Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - CERES ORION L.P. | y04523exv32w1.htm |
| EX-99.3 - EX-99.3 - CERES ORION L.P. | y04523exv99w3.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - CERES ORION L.P. | y04523exv31w1.htm |
| EX-99.1 - EX-99.1 - CERES ORION L.P. | y04523exv99w1.htm |
| EX-99.2 - EX-99.2 - CERES ORION L.P. | y04523exv99w2.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - CERES ORION L.P. | y04523exv31w2.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - CERES ORION L.P. | y04523exv32w2.htm |
| EX-10.3.A - EX-10.3.A - CERES ORION L.P. | y04523exv10w3wa.htm |
| EX-10.1.C - EX-10.1.C - CERES ORION L.P. | y04523exv10w1wc.htm |
| EX-10.2.B - EX-10.2.B - CERES ORION L.P. | y04523exv10w2wb.htm |
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON, D.C. 20549
FORM 10-K
| þ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010
OR
| o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the Transition period from
to
Commission File Number 0-50271
ORION FUTURES FUND L.P.
| New York | 22-3644546 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) |
|
c/o Ceres Managed Futures LLC
522 Fifth Avenue — 14th Fl.
New York, New York 10036
(Address and Zip Code of principal executive offices)
522 Fifth Avenue — 14th Fl.
New York, New York 10036
(212) 296-1999
(Registrant’s telephone number, including area code)
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act: None
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: Redeemable Units of Limited Partnership Interest
(Title of Class)
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of
the Securities Act.
Yes o
No þ
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or
Section 15(d) of the Act.
Yes o
No þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by
Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for
such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been
subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days.
Yes þ
No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its
corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted
pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months
(or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files).
Yes o
No o
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is
not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in
definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K
or any amendment to this form 10-K þ
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a
non-accelerated filer, or smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated
filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act.
(Check one):
| Large accelerated filer o | Accelerated filer o | Non-accelerated filer þ (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company o |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the
Exchange Act).
Yes o No þ
Limited Partnership Redeemable Units with an aggregate value of $1,196,360,843 were outstanding and
held by non-affiliates as of the last business day of the registrants most recently completed
second calendar month.
As of February 28, 2011, 429,610.4530 Limited Partnership Redeemable Units were outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
[None]
TABLE OF CONTENTS
PART I
Item 1. Business.
(a) General development of business. Orion Futures Fund L.P. (the “Partnership”), is a
limited partnership organized under the partnership laws of the State of New York on March 22, 1999 to engage, directly or indirectly, in the speculative trading of a diversified portfolio of
commodity interests including futures contracts, options, swaps and forward contracts. The sectors
traded include currencies, energy, grains, indices, U.S. and non-U.S. interest rates, livestock,
lumber, metals and softs. The commodity interests that are traded by the Partnership and the Funds
(as defined below) are volatile and involve a high degree of market risk.
During the initial offering period (March 31, 1999 through June 10, 1999) the Partnership sold
10,499 redeemable units of limited partnership interest (“Redeemable Units”) at $1,000 per
Redeemable Unit. The Partnership commenced trading activities on June 10, 1999. The Partnership
privately and continuously offers up to 600,000 Redeemable Units to qualified investors. There is
no maximum number of Redeemable Units that may be sold by the Partnership.
Subscriptions and redemptions of Redeemable Units and general partner contributions and
redemptions for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 are reported in the Statements of
Changes in Partners’ Capital on page 35 under “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary
Data.”
Ceres Managed Futures LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, acts as the general partner
(the “General Partner”) and commodity pool operator of the Partnership. The General Partner is
wholly owned by Morgan Stanley Smith Barney Holdings LLC (“MSSB Holdings”). Morgan Stanley, indirectly through various subsidiaries, owns
a majority equity interest in MSSB Holdings. Citigroup Global Markets Inc. (“CGM”), the commodity
broker and a selling agent for the Partnership, owns a minority equity interest in MSSB Holdings.
Citigroup Inc. (“Citigroup”), indirectly through various subsidiaries, wholly owns CGM. Prior to
July 31, 2009, the date as of which MSSB Holdings became its owner, the General Partner was wholly
owned by Citigroup Financial Products Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Citigroup Global Markets
Holdings Inc., the sole owner of which is Citigroup.
As of December 31, 2010, all trading decisions are made for the Partnership by Winton Capital
Management Limited (“Winton”), Willowbridge Associates Inc. (“Willowbridge”), and AAA Capital
Management Advisors, Ltd. (“AAA”) (each an “Advisor” and collectively, the “Advisors”), each of
which is a registered commodity trading advisor. Willowbridge trades the Argo, Vulcan, Consolidated
Commodities Fundamental and MStrategy trading systems for the Partnership. A description of the
trading activities and focus of the Advisors are included on
page 8 under “Item 7. Management’s
Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.” The Advisors are not
affiliated with one another, are not affiliated with the General Partner/managing member or CGM and
are not responsible for the organization or operation of the Partnership.
The General Partner and each limited partner share in the profits and losses of the
Partnership in proportion to the amount of Partnership interest owned by each except that no
limited partner shall be liable for obligations of the Partnership in excess of its capital
contribution and profits, if any, net of distributions.
The Partnership will be liquidated upon the first to occur of the following: December 31,
2019; the net asset value per Redeemable Unit of decreases to less than $400 as of a close of any
business day; a decline in net assets after trading commences to less than $1,000,000 or under
certain other circumstances as defined in the Limited Partnership Agreement of the Partnership (the
“Limited Partnership Agreement”).
On September 1, 2001, the assets allocated to AAA for trading were invested in AAA Master Fund
LLC (“AAA Master”), a limited liability company formed under the New York Limited Liability Company
Law. The Partnership purchased 5,173.4381 units of AAA Master with cash equal to $5,173,438. AAA
Master was formed in order to permit accounts managed now or in the future by AAA using the Energy
Program-Futures and Swaps, a proprietary, discretionary trading system, to invest together in one
trading vehicle. The General Partner is also the managing member of AAA Master. Individual and
pooled accounts currently managed by AAA, including the Partnership, are permitted to be
non-managing members of AAA Master. The General Partner and AAA believe that trading through this
structure should promote efficiency and economy in the trading process.
2
On November 1, 2004, the assets allocated to Winton for trading were invested in CMF Winton
Master L.P. (“Winton Master”), a limited partnership organized under the partnership laws of the
State of New York. The Partnership purchased 35,389.8399 units of Winton Master with cash equal to
$33,594,083 and a contribution of open commodity futures and forwards contracts with a fair value
of $1,795,757. Winton Master was formed in order to permit accounts managed now or in the future by
Winton using the Diversified Program, a proprietary, systematic trading system, to invest together
in one trading vehicle. The General Partner is also the general partner of Winton Master.
Individual and pooled accounts currently managed by Winton, including the Partnership are permitted
to be limited partners of Winton Master. The General Partner and Winton believe that trading
through this structure should promote efficiency and economy in the trading process.
On July 1, 2005, a portion of the assets allocated to Willowbridge for trading were invested
in CMF Willowbridge Argo Master Fund L.P. (“Willowbridge Master”), a limited partnership organized
under the partnership laws of the State of New York. The Partnership purchased 33,529.1186 units of
Willowbridge Master with cash equal to $29,866,194, and a contribution of open commodity futures
and forward contracts with a fair value of $3,662,925. Willowbridge Master was formed in order to
permit commodity pools managed now or in the future by Willowbridge using the Argo Trading System,
a proprietary, systematic trading system, to invest together in one trading vehicle. The General
Partner is also the general partner of Willowbridge Master. Individual and pooled accounts
currently managed by Willowbridge, including the Partnership, are permitted to be limited partners
of Willowbridge Master. The General Partner and Willowbridge believe that trading through this
structure should promote efficiency and economy in the trading process.
Additional assets allocated to Willowbridge are not invested in a separate limited partnership
established by the General Partner, but are held and traded by Willowbridge directly in separate
managed accounts in the Partnership’s name. Willowbridge trades the Partnership’s assets directly,
pursuant to its, Vulcan Trading System, Consolidated Commodities Fundamental Trading Program and
MStrategy Program. The Consolidated Commodities Technical Trading Program was terminated as of
October 31, 2010.
The General Partner is not aware of any material changes to the trading programs discussed
above during the year ended December 31, 2010.
AAA Master’s, Willowbridge Master’s and Winton Master’s (the “Funds”) and the Partnership’s
trading of futures, forward, swaps and options contracts, if applicable, on commodities is done
primarily on U.S. commodity exchanges and foreign commodity exchanges. The Funds and the
Partnership engage in such trading through commodity brokerage accounts maintained with CGM.
A limited partner/non-managing member may withdraw all or part of their capital contribution
and undistributed profits, if any, from the Funds in multiples of the net asset value per
Redeemable Unit as of the end of any day (the “Redemption Date”) after a request for redemption has
been made to the General Partner/managing member at least 3 days in advance of the Redemption Date.
The units are classified as a liability when the limited partner/non-managing member elects to
redeem and informs the Funds.
Management, administrative and incentive fees are charged at the Partnership level. All
exchange, clearing, user, give-up, floor brokerage and National
Futures Association (“NFA”) fees (collectively the “clearing fees”)
are borne by the Partnership directly and through its investment in the Funds. All other fees
including CGM’s direct brokerage commissions are charged at the Partnership level.
For the period January 1, 2010 through December 31, 2010, the approximate average market
sector distribution for the Partnership was as follows:
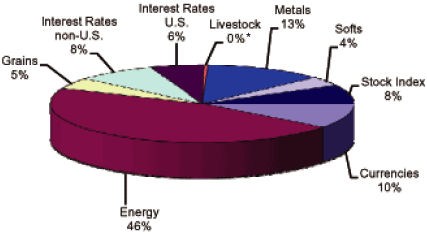
| * | Due to rounding. |
As of December 31, 2010, the Partnership owned approximately 28.7% of AAA Master, 61.9% of
Winton Master and 70.0% of Willowbridge Master. As of December 31, 2009, the Partnership owned
approximately 23.2% of AAA Master, 51.1% of Winton Master and 58.8% of Willowbridge Master. It is
AAA’s, Willowbridge’s and Winton’s intention to continue to invest the assets allocated to each by
the Partnership in AAA Master, Willowbridge Master and Winton Master, respectively. The performance
of the Partnership is directly affected by the performance of the Funds. Expenses to investors as a
result of investment in the Funds are approximately the same and the redemption rights are not
affected.
3
Under the amended and restated Limited Partnership Agreement, the General Partner has sole
responsibility for the administration of the business and affairs of the Partnership, but may
delegate trading discretion to one or more trading advisors. The Partnership pays the General
Partner a monthly administrative fee equal to 1/24 of 1% (0.5% per year) of month-end Net Assets.
Month-end Net Assets, for the purpose of calculating administrative fees are Net Assets, as defined
in the Limited Partnership Agreement, prior to the reduction of the current month’s incentive fee
accrual, the monthly management fees, the General Partner’s administrative fee and any redemptions
or distributions as of the end of such month.
Pursuant to the terms of the management agreements (the “Management Agreement”), the
Partnership will pay each Advisor a monthly management fee equal to 1/6 of 1% (2% a year) of
month-end Net Assets allocated to each Advisor, except for Winton, which will receive a monthly
management fee equal to 1/8 of 1% (1.5% a year) of month-end Net Assets allocated to the Advisor.
Month-end Net Assets, for the purpose of calculating management fees are Net Assets, as defined in
the Limited Partnership Agreement, prior to the reduction of the current month’s incentive fee
accrual, the monthly management fees, the General Partner’s administrative fee and any redemptions
or distributions as of the end of such month. Each Management Agreement may be terminated upon
notice by either party.
In addition, the Partnership is obligated to pay each Advisor an incentive fee, payable
quarterly, equal to 20% of the New Trading Profits, as defined in each Management Agreement, earned
by each Advisor for the Partnership during each calendar quarter.
The General Partner, on behalf of the Partnership has entered into a customer agreement (the
“Customer Agreement”) with CGM which provides that the Partnership will pay CGM brokerage
commissions at $18 per round turn for futures and forward transactions, $5 per round turn for swap
transactions and $9 per half turn for options transactions. Brokerage commissions are inclusive of
applicable floor brokerage. The brokerage commissions may be increased or decreased at any time at
CGM’s discretion upon written notice to the Partnership. CGM will pay a portion of its brokerage
commissions to other properly registered selling agents and to financial advisors who have sold
Redeemable Units. The Partnership directly and through its investment in the Funds will pay all
clearing fees. In addition, CGM will pay the Partnership interest on 100% of the average daily
equity maintained in cash in the Partnership’s (or the Partnership’s allocable portion of a Fund’s)
brokerage account during each month at a 30-day U.S. Treasury bill rate determined weekly by CGM
based on the average non-competitive yield on 3-month U.S. Treasury bills maturing in 30 days from
the date on which such weekly rate is determined. The
Customer Agreement gives the Partnership the legal right to net unrealized gains and losses. The
Customer Agreement may be terminated upon notice by either party.
(b) Financial Information about Segments. The Partnership’s business consists
of only one segment, speculative trading of commodity interests. The Partnership does not engage in
sales of goods or services. The Partnership’s net income (loss) from operations for the years ended
December 31, 2010, 2009, 2008, 2007 and 2006 are set forth under “Item 6. Selected Financial
Data.” The Partnership’s Capital as of December 31, 2010, was $1,169,565,735.
(c) Narrative Description of Business.
See Paragraphs (a) and (b) above.
(i) through (xii) — Not applicable.
(xiii) — The Partnership has no employees.
(d) Financial Information About Geographic Areas. The Partnership does not engage in
sales of goods or services or own any long-lived assets, and therefore this item is not applicable.
(e) Available Information. The Partnership does not have an Internet address. The
Partnership will provide paper copies of its annual report on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form
10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and any amendments to these reports free of charge upon request.
(f) Reports to Security Holders. Not applicable.
(g) Enforceability of Civil Liabilities Against Foreign Persons. Not applicable.
(h) Smaller Reporting Companies. Not applicable.
4
Item 1A. Risk Factors
As a result of leverage, small changes in the price of the Partnership’s positions may result
in major losses.
The trading of commodity interests is speculative, volatile and involves a high degree of
leverage. A small change in the market price of a commodity interest contract can produce major
losses for the Partnership. Market prices can be influenced by, among other things, changing supply
and demand relationships, governmental, agricultural, commercial and trade programs and policies,
national and international political and economic events, weather and climate conditions, insects
and plant disease, purchases and sales by foreign countries and changing interest rates.
An investor may lose all of their investment.
Due to the speculative nature of trading commodity interests, an investor could lose all of
their investment in the Partnership.
The Partnership will pay substantial fees and expenses regardless of profitability.
Regardless of its trading performance, the Partnership will incur fees and expenses, including
brokerage commissions, management and administrative fees. Substantial incentive fees may be paid to one or
more of the Advisors even if the Partnership experiences a net loss for the full year.
An investor’s ability
to redeem or transfer units is limited.
An investor’s ability to
redeem units is limited and no market exists for the
units.
Conflicts of interest exist.
The Partnership is subject to numerous conflicts of interest including those that arise from
the facts that:
| 1. | The General Partner and the Partnership’s/Funds’ commodity broker are affiliates; | ||
| 2. | Each of the Advisors, the Partnership’s/Funds’ commodity broker and their principals and affiliates may trade in commodity interests for their own accounts; and | ||
| 3. | An investor’s financial advisor will receive ongoing compensation for providing services to the investor’s account. |
Investing in units might not provide the desired diversification of an investor’s overall
portfolio.
The Partnership will not provide any benefit of diversification of an investor’s overall
portfolio unless it is profitable and produces returns that are independent from stock and bond
market returns.
Past performance is no assurance of future results.
The Advisors’ trading strategies may not perform as they have performed in the past. The
Advisors have from time to time incurred substantial losses in trading on behalf of clients.
An investor’s tax liability may exceed cash distributions.
Investors are taxed on their share of the Partnership’s income, even though the Partnership
does not intend to make any distributions.
The General Partner may allocate the Partnership’s assets to undisclosed advisors.
5
The General Partner at any time may select and allocate the Partnership’s assets to
undisclosed advisors. Investors may not be advised of such changes in advance. Investors must rely
on the ability of the General Partner to select commodity trading advisors and allocate assets
among them.
Regulatory changes could restrict the Partnership’s operations.
Regulatory changes could adversely affect the Partnership by restricting its markets or
activities, limiting its trading and/or increasing the taxes to which investors are subject.
Pursuant to the mandate of the Dodd-Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, signed
into law on July 21, 2010, the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (“CFTC”) and the Securities and
Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) may promulgate rules to regulate swaps dealers, require that swaps
be traded on an exchange or swap execution facilities, mandate additional reporting and disclosure
requirements and require that derivatives (such as those traded by the Partnership) be moved into
central clearinghouses. These rules, if promulgated, may negatively impact the manner in which
swap contracts are traded and/or settled and limit trading by speculators (such as the Partnership)
in futures and over-the-counter markets.
Speculative position and trading limits may reduce profitability.
The CFTC and U.S. exchanges have established speculative position limits on the maximum net
long or net short positions which any person may hold or control in particular futures and options
on futures. The trading instructions of an advisor may have to be modified, and positions held by
the Partnership may have to be liquidated in order to avoid exceeding these limits. Such
modification or liquidation could adversely affect the operations and profitability of the
Partnership by increasing transaction costs to liquidate positions and foregoing potential profits.
Item 2. Properties.
The Partnership does not own or lease any properties. The General Partner operates out of
facilities provided by MSSB Holdings.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
This section describes the major pending legal proceedings, other than ordinary routine
litigation incidental to the business, to which CGM is a party or to which any of their property is
subject. There are no material legal proceedings pending against the Partnership or the General
Partner.
CGM is a New York corporation with its principal place of business at 388 Greenwich St., New
York, New York 10013. CGM is registered as a broker-dealer and futures commission merchant (“FCM”),
and provides futures brokerage and clearing services for institutional and retail participants in
the futures markets. CGM and its affiliates also provide investment banking and other financial
services for clients worldwide.
There have been no material administrative, civil or criminal actions within the past five
years against CGM or any of its individual principals and no such actions are currently pending,
except as follows.
Credit-Crisis-Related Litigation and Other Matters
Citigroup and CGM continue to
cooperate fully in response to subpoenas and requests for information from the SEC, FINRA, the
Federal Housing Finance Agency, state attorneys general, the Department of Justice and
subdivisions thereof, bank regulators, and other government agencies and authorities,
in connection with various formal and informal inquiries concerning Citigroup’s
subprime and other mortgage-related conduct and business activities, as well as
other business activities affected by the credit crisis. These business activities
include, but are not limited to, Citigroup’s sponsorship, packaging, issuance, marketing,
servicing and underwriting of MBS and CDOs and its origination, sale or other transfer,
servicing, and foreclosure of residential mortgages.
Subprime Mortgage-Related Litigation and Other Matters
The SEC, among other regulators, is investigating Citigroup’s subprime
and other mortgage-related conduct and business activities, as well as other business activities
affected by the credit crisis, including an ongoing inquiry into Citigroup’s
structuring and sale of CDOs. Citigroup is cooperating fully with the
SEC’s inquiries.
On July 29, 2010, the SEC announced the settlement
of an investigation into certain of Citigroup’s 2007 disclosures
concerning its subprime-related business activities. On October 19, 2010, the
United States District Court for the District of Columbia entered a Final Judgment
approving the settlement, pursuant to which Citigroup agreed to pay a $75 million civil
penalty and to maintain certain disclosure policies, practices and procedures for a three-year
period. Additional information relating to this action is publicly available in court filings under
the docket number 10 Civ. 1277 (D.D.C.) (Huvelle, J.).
The Federal Reserve Bank, the OCC and the FDIC, among other federal and state
authorities, are investigating issues related to the conduct of certain mortgage servicing
companies, including Citigroup affiliates, in connection with mortgage foreclosures. Citigroup is
cooperating fully with these inquiries.
Certain of these regulatory matters assert claims for substantial or indeterminate damages.
Some of these matters already have been resolved, either through settlements or court proceedings,
including the complete dismissal of certain complaints or the rejection of certain claims following
hearings.
In the course of its business, CGM, as a major futures commission merchant and broker-dealer,
is a party to various civil actions, claims and routine regulatory investigations and proceedings
that the General Partner believes do not have a material effect on the business of CGM.
Item 4. [Removed and Reserved].
6
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity Related Stockholder Matters and Issuer Purchases
of Equity Securities.
(a) Market Information. The Partnership has issued no stock. There is no public market
for the Redeemable Units.
(b) Holders. The number of holders of Redeemable Units as of December 31, 2010, was
8,252.
(c) Dividends. The
Partnership did not declare a distribution in 2010 or 2009.
The Partnership does not intend to declare distributions in the foreseeable future.
(d) Securities Authorized for Issuance Under Equity Compensation Plans. None.
(e) Performance Graph. Not applicable.
(f) Recent
Sales of Unregistered Securities; Use of Proceeds from Registered Securities. For the twelve months ended December 31,
2010, there were additional subscriptions of 168,713.1893 Redeemable Units totaling $444,557,407
and 1,332.7362 General Partner unit equivalents totaling $3,500,000. For the twelve months ended
December 31, 2009, there were additional subscriptions of 124,540.6216 Redeemable Units totaling
$346,650,226 and 1,661.7798 General Partner unit equivalents totaling $4,500,000. For the twelve
months ended December 31, 2008, there were additional subscriptions of 73,057.0497 Redeemable Units
totaling $175,479,000 and 852.6005 General Partner unit equivalents totaling $1,973,412. The
Redeemable Units were issued in reliance upon applicable exceptions from registration under Section
4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 506 of Regulation D promulgated there
under. The Redeemable units were purchased by accredited investors as described in Regulation D.
Proceeds of net offering were used for the trading of commodity interests including futures
contracts, options, swaps and forward contracts.
