”) in the United States of America. The financial information included herein is unaudited; however, such financial information reflects all adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments, which are, in the opinion of USCF, necessary for the fair presentation of the condensed financial statements for the interim period.
NOTE 2 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Revenue Recognition
Commodity futures contracts, forward contracts, physical commodities and related options are recorded on the trade date. All such transactions are recorded on the identified cost basis and marked to market daily. Unrealized gains or losses on open contracts are reflected in the condensed statements of financial condition and represent the difference between the original contract amount and the market value (as determined by exchange settlement prices for futures contracts and related options and cash dealer prices at a predetermined time for forward contracts, physical commodities, and their related options) as of the last business day of the year or as of the last date of the condensed financial statements. Changes in the unrealized gains or losses between periods are reflected in the condensed statements of operations. USNG earns interest on its assets denominated in U.S. dollars on deposit with the futures commission merchant at the overnight Federal Funds Rate less 32 basis points. In addition, USNG earns income on funds held at the custodian or futures commission merchant at prevailing market rates earned on such investments.
8
Table of Contents
Investments in over-the-counter total return swap contracts (see Note 5) are arrangements to exchange a periodic payment for a market-linked return, each based on a notional amount. To the extent that the total return of the commodity future, security or index underlying the transaction exceeds or falls short of the offsetting periodic payment obligation, USNG receives a payment from, or makes a payment to, the swap counterparty. The over-the-counter swap contracts are valued daily based upon the appreciation or depreciation of the underlying securities subsequent to the effective date of the contract. Changes in the value of the swaps are reported as unrealized gains and losses and periodic payments are recorded as realized gains or losses in the accompanying condensed statements of operations.
Brokerage Commissions
Brokerage commissions on all open commodity futures contracts are accrued on a full-turn basis.
Swap Premiums
Upfront fees paid by USNG for over-the-counter swap contracts are reflected on the condensed statements of financial condition and represent payments made upon entering into a swap agreement to compensate for differences between the stated terms of the agreement and prevailing market conditions. The fees are amortized daily over the term of the swap agreement.
Income Taxes
USNG is not subject to federal income taxes; each partner reports his/her allocable share of income, gain, loss deductions or credits on his/her own income tax return.
In accordance with GAAP, USNG is required to determine whether a tax position is more likely than not to be sustained upon examination by the applicable taxing authority, including resolution of any tax related appeals or litigation processes, based on the technical merits of the position. USNG files an income tax return in the U.S. federal jurisdiction, and may file income tax returns in various U.S. states. USNG is not subject to income tax return examinations by major taxing authorities for years before 2008. The tax benefit recognized is measured as the largest amount of benefit that has a greater than fifty percent likelihood of being realized upon ultimate settlement. De-recognition of a tax benefit previously recognized results in USNG recording a tax liability that reduces net assets. However, USNG’s conclusions regarding this policy may be subject to review and adjustment at a later date based on factors including, but not limited to, on-going analysis of and changes to tax laws, regulations and interpretations thereof. USNG recognizes interest accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in income tax fees payable, if assessed. No interest expense or penalties have been recognized as of and for the period ended June 30, 2012.
Creations and Redemptions
Authorized Purchasers may purchase Creation Baskets or redeem Redemption Baskets only in blocks of 100,000 units at a price equal to the NAV of the units calculated shortly after the close of the core trading session on the NYSE Arca on the day the order is placed.
USNG receives or pays the proceeds from units sold or redeemed within three business days after the trade date of the purchase or redemption. The amounts due from Authorized Purchasers are reflected in USNG’s condensed statements of financial condition as receivable for units sold, and amounts payable to Authorized Purchasers upon redemption are reflected as payable for units redeemed.
Partnership Capital and Allocation of Partnership Income and Losses
Profit or loss shall be allocated among the partners of USNG in proportion to the number of units each partner holds as of the close of each month. USCF may revise, alter or otherwise modify this method of allocation as described in the LP Agreement.
Calculation of Per Unit Net Asset Value
USNG’s per unit NAV is calculated on each NYSE Arca trading day by taking the current market value of its total assets, subtracting any liabilities and dividing that amount by the total number of units outstanding. USNG uses the closing price for the contracts on the relevant exchange on that day to determine the value of contracts held on such exchange.
9
Table of Contents
Net Income (Loss) Per Unit
Net income (loss) per unit is the difference between the per unit NAV at the beginning of each period and at the end of each period. The weighted average number of units outstanding was computed for purposes of disclosing net income (loss) per weighted average unit. The weighted average units are equal to the number of units outstanding at the end of the period, adjusted proportionately for units added and redeemed based on the amount of time the units were outstanding during such period. There were no units held by USCF at June 30, 2012.
Offering Costs
Offering costs incurred in connection with the registration of additional units after the initial registration of units are borne by USNG. These costs include registration fees paid to regulatory agencies and all legal, accounting, printing and other expenses associated with such offerings. These costs are accounted for as a deferred charge and thereafter amortized to expense over twelve months on a straight-line basis or a shorter period if warranted.
Cash Equivalents
Cash equivalents include money market funds and overnight deposits or time deposits with original maturity dates of six months or less.
Reclassification
Certain amounts in the accompanying condensed financial statements were reclassified to conform to the current presentation.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of condensed financial statements in conformity with GAAP requires USCF to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amount of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the condensed financial statements, and the reported amounts of the revenue and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results may differ from those estimates and assumptions.
Other
On March 8, 2011, after the close of the NYSE Arca, USNG effected a 2-for-1 reverse unit split and post-split units of USNG began trading on March 9, 2011. The unaudited condensed financial information in this quarterly report on Form 10-Q gives effect to the reverse split and the post-split of units as if they had been completed on January 1, 2011.
On February 21, 2012, after the close of the NYSE Arca, USNG effected a 4-for-1 reverse unit split and post-split units of USNG began trading on February 22, 2012. The unaudited condensed financial information reported in this quarterly report on Form 10-Q gives effect to the reverse split and the post-split of units as if they had been completed on January 1, 2011.
The unaudited condensed financial information and pro forma financial information, as well as the historical financial information as of and for the year ended December 31, 2011, was derived from USNG’s historical financial statements and has been audited by Spicer Jeffries LLP. The financial information as of and for the six months ended June 30, 2012 is unaudited. The condensed financial statements in this quarterly report on Form 10-Q are presented in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification 260 for purposes of presenting the 2-for-1 reverse split and the 4-for-1 reverse split, respectively, on a historical basis for all periods reported.
NOTE 3 — FEES PAID BY THE FUND AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
USCF Management Fee
Under the LP Agreement, USCF is responsible for investing the assets of USNG in accordance with the objectives and policies of USNG. In addition, USCF has arranged for one or more third parties to provide administrative, custody, accounting, transfer agency and other necessary services to USNG. For these services, USNG is contractually obligated to pay USCF a fee, which is paid monthly, that is equal to 0.60% per annum of average daily total net assets of $1,000,000,000 or less and 0.50% per annum of average daily total net assets that are greater than $1,000,000,000.
10
Table of Contents
Ongoing Registration Fees and Other Offering Expenses
USNG pays all costs and expenses associated with the ongoing registration of its units subsequent to the initial offering. These costs include registration or other fees paid to regulatory agencies in connection with the offer and sale of units, and all legal, accounting, printing and other expenses associated with such offer and sale. For the six months ended June 30, 2012 and 2011, USNG incurred $0 and $56,110, respectively, in registration fees and other offering expenses.
Directors’ Fees and Expenses
USNG is responsible for paying its portion of the directors’ and officers’ liability insurance for USNG and the Related Public Funds and the fees and expenses of the independent directors who also serve as audit committee members of USNG and the Related Public Funds organized as limited partnerships and, as of July 8, 2011, the Related Public Funds organized as a series of a Delaware statutory trust. USNG shares the fees and expenses with each Related Public Fund, as described above, based on the relative assets of each fund computed on a daily basis. These fees and expenses for the year ending December 31, 2012 are estimated to be a total of $540,000 for USNG and the Related Public Funds.
Licensing Fees
As discussed in Note 4 below, USNG entered into a licensing agreement with the NYMEX on April 10, 2006, as amended on October 20, 2011. Pursuant to the agreement, through October 19, 2011, USNG and the Related Public Funds, other than USBO, USCI, CPER, USAG and USMI, paid a licensing fee that was equal to 0.04% for the first $1,000,000,000 of combined net assets of the funds and 0.02% for combined net assets above $1,000,000,000. On and after October 20, 2011, USNG and the Related Public Funds, other than USBO, USCI, CPER, USAG and USMI, pay a licensing fee that is equal to 0.015% on all net assets. During the six months ended June 30, 2012 and 2011, USNG incurred $68,000 and $267,191, respectively, under this arrangement.
Investor Tax Reporting Cost
The fees and expenses associated with USNG’s audit expenses and tax accounting and reporting requirements are paid by USNG. These costs are estimated to be $1,600,000 for the year ending December 31, 2012.
Other Expenses and Fees
In addition to the fees described above, USNG pays all brokerage fees, transaction costs for over-the-counter swaps and other expenses in connection with the operation of USNG, including the costs incurred with the preparation and execution of the reverse split, but excluding costs and expenses paid by USCF as outlined in Note 4 below.
NOTE 4 — CONTRACTS AND AGREEMENTS
USNG is party to a marketing agent agreement, dated as of April 17, 2007, as amended from time to time, with the Marketing Agent and USCF, whereby the Marketing Agent provides certain marketing services for USNG as outlined in the agreement. The fee of the Marketing Agent, which is borne by USCF, is equal to 0.06% on USNG’s assets up to $3 billion and 0.04% on USNG’s assets in excess of $3 billion.
The above fee does not include the following expenses, which are also borne by USCF: the cost of placing advertisements in various periodicals; web construction and development; or the printing and production of various marketing materials.
USNG is also party to a custodian agreement, dated March 5, 2007, as amended from time to time, with Brown Brothers Harriman & Co. (“BBH&Co.”) and USCF, whereby BBH&Co. holds investments on behalf of USNG. USCF pays the fees of the custodian, which are determined by the parties from time to time. In addition, USNG is party to an administrative agency agreement, dated March 5, 2007, as amended from time to time, with USCF and BBH&Co., whereby BBH&Co. acts as the administrative agent, transfer agent and registrar for USNG. USCF also pays the fees of BBH&Co. for its services under such agreement and such fees are determined by the parties from time to time.
Currently, USCF pays BBH&Co. for its services, in the foregoing capacities, a minimum amount of $75,000 annually for its custody, fund accounting and fund administration services rendered to USNG and each of the Related Public Funds, as well as a $20,000 annual fee for its transfer agency services. In addition, USCF pays BBH&Co. an asset-based charge of (a) 0.06% for the first $500 million of USNG’s, USOF’s, US12OF’s, UGA’s, USDHO’s, USSO’s, US12NG’s, USBO’s, USCI’s, CPER’s, USAG’s and USMI’s combined net assets, (b) 0.0465% for USNG’s, USOF’s, US12OF’s, UGA’s, USDHO’s, USSO’s, US12NG’s, USBO’s, USCI’s, CPER’s, USAG’s and USMI’s combined net assets greater than $500 million but less than $1 billion, and (c) 0.035% once USNG’s, USOF’s, US12OF’s, UGA’s, USDHO’s, USSO’s, US12NG’s, USBO’s, USCI’s, CPER’s, USAG’s and USMI’s combined net assets exceed $1 billion. The annual minimum amount will not apply if the asset-based charge for all accounts in the aggregate exceeds $75,000. USCF also pays transaction fees ranging from $7 to $15 per transaction.
11
Table of Contents
USNG has entered into a brokerage agreement with UBS Securities LLC (“UBS Securities”). The agreement requires UBS Securities to provide services to USNG in connection with the purchase and sale of Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments that may be purchased and sold by or through UBS Securities for USNG’s account. In accordance with the agreement, UBS Securities charges USNG commissions of approximately $7 to $15 per round-turn trade, including applicable exchange and NFA fees for Futures Contracts and options on Futures Contracts. Such fees include those incurred when purchasing Futures Contracts and options on Futures Contracts when USNG issues units as a result of a Creation Basket, as well as fees incurred when selling Futures Contracts and options on Futures Contracts when USNG redeems units as a result of a Redemption Basket. Such fees are also incurred when Futures Contracts and options on Futures Contracts are purchased or redeemed for the purpose of rebalancing the portfolio. USNG also incurs commissions to brokers for the purchase and sales of Futures Contracts, Other Natural Gas-Related Investments or Treasuries. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, total commissions accrued to brokers amounted to $1,950,611. Of this amount, $1,690,243 was a result of rebalancing costs and $260,368 was the result of trades necessitated by creation and redemption activity. By comparison, during the six months ended June 30, 2011, total commissions accrued to brokers amounted to $2,561,036. The decrease in the total commissions accrued to brokers for the six months ended June 30, 2012, as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2011, was primarily a function of decreased brokerage fees due to a lower number of Natural Gas Interests being held and traded during the six months ended June 30, 2012. As an annualized percentage of average daily total net assets, the figure for the six months ended June 30, 2012 represents approximately 0.43% of average daily total net assets. By comparison, the figure for the six months ended June 30, 2011 represented approximately 0.24% of average daily total net assets. However, there can be no assurance that commission costs and portfolio turnover will not cause commission expenses to rise in future quarters.
USNG and the NYMEX entered into a licensing agreement on April 10, 2006, as amended on October 20, 2011, whereby USNG was granted a non-exclusive license to use certain of the NYMEX’s settlement prices and service marks. Under the licensing agreement, USNG and the Related Public Funds, other than USBO, USCI, CPER, USAG and USMI, pay the NYMEX an asset-based fee for the license, the terms of which are described in Note 3. USNG expressly disclaims any association with the NYMEX or endorsement of USNG by the NYMEX and acknowledges that “NYMEX” and “New York Mercantile Exchange” are registered trademarks of the NYMEX.
NOTE 5 — FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS, OFF-BALANCE SHEET RISKS AND CONTINGENCIES
USNG engages in the trading of futures contracts, options on futures contracts, cleared swaps and over-the-counter swaps (collectively, “derivatives”). USNG is exposed to both market risk, which is the risk arising from changes in the market value of the contracts, and credit risk, which is the risk of failure by another party to perform according to the terms of a contract.
USNG may enter into futures contracts, options on futures contracts, cleared swaps and over-the-counter swaps to gain exposure to changes in the value of an underlying commodity. A futures contract obligates the seller to deliver (and the purchaser to accept) the future delivery of a specified quantity and type of a commodity at a specified time and place. Some futures contracts may call for physical delivery of the asset, while others are settled in cash. The contractual obligations of a buyer or seller may generally be satisfied by taking or making physical delivery of the underlying commodity or by making an offsetting sale or purchase of an identical futures contract on the same or linked exchange before the designated date of delivery. Cleared swaps are over-the-counter agreements that are eligible to be cleared by a clearinghouse, e.g., ICE Clear Europe, but which are not traded on an exchange. A cleared swap is created when the parties to an off-exchange over-the-counter transaction agree to extinguish their over-the-counter contract and replace it with a cleared swap. Cleared swaps are intended to provide the efficiencies and benefits that centralized clearing on an exchange offers to traders of futures contracts, including credit risk intermediation and the ability to offset positions initiated with different counterparties.
