Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-31.2 - EXHIBIT 31.2 - NANOSPHERE INC | c12557exv31w2.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EXHIBIT 32.2 - NANOSPHERE INC | c12557exv32w2.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EXHIBIT 32.1 - NANOSPHERE INC | c12557exv32w1.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EXHIBIT 23.1 - NANOSPHERE INC | c12557exv23w1.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EXHIBIT 31.1 - NANOSPHERE INC | c12557exv31w1.htm |
Table of Contents
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
Form 10-K
(Mark One)
| þ | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2010
OR
| o | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the transition period from to
Commission File Number 001-33775
Nanosphere, Inc.
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 36-4339870 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of | (I.R.S. Employer Identification No.) | |
| incorporation or organization) | ||
| 4088 Commercial Avenue | Northbrook, Illinois 60062 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (847) 400-9000
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| (Title of Each Class) | (Name of Each Exchange on Which Registered) | |
| Common Stock, par value $0.01 | NASDAQ Global Market |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in
Rule 405 of the Securities
Act.
o Yes
þ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to
Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the
Act.
o Yes
þ No
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant (1) has filed all reports required to be filed
by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or
for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been
subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes þ No o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its
corporate Web site, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted
pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T (§232.405 of this chapter) during the preceding 12 months
(or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes
o No o (the Registrant is not yet required to submit Interactive Data)
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation
S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in
definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K
or any amendment to this Form 10-K. o
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated
filer, a non-accelerated filer or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large
accelerated filer”, “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the
Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer o | Accelerated filer o | Non-accelerated filer þ | Smaller reporting company o |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of
the Exchange Act). Yes o No þ
As of June 30, 2010, the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second
fiscal quarter, the aggregate market value of the common stock held by non-affiliates of the
registrant was approximately $73,880,950 based on the closing sale price for the registrant’s
common stock on the NASDAQ Global Market on that date of $4.36 per share. This number is provided
only for the purpose of this report on Form 10-K and does not represent an admission by either the
registrant or any such person as to the status of such person.
As of February 10, 2011, there were 28,425,506 outstanding shares of common stock. The common
stock is listed on the NASDAQ Global Market (trading symbol “NSPH”).
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the registrant’s definitive proxy statement for fiscal year ended December 31,
2010 to be issued in conjunction with the registrant’s annual meeting of shareholders expected to
be held on June 1, 2011 are incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K. The
definitive proxy statement will be filed by the registrant with the SEC not later than 120 days
from the end of the registrant’s fiscal year ended December 31, 2010. Except as specifically
incorporated herein by reference, the above mentioned Proxy Statement is not deemed filed as part
of this report.
NANOSPHERE, INC.
INDEX
| Page | ||||||||
| 1 | ||||||||
| 13 | ||||||||
| 24 | ||||||||
| 24 | ||||||||
| 24 | ||||||||
| 24 | ||||||||
| 25 | ||||||||
| 27 | ||||||||
| 28 | ||||||||
| 37 | ||||||||
| 38 | ||||||||
| 55 | ||||||||
| 55 | ||||||||
| 56 | ||||||||
| 57 | ||||||||
| 57 | ||||||||
| 57 | ||||||||
| 57 | ||||||||
| 57 | ||||||||
| 58 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 23.1 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 31.1 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 31.2 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 32.1 | ||||||||
| Exhibit 32.2 | ||||||||
Table of Contents
Forward-Looking Statements
This Annual Report on Form 10-K contains forward-looking statements about us and our industry
that involve substantial risks and uncertainties. All statements, other than statements of
historical facts, included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K regarding our strategy, future
operations, future financial position, future net sales, projected expenses, prospects and plans
and objectives of management are forward-looking statements. These statements involve known and
unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our actual results, levels of
activity, performance or achievement to be materially different from those expressed or implied by
the forward-looking statements.
In some cases, you can identify forward-looking statements by terms such as “anticipate,”
“believe,” “estimate,” “expect,” “intend,” “may,” “might,” “plan,” “project,” “will,” “would,”
“should,” “could,” “can,” “predict,” “potential,” “continue,” “objective,” or the negative of these
terms, and similar expressions intended to identify forward-looking statements. However, not all
forward-looking statements contain these identifying words. These forward-looking statements
reflect our current views about future events and are based on assumptions and subject to risks and
uncertainties. Given these uncertainties, you should not place undue reliance on these
forward-looking statements. Actual events or results could differ materially from those expressed
or implied by these forward-looking statements as a result of various factors.
These forward-looking statements represent our estimates and assumptions only as of the date
of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Unless required by U.S. federal securities laws, we do not
intend to update any of these forward-looking statements to reflect circumstances or events that
occur after the statement is made or to conform these statements to actual results. The following
discussion should be read in conjunction with the consolidated financial statements and notes
thereto appearing elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. Our actual results may differ
materially from those anticipated in these forward-looking statements as a result of various
factors, including those set forth under “Item 1A — Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this Annual
Report on Form
10-K.
PART I.
Item 1. Business.
References herein to “we,” “us,” “our” or “the Company” refer to Nanosphere, Inc. unless the
context specifically requires otherwise.
Overview
We develop, manufacture and market an advanced molecular diagnostics platform, the Verigene
System, that enables simple, low cost and highly sensitive genomic and protein testing on a single
platform. Our proprietary nanoparticle technology provides the ability to run multiple tests
simultaneously on the same sample. The Verigene System includes a bench-top molecular diagnostics
workstation that is a universal platform for genomic and protein testing. While many systems
currently available on the market provide a diagnostic result for one test or a few tests within a
specific market niche, the Verigene System provides for multiple tests to be performed on a single
platform, including both genomic and protein assays, from a single sample.
The Verigene System is differentiated by its ease of use, rapid turnaround times and ability
to detect many targets on a single test, referred to as “multiplexing.” It provides lower cost for
laboratories already performing molecular diagnostic testing and enables smaller laboratories and
hospitals without advanced diagnostic capabilities to perform genetic testing. Our ability to
detect proteins, which can be as much as 100 times more sensitive than current technologies for
certain targets, may enable earlier detection of and intervention in diseases associated with known
biomarkers as well as the introduction of tests for new biomarkers that exist in concentrations too
low to be detected by current technologies. We are focused on the clinical diagnostics market.
1
Table of Contents
Our test menu is designed to fulfill the following unmet hospital laboratory needs:
| 1) | the conversion of microbiology to molecular methods to more rapidly pinpoint infectious diseases; | ||
| 2) | point-of-care pharmacogenetics to ensure that appropriate therapies are prescribed; and | ||
| 3) | earlier detection of life threatening disease through ultra-sensitive protein assays. |
The Verigene System is comprised of a microfluidics processor, a touchscreen reader and
disposable test cartridges. Certain assays, such as the Warfarin metabolism and hyper-coagulation
tests, were cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) for use with the original
Verigene System processor (the “Original Processor”). Subsequently, we developed and launched
a second generation Verigene System processor (the “Processor
SP”) that handles the same processing steps as the Original Processor and incorporates
sample preparation. Some of our current customers continue to use the Original Processor for
hyper-coagulation testing and Warfarin metabolism testing. Our development plans are focused on
expanding the menu of tests that will run on the Processor SP, and all future assays are expected
to be submitted to the FDA on the Processor SP.
Our Applications
The
following table summarizes the FDA and CE In-Vitro Diagnostic Mark
(“CE IVD Mark”) regulatory status of our near-term genomic and protein
assays on the Verigene System:
| Assay | FDA Status(1) | CE IVD Mark Status(2) | ||
Infectious Disease Assays |
||||
Respiratory Virus
|
510(k) cleared | |||
Respiratory Virus with Sub-Typing
|
510(k) cleared | CE IVD Marked | ||
Blood Infection Panels
|
In development | In development | ||
Human and Pharmacogenetic Assays |
||||
Warfarin Metabolism
|
510(k) cleared(3) | CE IVD Marked | ||
Hyper-Coagulation
|
510(k) cleared(3) | Pending | ||
Plavix® Metabolism (2C19)
|
Premarket approval filing submitted third quarter 2010 | Pending | ||
Ultra-Sensitive Protein Assays |
||||
Cardiac Troponin I
|
In development | In development | ||
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA)
|
Research use only |
| (1) | For further description of our FDA regulatory requirements, please refer to the section “Regulation by the United States Food and Drug Administration” within this Annual Report on Form 10-K. | |
| (2) | For further description of our CE IVD Mark regulatory requirements, please refer to the section “Foreign Government Regulation” within this Annual Report on Form 10-K. | |
| (3) | Currently cleared only for use with the Original Processor. |
Infectious Disease Assays
The conversion of microbiology to molecular methods is driven by the need to identify
infectious diseases more quickly, allowing a more rapid commencement of clinical intervention.
Microbiology labs need tests that can rapidly detect a wide range of potential infectious agents in
an automated system. The Verigene System provides the multiplexing, rapid turnaround and
ease-of-use needed by these labs. Our infectious disease menu and the Processor SP provide
microbiology labs with a compelling solution for conversion to molecular testing.
2
Table of Contents
We have received 510(k) clearance from the FDA for our respiratory panel that detects the
presence of influenza A and B as well as respiratory syncytial virus (“RSV”) A and B. Influenza is
commonly known as the seasonal flu and RSV is a respiratory virus that infects the lungs and
breathing passages. RSV is the most common cause of bronchitis and pneumonia in children under the
age of one year and has become a significant concern for older adults. Our respiratory panel
provides physicians with a highly accurate and fast determination of which virus is present. This
test result guides the most appropriate treatment therapy.
In the fourth quarter of 2009, we received 510(k) clearance from the FDA for our respiratory
panel on the Processor SP. We believe that our respiratory assay on the Processor SP offers a
simple-to-use molecular test for diagnosing respiratory infections and the flu, while providing
improved sensitivity over currently available rapid tests. We have received clearance for a package
insert change for this assay confirming that the novel H1N1 virus is detected as a positive
Influenza A when using our respiratory assay and the Processor SP.
In the first quarter of 2011, we received 510(k) clearance from the FDA and CE IVD Mark for
our respiratory assay that includes subtyping for seasonal H1 virus, seasonal H3 virus, and the
2009 novel H1N1 virus, commonly known as swine flu, as well as the targets on our previously
cleared respiratory assay. We believe this is the first sample-to-result molecular respiratory test
to include all of these viruses, thus lowering the cost of molecular respiratory testing for
hospitals and demonstrating the multiplexing capability of the Verigene System. The demand for this
test will be highly dependent upon the seasonality and prevalence of respiratory viruses.
We are developing three blood stream infection panels for the earlier detection of specific
bacteria present within patients with blood stream infections. Currently under development are gram
positive, gram negative and fungal panels. These assays are designed to enable physicians to
pinpoint bacterial strains infecting patients and thus prescribe the most appropriate antibiotic
regimen within 24 hours rather than after several days. Treatment is sometimes begun before assays
are complete and we believe that this early detection capability will allow patients to avoid
unnecessary treatments that may expose them to serious side effects. These assays will require
regulatory submission to the FDA along with corresponding CE mark
filings.
Our development efforts also include a C. difficile test and an enteric bacteria test. C.
difficile is a bacterium that can cause symptoms ranging from diarrhea to life-threatening
inflammation of the colon. Our enteric bacteria assay is being developed to detect and identify the
Enterobacteriaceae species that most often result from food poisoning. The enteric assay tests for
a wide spectrum of bacteria that are treated with various antibiotics and other anti-bacterial drug
therapies. These assays also will require regulatory submission to the FDA and corresponding
foreign regulatory bodies.
Human and Pharmacogenetic Assays
Hospitals need faster, less expensive and easier-to-use human and pharmacogenetic tests that
can be run for a single patient at the point-of-care. Our Verigene System and human and
pharmacogenetic test menu addresses these hospital needs. Pharmacogenomics is an emerging subset of
human genetic testing that correlates gene variation with a drug’s efficacy or toxicity. These
tests play a key role in the advancement of personalized medicine where drug therapies and dosing
are guided by each patient’s genetic makeup. There is a growing demand on laboratories to implement
molecular diagnostic testing, but the cost and complexity of existing technologies and the need for
specialized personnel and facilities have limited the number of laboratories with these
capabilities. The ease-of-use and reduced complexity of the Verigene System enables any hospital to perform these testing needs.
We have received 510(k) clearance from the FDA for a warfarin metabolism assay performed on
our Original Processor. This is a pharmacogenetic test to determine the existence of certain
genetic mutations that affect the metabolism of warfarin-based drugs, including
Coumadin®, the most-prescribed oral anticoagulant. This assay has been CE IVD
Marked during the first quarter of 2011, and we plan to submit an FDA application for this assay to
allow its use on the Processor SP.
In the third quarter of 2010, we filed a pre-market approval application (“PMA”) with the FDA
for our cytochrome P450 2C19 assay that detects genetic mutations associated with deficient
metabolism of clopidogrel, more commonly known by the trade name Plavix. Clopidogrel inhibits
platelet function and is a standard treatment to reduce the risk of thrombolytic events for
patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions. Clopidogrel metabolism is affected by the
cytochrome P-450 family of genes. Up to 50% of the population possess variations in these genes and
abnormally metabolize this drug, thus increasing the risk of adverse events. Our 2C19 assay is
designed to identify patients possessing certain of these variations so that alternative
therapeutic approaches can be prescribed to reduce clotting that can result in heart attack or
stroke. We plan to file for CE IVD Mark for this assay during the first quarter of 2011.
3
Table of Contents
We have also received 510(k) clearance from the FDA for a hyper-coagulation assay on the
Original Processor that determines an individual’s risk, based upon genetic information, for the
development of blood clots that can lead to pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. We plan to
submit an additional FDA application and file for CE IVD Mark to allow its use on the Processor SP.
Ultra-Sensitive Protein Assays
Our ability to detect proteins at sensitivity levels that can be up to 100 times greater than
current technologies may enable earlier detection of and intervention in diseases as well as enable
the introduction of tests for new biomarkers that exist in concentrations too low to be detected by
current technologies. We have developed or are currently developing diagnostic tests for markers
that reveal the existence of a variety of medical conditions including cardiovascular, respiratory,
cancer, autoimmune, neurodegenerative and other diseases.
The first ultra-sensitive protein test we plan to commercialize is for cardiac troponin I
(“cTnI”), which is the gold standard biomarker for diagnosis of myocardial
infarction, or heart attack, and identification of patients with acute coronary syndromes at risk for
subsequent cardiovascular events. We previously submitted a 510(k) application to the FDA to obtain
clearance for the cardiac troponin assay on the Original Processor. We have withdrawn this
application and plan to submit a new 510(k) application to obtain clearance for this assay on the
Processor SP. We plan to use patient samples from our FAST-TRAC clinical trial to run the clinical
trials in support of our new 510(k) submission. The FAST-TRAC clinical study is designed to
further demonstrate the clinical utility of ultra-sensitive cTnI measurements as a diagnostic tool
for use in the management of both acute and chronic cardiac disease.
In addition to the cardiac troponin I assay, we are developing an ultra-sensitive prostate-specific antigen (“PSA”) test for early diagnosis
of recurrent prostate cancer. Early testing data suggest this assay may serve as a more specific
test for PSA screening. We are also working on a multiplexed protein-based connective-tissue panel
for the detection of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and other related diseases. Finally, we are
investigating new biomarkers where our ultra-sensitive protein detection technology may enable
earlier detection of a broad range of diseases, such as cancer.
The Verigene System
The Verigene System is comprised of a microfluidics processor, a touchscreen reader and
disposable test cartridges. The microfluidics processor interacts with and manipulates various
functional components of the test cartridge, accomplishing a number of necessary steps including
target binding to the nucleic acid or protein array, nanoparticle probe hybridization, intermediate
washes and signal amplification. The reader houses the optical detection module that illuminates
the test slide and automated spot recognition software that analyzes the resulting signal
intensities and provides the test results. The reader also serves as the control station for the
Verigene System and features a simple and intuitive touchscreen interface that allows users to
track samples and test cartridges, initiate and monitor test processing, analyze results and
generate reports. The reader is web-enabled to allow remote access to results and reports.
To perform a test, the operator adds a prepared sample to a designated port in the test
cartridge, enters sample identification and test cartridge information into the reader using the
touchscreen keyboard or via the barcode wand, and inserts the test cartridge into the processor.
The processor assimilates information received from the reader and matches it to the inserted test
cartridge and initiates the specified test protocol. Once the assay process is complete the test
array is introduced into the reader for image analysis and result reporting.
Our Technology
We believe our technology will drive greater usage of ultra-sensitive and multiplexed protein
and genomic diagnostics in routine clinical laboratories, much as enzyme-linked immunosorbent
assay, or ELISA, accelerated the use of protein testing in the 1970s and 1980s and PCR catalyzed
the emergence of nucleic acid diagnostics in the 1990s.
Our Gold Nanoparticle Molecular Probes
At the core of our technology are gold nanoparticles which offer a unique set of physical
properties that can be exploited in the detection of biological molecules. In 1998, Dr. Chad
Mirkin, a director of the Company, and Dr. Robert Letsinger at Northwestern University
(“Northwestern”) developed a novel process to prepare stable probes by covalently attaching
oligonucleotides to gold
nanoparticles. This method, protected by patents, is exclusively assigned to or owned by us.
We have refined the synthesis methods to enable highly reproducible production of nanoparticle
probes with diameters in the 13-50 nanometer range required for highly sensitive biomedical
analysis. Subsequently, we have also developed methods for attaching antibodies to gold
nanoparticles, thereby producing highly stable probes for ultra-sensitive detection of proteins.
4
Table of Contents
The properties of nanoparticle probes can be tailored by controlling the size of the
particles, the density of recognition-oligomers or antibodies on the nanoparticles, the use of
diluent oligonucleotides, the use of spacer oligonucleotides and the salt concentration. Combined,
the optimization of these properties enables us to deliver superior analytical performance
characteristics versus other methods, for example:
| • | High Signal-to-Noise Ratio. Our nanoparticle probes deliver significantly stronger signals than the fluorescent probes, or fluorophores, used in most diagnostic platforms today. Nanoparticles are typically 10-100 nm in diameter and therefore significantly larger than conventional fluorophores. This size difference enables nanoparticles to produce up to 10,000 times more signal via light scattering than a fluorophore. A single nanoparticle can be detected with simple optical instrumentation with very high sensitivity, thus eliminating the need to employ our amplification techniques. | |
| • | Orders of Magnitude Greater Sensitivity and Lower Detection Limits. The sensitivity and limits of detection of our technology are further enhanced by a silver-staining step, which effectively amplifies the signal from each nanoparticle bound to a target molecule. In this process, silver is coated onto the gold nanoparticle surface, producing larger particles with enhanced optical properties. Whereas the leading technologies today can detect molecules at the picomolar range (10-12), our technology is capable of up to a million times higher sensitivity at the attomolar (10-18) range, enabling the unprecedented analysis of rarely expressed genes or low abundance proteins for early disease detection and diagnosis. | |
| • | Unparalleled Specificity. A key property of the oligonucleotide-linked gold nanoparticle is an extremely sharp melting curve. The melting curve is the temperature range during which the capture oligonucleotide dissociates with the complementary target oligonucleotide in the sample. Our nanoparticles exhibit dissociation transitions of less than one degree in Celsius temperature, whereas most alternative products are based on polymerase chain reaction, or PCR, which exhibits melt transitions typically in the 15-30 degree range. The narrow band of temperature in which binding and dissociation occurs, creates a significantly higher signal to noise ratio resulting in greater specificity. These qualities eliminate errors caused by mismatched nucleotide pairs, thereby allowing genomic targets differing by a single nucleotide (base pair) to be distinguished with unprecedented selectivity. Sharp melting curves are a proprietary feature of our nanoparticles and our patent portfolio includes issued patents protecting the methods and product performance related to melt transition curves. | |
| • | High Count Multiplexing. Our core technology enables high count multiplexing, or simultaneous multiple target identification in a single sample, using a simple low-density microarray. A sample and probe mixture is introduced simultaneously into a single self-contained reaction chamber pre-printed with multiple reaction spots, each containing capture strand oligonucleotides or proteins that are complementary to a specific target molecule of interest. By utilizing the sharp melt transition of the nanoparticle probes, multiple targets can be discretely identified in a single sample. This methodology eliminates the need for complex and costly means of physically isolating individual target molecules. | |
| • | Detection of Genomic and Protein Molecules Simultaneously. We are able to synthesize our gold nanoparticle probes for the simultaneous multiplexed detection of both protein and genomic targets in the same assay. | |
| • | Superior Reaction Kinetics. The sharp melt transition curves in our gold nanoparticles increase binding affinity thereby leading to improved assay kinetics and efficiency. | |
| • | Long-Term Stability. The high density of oligonucleotides per nanoparticle, serves both as a protective and recognition layer on the nanoparticle surface and ensures the long-term stability of our nanoparticles. We have patented approaches using localized salt and buffer concentrations that deliver long-shelf life for our technology and reagent set. |
5
Table of Contents
Assay Format
Our silver-enhanced gold nanoparticles and related optical detection technology are used for
diagnostic assays which detect genomic and proteomic targets captured onto microarrays as shown in
the “Schematic of Microarray Based Detection Using Nanoparticle Probes” below. The microarray
format enables high count multiplexing of assay targets, facilitating the development of a broad
menu of tests, including for complex diseases where multiple targets must be evaluated to provide a
diagnosis, in a simple, scalable format.
Two probe types can be used in a single assay. Oligonucleotide probes are used for genomic
assays and antibodies for protein assays. One probe, complementary to a specific site on the target
molecule, is attached to a surface such as a glass slide and the other probe, complementary to a
different site on the target molecule, is attached to the surface of gold nanoparticles. In the
presence of the target molecule of interest, the probes and target form a three dimensional,
cross-linked aggregate. After silver coating the gold nanoparticles, light scatter is measured on
the surface of the microarray slide. The silver-enhanced gold nanoparticle probes located on the
slide surface scatter light in proportion to the concentration of the target in the sample, which
is detected through optical imaging and translated into clinical results via our proprietary
software algorithms.
Schematic of Microarray Based Detection Using Nanoparticle Probes
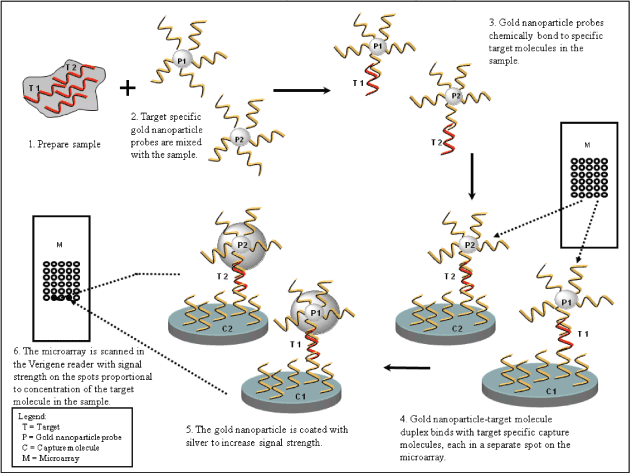
The above graphic depicts a genomic or proteomic assay utilizing a molecule attached to a gold
nanoparticle. In the case of a genomic assay, the molecule represents an oligonucleotide. In the
case of a proteomic assay, the molecule represents an antibody.
