Attached files
Table of Contents
As filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on January 28, 2011
Registration No. 333-171271
UNITED STATES SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D.C. 20549
AMENDMENT NO. 1
TO
FORM S-1
REGISTRATION STATEMENT
Under
The Securities Act of 1933
ServiceSource International, LLC
(Exact name of Registrant as specified in its charter)
| Delaware | 7380 | 81-0578975 | ||
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(Primary Standard Industrial Classification Code Number) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) |
634 Second Street
San Francisco, California 94107
(415) 901-6030
(Address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of Registrant’s principal executive offices)
Michael A. Smerklo
Chief Executive Officer
634 Second Street
San Francisco, California 94107
(415) 901-6030
(Name, address, including zip code, and telephone number, including area code, of agent for service)
Copies to:
| Jeffrey D. Saper Tony Jeffries Wilson Sonsini Goodrich & Rosati, P.C. 650 Page Mill Road Palo Alto, California 94304 (650) 493-9300 |
Paul D. Warenski Senior Vice President and General Counsel 634 Second Street San Francisco, California 94107 (415) 901-6030 |
Sarah K. Solum Davis Polk & Wardwell LLP 1600 El Camino Real Menlo Park, California 94025 (650) 752-2000 |
Approximate date of commencement of proposed sale to the public: As soon as practicable after this registration statement becomes effective.
If any of the securities being registered on this Form are to be offered on a delayed or continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933 check the following box: ¨
If this Form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, please check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this Form is a post effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
If this Form is a post effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same offering. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer | ¨ | Accelerated filer | ¨ | |||
| Non-accelerated filer | x (do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company | ¨ |
CALCULATION OF REGISTRATION FEE
| Title of Each Class of Securities to be Registered |
Proposed Maximum Aggregate Offering Price(1) |
Amount of Registration Fee(2) | ||
| Common Stock, par value $0.0001 per share |
$75,000,000 | $5,347.50 | ||
| (1) | Estimated solely for the purpose of calculating the registration fee in accordance with Rule 457(o) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended. Includes offering price of shares that the underwriters have the option to purchase to cover over-allotments, if any. |
| (2) | The Registrant previously paid this registration fee in connection with a previous filing of this Registration Statement. |
The registrant hereby amends this registration statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its effective date until the registrant shall file a further amendment which specifically states that this registration statement shall thereafter become effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 or until the registration statement shall become effective on such date as the Securities and Exchange Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may determine.
Table of Contents
EXPLANATORY NOTE
ServiceSource International, LLC, the registrant whose name appears on the cover of this registration statement, is a Delaware limited liability company. Prior to the issuance of any shares of common stock subject to this registration statement, ServiceSource International, LLC will convert into a Delaware corporation and change its name from ServiceSource International, LLC to ServiceSource International, Inc. Shares of the common stock of ServiceSource International, Inc. are being offered by the prospectus.
Table of Contents
The information in this prospectus is not complete and may be changed. Neither we nor the selling stockholders may sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This prospectus is not an offer to sell these securities, and we are not soliciting an offer to buy these securities in any state where the offer or sale is not permitted.
PROSPECTUS (Subject to Completion)
Issued January 28, 2011
Shares

COMMON STOCK
ServiceSource International, Inc. is offering shares of common stock and the selling stockholders are offering shares of common stock. We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of shares by the selling stockholders. This is our initial public offering and no public market exists for our shares. We anticipate that the initial public offering price will be between $ and $ per share.
We intend to apply for a listing of our common stock on The Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “ .”
Investing in our common stock involves risks. See “Risk Factors” beginning on page 11.
PRICE $ A SHARE
| Price to Public |
Underwriting |
Proceeds to |
Proceeds to | |||||
| Per share |
$ | $ | $ | $ | ||||
| Total |
$ | $ | $ | $ |
We and the selling stockholders have granted the underwriters the right to purchase up to an additional shares of common stock to cover over-allotments, with up to an additional shares sold by us and up to an additional shares sold by the selling stockholders.
The Securities and Exchange Commission and state securities regulators have not approved or disapproved these securities or determined if this prospectus is truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal offense.
The underwriters expect to deliver the shares of common stock to purchasers on , 2011.
| MORGAN STANLEY | DEUTSCHE BANK SECURITIES |
| WILLIAM BLAIR & COMPANY | LAZARD CAPITAL MARKETS | PIPER JAFFRAY |
JMP SECURITIES
, 2011
Table of Contents
Neither we, the selling stockholders nor the underwriters have authorized anyone to provide any information or to make any representations other than those contained in this prospectus or in any free writing prospectuses we have prepared. We take no responsibility for, and can provide no assurance as to the reliability of, any other information that others may give you. This prospectus is an offer to sell only the shares offered hereby but only under circumstances and in jurisdictions where it is lawful to do so. The information contained in this prospectus is current only as of its date. Our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects may have changed since that date.
Until , 2011 (the 25th day after the date of this prospectus), all dealers effecting transactions in these securities, whether or not participating in this offering, may be required to deliver a prospectus. This delivery requirement is in addition to the obligation of dealers to deliver a prospectus when acting as underwriters and with respect to their unsold allotments or subscriptions.
For investors outside the United States: Neither we, the selling stockholders nor the underwriters have done anything that would permit this offering or possession or distribution of this prospectus in any jurisdiction where action for that purpose is required, other than the United States. You are required to inform yourselves about and to observe any restrictions relating to this offering and the distribution of this prospectus outside of the United States.
ServiceSource is our registered trademark and Service Revenue Intelligence Platform, Channel Sales Cloud and our logo are our trademarks. All other trademarks and trade names appearing in this prospectus are the property of their respective owners.
i
Table of Contents
This summary highlights information contained elsewhere in this prospectus and does not contain all of the information you should consider in making your investment decision. Before deciding to invest in shares of our common stock, you should read this summary together with the more detailed information, including our consolidated financial statements and the related notes, elsewhere in this prospectus. You should carefully consider, among other things, the matters discussed in “Risk Factors,” our consolidated financial statements and related notes, and “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” in each case included elsewhere in this prospectus.
Except where the context otherwise requires or where otherwise indicated, the terms “ServiceSource,” “we,” “us,” “our,” “our company” and “our business” refer, prior to the conversion discussed below, to ServiceSource International, LLC and, after the conversion, to ServiceSource International, Inc., in each case together with its consolidated subsidiaries as a combined entity.
SERVICESOURCE INTERNATIONAL, INC.
Overview
ServiceSource is a leader in service revenue management, providing solutions that drive increased renewals of maintenance, support and subscription agreements for technology companies. Our integrated solution consists of a suite of cloud applications, dedicated service sales teams working under our customers’ brands and a proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform. By integrating software, managed services and data, we provide end-to-end management and optimization of the service contract renewals process, including data management, quoting, selling and service revenue business intelligence. Our business is built on our pay-for-performance model, whereby customers pay us based on renewal sales that we generate on their behalf. As of September 30, 2010, we managed over 90 engagements across more than 50 customers, representing over $5 billion in service revenue opportunity under management.
According to Gartner, total spending on maintenance and support agreements across the technology sector is expected to total $141 billion in 2010.1 We define service revenue as the revenue companies earn from the sale of maintenance and support agreements, as well as subscription contracts. Service revenue has become increasingly important for technology companies as it represents a significant and growing portion of total revenue, drives margin expansion and incremental profitability, can be highly recurring and correlates with end customer satisfaction. However, we believe the complexity of effective service revenue management, coupled with underinvestment in this area has led to suboptimal renewal rates on service contracts. Many technology companies lack the resources needed to maximize service revenue performance. These resources include enterprise systems and applications built specifically for service revenue data management as well as global service sales teams with the expertise to sell service contracts directly and through channel partners.
