Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EXCEL - IDEA: XBRL DOCUMENT - G III APPAREL GROUP LTD /DE/ | Financial_Report.xls |
| EX-21 - SUBSIDIARIES OF G-III - G III APPAREL GROUP LTD /DE/ | d312043dex21.htm |
| EX-31.1 - CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO RULE 302 - G III APPAREL GROUP LTD /DE/ | d312043dex311.htm |
| EX-32.1 - CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350 - G III APPAREL GROUP LTD /DE/ | d312043dex321.htm |
| EX-23.1 - CONSENT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM - G III APPAREL GROUP LTD /DE/ | d312043dex231.htm |
| EX-32.2 - CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO 18 U.S.C. SECTION 1350 - G III APPAREL GROUP LTD /DE/ | d312043dex322.htm |
| EX-31.2 - CERTIFICATION PURSUANT TO RULE 302 - G III APPAREL GROUP LTD /DE/ | d312043dex312.htm |
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) |
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the fiscal year ended January 31, 2012
OR
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) |
OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934
For the transition period from to
Commission file number 0-18183
G-III APPAREL GROUP, LTD.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 41-1590959 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of | (I.R.S. Employer | |
| incorporation or organization) | Identification No.) | |
| 512 Seventh Avenue, New York, New York | 10018 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code:
(212) 403-0500
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of Class |
Name of Exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, $0.01 par value | Nasdaq Global Select Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act:
None.
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K (§229.405 of this chapter) is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer ¨ | Accelerated filer x | Non-accelerated filer ¨ | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Act). Yes ¨ No x
As of July 31, 2011, the aggregate market value of the registrant’s voting stock held by non-affiliates of the registrant (based on the last sale price for such shares as quoted by the Nasdaq Global Select Market) was approximately $509,042,966.
The number of outstanding shares of the registrant’s Common Stock as of April 5, 2012 was 19,869,532. .
Documents incorporated by reference: Certain portions of the registrant’s definitive Proxy Statement relating to the registrant’s Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on or about June 5, 2012, to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 with the Securities and Exchange Commission, are incorporated by reference into Part III of this Report.
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
Various statements contained in this Form 10-K or incorporated by reference into this Form 10-K, in future filings by us with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”), in our press releases and in oral statements made from time to time by us or on our behalf constitute “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. Forward-looking statements are based on current expectations and are indicated by words or phrases such as “anticipate,” “estimate,” “expect,” “project,” “we believe,” “is or remains optimistic,” “currently envisions,” “forecasts” and similar words or phrases and involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from the future results, performance or achievements expressed in or implied by such forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements also include representations of our expectations or beliefs concerning future events that involve risks and uncertainties, including, but not limited to, those described in Part I, “Item 1A. Risk Factors” and the following:
| • | our dependence on licensed product; |
| • | costs and uncertainties with respect to expansion of our product offerings; |
| • | customer concentration; |
| • | the impact of the current economic and credit environment on our customers, suppliers and vendors; |
| • | the impact of the downturn in the global economy on consumer purchases of products that we offer for sale; |
| • | the performance of our products within the prevailing retail environment; |
| • | customer acceptance of new products; |
| • | our ability to make strategic acquisitions; |
| • | possible disruption from acquisitions; |
| • | consolidation of our retail customers; |
| • | price, availability and quality of materials used in our products; |
| • | seasonal nature of our business; |
| • | dependence on existing management; |
| • | the effects of competition in the markets in which we operate; |
| • | risks of operating a retail business; |
| • | need for additional financing; |
| • | our ability to import products in a timely and cost effective manner; |
| • | our reliance on foreign manufacturers; |
| • | our intention to introduce new products or enter into new alliances; |
| • | our ability to continue to maintain our reputation; |
| • | fluctuations in the price of our common stock; and |
| • | potential effect on the price of our common stock if actual results are worse than financial forecasts. |
These forward-looking statements are based largely on our expectations and judgments and are subject to a number of risks and uncertainties, many of which are unforeseeable and beyond our control. A detailed discussion of significant risk factors that have the potential to cause our actual results to differ materially from our expectations is described in Part I of this Form 10-K under the heading of “Risk Factors.” We undertake no obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, except as required by law.
2
WEBSITE ACCESS TO REPORTS
Our internet website is www.g-iii.com. We make available free of charge on our website (under the heading “Investor Relations”) our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file such material with, or furnish it to, the Securities and Exchange Commission. No information contained on our website is intended to be included as part of, or incorporated by reference into, this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Information relating to our corporate governance, including our Code of Ethics and Committee charters, is available at our website under “Investor Relations.” Paper copies of these filings and corporate governance documents are available to stockholders free of charge by written request to Investor Relations, G-III Apparel Group, Ltd., 512 Seventh Avenue, New York, New York 10018. Documents filed with the SEC are also available on the SEC’s website at www.sec.gov.
3
ITEM 1. BUSINESS.
Unless the context otherwise requires, “G-III”, “us”, “we” and “our” refer to G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and its subsidiaries. References to fiscal years refer to the year ended or ending on January 31 of that year. For example, our fiscal year ended January 31, 2012 is referred to as “fiscal 2012”.
Overview
G-III designs, manufactures and markets an extensive range of apparel, including outerwear, dresses, sportswear, women’s suits and women’s performance wear, as well as luggage and women’s handbags, small leather goods and cold weather accessories. We sell our products under our own proprietary brands, which include Andrew Marc, Marc New York and Marc Moto, licensed brands and private retail labels. We provide high quality apparel under recognized brands to a cross section of leading retailers such as Macy’s, Bloomingdale’s, Nordstrom, Lord & Taylor, The Bon-Ton Stores, Dillards, JC Penney, Belk and Kohl’s. We distribute our products through a diverse mix and a large number of retailers at a variety of price points, as well as through our own retail stores.
As of January 31, 2012, we operated 139 retail stores, of which 135 are outlet stores operated under the Wilsons Leather name and 4 are outlet stores operated under our Andrew Marc brand. During fiscal 2011, we formed a joint venture with The Camuto Group to open and operate footwear and accessory outlet stores under the name “Vince Camuto.” The joint venture opened the first Vince Camuto outlet store in April 2011 and, as of January 31, 2012, 11 of these stores were in operation.
We have expanded our portfolio of proprietary and licensed brands through acquisitions and by entering into license agreements for new brands or for additional product categories.
Selling products under well-known licensed brands is an important part of our strategy. We have licenses to produce branded fashion apparel under the Calvin Klein, Kenneth Cole, Cole Haan, Guess?, Tommy Hilfiger, Levi’s, Dockers, Jessica Simpson, Ellen Tracy, Kensie, Mac & Jac, Jones New York, Sean John and Nine West brands, among others. We also have sports licenses with the National Football League, National Basketball Association, Major League Baseball, National Hockey League, Touch by Alyssa Milano and over 100 U.S. colleges and universities.
G-III sells outerwear, dresses and handbags under our own Andrew Marc, Marc New York and Marc Moto brands and has licensed these brands to select third parties in certain product categories. Our other owned brands include, among others, Jessica Howard, Eliza J, Black Rivet, G-III, G-III Sports by Carl Banks and Winlit. We also work with a diversified group of retailers, such as JC Penney, Kohl’s and Express in developing private label product lines.
We have acquired businesses that have broadened our product offerings, expanded our ability to serve different tiers of distribution and added a retail component to our business. Our acquisitions are part of our strategy to expand our product offerings and increase the portfolio of proprietary and licensed brands that we offer through different tiers of retail distribution. We believe that our two most recent additions, Andrew Marc and the Wilsons outlet business, both of which were completed in fiscal 2009, leverage our core strength in outerwear and provide us with new avenues for growth. We also believe that these acquisitions complement our other licensed brands, G-III owned brands and private label programs.
We operate our business in three segments, wholesale licensed products, wholesale non-licensed products and retail operations. The wholesale licensed products segment includes sales of products under brands licensed by us from third parties. The wholesale non-licensed products segment principally includes sales of products under our own brands and private label brands. The retail operations segment consists almost entirely of our Wilsons outlet stores, and beginning in the second half of fiscal 2012, a limited number of Andrew Marc outlet stores. See Note K to our Consolidated Financial Statements for financial information with respect to these segments.
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. is a Delaware corporation that was formed in 1989. We and our predecessors have conducted our business since 1974.
4
Competitive Strengths
We believe that our broad portfolio of high-profile brands combined with our extensive distribution relationships position us for growth. We intend to capitalize on the following competitive strengths in order to achieve our goal of creating an all-season diversified apparel company:
Broad portfolio of recognized brands. We have built a broad and deep portfolio of over 30 licensed and proprietary brands. We believe we are a licensee of choice for well-known brands that have built a loyal following of both fashion-conscious consumers and retailers who desire high quality, well designed products. We have selectively added the licensing rights to premier brands in women’s, men’s and sports categories catering to a wide range of customers. In an environment of rapidly changing consumer fashion trends, we benefit from a balanced mix of well-established and newer brands. In addition to our licensed brands, we own several successful proprietary brands, including Andrew Marc, Marc New York and Marc Moto. Our experience in developing and acquiring licensed brands and proprietary labels, as well as our reputation for producing high quality, well-designed apparel, has led major department stores and retailers to select us as a designer and manufacturer for their private label programs.
We currently market apparel and other products under, among others, the following licensed and proprietary brand names:
| Women’s |
Men’s |
Sports | ||
| Licensed Brands |
||||
| Calvin Klein |
Calvin Klein | National Football League | ||
| ck Calvin Klein |
ck Calvin Klein | Major League Baseball | ||
| Guess |
Guess | National Basketball Association | ||
| Guess? |
Guess? | National Hockey League | ||
| Kenneth Cole NY |
Kenneth Cole NY | Touch by Alyssa Milano | ||
| Reaction Kenneth Cole |
Reaction Kenneth Cole | Collegiate Licensing Company | ||
| Cole Haan |
Cole Haan | Major League Soccer | ||
| Sean John |
Sean John | |||
| Levi’s |
Levi’s | |||
| Vince Camuto |
Vince Camuto | |||
| Jessica Simpson |
Dockers | |||
| Jones New York |
Tommy Hilfiger | |||
| Nine West |
||||
| Ellen Tracy |
||||
| Kensie |
||||
| Mac & Jac |
||||
| Proprietary Brands |
||||
| Andrew Marc |
Andrew Marc | G-III Sports by Carl Banks | ||
| Marc New York |
Marc New York | G-III for Her | ||
| Jessica Howard |
Marc Moto | |||
| Black Rivet |
Black Rivet | |||
| G-III |
G-III | |||
| Eliza J |
||||
| Marvin Richards |
||||
| Siena Studio |
||||
| Winlit |
||||
Diversified distribution base. We market our products at multiple price points and across multiple channels of distribution, allowing us to provide products to a broad range of consumers, while reducing our reliance on any one demographic segment, merchandise preference or distribution channel. Our products are sold
5
to approximately 2,400 customers, including a cross section of leading retailers such as Macy’s, Bloomingdale’s, Nordstrom, Lord & Taylor, The Bon-Ton Stores, Dillards, JC Penney, Belk and Kohl’s, and membership clubs such as Costco and Sam’s Club. As a result of our broad distribution platform, we are a licensee and supplier of choice and can more easily adapt to changes in the retail environment. We believe our strong relationships with retailers have been established through many years of personal customer service and adherence to meeting or exceeding retailer expectations. Our Wilsons and Andrew Marc outlet stores provide an additional distribution network for our products.
Superior design, sourcing and quality control. Our in-house design and merchandising team designs substantially all of our licensed, proprietary and private label products. Our designers work closely with our licensors and private label customers to create designs and styles that represent the look they want. We believe that our creative design team and our sourcing expertise give us an advantage in product development. We have a network of worldwide suppliers that allows us to negotiate competitive terms without relying on any single vendor. In addition, we employ a quality control team and a sourcing group in China to ensure the quality of our products. We believe we have developed a significant customer following and positive reputation in the industry as a result of our design capabilities, sourcing expertise, on-time delivery and high standards of quality control.
Leadership position in the wholesale business. As one of the largest outerwear wholesalers, we are widely recognized within the apparel industry for our high-quality and well-designed products. Our knowledge of the outerwear business and our industry-wide reputation provide us with an advantage when we are competing for outerwear licenses and private label business. Our expertise and reputation in designing, manufacturing and marketing outerwear have enabled us to build strong customer relationships. Our reputation and relationships, as well as the design skill demonstrated by our in-house team, provided us with the ability to become one of the leading dress suppliers in the United States over the past several years. Our historical position in outerwear and our market success after entering the dress business have allowed us to further expand into women’s sportswear, suits, performance wear and other product categories, including non-apparel categories such as luggage, handbags, small leather goods and accessories.
Experienced management team. Our executive management team has extensive experience in the apparel industry. Morris Goldfarb, our Chief Executive Officer, has been with us for over 35 years. Sammy Aaron, our Vice Chairman who joined us in 2005 when we acquired Marvin Richards, has more than 25 years of experience in the apparel industry, Jeanette Nostra, our President, has been with us for 30 years, and Wayne S. Miller, our Chief Operating Officer, has been with us for over ten years.
Growth Strategy
Our goal is to build an all-season diversified apparel company with a broad portfolio of brands that we offer in multiple channels of retail distribution through the following growth strategies:
Execute diversification initiatives. We are continually seeking opportunities to produce products for all seasons as we attempt to reduce our dependence on our third fiscal quarter for a significant portion of our net sales and our net income. We have initiated the following diversification efforts:
| • | We have continually expanded our relationship with Calvin Klein, which initially consisted of licenses for men’s and women’s outerwear. Since August 2005, we have added licenses for women’s suits, dresses, women’s performance wear and women’s better sportswear. In May 2010, we added two licenses with Calvin Klein, one for women’s handbags and small leather goods and the other for luggage and, in November 2011, we added a license to operate Calvin Klein Performance retail stores in the United States and China. |
| • | Our acquisition of Andrew Marc added a strong proprietary brand of men’s and women’s outerwear and women’s handbags to our portfolio. We believe the Andrew Marc brand can continue to be leveraged into a variety of new categories as we seek to create a meaningful lifestyle brand. We expanded the Andrew Marc family of brands by creating Marc Moto, a denim lifestyle brand that complements our Andrew Marc and Marc New York brands. We have entered into agreements to license the Andrew Marc, Marc New York and Marc Moto brands to select third parties in certain product categories. We have also developed Marc New York and Andrew Marc dress lines using our own in-house capabilities. |
6
| • | Our acquisition of the Wilsons outlet business in July 2008 added a vertical retail component to our business. These outlet stores have provided an additional distribution network for our outerwear products. Leveraging the capabilities of our Wilsons outlet business, in September 2010, we formed a joint venture to own and operate footwear and accessory outlet stores under the name “Vince Camuto.” The joint venture opened the first Vince Camuto outlet store in April 2011 and, as of January 31, 2012, 11 of these stores were in operation. In addition, our Wilsons team oversaw the opening and operation of our Andrew Marc outlet stores in fiscal 2012. As of January 31, 2012, we had 4 Andrew Marc outlet stores in operation. |
Continue to grow our outerwear business. We have been a leader in the outerwear business for many years and believe there is growth potential for us in this category. Specifically, our Calvin Klein men’s and women’s outerwear businesses benefit from Calvin Klein’s strong brand awareness and loyalty among consumers. Our acquisition of Andrew Marc added two well known proprietary brands in the men’s and women’s outerwear market, as well as licenses for men’s and women’s outerwear under the Levi’s and Dockers brands. More recently, we added a license for Vince Camuto men’s outerwear in May 2011 and Jessica Simpson women’s outerwear in November 2011.
Add new product categories. We have been able to leverage our expertise and experience in the outerwear business, our relationships with our licensors and our sourcing capabilities to expand our licenses to new product categories such as dresses, sportswear, women’s suits and women’s performance wear. Most recently, we expanded our licenses with Calvin Klein beyond apparel categories to include luggage, women’s handbags, small leather goods and cold weather accessories. In addition, we added luggage to the products we sell under the Tommy Hilfiger brand. We will attempt to expand our distribution of products in these and other categories under licensed brands, our own brands and private label brands.
Seek attractive acquisitions. We plan to pursue acquisitions of complementary product lines and businesses. We continually review acquisition opportunities. As a result of our acquisitions, we added name-brand licenses, including Calvin Klein, Guess?, Ellen Tracy, Tommy Hilfiger, Levi’s and Dockers, as well as proprietary labels and significant private label programs. We acquired the Jessica Howard and Eliza J dress businesses and Andrew Marc, which added to our portfolio two well-known proprietary brands, Andrew Marc and Marc New York. We also acquired the Wilsons Leather outlet store business. Our acquisitions have increased our portfolio of licensed and proprietary brands, allowed us to realize economies of scale and added a retail component to our business. We believe that our existing infrastructure and management depth will enable us to complete additional acquisitions in the apparel industry.
Products — Development and Design
G-III designs, manufactures and markets women’s and men’s apparel at a wide range of retail sales prices. Our product offerings primarily include outerwear, dresses, sportswear, women’s suits and women’s performance wear. We also market accessories including luggage, women’s handbags, small leather goods and cold weather accessories.
G-III’s licensed apparel consists of both women’s and men’s products. Our strategy is to seek licenses that will enable us to offer a range of products targeting different price points and different distribution channels.
G-III’s proprietary branded apparel also consists of both women’s and men’s products. The Andrew Marc line of women’s and men’s luxury apparel is sold to upscale department and specialty retail stores. The Marc New York line of women’s and men’s better priced outerwear is sold to upper tier stores. The Marc Moto line is a men’s denim lifestyle collection of sportswear and accessories. The Jessica Howard label is a moderate price dress line that sells to department stores, specialty stores and catalogs. Eliza J is a better dress line that sells to better department and specialty stores. The Black Rivet line of apparel consists of women’s and men’s outerwear. We sell men’s sports-related apparel under our G-III Sports by Carl Banks label.
We also work with a diversified group of retail chains, such as JC Penney, Kohl’s and Express, in developing product lines that are sold under their private label programs. We meet frequently with department and specialty chain store buyers who custom order products by color, fabric and style. These buyers may provide
7
samples to us or may select styles already available in our showrooms. We believe we have established a reputation among these buyers for our ability to produce high quality product on a reliable, expeditious and cost-effective basis.
Our in-house designers are responsible for the design and look of our licensed and non-licensed products. We work closely with our licensors to create designs and styles for each of our licensed brands. Licensors generally must approve products to be sold under their brand names prior to production. We respond to style changes in the apparel industry by maintaining a continuous program of style, color, leather and fabric selection. In designing new products and styles, we attempt to incorporate current trends and consumer preferences. We seek to design products in response to trends in consumer preferences, rather than attempt to create new market trends and styles.
Our design personnel meet regularly with our sales and merchandising department, as well as with the design and merchandising staffs of our licensors, to review market trends, sales results and the popularity of our latest products. In addition, our representatives regularly attend trade and fashion shows and shop at fashion forward stores in the United States, Europe and the Far East. Our designers present sample items along with their evaluation of the styles expected to be in demand in the United States. We also seek input from selected customers with respect to product design. We believe that our sensitivity to the needs of retailers, coupled with the flexibility of our production capabilities and our continual monitoring of the retail market, enables us to modify designs and order specifications in a timely fashion.
Licensing
The sale of licensed products is a key element of our strategy and we have continually expanded our offerings of licensed products for more than fifteen years. During the past year, we entered into a new license agreement with respect to Calvin Klein Performance retail stores in the United States and China which is in addition to our existing wholesale license for Calvin Klein performance wear. We expanded our relationship with Tommy Hilfiger by entering into a license for luggage and with Jessica Simpson by entering into a license for women’s outerwear. We added to our portfolio of brands with licenses for Vince Camuto dresses and men’s outerwear and with three licenses for products bearing the Kensie or Mac & Jac brand, (i) women’s sportswear, dresses, suits, active wear and sweaters, (ii) women’s cold weather accessories and (iii) women’s handbags.
Our new five-year license agreement with the National Football League became effective on April 1, 2012. This new license agreement provides us with exclusive rights to distribute outerwear to mass-market retailers and mid-tier department stores and with other rights to sell outerwear, sportswear and swimwear to better department stores, specialty stores, stadium stores and sporting good stores. Our license with Calvin Klein for women’s suits expired December 31, 2011. We continue to design, produce and market product for this line while we discuss the terms of an extension with Calvin Klein.
8
The following table sets forth, for each of our principal licenses, the date on which the current term ends and the date on which any potential renewal term ends
| License |
Date Current Term Ends |
Date Potential Renewal Term Ends | ||
| Fashion Licenses |
||||
| Calvin Klein (Men’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2015 | None | ||
| Calvin Klein (Women’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2013 | None | ||
| Calvin Klein (Women’s dresses) |
December 31, 2016 | None | ||
| Calvin Klein (Women’s suits) |
December 31, 2011 | None | ||
| Calvin Klein (Women’s performance wear) |
December 31, 2017 | None | ||
| Calvin Klein (Women’s better sportswear) |
December 31, 2012 | December 31, 2017 | ||
| Calvin Klein (Better luggage) |
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2020 | ||
| Calvin Klein (Women’s handbags and small leather goods) |
December 31, 2015 | December 31, 2020 | ||
| Calvin Klein (Women’s performance retail) |
December 31, 2017 | None | ||
| Cole Haan (Men’s and women’s outerwear) |
January 31, 2013 | January 31, 2015 | ||
| Dockers (Men’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2013 | December 31, 2016 | ||
| Ellen Tracy (Women’s outerwear, dresses and suits and men’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2014 | December 31, 2016 | ||
| Guess/Guess? (Men’s and women’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2013 | None | ||
| Guess/Guess? (Women’s dresses) |
December 31, 2013 | None | ||
| Jessica Simpson (Women’s dresses) |
January 31, 2013 | January 31, 2017 | ||
| Jessica Simpson (Women’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2014 | December 31, 2017 | ||
| Jones New York (Women’s outerwear) |
January 31, 2015 | None | ||
| Kenneth Cole NY/Reaction Kenneth Cole (Men’s and women’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2012 | December 31, 2015 | ||
| Kensie/Mac & Jac (Women’s sportswear, dresses, suits, active wear and sweaters) |
January 31, 2017 | January 31, 2022 | ||
| Kensie/Mac & Jac (Women’s cold weather accessories) |
January 31, 2017 | January 31, 2022 | ||
| Kensie/Mac & Jac (Women’s handbags) |
January 31, 2017 | January 31, 2022 | ||
| Levi’s (Men’s and women’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2013 | December 31, 2016 | ||
| Nine West (Women’s outerwear) |
January 31, 2013 | None | ||
| Sean John (Men’s outerwear) |
January 31, 2014 | None | ||
| Sean John (Women’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2013 | December 31, 2023 | ||
| Sean John (Boy’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2012 | None | ||
| Tommy Hilfiger (Men’s outerwear) |
March 31, 2013 | March 31, 2016 | ||
| Tommy Hilfiger (Luggage) |
December 31, 2014 | None | ||
| Vince Camuto (Women’s dresses) |
December 31, 2014 | December 31, 2017 | ||
| Vince Camuto (Men’s outerwear) |
December 31, 2014 | December 31, 2017 | ||
| Sports Licenses |
||||
| Collegiate Licensing Company |
March 31, 2013 | None | ||
| Major League Baseball |
October 31, 2013 | None | ||
| National Basketball Association |
September 30, 2012 | None | ||
| National Football League |
March 31, 2017 | None | ||
| National Hockey League |
June 30, 2012 | None |
Under our license agreements, we are generally required to achieve minimum net sales of licensed products, pay guaranteed minimum royalties, make specified royalty and advertising payments (usually based on a
9
percentage of net sales of licensed products), and receive prior approval of the licensor as to all design and other elements of a product prior to production. If we do not satisfy any of these requirements or otherwise fail to meet our obligations under a license agreement, a licensor usually will have the right to terminate our license.