6
Table of Contents
Intellectual Property
As of December 31, 2010, our patent portfolio is comprised, on a worldwide basis, of 151
issued patents and 52 pending patent applications which we own directly or for which we are the
exclusive licensee. Some of these patents and patent applications derive from a common parent
patent application or are foreign counterpart patent applications and relate to similar or
identical technological claims. The issued patents cover approximately 11 different technological
claims and the pending patent applications cover approximately four additional technological
claims.
Many of our issued and pending patents were exclusively licensed from the International
Institute for Nanotechnology at Northwestern in May 2000, and they generally cover our core
technology, including nanotechnology-based biodiagnostics and biobarcode technology. Our issued
patents expire between 2017 and 2025. We believe our patent portfolio provides protection against
other companies offering products employing the same technologies and methods as we have patented.
While we believe our patent portfolio establishes a proprietary position, there are many
competitive products utilizing other technologies that do not infringe on our patents.
In addition, as of December 31, 2010, we have non-exclusive licenses for at least 47 U.S.
patents that cover 12 different technological claims from various third parties. Most of these
license agreements require us to pay the licensor royalty fees that typically expire upon the
patent expiration dates, which range from 2011 to 2027. These license agreements are non-exclusive
and do not create a proprietary position. The expiration of these non-exclusive licenses will
result in the termination of certain royalty payments by us to the licensors.
Research and Development
Our research and development efforts are focused on:
| • | Expanding and Enhancing the Capabilities of Our Instrument Platform. Design elements and components of our current instrument platform will serve as the foundation for future generation development. The Processor SP incorporates sample preparation into our system. By adding this step, labs can now process a raw sample material, in most cases whole blood, in a single step. This feature is critical for analyzing infectious diseases and will further simplify the processing of clinical samples from swab, cerebrospinal fluid and serum. | ||
| We are also developing a fully automated instrument with increased high throughput and sample preparation for both infectious disease and human genetic tests for larger hospital based laboratories. By basing future generations of our instrument platform on existing design elements, each new generation of development will process assays developed for previous generations. | |||
| • | Developing Additional Genomic and Protein Assays. We are in various phases of developing and commercializing new assays for detecting protein biomarkers, infectious diseases and human genetic markers. Currently, we are researching additional human genetic, infectious disease and ultra-sensitive protein assays. | ||
| • | Validating and Commercializing New Biomarkers. We have a dedicated team of protein scientists and assay developers who conduct assay development to support feasibility testing and new protein biomarker validation. This team is collaborating with clinical researchers in academic and private settings to apply our ultra-sensitive protein detection technology to the researchers’ efforts to create diagnostic methods with greater clinical sensitivity and specificity. We are also applying our ultra-sensitivity methods to the development of established protein biomarkers that may lead to earlier detection of medical conditions including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders including Alzheimer’s disease, sepsis and mad cow disease, as well as for blood screening and veterinary applications. | ||
| • | Enhancing Performance of Established Product Systems and Developing New Applications. Our license agreement with Northwestern provides us with an exclusive license to certain patents and patent applications related to the application of nanotechnology to biodiagnostics and to biobarcode technology. This license covers all discoveries from the International Institute for Nanotechnology at Northwestern in the field of biodiagnostics through January 1, 2013. Nanosphere also has the right of first negotiation for an exclusive license on inventions after such date. Our research team utilizes the research and patents developed at Northwestern to develop diagnostic applications including additional genomic and protein testing assays for use in the Verigene System. |
7
Table of Contents
Employees
As of December 31, 2010, we had 115 full-time employees. Of these employees, 43 were in
research and development, 34 were in manufacturing (in support of both product sales and the
research and development function), 21 were in sales and marketing and 17 were in general and
administrative functions. We have never had a work stoppage and none of our employees are covered
by collective bargaining agreements or represented by a labor union. We believe our employee
relations are good.
Government Grants and Contracts
We have received grants over the last five years that have allowed for the evaluation and
development of new technologies and also allowed for development of market specific diagnostic
products.
We have benefited from Small Business Innovation Research grants to prove feasibility of gold
nanoparticle based detection technology as well as evaluate potential new technologies and medical
diagnostic applications.
We have received government contracts for the development of automated biological agent
detection systems using nanoparticle probes that are capable of rapidly detecting biological
warfare agents and biological toxins. These products have potential applications for both
government contractors and civilian first responders. Since inception, we have recorded revenue of
approximately $9 million under these grants and contracts.
Manufacturing
We assemble and package all our finished products at our corporate headquarters in Northbrook,
Illinois. Our manufacturing facility occupies approximately 12,000 square feet of the 40,945 square
feet which we lease at our Northbrook facility. There, we
manufacture our proprietary nanoparticle probes, assay reagents, test cartridges and instrumentation. We outsource much of the disposable component molding. Reagent
manufacturing and cartridge filling is performed under the current Good Manufacturing Practice —
Quality System Regulation as required by the FDA for the manufacture of in vitro diagnostic
products. These regulations carefully control the manufacture, testing and release of diagnostics
products as well as raw material receipt and control.
We have controlled methods for the consistent manufacturing of our proprietary nanoparticles
and production oligonucleotides at very high purity (greater than 95%). We also manufacture at our
Northbrook facility a proprietary linker to ensure stable bonding of the oligonucleotide to the
gold nanoparticle.
All quality control tests are validated to ensure product quality measurements are accurate.
Manufacturing of the Verigene System, including test cartridges, is tightly controlled with the use
of manufacturing batch records. These records control which product is produced and ensure that
each batch of product is manufactured consistently and according to the intended design.
We plan to continue to manufacture components that we determine are highly proprietary or
difficult to produce consistently while outsourcing commodity components. As we continue to
execute on our sales and market plans, we have ramped-up our manufacturing operations to meet
demand. We are likely to establish additional outsourcing partnerships as we manufacture additional
products. While we believe our current facilities and expansion rights are adequate to meet our
manufacturing needs for at least the next three years, we may need to lease additional space. Our
recently revised facilities lease includes a right of first offer on additional available space in
our building. While we do not need to expand our facilities to meet anticipated demand for 2011,
we will likely require expanded facilities to meet anticipated demand beyond 2011.
Sales and Marketing
As a part of our business strategy, we have a direct sales and marketing organization to
support the sales of the Verigene System and its initial menu of tests in the United States. This
organization comprises geographically dispersed sales representatives and clinical support
specialists as well as a centralized staff of market and product managers. We believe that the
primary market for our diagnostic applications will be hospital-based laboratories and academic
research institutions in the United States. A customer may purchase
the Verigene System instruments lease them
from a third party or enter into a reagent rental agreement. Our reagent rental agreements include
customer commitments to purchase a certain minimum volume of cartridges over the term of the
agreement. As part of these agreements, a portion of the charge for each cartridge is a rental fee
for use of the equipment.
8
Table of Contents
Our sales and marketing organization provides customer service related to order fulfillment,
technical service and product support, and distribution logistics.
We believe that the primary international customers for our diagnostic applications will be
hospital-based laboratories and academic research institutions. We have obtained CE IVD Mark
approval for sale of the Verigene System in European Union countries and will do so for each assay
we plan to market in Europe. Outside the United States, we anticipate initiating sales through
marketing partners and distributors. A distribution strategy is being developed for each relevant
international market. We expect to supplement marketing partnerships with specialists who will
train our partners’ sales forces and provide technical support.
Competition
We primarily face competition in the nucleic acid based testing market from companies that
provide PCR-based technologies. We believe that, over time, the Verigene System will compete with
these companies primarily on the following factors: (1) cost effectiveness; (2) ease of use; (3)
multiplexing capability; (4) range of tests offered; (5) immediacy of results; and (6) reliability.
We also face competition in the protein detection market from companies that provide mass
spectrometry systems. Although mass spectrometry systems offer high sensitivity, they are extremely
costly, require significant time and effort by sophisticated staff and cannot detect many complex,
disease-causing proteins. Due to these significant limitations we consider mass spectrometry
systems to be a lower competitive threat within commercial protein diagnostics laboratories.
The protein detection market also includes companies that provide ELISA-based testing systems.
We believe that our technology, which is at least 100 times more sensitive than ELISA-based
technologies provides a significant advantage because it can detect proteins at lower
concentrations equating to earlier detection of disease. This sensitivity will create new value for
existing biomarkers and allow the discovery of novel biomarkers for the treatment and monitoring of
disease where none exist today.
Regulation by the United States Food and Drug Administration
In the United States, the FDA regulates the sale and distribution, in interstate commerce, of
medical devices, including in vitro diagnostic test kits. Pursuant to the federal Food, Drug, and
Cosmetic Act, the FDA regulates the preclinical and clinical design, testing, manufacture,
labeling, distribution and promotion of medical devices. We will not be able to commence marketing
or commercial sales in the United States of new medical devices under development that fall within
the FDA’s jurisdiction until we receive clearance or approval from the FDA.
In the United States, medical devices are classified into one of three classes (i.e., Class I,
II or III) on the basis of the controls deemed necessary by the FDA to reasonably ensure their
safety and effectiveness. Class I devices are subject to general controls (e.g., establishment
registration, medical device listing, labeling regulations, possible
premarket notification, and adherence to current Good Manufacturing
Practice/Quality System Regulations (QSR)). However, most Class I devices are
exempt from premarket notification (510(k) clearance). Class II devices are subject to general and special controls (e.g., special labeling
requirements, mandatory performance standards, premarket notification (510(k) clearance) often with
guidance from an FDA special control guideline, adherence to current
Good Manufacturing Practice/QSR,
possible post-market surveillance). Generally, Class III devices are subject to general and special
controls and must receive premarket approval, or PMA, by the FDA to ensure their safety and
effectiveness (e.g., new devices for which insufficient information exists to assure safety and
effectiveness through general and special controls; often such devices are life-sustaining,
life-supporting and implantable). Many devices that have been approved by way of premarket approval
are required to perform post-market surveillance.
510(k) Clearance
The FDA will grant 510(k) clearance if the submitted information establishes that the proposed
device is “substantially equivalent” to a legally marketed Class I or Class II medical device or a
pre-amendment Class III medical device for which the FDA has not sought PMA. The FDA has recently
been requiring more rigorous demonstration of substantial equivalence than in the past. In some
cases, such as may be the case with our HFE and Cardiac Troponin I 510(k) submissions, the FDA may
require additional clinical data than it would have required in the past. The FDA may determine
that a proposed device is not substantially equivalent to a legally marketed device or that
additional information is needed before a substantial equivalence determination can be made. A “not
substantially equivalent” determination, or a request for additional information, could prevent or
delay the market introduction of new products that fall into this category. For any devices that
are cleared through the 510(k) process, modifications or enhancements that could significantly
affect safety or effectiveness, or constitute a major change in the intended use of the device,
require new 510(k) submissions and clearances.
9
Table of Contents
Premarket Approval
A PMA application must be filed if a proposed device is a new device not substantially
equivalent to a legally marketed Class I or Class II device, or if it is a pre-amendment Class III
device for which the FDA has sought PMA. A PMA application must be supported by valid scientific
evidence to demonstrate the safety and effectiveness of the device, typically including the results
of clinical investigations, bench tests, and laboratory and animal studies. The PMA application
must also contain a complete description of the device and its components and a detailed
description of the method, facilities and controls used to manufacture the device. In addition, the
submission must include the proposed labeling, advertising literature and any training materials.
The PMA process can be expensive, uncertain and lengthy, and a number of devices for which FDA
approval has been sought by other companies have never been approved for marketing.
Upon receipt of a PMA application, the FDA makes a threshold determination as to whether the
application is sufficiently complete to permit a substantive review. If the FDA determines that the
PMA application is complete, the FDA will accept the application for filing. Once the submission is
accepted, the FDA begins an in-depth review of the PMA. The FDA’s review of a PMA application
generally takes one to three years from the date the application is accepted, but may take
significantly longer. The review time is often extended by the FDA asking for more information or
clarification of information already provided in the submission. During the review period, an
advisory committee, typically a panel of clinicians and subject
matter experts, will likely be convened to review and evaluate
the application and provide recommendations to the FDA as to whether the device should be approved.
The FDA is not bound by the recommendation of the advisory panel. Toward the end of the PMA review
process, the FDA generally will conduct an inspection of the manufacturer’s facilities to ensure
that the facilities are in compliance with applicable current Good
Manufacturing Practices/QSR requirements.
If FDA evaluations of both the PMA application and the manufacturing facilities are favorable,
the FDA may issue either an approval letter or an approvable letter,
the latter of which contains a
number of conditions that must be met in order to secure final approval of the PMA. When and if
those conditions have been fulfilled to the satisfaction of the FDA, the agency will issue a
premarket approval letter, authorizing commercial marketing of the device for certain indications.
If the FDA’s evaluation of the PMA application or manufacturing facilities is not favorable, the
FDA will deny approval of the PMA application and issue a non-approvable letter. The FDA may
determine that additional clinical investigations are necessary, in which case the PMA may be
delayed for one or more years while additional clinical investigations are conducted and submitted
in an amendment to the PMA.
Modifications to a device that is the subject of an approved PMA, including its labeling or
manufacturing process, may require approval by the FDA of PMA supplements or new PMAs. Supplements
to an approved PMA often require the submission of the same type of information required for an
initial PMA, except that the supplement is generally limited to that information needed to support
the proposed change from the product covered by the original PMA. The
FDA also has the authority to withdraw or temporarily suspend PMA
approvals under specific circumstances.
Clinical Investigations
Before we can submit a medical device for 510(k) clearance, we may have to perform a short
(i.e., months) method comparison study at external clinical sites to
ensure that the test performs appropriately when conducted by end
users. This is a study in a clinical environment, and is considered a
clinical trial. However, the clinical out come information is most
often not required. Alternatively, when we submit a PMA, we generally must conduct a longer (i.e.,
years) clinical trial of the device which supports the clinical
utility of the device, demonstrating how the device will perform when
used with patients in the test’s intended use population.
Although clinical investigations of most devices are subject to the investigational device
exemption, or IDE requirements, clinical investigations of in vitro diagnostic tests, including our
products and products under development, are exempt from approval of
an IDE application prior to initiation of the clinical study, provided the testing is non-invasive, does not require an
invasive sampling procedure that presents a significant risk, does not intentionally introduce
energy into the subject, and is not used as a diagnostic procedure without confirmation by another
medically established test or procedure. In addition, our tests must be labeled “for research use
only” or “for investigational use only,” and distribution controls must be established to assure
that our tests distributed for research, method comparisons or clinical trials are used only for
those purposes.
10
Table of Contents
Obtaining FDA Clearance for Our Products
We
received 510(k) clearance from the FDA for commercial sale of the
initial tests for use on the Original Processor in the
second half of 2007. The first test is a warfarin metabolism assay, which is a pharmacogenomic test
to determine the existence of certain genetic information believed to affect the metabolism of
warfarin based drugs, including Coumadin, the most-prescribed oral anticoagulant in North America
and Europe. The second test is a hyper-coagulation assay, one of the highest volume human genetic
tests currently performed, to determine an individual’s risk, based upon genetic information, for
the development of blood clots, which can lead to stroke, pulmonary embolism and deep vein
thrombosis.
The third test is our respiratory panel which detects the presence of influenza A and B as
well as respiratory syncitial virus (“RSV”) A and B. Influenza is commonly known as the seasonal
flu and RSV is a respiratory virus that infects the lungs and breathing passages. RSV is the most
common cause of bronchitis and pneumonia in children under the age of one year and has become a
significant concern for older adults. Our respiratory panel provides physicians with a highly
accurate, fast determination of which virus is present which helps guide the most appropriate
treatment therapy. Most of the respiratory tests currently on the market take days to generate a
result, because they depend on culturing, or do not provide a reliable result, because they are
rapid tests which lack specificity. The fourth test is our cystic fibrosis test that enables
molecular laboratories to perform prenatal screening and diagnostic confirmations through
identification of the number of copies of each of the 23 most common gene mutations recognized by
the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists as markers for cystic fibrosis.
Most of our tests have special control guidances for 510(k) clearance. Some of our future
tests may be Class III devices. We also plan to conduct method
comparison studies and clinical
trials of our products currently under development, which we intend to distribute in the United
States. Our future developments may not be exempt from IDE
application approval requirements and may require us to
obtain approval from the FDA through the PMA process rather than 510(k) clearance. In addition, any
failure to maintain compliance with the IDE exemption requirements could result in, among other
things, the loss of the IDE exemption or the imposition of other restrictions on the distribution
of our products.
Regulation After FDA Approval or Clearance
Any devices we manufacture or distribute pursuant to clearance or approval by the FDA are
subject to pervasive and continuing regulation by the FDA and certain state agencies. We are
required to adhere to applicable regulations setting forth detailed current Good Manufacturing
Practices/QSR requirements, which include testing, control, design and documentation requirements.
Non-compliance with these standards can result in, among other things, fines, injunctions, civil
penalties, recalls or seizures of products, total or partial suspension of production, failure of
the government to grant 510(k) clearance PMA for devices, withdrawal of marketing approvals and
criminal prosecutions. We have designed and implemented our manufacturing facilities under the
current Good Manufacturing Practices/QSR requirements. Our manufacturing facility has been inspected by
the FDA and will continue to be periodically audited by the FDA.
Because we are a manufacturer of medical devices, we must also comply with medical device
reporting requirements by reporting to the FDA any incident in which our product may have caused or
contributed to a death or serious injury. We must also report any incident in which our product
malfunctioned if that malfunction would likely cause or contribute to a death or serious injury if
it were to recur. Labeling and promotional activities are subject to scrutiny by the FDA and, in
certain circumstances, by the Federal Trade Commission. Current FDA enforcement policy prohibits
the marketing of approved medical devices for unapproved uses.
We are also subject to numerous federal, state and local laws relating to such matters as safe
working conditions, manufacturing practices, environmental protection, fire hazard control and
disposal of hazardous or potentially hazardous substances. We have numerous policies and procedures
in place to ensure compliance with these laws and to minimize the risk of occupational exposure to
hazardous materials. In addition, we do not expect the operations of our products to produce
significant quantities of hazardous or toxic waste that would require extraordinary disposal
practices. Although the costs to comply with these applicable laws and regulations have not been
material, we cannot predict the impact on our business of new or amended laws or regulations, or
any changes in the way existing and future laws and regulations are interpreted or enforced.
Moreover, as we develop toxin and pathogen detection products for the food and agriculture markets,
we may be subject to the regulations of various food safety organizations, including the United
States Department of Agriculture.
11
Table of Contents
Export of Our Products
Export of products subject to the 510(k) notification requirements, but not yet cleared to
market, are permitted with FDA authorization provided certain requirements are met. Unapproved
products subject to the PMA requirements must be approved by the FDA for export. To obtain FDA
export approval, we must meet certain requirements, including, with some exceptions, documentation
demonstrating that the product is approved for import into the country to which it is to be
exported and, in some instances, safety data for the devices.
Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988
The use of our products is also affected by the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of
1988, or CLIA, and related federal and state regulations, which provide for regulation of
laboratory testing. These regulations mandate that clinical laboratories must be certified by the
federal government, by a federally-approved accreditation agency or by a state that has been deemed
exempt from the regulation’s requirements. Moreover, these laboratories must meet quality
assurance, quality control and personnel standards, and they must undergo proficiency testing and
inspections. The CLIA standards applicable to clinical laboratories are based on the complexity of
the method of testing performed by the laboratory, which range from “waived” to “moderately
complex” to “highly complex.” We expect that most of our products will be categorized as either
“moderately complex” or “highly complex.”
Foreign Government Regulation
We are beginning to market our products in certain foreign markets.
CE IVD Mark is a mandatory conformance mark under the
In-Vitro Diagnostic Directive 98/79/EC that addresses the essential
requirements that an in-vitro diagnostic device must meet before being marketed within the European Union.
We have
obtained CE IVD Mark approval for sale of the Verigene System in European Union countries and will
do so for any assay we plan to launch in Europe. Additional regulatory requirements exist in most foreign countries including, but not limited to, product standards, packaging requirements, labeling
requirements and import restrictions on devices. Each country has its own tariff regulations,
duties and tax requirements.
Other Information
Copies of the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current
Reports on Form 8-K, and amendments to those reports filed or furnished pursuant to Section 13(a)
or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 are available free of charge through the investor
relations section of the Company’s website (www.nanosphere.us) as soon as reasonably practicable
after the Company electronically files the material with, or furnishes it to, the Securities and
Exchange Commission.
12
Table of Contents
Item 1A. Risk Factors.
Our results from operations may be affected by the risk factors set forth below. All
investors should consider the following risk factors before deciding to purchase securities of the
Company. If any of the following events actually occur, our business, operating results, prospects
or financial condition could be materially and adversely affected. This could cause the trading
price of our common stock to decline and you may lose all or part of your investment. The risks
described below are not the only ones that we face. Additional risks not presently known to us or
that we currently deem immaterial may also significantly impair our business operations and could
result in a complete loss of your investment.
Risks Related to Our Business
We have a history of losses and we may never achieve or maintain profitability.
We have a limited operating history and have incurred significant losses in each fiscal year
since our inception, including net losses of $40.6 million, $33.9 million and $37.0 million in the
years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively. As of December 31, 2010, we had an
accumulated deficit of approximately $279.9 million. Our losses resulted principally from costs
incurred in our research and development programs and from our general and administrative expenses.
In recent years, we have incurred significant costs in connection with the development of the
Verigene System and its test menu. We expect our research and development expense levels to remain
high for the foreseeable future as we seek to enhance our existing product and develop new
products. These losses, among other things, have had and will continue to have an adverse effect on
our working capital, total assets and stockholders’ equity. Because of the numerous risks and
uncertainties associated with our product development and commercialization efforts, we are unable
to predict when we will become profitable, and we may never become profitable. If we fail to
achieve profitability in the future, the market price of our common stock could decline.
Our financial results depend on commercial acceptance of the Verigene System, its array of tests,
and the development of additional tests.
Our future depends on the success of the Verigene System, which depends primarily on its
acceptance by hospitals, research institutions, and independent diagnostic laboratories as a
reliable, accurate and cost-effective replacement for traditional molecular diagnostic measurement
methods. Many hospitals and laboratories already use expensive molecular diagnostic testing
instruments in their laboratories and may be reluctant to change their current procedures for
performing such analyses.