The foundation of our solution is our proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform, a data warehouse that incorporates transactional, analytical and industry data gathered from over two million service renewal transactions since our inception. The data housed within this platform fuels our applications, enables our service sales teams to improve service revenue performance, and allows us to provide analytical insights that we believe other third-party or internally-developed alternatives do not provide. Our suite of cloud applications increases visibility and control of service revenue management and is utilized by customers, channel partners, end customers and our service sales teams. Our dedicated service sales teams have specific expertise in our customers’ businesses, are deployed under our customers’ brands and follow a sales process tailored specifically to increase service contract renewals. Taken together, these elements of our solution help us increase our
| 1 | Gartner, Inc., IT Services Market Metrics Worldwide: Forecast Database, Kathryn Hale et al., September 9, 2010 |
1
Table of Contents
customers’ service revenue, drive their profitability and improve end customer satisfaction. Based on our analysis of customer renewal rates for new engagements added in 2009, we generated renewal rates on contracts delivered to us in the first half of 2010 that on a dollar value basis increased by an average of over 15 percentage points over historical customer renewal rates calculated in our Service Performance Analysis (“SPA”).
Our total revenue was $75.2 million, $100.3 million and $110.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively, and was $76.9 million and $108.5 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively. We had approximately 50, 60 and 80 engagements as of December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively, and over 90 engagements as of September 30, 2010.
Our Solution
We have developed an end-to-end solution to increase service revenue performance for our customers. The components of our integrated solution consist of a suite of cloud applications, dedicated service sales teams and our proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform. We deploy our solution through offerings that are tailored either to address specific challenges of the renewals process or to provide end-to-end management of this process. Our highly scalable solution allows us to sell globally on behalf of our customers in over 30 languages. It is designed to provide effective service revenue management irrespective of revenue models, distribution models, and segments within the technology and technology-enabled healthcare and life sciences industries, including hardware, software and software-as-a-service.
Key benefits of our solution include:
Financial Benefits
| • | Increased service revenue. Our solution is designed to increase customers’ service revenues. We actively monitor the service contract renewal rates we drive on behalf of our customers in each engagement. When we generate higher renewal rates, we drive incremental service revenue for both the associated period as well as for subsequent periods due to the recurring nature of service contracts. |
| • | Increased margin and profitability. We believe that the costs associated with delivering maintenance, support and subscription services by many of our customers can be relatively fixed, and thus growth of service revenue can benefit our customers’ bottom line. As a result, each incremental dollar of service revenue generated by our solution can drive greater profitability for our customers. |
Operational Benefits
| • | Improved end customer satisfaction. Our regular dialogue with end customers allows us to communicate the value of our customers’ maintenance, support and subscription services, and capture and address questions and concerns about our customers’ products. |
| • | Greater business insight and analytics. Our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform allows us to analyze our customers’ renewals against similar transactions and to identify areas for improvement, enabling greater insight into their renewals business. By tracking all transactions in our intelligence platform, we are able to provide benchmarking, end customer metrics, sales efficiency data and insight into successful and unsuccessful renewal efforts. The breadth of our data allows us to provide analysis across regions, industries, channel partners and product segments. |
| • | Greater visibility and forecasting tools. Our cloud applications deliver real-time analytics and visibility into a customer’s service revenue performance, sales efficiency and forecasts. CFOs and other executives utilize our cloud applications to assist in forecasting their company’s service revenue and to measure progress against their forecasts on a real-time basis. |
2
Table of Contents
| • | Strengthened channel loyalty. Our Channel Sales Cloud application and service sales teams empower our customers’ channel partners to generate higher sales by providing accurate, real-time data on their renewal opportunities and performance as well as tools to sell more effectively to end customers. These cloud applications help our customers develop a closer relationship with their channel partners. |
| • | Global consistency. We maintain a globally consistent renewals process for our customers as we leverage a unified intelligence platform. Our solution automates the application of best practices to the renewals process and provides a consistent view of the data. |
Our Competitive Advantages
We believe our business is difficult to replicate, as it incorporates a combination of several important and differentiated elements, including:
| • | Proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform. Our proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform aggregates transactional, analytical and industry data from over two million service renewal transactions. This intelligence platform allows us to improve service revenue performance for each customer’s unique business, enabling us to increase the effectiveness and accuracy of our SPA, the pricing and scoping of our solutions and customer benchmarking. We continue to enhance our intelligence platform with each renewal transaction. |
| • | Pay-for-performance business model. With our pay-for-perfomance business model, customers pay us based on the renewal sales that we generate on their behalf, with little or no upfront customer investment. This business model directly aligns our interests with our customers’ interests to drive greater service revenue. Our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform is the critical element that allows us to price effectively on a pay-for-performance basis. |
| • | Industry leadership. Our industry leadership, based on our nearly decade-long history, enables us to innovate best practices, continue to enhance our intelligence platform and attract new customers. |
| • | Service revenue focused solution. Our entire solution, combining software, managed services and data, is built from the ground up to deliver industry-leading service revenue performance across the key elements of the renewals process. |
| • | Renewal sales methodology. Our service sales teams leverage our intelligence platform, sales processes and best practices to manage the end customer relationship and enhance service contract renewal rates. We engage in extensive ongoing training of our service sales teams to ensure consistency of execution across our entire organization. |
| • | Global scale and expertise. Our service sales teams sell in over 30 languages from six sales centers around the globe, enabling them to deliver localized capabilities to better serve the increasingly global nature of our customers’ businesses. |
3
Table of Contents
Our Strategy
We intend to continue our industry leadership in service revenue management. The key elements of our strategy include:
| • | expanding our customer base within existing industry verticals; |
| • | continuing to build, deploy and increase the revenue we generate from our cloud applications; |
| • | increasing our footprint with existing customers to drive greater revenue per customer; |
| • | increasing our operating efficiency by developing additional technology; and |
| • | adding new customers from additional industry verticals and geographic markets. |
Selected Risk Factors
Investing in our common stock involves risks. You should carefully read “Risk Factors” beginning on page 12 for an explanation of these risks before investing in our common stock. In particular, the following considerations, among others, may offset our competitive strengths or have a negative effect on our growth strategy, which could cause a decline in the price of our common stock and result in a loss of all or a portion of your investment:
| • | our quarterly results of operations may fluctuate as a result of numerous factors, many of which may be outside of our control; |
| • | the market for our solution is relatively undeveloped and may not grow; |
| • | our estimates of service revenue opportunity under management and our analysis of renewal rates may prove inaccurate; |
| • | if close rates fall short of our predictions, our revenue will suffer and our ability to grow and achieve broader market acceptance of our solution could be harmed; |
| • | our revenue will decline if there is a decrease in the overall demand for our customers’ products and services for which we provide service revenue management; |
| • | if there is a widespread shift away from business consumers purchasing maintenance and support service contracts, we could be adversely impacted if we are not able to adapt to new trends or expand our target market; |
| • | if we are unable to compete effectively against current and future competitors, our business and operating results will be harmed; |
| • | the loss of one or more of our significant customers as a result of consolidation in the technology sector or otherwise, as occurred when Oracle acquired Sun Microsystems in 2010 and terminated its contract with us effective as of September 30, 2010, could slow our revenue growth and adversely impact our margins; and |
| • | upon the closing of this offering, our directors and executive officers and their affiliates will beneficially own a significant percentage of our outstanding common stock, and may, as a result, be able to determine substantially all matters requiring stockholder approval, including the election of directors and approval of significant corporate transactions. |
4
Table of Contents
Key Business Metrics
We refer to various key business metrics, including service revenue opportunity under management, engagements and renewal rates, in this Prospectus Summary and elsewhere in this prospectus. We describe how we calculate these metrics and material aspects and limitations of these metrics in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Key Business Metrics.”
Conversion to a Corporation
We are currently a Delaware limited liability company. Prior to the issuance of any of our shares of common stock in this offering, we will convert into a Delaware corporation and change our name from ServiceSource International, LLC to ServiceSource International, Inc. In conjunction with the conversion, all of our outstanding common shares will automatically be converted into shares of our common stock. See “Description of Capital Stock” for additional information regarding a description of the terms of our common stock following the conversion and the terms of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws as will be in effect upon the closing of this offering. While as a limited liability company our outstanding equity is called our common shares, in this prospectus for ease of comparison we refer to such common shares as our common stock for periods prior to the conversion, unless otherwise indicated in this prospectus. Similarly, unless otherwise indicated, we refer to members’ equity in this prospectus as stockholders’ equity. In this prospectus, we refer to all of the transactions related to our conversion to a corporation as the “Conversion.” See “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions—Conversion to a Corporation.”