(g) Purchases of Equity Securities by the Issuer and Affiliated Purchases.
The following chart sets forth the purchases of Redeemable Units by the Partnership.
| (d) Maximum Number | ||||||||||||||||
| (c) Total Number of | (or Approximate | |||||||||||||||
| Redeemable | Dollar Value) of | |||||||||||||||
| (b) Average | Units Purchased | Redeemable Units | ||||||||||||||
| (a) Total Number of | Price Paid per | as Part of | that May Yet Be | |||||||||||||
| Redeemable | Redeemable | Publicly Announced | Purchased Under the | |||||||||||||
| Period | Units Purchased* | Unit** | Plans or Programs | Plans or Programs | ||||||||||||
October 1,
2010 — October 31,
2010 |
5,860.1836 | $ | 2,689.64 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
November 1, 2010 —
November 30, 2010 |
6,208.7600 | $ | 2,651.12 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
December 1, 2010 —
December 31, 2010 |
4,127.3520 | $ | 2,754.39 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||
| 16,196.2956 | $ | 2,691.37 | ||||||||||||||
| * | Generally, limited partners are permitted to redeem their Redeemable Units as of the end of each month on three business days’ notice to the General Partner. Under certain circumstances, the General Partner can compel redemption, although to date the General Partner has not exercised this right. Purchases of Redeemable Units by the Partnership reflected in the chart above were made in the ordinary course of the Partnership’s business in connection with effecting redemptions for limited partners. | |
| ** | Redemptions of Redeemable Units are effected as of the last day of each month at the net asset value per Redeemable Unit as of that day. |
7
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
Net realized and unrealized trading gains (losses), interest income, net income (loss),
increase (decrease) in net asset value per unit and net asset value per unit for the years ended
December 2010, 2009, 2008, 2007 and 2006 and total assets at December 2010, 2009, 2008,
2007 and 2006 were as follows:
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||||||||||
Net realized and
unrealized trading
gains (losses) and
investments in Funds
net of brokerage
commissions (including
clearing fees) of
$11,840,857,
$7,831,507, $6,766,398,
$6,362,776 and
$6,049,901,
respectively |
$ | 65,843,981 | $ | (17,982,427 | ) | $ | 215,756,539 | $ | 65,513,200 | $ | 28,869,155 | ||||||||
Total interest income |
1,068,707 | 539,835 | 5,823,101 | 14,917,240 | 11,046,038 | ||||||||||||||
| $ | 66,912,688 | $ | (17,442,592 | ) | $ | 221,579,640 | $ | 80,430,440 | $ | 39,915,193 | |||||||||
Net income (loss) |
$ | 33,596,305 | $ | (39,246,801 | ) | $ | 166,805,886 | $ | 63,393,428 | $ | 29,048,211 | ||||||||
Increase (decrease) in
net asset value per
unit |
$ | 61.21 | $ | (143.75 | ) | $ | 704.34 | $ | 304.80 | $ | 216.46 | ||||||||
Net asset value per unit |
$ | 2,754.39 | $ | 2,693.18 | $ | 2,836.93 | $ | 2,132.59 | $ | 1,827.79 | |||||||||
Total
assets |
$ | 1,195,156,405 | $ | 827,864,934 | $ | 685,714,876 | $ | 469,271,467 | $ | 313,156,339 | |||||||||
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of
Operations.
Overview
The Partnership directly and through its investment in the Funds, seeks to achieve substantial
capital appreciation through speculative trading, directly or indirectly, in U.S. and international
markets for currencies, interest rates, stock indices, agricultural and energy products and
precious and base metals. The Partnership may employ futures, options on futures, and forward
contracts in those markets. The Partnership may also enter into swap transactions relating to the
value of crude oil and other energy related products.
The General Partner manages all business of the Partnership. The General Partner has delegated
its responsibility for the investment of the Partnership’s capital to AAA, Willowbridge, and
Winton. The General Partner employs a team of approximately 40 professionals whose primary emphasis
is on attempting to maintain quality control among the Advisors to the partnerships operated or
managed by the General Partner. A full-time staff of due diligence professionals use proprietary
technology and on-site evaluations to monitor new and existing futures money managers. The
accounting and operations staff provide processing of trading activity and reporting to limited
partners and regulatory authorities. In selecting the Advisors for the Partnership, the General
Partner considered past performance, trading style, volatility of markets traded and fee
requirements.
Responsibilities of the General Partner include:
| • | due diligence examinations of the Advisors; | ||
| • | selection, appointment and termination of the Advisors; | ||
| • | negotiation of the Management Agreements; and | ||
| • | monitoring the activity of the Advisors. |
In addition, the General Partner prepares the books and records and provides the
administrative and compliance services that are required by law or regulation, from time to time, in
connection with operation of the Partnership. These services include the preparation of required
books and records and reports to limited partners, government agencies and regulators; computation
of net asset value; calculation of fees; effecting subscriptions, redemptions and limited partner
communications; and preparation of offering documents and sales literature.
8
The General Partner seeks the best prices and services available in its commodity futures
brokerage transactions.
The programs traded by each Advisor on behalf of the Partnership are: AAA — Energy Program —
Futures and Swaps; Willowbridge — Argo; Vulcan, Consolidated Commodities Fundamental and MStrategy
Trading Systems; and Winton — Diversified Program. As of December 31, 2010, the Partnership’s
assets were allocated among the trading Advisors in the following approximate percentages: AAA,
24%, Willowbridge, 30%, and Winton, 46%. The General Partner may modify or terminate the allocation
of assets among trading advisors at any time and may allocate assets to additional advisors at any
time.
AAA Capital Management Advisors, Ltd.
The portion of the Partnership’s assets that are currently allocated to AAA for trading are
not invested in commodity interests directly. AAA’s allocation of the Partnership’s assets is
currently invested in AAA Master. AAA trades AAA Master’s, and thereby the Partnership’s, assets in
accordance with its Energy Program — Futures and Swaps, a proprietary, discretionary trading system.
AAA Master currently trades energy futures contracts and options on energy futures contracts
on domestic and international exchanges, as well as the Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (an index
future comprised of energy and other products) traded on the Chicago Mercantile Exchange. AAA
Master also currently engages in swap transactions involving crude oil and other energy related
products. References herein to energy and energy related products include all of the foregoing.
AAA generally bases its trading decisions on “fundamental” factors, namely supply and demand
for a particular group or type of commodity. AAA attempts to buy undervalued commodities and sell
overvalued commodities, often but not always simultaneously. AAA uses options to attempt either to
reduce or define risks.
AAA is aware of price trends but does not trade upon trends. AAA often takes profits in
positions with specific trends even though that trend may still be intact or perhaps even strong.
AAA occasionally establishes positions that are countertrend.
Effective risk management is a crucial aspect of AAA’s trading program. Account size,
expectation, volatility of the market traded and the nature of other positions taken are all
factors in determining the amount of equity committed to each trade. AAA Master is AAA’s largest
account.
Willowbridge Associates, Inc.
The portion of the Partnership’s assets that are currently allocated to Willowbridge for
trading are invested in commodity interests directly, and is also invested in Willowbridge Master.
Willowbridge trades the Partnership’s assets allocated to it in accordance with its Select
Investment Program, whereby the General Partner determined the initial allocation of the
Partnership’s assets among one or more of Willowbridge’s strategies and may determine subsequent
reallocations (if any). Of the Partnership’s assets allocated to
Willowbridge, 12% is currently
traded using the Vulcan Trading System (“Vulcan”), 12% is currently traded using the Argo Trading
System (“Argo”), 4% is currently traded using Consolidated Commodities Fundamental Trading System
(“CCF”) and 2% is currently traded using MStrategy Trading System (“MStrategy”) each of which is
described below.
For each of these systems, risk is managed on a market by market level as well as on an
overall portfolio level. On the market level, risk is managed primarily by utilizing proprietary
volatility filters. When these filters detect a certain excessive level of volatility in the
markets traded, they will signal that the systems should no longer be trading in the markets in
which the filters have detected excessive volatility. In this way, the systems do not participate
in markets in which there are extremes in market action. On the portfolio level, risk is managed by
utilizing a proprietary portfolio cutback rule. When cumulative profits have reached a certain
level, this rule determines that positions should be halved across the entire portfolio. In this
way, risk is reduced while allowing the systems to continue to participate in the markets, albeit
at a reduced level. After the portfolio has been traded at half, the portfolio cutback rule will
then determine when to increase positions to again trade at the full level.
Vulcan, which commenced trading in 1988, is a computerized technical trading system. It is not
a trend-following system, but does ride a trend when the opportunity arises. Vulcan uses the
concepts of pattern recognition, support/resistance levels, and counter-trend liquidations (as
defined below) in making trading decisions. In effect, Vulcan is more akin to a systematic
technical charting system, as opposed to most computer systems which are based on pure
trend-following calculations.
9
Vulcan is based on general technical trading principles. It applies these principles to a
diversified portfolio of commodities and currencies. Given that the system is based on general
principles, the system parameters used are the same for all items in the portfolio and are not
optimized. In this manner, the Vulcan minimizes the problem of data-fitting.
Argo commenced trading in 1988. Argo essentially incorporates Vulcan’s concepts of pattern
recognition, support/resistance levels and counter-trend liquidations (as defined below) to trade a
portfolio similar to Vulcan. However, Argo has a relatively slower time horizon than Vulcan and
attempts to capture longer-term price moves.
Pattern recognition, support/resistance levels and counter-trend liquidations are defined as
follows:
Pattern recognition is the ability to identify patterns that appear to have acted as
precursors of price advances or declines in the past.
A support level is a previous low—a price level under the current market price at which point
buying interest is expected to be sufficiently strong to overcome selling pressure.
A resistance level is a previous high—a price level over the current market price at which
point selling pressure is expected to overcome buying pressure and a price advance is expected to
be turned back.
A counter-trend liquidation is the closing out of a position after a significant price move on
the assumption that the market is due for a correction.
The Consolidated Commodities program is a trading approach through which Willowbridge’s
founder and principal trader makes discretionary decisions on a diversified portfolio of commodity
interests. These include energies, grains, tropical products, livestock, base metals and precious
metals. The trading decisions are based on reward-to risk expectations derived from the principal’s
experience in analyzing the fundamental outlook for the commodity markets as well as applying
anecdotal information and technical factors.
The MStrategy program is a discretionary trading
approach through which a Willowbridge trading principal uses extensive technical analysis and quantitative methodologies as the foundation
for trading decisions. MStrategy trades a diversified portfolio of exchange-traded futures contracts and options on futures
including commodities, currencies, fixed income and equity indices. There is a special focus on short-term movements, especially with
regard to equity indices trading. The approach combines traditional technical analysis, analogues and divergences with fundamental analysis and
anecdotal information.
Winton Capital Management Limited
The portion of the Partnership’s assets that are currently allocated to Winton for trading are
not invested in commodity interests directly. Winton’s allocation of the Partnership’s assets is
currently invested in Winton Master. Winton trades its Diversified Program on behalf of Winton
Master. The Diversified Program trades approximately 95 futures and forward contracts on U.S. and
non-U.S. exchanges and markets.
Winton employs a fully computerized, technical, trend-following trading system developed by
its principals. This system tracks the daily price movements from these markets around the world,
and carries out certain computations to determine each day how long or short the portfolio should
be in an attempt to maximize profit within a certain range of risk. If rising prices in a
particular market are anticipated, a long position will be established in that market; if prices in
a particular market are expected to fall, a short position in that market will be established.
Technical analysis refers to analysis based on data intrinsic to a market, such as price and
volume. In contrast, fundamental analysis relies on factors external to a market, such as supply
and demand. The Winton Program employs no fundamental factors.
A trend-following system is one that attempts to take advantage of the observable tendency of
the markets to trend, and to tend to make exaggerated movements in both upward and downward
directions as a result of such trends. These exaggerated movements are largely explained as a
result of the influence of crowd psychology or the “herd instinct” among market participants.
A trend-following system does not anticipate a trend. In fact, trend-following systems are
frequently unprofitable for long periods of time in particular markets or market groups, and
occasionally they are unprofitable for periods of more than a year. However, the principals believe
that such an approach will, in the long term, be profitable.
10
Trade selection is not subject to intervention by Winton’s principals and therefore is not
subject to the influences of individual judgment. As a mechanical trading system, the Winton model
embodies all the expert knowledge required to analyze market data and direct trades, thus
eliminating the risk of basing a trading program on one indispensable person. Equally as important
is the fact that mechanical systems can be tested in simulation for long periods of time and the
model’s empirical characteristics can be measured.
The system’s output is rigorously adhered to in trading the portfolio and intentionally no
importance is given to any external or fundamental factors. While it may be seen as unwise to
ignore information of obvious value, such as that pertaining to political or economic developments,
Winton believes that the disadvantage of this approach is far outweighed by the advantage of the
discipline that rigorous adherence to such a system instills. Winton believes that significant
profits may be realized by the Winton system by holding on to positions for much longer than
conventional wisdom would dictate. Winton believes that a trader who pays attention to day-to-day
events could be distracted from the chance of fully capitalizing on such trends.
The Winton system trades in all liquid U.S. and non-U.S. futures and forward contracts.
Forward markets include major currencies and precious and base metals, the latter two categories
being traded on the London Metal Exchange. Winton seeks out new opportunities to add additional
markets to the portfolio, with the goal of increasing the portfolio’s diversification.
Winton believes that taking positions in a variety of unrelated markets will, over time,
decrease system volatility. By employing a sophisticated and systematic method for placing orders
in a wide array of markets, Winton believes that profits can be realized over time.
No assurance can be given that Advisors’ strategies will be successful or that they will
generate profits for the Partnership.
For the period January 1, 2010 through
December 31, 2010, the average allocation by commodity
market sector for each of the Funds was as follows:
CMF Willowbridge Argo Master Fund L.P.
Currencies |
17.8 | % | ||
Energy |
18.7 | % | ||
Grains |
8.9 | % | ||
Interest Rates U.S. |
8.1 | % | ||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
16.7 | % | ||
Livestock |
0.6 | % | ||
Metals |
18.3 | % | ||
Softs |
10.9 | % |
AAA Master Fund LLC
Energy |
100 | % |
CMF Winton Master L.P.
Currencies |
21.0 | % | ||
Energy |
4.7 | % | ||
Grains |
5.3 | % | ||
Interest Rates U.S. |
12.6 | % | ||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
16.1 | % | ||
Livestock |
0.6 | % | ||
Metals |
13.3 | % | ||
Soft |
2.5 | % | ||
Stock Indices |
23.9 | % |
11
For the period January 1, 2010
through December 31, 2010, the average allocation by commodity
market sector for the portion of the Partnership’s assets traded directly by Willowbridge was as follows:
Currencies |
16.0 | % | ||
Energy |
20.3 | % | ||
Grains |
10.0 | % | ||
Interest Rates U.S. |
8.8 | % | ||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
15.6 | % | ||
Livestock |
0.5 | % | ||
Metals |
18.2 | % | ||
Softs |
10.6 | % |
(a) Liquidity.
The Partnership does not engage in sales of goods or services. The Partnership’s assets
are its (i) investment in Funds, (ii) equity in its trading account, consisting of cash and cash
equivalents, net unrealized appreciation on open forward contracts, and (iii) interest receivable.
Because of the low margin deposits normally required in commodity futures trading, relatively small
price movements may result in substantial losses to the Partnership. While substantial losses could
lead to a material decrease in liquidity, no such illiquidity occurred during the year ended
December 31, 2010.
To minimize the risk relating to low margin deposits, the Partnership and Funds follow
certain trading policies, including:
| (i) | The Partnership and Funds invest their assets only in commodity interests that the Advisors believe are traded in sufficient volume to permit ease of taking and liquidating positions. Sufficient volume, in this context, refers to a level of liquidity that the Advisors believe will permit it to enter and exit trades without noticeably moving the market. | ||
| (ii) | An Advisor will not initiate additional positions in any commodity if these positions would result in aggregate positions requiring a margin of more than 66 2/3% of the Partnership’s net assets allocated to that Advisor. | ||
| (iii) | The Partnership and Funds may occasionally accept delivery of a commodity. Unless such delivery is disposed of promptly by retendering the warehouse receipt representing the delivery to the appropriate clearinghouse, the physical commodity position is fully hedged. | ||
| (iv) | The Partnership and Funds do not employ the trading technique commonly known as “pyramiding,” in which the speculator uses unrealized profits on existing positions as margin for the purchases or sale of additional positions in the same or related commodities. | ||
| (v) | The Partnership and Funds do not utilize borrowings other than short-term borrowings if the Partnership/Funds take delivery of any cash commodities. | ||
| (vi) | The Advisors may, from time to time, employ trading strategies such as spreads or straddles on behalf of the Partnership/Funds. “Spreads” and “Straddles” describe commodity futures trading strategies involving the simultaneous buying and selling of futures contracts on the same commodity but involving different delivery dates or markets. | ||
| (vii) | The Partnership/Funds will not permit the churning of its commodity trading account. The term “churning” refers to the practice of entering and exiting trades with a frequency unwarranted by legitimate efforts to profit from the trades, indicating the desire to generate commission income. |
From January 1, 2010 through December 31, 2010, the Partnership’s average margin to equity
ratio (i.e., the percentage of assets on deposit required for margin) was approximately 9.7%. The
foregoing margin to equity ratio takes into account cash held in the Partnership’s name, as well as
the allocable value of the positions and cash held on behalf of the Partnership in the name of the
Funds.
In the normal course of business, the Partnership and the Funds are parties to financial
instruments with off-balance sheet risk, including derivative financial instruments and derivative
commodity instruments. These financial instruments include forwards, futures, options and swaps,
whose values are based upon an underlying asset, index or reference rate, and generally represent
future commitments to exchange currencies or cash balances, or to purchase or sell other financial
instruments at specified terms at specified future dates, or, in the case of derivative commodity
instruments, to have a reasonable possibility to be settled in cash, through physical delivery or
with another financial instrument. These instruments may be traded on an exchange or
over-the-counter (“OTC”). Exchange-traded instruments are standardized and include futures and
certain forwards and option contracts. OTC contracts are negotiated between contracting parties and
include swaps and certain forwards and option contracts. Each of these instruments is
12
subject to various risks similar to those relating to the underlying financial instruments
including market and credit risk. In general, the risks associated with OTC contracts are greater
than those associated with exchange-traded instruments because of the greater risk of default by
the counterparty to an OTC contract.
The risk to the limited partners that have purchased interests in the Partnership is limited
to the amount of their capital contributions to the Partnership and their share of the
Partnership’s assets and undistributed profits. This limited liability is a consequence of the
organization of the Partnership as a limited partnership under applicable law.
Market risk is the potential for changes in the value of the financial instruments traded by
the Partnership and Funds due to market changes, including interest and foreign exchange rate
movements and fluctuations in commodity or security prices. Market risk is directly impacted by the
volatility and liquidity in the markets in which the related underlying assets are traded. The
Partnership and the Funds are exposed to a market risk equal to the value of futures and forward
contracts purchased and unlimited liability on such contracts sold short.
Credit risk is the possibility that a loss may occur due to the failure of a counterparty to
perform according to the terms of a contract. The Partnership and the Funds’ risk of loss in the
event of counterparty default is typically limited to the amounts recognized in the Statements of
Financial Condition and not represented by the contract or notional amounts of the instruments. The
Partnership and the Fund’s risk of loss is reduced through the use of legally enforceable master
netting agreements with counterparties that permit the Partnership and the Funds to offset
unrealized gains and losses and other assets and liabilities with such counterparties upon the
occurrence of certain events. The Partnership and the Funds have credit risk and concentration risk
because the sole counterparty or broker with respect to the Partnership and the Funds assets is CGM
or a CGM affiliate. Credit risk with respect to exchange traded instruments is reduced to the
extent that, through CGM, the Partnership and the Fund’s counterparty is an exchange or clearing
organization.
As both a buyer and seller of options, the Partnership/Funds pay or receive a premium at the
outset and then bear the risk of unfavorable changes in the price of the contract underlying the
option. Written options expose the Partnership/Funds to potentially unlimited liability; for
purchased options the risk of loss is limited to the premiums paid. Certain written put options
permit cash settlement and do not require the option holder to own the reference asset. The
Partnership/Funds do not consider these contracts to be guarantees.
The General Partner/managing member monitors and attempts to control the Partnership’s/Funds’
risk exposure on a daily basis through financial, credit and risk management monitoring systems,
and accordingly, believes that it has effective procedures for evaluating and limiting the credit
and market risks to which the Partnership/Funds may be subject. These monitoring systems generally
allow the General Partner/managing member to statistically analyze actual trading results with risk
adjusted performance indicators and correlation statistics. In addition, on-line monitoring systems
provide account analysis of futures, forwards and options positions by sector, margin requirements,
gain and loss transactions and collateral positions. (See also “Item 8. Financial Statements
and Supplementary Data” for further information on financial instrument risk included in the
notes to financial statements.)
Other than the risks inherent in commodity futures and other derivatives trading, the
Partnership knows of no trends, demands, commitments, events or uncertainties which will result in
or which are reasonably likely to result in the Partnership’s liquidity increasing or decreasing in
any material way. The Limited Partnership Agreement provides that the Partnership shall terminate
under certain circumstances including a decrease in net asset value per Redeemable Unit to less
than $400 as of the close of business on any business day.
(b) Capital Resources.
(i) The Partnership has made no material commitments for capital expenditures.
(ii) The Partnership’s capital consists of the capital contributions of the partners as
increased or decreased by gains or losses on trading and by expenses, interest income, redemptions
of Redeemable Units and distributions of profits, if any. Gains or losses on trading cannot be
predicted. Market movements in commodities are dependent upon fundamental and technical factors
which the Advisors may or may not be able to identify, such as changing supply and demand
relationships, weather, government agricultural, commercial and trade programs and policies,
national and international political and economic events and changes in interest rates. Partnership
expenses consist of, among other things, brokerage commissions, advisory fees and administrative
fees. The level of these
13
expenses is dependent upon trading performance and the level of Net Assets maintained. In
addition, the amount of interest income payable by CGM is dependent upon interest rates over which
the Partnership has no control.