The purchase and sale of futures contracts, options on futures contracts and cleared swaps require margin deposits with a futures commission merchant. Additional deposits may be necessary for any loss on contract value. The Commodity Exchange Act requires a futures commission merchant to segregate all customer transactions and assets from the futures commission merchant’s proprietary activities.
12
Table of Contents
Futures contracts and cleared swaps involve, to varying degrees, elements of market risk (specifically commodity price risk) and exposure to loss in excess of the amount of variation margin. The face or contract amounts reflect the extent of the total exposure USNG has in the particular classes of instruments. Additional risks associated with the use of futures contracts are an imperfect correlation between movements in the price of the futures contracts and the market value of the underlying securities and the possibility of an illiquid market for a futures contract.
All of USNG’s investment contracts were exchange-traded futures contracts, cleared swaps or fully-collateralized over-the-counter swaps through June 30, 2012. The liquidity and credit risks associated with exchange-traded contracts and cleared swaps are generally perceived to be less than those associated with over-the-counter transactions since, in over-the-counter transactions, a party must rely solely on the credit of its respective individual counterparties. At June 30, 2012, USNG maintained over-the-counter transactions with two counterparties, JPMorgan and Deutsche Bank. Over-the-counter transactions subject USNG to the credit risk associated with counterparty non-performance. The credit risk from counterparty non-performance associated with such instruments is the net unrealized gain, if any, on the transaction. USNG has credit risk under its futures contracts since the sole counterparty to all domestic and foreign futures contracts is the clearinghouse for the exchange on which the relevant contracts are traded. However, as compared to its over-the-counter transactions, it may more easily realize value by reselling its futures contracts. In addition, USNG bears the risk of financial failure by the clearing broker.
At June 30, 2012, USNG’s counterparties posted $9,100,249 in cash and $0 in securities as collateral with USNG’s custodian, as compared with $506 in cash and $0 in securities at June 30, 2011. Under these over-the-counter swap agreements, USNG posted collateral with respect to its obligations of $13,905,308 in cash and $18,471,865 in securities, such as Treasuries, at June 30, 2012, as compared with $151,376,650 in cash and $35,259,611 in securities at June 30, 2011.
USNG’s cash and other property, such as short-term obligations of the United States of two years or less (“Treasuries”), deposited with a futures commission merchant are considered commingled with all other customer funds, subject to the futures commission merchant’s segregation requirements. In the event of a futures commission merchant’s insolvency, recovery may be limited to a pro rata share of segregated funds available. It is possible that the recovered amount could be less than the total of cash and other property deposited. The insolvency of a futures commission merchant could result in the complete loss of USNG’s assets posted with that futures commission merchant; however, the majority of USNG’s assets are held in Treasuries, cash and/or cash equivalents with USNG’s custodian and would not be impacted by the insolvency of a futures commission merchant. The failure or insolvency of USNG’s custodian, however, could result in a substantial loss of USNG’s assets.
USCF invests a portion of USNG’s cash in money market funds that seek to maintain a stable per unit NAV. USNG is exposed to any risk of loss associated with an investment in such money market funds. As of June 30, 2012 and December 31, 2011, USNG held investments in money market funds in the amounts of $402,541,971 and $602,490,800, respectively. USNG also holds cash deposits with its custodian. Pursuant to a written agreement with BBH&Co., uninvested overnight cash balances are swept to offshore branches of U.S. regulated and domiciled banks located in Toronto, Canada, London, United Kingdom, Grand Cayman, Cayman Islands and Nassau, Bahamas, which are subject to U.S. regulation and regulatory oversight. As of June 30, 2012 and December 31, 2011, USNG held cash deposits and investments in Treasuries in the amounts of $580,513,754 and $542,816,065, respectively, with the custodian and futures commission merchant. Some or all of these amounts may be subject to loss should USNG’s custodian and/or futures commission merchant cease operations.
For derivatives, risks arise from changes in the market value of the contracts. Theoretically, USNG is exposed to market risk equal to the value of futures contracts purchased and unlimited liability on such contracts sold short. As both a buyer and a seller of options, USNG pays or receives a premium at the outset and then bears the risk of unfavorable changes in the price of the contract underlying the option.
USNG’s policy is to continuously monitor its exposure to market and counterparty risk through the use of a variety of financial, position and credit exposure reporting controls and procedures. In addition, USNG has a policy of requiring review of the credit standing of each broker or counterparty with which it conducts business.
13
Table of Contents
The financial instruments held by USNG are reported in its condensed statements of financial condition at market or fair value, or at carrying amounts that approximate fair value, because of their highly liquid nature and short-term maturity.
NOTE 6 — FINANCIAL HIGHLIGHTS
The following table presents per unit performance data and other supplemental financial data for the six months ended June 30, 2012 and 2011 for the unitholders. This information has been derived from information presented in the condensed financial statements.
| For the six months ended June 30, 2012 (Unaudited) |
For the six months ended June 30, 2011 (Unaudited) |
|||||||
| Per Unit Operating Performance: |
||||||||
| Net asset value, beginning of period |
$ | 25.88 | * | $ | 48.00 | * | ||
| Total income (loss) |
(6.50 | ) | (3.71 | )* | ||||
| Total expenses |
(0.11 | ) | (0.21 | )* | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net decrease in net asset value |
(6.61 | ) | (3.92 | )* | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net asset value, end of period |
$ | 19.27 | $ | 44.08 | * | |||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total Return |
(25.54 | ) % | (8.17 | ) % | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Ratios to Average Net Assets |
||||||||
| Total income (loss) |
(26.25 | ) % | (4.95 | ) % | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Expenses excluding management fees** |
0.60 | % | 0.41 | % | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Management fees** |
0.60 | % | 0.55 | % | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net income (loss) |
(26.85 | ) % | (5.42 | ) % | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| * | On February 21, 2012, there was a 4-for-1 reverse unit split. The Financial Highlights (Unaudited) have been adjusted for the periods shown to reflect the 4-for-1 reverse unit split on a retroactive basis. |
| ** | Annualized |
Total returns are calculated based on the change in value during the period. An individual unitholder’s total return and ratio may vary from the above total returns and ratios based on the timing of contributions to and withdrawals from USNG.
NOTE 7 — FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
USNG values its investments in accordance with Accounting Standards Codification 820 – Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures (“ASC 820”). ASC 820 defines fair value, establishes a framework for measuring fair value in generally accepted accounting principles, and expands disclosures about fair value measurement. The changes to past practice resulting from the application of ASC 820 relate to the definition of fair value, the methods used to measure fair value, and the expanded disclosures about fair value measurement. ASC 820 establishes a fair value hierarchy that distinguishes between: (1) market participant assumptions developed based on market data obtained from sources independent of USNG (observable inputs) and (2) USNG’s own assumptions about market participant assumptions developed based on the best information available under the circumstances (unobservable inputs). The three levels defined by the ASC 820 hierarchy are as follows:
Level I – Quoted prices (unadjusted) in active markets for identical assets or liabilities that the reporting entity has the ability to access at the measurement date.
Level II – Inputs other than quoted prices included within Level I that are observable for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. Level II assets include the following: quoted prices for similar assets or liabilities in active markets, quoted prices for identical or similar assets or liabilities in markets that are not active, inputs other than quoted prices that are observable for the asset or liability, and inputs that are derived principally from or corroborated by observable market data by correlation or other means (market-corroborated inputs).
14
Table of Contents
Level III – Unobservable pricing input at the measurement date for the asset or liability. Unobservable inputs shall be used to measure fair value to the extent that observable inputs are not available.
In some instances, the inputs used to measure fair value might fall within different levels of the fair value hierarchy. The level in the fair value hierarchy within which the fair value measurement in its entirety falls shall be determined based on the lowest input level that is significant to the fair value measurement in its entirety.
The following table summarizes the valuation of USNG’s securities at June 30, 2012 using the fair value hierarchy:
| At June 30, 2012 | Total | Level I | Level II | Level III | ||||||||||||
| Short-Term Investments |
$ | 652,498,554 | $ | 652,498,554 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
| Exchange-Traded Futures Contracts |
71,552,700 | 71,552,700 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Exchange-Traded Cleared Swap Contracts |
23,762,812 | 23,762,812 | — | — | ||||||||||||
| Over-the-Counter Total Return Swap Contracts |
10,537,264 | — | — | 10,537,264 | ||||||||||||
During the six months ended June 30, 2012, there were no transfers between Level I and Level II.
Following is a reconciliation of assets in which significant observable inputs (Level III) were used in determining fair value:
| Total Return Swap Contracts |
||||
| Beginning balance as of 12/31/11 |
$ | (12,805,692 | ) | |
| Realized gain (loss)* |
— | |||
| Change in unrealized gain (loss) |
23,342,956 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Ending balance as of 06/30/12 |
$ | 10,537,264 | ||
|
|
|
| * | The realized gain (loss) incurred during the six months ended June 30, 2012 for total return swaps was $(86,284,041). |
The following table summarizes the valuation of USNG’s securities at December 31, 2011 using the fair value hierarchy:
| At December 31, 2011 | Total | Level I | Level II | Level III | ||||||||||||
| Short-Term Investments |
$ | 852,474,966 | $ | 852,474,966 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
| Exchange-Traded Futures Contracts |
(28,631,262 | ) | (28,631,262 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Exchange-Traded Cleared Swap Contracts |
(20,361,043 | ) | (20,361,043 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||
| Over-the-Counter Total Return Swap Contracts |
(12,805,692 | ) | — | — | (12,805,692 | ) | ||||||||||
During the year ended December 31, 2011, there were no transfers between Level I and Level II.
Following is a reconciliation of assets in which significant observable inputs (Level III) were used in determining fair value:
| Total Return Swap Contracts |
||||
| Beginning balance as of 12/31/10 |
$ | 27,200,226 | ||
| Realized gain (loss)* |
— | |||
| Change in unrealized gain (loss) |
(40,005,918 | ) | ||
|
|
|
|||
| Ending balance as of 12/31/11 |
$ | (12,805,692 | ) | |
|
|
|
| * | The realized gain (loss) incurred during the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011 for total return swaps was $(275,985,809). |
15
Table of Contents
Effective January 1, 2009, USNG adopted the provisions of Accounting Standards Codification 815 — Derivatives and Hedging, which require presentation of qualitative disclosures about objectives and strategies for using derivatives, quantitative disclosures about fair value amounts and gains and losses on derivatives.
Fair Value of Derivative Instruments
| Derivatives not Accounted for as Hedging Instruments |
Condensed Statements of Financial Condition Location |
Fair Value At June 30, 2012 |
Fair Value At December 31, 2011 |
|||||||
| Futures - Commodity Contracts |
Assets | $ | 95,315,512 | $ | (48,992,305 | ) | ||||
| Swaps - Commodity Contracts | Assets | 10,537,264 | (12,805,692 | ) | ||||||
The Effect of Derivative Instruments on the Condensed Statements of Operations
| For the six months ended June 30, 2012 |
For the six months ended June 30, 2011 |
|||||||||||||||||
| Derivatives not Accounted for as Hedging Instruments |
Location of Gain or (Loss) on Derivatives Recognized in Income |
Realized Gain or (Loss) on Derivatives Recognized in Income |
Change in Unrealized Gain or (Loss) on Derivatives Recognized in Income |
Realized Gain or (Loss) on Derivatives Recognized in Income |
Change in Unrealized Gain or (Loss) on Derivatives Recognized in Income |
|||||||||||||
| Futures - Commodity Contracts |
Realized gain (loss) on closed futures positions | $ | (320,916,173 | ) | $ | 59,088,085 | ||||||||||||
| Change in unrealized gain (loss) on open futures positions | $ | 144,307,817 | $ | (111,622,973 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Swaps - Commodity Contracts |
Realized loss on closed swap contracts | (86,284,041 | ) | (25,001,019 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Change in unrealized gain (loss) on open swap contracts | 23,342,956 | (31,297,867 | ) | |||||||||||||||
NOTE 8 — RECENT ACCOUNTING PRONOUNCEMENTS
In December 2011, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) No. 2011-11, “Balance Sheet (Topic 210): Disclosures about Offsetting Assets and Liabilities.” The amendments in ASU No. 2011-11 require an entity to disclose information about offsetting and related arrangements to enable users of its financial statements to understand the effect of those arrangements on its financial position. ASU No. 2011-11 is effective for annual reporting periods beginning on or after January 1, 2013, and interim periods within those annual periods. The guidance requires retrospective application for all comparative periods presented. USCF is currently evaluating the impact ASU No. 2011-11 will have on USNG’s financial statements.
NOTE 9 — SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
USNG has performed an evaluation of subsequent events through the date the financial statements were issued. This evaluation did not result in any subsequent events that necessitated disclosures and/or adjustments.
16
Table of Contents
| Item 2. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations. |
The following discussion should be read in conjunction with the condensed financial statements and the notes thereto of the United States Natural Gas Fund, LP (“USNG”) included elsewhere in this quarterly report on Form 10-Q.
Forward-Looking Information
This quarterly report on Form 10-Q, including this “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” contains forward-looking statements regarding the plans and objectives of management for future operations. This information may involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause USNG’s actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by any forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements, which involve assumptions and describe USNG’s future plans, strategies and expectations, are generally identifiable by use of the words “may,” “will,” “should,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “estimate,” “believe,” “intend” or “project,” the negative of these words, other variations on these words or comparable terminology. These forward-looking statements are based on assumptions that may be incorrect, and USNG cannot assure investors that the projections included in these forward-looking statements will come to pass. USNG’s actual results could differ materially from those expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements as a result of various factors.
USNG has based the forward-looking statements included in this quarterly report on Form 10-Q on information available to it on the date of this quarterly report on Form 10-Q, and USNG assumes no obligation to update any such forward-looking statements. Although USNG undertakes no obligation to revise or update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, investors are advised to consult any additional disclosures that USNG may make directly to them or through reports that USNG in the future files with the U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), including annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q and current reports on Form 8-K.
Introduction
USNG, a Delaware limited partnership, is a commodity pool that issues units that may be purchased and sold on the NYSE Arca, Inc. (the “NYSE Arca”). The investment objective of USNG is for the daily changes in percentage terms of its units’ per unit net asset value (“NAV”) to reflect the daily changes in percentage terms of the spot price of natural gas delivered at the Henry Hub, Louisiana, as measured by the daily changes in the price of the futures contract for natural gas traded on the New York Mercantile Exchange (the “NYMEX”) that is the near month contract to expire, except when the near month contract is within two weeks of expiration, in which case it will be measured by the futures contract that is the next month contract to expire (the “Benchmark Futures Contract”), less USNG’s expenses. “Near month contract” means the next contract traded on the NYMEX due to expire. “Next month contract” means the first contract traded on the NYMEX due to expire after the near month contract. It is not the intent of USNG to be operated in a fashion such that the per unit NAV will equal, in dollar terms, the spot price of natural gas or any particular futures contract based on natural gas. It is not the intent of USNG to be operated in a fashion such that its per unit NAV will reflect the percentage change of the price of any particular futures contract as measured over a time period greater than one day. The general partner of USNG, United States Commodity Funds LLC (“USCF”), believes that it is not practical to manage the portfolio to achieve such an investment goal when investing in Futures Contracts (as defined below) and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments (as defined below).