Corporate Information
Our principal executive offices are located at 634 Second Street, San Francisco, California 94107, and our telephone number is (415) 901-6030. Our website address is www.servicesource.com. Information contained on or accessible through our website is not incorporated by reference into this prospectus, and should not be considered to be part of this prospectus.
5
Table of Contents
THE OFFERING
| Shares of common stock offered by us |
shares |
| Shares of common stock offered by the selling stockholders |
shares |
| Total |
shares |
| Over-allotment option to be offered by us |
shares |
| Over-allotment option to be offered by the selling stockholders |
shares |
| Shares of common stock to be outstanding after this offering |
shares ( shares if the over-allotment option is exercised in full) |
| Use of proceeds |
We expect our net proceeds from this offering will be approximately $ , after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. We intend to use the net proceeds of the offering to repay the loan balances outstanding under our credit facility and for working capital and other general corporate purposes. We may also use a portion of the proceeds from the offering to acquire other businesses or technologies. We will not receive any of the proceeds from the shares of common stock sold by the selling stockholders. See “Use of Proceeds.” |
| Risk factors |
You should read the “Risk Factors” section of this prospectus for a discussion of factors to consider carefully before deciding to invest in shares of our common stock. |
| Proposed Nasdaq Global Market symbol |
“ ” |
The number of shares of our common stock to be outstanding following this offering is based on 57,426,218 shares of our common stock outstanding as of September 30, 2010 after giving effect to the Conversion described under “Certain Relationships and Related Party Transactions—Conversion to a Corporation” and excludes:
| • | 15,726,057 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of options outstanding as of September 30, 2010, with a weighted average exercise price of $4.09 per share; |
| • | 2,315,428 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of options granted after September 30, 2010, at an exercise price of $5.80 per share; and |
| • | shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan, which will become effective in connection with this offering. |
Unless otherwise noted, the information in this prospectus reflects and assumes the following:
| • | the consummation of the Conversion prior to the closing of this offering; |
| • | no exercise of outstanding options; and |
| • | no exercise by the underwriters of their over-allotment option. |
6
Table of Contents
SUMMARY CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL DATA
We have derived the summary consolidated statements of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 from our audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. We have derived the summary consolidated statements of operations data for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010 and the consolidated balance sheet data as of September 30, 2010 from our unaudited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. We have prepared the unaudited consolidated financial statement data on a basis consistent with our audited consolidated financial statements, and, in the opinion of our management, the unaudited consolidated financial data reflects all adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments necessary for a fair statement of such data. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results that may be expected in the future, and the results for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected for the full year or for any other period. The following summary consolidated financial data should be read in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus. The additional financial data presented is used in addition to the financial measures reflected in the consolidated statements of operations and balance sheet data to help us evaluate our business.
7
Table of Contents
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months
Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Statements of Operations Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue |
$ | 75,189 | $ | 100,280 | $ | 110,676 | $ | 76,889 | $ | 108,468 | ||||||||||
| Cost of revenue(1) |
39,224 | 56,965 | 58,877 | 41,577 | 63,841 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
35,965 | 43,315 | 51,799 | 35,312 | 44,627 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing(1) |
13,119 | 20,486 | 23,182 | 16,802 | 25,640 | |||||||||||||||
| Research and development(1) |
— | 1,160 | 2,054 | 1,647 | 3,927 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative(1) |
10,475 | 10,571 | 13,777 | 10,214 | 13,806 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
912 | 857 | 68 | 68 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
24,506 | 33,074 | 39,081 | 28,731 | 43,373 | |||||||||||||||
| Income from operations |
11,459 | 10,241 | 12,718 | 6,581 | 1,254 | |||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(2,305 | ) | (2,209 | ) | (1,116 | ) | (772 | ) | (940 | ) | ||||||||||
| Loss on extinguishment of debt |
— | (561 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Other income (expenses), net |
(118 | ) | (1,497 | ) | 639 | 465 | (202 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Income (loss) before provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
9,036 | 5,974 | 12,241 | 6,274 | 112 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax (benefit) provision |
(632 | ) | 1,153 | 1,866 | 730 | 1,368 | ||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 9,668 | $ | 4,821 | $ | 10,375 | $ | 5,544 | $ | (1,256 | ) | |||||||||
| Net income (loss) per common share(2): |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.17 | $ | 0.09 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.10 | $ | (0.02 | ) | |||||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.16 | $ | 0.08 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.09 | $ | (0.02 | ) | |||||||||
| Cash distributions per common share(3) |
$ | 0.09 | $ | 0.09 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.04 | ||||||||||
| Weighted-average shares used in computing net income (loss) per common share(2): |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
55,936 | 56,209 | 56,750 | 56,702 | 57,167 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
58,706 | 58,733 | 58,912 | 58,510 | 57,167 | |||||||||||||||
| Pro forma net income (loss) per common share(4): |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
$ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma weighted-average shares used in computing net income (loss) per common share(4): |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Effective January 1, 2006, we adopted FASB ASC Topic 718, Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation. Reported balances include stock-based compensation expense as follows: |
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months
Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 1,096 | $ | 1,271 | $ | 914 | $ | 672 | $ | 843 | ||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
1,100 | 1,570 | 2,340 | 1,706 | 2,214 | |||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
— | — | 541 | 399 | 598 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
1,680 | 2,608 | 2,265 | 1,663 | 2,362 | |||||||||||||||
| Total stock-based compensation |
$ | 3,876 | $ | 5,449 | $ | 6,060 | $ | 4,440 | $ | 6,017 | ||||||||||
8
Table of Contents
| (2) | Our basic net income (loss) per common share is calculated by dividing the net income (loss) by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding for the period. |
| (3) | Pursuant to our limited liability company agreement, we were required to pay cash distributions to our members to fund their tax obligations in respect of their equity interests. All other distributions are determined by our directors in their sole discretion. Tax distributions to members were $4.9 million, $5.1 million, $5.2 million and $0 in 2006, 2007, 2008 and 2009, and $0 and $2.5 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively. In 2006, the directors approved an additional $15.0 million distribution to all members. |
| (4) | Our pro forma net income (loss) per common share gives effect to the Conversion and to an assumed issuance of only that number of shares that would have been required to be issued to repay the loan balances outstanding under our credit facility as of September 30, 2010 assuming the issuance of such shares at an initial public offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus). The diluted pro forma net income (loss) per common share calculation also assumes the conversion, exercise, or issuance of all potential common shares, unless the effect of inclusion would result in the reduction of a loss or the increase in net income per common share. |
Other Financial Data:
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months
Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA(1)(2) |
$ | 17,931 | $ | 19,046 | $ | 22,305 | $ | 13,388 | $ | 11,707 | ||||||||||
| (1) | We present Adjusted EBITDA, which we define as net income (loss), plus: income tax provision (benefit); loss on extinguishment of debt; interest expense; other (income) expense, net; depreciation; amortization of intangible assets; and stock-based compensation. Adjusted EBITDA is a financial measure that is not calculated in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles (“GAAP”). We have provided a reconciliation of Adjusted EBITDA, a non-GAAP financial measure, to net income (loss), the most directly comparable financial measure calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP. Adjusted EBITDA should not be considered as an alternative to net income (loss), operating income or any other measure of financial performance calculated and presented in accordance with GAAP. Our Adjusted EBITDA may not be comparable to similarly titled measures of other organizations because other organizations may not calculate Adjusted EBITDA in the same manner as we do. We have included Adjusted EBITDA in this prospectus because it is a basis upon which our management assesses financial performance and it eliminates the impact of items that we do not consider indicative of our core operating performance. In evaluating Adjusted EBITDA, you should be aware that in the future we will incur expenses similar to the adjustments in this presentation. Our presentation of Adjusted EBITDA should not be construed as an inference that our future results will be unaffected by these expenses or any unusual or non-recurring items. |
| (2) | We reconcile net income (loss) to Adjusted EBITDA as follows: |
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine
Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 9,668 | $ | 4,821 | $ | 10,375 | $ | 5,544 | $ | (1,256 | ) | |||||||||
| Income tax (benefit) provision |
(632 | ) | 1,153 | 1,866 | 730 | 1,368 | ||||||||||||||
| Loss on extinguishment of debt |
— | 561 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