The Verigene System currently does not process a sufficiently broad menu of tests for some
hospitals and laboratories to consider adopting it. Although we continue to develop additional
tests to respond to hospitals’ and laboratories’ needs, we cannot guarantee that we will be able to
develop enough additional tests quickly enough or in a manner that is cost-effective or at all. The
development of new or enhanced products is a complex and uncertain process requiring the accurate
anticipation of technological and market trends, as well as precise technological execution. We are
currently not able to estimate when or if we will be able to develop, commercialize or sell
additional tests or enhance existing products. If we are unable to increase sales of the Verigene
System and its tests or to successfully develop and commercialize other products or tests, our
revenues and our ability to achieve profitability would be impaired.
The regulatory approval process is expensive, time consuming and uncertain and the failure to
obtain such approvals will prevent us from commercializing our future products.
Our products are subject to approval or clearance by the FDA or foreign governmental entities
prior to their marketing for commercial use. The 510(k) clearance and premarket approval processes
as well as the foreign approvals required to initiate sales outside the United States can be
expensive, time consuming and uncertain. It may take as long as eighteen months or longer from
submission to obtain 510(k) clearance, and from one to three years from submission to obtain
premarket approval; however, it may take longer, and 510(k) clearance or premarket approval may
never be obtained. Delays in receipt of, or failure to obtain, clearances or
approvals for future products, including tests that are currently in development, would result
in delayed, or no, realization of revenues from such products and in substantial additional costs
which could decrease our profitability. We have limited experience in filing FDA applications for
510(k) clearance and premarket approval. There are no assurances that we will obtain any required
clearance or approval. Any such failure, or any material delay in obtaining the clearance or
approval, could harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
13
Table of Contents
We and our customers are subject to various governmental regulations, and we may incur significant
expenses to comply with, and experience delays in our product commercialization as a result of,
these regulations.
The products we develop, manufacture and market are subject to regulation by the FDA and
numerous other federal, state and foreign governmental authorities. We generally are prohibited
from marketing our products in the United States unless we obtain either 510(k) clearance or
premarket approval from the FDA.
In addition, we are required to continue to comply with applicable FDA and other regulatory
requirements once we have obtained clearance or approval for a product. These requirements include
the Quality System Regulation, labeling requirements, the FDA’s general prohibition against
promoting products for unapproved or “off-label” uses and adverse event reporting regulations.
Failure to comply with applicable FDA product regulatory requirements could result in warning
letters, fines, injunctions, civil penalties, repairs, replacements, refunds, recalls or seizures
of products, total or partial suspension of production, the FDA’s refusal to grant future
pre-market clearances or approvals, withdrawals or suspensions of current product applications and
criminal prosecution. Any of these actions, in combination or alone, could prevent us from selling
our products and would likely harm our business.
Our manufacturing facilities are subject to periodic regulatory inspections by the FDA and
other federal and state regulatory agencies. The use of our diagnostic products by our customers is
also affected by the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments of 1988, or CLIA, and related
federal and state regulations that provide for regulation of laboratory testing. CLIA is intended
to ensure the quality and reliability of clinical laboratories in the United States by mandating
specific standards in the areas of personnel qualifications, administration, participation in
proficiency testing, patient test management, quality and inspections. Current or future CLIA
requirements or the promulgation of additional regulations affecting laboratory testing may prevent
some laboratories from using some or all of our diagnostic products.
The FDA and foreign governmental regulators have made, and may continue to make, changes in
approval requirements and processes. We cannot predict what these changes will be, how or when they
will occur or what effect they will have on the regulation of our products. Any new regulations,
including regulations specifically related to nanotechnology, may impose additional costs or
lengthen review times of our products. Delays in receipt of or failure to receive regulatory
approvals or clearances for our new products would have a material adverse effect on our business,
financial condition and results of operations.
If third-party payors do not reimburse our customers for the use of our clinical diagnostic
products or if they reduce reimbursement levels, our ability to sell our products will be harmed.
We intend to sell our products primarily to hospital-based laboratories and academic research
institutions, substantially all of which receive reimbursement for the health care services they
provide to their patients from third-party payors, such as Medicare, Medicaid and other domestic
and international government programs, private insurance plans and managed care programs. Most of
these third-party payors may deny reimbursement if they determine that a medical product was not
used in accordance with cost-effective treatment methods, as determined by the third-party payor,
or was used for an unapproved indication. Third-party payors also may refuse to reimburse for
procedures and devices deemed to be experimental.
In the United States, the American Medical Association assigns specific Current Procedural
Terminology, or CPT, codes, which are necessary for reimbursement of diagnostic tests. Once the CPT
code is established, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services establish reimbursement payment
levels and coverage rules under Medicaid and Medicare, and private payors establish rates and
coverage rules independently. Although the tests performed by our assays in development have
previously assigned CPT Codes, we cannot guarantee that our assays are covered by such CPT codes
and are therefore approved for reimbursement by Medicare and Medicaid as well as most third-party
payors. Additionally, certain of our future products may not be approved for reimbursement.
Third-party payors may choose to reimburse our customers on a per test basis, rather than on the
basis of the number of results given by the test. This may result in reference laboratories, public
health institutions and hospitals electing to use separate tests to screen for each disease so that
they can receive reimbursement for each test they conduct. In that event, these entities likely
would purchase separate tests for each disease, rather than products that multiplex.
Third-party payors are increasingly attempting to contain health care costs by limiting both
coverage and the level of reimbursement for medical products and services. Increasingly, Medicare,
Medicaid and other third-party payors are challenging the prices charged for medical services,
including clinical diagnostic tests. Levels of reimbursement may decrease in the future, and future
legislation, regulation or reimbursement policies of third-party payors may adversely affect the
demand for and price levels of our products. If our customers are not reimbursed for our products,
they may reduce or discontinue purchases of our products, which would cause our revenues to
decline.
14
Table of Contents
We may fail to receive positive clinical results from the diagnostic tests currently in development
that require clinical trials, and even if we receive positive clinical results, we may still fail
to receive the necessary clearances or approvals to market our products.
We are investing in the research and development of new products to expand the menu of testing
options for the Verigene System. In order to commercialize our products, we are required to
undertake time consuming and costly development activities, sometimes including clinical trials for
which the outcome is uncertain. Products that appear promising during early development and
preclinical studies may, nonetheless, fail to demonstrate the results needed to support regulatory
approval. Even if we receive positive clinical results, we may still fail to obtain the necessary
FDA clearance and approvals.
Our operating results may be variable and unpredictable.
The sales cycles for our products may be lengthy, which will make it difficult for us to
accurately forecast revenues in a given period, and may cause revenues and operating results to
vary significantly from period to period. In addition to its length, the sales cycle associated
with our products is subject to a number of significant risks, including the budgetary constraints
of our customers, their inventory management practices and possibly internal acceptance reviews,
all of which are beyond our control. Sales of our products will also involve the purchasing
decisions of large, medium and small hospitals and laboratories which can require many levels of
pre-approvals, further lengthening sales time. As a result, we may expend considerable resources on
unsuccessful sales efforts or we may not be able to complete transactions on the scheduled
anticipated.
If we do not achieve significant product revenue, we may not be able to meet our cash requirements
without obtaining additional capital from external sources, and if we are unable to do so, we may
have to curtail or cease operations.
We expect capital outlays and operating expenditures to increase over the next few years as we
expand our infrastructure, commercialization, manufacturing, and research and development
activities. We anticipate that our current cash and cash equivalents, which include the net
proceeds of our initial and secondary public offerings, will be sufficient to meet our estimated
needs for at least twelve months. However, we operate in a market that makes our prospects
difficult to evaluate, and we will need additional financing to execute on our current or future
business strategies. The amount and the timing of the additional capital we will need to raise
depends on many factors, including:
| • | the level of research and development investment required to maintain and improve our technology; | ||
| • | the amount and growth rate, if any, of our revenues; | ||
| • | changes in product development plans needed to address any difficulties in manufacturing or commercializing the Verigene System and enhancements to our system; | ||
| • | the costs of filing, prosecuting, defending and enforcing patent claims and other intellectual property rights; | ||
| • | competing technological and market developments; | ||
| • | our need or decision to acquire or license complementary technologies or acquire complementary businesses; | ||
| • | the expansion of our sales force; and | ||
| • | changes in regulatory policies, practices or laws that affect our operations, including clearance to market our products. |
We cannot be certain that additional capital will be available when and as needed or that our
actual cash requirements will not be greater than anticipated. If we require additional capital at
a time when investment in diagnostics companies or in the marketplace in general is limited due to
the then prevailing market or other conditions, we may not be able to raise such funds at the time
that we desire or any time thereafter. In addition, if we raise additional funds through the
issuance of common stock or convertible securities, the percentage ownership of our stockholders
could be significantly diluted, and these newly issued securities may have rights, preferences or
privileges senior to those of existing stockholders. If we obtain additional debt financing, a
substantial portion of our operating cash flow may be dedicated to the payment of principal and
interest on such indebtedness, and the terms of the debt securities issued could impose significant
restrictions on our operations. If we raise additional funds through collaborations and licensing
arrangements, we might be required to relinquish significant rights to our technologies or
products, or grant licenses on terms that are not favorable to us.
15
Table of Contents
The adverse capital and credit market conditions could affect our liquidity.
Adverse capital and credit market conditions could affect our ability to meet liquidity needs,
as well as our access to capital and cost of capital. The capital and credit markets have been
experiencing extreme volatility and disruption for more than 12 months. In recent months, the
volatility and disruption have reached unprecedented levels and the markets have exerted downward
pressure on availability of liquidity and credit capacity for certain issuers. For example,
recently credit spreads have widened considerably. Our results of operations, financial condition,
cash flows and capital position could be materially adversely affected by continued disruptions in
the capital and credit markets.
If our products do not perform as expected or the reliability of the technology on which our
products are based is questioned, we could experience lost revenue, delayed or reduced market
acceptance of our products, increased costs and damage to our reputation.
Our success depends on the market’s confidence that we can provide reliable, high-quality
diagnostics systems. We believe that customers in our target markets are likely to be particularly
sensitive to product defects and errors.
Our reputation and the public image of our products or technologies may be impaired if our
products fail to perform as expected or our products are perceived as difficult to use. Our
products are complex and may develop or contain undetected defects or errors. Any defects or errors
could lead to the filing of product liability claims, which could be costly and time-consuming to
defend and result in substantial damages. If we experience a sustained material defect or error,
this could result in loss or delay of revenues, delayed market acceptance, damaged reputation,
diversion of development resources, legal claims, increased insurance costs or increased service
and warranty costs, any of which could materially harm our business. We cannot assure you that our
product liability insurance would protect our assets from the financial impact of defending a
product liability claim. A product liability claim could have a serious adverse effect on our
business, financial condition and results of operations.
We rely on third-party license agreements for patents and other technology related to our products,
and the termination of these agreements could delay or prevent us from being able to commercialize
our products.
As of December 31, 2010, our patent portfolio is comprised, on a worldwide basis, of 151
issued patents and 52 pending patent applications which we own directly or for which we are the
exclusive licensee. Some of these patents and patent applications derive from a common parent
patent application or are foreign counterpart patent applications and relate to similar or
identical technological claims. The issued patents cover approximately 11 different technological
claims and the pending patent applications cover approximately 4 additional technological claims.
Many of our issued and pending patents were exclusively licensed from the International
Institute for Nanotechnology at Northwestern University (“Northwestern”) in May 2000 and they
generally cover our core technology, including nanotechnology based biodiagnostics and biobarcode
technology. Our issued patents expire between 2017 and 2025. Our patent portfolio provides
protection against other companies offering products employing the same technologies and methods as
we have patented. While we believe our patent portfolio establishes a proprietary position, there
are many competitive products utilizing other technologies that do not infringe on our patents.
In addition, we have non-exclusive licenses for 47 patents that cover 12 different
technological claims from various third parties. Most of these license agreements require us to pay
the licensor royalty fees that typically expire upon the patent expiration dates
which range from 2011 to 2027. These license agreements are nonexclusive and do not create a
proprietary position. The expiration of these non-exclusive licenses will result in the termination
of certain royalty payments by us to the licensors.
If we are unable to obtain, maintain and enforce intellectual property protection covering our
products, others may be able to make, use, or sell our products, which could adversely affect our
ability to compete in the market.
Our success is dependent in part on obtaining, maintaining and enforcing intellectual property
rights, including patents. If we are unable to obtain, maintain and enforce intellectual property
legal protection covering our products, others may be able to make, use or sell products that are
substantially identical to ours without incurring the sizeable discovery, development and licensing
costs that we have incurred, which would adversely affect our ability to compete in the market.
16
Table of Contents
We seek to obtain and maintain patents and other intellectual property rights to restrict the
ability of others to market products that compete with our products. Currently, our patent
portfolio is comprised, on a worldwide basis, of 151 issued patents and 52 pending patent
applications which, in either case, we own directly or for which we are the exclusive licensee.
However, patents may not be issued from any pending or future patent applications owned by or
licensed to us, and moreover, issued patents owned or licensed to us now or in the future may be
found by a court to be invalid or otherwise unenforceable. Also, even if our patents are determined
by a court to be valid and enforceable, they may not be sufficiently broad to prevent others from
marketing products similar to ours or designing around our patents, despite our patent rights, nor
provide us with freedom to operate unimpeded by the patent rights of others.
Furthermore, we cannot be certain that we were the first to make the invention claimed in our
United States issued patents or pending patent applications, or that we were the first to file for
protection of the inventions claimed in our foreign issued patents or pending patent applications.
We may become subject to interference proceedings conducted in the patent and trademark offices of
various countries to determine our entitlement to patents, and these proceedings may conclude that
other patents or patent applications have priority over our patents or patent applications. It is
also possible that a competitor may successfully challenge our patents through various proceedings
and those challenges may result in the elimination or narrowing of our patents, and therefore
reduce our patent protection. Accordingly, rights under any of our issued patents, patent
applications or future patents may not provide us with commercially meaningful protection for our
products or afford us a commercial advantage against our competitors or their competitive products
or processes.
We have a number of foreign patents and applications. However, the laws of some foreign
jurisdictions do not protect intellectual property rights to the same extent as laws in the United
States, and many companies have encountered significant difficulties in protecting and defending
such rights in foreign jurisdictions. If we encounter such difficulties or we are otherwise
precluded from effectively protecting our intellectual property rights in foreign jurisdictions,
our business prospects could be substantially harmed.
We may initiate litigation to enforce our patent rights, which may prompt our adversaries in
such litigation to challenge the validity, scope or enforceability of our patents. Patent
litigation is complex and often difficult and expensive, and would consume the time of our
management and other significant resources. In addition, the outcome of patent litigation is
uncertain. If a court decides that our patents are not valid, not enforceable or of a limited
scope, we may not have the right to stop others from using the subject matter covered by those
patents.
We also rely on trade secret protection to protect our interests in proprietary know-how and
for processes for which patents are difficult to obtain or enforce. We may not be able to protect
our trade secrets adequately. In addition, we rely on non-disclosure and confidentiality agreements
with our employees, consultants and other parties to protect, in part, our trade secrets and other
proprietary technology. These agreements may be breached and we may not have adequate remedies for
any breach. Moreover, others may independently develop equivalent proprietary information, and
third parties may otherwise gain access to our trade secrets and proprietary knowledge. Any
disclosure of confidential data into the public domain or to third parties could allow our
competitors to learn our trade secrets and use the information in competition against us.
Our products could infringe patent rights of others, which may require costly litigation and, if we
are not successful, could cause us to pay substantial damages or limit our ability to commercialize
our products.
Our commercial success depends on our ability to operate without infringing the patents and
other proprietary rights of third parties. We are aware of third party patents that may relate to
our products and technology. There may also be other patents that relate to our products and
technology of which we are not aware. We may unintentionally infringe upon valid patent rights of
third parties. Although we are currently not involved in any material litigation involving patents,
a third party patent holder could assert a claim of patent infringement against us in the future.
Alternatively, we may initiate litigation against the third party patent holder to request that
a court declare that we are not infringing the third party’s patent and/or that the third
party’s patent is invalid or unenforceable. If a claim of infringement is asserted against us and
is successful, and therefore we are found to infringe, we could be required to pay damages for
infringement, including treble damages if it is determined that we knew or became aware of such a
patent and we failed to exercise due care in determining whether or not we infringed the patent. If
we have supplied infringing products to third parties or have licensed third parties to
manufacture, use or market infringing products, we may be obligated to indemnify these third
parties for damages they may be required to pay to the patent holder and for any losses they may
sustain. We can also be prevented from selling or commercializing any of our products that use the
infringing technology in the future, unless we obtain a license from such third party. A license
may not be available from such third party on commercially reasonable terms, or may not be
available at all. Any modification to include a non-infringing technology may not be possible or if
possible may be difficult or time-consuming to develop, and require revalidation, which could delay
our ability to commercialize our products.
17
Table of Contents
Any infringement action asserted against us, even if we are ultimately successful in defending
against such action, would likely delay the regulatory approval process of our products, harm our
competitive position, be expensive and require the time and attention of our key management and
technical personnel.
We have limited experience in sales and marketing and may be unable to successfully commercialize
our Verigene System, or it may be difficult to build brand loyalty.
We have limited marketing, sales and distribution experience and capabilities. Our ability to
achieve profitability depends on attracting customers for the Verigene System and building brand
loyalty. To successfully perform sales, marketing, distribution and customer support functions
ourselves, we will face a number of risks, including:
| • | our ability to attract and retain the skilled support team, marketing staff and sales force necessary to commercialize and gain market acceptance for our technology and our products; | ||
| • | the ability of our sales and marketing team to identify and penetrate the potential customer base including hospitals, research institutions, and independent diagnostic laboratories; | ||
| • | the time and cost of establishing a support team, marketing staff and sales force; and | ||
| • | the difficulty of establishing brand recognition and loyalty for our products. |
In addition, we may seek to enlist one or more third parties to assist with sales,
distribution and customer support globally or in certain regions of the world. If we do seek to
enter into such arrangements, we may not be successful in attracting desirable sales and
distribution partners, or we may not be able to enter into such arrangements on favorable terms. If
our sales and marketing efforts, or those of any third-party sales and distribution partners, are
not successful, our technologies and products may not gain market acceptance, which would
materially impact our business operations.
We may be unsuccessful in our long-term goal of expanding our product offerings outside the United
States.
To the extent we begin to offer our products broadly outside the United States, we expect that
we will be dependent on third-party distribution relationships. Distributors may not commit the
necessary resources to market and sell our products to the level of our expectations. If
distributors do not perform adequately, or we are unable to locate distributors in particular
geographic areas, our ability to realize long-term international revenue growth would be materially
adversely affected.
Additionally, our products may require regulatory clearances and approvals from jurisdictions
outside the United States. These products may not be sold in these jurisdictions until the required
clearances and approvals are obtained. We cannot assure you that we will be able to obtain these
clearances or approvals on a timely basis, or at all.
Manufacturing risks and inefficiencies may adversely affect our ability to produce products.
We must manufacture or engage third parties to manufacture components of our products in
sufficient quantities and on a timely basis, while maintaining product quality and acceptable
manufacturing costs and complying with regulatory requirements. In determining the required
quantities of our products and the manufacturing schedule, we must make significant judgments and
estimates based on historical experience, inventory levels, current market trends and other related
factors. Because of the inherent nature of estimates, there could be significant differences
between our estimates and the actual amounts of products we require. Additionally, some of the
components of the Verigene System are custom-made by only a few outside vendors, and we do not have
long-term supply contracts for the materials or components supplied by any of our vendors. If
we are unable to obtain from one or more of these vendors the needed materials or components that
meet our specifications on commercially reasonable terms, or at all, we may not be able to meet the
demand for our products. We have not arranged for alternate suppliers, and it may be difficult to
find alternate suppliers in a timely manner and on terms acceptable to us.
We manufacture in one facility. If there were to be a significant disruption in our ability
to use this facility, it would take significant time to setup and validate an alternative
manufacturing facility. Disruptions due to lack of power, flooding, fire and environmental
controls could adversely impact our ability to manufacture. In addition, we have been steadily
increasing manufacturing capacity to meet demand for our products. A disruption of our
manufacturing operations resulting from scale-up related challenges such as obtaining sufficient
raw materials, hiring of qualified factory personnel, installation and efficient operation of new
equipment, and management of our quality controls could cause us to cease, delay, or limit our
manufacturing operations and consequently adversely impact our business, our results of operations
and our financial condition.
18
Table of Contents
We may experience unforeseen technical complications in the processes we use to develop,
manufacture, customize or receive orders for our products. These complications could materially
delay or limit the use of products we attempt to commercialize, substantially increase the
anticipated cost of our products or prevent us from implementing our processes at appropriate
quality and scale levels, thereby causing our business to suffer. In addition, our manufacturing
operations use highly technical processes involving unique, proprietary techniques that our
manufacturing personnel must continuously monitor and update, especially as we develop more
products. In order to be profitable, we must manufacture greater quantities of products than we
have to date and we must do this more efficiently than we have in the past. We may not be able to
do so.
We will need to develop manufacturing capacity by ourselves or with third parties.
We will need to either continue to build internal manufacturing capacity or contract with one
or more manufacturing partners, or both. We currently use a combination of outsourced and internal
manufacturing activities. We may encounter difficulties in manufacturing our products and, due to
the complexity of our technology and our manufacturing process, we cannot be sure we fully
understand all of the factors that affect our manufacturing processes or product performance. We
may not be able to build manufacturing capacity internally or find one or more suitable
manufacturing partners, or both, to meet the volume and quality requirements necessary to be
successful in the market. If our products do not consistently meet our customers’ performance
expectations, we may be unable to generate sufficient revenues to become profitable. Significant
additional resources, implementation of additional manufacturing equipment and changes in our
manufacturing processes and organization may be required for the scale-up of each new product prior
to commercialization or to meet increasing customer demand once commercialization begins, and this
work may not be successfully or efficiently completed. Any delay in establishing or inability to
expand our manufacturing capacity could delay our ability to develop or sell our products, which
would result in lost revenue and seriously harm our business, financial condition and results of
operations.
Our business and future operating results may be adversely affected by events outside of our
control.
We
develop and manufacture the Verigene System instruments and assays in our facility located in
Northbrook, Illinois. This facility and the manufacturing equipment we use would be costly to
replace and could require substantial lead time to repair or replace. Our business and operating
results may be harmed due to interruption of our manufacturing by events outside of our control,
including earthquakes, tornadoes and fires. Other possible disruptions may include power loss and
telecommunications failures. In the event of a disruption, we may lose customers and we may be
unable to regain those customers thereafter. Our insurance may not be sufficient to cover all of
our potential losses and may not continue to be available to us on acceptable terms, or at all.