USNG invests in futures contracts for natural gas, crude oil, heating oil, gasoline and other petroleum-based fuels that are traded on the NYMEX, ICE Futures or other U.S. and foreign exchanges (collectively, “Futures Contracts”) and other natural gas-related investments such as cash-settled options on Futures Contracts, forward contracts for natural gas, cleared swap contracts and over-the-counter transactions that are based on the price of natural gas, crude oil and other petroleum-based fuels, Futures Contracts and indices based on the foregoing (collectively, “Other Natural Gas-Related Investments”). For convenience and unless otherwise specified, Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments collectively are referred to as “Natural Gas Interests” in this quarterly report on Form 10-Q. Due, in part, to USNG’s obligation to comply with current and potential regulatory limits, it has invested in, and may continue to invest in, Other Natural Gas-Related Investments in order to fulfill its investment objective.
17
Table of Contents
USNG seeks to achieve its investment objective by investing in a combination of Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments such that daily changes in its per unit NAV, measured in percentage terms, will closely track the daily changes in the price of the Benchmark Futures Contract, also measured in percentage terms. USCF believes the daily changes in the price of the Benchmark Futures Contract have historically exhibited a close correlation with the daily changes in the spot price of natural gas. It is not the intent of USNG to be operated in a fashion such that the per unit NAV will equal, in dollar terms, the spot price of natural gas or any particular futures contract based on natural gas. It is not the intent of USNG to be operated in a fashion such that its per unit NAV will reflect the percentage change of the price of any particular futures contract as measured over a time period greater than one day. USCF believes that it is not practical to manage the portfolio to achieve such an investment goal when investing in Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments.
In addition, due to potential regulatory limitations, USNG may determine to hold greater amounts of cash and cash equivalents and lesser amounts of Natural Gas Interests, or greater amounts of Other Natural Gas-Related Investments if it determines that this will most appropriately satisfy USNG’s investment objective. Holding more cash and cash equivalents and fewer Natural Gas Interests, or more Other Natural Gas-Related Investments for some period of time may result in increased tracking error. Increasing USNG’s investments in Other Natural Gas-Related Investments, such as through increased investments in over-the-counter swaps, may result in increased tracking error due to the fact that transaction costs for over-the-counter swaps are significantly higher as compared to those for exchange-traded Natural Gas Interests, which to date are the principal investment of USNG. In the event that USNG determines that suitable Other Natural Gas-Related Investments are not obtainable, USNG will need to consider other actions to protect its unitholders and to permit USNG to achieve its investment objective.
Impact of Accountability Levels, Position Limits and Price Fluctuation Limits. Futures contracts include typical and significant characteristics. Most significantly, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (the “CFTC”) and U.S. designated contract markets such as the NYMEX have established accountability levels and position limits on the maximum net long or net short futures contracts in commodity interests that any person or group of persons under common trading control (other than as a hedge, which an investment by USNG is not) may hold, own or control. The net position is the difference between an individual’s or firm’s open long contracts and open short contracts in any one commodity. In addition, most U.S.-based futures exchanges, such as the NYMEX, limit the daily price fluctuation for futures contracts. Currently, the ICE Futures imposes position and accountability limits that are similar to those imposed by U.S.-based futures exchanges but does not limit the maximum daily price fluctuation, while some other non-U.S. futures exchanges have not adopted such limits.
The accountability levels for the Benchmark Futures Contract and other Futures Contracts traded on U.S.-based futures exchanges, such as the NYMEX, are not a fixed ceiling, but rather a threshold above which the NYMEX may exercise greater scrutiny and control over an investor’s positions. The current accountability level for investments for any one-month in the Benchmark Futures Contract is 6,000 net contracts. In addition, the NYMEX imposes an accountability level for all months of 12,000 net futures contracts for natural gas. If USNG and the Related Public Funds (as defined below) exceed these accountability levels for investments in the futures contract for natural gas, the NYMEX will monitor such exposure and ask for further information on their activities, including the total size of all positions, investment and trading strategy, and the extent of liquidity resources of USNG and the Related Public Funds. If deemed necessary by the NYMEX, it could also order USNG and the Related Public Funds to reduce their aggregate net position back to the accountability level. As of June 30, 2012, USNG held 22,244 NYMEX Natural Gas Futures NG contracts and 17,952 NYMEX Natural Gas Futures NN contracts. As of June 30, 2012, USNG held 31,178 natural gas cleared-swap contracts traded on the ICE Futures. USNG exceeded accountability levels of the NYMEX during the six months ended June 30, 2012, when on June 11, 2012, it held 21,418 Natural Gas Futures NG contracts, exceeding both the “any” and “all” month limits. No action was taken by the NYMEX and USNG reduced the number of Futures Contracts held. USNG did not exceed accountability levels imposed by the ICE Futures for the six months ended June 30, 2012.
Position limits differ from accountability levels in that they represent fixed limits on the maximum number of futures contracts that any person may hold and cannot allow such limits to be exceeded without express CFTC authority to do so. In addition to accountability levels and position limits that may apply at any time, the NYMEX and the ICE Futures impose position limits on contracts held in the last few days of trading in the near month contract to expire. It is unlikely that USNG will run up against such position limits because USNG’s investment strategy is to close out its positions and “roll” from the near month contract to expire to the next month contract during a four-day period beginning two weeks from expiration of the contract. For the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG did not exceed any position limits imposed by the NYMEX and ICE Futures.
18
Table of Contents
On October 18, 2011, the CFTC adopted new rules, which establish position limits and limit formulas for certain physical commodity futures including Futures Contracts and options on Futures Contracts, executed pursuant to the rules of designated contract markets (i.e., certain regulated exchanges) and commodity swaps that are economically equivalent to such futures and options contracts. See Introduction – Futures Contracts and Position Limits in this quarterly report on Form 10-Q for information regarding the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act (the “Dodd-Frank Act”).
The regulation of commodity interests in the United States is subject to ongoing modification by governmental and judicial action. On July 21, 2010, a broad financial regulatory reform bill, the Dodd-Frank Act, was signed into law. All of the Dodd-Frank Act’s provisions became effective on July 16, 2011, but the actual implementation of some of the provisions is subject to continuing uncertainty because implementing rules and regulations have not been completely finalized and have been challenged in court. Pending final resolution of all applicable regulatory requirements, some specific examples of how the new Dodd-Frank Act provisions and rules adopted thereunder could impact USNG are discussed below.
Futures Contracts and Position Limits
Provisions in the Dodd-Frank Act include the requirement that position limits be established on a wide range of commodity interests including energy-based and other commodity futures contracts, certain cleared commodity swaps and certain over-the-counter commodity contracts; new registration, recordkeeping, capital and margin requirements for “swap dealers” and “major swap participants” as determined by the new law and applicable regulations; and the forced use of clearinghouse mechanisms for many swap transactions that are currently entered into in the over-the-counter market. The new law and the rules thereunder may negatively impact USNG’s ability to meet its investment objective either through limits or requirements imposed on it or upon its counterparties. Further, increased regulation of, and the imposition of additional costs on, swap transactions under the new legislation and implementing regulations could cause a reduction in the swap market and the overall derivatives markets, which could restrict liquidity and adversely affect USNG. In particular, new position limits imposed on USNG or its counterparties may impact USNG’s ability to invest in a manner that most efficiently meets its investment objective, and new requirements, including capital and mandatory clearing, may increase the cost of USNG’s investments and doing business, which could adversely impact the ability of USNG to achieve its investment objective.
On October 18, 2011, the CFTC adopted regulations implementing position limits and limit formulas for 28 core physical commodity futures contracts, including the Futures Contracts and options on Futures Contracts, executed pursuant to the rules of designated contract markets (i.e., certain regulated exchanges) and commodity swaps that are economically equivalent to such futures and options contracts (collectively, “Referenced Contracts”). The new regulations require, among other things, aggregation of position limits that would apply across different trading venues to contracts based on the same underlying commodity. However, the regulations would require aggregation of Referenced Contracts held by separate Related Public Funds (as defined below) only if such Related Public Funds had “identical trading strategies.” USCF does not believe any of the Related Public Funds should be viewed as having identical trading strategies for purposes of the CFTC’s aggregation rules.
Although the regulations became effective on January 17, 2012, the position limit rules will be implemented in two phases: spot-month position limits and non-spot-month position limits. Spot-month limits will be effective sixty days after the term “swap” is defined under the Dodd-Frank Act (see below). The limits adopted will be based on the spot-month position limit levels currently in place at applicable futures exchanges (or designated contract market or “DCM”). Thereafter, the spot-month limits will be adjusted annually for energy contracts. These subsequent limits will be based on the CFTC’s determination of deliverable supply in consultation with the futures exchanges. Spot-month position limit levels will be set generally at 25% of estimated deliverable supply, and limits will be applied separately for physical-delivery and cash-settled contracts in the same commodity. Cash-settled NYMEX Henry Hub Natural Gas contracts, however, will be subject to a cash-settled spot-month position limit and an aggregate limit (extending across positions in both physical-delivery and cash-settled natural gas contracts), each set at five-times the limit that applies to the physical-delivery NYMEX Henry Hub Natural Gas contract.
19
Table of Contents
Non-spot-month position limits will go into effect by CFTC order after the CFTC has received one year of open interest data on physical commodity cleared and uncleared swaps under the swaps large trader reporting rule. The non-spot month limits will be adjusted biennially based on Referenced Contract open interest. Non-spot-month position limits (i.e., limits applied to positions in all contract months combined or in a single contract month) will be set using the 10/2.5 percent formula: 10 percent of the contract’s first 25,000 of open interest and 2.5 percent thereafter. These limits will be reset biennially based on two years of open interest data.
On December 2, 2011, the Securities Industry and Financial Markets Association (“SIFMA”) and the International Swaps and Derivatives Association (“ISDA”) filed a lawsuit challenging the CFTC’s position limits rule. The lawsuit asserts that the position limits rule inadequately fulfills the required cost-benefit analysis. It is not known at this time what effect this lawsuit will have on the implementation of the new position limits rule.
Based on its current understanding of the final position limit regulations, USCF does not anticipate significant negative impact on the ability of USNG to achieve its investment objective. However, as of the filing of this quarterly report on Form 10-Q, additional studies are required to be conducted before all requirements of the final rules are implemented, and therefore, it cannot be determined with certainty what impact such regulations will have on USNG.
“Swap” Transactions
The Dodd-Frank Act imposes new regulatory requirements on certain “swap” transactions that USNG is authorized to engage in that may ultimately impact the ability of USNG to meet its investment objective. On May 23, 2011, the CFTC and the SEC published joint proposed rules defining the term “swap” and thus providing more clarity regarding which transactions will be regulated as such under the Dodd-Frank Act. On July 13, 2012, the CFTC published a pre-publication version of the joint CFTC and SEC final rules that provide further definition of the terms “swap” and “security-based swap.” The term “swap” is broadly defined to include various types of over-the-counter derivatives, including swaps and options. The effective date of these final rules will be 60 days after the publication of such final rules in the Federal Register, which has not occurred as of the date of filing of this quarterly report on Form 10-Q.
The Dodd-Frank Act requires that certain transactions ultimately falling within the definition of “swap” be executed on organized exchanges or “swap execution facilities” and cleared through regulated clearing organizations (which are referred to in the Dodd-Frank Act as “derivative clearing organizations” (“DCOs”)). However, as described above, it is currently unknown which swaps will be subject to such trading and clearing requirements. If a swap is required to be cleared, the initial margin will be set by the clearing organization, subject to certain regulatory requirements and guidelines. Initial and variation margin requirements for swap dealers and major swap participants who enter into uncleared swaps and capital requirements for swap dealers and major swap participants who enter into both cleared and uncleared trades will be set by the CFTC, the SEC or the applicable Prudential Regulator. On May 23, 2012, the CFTC published final regulations, which are not yet effective, to determine which entities will be regulated as “swap dealers” and “major swap participants” and thus have to comply with these capital and margin requirements (as well as a multitude of other requirements under the Dodd-Frank Act). In general, increased regulation of, and the imposition of additional costs on, swap transactions could have an adverse effect on USNG by, for example, reducing the size of and therefore liquidity in the derivatives market, increasing transaction costs and decreasing the ability to customize derivative transactions. The final rule regarding review of swaps for mandatory clearing went effective September 26, 2011.
On July 14, 2011, the CFTC issued an order providing temporary relief from certain swaps-related provisions of Title VII that would have automatically taken effect on July 16, 2011. The final order granted temporary exemptive relief that, by its terms, expires upon the earlier of the effective date of the required final rulemaking or December 31, 2011. On October 18, 2011, the CFTC issued an order, which modified the July 14, 2011 order by extending the temporary exemptive relief to the earlier of the effective date of the required final rulemaking or July 16, 2012. On July 13, 2012, the CFTC issued an order to, in pertinent part, extend the temporary exemptive relief to December 31, 2012.
On February 7, 2012, the CFTC published a rule requiring each futures commission merchant (“FCM”) and DCO to segregate cleared swaps and related collateral posted by a customer of the FCM from the assets of the FCM or DCO, although such property can be commingled with the property of other cleared swaps customers of the FCM or DCO. This rule addresses losses incurred by a DCO in a so-called “double default” scenario in which a customer of a FCM defaults in its obligations to the FCM and the FCM, in turn, defaults in its obligations to the DCO. Under this scenario, the DCO can only access the collateral attributable to other customers of the DCO whose cleared swap positions are in a loss position following the primary customer’s default. This rule is scheduled to become effective on November 8, 2012. Some market participants have expressed concern that the requirements of this segregation rule may result in higher initial margins or higher fees. USNG does not anticipate any impact to its operations in order to meet the requirements of the new rule.
20
Table of Contents
Additionally, the CFTC published rules on February 17, 2012 and April 3, 2012 that require “swap dealers” and “major swap participants” to: 1) adhere to business conduct standards, 2) implement policies and procedures to ensure compliance with the Commodity Exchange Act and 3) maintain records of such compliance. These new requirements may impact the documentation requirements for both cleared and non-cleared swaps and cause swap dealers and major swap participants to face increased compliance costs that, in turn, may be passed along to counterparties (such as USNG) in the form of higher fees and expenses that related to trading swaps.
On February 24, 2012, the CFTC amended certain disclosure obligations to require that the operator of a commodity pool that invests in swaps include standardized swap risk disclosures in the pool’s disclosure documents by December 31, 2012.
The CFTC issued a final rule on May 23, 2012 interpreting the definition of “eligible contract participant,” as amended by the Dodd-Frank Act, in such a manner that USNG may be limited as to the counterparties with which it may enter into currency forward contracts. Additionally, USNG may under certain circumstances related to the amount of assets under management no longer qualify as an eligible contract participant. USNG’s ability to maintain a certain minimum level of assets to qualify as an eligible contract participant allows USNG to enter into swaps on swap execution facilities as well as on a bilateral, off-exchange basis. The loss of status as an eligible contract participant and the resulting loss of eligible counterparties and investment options could impact USNG’s ability to achieve its investment objective.
The effect of the future regulatory change on USNG is impossible to predict, but it could be substantial and adverse.
USCF, which is registered as a commodity pool operator (“CPO”) with the CFTC, is authorized by the Third Amended and Restated Agreement of Limited Partnership of USNG (the “LP Agreement”) to manage USNG. USCF is authorized by USNG in its sole judgment to employ and establish the terms of employment for, and termination of, commodity trading advisors or FCMs.