2,305 | 2,209 | 1,116 | 772 | 940 | |||||||||||||||
| Other (income) expense net |
118 | 1,497 | (639 | ) | (465 | ) | 202 | |||||||||||||
| Depreciation |
1,684 | 2,499 | 3,459 | 2,299 | 4,436 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
912 | 857 | 68 | 68 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation |
3,876 | 5,449 | 6,060 | 4,440 | 6,017 | |||||||||||||||
| Adjusted EBITDA |
$ | 17,931 | $ | 19,046 | $ | 22,305 | $ | 13,388 | $ | 11,707 | ||||||||||
9
Table of Contents
| As of September 30, 2010 | ||||||||||||
| Actual | Pro Forma(1) | Pro Forma As Adjusted(2) |
||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 23,231 | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Working capital(3) |
18,887 | |||||||||||
| Total assets |
99,136 | |||||||||||
| Term loan, current and non-current |
15,834 | |||||||||||
| Obligations under capital leases, current and non-current |
1,956 | |||||||||||
| Total members’/stockholders’ equity |
32,920 | |||||||||||
| (1) | The pro forma column in the summary consolidated balance sheet data above reflects the effect of the Conversion. |
| (2) | The pro forma as adjusted column in the summary consolidated balance sheet data above reflects the effect of: (i) the Conversion; (ii) our sale of shares of common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the front cover of this prospectus, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us; and (iii) the repayment of the $15.8 million outstanding under our loans as of September 30, 2010 with a portion of the net proceeds from this offering. See “Use of Proceeds” for additional information. A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) cash and each of working capital, total assets and total stockholders’ equity by $ million, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same, and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. Each increase of 1.0 million shares in the number of shares offered by us would increase cash and each of working capital, total assets and total stockholders’ equity by approximately $ million. Similarly, each decrease of 1.0 million shares in the number of shares offered by us would decrease cash and each of working capital, total assets and total stockholders’ equity by approximately $ million. The pro forma as adjusted information discussed above is illustrative only and will be adjusted based on the actual public offering price and other terms of this offering determined at pricing. |
| (3) | Working capital is defined as current assets less current liabilities. |
10
Table of Contents
Investing in our common stock involves a high degree of risk. You should consider carefully the risks and uncertainties described below, together with all of the other information in this prospectus, including our consolidated financial statements and related notes, before deciding whether to purchase shares of our common stock. If any of the following risks is realized, our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects could be materially and adversely affected. In that event, the price of our common stock could decline and you could lose part or all of your investment.
Risks Related to Our Business and Industry
Our quarterly results of operations may fluctuate as a result of numerous factors, many of which may be outside of our control.
Our quarterly operating results are likely to fluctuate. Some of the important factors that may cause our revenue, operating results and cash flows to fluctuate from quarter to quarter include:
| • | our ability to attract new customers and retain existing customers; |
| • | fluctuations in the value of end customer contracts delivered to us; |
| • | fluctuations in close rates; |
| • | changes in our commission rates; |
| • | seasonality; |
| • | loss of customers for any reason including due to acquisition; |
| • | the mix of new customers as compared to existing customers; |
| • | the length of the sales cycle for our solution, and our level of upfront investments prior to the period we begin generating sales associated with such investments; |
| • | the timing of customer payments and payment defaults by customers; |
| • | the amount and timing of operating costs and capital expenditures related to the operations of our business; |
| • | the rate of expansion and productivity of our direct sales force; |
| • | the cost and timing of the introduction of new technologies or new services, including additional investments in our cloud applications; |
| • | general economic conditions; |
| • | technical difficulties or interruptions in delivery of our solution; |
| • | changes in foreign currency exchange rates; |
| • | changes in the effective tax rates; |
| • | regulatory compliance costs, including with respect to data privacy; |
| • | costs associated with acquisitions of companies and technologies; |
| • | extraordinary expenses such as litigation or other dispute-related settlement payments; and |
| • | the impact of new accounting pronouncements. |
Many of the above factors are discussed in more detail elsewhere in these Risk Factors. Many of these factors are outside our control, and the variability and unpredictability of such factors could result in our failing to meet our revenue or operating results expectations for a given period. In addition, the occurrence of one or more of these factors might cause our operating results to vary widely which could lead to negative impacts on
11
Table of Contents
our margins, short-term liquidity or ability to retain or attract key personnel, and could cause other unanticipated issues. Accordingly, we believe that quarter-to-quarter comparisons of our revenue, operating results and cash flows may not be meaningful and should not be relied upon as an indication of future performance.
The market for our solution is relatively undeveloped and may not grow.
The market for service revenue management is still relatively undeveloped, has not yet achieved widespread acceptance and may not grow quickly or at all. Our success will depend to a substantial extent on the willingness of companies to engage a third party such as us to manage the sales of their support, maintenance and subscription contracts. Many companies have invested substantial personnel, infrastructure and financial resources in their own internal service revenue organizations and therefore may be reluctant to switch to a solution such as ours. Companies may not engage us for other reasons, including a desire to maintain control over all aspects of their sales activities and customer relations, concerns about end customer reaction, a belief that they can sell their support, maintenance and subscription services more cost-effectively using their internal sales organizations, perceptions about the expenses associated with changing to a new approach and the timing of expenses once they adopt a new approach, general reluctance to adopt any new and different approach to old ways of doing business, or other considerations that may not always be evident. New concerns or considerations may also emerge in the future. Particularly because our market is undeveloped, we must address our potential customers concerns and explain the benefits of our approach in order to convince them to change the way that they manage the sales of support, maintenance and subscription contracts. If companies are not sufficiently convinced that we can address their concerns and that the benefits of our solution are sufficient, then the market for our solution may not develop as we anticipate and our business will not grow.
Our estimates of service revenue opportunity under management and our analysis of renewal rates and other metrics may prove inaccurate.
We use various estimates in formulating our business plans and analyzing our potential and historical performance, including our estimate of service revenue opportunity under management. We base our estimates upon a number of assumptions that are inherently subject to significant business and economic uncertainties and contingencies, many of which are beyond our control. Our estimates therefore may prove inaccurate.
Service revenue opportunity under management (“opportunity under management”) is our estimate, as of a given date, of the value of all end customer service contracts that we will have the opportunity to sell on behalf of our customers over the subsequent twelve-month period. We estimate the value of such end customer contracts based on a combination of factors, including the value of end customer contracts made available to us by customers in past periods, the minimum value of end customer contracts that our customers are required to give us the opportunity to sell pursuant to the terms of their contracts with us, periodic internal business reviews of our expectations as to the value of end customer contracts that will be made available to us by customers, the value of end customer contracts included in the SPA and collaborative discussions with our customers assessing their expectations as to the value of service contracts that they will make available to us for sale. While the minimum value of end customer contracts that our customers are required to give us represents a portion of our estimated opportunity under management, a significant portion of the opportunity under management is estimated based on the other factors described above.
When estimating service revenue opportunity under management, we must, to a large degree, rely on the assumptions described above, which may prove incorrect. These assumptions are inherently subject to significant business and economic uncertainties and contingencies, many of which are beyond our control. Our estimates therefore may prove inaccurate, causing the actual value of end customer contracts delivered to us in a given twelve-month period to differ from our estimate of opportunity under management. These factors include:
| • | the extent to which customers deliver a greater or lesser value of end customer contracts than may be required or otherwise expected; |
| • | roll-overs of unsold service contract renewals from prior periods to the current period or future periods; |
12
Table of Contents
| • | changes in the pricing or terms of service contracts offered by our customers; |
| • | increases or decreases in the end customer base of our customers; |
| • | the extent to which the renewal rates we achieve on behalf of a customer early in an engagement affect the amount of opportunity that the customer makes available to us later in the engagement; |
| • | customer cancellations of their contracts with us due to acquisitions or otherwise; and |
| • | changes in our customers’ businesses, sales organizations, sales processes or priorities. |
In addition, opportunity under management reflects our estimate for a forward twelve-month period and should not be used to estimate our opportunity for any particular quarter within that period. The value of end customer contracts actually delivered during a twelve-month period should not be expected to occur in even quarterly increments due to seasonality and other factors impacting our customers and their end customers.