No forecast can be made as to the level of redemptions in any given period. A limited partner
may require the Partnership to redeem their Redeemable Units at the net asset value per Redeemable
Unit as of the last day of any month on three business days notice to the General Partner. There is
no fee charged to limited partners in connection with redemptions. Redemptions generally are funded
out of the Partnership’s cash holdings. For the year ended December 31, 2010, 48,335.2496
Redeemable Units were redeemed totaling $127,874,531. For the year ended December 31, 2009,
52,022.5263 Redeemable Units were redeemed totaling $145,003,724. For the year ended December 31,
2008, 61,071.3615 Redeemable Units were redeemed totaling $155,777,201.
The Partnership continues to offer Redeemable Units at the net asset value per Redeemable Unit
as of the end of each month. For the year ended December 31, 2010, there were additional
subscriptions of 168,713.1893 Redeemable Units totaling $444,557,407 and 1,332.7362 General Partner
unit equivalents totaling $3,500,000. For the year ended December 31, 2009, there were additional
subscriptions of 124,540.6216 Redeemable Units totaling $346,650,226 and 1,661.7798 General Partner
unit equivalents totaling $4,500,000. For the year ended December 31, 2008, there were additional
subscriptions of 73,057.0497 Redeemable Units totaling $175,479,000 and 852.6005 General Partner
unit equivalents totaling $1,973,412.
(c) Results of Operations.
For the year ended December 31, 2010 the net asset value per unit increased 2.3% from
$2,693.18 to $2,754.39. For the year ended December 31, 2009 the net asset value per unit decreased
5.1% from $2,836.93 to $2,693.18. For the year ended December 31, 2008 the net asset value per unit
increased 33.0% from $2,132.59 to $2,836.93.
The Partnership experienced a net trading gain of $77,684,838 before brokerage commissions and
expenses in 2010. Gains were primarily attributable to the Partnership’s/Funds’ trading in
currencies, grains, U.S. and non-U.S. interest rates, metals and softs and were partially offset by
losses in energy, indices and livestock. The net trading gain (or loss) realized from the Partnership and the
Funds is disclosed on page 34 under “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.”
The most significant trading gains were experienced within the
fixed-income sector from long positions in European, U.S.,
and Japanese fixed-income futures. In this sector, prices increased
during the first quarter on concerns that lending restrictions in China,
possible reductions in U.S. stimulus measures, and Greece’s
fiscal struggles might stifle the global economic rebound.
Prices were then pressured higher during the second quarter
amid an unexpected drop in U.S. consumer confidence,
increased regulatory scrutiny of the financial industry,
and the growing European debt crisis. During the third quarter,
prices continued to climb higher due to concern that European
governments may struggle to repay their debt and Chinese
economic growth may be slowing. In the metals markets,
gains were recorded throughout September, October, November,
and December as long futures positions in silver and gold resulted in
additional gains for the metals sector as prices rose amid increased
demand for the precious metals due to a drop in the value of the U.S.
dollar, with silver futures rallying to a 30-year high and
gold prices reaching a new all-time high. Within the currency
markets, gains were achieved primarily during May, September and
December. During May, short positions in the euro versus the U.S.
dollar posted gains as the euro continued to weaken amid concerns
over the Greek debt crisis. During September, long positions in the
Australian dollar versus the U.S. dollar resulted in gains as the value of the Australian
dollar rose against the U.S. dollar amid speculation that the Reserve
Bank of Australia may raise interest rates in October.
During December, gains were achieved due to long positions in the
Australian dollar, Swiss franc, and Japanese yen versus the U.S.
dollar as the value of these currencies rose against the U.S. dollar
after better-than-expected economic data diminished demand for the U.S.
dollar as a “safe-haven”, and spurred speculation that global
growth is gathering momentum, boosting demand for higher-yielding and
commodity-driven currencies
A portion of the Partnership’s gains
for the year was offset by losses recorded in the energy
markets from long futures positions in crude oil and its
related products as prices declined amid speculation that
China’s economic activity and
energy demand may ease. Throughout May, long futures positions in crude
oil and its related products resulted in additional
losses as prices declined on continued worries that Europe’s debt
troubles might slow down the global economic recovery and thereby
weaken energy demand. Losses were also recorded in short
positions in natural gas as prices unexpectedly rallied due to
higher demand for electricity in the summer due to higher than expected temperatures.
The Partnership experienced a net trading loss of $10,150,920 before brokerage commissions and
expenses in 2009. Losses were primarily attributable to the Partnership’s/Funds’ trading in
currencies, grains, indices, U.S. and non-U.S. interest rates, livestock and softs and were
partially offset by gains in energy and metals.
2009 was a volatile year for the financial markets. The U.S. stock market entered 2009 reeling
from the financial turmoil of 2008. The results of the sub-prime fallout, bank bailouts, auto
industry bankruptcies, and capitulating economic data overwhelmed not just stock prices, but fueled
extraordinarily high levels of risk aversion. The market’s recovery was driven by stability in the
banking sector and a rapid recovery in global markets. By mid-year 2009, the market had hit bottom,
in March, banks were seeking to return TARP bailout money and leading indicators were recovering.
The Partnership realized losses as trends were volatile and sensitivity to news shocks and contrary
economic data.
Losses
were realized in trading fixed-income instruments. With the economic backdrop of 2009,
yields started to exhibit asymmetric volatility due to extreme uncertainty prevailing in the longer
time horizon. Encouraged by the continuing efforts of the Obama administration to stabilize the
U.S. economy, the markets finally began to recover a degree of risk-taking confidence in March,
resulting in the reversal of many of the trends that had driven returns in late 2008. Losses were
also taken in trading currencies, primarily in December, as the Japanese yen reversed sharply on
Japanese Prime Minister Yukio Hatoyama’s dissatisfaction over the high value of the Japanese yen. In
agricultural commodities, losses were realized primarily in corn and wheat. Prices of corn and
wheat both unexpectedly rallied in October as cold and wet weather threatened to delay harvest and
concerns arose over the acres likely to be seeded for the new crop. Losses were incurred in sugar after prices hit a 28 year high, which led many
countries to reduce their expected sugar imports.
14
Interest income is earned on 100% of the Partnership’s average daily equity maintained in cash
in the Partnership’s (or the Partnership’s allocable portion of a Fund’s) brokerage account was
earned at a 30-day U.S. Treasury bill rate determined weekly by CGM based on the average
non-competitive yield on 3-month U.S. Treasury bills maturing in 30 days from the date on which
such weekly rate is determined. Interest income for the three and twelve months ended December 31,
2010 increased by $272,685 and $528,872, respectively as compared to the corresponding periods in
2009. The increase in interest income is primarily due to higher average daily equity maintained in
cash for the Partnership during the three and twelve months ended December 31, 2010, as compared to
the corresponding periods in 2009. Interest earned by the Partnership will increase the net asset
value of the Partnership. The amount of interest income earned by the Partnership depends on the
average daily equity in the Partnership’s and the Fund’s accounts and upon interest rates over
which neither the Partnership nor CGM has control.
Brokerage commissions are based on the number of trades executed by the Advisors. Accordingly,
they must be compared in relation to the number of trades executed during the period. Brokerage
commissions and fees for the three and twelve months ended December 31, 2010 increased by
$367,976 and $4,009,350, respectively, as compared to the corresponding periods in 2009. The
increase in brokerage commissions and fees is primarily due to an increase in the number of trades
during the three and twelve months ended December 31, 2010, as compared to the corresponding
periods in 2009.
Management fees are calculated as a percentage of the Partnership’s net asset value as of the
end of each month and are affected by trading performance, subscriptions and redemptions. Management
fees for the three and twelve months ended December 31, 2010,
increased by $1,387,196 and $5,027,236,
respectively, as compared to the corresponding periods in 2009. The increase in management fees is
due to an increase in average net assets for the three and twelve months ended December 31, 2010,
as compared to the corresponding periods in 2009.
Administrative fees are paid to the General Partner for administering the business and affairs
of the Partnership, These fees are calculated as a percentage of the Partnership’s net asset value
as of the end of each month and are affected by trading performance, subscriptions and redemptions.
Administrative fees for the three and twelve months ended
December 31, 2010 increased by $423,505 and $1,510,175, respectively, as compared to the corresponding periods in 2009. The increase in
administrative fees is due to an increase in average net assets during the three and twelve months
ended December 31, 2010, as compared to the corresponding periods in 2009.
Incentive fees are based on the new trading profits generated by the Advisor at the end of the
year as defined in the management agreements between the Partnership, the General Partner and each
Advisor. Trading performance for the three and twelve months ended December 31, 2010 resulted in
incentive fees of $4,494,823 and $8,890,045, respectively. There were
no incentive fees earned for the three months ended December 31,
2009. Trading performance for the twelve months ended December
31, 2009 resulted in incentive fees of $4,138,088.
The Partnership pays professional fees, which generally include legal and accounting expenses.
Professional fees for the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009 were $708,692 and $495,318,
respectively.
The Partnership pays other expenses, which generally include filing, reporting and data
processing fees. Other expenses for the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009 were $120,545 and
$111,113, respectively.
The Partnership experienced a net trading gain of $222,522,937 before brokerage commissions
and expenses in 2008. Gains were primarily attributable to the Partnership’s/Funds’ trading in
currencies, energy, grains, indices, U.S. and non-U.S. interest rates, livestock, lumber and metals
and were partially offset by losses in softs.
In 2008, the liquidity crisis that began in 2007 rapidly spread to all corners of the globe,
significantly pushing down global economic growth and presenting the U.S. economy with the hardest
challenges since the Great Depression. During the year, the world’s credit markets virtually seized
up, commodity prices plunged and most major equity indices declined dramatically, while some of the
largest U.S. financial institutions were under pressure. Faced with unprecedented rapid
deterioration in economic data and outlook, and fearing a snowball adverse effect of the credit
crunch, global central banks reacted with aggressive campaigns of interest rate cuts and
coordinated capital injections. As the markets re-priced the cost of risk, several strong trends
emerged. The Partnership strongly capitalized on the trends and was profitable in almost every
sector.
15
Profits were primarily realized from trading in energy, fixed income, and currency. The
Partnership realized most of the profits in the energy sector by capturing both the bullish and the
bearish trends. In the earlier part of the year, crude oil pushed towards a historic high of $147
per barrel and in the latter part, the trend suddenly reversed and a strong negative trend emerged
with crude oil dropping to about $32 per barrel. Natural gas also contributed to profits as prices
plunged from $14 to about $5 per MMBtu. The Partnership was also profitable in interest rates as the
yield on short term notes dropped significantly. Short term U.S. Treasury bills were in such high
demand due to flight-to-quality that the yields had dropped below zero during the year. While the
10-year U.S. Treasury bill yielded on an average between 3.5%-4% most of the year, the yield dropped to 2% in
December. Non-U.S. interest rates also showed tremendous volatility as the rates dropped
precipitously due to the actions of the central banks. The Partnership also benefited from strong
trends that emerged in the currencies and realized gains for the year. The U.S. dollar was relatively
strong compared with most of the other developed economy currencies. The euro was put to its first
major test since its inception. UK, Germany and France continued to show weak growth earlier in the
year and as the situations worsened in the later part of the year, these countries officially
entered a recession. As investors sought U.S. dollar denominated assets for relative safety, the U.S.
dollar emerged stronger relative to other currencies. The Japanese yen remained an exception and showed
extraordinary strength as the carry trade reversed. Slightly offsetting gains were small losses in
soft commodities such as coffee.
In the General Partner’s opinion, the Partnership’s Advisors continue to employ trading
methods consistent with the objectives of the Partnership/Funds. The General Partner/Managing
Member monitors the Advisors’ performance on a daily, weekly, monthly and annual basis to assure
these objectives are met.
Commodity markets are highly volatile. Broad price fluctuations and
rapid inflation increase the risks involved in commodity trading, but also increase the possibility
of profit. The profitability of the Funds and the Partnership depends on the Advisors’ ability to
forecast changes in energy and energy related commodities. Such price changes are influenced by,
among other things, changing supply and demand relationships, weather, governmental, agricultural,
commercial and trade programs and policies, national and international political and economic
events and changes in interest rates. To the extent that the Advisors correctly make such
forecasts, the Funds and the Partnership expect to increase capital through operations.
In allocating the assets of the Partnership among the Advisors, the General Partner considered
past performance, trading style, volatility of markets traded and fee requirements. The General
Partner may modify or terminate the allocation of assets among the Advisors and may allocate assets
to additional advisors at any time. Each Advisors’ percentage allocation and trading program is described in the
“overview” section of this Item 7.
(d) Off-balance Sheet Arrangements. None
(e) Contractual Obligations. None
(f) Operational Risk.
The Partnership is directly exposed to market risk and credit risk, which arise in the normal
course of its business activities. Slightly less direct, but of critical importance, are risks
pertaining to operational and back office support. This is particularly the case in a rapidly
changing and increasingly global environment with increasing transaction volumes and an expansion
in the number and complexity of products in the marketplace.
Such risks include:
Operational/Settlement Risk — the risk of financial and opportunity loss and legal liability
attributable to operational problems, such as inaccurate pricing of transactions, untimely trade
execution, clearance and/or settlement, or the inability to process large volumes of transactions.
The Partnership/Funds are subject to increased risks with respect to its trading activities in
emerging market securities, where clearance, settlement, and custodial risks are often greater than
in more established markets.
Technological Risk — the risk of loss attributable to technological limitations or hardware
failure that constrain the Partnership’s/Funds’ ability to gather, process, and communicate information
efficiently and securely, without interruption, to customers and in the markets where the
Partnership/Funds participates.
16
Legal/Documentation Risk — the risk of loss attributable to deficiencies in the documentation
of transactions (such as trade confirmations) and customer relationships (such as master netting
agreements) or errors that result in noncompliance with applicable legal and regulatory
requirements.
Financial Control Risk — the risk of loss attributable to limitations in financial systems
and controls. Strong financial systems and controls ensure that assets are safeguarded, that
transactions are executed in accordance with management’s authorization, and that financial
information utilized by management and communicated to external parties, including the
Partnership’s Redeemable Unit holders, creditors, and regulators, is free of material errors.
(g) Critical Accounting Policies.
Partnership’s and the Funds’ Investments. All commodity interests held by the Partnership and
the Funds (including derivative financial instruments and derivative commodity instruments) are
held for trading purposes. The commodity interests are recorded on trade date and open contracts
are recorded at fair value (as described below) at the measurement date. Investments in commodity
interests denominated in foreign currencies are translated into U.S. dollars at the exchange rates
prevailing at the measurement date. Gains or losses are realized when contracts are liquidated.
Unrealized gains or losses on open contracts are included as a component of equity in trading
account on the Statements of Financial Condition. Realized gains or losses and any change in net
unrealized gains or losses from the preceding period are reported in the Statements of Income and
Expenses.
Partnership’s and the Funds’ Fair Value Measurements. Fair value is defined as the price that
would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a liability in an orderly transaction
between market participants at the measurement date under current market conditions. The fair value
hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical
assets or liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest priority to fair values derived from unobservable
inputs (Level 3). The level in the fair value hierarchy within which the fair value measurement in
its entirety falls shall be determined based on the lowest level input that is significant to the
fair value measurement in its entirety. Management has concluded that based on available
information in the marketplace, the Partnership’s and the Funds’ Level 1 assets and liabilities are
actively traded.
Accounting
principles generally accepted in the United States of America
(“GAAP”) also requires the need to use judgment in determining if a formerly active market has
become inactive and in determining fair values when the market has become inactive. Management has
concluded that based on available information in the marketplace, there has not been a significant
decrease in the volume and level of activity in the Partnership’s and the Funds’ Level 2 assets and
liabilities.
The Partnership and the Funds will separately present purchases, sales, issuances, and
settlements in their reconciliation of Level 3 fair value measurements (i.e. to present such items
on a gross basis rather than on a net basis), and make disclosures regarding the level of
disaggregation and the inputs and valuation techniques used to measure fair value for measurements
that fall within either Level 2 or Level 3 of the fair value hierarchy as required under GAAP.
The Partnership and the Funds consider prices for exchange-traded commodity futures, forwards
and options contracts to be based on unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets (Level
1). The values of non exchange-traded forwards, swaps and certain options contracts for which
market quotations are not readily available, are priced by broker-dealers who derive fair values
for those assets from observable inputs (Level 2). Investments in funds (other commodity pools)
where there are no other rights or obligations inherent within the ownership interest held by the
Partnership are priced based on the end of the day net asset value (Level 2). The value of the
Partnership’s investment in the Funds reflects its proportional interest in the Funds. As of and for
the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009, the Partnership and the Funds did not hold any
derivative instruments that are priced at fair value using unobservable inputs through the
application of management’s assumptions and internal valuation pricing models (Level 3).
Futures
Contracts. The Partnership and the Funds trade futures contracts
and exchange-cleared
swaps. Exchange-cleared swaps are swaps that are traded as futures. A futures contract is a firm
commitment to buy or sell a specified quantity of investments, currency or a standardized amount of
a deliverable grade commodity, at a specified price on a specified future date, unless the contract
is closed before the delivery date or if the delivery quantity is something where physical delivery
cannot occur (such as the S&P 500 Index), whereby such contract is settled in cash. Payments
(“variation margin”) may be made or received by the Partnership and the Funds each business day,
depending on the daily fluctuations in the value of the underlying contracts, and are recorded as
unrealized gains or losses by the Partnership and the Funds. When the contract is closed, the
Partnership and the Funds record a realized gain or loss equal to the difference between the value
of the contract at the time it was opened and the value at the time it was closed. Transactions in
17
futures contracts require participants to make both initial margin deposits of cash or other
assets and variation margin deposits, through the futures broker, directly with the exchange on
which the contracts are traded. Realized gains (losses) and changes in unrealized gains (losses) on
futures contracts are included in the Statements of Income and Expenses.
Forward Foreign Currency Contracts. Foreign currency contracts are those contracts where the
Funds agrees to receive or deliver a fixed quantity of foreign currency for an agreed-upon price on
an agreed future date. Foreign currency contracts are valued daily, and the Funds’ net equity
therein, representing unrealized gain or loss on the contracts as measured by the difference
between the forward foreign exchange rates at the dates of entry into the contracts and the forward
rates at the reporting date, is included in the Statements of Financial Condition. Realized gains
(losses) and changes in unrealized gains (losses) on foreign currency contracts are recognized in
the period in which the contract is closed or the changes occur, respectively and are included in
the Statements of Income and Expenses.
The Funds do not isolate that portion of the results of operations arising from the effect of
changes in foreign exchange rates on investments from fluctuations from changes in market prices of
investments held. Such fluctuations are included in net gain (loss) on investments in the
Statements of Income and Expenses.
London Metals Exchange Forward Contracts. Metal contracts traded on the London Metals Exchange
(“LME”) represent a firm commitment to buy or sell a specified quantity of aluminum, copper, lead,
nickel, tin or zinc. LME contracts traded by the Partnership and the Funds are cash settled based on prompt dates
published by the LME. Payments (“variation margin”) may be made or received by the Partnership and the Funds each
business day, depending on the daily fluctuations in the value of the underlying contracts, and are
recorded as unrealized gains or losses by the Partnership and the Funds. A contract is considered offset when all long
positions have been matched with a like number of short positions settling on the same prompt date.
When the contract is closed at the prompt date, the Partnership and the Funds record a realized gain or loss equal to
the difference between the value of the contract at the time it was opened and the value at the
time it was closed. Transactions in LME contracts require participants to make both initial margin
deposits of cash or other assets and variation margin deposits, through the broker, directly with
the LME. Realized gains (losses) and changes in unrealized gains (losses) on metal contracts are
included in the Statements of Income and Expenses.
Options. The Partnership and the Funds may purchase and write (sell) both exchange-listed and OTC options on
commodities or financial instruments. An option is a contract allowing, but not requiring, its
holder to buy (call) or sell (put) a specific or standard commodity or financial instrument at a
specified price during a specified time period. The option premium is the total price paid or
received for the option contract. When the Partnership and the Funds write an option, the premium received is recorded
as a liability in the Statements of Financial Condition and marked to market daily. When the Partnership and the Funds
purchase an option, the premium paid is recorded as an asset in the Statements of Financial
Condition and marked to market daily. Realized gains (losses) and changes in unrealized gains
(losses) on options contracts are included in the Statements of Income and Expenses.
Brokerage Commissions. Commission charges to open and close futures and exchange traded swap
contracts are expensed at the time the positions are opened. Commission charges on option contracts
are expensed at the time the position is established and when the option contract is closed.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk
The Partnership/Funds are speculative commodity pools. The market sensitive instruments held
by the Partnership/Funds are acquired for speculative trading purposes, and all or substantially
all of the Partnership’s/Funds’ assets are subject to the risk of trading loss. Unlike an operating
company, the risk of market sensitive instruments is integral, not incidental, to the Partnership’s
main line of business.
The risk to the limited partners that have purchased interests in the Partnership is limited
to the amount of their capital contributions to the Partnership and their share of the
Partnership’s assets and undistributed profits. This limited liability is a consequence of the
organization of the Partnership as a limited partnership under applicable law.
Market movements result in frequent changes in the fair value of the Partnership’s/Funds’ open
positions and, consequently, in its earnings and cash balances. The Partnership’s/Funds’ market
risk is influenced by a wide variety of factors. These primarily include factors which affect
energy price levels, including supply factors and weather conditions, but could also include the
level and volatility
18
of interest rates, exchange rates, equity price levels, the market value of financial
instruments and contracts, the diversification effects among the Partnership’s/Funds’ open
positions and the liquidity of the markets in which it trades.
The Partnership/Funds rapidly acquire and liquidate both long and short positions in a wide
range of different markets. Consequently, it is not possible to predict how a particular future
market scenario will affect performance, and the Partnership’s or a Fund’s past performance is not necessarily
indicative of its future results.
