Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 8-K - FORM 8-K - REVA Medical, Inc. | d304457d8k.htm |
Exhibit 99.1

| Novel Bioresorbable Polymer Based Drug Eluting Scaffolds J. Zeltinger |

| Purpose of Metal DES Provide Strength Enlarge lumen acutely Maintain support throughout healing process Assist Healing Manage post-treatment stenosis by elution of an effective anti-proliferative |

| Risks of Metal DES Overstays it's welcome Long-term thrombosis Rigid device, alters vascular mechanics and flow Theoretically, may induce subsequent downstream disease |
| Benefits of Bioresorbable Scaffolds Provides the benefits of metal DES stents without their permanency Resorption Dissolves and leaves patient free of a permanent implant Allows favorable geometric remodeling Return of arterial compliance Return of vasomotor function Less risk for long-term thrombosis Enhances retreatment options |
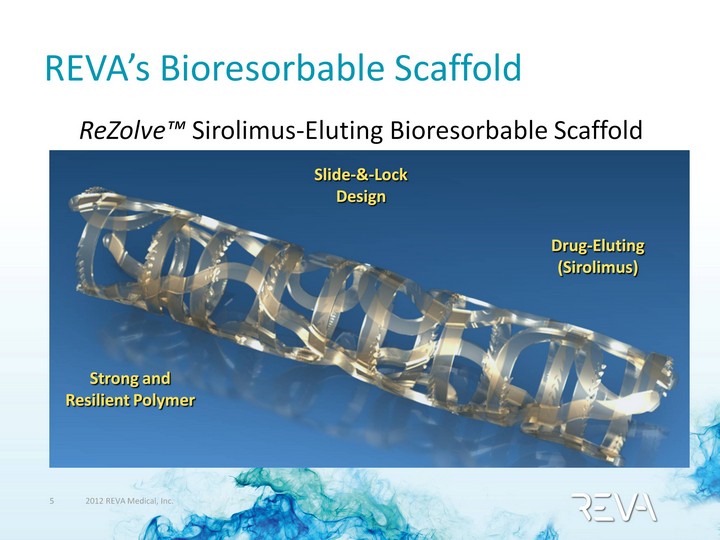
| REVA's Bioresorbable Scaffold Drug-Eluting (Sirolimus) Strong and Resilient Polymer Slide-&-Lock Design ReZolve(tm) Sirolimus-Eluting Bioresorbable Scaffold |
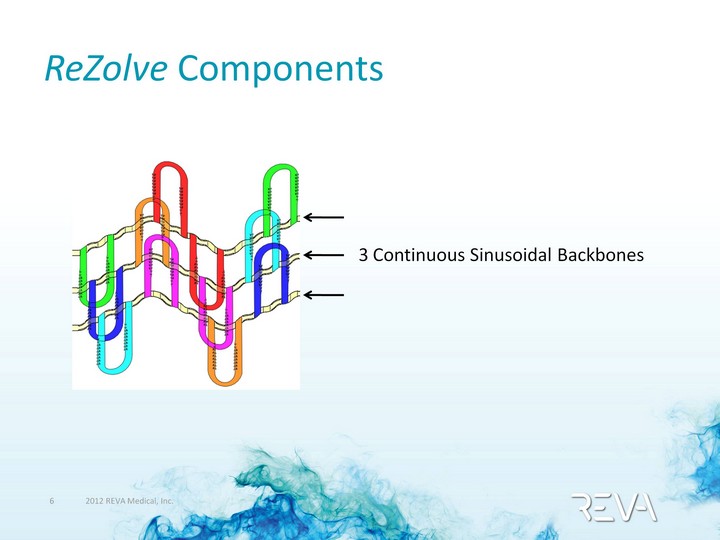
| ReZolve Components 3 Continuous Sinusoidal Backbones |
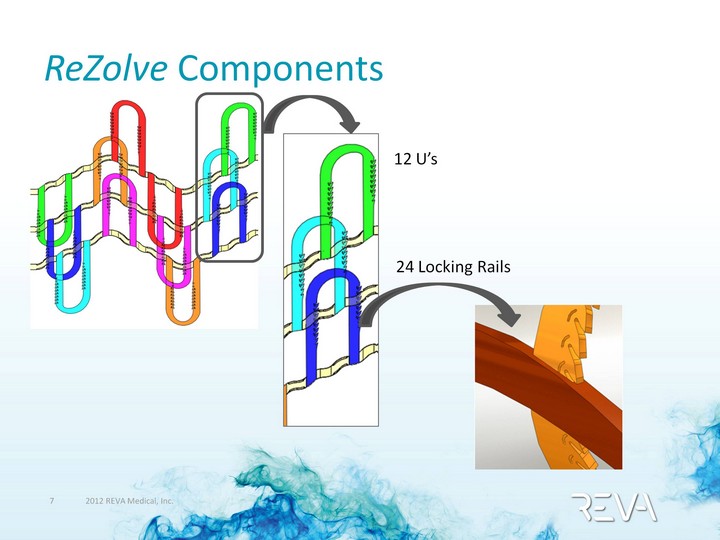
| ReZolve Components 12 U's 24 Locking Rails |

| ReZolve Slide & Lock Deployment |

| ReZolve Elutes Sirolimus 80µg dose Sirolimus with abluminal delivery 5µm drug layer embedded on scaffold surface Delivery kinetics match commercial -limus eluting stents Coated Bare |
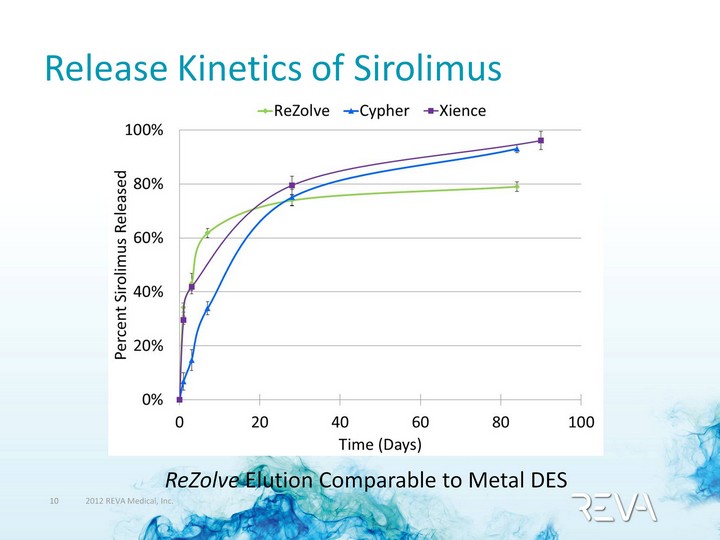
| Release Kinetics of Sirolimus ReZolve Elution Comparable to Metal DES |
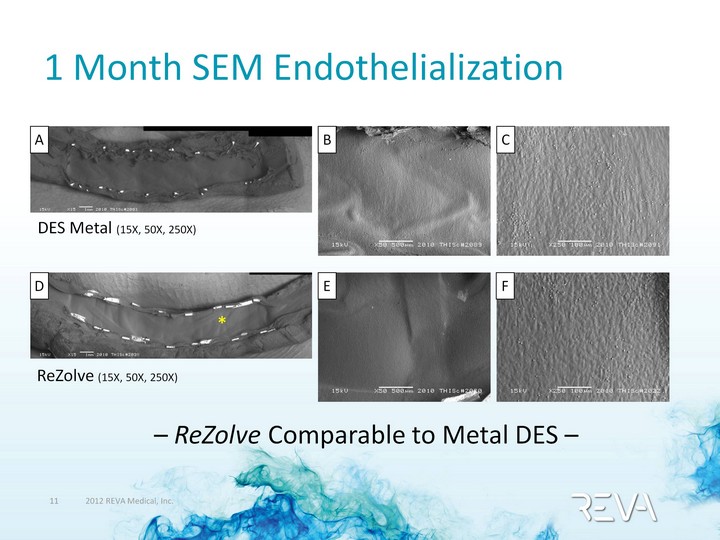