In addition, we analyze various metrics in evaluating our potential and historical performance. We analyze the renewal rates we achieve on behalf of our customers. We compare the renewal rates we achieve on behalf of our customers to the renewal rates that we calculate during the SPA, based on the data provided to us by the customer. In calculating renewal rates, we cannot provide any assurance as to the accuracy or completeness of the customer renewal data we receive during the SPA. To the extent that the actual data and information provided by our customers for use in the SPA is inaccurate, insufficient or misrepresents the contracts we would receive for renewal in future periods, our calculation of renewal rates may be inaccurate.
We also analyze our contribution margin for a period as the excess of the revenue recognized from a customer over the estimated expenses for the period associated with supporting the customer and managing the service contract renewals process for them, expressed as a percentage of associated revenue. Although we believe the estimates and assumptions we use in calculating contribution margin are reasonable, the estimated expenses and resulting contribution margin could vary significantly from the amounts disclosed herein had we used different estimates and assumptions. Moreover, we cannot assure you that we will experience similar contribution margins from customers added in other years or in future periods. You should not rely on the estimated expenses or contribution margin as being indicative of our future performance. Because of our growing customer base, we expect that there will be times when large numbers of our customers are in the initial phases of their customer relationship with us or have a material expansion of their existing engagements with us. In these scenarios, we may not be able to achieve profitability even if many of our customer relationships generate a positive contribution margin.
If close rates fall short of our predictions, our revenue will suffer and our ability to grow and achieve broader market acceptance of our solution could be harmed.
Given our pay-for-performance pricing model, our revenue is directly tied to close rates. Close rates represent the percentage of the actual opportunity delivered that we renew on behalf of our customers. If the close rate for a particular customer is lower than anticipated, then our revenue for that customer will also be lower than projected. If close rates fall short of expectations across a broad range of customers, or if they fall below expectations for a particularly large customer, then the impact on our revenue and our overall business will be significant. In the event close rates are lower than expected for a given customer, our margins will suffer because we will have already incurred a certain level of costs in both personnel and infrastructure to support the engagement. This risk is compounded by the fact that many of our customer relationships are terminable if we fail to meet certain specified sales targets over a sustained period of time. If actual close rates fall to a level at which our revenue and customer contracts are at risk, then our financial performance will decline and we will be severely compromised in our ability to retain and attract customers. Increasing our customer base and achieving broader market acceptance of our solution depends, to a large extent, on how effectively our solution increases service sales. As a result, poor performance with respect to our close rates, in addition to causing our revenue, margins and earnings to suffer, will likely damage our reputation and prevent us from effectively developing and
13
Table of Contents
maintaining awareness of our brand or achieving widespread acceptance of our solution, in which case we could fail to grow our business and our revenue, margins and earnings would suffer.
Our revenue will decline if there is a decrease in the overall demand for our customers’ products and services for which we provide service revenue management.
Our revenue is based on a pay-for-performance model under which we are paid a percentage commission based on the service contracts we sell on behalf of our customers. If a particular customer’s products or services fail to appeal to its end customers, our revenue may decline. In addition, if end customer demand decreases for other reasons, such as negative news regarding our customers or their products, unfavorable economic conditions, shifts in strategy by our customers away from promoting the service contracts we sell in favor of selling their other products or services to their end customers, or if end customers experience financial constraints and fail to renew the service contracts we sell, we may experience a decrease in our revenue as the demand for our customers’ service contracts declines.
If there is a widespread shift away from business consumers purchasing maintenance and support service contracts, we could be adversely impacted if we are not able to adapt to new trends or expand our target markets.
As a result of our historical concentration in the software and hardware industries, a significant portion of our revenue comes from the sale of maintenance and support service contracts for the software and hardware products used by our customers’ end customers. Although we also sell other types of renewals, such as subscriptions to software-as-a-service offerings, those sales have to date constituted a relatively small portion of our revenue. The emergence of cloud computing and other alternative technology purchasing models, in which technology services are provided on a remote-access basis, may have a significant impact on the size of the market for traditional maintenance and support contracts. If these alternative models continue gaining traction and reduce the size of our traditional market, we will need to continue to adapt our solution to capitalize on these trends or our results of operations will suffer.
If we are unable to compete effectively against current and future competitors, our business and operating results will be harmed.
The market for service revenue management is evolving. Historically, technology companies have managed their service renewals through internal personnel and relied upon technology ranging from Excel spreadsheets to internally-developed software to customized versions of traditional business intelligence tools and CRM or ERP software from vendors such as Oracle, SAP, salesforce.com and NetSuite. Some companies have made further investments in this area using firms such as Accenture and McKinsey for technology consulting and education services focused on service renewals. These internally-developed solutions represent the primary alternative to our integrated approach. We also face direct competition from smaller companies that offer specialized service revenue management solutions, typically providing technology for their customers to use internal personnel for their sales efforts.
We believe the principal competitive factors in our markets include the following:
| • | service revenue industry expertise, best practices, and benchmarks; |
| • | performance-based pricing of solutions; |
| • | ability to increase service revenue, renewal rates, and close rates; |
| • | global capabilities; |
| • | completeness of solution; |
| • | ability to effectively represent customer brands to end customers and channel partners; |
14
Table of Contents
| • | size of upfront investment; and |
| • | size and financial stability of operations. |
We believe that more competitors will emerge. These competitors may have greater name recognition, longer operating histories, well-established relationships with customers in our markets and substantially greater financial, technical, personnel and other resources than we have. Potential competitors of any size may be able to respond more quickly and effectively than we can to new or changing opportunities, technologies, standards or customer or end customer requirements. Even if our solution is more effective than competing solutions, potential customers might choose new entrants unless we can convince them of the advantages of our integrated solution. We expect competition and competitive pressure, from both new and existing competitors, to increase in the future.
The loss of one or more of our key customers could slow our revenue growth or cause our revenue to decline.
A substantial portion of our revenue has to date come from a relatively small number of customers. During the nine months ended September 30, 2010, our top ten customers accounted for 57% of our revenue, with our largest customer, Sun Microsystems, accounting for 17% of our revenue. During the year ended December 31, 2009, our top ten customers accounted for 64% of our revenue, with Sun Microsystems accounting for 24% of our revenue. Oracle terminated our contracts with Sun Microsystems effective as of September 30, 2010. A relatively small number of customers may continue to account for a significant portion of our revenue for the foreseeable future. The loss of any of our significant customers for any reason, including the failure to renew our contracts, a change of relationship with any of our key customers or their acquisition as discussed below, may cause a significant decrease in our revenue.
Consolidation in the technology sector is continuing at a rapid pace, which could harm our business in the event that our customers are acquired and their contracts are cancelled.
Consolidation among technology companies in our target market has been robust in recent years, and this trend poses a risk for us. Acquisitions of our customers could lead to cancellation of our contracts with those customers by the acquiring companies and could reduce the number of our existing and potential customers. For example, Oracle has acquired a number of our customers in recent years, including our then largest customer, Sun Microsystems, in January 2010, and another customer, BEA Systems, in April 2008. Oracle has elected to terminate our service contracts with each customer because Oracle conducts its service revenue management internally. If mergers and acquisitions in the technology industry continue unabated or increase, we expect that some of the acquiring companies, and Oracle in particular, will terminate, renegotiate and/or elect not to renew our contracts with the companies they acquire, which could reduce our revenue.
Supporting our existing and growing customer base could strain our personnel resources and infrastructure, and if we cannot scale our operations and increase productivity, we may be unsuccessful in implementing our business plan.
Since 2003, we have experienced significant growth in our customer base, which has placed a strain on our management, administrative, operational and financial infrastructure. We anticipate that additional investments in sales personnel, infrastructure and research and development spending will be required to:
| • | scale our operations and increase productivity; |
| • | address the needs of our customers; |
| • | further develop and enhance our solution and offerings; |
| • | develop new technology; and |
| • | expand our markets and opportunity under management, including into new industry verticals and geographic areas. |
15
Table of Contents
Our success will depend in part upon our ability to manage our growth effectively. To do so, we must continue to increase the productivity of our existing employees and to hire, train and manage new employees as needed. To manage domestic and international growth of our operations and personnel, we will need to continue to improve our operational, financial and management controls and our reporting processes and procedures, and implement more extensive and integrated financial and business information systems. These additional investments will increase our operating costs, which will make it more difficult for us to offset any future revenue shortfalls by reducing expenses in the short term. Moreover, if we fail to scale our operations successfully and increase productivity, our overall business will be at risk.