“Value at Risk” is a measure of the maximum amount which the Partnership/Funds could reasonably
be expected to lose in a given market sector. However, the inherent uncertainty of the
Partnership’s/Funds’ speculative trading and the recurrence in the markets traded by the
Partnership/Funds of market movements far exceeding expectations could result in actual trading or
non-trading losses far beyond the indicated Value at Risk or the
Partnership’s/Funds’ experience to date (i.e., “risk of ruin”). In light of the foregoing as well
as the risks and uncertainties intrinsic to all future projections, the inclusion of the
quantification included in this section should not be considered to constitute any assurance or
representation that the Partnership’s/Funds’ losses in any market sector will be limited to Value
at Risk or by the Partnership’s/Funds’ attempts to manage their market risk.
Materiality as used in this section, “Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market
Risk,” is based on an assessment of reasonably possible market movements and the potential losses
caused by such movements, taking into account the leverage, optionality and multiplier features of
the Partnership’s/Funds’ market sensitive instruments.
Quantifying the Partnership’s Trading Value at Risk
The following quantitative disclosures regarding the Partnership’s/Funds’ market risk
exposures contain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the safe harbor from civil
liability provided for such statements by the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995 (set
forth in Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Securities Act”) and Section
21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended (the “Exchange Act”)). All quantitative
disclosures in this section are deemed to be forward-looking statements for purposes of the safe
harbor except for statements of historical fact (such as the terms of particular contracts and the
number of market risk sensitive instruments held during or at the end of the reporting period).
The Partnership’s/Funds’ risk exposure in the various market sectors traded by the Advisors is
quantified below in terms of Value at Risk. Due to the Partnership’s/Funds’ mark-to-market
accounting, any loss in the fair value of the Partnership’s open positions is directly reflected in
the Partnership’s earnings (realized or unrealized) and cash balance.
Exchange maintenance margin
requirements have been used by the Partnership/Funds as the measure of
their Value at Risk. Maintenance margin requirements are set by exchanges to equal or exceed the
maximum losses reasonably expected to be incurred in the fair value of any given contract in
95%—99% of any one-day interval. The maintenance margin levels are established by dealers and
exchanges using historical price studies as well as an assessment of current market volatility
(including the implied volatility of the options on a given futures contract) and economic
fundamentals to provide a probabilistic estimate of the maximum expected near-term one-day price
fluctuation. Maintenance margin has been used rather than the more generally available initial
margin, because initial margin includes a credit risk component which is not relevant to Value at
Risk.
In the case of market sensitive instruments which are not exchange-traded (almost exclusively
currencies in the case of the Partnership/Funds), the margin requirements for the equivalent
futures positions have been used as Value at Risk. In those rare cases in which a
futures-equivalent margin is not available, dealers’ margins have been used.
The fair value of the Partnership’s/Funds’ futures and forward positions does not have any
optionality component. However, the Advisors do trade commodity options. Where this instrument is
a futures contract, the futures margin, and where this instrument is a physical commodity, the
futures-equivalent maintenance margin has been used. This calculation is conservative in that it
assumes that the fair value of an option will decline by the same amount as the fair value of the
underlying instrument, whereas, in fact, the fair values of the options traded by the
Partnership/Funds in almost all cases fluctuate to a lesser extent than those of the underlying
instruments.
In quantifying the Partnership’s/Funds’ Value at Risk, 100% positive correlation in the
different positions held in each market risk category has been assumed. Consequently, the margin
requirements applicable to the open contracts have simply been added to
19
determine each trading category’s aggregate Value at Risk. The diversification effects
resulting from the fact that the Partnership’s positions are rarely, if ever, 100% positively
correlated have not been reflected.
The Partnership’s Trading Value at Risk in Different Market Sectors
Value at Risk tables represent a probabilistic assessment of the risk of loss in market risk
sensitive instruments. With the exception of Willowbridge, the Advisors currently
trade the Partnership’s assets indirectly in master fund managed accounts over which they have been
granted limited authority to make trading decisions. Willowbridge directly trades managed accounts
in the Partnership’s name. The first two trading Value at Risk tables reflect the market sensitive
instruments held by the Partnership directly and through its investment in the Funds. The remaining
trading Value at Risk tables reflect the market sensitive instruments held by the Partnership
directly (i.e., in the managed account in the Partnership’s name traded by Willowbridge) and
indirectly by each Fund separately.
The following tables indicate the trading Value at Risk associated with the Partnership’s open
positions by market category as of December 31, 2010 and 2009. As of December 31, 2010, the
Partnership’s total capitalization was $1,169,565,735.
December 31, 2010
| % of Total | ||||||||
| Market Sector | Value at Risk | Capitalization | ||||||
Currencies |
$ | 8,784,775 | 0.75 | % | ||||
Energy |
20,307,536 | 1.74 | % | |||||
Grains |
5,909,516 | 0.50 | % | |||||
Indices |
9,896,381 | 0.85 | % | |||||
Interest Rates U.S. |
1,998,797 | 0.17 | % | |||||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
4,235,023 | 0.36 | % | |||||
Livestock |
358,716 | 0.03 | % | |||||
Lumber |
26,863 | 0.00 | % * | |||||
Metals |
21,262,991 | 1.82 | % | |||||
Softs |
4,072,438 | 0.35 | % | |||||
Total |
$ | 76,853,036 | 6.57 | % | ||||
* Due to rounding
As of December 31, 2009, the Partnership’s total capitalization was $815,786,554.
December 31, 2009
| % of Total | ||||||||
| Market Sector | Value at Risk | Capitalization | ||||||
Currencies |
$ | 7,775,289 | 0.95 | % | ||||
Energy |
34,037,491 | 4.17 | % | |||||
Grains |
1,725,521 | 0.21 | % | |||||
Indices |
8,476,985 | 1.04 | % | |||||
Interest Rates U.S. |
2,269,333 | 0.28 | % | |||||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
5,514,333 | 0.68 | % | |||||
Livestock |
153,968 | 0.02 | % | |||||
Metals |
6,828,589 | 0.84 | % | |||||
Softs |
2,686,366 | 0.33 | % | |||||
Total |
$ | 69,467,875 | 8.52 | % | ||||
20
The following tables indicate the trading Value at Risk associated with the Partnership’s
direct investments and indirect investments in the Funds by market category as of December 31, 2010
and December 31, 2009, the highest and lowest value at any point and the average value during the
years. All open position trading risk exposures have been included in calculating the figures set
forth below. As of December 31, 2010, the Partnership’s Value at Risk for the portion of its assets
that are traded directly by Willowbridge was as follows:
December 31, 2010
| Value at | % of Total | High | Low | Average Value | ||||||||||||||||
| Market Sector | Risk | Capitalization | Value at Risk | Value at Risk | at Risk* | |||||||||||||||
Currencies |
$ | 1,669,739 | 0.15 | % | $ | 3,324,728 | $ | 250,058 | $ | 1,570,799 | ||||||||||
Energy |
1,572,750 | 0.13 | % | 6,356,500 | 56,500 | 2,141,045 | ||||||||||||||
Grains |
1,994,050 | 0.17 | % | 4,029,150 | 228,250 | 1,329,487 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates U.S. |
598,250 | 0.05 | % | 1,911,600 | 102,000 | 691,446 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
719,311 | 0.06 | % | 2,737,047 | 231,820 | 1,207,028 | ||||||||||||||
Livestock |
114,300 | 0.01 | % | 394,450 | 8,000 | 125,388 | ||||||||||||||
Metals |
14,637,181 | 1.25 | % | 15,575,295 | 260,649 | 6,248,420 | ||||||||||||||
Softs |
1,792,700 | 0.15 | % | 2,829,825 | 12,500 | 1,230,146 | ||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 23,098,281 | 1.97 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| * | Annual average of month-end Value at Risk |
As of December 31, 2009, the Partnership’s Value at Risk for the portion of its assets that
are traded directly by Willowbridge was as follows:
December 31, 2009
| Value at | % of Total | High | Low | Average Value | ||||||||||||||||
| Market Sector | Risk | Capitalization | Value at Risk | Value at Risk | at Risk* | |||||||||||||||
Currencies |
$ | 1,913,804 | 0.23 | % | $ | 2,683,324 | $ | 10,800 | $ | 1,252,370 | ||||||||||
Energy |
1,443,000 | 0.18 | % | 4,846,643 | 45,000 | 1,509,395 | ||||||||||||||
Grains |
542,000 | 0.07 | % | 1,484,580 | 209,000 | 666,509 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates U.S. |
590,550 | 0.07 | % | 1,174,500 | 92,400 | 476,078 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
1,209,738 | 0.15 | % | 2,000,036 | 212,338 | 838,430 | ||||||||||||||
Livestock |
67,200 | 0.01 | % | 71,280 | 5,250 | 27,451 | ||||||||||||||
Metals |
1,910,916 | 0.23 | % | 2,273,753 | 23,717 | 1,414,320 | ||||||||||||||
Softs |
595,900 | 0.07 | % | 653,340 | 54,600 | 342,739 | ||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 8,273,108 | 1.01 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| * | Annual average of month-end Value at Risk |
As of December 31, 2010, AAA Master’s total capitalization was $980,369,638. The Partnership owned
approximately 28.7% of AAA Master. As of December 31, 2010, AAA Master’s Value at Risk for its
assets (including the portion of the Partnership’s assets allocated to AAA for trading) was as
follows:
December 31, 2010
| Value at | % of Total | High | Low | Average Value | ||||||||||||||||
| Market Sector | Risk | Capitalization | Value at Risk | Value at Risk | at Risk* | |||||||||||||||
Energy |
$ | 51,518,525 | 5.26 | % | $ | 143,609,109 | $ | 51,518,525 | $ | 94,568,057 | ||||||||||
Lumber |
93,600 | 0.01 | % | 126,800 | 22,200 | 57,792 | ||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 51,612,125 | 5.27 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| * | Annual average of month-end Value at Risk |
21
As of December 31, 2009, AAA Master’s total capitalization was $1,229,195,192. The
Partnership owned approximately 23.2% of AAA Master. As of December 31, 2009, AAA Master’s Value
at Risk for its assets (including the portion of the Partnership’s assets allocated to AAA for
trading) was as follows:
December 31, 2009
| Value at | % of Total | High | Low | Average Value | ||||||||||||||||
| Market Sector | Risk | Capitalization | Value at Risk | Value at Risk | at Risk* | |||||||||||||||
Energy |
$ | 133,905,240 | 10.89 | % | $ | 352,329,038 | $ | 4,405,231 | $ | 166,882,818 | ||||||||||
Total |
$ | 133,905,240 | 10.89 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| * | Annual average of month-end Values at Risk |
As of December 31, 2010, Willowbridge Master’s total capitalization was $216,298,633. The
Partnership owned 70.0% of Willowbridge Master. As of December 31, 2010, Willowbridge Master’s
Value at Risk for its assets (including the portion of the Partnership’s assets allocated to
Willowbridge for trading) was as follows:
December 31, 2010
| Value at | % of Total | High | Low | Average Value | ||||||||||||||||
| Market Sector | Risk | Capitalization | Value at Risk | Value at Risk | at Risk* | |||||||||||||||
Currencies |
$ | 2,232,591 | 1.03 | % | $ | 7,096,121 | $ | 940,854 | 3,547,819 | |||||||||||
Energy |
2,742,900 | 1.27 | % | 6,539,400 | 460,750 | 2,570,821 | ||||||||||||||
Grains |
2,062,750 | 0.95 | % | 3,762,750 | 207,200 | 1,238,276 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates U.S. |
774,255 | 0.36 | % | 3,269,700 | 243,600 | 1,143,161 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
1,908,692 | 0.88 | % | 5,489,653 | 289,858 | 2,700,503 | ||||||||||||||
Livestock |
112,000 | 0.05 | % | 171,200 | 44,800 | 92,018 | ||||||||||||||
Metals |
3,791,000 | 1.75 | % | 5,643,396 | 710,500 | 2,729,785 | ||||||||||||||
Softs |
2,024,400 | 0.94 | % | 3,388,150 | 198,000 | 1,542,246 | ||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 15,648,588 | 7.23 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| * | Annual average of month-end Value at Risk |
As of December 31, 2009, Willowbridge Master’s total capitalization was $231,105,317. The
Partnership owned 58.8% of Willowbridge Master. As of December 31, 2009, Willowbridge Master’s
Value at Risk for its assets (including the portion of the Partnership’s assets allocated to
Willowbridge for trading) was as follows:
December 31, 2009
| Value at | % of Total | High | Low | Average Value | ||||||||||||||||
| Market Sector | Risk | Capitalization | Value at Risk | Value at Risk | at Risk* | |||||||||||||||
Currencies |
$ | 5,974,364 | 2.58 | % | $ | 14,208,480 | $ | 1,008,000 | $ | 7,206,662 | ||||||||||
Energy |
2,116,000 | 0.92 | % | 13,037,019 | 391,000 | 5,515,268 | ||||||||||||||
Grains |
1,058,000 | 0.46 | % | 5,919,480 | 259,875 | 2,320,519 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates U.S. |
1,959,945 | 0.85 | % | 9,939,105 | 280,500 | 2,836,425 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
3,403,449 | 1.47 | % | 14,168,324 | 455,649 | 4,852,602 | ||||||||||||||
Metals |
3,968,558 | 1.72 | % | 8,372,754 | 1,909,575 | 3,799,612 | ||||||||||||||
Softs |
2,725,100 | 1.18 | % | 3,202,100 | 237,900 | 1,531,645 | ||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 21,205,416 | 9.18 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| * | Annual average of month-end Value at Risk |
22
As of December 31, 2010, Winton Master’s total capitalization was $883,719,871. The
Partnership owned 61.9% of Winton Master. As of December 31, 2010, Winton Master’s Value at Risk
for its assets (including the portion of the Partnership’s assets allocated to Winton for trading)
was as follows:
December 31. 2010
| Value at | % of Total | High | Low | Average Value | ||||||||||||||||
| Market Sector | Risk | Capitalization | Value at Risk | Value at Risk | at Risk* | |||||||||||||||
Currencies |
$ | 8,969,665 | 1.01 | % | $ | 13,529,797 | $ | 3,127,432 | $ | 9,858,603 | ||||||||||
Energy |
3,277,769 | 0.37 | % | 4,944,082 | 236,988 | 2,213,508 | ||||||||||||||
Grains |
3,992,796 | 0.45 | % | 4,064,389 | 556,164 | 2,285,359 | ||||||||||||||
Indices |
15,987,691 | 1.81 | % | 22,020,780 | 2,382,812 | 12,021,182 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates U.S. |
1,387,025 | 0.16 | % | 10,348,050 | 275,672 | 5,195,958 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
3,521,207 | 0.40 | % | 13,490,861 | 1,949,046 | 7,347,287 | ||||||||||||||
Livestock |
268,200 | 0.03 | % | 437,350 | 158,080 | 263,226 | ||||||||||||||
Metals |
6,416,979 | 0.73 | % | 8,963,451 | 3,939,668 | 5,989,765 | ||||||||||||||
Softs |
1,393,632 | 0.16 | % | 2,071,953 | 538,916 | 1,029,710 | ||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 45,214,964 | 5.12 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| * | Annual average of month-end Value at Risk |
As of December 31, 2009, Winton Master’s total capitalization was $574,408,313. The
Partnership owned 51.1% of Winton Master. As of December 31, 2009, Winton Master’s Value at Risk
for its assets (including the portion of the Partnership’s assets allocated to Winton for
trading) was as follows:
December 31. 2009
| Value at | % of Total | High | Low | Average Value | ||||||||||||||||
| Market Sector | Risk | Capitalization | Value at Risk | Value at Risk | at Risk* | |||||||||||||||
Currencies |
$ | 4,596,005 | 0.80 | % | $ | 10,700,900 | $ | 3,479,307 | $ | 6,740,750 | ||||||||||
Energy |
556,296 | 0.10 | % | 2,627,998 | 228,335 | 1,092,646 | ||||||||||||||
Grains |
1,098,663 | 0.19 | % | 1,976,399 | 864,083 | 1,388,868 | ||||||||||||||
Indices |
16,589,011 | 2.89 | % | 16,589,011 | 1,261,608 | 6,511,470 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates U.S. |
1,030,011 | 0.18 | % | 6,518,610 | 716,705 | 2,896,261 | ||||||||||||||
Interest Rates Non-U.S. |
4,507,567 | 0.78 | % | 11,661,822 | 2,841,339 | 5,786,393 | ||||||||||||||
Livestock |
169,800 | 0.03 | % | 425,655 | 59,475 | 207,937 | ||||||||||||||
Metals |
5,057,067 | 0.88 | % | 5,057,067 | 849,000 | 2,780,563 | ||||||||||||||
Softs |
955,200 | 0.17 | % | 1,269,508 | 385,375 | 791,384 | ||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 34,559,620 | 6.02 | % | ||||||||||||||||
| * | Annual average of month-end Value at Risk |
Material Limitations on Value at Risk as an Assessment of Market Risk
The face value of the market sector instruments held by the Partnership/Funds is typically
many times the applicable maintenance margin requirement (margin requirements generally range
between 2% and 15% of contract face value) as well as many times the capitalization of the
Partnership/Funds. The magnitude of the Partnership’s/Funds’ open positions creates a “risk of
ruin” not typically found in most other investment vehicles. Because of the size of its positions,
certain market conditions—unusual, but historically recurring from time to time —could cause the
Partnership/Funds to incur severe losses over a short period of time. The foregoing Value at Risk
table—as well as the past performance of the Partnership/Funds—give no indication of this “risk
of ruin.”
23
Non-Trading Risk
The Partnership/Funds have non-trading market risk on their cash balances not needed for
margin. However, these balances (as well as any market risk they represent) are immaterial.
Materiality as used in this section, “Qualitative and Quantitative Disclosures About Market
Risk,” is based on an assessment of reasonably possible market movements and the potential losses
caused by such movements, taking into account the leverage, optionality and multiplier features of
the Partnership’s/Funds’ market sensitive instruments.
Qualitative Disclosures Regarding Primary Trading Risk Exposures
The following qualitative disclosures regarding the Partnership’s/Funds’ market risk exposures
— except for (i) those disclosures that are statements of historical fact and (ii) the
descriptions of how the Partnership manages its primary market risk exposures—constitute
forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of the Securities Act of 1933 and
Section 21E of the Exchange Act. The Partnership’s/Funds’ primary market risk exposures as well as
the strategies used and to be used by the General Partner and the Advisors for managing such
exposures are subject to numerous uncertainties, contingencies and risks, any one of which could
cause the actual results of the Partnership’s/Funds’ risk control to differ materially from the
objectives of such strategies. Government interventions, defaults and expropriations, illiquid
markets, the emergence of dominant fundamental factors, political upheavals, changes in historical
price relationships, an influx of new market participants, increased regulation and many other
factors could result in material losses as well as in material changes to the risk exposures and
the management strategies of the Partnership/Funds. There can be no assurance that the
Partnership’s/Funds’ current market exposure and/or risk management strategies will not change
materially or that any such strategies will be effective in either the short or long term.
Investors must be prepared to lose all or substantially all of their investment in the Partnership.
The following were the primary trading risk exposures of the Partnership as of December 31,
2010, by market sector.
Interest Rates. Interest rate movements directly affect the price of the futures
positions held by the Partnership/Funds and indirectly the value of its stock index and currency
positions. Interest rate movements in one country as well as relative interest rate movements
between countries materially impact the Partnership’s/Funds’ profitability. The
Partnership’s/Funds’ primary interest rate exposure is to interest rate fluctuations in the United
States and the other G-8 countries. However, the Partnership/Funds also take futures positions on
the government debt of smaller nations — e.g., Australia.
Currencies. The Partnership’s/Funds’ currency exposure is to exchange rate
fluctuations, primarily fluctuations which disrupt the historical pricing relationships between
different currencies and currency pairs. These fluctuations are influenced by interest rate changes
as well as political and general economic conditions, the General Partner does not anticipate that
the risk profile of the Partnership’s/Funds’ currency sector will change significantly in the
future. The currency trading Value at Risk figure includes foreign margin amounts converted into
U.S. dollars with an incremental adjustment to reflect the exchange rate risk inherent to the
dollar-based Partnership/Funds in expressing Value at Risk in functional currency other than
dollars.
Metals. The Partnership’s/Funds’ primary metal market exposure is to fluctuations in
the price of copper. Although certain that the Advisors will from time to time trade base metals
such as silver and copper, the principal market exposures of the Partnership/Funds have
consistently been in the precious metals, including gold.
Softs. The Partnership’s/Funds’ primary commodities exposure is to agricultural price
movements which are often directly affected by severe or unexpected weather conditions. Cocoa and
cotton accounted for the bulk of the Partnership’s/Funds’ commodity exposure as of December 31,
2010.
Energy. The Partnership’s/Funds’ primary energy market exposure is to natural gas and
oil price movements, often resulting from political developments in the Middle East. Oil prices can
be volatile and substantial profits and losses have been are expected to continue to be experienced
in this market.
Grains. The Partnership’s/Funds’ commodities exposure is to agricultural price
movements which are often directly affected by severe or unexpected weather conditions.
24
Qualitative Disclosures Regarding Non-Trading Risk Exposure
The following were the only non-trading risk exposures of the Partnership/Funds as of December
31, 2010.
Foreign Currency Balances. The Partnership’s/Funds’ primary foreign currency balances
are in Japanese yen, euro and British pounds. The Advisors regularly convert foreign currency
balances to dollars in an attempt to control the Partnership’s/Funds’ non-trading risk.
Qualitative Disclosures Regarding Means of Managing Risk Exposure
The General Partner/managing member monitors
and attempts to control the Partnership’s/ Funds’ risk
exposure on a daily basis through financial, credit and risk management monitoring systems and
accordingly, believes that it has effective procedures for evaluating and limiting the credit and
market risks to which the Partnership/Funds may be subject.