Price Movements
Natural gas futures prices were volatile during the six months ended June 30, 2012. The price of the Benchmark Futures Contract started the period at $2.989. The low of the period was on April 4, 2012, when the price dropped to $1.983 per million British thermal units (“MMBtu”). The high of the period was on January 4, 2012, when the price reached $3.096 per MMBtu. The period ended with the Benchmark Futures Contract at $2.824 per MMBtu, a decrease of approximately 5.52% over the period. USNG’s per unit NAV initially rose during the period, taking into account the reverse split, from a starting level of $25.88* to a high on January 4, 2012 of $26.82*. USNG’s per unit NAV reached its low for the period on April 19, 2012 at $14.29. The per unit NAV on June 30, 2012 was $19.27, a decrease of approximately 25.54% over the period. The Benchmark Futures Contract prices listed above began with the February 2012 contracts and ended with the August 2012 contracts. The decrease of approximately 5.52% on the Benchmark Futures Contract listed above is a hypothetical return only and could not actually be achieved by an investor holding Futures Contracts. An investment in natural gas Futures Contracts would need to be rolled forward during the time period described in order to simulate such a result. Furthermore, the change in the nominal price of these differing natural gas Futures Contracts, measured from the start of the period to the end of the period, does not represent the actual benchmark results that USNG seeks to track, which are more fully described below in the section titled “Tracking USNG’s Benchmark.”
During the six months ended June 30, 2012, the natural gas futures market was in a state of contango, meaning that the price of the near month natural gas Futures Contract was lower than the price of the next month natural gas Futures Contract, or contracts further away from expiration. A contango market is one in which the price of the near month natural gas Futures Contract is less than the price of the next month natural gas Futures Contract, or contracts further away from expiration. As a result of contango or backwardation, as the case may be, the return of approximately (5.52)% on the Benchmark Futures Contract listed above is a hypothetical return only and could not actually be achieved by an investor holding futures contracts. For a discussion of the impact of backwardation and contango on total returns, see “Term Structure of Natural Gas Futures Prices and the Impact on Total Returns” below.
| * | Adjusted to give effect to the reverse unit split of 4-for-1 executed on February 21, 2012. |
21
Table of Contents
Valuation of Futures Contracts and the Computation of the Per Unit NAV
The per unit NAV of USNG’s units is calculated once each NYSE Arca trading day. The per unit NAV for a particular trading day is released after 4:00 p.m. New York time. Trading during the core trading session on the NYSE Arca typically closes at 4:00 p.m. New York time. USNG’s administrator uses the NYMEX closing price (determined at the earlier of the close of the NYMEX or 2:30 p.m. New York time) for the contracts held on the NYMEX, but calculates or determines the value of all other USNG investments, including cleared swaps or other futures contracts, as of the earlier of the close of the NYSE Arca or 4:00 p.m. New York time.
Results of Operations and the Natural Gas Market
Results of Operations. On April 18, 2007, USNG listed its units on the American Stock Exchange (the “AMEX”) under the ticker symbol “UNG.” On that day, USNG established its initial offering price at $50.00 per unit and issued 200,000 units to the initial authorized purchaser, Merrill Lynch Professional Clearing Corp., in exchange for $10,001,000 in cash. As a result of the acquisition of the AMEX by NYSE Euronext, USNG’s units no longer trade on the AMEX and commenced trading on the NYSE Arca on November 25, 2008.
Since its initial offering of 30,000,000 units, USNG has registered four subsequent offerings of its units: 50,000,000 units which were registered with the SEC on November 21, 2007, 100,000,000 units which were registered with the SEC on August 28, 2008, 300,000,000 units which were registered with the SEC on May 6, 2009 and 1,000,000,000 units which were registered with the SEC on August 12, 2009. Units offered by USNG in the subsequent offerings were sold by it for cash at the units’ per unit NAV as described in the applicable prospectus. On March 8, 2011, after the close of trading on the NYSE Arca, USNG effected a 2-for-1 reverse unit split and post-split units of USNG began trading on March 9, 2011. As a result of the reverse unit split, every two pre-split units of USNG were automatically exchanged for one post-split unit. Immediately prior to the reverse unit split, there were 447,200,000 units of USNG issued and outstanding, representing a per unit NAV of $5.16. Immediately after the reverse unit split, the number of issued and outstanding units of USNG decreased to 223,600,000, not accounting for fractional units, and the per unit NAV increased to $10.31. On February 21, 2012, after the close of trading on the NYSE Arca, USNG effected a 4-for-1 reverse unit split and post-split units of USNG began trading on February 22, 2012. As a result of the reverse unit split, every four pre-split units of USNG were automatically exchanged for one post-split unit. Immediately prior to the reverse unit split, there were 174,297,828 units of USNG issued and outstanding, representing a per unit NAV of $5.51. Immediately after the reverse unit split, the number of issued and outstanding units of USNG decreased to 43,574,457, not accounting for fractional units, and the per unit NAV increased to $22.06. As of June 30, 2012, USNG had issued 1,163,100,000 units, 60,266,476 of which were outstanding. As of June 30, 2012, there were 316,900,000 units registered but not yet issued.
More units may have been issued by USNG than are outstanding due to the redemption of units. Unlike funds that are registered under the Investment Company Act of 1940, as amended, units that have been redeemed by USNG cannot be resold by USNG. As a result, USNG contemplates that additional offerings of its units will be registered with the SEC in the future in anticipation of additional issuances and redemptions.
As of June 30, 2012, USNG had the following authorized purchasers: ABN Amro, Banc of America Securities LLC, Citadel Securities LLC, Citigroup Global Markets Inc., Credit Suisse Securities USA LLC, Deutsche Bank Securities Inc., Fimat USA LLC, Goldman Sachs & Company, Goldman Sachs Execution & Clearing LP, JP Morgan Securities Inc., Knight Clearing Services LLC, Merrill Lynch Professional Clearing Corp., Morgan Stanley & Company Inc., Nomura Securities International Inc., RBC Capital Markets Corporation, SG Americas Securities LLC, Virtu Financial Capital Markets and Virtu Financial DB LLC.
For the Six Months Ended June 30, 2012 Compared to the Six Months Ended June 30, 2011
As of June 30, 2012, the total unrealized gain on Futures Contracts, cleared swap contracts and over-the-counter swap contracts owned or held on that day was $105,852,776 and USNG established cash deposits and investments in short-term obligations of the United States of two years or less (“Treasuries”) and money market funds that were equal to $983,055,725. USNG held 84.74% of its cash assets in overnight deposits, Treasuries and money market funds at its custodian bank, while 15.26% of the cash balance was held as Treasuries and as margin deposits for the Futures Contracts purchased. The ending per unit NAV on June 30, 2012 was $19.27.
22
Table of Contents
By comparison, as of June 30, 2011, the total unrealized loss on Futures Contracts, cleared swap contracts and over-the-counter swap contracts owned or held on that day was $28,315,334 and USNG established cash deposits and investments in Treasuries and money market funds that were equal to $1,921,746,217. USNG held 88.74% of its cash assets in overnight deposits, Treasuries and money market funds at its custodian bank, while 11.26% of the cash balance was held as margin deposits for the Futures Contracts purchased. The decrease in cash assets in overnight deposits, Treasuries and money market funds for June 30, 2012 as compared to June 30, 2011, was the result of USNG’s smaller size during the six months ended June 30, 2012 as measured by total net assets. The ending per unit NAV on June 30, 2011 was $44.08*. The decrease in the per unit NAV for June 30, 2012 as compared to June 30, 2011, was primarily a result of sharply lower prices for natural gas and the related decline in the value of the Futures Contracts, cleared swap contracts, and over-the-counter swap contracts that USNG had invested in between the period ended June 30, 2011 and the period ended June 30, 2012.
| * | Adjusted to give effect to the reverse unit split of 4-for-1 executed on February 21, 2012. |
Portfolio Expenses. USNG’s expenses consist of investment management fees, brokerage fees and commissions, certain offering costs, licensing fees, the fees and expenses of the independent directors of USCF and expenses relating to tax accounting and reporting requirements. The management fee that USNG pays to USCF is calculated as a percentage of the total net assets of USNG. For total net assets of up to $1 billion, the management fee is 0.60%. For total net assets over $1 billion, the management fee is 0.50% on the incremental amount of total net assets. The fee is accrued daily and paid monthly.
During the six months ended June 30, 2012, the average daily total net assets of USNG were $911,651,594. The management fee incurred by USNG during the period amounted to $2,715,198, which was calculated at the 0.60% rate on total net assets up to and including $1 billion and at the rate of 0.50% on total net assets over $1 billion, and accrued daily. Management fees as a percentage of average daily total net assets averaged 0.60% over the course of this six month period. By comparison, during the six months ended June 30, 2011, the average daily total net assets of USNG were $2,191,053,553. The management fee paid by USNG during this six month period amounted to $5,928,503, which was calculated at the 0.60% rate for total net assets up to and including $1 billion and at the rate of 0.50% on total net assets over $1 billion, and accrued daily. Management fees as a percentage of average daily total net assets averaged 0.55% over the course of this six month period. USNG’s management fees as a percentage of average daily total net assets were higher for the six months ended June 30, 2012 compared to the six months ended June 30, 2011 due to the fact that there were fewer days with assets over $1 billion that were charged at the lower 0.50% rate during the six months ended June 30, 2012.
In addition to the management fee, USNG pays all brokerage fees, transaction costs for over-the-counter swaps and other expenses, including tax reporting costs, licensing fees for the use of intellectual property, ongoing registration or other fees paid to the SEC, the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (“FINRA”) and any other regulatory agency in connection with offers and sales of its units subsequent to the initial offering and all legal, accounting, printing and other expenses associated therewith. The total of these fees and expenses for the six months ended June 30, 2012 was $2,699,382, as compared to $4,408,717 for the six months ended June 30, 2011. The decrease in total expenses excluding management fees for the six months ended June 30, 2012 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2011, was primarily due to reduced trading activity and reduced variable costs resulting from USNG’s lower average daily total net assets during the six months ended June 30, 2012. For the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG incurred $(19,388) in ongoing registration fees and other expenses relating to the registration and offering of additional units. By comparison, for the six months ended June 30, 2011, USNG incurred $56,110 in ongoing registration fees and other expenses relating to the registration and offering of additional units. The decrease in registration fees and expenses incurred by USNG for the six months ended June 30, 2012 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2011, was due to the fact that these expenses were completely amortized by December 31, 2011. The positive impact (negative expense) during the six months ended June 30, 2012 was a result of an over accrual of a portion of the registration fees and expenses for the year ended December 31, 2011. This amount was adjusted for the six months ended June 30, 2012, thereby offsetting other expenses by 12.65%.
23
Table of Contents
USNG is responsible for paying its portion of the directors’ and officers’ liability insurance of USNG and the United States Oil Fund, LP, the United States 12 Month Oil Fund, LP, the United States Gasoline Fund, LP, the United States Diesel-Heating Oil Fund, LP (formerly, the United States Heating Oil Fund, LP), the United States Short Oil Fund, LP, the United States 12 Month Natural Gas Fund, LP, the United States Brent Oil Fund, LP, the United States Commodity Index Fund, the United States Copper Index Fund, the United States Agriculture Index Fund and the United States Metals Index Fund (collectively, the “Related Public Funds”) and the fees and expenses of the independent directors who also serve as audit committee members of USNG and the Related Public Funds organized as limited partnerships and, as of July 8, 2011, the Related Public Funds organized as a series of a Delaware statutory trust. USNG shares the fees and expenses with each Related Public Fund, as described above, based on the relative assets of each fund computed on a daily basis. These fees and expenses for the year ending December 31, 2012 are estimated to be a total of $540,000 for USNG and the Related Public Funds. By comparison, for the year ended December 31, 2011, these fees and expenses amounted to a total of $607,582 for USNG and the Related Public Funds. USNG’s portion of such fees and expenses was $290,377.
USNG also incurs commissions to brokers for the purchase and sale of Futures Contracts, Other Natural Gas-Related Investments or Treasuries. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, total commissions accrued to brokers amounted to $1,950,611. Of this amount, $1,690,243 was a result of rebalancing costs and $260,368 was the result of trades necessitated by creation and redemption activity. By comparison, during the six months ended June 30, 2011, total commissions accrued to brokers amounted to $2,561,036. The decrease in the total commissions accrued to brokers for the six months ended June 30, 2012 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2011, was primarily a function of decreased brokerage fees due to a lower number of Natural Gas Interests being held and traded during the six months ended June 30, 2012. As an annualized percentage of average daily total net assets, the figure for the six months ended June 30, 2012 represents approximately 0.43% of average daily total net assets. By comparison, the figure for the six months ended June 30, 2011 represented approximately 0.24% of average daily total net assets. However, there can be no assurance that commission costs and portfolio turnover will not cause commission expenses to rise in future quarters.
USNG incurred $441,246 in transaction costs during the six months ended June 30, 2012 as compared to $2,379,686 in transaction costs during the six months ended June 30, 2011. USNG’s transaction costs were lower during the six months ended June 30, 2012 as compared to the six months ended June 30, 2011, due to reduced investment in Other Natural Gas-Related Investments, including over-the-counter swaps, during the six months ended June 30, 2012. However, these costs remain somewhat higher as compared to those for exchange-traded Natural Gas Interests.
The fees and expenses associated with USNG’s audit expenses and tax accounting and reporting requirements are paid by USNG. These costs are estimated to be $1,600,000 for the year ending December 31, 2012.
Dividend and Interest Income. USNG seeks to invest its assets such that it holds Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments in an amount equal to the total net assets of its portfolio. Typically, such investments do not require USNG to pay the full amount of the contract value at the time of purchase, but rather require USNG to post an amount as a margin deposit against the eventual settlement of the contract. As a result, USNG retains an amount that is approximately equal to its total net assets, which USNG invests in Treasuries, cash and/or cash equivalents. This includes both the amount on deposit with the FCM as margin, as well as unrestricted cash and cash equivalents held with USNG’s custodian bank. The Treasuries, cash and/or cash equivalents earn income that accrues on a daily basis. For the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG earned $117,668 in dividend and interest income on such cash and/or cash equivalents. Based on USNG’s average daily total net assets, this was equivalent to an annualized yield of 0.03%. USNG purchased Treasuries during the six months ended June 30, 2012 and also held cash and/or cash equivalents during this time period. By comparison, for the six months ended June 30, 2011, USNG earned $306,597 in dividend and interest income on such cash and/or cash equivalents. Based on USNG’s average daily total net assets, this was equivalent to an annualized yield of 0.03%. USNG purchased Treasuries during the six months ended June 30, 2011 and also held cash and/or cash equivalents during this time period. Interest rates on short-term investments held by USNG, including cash, cash equivalents and Treasuries, were approximately unchanged during the six months ended June 30, 2012 compared to the six months ended June 30, 2011. As a result, the amount of income earned by USNG as a percentage of average daily total net assets was unchanged during the six months ended June 30, 2012 compared to the six months ended June 30, 2011.