Our ability to renew the current term of a license agreement is usually subject to attaining minimum sales and/or royalty levels and to our compliance with the terms of the agreement. Other criteria may also impact our ability to renew a license. As a result, we cannot be sure that we will be able to renew a license agreement when it expires if we desire to do so. We believe that brand owners are looking to consolidate the number of licensees they engage to develop product and to choose licensees who have a successful track record of developing brands. We continue to seek other opportunities to enter into license agreements in order to expand our product offerings under well-known labels and broaden the markets that we serve.
Revenues from the sale of wholesale licensed products accounted for 65.5% of our net sales in fiscal 2012 compared to 67.6% of our net sales in fiscal 2011 and 65.4% of our net sales in fiscal 2010.
Proprietary Brands
Dating back to the beginning of our company, G-III has sold apparel under our own proprietary brands. Over the years, we developed or acquired brands such as G-III, Black Rivet, G-III Sports by Carl Banks, Jessica Howard and Eliza J.
We acquired Andrew Marc and Marc New York as additional upscale company owned brands. We have also developed the Marc Moto brand, a men’s denim lifestyle collection, as a complement to these two brands. We utilize our own in-house capabilities to create our core women’s and men’s outerwear, as well as our women’s dress lines for Andrew Marc and Marc New York.
One of our important initiatives has been to develop the Andrew Marc family of brands into a meaningful lifestyle brand. In addition to the core products that we develop and market for these brands, we have sought to expand the reach of these brands by entering into license agreements with third parties for women’s footwear, women’s handbags, men’s accessories, men’s cold weather accessories, men’s denim and related sportswear, men’s dress shirts, men’s tailored clothing, men’s footwear, eyewear, watches, neckwear and sweaters. We have entered into agreements that terminate the license agreements with respect to women’s handbags and men’s denim and related sportswear, and are pursuing these initiatives in-house. We continually look for new opportunities to leverage these brands.
Revenues from the sale of wholesale non-licensed products accounted for 21.7% of our net sales in fiscal 2012 compared to 22.9% of our net sales in fiscal 2011 and 23.5% of our net sales in fiscal 2010.
Retail Operations
Our outlet store business is a national retailer of outerwear and accessories, which as of January 31, 2012, operates 139 outlet stores in 38 states, of which 135 are outlet stores operated under the name Wilsons Leather Outlets and 4 are outlet stores operated under our Andrew Marc brand. Substantially all of our outlet stores are located in larger outlet centers and average approximately 3,900 total leased square feet. We currently plan to open approximately 14 new outlet stores in fiscal 2013.
Our outlet stores sell men’s and women’s outerwear and accessories. Outerwear sold in our stores includes products primarily manufactured by us and accessories which are purchased from third parties. Merchandise for our stores is shipped directly from domestic merchandise vendors or overseas manufacturers to our outlet distribution center located in Brooklyn Park, Minnesota. Merchandise is shipped from our Brooklyn Park, Minnesota distribution center to replenish stores as needed with key styles and to build inventory for the peak holiday selling season.
In August 2010, we formed a joint venture with The Camuto Group to operate footwear and accessory outlet stores under the name “Vince Camuto.” The Camuto Group provides product and merchandises the stores. Through our Wilsons team, we provide the infrastructure and expertise for operation of the stores, including real estate, distribution, information systems, finance and administration. Both companies share equally in the capital costs of the joint venture. The joint venture opened the first Vince Camuto outlet store in April 2011 and, as of January 31, 2012, 11 of these stores were in operation.
10
In November 2011, we entered into a license agreement to operate Calvin Klein Performance retail stores in the United States and China. We opened our first Calvin Klein Performance store in Scottsdale, Arizona in February 2012 and expect to open approximately 2 additional stores in the U.S. in fiscal 2013. In March 2012, we entered into a joint venture agreement with Finity Apparel Retail Limited to open and operate Calvin Klein Performance retail stores in China and Hong Kong. G-III will retain 51% ownership of the joint venture which expects to begin operating retail locations in major Chinese markets beginning in Fall 2012.
Revenues from our retail operations accounted for 12.8% of our net sales in fiscal 2012 compared to 13.4% of our net sales in fiscal 2011 and 15.8% of our net sales in fiscal 2010.
Manufacturing and Sourcing
G-III arranges for the production of products from independent manufacturers located primarily in China and, to a lesser extent, in Vietnam, India, Indonesia, Thailand, Sri Lanka, Taiwan, Central and South America, Pakistan, Bangladesh and Turkey. A small portion of our garments are manufactured in the United States.
We currently have representative offices in Hangzhou, Nanjing and Qingdao, China. These offices act as a liaison between us and manufacturers in the Far East. At January 31, 2012, we had 158 employees in these representative offices.
G-III’s headquarters provides these liaison offices with production orders stating the quantity, quality, delivery time and types of garments to be produced. Liaison office personnel assist in the negotiation and placement of orders with manufacturers. In allocating production among independent suppliers, we consider a number of criteria, including, but not limited to, quality, availability of production capacity, pricing and ability to meet changing production requirements.
To facilitate better service for our customers and accommodate the volume of manufacturing in the Far East, we also have a subsidiary in Hong Kong. The Hong Kong subsidiary supports third party production of products on an agency fee basis. Our Hong Kong office acts as an agent for substantially all of our production. Our China and Hong Kong offices monitor production at manufacturers’ facilities to ensure quality control, compliance with our specifications and timely delivery of finished garments to our distribution facilities and, in some cases, direct to our customers. At January 31, 2012, we had 9 employees in our Hong Kong office.
In connection with the foreign manufacture of our products, manufacturers purchase leather, wool and other fabrics under our direction. In addition, they purchase necessary “submaterials” (such as linings, zippers, buttons and trimmings) according to parameters specified by us. Prior to commencing the manufacture of products, samples of raw materials or submaterials are sent to us for approval. We regularly inspect and supervise the manufacture of our products in order to ensure timely delivery, maintain quality control and monitor compliance with our manufacturing specifications. We also inspect finished products at the factory site.
The manufacture of the substantial majority of our products is performed manually. A pattern is used in cutting fabric to panels that are assembled in the factory. All submaterials are also added at this time. We inspect products throughout this process to insure that the design and quality specifications of the order are being maintained as the garment is assembled. After pressing, cleaning and final inspection, the product is labeled and ready for shipment. A final random inspection by us occurs when the products are packed for shipment.
We generally arrange for the production of products on a purchase order basis with completed products manufactured to our design specifications. We assume the risk of loss predominantly on a Freight-On-Board (F.O.B.) basis when goods are delivered to a shipper and are insured against casualty losses arising during shipping.
As is customary, we have not entered into any long-term contractual arrangements with any contractor or manufacturer. We believe that the production capacity of foreign manufacturers with which we have developed, or are developing, a relationship is adequate to meet our production requirements for the foreseeable future. We believe that alternative foreign manufacturers are readily available.
A majority of all finished goods manufactured for us is shipped to our New Jersey warehouse and distribution facilities or to designated third party facilities for final inspection and allocation, as well as reshipment to customers. The goods are delivered to our customers and us by independent shippers. We choose the form of shipment (principally ship, truck or air) based upon a customer’s needs, cost and timing considerations.
11
Quotas, Customs and Import Restrictions
Our arrangements with textile manufacturers and suppliers are subject to requisite customs clearances for textile apparel and the imposition of export duties. United States Customs duties on our textile apparel presently range from duty free to 28%, depending upon the type of fabric used, how the garment is constructed and the country of export. Quotas represent the right to export restricted amounts of certain categories of merchandise into a country or territory pursuant to a visa or a license. Countries in which our products are manufactured and sold may, from time to time, impose new duties, tariffs, surcharges or other import controls or restrictions or adjust prevailing duty or tariff levels. The products we are currently importing are not subject to quota restrictions. We continually monitor duty, tariff and other import restriction developments. We seek to minimize our potential exposure to import related risks through, among other measures, geographical diversification of manufacturing sources and shifts of production among countries and manufacturers.
Apparel and other products sold by us are also subject to regulations that relate to product labeling, content and safety requirements, licensing requirements and flammability testing. We believe that we are in substantial compliance with those regulations, as well as applicable federal, state, local, and foreign regulations relating to the discharge of materials hazardous to the environment.
Raw Materials
During fiscal 2012, demand for raw materials, including textiles, wool and leather, significantly increased while supplies of those raw materials declined due to adverse climate and other factors. As a result, we and other apparel manufacturers experienced increases in raw material prices. These conditions are expected to moderate in fiscal 2013.
We purchase most products manufactured for us on a finished goods basis. We coordinate the sourcing of raw materials used in the production of our products which are generally available from numerous sources. The apparel industry competes with manufacturers of many other products for the supply of raw materials.
Marketing and Distribution
G-III’s products are sold primarily to department, specialty and mass merchant retail stores in the United States. We sell to approximately 2,400 customers, ranging from national and regional chains to small specialty stores. We also distribute our products through our outlet stores and, to a lesser extent, through our Wilson’s Leather and Andrew Marc websites.
Sales to our 10 largest customers accounted for 63.3% of our net sales in fiscal 2012 compared to 62.7% of our net sales in fiscal 2011 and 55.0% of our net sales in fiscal 2010. Sales to Macy’s, which includes sales to its Macy’s and Bloomingdale’s store chains, accounted for an aggregate of 18.7% of our net sales in fiscal 2012, 17.3% of our net sales in fiscal 2011 and 16.8% of our net sales in fiscal 2010. Sales to the Marmaxx Group, which includes sales to the T.J. Maxx and Marshalls store chains, accounted for 12.3% of our net sales in fiscal 2012, 12.4% of our net sales in fiscal 2011 and 8.8% of our net sales in fiscal 2010. The loss of either of these customers, or a significant reduction in purchases by these customers, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Almost all of our sales are made in the United States. We also market our products in Canada, Europe and the Far East, which, on a combined basis, accounted for approximately 4% of our wholesale net sales in fiscal 2012.
G-III’s products are sold primarily through a direct sales force consisting of 122 employees at January 31, 2012. Our principal executives are also actively involved in sales of our products. Some of our products are also sold by various retail buying offices and independent sales representatives located throughout the United States. Sales outside of the United States are managed by two salespeople in our China office. The Canadian market is serviced by a sales and customer service team based both in the United States and in Canada.
Brand name products sold by us pursuant to a license agreement are promoted by institutional and product advertisements placed by the licensor. Our license agreements generally require us to pay the licensor a fee, based on a percentage of net sales of licensed product, to pay for a portion of these advertising costs. We may also be required to spend a specified percentage of net sales of a licensed product on advertising placed by us.
12
We advertise our Andrew Marc brand and are engaged in both cooperative advertising programs with retailers and direct to the consumer. We are focused on creating an image that will broaden the lifestyle appeal of our Andrew Marc brands. Our marketing strategy is focused on media, public relations and channel marketing. Our media strategy for Andrew Marc includes traditional print and outdoor advertising, as well as digital and social media initiatives. We continue to allocate marketing and advertising resources to support the growth of our Andrew Marc brand.
We believe we have developed awareness of our other owned labels primarily through our reputation, consumer acceptance and the fashion press. We primarily rely on our reputation and relationships to generate business in the private label portion of our non-licensed segment. We believe we have developed a significant customer following and positive reputation in the industry as a result of, among other things, our standards of quality control, on-time delivery, competitive pricing and willingness and ability to assist customers in their merchandising of our products.
Seasonality
Retail sales of outerwear have traditionally been seasonal in nature. Sales of outerwear constitute a significant portion of our sales. In prior years, we have been dependent on our sales from July through November for the substantial majority of our net sales and net income. Although we sell our products throughout the year, net sales in the months of July through November accounted for approximately 60% of our net sales in each of fiscal 2012 and fiscal 2011, and 64% of our net sales in fiscal 2010. Our Wilsons outlet business is also highly seasonal, with the third and fourth fiscal quarters accounting for a significant majority of its sales and operating income. As a result, the second half of our fiscal year is expected to provide a disproportionate amount of our net sales and a substantial majority of our net income.
Order Book
A portion of our orders consists of short-term purchase orders from customers who place orders on an as-needed basis. Information relative to open purchase orders at any date may also be materially affected by, among other things, the timing of the initial showing of apparel to the trade, as well as by the timing of recording of orders and shipments. As a result, we do not believe that disclosure of the amount of our unfilled customer orders at any time is meaningful.
Competition
We have numerous competitors with respect to the sale of our products, including distributors that import products from abroad and domestic retailers with established foreign manufacturing capabilities. Some of our competitors have greater financial and marketing resources and greater manufacturing capacity than we do. We also compete with vertically integrated manufacturers that also own retail stores. Our outlet business competes against a diverse group of retailers, including, among others, other outlet stores, department stores, specialty stores, warehouse clubs and e-commerce retailers. Sales of our products are affected by style, price, quality, brand reputation and general fashion trends.
Trademarks
We own the trademarks used by us in connection with our wholesale non-licensed product segment and act as licensee of certain trademarks owned by third parties that are used in connection with our wholesale licensed product segment. The principal brands that we license are summarized under the heading “Licensing” above. We own a number of proprietary brands that we use in connection with our business and products including, among others, Andrew Marc, Marc New York, Marc Moto, Jessica Howard, Eliza J., Black Rivet, Marvin Richards, Winlit, G-III and G-III Sports by Carl Banks. We have registered, or applied for registration of, many of our trademarks in multiple jurisdictions for use on a variety of apparel and related other products, as well as for retail services.
In markets outside of the U.S., our rights to some of our trademarks may not be clearly established. In the course of our attempts to expand into foreign markets, we may experience conflicts with various third parties
13
who have acquired ownership rights in certain trademarks that would impede our use and registration of some of our trademarks. Such conflicts are common and may arise from time to time as we pursue international expansion. Although we have not in the past suffered any material restraints or restrictions on doing business in desirable markets or in new product categories, we cannot be sure that significant impediments will not arise in the future as we expand product offerings and introduce additional brands to new markets.
We regard our trademarks and other proprietary rights as valuable assets and believe that they have value in the marketing of our products. We vigorously protect our trademarks and other intellectual property rights against infringement.
Employees
As of January 31, 2012, we had 2,592 employees, of whom 228 worked in executive or administrative capacities, 499 worked in design, merchandising and sourcing, 618 worked in warehouse and distribution facilities, 122 worked in wholesale sales, and 1,125 worked in our outlet stores. Additionally, during our peak retail selling season from October through January, we employed approximately 1,038 additional seasonal associates in our outlet stores. We employ both union and non-union personnel and believe that our relations with our employees are good. We have not experienced any interruption of any of our operations due to a labor disagreement with our employees and do not believe any interruption will occur if the labor agreements referred to below are not renewed.
We are a party to agreements with two labor unions. One agreement covers approximately 438 of our full-time employees as of January 31, 2012 and is currently in effect through October 31, 2015. The other agreement covers approximately 10 full-time employees of our Andrew Marc division and is currently in effect through December 31, 2014.
14
EXECUTIVE OFFICERS OF THE REGISTRANT
The following table sets forth certain information with respect to our executive officers.
| Name |
Age | Position | ||||
| Morris Goldfarb |
61 | Chairman of the Board, Chief Executive Officer and Director | ||||
| Sammy Aaron |
52 | Vice Chairman and Director | ||||
| Jeanette Nostra |
60 | President | ||||
| Wayne S. Miller |
54 | Chief Operating Officer and Secretary | ||||
| Neal S. Nackman |
52 | Chief Financial Officer and Treasurer | ||||
Morris Goldfarb is our Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer, as well as one of our directors. Mr. Goldfarb has served as an executive officer of G-III and our predecessors since our formation in 1974. Mr. Goldfarb is also a director of Christopher & Banks Corporation, RLJ Acquisition, Inc. and Ante5, Inc. Mr. Goldfarb served as a director of Lakes Entertainment, Inc. from June 1998 until March 2010.
Sammy Aaron has been our Vice Chairman, as well as one of our directors, since we acquired the Marvin Richards business in July 2005. Mr. Aaron also oversees the operations of our Calvin Klein division. Prior to joining G-III, Mr. Aaron served as the President of Marvin Richards from 1998 until July 2005.
Jeanette Nostra became our President in April 1997. From March 2008 to July 2011, Ms. Nostra also acted as President of our Andrew Marc division. Ms. Nostra’s responsibilities include sales, marketing, product development and licensing for selected divisions, as well as business development for international sales. We have employed Ms. Nostra since 1981.
Wayne S. Miller has been our Chief Operating Officer since December 2003 and our Secretary since November 1998. He also served as our Chief Financial Officer from April 1998 until September 2005 and as our Treasurer from November 1998 until April 2006.
Neal S. Nackman has been our Chief Financial Officer since September 2005 and was elected Treasurer in April 2006. Mr. Nackman served as Vice President — Finance from December 2003 until April 2006. Prior to joining G-III, Mr. Nackman was a financial consultant with Jefferson Wells International from January 2003 until December 2003. From May 2001 until October 2002, he was Senior Vice President — Controller of Martha Stewart Living Omnimedia, Inc. From May 1999 until May 2001, he was Chief Financial Officer of Perry Ellis International Inc. From August 1995 until May 1999, he was the Vice-President — Finance with Nautica Enterprises, Inc.
Carl Katz, one of our directors, and Jeanette Nostra are married to each other. Jeffrey Goldfarb, one of our directors and our Director of Business Development, is the son of Morris Goldfarb.
15
ITEM 1A. RISK FACTORS.
The following risk factors should be read carefully in connection with evaluating our business and the forward-looking statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Any of the following risks could materially adversely affect our business, our prospects, our operating results, our financial condition, the trading prices of our securities and the actual outcome of matters as to which forward-looking statements are made in this report. Additional risks that we do not yet know of or that we currently think are immaterial may also affect our business operations.
Risk Factors Relating to Our Licensed and Non-Licensed Wholesale Products Business
The failure to maintain our license agreements could cause us to lose significant revenues and have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We are dependent on sales of licensed product for a substantial portion of our revenues. In fiscal 2012, net sales of wholesale licensed product accounted for 65.5% of our net sales (75.2% of our net sales of wholesale products) compared to 67.6% of our net sales (74.6% of our net sales of wholesale products) in fiscal 2011 and 65.4% of our net sales (73.5% of our net sales of wholesale products) in fiscal 2010.
We are generally required to achieve specified minimum net sales, make specified royalty and advertising payments and receive prior approval of the licensor as to all design and other elements of a product prior to production. License agreements also may restrict our ability to enter into other license agreements for competing products. If we do not satisfy any of these requirements, a licensor usually will have the right to terminate our license. Even if a licensor does not terminate our license, the failure to achieve net sales sufficient to cover our required minimum royalty payments could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. If a license contains a renewal provision, there are usually minimum sales and other conditions that must be met in order to be able to renew a license. Even if we comply with all the terms of a license agreement, we cannot be sure that we will be able to renew an agreement when it expires even if we desire to do so. The failure to maintain our license agreements could cause us to lose significant revenue and have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
Our success is dependent on the strategies and reputation of our licensors, including in particular, Calvin Klein.
Our business strategy is to offer our products on a multiple brand, multiple channel and multiple price point basis. As a part of this strategy, we license the names and brands of numerous recognized companies, designers and celebrities. In entering into these license agreements, we plan our products to be targeted towards different market segments based on consumer demographics, design, suggested pricing and channel of distribution. If any of our licensors decides to “reposition” its products under the brands we license from them, introduce similar products under similar brand names or otherwise change the parameters of design, pricing, distribution, target market or competitive set, we could experience a significant downturn in that brand’s business, adversely affecting our sales and profitability. In addition, as licensed products may be personally associated with designers or celebrities, our sales of those products could be materially and adversely affected if any of those individuals’ images, reputations or popularity were to be negatively impacted.
We have nine different license agreements relating to a variety of products sold under the Calvin Klein brand that is owned by Phillips-Van Heusen Corporation. Sales of Calvin Klein product constitute a majority of our sales of licensed products. Any change by Phillips-Van Heusen in the marketing of products sold under the Calvin Klein label or any adverse change in the consumer’s perception of the Calvin Klein brand could have a material adverse affect on our results of operations. We have two license agreements for products sold under the Tommy Hilfiger brand, which is also owned by Phillips-Van Heusen. Any adverse change in our relationship with Phillips-Van Heusen would have a material adverse affect on our results of operations.
If we are unable to successfully translate market trends into attractive product offerings, our sales and profitability could suffer.
Our ability to successfully compete depends on a number of factors, including our ability to effectively anticipate, gauge and respond to changing consumer demands and tastes across multiple product lines and tiers of dis-
16
tribution. We are required to translate market trends into attractive product offerings and operate within substantial production and delivery constraints. We cannot be sure we will continue to be successful in this regard. We need to anticipate and respond to changing trends quickly, efficiently and effectively in order to be successful.
Expansion of our product offerings involves significant costs and uncertainty and could adversely affect our results of operations.
An important part of our strategy is to expand the types of products we offer. During the past few years, we have added licenses for new lines of women’s suits, dresses, performance wear and sportswear, as well as luggage and women’s handbags and small leather goods. In addition, we acquired a dress and sportswear manufacturer. We had limited prior experience designing, manufacturing and marketing these types of products. We intend to continue to add additional product lines in the future. As is typical with new products, demand and market acceptance for any new products we introduce will be subject to uncertainty. Designing, producing and marketing new products require substantial expenditures. We cannot be certain that our efforts and expenditures will successfully generate sales or that sales that are generated will be sufficient to cover our expenditures.
If our customers change their buying patterns, request additional allowances, develop their own private label brands or enter into agreements with national brand manufacturers to sell their products on an exclusive basis, our sales to these customers could be materially adversely affected.
Our customers’ buying patterns, as well as the need to provide additional allowances to customers, could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. Customers’ strategic initiatives, including developing their own private labels brands, selling national brands on an exclusive basis or reducing the number of vendors they purchase from, could also impact our sales to these customers. There is a trend among major retailers to concentrate purchasing among a narrowing group of vendors. To the extent that any of our key customers reduces the number of its vendors and, as a result, reduces or eliminates purchases from us, there could be a material adverse effect on us.