The General Partner/managing member monitors the Partnership’s/Funds’ performance and the
concentration of its open positions, and consults with the Advisors concerning the
Partnership’s/Funds’ overall risk profile. If the General Partner/managing member felt it necessary
to do so, the General Partner/managing member could require the Advisors to close out positions as well
as enter positions traded on behalf of the Partnership/Funds. However, any such intervention would be a
highly unusual event. The General Partner/managing member primarily relies on the Advisors’ own risk control
policies while maintaining a general supervisory overview of the Partnership’s/Funds’ market risk
exposures.
The Advisors apply their own risk management policies to their trading. The Advisors often
follow diversification guidelines, margin limits and stop loss points to exit a position. The
Advisors’ research of risk management often suggests ongoing modifications to their trading
programs.
As part of the General Partner’s/managing member’s risk management, the General Partner/managing member periodically meets with
the Advisors to discuss its risk management and to look for any material changes to the Advisor’s
portfolio balance and trading techniques. The Advisors are required to notify the General Partner/managing member
of any material changes to its programs.
25
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
ORION FUTURES FUND L.P.
The following financial statements and related items of the Partnership are filed under this Item 8: Oath or Affirmation, Management's Report on Internal
Control over Financial Reporting, Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firms, for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008; Statements of
Financial Condition at December 31, 2010 and 2009; Condensed Schedules of Investments at December 31, 2010 and 2009; Statements of Income and Expenses for the years ended December 31,
2010, 2009, and 2008; Statements of Changes in Partners' Capital for the years ended December 2010, 2009, and 2008; and Notes to Financial Statements. Additional financial
information has been filed as Exhibits to this Form 10-K.
26
To the Limited
Partners of
Orion Futures Fund L.P.
Orion Futures Fund L.P.
To the best of the knowledge and belief of the undersigned, the
information contained herein is accurate and complete.
| By: | Walter Davis |
President and Director
Ceres Managed Futures LLC
General Partner,
Orion Futures Fund L.P.
Ceres Managed Futures LLC
General Partner,
Orion Futures Fund L.P.
Ceres Managed Futures LLC
522 Fifth Avenue
14th Floor
New York, N.Y. 10036
212-296-1999
14th Floor
New York, N.Y. 10036
212-296-1999
27
Management’s
Report on Internal Control Over
Financial Reporting
Financial Reporting
The management of Orion Futures Fund L.P., (the Partnership),
Ceres Managed Futures LLC, is responsible for establishing and
maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting
as defined in Rules 13a – 15(f) and
15d – 15(f) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934
and for our assessment of internal control over financial
reporting. The Partnership’s internal control over
financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable
assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and
the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in
accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the
United States of America. The Partnership’s internal
control over financial reporting includes those policies and
procedures that:
(i) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in
reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the
transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Partnership;
(ii) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are
recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial
statements in accordance with accounting principles generally
accepted in the United States of America, and that receipts and
expenditures of the Partnership are being made only in
accordance with authorizations of management and directors of
the Partnership; and
(iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or
timely detection and correction of unauthorized acquisition, use
or disposition of the Partnership’s assets that could have
a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over
financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements.
Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future
periods are subject to the risk that controls may become
inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree
of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
The management of Orion Futures Fund L.P. has assessed the
effectiveness of the Partnership’s internal control over
financial reporting as of December 31, 2010. In making this
assessment, management used the criteria set forth in the
Internal Control-Integrated Framework issued by the
Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission
(COSO). Based on our assessment, management concluded that the
Partnership maintained effective internal control over financial
reporting as of December 31, 2010 based on the criteria
referred to above.
|

|
|
|
Walter Davis President and Director Ceres Managed Futures LLC General Partner, Orion Futures Fund L.P. |
Jennifer Magro Chief Financial Officer and Director Ceres Managed Futures LLC General Partner, Orion Futures Fund L.P. |
28
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Partners of
Orion Futures Fund L.P.:
Orion Futures Fund L.P.:
We have audited the accompanying statements of financial condition of Orion Futures
Fund L.P. (the “Partnership”), including the condensed schedules of investments, as of
December 31, 2010 and 2009, and the related statements of income and expenses, and
changes in partners’ capital for the years then ended. These financial statements are
the responsibility of the Partnership’s management. Our responsibility is to express an
opinion on these financial statements based on our audits. The financial statements of
the Partnership for the year ended December 31, 2008 were audited by other auditors
whose report, dated March 26, 2009, expressed an unqualified opinion on those
statements.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company
Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and
perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial
statements are free of material misstatement. The Partnership is not required to have,
nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control over financial reporting.
Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial reporting as a basis
for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but not for the
purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Partnership’s internal
control over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also
includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in
the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant
estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement
presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such 2010 and 2009 financial statements present fairly, in all material
respects, the financial position of Orion Futures Fund L.P. as of December 31, 2010 and
2009, and the results of its operations and its changes in partners’ capital for the years
then ended, in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United
States of America.
/s/ Deloitte & Touche LLP
New York, New York
March 23, 2011
New York, New York
March 23, 2011
29
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Partners of
Orion Futures Fund L.P.:
Orion Futures Fund L.P.:
In our opinion, the accompanying statement of income and expenses, and statement of changes in
partners’ capital present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Orion Futures
Fund L.P. (formerly known as Citigroup Orion Futures Fund L.P.) at December 31, 2008 and the
results of its operations for the year then ended in conformity with accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States of America. Also in our opinion, the Partnership
maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of
December 31, 2008, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued
by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). The Partnership’s
management is responsible for these financial statements, for maintaining effective internal
control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control
over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over
Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express opinions on these financial statements and
on the Partnership’s internal control over financial reporting based on our integrated audit. We
conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight
Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain
reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement and
whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material
respects. Our audit of the financial statements included examining, on a test basis, evidence
supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting
principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial
statement presentation. Our audit of internal control over financial reporting included obtaining
an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material
weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal
control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we
considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis
for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable
assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial
statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A
company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (i)
pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the
transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (ii) provide reasonable assurance that
transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance
with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company
are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company;
and (iii) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized
acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the
financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or
detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are
subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that
the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
/s/ PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP
New York, New York
March 26, 2009
March 26, 2009
30
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Statements of Financial Condition
December 31, 2010 and 2009
Statements of Financial Condition
December 31, 2010 and 2009
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
|
Assets:
|
||||||||
|
Investment in Funds, at fair value (Note 5)
|
$ | 981,904,411 | $ | 714,110,396 | ||||
|
Equity in trading account:
|
||||||||
|
Cash (Note 3c)
|
172,054,703 | 100,683,304 | ||||||
|
Cash margin (Note 3c)
|
22,755,878 | 9,063,690 | ||||||
|
Net unrealized appreciation on open futures contracts
|
— | 3,055,807 | ||||||
|
Net unrealized appreciation on open forward contracts
|
13,090,568 | 950,175 | ||||||
|
Options purchased, at fair value (cost $2,992,890 at
December 31, 2010)
|
5,335,173 | — | ||||||
| 1,195,140,733 | 827,863,372 | |||||||
|
Interest receivable (Note 3c)
|
15,672 | 1,562 | ||||||
|
Total assets
|
$ | 1,195,156,405 | $ | 827,864,934 | ||||
|
Liabilities and Partners’ Capital:
|
||||||||
|
Liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Options premium received, at fair value (cost $45,720 at
December 31, 2010)
|
$ | 14,130 | $ | — | ||||
|
Net unrealized depreciation on open futures contracts
|
5,247,768 | — | ||||||
|
Accrued expenses:
|
||||||||
|
Brokerage commissions (Note 3c)
|
2,109,769 | 1,986,385 | ||||||
|
Management fees (Note 3b)
|
1,751,605 | 1,254,174 | ||||||
|
Administrative fees (Note 3a)
|
494,865 | 344,078 | ||||||
|
Incentive fees (Note 3b)
|
4,494,823 | — | ||||||
|
Professional fees
|
90,611 | 79,253 | ||||||
|
Other
|
18,762 | 13,850 | ||||||
|
Redemptions payable (Note 6)
|
11,368,337 | 8,400,640 | ||||||
|
Total liabilities
|
25,590,670 | 12,078,380 | ||||||
|
Partners’ Capital: (Notes 1 and 6)
|
||||||||
|
General Partner, 4,276.0755 and 2,943.3393 unit equivalents
outstanding at December 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively
|
11,777,980 | 7,926,943 | ||||||
|
Limited Partners, 420,343.0232 and 299,965.0835 Redeemable Units
outstanding at December 31, 2010 and 2009, respectively
|
1,157,787,755 | 807,859,611 | ||||||
|
Total partners’ capital
|
1,169,565,735 | 815,786,554 | ||||||
|
Total liabilities and partners’ capital
|
$ | 1,195,156,405 | $ | 827,864,934 | ||||
|
Net asset value per unit
|
$ | 2,754.39 | $ | 2,693.18 | ||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
31
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Condensed Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2010
Condensed Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2010
|
Notional ($)/ |
% of Partners’ |
|||||||||||
| Number of Contracts | Fair Value | Capital | ||||||||||
|
Futures Contracts Purchased
|
||||||||||||
|
Currencies
|
520 | $ | 953,808 | 0.08 | % | |||||||
|
Energy
|
407 | 1,063,222 | 0.09 | |||||||||
|
Grains
|
1,143 | 2,154,944 | 0.18 | |||||||||
|
Interest Rates U.S.
|
380 | 35,017 | 0.00 | * | ||||||||
|
Interest Rates
Non-U.S.
|
238 | 8,350 | 0.00 | * | ||||||||
|
Livestock
|
111 | 95,380 | 0.01 | |||||||||
|
Metals
|
390 | 3,589,090 | 0.31 | |||||||||
|
Softs
|
518 | 2,648,939 | 0.23 | |||||||||
|
Total futures contracts purchased
|
10,548,750 | 0.90 | ||||||||||
|
Futures Contracts Sold
|
||||||||||||
|
Currencies
|
95 | 26,292 | 0.00 | * | ||||||||
|
Grains
|
240 | (123,200 | ) | (0.01 | ) | |||||||
|
Interest Rates U.S.
|
12 | (6,375 | ) | (0.00 | )* | |||||||
|
Interest Rates
Non-U.S.
|
95 | 102,828 | 0.01 | |||||||||
|
Metals
|
1,428 | (15,796,063 | ) | (1.35 | ) | |||||||
|
Total futures contracts sold
|
(15,796,518 | ) | (1.35 | ) | ||||||||
|
Unrealized Appreciation on Open Forward Contracts
|
||||||||||||
|
Metals
|
3,976 | 67,511,368 | 5.77 | |||||||||
|
Total unrealized appreciation on open forward contracts
|
67,511,368 | 5.77 | ||||||||||
|
Unrealized Depreciation on Open Forward Contracts
|
||||||||||||
|
Currencies
|
$ | 75,375 | (313 | ) | 0.00 | * | ||||||
|
Metals
|
3,256 | (54,420,487 | ) | (4.65 | ) | |||||||
|
Total unrealized depreciation on open forward contracts
|
(54,420,800 | ) | (4.65 | ) | ||||||||
|
Options Purchased
|
||||||||||||
|
Call
|
||||||||||||
|
Grains
|
200 | 55,000 | 0.00 | * | ||||||||
|
Metals
|
225 | 5,280,173 | 0.45 | |||||||||
|
Total options purchased
|
5,335,173 | 0.45 | ||||||||||
|
Options Premium Received
|
||||||||||||
|
Call
|
||||||||||||
|
Metals
|
60 | (14,130 | ) | (0.00 | )* | |||||||
|
Total options premium received
|
(14,130 | ) | (0.00 | )* | ||||||||
|
Investment in Funds
|
||||||||||||
|
AAA Master Fund LLC
|
283,238,250 | 24.22 | ||||||||||
|
CMF Willowbridge Argo Master Fund LP
|
151,432,714 | 12.95 | ||||||||||
|
CMF Winton Master Fund LP
|
547,233,447 | 46.79 | ||||||||||
|
Total investment in Funds
|
981,904,411 | 83.96 | ||||||||||
|
Total fair value
|
$ | 995,068,254 | 85.08 | % | ||||||||
| * | Due to rounding |
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
32
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Condensed Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2009
Condensed Schedule of Investments
December 31, 2009
|
Number of |
% of Partners’ |
|||||||||||
| Contracts | Fair Value | Capital | ||||||||||
|
Futures Contracts Purchased
|
||||||||||||
|
Currencies
|
254 | $ | 419,773 | 0.05 | % | |||||||
|
Energy
|
364 | 129,842 | 0.02 | |||||||||
|
Grains
|
402 | 91,185 | 0.01 | |||||||||
|
Interest Rates
Non-U.S.
|
127 | (21,825 | ) | (0.00 | )* | |||||||
|
Livestock
|
84 | 38,440 | 0.00 | * | ||||||||
|
Metals
|
222 | (140,327 | ) | (0.02 | ) | |||||||
|
Softs
|
342 | 560,264 | 0.07 | |||||||||
|
Total futures contracts purchased
|
1,077,352 | 0.13 | ||||||||||
|
Futures Contracts Sold
|
||||||||||||
|
Currencies
|
635 | 1,761,778 | 0.22 | |||||||||
|
Energy
|
5 | 10,950 | 0.00 | * | ||||||||
|
Interest Rates U.S.
|
381 | 438,625 | 0.05 | |||||||||
|
Interest Rates Non-U.S.
|
413 | 61,615 | 0.01 | |||||||||
|
Metals
|
58 | (294,513 | ) | (0.04 | ) | |||||||
|
Total futures contracts sold
|
1,978,455 | 0.24 | ||||||||||
|
Unrealized Appreciation on Open Forward Contracts
|
||||||||||||
|
Metals
|
287 | 3,563,843 | 0.44 | |||||||||
|
Total unrealized appreciation on open forward contracts
|
3,563,843 | 0.44 | ||||||||||
|
Unrealized Depreciation on Open Forward Contracts
|
||||||||||||
|
Metals
|
222 | (2,613,668 | ) | (0.32 | ) | |||||||
|
Total unrealized depreciation on open forward contracts
|
(2,613,668 | ) | (0.32 | ) | ||||||||
|
Investment in Funds
|
||||||||||||
|
AAA Master Fund LLC
|
284,764,800 | 34.91 | ||||||||||
|
CMF Willowbridge Argo Master Fund LP
|
135,945,983 | 16.66 | ||||||||||
|
CMF Winton Master LP
|
293,399,613 | 35.97 | ||||||||||
|
Total investment in Funds
|
714,110,396 | 87.54 | ||||||||||
|
Total fair value
|
$ | 718,116,378 | 88.03 | % | ||||||||
* Due to rounding
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
33
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Statements of Income and Expenses
for the years ended
December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008
Statements of Income and Expenses
for the years ended
December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
|
Income:
|
||||||||||||
|
Net gains (losses) on trading of commodity interests and
investment in Funds:
|
||||||||||||
|
Net realized gains (losses) on closed contracts
|
$ | 14,795,114 | $ | (12,572,238 | ) | $ | 12,376,626 | |||||
|
Net realized gains (losses) on investment in Funds
|
25,334,101 | 81,850,071 | 177,104,310 | |||||||||
|
Change in net unrealized gains (losses) on open contracts
|
6,210,691 | 2,335,509 | 1,079,599 | |||||||||
|
Change in net unrealized gains (losses) on investment in Funds
|
31,344,932 | (81,764,262 | ) | 31,962,402 | ||||||||
|
Gain (loss) from trading, net
|
77,684,838 | (10,150,920 | ) | 222,522,937 | ||||||||
|
Interest income (Note 3c)
|
201,642 | 67,628 | 689,057 | |||||||||
|
Interest income from investment in Funds
|
867,065 | 472,207 | 5,134,044 | |||||||||
|
Total income (loss)
|
78,753,545 | (9,611,085 | ) | 228,346,038 | ||||||||
|
Expenses:
|
||||||||||||
|
Brokerage commissions including clearing fees (Note 3c)
|
11,840,857 | 7,831,507 | 6,766,398 | |||||||||
|
Management fees (Note 3b)
|
18,444,754 | 13,417,518 | 10,925,864 | |||||||||
|
Administrative fees (Note 3a)
|
5,152,347 | 3,642,172 | 2,980,531 | |||||||||
|
Incentive fees (Note 3b)
|
8,890,045 | 4,138,088 | 40,256,797 | |||||||||
|
Professional fees
|
708,692 | 495,318 | 520,640 | |||||||||
|
Other
|
120,545 | 111,113 | 89,922 | |||||||||
|
Total expenses
|
45,157,240 | 29,635,716 | 61,540,152 | |||||||||
|
Net income (loss)
|
$ | 33,596,305 | $ | (39,246,801 | ) | $ | 166,805,886 | |||||
|
Net income (loss) per unit (Note 7)
|
$ | 61.21 | $ | (143.75 | ) | $ | 704.34 | |||||
|
Weighted average units outstanding
|
388,634.8551 | 261,677.7144 | 236,302.6401 | |||||||||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
34
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Statements of Changes in Partners’ Capital
for the years ended
December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008
Statements of Changes in Partners’ Capital
for the years ended
December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008
|
Limited |
General |
|||||||||||
| Partners | Partner | Total | ||||||||||
|
Partners’ Capital at December 31, 2007
|
$ | 459,490,962 | $ | 914,794 | $ | 460,405,756 | ||||||
|
Net income (loss)
|
166,058,397 | 747,489 | 166,805,886 | |||||||||
|
Subscriptions of 73,057.0497 Redeemable Units and 852.6005
General Partner unit equivalents
|
175,479,000 | 1,973,412 | 177,452,412 | |||||||||
|
Redemptions of 61,071.3615 Redeemable Units
|
(155,777,201 | ) | — | (155,777,201 | ) | |||||||
|
Partners’ Capital at December 31, 2008
|
645,251,158 | 3,635,695 | 648,886,853 | |||||||||
|
Net income (loss)
|
(39,038,049 | ) | (208,752 | ) | (39,246,801 | ) | ||||||
|
Subscriptions of 124,540.6216 Redeemable Units and 1,661.7798
General Partner unit equivalents
|
346,650,226 | 4,500,000 | 351,150,226 | |||||||||
|
Redemptions of 52,022.5263 Redeemable Units
|
(145,003,724 | ) | — | (145,003,724 | ) | |||||||
|
Partners’ Capital at December 31, 2009
|
807,859,611 | 7,926,943 | 815,786,554 | |||||||||
|
Net income (loss)
|
33,245,268 | 351,037 | 33,596,305 | |||||||||
|
Subscriptions of 168,713.1893 Redeemable Units and 1,332.7362
General Partner unit equivalents
|
444,557,407 | 3,500,000 | 448,057,407 | |||||||||
|
Redemptions of 48,335.2496
|
(127,874,531 | ) | — | (127,874,531 | ) | |||||||
|
Partners’ Capital at December 31, 2010
|
$ | 1,157,787,755 | $ | 11,777,980 | $ | 1,169,565,735 | ||||||
|
Net asset value per unit:
|
||||||||||||
|
2008:
|
$ | 2,836.93 | ||
|
2009:
|
$ | 2,693.18 | ||
|
2010:
|
$ | 2,754.39 | ||
See accompanying notes to financial statements.
35
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
| 1. | Partnership Organization: |
Orion Futures Fund L.P. (the “Partnership”)
is a limited partnership organized under the partnership laws of
the State of New York on March 22, 1999 to engage,
directly or indirectly, in the speculative trading of a
diversified portfolio of commodity interests including futures
contracts, options, swaps and forward contracts. The sectors
traded include currencies, energy, grains, indices, U.S. and
non-U.S.
interest rates, livestock, lumber, metals and softs. The
commodity interests that are traded by the Partnership and the
Funds (as defined in Note 5 “Investment in
Funds”) are volatile and involve a high degree of
market risk.
Between March 31, 1999 (commencement of the initial
offering period) and June 10, 1999, 10,499 redeemable units
of limited partnership interest (“Redeemable Units”)
were sold at $1,000 per Redeemable Unit. The proceeds of the
initial offering were held in an escrow account until
June 10, 1999, at which time they were turned over to the
Partnership for trading. The Partnership privately and
continuously offers up to 600,000 Redeemable Units to qualified
investors. There is no maximum number of Redeemable Units that
may be sold by the Partnership.
Ceres Managed Futures LLC, a Delaware limited liability company,
acts as the general partner (the “General Partner”)
and commodity pool operator of the Partnership. The General
Partner is wholly owned by Morgan Stanley Smith Barney Holdings
LLC (“MSSB Holdings”). Morgan Stanley, indirectly
through various subsidiaries, owns a majority equity interest in
MSSB Holdings. Citigroup Global Markets Inc. (“CGM”),
the commodity broker and a selling agent for the Partnership,
owns a minority equity interest in MSSB Holdings. Citigroup Inc.
(“Citigroup”), indirectly through various
subsidiaries, wholly owns CGM. Prior to July 31, 2009, the
date as of which MSSB Holdings became its owner, the General
Partner was wholly owned by Citigroup Financial Products Inc., a
wholly owned subsidiary of Citigroup Global Markets Holdings
Inc., the sole owner of which is Citigroup. As of
December 31, 2010, all trading decisions for the
Partnership are made by the Advisors (defined below).
The General Partner and each limited partner share in the
profits and losses of the Partnership in proportion to the
amount of Partnership interest owned by each except that no
limited partner shall be liable for obligations of the
Partnership in excess of its initial capital contribution and
profits, if any, net of distributions.