We face intense competition from established and new companies in the molecular diagnostics field.
We compete with companies that design, manufacture and market already existing and new
molecular diagnostics systems, and single target or low count multiplexing systems and assays are
abundant. We anticipate that we will face increased competition in the future as new companies
enter the market with new technologies and our competitors improve their current products. One or
more of our competitors may offer technology superior to ours and render our technology obsolete or
uneconomical. If a competitor were able to deliver a testing application that offers simplicity
and ease of use, high count multiplexing and high throughput and fast turnaround, our ability to
successfully market our products would be materially adversely affected. Most of our current
competitors, as well as many of our potential competitors, have greater name recognition, more
substantial intellectual property portfolios, longer operating histories, significantly greater
resources to invest in new technologies and more substantial experience in new product development,
regulatory expertise, manufacturing capabilities and the distribution channels to deliver
products to customers. If we are not able to compete successfully, we may not generate sufficient
revenue to become profitable.
Our success may depend upon how we and our competitors anticipate and adapt to market conditions.
The markets for our products are characterized by rapidly changing technology, evolving
industry standards, changes in customer needs, emerging competition and new product introductions.
The success of our products will depend on our ability to continue to increase their performance
and decrease their price. New technologies, techniques or products could emerge with similar or
better price-performance than our system and could exert pricing pressures on our products. It is
critical to our success for us to anticipate changes in technology and customer requirements and to
successfully introduce enhanced and competitive technology to meet our customers’ and prospective
customers’ needs on a timely basis. We may not be able to maintain our technological advantages
over emerging technologies in the future and we will need to respond to technological innovation in
a rapidly changing industry. If we fail to keep pace with emerging technologies our system will
become uncompetitive, our market share will decline and our business, revenue, financial condition
and operating results could suffer materially.
19
Table of Contents
We may not be able to manage our anticipated growth, and we may experience constraints or
inefficiencies caused by unanticipated acceleration and deceleration of customer demand.
Demand for our respiratory products is directly proportionate to the size and duration of
influenza and other respiratory illnesses. Unanticipated acceleration and deceleration of customer
demand for our products may result in constraints or inefficiencies related to our manufacturing,
sales force, implementation resources and administrative infrastructure. Such constraints or
inefficiencies may adversely affect us as a result of delays, lost potential product sales or loss
of current or potential customers due to their dissatisfaction. Similarly, over-expansion or
investments in anticipation of growth that does not materialize, or develops more slowly than we
expect, could harm our financial results and result in overcapacity.
To manage our anticipated future growth effectively, we must enhance our manufacturing
capabilities and operations, information technology infrastructure, and financial and accounting
systems and controls. Organizational growth and scale-up of operations could strain our existing
managerial, operational, financial and other resources. Our growth could require significant
capital expenditures and may divert financial resources from other projects, such as the
development of new products or enhancements of existing products. If our management is unable to
effectively manage our growth, our expenses may increase more than expected, our revenue could grow
more slowly than expected and we may not be able to achieve our research and development and
commercialization goals. Our failure to manage our anticipated growth effectively could have a
material adverse effect on our business, operating results or financial condition.
We use hazardous chemicals, biological materials, and infectious diseases in our business. Any
claims relating to improper handling, storage or disposal of these materials could be time
consuming and costly.
Our research and development and manufacturing processes involve the controlled use of
hazardous materials, including chemicals, biological materials and infectious diseases. Our
operations produce hazardous waste products. We cannot eliminate the risk of accidental
contamination or discharge and any resultant injury from these materials. We may be sued for any
injury or contamination that results from our use or the use by third parties of these materials,
and our liability may exceed our insurance coverage and our total assets. Federal, state and local
laws and regulations govern the use, manufacture, storage, handling and disposal of these hazardous
materials and specified waste products, as well as the discharge of pollutants into the environment
and human health and safety matters. Compliance with environmental laws and regulations may be
expensive, and may impair our research, development and production efforts. If we fail to comply
with these requirements, we could incur substantial costs, including civil or criminal fines and
penalties, clean-up costs, or capital expenditures for control equipment or operational changes
necessary to achieve and maintain compliance. In addition, we cannot predict the impact on our
business of new or amended environmental laws or regulations, or any changes in the way existing
and future laws and regulations are interpreted and enforced.
If we are unable to recruit and retain key executives and scientists, we may be unable to achieve
our goals.
Our performance is substantially dependent on the performance of our senior management and key
scientific and technical personnel. The loss of the services of any member of our senior management
or our scientific or technical staff could divert management’s attention to transition matters and
identification of suitable replacements, if any, and have a material adverse effect on our
business, operating results and financial condition. Each of our executive officers and other key
employees could terminate his or her relationship with us at any time. We do not maintain key man
life insurance on any of our employees.
In addition, our product development and marketing efforts could be delayed or curtailed if we
are unable to attract, train and retain highly skilled employees and scientific advisors,
particularly our management team, senior scientists and engineers and sales and marketing
personnel. To expand our research, product development and sales efforts we need additional people
skilled in areas such as protein science, information services, manufacturing, sales, marketing and
technical support. Because of the complex and technical nature of our system and the dynamic market
in which we compete, any failure to attract and retain a sufficient number of qualified employees
could materially harm our ability to develop and commercialize our technology. We may not be
successful in hiring or retaining qualified personnel and our failure to do so could have a
material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of operations.
20
Table of Contents
Healthcare reform and restrictions on reimbursement may adversely affect our profitability.
In the United States, healthcare providers that purchase our products and other diagnostic
products generally rely on third-party payors to reimburse all or part of the cost of the
procedure. In international markets, reimbursement and healthcare payment systems vary
significantly by country, and include both government-sponsored healthcare and private insurance.
Third-party payors can affect the pricing or the relative attractiveness of our products by
regulating the maximum amount of reimbursement provided by such payors for laboratory testing
services. Lower-than-expected or decreases in reimbursement amounts for tests performed using our
products may decrease amounts physicians and other practitioners are able to charge patients, which
in turn may adversely affect the willingness of physicians and other practitioners to purchase our
products at prices we target, or at all. If we were not able to sell our products at target prices,
then we will suffer a decrease in expected profitability that would likely adversely affect our
business, financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, political, economic and regulatory influences are subjecting the healthcare
industry to potential fundamental changes that could substantially affect our results of
operations. Government and private sector initiatives to limit the growth of healthcare costs,
including price regulation, competitive pricing, coverage and payment policies, comparative
effectiveness of therapies, technology assessments and managed-care arrangements, are continuing.
These changes are causing the marketplace to put increased emphasis on the delivery of more
cost-effective treatments. In addition, uncertainty remains regarding proposed significant reforms
to the U.S. healthcare system, including the potential innovation tax on medical device companies.
Risks Related to Our Common Stock
The market price of our common stock may be volatile and fluctuate significantly, which could
result in substantial losses for investors and subject us to securities class action litigation.
Market prices of diagnostics companies have been volatile. Among the factors that may cause
the market price of our common stock to fluctuate are the risks described in this “Risk Factors”
section and other factors, including:
| • | fluctuations in our quarterly operating results or the operating results of our competitors; | |
| • | changes in estimates of our financial results or recommendations by securities analysts; | |
| • | variance in our financial performance from the expectations of securities analysts; | |
| • | changes in the estimation of the future size and growth rate of our markets; | |
| • | changes in accounting principles or changes in interpretations of existing principles, which could affect our financial results; | |
| • | failure of our products to achieve or maintain market acceptance or commercial success; | |
| • | conditions and trends in the markets we serve; | |
| • | changes in general economic, industry and market conditions; | |
| • | success of competitive products and services; | |
| • | changes in market valuations or earnings of our competitors; | |
| • | changes in our pricing policies or the pricing policies of our competitors; | |
| • | announcements of significant new products, contracts, acquisitions or strategic alliances by us or our competitors; | |
| • | changes in legislation or regulatory policies, practices, or actions; | |
| • | the commencement or outcome of litigation involving our company, our general industry or both; | |
| • | recruitment or departure of key personnel; | |
| • | changes in our capital structure, such as future issuances of securities or the incurrence of additional debt; | |
| • | actual or expected sales of our common stock by our stockholders; and | |
| • | the trading volume of our common stock. |
21
Table of Contents
In addition, the stock market in general, the NASDAQ Global Market and the market for
diagnostics companies in particular, may experience a loss of investor confidence. Such loss of
investor confidence may result in extreme price and volume fluctuations in our common stock that
are unrelated or disproportionate to the operating performance of our business, financial condition
or results of operations. These broad market and industry factors may materially harm the market
price of our common stock and expose us to securities class action litigation. Such litigation,
even if unsuccessful, could be costly to defend and divert management’s attention and resources,
which could further materially harm our financial condition and results of operations.
If equity research analysts do not publish research or reports about our business or if they issue
unfavorable commentary or downgrade our common stock, the price of our common stock could decline.
The liquidity of the trading market for our common stock may be affected in part by the
research and reports that equity research analysts publish about us and our business. We do not
control the opinions of these analysts. The price of our stock could decline if one or more equity
analysts downgrade our stock or if those analysts issue other unfavorable commentary or cease
publishing reports about us or our business.
Certain provisions of our corporate governing documents could make an acquisition of our company
more difficult.
Certain provisions of our organizational documents could discourage potential acquisition
proposals, delay or prevent a change in control of us or limit the price that investors may be
willing to pay in the future for shares of our common stock. For example, our amended and restated
certificate of incorporation and amended and restated by-laws:
| • | authorize the issuance of preferred stock that can be created and issued by our board of directors without prior stockholder approval, commonly referred to as “blank check” preferred stock, with rights senior to those of our common stock; | |
| • | limit the persons who can call special stockholder meetings; | |
| • | provide that a majority vote of our stockholders is required to amend our amended and restated certificate of incorporation and amended and restated by-laws; | |
| • | establish advance notice requirements to nominate persons for election to our board of directors or to propose matters that can be acted on by stockholders at stockholder meetings; | |
| • | not provide for cumulative voting in the election of directors; and | |
| • | provide for the filling of vacancies on our board of directors by action of a majority of the directors and not by the stockholders. |
These and other provisions in our organizational documents could allow our board of directors
to affect your rights as a stockholder in a number of ways, including making it more difficult for
stockholders to replace members of the board of directors. Because our board of directors is
responsible for approving the appointment of members of our management team, these provisions could
in turn affect any attempt to replace the current management team. These provisions could also
limit the price that investors would be willing to pay in the future for shares of our common
stock.
Our amended and restated articles of incorporation provide that Section 203 of the Delaware
General Corporation Law, an anti-takeover law, will not apply to us. Section 203 generally
prohibits an interested stockholder from engaging in certain types of business combinations with a
Delaware corporation for three years after becoming an interested stockholder. An “interested
stockholder” is a person who, together with affiliates and associates, owns 15% or more of the
corporation.
22
Table of Contents
Our 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan includes an automatic share replenishment, or “evergreen,”
provision that, unless our board of directors takes action to the contrary, will automatically
increase the number of shares of our common stock reserved for issuance under this plan each year.
Issuances of awards under this Plan would cause further dilution to existing stockholders.
In March 2007 our board of directors adopted and our shareholders approved our 2007 Long-Term
Incentive Plan (the “2007 Plan”). The 2007 Plan authorizes the grant of stock options, share
appreciation rights, restricted shares, restricted share units, unrestricted shares, incentive
stock options, deferred share units and performance awards. The total awards originally authorized
under the 2007 Plan was 4,106,009 shares, plus up to an additional 773,591 shares of common stock
that will become available in the event that awards made under our 2000 Equity Incentive Plan
expire, are forfeited or cancelled, plus an annual increase in the number of shares pursuant to the
evergreen provision equal to the least of: 900,000 shares of common stock; 4.0% of our outstanding
shares of common stock as of fiscal year end; and an amount determined by the board of directors.
At December 31, 2010, there were 28,408,506 outstanding shares of our common stock. In
addition, there were outstanding options to purchase 4,208,830 shares of our common stock
(including 479,412 shares authorized pursuant to the evergreen provision of the Plan), of which
2,000 were in-the-money based on our December 31, 2010 closing stock price. Pursuant to the
evergreen provision, an additional 900,000 shares of our common stock were authorized for issuance
under the 2007 Plan as of January 1, 2011. Collectively, the outstanding shares as of December 31,
2010, the in-the-money options and warrants as of December 31, 2010 and the additional shares
authorized on January 1, 2011 pursuant to the evergreen provision were 29,310,506 (the “Adjusted
Outstanding Shares”).
On January 1, 2012, a maximum of 900,000 additional shares may be authorized under our 2007
Plan as a result of this evergreen provision. If the maximum number of shares under the evergreen
provision were to be authorized and issued, the future shares issued under the evergreen provision
would result in an approximate 3% increase in the Adjusted Outstanding Shares as of December 31,
2010.
The evergreen provision of the 2007 Plan will increase the likelihood that we will not request
existing stockholders to authorize additional shares for issuance under the 2007 Plan or a new
plan. However, other factors, such as a material increase in the number of our award-eligible
employees, or competitive conditions to attract or keep valuable employees, may affect the
likelihood of our requesting stockholders to authorize additional shares under this plan or a new
plan. The issuance, perception that issuance may occur, or exercise of these options may have a
dilutive impact on other stockholders and could have a material negative effect on the market price
of our common stock.
We do not currently intend to pay dividends on our capital stock and, consequently, your ability to
achieve a return on your investment will depend on appreciation in the price of our common stock.
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock, and we currently intend
to invest our future earnings, if any, to fund the development and growth of our business.
Therefore, we do not anticipate declaring or paying cash dividends on our common stock in the
foreseeable future. The payment of dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors
and will depend on our results of operations, capital requirements, financial condition, future
prospects, contractual arrangements, restrictions imposed by applicable law, any limitations on
payments of dividends present in our current and future debt agreements, and other factors our
board of directors may deem relevant. If we do not pay dividends, your ability to achieve a return
on your investment in our company will depend on any future appreciation in the market price of our
common stock. There is no guarantee that shares of our common stock will appreciate in value or
even maintain the price at which our stockholders have purchased their shares.
We will continue to incur costs and demands upon management as a result of complying with the laws
and regulations affecting public companies, which may adversely affect our operating results and
failure to achieve and maintain effective internal controls in accordance with Section 404 of the
Sarbanes-Oxley Act could cause investors to lose confidence in our operating results and in the
accuracy of our financial reports and could have a material adverse effect on our business and on
the price of our common stock.
As a public company, we are required, pursuant to Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of
2002, to furnish a report by management on, among other things, the effectiveness of our internal
control over financial reporting for our 2010 fiscal year. Management is responsible for
implementing controls and other procedures designed to ensure that information required to be
disclosed by us in the reports that we file with the SEC is disclosed accurately and is recorded,
processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the SEC’s rules and forms.
While we have implemented the internal controls that we feel are necessary to comply with Section
404 of the Sarbanes Oxley Act, these controls may become inadequate because of changes in
conditions or the degree of compliance with these policies or procedures may deteriorate.
23
Table of Contents
Furthermore, as a public company, changing laws, regulations and standards relating to
corporate governance and public disclosure, including regulations implemented by the Securities and
Exchange Commission and the NASDAQ may increase legal and financial compliance costs and make some
activities more time consuming. These laws, regulations and standards are subject to varying
interpretations and, as a result, their application in practice may evolve over time as new
guidance is provided by regulatory and governing bodies. We intend to invest resources to comply
with evolving laws, regulations and standards, and this investment may result in increased general
and administrative expenses and a diversion of management’s time and attention from
revenue-generating activities to compliance activities. If notwithstanding our efforts to comply
with new laws, regulations and standards, we fail to comply, regulatory authorities may initiate
legal proceedings against us and our business may be harmed.
Failure to comply with these rules might also make it more difficult for us to obtain certain
types of insurance, including director and officer liability insurance, and we might be forced to
accept reduced policy limits and coverage and/or incur substantially higher costs to obtain the
same or similar coverage. The impact of these events could also make it more difficult for us to
attract and retain qualified persons to serve on our board of directors, on committees of our board
of directors, or as executive officers.
Concentration of ownership among some of our stockholders, including directors and management may
limit your ability to influence corporate matters.
As of February 10, 2011, approximately 75% of our common stock including the exercise of all
outstanding warrants and exercisable options to purchase our common stock will be beneficially held
by our directors, our executive officers, and greater than five percent stockholders and their
respective affiliates. Lurie Investment Fund, L.L.C., Lurie Investments, Inc., AOQ Trust,
Alfa-Tech, L.L.C., and their respective affiliates, own 29% of our common stock, and Bain Capital
Venture Fund 2005, L.P. and their respective affiliates own 7% of our common stock. Consequently, a
small number of our stockholders may be able to substantially influence our management and affairs.
If they choose to act together, they would be able to influence most matters requiring approval by
our stockholders, including the election of directors, any merger, consolidation or sale of all or
substantially all of our assets and any other transaction. The concentration of ownership may also
delay or prevent a change in control of us even if such changes might otherwise be beneficial to
our stockholders. In addition the significant concentration of share ownership may adversely affect
the trading price of our common stock because investors often perceive disadvantages in owning
shares in companies with controlling stockholders.
Item 1B. Unresolved Staff Comments.
None.
Item 2. Properties.
Our executive, research and development and manufacturing functions are all located at a
40,945 square foot leased facility in Northbrook, Illinois. The lease for our Northbrook facility
expires in May 2014. Our recently revised facilities lease includes the right of first offer on
additional available space in our building. While we do not need to expand our facilities to meet
anticipated demand for 2011, we will likely require expanded facilities to meet anticipated demand
beyond 2011.
We do not own any real property.
Item 3. Legal Proceedings.
We are from time to time subject to various claims and legal actions during the ordinary
course of our business. We believe that there are currently no claims or legal actions that would,
in management’s judgment based on information currently available, have a material adverse effect
on our results of operations or financial condition.
Item 4. (Removed and Reserved).
24
Table of Contents
PART II
Item 5. Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Stockholder Matters, and Issuer Purchases
of Equity Securities.
Market Information
Our common stock has been traded on the NASDAQ Global Market since November 1, 2007 under the
symbol “NSPH”. The following table sets forth the high and low sale prices for our common stock for
each quarter of our two most recent fiscal years, as reported on the NASDAQ Global Market for the
period indicated.
| High | Low | |||||||
Fiscal year ended December 31, 2010 |
||||||||
First Quarter |
$ | 6.80 | $ | 3.15 | ||||
Second Quarter |
6.46 | 4.20 | ||||||
Third Quarter |
5.09 | 2.91 | ||||||
Fourth Quarter |
5.95 | 4.16 | ||||||
Fiscal year ended December 31, 2009 |
||||||||
First Quarter |
$ | 6.26 | $ | 2.71 | ||||
Second Quarter |
5.58 | 2.95 | ||||||
Third Quarter |
8.61 | 3.94 | ||||||
Fourth Quarter |
7.85 | 5.60 | ||||||
Stockholders
The last reported sale price of common stock on February 10, 2011 as reported on the NASDAQ
Global Market was $3.54. As of February 10, 2011, there were 194 holders of record of our common
stock.
Dividend Policy
We have never declared or paid any cash dividends on our common stock and do not expect to pay
any dividends for the foreseeable future. We currently intend to retain any future earnings to fund
the operation, development and expansion of our business. Any future determination to pay dividends
will be at the sole discretion of our board of directors and will depend upon a number of factors,
including our results of operations, capital requirements, financial condition, future prospects,
contractual arrangements, restrictions imposed by applicable law, any limitations on payments of
dividends present in our current and future debt arrangements, and other factors our board of
directors may deem relevant.
25
Table of Contents
Stock Performance Graph
The following graph shows a comparison of cumulative total stockholder returns for our common
stock, the NASDAQ Composite Index and the NASDAQ Biotechnology Index. The graph assumes the
investment of $100 on November 1, 2007, the date of our initial public offering and listing of our
common stock on the NASDAQ Global Market, and the reinvestment of all dividends. The performance
shown is not necessarily indicative of future performance.
| November | December | December | December | December | ||||||||||||||||
| Investment Return Analysis | 2007 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||
Nanosphere |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 99.93 | $ | 34.00 | $ | 46.00 | $ | 31.14 | ||||||||||
NASDAQ Composite |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 93.55 | $ | 55.63 | $ | 80.04 | $ | 93.58 | ||||||||||
NASDAQ Biotechnology |
$ | 100.00 | $ | 94.07 | $ | 82.19 | $ | 95.04 | $ | 109.30 | ||||||||||
The information contained in the graph above shall not be deemed to be “soliciting material”
or to be “filed” with the SEC, nor shall such information be incorporated by reference into any
future filing under the Securities Act or the Exchange Act, or subject to Regulation 14A or 14C
promulgated under the Exchange Act, other than as provided in Item 402 of the SEC’s Regulation S-K,
or to the liabilities of Section 18 of the Exchange Act, except to the extent that Nanosphere
specifically requests that the information be treated as soliciting material or specifically
incorporates it by reference in such filing.
26
Table of Contents
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table provides information as of December 31, 2010 with respect to shares of the
Company’s common stock that may be issued under the 2007 Plan, which is the Company’s only existing
equity compensation plan under which grants can be made. Stockholders approved the Company’s 2007
Plan on March 27, 2007.
Equity Compensation Plan Information
| Number of securities | ||||||||||||
| remaining available for | ||||||||||||
| future issuance under | ||||||||||||
| equity compensation | ||||||||||||
| Number of securities to | Weighted Average | plans (excluding | ||||||||||
| be issued upon exercise | exercise price of | securities reflected in | ||||||||||
| of outstanding awards | outstanding awards | column(a)) | ||||||||||
| Plan Category | (a) | (b) | (c) | |||||||||
Equity compensation plans approved by stockholders |
4,208,830 | $ | 5.60 | 1,309,736 | ||||||||
Equity compensation plans not approved by stockholders |
— | — | — | |||||||||
Total |
4,208,830 | $ | 5.60 | 1,309,736 | ||||||||
Pursuant to the evergreen provision, an additional 900,000 shares of common stock were
authorized for issuance under the 2007 Plan as of January 1, 2011.
Item 6. Selected Financial Data.