24
Table of Contents
For the Three Months Ended June 30, 2012 Compared to the Three Months Ended June 30, 2011
Portfolio Expenses. During the three months ended June 30, 2012, the average daily total net assets of USNG were $896,755,397. The management fee incurred by USNG during the period amounted to $1,335,505, which was calculated at the 0.60% rate on total net assets up to and including $1 billion and at the rate of 0.50% on total net assets over $1 billion, and accrued daily. Management fees as a percentage of average daily total net assets averaged 0.60% over the course of this three month period. By comparison, during the three months ended June 30, 2011, the average daily total net assets of USNG were $2,001,352,694. The management fee paid by USNG during this three month period amounted to $2,744,152, which was calculated at the 0.60% rate for total net assets up to and including $1 billion and at the rate of 0.50% on total net assets over $1 billion, and accrued daily. Management fees as a percentage of average daily total net assets averaged 0.55% over the course of this three month period. USNG’s management fees as a percentage of average daily total net assets were higher for the three months ended June 30, 2012 compared to the three months ended June 30, 2011 due to the fact that there were fewer days with assets over $1 billion that were charged at the lower 0.50% rate during the three months ended June 30, 2012.
In addition to the management fee, USNG pays all brokerage fees, transaction costs for over-the-counter swaps and other expenses, including tax reporting costs, licensing fees for the use of intellectual property, ongoing registration or other fees paid to the SEC, FINRA and any other regulatory agency in connection with offers and sales of its units subsequent to the initial offering and all legal, accounting, printing and other expenses associated therewith. The total of these fees and expenses for the three months ended June 30, 2012 was $1,320,308, as compared to $2,029,981 for the three months ended June 30, 2011. The decrease in total expenses excluding management fees for the three months ended June 30, 2012 as compared to the three months ended June 30, 2011, was primarily due to reduced trading activity and reduced variable costs resulting from USNG’s lower average daily total net assets during the three months ended June 30, 2012. For the three months ended June 30, 2012, USNG incurred $0 in ongoing registration fees and other expenses relating to the registration and offering of additional units. By comparison, for the three months ended June 30, 2011, USNG incurred $28,210 in ongoing registration fees and other expenses relating to the registration and offering of additional units. The decrease in registration fees and expenses incurred by USNG for the three months ended June 30, 2012 as compared to the three months ended June 30, 2011, was due to the fact that these expenses were completely amortized by December 31, 2011.
USNG is responsible for paying its portion of the directors’ and officers’ liability insurance of USNG and the Related Public Funds and the fees and expenses of the independent directors who also serve as audit committee members of USNG and the Related Public Funds organized as limited partnerships and, as of July 8, 2011, the Related Public Funds organized as a series of a Delaware statutory trust. USNG shares the fees and expenses with each Related Public Fund, as described above, based on the relative assets of each fund computed on a daily basis. These fees and expenses for the year ending December 31, 2012 are estimated to be a total of $540,000 for USNG and the Related Public Funds. By comparison, for the year ended December 31, 2011, these fees and expenses amounted to a total of $607,582 for USNG and the Related Public Funds. USNG’s portion of such fees and expenses was $290,377.
USNG also incurs commissions to brokers for the purchase and sale of Futures Contracts, Other Natural Gas-Related Investments or Treasuries. During the three months ended June 30, 2012, total commissions accrued to brokers amounted to $929,220. Of this amount, $772,273 was a result of rebalancing costs and $156,947 was the result of trades necessitated by creation and redemption activity. By comparison, during the three months ended June 30, 2011, total commissions accrued to brokers amounted to $1,164,253. The decrease in the total commissions accrued to brokers for the three months ended June 30, 2012 as compared to the three months ended June 30, 2011, was primarily a function of decreased brokerage fees due to a lower number of Natural Gas Interests being held and traded during the three months ended June 30, 2012. As an annualized percentage of average daily total net assets, the figure for the three months ended June 30, 2012 represents approximately 0.42% of average daily total net assets. By comparison, the figure for the three months ended June 30, 2011 represented approximately 0.23% of average daily total net assets. However, there can be no assurance that commission costs and portfolio turnover will not cause commission expenses to rise in future quarters.
USNG incurred $211,316 in transaction costs during the three months ended June 30, 2012 as compared to $1,093,578 in transaction costs during the three months ended June 30, 2011. USNG’s transaction costs were lower during the three months ended June 30, 2012 as compared to the three months ended June 30, 2011, due to reduced investment in Other Natural Gas-Related Investments, including over-the-counter swaps, during the three months ended June 30, 2012. However, these costs remain somewhat higher as compared to those for exchange-traded Natural Gas Interests.
The fees and expenses associated with USNG’s audit expenses and tax accounting and reporting requirements are paid by USNG. These costs are estimated to be $1,600,000 for the year ending December 31, 2012.
25
Table of Contents
Dividend and Interest Income. USNG seeks to invest its assets such that it holds Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments in an amount equal to the total net assets of its portfolio. Typically, such investments do not require USNG to pay the full amount of the contract value at the time of purchase, but rather require USNG to post an amount as a margin deposit against the eventual settlement of the contract. As a result, USNG retains an amount that is approximately equal to its total net assets, which USNG invests in Treasuries, cash and/or cash equivalents. This includes both the amount on deposit with the FCM as margin, as well as unrestricted cash and cash equivalents held with USNG’s custodian bank. The Treasuries, cash and/or cash equivalents earn income that accrues on a daily basis. For the three months ended June 30, 2012, USNG earned $63,229 in dividend and interest income on such cash and/or cash equivalents. Based on USNG’s average daily total net assets, this was equivalent to an annualized yield of 0.03%. USNG purchased Treasuries during the three months ended June 30, 2012 and also held cash and/or cash equivalents during this time period. By comparison, for the three months ended June 30, 2011, USNG earned $93,680 in dividend and interest income on such cash and/or cash equivalents. Based on USNG’s average daily total net assets, this was equivalent to an annualized yield of 0.02%. USNG purchased Treasuries during the three months ended June 30, 2011 and also held cash and/or cash equivalents during this time period. Interest rates on short-term investments held by USNG, including cash, cash equivalents and Treasuries, were approximately the same during the three months ended June 30, 2012 compared to the three months ended June 30, 2011. As a result, the amount of income earned by USNG as a percentage of average daily total net assets was approximately unchanged during the three months ended June 30, 2012 compared to the three months ended June 30, 2011.
Tracking USNG’s Benchmark
USCF seeks to manage USNG’s portfolio such that changes in its average daily per unit NAV, on a percentage basis, closely track the daily changes in the average price of the Benchmark Futures Contract, also on a percentage basis. Specifically, USCF seeks to manage the portfolio such that over any rolling period of 30-valuation days, the average daily change in USNG’s per unit NAV is within a range of 90% to 110% (0.9 to 1.1) of the average daily change in the price of the Benchmark Futures Contract. As an example, if the average daily movement of the price of the Benchmark Futures Contract for a particular 30-valuation day time period was 0.50% per day, USCF would attempt to manage the portfolio such that the average daily movement of the per unit NAV during that same time period fell between 0.45% and 0.55% (i.e., between 0.9 and 1.1 of the benchmark’s results). USNG’s portfolio management goals do not include trying to make the nominal price of USNG’s per unit NAV equal to the nominal price of the current Benchmark Futures Contract or the spot price for natural gas. USCF believes that it is not practical to manage the portfolio to achieve such an investment goal when investing in listed Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments.
For the 30-valuation days ended June 30, 2012, the simple average daily change in the Benchmark Futures Contract was 0.205%, while the simple average daily change in the per unit NAV of USNG over the same time period was 0.199%. The average daily difference was (0.006)% (or (0.6) basis points, where 1 basis point equals 1/100 of 1%). As a percentage of the daily movement of the Benchmark Futures Contract, the average error in daily tracking by the per unit NAV was (0.316)%, meaning that over this time period USNG’s tracking error was within the plus or minus 10% range established as its benchmark tracking goal. The first chart below shows the daily movement of USNG’s per unit NAV versus the daily movement of the Benchmark Futures Contract for the 30-valuation day period ended June 30, 2012. The second chart below shows the monthly total returns of USNG as compared to the monthly value of the Benchmark Futures Contract since inception.
Since the commencement of the offering of USNG’s units to the public on April 18, 2007 to June 30, 2012, the simple average daily change in the Benchmark Futures Contract was (0.185)%, while the simple average daily change in the per unit NAV of USNG over the same time period was (0.186)%. The average daily difference was 0.001% (or 0.1 basis points, where 1 basis point equals 1/100 of 1%). As a percentage of the daily movement of the Benchmark Futures Contract, the average error in daily tracking by the per unit NAV was (0.373)%, meaning that over this time period USNG’s tracking error was within the plus or minus 10% range established as its benchmark tracking goal.
26
Table of Contents
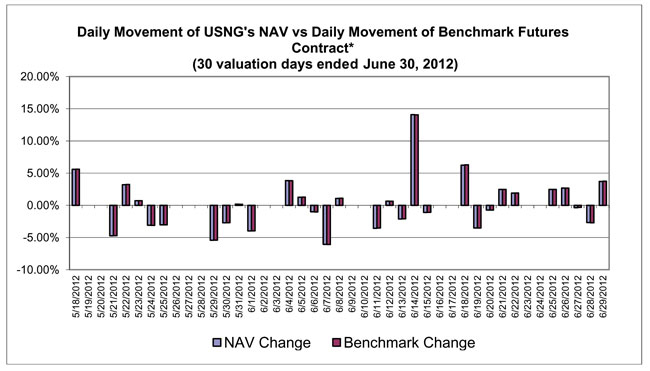
*PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS
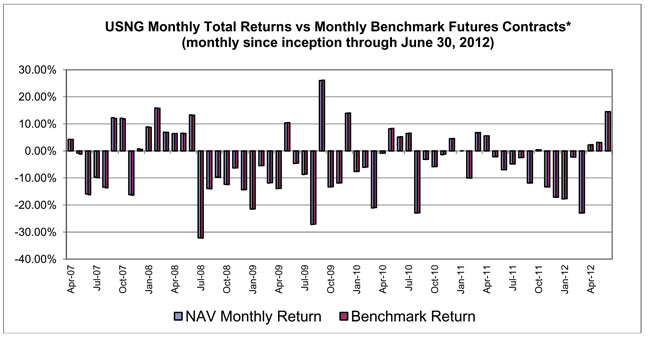
*PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS
An alternative tracking measurement of the return performance of USNG versus the return of its Benchmark Futures Contract can be calculated by comparing the actual return of USNG, measured by changes in its NAV, versus the expected changes in its per unit NAV under the assumption that USNG’s returns had been exactly the same as the daily changes in its Benchmark Futures Contract.
27
Table of Contents
For the six months ended June 30, 2012, the actual total return of USNG as measured by changes in its per unit NAV was (25.54)%. This is based on an initial per unit NAV, taking into account the reverse split, of $25.88* on December 31, 2011 and an ending per unit NAV as of June 30, 2012 of $19.27. During this time period, USNG made no distributions to its unitholders. However, if USNG’s daily changes in its per unit NAV had instead exactly tracked the changes in the daily total return of the Benchmark Futures Contract, USNG would have had an estimated per unit NAV of $19.38 as of June 30, 2012, for a total return over the relevant time period of (25.12)%. The difference between the actual per unit NAV total return of USNG of (25.54)% and the expected total return based on the Benchmark Futures Contract of (25.12)% was an error over the time period of (0.42)%, which is to say that USNG’s actual total return underperformed the benchmark result by that percentage. USCF believes that a portion of the difference between the actual total return and the expected benchmark total return can be attributed to the net impact of the expenses that USNG pays, offset in part by the income that USNG collects on its cash and cash equivalent holdings. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG earned dividend and interest income of $117,668, which is equivalent to a weighted average income rate of 0.03% for such period. In addition, during the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG also collected $106,000 from its Authorized Purchasers for creating or redeeming baskets of units. This income contributed to USNG’s actual total return. However, if the total assets of USNG increase, USCF believes that the impact on total returns of these fees from creations and redemptions will diminish as a percentage of the total return. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG incurred total expenses of $5,414,580. Income from dividends and interest and Authorized Purchaser collections net of expenses was $(5,190,912), which is equivalent to an annualized weighted average net income rate of (1.15)% for the six months ended June 30, 2012.
| * | Adjusted to give effect to the reverse unit split of 4-for-1 executed on February 21, 2012. |
By comparison, for the six months ended June 30, 2011, the actual total return of USNG as measured by changes in its per unit NAV was (8.17)%. This was based on an initial per unit NAV, taking into account the reverse unit split, of $48.00* on December 31, 2010 and an ending per unit NAV as of June 30, 2011 of $44.08**. During this time period, USNG made no distributions to its unitholders. However, if USNG’s daily changes in its per unit NAV had instead exactly tracked the changes in the daily total return of the Benchmark Futures Contract, USNG would have had an estimated per unit NAV of $11.08 as of June 30, 2011, for a total return over the relevant time period of (7.67)%. The difference between the actual per unit NAV total return of USNG of (8.17)% and the expected total return based on the Benchmark Futures Contract of (7.67)% was an error over the time period of (0.50)%, which is to say that USNG’s actual total return underperformed the benchmark result by that percentage. USCF believes that a portion of the difference between the actual total return and the expected benchmark total return can be attributed to the net impact of the expenses that USNG paid, offset in part by the income that USNG collected on its cash and cash equivalent holdings. During the six months ended June 30, 2011, USNG earned dividend and interest income of $306,597, which is equivalent to a weighted average income rate of 0.03% for such period. In addition, during the six months ended June 30, 2011, USNG also collected $97,000 from its Authorized Purchasers for creating or redeeming baskets of units. This income also contributed to USNG’s actual total return. During the six months ended June 30, 2011, USNG incurred total expenses of $10,337,220. Income from dividends and interest and Authorized Purchaser collections net of expenses was $(9,933,623), which is equivalent to an annualized weighted average net income rate of (0.91)% for the six months ended June 30, 2011.
| * | Adjusted to give effect to the reverse unit split of 2-for-1 executed on March 8, 2011 and the reverse unit split of 4-for-1 executed on February 21, 2012. |
| ** | Adjusted to give effect to the reverse unit split of 4-for-1 executed on February 21, 2012. |
There are currently three factors that have impacted or are most likely to impact USNG’s ability to accurately track its Benchmark Futures Contract.
First, USNG may buy or sell its holdings in the then current Benchmark Futures Contract at a price other than the closing settlement price of that contract on the day during which USNG executes the trade. In that case, USNG may pay a price that is higher, or lower, than that of the Benchmark Futures Contract, which could cause the changes in the daily per unit NAV of USNG to either be too high or too low relative to the daily changes in the Benchmark Futures Contract. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USCF attempted to minimize the effect of these transactions by seeking to execute its purchase or sale of the Benchmark Futures Contract at, or as close as possible to, the end of the day settlement price. However, it may not always be possible for USNG to obtain the closing settlement price and there is no assurance that failure to obtain the closing settlement price in the future will not adversely impact USNG’s attempt to track the Benchmark Futures Contract over time.