The Partnership will be liquidated upon the first to occur of
the following: December 31, 2019; the net asset value per
Redeemable Unit decreases to less than $400 per Redeemable Unit
as of a close of any business day; a decline in net assets after
trading commences to less than $1,000,000; or under certain
other circumstances as defined in the Limited Partnership
Agreement of the Partnership (the “Limited Partnership
Agreement”).
| 2. | Accounting Policies: |
| a. | Use of Estimates. The preparation of financial statements and accompanying notes in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities, income and expenses, and related disclosures of contingent assets and liabilities in the financial statements and accompanying notes. As a result, actual results could differ from these estimates. |
36
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
| b. | Statement of Cash Flows. The Partnership is not required to provide a Statement of Cash Flows. | |
| c. | Partnership’s and the Funds’ Investments. All commodity interests held by the Partnership and the Funds (including derivative financial instruments and derivative commodity instruments) are held for trading purposes. The commodity interests are recorded on trade date and open contracts are recorded at fair value (as described below) at the measurement date. Investments in commodity interests denominated in foreign currencies are translated into U.S. dollars at the exchange rates prevailing at the measurement date. Gains or losses are realized when contracts are liquidated. Unrealized gains or losses on open contracts are included as a component of equity in trading account on the Statements of Financial Condition. Realized gains or losses and any change in net unrealized gains or losses from the preceding period are reported in the Statements of Income and Expenses. |
Partnership’s and the Funds’ Fair Value
Measurements. Fair value is defined as the price
that would be received to sell an asset or paid to transfer a
liability in an orderly transaction between market participants
at the measurement date under current market conditions. The
fair value hierarchy gives the highest priority to unadjusted
quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or
liabilities (Level 1) and the lowest priority to fair
values derived from unobservable inputs (Level 3). The
level in the fair value hierarchy within which the fair value
measurement in its entirety falls shall be determined based on
the lowest level input that is significant to the fair value
measurement in its entirety. Management has concluded that based
on available information in the marketplace, the
Partnership’s and the Funds’ Level 1 assets and
liabilities are actively traded.
GAAP also requires the need to use judgment in determining if a
formerly active market has become inactive and in determining
fair values when the market has become inactive. Management has
concluded that based on available information in the
marketplace, that there has not been a significant decrease in
the volume and level of activity in the Partnership’s and
the Funds’ Level 2 assets and liabilities.
The Partnership and the Funds will separately present purchases,
sales, issuances, and settlements in their reconciliation of
Level 3 fair value measurements (i.e. to present such items on a
gross basis rather than on a net basis), and make disclosures
regarding the level of disaggregation and the inputs and
valuation techniques used to measure fair value for measurements
that fall within either Level 2 or Level 3 of the fair value
hierarchy as required under GAAP.
The Partnership and the Funds consider prices for
exchange-traded
commodity futures, forwards and options contracts to be based on
unadjusted quoted prices in active markets for identical assets
(Level 1). The values of non exchange-traded forwards,
swaps and certain options contracts for which market quotations
are not readily available are priced by broker-dealers that
derive fair values for those assets from observable inputs
(Level 2). Investments in funds (other commodity pools)
where there are no other rights or obligations inherent within
the ownership interest held by the Partnership are priced based
on the end of the day net asset value (Level 2). The value
of the Partnership’s investments in the Funds reflects its
proportional interest in the Funds. As of and for the years
ended December 31, 2010 and 2009, the Partnership and the
Funds did not hold any derivative instruments that are priced at
fair value using unobservable inputs through the application of
management’s assumptions and internal valuation pricing
37
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
models (Level 3). The gross presentation of the fair value
of the Partnership’s derivatives by instrument type is
shown in Note 4, “Trading Activities”.
|
Quoted Prices in |
||||||||||||||||
|
Active Markets |
Significant Other |
Significant |
||||||||||||||
|
for Identical |
Observable Inputs |
Unobservable |
||||||||||||||
| 12/31/2010 | Assets (Level 1) | (Level 2) | Inputs (Level 3) | |||||||||||||
|
Assets
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Forwards
|
$ | 13,090,881 | $ | 13,090,881 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
|
Options purchased
|
5,335,173 | 5,335,173 | — | — | ||||||||||||
|
Investment in Funds
|
981,904,411 | — | 981,904,411 | — | ||||||||||||
|
Total assets
|
1,000,330,465 | 18,426,054 | 981,904,411 | — | ||||||||||||
|
Liabilities
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Futures
|
5,247,768 | 5,247,768 | — | — | ||||||||||||
|
Forwards
|
313 | — | 313 | — | ||||||||||||
|
Options premium received
|
14,130 | 14,130 | — | — | ||||||||||||
|
Total liabilities
|
5,262,211 | 5,261,898 | 313 | — | ||||||||||||
|
Total fair value
|
$ | 995,068,254 | $ | 13,164,156 | $ | 981,904,098 | $ | — | ||||||||
|
Quoted Prices in |
||||||||||||||||
|
Active Markets |
Significant Other |
Significant |
||||||||||||||
|
for Identical |
Observable Inputs |
Unobservable |
||||||||||||||
| 12/31/2009 | Assets (Level 1) | (Level 2) | Inputs (Level 3) | |||||||||||||
|
Assets
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Futures
|
$ | 3,055,807 | $ | 3,055,807 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
|
Forwards
|
950,175 | 950,175 | — | — | ||||||||||||
|
Investment in Funds
|
714,110,396 | — | 714,110,396 | — | ||||||||||||
|
Total assets
|
718,116,378 | 4,005,982 | 714,110,396 | — | ||||||||||||
|
Total fair value
|
$ | 718,116,378 | $ | 4,005,982 | $ | 714,110,396 | $ | — | ||||||||
| d. | Futures Contracts. The Partnership and the Funds trade futures contracts and exchange-cleared swaps. Exchange-cleared swaps are swaps that are traded as futures. A futures contract is a firm commitment to buy or sell a specified quantity of investments, currency or a standardized amount of a deliverable grade commodity, at a specified price on a specified future date, unless the contract is closed before the delivery date, or if the delivery quantity is something where physical delivery cannot occur (such as the S&P 500 Index), whereby such contract is settled in cash. Payments (“variation margin”) may be made or received by the Partnership and the Funds each business day, depending on the daily fluctuations in the value of the underlying contracts, and are recorded as unrealized gains or losses by the Partnership and the Funds. When the contract is closed, the Partnership and the Funds record a realized gain or loss equal to the difference between the value of the contract at the time it was opened and the value at the time it was closed. Transactions in futures contracts require participants to make both initial margin deposits of cash or other assets and variation margin deposits, through the futures broker, directly with the exchange on which the contracts are traded. Realized gains (losses) and changes in unrealized gains (losses) on futures contracts are included in the Statements of Income and Expenses. | |
| e. | Forward Foreign Currency Contracts. Foreign currency contracts are those contracts where the Funds agree to receive or deliver a fixed quantity of foreign currency for an agreed-upon price on an agreed future date. Foreign currency contracts are valued daily, and the Funds’ net equity therein, representing unrealized gain or loss on the contracts as measured by the difference between the forward foreign exchange rates at the dates of entry into the contracts and the forward rates at the reporting date, is included in the Statements of Financial Condition. Realized |
38
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
| gains (losses) and changes in unrealized gains (losses) on foreign currency contracts are recognized in the period in which the contract is closed or the changes occur, respectively, and are included in the Statements of Income and Expenses. |
The Funds do not isolate that portion of the results of
operations arising from the effect of changes in foreign
exchange rates on investments from fluctuations from changes in
market prices of investments held. Such fluctuations are
included in net gain (loss) on investments in the Statements of
Income and Expenses.
| f. | London Metals Exchange Forward Contracts. Metal contracts traded on the London Metals Exchange (“LME”) represent a firm commitment to buy or sell a specified quantity of aluminum, copper, lead, nickel, tin or zinc. LME contracts traded by the Partnership and the Funds are cash settled based on prompt dates published by the LME. Payments (“variation margin”) may be made or received by the Partnership and the Funds each business day, depending on the daily fluctuations in the value of the underlying contracts, and are recorded as unrealized gains or losses by the Partnership and the Funds. A contract is considered offset when all long positions have been matched with a like number of short positions settling on the same prompt date. When the contract is closed at the prompt date, the Partnership and the Funds record a realized gain or loss equal to the difference between the value of the contract at the time it was opened and the value at the time it was closed. Transactions in LME contracts require participants to make both initial margin deposits of cash or other assets and variation margin deposits, through the broker, directly with the LME. Realized gains (losses) and changes in unrealized gains (losses) on metal contracts are included in the Statements of Income and Expenses. |
| g. | Options. The Partnership and the Funds may purchase and write (sell) both exchange listed and over-the-counter (“OTC”) options on commodities or financial instruments. An option is a contract allowing, but not requiring, its holder to buy (call) or sell (put) a specific or standard commodity or financial instrument at a specified price during a specified time period. The option premium is the total price paid or received for the option contract. When the Partnership and the Funds write an option, the premium received is recorded as a liability in the Statements of Financial Condition and marked to market daily. When the Partnership and the Funds purchase an option, the premium paid is recorded as an asset in the Statements of Financial Condition and marked to market daily. Realized gains (losses) and changes in unrealized gains (losses) on options contracts are included in the Statements of Income and Expenses. | |
| h. | Brokerage Commissions. Commission charges to open and close futures and exchange traded swap contracts are expensed at the time the positions are opened. Commission charges on option contracts are expensed at the time the position is established and when the option contract is closed. |
| i. | Income Taxes. Income taxes have not been provided as each partner is individually liable for the taxes, if any, on its share of the Partnership’s income and expenses. |
GAAP provides guidance for how uncertain tax positions should be
recognized, measured, presented and disclosed in the financial
statements and requires the evaluation of tax positions taken or
expected to be taken in the course of preparing the
Partnership’s financial statements to determine whether the
tax positions are “more-likely-than-not” to be
sustained by the applicable tax authority. Tax positions with
respect to tax at the Partnership level not deemed to meet the
“more-likely-than-not” threshold would be recorded as
a tax benefit or expense in the current year. The General
Partner has concluded that no provision for income tax is
required in the Partnership’s financial statements.
The Partnership files U.S. federal and various state and
local tax returns. No income tax returns are currently under
examination. Generally, the 2007 through 2010 tax years remain
subject to
39
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
examination by U.S. federal and most state tax authorities.
Management does not believe that there are any uncertain tax
positions that require recognition of a tax liability.
| j. | Subsequent Events. Management of the Partnership evaluates events that occur after the balance sheet date but before financial statements are filed. Management has assessed the subsequent events through the date of filing and determined that there were no subsequent events requiring adjustment of or disclosure in the financial statements. |
| k. | Net Income (loss) per Unit. Net income (loss) per unit is calculated in accordance with investment company guidance. See Note 7, “Financial Highlights”. |
| 3. | Agreements: |
| a. | Limited Partnership Agreement: |
The General Partner administers the business and affairs of the
Partnership including selecting one or more advisors to make
trading decisions for the Partnership. The Partnership pays the
General Partner a monthly administrative fee equal to
1/24
of 1% (0.5% per year) of month-end Net Assets. Month-end Net
Assets, for the purpose of calculating administrative fees are
Net Assets, as defined in the Limited Partnership Agreement,
prior to the reduction of the current month’s incentive fee
accruals, the monthly management fees, the General
Partner’s administrative fee and any redemptions or
distributions as of the end of such month.
| b. | Management Agreement: |
The General Partner, on behalf of the Partnership, has entered
into management agreements (the “Management
Agreement”) with Winton Capital Management Limited
(“Winton”), Willowbridge Associates Inc.
(“Willowbridge”), and AAA Capital Management Advisors,
Ltd. (“AAA”) (each an “Advisor” and
collectively, the “Advisors”), each of which is a
registered commodity trading advisor. Willowbridge trades the
Argo, Vulcan, Consolidated Commodities Fundamental and MStrategy
trading systems for the Partnership. The Advisors are not
affiliated with one another, are not affiliated with the General
Partner or CGM, and are not responsible for the organization or
operation of the Partnership. The Partnership will pay each
Advisor a monthly management fee equal to
1/6
of 1% (2% a year), except for Winton, which is paid a monthly
management fee equal to
1/8
of 1% (1.5% a year), of month-end Net Assets allocated
to each Advisor. Month-end Net Assets, for the purpose of
calculating management fees are Net Assets, as defined in the
Limited Partnership Agreement, prior to the reduction of the
current month’s incentive fee accruals, the monthly
management fees, the General Partner’s administrative fee
and any redemptions or distributions as of the end of such
month. Each Management Agreement may be terminated upon notice
by either party.
In addition, the Partnership is obligated to pay each Advisor an
incentive fee, payable quarterly, equal to 20% of the New
Trading Profits, as defined in each Management Agreement, earned
by each Advisor for the Partnership during each calendar quarter.
In allocating the assets of the Partnership to the Advisors, the
General Partner considers past performance, trading style,
volatility of markets traded and fee requirements. The General
Partner may modify or terminate the allocation of assets to the
Advisors and may allocate the assets to additional advisors at
any time.
| c. | Customer Agreement: |
The Partnership has entered into a customer agreement (the
“Customer Agreement”) which provides that the
Partnership will pay CGM brokerage commissions at $18 per
round turn for futures and forwards transactions, $5 per
round turn for swap transactions and $9 per half turn for
options transactions. Brokerage commissions are inclusive of
applicable floor brokerage. The
40
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
brokerage commissions may be increased or decreased at any time
at CGM’s discretion upon written notice to the Partnership.
CGM will pay a portion of its brokerage commissions to other
properly registered selling agents and to financial advisors who
have sold Redeemable Units. The Partnership directly and through
its investment in the Funds will pay CGM for National Futures
Association fees, as well as exchange, clearing, user and
give-up fees
(collectively the “clearing fees”). All of the
Partnership’s assets not held in the Funds’ accounts
at CGM are deposited in the Partnership’s account at CGM.
The Partnership’s cash is deposited by CGM in segregated
bank accounts to the extent required by Commodity Futures
Trading Commission regulations. At December 31, 2010 and
2009, the amounts of cash held for margin requirements were
$22,755,878 and $9,063,690, respectively. CGM will pay the
Partnership interest on 100% of the average daily equity
maintained in cash in the Partnership’s (or the
Partnership’s allocable portion of a Fund’s) brokerage
account during each month at a
30-day U.S.
Treasury bill rate determined weekly by CGM based on the average
noncompetitive yield on
3-month U.S.
Treasury bills maturing in 30 days from the date on which
such weekly rate is determined. The Customer Agreement may be
terminated upon notice by either party.
| 4. | Trading Activities: |
The Partnership was formed for the purpose of trading contracts
in a variety of commodity interests, including derivative
financial instruments and derivative commodity interests. The
results of the Partnership’s trading activities are shown
in the Statements of Income and Expenses.
The Customer Agreements between the Partnership and CGM and the
Funds and CGM give the Partnership and the Funds, the legal
right to net unrealized gains and losses on open futures and
forward contracts. The Partnership and the Funds net, for
financial reporting purposes, the unrealized gains and losses on
open futures and forward contacts on the Statements of Financial
Condition.
All of the commodity interests owned by the Partnership are held
for trading purposes. All of the commodity interests owned by
the Funds are held for trading purposes. The average number of
futures contracts traded directly by the Partnership for the
years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009 based on a monthly
calculation, were 5,579 and 2,300, respectively. The average
number of metals forward contracts traded directly by the
Partnership for the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009
based on a monthly calculation, were 5,017 and 476,
respectively. The average notional values of currency forward
contracts held directly by the Partnership for the years ended
December 31, 2010 and 2009 based on a monthly calculation,
were $19,374,274 and $11,571,131, respectively. The average
number of options contracts traded directly by the Partnership
for the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009 based on a
monthly calculation, were 435 and 4, respectively. In prior
year, the average contracts and average notional values were
based on a quarterly and not a monthly calculation. The amounts
for the year ended December 31, 2009 have been revised
accordingly.
Brokerage commissions are based on the number of trades executed
by the Advisors.
41
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
The following tables indicate the gross fair values of
derivative instruments of futures, forward and options contracts
as separate assets and liabilities as of December 31, 2010
and 2009.
|
December 31, |
||||
| 2010 | ||||
|
Assets
|
||||
|
Futures Contracts
|
||||
|
Currencies
|
$ | 1,023,400 | ||
|
Energy
|
1,076,962 | |||
|
Grains
|
2,158,741 | |||
|
Interest Rates U.S.
|
35,017 | |||
|
Interest Rates
Non-U.S.
|
113,936 | |||
|
Livestock
|
95,380 | |||
|
Metals
|
3,589,089 | |||
|
Softs
|
2,714,932 | |||
|
Total unrealized appreciation on open futures contracts
|
$ | 10,807,457 | ||
|
Liabilities
|
||||
|
Futures Contracts
|
||||
|
Currencies
|
$ | (43,300 | ) | |
|
Energy
|
(13,740 | ) | ||
|
Grains
|
(126,997 | ) | ||
|
Interest Rates U.S.
|
(6,375 | ) | ||
|
Interest Rates
Non-U.S.
|
(2,758 | ) | ||
|
Metals
|
(15,796,062 | ) | ||
|
Softs
|
(65,993 | ) | ||
|
Total unrealized depreciation on open futures contracts
|
$ | (16,055,225 | ) | |
|
Net unrealized depreciation on open futures contracts
|
$ | (5,247,768 | )* | |
| * | This amount is in “Net unrealized depreciation on open futures contracts” on the Statements of Financial Condition. |
42
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
|
December 31, |
||||
| 2010 | ||||
|
Assets
|
||||
|
Forward Contracts
|
||||
|
Metals
|
$ | 67,511,368 | ||
|
Total unrealized appreciation on open forward contracts
|
$ | 67,511,368 | ||
|
Liabilities
|
||||
|
Forward Contracts
|
||||
|
Currencies
|
$ | (313 | ) | |
|
Metals
|
(54,420,487 | ) | ||
|
Total unrealized depreciation on open forward contracts
|
$ | (54,420,800 | ) | |
|
Net unrealized appreciation on open forward contracts
|
$ | 13,090,568 | ** | |
|
Assets
|
||||
|
Options Purchased
|
||||
|
Grains
|
$ | 55,000 | ||
|
Metals
|
5,280,173 | |||
|
Total options purchased
|
$ | 5,335,173 | *** | |
|
Liabilities
|
||||
|
Options Premium Received
|
||||
|
Metals
|
$ | (14,130 | ) | |
|
Total options premium received
|
$ | (14,130 | )**** | |
| ** | This amount is in “Net unrealized appreciation on open forward contracts” on the Statements of Financial Condition. | |
| *** | This amount is in “Options purchased, at fair value” on the Statements of Financial Condition. | |
| **** | This amount is in “Options premium received, at fair value” on the Statements of Financial Condition. |
43
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
|
December 31, |
||||
| 2009 | ||||
|
Assets
|
||||
|
Futures Contracts
|
||||
|
Currencies
|
$ | 2,181,550 | ||
|
Energy
|
199,794 | |||
|
Grains
|
110,773 | |||
|
Interest Rates U.S.
|
438,625 | |||
|
Interest Rates Non-U.S.
|
210,400 | |||
|
Livestock
|
38,440 | |||
|
Metals
|
181,742 | |||
|
Softs
|
663,038 | |||
|
Total unrealized appreciation on open futures contracts
|
$ | 4,024,362 | ||
|
Liabilities
|
||||
|
Futures Contracts
|
||||
|
Energy
|
$ | (59,002 | ) | |
|
Grains
|
(19,587 | ) | ||
|
Interest Rates Non-U.S.
|
(170,609 | ) | ||
|
Metals
|
(616,583 | ) | ||
|
Softs
|
(102,774 | ) | ||
|
Total unrealized depreciation on open futures contracts
|
$ | (968,555 | ) | |
|
Net unrealized appreciation on open futures contracts
|
$ | 3,055,807 | * | |
|
Assets
|
||||
|
Forward Contracts
|
||||
|
Metals
|
$ | 3,563,843 | ||
|
Total unrealized appreciation on open forward contracts
|
$ | 3,563,843 | ||
|
Liabilities
|
||||
|
Forward Contracts
|
||||
|
Metals
|
$ | (2,613,668 | ) | |
|
Total unrealized depreciation on open forward contracts
|
$ | (2,613,668 | ) | |
|
Net unrealized appreciation on open forward contracts
|
$ | 950,175 | ** | |
| * | This amount is in “Net unrealized appreciation on open futures contracts” on the Statements of Financial Condition. | |
| ** | This amount is in “Net unrealized appreciation on open forward contracts” on the Statements of Financial Condition. |
44
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
The following tables indicate the Partnership’s trading
gains and losses, by market sector, on derivative instruments
for the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009.
|
December 31, 2010 |
December 31, 2009 |
|||||||
|
Sector
|
Gain (loss) from trading | Gain (loss) from trading | ||||||
|
Currencies
|
$ | 8,442,431 | $ | (1,780,147 | ) | |||
|
Energy
|
(18,679,717 | ) | (2,447,142 | ) | ||||
|
Grains
|
7,417,695 | (598,463 | ) | |||||
|
Indices
|
(139,663 | ) | — | |||||
|
Interest Rates U.S.
|
2,310,098 | (2,079,594 | ) | |||||
|
Interest Rates
Non-U.S.
|
6,831,370 | (2,180,445 | ) | |||||
|
Livestock
|
(502,640 | ) | (89,640 | ) | ||||
|
Metals
|
8,737,672 | 1,203,412 | ||||||
|
Softs
|
6,588,559 | (2,264,710 | ) | |||||
|
Total
|
$ | 21,005,805 | $ | (10,236,729 | ) | |||
| 5. | Investments in Funds: |
On September 1, 2001, the assets allocated to AAA for
trading were invested in AAA Master Fund LLC (“AAA
Master”), a limited liability company formed under the
New York Limited Liability Company Law. The Partnership
purchased 5,173.4381 units of AAA Master with cash equal to
$5,173,438. AAA Master was formed in order to permit accounts
managed now or in the future by AAA using the Energy
Program-Futures and Swaps, a proprietary, discretionary trading
system, to invest together in one trading vehicle. The General
Partner is also the managing member of AAA Master. Individual
and pooled accounts currently managed by AAA, including the
Partnership, are permitted to be non-managing members of AAA
Master. The General Partner and AAA believe that trading through
this structure should promote efficiency and economy in the
trading process.