The following selected financial data should be read in conjunction with, and is qualified by
reference to, our financial statements and related notes and “Item 7. Management’s Discussion and
Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” appearing elsewhere in this report.
| As of December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statements of Operations Data: | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Total revenue |
$ | 2,026 | $ | 2,214 | $ | 1,367 | $ | 1,167 | $ | 1,138 | ||||||||||
Research and development expense |
18,821 | 18,608 | 23,675 | 21,446 | 18,186 | |||||||||||||||
Sales, general and administrative expense |
22,007 | 14,472 | 13,616 | 13,443 | 5,416 | |||||||||||||||
Net loss |
(40,612 | ) | (33,949 | ) | (37,042 | ) | (53,199 | ) | (24,270 | ) | ||||||||||
Net loss attributable to common stock |
(40,612 | ) | (33,949 | ) | (37,042 | ) | (59,284 | ) | (46,421 | ) | ||||||||||
Net loss per common share: |
||||||||||||||||||||
basic and diluted |
(1.46 | ) | (1.46 | ) | (1.67 | ) | (14.18 | ) | (53.63 | ) | ||||||||||
Weighted average number of common shares: |
||||||||||||||||||||
basic and diluted (1)(2) |
27,755 | 23,302 | 22,213 | 4,181 | 866 | |||||||||||||||
| As of December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data: | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents (1)(2) |
$ | 39,628 | $ | 76,689 | $ | 75,357 | $ | 114,313 | $ | 29,112 | ||||||||||
Working capital (1)(2) |
37,426 | 71,152 | 69,027 | 107,685 | 27,332 | |||||||||||||||
Total assets (1)(2) |
51,375 | 88,669 | 86,896 | 125,964 | 37,968 | |||||||||||||||
Long-term debt |
— | — | 3,352 | 7,462 | 59 | |||||||||||||||
Convertible preferred stock (2) |
— | — | — | — | 108,868 | |||||||||||||||
Stockholders’ equity (deficit) (1)(2) |
44,524 | 79,082 | 74,541 | 109,200 | (108,308 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| (1) | In October 2009, we completed our underwritten public offering of 5,405,000 shares of common stock at $7.00 per share. We received approximately $35.4 million of net proceeds from the offering. | |
| (2) | In November 2007, we completed our initial public offering of 8,050,000 shares of common stock at $14.00 per share. We received approximately $102 million of net proceeds from the offering. All shares of convertible preferred stock were converted to common stock upon the closing of the initial public offering. |
27
Table of Contents
Item 7. Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.
The following discussion and analysis is based primarily on the financial statements of
Nanosphere, Inc. for the years presented and should be read together with the notes thereto
contained in this annual report on Form 10-K. Terms employed herein as defined terms, but without
definition, have the meanings set forth in the notes to the financial statements (see “Item 8.
Financial Statements and Supplementary Data”).
Business Overview
We develop, manufacture and market an advanced molecular diagnostics platform, the Verigene
System, that enables simple, low cost and highly sensitive genomic and protein testing on a single
platform. Our proprietary nanoparticle technology provides the ability to run multiple tests
simultaneously on the same sample. The Verigene System includes, a bench-top molecular diagnostics
workstation that is a universal platform for genomic and protein testing. While many systems
currently available on the market provide a diagnostic result for one test or a few tests within a
specific market niche, the Verigene System provides for multiple tests to be performed on a single
platform, including both genomic and protein assays, from a single sample.
The Verigene System is differentiated by its ease of use, rapid turnaround times and ability
to detect many targets on a single test, referred to as “multiplexing.” It provides lower cost for
laboratories already performing molecular diagnostic testing and enables smaller laboratories and
hospitals without advanced diagnostic capabilities to perform genetic testing. Our ability to
detect proteins, which can be as much as 100 times more sensitive than current technologies for
certain targets, may enable earlier detection of and intervention in diseases associated with known
biomarkers as well as the introduction of tests for new biomarkers that exist in concentrations too
low to be detected by current technologies. We are focused on the clinical diagnostics market.
Our test menu is designed to fulfill the following unmet hospital laboratory needs:
| 1) | the conversion of microbiology to molecular methods to more rapidly pinpoint infectious diseases; | ||
| 2) | point-of-care pharmacogenetics to ensure that appropriate therapies are prescribed; and | ||
| 3) | earlier detection of life threatening disease through ultra-sensitive protein assays. |
The Verigene System is comprised of a microfluidics processor, a touchscreen reader and
disposable test cartridges. Certain assays, such as the Warfarin metabolism test and the
hyper-coagulation test, were cleared by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (“FDA”) for use with the original Verigene System processor
(the “Original Processor”). Subsequently, we developed and launched a second generation Verigene System
processor (the “Processor SP”) that handles
the same processing steps as the Original Processor and incorporates sample preparation. Some of
our current customers continue to use the Original Processor for hyper-coagulation testing and
Warfarin metabolism testing. Our development plans are focused on expanding the menu of tests that
will run on the Processor SP, and all future assays are expected to be submitted to the FDA on the
Processor SP.
28
Table of Contents
Our Applications
The
following table summarizes the FDA and CE IVD Mark regulatory status
of our near-term genomic and protein assays on the Verigene System:
| Assay | FDA Status | CE IVD Mark Status | ||
Infectious Disease Assays |
||||
Respiratory Virus
|
510(k) cleared | |||
Respiratory Virus with Sub-Typing
|
510(k) cleared | CE IVD Marked | ||
Blood Infection Panels
|
In development | In development | ||
Human and Pharmacogenetic Assays |
||||
Warfarin Metabolism
|
510(k) cleared(1) | CE IVD Marked | ||
Hyper-Coagulation
|
510(k) cleared(1) | Pending | ||
Plavix® Metabolism (2C19)
|
Premarket approval filing submitted third quarter 2010 |
Pending | ||
Ultra-Sensitive Protein Assays |
||||
Cardiac Troponin I
|
In development | In development | ||
Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA)
|
Research use only |
| (1) | Currently cleared only for use with the Original Processor. |
Infectious Disease Assays
The conversion of microbiology to molecular methods is driven by the need to identify
infectious diseases more quickly, allowing a more rapid commencement of clinical intervention.
Microbiology labs need tests that can rapidly detect a wide range of potential infectious agents in
an automated system. The Verigene System provides the multiplexing, rapid turnaround and
ease-of-use needed by these labs. Our infectious disease menu and the Processor SP provide
microbiology labs with a compelling solution for conversion to molecular testing.
We have received 510(k) clearance from the FDA for our respiratory panel that detects the
presence of influenza A and B as well as respiratory syncytial virus (“RSV”) A and B. Influenza is
commonly known as the seasonal flu and RSV is a respiratory virus that infects the lungs and
breathing passages. RSV is the most common cause of bronchitis and pneumonia in children under the
age of one year and has become a significant concern for older adults. Our respiratory panel
provides physicians with a highly accurate and fast determination of which virus is present. This
test result guides the most appropriate treatment therapy.
In the fourth quarter of 2009, we received 510(k) clearance from the FDA for our respiratory
panel on the Processor SP. We believe that our respiratory assay on the Processor SP offers a
simple-to-use molecular test for diagnosing respiratory infections and the flu, while providing
improved sensitivity over currently available rapid tests. We have received clearance for a package
insert change for this assay confirming that the novel H1N1 virus is detected as a positive
Influenza A when using our respiratory assay and the Processor SP.
In the first quarter of 2011, we received 510(k) clearance from the FDA and CE IVD Mark for
our respiratory assay that includes subtyping for seasonal H1 virus, seasonal H3 virus, and the
2009 novel H1N1 virus, commonly known as swine flu, as well as the targets on our previously
cleared respiratory assay. We believe this is the first sample-to-result molecular respiratory test
to include all
of these viruses, thus lowering the cost of molecular respiratory testing for hospitals and
demonstrating the multiplexing capability of the Verigene System. The demand for this test will be
highly dependent upon the seasonality and prevalence of respiratory viruses.
29
Table of Contents
We are developing three blood stream infection panels for the earlier detection of specific
bacteria present within patients with blood stream infections. Currently under development are gram
positive, gram negative and fungal panels. These assays are designed to enable physicians to
pinpoint bacterial strains infecting patients and thus prescribe the most appropriate antibiotic
regimen within 24 hours rather than after several days. Treatment is sometimes begun before assays
are complete and we believe that this early detection capability will allow patients to avoid
unnecessary treatments that may expose them to serious side effects. These assays will require
regulatory submission to the FDA along with corresponding CE mark
filings.
Our development efforts also include a C. difficile test and an enteric bacteria test. C.
difficile is a bacterium that can cause symptoms ranging from diarrhea to life-threatening
inflammation of the colon. Our enteric bacteria assay is being developed to detect and identify the
Enterobacteriaceae species that most often result from food poisoning. The enteric assay tests for
a wide spectrum of bacteria that are treated with various antibiotics and other anti-bacterial drug
therapies. These assays also will require regulatory submission to the FDA and corresponding
foreign regulatory bodies.
Human and Pharmacogenetic Assays
Hospitals need faster, less expensive and easier-to-use human and pharmacogenetic tests that
can be run for a single patient at the point-of-care. Our Verigene System and human and
pharmacogenetic test menu addresses these hospital needs. Pharmacogenomics is an emerging subset of
human genetic testing that correlates gene variation with a drug’s efficacy or toxicity. These
tests play a key role in the advancement of personalized medicine where drug therapies and dosing
are guided by each patient’s genetic makeup. There is a growing demand on laboratories to implement
molecular diagnostic testing, but the cost and complexity of existing technologies and the need for
specialized personnel and facilities have limited the number of laboratories with these
capabilities. The ease-of-use and reduced complexity of the Verigene System enables any hospital to perform these testing needs.
We have received 510(k) clearance from the FDA for a warfarin metabolism assay performed on
our Original Processor. This is a pharmacogenetic test to determine the existence of certain
genetic mutations that affect the metabolism of warfarin-based drugs, including
Coumadin®, the most-prescribed oral anticoagulant. This assay has been CE IVD
Marked during the first quarter of 2011, and we plan to submit an FDA application for this assay to
allow its use on the Processor SP.
In the third quarter of 2010, we filed a pre-market approval application (“PMA”) with the FDA
for our cytochrome P450 2C19 assay that detects genetic mutations associated with deficient
metabolism of clopidogrel, more commonly known by the trade name Plavix. Clopidogrel inhibits
platelet function and is a standard treatment to reduce the risk of thrombolytic events for
patients undergoing percutaneous coronary interventions. Clopidogrel metabolism is affected by the
cytochrome P-450 family of genes. Up to 50% of the population possess variations in these genes and
abnormally metabolize this drug, thus increasing the risk of adverse events. Our 2C19 assay is
designed to identify patients possessing certain of these variations so that alternative
therapeutic approaches can be prescribed to reduce clotting that can result in heart attack or
stroke. We plan to file for CE IVD Mark for this assay during the first quarter of 2011.
We have also received 510(k) clearance from the FDA for a hyper-coagulation assay on the
Original Processor that determines an individual’s risk, based upon genetic information, for the
development of blood clots that can lead to pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis. We plan to
submit an additional FDA application and file for CE IVD Mark to allow its use on the Processor SP.
Ultra-Sensitive Protein Assays
Our ability to detect proteins at sensitivity levels that can be up to 100 times greater than
current technologies may enable earlier detection of and intervention in diseases as well as enable
the introduction of tests for new biomarkers that exist in concentrations too low to be detected by
current technologies. We have developed or are currently developing diagnostic tests for markers
that reveal the existence of a variety of medical conditions including cardiovascular, respiratory,
cancer, autoimmune, neurodegenerative and other diseases.
The first ultra-sensitive protein test we plan to commercialize is for cardiac troponin I
(“cTnI”), which is the gold standard biomarker for diagnosis of myocardial
infarction, or heart attack, and identification of patients with acute coronary syndromes at risk for
subsequent cardiovascular events. We previously submitted a 510(k) application to the FDA to obtain
clearance for the cardiac troponin assay on the Original Processor. We have withdrawn this
application and plan to submit a new 510(k)
application to obtain clearance for this assay on the Processor SP. We plan to use patient
samples from our FAST-TRAC clinical trial to run the clinical trials in support of our new 510(k)
submission. The FAST-TRAC clinical study is designed to further demonstrate the clinical
utility of ultra-sensitive cTnI measurements as a diagnostic tool for use in the management of both
acute and chronic cardiac disease.
30
Table of Contents
In addition to the cardiac troponin I assay, we are developing an ultra-sensitive prostate-specific antigen (“PSA”) test for early diagnosis
of recurrent prostate cancer. Early testing data suggest this assay may serve as a more specific
test for PSA screening. We are also working on a multiplexed protein-based connective-tissue panel
for the detection of rheumatoid arthritis, lupus and other related diseases. Finally, we are
investigating new biomarkers where our ultra-sensitive protein detection technology may enable
earlier detection of a broad range of diseases, such as cancer.
Intellectual Property
As of December 31, 2010, our patent portfolio is comprised, on a worldwide basis, of 151
issued patents and 52 pending patent applications which we own directly or for which we are the
exclusive licensee. Some of these patents and patent applications derive from a common parent
patent application or are foreign counterpart patent applications and relate to similar or
identical technological claims. The issued patents cover approximately 11 different technological
claims and the pending patent applications cover approximately four additional technological
claims.
Many of our issued and pending patents were exclusively licensed from the International
Institute for Nanotechnology at Northwestern University (“Northwestern”) in May 2000, and they
generally cover our core technology, including nanotechnology-based biodiagnostics and biobarcode
technology. Our issued patents expire between 2017 and 2025. We believe our patent portfolio
provides protection against other companies offering products employing the same technologies and
methods as we have patented. While we believe our patent portfolio establishes a proprietary
position, there are many competitive products utilizing other technologies that do not infringe on
our patents.
In addition, as of December 31, 2010, we have non-exclusive licenses for at least 47 U.S.
patents that cover 12 different technological claims from various third parties. Most of these
license agreements require us to pay the licensor royalty fees that typically expire upon the
patent expiration dates, which range from 2011 to 2027. These license agreements are non-exclusive
and do not create a proprietary position. The expiration of these non-exclusive licenses will
result in the termination of certain royalty payments by us to the licensors.
Since inception we have incurred net losses each year, and we expect to continue to incur
losses for the foreseeable future. Our net loss was approximately $40.6 million for fiscal 2010. As
of December 31, 2010, we had an accumulated deficit of approximately $279.9 million. Our operations
to date have been funded principally through capital contributions from investors in two
underwritten direct public offerings of common stock, and prior thereto in our convertible
preferred stock, which was converted to common stock in 2007, and our debt borrowings.
In November 2007, we completed our initial public offering of 8,050,000 shares of common stock
at $14.00 per share. We received approximately $102 million of net proceeds from our initial
public offering. In October 2009, we completed a public offering of 5,405,000 shares of our common
stock at $7.00 per share. We received approximately $35.4 million of net proceeds from this
offering.
Financial Operations Overview
Revenue
Product sales revenue is derived from the sale or lease of the Verigene System, including
cartridges and related products sold to research laboratories and hospitals. Grant and contract
revenue consists of funds received under contracts and government grants, including funds for the
reimbursement of certain research and development expenses. Our market efforts are primarily
focused on driving product sales rather than grants and contracts. However, the Company recently
completed development of certain custom pharmacogenetic assays to be used in conjunction with the
clinical trials associated with new therapeutic drugs for a major pharmaceutical company. We will
continue to be opportunistic with regard to future contract and grant opportunities.
31
Table of Contents
Cost of Sales
Cost of sales represents the cost of materials, direct labor and other manufacturing overhead
costs incurred to produce Verigene cartridges and instruments, as well as royalties on product
sales, amortization of purchased intellectual property relevant to products available for sale and
depreciation of instrument leases and rentals. Costs associated with custom assay development
contracts also include labor associated with assay development, validation and testing.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses primarily include all costs incurred during the development
of the Verigene System instruments and assays, and the expenses associated with fulfilling our development
obligations related to the United States government contracts and grants. Such expenses include
salaries and benefits for research and development personnel, consulting services, materials,
patent-related costs and other expenses. We expense all research and development costs in the
periods in which they are incurred. We expect research and development expenses to grow modestly as
we continue to develop future generations of the Verigene System instruments and additional genomic and
protein tests.
Sales, General and Administrative Expenses
Sales, general and administrative expenses principally include compensation for employees in
our sales, customer service, marketing, management and administrative functions. We also include
professional services, facilities, technology, communications and administrative expenses in sales,
general and administrative. The professional services costs primarily consist of legal and
accounting costs. We expect sales and marketing expenses will increase as additional sales and
customer support are needed to drive and support customer growth.
Interest Income
Interest income principally includes interest earned on our excess cash balances. Such
balances are primarily invested in money market and bank checking accounts at major financial
institutions. We expect that continued low interest rates will significantly limit our interest
income in the near term.
Interest Expense
Interest expense includes the interest charges related to our debt borrowings, including
non-cash amortization of debt discount and issuance costs.
Fiscal 2010 Compared to 2009
Revenues
Revenues were $2.0 million for fiscal 2010, as compared to $2.2 million for fiscal 2009.
Product sales increased from $1.1 million for fiscal 2009 to $1.4 million for fiscal 2010, driven
by an increase in consumables revenue and system sales. Service revenue related to an assay
development contract with a major pharmaceutical company was $0.6 million for 2010 as compared to
$1.0 million for 2009. This assay development contract was substantially completed in the first
half of 2010.
Cost of Sales
For fiscal 2010, cost of sales was $2.6 million, as compared to $2.2 million for fiscal 2009.
During 2010, the Company established a valuation reserve of $0.7 million for the Original Processor
inventory. This reserve was taken based on the Company’s plan to submit future assay applications
to the FDA for use only on the Processor SP. In addition, the Company withdrew its 510(k)
application to the FDA for the cardiac troponin assay on the Original Processor and plans to submit
a new 510(k) application for this assay on the Processor SP. Partially offsetting the impact of
this inventory reserve was a decrease in cost of sales due to lower service revenue.
32
Table of Contents
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses have remained relatively consistent at $18.8 million for
fiscal 2010 as compared to $18.6 million for fiscal 2009.
Sales, General and Administrative Expenses
Sales, general and administrative expenses increased from $14.5 million for fiscal 2009 to
$22.0 million for fiscal 2010, an increase due to litigation settlement expenses of $3.5 million as
well as a $2.6 million increase in litigation defense expenses related to the Eppendorf AG
litigation. In addition, non-cash share-based compensation increased $2.4 million due to options
and restricted stock granted in the fourth quarter of 2009. Clinical trial expenses associated with
the FAST-TRAC Troponin I study decreased approximately $1.5 million during 2010 due to the
substantial completion of patient enrollment in 2009.
U.S. Treasury Grant
During fiscal 2010, the United States Department of the Treasury awarded the Company a grant
of $1.0 million for investments in qualifying therapeutic discovery projects under section 48D of
the Internal Revenue Code.
Interest Expense
Interest expense was $0.3 million for fiscal 2010, as compared to $1.3 million for fiscal
2009. The decrease in interest expense in 2010 resulted from a decrease in the scheduled
amortization in accordance with the loan and security agreements with Venture Lending and Leasing.
The balance of this debt was fully repaid in August 2010.
Interest Income
Interest income was less than $0.1 million for 2010 and $0.4 million for 2009. The decrease
in interest income during the fiscal 2010 resulted from lower interest rates during 2010 as
compared to the same period in 2009. In addition, the average cash balance was lower during 2010 as
compared to 2009.
Fiscal 2009 Compared to 2008
Revenues
Revenues were $2.2 million for fiscal 2009 as compared to $1.4 million for fiscal 2008.
Product sales increased slightly to $1.1 million for fiscal 2009 as compared to $1.0 million for
fiscal 2008. The change in product sales was driven by a 47% increase in consumables revenue and a
50% reduction in system sales. Fiscal 2009 revenues also included $1.0 million of service revenue
related primarily to the assay development contracts with a major pharmaceutical company. Revenues
from government grants were $0.3 million for fiscal 2008.
Cost of Sales
For fiscal 2009, cost of sales was $2.2 million, as compared to $1.5 million for fiscal 2008.
The $0.7 million increase in cost of sales for fiscal 2009 resulted from the costs associated with
assay development revenue from our commercial contracts, the increase in product sales and the
fixed amortization of license fees.
Research and Development Expenses
Research and development expenses decreased from $23.7 million in fiscal 2008 to $18.6 million
in fiscal 2009. The $5.1 million decrease in research and development expenses for fiscal 2009
consists primarily of $2.0 million in staffing, $1.5 million of materials spending and $1.0 million
in reduced facilities and depreciation expense. The staffing reduction was driven by a more narrow
focus on core research and development projects. The materials reduction was primarily related to
the completion of the up-front investment in Processor SP development activities.
Sales, General and Administrative Expenses
Sales, general and administrative expenses increased from $13.6 million for fiscal 2008 to
$14.5 million for fiscal 2009. The increase in sales, general and administrative expenses for
fiscal 2009 consists primarily of a $1.4 million increase in clinical trial
expenses associated with the FAST-TRAC Troponin I study intended to create market
differentiation for this assay, partially offset by a decrease in spending due to the completion of
the initial implementation of our Sarbanes-Oxley compliance program.
33
Table of Contents
Interest Expense
Interest expense was $1.3 million for fiscal 2009 as compared to $2.1 million for fiscal 2008.
The decrease in interest expense for fiscal 2009 resulted from increased principal payments and
lower interest, in accordance with our loan and security agreements.
Interest Income
Interest income was $0.4 million and $2.5 million for fiscal 2009 and 2008, respectively. The
decrease in interest income during fiscal 2009 resulted from a lower average cash balance during
this period as compared to fiscal 2008. In addition, interest rates declined significantly for
fiscal 2009 as compared to fiscal 2008.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
From our inception in December 1999 through December 31, 2010, we have received net proceeds
of $103.9 million from the sale of convertible preferred stock and issuance of notes payable that
were exchanged for convertible preferred stock, $102.2 million from our November 2007 initial
public offering, $35.4 million from our October 2009 underwritten public offering and $10.3 million
from government grants. We have devoted substantially all of these funds to research and
development and sales, general and administrative expenses. Since our inception, we have generated
minimal revenues from the sale of the Verigene System, including consumables and related products,
to our initial clinical customers, research laboratories and government agencies. We also incurred
significant losses and, as of December 31, 2010, we had an accumulated deficit of approximately
$279.9 million. While we are currently in the commercialization stage of operations, we have not
yet achieved profitability and anticipate that we will continue to incur net losses in the
foreseeable future.
Because we recently began to commercialize our products, we do not anticipate achieving
positive operating cash flow in the next three years. During this period we expect to increase
investment in additional manufacturing scale-up, research and development costs to expand our assay
menu and to develop a fully automated instrument with increased throughput, and to add to sales and
marketing personnel. Achievement of positive cash flow from operations will depend upon revenue
resulting from adoption of both our current products and future products that depend upon
regulatory clearance. Demand for our respiratory products is directly proportional to the size and
duration of the annual season for influenza and other respiratory illnesses. Any unanticipated
acceleration or deceleration of customer demand for our products relative to projections will have
a material effect on our cash flows. While the Company anticipates that capital resources will be
sufficient to meet estimated needs for at least twelve months, the Company operates in a market
that makes its prospects difficult to evaluate, and the Company will need additional financing in
the future to execute on its current or future business strategies. Capital outlays and operating
expenditures may increase over the next few years as the Company expands its infrastructure,
commercialization, manufacturing, and research and development activities.