We have significant customer concentration, and the loss of one of our large customers could adversely affect our business.
Our 10 largest customers accounted for approximately 63.3% of our net sales in fiscal 2012, 62.7% of our net sales in fiscal 2011 and 55.0% of our net sales in fiscal 2010, with Macy’s Inc. accounting for 18.7% of our net sales and the Marmaxx Group accounting for 12.3% of our net sales in fiscal 2012. Consolidation in the retail industry could increase the concentration of our sales to our largest customers. We do not have long-term contracts with any customers, and sales to customers generally occur on an order-by-order basis that may be subject to cancellation or rescheduling by the customer. A decision by our major customers to decrease the amount of merchandise purchased from us, increase the use of their own private label brands, sell a national brand on an exclusive basis or change the manner of doing business with us could reduce our revenues and materially adversely affect our results of operations. The loss of any of our large customers, or the bankruptcy or serious financial difficulty of any of our large customers, could have a material adverse effect on us.
If we miscalculate the market for our products, we may end up with significant excess inventories for some products and missed opportunities for others.
We often produce products to hold in inventory in order to meet our customers’ delivery requirements and to be able to quickly fulfill reorders. If we misjudge the market for our products, we may be faced with significant excess inventories for some products and missed opportunities for others. In addition, weak sales and resulting markdown requests from customers could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
We are subject to the risks of doing business abroad.
Our arrangements with foreign manufacturers are subject to the usual risks of doing business abroad, including currency fluctuations, political or labor instability and potential import restrictions, duties and tariffs. We do not maintain insurance for the potential lost profits due to disruptions of our overseas manufacturers. Because our products are produced abroad, primarily in China, political or economic instability in China or elsewhere could
17
cause substantial disruption in the business of our foreign manufacturers. For example, in the past, the Chinese government has reduced tax rebates to factories for the manufacture of textile and leather garments. The rebate reduction resulted in factories seeking to recoup more of their costs from customers, resulting in higher prices for goods imported from China. This tax rebate has been reinstated in certain instances. However, new or increased reductions in this rebate would cause an increase in the cost of finished products from China which could materially adversely affect our financial condition and results of operations.
Heightened terrorism security concerns could subject imported goods to additional, more frequent or more thorough inspections. This could delay deliveries or increase costs, which could adversely impact our results of operations. In addition, since we negotiate our purchase orders with foreign manufacturers in United States dollars, the decline in value of the United States dollar against local currencies would negatively impact our cost in dollars of product sourced from these manufacturers. We are not currently engaged in any hedging activities to protect against currency risks. If there is downward pressure on the value of the dollar, our purchase prices for our products could increase. We may not be able to offset an increase in product costs with a price increase to our customers.
Fluctuations in the price, availability and quality of materials used in our products could have a material adverse effect on our cost of goods sold and our ability to meet our customers’ demands.
Fluctuations in the price, availability and quality of raw materials used in our products could have a material adverse effect on our cost of sales or our ability to meet our customers’ demands. We compete with numerous entities for supplies of materials and manufacturing capacity. Raw materials are vulnerable to adverse climate conditions, animal diseases and natural disasters that can affect the supply and price of raw materials. We may not be able to pass on all or any portion of higher material prices to our customers. Increases in the price of raw materials, as occurred during fiscal 2012, could have an adverse effect on our results of operations.
Any raw material price increase or increase in costs related to the transport of our products (primarily petroleum costs) could increase our cost of sales and decrease our profitability unless we are able to pass higher prices on to our customers. In addition, if one or more of our competitors is able to reduce its production costs by taking greater advantage of any reductions in raw material prices, favorable sourcing agreements or new manufacturing technologies (which enable manufacturers to produce goods on a more cost-effective basis) we may face pricing pressures from those competitors and may be forced to reduce our prices or face a decline in net sales, either of which could have an adverse effect on our business, results of operations or financial condition.
Our trademark and other intellectual property rights may not be adequately protected.
We believe that our trademarks and other proprietary rights are important to our success and our competitive position. We may, however, experience conflict with various third parties who acquire or claim ownership rights in certain trademarks. We cannot be sure that the actions we have taken to establish and protect our trademarks and other proprietary rights will be adequate to prevent imitation of our products by others or to prevent others from seeking to block sales of our products as a violation of the trademarks and proprietary rights of others.
In the course of our attempts to expand into foreign markets, we may experience conflicts with various third parties who have acquired ownership rights in certain trademarks, which would impede our use and registration of some of our trademarks. Such conflicts are common and may arise from time to time as we pursue international expansion. In addition, the laws of certain foreign countries may not protect proprietary rights to the same extent as the laws of the United States. Enforcing rights to our intellectual property may be difficult and expensive, and we may not be successful in combating counterfeit products and stopping infringement of our intellectual property rights, which could make it easier for competitors to capture market share. Furthermore, our efforts to enforce our trademark and other intellectual property rights may be met with defenses, counterclaims and countersuits attacking the validity and enforceability of our trademark and other intellectual property rights. If we are unsuccessful in protecting and enforcing our intellectual property rights, continued sales of such competing products by third parties could harm our brands and adversely impact our business, financial condition and results of operations.
18
Risks Relating to Our Outlet Business
Operation of our retail business could divert the attention of our management or impact our relationship with our licensors and customers.
As of January 31, 2012, we operated 139 outlet stores. Managing the outlet stores requires the expenditure of our time and resources. Operation of a retail chain could divert our management’s time and resources from our core wholesale apparel business. Operation of a retail chain could be viewed as competitive by our licensors and existing retail customers and adversely affect our relationships with them. Accordingly, the operation of the Wilsons outlet business could negatively impact our results of operations. In addition, the development and opening of Vince Camuto outlet stores and Calvin Klein Performance stores will take up the time of the management of our retail group that could divert their attention from the operation of the Wilsons outlet stores.
We will need to continue to improve the results of operations of our Wilsons outlet stores in order for these stores to operate profitably for us on an ongoing basis. We had no experience operating a retail chain prior to our acquisition of Wilsons.
Prior to our acquisition of the Wilsons outlet stores in 2008, these stores as a whole were experiencing declines in comparable store sales, sales per square foot and gross margins. The operation of these stores negatively impacted our results of operations in fiscal 2009 and 2010. In fiscal 2011 and fiscal 2012, we achieved an operating profit for our Wilsons outlet stores. We will need to further improve store operations and upgrade merchandise offered at these stores in order for these stores to continue to operate profitably for us. We cannot be sure we will be able to improve the operations of these stores on a long-term basis. If we cannot maintain or improve the results of operations of these stores on an ongoing basis, our retail division could have a material adverse effect on our result of operations.
Leasing of significant amounts of real estate exposes us to possible liabilities and losses.
All of the stores operated by us are leased. Accordingly, we are subject to all of the risks associated with leasing real estate. Store leases generally require us to pay a fixed minimum rent and a variable amount based on a percentage of annual sales at that location. We generally cannot cancel our leases. If an existing or future store is not profitable, and we decide to close it, we may be committed to perform certain obligations under the applicable lease including, among other things, paying rent for the balance of the applicable lease term. As each of our leases expires, if we do not have a renewal option, we may be unable to negotiate a renewal, on commercially acceptable terms or at all, which could cause us to close stores in desirable locations. In addition, we may not be able to close an unprofitable store due to an existing operating covenant, which may cause us to operate the location at a loss and prevent us from finding a more desirable location.
Our outlet stores are heavily dependent on the ability and desire of consumers to travel and shop. A reduction in the volume of outlet mall traffic could adversely affect our retail sales.
Our outlet stores are located in outlet malls, which are typically located in or near vacation destinations or away from large population centers where department stores and other traditional retailers are concentrated. Factors, such as the current economic uncertainty in the U.S., fuel shortages, increased fuel prices, travel concerns and other circumstances, which would lead to decreased travel, could have a material adverse affect on sales at our outlet stores. Other factors which could affect the success of our outlet stores include:
| • | the location of the outlet mall or the location of a particular store within the mall; |
| • | the other tenants occupying space at the outlet mall; |
| • | increased competition in areas where the outlet malls are located; |
| • | a continued downturn in the economy generally or in a particular area where an outlet mall is located; and |
| • | the amount of advertising and promotional dollars spent on attracting consumers to the outlet malls. |
Sales at our stores are derived, in part, from the volume of traffic at the malls where our stores are located. Our stores benefit from the ability of a mall’s other tenants and other area attractions to generate consumer traffic
19
in the vicinity of our stores and the continuing popularity of outlet malls as shopping destinations. A reduction in outlet mall traffic as a result of these or other factors could materially adversely affect our business.
The retail business is intensely competitive and increased or new competition could have a material adverse effect on us.
The retail industry is intensely competitive. We compete against a diverse group of retailers, including, among others, other outlet stores, department stores, specialty stores, warehouse clubs and e-commerce retailers. We also compete in particular markets with a number of retailers that specialize in the products that we sell. A number of different competitive factors could have a material adverse effect on our retail business, results of operations and financial condition including:
| • | increased operational efficiencies of competitors; |
| • | competitive pricing strategies, including deep discount pricing by a broad range of retailers during periods of poor consumer confidence or economic instability; |
| • | expansion of product offerings by existing competitors; |
| • | entry by new competitors into markets in which we operate retail stores; and |
| • | adoption by existing competitors of innovative retail sales methods. |
We may not be able to continue to compete successfully with our existing or new competitors, or be assured that prolonged periods of deep discount pricing by our competitors will not have a material adverse effect on our business.
A privacy breach could adversely affect our business.
The protection of customer, employee, and company data is critical to us. The regulatory environment surrounding information security and privacy is increasingly demanding, with the frequent imposition of new and constantly changing requirements across business units. In addition, customers have a high expectation that we will adequately protect their personal information. A significant breach of customer, employee, or company data could damage our reputation and result in lost sales, fines, or lawsuits.
Risk Factors Relating to the Operation of Our Business
If we lose the services of our key personnel, our business will be harmed.
Our future success depends on Morris Goldfarb, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, and other key personnel. The loss of the services of Mr. Goldfarb and any negative market or industry perception arising from the loss of his services could have a material adverse effect on us and the price of our shares. Our other executive officers have substantial experience and expertise in our business and have made significant contributions to our success. The unexpected loss of services of one or more of these individuals could also adversely affect us.
We have expanded our business through acquisitions that could result in diversion of resources, an inability to integrate acquired operations and extra expenses. This could disrupt our business and adversely affect our financial condition.
Part of our growth strategy is to pursue acquisitions. The negotiation of potential acquisitions as well as the integration of acquired businesses could divert our management’s time and resources. Acquired businesses may not be successfully integrated with our operations. We may not realize the intended benefits of any acquisition. For example, the results of Wilsons adversely affected our results of operations in fiscal 2009 and 2010.
Acquisitions could also result in:
| • | substantial cash expenditures; |
| • | potentially dilutive issuances of equity securities; |
| • | the incurrence of debt and contingent liabilities; |
20
| • | a decrease in our profit margins; |
| • | amortization of intangibles and potential impairment of goodwill; |
| • | reduction of management attention to other parts of our business; |
| • | failure to generate expected financial results or reach business goals; and |
| • | increased expenditures on human resources and related costs. |
If acquisitions disrupt our operations, our business may suffer.
We may need additional financing to continue to grow.
The continued growth of our business depends on our access to sufficient funds to support our growth. Our primary source of working capital to support our growth is our line of credit which currently extends to July 2013. Our need for working capital has increased significantly as a result of our five acquisitions since July 2005, our addition of new licenses and the expansion of our business. The maximum available under our line of credit has increased from $110 million prior to our acquisitions in July 2005 to its current level of $300 million. Our growth is dependent on our ability to continue to be able to extend and increase our line of credit. If we are unable to refinance our debt, we cannot be sure we will be able to secure alternative financing on satisfactory terms or at all. The loss of the use of this credit facility or the inability to replace this facility when it expires would materially impair our ability to operate our business.
Our business is highly seasonal. Our results of operations may suffer in the event that the weather is unusually warm during the peak outerwear selling season.
Retail sales of outerwear have traditionally been seasonal in nature. Sales of outerwear constitute a significant portion of our sales. In prior years we have been dependent on our sales from July through November for the substantial majority of our net sales and net income. Net sales in the months of July through November accounted for approximately 60% of our net sales in each of fiscal 2012 and fiscal 2011 and 64% of our net sales in fiscal 2010. Our Wilsons outlet business is also highly seasonal, with the third and fourth fiscal quarters accounting for a significant majority of its sales and operating income. As a result, we are highly dependent on our results of operations during the second half of our fiscal year. Any difficulties we may encounter during this period as a result of weather or disruption of manufacturing or transportation of our products will have a magnified effect on our net sales and net income for the year. In addition, because of the large amount of outerwear we sell at both wholesale and retail, unusually warm weather conditions during the peak fall and winter outerwear selling season, including as a result of any change in historical climate patterns, could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations. Our quarterly results of operations for our retail business also may fluctuate based upon such factors as the timing of certain holiday seasons, the number and timing of new store openings, the acceptability of seasonal merchandise offerings, the timing and level of markdowns, store closings and remodels, competitive factors, weather and general economic conditions. The second half of the year is expected to continue to provide a disproportionate amount of our net sales and a substantial majority of our net income for the foreseeable future.
We are dependent upon foreign manufacturers.
We do not own or operate any manufacturing facilities. We also do not have long-term written agreements with any of our manufacturers. As a result, any of these manufacturers may unilaterally terminate its relationship with us at any time. Almost all of our products are imported from independent foreign manufacturers. The failure of these manufacturers to meet required quality standards could damage our relationships with our customers. In addition, the failure by these manufacturers to ship products to us in a timely manner could cause us to miss the delivery date requirements of our customers. The failure to make timely deliveries could cause customers to cancel orders, refuse to accept delivery of products or demand reduced prices.
We are also dependent on these manufacturers for compliance with our policies and the policies of our licensors and customers regarding labor practices employed by factories that manufacture product for us. Any failure by these manufacturers to comply with required labor standards or any other divergence in their labor or
21
other practices from those generally considered ethical in the United States, and the potential negative publicity relating to any of these events, could result in a violation by us of our license agreements and harm us and our reputation. In addition, a manufacturer’s failure to comply with safety or content regulations and standards could result in substantial liability and harm to our reputation.
If we do not successfully upgrade, maintain and secure our information systems to support the needs of our organization, this could have an adverse impact on the operation of our business.
We rely heavily on information systems to manage operations, including a full range of financial, sourcing, retail and merchandising systems, and regularly make investments to upgrade, enhance or replace these systems. The reliability and capacity of information systems is critical. Despite our preventative efforts, our systems are vulnerable from time to time to damage or interruption from, among other things, security breaches, computer viruses, power outages and other technical malfunctions. Any disruptions affecting our information systems, or any delays or difficulties in transitioning to new systems or in integrating them with current systems, could have a material adverse impact on the operation of our business. In addition, our ability to continue to operate our business without significant interruption in the event of a disaster or other disruption depends in part on the ability of our information systems to operate in accordance with our disaster recovery and business continuity plans.
Risk Factors Relating to the Economy and the Apparel Industry
Recent and future economic conditions, including turmoil in the financial and credit markets, may adversely affect our business.
The economic and credit environment has had and could continue to have a negative impact on businesses around the world. The impact of the environment on the apparel industry and our major customers has been significant. Conditions may be depressed or may be subject to deterioration which could lead to a reduction in consumer spending overall, which could have an adverse impact on sales of our products. A disruption in the ability of our significant customers to access liquidity could cause serious disruptions or an overall deterioration of their businesses which could lead to a significant reduction in their orders of our products and the inability or failure on their part to meet their payment obligations to us, any of which could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations and liquidity. A significant adverse change in a customer’s financial and/or credit position could also require us to assume greater credit risk relating to that customer’s receivables or could limit our ability to collect receivables related to previous purchases by that customer. As a result, our reserves for doubtful accounts and write-offs of accounts receivable may increase.
Our ability to continue to have the necessary liquidity to operate our business may be adversely impacted by a number of factors, including a continuation of the uncertain conditions in the credit and financial markets which could limit the availability and increase the cost of financing. A deterioration of our results of operations and cash flow resulting from decreases in consumer spending, could, among other things, impact our ability to comply with financial covenants in our existing credit facility.
Our historical sources of liquidity to fund ongoing cash requirements include cash flows from operations, cash and cash equivalents, and borrowings through our loan agreement (which includes revolving and trade letter of credit facilities). The sufficiency and availability of credit may be adversely affected by a variety of factors, including, without limitation, the tightening of the credit markets, including lending by financial institutions who are sources of credit for our borrowing and liquidity; an increase in the cost of capital; the reduced availability of credit; our ability to execute our strategy; the level of our cash flows, which will be impacted by retailer and consumer acceptance of our products and the level of consumer discretionary spending; maintenance of financial covenants included in our loan agreement; and interest rate fluctuations. We cannot be certain that any additional required financing, whether debt or equity, will be available in amounts needed or on terms acceptable to us, if at all.
As of January 31, 2012, we were in compliance with the financial covenants in our loan agreement. Compliance with these financial covenants is dependent on the results of our operations, which are subject to a number of factors including current economic conditions. The current economic environment has resulted generally in lower consumer confidence and lower retail sales. A continuation of this trend may lead to reduced consumer spending which could adversely impact our net sales and cash flow, which could affect our compliance with our
22
financial covenants. A violation of our covenants could limit access to our credit facilities. Should such restrictions on our credit facilities and these factors occur, they could have a material adverse effect on our business and results of operations.
The cyclical nature of the apparel industry and uncertainty over future economic prospects and consumer spending could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations.
The apparel industry is cyclical. Purchases of outerwear, sportswear and other apparel tend to decline during recessionary periods and may decline for a variety of other reasons, including changes in fashion trends and the introduction of new products or pricing changes by our competitors. Uncertainties regarding future economic prospects may affect consumer-spending habits and could have an adverse effect on our results of operations. Uncertainty with respect to consumer spending as a result of weak economic conditions has, at times, caused our customers to delay the placing of initial orders and to slow the pace of reorders during the seasonal peak of our business. Weak economic conditions have had a material adverse effect on our results of operations at times in the past and could have a material adverse effect on our results of operations in the future as well.
The competitive nature of the apparel industry may result in lower prices for our products and decreased gross profit margins.
The apparel business is highly competitive. We have numerous competitors with respect to the sale of apparel, including distributors that import apparel from abroad and domestic retailers with established foreign manufacturing capabilities. Many of our competitors have greater financial and marketing resources and greater manufacturing capacity than we do. We also compete with vertically integrated apparel manufacturers that also own retail stores. The general availability of contract manufacturing capacity also allows ease of access by new market entrants. The competitive nature of the apparel industry may result in lower prices for our products and decreased gross profit margins, either of which may materially adversely affect our sales and profitability. Sales of our products are affected by style, price, quality, brand reputation and general fashion trends.
If major department, mass merchant and specialty store chains continue to consolidate, our business could be negatively affected.
We sell our products to major department, mass merchant and specialty store chains. Continued consolidation in the retail industry could negatively impact our business. Consolidation could reduce the number of our customers and potential customers. With increased consolidation in the retail industry, we are increasingly dependent on retailers whose bargaining strength may increase and whose share of our business may grow. As a result, we may face greater pressure from these customers to provide more favorable terms, including increased support of their retail margins. As purchasing decisions become more centralized, the risks from consolidation increase. A store group could decide to decrease the amount of product purchased from us, modify the amount of floor space allocated to outerwear or other apparel in general or to our products specifically or focus on promoting private label products or national brand products for which it has exclusive rights rather than promoting our products. Customers are also concentrating purchases among a narrowing group of vendors. These types of decisions by our key customers could adversely affect our business.
A significant increase in fuel prices could adversely affect our results of operations.
Fuel prices have increased significantly at times during the past few years, and continued at relatively high levels in fiscal 2012. Increased gasoline prices could adversely affect consumer spending, including discretionary spending on apparel and accessories. In addition, higher fuel prices have caused our operating expenses to increase, particularly for freight. Any significant decrease in sales or increase in expenses as a result of higher fuel prices could adversely affect our results of operations.
If new legislation restricting the importation or increasing the cost of textiles and apparel produced abroad is enacted, our business could be adversely affected.
Legislation that would restrict the importation or increase the cost of textiles and apparel produced abroad has been periodically introduced in Congress. The enactment of new legislation or international trade regulation,
23
or executive action affecting international textile or trade agreements, could adversely affect our business. International trade agreements that can provide for tariffs and/or quotas can increase the cost and limit the amount of product that can be imported.
China’s accession agreement for membership in the World Trade Organization provides that member countries, including the United States, may impose safeguard quotas on specific products. In May 2005, the United States imposed unilateral quotas on several product categories, limiting growth in imports of these categories to 7.5% a year. These safeguard quotas were eliminated in 2009. We are unable to assess the potential for future action by the United States government with respect to any product category in the event that the quantity of imported apparel significantly disrupts the apparel market in the United States. Future action by the United States in response to a disruption in its apparel markets could limit our ability to import apparel and increase our costs.
The effects of war or acts of terrorism could adversely affect our business.
The continued threat of terrorism, heightened security measures and military action in response to acts of terrorism has, at times, disrupted commerce and intensified concerns regarding the United States economy. Any further acts of terrorism or new or extended hostilities may disrupt commerce and undermine consumer confidence, which could negatively impact our sales and results of operations.
Other Risks Relating to Ownership of Our Common Stock
Our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer may be in a position to control matters requiring a stockholder vote.
As of April 1, 2012, Morris Goldfarb, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, beneficially owned approximately 15.5% of our common stock. His significant role in our management and his reputation in the apparel industry could make his support crucial to the approval of any major transaction involving us. As a result, he may have the ability to control the outcome on matters requiring stockholder approval including, but not limited to, the election of directors and any merger, consolidation or sale of all or substantially all of our assets. He also may have the ability to control our management and affairs.
The price of our common stock has fluctuated significantly and could continue to fluctuate significantly.
Between February 1, 2009 and April 1, 2012, the market price of our common stock has ranged from a low of $3.24 to a high of $45.38 per share. The market price of our common stock may change significantly in response to various factors and events beyond our control, including:
| • | fluctuations in our quarterly revenues or those of our competitors as a result of seasonality or other factors; |
| • | a shortfall in revenues or net income from that expected by securities analysts and investors; |
| • | changes in securities analysts’ estimates of our financial performance or the financial performance of our competitors or companies in our industry generally; |
| • | announcements concerning our competitors; |
| • | changes in product pricing policies by our competitors or our customers; |
| • | general conditions in our industry; and |
| • | general conditions in the securities markets. |
Our actual financial results might vary from our publicly disclosed financial forecasts.