28
Table of Contents
Second, USNG earns dividend and interest income on its cash, cash equivalents and Treasuries. USNG is not required to distribute any portion of its income to its unitholders and did not make any distributions to unitholders during the six months ended June 30, 2012. Interest payments, and any other income, were retained within the portfolio and added to USNG’s NAV. When this income exceeds the level of USNG’s expenses for its management fee, brokerage commissions and other expenses (including ongoing registration fees, licensing fees and the fees and expenses of the independent directors of USCF), USNG will realize a net yield that will tend to cause daily changes in the per unit NAV of USNG to track slightly higher than daily changes in the Benchmark Futures Contract. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG earned, on an annualized basis, approximately 0.03% on its cash and cash equivalent holdings. It also incurred cash expenses on an annualized basis of 0.60% for management fees, approximately 0.43% in brokerage commission costs related to the purchase and sale of futures contracts and approximately 0.17% for other expenses. The foregoing fees and expenses resulted in a net yield on an annualized basis of approximately (1.17)% and affected USNG’s ability to track its benchmark. If short-term interest rates rise above the current levels, the level of deviation created by the yield would decrease. Conversely, if short-term interest rates were to decline, the amount of error created by the yield would increase. When short-term yields drop to a level lower than the combined expenses of the management fee and the brokerage commissions, then the tracking error becomes a negative number and would tend to cause the daily returns of the per unit NAV to underperform the daily returns of the Benchmark Futures Contract.
Third, USNG may hold Other Natural Gas-Related Investments in its portfolio that may fail to closely track the Benchmark Futures Contract’s total return movements. In that case, the error in tracking the Benchmark Futures Contract could result in daily changes in the per unit NAV of USNG that are either too high, or too low, relative to the daily changes in the Benchmark Futures Contract. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG held Other Natural Gas-Related Investments. These holdings included a financially settled natural gas futures contract traded on NYMEX whose settlement price tracks the settlement price of the Benchmark Futures Contract. USNG also held investments in cleared swaps traded on the ICE Futures whose settlement price also tracks the settlement price of the Benchmark Futures Contract and fully-collateralized over-the-counter swaps designed to track the settlement price of the Benchmark Futures Contract. Due, in part, to the increased size of USNG over the last several quarters and its obligations to comply with current and potential regulatory limits, USNG has invested in Other Natural Gas-Related Investments, such as over-the-counter swaps, which have increased transaction-related expenses and may result in increased tracking error. Over-the-counter swaps increase transaction-related expenses due to the fact that USNG must pay to the swap counterparty certain fees that USNG does not have to pay for transactions executed on an exchange. Finally, due to potential regulatory limitations, USNG may determine to hold greater amounts of cash and cash equivalents and lesser amounts of Natural Gas Interests, if it determines that will most appropriately satisfy USNG’s investment objective. Holding more cash and cash equivalents and less Natural Gas Interests for some period of time may result in increased tracking error. There are additional Other Natural Gas-Related Investments that USNG is permitted to invest in whose price movements may not track the settlement price of the Benchmark Futures Contract.
USCF anticipates that interest rates will continue to remain at historical lows and therefore, it is anticipated that fees and expenses paid by USNG will continue to be higher than interest earned by USNG. As such, USCF anticipates that USNG will continue to underperform its benchmark until such a time when interest earned at least equals or exceeds the fees and expenses paid by USNG.
Term Structure of Natural Gas Futures Prices and the Impact on Total Returns. Several factors determine the total return from investing in a futures contract position. One factor that impacts the total return that will result from investing in near month futures contracts and “rolling” those contracts forward each month is the price relationship between the current near month contract and the next month contract. For example, if the price of the near month contract is higher than the next month contract (a situation referred to as “backwardation” in the futures market), then absent any other change there is a tendency for the price of a next month contract to rise in value as it becomes the near month contract and approaches expiration. Conversely, if the price of a near month contract is lower than the next month contract (a situation referred to as “contango” in the futures market), then absent any other change there is a tendency for the price of a next month contract to decline in value as it becomes the near month contract and approaches expiration.
29
Table of Contents
As an example, assume that the price of natural gas for immediate delivery (the “spot” price), was $7 per MMBtu, and the value of a position in the near month futures contract was also $7. Over time, the price of 10,000 MMBtu of natural gas will fluctuate based on a number of market factors, including demand for natural gas relative to its supply. The value of the near month contract will likewise fluctuate in reaction to a number of market factors. If investors seek to maintain their position in a near month contract and not take delivery of the natural gas, every month they must sell their current near month contract as it approaches expiration and invest in the next month contract.
If the futures market is in backwardation, e.g., when the expected price of natural gas in the future would be less, the investor would be buying a next month contract for a lower price than the current near month contract. Using the $7 per MMBtu price above to represent the front month price, the price of the next month contract could be $6.86 per barrel, that is, 2% cheaper than the front month contract. Hypothetically, and assuming no other changes to either prevailing natural gas prices or the price relationship between the spot price, the near month contract and the next month contract (and ignoring the impact of commission costs and the income earned on cash and/or cash equivalents), the value of the $6.86 next month contract would rise as it approaches expiration and becomes the new near month contract with a price of $7. In this example, the value of an investment in the second month contract would tend to rise faster than the spot price of natural gas, or fall slower. As a result, it would be possible in this hypothetical example for the spot price of natural gas to have risen 10% after some period of time, while the value of the investment in the second month futures contract would have risen 12%, assuming backwardation is large enough or enough time has elapsed. Similarly, the spot price of natural gas could have fallen 10% while the value of an investment in the futures contract could have fallen only 8%. Over time, if backwardation remained constant, the difference would continue to increase.
If the futures market is in contango, the investor would be buying a next month contract for a higher price than the current near month contract. Using again the $7 per MMBtu price above to represent the front month price, the price of the next month contract could be $7.14 per barrel, that is, 2% more expensive than the front month contract. Hypothetically, and assuming no other changes to either prevailing natural gas prices or the price relationship between the spot price, the near month contract and the next month contract (and ignoring the impact of commission costs and the income earned on cash and/or cash equivalents), the value of the next month contract would fall as it approaches expiration and becomes the new near month contract with a price of $7. In this example, it would mean that the value of an investment in the second month would tend to rise slower than the spot price of natural gas, or fall faster. As a result, it would be possible in this hypothetical example for the spot price of natural gas to have risen 10% after some period of time, while the value of the investment in the second month futures contract will have risen only 8%, assuming contango is large enough or enough time has elapsed. Similarly, the spot price of natural gas could have fallen 10% while the value of an investment in the second month futures contract could have fallen 12%. Over time, if contango remained constant, the difference would continue to increase.
The chart below compares the price of the near month contract to the average price of the near 12 month contracts over the last 10 years (2002-2011) for natural gas. When the price of the near month contract is higher than the average price of the near 12 month contracts, the market would be described as being in backwardation. When the price of the near month contract is lower than the average price of the near 12 month contracts, the market would be described as being in contango. Although the prices of the near month contract and the average price of the near 12 month contracts do tend to move up or down together, it can be seen that at times the near month prices are clearly higher than the average price of the near 12 month contracts (backwardation), and other times they are below the average price of the near 12 month contracts (contango). In addition, investors can observe that natural gas prices, both front month and the average of the near 12 months, often display a seasonal pattern in which the price of natural gas tends to rise in the early winter months and decline in the summer months. This mirrors the physical demand for natural gas, which typically peaks in the winter.
30
Table of Contents
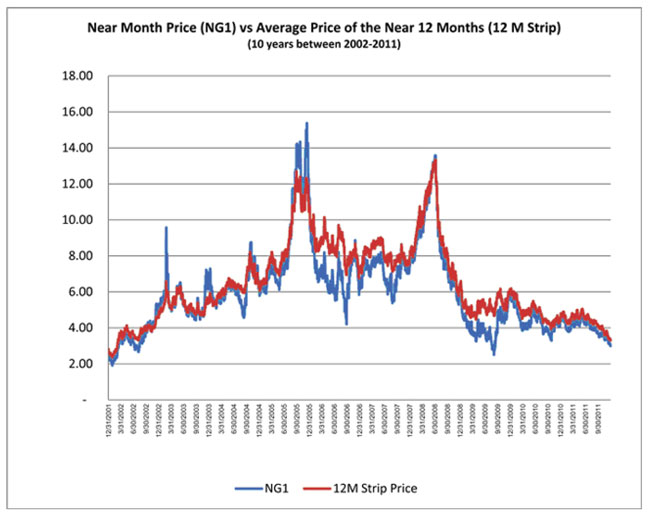
*PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS
An alternative way to view backwardation and contango data over time is to subtract the dollar price of the near month natural gas Futures Contract from the dollar price of the near 12 month natural gas Futures Contracts. If the resulting number is a positive number, then the near month price is higher than the average price of the near 12 months and the market could be described as being in backwardation. If the resulting number is a negative number, then the near month price is lower than the average price of the near 12 months and the market could be described as being in contango. The chart below shows the results from subtracting the average dollar price of the near 12 month contracts from the near month price for the 10 year period between 2002 and 2011. Investors will note that the natural gas market spent time in both backwardation and contango. Investors will further note that the markets display a seasonal pattern that corresponds to the seasonal demand patterns for natural gas above. That is, in many, but not all, cases the average price of the near 12 month contracts is higher than the near month during the approach to the winter months as the price of natural gas for delivery in those winter months rises on expectations of demand. At the same time, the price of the near month, when that month is just before the onset of winter, does not rise as far or as fast as the average price of the near 12 month contracts whose delivery falls during the winter season.
31
Table of Contents
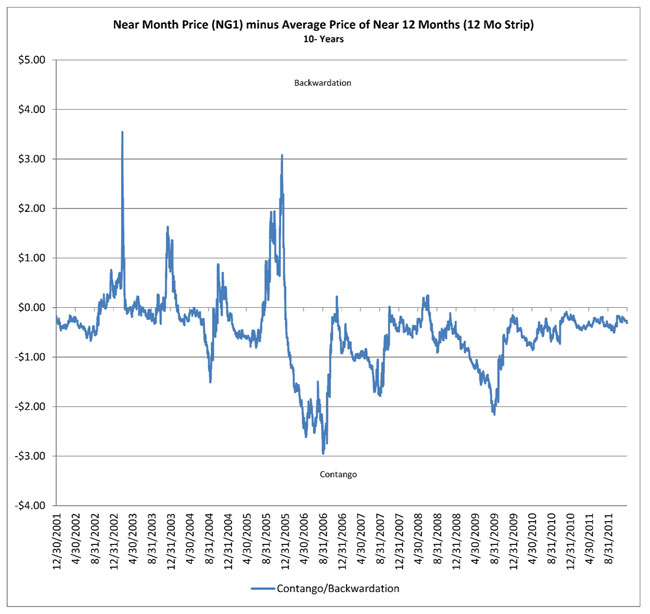
*PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS
An investment in a portfolio that involved owning only the near month contract would likely produce a different result than an investment in a portfolio that owned an equal number of each of the near 12 months’ worth of contracts. Generally speaking, when the natural gas futures market is in backwardation, the near month only portfolio would tend to have a higher total return than the 12 month contract portfolio. Conversely, if the natural gas futures market was in contango, the portfolio containing 12 months’ worth of contracts would tend to outperform the near month only portfolio. The chart below shows the annual results of owning a portfolio consisting of the near month contract and a portfolio containing the near 12 months’ worth of contracts. In addition, the chart shows the annual change in the spot price of natural gas. In this example, each month, the near month only portfolio would sell the near month contract at expiration and buy the next month out contract. The portfolio holding an equal number of the near 12 months’ worth of contracts would sell the near month contract at expiration and replace it with the contract that becomes the new twelfth month contract.
32
Table of Contents
*PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS
HYPOTHETICAL PERFORMANCE RESULTS HAVE MANY INHERENT LIMITATIONS, SOME OF WHICH ARE DESCRIBED BELOW. NO REPRESENTATION IS BEING MADE THAT USNG WILL OR IS LIKELY TO ACHIEVE PROFITS OR LOSSES SIMILAR TO THOSE SHOWN. IN FACT, THERE ARE FREQUENTLY SHARP DIFFERENCES BETWEEN HYPOTHETICAL PERFORMANCE RESULTS AND THE ACTUAL RESULTS ACHIEVED BY ANY PARTICULAR TRADING PROGRAM.
ONE OF THE LIMITATIONS OF HYPOTHETICAL PERFORMANCE RESULTS IS THAT THEY ARE GENERALLY PREPARED WITH THE BENEFIT OF HINDSIGHT. IN ADDITION, HYPOTHETICAL TRADING DOES NOT INVOLVE FINANCIAL RISK, AND NO HYPOTHETICAL TRADING RECORD CAN COMPLETELY ACCOUNT FOR THE IMPACT OF FINANCIAL RISK IN ACTUAL TRADING.
FOR EXAMPLE, THE ABILITY TO WITHSTAND LOSSES OR TO ADHERE TO A PARTICULAR TRADING PROGRAM IN SPITE OF TRADING LOSSES ARE MATERIAL POINTS WHICH CAN ALSO ADVERSELY AFFECT ACTUAL TRADING RESULTS. THERE ARE NUMEROUS OTHER FACTORS RELATED TO THE MARKETS IN GENERAL OR TO THE IMPLEMENTATION OF ANY SPECIFIC TRADING PROGRAM WHICH CANNOT BE FULLY ACCOUNTED FOR IN THE PREPARATION OF HYPOTHETICAL PERFORMANCE RESULTS AND ALL OF WHICH CAN ADVERSELY AFFECT ACTUAL TRADING RESULTS.
BECAUSE THERE ARE NO ACTUAL TRADING RESULTS TO COMPARE TO THE HYPOTHETICAL PERFORMANCE RESULTS, INVESTORS SHOULD BE PARTICULARLY WARY OF PLACING UNDUE RELIANCE ON THESE HYPOTHETICAL PERFORMANCE RESULTS.
As seen in the chart above, there have been periods of both positive and negative annual total returns for both hypothetical portfolios over the last 10 years. In addition, there have been periods during which the near month only approach had higher returns, and periods where the 12 month approach had higher total returns. The above chart does not represent the performance history of USNG or any Related Public Fund.
33
Table of Contents
Historically, the natural gas futures markets have experienced periods of contango and backwardation. Because natural gas demand is seasonal, it is possible for the price of Futures Contracts for delivery within one or two months to rapidly move from backwardation into contango and back again within a relatively short period of time of less than one year. While the investment objective of USNG is not to have the market price of its units match, dollar for dollar, changes in the spot price of natural gas, contango impacted the total return on an investment in USNG units during the six months ended June 30, 2012 relative to a hypothetical direct investment in natural gas. For example, an investment in USNG units made on December 31, 2011 and held to June 30, 2012 decreased, based upon the changes in the per unit NAV for USNG units on those days, by approximately 25.54%, while the spot price of natural gas for immediate delivery during the same period decreased by approximately 5.52% (note: this comparison ignores the potential costs associated with physically owning and storing natural gas, which could be substantial). By comparison, during the period from December 31, 2010 to June 30, 2011, contango impacted the total return on an investment in USNG units relative to a hypothetical direct investment in natural gas. For example, an investment in USNG units made on December 31, 2010 and held to June 30, 2011 decreased, based upon the changes in the per unit NAV for USNG units on those days, by approximately 8.17%, while the spot price of natural gas for immediate delivery during the same period decreased by approximately 0.70% (note: this comparison ignores the potential costs associated with physically owning and storing natural gas, which could be substantial).