| 1 Month SEM Endothelialization DES Metal (15X, 50X, 250X) A B C ReZolve (15X, 50X, 250X) D E F * - ReZolve Comparable to Metal DES - |

| 3 Month SEM Endothelialization DES Metal (15X, 50X, 250X) A B C ReZolve (15X, 50X , 250X) D E F ReZolve Endothelium Matures More Rapidly than Metal DES |
| ReZolve Deployment - In Vivo |
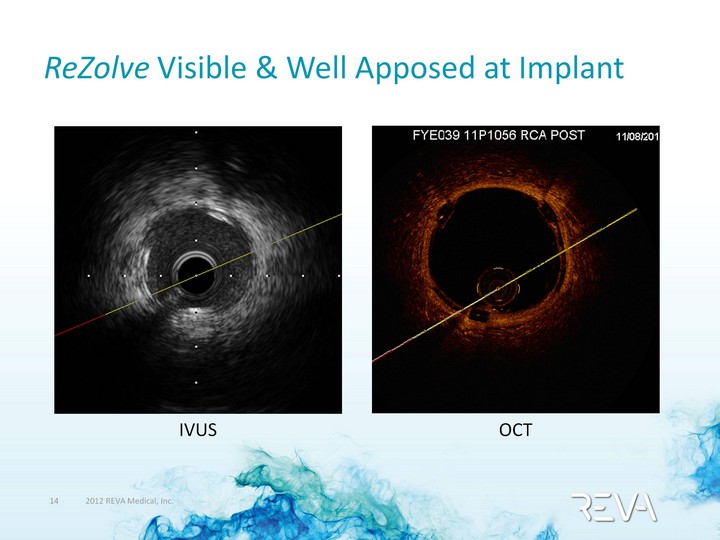
| ReZolve Visible & Well Apposed at Implant IVUS OCT |
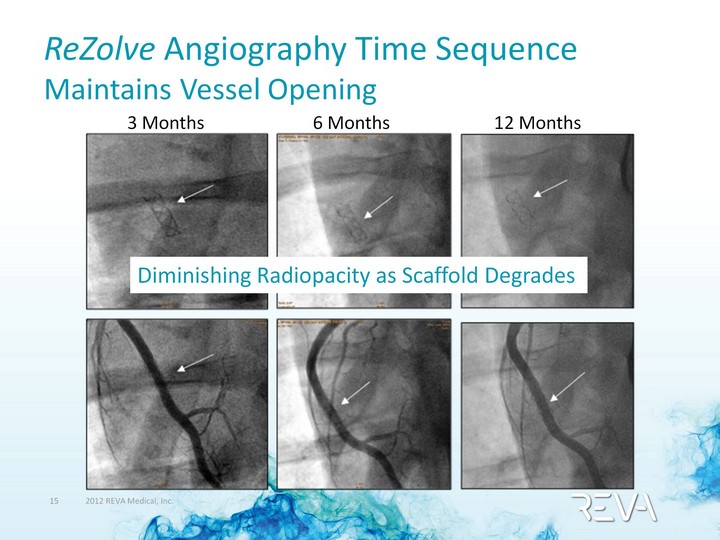
| ReZolve Angiography Time Sequence Maintains Vessel Opening 3 Months 6 Months 12 Months Diminishing Radiopacity as Scaffold Degrades |
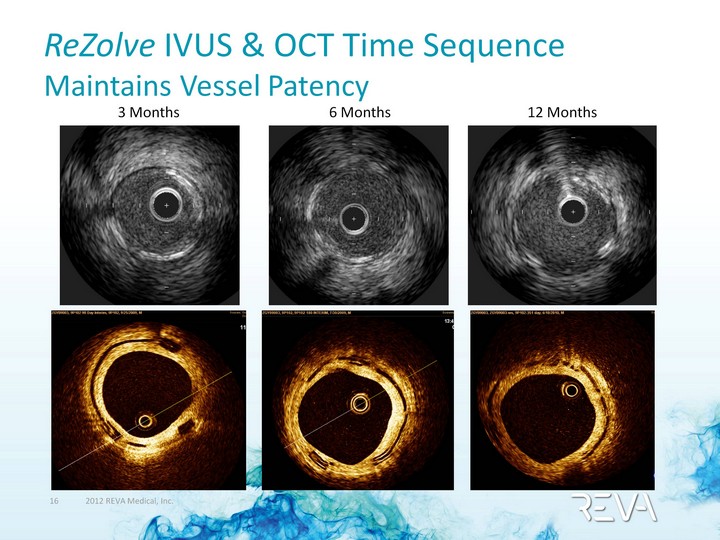
| 3 Months ReZolve IVUS & OCT Time Sequence Maintains Vessel Patency 6 Months 12 Months |
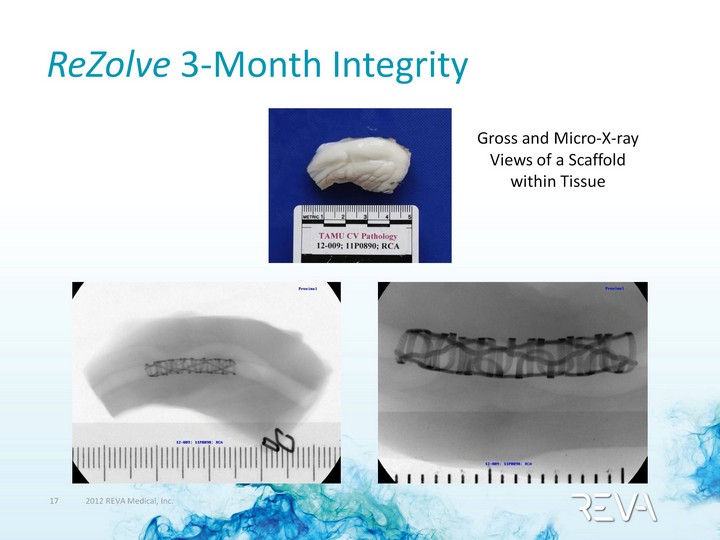
| ReZolve 3-Month Integrity Gross and Micro-X-ray Views of a Scaffold within Tissue |