From time to time, we publicly disclose financial forecasts. Our forecasts reflect numerous assumptions concerning our expected performance, as well as other factors that are beyond our control and that might not turn out to be correct. As a result, variations from our forecasts could be material. Our financial results are subject to numerous risks and uncertainties, including those identified throughout this “Risk Factors” section and elsewhere in this Annual Report and in the documents incorporated by reference in this Annual Report. If our actual financial results are worse than our financial forecasts, the price of our common stock may decline.
24
We are subject to significant corporate regulation as a public company and failure to comply with all applicable regulations could subject us to liability or negatively affect our stock price.
As a publicly traded company, we are subject to a significant body of regulation, including the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act of 2010. While we have developed and instituted corporate compliance programs and continue to update our programs in response to newly implemented or changing regulatory requirements, we cannot provide assurance that we are or will be in compliance with all potentially applicable corporate regulations. If we fail to comply with any of these regulations, we could be subject to a range of regulatory actions, fines or other sanctions or litigation.
The internal control over financial reporting required by the Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act may not prevent or detect misstatements because of certain of its limitations, including the possibility of human error, the circumvention or overriding of controls, or fraud. As a result, even effective internal controls may not provide reasonable assurances with respect to the preparation and presentation of financial statements. We cannot provide assurance that, in the future, our management will not find a material weakness in connection with its annual review of our internal control over financial reporting pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act. We also cannot provide assurance that we could correct any such weakness to allow our management to assess the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting as of the end of our fiscal year in time to enable our independent registered public accounting firm to state that such assessment will have been fairly stated in our Annual Report on Form 10-K or state that we have maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of the end of our fiscal year. If we must disclose any material weakness in our internal control over financial reporting, our stock price could decline.
ITEM 1B. UNRESOLVED STAFF COMMENTS.
None.
ITEM 2. PROPERTIES.
Our executive offices, sales showrooms and support staff are located at 512 Seventh Avenue in New York City. During 2010, we entered into amendments to our leases related to our space in 512 Seventh Avenue that extended the term of our leases and provided for a common expiration date of March 31, 2023 for all of our space in this building, with a five year renewal option. We currently lease approximately 149,000 square feet of office and showroom space in this building. Our rent for our space at 512 Seventh Avenue is expected to be approximately $4.4 million in fiscal 2013. In March 2012, we added a lease for an additional space in this building of approximately 3,500 square feet which expires in June 2017. The rent for this space is approximately $128,000 for fiscal 2013.
We also have a lease for showroom and office space located at 209 West 38th Street in New York City for a term that commences August 2012 and ends in July 2015. This space consists of approximately 3,740 square feet of space. The rent for the premises is approximately $59,000 for fiscal 2013.
We had leases in New York City for an additional approximately 21,000 square feet of office and showroom space at 570 Seventh Avenue. A portion of the leased premises was surrendered to the landlord in January 2011 as a result of consolidation of some of these offices into our additional space at 512 Seventh Avenue. The lease for the remaining portion, approximately 16,000 square feet, has been extended through December 31, 2013. The current aggregate annual rent for this space is approximately $532,000. In October 2011, we added a lease for an additional space in this building of approximately 1,300 square feet which also expires December 31, 2013. Annual rent for this space is approximately $57,000.
We have a lease for a warehouse and distribution facility, located in Secaucus, New Jersey, through February 2014 covering an aggregate of approximately 205,000 square feet. Annual rent for the premises is approximately $1.0 million.
We have a lease through January 2014 for another distribution center in South Brunswick, New Jersey. This facility contains approximately 305,000 square feet of space which is used by us for product distribution. Annual rent for this facility is approximately $1.4 million.
25
We have a lease for another distribution center located in Jamesburg, New Jersey, for a term that commenced June 1, 2010 and ends December 31, 2020. We also have one five year renewal option. The distribution center consists of approximately 583,000 square feet which we utilize for the warehousing and distribution of our products. The initial fixed rent is approximately $2.0 million per year, with periodic set increases beginning in January 2013.
A majority of our finished goods is shipped to our New Jersey warehouse and distribution facilities for final reshipment to customers. We also use third-party warehouses to accommodate our finished goods storage and reshipment needs.
In connection with our retail operations, we have a lease in Brooklyn Park, Minnesota for an office, warehouse and distribution facility of approximately 158,000 square feet at a current aggregate annual rent of approximately $627,000. This lease commenced in June 2009 and expires in April 2015.
As of January 31, 2012, we operated 139 leased store locations, of which 135 are Wilsons stores located in outlet centers. Most leases require us to pay annual minimum rent plus a contingent rent dependent on the store’s annual sales in excess of a specified threshold. In addition, the leases generally require us to pay costs such as real estate taxes and common area maintenance costs. Outlet store leases are typically 5 to 10 years in duration. Our leases expire at varying dates through 2022. During fiscal 2012, we entered into 20 new store leases, renewed 27 store leases and terminated or allowed to expire, 11 store leases. The following table indicates the periods during which our retail leases expire.
| Fiscal Year Ending |
Number of Stores |
|||
| 2013 |
21 | |||
| 2014 |
21 | |||
| 2015 |
8 | |||
| 2016 |
17 | |||
| 2017 and thereafter |
72 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| Total |
139 | |||
|
|
|
|||
ITEM 3. LEGAL PROCEEDINGS.
In the ordinary course of our business, we are subject to periodic lawsuits, investigations and claims. Although we cannot predict with certainty the ultimate resolution of lawsuits, investigations and claims asserted against us, we do not believe that any currently pending legal proceeding or proceedings to which we are a party will have a material adverse effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations.
ITEM 4. MINE SAFETY DISCLOSURES.
Not applicable.
26
PART II
| ITEM 5. | MARKET FOR THE REGISTRANT’S COMMON EQUITY, RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS AND ISSUER REPURCHASES OF EQUITY SECURITIES. |
Market For Common Stock
Our Common Stock is quoted on the Nasdaq Global Select Market under the trading symbol “GIII”. The following table sets forth, for the fiscal periods shown, the high and low sales prices for our Common Stock, as reported by the Nasdaq.
| High Prices | Low Prices | |||||||
| Fiscal 2011 |
||||||||
| Fiscal Quarter ended April 30, 2010 |
$ | 30.99 | $ | 16.88 | ||||
| Fiscal Quarter ended July 31, 2010 |
$ | 31.20 | $ | 20.99 | ||||
| Fiscal Quarter ended October 31, 2010 |
$ | 32.58 | $ | 22.02 | ||||
| Fiscal Quarter ended January 31, 2011 |
$ | 36.99 | $ | 24.40 | ||||
| Fiscal 2012 |
||||||||
| Fiscal Quarter ended April 30, 2011 |
$ | 45.38 | $ | 33.34 | ||||
| Fiscal Quarter ended July 31, 2011 |
$ | 45.15 | $ | 29.26 | ||||
| Fiscal Quarter ended October 31, 2011 |
$ | 31.33 | $ | 20.44 | ||||
| Fiscal Quarter ended January 31, 2012 |
$ | 28.99 | $ | 17.31 | ||||
| Fiscal 2013 |
||||||||
| Fiscal Quarter ending April 30, 2012 (through April 5, 2012) |
$ | 29.62 | $ | 22.87 | ||||
The last sales price of our Common Stock as reported by the Nasdaq Global Select Market on April 5, 2012 was $27.54 per share.
On April 5, 2012, there were 42 holders of record and, we believe, approximately 3,300 beneficial owners of our Common Stock.
Dividend Policy
Our Board of Directors currently intends to follow a policy of retaining any earnings to finance the growth and development of our business and does not anticipate paying cash dividends in the foreseeable future. Any future determination as to the payment of cash dividends will be dependent upon our financial condition, results of operations and other factors deemed relevant by the Board. Our loan agreement limits payments for cash dividends and stock redemptions to $1.5 million plus an additional amount based on the proceeds of sales of equity securities. See “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations — Liquidity and Capital Resources” in Item 7 below and Note E to our Condensed Consolidated Financial Statements.
Performance Graph
The following Performance Graph and related information shall not be deemed to be “soliciting material” or “filed” with the Securities and Exchange Commission, nor shall such information be incorporated by reference into any future filing under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, each as amended, except to the extent that we specifically request that it be treated as soliciting material or incorporate it by reference into such filing.
27
The Securities and Exchange Commission requires us to present a chart comparing the cumulative total stockholder return on our Common Stock with the cumulative total stockholder return of (i) a broad equity market index and (ii) a published industry index or peer group. This chart compares the Common Stock with (i) the S&P 500 Composite Index and (ii) the S&P Textiles Index, and assumes an investment of $100 on January 31, 2007 in each of the Common Stock, the stocks comprising the S&P 500 Composite Index and the stocks comprising the S&P Textile Index.
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.
Comparison of Cumulative Total Return
(January 31, 2007 — January 31, 2012)
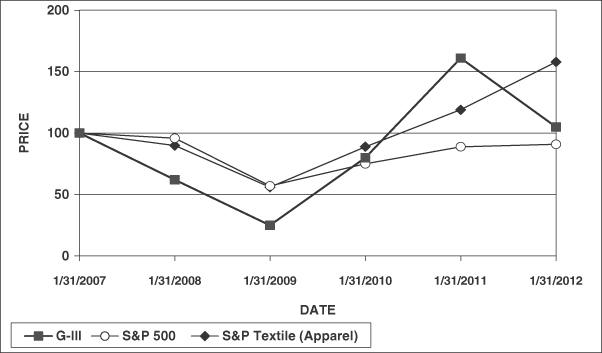
28
ITEM 6. SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA.
The selected consolidated financial data set forth below as of and for the years ended January 31, 2008, 2009, 2010, 2011 and 2012, have been derived from our audited consolidated financial statements. Our audited consolidated balance sheets as of January 31, 2008, 2009 and 2010, and our audited consolidated statements of income for the years ended January 31, 2008 and 2009 are not included in this filing. The selected consolidated financial data should be read in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” (Item 7 of this Report) and the audited consolidated financial statements and related notes thereto included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| Year Ended January 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Income Statement Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 518,868 | $ | 711,146 | $ | 800,864 | $ | 1,063,404 | $ | 1,231,201 | ||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
379,417 | 510,455 | 533,996 | 712,359 | 860,485 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Gross profit |
139,451 | 200,691 | 266,868 | 351,045 | 370,716 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
101,669 | 164,098 | 205,281 | 248,380 | 277,019 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
5,427 | 6,947 | 5,380 | 5,733 | 7,473 | |||||||||||||||
| Goodwill and trademark impairment |
— | 33,523 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Operating profit (loss) |
32,355 | (3,877 | ) | 56,207 | 96,932 | 86,224 | ||||||||||||||
| Equity loss in joint venture |
— | — | — | — | 1,271 | |||||||||||||||
| Interest and financing charges, net |
3,158 | 5,564 | 4,705 | 4,027 | 5,713 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
29,197 | (9,441 | ) | 51,502 | 92,905 | 79,240 | ||||||||||||||
| Income tax expense |
11,707 | 4,588 | 19,784 | 36,223 | 29,620 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 17,490 | $ | (14,029 | ) | $ | 31,718 | $ | 56,682 | $ | 49,620 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Basic earnings (loss) per share |
$ | 1.09 | $ | (0.85 | ) | $ | 1.87 | $ | 2.96 | $ | 2.51 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding — basic |
16,119 | 16,536 | 16,990 | 19,175 | 19,796 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted earnings (loss) per share |
$ | 1.05 | $ | (0.85 | ) | $ | 1.83 | $ | 2.88 | $ | 2.46 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Weighted average shares outstanding — diluted |
16,670 | 16,536 | 17,358 | 19,705 | 20,192 | |||||||||||||||
| As of January 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Working capital |
$ | 120,414 | $ | 99,154 | $ | 174,082 | $ | 239,494 | $ | 288,259 | ||||||||||
| Total assets |
237,698 | 280,960 | 332,015 | 447,921 | 546,103 | |||||||||||||||
| Short-term debt |
13,060 | 29,048 | — | — | 30,050 | |||||||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity |
173,874 | 162,229 | 232,210 | 303,494 | 357,972 | |||||||||||||||
29
| ITEM 7. | MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATION. |
Unless the context otherwise requires, “G-III”, “us”, “we” and “our” refer to G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and its subsidiaries. References to fiscal years refer to the year ended or ending on January 31 of that year. For example, our fiscal year ended January 31, 2012 is referred to as “fiscal 2012.”
The following presentation of management’s discussion and analysis of our consolidated financial condition and results of operations should be read in conjunction with our financial statements, the accompanying notes and other financial information appearing elsewhere in this Report.
Overview
G-III designs, manufactures, and markets an extensive range of apparel, including outerwear, dresses, sportswear, women’s suits and women’s performance wear, as well as luggage and women’s handbags, small leather goods and cold weather accessories. We sell our products under our own proprietary brands, which include Andrew Marc, Marc New York and Marc Moto, licensed brands and private retail labels. As of January 31, 2012, G-III operated 139 retail stores, of which 135 are outlet stores operated under the Wilsons Leather name and 4 are outlet stores operated under our Andrew Marc brand. As of January 31, 2012, our joint venture with the Camuto Group operated 11 Vince Camuto outlet stores.
While our products are sold at a variety of price points through a broad mix of retail partners and our own outlet stores, a majority of our sales are concentrated with our ten largest customers. Sales to our ten largest customers comprised 55.0% of our net sales in fiscal 2010, 62.7% of our net sales in 2011 and 63.3% of our net sales in fiscal 2012.
Our business is dependent on, among other things, retailer and consumer demand for our products. We believe that economic uncertainty and a slowdown in the global macroeconomic environment continue to negatively impact the level of consumer spending for discretionary items. The current uncertain economic environment has been characterized by a decline in consumer discretionary spending that may affect retailers and sellers of consumer goods, particularly those whose goods are viewed as discretionary purchases, such as fashion apparel and related products, such as ours. We cannot predict the direction in which the current economic environment will move. Continued uncertain macroeconomic conditions may have a negative impact on our results for fiscal 2013.
We operate in fashion markets that are intensely competitive. Our ability to continuously evaluate and respond to changing consumer demands and tastes, across multiple market segments, distribution channels and geographies is critical to our success. Although our portfolio of brands is aimed at diversifying our risks in this regard, misjudging shifts in consumer preferences could have a negative effect on our business. Our success in the future will depend on our ability to design products that are accepted in the marketplace, source the manufacture of our products on a competitive basis, and continue to diversify our product portfolio and the markets we serve.
We operate our business in three segments, wholesale licensed products, wholesale non-licensed products and retail operations. The wholesale licensed products segment includes sales of products under brands licensed by us from third parties. The wholesale non-licensed products segment includes sales of products under our own brands and private label brands. The retail operations segment consists almost entirely of the operations of our Wilsons outlet stores, and beginning in the second half of fiscal 2012, a limited number of Andrew Marc outlet stores.
We have expanded our portfolio of proprietary and licensed brands through acquisitions and by entering into license agreements for new brands or for additional products under previously licensed brands. Our acquisitions have helped to broaden our product offerings, expand our ability to serve different tiers of distribution and add a retail component to our business.
Our acquisitions are part of our strategy to expand our product offerings and increase the portfolio of proprietary and licensed brands that we offer through different tiers of retail distribution and at a variety of price points.
30
We believe that both Andrew Marc and the Wilsons outlet business leverage our core strength in outerwear and provide us with new avenues for growth. We also believe that these acquisitions complement our other licensed brands, G-III owned labels and private label programs.
We have used the capabilities of companies we acquired to help us expand our product offerings. The Jessica Howard dress operations we acquired expanded and complemented our dress business that began shipping under the Calvin Klein label in September 2006. We added to our dress business when we expanded our license with Ellen Tracy to include dresses and again when we entered into a license agreement for Jessica Simpson dresses. We continued to grow our dress business when we expanded our relationship with Guess in 2010 to include dresses and added licenses in 2011 for dresses with each of Vince Camuto and Kensie. We also intend to grow our Jessica Howard and Eliza J brands and expand private label programs to further develop our dress business.
When we acquired Andrew Marc, it was a supplier of fine outerwear and handbags for both men and women to upscale specialty and department stores. We have since expanded our product categories and product offerings for Andrew Marc, both in house and through licensing arrangements. We have expanded the distribution of outerwear by penetrating additional doors and selling into new channels of distribution. We enhanced our website for Andrew Marc (www.andrewmarc.com) to expand our online product offerings. We launched Andrew Marc and Marc New York dress lines which began shipping in Fall 2009, leveraging our G-III dress capabilities and our manufacturing sources.
We added to the Andrew Marc family of brands by creating the Marc Moto brand, The Marc Moto offering contains vintage inspired product that embraces legendary style. It is a denim lifestyle collection targeted toward young, independent men.
We began a program to license our Andrew Marc and Marc New York brands and have entered into agreements to license these brands for women’s footwear, men’s accessories, women’s handbags, men’s cold weather accessories, men’s denim and related sportswear, eyewear, men’s dress shirts, men’s tailored clothing, men’s footwear, watches, neckwear and sweaters. We have entered into agreements that terminate the license agreements with respect to women’s handbags and men’s denim and related sportswear, and are now pursuing these initiatives in-house.
Our retail operations segment, which consists almost entirely of our Wilsons outlet store business, had an operating loss during fiscal 2009 and fiscal 2010, although it achieved an operating profit in fiscal 2011 and fiscal 2012. Beginning in fiscal 2010, we undertook the following initiatives to improve the performance of our outlet business:
| • | Improve the merchandise mix of outerwear at our stores, with increased emphasis on leather outerwear and a stronger assortment of private label product; |
| • | Emphasize presentation of product in our stores and training of our sales associates; and |
| • | Incorporate an improved mix of private label and branded accessories. |
As a result of these initiatives, the amount of the operating loss in our retail segment was reduced in fiscal 2010, and the retail segment achieved an operating profit in each of fiscal 2011 and 2012. We continue to believe that operation of the Wilsons outlet stores is part of our core competency, as outerwear comprised about one-half of our net sales at Wilsons in fiscal 2012. We expect to continue to implement and refine these initiatives with a view to creating a store concept that is capable of building growth and profitability over the long-term. During fiscal 2012, we increased the number of our Wilson outlet stores by 5 and opened 4 new Andrew Marc outlet stores. We expect to add approximately 14 new outlet stores in fiscal 2013.
During the third quarter of fiscal 2011, we formed a joint venture with The Camuto Group to operate footwear and accessory outlet stores under the name “Vince Camuto.” The Camuto Group provides product and merchandises the stores. We provide the infrastructure and expertise for operation of the stores, including real estate, distribution, information systems, finance and administration. Both companies share equally in the capital costs of the joint venture. The joint venture opened the first Vince Camuto outlet store in April 2011 and, as of January 31, 2012, 11 of these stores were in operation. We are accounting for our share of this joint venture under the equity method.
31
In November 2011, we entered into a license agreement granting us the retail rights to distribute and market Calvin Klein women’s performance apparel in the United States and China. We opened our first Calvin Klein Performance store in Scottsdale, Arizona in February 2012 and expect to open approximately 2 additional stores in the U.S. in fiscal 2013. In March 2012, we entered into a joint venture agreement with Finity Apparel Retail Limited to open and operate Calvin Klein Performance retail stores in China and Hong Kong. G-III will retain 51% ownership of the joint venture which expects to begin operating retail locations in major Chinese markets beginning in Fall 2012.
The sale of licensed product has been a key element of our business strategy for many years. Sales of wholesale licensed product accounted for 65.5% of our net sales in fiscal 2012, 67.6% of our net sales in fiscal 2011 and 65.4% of our net sales in fiscal 2010.
Our most significant licensor is Calvin Klein with whom we have nine different license agreements. In May 2010, we added licenses for Calvin Klein luggage and for Calvin Klein women’s handbags and small leather goods. The first shipment of these products in the United States commenced for the Spring 2011 season. We have also entered into distribution agreements with respect to Calvin Klein luggage in a limited number of countries in Asia, Europe and North America.
In September 2010, we entered into an extended and expanded license agreement with the National Football League to manufacture and market men’s and women’s outerwear, sportswear, and swimwear products in the United States under a variety of NFL trademarks. This license agreement is for five additional years and commenced on April 1, 2012.
In May 2011, we entered into two new agreements with the Camuto Group, expanding our relationship with Camuto to include licenses for dresses and men’s outerwear. Dresses under the Camuto label begin shipping for Spring 2012 and men’s outerwear is expected to begin shipping for the Fall 2012 season. In June 2011, we also expanded our product categories with Tommy Hilfiger to include luggage, which began shipping in August 2011. In November 2011, we entered into a license agreement to develop sportswear, dresses, tailored clothing, active wear and sweaters under the Kensie and Mac & Jac brands for the U.S. and Canadian markets. In December 2011, we added licenses under these brands for women’s handbags and women’s cold weather accessories. We began shipping Kensie sportswear in the first quarter of fiscal 2012 and plan to follow with the launch of additional categories. In December 2011, we entered into a license agreement that expanded our Jessica Simpson products to include women’s outerwear. We expect to begin shipping Jessica Simpson outerwear for the Fall 2012 season.
We believe that consumers prefer to buy brands they know and we have continually sought licenses that would increase the portfolio of name brands we can offer through different tiers of retail distribution, for a wide array of products and at a variety of price points. We believe that brand owners will look to consolidate the number of licensees they engage to develop product and they will seek licensees with a successful track record of expanding brands into new categories. It is our objective to continue to expand our product offerings and we are continually discussing new licensing opportunities with brand owners.
Trends
Significant trends that affect the apparel industry include increases in raw material, manufacturing and transportation costs, the continued consolidation of retail chains and the desire on the part of retailers to consolidate vendors supplying them.
During fiscal 2012, we and other apparel manufacturers experienced increases in raw material prices and other costs. These conditions are expected to moderate during fiscal 2013.
Retailers are seeking to expand the differentiation of their offerings by devoting more resources to the development of exclusive products, whether by focusing on their own private label products or on products produced exclusively for a retailer by a national brand manufacturer. Retailers are placing more emphasis on building strong images for their private label and exclusive merchandise. Exclusive brands are only made available to a specific retailer, and thus customers loyal to their brands can only find them in the stores of that retailer.
A number of retailers are experiencing financial difficulties, which in some cases has resulted in bankruptcies, liquidations and/or store closings. The financial difficulties of a retail customer of ours could result in
32
reduced business with that customer. We may also assume higher credit risk relating to receivables of a retail customer experiencing financial difficulty that could result in higher reserves for doubtful accounts or increased write-offs of accounts receivable. We attempt to lower credit risk from our customers by closely monitoring accounts receivable balances and shipping levels, as well as the ongoing financial performance and credit standing of customers.
We have attempted to respond to these trends by continuing to focus on selling products with recognized brand equity, by attention to design, quality and value and by improving our sourcing capabilities. We have also responded with the strategic acquisitions made by us and new license agreements entered into by us that have added additional licensed and proprietary brands and helped diversify our business by adding new product lines, additional distribution channels and a retail component to our business. We believe that our broad distribution capabilities help us to respond to the various shifts by consumers between distribution channels and that our operational capabilities will enable us to continue to be a vendor of choice for our retail partners.