On November 1, 2004, the assets allocated to Winton for
trading were invested in CMF Winton Master L.P. (“Winton
Master”), a limited partnership organized under the
partnership laws of the State of New York. The Partnership
purchased 35,389.8399 units of Winton Master with cash equal to
$33,594,083 and a contribution of open commodity futures and
forward contracts with a fair value of $1,795,757. Winton Master
was formed in order to permit accounts managed now or in the
future by Winton using the Diversified Program, a proprietary,
systematic trading system, to invest together in one trading
vehicle. The General Partner is also the general partner of
Winton Master. Individual and pooled accounts currently managed
by Winton, including the Partnership, are permitted to be
limited partners of Winton Master. The General Partner and
Winton believe that trading through this structure should
promote efficiency and economy in the trading process.
On July 1, 2005, a portion of the assets allocated to
Willowbridge for trading were invested in CMF Willowbridge Argo
Master Fund L.P. (“Willowbridge Master”), a
limited partnership organized under the partnership laws of the
State of New York. The Partnership purchased 33,529.1186 units
of Willowbridge Master with cash equal to $29,866,194, and a
contribution of open commodity futures and forward contracts
with a fair value of $3,662,925. Willowbridge Master was formed
in order to permit commodity pools managed now or in the future
by Willowbridge using the Argo Trading System, a proprietary,
systematic trading system, to invest together in one trading
vehicle. The General Partner is also the general partner of
Willowbridge Master. Individual and pooled accounts currently
managed by Willowbridge, including the Partnership, are
permitted to be limited partners of Willowbridge Master. The
General Partner and Willowbridge believe that trading through
this structure should promote efficiency and economy in the
trading process.
45
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Additional assets allocated to Willowbridge are not invested in
a separate limited partnership established by the General
Partner, but are held and traded by Willowbridge directly in
separate managed accounts in the Partnership’s name.
Willowbridge trades the Partnership’s assets directly
pursuant to its Vulcan Trading System, Consolidated Commodities
Fundamental Trading Program and MStrategy Program. The
Consolidated Commodities Technical Trading Program was
terminated as of October 31, 2010.
The General Partner is not aware of any material changes to the
trading programs discussed above during the year ended
December 31, 2010.
AAA Master’s, Willowbridge Master’s and Winton
Master’s (collectively, the “Funds”) and the
Partnership’s trading of futures, forward, swaps and
options contracts, if applicable, on commodities is done
primarily on U.S. commodity exchanges and foreign commodity
exchanges. The Funds and the Partnership engage in such trading
through commodity brokerage accounts maintained with CGM.
A limited partner/non-managing member may withdraw all or part
of their capital contribution and undistributed profits, if any,
from the Funds in multiples of the net asset value per unit as
of the end of any day (the “Redemption Date”)
after a request for redemption has been made to the General
Partner/managing member at least 3 days in advance of the
Redemption Date. The units are classified as a liability
when the limited partner/non-managing member elect to redeem and
informs the Funds.
Management, administrative and incentive fees are charged at the
Partnership level. All clearing fees are borne by the
Partnership directly and through its investment in the Funds.
All other fees including CGM’s direct brokerage commissions
are charged at the Partnership level.
As of December 31, 2010, the Partnership owned
approximately 28.7% of AAA Master, 61.9% of Winton Master and
70.0% of Willowbridge Master. As of December 31, 2009, the
Partnership owned approximately 23.2% of AAA Master, 51.1% of
Winton Master and 58.8% of Willowbridge Master. It is
AAA’s, Willowbridge’s and Winton’s intention to
continue to invest the assets allocated to each by the
Partnership in AAA Master, Willowbridge Master and Winton
Master, respectively. The performance of the Partnership is
directly affected by the performance of the Funds. Expenses to
investors as a result of investment in the Funds are
approximately the same and redemption rights are not affected.
Summarized information reflecting the total assets, liabilities
and capital for the Funds are shown in the following tables.
| December 31, 2010 | ||||||||||||
| Total Assets | Total Liabilities | Total Capital | ||||||||||
|
AAA Master
|
$ | 1,234,677,140 | $ | 254,307,502 | $ | 980,369,638 | ||||||
|
Willowbridge Master
|
216,360,362 | 61,729 | 216,298,633 | |||||||||
|
Winton Master
|
883,842,483 | 122,612 | 883,719,871 | |||||||||
|
Total
|
$ | 2,334,879,985 | $ | 254,491,843 | $ | 2,080,388,142 | ||||||
| December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||
|
Total |
Total |
Total |
||||||||||
| Assets | Liabilities | Capital | ||||||||||
|
AAA Master
|
$ | 1,632,583,054 | $ | 403,387,862 | $ | 1,229,195,192 | ||||||
|
Willowbridge Master
|
231,147,799 | 42,482 | 231,105,317 | |||||||||
|
Winton Master
|
574,479,690 | 71,377 | 574,408,313 | |||||||||
|
Total
|
$ | 2,438,210,543 | $ | 403,501,721 | $ | 2,034,708,822 | ||||||
46
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Summarized information reflecting the net gain (loss) from
trading, total income (loss) and net income (loss) for the Funds
are shown in the following tables.
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2010 | ||||||||||||
|
Gain (Loss) from |
||||||||||||
| Trading, net | Total income (Loss) | Net income (Loss) | ||||||||||
|
AAA Master
|
$ | (44,917,645 | ) | $ | (44,199,399 | ) | $ | (48,102,394 | ) | |||
|
Willowbridge Master
|
(8,681,294 | ) | (8,453,112 | ) | (8,840,226 | ) | ||||||
|
Winton Master
|
122,196,753 | 122,968,789 | 122,204,611 | |||||||||
|
Total
|
$ | 68,597,814 | $ | 70,316,278 | $ | 65,261,991 | ||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||
|
Gain (Loss) from |
||||||||||||
| Trading, net | Total income (Loss) | Net income (Loss) | ||||||||||
|
AAA Master
|
$ | 154,505,739 | $ | 155,167,589 | $ | 151,195,430 | ||||||
|
Willowbridge Master
|
(42,016,964 | ) | (41,821,187 | ) | (42,198,191 | ) | ||||||
|
Winton Master
|
(25,033,464 | ) | (24,623,815 | ) | (25,021,263 | ) | ||||||
|
Total
|
$ | 87,455,311 | $ | 88,722,587 | $ | 83,975,976 | ||||||
Summarized information reflecting the Partnership’s
investments in, and the operations of, the Funds are shown in
the following tables.
|
% of |
Net |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Partnership’s |
Expenses |
Income |
Investment |
Redemption |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Funds
|
Net Assets | Fair Value | Income (Loss) | Commissions | Other | (loss) | Objective | Permitted | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
For the year ended December 31, 2010
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AAA Master
|
24.22 | % | $ | 283,238,250 | $ | (11,370,085 | ) | $ | 821,888 | $ | 193,207 | $ | (12,385,180 | ) |
Energy Portfolio |
Monthly | ||||||||||||
|
Willowbridge Master
|
12.95 | % | 151,432,714 | (3,111,326 | ) | 185,077 | 67,635 | (3,364,038 | ) |
Commodity Portfolio |
Monthly | |||||||||||||||||
|
Winton Master
|
46.79 | % | 547,233,447 | 72,027,509 | 369,033 | 70,709 | 71,587,767 |
Commodity Portfolio |
Monthly | |||||||||||||||||||
|
Total
|
$ | 981,904,411 | $ | 57,546,098 | $ | 1,375,998 | $ | 331,551 | $ | 55,838,549 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
% of |
Net |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Partnership’s |
Expenses |
Income |
Investment |
Redemption |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Funds
|
Net Assets | Fair Value | Income (Loss) | Commissions | Other | (loss) | Objective | Permitted | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
For the year ended December 31, 2009
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
AAA Master
|
34.91 | % | $ | 284,764,800 | $ | 32,116,575 | $ | 734,680 | $ | 135,448 | $ | 31,246,447 |
Energy Portfolio |
Monthly | ||||||||||||||
|
Willowbridge Master
|
16.66 | % | 135,945,983 | (21,885,805 | ) | 174,549 | 33,695 | (22,094,049 | ) |
Commodity Portfolio |
Monthly | |||||||||||||||||
|
Winton Master
|
35.97 | % | 293,399,613 | (9,672,754 | ) | 150,897 | 25,626 | (9,849,277 | ) |
Commodity Portfolio |
Monthly | |||||||||||||||||
|
Total
|
$ | 714,110,396 | $ | 558,016 | $ | 1,060,126 | $ | 194,769 | $ | (696,879 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| 6. | Subscriptions, Distributions and Redemptions: |
Subscriptions are accepted monthly from investors and they
become limited partners on the first day of the month after
their subscription is processed. Distributions of profits, if
any, will be made at the sole discretion of the General Partner
and at such times as the General Partner may decide. A limited
partner may require the Partnership to redeem their Redeemable
Units at the net asset value per Redeemable Unit as of the last
day of any month on three business days’ notice to the
General Partner. There is no fee charged to limited partners in
connection with redemptions.
47
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
| 7. | Financial Highlights: |
Changes in the net asset value per unit for the years ended
December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 were as follows:
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
|
Net realized and unrealized gains (losses)*
|
$ | 142.91 | $ | (60.42 | ) | $ | 910.82 | |||||
|
Interest income
|
2.70 | 2.15 | 24.80 | |||||||||
|
Expenses**
|
(84.40 | ) | (85.48 | ) | (231.28 | ) | ||||||
|
Increase (decrease) for the year
|
61.21 | (143.75 | ) | 704.34 | ||||||||
|
Net asset value per unit, beginning of year
|
2,693.18 | 2,836.93 | 2,132.59 | |||||||||
|
Net asset value per unit, end of year
|
$ | 2,754.39 | $ | 2,693.18 | $ | 2,836.93 | ||||||
| * | Includes brokerage commissions. | |
| ** | Excludes brokerage commissions. |
| 2010 |
2009
|
2008 | ||||||||||
|
Ratios to average net assets:
|
||||||||||||
|
Net investment income (loss) before incentive fees***
|
(3.5 | )% | (3.5 | )% | (2.7 | )% | ||||||
|
Operating expenses
|
3.6 | % | 3.6 | % | 3.8 | % | ||||||
|
Incentive fees
|
0.9 | % | 0.6 | % | 7.1 | % | ||||||
|
Total expenses
|
4.5 | % | 4.2 | % | 10.9 | % | ||||||
|
Total return:
|
||||||||||||
|
Total return before incentive fees
|
3.1 | % | (4.6 | )% | 41.3 | % | ||||||
|
Incentive fees
|
(0.8 | )% | (0.5 | )% | (8.3 | )% | ||||||
|
Total return after incentive fees
|
2.3 | % | (5.1 | )% | 33.0 | % | ||||||
| *** | Interest income less total expenses. |
The above ratios may vary for individual investors based on the
timing of capital transactions during the year. Additionally,
these ratios are calculated for the limited partner class using
the limited partners’ share of income, expenses and average
net assets.
| 8. | Financial Instrument Risks: |
In the normal course of business, the Partnership and the Funds,
are parties to financial instruments with off-balance sheet
risk, including derivative financial instruments and derivative
commodity instruments. These financial instruments may include
forwards, futures, options and swaps, whose values are based
upon an underlying asset, index, or reference rate, and
generally represent future commitments to exchange currencies or
cash balances, or to purchase or sell other financial
instruments at specific terms at specified future dates, or, in
the case of derivative commodity instruments, to have a
reasonable possibility to be settled in cash, through physical
delivery or with another financial instrument. These instruments
may be traded on an exchange or OTC. Exchange-traded instruments
are standardized and include futures and option contracts. OTC
contracts are negotiated between contracting parties and include
certain forwards and option contracts. Each of these instruments
is subject to various risks similar to those related to the
underlying financial instruments including market and credit
risk. In general, the risks associated with OTC contracts are
greater than those associated with exchange-traded instruments
because of the greater risk of default by the counterparty to an
OTC contract.
The risk to the limited partners that have purchased interests
in the Partnership is limited to the amount of their capital
contributions to the Partnership and their share of the
Partnership’s assets and
48
Orion Futures
Fund L.P.
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
Notes to Financial Statements
December 31, 2010
undistributed profits. This limited liability is a consequence
of the organization of the Partnership as a limited partnership
under applicable law.
Market risk is the potential for changes in the value of the
financial instruments traded by the Partnership/Funds due to
market changes, including interest and foreign exchange rate
movements and fluctuations in commodity or security prices.
Market risk is directly impacted by the volatility and liquidity
in the markets in which the related underlying assets are
traded. The Partnership/Fund is exposed to a market risk equal
to the value of futures and forward contracts purchased and
unlimited liability on such contracts sold short.
Credit risk is the possibility that a loss may occur due to the
failure of a counterparty to perform according to the terms of a
contract. The Partnership’s and the Funds’ risk of
loss in the event of a counterparty default is typically limited
to the amounts recognized in the Statements of Financial
Condition and not represented by the contract or notional
amounts of the instruments. The Partnership’s and the
Funds’ risk of loss is reduced through the use of legally
enforceable master netting agreements with counterparties that
permit the Partnership and the Funds to offset unrealized gains
and losses and other assets and liabilities with such
counterparties upon the occurrence of certain events. The
Partnership and the Funds have credit risk and concentration
risk because the sole counterparty or broker with respect to the
Partnership’s and the Funds’ assets is CGM or a CGM
affiliate. Credit risk with respect to exchange-traded
instruments is reduced to the extent that through CGM, the
Partnership’s and the Funds’ counterparty is an
exchange or clearing organization.
As both a buyer and seller of options, the Partnership/Funds pay
or receive a premium at the outset and then bear the risk of
unfavorable changes in the price of the contract underlying the
option. Written options expose the Partnership/Funds to
potentially unlimited liability; for purchased options the risk
of loss is limited to the premiums paid. Certain written put
options permit cash settlement and do not require the option
holder to own the reference asset. The Partnership/Funds do not
consider these contracts to be guarantees.
The General Partner/managing member monitors and attempts to
control the Partnership’s/Funds’ risk exposure on a
daily basis through financial, credit and risk management
monitoring systems, and accordingly, believes that it has
effective procedures for evaluating and limiting the credit and
market risks to which the Partnership/Funds may be subject.
These monitoring systems generally allow the General
Partner/managing member to statistically analyze actual trading
results with risk-adjusted performance indicators and
correlation statistics. In addition, on line monitoring systems
provide account analysis of futures, forwards and options
positions by sector, margin requirements, gain and loss
transactions and collateral positions.
The majority of these instruments mature within one year of the
inception date. However, due to the nature of the
Partnership’s/Funds’ business, these instruments may
not be held to maturity.
49
Selected unaudited quarterly financial data for the years ended December 31, 2010 and 2009 are summarized below:
| For the period from | For the period from | For the period from | For the period from | |||||||||||||
| October 1, 2010 to | July 1, 2010 to | April 1, 2010 to | January 1, 2010 to | |||||||||||||
| December 31, 2010 | September 30, 2010 | June 30, 2010 | March 31, 2010 | |||||||||||||
Net realized and
unrealized trading
gains (losses) net of
brokerage commissions and
clearing fees including
interest income |
$ | 59,255,667 | $ | 24,896,125 | $ | (5,081,090 | ) | $ | (12,158,014 | ) | ||||||
Net income (loss) |
$ | 47,998,682 | $ | 16,063,446 | $ | (12,991,075 | ) | $ | (17,474,748 | ) | ||||||
Increase (decrease) in
net asset value per unit |
$ | 112.18 | $ | 39.10 | $ | (33.04 | ) | $ | (57.03 | ) | ||||||
| For the period from | For the period from | For the period from | For the period from | |||||||||||||
| October 1, 2009 to | July 1, 2009 to | April 1, 2009 to | January 1, 2009 to | |||||||||||||
| December 31, 2009 | September 30, 2009 | June 30, 2009 | March 31, 2009 | |||||||||||||
Net realized and
unrealized trading
gains (losses) net of
brokerage commissions and
clearing fees including
interest income |
$ | (12,753,163 | ) | $ | (4,432,679 | ) | $ | 7,069,723 | $ | (7,326,473 | ) | |||||
Net income (loss) |
$ | (17,732,212 | ) | $ | (9,949,410 | ) | $ | 2,894,930 | $ | (14,460,109 | ) | |||||
Increase (decrease) in
net asset value per unit |
$ | (56.34 | ) | $ | (37.87 | ) | $ | 11.53 | $ | (61.07 | ) | |||||
50
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements with Accountants on Accounting and Financial
Disclosure.
PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP (“PwC”) was previously the principal accountant for the Partnership
through July 22, 2009. On July 22, 2009, PwC was dismissed as principal accountant and on July 23,
2009, Deloitte & Touche LLP (“Deloitte”) was engaged as the independent registered public
accounting firm. The decision to change accountants was approved by the General Partner of the
Partnership.
In connection with the audit of the fiscal year ended December 31, 2008, and through July 22,
2009, there were no disagreements with PwC, on any matter of accounting principles or practices,
financial statement disclosure, or auditing scope or procedures, which disagreements if not
resolved to their satisfaction would have caused them to make reference thereto in their report on
the financial statements for the corresponding year.
The audit report of PwC on the financial statements of the Partnership as of and
for the year ended December 31, 2008, did not contain any adverse opinion or disclaimer of opinion,
nor was it qualified or modified as to uncertainty, audit scope, or accounting principle.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
The Partnership’s disclosure controls and procedures are designed to ensure that information
required to be disclosed by the Partnership on the reports that it files or submits under the
Securities Exchange Act of 1934 (the “Exchange Act”) is recorded, processed, summarized and reported
within the time periods expected in the Securities and Exchange Commission’s (the “SEC”) rules and
forms. Disclosure controls and procedures include controls and procedures designed to ensure that
information required to be disclosed by the Partnership in the reports it files is accumulated and
communicated to management, including the Chief Executive Officer (“CEO”) and Chief Financial
Officer (“CFO”) of the General Partner, to allow for timely decisions regarding required disclosure
and appropriate SEC filings.
Management is responsible for ensuring that there is an adequate and effective process for
establishing, maintaining and evaluating disclosure controls and procedures for the Partnership’s
external disclosures.
The General Partner’s CEO and CFO have evaluated the effectiveness of the Partnership’s
disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) under the Exchange
Act) as of December 31, 2010 and, based on that evaluation, the General Partner’s CEO and CFO have
concluded that at that date the Partnership’s disclosure controls and procedures were effective.
The Partnership’s internal control over financial reporting is a process under the supervision
of the General Partner’s CEO and CFO to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of
financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP. These
controls include policies and procedures that:
| • | pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Partnership; | ||
| • | provide reasonable assurance that (i) transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with GAAP, and (ii) the Partnership’s receipts are handled and expenditures are made only pursuant to authorizations of the General Partner; and | ||
| • | provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Partnership’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
The report included in “Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.” includes
management’s report on internal control over financial reporting (“Management’s Report”).
There were no changes in the Partnership’s internal control over financial reporting during
the fiscal quarter ended December 31, 2010 that materially affected, or are reasonably likely to
materially affect, the Partnership’s internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B: Other Information. None.
51
PART III
Item 10. Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance.
The
Partnership has no officers, directors or employees and its affairs are managed by its General
Partner. Investment decisions are made by the Advisors.
The officers and directors of the General Partner are Walter Davis (President and Chairman of
the Board of Directors), Jennifer Magro (Chief Financial Officer and Director), Michael McGrath
(Director), Douglas J. Ketterer (Director), Ian Bernstein (Director), Harry Handler (Director),
Patrick T. Egan (Director) and Alper Daglioglu (Director). Each director of the General Partner holds office until the
earlier of his or her death, resignation or removal. Vacancies on the board of directors may be
filled by either (i) the majority vote of the remaining directors or (ii) Morgan Stanley Smith
Barney Holdings LLC, as the sole member of the General Partner. The officers of the General
Partner are designated by the General Partner’s board of directors. Each officer will hold office
until his or her successor is designated and qualified or until his or her death, resignation or
removal.
Walter
Davis, age 46, is President and Chairman of the Board of Directors of the General
Partner (since June 2010). Mr. Davis was registered as an associated person of the General Partner
and listed as a principal in June 2010. Mr. Davis is responsible for the oversight of the General
Partner’s funds and accounts. Prior to the combination of Demeter Management LLC (“Demeter”) and the General Partner
effective December 1, 2010, Mr. Davis served as Chairman of the Board of Directors and President of
Demeter, a registered commodity pool operator. Mr. Davis was a principal and associated person of
Demeter from May 2006 to December 2010 and July 2006 to December 2010, respectively. Mr. Davis was
an associated person of Morgan Stanley DW Inc., a financial services firm, from August 2006 to
April 2007, when, because of the merger of Morgan Stanley DW Inc. into Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated (“MS & Co.”), a global financial
services firm, he became an associated person of MS & Co. (due to the transfer of his original
registration as an associated person of Morgan Stanley DW Inc.). Prior to becoming an associated
person in August 2006, Mr. Davis was responsible for overseeing the sales and marketing of MS &
Co.’s managed futures funds to high net worth and institutional investors on a global basis. Mr.
Davis withdrew as an associated person of MS & Co. in June 2009. Mr. Davis has been an associated
person of Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC since June 2009. Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC is
registered as a broker-dealer with FINRA, an investment adviser with the SEC and a futures
commission merchant with the CFTC. Mr. Davis is a Managing Director of Morgan Stanley Smith Barney
LLC and the Director of Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC’s Managed Futures Department. Prior to
joining Morgan Stanley in September 1999, Mr. Davis worked for Chase Manhattan Bank’s Alternative
Investment Group from January 1992 until September 1999, where his principal duties included
marketing managed futures funds to high net worth investors, as well as developing and structuring
managed futures funds. Throughout his career, Mr. Davis has been involved with the development,
management and marketing of a diverse array of commodity pools, hedge funds and other alternative
investment vehicles. Mr. Davis received an MBA in Finance and International Business from the
Columbia University Graduate School of Business in 1992 and a BA in Economics from the University
of the South in 1987.