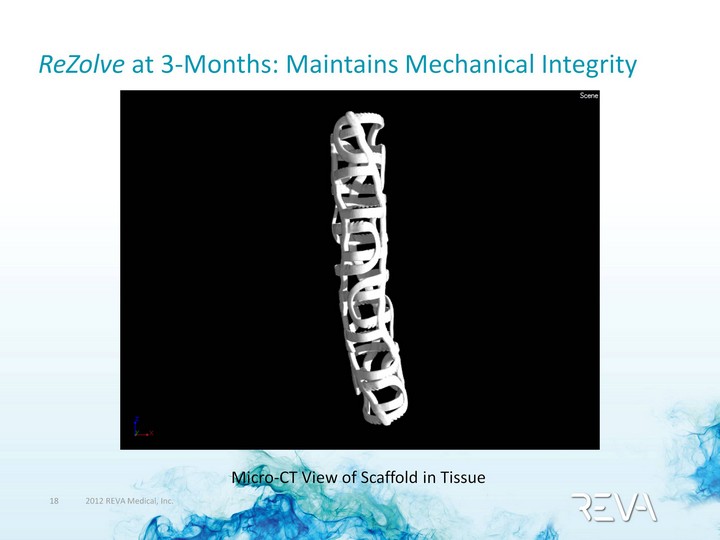
| ReZolve at 3-Months: Maintains Mechanical Integrity Micro-CT View of Scaffold in Tissue |
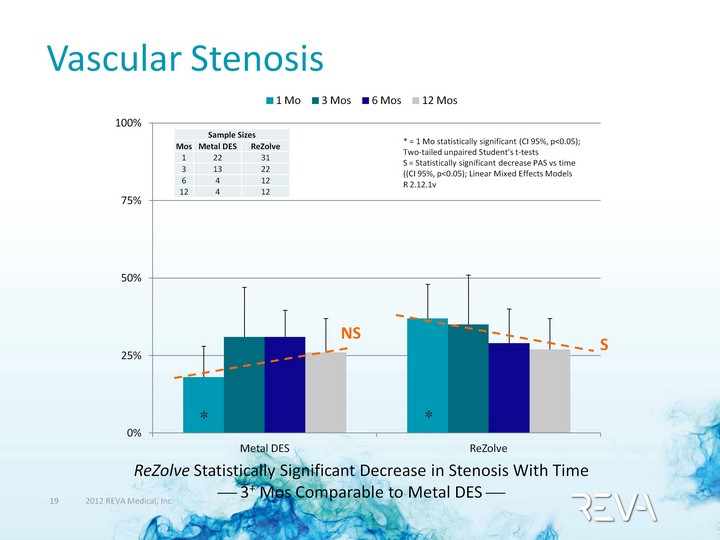
| (CHART) Vascular Stenosis Sample Sizes Sample Sizes Sample Sizes Mos Metal DES ReZolve 1 22 31 3 13 22 6 4 12 12 4 12 * = 1 Mo statistically significant (CI 95%, p<0.05); Two-tailed unpaired Student's t-tests S = Statistically significant decrease PAS vs time ((CI 95%, p<0.05); Linear Mixed Effects Models R 2.12.1v ? ? NS ReZolve Statistically Significant Decrease in Stenosis With Time ? 3+ Mos Comparable to Metal DES ? |
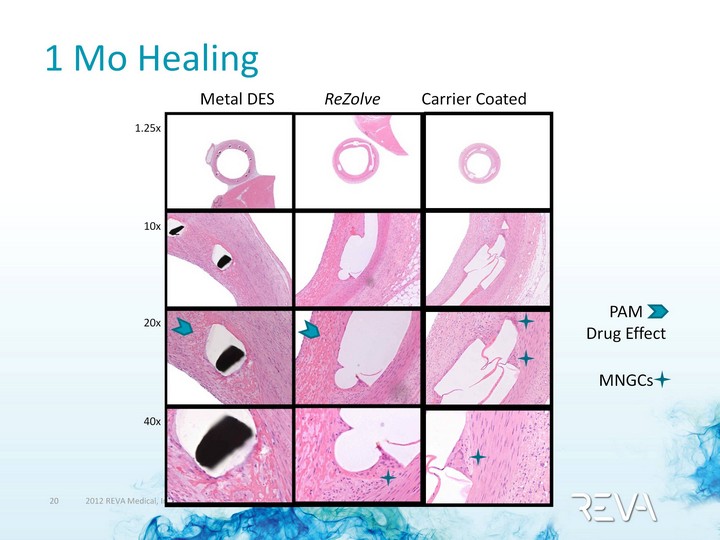
| 1 Mo Healing 1.25x 10x 20x 40x Metal DES ReZolve Carrier Coated PAM Drug Effect MNGCs |
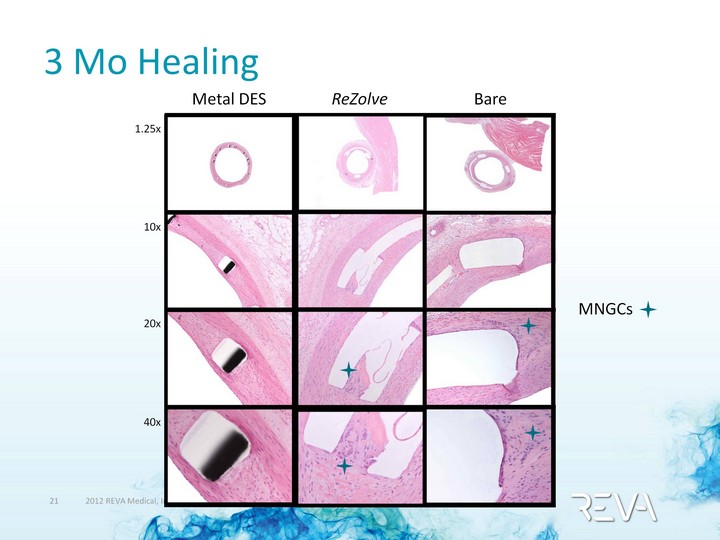
| 3 Mo Healing MNGCs 1.25x 10x 20x 40x Metal DES ReZolve Bare |