Use of Estimates and Critical Accounting Policies
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with generally accepted accounting principles requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements and revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Significant accounting policies employed by us, including the use of estimates, are presented in the notes to our consolidated financial statements.
Critical accounting policies are those that are most important to the portrayal of our financial condition and our results of operations, and require management’s most difficult, subjective and complex judgments, as a result of the need to make estimates about the effect of matters that are inherently uncertain. Our most critical accounting estimates, discussed below, pertain to revenue recognition, accounts receivable, inventories, income taxes, goodwill and intangible assets and equity awards. In determining these estimates, management must use amounts that are based upon its informed judgments and best estimates. On an on-going basis, we evaluate our estimates, including those related to customer allowances and discounts, product returns, bad debts and inventories, and carrying values of intangible assets. We base our estimates on historical experience and on various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under the circumstances. The results of these estimates form the basis for making judgments about the carrying values of assets and liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results may differ from these estimates under different assumptions and conditions.
Revenue Recognition
Goods are shipped to retailers in accordance with specific customer orders. We recognize wholesale sales when the risks and rewards of ownership have transferred to the customer, determined by us to be when title to the merchandise passes to the customer. In addition, we act as an agent in brokering sales between customers and overseas factories. On these transactions, we recognize commission fee income on sales that are financed by and shipped directly to our customers. Title to goods shipped by overseas vendors, transfers to customers when the goods have been delivered to the customer. We recognize commission income upon the completion of the delivery by our vendors to the customer. We recognize retail sales upon customer receipt of our merchandise, generally at the point of sale. Our sales are recorded net of applicable sales tax. Net sales take into account reserves for returns and allowances. We estimate the amount of reserves and allowances based on current and historical information and trends. Sales are reported net of returns, discounts and allowances. Discounts, allowances and estimates of future returns are recognized when the related revenues are recognized.
Accounts Receivable
In the normal course of business, we extend credit to our wholesale customers based on pre-defined credit criteria. Accounts receivable, as shown on our consolidated balance sheet, are net of allowances and anticipated discounts. In circumstances where we are aware of a specific customer’s inability to meet its financial obligation (such as in the case of bankruptcy filings, extensive delay in payment or substantial downgrading by credit sources), a specific reserve for bad debts is recorded against amounts due to reduce the net recognized receivable to the amount
33
reasonably expected to be collected. For all other wholesale customers, an allowance for doubtful accounts is determined through analysis of the aging of accounts receivable at the date of the financial statements, assessments of collectability based on historical trends and an evaluation of the impact of economic conditions.
An allowance for discounts is based on reviews of open invoices where concessions have been extended to customers. Costs associated with allowable deductions for customer advertising expenses are charged to advertising expenses in the selling, general and administrative section of our consolidated statements of income. Costs associated with markdowns and other operational charge backs, net of historical recoveries, are included as a reduction of net sales. All of these are part of the allowances included in accounts receivable. We reserve against known charge backs, as well as for an estimate of potential future deductions by customers. These provisions result from seasonal negotiations with our customers as well as historical deduction trends, net of historical recoveries and the evaluation of current market conditions.
Inventories
Wholesale inventories are stated at lower of cost (determined by the first-in, first-out method) or market. The cost elements included in inventory consist of all direct costs of merchandise, inbound freight and merchandise acquisition costs such as commissions and import fees. Retail inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market as determined by the retail inventory method. Retail inventory cost includes the cost of merchandise, inbound freight, duty and other merchandise-specific charges.
We continually evaluate the composition of our inventories, assessing slow-turning, ongoing product as well as fashion product from prior seasons. The market value of distressed inventory is based on historical sales trends of our individual product lines, the impact of market trends and economic conditions, expected permanent retail markdowns and the value of current orders for this type of inventory. A provision is recorded to reduce the cost of inventories to the estimated net realizable values, if required.
Income Taxes
As part of the process of preparing our consolidated financial statements, we are required to estimate our income taxes in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate. This process involves estimating our actual current tax exposure, together with assessing temporary differences resulting from differing treatment of items for tax and accounting purposes. These differences result in deferred tax assets and liabilities, which are included within our consolidated balance sheet.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
ASC 350 requires that goodwill and intangible assets with an indefinite life be tested for impairment at least annually and are required to be written down when impaired. We perform our test in the fourth fiscal quarter of each year, or more frequently, if events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying amount of such assets may be impaired. Goodwill and intangible assets with an indefinite life are tested for impairment by comparing the fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying value. Fair value is generally determined using discounted cash flows, market multiples and market capitalization. Significant estimates used in the fair value methodologies include estimates of future cash flows, future short-term and long-term growth rates, weighted average cost of capital and estimates of market multiples of the reportable unit. If these estimates or their related assumptions change in the future, we may be required to record impairment charges for our goodwill and intangible assets with an indefinite life. Our annual impairment test is performed in the fourth quarter each year.
The process of evaluating the potential impairment of goodwill is subjective and requires significant judgment at many points during the analysis. In estimating the fair value of a reporting unit for the purposes of our annual or periodic analyses, we make estimates and judgments about the future cash flows of that reporting unit. Although our cash flow forecasts are based on assumptions that are consistent with our plans and estimates we are using to manage the underlying businesses, there is significant exercise of judgment involved in determining the cash flows attributable to a reporting unit over its estimated remaining useful life. In addition, we make certain judgments about allocating shared assets to the estimated balance sheets of our reporting units. We also consider our and our competitor’s market capitalization on the date we perform the analysis. Changes in judgment on these assumptions and estimates could result in a goodwill impairment charge.
34
We have allocated the purchase price of the companies we acquired to the tangible and intangible assets acquired and liabilities we assumed, based on their estimated fair values. These valuations require management to make significant estimations and assumptions, especially with respect to intangible assets. Critical estimates in valuing intangible assets include future expected cash flows from license agreements, trade names and customer relationships. In addition, other factors considered are the brand awareness and market position of the products sold by the acquired companies and assumptions about the period of time the brand will continue to be used in the combined company’s product portfolio. Management’s estimates of fair value are based on assumptions believed to be reasonable, but which are inherently uncertain and unpredictable.
If we did not appropriately allocate these components or we incorrectly estimate the useful lives of these components, our computation of amortization expense may not appropriately reflect the actual impact of these costs over future periods, which may affect our results of operations.
Trademarks having finite lives are amortized over their estimated useful lives and measured for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying value may be impaired.
Equity Awards
All share-based payments to employees, including grants of restricted stock units and employee stock options, are recognized as compensation expense over the service period (generally the vesting period) in the consolidated financial statements based on their fair values. Restricted stock units that do not have a market condition are valued based on the quoted market price on date of grant. Restricted stock units with a market condition are valued using a valuation expert. Stock options are valued using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The Black-Scholes model requires subjective assumptions regarding dividend yields, expected volatility, expected life of options and risk-free interest rates. These assumptions reflect management’s best estimates. Changes in these inputs and assumptions can materially affect the estimate of fair value and the amount of our compensation expenses for stock options.
35
Results of Operations
The following table sets forth selected operating data as a percentage of our net sales for the fiscal years indicated below:
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | ||||||||||
| Net sales |
100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | 100.0 | % | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
66.7 | 67.0 | 69.9 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross profit |
33.3 | 33.0 | 30.1 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
25.6 | 23.4 | 22.5 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
0.7 | 0.5 | 0.6 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating profit |
7.0 | 9.1 | 7.0 | |||||||||
| Equity loss in joint venture |
— | — | 0.1 | |||||||||
| Interest and financing charges, net |
0.6 | 0.4 | 0.5 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income before income taxes |
6.4 | 8.7 | 6.4 | |||||||||
| Income taxes |
2.4 | 3.4 | 2.4 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income |
4.0 | % | 5.3 | % | 4.0 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Year ended January 31, 2012 (“fiscal 2012”) compared to year ended January 31, 2011 (“fiscal 2011”)
Net sales for fiscal 2012 increased to $1.23 billion from $1.06 billion in the prior year. Net sales of wholesale licensed product accounted for 65.5% of our net sales in fiscal 2012 compared to 67.6% of our net sales in fiscal 2011. Excluding net sales in the retail segment, net sales of wholesale licensed product accounted for 75.2% of net sales of wholesale product in fiscal 2012 and 74.6% of net sales of wholesale product in fiscal 2011. Net sales of wholesale licensed product increased to $840.7 million in fiscal 2012 from $718.5 million in fiscal 2011. This increase was primarily the result of an increase of $85.8 million in net sales of Calvin Klein licensed product, mainly due to the introduction of Calvin Klein handbag, accessory and luggage lines, a $11.9 million increase in net sales of licensed sports apparel and a $11.1 million increase in net sales of Jessica Simpson dresses.
Net sales of wholesale non-licensed product increased to $277.6 million in fiscal 2012 from $244.0 million in fiscal 2011, primarily due to an increase of $33.7 million in net sales of private label outerwear.
Net sales of our retail operations increased to $164.3 million in fiscal 2012 from $142.3 million in fiscal 2011 primarily as a result of an increase in the number of stores in fiscal 2012, as well as a comparative store sales increase of 6.6%. Net sales resulting from new stores opened in fiscal 2012 were approximately $8.4 million.
Gross profit increased to $370.7 million, or 30.1% of net sales, for fiscal 2012 from $351.0 million, or 33.0% of net sales, for fiscal 2011. The gross profit in our wholesale licensed product segment increased to $223.0 million, or 26.5% of net sales, in fiscal 2012 from $213.6 million, or 29.7% of net sales, in the prior year. The gross profit in our wholesale non-licensed product segment increased to $72.1 million in fiscal 2012, or 26% of net sales, from $70.5 million, or 28.9% of net sales, in fiscal 2011. The gross profit in our retail operations segment increased to $75.6 million, or 46.0% of net sales, for fiscal 2012 from $67.0 million, or 47.1% of net sales, for fiscal 2011. We experienced significant increases in wholesale product costs during the year and were not always able to increase selling prices to offset cost increases. The gross margins in all three segments were impacted by promotional activity throughout the year and also by the unseasonably warm weather in our fourth fiscal quarter, which resulted in lower discounted initial selling prices and additional markdown support.
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased to $277.0 million in fiscal 2012 from $248.4 million in the prior year. Selling, general and administrative expenses increased primarily as a result of increases in personnel costs ($8.3 million), advertising and promotion expenses ($7.2 million) and third party warehousing costs ($5.2 million). Personnel costs increased primarily as a result of the addition of new product lines as well as an
36
increase in personnel to staff additional outlet stores in our retail division, offset in part by reduced bonus payments as a result of lower profitability. Advertising costs increased because sales of licensed product increased and we typically pay an advertising fee under our license agreements based on a percentage of sales of licensed product. We also experienced an increase in advertising chargebacks by customers. Third party warehousing costs increased as a result of our increased shipping volume as well as higher inventory balances compared to last year.
Depreciation and amortization increased to $7.5 million in fiscal 2012 from $5.7 million in the prior year primarily as a result of leasehold improvements and fixtures added during fiscal 2011 for the additional showroom and office space we leased.
Equity loss in joint venture of $1.3 million in fiscal 2012 represents our share of the loss in the joint venture relating to the operation of Vince Camuto outlet stores. As this joint venture commenced operations in the fourth quarter of fiscal 2011, there is no amount for this item in the prior year.
Interest and finance charges, net for fiscal 2012 increased to $5.7 million from $4.0 million in the prior year. Our interest charges were higher because of higher average borrowings under our credit facility, primarily as a result of higher inventory levels.
Income tax expense for fiscal 2012 decreased to $29.6 million from $36.2 million in the prior year. The effective rate for fiscal 2012 was 37.4% compared to an effective tax rate for fiscal 2011 of 39.0%. The effective tax rate is lower primarily due to foreign tax savings realized during the current period.
Year ended January 31, 2011 (“fiscal 2011”) compared to year ended January 31, 2010 (“fiscal 2010”)
Net sales for fiscal 2011 increased to $1.06 billion from $800.9 million in the prior year. Net sales of wholesale licensed product accounted for 67.6% of our net sales in fiscal 2011 compared to 65.4% of our net sales in fiscal 2010. Excluding net sales in the retail segment, net sales of wholesale licensed product accounted for 74.6% of net sales of wholesale product in fiscal 2011 and 73.5% of net sales of wholesale product in fiscal 2010. Net sales of wholesale licensed product increased to $718.5 million in fiscal 2011 from $523.6 million in fiscal 2010. This increase was primarily the result of an increase of $143.6 million in net sales of Calvin Klein licensed product, primarily attributable to increased sales of dresses and women’s sportswear, as well as increased net sales of $19.9 million in Guess outerwear and $16.2 million in Kenneth Cole outerwear.
Net sales of wholesale non-licensed product increased to $244.0 million in fiscal 2011 from $188.3 million in fiscal 2010, primarily due to increased net sales of $32.1 million in private label outerwear, $12.9 million in our Andrew Marc products and $10.8 million in our Jessica Howard/Eliza J dresses.
Net sales of our retail operations increased to $142.3 million in fiscal 2011 from $126.6 million in fiscal 2010 primarily as a result of various performance improvement initiatives we implemented beginning in fiscal 2010 and continued in fiscal 2011, as well as an increase in the number of stores in fiscal 2011. Net sales resulting from new stores opened in fiscal 2011 were approximately $5.7 million.
Gross profit increased to $351.0 million, or 33.0% of net sales, for fiscal 2011 from $266.9 million, or 33.3% of net sales, in the prior year. The gross profit in our wholesale licensed product segment increased to $213.6 million, or 29.7% of net sales, for fiscal 2011 from $156.2 million, or 29.8% of net sales, in the prior year. The gross profit in our wholesale non-licensed product segment increased to $70.5 million in fiscal 2011, or 28.9% of net sales, from $53.7 million, or 28.5% of net sales, in fiscal 2010. The gross profit in our retail operations segment increased to $67.0 million, or 47.1% of net sales, for fiscal 2011 from $57.0 million, or 45.0% of net sales, for fiscal 2010. The gross profit in our retail operations segment increased primarily as a result of higher initial margins and less markdown activity across all product categories.
Selling, general and administrative expenses increased to $248.4 million in fiscal 2011 from $205.3 million in the prior year. Selling, general and administrative expenses increased primarily as a result of increases in personnel costs ($19.0 million), advertising and promotion expenses ($6.6 million), facility costs ($5.4 million) and third party warehousing costs ($5.1 million). Personnel costs increased primarily as a result of higher bonus payments associated with higher profitability and an increase in headcount. Advertising costs increased because sales of licensed product increased and we typically pay an advertising fee under our license agreements based on
37
a percentage of sales of licensed product. Facility costs increased primarily as a result of rent and related occupancy costs associated with our new warehouse facility space which became fully operational during fiscal 2011 and the additional showroom space we leased. Third party warehousing costs increased as a result of our increased shipping volume.
Depreciation and amortization increased to $5.7 million in fiscal 2011 from $5.4 million for the prior year primarily as a result of increased capital expenditures during fiscal 2011 relating to our new office and warehouse leases.
Interest and finance charges, net for fiscal 2011 decreased to $4.0 million from $4.7 million in the prior year. Our interest charges were lower primarily due to a lower average loan balance compared to the prior fiscal year as a result of the proceeds received from our public offering in December 2009.
Income tax expense for fiscal 2011 increased to $36.2 million from $19.8 million in the prior year. The effective rate for fiscal 2011 was 39.0% compared to an effective tax rate for fiscal 2010 of 38.4%. The effective rate in the prior year was positively impacted by additional net operating losses recorded in connection with the acquisition of Andrew Marc.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Our primary operating cash requirements are to fund our seasonal buildup in inventories and accounts receivable, primarily during the second and third fiscal quarters each year. Due to the seasonality of our business, we generally reach our peak borrowings under our asset-based credit facility during our third fiscal quarter. The primary sources to meet our operating cash requirements have been borrowings under this credit facility and cash generated from operations. We also raised cash from an offering of our common stock in December 2009 as described below. We had a net debt position of $5.4 million at January 31, 2012 compared to cash of $10.0 million at January 31, 2011.
Public Offering
In December 2009, we sold 1,907,010 shares of our common stock, including 207,010 shares sold pursuant to the exercise of the underwriters’ over-allotment option, at a public offering price of $19.50 per share. We received net proceeds of $34.7 million from this offering after payment of the underwriting discount and expenses of the offering. The net proceeds we received were used for general corporate purposes to support the growth of our business.
Financing Agreement
We have a financing agreement with JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A., as Agent for a consortium of banks. The financing agreement is a senior secured revolving credit facility. The financing agreement was amended in May 2010 to (a) increase the maximum line of credit from $250 million to $300 million, (b) reduce the interest rate on borrowings by 0.25% to, at our option, the prime rate plus 0.50% or LIBOR plus 2.75%, (c) extend the maturity of the loan from July 11, 2011 to July 31, 2013, and (d) revise the maximum senior leverage ratio that we must maintain.
The financing agreement provides for a maximum revolving line of credit of $300 million. Amounts available under the line are subject to borrowing base formulas and over advances as specified in the financing agreement. Borrowings under the line of credit bear interest, at our option, at the prime rate plus 0.50% (3.75% at March 31, 2012) or LIBOR plus 2.75% (2.99% at March 31, 2012).
The amount borrowed under the line of credit has varied based on our seasonal requirements. The maximum amount outstanding, including open letters of credit, under our line of credit was approximately $212.5 million in fiscal 2010, $206.2 million in fiscal 2011 and $292.2 million in fiscal 2012. At January 31, 2011, there were no direct borrowings outstanding compared to $30.1 million of outstanding borrowings at January 31, 2012. Our contingent liability under open letters of credit was approximately $20.1 million at January 31, 2011 and $11.3 million at January 31, 2012.
38
The financing agreement requires us, among other things, to maintain a maximum senior leverage ratio and minimum fixed charge coverage ratio, as defined. It also limits payments for cash dividends and stock redemption to $1.5 million plus an additional amount based on the proceeds of sales of equity securities. As of January 31, 2012, we were in compliance with these covenants. The financing agreement is secured by all of our assets.
Share Repurchase Program
In September 2011, our board of directors authorized a program to repurchase up to two million shares of our common stock. The timing and actual number of shares repurchased will depend upon a number of factors, including market conditions and prevailing stock prices. Share repurchases may take place on the open market, in privately negotiated transactions or by other means, and would be made in accordance with applicable securities laws. Pursuant to the share repurchase program, during fiscal 2012, we repurchased 125,000 shares of our common stock for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $2.9 million. Repurchased shares are accounted for as treasury stock at cost and will be held in treasury for future use.
Cash from Operating Activities
At January 31, 2012, we had cash and cash equivalents of $24.7 million. We generated $6.8 million of cash from operating activities in fiscal 2012. Cash was generated primarily from our net income of $49.6 million, non-cash charges of $7.5 million for depreciation and amortization, an increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses of $6.2 million primarily associated with accrued royalty expenses relating to sales of licensed products, a net increase in taxes payable of $6.0 million and $5.2 million for non-cash equity-based compensation offset in part by an increase in inventory of $48.5 million primarily as a result of our purchase of inventory for our most recently added luggage and handbag product lines and the growth in our dress lines and an increase in accounts receivable of $24.2 million associated with increased fourth quarter net sales.
The main reasons for the change in cash provided by (used in) operations for fiscal 2012 compared to fiscal 2011 is a smaller increase in accounts receivable and inventory at January 31, 2012 compared to January 31, 2011, offset by the relative insignificant change in accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities at January 31, 2012 compared to January 31, 2011, compared to the significant increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses at January 31, 2010 as compared to the prior period.
At January 31, 2011, we had cash and cash equivalents of $10.0 million. We used $28.6 million of cash for operating activities in fiscal 2011 primarily from an increase in accounts receivable of $64.9 million due to increased fourth quarter net sales and an increase in inventory of $85.1 million primarily due to accelerated receipts to take advantage of early buying opportunities and as a result of the earlier Chinese New Year holiday, offset in part by our net income of $56.7 million and an increase in accounts payable and accrued expenses of $63.5 million primarily associated with higher inventory levels.
At January 31, 2010, we had cash and cash equivalents of $46.8 million. We generated $44.0 million of cash from operating activities in fiscal 2010. Cash was generated primarily from our net income of $31.7 million, an increase in accrued expenses of $10.0 million and non-cash depreciation and amortization charges of $5.4 million. Accrued expenses increased primarily as a result of higher accrued bonuses associated with higher profitability.
Cash from Investing Activities
In fiscal 2012, we used $21.1 million of cash in investing activities, of which $17.4 million were for capital expenditures and $3.7 million were for an investment in the joint venture relating to the Vince Camuto outlet stores. The capital expenditures related primarily to build out and renovation costs with respect to the amended and extended leases we entered into in March 2010 relating to our existing and additional showrooms and offices and the addition of new outlet stores.
In fiscal 2011, we used $19.4 million of cash for investing activities primarily for capital expenditures, which were primarily for the new warehouse facility leased in December 2009, which became fully operational in June 2010, and renovations associated with additional office and showroom space.
39
In fiscal 2010, we used $7.0 million of cash for investing activities. We used $5.5 million of cash in connection with contingent payments earned as a result of the fiscal 2009 operating results of our Marvin Richards and Winlit divisions. Fiscal 2009 was the last year we were obligated to make these payments. We also used $1.5 million of cash for capital expenditures, primarily for renovating existing showroom space.
Cash from Financing Activities
Cash flows from financing activities provided $28.9 million in fiscal 2012 primarily as a result of net proceeds of $30.1 million of borrowings under our revolving credit facility offset by the use of approximately $2.9 million to repurchase shares of our common stock. We increased our borrowings primarily to pay for purchases of inventory.
Cash flows from financing activities provided $11.3 million in fiscal 2011 primarily as a result of $4.4 million from tax benefits recognized from the vesting or exercise of equity awards, $4.1 million in proceeds received from the exercise of stock warrants issued in connection with a private placement of our common stock and warrants in 2006 and $2.8 million in proceeds received from the exercise of stock options.
Cash flows from financing activities provided $7.4 million in fiscal 2010 primarily as a result of net proceeds of $34.7 million from our public offering of common stock in December 2009 offset, in part, by repayments of $29.0 of outstanding borrowings.
Financing Needs
We believe that our cash on hand and cash generated from operations, together with funds available from our line of credit, are sufficient to meet our expected operating and capital expenditure requirements, as well as to fund any repurchase of shares we elect to make. We may seek to acquire other businesses in order to expand our product offerings. We may need additional financing in order to complete one or more acquisitions. We cannot be certain that we will be able to obtain additional financing, if required, on acceptable terms or at all.
New Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2011, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued an Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) ASU 2011-12, “Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Deferral of the Effective Date for Amendments to the Presentation of Reclassifications of Items Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income in Accounting Standards Update No. 2011-05.” ASU 2011-12 defers the specific requirement to present items that are reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income to net income separately with their respective components of net income and other comprehensive income. ASU 2011-12 did not defer the requirement to report comprehensive income either in a single continuous statement or in two separate but consecutive financial statements. The amendments are effective at the same time as the amendments in ASU 2011-05.