We enter into long-term, commission-based contracts with our customers, and our failure to correctly price these contracts may negatively affect our profitability.
We enter into long-term contracts with our customers that are priced based on multiple factors determined in large part by the SPA we conduct for our customers. These factors include opportunity size, anticipated close rates and expected commission rates at various levels of sales performance. Some of these factors require forward looking assumptions that may prove incorrect. If our assumptions are inaccurate, or if we otherwise fail to correctly price our customer contracts, particularly those with lengthy contract terms, then our revenue, profitability and overall business operations may suffer. Further, if we fail to anticipate any unexpected increase in our cost of providing services, including the costs for employees, office space or technology, we could be exposed to risks associated with cost overruns related to our required performance under our contracts, which could have a negative effect on our margins and earnings.
Many of our customer contracts allow termination for failure to meet certain performance conditions.
Although most of our customer contracts are subject to multi-year terms, these agreements often have termination rights if we fail to meet specified sales targets. During the SPA and contract negotiation phase with a customer, we typically negotiate minimum performance levels for the engagement. If we fail to meet our required targets and our customers choose to exercise their termination rights, our revenue could decline. These termination rights may also create instability in our revenue forecasts and other forward looking financial metrics.
Our business may be harmed if our customers rely upon our service revenue forecasts in their business and actual results are materially different.
The contracts that we enter into with our customers provide for sharing of information with respect to forecasts and plans for the renewal of maintenance, support and subscription agreements of our customers. Our customers may use such forecasted data for a variety of purposes related to their business. Our forecasts are based upon the data our customers provide to us, and are inherently subject to significant business, economic and competitive uncertainties, many of which are beyond our control. In addition, these forecasted expectations are based upon historical trends and data that may not be true in subsequent periods. Any material inaccuracies related to these forecasts could lead to claims on the part of our customers related to the accuracy of the forecasted data we provide to them, or the appropriateness of our methodology. Any liability that we incur or any harm to our brand that we suffer because of inaccuracies in the forecasted data we provide to our customers could impact our ability to retain existing customers and harm our brand and, ultimately, our business.
Changing global economic conditions and large scale economic shifts may impact our business.
Our overall performance depends in part on worldwide economic conditions that impact the technology and technology-enabled healthcare and life sciences industries. For example, the recent economic downturn resulted in many businesses deferring technology investments, including purchases of new software, hardware and other equipment, and purchases of additional or supplemental maintenance, support and subscription services. To a certain extent, these businesses also slowed the rate of renewals of maintenance, support and subscription
16
Table of Contents
services for their existing technology base. A future downturn could cause business customers to stop renewing their existing maintenance, support and subscription agreements or contracting for additional maintenance services as they look for ways to further cut expenses, in which case our business could suffer.
Conversely, a significant upturn in global economic conditions could cause business purchasers to purchase new hardware, software and other technology products, which we generally do not sell, instead of renewing or otherwise purchasing maintenance, support and subscription services for their existing products. A general shift toward new product sales could reduce our near term opportunities for these contracts, which could lead to a decline in our revenue.
Our inability to expand our target markets could adversely impact our business and operating results.
We derive substantially all of our revenue from customers in certain sectors in the technology and technology-enabled healthcare and life sciences industries, and an important part of our strategy is to expand our existing customer base and win new customers in these industries. In addition, because of the service revenue opportunities that we believe exist beyond these industries, we intend to target new customers in additional industry vertical markets. In connection with the expansion of our target markets, we may not have familiarity with such additional industry verticals, and our execution of such expansion could face risks where our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform is less developed within a particular new vertical. We may encounter customers in these previously untapped markets that have different pricing and other business sensitivities than we are used to managing. As a result of these and other factors, our efforts to expand our solution to additional industry vertical markets may not succeed, may divert management resources from our existing operations and may require us to commit significant financial resources to unproven parts of our business, all of which may harm our financial performance.
Our business and growth depend substantially on customers renewing their agreements with us and expanding their use of our solution for additional available markets. Any decline in our customer renewals or failure to expand their relationships with us could harm our future operating results.
In order for us to improve our operating results and grow, it is important that our customers renew their agreements with us when the initial contract term expires and that we expand our customer relationships to add new market opportunities and related service revenue opportunity under management. Our customers have no obligation to renew their contracts with us after the initial terms have expired, and we cannot assure you that our customers will renew service contracts with us at the same or higher level of service, if at all, or provide us with the opportunity to manage additional opportunity. Although our renewal rates have been historically higher than those achieved by our customers prior to their using our solution, some customers have elected not to renew their agreements with us. Our customers’ renewal rates may decline or fluctuate as a result of a number of factors, including their satisfaction or dissatisfaction with our solution and results, our pricing, mergers and acquisitions affecting our customers or their end customers, the effects of economic conditions or reductions in our customers’ or their end customers’ spending levels. If our customers do not renew their agreements with us, renew on less favorable terms or fail to contract with us for additional service revenue management opportunities, our revenue may decline and we may not realize improved operating results and growth from our customer base.
A substantial portion of our business consists of supporting our customers’ channel partners in the sale of service contracts. If those channel partners become unreceptive to our solution, our business could be harmed.
Many of our customers, including some of our largest customers, sell service contracts through their channel partners and engage our solution to help those channel partners become more effective at selling service contract renewals. These channel partners may have access to some of our cloud applications, such as our Channel Sales Cloud, in addition to other sales support services we provide. In this context, the ultimate buyers of the service contracts are end customers of those channel partners, who then receive the actual services from our customers.
17
Table of Contents
In the event our customers’ channel partners become unreceptive to our involvement in the renewals process, those channel partners could discourage our current or future customers from engaging our solution to support channel sales. This risk is compounded by the fact that large channel partners may have relationships with more than one of our customers or prospects, in which case the negative reaction of one or more of those large channel partners could impact multiple customer relationships. Accordingly, with respect to those customers and prospective customers who sell service contracts through channel partners, any significant resistance to our solution by their channel partners could harm our ability to attract or retain customers, which would damage our overall business operations.
We face long sales cycles to secure new customer contracts, making it difficult to predict the timing of specific new customer relationships.
We face a variable selling cycle to secure new customer agreements, typically spanning a number of months and requiring our effort to obtain and analyze our prospect’s business through the SPA, for which we are not paid. Moreover, even if we succeed in developing a relationship with a potential new customer, the scope of the potential service revenue management engagement frequently changes over the course of the business discussions and, for a variety of reasons, our sales discussions may fail to result in new customer acquisitions. Consequently, we have only a limited ability to predict the timing and size of specific new customer relationships.
If we experience significant fluctuations in our anticipated growth rate and fail to balance our expenses with our revenue forecasts, our results could be harmed.
Due to our evolving business model, the uncertain size of our markets and the unpredictability of future general economic and financial market conditions, we may not be able to accurately forecast our growth rate. We plan our expense levels and investments based on estimates of future sales performance for our customers with respect to their end customers, future revenue and future customer acquisition. If our assumptions prove incorrect, we may not be able to adjust our spending quickly enough to offset the resulting decline in growth and revenue. Consequently, we expect that our gross margins, operating margins and cash flows may fluctuate significantly on a quarterly basis.
If we cannot efficiently implement our offering for customers, we may be delayed in generating revenue, fail to generate revenue and/or incur significant costs.
In general, our customer engagements are complex and may require lengthy and significant work to implement our offerings. As a result, we generally incur sales and marketing expenses related to the commissions owed to our sales representatives and make upfront investments in technology and personnel to support the engagements one to three months before we begin selling end customer contracts. Each customer’s situation may be different, and unanticipated difficulties and delays may arise as a result of our failure, or that of our customer, to meet respective implementation responsibilities. If the customer implementation process is not executed successfully or if execution is delayed, we could incur significant costs without yet generating revenue, and our relationships with some of our customers may be adversely impacted.