A customer may purchase the Verigene System instruments lease them from a third party or enter into a
reagent rental agreement. Our reagent rental agreements include customer commitments to purchase a
certain minimum volume of cartridges over the term of the agreement. As part of these agreements, a
portion of the charge for each cartridge is a rental fee for use of the equipment. To date, our
aggregate investment in systems rented to customers has not been material. However, we may need to
increase our investment in such systems to support future product placements under reagent rental
agreements. We have established a relationship with a third party financing company to provide our
customers with lease financing for Verigene equipment. This arrangement may help mitigate the
demand on our capital resources as it allows us to recover the cost of such systems immediately,
instead of over three to five years.
As of December 31, 2010, we had $39.6 million in cash and cash equivalents, compared to $76.7
million at December 31, 2009. Cash used in operations increased to $31.6 million for 2010 as
compared to $27.9 million in 2009 due primarily to the lump sum payment to Eppendorf AG to settle a
patent litigation dispute. Accounts payable at December 31, 2010 includes approximately $2.0
million of legal defense expenses that will be paid in 2011. Cash used in operations decreased to
$27.9 million for 2009 as compared to $32.0 million in 2008 due to a decrease in research and
development expenses during 2009.
Net cash used in investing activities remained relatively consistent at $1.6 million for the
year ended December 31, 2010 compared to $1.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2009.
Investments in property and equipment decreased $1.0 million from 2008 to 2009 due to the
significant spending in 2008 to scale-up manufacturing for the commencement of product
commercialization activities.
34
Table of Contents
Net cash used in financing activities was $3.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2010,
compared to cash provided by financing activities of $31.1 million for the year ended December 31,
2009. Cash used in financing activities during 2008 was $4.2 million. Cash was used in financing
activities during 2008 through 2010 to repay our long-term debt that was fully repaid in the third
quarter of 2010. In October 2009, we completed our public offering of 5,405,000 shares of common
stock at $7.00 per share. We received approximately $35.4 million of net proceeds from this
offering.
We may need to increase our capital outlays and operating expenditures over the next several
years as we expand our product offering, drive product adoption, further scale-up manufacturing and
implement product cost savings. The amount and the timing of the additional capital we will need to
raise depends on many factors, including:
| • | the level of research and development investment required to maintain and improve our technology; |
| • | the amount and growth rate of our revenues; |
| • | changes in product development plans needed to address any difficulties in manufacturing or commercializing the Verigene System and enhancements to our system; |
| • | the costs of filing, prosecuting, defending and enforcing patent claims and other intellectual property rights; |
| • | competing technological and market developments; |
| • | our need or decision to acquire or license complementary technologies or acquire complementary businesses; and |
| • | changes in regulatory policies or laws that affect our operations. |
We cannot be certain that additional capital will be available when and as needed or that our
actual cash requirements will not be greater than anticipated. If we require additional capital at
a time when investment in diagnostics companies or in the marketplace in general is limited due to
the then prevailing market or other conditions, we may not be able to raise such funds at the time
that we desire or any time thereafter. In addition, if we raise additional funds through the
issuance of equity or convertible debt securities, the percentage ownership of our stockholders
could be significantly diluted, and these newly-issued securities may have rights, preferences or
privileges senior to those of existing stockholders. If we obtain additional debt financing, a
substantial portion of our operating cash flow may be dedicated to the payment of principal and
interest on such indebtedness, and the terms of the debt securities issued could impose significant
restrictions on our operations. If we raise additional funds through collaborations and licensing
arrangements, we might be required to relinquish significant rights to our technologies or
products, or grant licenses on terms that are not favorable to us.
Income Taxes
Since inception, we have incurred operating losses and, accordingly, have not recorded a
provision for income taxes for any of the periods presented. As of December 31, 2010, we had net
operating loss carryforwards for federal and state income tax purposes of $191 million. The Company
also has federal research and development tax credit carryforwards of $9 million which will begin
to expire in 2020. Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code subjects the utilization of net
operating loss and credit carryforwards to an annual limitation that is applicable if the Company
experiences an ownership change. The Company believes its public offerings and/or prior equity
investments may have triggered an ownership change as defined by the Internal Revenue Code.
However, the Company has yet to perform the computations under Section 382 which would determine
the amount of annual limitation on its utilization of its net operating loss and tax credit
carryforwards. The annual limitation may result in the expiration of the Company’s net operating
loss and tax credit carryforwards before they can be used.
35
Table of Contents
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
As of December 31, 2010, the annual amounts of future minimum payments under certain of our
contractual obligations were (in thousands):
| Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations | Total | Less than 1 Year | 1-3 Years | 3-5 Years | More than 5 Years | |||||||||||||||
Operating lease |
$ | 1,507 | $ | 427 | $ | 890 | $ | 190 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Obligations under license agreements |
3,280 | 526 | 1,731 | 423 | 600 | |||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 4,787 | $ | 953 | $ | 2,621 | $ | 613 | $ | 600 | ||||||||||
On July 9, 2010, the Company executed a worldwide non-exclusive license agreement (the
Agreement”) to utilize certain patented technology believed by the Company to be useful in the
manufacture of certain of its current and future products. Under the terms of the Agreement, the
Company will pay a license and technology transfer fee of $1,865,000, payable in four installments.
The first installment of $165,000 was due upon the execution of the Agreement, and the remaining
installments of $350,000, $600,000 and $750,000 are payable on July 9, 2011, 2012 and 2013,
respectively. These fees represent full payment for use of the licensed patents during the term of
the Agreement, which ends on the expiration date of the last patent issued and licensed under the
Agreement.
License Agreements
We have entered into several nonexclusive license agreements with various companies covering
certain technologies which are embedded in the Company’s diagnostic instruments and diagnostic test
products. Since inception, we have paid aggregate initial license fees of $2.8 million for these
licenses, and have agreed to pay a percentage of net sales as royalties, in percentage amounts
ranging from less than 1% to 12%. Certain of the license agreements have minimum annual royalty
payments, and such minimum payments are as shown above. These licenses expire at various times,
corresponding to the subject patents expirations, which currently range from 2011 to 2027.
We have entered into a license agreement with Northwestern which provides us with an exclusive
license to certain patents and patent applications related to the application of nanotechnology to
biodiagnostics and to biobarcode technology. This license covers all discoveries from the
International Institute for Nanotechnology at Northwestern in the field of biodiagnostics through
January 1, 2013. Nanosphere also has the right of first negotiation for an exclusive license on
inventions after such date. Our research team utilizes the research and patents developed at
Northwestern to develop diagnostic applications including additional genomic and protein testing
assays for use in the Verigene System.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any off-balance sheet financing or unconsolidated special-purpose entities.
Critical Accounting Policies and Significant Judgments and Estimates
This discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations is
based on our financial statements, which have been prepared in conformity with accounting
principles generally accepted in the United States of America. The preparation of these financial
statements requires management to make estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of
assets, liabilities and expenses and the disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the
date of the financial statements, as well as revenues and expenses during the reporting periods. We
evaluate our estimates and judgments on an ongoing basis. We base our estimates on historical
experience and on various other factors we believe are reasonable under the circumstances, the
results of which form the basis for making judgments about the carrying value of assets and
liabilities that are not readily apparent from other sources. Actual results could therefore differ
materially from those estimates under different assumptions or conditions.
Our significant accounting policies are described in Note 3 to our consolidated financial
statements included elsewhere in this Annual Report on Form 10-K. We believe the following critical
accounting policies reflect our more significant estimates and assumptions used in the preparation
of our financial statements.
36
Table of Contents
Revenue Recognition
We recognize revenue under grants and contracts and for reimbursement of related research and
development expenses at the time the relevant expenses are incurred. For product sales, revenue is
recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, title and risk of loss is transferred
to customers, the price to the buyer is fixed or determinable, and collectability is reasonably
assured.
Verigene System instrument units are sold outright to customers or leased to customers
pursuant to operating leases. We recognize revenue from sales of the Verigene System, including
cartridges and related products, when the risks and rewards of ownership are transferred to the
customer. Revenue for Verigene System instrument units leased under operating lease arrangements is
recognized on an installment basis over the life of the lease while the cost of the leased
equipment is carried on the Company’s balance sheet and fully amortized over the life of lease
arrangements.
Stock-Based Compensation Expense
We have granted share-based compensation consisting of restricted stock and common stock
options issued to employees, consultants and founders. Compensation expense is recognized based on
the fair value of the stock-based awards granted utilizing various assumptions regarding the
underlying attributes of the options and our common stock. The estimated fair value of options
granted, net of forfeitures expected to occur during the vesting period, is determined using the
Black-Scholes option-pricing model and then amortized as compensation expense on a straight-line
basis over the vesting period of the options. All of the stock options granted prior to November
2007 have exercise prices at or above the estimated fair value of the common stock on the date of
grant, as determined by our board of directors prior to our initial public offering in November
2007, who used their knowledge of us and our affairs along with third-party valuation assessments,
to determine the fair value of our common stock. For option grants after our initial public
offering, we use the fair value of our common stock as determined by the closing price of our
common stock on NASDAQ on the date of grant. In addition to the grant date fair value of our
common stock, the Black-Scholes model requires inputs for risk-free interest rate, dividend yield,
volatility and expected lives of the options. Due to the Company’s limited period of trading
activity as a public company from 2007 through the third quarter of 2009, the expected volatility
of option grants prior to the fourth quarter of 2009 was based on historical data from various peer
public companies with similar product portfolios. The expected volatility for option awards granted
during 2010 and in the fourth quarter of 2009 was based on the Company’s actual historical
volatility. The expected life of options that vest ratably over four years of service is derived
from the average of the vesting period and the term of the option following the guidance in SEC
Staff Accounting Bulletins No. 107 and 110. The Company estimates the expected life of options with
accelerated vesting terms giving consideration to the dates that the Company expects to achieve key
milestones under the option agreements and the term of the option. The risk-free rate for periods
within the contractual life of the option is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at
the time of the grant.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In October 2009, the FASB issued authoritative guidance that amends existing guidance for
identifying separate deliverables in a revenue-generating transaction where multiple deliverables
exist, and provides guidance for allocating and recognizing revenue based on those separate
deliverables. The guidance is expected to result in more multiple-deliverable arrangements being
separable than under current guidance. This guidance is effective for the Company beginning on
January 1, 2011 and is required to be applied prospectively to new or significantly modified
revenue arrangements. The Company does not expect this guidance to have a material impact on its
financial statements in future periods.
Item 7A. Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk.
Our exposure to market risk is currently confined to our cash and cash equivalents. We have
not used derivative financial instruments for speculation or trading purposes. The primary
objective of our investment activities is to preserve our capital for the purpose of funding
operations while at the same time maximizing the income we receive from our investments without
significantly increasing risk. To achieve these objectives, our investment policy allows us to
maintain a portfolio of cash equivalents and short-term investments through a variety of
securities, including commercial paper, money market funds and corporate debt securities. Our cash
and cash equivalents through December 31, 2010 included amounts in bank checking and liquid money
market accounts. As a result, we believe we have minimal interest rate risk; however, a one
percentage point decrease in the average interest rate on our portfolio, if such a decrease were
possible, would have reduced our interest income to $0 for the twelve month period ended December
31, 2010.
37
Table of Contents
Item 8. Financial Statements and Supplementary Data.
The following financial statements and the related notes thereto, of Nanosphere, Inc. and the
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm, Deloitte & Touche LLP, are filed as a part
of this Form 10-K.
| Page | ||||
| 39 | ||||
| 41 | ||||
| 42 | ||||
| 43 | ||||
| 44 | ||||
| 45-54 | ||||
38
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Nanosphere, Inc.
Northbrook, Illinois
Northbrook, Illinois
We have audited the accompanying balance sheets of Nanosphere, Inc. (the “Company”) as of December
31, 2010 and 2009, and the related statements of operations, stockholders’ equity (deficit), and
cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2010. These financial
statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an
opinion on these financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight
Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain
reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An
audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the
financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and
significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement
presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, such financial statements present fairly, in all material respects, the financial
position of the Company as of December 31, 2010 and 2009, and the results of their operations and
their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2010, in conformity
with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight
Board (United States), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31,
2010, based on the criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the
Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and
our report dated February 16,
2011 expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
Chicago, Illinois
February 16, 2011
February 16, 2011
39
Table of Contents
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Stockholders of Nanosphere, Inc.
Northbrook, Illinois
Northbrook, Illinois
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of Nanosphere, Inc. (the “Company”)
as of December 31, 2010, based on criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework
issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. The Company’s
management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and
for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in
the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our
responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting
based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight
Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain
reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was
maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal
control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and
evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk,
and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe
that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the
supervision of, the company’s principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons
performing similar functions, and effected by the company’s board of directors, management, and
other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting
and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally
accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes
those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable
detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the
company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit
preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles,
and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with
authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance
regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the
company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including the
possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements due to
error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any
evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods
are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions,
or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over
financial reporting as of December 31, 2010, based on the criteria established in Internal Control
— Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway
Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight
Board (United States), the financial statements as of and for the year ended December 31, 2010 of
the Company and our report dated February 16, 2011 expressed an unqualified opinion on those
financial statements.
/s/ DELOITTE & TOUCHE LLP
Chicago, Illinois
February 16, 2011
February 16, 2011
40
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Balance Sheets
(dollars in thousands)
| As of December 31, | ||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
CURRENT ASSETS: |
||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 39,628 | $ | 76,689 | ||||
Accounts receivable |
198 | 735 | ||||||
Inventories |
2,428 | 2,941 | ||||||
Other current assets |
673 | 374 | ||||||
Total current assets |
42,927 | 80,739 | ||||||
PROPERTY AND EQUIPMENT — Net |
5,142 | 6,145 | ||||||
INTANGIBLE ASSETS — Net of accumulated amortization |
3,231 | 1,710 | ||||||
OTHER ASSETS |
75 | 75 | ||||||
TOTAL |
$ | 51,375 | $ | 88,669 | ||||
CURRENT LIABILITIES: |
||||||||
Accounts payable |
$ | 3,352 | $ | 2,509 | ||||
Accrued compensation |
794 | 955 | ||||||
Other current liabilities |
1,355 | 2,304 | ||||||
Long-term debt — current portion |
— | 3,819 | ||||||
Total current liabilities |
5,501 | 9,587 | ||||||
LONG-TERM LIABILITIES: |
||||||||
Other noncurrent liabilities |
1,350 | — | ||||||
Total liabilities |
6,851 | 9,587 | ||||||
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES |
||||||||
STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY: |
||||||||
Common stock, $0.01 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; 28,408,506 shares
and 28,422,461 shares issued and outstanding as of December 31, 2010 and 2009,
respectively |
284 | 284 | ||||||
Preferred stock, $0.01 par value; 10,000,000 shares authorized; no shares issued |
— | — | ||||||
Additional paid-in capital |
318,714 | 312,660 | ||||||
Warrants to acquire common stock |
5,424 | 5,424 | ||||||
Accumulated deficit |
(279,898 | ) | (239,286 | ) | ||||
Total stockholders’ equity |
44,524 | 79,082 | ||||||
TOTAL |
$ | 51,375 | $ | 88,669 | ||||
See notes to financial statements.
41
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Statements of Operations
(dollars and shares in thousands except per share data)
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
REVENUE: |
||||||||||||
Grant and contract revenue |
$ | 610 | $ | 1,090 | $ | 346 | ||||||
Product sales |
1,416 | 1,124 | 1,021 | |||||||||
Total revenue |
2,026 | 2,214 | 1,367 | |||||||||
COSTS AND EXPENSES: |
||||||||||||
Cost of sales |
2,597 | 2,175 | 1,464 | |||||||||
Research and development |
18,821 | 18,608 | 23,675 | |||||||||
Sales, general, and administrative |
22,007 | 14,472 | 13,616 | |||||||||
Total costs and expenses |
43,425 | 35,255 | 38,755 | |||||||||
Loss from operations |
(41,399 | ) | (33,041 | ) | (37,388 | ) | ||||||
OTHER INCOME (EXPENSE): |
||||||||||||
Foreign exchange gain (loss) |
4 | (4 | ) | (23 | ) | |||||||
U.S. Treasury grant |
978 | — | — | |||||||||
Interest expense |
(274 | ) | (1,258 | ) | (2,081 | ) | ||||||
Interest income |
79 | 354 | 2,450 | |||||||||
Total other income (expense) |
787 | (908 | ) | 346 | ||||||||
NET LOSS |
$ | (40,612 | ) | $ | (33,949 | ) | $ | (37,042 | ) | |||
Net loss per common share — basic and diluted |
$ | (1.46 | ) | $ | (1.46 | ) | $ | (1.67 | ) | |||
Weighted average number of common shares
outstanding — basic and diluted |
27,755 | 23,302 | 22,213 | |||||||||
See notes to financial statements.
42
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Statements of Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit)
(dollars and shares in thousands)
| Warrants | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Additional | To Acquire | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common Stock | Paid-In | Common | Accumulated | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Par Value | Capital | Stock | Deficit | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
BALANCE — January 1, 2008 |
22,192 | $ | 305 | $ | 271,765 | $ | 5,425 | $ | (168,295 | ) | $ | 109,200 | ||||||||||||
Share-based compensation |
2,218 | 2,218 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options on common stock |
36 | — | 164 | 164 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of warrants |
1 | — | 3 | (1 | ) | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
Other |
(83 | ) | 82 | (1 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
(37,042 | ) | (37,042 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
BALANCE — December 31, 2008 |
22,229 | 222 | 274,232 | 5,424 | (205,337 | ) | 74,541 | |||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation |
672 | 7 | 2,528 | 2,535 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options on common stock |
116 | 1 | 521 | 522 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock from public
offering, net of offering expenses |
5,405 | 54 | 35,379 | 35,433 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
(33,949 | ) | (33,949 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
BALANCE — December 31, 2009 |
28,422 | 284 | 312,660 | 5,424 | (239,286 | ) | 79,082 | |||||||||||||||||
Share-based compensation |
6,019 | 6,019 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Exercise of stock options on common stock |
9 | — | 35 | 35 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Forfeiture of restricted stock |
(22 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net loss |
(40,612 | ) | (40,612 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
BALANCE — December 31, 2010 |
28,409 | $ | 284 | $ | 318,714 | $ | 5,424 | $ | (279,898 | ) | $ | 44,524 | ||||||||||||
See notes to financial statements.
43
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Statements of Cash Flows
(dollars in thousands)
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES: |
||||||||||||
Net loss |
$ | (40,612 | ) | $ | (33,949 | ) | $ | (37,042 | ) | |||
Adjustments to reconcile net loss to net cash used in operating activities: |
||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
3,343 | 3,067 | 3,170 | |||||||||
Amortization of financing costs and accretion of debt discount |
119 | 499 | 762 | |||||||||
Loss from write-off of intangible assets |
292 | — | 245 | |||||||||
Loss from disposal of fixed assets |
21 | 3 | 326 | |||||||||
Share-based compensation |
6,019 | 2,534 | 2,218 | |||||||||
Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
Accounts receivable |
537 | (349 | ) | (285 | ) | |||||||
Inventories |
(865 | ) | (1,335 | ) | (1,079 | ) | ||||||
Other current assets |
(318 | ) | 205 | 111 | ||||||||
Other assets |
— | — | 3 | |||||||||
Accounts payable |
1,036 | 519 | (209 | ) | ||||||||
Accrued and other current liabilities |
(1,199 | ) | 856 | (195 | ) | |||||||
Net cash used in operating activities |
(31,627 | ) | (27,950 | ) | (31,975 | ) | ||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES: |
||||||||||||
Purchases of property and equipment |
(710 | ) | (1,327 | ) | (2,332 | ) | ||||||
Investments in intangible assets |
(865 | ) | (507 | ) | (401 | ) | ||||||
Other |
23 | — | — | |||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities |
(1,552 | ) | (1,834 | ) | (2,733 | ) | ||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
||||||||||||
Repayment of long-term debt |
(3,917 | ) | (4,818 | ) | (3,598 | ) | ||||||
Payments on capital lease obligation |
— | (21 | ) | (37 | ) | |||||||
Proceeds from the issuance of common stock, net of offering expenses |
— | 35,433 | (779 | ) | ||||||||
Proceeds from warrant redemptions |
— | — | 2 | |||||||||
Proceeds from stock option exercises |
35 | 522 | 164 | |||||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by financing activities |
(3,882 | ) | 31,116 | (4,248 | ) | |||||||
NET (DECREASE) INCREASE IN CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
(37,061 | ) | 1,332 | (38,956 | ) | |||||||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS — Beginning of year |
76,689 | 75,357 | 114,313 | |||||||||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS — End of year |
$ | 39,628 | $ | 76,689 | $ | 75,357 | ||||||
NONCASH INVESTING AND FINANCING ACTIVITIES: |
||||||||||||
Capital expenditures included in accounts payable |
$ | — | $ | 206 | $ | — | ||||||
License costs capitalized and included in other current liabilities |
350 | 278 | 225 | |||||||||
License costs capitalized and included in other noncurrent liabilities |
1,350 | — | — | |||||||||
Reclassification of inventory to property and equipment |
1,378 | 252 | 1,254 | |||||||||
See notes to financial statements.
44
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements
As of December 31, 2010 and 2009, and
For the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008
As of December 31, 2010 and 2009, and
For the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008
1. Description of Business
Nanosphere, Inc. (the “Company”) develops, manufactures and markets an advanced molecular
diagnostics platform, the Verigene System, that enables simple, low cost, and highly sensitive
genomic and protein testing on a single platform.
Basis of Presentation — The accompanying financial statements have been prepared on a
going-concern basis, which contemplates the realization of assets and the satisfaction of
liabilities in the normal course of business.
2. Liquidity and Capital Resources
The Company has incurred net losses attributable to common stock of $279.9 million since
inception, and has funded those losses primarily through the sale and issuance of equity securities
and secondarily through the issuance of debt. While the Company is no longer in the development
stage and the focus of the Company’s business activities has turned towards commercialization of
its products, because of the numerous risks and uncertainties associated with its product
development and commercialization efforts, the Company is unable to predict when it will become
profitable, and the Company may never become profitable. While the Company anticipates that capital
resources will be sufficient to meet estimated needs for at least twelve months, the Company
operates in a market that makes its prospects difficult to evaluate, and the Company will need
additional financing in the future to execute on its current or future business strategies. Capital
outlays and operating expenditures may increase over the next few years as the Company expands its
infrastructure, commercialization, manufacturing, and research and development activities.
3. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Cash and Cash Equivalents — The Company considers all highly liquid investments with a
maturity of three months or less, at date of purchase, to be cash equivalents. The majority of
these funds are held in interest-bearing money market and bank checking accounts. Interest income
is recorded on the accrual basis as earned.
Receivables — Accounts receivable consists of amounts due to the Company for sales of the
Verigene system as well as amounts due under various contracts and government grants. An allowance
for doubtful accounts is not recorded because the Company has no history of uncollectible
receivables and there are no specifically identified uncollectible accounts.
Inventories — Inventories are carried at the lower of cost or market, using the first-in,
first-out method. Certain finished goods inventory is ultimately leased rather than sold, and upon
the lease date is transferred to Property and equipment and subsequently depreciated to Cost of
sales over the period indicated below.
Property and Equipment — Property and equipment are recorded at cost and depreciated using
the straight-line method over the assets’ estimated useful lives, which are:
Equipment with customers |
3-5 years | |||
Computers and office equipment |
3 years | |||
Engineering and laboratory equipment, including tooling |
3-5 years | |||
Furniture and fixtures |
7 years | |||
Manufacturing equipment |
5-7 years |
The economic life of the Company’s equipment with customers is based on the original term of
the lease, which is typically three years. The Company believes that this is representative of the
period during which the instrument is expected to be economically usable.
Assets classified as leasehold improvements are amortized over the shorter of their estimated
useful lives or the lease term using the straight-line method. Maintenance and repair costs are
expensed as incurred.
45
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
Intangible Assets — Intangible assets are stated at cost less accumulated amortization and
consist of purchased intellectual property. Purchased intellectual property represents licenses and
is associated with patents owned by third-parties for technologies which are embedded in the
Company’s diagnostic instruments and diagnostic test products that the Company licensed in
anticipation of sales of such products. Amortization of upfront license fees begins upon the
Company obtaining FDA clearance to sell products containing the licensed technology and is
calculated using the straight-line method over the remaining expected lives of the licensed
technology, which range from less than one year to 16.25 years. Such amortization of upfront license fees is
classified in Cost of sales on the statement of operations. Purchased intellectual property also
includes purchased patents and patent rights. These patents and patent rights are amortized using a
straight-line method over the remaining 9.5 years of the patent, and the amortization expense is
classified in research and development expense on the statement of operations.
Deferred Financing Costs — Deferred financing costs of $0.1 million incurred in connection
with the Company’s issuance of debt are amortized over the life of the debt using the effective
interest rate method with amortization of such costs being charged to interest expense.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets — The Company assesses the recoverability of long-lived
assets, including intangible assets, by periodically evaluating the carrying value of such assets
whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of such assets may
not be recoverable. If impairment is indicated, the Company will value the asset at its estimated
fair value.
Use of Estimates — The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting
principles generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make estimates
and assumptions that affect the amounts reported in the financial statements and the notes thereto.
The Company’s significant estimates included in the preparation of the financial statements are
related to inventories, property and equipment, intangible assets, service revenue and share-based
compensation. Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Revenue Recognition — The Company recognizes revenue from product sales and contract
arrangements. The Company recognizes revenue from product sales when there is persuasive evidence
that an arrangement exists, delivery has occurred, the price is fixed or determinable and
collectability is reasonably assured. Verigene System instrument units are sold outright to
customers or leased to customers pursuant to operating leases. The Company recognizes revenue from
sales of the Verigene System, including cartridges and related products, when the risks and rewards
of ownership are transferred to the customer. Revenue for Verigene System instrument units sold
under operating lease arrangements is recognized on an installment basis over the life of the lease
while the cost of the leased equipment is carried on the Company’s balance sheet in Property and
equipment and depreciated over its estimated useful life to Cost of sales.
Shipping and handling costs are expensed as incurred and included in Cost of sales. In those
cases where the Company bills shipping and handling costs to customers, the amounts billed are
classified as product sales.
Grant and government sponsored research revenue and contract revenue related to research and
development services are recognized as the related services are performed based on the performance
requirements of the relevant contract. Under such agreements, the Company is required to perform
specific research and development activities and is compensated either based on the costs or costs
plus a mark-up associated with each specific contract over the term of the agreement or when
certain milestones are achieved.
Research and Development Costs — Research and development costs are expensed as incurred.
U.S. Treasury Grant — During 2010, the United States Department of the Treasury awarded the
Company a grant of approximately $1.0 million for investments in qualifying therapeutic discovery
projects under section 48D of the Internal Revenue Code. The proceeds from this grant are
classified in “Other income (expense) — U.S. Treasury Grant” on the statement of operations.
Income Taxes — The Company accounts for income taxes, including uncertain tax positions,
under the provisions of Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) Accounting Standards
Codification (“ASC”) Topic 740 “Accounting for Income Taxes”. This Topic requires recognition of
deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of events that have
been included in the financial statements or tax returns. Under this method, deferred tax assets
and liabilities are determined based on the differences between the financial reporting and tax
bases of assets and liabilities using enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the
differences are expected to reverse. An allowance is provided to reduce net deferred tax assets to
the amount management believes will, more likely than not, be recovered.
46
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
Share-Based Compensation — The Company recognizes share-based compensation expense related to
restricted stock and common stock options issued to employees, consultants and directors. ASC Topic
718 “Stock Compensation” provides for recognition of compensation expense based on the fair value
of the stock-based compensation utilizing various assumptions regarding the underlying attributes
of the options and stock. The estimated fair value of options granted, net of forfeitures expected
to occur during the vesting period, is amortized as compensation expense on a straight-line basis
over the service period of the options.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments — The carrying amount of the Company’s financial
instruments, including cash and cash equivalents, accounts receivable and accounts payable
approximate their fair values.
New Accounting Standards — In October 2009, the FASB issued authoritative guidance that
amends existing guidance for identifying separate deliverables in a revenue-generating transaction
where multiple deliverables exist, and provides guidance for allocating and recognizing revenue
based on those separate deliverables. The guidance is expected to result in more
multiple-deliverable arrangements being separable than under current guidance. This guidance is
effective for the Company beginning on January 1, 2011 and is required to be applied prospectively
to new or significantly modified revenue arrangements. The Company does not expect this guidance to
have a material impact on its financial statements in future periods.
Net Loss Per Common Share — Basic and diluted net loss per common share have been calculated
in accordance with ASC Topic 260, “Earnings Per Share”, for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009
and 2008. As the Company had a net loss in each of the periods presented, basic and diluted net
loss per common share are the same.
The computation of basic net loss per common share for the years ended December 31, 2010 and
2009 excluded 650,000 and 672,500 shares of restricted stock, respectively (see Note 6). While
these restricted shares of stock are included in outstanding shares on the balance sheet at
December 31, 2010 and 2009, these restricted shares are excluded from basic net loss per common
share in accordance with ASC Topic 260 due to the forfeiture provisions associated with these
shares.
The computations of diluted net loss per common share for the years ended December 31, 2010,
2009 and 2008 did not include the outstanding shares of restricted stock as well as the effects of
the following options to acquire common stock and common stock warrants as the inclusion of these
securities would have been antidilutive:
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
Restricted stock |
650,000 | 672,500 | — | |||||||||
Stock options |
4,208,830 | 4,338,695 | 3,362,721 | |||||||||
Common stock warrants |
1,300,119 | 1,300,119 | 1,300,119 | |||||||||
| 6,158,949 | 6,311,314 | 4,662,840 | ||||||||||
4. Intangible Assets
Intangible assets, consisting of purchased intellectual property, as of December 31, 2010 and
2009 comprise the following (in thousands):
| December 31, 2010 | December 31, 2009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Accumulated | Accumulated | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost | Amortization | Net | Cost | Amortization | Net | |||||||||||||||||||
Intellectual property — licenses |
$ | 4,036 | $ | (1,241 | ) | $ | 2,795 | $ | 2,438 | $ | (728 | ) | $ | 1,710 | ||||||||||
Patents |
455 | (19 | ) | $ | 436 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||
| $ | 4,491 | $ | (1,260 | ) | $ | 3,231 | $ | 2,438 | $ | (728 | ) | $ | 1,710 | |||||||||||
On July 9, 2010, the Company executed a worldwide non-exclusive license agreement (“the
License Agreement”) to utilize certain patented technology believed by the Company to be useful in
the manufacture of certain of its current and future products. Under the terms of the License
Agreement, the Company will pay a license and technology transfer fee, payable in four
installments. The license fee of $1,850,000 is reflected in “Intangible Assets — Net of
accumulated amortization” on the balance sheet as of December 31, 2010. The first installment of
$165,000, including a $15,000 of technology transfer fee, was paid upon the execution of the
License Agreement. The second installment of $350,000 is payable on July 9, 2011 and is reflected
in “Current Liabilities — Other Current Liabilities” on the balance sheet as of December 31, 2010.
The final two installments of $600,000 and $750,000 are payable on July 9, 2012 and 2013,
respectively, and are reflected in “Long-Term Liabilities — Other Noncurrent Liabilities” on the
balance sheet as of December 31, 2010. These fees represent full payment for use of the licensed
patents during the term of the License Agreement, which ends on the expiration date of the last
patent issued and licensed under the License Agreement.
47
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
The Company acquired patents and patent rights from Eppendorf AG on August 18, 2010. See Note
10.
Amortization expense for intangible assets was $0.5 million, $0.3 million and $0.3 million for
the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively. Estimated future amortization
expense is as follows (in thousands):
| Years Ending December 31 | ||||
2011 |
$ | 176 | ||
2012 |
176 | |||
2013 |
176 | |||
2014 |
176 | |||
2015 |
171 | |||
Thereafter |
522 |
Licenses are amortized from the date of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (the “FDA”)
clearance of products associated with the licensed technology and such amortization continues over
the remaining life of the license. The future amortization expense reflected above is based on
licenses related to products cleared by the FDA as of December 31, 2010. The amortization period
related to $1.8 million of licenses is not known as the diagnostic test products associated with
the licensed technology have not been cleared by the FDA and, accordingly, amortization has not
begun and no expense associated with the licenses is included in the table above. During the year
ended December 31, 2010 and 2008, the Company wrote off capitalized license fees of $0.3 million
and $0.2 million, respectively, associated with licenses which the Company did not plan to utilize
in the Verigene System. There were no license costs written off in the year ended December 31,
2009.
5. Related Party Transactions
Dr. Chad Mirkin, a co-founder of the Company, provides contracted research and development
services to the Company and is reimbursed for these services based upon negotiated contract rates.
The Company incurred expenses of $0.1 million for these services in each of the years ended
December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008.
AOQ Trust, a 5% stockholder of the Company, and LFT Partnership, an affiliate of AOQ Trust,
purchased 337,849 shares and 162,151 shares of the Company’s common stock, respectively, at $7.00
per share in the Company’s October 2009 underwritten public offering. Mark Slezak, a director of
the Company, is a trustee of AOQ Trust and the investment manager of LFT Partnership.
6. Equity Incentive Plans
The Company’s 2000 Equity Incentive Plan, as amended (the “2000 Plan”), permitted the grant of
options to employees, founders, and consultants for up to 1,600,000 shares of common stock. Option
awards are generally granted with an exercise price equal to the fair value of the Company’s common
stock at the date of grant; those option awards have various vesting structures and have 10 year
contractual terms. In connection with the approval of the 2007 Plan as defined below, the Company
terminated the 2000 Plan and therefore, the Company may not make any further awards of options,
share appreciations rights or restricted shares under the 2000 Plan.
In March 2007, the Company’s board of directors adopted and its shareholders approved the
Nanosphere 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan (the “2007 Plan”). The 2007 Plan authorizes the grant of
stock options, share appreciation rights, restricted shares, restricted share units, unrestricted
shares, incentive stock options, deferred share units and performance awards. The total awards
originally authorized under the 2007 Plan was 4,106,009 shares, plus up to an additional 773,591
shares of common stock that will become available in the event that awards made under the 2000 Plan
expire, are forfeited or cancelled, plus an annual increase in the number of shares pursuant to the
evergreen provision equal to the least of: 900,000 shares of common stock; 4.0% of the Company’s
outstanding shares of common stock as of fiscal year end; and an amount determined by the board of
directors. Pursuant to the evergreen provision, an additional 900,000 shares of common stock were
authorized for issuance under the 2007 Plan as of January 1, 2010 and 2011.
Certain options vest ratably over four years of service, while other options vest after seven
years of service but provide for accelerated vesting contingent upon the achievement of various
company-wide performance goals, such as decreasing time to market for new products and entering
into corporate collaborations (as defined in the option grant agreements). For these “accelerated
vesting” options, 20-25% of the granted option shares will vest upon the achievement of each of
four or five milestones as defined in
the option grant agreements, with any remaining unvested options vesting on the seven year
anniversary of the option grant dates. Approximately 46% of the options granted and outstanding
contain “accelerated vesting” provisions. The service period over which compensation expense is
recognized for options which include the accelerated vesting provision is the shorter of the seven
year cliff term or the projected timeframe for achieving the company-wide performance goals.
48
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
The fair values of the Company’s option awards were estimated at the dates of grant using the
Black-Scholes option pricing model with the following assumptions:
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
Expected dividend yield |
0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||||||
Expected volatility |
100 | % | 97 | % | 68 | % | ||||||
Risk free interest rate |
2.46 | % | 2.42 | % | 3.02 | % | ||||||
Weighted-average expected option life |
6.1 years | 6.1 years | 6.4 years | |||||||||
Estimated weighted-average fair value on the
date of grant based on the above assumptions |
$ | 3.99 | $ | 4.59 | $ | 6.97 | ||||||
Estimated forfeiture rate for unvested options |
11.9 | % | 4.4 | % | 4.6 | % | ||||||
Due to the Company’s limited period of trading activity as a public company from 2007 through
the third quarter of 2009, the expected volatility was based on historical data from various peer
public companies with similar product portfolios. The expected volatility for option awards granted
in the fourth quarter of 2009 and during 2010 was based on the Company’s actual historical
volatility. The risk-free rate is based on the U.S. Treasury yield curve in effect at the time of
the grants for periods consistent with the expected life of the option. The expected life of
options that vest ratably over four years of service is derived from the average of the vesting
period and the term of the option as defined in the Plans, following the guidance in Securities and
Exchange Commission (“SEC”) Staff Accounting Bulletin Nos. 107 and 110. The Company estimates the
expected life of options with accelerated vesting terms giving consideration to the dates that the
Company expects to achieve key milestones under the option agreements and the term of the option.
Total compensation cost associated with the option awards was $4.5 million, $2.4 million and $2.2
million 2010, 2009, and 2008, respectively.
As of December 31, 2010, the total compensation cost not yet recognized related to the
nonvested awards is approximately $5.4 million, which amount is expected to be recognized over the
next two years, which is a weighted average term. Certain milestone events are deemed probable of
achievement prior to their seven year vesting term, and the acceleration of vesting resulting from
the achievement of such milestone events has been factored into the weighted average vesting term.
While the Company does not have a formally established policy, as a practice the Company has
delivered newly issued shares of its common stock upon the exercise of stock options.
A summary of option activity under the Plan as of December 31, 2010, and for the year then
ended is presented below:
| Weighted | ||||||||||||||||
| Weighted | Average | |||||||||||||||
| Average | Remaining | Aggregate | ||||||||||||||
| Number of | Exercise | Contractual | Intrinsic | |||||||||||||
| Options | Shares | Price | Term | Value of Options | ||||||||||||
Outstanding — January 1, 2010 |
4,338,695 | $ | 5.75 | |||||||||||||
Granted |
155,945 | $ | 5.07 | |||||||||||||
Exercised |
(8,545 | ) | $ | 4.13 | ||||||||||||
Expired |
(115,603 | ) | $ | 9.69 | ||||||||||||
Forfeited |
(161,662 | ) | $ | 6.30 | ||||||||||||
Outstanding — December 31, 2010 |
4,208,830 | $ | 5.60 | 6.99 | $ | 2,500 | ||||||||||
Exercisable — December 31, 2010 |
1,892,369 | $ | 5.57 | 6.14 | $ | 938 | ||||||||||
Vested and Expected to Vest — December 31, 2010 |
4,102,273 | $ | 5.60 | 6.98 | $ | 2,428 | ||||||||||
The intrinsic value of options exercised in 2010 was less than $0.1 million. The intrinsic
value of options exercised in 2009 and 2008 was $0.2 million in each year.
Included in the number of options outstanding at December 31, 2010, are 1,928,516 options with
a weighted average exercise price of $5.28 per share and accelerated vesting provisions based on
the criteria mentioned above. During 2009, two of the five milestones as defined in the 2000 Plan
were achieved, and one of the four milestones as defined in the 2007 Plan was achieved. As a
result, 40% of the outstanding options under the 2000 Plan with accelerated vesting provisions were
vested as of December 31, 2010 and 25% of
the outstanding options under the 2007 Plan with accelerated vesting provisions were vested as
of December 31, 2010. The total fair value of shares vested during 2010, 2009 and 2008 was $2.0
million, $3.1 million and $1.3 million, respectively.
49
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
In November 2009, the Company granted 672,500 shares of restricted stock under the 2007 Plan,
of which 50% vest on the two-year anniversary of the grant date and are subject to forfeiture until
vested, and 50% vest on the four-year anniversary of the grant date and are subject to forfeiture
until vested. The weighted average grant-date fair value was $6.06 per share. During fiscal 2010,
22,500 shares of restricted stock were forfeited. The Company recognized $1.5 million and $0.1
million in compensation expense associated with the restricted stock during 2010 and 2009,
respectively. As of December 31, 2010, the total compensation cost not yet recognized related to
the nonvested restricted stock awards is approximately $2.4 million, which amount is expected to be
recognized over a weighted average term of two years.
7. Income Taxes
Deferred tax assets consist primarily of net operating loss (“NOL”) carryforwards related to
U.S. federal and state taxes and research and development tax credits. Realization of future tax
benefits related to deferred tax assets is dependent on many factors, including the Company’s
ability to generate future taxable income. Due to the Company’s history of operating losses, the
Company has recorded a full valuation allowance against these assets.
NOL carryforwards of approximately $191 million for income tax purposes are available to
offset future taxable income. If not used, these carryforwards will expire in varying amounts from
2020 through 2030. The Company also has federal research and development tax credit carryforwards
of $9 million which will expire from 2020 through 2030. Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code
subjects the utilization of net operating loss and credit carryforwards to an annual limitation
that is applicable if the Company experiences an ownership change. The Company believes its public
offerings and/or prior equity investments may have triggered an ownership change as defined by the
Internal Revenue Code. However, the Company has yet to perform the computations under Section 382
which would determine the amount of annual limitation on its utilization of its net operating loss
and tax credit carryforwards. The annual limitation may result in the expiration of the Company’s
net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards before they can be used.
The following is a summary of the components of the Company’s deferred tax assets and
liabilities as of December 31, 2010 and 2009 (in thousands):
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
Deferred tax assets: |
||||||||
Net operating losses |
$ | 74,125 | $ | 60,449 | ||||
Research and development credits |
9,100 | 8,033 | ||||||
Share-based compensation |
1,549 | 777 | ||||||
Amortization of intangible assets |
1,169 | 1,202 | ||||||
Other |
542 | 566 | ||||||
| 86,485 | 71,027 | |||||||
Valuation allowance |
(86,137 | ) | (70,476 | ) | ||||
Net deferred tax assets after valuation allowance |
348 | 551 | ||||||
Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||
Depreciation on property and equipment |
(348 | ) | (551 | ) | ||||
Deferred tax assets — net |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||
The reconciliation of the federal statutory rate to the Company’s effective tax rate of zero
percent for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 is as follows:
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
Tax provision at the statutory federal rate |
34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | ||||||
State income taxes, net of federal income tax benefit |
4.8 | % | 4.8 | % | 4.8 | % | ||||||
Other |
(6.7 | )% | (5.5 | )% | (5.8 | )% | ||||||
Valuation allowance |
(32.1 | )% | (33.3 | )% | (33.0 | )% | ||||||
| 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | 0.0 | % | |||||||
50
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
As of December 31, 2010 and 2009, the Company had no liability recorded for unrecognized tax
benefits. The Company classifies penalties and interest expense related to income tax liabilities
as an income tax expense. There are no interest and penalties recognized in the statements of
operations for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 or accrued on the balance sheets as
of December 31, 2010 and 2009.
The Company files tax returns in the U.S. and various states. All tax years since 1999 remain
open to examination by the major taxing jurisdictions to which the Company is subject. The Company
has not made any cash payments for income taxes since its inception.
8. License Agreements
In 2006, the Company entered into a license agreement with Northwestern University
(“Northwestern”), which provides the Company with an exclusive license to certain existing patents
and patent applications owned by Northwestern and future inventions developed by Northwestern that
are related to (1) nanotechnology, which technology involves a particle where no single dimension
is greater than 100 nanometers, or Nanotechnology, and (2) biobarcode technology, which is analysis
where oligonucleotides act as surrogate targets or reporter molecules, or Biobarcode Technology.
The license is limited to the “Biodiagnostics Field” defined as qualitative or quantitative in
vitro analysis, testing, measurement, or detection of various biodiagnostics field subjects and
target combinations.
The Company has entered into several nonexclusive license agreements with various companies
covering certain technologies which are embedded in the Company’s diagnostic instruments and
diagnostic test products. As of December 31, 2010, the Company has paid aggregate initial license
fees of $2.8 million for these licenses, and has agreed to pay a percentage of net sales as
royalties, in percentage amounts ranging from less than 1% to 12.0%. Royalties on net sales are
classified in Cost of sales. Certain of the license agreements have minimum annual royalty
payments, and such minimum payments are $0.2 million in each of the fiscal years 2011, 2012, 2013,
2014 and 2015 and are approximately $0.1 million annually thereafter through the dates the
respective licenses terminate. These licenses expire at various times, corresponding to the subject
patents expirations, which currently range from 2011 to 2027.
9. Stockholders’ Equity
Common Stock
During 2007, the Company closed on the sale of 8,050,000 shares related to the initial public
offering at $14.00 per share, less underwriting discounts and commissions. Net proceeds from the
initial public offering were approximately $102 million, net of transaction expenses.
Approximately $0.8 million of the transaction expenses were paid in 2008.
The Company completed an underwritten public offering of 5,405,000 shares of common stock on
October 21, 2009 at a public offering price of $7.00 per share, less underwriting discounts and
commissions. Net proceeds from the public offering were approximately $35.4 million.