Jennifer Magro, age 39, is Chief Financial Officer and Director of the General Partner (since
October 2006 and May 2005, respectively). Ms. Magro was listed as a principal in June 2005. Ms.
Magro served as Vice President and Secretary of the General Partner from August 2001 to December
2010 and June 2010 to December 2010, respectively. She was also a Managing Director of Citi
Alternative Investments (“CAI”), a division of Citigroup that administered its hedge fund and fund
of funds business, and was Chief Operating Officer of CAI’s Hedge Fund Management Group from
October 2006 to July 2009. Ms. Magro is responsible for the financial, administrative and
operational functions of the General Partner. She is also responsible for the accounting and
financial and regulatory reporting of the General Partner’s managed futures funds. From March 1999
to July 2009, Ms. Magro was responsible for the accounting and financial and regulatory reporting
of Citigroup’s managed futures funds. She had similar responsibilities with CAI’s Hedge Fund
Management Group (from October 2006 to July 2009). Prior to joining the General Partner in January
1996, Ms. Magro was employed by Prudential Securities Inc., a securities brokerage services
company, (from July 1994) as a staff accountant whose duties included the calculation of net asset
values for commodity pools and real estate investment products. Ms. Magro received a BS in
Accounting from the State University of New York, Oswego in 1993.
Michael McGrath, age 41, has been a Director of the General Partner since June 2010. Mr.
McGrath was listed as a principal in June 2010. Mr. McGrath was a principal and Director of
Demeter from May 2006 until Demeter’s combination with the General Partner in December 2010. Mr.
McGrath is a Managing Director of Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC and currently serves as the Head
of Alternative Investments for the Global Wealth Management Group of Morgan Stanley Smith Barney
LLC. He also serves on
52
the Management Committee of the Global Wealth Management Group. Prior to his current role,
Mr. McGrath served as the Director of Product Management for the Consulting Services Group in
Morgan Stanley as well as the Chief Operating Officer for Private Wealth Management North America
and Private Wealth Management Latin America (the Americas) and the Director of Product Development
for Morgan Stanley’s Global Wealth Management Group. Mr. McGrath served as a Managing Director of
Morgan Stanley from May 2004 until May 2009, when Mr. McGrath became a Managing Director of Morgan
Stanley Smith Barney LLC. Mr. McGrath joined Morgan Stanley from Nuveen Investments, a publicly
traded investment management company headquartered in Chicago, Illinois, where he worked from July
2001 to May 2004. At Nuveen Investments, Mr. McGrath served as a Managing Director and oversaw the
development of alternative investment products catering to high net worth investors. Mr. McGrath
received his BA degree from Saint Peters College in 1990, and currently serves on the school’s
Board of Regents. He received his MBA in Finance from New York University in 1996.
Douglas J. Ketterer, age 45, has been a Director of the General Partner since December 2010.
Mr. Ketterer was listed as a principal in December 2010. Mr. Ketterer was a principal of Demeter
from October 2003 until Demeter’s combination with the General Partner in December 2010. Mr.
Ketterer is a Managing Director and Head of the U.S. Private Wealth Management Group within Morgan
Stanley Smith Barney LLC. Mr. Ketterer joined MS & Co. in March 1990 and has served in many roles
in the corporate finance/investment banking, asset management, and wealth management divisions of
the firm; most recently as Chief Operating Officer, Wealth Management Group and Head of the
Products Group with responsibility for a number of departments (including, among others, the
Alternative Investments Group, Consulting Services Group, Annuities & Insurance Department and
Retirement & Equity Solutions Group) which offered products and services through MS & Co.’s Global
Wealth Management Group. Mr. Ketterer received his MBA from New York University’s Leonard N. Stern
School of Business and his BS in Finance from the University at Albany’s School of Business.
Ian Bernstein, age 48, is a Director of the General Partner. Mr. Bernstein has been a
Director, and listed as a principal of the General Partner since December 2010. Mr. Bernstein held
various positions, including Managing Director, within the Capital Markets group at Morgan Stanley
DW Inc. from October 1984 to April 2007, when Morgan Stanley DW Inc. was merged into, its
institutional affiliate, MS & Co. and became the Global Wealth Management Division of MS & Co. Mr.
Bernstein first served as a Managing Director with MS & Co. in March 2004, prior to its merger with
Morgan Stanley DW Inc. Since June 1, 2009, Mr. Bernstein has served as a Managing Director of
Capital Markets at Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, a new broker-dealer formed as a result of a
joint venture between Citigroup and Morgan Stanley. The respective retail business of MS & Co. and
Citigroup (formerly known as Smith Barney) was contributed to Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC. Mr.
Bernstein has continued as Managing Director of both Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC, the retail
broker-dealer, and MS & Co., the institutional broker-dealer, up to the present. Mr. Bernstein
received his MBA from New York University’s Leonard N. Stern School of Business in 1988, and his BA
from the University of Buckingham in 1980.
Harry Handler, age 51, has been a Director of the General Partner since December 2010. Mr.
Handler became registered as an associated person of the General Partner and listed as a principal
in December 2010. Mr. Handler was a principal and associated person of Demeter from May 2005 until
Demeter’s combination with the General Partner in December 2010, and from April 2006 until December
2010, respectively. He has been an associate member of the NFA since August 1985. Mr. Handler was
an associated person of Morgan Stanley DW Inc., a financial services firm, from February 1984 to
April 2007, when, because of the merger of Morgan Stanley DW Inc. into MS & Co., he became an
associated person of MS & Co. due to the transfer of his original registration as an associated
person of Morgan Stanley DW Inc. Mr. Handler withdrew as an associated person of MS & Co. in June
2009. Mr. Handler has been an associated person of Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC since June
2009. Mr. Handler serves as an Executive Director at Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC in the Global
Wealth Management Group. Mr. Handler works in the Capital Markets Division and is responsible for
Electronic Equity and Securities Lending. Additionally, Mr. Handler serves as Chairman of the
Global Wealth Management Group’s Best Execution Committee. In his prior position, Mr. Handler was
a Systems Director in Information Technology, in charge of Equity and Fixed Income Trading Systems
along with the Special Products, such as Unit Trusts, Managed Futures, and Annuities. Prior to his
transfer to the Information Technology Area, Mr. Handler managed the Foreign Currency and Precious
Metals Trading Desk of Dean Witter, a financial services firm and predecessor company to Morgan
Stanley, from July 1982 until January 1984. He also held various positions in the Futures Division
where he helped to build the Precious Metals Trading Operation at Dean Witter. Before joining Dean
Witter, Mr. Handler worked at Mocatta Metals, a precious metals trading firm and futures broker
that was sold to Standard Charted Bank in the 1980’s, as an Assistant to the Chairman from March
1980 until June 1982. His roles at Mocatta Metals included positions on the Futures Order Entry
Desk and the Commodities Exchange Trading Floor. Additional work included building a computerized
Futures Trading System and writing a history of the company. Mr. Handler
53
graduated on the Dean’s List from the University of Wisconsin-Madison with a BA degree and a
double major in History and Political Science.
Patrick T. Egan, age 41, has been a Director of the General Partner since December 2010. Mr.
Egan became registered as an associated person of the General Partner and listed as a principal in
December 2010. Mr. Egan has been an associate member of the NFA since December 1997. He has been
an associated person of Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC since November 2010. Mr. Egan was an
associated person of Morgan Stanley DW Inc., a financial services firm, from February 1998 to April
2007, when, because of the merger of Morgan Stanley DW Inc. into MS & Co., he became an associated
person of MS & Co. due to the transfer of his original registration as an associated person of
Morgan Stanley DW Inc. Mr. Egan withdrew as an associated person of MS & Co. in November 2010.
Mr. Egan is an Executive Director at Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC and currently serves as the
Co- Chief Investment Officer for Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC’s Managed Futures Department.
Prior to his current role, Mr. Egan served as the Head of Due Diligence & Manager Research for
Morgan Stanley’s Managed Futures Department from October 2003 until the formation of Morgan Stanley
Smith Barney LLC in June 2009. From March 1993 through September 2003, Mr. Egan was an analyst and
manager within the Managed Futures Department for Morgan Stanley DW Inc., and its predecessor firm,
Dean Witter Reynolds, Inc., a financial services firm, with his primary responsibilities being
dedicated to the product development, due diligence, investment analysis and risk management of the
firm’s commodity pools. Mr. Egan began his career in August 1991, joining Dean Witter
Intercapital, the asset management arm of Dean Witter Reynolds, Inc., until March 1993 when he
joined the firm’s Managed Futures Department. Mr. Egan received a Bachelor of Business
Administration with a concentration in Finance from the University of Notre Dame in May 1991. Mr.
Egan is a former Director to the Managed Funds Association’s Board of Directors, a position he was
elected to by industry peers for two consecutive two-year terms, from November 2004 to October 2006
and November 2006 to October 2008.
Alper Daglioglu, age 33, has been a Director, and listed as a principal of the General Partner
since December 2010. Mr. Daglioglu is an Executive Director at Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC and
the Co-Chief Investment Officer for Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC’s Managed Futures Department.
Mr. Daglioglu also serves on the Alternative Investments Product Review Committee of Morgan Stanley
Smith Barney LLC’s Alternative Investments Group. Prior to his current role, Mr. Daglioglu was a
Senior Analyst at the Product Origination Group within Morgan Stanley Managed Futures Department
from December 2003 until the formation of Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC in June 2009. In
addition to his responsibilities within Managed Futures Department, Mr. Daglioglu was also the lead
investment analyst for Global Macro and Managed Futures strategies within Morgan Stanley Graystone
Research Group from February 2007 to June 2009. Mr. Daglioglu served as a consultant at the
Product Origination Group within Morgan Stanley Managed Futures Department from June 2003 to
November 2003. Mr. Daglioglu received a BS degree in Industrial Engineering from Galatasaray
University in June 2000 and a MBA degree in Finance from the University of Massachusetts-Amherst’s
Isenberg School of Management in May 2003. Mr. Daglioglu was awarded a full merit scholarship and
research assistantship at the Center for International Securities and Derivatives Markets during
his graduate studies. In this capacity, he worked with various major financial institutions in
performance monitoring, asset allocation and statistical analysis projects and specialized on
alternative approaches to risk assessment for hedge funds and managed futures. Mr. Daglioglu wrote
and published numerous research papers on alternative investments. Mr. Daglioglu is a Chartered
Alternative Investment Analyst charterholder.
The Partnership has not adopted a code of ethics that applies to officers because it has no
officers. In addition, the Partnership has not adopted any procedures by which investors may
recommend nominees to the Partnership’s board of directors, and has not established an audit
committee because it has no board of directors.
Item 11. Executive Compensation.
The Partnership has no directors or officers. Its affairs are managed by the General Partner,
which receives compensation for its services, as set forth under “Item 1. Business.” CGM,
an affiliate of the General Partner, is the commodity broker for the Partnership and receives
brokerage commissions for such services, as described under “Item 1. Business.” Brokerage
commissions and clearing fees of $11,840,857 were earned by CGM for the year ended December 31,
2010. Management fees of $18,444,754 were earned by the Advisors for the year ended December 31,
2010. Administrative fees of $5,152,347 were earned by the General Partner for the year ended
December 31, 2010. Incentive fees of $8,890,045 were earned by the Advisors for the year ended
December 31, 2010.
Item 12. Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder
Matters.
(a) Security ownership of certain beneficial owners. As of February 28, 2011, the
Partnership knows of no person who beneficially owns more than five percent (5%) of the Redeemable
Units outstanding.
54
(b) Security ownership of management. Under the terms of the Limited Partnership
Agreement, the Partnership’s affairs are managed by the General Partner.
The following table indicates securities owned by management as of December 31, 2010:
| (3) Amount and | ||||||||||||
| (2) Name of | Nature of | |||||||||||
| Beneficial | Beneficial | (4) Percent of | ||||||||||
| (1) Title of Class | Owner | Ownership | Class | |||||||||
General Partner unit equivalents |
General Partner | 4,276.0755 | 1.1 | % | ||||||||
(c) Changes in control. None.
Item 13.
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
(a) Transactions with related persons. None.
(b) Review, approval or ratification of transactions with related persons. Not applicable.
(c) Promoters and certain control persons.
CGM and the General Partner would be considered promoters for purposes of item 404(d) of
Regulation S-K. The nature and the amounts of compensation each promoter will receive, if any, from
the Partnership are set forth under “Item 1. Business” and “Item 11. Executive
Compensation.”
Item 14. Principal Accountant Fees and Services.
(1) Audit Fees. The
aggregate fees billed for each of the last two fiscal years for
professional services rendered by Deloitte in the year ended December 31,
2010 and the period from July 23, 2009 through December 31, 2009, PwC in the period from January 1, 2009 through July 22, 2009 for the audit of the Partnership’s
annual financial statements, review of financial statements included in the Partnership’s Forms
10-Q and 10-K and other services normally provided in connection with regulatory filings or
engagements were:
Deloitte |
PwC |
|||||||
2010 |
$ | 116,900 | N/A | |||||
2009 |
$ | 129,200 | (1) | $ | 22,700 | (2) | ||
(1) For the period July 23, 2009 to December 31, 2009.
(2) For the period January 1, 2009 to July 22, 2009.
(2) Audit-Related Fees. None
(3) Tax Fees. In the last two fiscal years, Deloitte did not provide any professional
services for tax compliance, tax advice or tax planning. The aggregate fees billed for each of the
last two fiscal years for professional services rendered by PwC for tax compliance and tax advice
given in the preparation of the Partnership’s Schedule K1s, the preparation of the Partnership’s
Form 1065 and preparation of all State Tax Returns were:
2010
|
$ | 44,100 | ||
2009
|
$ | 42,000 |
(4) All Other Fees. None.
(5) Not Applicable.
(6) Not Applicable.
55
PART IV
Item 15.
Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
| (a) | (1) Financial Statements: |
Statements of Financial Condition at December 31, 2010 and 2009.
Condensed
Schedules of Investments at December 31, 2010 and 2009.
Statements of Income and Expenses for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008.
Statements of Changes in Partners’ Capital for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and
2008.
Notes to Financial Statements
(2) Exhibits:
| 3.1 | Second Amended and Restated Limited Partnership Agreement (filed as Exhibit 3.1 to current report on Form 8-K/A filed on December 28, 2009). | |
| 3.2 | Certificate of Limited Partnership of the Partnership as filed in the office of the Secretary of State of the State of the State of New York (filed as Exhibit 3.(I) to the general form for registration of securities on Form 10 filed on May 1, 2003). |
| (a) | 1st Certificate of Amendment to the Certificate of Limited Partnership as filed in the office of the Secretary of State of the State of New York, dated April 3, 2001 (filed as Exhibit 3.(I) to the general form for registration of securities on Form 10 filed on May 1, 2003). | ||
| (b) | 2nd Certificate of Amendment to the Certificate of Limited Partnership as filed in the office of the Secretary of State of the State of New York, dated May 21, 2003 (filed as Exhibit 3.2(b) to the Form 10-Q filed on November 16, 2009). | ||
| (c) | 3rd Certificate of Amendment to the Certificate of Limited Partnership as filed in the office of the Secretary of State of the State of New York, dated September 21, 2005 (filed as Exhibit 3.2(c) to the Form 10-Q filed on November 16, 2009). | ||
| (d) | 4th Certificate of Amendment to the Certificate of Limited Partnership as filed in the office of the Secretary of State of the State of New York, dated August 27, 2008 (filed as Exhibit 99.1 to current report on Form 8-K filed on September 2, 2008). | ||
| (e) | 5th Certificate of Amendment to the Certificate of Limited Partnership as filed in the office of the Secretary of State of the State of New York, dated September 19, 2008 (filed as Exhibit 3.2(e) to the Form 10-Q filed on November 16, 2009). | ||
| (f) | 6th Certificate of Amendment to the Certificate of Limited Partnership as filed in the office of the Secretary of State of the State of New York, dated September 30, 2009 (filed as Exhibit 99.1(a) to current report on Form 8-K filed on September 30, 2009). | ||
| (g) | 1st Certificate of Change to the Certificate of Limited Partnership as filed in the office of the Secretary of State of the State of New York, dated January 31, 2000 (filed as Exhibit 3.2(g) to the Form 10-Q filed on November 16, 2009). | ||
| (h) | Certificate of Amendment to the Certificate of Limited Partnership as filed in the office of the Secretary of State of the State of New York, dated June 29, 2010 (filed as Exhibit 3.1(h) to the Form 8-K filed on July 2, 2010). |
| 10.1 | Management Agreement among the Partnership, Smith Barney Futures Management Inc., SFG Global Investments, Inc. and AAA Capital Management Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10 to the general form for registration of securities on Form 10 filed on May 1, 2003). |
56
| 10.1(a) | First Amendment to the Management Agreement among the Partnership, Smith Barney Futures Management Inc., SFG Global Investments, Inc. and AAA Capital Management Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10 to the general form for registration of securities on Form 10 filed on May 1, 2003). | |
| 10.1(b) | Second Amendment to the Management Agreement among Citigroup Managed Futures LLC and AAA Capital Management Inc. (filed as Exhibit 33 to the quarterly report on Form 10-Q filed on August 14, 2006). | |
| 10.1(c) | Letter extending the Management Agreements between the General Partner and AAA Capital Management Inc. for 2010 (filed herein). | |
| 10.2 | Management Agreement among the Partnership, Smith Barney Futures Management Inc., SFG Global Investments, Inc. and Willowbridge Associates Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10 to the general form for registration of securities on Form 10 filed on May 1, 2003). | |
| 10.2(a) | First Amendment to the Management Agreement among the Partnership, Smith Barney Futures Management Inc., SFG Global Investments, Inc. and Willowbridge Associates Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10 to the general form for registration of securities on Form 10 filed on May 1, 2003). | |
| 10.2(b) | Letter extending the Management Agreement between the General Partner and Willowbridge Associates Inc. for 2010 (filed herein). | |
| 10.3 | Management Agreement among the Partnership, Citigroup Managed Futures LLC and Winton Capital Management Limited (filed as Exhibit 10 to the annual report on Form 10-K filed on March 15, 2004). | |
| 10.3(a) | Letter extending the Management Agreement between the General Partner and Winton Capital Management Limited for 2010 (filed herein). | |
| 10.4 | Amended and Restated Customer Agreement between the Partnership and Salomon Smith Barney Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10 to the general form for registration of securities on Form 10 filed on May 1, 2003). | |
| 10.5 | Second Amended and Restated Agency Agreement between the Partnership, Ceres Managed Futures LLC, Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC and Citigroup Global Markets Inc. (filed as Exhibit 10.5 to the Form 10-Q filed on November 16, 2009). | |
| 10.6 | Form of Subscription Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10.5 to the Form 10-Q filed on November 16, 2009). | |
| 10.7 | Form of Third-Party Subscription Agreement (filed as Exhibit 10.5 to the Form 10-Q filed on November 16, 2009). | |
| 10.8 | Joinder Agreement among Citigroup Managed Futures LLC, Citigroup Global Markets Inc. and Morgan Stanley Smith Barney LLC (filed as Exhibit 10 to the quarterly report on Form 10-Q filed on August 14, 2009). | |
| 16.1 | Letter dated July 23, 2009 from PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP regarding Change in Certifying Accountant (filed as Exhibit 16.1 to the Form 8-K filed on July 24, 2009). | |
| 16.2 | Letter dated June 26, 2008 from KPMG LLP regarding Change in Certifying Accountant (filed as Exhibit 16.1 to the Form 8-K filed on July 1, 2008). | |
| 99.1 | Financial Statements of AAA Master Fund LLC. | |
| 99.2 | Financial Statements of CMF Winton Master L.P. | |
| 99.3 | Financial Statements of CMF Willowbridge Argo Master Fund L.P. |
The exhibits required to be filed by Item 601 of Regulations S-K are incorporated herein by
reference.
31.1 — Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certification (Certification of President and Director).
31.2 — Rule 13a-14(a)/15d-14(a) Certification (Certification of Chief Financial Officer and
Director).
32.1 — Section 1350 Certification (Certification of President and Director).
32.2 — Section 1350 Certification (Certification of Chief Financial Officer and Director).
57
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934,
the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto
duly authorized.
ORION FUTURES FUND L.P.
By: Ceres Managed Futures LLC
(General Partner)
| By: | /s/ Walter Davis | |||
| Walter Davis, President & Director Date: March 31, 2011 |
||||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been
signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on the
date indicated.
/s/ Walter Davis
|
/s/ Ian Bernstein | /s/ Patrick T. Egan | ||
Walter Davis
|
Ian Bernstein | Patrick T. Egan | ||
President and Director
|
Director | Director | ||
Ceres Managed Futures LLC
|
Ceres Managed Futures LLC | Ceres Managed Futures LLC | ||
Date: March 31, 2011
|
Date: March 31, 2011 | Date: March 31, 2011 | ||
/s/ Jennifer Magro
|
/s/ Michael McGrath | /s/ Alper Daglioglu | ||
Jennifer Magro
|
Michael McGrath | Alper Daglioglu | ||
Chief Financial Officer and Director
|
Director | Director | ||
(Principal Accounting Officer)
|
Ceres Managed Futures LLC | Ceres Managed Futures LLC | ||
Ceres Managed Futures LLC |
Date: March 31, 2011 | Date: March 31, 2011 | ||
Date: March 31, 2011
|
||||
/s/ Douglas J. Ketterer
|
/s/ Harry Handler | |||
Douglas J. Ketterer
|
Harry Handler | |||
Director
|
Director | |||
Ceres Managed Futures LLC
|
Ceres Managed Futures LLC | |||
Date: March 31, 2011
|
Date: March 31, 2011 |
Supplemental Information to be Furnished With Reports Filed Pursuant to Section 15(d) of the
Act by Registrants Which Have Not Registered Securities Pursuant to Section 12 of the Act.
Annual Report to Limited Partners
No proxy material has been sent to Limited Partners.
58