In September 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-08, “Intangibles — Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Testing Goodwill for Impairment.” ASU 2011-08 simplifies how entities, both public and nonpublic, test goodwill for impairment and permits an entity to first assess qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount as a basis for determining whether it is necessary to perform the two-step goodwill impairment test described in Topic 350. The amendments are effective for annual and interim goodwill impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2011. Early adoption is permitted, including for annual and interim goodwill impairment tests performed as of a date before September 15, 2011, if an entity’s financial statements for the most recent annual or interim period have not yet been issued or, for nonpublic entities, have not yet been made available for issuance. The adoption of ASU 2011-08 is not expected to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In June 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-05, Presentation of Comprehensive Income. Under the amendments to Topic 220, Comprehensive Income, an entity has the option to present the total of comprehensive income, the components of net income, and the components of other comprehensive income either in a single continuous statement of comprehensive income or in two separate but consecutive statements. In both choices, an entity is required to present each component of net income along with total net income, each component of other comprehensive income along with a total for other comprehensive income, and a total amount for comprehensive
40
income. This eliminates the option to present the components of other comprehensive income as part of the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity. The amendments do not change the items that must be reported in other comprehensive income or when an item of other comprehensive income must be reclassified to net income. The guidance in ASU 2011-05 is effective for public companies for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years beginning after December 15, 2011. We do not expect that ASU 2011-05 will have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In May 2011, the FASB issued ASU No. 2011-04, “Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Amendments to Achieve Common Fair Value Measurement and Disclosure Requirements in U.S. GAAP and IFRSs.” ASU 2011-04 amends Topic 820 to provide common fair value measurement and disclosure requirements in U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“U.S. GAAP”) and International Financial Reporting Standards. Consequently, the amendments change the wording used to describe many of the requirements in U.S. GAAP for measuring fair value and for disclosing information about fair value measurements, as well as providing guidance on how fair value should be applied where its use is already required or permitted by other standards within U.S. GAAP. ASU No. 2011-04 is to be applied prospectively, and early adoption is not permitted. For public entities, the amendments are effective during interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2011. The adoption of ASU No. 2011-04 is not expected to have a material impact on our results of operations or financial position.
Off Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any “off-balance sheet arrangements” as such term is defined in Item 303 of Regulation S-K of the SEC rules.
Tabular Disclosure of Contractual Obligations
As of January 31, 2012, our contractual obligations were as follows (in thousands):
| Payments Due By Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations |
Total | Less than 1 Year |
1-3 Years |
3-5 Years |
More than 5 Years |
|||||||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations |
$ | 163,807 | $ | 24,288 | $ | 42,141 | $ | 32,765 | $ | 64,613 | ||||||||||
| Minimum royalty payments(1) |
172,476 | 62,236 | 65,379 | 42,861 | 2,000 | |||||||||||||||
| Purchase obligations(2) |
10,595 | 10,595 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 346,878 | $ | 97,119 | $ | 107,520 | $ | 75,626 | $ | 66,613 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | Includes obligations to pay minimum scheduled royalty, advertising and other required payments under various license agreements. |
| (2) | Includes outstanding trade letters of credit, which represent inventory purchase commitments, which typically mature in less than six months. |
ITEM 7A. QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK.
Foreign Currency Exchange Rate Risks and Commodity Price Risk
Our results of operations for the periods discussed have not been significantly affected by foreign currency fluctuation. We negotiate our purchase orders with foreign manufacturers in United States dollars. Thus, notwithstanding any fluctuation in foreign currencies, our cost for any purchase order is not subject to change after the time the order is placed. However, if the value of the United States dollar against local currencies were to decrease, manufacturers might increase their United States dollar prices for products.
We believe that the increase in commodity prices did not have a material effect on our costs and gross margins prior to fiscal 2012. During 2012, we experienced increases in the cost our raw materials, including textiles, wool and leather. We are exposed to market risks for the pricing of our raw materials and are anticipating that the cost of our raw materials will experience moderate increases for 2013 as compared to 2012. To manage the risks of raw material prices, we negotiate the purchase of such materials in advance when possible. We have not, and do not anticipate using, derivative instruments to manage these price exposures.
41
Interest Rate Exposure
We are subject to market risk from exposure to changes in interest rates relating primarily to our line of credit. We borrow under our line of credit to support general corporate purposes, including capital expenditures and working capital needs. We do not expect changes in interest rates to have a material adverse effect on income or cash flows in fiscal 2013. Based on our average borrowings during fiscal 2012, we estimate that each 100 basis point increase in our borrowing rates would result in additional interest expense to us of approximately $1.2 million.
| ITEM 8. | FINANCIAL STATEMENTS AND SUPPLEMENTARY DATA. |
Financial statements and supplementary data required pursuant to this Item begin on page F-1 of this Report.
| ITEM 9. | CHANGES IN AND DISAGREEMENTS WITH ACCOUNTANTS ON ACCOUNTING AND FINANCIAL DISCLOSURE. |
None.
ITEM 9A. CONTROLS AND PROCEDURES.
As of January 31, 2012, our management, including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, carried out an evaluation of the effectiveness of the design and operation of our disclosure controls and procedures (as such term is defined in Rule 13a-15(e) under the Exchange Act). Based on that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by us in the reports that we file or submit under the Exchange Act is (i) recorded, processed, summarized and reported, within the time periods specified in the Commission’s rules and forms and (ii) accumulated and communicated to our management, including our principal executive and principal financial officers, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure, and thus, are effective in making known to them material information relating to G-III required to be included in this report.
Changes in Internal Control over Financial Reporting
During our last fiscal quarter, there were no changes in our internal control over financial reporting that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting
Management is responsible for establishing and maintaining an adequate system of internal control over our financial reporting. In order to evaluate the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, as required by Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act, management has conducted an assessment, including testing, using the criteria on Internal Control-Integrated Framework, issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Our system of internal control over financial reporting is designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation and fair presentation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Therefore, even those systems determined to be effective can provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation and presentation. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Based on its assessment, management has concluded that we maintained effective internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2012, based on criteria in Internal Control-Integrated Framework, issued by the COSO.
42
Our independent auditors, Ernst & Young LLP, a registered public accounting firm, have audited and reported on our consolidated financial statements and the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting. The reports of our independent auditors appear on pages F-2 and F-3 of this Form 10-K and express unqualified opinions on the consolidated financial statements and the effectiveness of our internal control over financial reporting.
ITEM 9B. OTHER INFORMATION.
None.
43
PART III
ITEM 10. DIRECTORS, EXECUTIVE OFFICERS AND CORPORATE GOVERNANCE.
We have adopted a code of ethics and business conduct, or Code of Ethics, which applies to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller and persons performing similar functions. Our Code of Ethics is located on our Internet website at www.g-iii.com under the heading “Investor Relations.” Any amendments to, or waivers from, a provision of our Code of Ethics that apply to our principal executive officer, principal financial officer, principal accounting officer or controller and persons performing similar functions will be disclosed on our internet website within five business days following such amendment or waiver. The information contained on or connected to our Internet website is not incorporated by reference into this Form 10-K and should not be considered part of this or any other report we file with or furnish to the Securities and Exchange Commission.
The information required by Item 401 of Regulation S-K regarding directors is contained under the heading “Proposal No. 1 — Election of Directors” in our definitive Proxy Statement (the “Proxy Statement”) relating to our Annual Meeting of Stockholders to be held on or about June 5, 2012, to be filed pursuant to Regulation 14A of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 with the Securities and Exchange Commission, and is incorporated herein by reference. For information concerning our executive officers, see “Business-Executive Officers of the Registrant” in Item 1 above in this Report.
The information required by Item 405 of Regulation S-K is contained under the heading “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in our Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference. The information required by Items 407(c)(3), (d)(4), and (d)(5) of Regulation S-K is contained under the heading “Corporate Governance” in our Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
ITEM 11. EXECUTIVE COMPENSATION.
The information required by this Item 11 is contained under the headings “Executive Compensation” and “Compensation Committee Report” in our Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 12. | SECURITY OWNERSHIP OF CERTAIN BENEFICIAL OWNERS AND MANAGEMENT AND RELATED STOCKHOLDER MATTERS. |
Security ownership information of certain beneficial owners and management as called for by this Item 12 is incorporated by reference to the information set forth under the heading “Beneficial Ownership of Common Stock by Certain Stockholders and Management” in our Proxy Statement.
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table provides information as of January 31, 2012, the last day of fiscal 2012, regarding securities issued under G-III’s equity compensation plans that were in effect during fiscal 2012.
| Plan Category |
Number of Securities to be Issued Upon Exercise of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights (a) |
Weighted Average Exercise Price of Outstanding Options, Warrants and Rights (b) |
Number of Securities Remaining Available for Future Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans (Excluding Securities Reflected in Column (a)) (c) |
|||||||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by stockholders |
417,722 | $ | 16.59 | 1,409,079 | ||||||||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by stockholders |
N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total |
417,722 | $ | 16.59 | 1,409,079 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
44
| ITEM 13. CERTAIN | RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED TRANSACTIONS, AND DIRECTOR INDEPENDENCE. |
The information required by this Item 13 is contained under the headings “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” and “Corporate Governance” in our Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
| ITEM 14. PRINCIPAL | ACCOUNTING FEES AND SERVICES. |
The information required by this Item 14 is contained under the heading “Principal Accounting Fees and Services” in our Proxy Statement and is incorporated herein by reference.
PART IV
ITEM 15. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
1. Financial Statements.
2. Financial Statement Schedules.
The Financial Statements and Financial Statement Schedules are listed in the accompanying index to consolidated financial statements beginning on page F-1 of this report. All other schedules, for which provision is made in the applicable accounting regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission are not required under the related instructions, are shown in the financial statements or are not applicable and therefore have been omitted.
3. Exhibits:
(a) The following exhibits filed as part of this report or incorporated herein by reference are management contracts or compensatory plans or arrangements: Exhibits 10.1, 10.1(a), 10.1(b), 10.7, 10.7(a), 10.8, 10.8(a), 10.9, 10.9(a), 10.9(b), 10.9(c), 10.9(d), 10.9(e), 10.9(f), 10.10, 10.11, 10.11(a), 10.11(b) and 10.14.
| 3.1 | Certificate of Incorporation. 1 | |
| 3.1(a) | Certificate of Amendment of Certificate of Incorporation, dated June 8, 2006. 2 | |
| 3.1(b) | Certificate of Amendment of Certificate of Incorporation, dated June 7, 2011. 18 | |
| 3.2 | By-Laws, as amended, of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. (‘‘G-III’’) 20 | |
| 10.1 | Employment Agreement, dated February 1, 1994, between G-III and Morris Goldfarb. 3 | |
| 10.1(a) | Amendment, dated October 1, 1999, to the Employment Agreement, dated February 1, 1994, between G-III and Morris Goldfarb. 3 | |
| 10.1(b) | Amendment, dated January 28, 2009, to Employment Agreement, dated February 1, 1994, between G-III and Morris Goldfarb. 10 | |
| 10.2 | Amended and Restated Financing Agreement, dated as of April 3, 2008 (“Financing Agreement”), by and among The CIT Group/Commercial Services, Inc., as Agent, the Lenders that are parties thereto, G-III Leather Fashions, Inc., J. Percy For Marvin Richards, Ltd., CK Outerwear, LLC, A. Marc & Co., Inc. and Andrew and Suzanne Company Inc.16 | |
| 10.2(a) | Joinder and Amendment No. 1, dated July 21, 2008, to Financing Agreement.11 | |
| 10.2(b) | Amendment No. 2, dated April 20, 2009, to Financing Agreement.12 | |
| 10.2(c) | Amendment No. 3, dated September 11, 2009, to Financing Agreement.13 | |
| 10.2(d) | Amendment No. 4, dated May 13, 2010, to Financing Agreement. 15 | |
| 10.3 | Lease, dated September 21, 1993, between Hartz Mountain Associates and G-III. 3 | |
| 10.3(a) | Lease renewal, dated May 27, 1999, between Hartz Mountain Associates and G-III. 3 | |
| 10.3(b) | Lease modification agreement, dated March 10, 2004, between Hartz Mountain Associates and G-III. 4 |
45
| 10.3(c) | Lease modification agreement, dated February 23, 2005, between Hartz Mountain Associates and G-III.5 | |
| 10.4 | Lease, dated June 1, 1993, between 512 Seventh Avenue Associates (‘‘512’’) and G-III Leather Fashions, Inc (“G-III Leather”)(34th and 35th floors). 3 | |
| 10.4(a) | Lease amendment, dated July 1, 2000, between 512 and G-III Leather(34th and 35th floors). 3 | |
| 10.4(b) | Second Amendment of Lease, dated March 26, 2010, between 500-512 Seventh Avenue Limited Partnership, the successor to 512 (collectively, “512”) and G-III Leather (34th and 35th floors).16 | |
| 10.5 | Lease, dated January 31, 1994, between 512 and G-III(33rd floor). 3 | |
| 10.5(a) | Lease amendment, dated July 1, 2000, between 512 and G-III(33rd floor). 3 | |
| 10.5(b) | Second Amendment of Lease, dated March 26, 2010, between 512 and G-III Leather (33rd floor).16 | |
| 10.5(c) | Second Amendment of Lease, dated March 26, 2010, between 512 and G-III Leather (10th floor).16 | |
| 10.5(d) | Third Amendment of Lease, dated March 26, 2010, between 512 and G-III Leather (36th, 21st, 22nd, 23rd and 24th floors). 16 | |
| 10.6 | Lease, dated February 10, 2009, between IRET Properties and AM Retail Group, Inc. 16 | |
| 10.7 | G-III 1997 Stock Option Plan, as amended the “1997 Plan”. 4 | |
| 10.7(a) | Form of Option Agreement for awards made pursuant to the G-III 1997 Plan.5 | |
| 10.8 | G-III 1999 Stock Option Plan for Non-Employee Directors, as amended the “1999 Plan”.6 | |
| 10.8(a) | Form of Option Agreement for awards made pursuant to the 1999 Plan. 11 | |
| 10.9 | G-III 2005 Amended and Restated Stock Incentive Plan, the “2005 Plan”. 16 | |
| 10.9(a) | Form of Option Agreement for awards made pursuant to the 2005 Plan.11 | |
| 10.9(b) | Form of Restricted Stock Agreement for restricted stock awards made pursuant to the 2005 Plan. 7 | |
| 10.9(c) | Form of Deferred Stock Award Agreement for restricted stock unit awards made pursuant to the 2005 Plan. 8 | |
| 10.9(d) | Form of Deferred Stock Award Agreement for April 15, 2009 restricted stock unit grants.12 | |
| 10.9(e) | Form of Deferred Stock Award Agreement for March 17, 2010 restricted stock unit grants.14 | |
| 10.9(f) | Form of Deferred Stock Award Agreement for June 29, 2011 restricted stock unit grants. 19 | |
| 10.10 | Form of Executive Transition Agreement, as amended.17 | |
| 10.11 | Employment Agreement, dated as of July 11, 2005, by and between Sammy Aaron and G-III. 16 | |
| 10.11(a) | Amendment, dated October 3, 2008, to Employment Agreement, dated as of July 11, 2005, by and between Sammy Aaron and G-III. 9 | |
| 10.11(b) | Amendment, dated January 28, 2009, to Employment Agreement, dated as of July 11, 2005, by and between Sammy Aaron and G-III. 10 | |
| 10.12 | Lease agreement dated June 29, 2006 between The Realty Associates Fund VI, LP and G-III.2 | |
| 10.13 | Lease Agreement, dated December 21, 2009 and effective December 28, 2009, by and between G-III, as Tenant, and Granite South Brunswick LLC, as Landlord. 16 | |
| 10.14 | Form of Indemnification Agreement. 16 | |
| 21* | Subsidiaries of G-III. | |
| 23.1* | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, Ernst & Young LLP. | |
| 31.1* | Certification by Morris Goldfarb, Chief Executive Officer of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd., pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, in connection with G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2012. | |
| 31.2* | Certification by Neal S. Nackman, Chief Financial Officer of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd., pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, in connection with G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2012. | |
| 32.1** | Certification by Morris Goldfarb, Chief Executive Officer of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd., pursuant to 16 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, in connection with G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2012. |
46
| 32.2** | Certification by Neal S. Nackman, Chief Financial Officer of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd., pursuant to 16 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, in connection with G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the year ended January 31, 2012. | |
| 101.INS*** | XBRL Instance Document. | |
| 101.SCH*** | XBRL Schema Document. | |
| 101.CAL*** | XBRL Calculation Linkbase Document. | |
| 101.LAB*** | XBRL Label Linkbase Document. | |
| 101.PRE*** | XBRL Presentation Linkbase Document. |
| * | Filed herewith. |
| ** | Exhibits 32.1 and 32.2 shall not be deemed “filed” for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, or otherwise subject to the liability of that Section. Such exhibits shall not be deemed incorporated by reference into any filing under the Securities Act of 1933 or the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. |
| *** | Pursuant to Rule 406T of Regulation S-T, the Interactive Data Files on Exhibit 101 hereto are deemed not filed or part of a registration statement or prospectus for purposes of Sections 11 or 12 of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, are deemed not filed for purposes of Section 18 of the Securities and Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, and otherwise are not subject to liability under those sections. |
| (1) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (no. 33-31906), which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (2) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the fiscal quarter ended July 31, 2006, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (3) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Annual Report on Form 10-K/A for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2006, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (4) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2004, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (5) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2005, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (6) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2006, filed on May 1, 2006, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (7) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on June 15, 2005, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (8) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on July 2, 2008, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (9) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on October 6, 2008, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (10) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on February 3, 2009, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (11) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2009, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (12) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on April 21, 2009, which is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (13) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on September 16, 2009, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (14) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on March 23, 2010, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (15) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the fiscal quarter ended April 30, 2010, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
47
| (16) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q for the fiscal quarter ended October 31, 2010, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (17) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on February 16, 2011, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (18) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on June 9, 2011, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (19) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on July 1, 2011, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
| (20) | Previously filed as an exhibit to G-III’s Report on Form 8-K filed on December 9, 2011, which exhibit is incorporated herein by reference. |
Exhibits have been included in copies of this Report filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission. We will provide, without charge, a copy of these exhibits to each stockholder upon the written request of any such stockholder. All such requests should be directed to G-III Apparel Group, Ltd., 512 Seventh Avenue, 35th floor, New York, New York 10018, Attention: Mr. Wayne S. Miller, Secretary.
48
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| G-III APPAREL GROUP, LTD. | ||
| By: | /s/ Morris Goldfarb | |
| Morris Goldfarb, | ||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||
April 11, 2012
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||
| /s/ Morris Goldfarb Morris Goldfarb |
Director, Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer (principal executive officer) |
April 11, 2012 | ||
| /s/ Neal S. Nackman Neal S. Nackman |
Chief Financial Officer (principal financial and accounting officer) |
April 11, 2012 | ||
| /s/ Sammy Aaron Sammy Aaron |
Director and Vice Chairman |
April 11, 2012 | ||
| /s/ Thomas J. Brosig Thomas J. Brosig |
Director |
April 11, 2012 | ||
| /s/ Alan Feller Alan Feller |
Director |
April 11, 2012 | ||
| /s/ Jeffrey Goldfarb Jeffrey Goldfarb |
Director |
April 11, 2012 | ||
| /s/ Carl Katz Carl Katz |
Director |
April 11, 2012 | ||
| /s/ Laura Pomerantz Laura Pomerantz |
Director |
April 11, 2012 | ||
| /s/ Willem van Bokhorst Willem van Bokhorst |
Director |
April 11, 2012 | ||
| /s/ Cheryl Vitali Cheryl Vitali |
Director |
April 11, 2012 | ||
| /s/ Richard White Richard White |
Director |
April 11, 2012 | ||
49
EXHIBIT INDEX
| 21 | Subsidiaries of G-III. | |
| 23.1 | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, Ernst & Young LLP. | |
| 31.1 | Certification by Morris Goldfarb, Chief Executive Officer of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd., pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, in connection with G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2012. | |
| 31.2 | Certification by Neal S. Nackman, Chief Financial Officer of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd., pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, in connection with G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2012. | |
| 32.1 | Certification by Morris Goldfarb, Chief Executive Officer of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd., pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, in connection with G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2012. | |
| 32.2 | Certification by Neal S. Nackman, Chief Financial Officer of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd., pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, in connection with G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.’s Annual Report on Form 10-K for the fiscal year ended January 31, 2012. | |
| 101.INS | XBRL Instance Document. | |
| 101.SCH | XBRL Schema Document. | |
| 101.CAL | XBRL Calculation Linkbase Document. | |
| 101.LAB | XBRL Label Linkbase Document. | |
| 101.PRE | XBRL Presentation Linkbase Document. |
50
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULE
(Item 15(a))
| Page | ||||
| F-2 | ||||
| Financial Statements |
||||
| F-4 | ||||
| Consolidated Statements of Income — Years Ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 |
F-5 | |||
| Consolidated Statements of Stockholders’ Equity — Years Ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 |
F-6 | |||
| Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows — Years Ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 |
F-7 | |||
| F-8 | ||||
| Financial Statement Schedule |
||||
| S-1 | ||||
All other schedules for which provision is made in the applicable regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission are not required under the related instructions or are inapplicable and, accordingly, are omitted.
F-1
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and subsidiaries as of January 31, 2012 and 2011, and the related consolidated statements of income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended January 31, 2012. Our audits also included the financial statement schedule listed in the index at Item 15(a). These financial statements and schedule are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements and schedule based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the consolidated financial position of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and subsidiaries at January 31, 2012 and 2011, and the consolidated results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended January 31, 2012, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles. Also, in our opinion, the related financial statement schedule, when considered in relation to the basic financial statements taken as a whole, presents fairly in all material respects, the information set forth therein.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and subsidiaries’ internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2012, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated April 11, 2012 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
/s/ ERNST & YOUNG LLP
New York, New York
April 11, 2012
F-2
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders
of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd.
We have audited G-III Apparel Group Ltd. and subsidiaries internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2012, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (the COSO criteria). G-III Apparel Group Ltd. and subsidiaries management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting, and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk, and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and subsidiaries maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of January 31, 2012, based on the COSO criteria.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and subsidiaries as of January 31, 2012 and 2011, and the related consolidated statements of income, stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended January 31, 2012 of G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and subsidiaries, and our report dated April 11, 2012 expressed an unqualified opinion thereon.