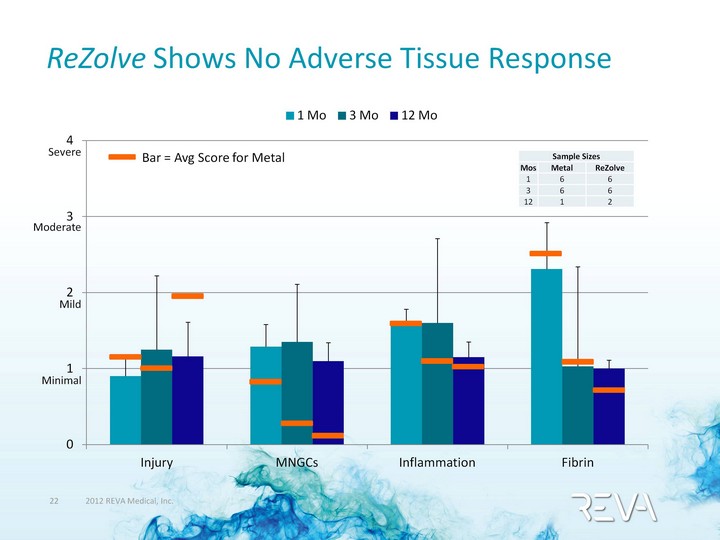
| (CHART) ReZolve Shows No Adverse Tissue Response Sample Sizes Sample Sizes Sample Sizes Mos Metal ReZolve 1 6 6 3 6 6 12 1 2 Severe Moderate Mild Minimal Bar = Avg Score for Metal |

| Degradation and Resorption Are We There Yet? |

| RESORB FIM Scaffold AND ReZolve |
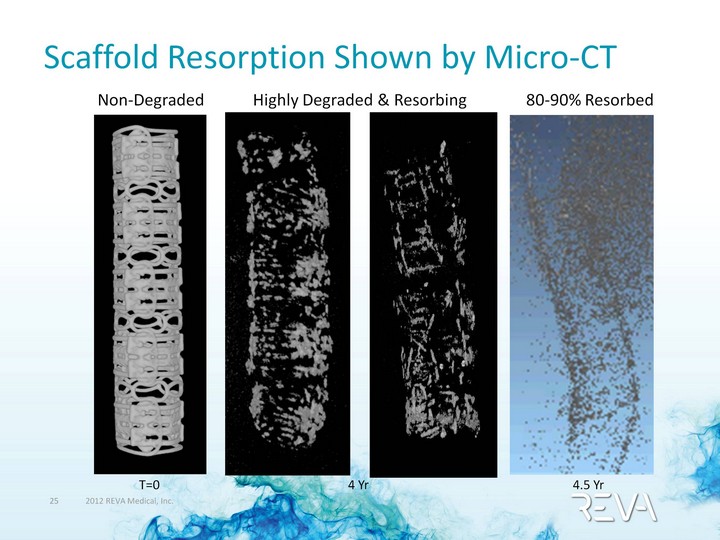
| Scaffold Resorption Shown by Micro-CT Non-Degraded 80-90% Resorbed Highly Degraded & Resorbing T=0 4.5 Yr 4 Yr |

| Micro-CT of Resorbing Scaffold |

| SEM Time Lapse - In Vivo Structural Degradation Solid Surface Deep Microcracks Microcracks 150X 4KX 8KX Bulk Erosion Microporous |

| SEM Time Lapse - Degrading & Resorbing Struts Non-Degraded 80-90% Resorbed RESORB Scaffolds Highly Degraded & Resorbing |
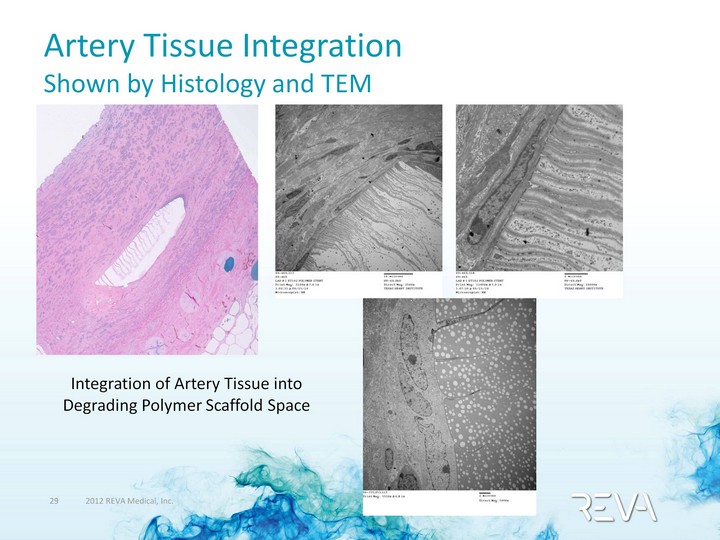