Delayed or unsuccessful investment in new technology, services and markets may harm our financial results.
We plan to continue to invest significant resources in research and development in order to enhance our existing offerings and introduce new offerings that will appeal to customers and potential customers. We have undertaken the development of new technology to offer improved and more scalable service revenue management, including enhancements to our applications. The development of new products and services entails a number of risks that could adversely affect our business and operating results, including:
| • | the risk of diverting the attention of our management and our employees from the day-to-day operations of the business; |
18
Table of Contents
| • | insufficient revenue to offset increased expenses associated with research, development, operational and marketing activities; and |
| • | write-offs of the value of such technology investments as a result of unsuccessful implementation or otherwise. |
If our new or modified technology does not work as intended, is not responsive to user preferences or industry or regulatory changes, is not appropriately timed with market opportunity, or is not effectively brought to market, we may lose existing and potential customers or related service revenue opportunities, in which case our results of operations may suffer. The cost of future development of new service revenue management offerings or technologies also could require us to raise additional debt or equity financing. These actions could negatively impact the ownership percentages of our existing stockholders, our financial condition or our results of operations.
The length of time it takes our newly-hired sales representatives to become productive could adversely impact our success rate, the execution of our overall business plan and our costs.
It can take twelve months or longer before our sales representatives are fully trained and productive in selling our solution to prospects and customers. This long ramp period presents a number of operational challenges as the cost of recruiting, hiring and carrying new sales representatives cannot be offset by the revenue such new sales representatives produce until after they complete their long ramp periods. Further, given the length of the ramp period, we often cannot determine if a sales representative will succeed until he or she has been employed for a year or more. If we cannot reliably develop our sales representatives to a productive level, or if we lose productive representatives in whom we have heavily invested, our future growth rates and revenue will suffer.
If we lose our top executives, or if we are unable to attract, hire, integrate and retain key personnel and other necessary employees, our business will be harmed.
Our future success depends on the continued contributions of our executives, each of whom may be difficult to replace. Our future success also depends in part on our ability to attract, hire, integrate and retain qualified service sales personnel, sales representatives and management level employees to oversee such sales forces. In particular, Michael Smerklo, our chairman of the board of directors and chief executive officer, is critical to the management of our business and operations and the development of our strategic direction. The loss of Mr. Smerklo’s services or those of our other executives, or our inability to continue to attract and retain high-quality talent, could harm our business.
Because competition for our target employees is intense, we may be unable to attract and retain the highly skilled employees we need to support our planned growth.
To continue to execute on our growth plan, we must attract and retain highly qualified sales representatives, engineers and other key employees in the international markets in which we have operations. Competition for these personnel is intense, especially for highly educated, qualified sales representatives. We have from time to time in the past experienced, and we expect to continue to experience in the future, difficulty in hiring and retaining highly skilled key employees with appropriate qualifications. If we fail to attract new sales representatives, engineers and other key employees, or fail to retain and motivate our most successful employees, our business and future growth prospects could be harmed.
We depend on revenue from sources outside the United States, and our international business operations and expansion plans are subject to risks related to international operations, and may not increase our revenue growth or enhance our business operations.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, approximately 33% of our revenue was generated from sales centers located outside of the United States. As a result of our continued focus on international markets, we
19
Table of Contents
expect that future revenue derived from international sources will continue to represent a significant portion of our total revenue.
A portion of the sales commissions paid by our international customers is paid in foreign currencies. As a result, fluctuations in the value of these foreign currencies may make our solution more expensive or cause resulting fluctuations in cost for international customers, which could harm our business. We currently do not undertake hedging activities to manage these currency fluctuations. In addition, if the effective price of the contracts we sell to the end customers were to increase as a result of fluctuations in the exchange rate of the relevant currencies, demand for such contracts could fall, which in turn would reduce our revenue.
Our growth strategy includes further expansion into international markets. Our international expansion may require significant additional financial resources and management attention, and could negatively affect our financial condition, cash flows and operating results. In addition, we may be exposed to associated risks and challenges, including:
| • | the need to localize and adapt our solution for specific countries, including translation into foreign languages and associated expenses; |
| • | difficulties in staffing and managing foreign operations; |
| • | different pricing environments, longer sales cycles and longer accounts receivable payment cycles and difficulties in collecting accounts receivable; |
| • | new and different sources of competition; |
| • | weaker protection for our intellectual property than in the United States and practical difficulties in enforcing our rights abroad; |
| • | laws and business practices favoring local competitors; |
| • | compliance obligations related to multiple, conflicting and changing foreign governmental laws and regulations, including employment, tax, privacy and data protection laws and regulations; |
| • | increased financial accounting and reporting burdens and complexities; |
| • | restrictions on the transfer of funds; |
| • | adverse tax consequences; and |
| • | unstable regional and economic political conditions. |
We cannot assure you we will succeed in creating additional international demand for our solution or that we will be able to effectively sell service agreements in all of the international markets we enter.
If we do not adequately protect our intellectual property rights, our competitive position and our business may suffer.
We rely upon a combination of trademark, copyright and trade secret law and contractual terms to protect our intellectual property rights, all of which provide only limited protection. Our success depends, in part, upon our ability to establish, protect and enforce our intellectual property and other proprietary rights. If we fail to protect or effectively enforce our intellectual property rights, others may be able to compete against us using intellectual property that is the same as or similar to our own. In addition, we cannot assure you that our intellectual property rights are sufficient to provide us with a competitive advantage against others who offer services similar to ours.
While we have no patents or pending patent applications, we may file patent applications in the future. If we do file patent applications, we cannot assure you that any issued patents arising from future applications will provide the protection we seek, or that any future patents issued to us will not be challenged, invalidated or
20
Table of Contents
circumvented. Also, we cannot assure you that we will obtain any copyright or trademark registrations from our pending or future applications or that any of our trademarks will be enforceable or provide adequate protection of our proprietary rights.
We also rely in some circumstances on trade secrets to protect our technology. Trade secrets may lose their value if not properly protected. We endeavor to enter into non-disclosure agreements with our employees, customers, contractors and business partners to limit access to and disclosure of our proprietary information. The steps we have taken, however, may not prevent unauthorized use of our technology, and adequate remedies may not be available in the event of unauthorized use or disclosure of our trade secrets and proprietary technology. However, trade secret protection does not prevent others from reverse engineering or independently developing similar technologies. In addition, reverse engineering, unauthorized copying or other misappropriation of our trade secrets could enable third parties to benefit from our technology without paying for it.
Accordingly, despite our efforts, we may be unable to prevent third parties from infringing or misappropriating our intellectual property and using our technology for their competitive advantage. Any such infringement or misappropriation could have a material adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition. Monitoring infringement of our intellectual property rights can be difficult and costly, and enforcement of our intellectual property rights may require us to bring legal actions against infringers. Infringement actions are inherently uncertain and therefore may not be successful, even when our rights have been infringed. Even if such actions are successful, they may require a substantial amount of resources and divert our management’s attention.
Claims by others that we infringe or violate their intellectual property could force us to incur significant costs and require us to change the way we conduct our business.
Numerous technology companies including potential competitors protect their intellectual property rights by means such as patents, trade secrets, copyrights and trademarks. We have not conducted an independent review of patents issued to third parties. Additionally, because patent applications in the United States and many other jurisdictions are kept confidential for 18 months before they are published, we may be unaware of pending patent applications that relate to our proprietary technology. From time to time we may receive letters from other parties alleging, or inquiring about, possible breaches of their intellectual property rights.