Registration Rights
Pursuant to an agreement between the Company and certain of its stockholders, the Company has
granted the following demand registration rights to Mr. Mark Slezak and Ms. Sheli Rosenberg, who
are members of the Company’s board of directors, AOQ Trust, Alfa-Tech, LLC, Lurie Investment Fund,
LLC, Lurie Investments, Inc. and their respective affiliates, and Bain Capital Venture Fund 2005,
L.P., Brookside Capital Partners Fund, L.P., and their respective affiliates and other
stockholders. Mr. William P. Moffitt, III, the Company’s chief executive officer and a member of
the board of directors, and Dr. Chad Mirkin, a member of the board of directors, are parties to
this agreement, but do not have the right to demand registration. At any time after the earlier to
occur of (1) 120 days after the closing of an initial public offering, which occurred on November
6, 2007, or (2) April 1, 2010:
| • | Long-Form Registrations. Stockholders holding at least 20% of the then outstanding shares of the Company’s common stock that are subject to the registration rights agreement, which are referred to as registrable securities, have the right to demand that the Company file a registration statement under the Securities Act on Form S-1 or any similar long-form registration covering their registrable securities. However, the Company is not obligated to file a long-form registration statement on more than three occasions upon the request of the stockholders. | ||
| • | Short-Form Registrations. Stockholders holding at least 10% of the then outstanding registrable securities have the right to demand that the Company file a registration statement on Form S-3 or any similar short-form registration covering their registrable securities, provided that such short-form registration is then available to the Company under applicable law. Such stockholders are entitled to request an unlimited number of short-form registrations. |
51
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
If the Company’s board of directors believes in its reasonable good faith that any demand
registration would require premature disclosure of a proposal or plan that the Company intends to
undertake, and such disclosure would have a material adverse effect on the Company, then it may
delay the registration once in any twelve month period for up to 90 days. Moreover, if the demand
registration is an underwritten offering, the Company may reduce the number of shares of
registrable securities to be registered upon the advice of the underwriters that such offering
exceeds the number of securities that can be sold in an orderly manner within an acceptable price
range. If shares of the Company’s common stock requested to be included in a registration must be
excluded pursuant to the underwriters’ advice, the Company will generally register a pro rata
portion of the shares requested to be registered.
Under the piggyback registration provisions, if the Company proposes to register any
securities under the Securities Act, other than pursuant to a demand registration, and the
registration form to be used may be used for the registration of registrable securities,
stockholders holding such registrable securities have the right to include their shares in the
registration statement. However, if the registration is an underwritten offering, the Company may
reduce the number of shares to be registered under the piggyback registration provisions upon the
advice of the underwriters that such offering exceeds the number of securities that can be sold in
an orderly manner within an acceptable price range. If shares of the Company’s common stock
requested to be included in a registration must be excluded pursuant to the underwriters’ advice,
the Company will generally register a pro rata portion of the shares requested to be registered
under the piggyback registration provisions. The piggyback registration rights granted under the
registration rights agreement have no expiration date.
Expenses of Registration. The Company will generally pay all registration expenses in
connection with the demand and piggyback registrations described above, including all registration
and filing fees, expenses and fees of compliance with securities laws, and fees and disbursements
of all counsel, independent certified public accountants, underwriters (excluding discounts and
commissions) and other persons retained by the Company. The Company will also pay the reasonable
fees and disbursements of one counsel chosen by the selling stockholders in each demand or
piggyback registration.
Transferability. The demand and piggyback registration rights described above are generally
transferable to any subsequent holder of registrable securities.
Warrants
Prior to the completion of the Company’s initial public offering, the Company issued warrants
to purchase shares of convertible preferred stock in connection with certain of the convertible
preferred stock financings. Certain of these warrants were converted to common stock warrants upon
the closing of the initial public offering. As of December 31, 2010 and 2009, there were
outstanding warrants to acquire shares of common stock of 1,300,119. The expiration dates of the
warrants outstanding at December 31, 2010 are as follows:
| Series of Stock to | Number of | Expiration | ||||||
| which the Warrant is Exercisable | Warrants | Date | ||||||
Common — exercise price of $17.50 per share |
1,135,194 | April 2011 | ||||||
Common — exercise price of $8.75 per share |
164,925 | April 2013 | ||||||
In April 2010 the exercise price on the common stock warrants increased from $15.32 per share
to $17.50 per share.
10. Commitments and Contingencies
In August 2009, the Company executed a lease renewal which commenced in June 2010 and ends in
May 2014. Under the terms of the lease renewal, the Company has two successive three year options
to renew the lease, and the Company has the right of first refusal to lease additional space within
the facility.
Rent and operating expenses associated with the office and laboratory space were $0.6 million,
$0.5 million and $0.8 million in 2010, 2009 and 2008, respectively.
52
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
Annual future minimum obligations for the operating lease as of December 31, 2010 are as
follows (in thousands):
| Operating | ||||
| Years Ending December 31 | Lease | |||
2011 |
$ | 427 | ||
2012 |
439 | |||
2013 |
451 | |||
2014 |
190 | |||
Total minimum lease payments |
$ | 1,507 | ||
In July 2009, the Company was named as a defendant in a lawsuit filed in the United States
District Court for the District of Delaware by Eppendorf AG alleging infringement of a patent owned
by the plaintiff. On August 18, 2010, the Company executed a Settlement Agreement and Intellectual
Property Purchase Agreement (the “Settlement and Purchase Agreement”) with Eppendorf AG. The
Settlement and Purchase Agreement provides for, among other things, a lump sum payment of $4
million to settle a patent litigation dispute between the companies, the Company’s acquisition from
Eppendorf of certain patents and patent rights, and a limited license back to service existing
Eppendorf customers and licenses previously issued that relate to the purchased patents and patent
rights. Pursuant to the Settlement and Purchase Agreement, the Company paid $4 million to Eppendorf
AG during the third quarter of 2010. The Company has allocated $3.5 million of the lump sum
payment to settlement expense and $0.5 million to intangible assets for the fair value of the
acquired patents and patent rights.
11. Long-Term Debt
In February 2007, the Company entered into two loan and security agreements, with commitments
for debt financing with Venture Lending & Leasing IV, Inc., and Venture Lending & Leasing V, Inc.
The Company borrowed $12.5 million under these agreements in February 2007. Interest rates under
the agreements were 12.5% for the initial twelve month period and 10.0% during the following thirty
month period. Notes issued pursuant to this commitment were secured by a first security lien on all
of the Company’s assets including intellectual property. This debt matured in August 2010.
The $12.5 million of proceeds received were allocated to debt and the Series D Convertible
Preferred Stock based on their fair values at the borrowing date with $1.9 million allocated to
Series D Convertible Preferred Stock and the remaining $10.6 million allocated to debt. The
discount on the debt of $1.9 million resulted in an effective interest rate on the debt of 21% and
the discount was amortized as interest expense over the term of the debt following the interest
method. Interest expense on this debt for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 was $0.3
million, $1.2 million and $2.0 million, respectively, which included $0.1 million, $0.5 million and
$0.7 million of discount amortization, respectively. Cash interest paid on this debt was $0.2
million, $0.8 million and $1.3 million for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008,
respectively.
12. Supplemental Financial Information
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
Inventories: |
||||||||
Raw materials |
$ | 760 | $ | 1,062 | ||||
Work-in-process |
69 | — | ||||||
Finished goods |
1,599 | 1,879 | ||||||
Total |
$ | 2,428 | $ | 2,941 | ||||
During 2010, the Company established a valuation reserve of $0.7 million for most of the
original Verigene System processor inventory. All near-term assay submissions are expected to be on
the Processor SP.
53
Table of Contents
Nanosphere, Inc.
Notes to Financial Statements — (Continued)
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
Property and Equipment — Net: |
||||||||
Equipment with customers |
$ | 2,164 | $ | 1,568 | ||||
Computer equipment and software |
935 | 1,016 | ||||||
Laboratory equipment |
5,725 | 4,721 | ||||||
Furniture and fixtures |
269 | 269 | ||||||
Leasehold improvements |
2,878 | 2,869 | ||||||
Manufacturing equipment |
4,298 | 4,143 | ||||||
Office equipment |
67 | 67 | ||||||
Tooling |
1,423 | 1,377 | ||||||
Total property and equipment — at cost |
17,759 | 16,030 | ||||||
Less accumulated depreciation |
(12,617 | ) | (9,885 | ) | ||||
Property and Equipment — Net |
$ | 5,142 | $ | 6,145 | ||||
| 2010 | 2009 | |||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
Other Current Liabilities: |
||||||||
Accrued clinical trial expenses |
$ | 603 | $ | 940 | ||||
All other |
752 | 1,364 | ||||||
Total |
$ | 1,355 | $ | 2,304 | ||||
13. Selected Quarterly Financial Data (Unaudited)
| 2010 Quarters | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||
| First | Second | Third | Fourth | |||||||||||||
Total revenue |
$ | 826 | $ | 517 | $ | 373 | $ | 310 | ||||||||
Loss from operations |
$ | (8,416 | ) | $ | (13,689 | ) | $ | (10,920 | ) | $ | (8,374 | ) | ||||
Net loss |
$ | (8,551 | ) | $ | (13,759 | ) | $ | (10,919 | ) | $ | (7,383 | ) | ||||
Per share data: |
||||||||||||||||
Net loss per common share — basic and diluted |
$ | (0.31 | ) | $ | (0.50 | ) | $ | (0.39 | ) | $ | (0.27 | ) | ||||
| 2009 Quarters | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||
| First | Second | Third | Fourth | |||||||||||||
Total revenue |
$ | 255 | $ | 402 | $ | 729 | $ | 828 | ||||||||
Loss from operations |
$ | (7,982 | ) | $ | (8,131 | ) | $ | (7,996 | ) | $ | (8,932 | ) | ||||
Net loss |
$ | (8,193 | ) | $ | (8,384 | ) | $ | (8,242 | ) | $ | (9,130 | ) | ||||
Per share data: |
||||||||||||||||
Net loss per common share — basic and diluted |
$ | (0.37 | ) | $ | (0.38 | ) | $ | (0.37 | ) | $ | (0.34 | ) | ||||
14. Subsequent Events
In January 2011, the Company received FDA 510(k) clearance as well as CE IVD Mark approval for
the Verigene Respiratory Virus Plus Nucleic Acid Test (RV+) on the Processor SP. The RV+ test
expands the Company’s existing test capabilities for the detection of respiratory viruses. In a
single test, the RV+ provides Influenza A, Influenza B, RSV A, and RSV B detection, and further
subtypes Influenza A as H1, H3, or 2009 H1N1. In addition, the Company’s warfarin metabolism assay
was CE IVD Marked during the first quarter of 2011.
54
Table of Contents
Item 9. Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure.
We have had no disagreements with our independent registered public accounting firm on any
matter of accounting principles or practices or financial statement disclosure.
Item 9A. Controls and Procedures.
(a) Evaluation of Disclosure Controls and Procedures
Management of the Company, with the participation of the Chief Executive Officer and the Chief
Financial Officer, evaluated the effectiveness of the design and operation of the Company’s
disclosure controls and procedures (as defined in Rules 13a-15(e) and 15d-15(e) of the Securities
Exchange Act of 1934, as amended) as of December 31, 2010. The Company’s disclosure controls and
procedures are designed to ensure that information required to be disclosed by the Company in the
reports it files or submits under the Exchange Act is recorded, processed, summarized and reported
on a timely basis and that such information is accumulated and communicated to management,
including the Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate, to allow timely
decisions regarding disclosure. Based upon this evaluation, the Chief Executive Officer and the
Chief Financial Officer have concluded that the Company’s disclosure controls and procedures were
effective as of December 31, 2010.
(b) Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
Internal control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Rules 13a-15(f) and
15d-15(f) under the Exchange Act, is a process designed by, or under the supervision of, the
Company’s chief executive officer and chief financial officer, or persons performing similar
functions, and effected by the Company’s board of directors, management and other personnel, to
provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation
of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting
principles. The Company’s management, with the participation of the Company’s chief executive
officer and chief financial officer, has established and maintained policies and procedures
designed to maintain the adequacy of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting, and
includes those policies and procedures that:
| (1) | Pertain to the maintenance of records that in reasonable detail accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the Company; | ||
| (2) | Provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the Company; and | ||
| (3) | Provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use or disposition of the Company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. |
The Company’s management is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal
control over financial reporting, as such term is defined in Exchange Act Rules 13a-15(f). The
Company’s management conducted an evaluation of the effectiveness of internal control over
financial reporting based on the framework in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by
the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission. Based on its evaluation under
the framework in Internal Control — Integrated Framework, the Company’s management concluded that
internal control over financial reporting was effective as of December 31, 2010.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent
or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are
subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that
the degree or compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
The Company’s independent registered public accounting firm, Deloitte & Touche LLP, has issued
an attestation report on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31,
2010. Their report is included in this Form 10-K.
55
Table of Contents
(c) Changes in Internal Controls Over Financial Reporting
There have been no changes to the Company’s internal control over financial reporting during
the most recent fiscal quarter that have materially affected, or are reasonably likely to
materially affect, the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
Item 9B. Other Information.
None.
56
Table of Contents
PART III.
Item 10. Directors and Executive Officers of the Registrant.
The information required by Item 10 will be set forth in the Company’s definitive proxy
statement for its annual meeting of shareholders expected to be held on June 1, 2011, and is
incorporated herein by reference.
| Item 11. Executive Compensation. | ||
The information required by Item 11 will be set forth in the Company’s definitive proxy statement
for its annual meeting of shareholders expected to be held on June 1, 2011, and is incorporated
herein by reference.
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Stockholder Matters. |
The information required by Item 12 will be set forth in the Company’s definitive proxy
statement for its annual meeting of shareholders expected to be held on June 1, 2011, and is
incorporated herein by reference.
Item 13. Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence.
The information required by Item 13 will be set forth in the Company’s definitive proxy statement
for its annual meeting of shareholders expected to be held on June 1, 2011, and is incorporated
herein by reference.
Item 14. Principal Accounting Fees and Services.
The information required by Item 14 will be set forth in the Company’s definitive proxy
statement for its annual meeting of shareholders expected to be held on June 1, 2011, and is
incorporated herein by reference.
57
Table of Contents
PART IV.
Item 15. Exhibits, Financial Statement Schedules.
| (a)(1) | Financial Statements |
| Reports of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | |||
| Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2010 and 2009 | |||
| Statements of Operations for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 | |||
| Statements of Stockholders’ Equity (Deficit) for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 | |||
| Statements of Cash Flows for the years ended December 31, 2010, 2009 and 2008 | |||
| Notes to Financial Statements | |||
| (a)(2) Financial Statement Schedules | |||
| None | |||
| (a)(3) Exhibits required by Item 601 of Regulation S-K. | |||
| Exhibit Number | Exhibit Description | |||
| 3.1 | Second Amended and Restated Certificate of Incorporation of Nanosphere, Inc. (3) (Exhibit 3.1) |
|||
| 3.2 | Amended and Restated Bylaws of Nanosphere, Inc. (3) (Exhibit 3.2) |
|||
| 4.1 | Specimen of common stock certificate (4) (Exhibit 4.3) |
|||
| 10.1 | Nanosphere, Inc. 2000 Equity Incentive Plan (1) (Exhibit 10.1) |
|||
| 10.2 | Form of Nanosphere, Inc. 2000 Equity Incentive Plan Non-Qualified Stock Option Award Agreement, as
amended (1) (Exhibit 10.2) |
|||
| 10.3 | Form of Nanosphere, Inc. 2000 Equity Incentive Plan Option Award Agreement (1) (Exhibit 10.3) |
|||
| 10.4 | Nanosphere, Inc. 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan, as amended and restated (4) (Exhibit 10.4) |
|||
| 10.5 | Form of Nanosphere, Inc. 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan Incentive Stock Option Award Agreement (Time
Vested) (1) (Exhibit 10.5) |
|||
| 10.6 | Form of Nanosphere, Inc. 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan Non-Qualified Stock Option Award Agreement
(Time Vested) (1) (Exhibit 10.6) |
|||
| 10.7 | Form of Nanosphere, Inc. 2007 Long-Term Incentive Plan Option Award Agreement (Cliff-vested,
performance-accelerated) (1) (Exhibit 10.7) |
|||
| 10.8 | Employment Agreement, dated as of July 19, 2004, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and William P.
Moffitt III, as amended (1) (Exhibit 10.8) |
|||
| 10.9 | Restricted Stock Purchase Agreement, dated as of March 16, 2006, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and
William P. Moffitt III (3) (Exhibit 10.9) |
|||
| 10.10 | Employment Agreement, dated January 2, 2001, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and William Cork (4)
(Exhibit 10.10) |
|||
| 10.11 | Employment Agreement, dated May 13, 2005, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and Gregory Shipp (1)
(Exhibit 10.11) |
|||
| 10.12 | Employment Agreement, dated September 5, 2005, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and Michael McGarrity
(1) (Exhibit 10.12) |
|||
| 10.13 | Employment Agreement, dated April 25, 2007, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and J. Roger Moody, Jr.
(1) (Exhibit 10.13) |
|||
| 10.14 | Employment Agreement, dated May 31, 2007, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and Winton Gibbons (1)
(Exhibit 10.14) |
|||
| 10.15 | Severance Agreement, dated as of June 4, 2007, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and Stephen Wasko (1)
(Exhibit 10.15) |
|||
58
Table of Contents
| Exhibit Number | Exhibit Description | |||
| 10.16 | License Agreement, dated as of January 1, 2006, by and between Northwestern University and Nanosphere,
Inc. (2)# (Exhibit 10.16) |
|||
| 10.17 | Non-Exclusive License Agreement, dated as of December 20, 2002, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and
Abbott Laboratories (2)# (Exhibit 10.17) |
|||
| 10.18 | Lease with Motorola, Inc., dated as of March 24, 2003, as amended (1) (Exhibit 10.18) |
|||
| 10.19 | Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of February 7, 2007, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and Venture
Lending & Leasing IV, Inc. (1) (Exhibit 10.19) |
|||
| 10.20 | Loan and Security Agreement, dated as of February 21, 2007, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and
Venture Lending & Leasing V, Inc. (1) (Exhibit 10.20) |
|||
| 10.21 | Consulting and Non-Competition Agreement, dated as of October 31, 2002, by and between Nanosphere,
Inc. and Chad A. Mirkin, as amended (1) (Exhibit 10.21) |
|||
| 10.22 | Bonus Agreement, dated as of March 16, 2006, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and William P. Moffitt
III, as amended (2) (Exhibit 10.22) |
|||
| 10.23 | Series D Preferred Stock and Warrant Purchase Agreement, dated as of April 12, 2006 (2) (Exhibit 10.24) |
|||
| 10.24 | Note Purchase Agreement, dated as of March 15, 2006, by and between Nanosphere, Inc. and Lurie
Investment Fund, L.L.C. (2) (Exhibit 10.28) |
|||
| 10.25 | Form of Indemnification Agreement (3) (Exhibit 10.29) |
|||
| 10.26 | Non-Exclusive Financial Advisory Services Engagement Letter, dated as of August 8, 2007, by and
between Nanosphere, Inc. and Allen & Company LLC (4) (Exhibit 10.30) |
|||
| 10.27 | Amended and Restated Employment Agreement dated as of January 1, 2009, between Nanosphere, Inc. and
Mr. William P. Moffitt (5) (Exhibit 10.31) |
|||
| 10.28 | Second Amended and Restated Registration Rights Agreement, dated August 19, 2009 (6) (Exhibit 10.1) |
|||
| 10.29 | Lease Agreement, dated August 28, 2009, between Nanosphere, Inc. and Northbrook Commercial Properties,
LLC (7) (Exhibit 10.1) |
|||
| 10.30 | License Agreement, dated July 9, 2010, between Nanosphere, Inc. and Accelr8 Technology Corporation (8)
(Exhibit 10.1) |
|||
| 10.31 | Settlement Agreement and Intellectual Property Purchase Agreement, dated August 18, 2010, between
Nanosphere, Inc. and Eppendorf AG (9) (Exhibit 10.1) |
|||
| 23.1 | Consent of Deloitte & Touche LLP* |
|||
| 31.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a), as
adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 * |
|||
| 31.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to Exchange Act Rules 13a-14(a) and 15d-14(a), as
adopted pursuant to Section 302 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 * |
|||
| 32.1 | Certification of Chief Executive Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to
Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 * |
|||
| 32.2 | Certification of Chief Financial Officer pursuant to 18 U.S.C. Section 1350, as adopted pursuant to
Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 * |
|||
| * | Filed herewith | |
| # | Confidential treatment has been requested with respect to certain provisions of this agreement. Omitted portions have been filed separately with the SEC. | |
| (1) | Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on August 13, 2007. The exhibit reference in parentheses indicates the corresponding exhibit number in such Registration Statement. | |
| (2) | Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Amendment No. 1 to Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 27, 2007. The exhibit reference in parentheses indicates the corresponding exhibit number in such Amendment. | |
| (3) | Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Amendment No. 2 to Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 17, 2007. The exhibit reference in parentheses indicates the corresponding exhibit number in such Amendment. |
59
Table of Contents
| (4) | Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Amendment No. 3 to Form S-1 as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on October 29, 2007. The exhibit reference in parentheses indicates the corresponding exhibit number in such Amendment. | |
| (5) | Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on March 5, 2009. The exhibit reference in parentheses indicates the corresponding exhibit number in such Current Report. | |
| (6) | Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Quarterly Report on Form 10-Q as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on November 5, 2009. The exhibit reference in parentheses indicates the corresponding exhibit number in such Quarterly Report. | |
| (7) | Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on September 1, 2009. The exhibit reference in parentheses indicates the corresponding exhibit number in such Current Report. | |
| (8) | Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on July 15, 2010. The exhibit reference in parentheses indicates the corresponding exhibit number in such Current Report. | |
| (9) | Incorporated by reference from the Company’s Current Report on Form 8-K as filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on August 24, 2010. The exhibit reference in parentheses indicates the corresponding exhibit number in such Current Report. |
60
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934,
the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned,
thereunto duly authorized.
| NANOSPHERE, INC. |
||||
| By: | /s/ William P. Moffitt | |||
| William P. Moffitt | ||||
| Date: February 16, 2011 | President and Chief Executive Officer | |||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been
signed below by the following persons on behalf of the Registrant and in the capacities and on
the dates indicated:
| Signature | Title(s) | Date | ||
/s/ William P. Moffitt
|
President, Chief Executive Officer, Director (principal executive officer) |
February 16, 2011 | ||
/s/ Roger Moody
|
Chief Financial Officer, Treasurer (principal financial officer and principal accounting officer) |
February 16, 2011 | ||
/s/ Mark Slezak
|
Chairman of the board of directors | February 16, 2011 | ||
/s/ Jeffrey R. Crisan
|
Director | February 16, 2011 | ||
/s/ André de Bruin
|
Director | February 16, 2011 | ||
/s/ Chad A. Mirkin
|
Director | February 16, 2011 | ||
/s/ James J. Nahirny
|
Director | February 16, 2011 | ||
/s/ Sheli Z. Rosenberg
|
Director | February 16, 2011 | ||
/s/ Lorin J. Randall
|
Director | February 16, 2011 |
61