| Artery Tissue Integration Shown by Histology and TEM Integration of Artery Tissue into Degrading Polymer Scaffold Space |
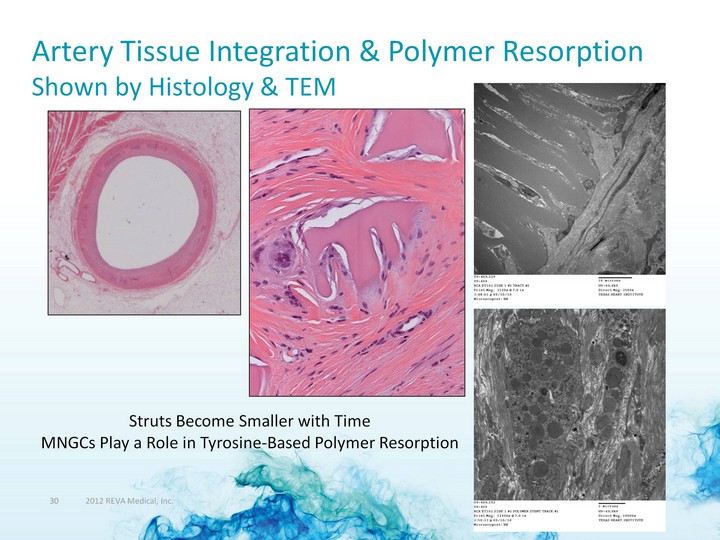
| Artery Tissue Integration & Polymer Resorption Shown by Histology & TEM Struts Become Smaller with Time MNGCs Play a Role in Tyrosine-Based Polymer Resorption |
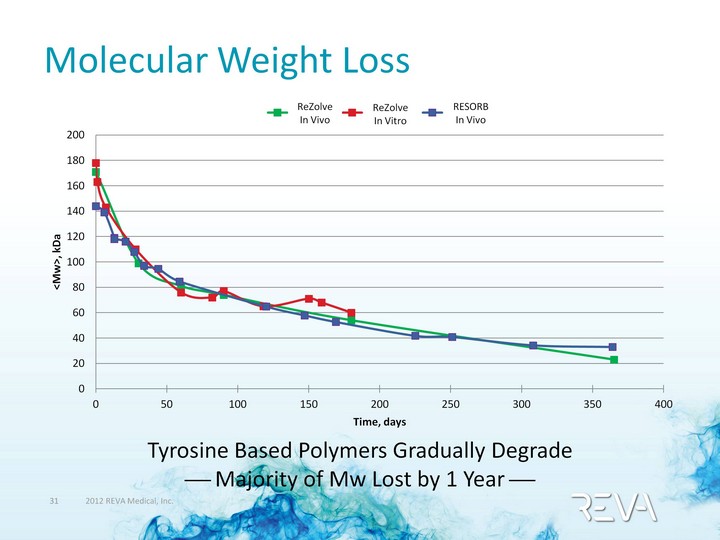
| Molecular Weight Loss Molecular Weight Loss ReZolve In Vivo ReZolve In Vitro RESORB In Vivo Tyrosine Based Polymers Gradually Degrade ? Majority of Mw Lost by 1 Year ? |
| Predictable & Safe Breakdown Products 1H-NMR ? by 3 Months+ Confirmed hydrolytic breakdown Cleavage of the ethyl ester bond initiated HPLC ? 6 Months+ Detected free monomers (I2DTE, I2DT and I2DAT) Mass Spectroscopy ? 12 Months+ Confirmed significant molecular weight loss by detection of short chain oligomers (<10,000 Da) I2DTE, I2DT, I2DAT, I2, DT |