Ernst & Young LLP
New York, New York
April 11, 2012
F-3
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
January 31,
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| (In thousands, except share and per share amounts) |
||||||||
| ASSETS | ||||||||
| CURRENT ASSETS |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 24,660 | $ | 10,045 | ||||
| Accounts receivable, net of allowance for doubtful accounts and sales discounts of $34,436 and $32,174, respectively |
162,510 | 138,341 | ||||||
| Inventories |
253,521 | 204,995 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
9,559 | 10,035 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
14,528 | 13,390 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current assets |
464,778 | 376,806 | ||||||
| INVESTMENT IN JOINT VENTURE |
2,419 | 40 | ||||||
| PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT, NET |
33,365 | 22,556 | ||||||
| DEFERRED INCOME TAXES |
— | 1,803 | ||||||
| OTHER ASSETS |
1,830 | 2,133 | ||||||
| INTANGIBLES, NET |
17,611 | 18,483 | ||||||
| GOODWILL |
26,100 | 26,100 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 546,103 | $ | 447,921 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| LIABILITIES AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY | ||||||||
| CURRENT LIABILITIES |
||||||||
| Notes payable |
$ | 30,050 | $ | — | ||||
| Income taxes payable |
6,212 | 41 | ||||||
| Accounts payable |
96,727 | 103,012 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses |
43,530 | 34,259 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total current liabilities |
176,519 | 137,312 | ||||||
| DEFERRED INCOME TAXES |
1,289 | — | ||||||
| OTHER NON- CURRENT LIABILITIES |
10,323 | 7,115 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| TOTAL LIABILITIES |
188,131 | 144,427 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
| |||||||
| Preferred stock; 1,000,000 shares authorized; No shares issued and outstanding |
||||||||
| Common stock — $.01 par value; 80,000,000 and 40,000,000 shares authorized; 20,279,132 and 20,056,132 shares issued |
203 | 201 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
160,102 | 152,340 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
4 | (19 | ) | |||||
| Retained earnings |
201,562 | 151,942 | ||||||
| Common stock held in treasury, at cost — 492,225 and 367,225 shares |
(3,899 | ) | (970 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 357,972 | 303,494 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 546,103 | $ | 447,921 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these statements.
F-4
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF INCOME
| Year Ended January 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands, except per share amounts) | ||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 1,231,201 | $ | 1,063,404 | $ | 800,864 | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
860,485 | 712,359 | 533,996 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Gross profit |
370,716 | 351,045 | 266,868 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative expenses |
277,019 | 248,380 | 205,281 | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
7,473 | 5,733 | 5,380 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Operating profit |
86,224 | 96,932 | 56,207 | |||||||||
| Equity loss in joint venture |
1,271 | — | — | |||||||||
| Interest and financing charges, net |
5,713 | 4,027 | 4,705 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income before income taxes |
79,240 | 92,905 | 51,502 | |||||||||
| Income tax expense |
29,620 | 36,223 | 19,784 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net income |
$ | 49,620 | $ | 56,682 | $ | 31,718 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| NET INCOME PER COMMON SHARE: |
||||||||||||
| Basic: |
||||||||||||
| Net income per common share |
$ | 2.51 | $ | 2.96 | $ | 1.87 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted average number of shares outstanding |
19,796 | 19,175 | 16,990 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted: |
||||||||||||
| Net income per common share |
$ | 2.46 | $ | 2.88 | $ | 1.83 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Weighted average number of shares outstanding |
20,192 | 19,705 | 17,358 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these statements.
F-5
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
| Common Stock |
Additional Paid-in Capital |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
Retained Earnings |
Common Stock Held in Treasury |
Total | |||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of January 31, 2009 |
$ | 171 | $ | 99,486 | $ | — | $ | 63,542 | $ | (970 | ) | $ | 162,229 | |||||||||||
| Equity awards exercised/vested |
2 | 1,186 | 1,188 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise/vesting of equity awards |
859 | 859 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Taxes paid for net share settlements |
(296 | ) | (296 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of share-based compensation |
1,891 | 1,891 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares issued in connection with public offering, net |
19 | 34,638 | 34,657 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes |
(36 | ) | (36 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
31,718 | 31,718 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance as of January 31, 2010 |
192 | 137,764 | (36 | ) | 95,260 | (970 | ) | 232,210 | ||||||||||||||||
| Equity awards exercised/vested |
5 | 2,781 | 2,786 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise/vesting of equity awards |
4,356 | 4,356 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of share-based compensation |
3,314 | 3,314 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock warrants exercised |
4 | 4,125 | 4,129 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes |
17 | 17 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
56,682 | 56,682 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance as of January 31, 2011 |
201 | 152,340 | (19 | ) | 151,942 | (970 | ) | 303,494 | ||||||||||||||||
| Equity awards exercised/vested |
2 | 617 | 619 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise/vesting of equity awards |
1,945 | 1,945 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of share-based compensation |
5,200 | 5,200 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes |
23 | 23 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
49,620 | 49,620 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Treasury share purchase |
(2,929 | ) | (2,929 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Balance as of January 31, 2012 |
$ | 203 | $ | 160,102 | $ | 4 | $ | 201,562 | $ | (3,899 | ) | $ | 357,972 | |||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these statements.
F-6
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| Year Ended January 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities |
||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 49,620 | $ | 56,682 | $ | 31,718 | ||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income to net cash provided by (used) in operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
7,473 | 5,733 | 5,380 | |||||||||
| Equity based compensation |
5,200 | 3,314 | 1,891 | |||||||||
| Tax benefit from exercise/vesting of equity awards |
809 | — | — | |||||||||
| Deferred financing charges |
425 | 844 | 591 | |||||||||
| Equity loss in joint venture |
1,271 | — | — | |||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
3,568 | 6,125 | (2,984 | ) | ||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
(24,169 | ) | (64,885 | ) | (3,761 | ) | ||||||
| Inventories |
(48,526 | ) | (85,118 | ) | (3,265 | ) | ||||||
| Income taxes, net |
6,171 | (10,833 | ) | 5,652 | ||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
(1,324 | ) | (2,935 | ) | (375 | ) | ||||||
| Other assets, net |
64 | (1,055 | ) | (456 | ) | |||||||
| Accounts payable, accrued expenses and other liabilities |
6,194 | 63,479 | 9,608 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by (used in) operating activities |
6,776 | (28,649 | ) | 43,999 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities |
||||||||||||
| Investment in equity of joint venture |
(3,650 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
(17,410 | ) | (19,407 | ) | (1,477 | ) | ||||||
| Contingent purchase price paid |
— | — | (5,541 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(21,060 | ) | (19,407 | ) | (7,018 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities |
||||||||||||
| Proceeds from (repayment of) notes payable, net |
30,050 | — | (29,048 | ) | ||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of common stock, net |
— | — | 34,657 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of stock warrants |
— | 4,129 | — | |||||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of equity awards |
619 | 2,786 | 1,188 | |||||||||
| Stock repurchase |
(2,929 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Excess tax benefit from exercise/vesting of equity awards |
1,136 | 4,356 | 859 | |||||||||
| Taxes paid for net share settlements |
— | — | (296 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities |
28,876 | 11,271 | 7,360 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes |
23 | 17 | (36 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
14,615 | (36,768 | ) | 44,305 | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of year |
10,045 | 46,813 | 2,508 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents at end of year |
$ | 24,660 | $ | 10,045 | $ | 46,813 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Supplemental disclosures of cash flow information: |
||||||||||||
| Cash paid during the year for: |
||||||||||||
| Interest |
$ | 5,228 | $ | 4,145 | $ | 5,002 | ||||||
| Income taxes |
18,243 | 36,548 | 8,085 | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these statements.
F-7
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
NOTE A — SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
A summary of the significant accounting policies consistently applied in the preparation of the accompanying consolidated financial statements follows:
1. Business Activity and Principles of Consolidation
As used in these financial statements, the term “Company” or “G-III” refers to G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and its subsidiaries. The Company designs, manufactures and markets an extensive range of apparel, including outerwear, dresses, sportswear, women’s suits and women’s performance wear, as well as luggage and women’s handbags, small leather goods and cold weather accessories which is sold to retailers primarily in the United States. The Company also operates outlet stores.
The Company consolidates the accounts of all its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All material intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated.
Investments in entities that the Company does not control but has the ability to exercise significant influence are accounted for using the equity method of accounting. Equity method investments are recorded initially at cost in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Those amounts are adjusted to recognize the Company’s proportional share of the investee’s earnings after the date of the investment. The Company’s share of net income or loss of these investments is included in the Consolidated Statements of Income.
During the third quarter of fiscal 2011, the Company formed a joint venture with The Camuto Group to operate footwear and accessory outlet stores under the name “Vince Camuto.” Both companies share equally in the capital costs of the joint venture. We are accounting for our share of this joint venture under the equity method. Results of operations of the joint venture are included in the retail segment.
References to fiscal years refer to the year ended or ending on January 31 of that year.
2. Cash Equivalents
The Company considers all highly liquid investments purchased with a maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents.
3. Revenue Recognition
Goods are shipped to retailers in accordance with specific customer orders. The Company recognizes wholesale sales when the risks and rewards of ownership have transferred to the customer, determined by the Company to be when title to the merchandise passes to the customer. In addition, the Company acts as an agent in brokering sales between customers and overseas factories. On these transactions, the Company recognizes commission fee income on sales that are financed by and shipped directly to the customers. Title to goods shipped by overseas vendors, transfers to customers when the goods have been delivered to the customer.
The Company recognizes commission income upon the completion of the delivery by its vendors to the customer. The Company recognizes retail sales upon customer receipt of the merchandise generally at the point of sale. The Company’s sales are recorded net of applicable sales taxes. Both wholesale and retail store revenues are shown net of returns, discounts and other allowances.
4. Returns and Allowances
The Company reserves against known chargebacks, as well as for an estimate of potential future deductions and returns by customers. The Company establishes these reserves for returns and allowances based on current and historical information and trends. Allowances are established for trade discounts, markdowns, customer advertising agreements and operational chargebacks. Estimated costs associated with allowable deductions for
F-8
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
customer advertising expenses are reflected as selling, general and administrative expenses. Estimated costs associated with trade discounts and markdowns, and reserves for returns are reflected as a reduction of net sales. All of these reserves are part of the allowances netted against accounts receivable.
The Company estimates an allowance for doubtful accounts based on the creditworthiness of its customers as well as general economic conditions. Consequently, an adverse change in those factors could affect the Company’s estimate. The Company writes off uncollectible trade receivables once collection efforts have been exhausted.
5. Inventories
Wholesale inventories are stated at the lower of cost (determined by the first-in, first-out method) or market. Retail inventories are valued at the lower of cost or market as determined by the retail inventory method.
6. Goodwill and Other Intangibles
Goodwill represents the excess of purchase price over the fair value of net assets acquired in business combinations accounted for under the purchase method of accounting. Goodwill and intangible assets deemed to have indefinite lives are not amortized, but are subject to annual impairment tests, using a test combining a discounted cash flow approach and a market approach. Other intangibles with determinable lives, including license agreements, trademarks, customer lists and non-compete agreements are amortized on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful lives of the assets (currently ranging from 5 to 15 years). Impairment losses, if any, on intangible assets with finite lives are recorded when indicators of impairment are present and the discounted cash flows estimated to be derived from those assets are less than the assets’ carrying amounts.
7. Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation and amortization are provided for by straight-line methods in amounts sufficient to relate the cost of depreciable assets to operations over their estimated useful lives.
The following are the estimated lives of the Company’s fixed assets:
| Machinery and equipment |
4 to 5 years | |||
| Furniture and fixtures |
3 to 5 years | |||
| Computer equipment and software |
2 to 3 years |
Leasehold improvements are amortized over the lease term of the respective leases or the useful lives of the improvement, whichever is shorter.
8. Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
In accordance with Statements of Financial Accounting Standards ASC Topic 360, Property, Plant and Equipment, the Company annually evaluates the carrying value of its long-lived assets to determine whether changes have occurred that would suggest that the carrying amount of such assets may not be recoverable based on the estimated future undiscounted cash flows of the businesses to which the assets relate. Any impairment loss would be equal to the amount by which the carrying value of the assets exceeded its fair value.
9. Income Taxes
The Company accounts for income taxes and uncertain tax positions in accordance with ASC Topic 740 – Income Taxes. ASC 740 prescribes a recognition threshold and measurement attribute for the financial statement recognition and measurement of a tax position taken or expected to be taken in a return, as well as guidance on de-recognition, classification, interest and penalties and financial statement reporting disclosures.
Deferred income taxes reflect the tax effects of temporary differences between the carrying amounts of assets and liabilities for financial reporting purposes and the amounts used for income tax purposes.
F-9
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
10. Net Income Per Common Share
Basic net income per common share has been computed using the weighted average number of common shares outstanding during each period. Diluted net income per share, when applicable, is computed using the weighted average number of common shares and potential dilutive common shares, consisting of stock options, stock purchase warrants and unvested restricted stock awards, outstanding during the period. Approximately 20,000 shares for the years ended January 31, 2012 and 2011 and 407,850 shares for the year ended January 31, 2010 have been excluded from the diluted per share calculation as their inclusion would be been anti-dilutive. The Company issued 223,000, 488,428 and 222,692 shares of common stock in connection with the exercise or vesting of equity awards during the years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively. In December 2010, the Company also issued 375,000 shares of common stock in connection with the exercise of all of its outstanding warrants.
A reconciliation between basic and diluted net income per share is as follows:
| Year Ended January 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands, except per share amounts) | ||||||||||||
| Net income |
$ | 49,620 | $ | 56,682 | $ | 31,718 | ||||||
| Basic net income per share: |
||||||||||||
| Basic common shares |
19,796 | 19,175 | 16,990 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Basic net income per share |
$ | 2.51 | $ | 2.96 | $ | 1.87 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted net income per share: |
||||||||||||
| Basic common shares |
19,796 | 19,175 | 16,990 | |||||||||
| Stock options, stock warrants and restricted stock awards |
396 | 530 | 368 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted common shares |
20,192 | 19,705 | 17,358 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Diluted net income per share |
$ | 2.46 | $ | 2.88 | $ | 1.83 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
11. Equity Award Compensation
ASC Topic 718, Compensation — Stock Compensation, requires all share-based payments to employees, including grants of employee stock options and restricted stock awards, to be recognized as compensation expense over the service period (generally the vesting period) based on their fair values. The impact of forfeitures that may occur prior to vesting is estimated and considered in the amount recognized.
It is the Company’s policy to grant stock options at prices not less than the fair market value on the date of the grant. Option terms, vesting and exercise periods vary, except that the term of an option may not exceed ten years.
Restricted stock awards generally vest over a four or five year period and certain awards that have been granted also include a market condition that provides for the award to vest only after the Company’s stock price trades above a predetermined market level for a period of twenty consecutive trading days. All awards are expensed on a straight line basis.
12. Cost of Goods Sold
Cost of goods sold includes the expenses incurred to acquire, produce and prepare inventory for sale, including product costs, warehouse staff wages, freight in, import costs, packaging materials, the cost of operating our overseas offices and royalty expense. Our gross margins may not be directly comparable to those of our competitors, as income statement classifications of certain expenses may vary by company.
F-10
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
13. Shipping and Handling Costs
Shipping and handling costs for wholesale operations consist of warehouse facility costs, third party warehousing, freight out costs, and warehouse supervisory wages and are included in selling, general and administrative expense. Wholesale shipping and handling costs included in selling, general and administrative expenses were $44.9 million, $38.1 million and $26.1 million for the years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
14. Advertising Costs
The Company expenses advertising costs as incurred and includes these costs in selling, general and administrative expense. Advertising paid as a percentage of sales under license agreements are expensed in the period in which the sales occur or are accrued to meet guaranteed minimum requirements under license agreements. Advertising expense was $43.8 million, $36.4 million and $29.8 million for the years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively. Prepaid advertising, which represents advance payments to licensors for minimum guaranteed payments for advertising under our licensing agreements, was $3.9 million and $4.2 million at January 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
15. Use of Estimates
In preparing financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States, management is required to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenues and expenses during the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
16. Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The carrying amount of the Company’s variable rate debt approximates the fair value, as interest rates change with the market rates. Furthermore, the carrying value of all other financial instruments potentially subject to valuation risk (principally consisting of cash, accounts receivable and accounts payable) also approximates fair value due to the short-term nature of their maturity.
17. Foreign Currency Translation
The financial statements of subsidiaries outside the United States are measured using local currency as the functional currency. Assets and liabilities are translated at the rates of exchange at the balance sheet date. Income and expense items are translated at average monthly rates of exchange. Gains and losses from foreign currency transactions of these subsidiaries are included in net earnings.
18. Effects of Recently Issued Accounting Pronouncements
In December 2011, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued an Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) ASU 2011-12, “Comprehensive Income (Topic 220): Deferral of the Effective Date for Amendments to the Presentation of Reclassifications of Items Out of Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income in Accounting Standards Update No. 2011-05.” ASU 2011-12 defers the specific requirement to present items that are reclassified from accumulated other comprehensive income to net income separately with their respective components of net income and other comprehensive income. ASU 2011-12 did not defer the requirement to report comprehensive income either in a single continuous statement or in two separate but consecutive financial statements. The Company’s other comprehensive income represents foreign currency translation adjustments. The amendments are effective at the same time as the amendments in ASU 2011-05. The adoption of ASU 2011-12 is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
F-11
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
In September 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-08, “Intangibles — Goodwill and Other (Topic 350): Testing Goodwill for Impairment.” ASU 2011-08 simplifies how entities, both public and nonpublic, test goodwill for impairment and permits an entity to first assess qualitative factors to determine whether it is more likely than not that the fair value of a reporting unit is less than its carrying amount as a basis for determining whether it is necessary to perform the two-step goodwill impairment test described in Topic 350. The amendments are effective for annual and interim goodwill impairment tests performed for fiscal years beginning after December 15, 2011. Early adoption is permitted, including for annual and interim goodwill impairment tests performed as of a date before September 15, 2011, if an entity’s financial statements for the most recent annual or interim period have not yet been issued or, for nonpublic entities, have not yet been made available for issuance. The adoption of ASU 2011-08 is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In June 2011, the FASB issued ASU 2011-05, Presentation of Comprehensive Income. Under the amendments to Topic 220, Comprehensive Income, an entity has the option to present the total of comprehensive income, the components of net income, and the components of other comprehensive income either in a single continuous statement of comprehensive income or in two separate but consecutive statements. In both choices, an entity is required to present each component of net income along with total net income, each component of other comprehensive income along with a total for other comprehensive income, and a total amount for comprehensive income. This eliminates the option to present the components of other comprehensive income as part of the statement of changes in stockholders’ equity. The amendments do not change the items that must be reported in other comprehensive income or when an item of other comprehensive income must be reclassified to net income. The guidance in ASU 2011-05 is effective for public companies for fiscal years, and interim periods within those years beginning after December 15, 2011. The Company expects that ASU 2011-05 will not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In May 2011, the FASB issued ASU No. 2011-04, “Fair Value Measurement (Topic 820): Amendments to Achieve Common Fair Value Measurement and Disclosure Requirements in U.S. GAAP and IFRSs.” ASU 2011-04 amends Topic 820 to provide common fair value measurement and disclosure requirements in U.S. Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (“U.S. GAAP”) and International Financial Reporting Standards. Consequently, the amendments change the wording used to describe many of the requirements in U.S. GAAP for measuring fair value and for disclosing information about fair value measurements, as well as providing guidance on how fair value should be applied where its use is already required or permitted by other standards within U.S. GAAP. ASU No. 2011-04 is to be applied prospectively, and early adoption is not permitted. For public entities, the amendments are effective during interim and annual periods beginning after December 15, 2011. The adoption of ASU No. 2011-04 is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s results of operations or financial position.
NOTE B — INVENTORIES
Inventories consist of:
| January 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||
| Finished goods |
$ | 244,884 | $ | 199,292 | ||||
| Raw materials and work-in-process |
8,637 | 5,703 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 253,521 | $ | 204,995 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Raw materials of $8.1 million and $5.3 million, net of allowances, were maintained in China at January 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
F-12
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
NOTE C — PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT
Property and equipment at cost consist of:
| January 31, | ||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||
| Machinery and equipment |
$ | 1,655 | $ | 1,442 | ||||
| Leasehold improvements |
35,335 | 26,445 | ||||||
| Furniture and fixtures |
11,889 | 5,060 | ||||||
| Computer equipment |
3,949 | 2,994 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| 52,828 | 35,941 | |||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation |
19,463 | 13,385 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| $ | 33,365 | $ | 22,556 | |||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
The Company had fixed asset disposals of approximately $523,000 in fiscal 2012. Disposals in prior years were not significant. Depreciation expense amounted to $6.6 million, $4.4 million and $3.8 million for the years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
NOTE D — ACQUISITIONS AND INTANGIBLES
Intangible assets consist of:
| January 31, | ||||||||||
| Estimated Life | 2012 | 2011 | ||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||
| Gross carrying amounts |
||||||||||
| Licenses |
3.5 - 5.5 years | $ | 12,573 | $ | 12,573 | |||||
| Trademarks |
8 - 12 years | 2,194 | 2,194 | |||||||
| Customer relationships |
5 - 15 years | 5,900 | 5,900 | |||||||
| Non-compete agreements |
3.5 - 4.0 years | 1,058 | 1,058 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Subtotal |
21,725 | 21,725 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Accumulated amortization |
||||||||||
| Licenses |
12,533 | 12,493 | ||||||||
| Trademarks |
1,374 | 1,072 | ||||||||
| Customer relationships |
2,359 | 1,859 | ||||||||
| Non-compete agreements |
1,058 | 1,028 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Subtotal |
17,324 | 16,452 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Net |
||||||||||
| Licenses |
40 | 80 | ||||||||
| Trademarks |
820 | 1,122 | ||||||||
| Customer relationships |
3,541 | 4,041 | ||||||||
| Non-compete agreements |
— | 30 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Subtotal |
4,401 | 5,273 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Unamortized intangible assets |
||||||||||
| Goodwill (Deductible for tax purposes) |
26,100 | 26,100 | ||||||||
| Trademark |
13,210 | 13,210 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Subtotal |
39,310 | 39,310 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Total intangible assets, net |
$ | 43,711 | $ | 44,583 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
F-13
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Intangible amortization expense amounted to approximately $900,000, $1.3 million and $1.6 million for the years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
The estimated intangible amortization expense for the next five years is as follows:
| Year Ending January 31, |
Amortization Expense | |||
| (In thousands) | ||||
| 2013 |
$ | 759 | ||
| 2014 |
559 | |||
| 2015 |
559 | |||
| 2016 |
430 | |||
| 2017 |
386 | |||
Goodwill represents the excess of the purchase price and related costs over the value assigned to net tangible and identifiable intangible assets of businesses acquired and accounted for under the purchase method. The Company reviews and tests its goodwill and intangible assets with indefinite lives for impairment at least annually, or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may be impaired. We perform our test in the fourth fiscal quarter of each year using a combination of a discounted cash flow analysis and a market approach. The discounted cash flow approach requires that certain assumptions and estimates be made regarding industry economic factors and future profitability. The market approach estimates the fair value based on comparisons with the market values and market multiples of earnings and revenues of similar public companies.