Periods of contango or backwardation do not materially impact USNG’s investment objective of having the daily percentage changes in its per unit NAV track the daily percentage changes in the price of the Benchmark Futures Contract since the impact of backwardation and contango tend to equally impact the daily percentage changes in price of both USNG’s units and the Benchmark Futures Contract. It is impossible to predict with any degree of certainty whether backwardation or contango will occur in the future. It is likely that both conditions will occur during different periods and, because of the seasonal nature of natural gas demand, both may occur within a single year’s time.
Natural Gas Market. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, natural gas prices in the United States were impacted by several factors. As of June 30, 2012, the amount of natural gas in storage had reached 3.102 billion cubic feet, which was approximately 22% and 23% above the five-year average and 2011 levels, respectively. Prices were volatile and sharply higher during the second quarter of 2012 but lower for the six months ended June 30, 2012. Reduced natural gas production and a decline of surplus storage over historical levels contributed to an increase in natural gas prices during the second quarter of 2012. However, the continued existence of a historic storage surplus ultimately led to a decline in prices for the six months ended June 30, 2012, with prices reaching a low of $1.983 on April 12, 2012.
Natural Gas Price Movements in Comparison to Other Energy Commodities and Investment Categories. USCF believes that investors frequently measure the degree to which prices or total returns of one investment or asset class move up or down in value in concert with another investment or asset class. Statistically, such a measure is usually done by measuring the correlation of the price movements of the two different investments or asset classes over some period of time. The correlation is scaled between 1 and -1, where 1 indicates that the two investment options move up or down in price or value together, known as “positive correlation,” and -1 indicates that they move in completely opposite directions, known as “negative correlation.” A correlation of 0 would mean that the movements of the two are neither positively nor negatively correlated, known as “non-correlation.” That is, the investment options sometimes move up and down together and other times move in opposite directions.
For the ten-year time period between June 30, 2002 and June 30, 2012, the chart below compares the monthly movements of natural gas prices versus the monthly movements of the prices of several other energy commodities, such as crude oil, heating oil, and unleaded gasoline, as well as several major non-commodity investment asset classes, such as large cap U.S. equities, U.S. government bonds and global equities. It can be seen that over this particular time period, the movement of natural gas on a monthly basis was not strongly correlated with the movements of unleaded gasoline, crude oil, large cap U.S. equities, U.S. government bonds or global equities. Movements in natural gas had a positive, yet moderate, correlation to movements in heating oil.
34
Table of Contents
| Correlation Matrix June 30, 2002-2012 |
Large Cap U.S. Equities (S&P 500) |
U.S. Gov’t. Bonds (EFFAS U.S. Gov’t. Bond Index) |
Global Equities (FTSE World Index) |
Crude Oil |
Heating Oil |
Unleaded Gasoline |
Natural Gas |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap U.S. Equities (S&P 500) |
1.000 | (0.337 | ) | 0.968 | 0.282 | 0.234 | 0.189 | 0.042 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Gov’t. Bonds (EFFAS U.S. Gov’t. Bond Index) |
1.000 | (0.315 | ) | (0.184 | ) | (0.130 | ) | (0.222 | ) | 0.074 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Global Equities (FTSE World Index) |
1.000 | 0.369 | 0.314 | 0.247 | 0.092 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crude Oil |
1.000 | 0.833 | 0.724 | 0.391 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heating Oil |
1.000 | 0.707 | 0.505 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unleaded Gasoline |
1.000 | 0.281 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural Gas |
1.000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Bloomberg, NYMEX
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS
The chart below covers a more recent, but much shorter, range of dates than the above chart. It can be seen that over this particular time period, the movement of natural gas on a monthly basis was essentially non-correlated with large-cap U.S. equities, U.S. government bonds, global equities, crude oil and heating oil and had a negative, yet moderate, correlation with unleaded gasoline.
| Correlation Matrix 12 Months ended June 30, 2012 |
Large Cap U.S. Equities (S&P 500) |
U.S. Gov’t. Bonds (EFFAS U.S. Gov’t. Bond Index) |
Global Equities (FTSE World Index) |
Crude Oil |
Heating Oil |
Unleaded Gasoline |
Natural Gas |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Large Cap U.S. Equities (S&P 500) |
1.000 | (0.777 | ) | 0.980 | 0.803 | 0.748 | 0.637 | 0.142 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| U.S. Gov’t. Bonds (EFFAS U.S. Gov’t. Bond Index) |
1.000 | (0.744 | ) | (0.506 | ) | (0.385 | ) | (0.532 | ) | (0.008 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Global Equities (FTSE World Index) |
1.000 | 0.783 | 0.790 | 0.629 | 0.187 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Crude Oil |
1.000 | 0.850 | 0.456 | 0.160 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Heating Oil |
1.000 | 0.658 | 0.045 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Unleaded Gasoline |
1.000 | (0.441 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Natural Gas |
1.000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Source: Bloomberg, NYMEX
PAST PERFORMANCE IS NOT NECESSARILY INDICATIVE OF FUTURE RESULTS
Investors are cautioned that the historical price relationships between natural gas and various other energy commodities, as well as other investment asset classes, as measured by correlation may not be reliable predictors of future price movements and correlation results. The results pictured above would have been different if a different range of dates had been selected. USCF believes that natural gas has historically not demonstrated a strong correlation with equities or bonds over long periods of time. However, USCF also believes that in the future it is possible that natural gas could have long-term correlation results that indicate prices of natural gas more closely track the movements of equities or bonds. In addition, USCF believes that, when measured over time periods shorter than ten years, there will always be some periods where the correlation of natural gas to equities and bonds will be either more strongly positively correlated or more strongly negatively correlated than the long term historical results suggest.
35
Table of Contents
The correlations between natural gas, crude oil, heating oil and gasoline are relevant because USCF endeavors to invest USNG’s assets in natural gas Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments so that daily changes in percentage terms in USNG’s per unit NAV correlate as closely as possible with daily changes in percentage terms in the price of the Benchmark Futures Contract. If certain other fuel-based commodity futures contracts do not closely correlate with the natural gas Futures Contract, then their use could lead to greater tracking error. As noted above, USCF also believes that the changes in percentage terms in the price of the Benchmark Futures Contract will closely correlate with changes in percentage terms in the spot price of natural gas.
Critical Accounting Policies
Preparation of the condensed financial statements and related disclosures in compliance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires the application of appropriate accounting rules and guidance, as well as the use of estimates. USNG’s application of these policies involves judgments and actual results may differ from the estimates used.
USCF has evaluated the nature and types of estimates that it makes in preparing USNG’s condensed financial statements and related disclosures and has determined that the valuation of its investments, which are not traded on a United States or internationally recognized futures exchange (such as forward contracts and over-the-counter contracts) involves a critical accounting policy. The values which are used by USNG for its Futures Contracts are provided by its commodity broker who uses market prices when available, while over-the-counter contracts are valued based on the present value of estimated future cash flows that would be received from or paid to a third party in settlement of these derivative contracts prior to their delivery date and valued on a daily basis. In addition, USNG estimates interest and dividend income on a daily basis using prevailing rates earned on its cash and cash equivalents. These estimates are adjusted to the actual amount received on a monthly basis and the difference, if any, is not considered material.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
USNG has not made, and does not anticipate making, use of borrowings or other lines of credit to meet its obligations. USNG has met, and it is anticipated that USNG will continue to meet, its liquidity needs in the normal course of business from the proceeds of the sale of its investments, or from the Treasuries, cash and/or cash equivalents that it intends to hold at all times. USNG’s liquidity needs include: redeeming units, providing margin deposits for its existing Futures Contracts or the purchase of additional Futures Contracts and posting collateral for its over-the-counter contracts and payment of its expenses, summarized below under “Contractual Obligations.”
USNG currently generates cash primarily from: (i) the sale of baskets consisting of 100,000 units (“Creation Baskets”) and (ii) income earned on Treasuries, cash and/or cash equivalents. USNG has allocated substantially all of its net assets to trading in Natural Gas Interests. USNG invests in Natural Gas Interests to the fullest extent possible without being leveraged or unable to satisfy its current or potential margin or collateral obligations with respect to its investments in Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments. A significant portion of USNG’s NAV is held in cash and cash equivalents that are used as margin and as collateral for its trading in Natural Gas Interests. The balance of the assets is held in USNG’s account at its custodian bank and in Treasuries at the FCM. Income received from USNG’s money market funds and Treasuries is paid to USNG. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG’s expenses exceeded the income USNG earned and the cash earned from the sale of Creation Baskets and the redemption of Redemption Baskets. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG was forced to use other assets to pay expenses, which could cause a drop in USNG’s NAV over time. To the extent expenses exceed income, USNG’s NAV will be negatively impacted.
USNG’s investments in Natural Gas Interests may be subject to periods of illiquidity because of market conditions, regulatory considerations and other reasons. For example, most commodity exchanges limit the fluctuations in futures contracts prices during a single day by regulations referred to as “daily limits.” During a single day, no trades may be executed at prices beyond the daily limit. Once the price of a futures contract has increased or decreased by an amount equal to the daily limit, positions in the contracts can neither be taken nor liquidated unless the traders are willing to effect trades at or within the specified daily limit. In addition, USNG’s over-the-counter contracts have very limited liquidity since they are negotiated agreements that are not transferable by USNG except with the consent of its counterparty, and even if consent were granted, there may not be an available transferee. Such market conditions or contractual limits could prevent USNG from promptly liquidating its positions in Natural Gas Interests. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG was not forced to purchase or liquidate any of its positions while daily limits were in effect; however, USNG cannot predict whether such an event may occur in the future.
36
Table of Contents
Since the initial offering of units, USNG has been responsible for expenses relating to: (i) management fees, (ii) brokerage fees and commissions and fees associated with its over-the-counter transactions, (iii) licensing fees for the use of intellectual property, (iv) ongoing registration expenses in connection with offers and sales of its units subsequent to the initial offering, (v) other expenses, including tax reporting costs, (vi) fees and expenses of the independent directors of USCF and (vii) other extraordinary expenses not in the ordinary course of business, while USCF has been responsible for expenses relating to the fees of USNG’s Marketing Agent, Administrator and Custodian and registration expenses relating to the initial offering of units. If USCF and USNG are unsuccessful in raising sufficient funds to cover these respective expenses or in locating any other source of funding, USNG will terminate and investors may lose all or part of their investment.
Market Risk
Trading in Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments, such as forwards, involves USNG entering into contractual commitments to purchase or sell natural gas at a specified date in the future. The aggregate market value of the contracts will significantly exceed USNG’s future cash requirements since USNG intends to close out its open positions prior to settlement. As a result, USNG is generally only subject to the risk of loss arising from the change in value of the contracts. USNG considers the “fair value” of its derivative instruments to be the unrealized gain or loss on the contracts. The market risk associated with USNG’s commitments to purchase natural gas is limited to the aggregate market value of the contracts held. However, should USNG enter into a contractual commitment to sell natural gas, it would be required to make delivery of the natural gas at the contract price, repurchase the contract at prevailing prices or settle in cash. Since there are no limits on the future price of natural gas, the market risk to USNG could be unlimited.
USNG’s exposure to market risk depends on a number of factors, including the markets for natural gas, the volatility of interest rates and foreign exchange rates, the liquidity of the Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments markets and the relationships among the contracts held by USNG. Drastic market occurrences could ultimately lead to the loss of all or substantially all of an investor’s capital.
Credit Risk
When USNG enters into Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments, it is exposed to the credit risk that the counterparty will not be able to meet its obligations. The counterparty for the Futures Contracts traded on the NYMEX and on most other futures exchanges is the clearinghouse associated with the particular exchange. In general, in addition to margin required to be posted by the clearinghouse in connection with cleared trades, clearinghouses are backed by their members who may be required to share in the financial burden resulting from the nonperformance of one of their members and, therefore, this additional member support should significantly reduce credit risk. Some foreign exchanges are not backed by their clearinghouse members but may be backed by a consortium of banks or other financial institutions. There can be no assurance that any counterparty, clearinghouse, or their members or their financial backers will satisfy their obligations to USNG in such circumstances.
During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG entered into fully collateralized over-the-counter transactions with two counterparties, JPMorgan Chase Bank, NA (“JPMorgan”) and Deutsche Bank AG (“Deutsche Bank”). Unlike most exchange-traded futures contracts, cleared swaps or exchange-traded options on such futures, each party to an over-the-counter contract bears the credit risk that the other party may not be able to perform its obligations under its contract. See “Item 3. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk” of this quarterly report on Form 10-Q for a discussion of over-the-counter contracts.
37
Table of Contents
USCF attempts to manage the credit risk of USNG by following various trading limitations and policies. In particular, USNG generally posts margin and/or holds liquid assets that are approximately equal to the market value of its obligations to counterparties under the Futures Contracts and Other Natural Gas-Related Investments it holds. USCF has implemented procedures that include, but are not limited to, executing and clearing trades only with creditworthy parties and/or requiring the posting of collateral or margin by such parties for the benefit of USNG to limit its credit exposure. UBS Securities LLC, USNG’s commodity broker, or any other broker that may be retained by USNG in the future, when acting as USNG’s FCM in accepting orders to purchase or sell Futures Contracts on United States exchanges, is required by CFTC regulations to separately account for and segregate as belonging to USNG, all assets of USNG relating to domestic Futures Contracts trading. These FCMs are not allowed to commingle USNG’s assets with their other assets. In addition, the CFTC requires commodity brokers to hold in a secure account USNG’s assets related to foreign Futures Contracts trading and, in some cases, to cleared swaps executed through the FCM. Similarly, under its current over-the-counter agreements, USNG requires that collateral it posts or receives be posted with its custodian and, under agreements among the custodian, USNG and its counterparties, such collateral is segregated.
See “Item 3. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk” in this quarterly report on Form 10-Q for a discussion of over-the-counter contracts.
As of June 30, 2012, USNG held cash deposits and investments in Treasuries and money market funds in the amount of $983,055,725 with the custodian and FCM. Some or all of these amounts may be subject to loss should USNG’s custodian and/or FCM cease operations.
Off Balance Sheet Financing
As of June 30, 2012, USNG had no loan guarantee, credit support or other off-balance sheet arrangements of any kind other than agreements entered into in the normal course of business, which may include indemnification provisions relating to certain risks that service providers undertake in performing services which are in the best interests of USNG. While USNG’s exposure under these indemnification provisions cannot be estimated, they are not expected to have a material impact on USNG’s financial position.
European Sovereign Debt
USNG had no direct exposure to European sovereign debt as of June 30, 2012 and has no direct exposure to European sovereign debt as of the filing of this quarterly report on Form 10-Q.
Redemption Basket Obligation
In order to meet its investment objective and pay its contractual obligations described below, USNG requires liquidity to redeem units, which redemptions must be in blocks of 100,000 units called “Redemption Baskets.” USNG has to date satisfied this obligation by paying from the cash or cash equivalents it holds or through the sale of its Treasuries in an amount proportionate to the number of units being redeemed.
Contractual Obligations
USNG’s primary contractual obligations are with USCF. In return for its services, USCF is entitled to a management fee calculated monthly as a fixed percentage of USNG’s NAV, currently 0.60% for a NAV of $1 billion or less, and thereafter 0.50% for a NAV above $1 billion.
USCF agreed to pay the start-up costs associated with the formation of USNG, primarily its legal, accounting and other costs in connection with USCF’s registration with the CFTC as a CPO and the registration and listing of USNG and its units with the SEC, FINRA and NYSE Arca (formerly, AMEX), respectively. However, since USNG’s initial offering of units, offering costs incurred in connection with registering and listing additional units of USNG have been directly borne on an ongoing basis by USNG, and not by USCF.