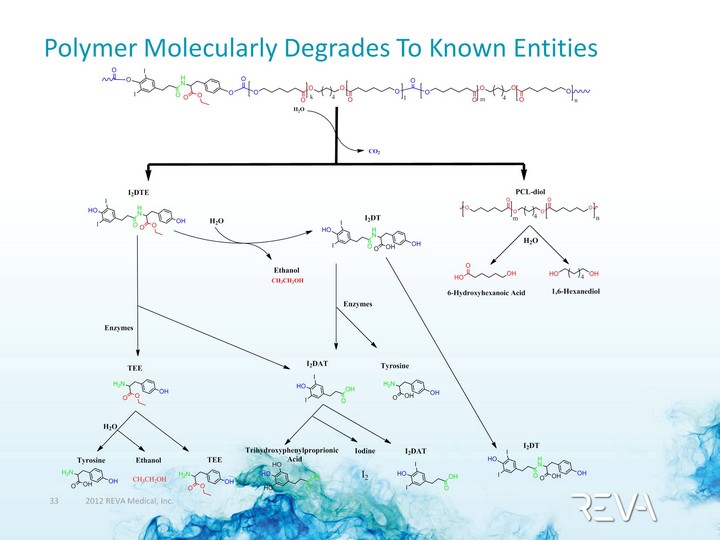
| Polymer Molecularly Degrades To Known Entities |
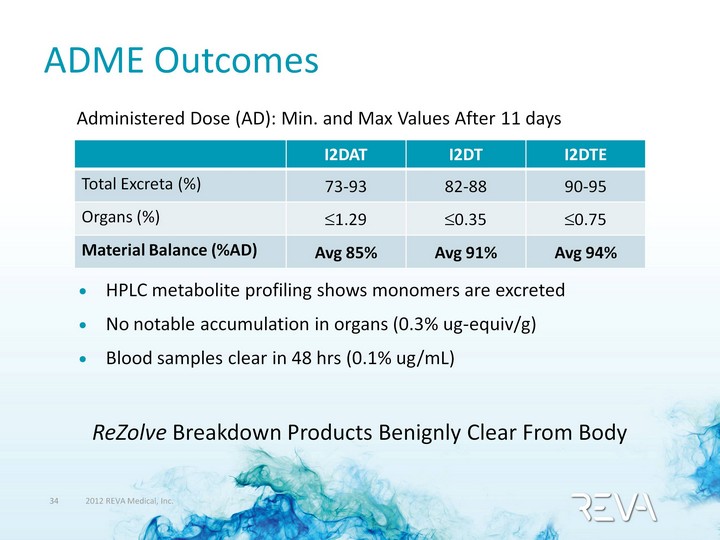
| ADME Outcomes Administered Dose (AD): Min. and Max Values After 11 days HPLC metabolite profiling shows monomers are excreted No notable accumulation in organs (0.3% ug-equiv/g) Blood samples clear in 48 hrs (0.1% ug/mL) I2DAT I2DT I2DTE Total Excreta (%) 73-93 82-88 90-95 Organs (%) ?1.29 ?0.35 ?0.75 Material Balance (%AD) Avg 85% Avg 91% Avg 94% ReZolve Breakdown Products Benignly Clear From Body |
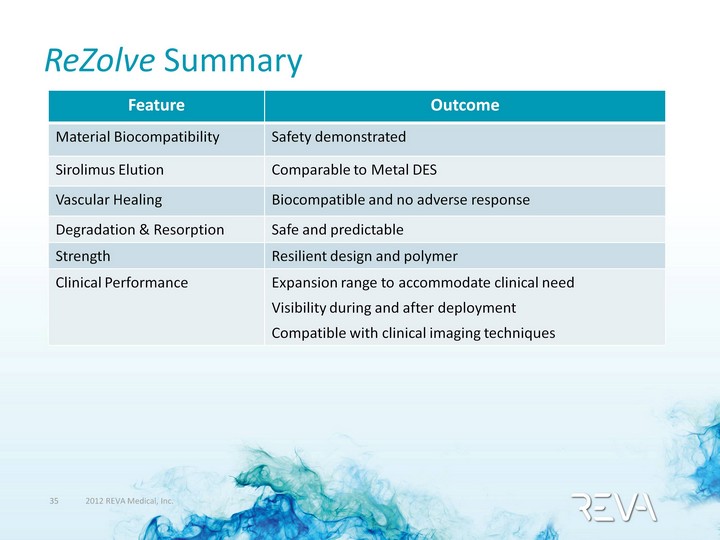
| ReZolve Summary Feature Outcome Material Biocompatibility Safety demonstrated Sirolimus Elution Comparable to Metal DES Vascular Healing Biocompatible and no adverse response Degradation & Resorption Safe and predictable Strength Resilient design and polymer Clinical Performance Expansion range to accommodate clinical need Visibility during and after deployment Compatible with clinical imaging techniques |

| RESTORE Clinical Trial ReZolve Sirolimus-Eluting Bioresorbable Coronary Scaffold Pilot Safety Study 50 Patient enrollment Sites in Brazil & Europe Patient Enrollment Initiated 12/21/11 Principal Investigator: Dr. Alexandre Abizaid Primary Endpoints Freedom from ischemic-driven target lesion revascularization at 6 months Quantitative measurements at 12 months (QCA/IVUS) |

| Thank You to the Audience and REVA's Many Colleagues! Pathology Dr. Fred J. Clubb, TAMU Dr. Marian Rippy, Rippy Pathology Solutions, Inc. Pamela Potts & Team at Texas Heart Institute (THI) IVUS and OCT Analysis Drs. Greg Kaluza and Yanping Cheng, Skirball - CRF And everyone at "TEAM REVA" San Diego, CA |