Trademarks having finite lives are amortized over their estimated useful lives and measured for impairment when events or circumstances indicate that the carrying value may be impaired.
Goodwill has been allocated to the reporting segments based upon the relative fair values of the licenses (wholesale licensed product segment) and trademarks (wholesale non-licensed product segment) acquired. The carrying amount of goodwill in the wholesale licensed product segment was $26.1 million for the years ended January 31, 2012 and 2011.
NOTE E — NOTES PAYABLE
The Company has a financing agreement with JPMorgan Chase Bank, N.A. as Agent for a consortium of banks. The financing agreement is a senior secured revolving credit facility. The financing agreement was amended in May 2010 to (a) increase the maximum line of credit from $250 million to $300 million, (b) reduce the interest rate on borrowings by 0.25% to, at the Company’s option, the prime rate plus 0.50% or LIBOR plus 2.75%, (c) extend the maturity of the loan from July 11, 2011 to July 31, 2013, and (d) revise the maximum senior leverage ratio that must be maintained. Amounts available under this facility are subject to borrowing base formulas and over advances as specified in the financing agreement. At January 31, 2012, the Company had outstanding borrowings of $30.1 million compared to no direct borrowings outstanding at January 31, 2011.
The financing agreement requires the Company, among other things, to maintain a maximum senior leverage ratio and minimum fixed charge coverage ratio, as defined, and also limits payments for cash dividends and stock redemptions. As of January 31, 2012, the Company was in compliance with these covenants. The financing agreement is secured by all of the Company’s assets.
The weighted average interest rate for amounts borrowed under the credit facility was 3.1% and 3.4% for the years ended January 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The Company was contingently liable under letters of credit in the amount of approximately $11.3 million and $20.1 million at January 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively.
F-14
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
NOTE F — INCOME TAXES
The income tax provision is comprised of the following:
| Year Ended January 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Current |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | 19,206 | $ | 24,705 | $ | 18,608 | ||||||
| State and city |
4,449 | 5,368 | 4,152 | |||||||||
| Foreign |
2,396 | 25 | 8 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| 26,051 | 30,098 | 22,768 | ||||||||||
| Deferred tax benefit |
3,569 | 6,125 | (2,984 | ) | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income tax expense |
$ | 29,620 | $ | 36,223 | $ | 19,784 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
||||||||||||
| United States |
$ | 64,940 | $ | 92,933 | $ | 51,454 | ||||||
| Non-United States |
14,300 | (28 | ) | 48 | ||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| $ | 79,240 | $ | 92,905 | $ | 51,502 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The significant components of the Company’s net deferred tax asset at January 31, 2012 and 2011 are summarized as follows:
| 2012 | 2011 | |||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||
| Deferred tax assets |
||||||||
| Compensation |
$ | 1,995 | $ | 2,307 | ||||
| Provision for bad debts and sales allowances |
7,474 | 7,676 | ||||||
| Inventory write-downs |
1,964 | 2,033 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Deferred tax assets, current |
11,433 | 12,016 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Compensation |
2,859 | 1,685 | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
— | 4,493 | ||||||
| Straight-line lease |
2,596 | 1,798 | ||||||
| Supplemental employee retirement plan |
405 | 317 | ||||||
| Net operating loss |
242 | — | ||||||
| Other |
193 | 11 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Deferred tax assets, non-current |
6,295 | 8,304 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Total deferred tax assets |
17,728 | 20,320 | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Deferred tax liabilities |
||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other, current |
(1,874 | ) | (1,981 | ) | ||||
| Depreciation and amortization, non-current |
(1,140 | ) | — | |||||
| Intangibles, non-current |
(6,444 | ) | (6,501 | ) | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
| Net deferred tax assets |
$ | 8,270 | $ | 11,838 | ||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
F-15
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The following is a reconciliation of the statutory federal income tax rate to the effective rate reported in the financial statements for the years ended January 31:
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||
| Provision for Federal income taxes at the statutory rate |
35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | 35.0 | % | ||||||
| State and local income taxes, net of Federal tax benefit |
3.3 | 4.9 | 4.9 | |||||||||
| Permanent differences resulting in Federal taxable income |
5.5 | 0.4 | 0.5 | |||||||||
| Foreign tax rate differential |
(3.4 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Foreign tax credit |
(2.5 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Other, net |
(0.5 | ) | (1.3 | ) | (2.0 | ) | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| Actual provision for income taxes |
37.4 | % | 39.0 | % | 38.4 | % | ||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
The Company accounts for uncertain income tax positions in accordance with ASC Topic 740 Income Taxes. As of January 31, 2012, the Company had no material unrecognized tax benefits. The Company files income tax returns in the U.S. federal jurisdiction and various state and foreign jurisdictions. The Company is currently under audit by various state and local jurisdiction for the years ended January 31, 2008 through January 31, 2011. As of January 31, 2012, the federal tax examination for the year ended January 31, 2009 has been concluded with no change.
The Company’s policy on classification is to include interest in “interest and financing charges” and penalties in “selling, general and administrative expense” in the accompanying Consolidated Statements of Income. The Company and certain of its subsidiaries are subject to U.S. Federal income tax as well as income tax of multiple state, local, and foreign jurisdictions. U.S. Federal income tax returns have been examined through January 31, 2009.
Undistributed earnings of the Company’s foreign subsidiaries amounted to approximately $13.6 million at January 31, 2012. Those earnings are considered indefinitely reinvested and, accordingly, no provision for U.S. income taxes has been provided thereon. Upon distribution of those earnings in the form of dividends or otherwise, the Company would be subject to both U.S. income taxes (subject to an adjustment for foreign tax credits) and withholding taxes payable to the various foreign countries, as applicable.
NOTE G — COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
Lease Agreements
The Company leases warehousing, executive and sales facilities, retail stores, equipment and vehicles under operating leases with options to renew at varying terms. Leases with provisions for increasing rents have been accounted for on a straight-line basis over the life of the lease.
Certain leases provide for contingent rents, which are determined as a percentage of gross sales. The Company records a contingent rent liability in accrued expenses on the Consolidated Balance Sheets and the corresponding rent expense on the Consolidated Statements of Income when management determines that achieving the specified levels during the fiscal year is probable.
F-16
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The following schedule sets forth the future minimum rental payments for operating leases having non-cancelable lease periods in excess of one year at January 31, 2012:
| Operating Leases | ||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Year Ending January 31, |
Wholesale | Retail | Total | |||||||||
| 2013 |
$ | 10,131 | $ | 14,157 | $ | 24,288 | ||||||
| 2014 |
10,276 | 12,859 | 23,135 | |||||||||
| 2015 |
7,225 | 11,781 | 19,006 | |||||||||
| 2016 |
7,327 | 9,880 | 17,207 | |||||||||
| 2017 |
7,372 | 8,186 | 15,558 | |||||||||
| Thereafter |
43,263 | 21,350 | 64,613 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
| $ | 85,594 | $ | 78,213 | $ | 163,807 | |||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||
Rent expense on the above operating leases for the years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010 was approximately $25.9 million, $22.4 million and $20.7 million, respectively.
License Agreements
The Company has entered into license agreements that provide for royalty payments ranging from 4% to 19% of net sales of licensed products as set forth in the agreements. The Company incurred royalty expense (included in cost of goods sold) of approximately $68.7 million, $56.8 million and $44.4 million for the years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively. Contractual advertising expense, which is normally based on a percentage of net sales, associated with certain license agreements (included in selling, general and administrative expense) was $22.9 million, $18.8 million and $14.0 million for the years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively. Based on minimum sales requirements, future minimum royalty and advertising payments required under these agreements are:
| Year Ending January 31, |
Amount | |||
| (In thousands) | ||||
| 2013 |
$ | 62,236 | ||
| 2014 |
37,220 | |||
| 2015 |
28,159 | |||
| 2016 |
24,460 | |||
| 2017 |
18,401 | |||
|
|
|
|||
| $ | 170,476 | |||
|
|
|
|||
NOTE H — STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Public Offering
On December 21, 2009, the Company completed a public offering of 1,700,000 shares of common stock at a public offering price of $19.50 per share. The Company received net proceeds of $30.9 million from this offering after payment of the underwriting discount and expenses of the offering. On December 30, 2009, the Company received additional net proceeds of $3.8 million in connection with the sale of 207,010 shares of common stock pursuant to the exercise of the underwriters’ overallotment option.
Share Repurchase Program
In September 2011, the Company’s board of directors authorized a program to repurchase up to two million shares of its common stock. The timing and actual number of shares repurchased will depend upon a number of
F-17
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
factors, including market conditions and prevailing stock prices. Share repurchases may take place on the open market, in privately negotiated transactions or by other means, and would be made in accordance with applicable securities laws. Pursuant to the share repurchase program, during fiscal 2012, the Company repurchased 125,000 shares of its common stock for an aggregate purchase price of approximately $2.9 million. Repurchased shares are accounted for as treasury stock at cost and will be held in treasury for future use.
Stock Plans
As of January 31, 2012, the Company has 1,409,079 shares available for grant under its stock plans. The plans provide for the grant of equity and cash awards, including stock options, restricted stock awards and other stock unit awards to directors, officers and employees. It is the Company’s policy to grant stock options at prices not less than the fair market value on the date of the grant. Option terms, vesting and exercise periods vary, except that the term of an option may not exceed ten years. Restricted stock unit awards vest over a three to five year period and generally include a price vesting market condition in addition to the time vesting condition.
Stock Options
Information regarding all stock options for fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010 is as follows:
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Shares | Weighted Average Exercise Price |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Stock options outstanding at beginning of year |
514,190 | $ | 14.54 | 817,050 | $ | 11.23 | 1,003,750 | $ | 10.33 | |||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
(60,668 | ) | $ | 10.21 | (339,010 | ) | $ | 8.23 | (189,250 | ) | $ | 6.28 | ||||||||||||
| Granted |
40,000 | $ | 27.13 | 38,000 | $ | 29.59 | 18,000 | $ | 11.10 | |||||||||||||||
| Cancelled or forfeited |
(75,800 | ) | $ | 13.35 | (1,850 | ) | $ | 18.40 | (15,450 | ) | $ | 12.87 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Stock options outstanding at end of year |
417,722 | $ | 16.59 | 514,190 | $ | 14.54 | 817,050 | $ | 11.23 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| Exercisable |
245,556 | $ | 14.18 | 260,990 | $ | 12.32 | 471,950 | $ | 8.82 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
The following table summarizes information about stock options outstanding:
| Range of Exercise Prices |
Number Outstanding as of January 31, 2012 |
Weighted Average Remaining Contractual Life |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
Number Exercisable as of January 31, 2012 |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
|||||||||||||||
| $ 3.00 - $ 8.00 |
59,857 | 1.56 | $ | 5.45 | 59,857 | $ | 5.45 | |||||||||||||
| $ 8.01 - $ 12.00 |
47,000 | 5.53 | $ | 10.34 | 16,200 | $ | 9.38 | |||||||||||||
| $ 12.01 - $ 16.00 |
87,100 | 6.13 | $ | 14.03 | 51,500 | $ | 13.88 | |||||||||||||
| $ 16.01 - $ 40.00 |
223,765 | 6.39 | $ | 21.88 | 117,999 | $ | 19.40 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
| 417,722 | 245,556 | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||||||
F-18
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The fair value of stock options was estimated using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. This model requires the input of subjective assumptions that will usually have a significant impact on the fair value estimate. The following table summarizes the weighted average assumptions used in the Black-Scholes option pricing model for grants in fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively:
| 2012 |
2011 |
2010 | ||||
| Expected stock price volatility |
68.5% | 64.1% | 56.5% | |||
| Expected lives of options |
||||||
| Directors and officers |
7 years | 7 years | 7 years | |||
| Employees |
6 years | 6 years | n/a | |||
| Risk-free interest rate |
1.2% | 2.3% - 3.4% | 3.5% | |||
| Expected dividend yield |
0% | 0% | 0% |
The weighted average volatility for the current period was developed using historical volatility for periods equal to the expected term of the options.
The risk-free interest rate was developed using the U.S. Treasury yield curve for periods equal to the expected term of the options on the grant date. An increase in the risk-free interest rate will increase stock compensation expense.
The dividend yield is a ratio that estimates the expected dividend payments to shareholders. The Company has not declared a cash dividend and has estimated dividend yield at 0%.
The expected term of stock option grants was developed after considering vesting schedules, life of the option, and historical experience. An increase in the expected holding period will increase stock compensation expense.
The Company is required to recognize stock-based compensation based on the number of awards that are ultimately expected to vest. As a result, for most awards, recognized stock compensation was reduced for estimated forfeitures prior to vesting primarily based on an historical annual forfeiture rate. Estimated forfeitures will be reassessed in subsequent periods and may change based on new facts and circumstances.
The weighted average remaining term for stock options outstanding was 5.6 years at January 31, 2012. The aggregate intrinsic value at January 31, 2012 was $3.0 million for stock options outstanding and $2.2 million for stock options exercisable. The intrinsic value for stock options is calculated based on the exercise price of the underlying awards and the market price of our common stock as of January 31, 2012, the reporting date.
Proceeds received from the exercise of stock options were approximately $620,000 and $2.8 million during the years ended January 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. The intrinsic value of stock options exercised was $1.4 million and $6.8 million for the years ended January 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively. A portion of this amount is currently deductible for tax purposes.
The Company recognized approximately $798,000 and $987,000 in compensation expense for the years ended January 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively, related to equity option award grants. As of January 31, 2012, approximately $1.3 million related to unrecognized stock compensation related to unvested option awards (net of estimated forfeitures) is expected to be recognized through the year ending January 31, 2017.
The weighted average fair value at date of grant for options granted during fiscal 2012, 2011 and 2010 was $12.97, $18.01 and $6.67 per option, respectively.
F-19
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
Restricted Stock
| Awards Outstanding |
Weighted Average Grant Date Fair Value |
|||||||
| Unvested as of January 31, 2010 |
522,250 | $ | 8.08 | |||||
| Granted |
286,050 | $ | 21.28 | |||||
| Vested |
(149,418 | ) | $ | 7.87 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Unvested as of January 31, 2011 |
658,882 | $ | 13.86 | |||||
| Granted |
437,850 | $ | 30.80 | |||||
| Vested |
(162,332 | ) | $ | 9.16 | ||||
| Canceled |
(8,500 | ) | $ | 24.03 | ||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| Unvested as of January 31, 2012 |
925,900 | $ | 22.60 | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
The Company recognized $4.4 million and $2.5 million in compensation expense for the years ended January 31, 2012 and 2011, respectively, related to restricted stock grants. At January 31, 2012 and 2011, unrecognized costs related to the restricted stock units totaled approximately $16.0 million and $7.0 million, respectively.
Stock Warrants
In connection with its private placement in July 2006, the Company issued five year warrants to purchase an aggregate of up to 375,000 shares of its Common Stock at an exercise price of $11.00 per share, subject to adjustment upon the occurrence of specified events, including customary weighted average price anti-dilution adjustments. These warrants were exercised on December 30, 2010. As a result, the Company received proceeds of $4.1 million.
NOTE I — MAJOR CUSTOMERS
One customer accounted for 18.7%, 17.3% and 16.8% of the Company’s net sales for the years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively. A second customer accounted for 12.3%, 12.4% and 8.8% of the Company’s net sales for the years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
NOTE J — EMPLOYEE BENEFIT PLANS
The Company maintains a 401(k) plan and trust for nonunion employees. At the discretion of the Company, the Company may elect to match 50% of employee contributions up to 3% of the participant’s compensation. The Company made matching contributions of approximately $869,000 $853,000 and $800,000 for the years ended January 31, 2012, January 31, 2011 and 2010, respectively.
F-20
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
NOTE K — SEGMENTS
The Company’s reportable segments are business units that offer products through different channels of distribution and are managed separately. The Company operates in three segments; wholesale licensed product, wholesale non-licensed product and retail operations. There is substantial intersegment cooperation, cost allocations and sharing of assets. As a result, the Company does not represent that these segments, if operated independently, would report the operating results set forth in the table below. The following information, in thousands, is presented for the fiscal years ended:
| January 31, 2012 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wholesale Licensed |
Wholesale Non- Licensed |
Retail | Elimination(1) | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 840,717 | $ | 277,615 | $ | 164,343 | $ | (51,474 | ) | $ | 1,231,201 | |||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
617,716 | 205,504 | 88,739 | (51,474 | ) | 860,485 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Gross profit |
223,001 | 72,111 | 75,604 | — | 370,716 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
164,070 | 42,295 | 70,654 | — | 277,019 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
1,360 | 4,126 | 1,987 | — | 7,473 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Operating profit |
$ | 57,571 | $ | 25,690 | $ | 2,963 | $ | — | $ | 86,224 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| January 31, 2011 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wholesale Licensed |
Wholesale Non- Licensed |
Retail | Elimination(1) | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 718,537 | $ | 244,031 | $ | 142,292 | $ | (41,456 | ) | $ | 1,063,404 | |||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
504,935 | 173,578 | 75,302 | (41,456 | ) | 712,359 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Gross profit |
213,602 | 70,453 | 66,990 | — | 351,045 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
142,510 | 42,521 | 63,349 | — | 248,380 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
719 | 3,615 | 1,399 | — | 5,733 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Operating profit |
$ | 70,373 | $ | 24,317 | $ | 2,242 | $ | — | $ | 96,932 | ||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| January 31, 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Wholesale Licensed |
Wholesale Non- Licensed |
Retail | Elimination(1) | Total | ||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$523,606 | $ | 188,318 | $ | 126,608 | $ | (37,668 | ) | $ | 800,864 | ||||||||||
| Cost of goods sold |
367,416 | 134,600 | 69,648 | (37,668 | ) | 533,996 | ||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Gross profit |
156,190 | 53,718 | 56,960 | — | 266,868 | |||||||||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
111,075 | 35,099 | 59,107 | — | 205,281 | |||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
837 | 3,338 | 1,205 | — | 5,380 | |||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| Operating profit (loss) |
$ | 44,278 | $ | 15,281 | $ | (3,352 | ) | $ | — | $ | 56,207 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
| (1) | Represents intersegment sales to the Company’s retail operations. |
F-21
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS — (Continued)
The Company allocates overhead to its business segments on various bases, which include units shipped, space utilization, inventory levels, and relative sales levels, among other factors. The method of allocation is consistent on a year-to-year basis.
| 2012 | 2011 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Geographic Region |
Revenues | Long-Lived Assets |
Revenues | Long-Lived Assets |
Revenues | Long-Lived Assets |
||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| United States |
$ | 1,185,800 | $ | 87,103 | $ | 1,025,763 | $ | 77,042 | $ | 782,285 | $ | 65,677 | ||||||||||||
| Non-United States |
45,401 | 517 | 37,641 | 574 | 18,579 | 184 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
| $ | 1,231,201 | $ | 87,620 | $ | 1,063,404 | $ | 77,616 | $ | 800,864 | $ | 65,861 | |||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||||
Capital expenditures for locations outside of the United States were not significant in each of the fiscal years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010. For the year ended January 31, 2012, capital expenditures were $10.7 million and $6.7 million for the wholesale and retail segments, respectively. For the year ended January 31, 2011, capital expenditures were $16.6 million and $2.8 million for the wholesale and retail segments, respectively.
Included in finished goods inventory at January 31, 2012 are approximately $170.4 million, $35.2 million and $39.3 million of inventories for wholesale licensed product, wholesale non-licensed product and retail operations, respectively. Included in finished goods inventory at January 31, 2011 are approximately $135.3 million, $32.8 million and $31.2 million of inventories for wholesale licensed product, wholesale non-licensed product and retail operations, respectively. Substantially all other assets are commingled.
NOTE L — QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (UNAUDITED)
Summarized quarterly financial data in thousands, except per share amounts, for the fiscal years ended January 31, 2012 and 2011 are as follows:
| Quarter Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| April 30, 2011 |
July 31, 2011 |
October 31, 2011 |
January 31, 2012 |
|||||||||||||
| January 31, 2012 |
||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 196,871 | $ | 229,975 | $ | 510,009 | $ | 294,346 | ||||||||
| Gross profit |
59,455 | 65,571 | 162,275 | 83,415 | ||||||||||||
| Net income/(loss) |
(520 | ) | 1,565 | 43,555 | 5,020 | |||||||||||
| Net income/(loss) per common share |
||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | (0.03 | ) | $ | 0.08 | $ | 2.19 | $ | 0.25 | |||||||
| Diluted |
$ | (0.03 | ) | $ | 0.08 | $ | 2.16 | $ | 0.25 | |||||||
| Quarter Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| April 30, 2010 |
July 31, 2010 |
October 31, 2010 |
January 31, 2011 |
|||||||||||||
| January 31, 2011 |
||||||||||||||||
| Net sales |
$ | 154,278 | $ | 188,960 | $ | 450,002 | $ | 270,164 | ||||||||
| Gross profit |
49,037 | 60,754 | 153,947 | 87,307 | ||||||||||||
| Net income/(loss) |
(1,372 | ) | 2,999 | 42,722 | 12,333 | |||||||||||
| Net income/(loss) per common share |
||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | (0.07 | ) | $ | 0.16 | $ | 2.22 | $ | 0.63 | |||||||
| Diluted |
$ | (0.07 | ) | $ | 0.15 | $ | 2.16 | $ | 0.62 | |||||||
F-22
Schedule VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
G-III Apparel Group, Ltd. and Subsidiaries
SCHEDULE II — VALUATION AND QUALIFYING ACCOUNTS
Years ended January 31, 2012, 2011 and 2010
| Description |
Balance at Beginning of Period |
Charged to Costs and Expenses |
Deductions (a) |
Balance at End of Period |
||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Year ended January 31, 2012 |
||||||||||||||||
| Deducted from asset accounts |
||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 1,350 | $ | 643 | $ | 510 | $ | 1,483 | ||||||||
| Reserve for sales allowances(b) |
30,824 | 77,764 | 75,635 | 32,953 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| $ | 32,174 | $ | 78,407 | $ | 76,145 | $ | 34,436 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Year ended January 31, 2011 |
||||||||||||||||
| Deducted from asset accounts |
||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 1,589 | $ | 371 | $ | 610 | $ | 1,350 | ||||||||
| Reserve for sales allowances(b) |
27,503 | 60,329 | 57,008 | 30,824 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| $ | 29,092 | $ | 60,700 | $ | 57,618 | $ | 32,174 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| Year ended January 31, 2010 |
||||||||||||||||
| Deducted from asset accounts |
||||||||||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
$ | 1,525 | $ | 672 | $ | 608 | $ | 1,589 | ||||||||
| Reserve for sales allowances(b) |
19,464 | 57,150 | 49,111 | 27,503 | ||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| $ | 20,989 | $ | 57,822 | $ | 49,719 | $ | 29,092 | |||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||
| (a) | Accounts written off as uncollectible, net of recoveries. |
| (b) | See Note A in the accompanying Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for a description of sales allowances. |
S-1