USCF pays the fees of USNG’s marketing agent, ALPS Distributors, Inc., and the fees of the custodian and transfer agent, Brown Brothers Harriman & Co. (“BBH&Co.”), as well as BBH&Co.’s fees for performing administrative services, including those in connection with the preparation of USNG’s condensed financial statements and its SEC, NFA and CFTC reports. USCF and USNG have also entered into a licensing agreement with the NYMEX pursuant to which USNG and the Related Public Funds, other than USBO, USCI, CPER, USAG and USMI, pay a licensing fee to the NYMEX. USNG also pays the fees and expenses associated with its tax accounting and reporting requirements.
38
Table of Contents
In addition to USCF’s management fee, USNG pays its brokerage fees (including fees to a FCM), over-the-counter dealer spreads and up-front fees, any licensing fees for the use of intellectual property, and, subsequent to the initial offering, registration and other fees paid to the SEC, FINRA, or other regulatory agencies in connection with the offer and sale of units, as well as legal, printing, accounting and other expenses associated therewith, and extraordinary expenses. The latter are expenses not incurred in the ordinary course of USNG’s business, including expenses relating to the indemnification of any person against liabilities and obligations to the extent permitted by law and under the LP Agreement, the bringing or defending of actions in law or in equity or otherwise conducting litigation and incurring legal expenses and the settlement of claims and litigation. Commission payments to a FCM are on a contract-by-contract, or round turn, basis. USNG also pays a portion of the fees and expenses of the independent directors of USCF. See Note 3 to the Notes to Condensed Financial Statements (Unaudited) in Item 1 of this quarterly report on Form 10-Q.
The parties cannot anticipate the amount of payments that will be required under these arrangements for future periods, as USNG’s per unit NAVs and trading levels to meet its investment objective will not be known until a future date. These agreements are effective for a specific term agreed upon by the parties with an option to renew, or, in some cases, are in effect for the duration of USNG’s existence. Either party may terminate these agreements earlier for certain reasons described in the agreements.
As of June 30, 2012, USNG’s portfolio consisted of 22,244 Natural Gas NG Futures August 2012 Contracts traded on the NYMEX, 17,952 Natural Gas NN Financially Settled Futures August 2012 Contracts traded on the NYMEX, 31,178 cleared swaps traded on the ICE Futures and total return swaps with an aggregate market value of $10,537,264. For a list of USNG’s current holdings, please see USNG’s website at www.unitedstatesnaturalgasfund.com.
| Item 3. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk. |
Over-the-Counter Derivatives (Including Spreads and Straddles)
At June 30, 2012, USNG maintained fully-collateralized over-the-counter swap transactions (“OTC Contracts”) with two counterparties, JPMorgan and Deutsche Bank. Unlike most exchange-traded futures contracts, cleared swaps or exchange-traded options on such futures, each party to an OTC Contract bears the credit risk that the other party may not be able to perform its obligations under its contract.
To reduce the credit risk that arises in connection with such contracts, USNG will generally enter into an agreement with each counterparty based on the Master Agreement published by ISDA that provides for the netting of its overall exposure to its counterparty, if the counterparty is unable to meet its obligations to USNG due to the occurrence of a specified event, such as the insolvency of the counterparty.
USCF assesses or reviews, as appropriate, the creditworthiness of each potential or existing counterparty to an OTC Contract pursuant to guidelines approved by USCF’s board of directors (the “Board”). Furthermore, USCF on behalf of USNG only enters into OTC Contracts with counterparties who are, or are affiliates of, (a) banks regulated by a United States federal bank regulator, (b) broker-dealers regulated by the SEC, (c) insurance companies domiciled in the United States, or (d) producers, users or traders of energy, whether or not regulated by the CFTC. Any entity acting as a counterparty shall be regulated in either the United States or the United Kingdom unless otherwise approved by the Board after consultation with its legal counsel. Existing counterparties are also reviewed periodically by USCF. USNG will also require that the counterparty be highly rated and/or provide collateral or other credit support. Even if collateral is used to reduce counterparty credit risk, sudden changes in the value of OTC transactions may leave a party open to financial risk due to a counterparty default since the collateral held may not cover a party’s exposure on the transaction in such situations.
Both the Board and its audit committee review statistics and data pertaining to each of USNG’s over-the-counter counterparties. Reports are provided verbally and in writing by USCF’s management at least quarterly and more frequently when deemed necessary. Data reviewed includes, but is not limited to, short-term and long-term credit ratings by Moody’s Investor Service, Inc., Standard & Poor’s Financial Services LLC and Fitch Ratings; changes in market capitalization and stock prices over the last five years; numerous financial ratios including capital and leverage ratios; and credit default swap yields and spreads. Additionally, members of USCF’s Board, audit committee and management team may note general economic or company specific news that necessitates a review of a counterparty’s creditworthiness outside of the regular review cycle. Board members and audit committee members may conduct their own analysis and contact USCF’s management team at their discretion to request further information or action. Board members are apprised of open positions as well as changes to positions and counterparties utilized by USNG on an ongoing basis. Significant changes to USNG’s over-the-counter contract holdings are reported to the Board in a timely manner.
39
Table of Contents
In general, valuing OTC derivatives is less certain than valuing actively traded financial instruments such as exchange-traded futures contracts and securities or cleared swaps because the price and terms on which such OTC derivatives are entered into or can be terminated are individually negotiated, and those prices and terms may not reflect the best price or terms available from other sources. In addition, while market makers and dealers generally quote indicative prices or terms for entering into or terminating OTC Contracts, they typically are not contractually obligated to do so, particularly if they are not a party to the transaction. As a result, it may be difficult to obtain an independent value for an outstanding OTC derivatives transaction.
During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG employed hedging methods such as those described above to the extent it invested in fully-collateralized over-the-counter swap transactions designed to track percentage changes in the price of the Benchmark Futures Contract. During the six months ended June 30, 2012, USNG was exposed to counterparty risk on its fully-collateralized over-the-counter swap transactions with two counterparties, JPMorgan and Deutsche Bank.
The counterparty credit ratings for the exposure on over-the-counter swap transactions to which USNG was a party that would be owed to USNG due to a default or early termination by USNG’s counterparties at June 30, 2012, December 31, 2011 and June 30, 2011 were:
| June 30, 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Moody’s Credit Rating |
Number of Counterparties |
Notional Value |
Credit Exposure |
Collateral Held |
Exposure, Net of Collateral* |
|||||||||||||||
| Aa3 |
2 | $ | 175,792,038 | $ | 10,559,615 | $ | 9,100,249 | $ | 1,459,366 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
2 | $ | 175,792,038 | $ | 10,559,615 | $ | 9,100,249 | $ | 1,459,366 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| December 31, 2011 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Moody’s Credit Rating |
Number of Counterparties |
Notional Value |
Credit Exposure |
Collateral Held |
Exposure, Net of Collateral* |
|||||||||||||||
| Aa3 |
2 | $ | 261,626,092 | $ | (12,774,598 | ) | $ | 990,210 | $ | (13,764,808 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
2 | $ | 261,626,092 | $ | (12,774,598 | ) | $ | 990,210 | $ | (13,764,808 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| June 30, 2011 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Moody’s Credit Rating |
Number of Counterparties |
Notional Value |
Credit Exposure |
Collateral Held |
Exposure, Net of Collateral* |
|||||||||||||||
| A2 |
1 | $ | 256,803,836 | $ | (22,738,262 | ) | $ | 75,757,094 | $ | (22,738,262 | ) | |||||||||
| Aa2 |
1 | 106,167,330 | (7,968,361 | ) | 22,199,236 | (7,968,361 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Aa3 |
2 | 472,493,919 | (3,895,182 | ) | 88,679,930 | 88,679,039 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
4 | $ | 835,465,085 | $ | (34,601,805 | ) | $ | 186,636,260 | $ | (34,602,311 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| * | The difference reflects minimum transfer amounts for collateral and potentially one day’s movement in the underlying total return, which would be collateralized the following business day. |
The aggregate notional amount of USNG’s over-the-counter derivative transactions, which consisted of total return swaps, decreased to $175,792,038 at June 30, 2012, as compared to $835,465,085 at June 30, 2011. The aggregate notional amount of these derivative transactions, which is not included in the Condensed Schedule of Investments (Unaudited), is indicative of USNG’s activities in derivative transactions, but is not an indicator of the level of credit risk associated with these transactions. The aggregate notional amount of USNG’s over-the-counter swap transactions represented 14.97% of USNG’s total assets as of June 30, 2012.
USNG maintains, in conjunction with its counterparties, collateral in the form of both cash and Treasuries, depending on the specific arrangements with each counterparty. USNG is required to post an independent amount based on a percentage of the initial notional amount of each position at the inception of each over-the-counter contract. In addition, between reset periods, USNG posts collateral for the benefit of its counterparties that approximately corresponds to any unrealized loss that would be realized by USNG if the over-the-counter contract were closed on any given valuation date. Likewise, USNG’s counterparties post collateral for USNG’s benefit that approximately corresponds to any unrealized gain that would be realized by USNG if the over-the-counter contract were to be closed on any given valuation date. At each reset date, USNG will make or receive settlement payments to or from its counterparties, and collateral posted by or for USNG will be returned to the appropriate party to offset the settlement payment made. Collateral is held by an independent third party and governed by tri-party agreements between USNG, its custodian, BBH&Co, and each counterparty.
40
Table of Contents
At June 30, 2012, USNG’s counterparties posted $9,100,249 in cash and $0 in securities as collateral with USNG’s custodian, as compared with $506 in cash and $0 in securities at June 30, 2011. Under these over-the-counter swap agreements, USNG posted collateral with respect to its obligations of $13,905,308 in cash and $18,471,865 in securities, such as U.S. Treasuries, at June 30, 2012, as compared with $151,376,650 in cash and $35,259,611 in securities at June 30, 2011.
USNG anticipates that the use of Other Natural Gas-Related Investments together with its investments in Futures Contracts will produce price and total return results that closely track the investment goals of USNG. However, there can be no assurance of this. OTC Contracts may result in higher transaction-related expenses than the brokerage commissions paid in connection with the purchase of Futures Contracts, which may impact USNG’s ability to successfully track the Benchmark Futures Contract.
| Item 4. | Controls and Procedures. |
Disclosure Controls and Procedures
USNG maintains disclosure controls and procedures that are designed to ensure that material information required to be disclosed in USNG’s periodic reports filed or submitted under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, is recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time period specified in the SEC’s rules and forms.
The duly appointed officers of USCF, including its chief executive officer and chief financial officer, who perform functions equivalent to those of a principal executive officer and principal financial officer of USNG if USNG had any officers, have evaluated the effectiveness of USNG’s disclosure controls and procedures and have concluded that the disclosure controls and procedures of USNG have been effective as of the end of the period covered by this quarterly report on Form 10-Q.
Change in Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
There were no changes in USNG’s internal control over financial reporting during USNG’s last fiscal quarter that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, USNG’s internal control over financial reporting.
| Item 1. | Legal Proceedings. |
Not applicable.
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors. |
There have been no material changes to the risk factors previously disclosed in USNG’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended December 31, 2011, filed on February 29, 2012, except for the addition of the risk factor set forth below.
USNG is organized and operated as a limited partnership in accordance with the provisions of the LP Agreement and applicable state law, and therefore, USNG has a more complex tax treatment than traditional mutual funds.
USNG is organized and operated as a limited partnership in accordance with the provisions of the LP Agreement and applicable state law. No U.S. federal income tax is paid by USNG on its income. Instead, USNG will furnish unitholders each year with tax information on IRS Schedule K-1 (Form 1065) and each U.S. unitholder is required to report on its U.S. federal income tax return its allocable share of the income, gain, loss and deduction of USNG. This must be reported without regard to the amount (if any) of cash or property the unitholder receives as a distribution from USNG during the taxable year. A unitholder, therefore, may be allocated income or gain by USNG but receive no cash distribution with which to pay the tax liability resulting from the allocation, or may receive a distribution that is insufficient to pay such liability.
41
Table of Contents
In addition to federal income taxes, unitholders may be subject to other taxes, such as state and local income taxes, unincorporated business taxes, business franchise taxes, and estate, inheritance or intangible taxes that may be imposed by the various jurisdictions in which USNG does business or owns property or where the unitholders reside. Although an analysis of those various taxes is not presented here, each prospective unitholder should consider their potential impact on its investment in USNG. It is each unitholder’s responsibility to file the appropriate U.S. federal, state, local and foreign tax returns.
| Item 2. | Unregistered Sales of Equity Securities and Use of Proceeds. |
Not applicable.
| Item 3. | Defaults Upon Senior Securities. |
Not applicable.
| Item 4. | Mine Safety Disclosures. |
Not applicable.
| Item 5. | Other Information. |
Monthly Account Statements
Pursuant to the requirement under Rule 4.22 under the Commodity Exchange Act, each month USNG publishes an account statement for its unitholders, which includes a Statement of Income (Loss) and a Statement of Changes in Net Asset Value. The account statement is furnished to the SEC on a current report on Form 8-K pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange Act and posted each month on USNG’s website at www.unitedstatesnaturalgasfund.com.
| Item 6. | Exhibits. |
Listed below are the exhibits, which are filed as part of this quarterly report on Form 10-Q (according to the number assigned to them in Item 601 of Regulation S-K):
| Exhibit Number |
Description of Document | |
| 10.1(1) |
Second Amendment Agreement to the Administrative Agency Agreement. | |
| 10.2(1) |
Second Amendment Agreement to the Custodian Agreement. | |
| 10.3(1) |
Second Amendment Agreement to the Marketing Agent Agreement. | |
| 31.1(1) |
Certification by Principal Executive Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 31.2(1) |
Certification by Principal Financial Officer Pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 32.1(1) |
Certification by Principal Executive Officer Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 32.2(1) |
Certification by Principal Financial Officer Pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as Adopted Pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002. | |
| 101.INS(2) |
XBRL Instance Document. | |
| 101.SCH(2) |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Schema. | |
| 101.CAL(2) |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Calculation Linkbase. | |
| 101.DEF(2) |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Definition Linkbase. | |
| 101.LAB(2) |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Label Linkbase. | |
| 101.PRE(2) |
XBRL Taxonomy Extension Presentation Linkbase. |
| (1) | Filed herewith. |
| (2) | In accordance with Rule 406T of Regulation S-T, the information in these exhibits is furnished and deemed not filed or part of a registration statement or prospectus for purposes of Sections 11 or 12 of the Securities Act of 1933, is deemed not filed for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, and otherwise is not subject to liability under these sections. |
42
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned thereunto duly authorized.
| United States Natural Gas Fund, LP (Registrant) | ||
| By: United States Commodity Funds LLC, its general partner | ||
| By: | /s/ Nicholas D. Gerber | |
| Nicholas D. Gerber | ||
| President and Chief Executive Officer | ||
| (Principal executive officer) | ||
| Date: August 9, 2012 | ||
| By: | /s/ Howard Mah | |
| Howard Mah | ||
| Chief Financial Officer | ||
| (Principal financial and accounting officer) | ||
| Date: August 9, 2012 | ||
43