Any party asserting that we infringe its proprietary rights would force us to defend ourselves, and possibly our customers, against the alleged infringement. The technology industry is characterized by the existence of a large number of patents, copyrights, trademarks and trade secrets and by frequent litigation based on allegations of infringement or other violations of intellectual property rights. Moreover, the risk of such a lawsuit will likely increase as we become larger, the scope of our solution and technology expands and the number of competitors in our market increases. Any such claims or litigation could:
| • | be time-consuming and expensive to defend, and deplete our financial resources, whether meritorious or not; |
| • | require us to stop providing the services that use the technology that infringes the other party’s intellectual property; |
| • | divert the attention of our technical and managerial resources away from our business; |
| • | require us to enter into royalty or licensing agreements with third parties, which may not be available on terms that we deem acceptable, if at all; |
| • | prevent us from operating all or a portion of our business or force us to redesign our technology, which could be difficult and expensive and may make the performance or value of our solution less attractive; |
| • | subject us to significant liability for damages or result in significant settlement payments; or |
21
Table of Contents
| • | require us to indemnify our customers as we are required by contract to indemnify some of our customers for certain claims based upon the infringement or alleged infringement of any third party’s intellectual property rights resulting from our customers’ use of our intellectual property. |
During the course of any intellectual property litigation, confidential information may be disclosed in the form of documents or testimony in connection with discovery requests, depositions or trial testimony. Disclosure of our confidential information and our involvement in intellectual property litigation could harm us. In addition, any uncertainties resulting from the initiation and continuation of any litigation could significantly limit our ability to continue our operations and could harm our relationships with current and prospective customers. Any of the foregoing could disrupt our business and have a material adverse effect on our operating results and financial condition.
In addition, we may incorporate open source software into our technology solution. The terms of many open source licenses have not been interpreted by United States or foreign courts, and there is a risk that such licenses could be construed in a manner that imposes unanticipated conditions or restrictions on our commercialization of any of our solutions that may include open source software. As a result, we will be required to analyze and monitor our use of open source software closely. As a result of the use of open source software, we could be required to seek licenses from third parties in order to develop such future products, re-engineer our products, discontinue sales of our solutions or release our software code under the terms of an open source license to the public. Given the nature of open source software, there is also a risk that third parties may assert copyright and other intellectual property infringement claims against us based on any use of such open source software, as more generally discussed with respect to general intellectual property claims.
Changes in the U.S. and foreign legal and regulatory environment that affect our operations, including those relating to privacy, data security and cross-border data flows, could pose a significant risk to our company by disrupting our business and increasing our expenses.
We are subject to a wide variety of laws and regulations in the United States and the other jurisdictions in which we operate, and changes in the level of government regulation of our business have the potential to materially alter our business practices with resultant increases in costs and decreases in profitability. Depending on the jurisdiction, those changes may come about through new legislation, the issuance of new regulations or changes in the interpretation of existing laws and regulations by a court, regulatory body or governmental official. Sometimes those changes may have both prospective and retroactive effect, which is particularly true when a change is made through reinterpretation of laws or regulations that have been in effect for some time.
Privacy and data security are rapidly evolving areas of regulation, and additional regulation in those areas, some of it potentially difficult and costly for us to accommodate, is frequently proposed and occasionally adopted. Laws in many countries and jurisdictions, particularly in the European Union and Canada, govern the requirements related to how we store, transfer or otherwise process the private data provided to us by our customers. In addition, the centralized nature of our information systems at the data and operations centers that we use requires the routine flow of data relating to our customers and their respective end customers across national borders, both with respect to the jurisdictions within which we have operations and the jurisdictions in which we provide services to our customers. If this flow of data becomes subject to new or different restrictions, our ability to serve our customers and their respective customers could be seriously impaired for an extended period of time. For example, we participate in the U.S. Department of Commerce’s safe harbor program to govern our treatment of data and data flow with respect to our customers and their respective customers across various jurisdictions. We also have entered into various model contracts and related contractual provisions to enable these data flows. For any jurisdictions in which these measures are not recognized or otherwise not compliant with the laws of the countries in which we process data, or where more stringent data privacy laws are enacted irrespective of the guidelines, we could face increased compliance expenses and face penalties for violating such laws or be excluded from those markets altogether, in which case our operations could be materially damaged.
22
Table of Contents
Various risks could affect our worldwide operations, including numerous events outside of our control, exposing us to significant costs that could adversely affect our operations and customer confidence.
We conduct operations throughout the world, including our headquarters in the United States and various operations in Ireland, Malaysia, Singapore and the United Kingdom. Such worldwide operations expose us to potential operational disruptions and costs as a result of a wide variety of events, including local inflation or economic downturn, currency exchange fluctuations, political turmoil, labor issues, terrorism, natural disasters and pandemics. Any such disruptions or costs could have a negative effect on our ability to provide our solution or meet our contractual obligations, the cost of our solution, customer satisfaction, our ability to attract or maintain customers, and, ultimately, our profits.
Natural disasters or other catastrophic events may cause damage or disruption to our operations, international commerce and the global economy, and thus could have a strong negative effect on us. Our business operations are subject to interruption by natural disasters, fire, power shortages, pandemics and other events beyond our control. Such events could make it difficult or impossible for us to deliver our solution to our customers, and could decrease demand for our solution. The majority of our research and development activities, corporate headquarters, information technology systems and other critical business operations are located near major seismic faults in the San Francisco Bay Area. Because we may not have insurance coverage that would cover quake-related losses, and significant recovery time could be required to resume operations, our financial condition and operating results could be materially adversely affected in the event of a major earthquake or catastrophic event.
Terrorist attacks and other acts of violence or war may adversely affect worldwide financial markets and could potentially lead to economic recession, which could adversely affect our business, results of operations, financial condition and cash flows. These events could adversely affect our customers’ levels of business activity and precipitate sudden significant changes in regional and global economic conditions and cycles.
If our security measures are breached or fail, resulting in unauthorized access to customer data, our solution may be perceived as insecure, the attractiveness of our solution to current or potential customers may be reduced and we may incur significant liabilities.
Our solution involves the storage and transmission of the proprietary information and protected data that we receive from our customers. We rely on proprietary and commercially available systems, software, tools and monitoring, as well as other processes, to provide security for processing, transmission and storage of such information. If our security measures are breached or fail as a result of third-party action, employee negligence, error, malfeasance or otherwise, unauthorized access to customer or end customer data may occur. Improper activities by third parties, advances in computer and software capabilities and encryption technology, new tools and discoveries and other events or developments may facilitate or result in a compromise or breach of our computer systems. Techniques used to obtain unauthorized access or to sabotage systems change frequently and generally are not recognized until launched against a target, and we may be unable to anticipate these techniques or implement adequate preventive measures. Our security measures may not be effective in preventing these types of activities, and the security measures of our third-party data centers and service providers may not be adequate.
Our customer contracts generally provide that we will indemnify our customers for data privacy breaches. If such a breach occurs, we could face contractual damages, damages and fees arising from our indemnification obligations, penalties for violation of applicable laws or regulations, possible lawsuits by affected individuals and significant remediation costs and efforts to prevent future occurrences. In addition, whether there is an actual or a perceived breach of our security, the market perception of the effectiveness of our security measures could be harmed significantly and we could lose current or potential customers.
We may be liable to our customers or third parties if we make errors in providing our solution or fail to properly safeguard their confidential information.
The solution we offer is complex, and we make errors from time to time. These may include human errors made in the course of managing the sales process for our customers as we interact with their end customers, or
23
Table of Contents
errors arising from our technology solution as it interacts with our customers’ systems and the disparate data contained on such systems. The costs incurred in correcting any material errors may be substantial. In addition, as part of our business, we collect, process and analyze confidential information provided by our customers and prospective customers. Although we take significant steps to safeguard the confidentiality of customer information, we could be subject to claims that we disclosed their information without appropriate authorization or used their information inappropriately. Any claims based on errors or unauthorized disclosure or use of information could subject us to exposure for damages, significant legal defense costs, adverse publicity and reputational harm, regardless of the merits or eventual outcome of such claims.
The technology we currently use may not operate properly, which could damage our reputation, give rise to claims against us or divert application of our resources from other purposes, any of which could harm our business and operating results.
The technology we currently use, which includes our cloud based applications as well as the technology components of our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform, may contain or develop unexpected defects or errors. There can be no assurance that performance problems or defects in our technology will not arise in the future. Errors may result from receipt, entry or interpretation of customer or end customer information or from the interface of our technology with legacy systems and data that are outside of our control. Despite testing, defects or errors may arise in our solution. Any defects and errors that we discover in our technology and any failure by us to identify and effectively address them could result in loss of revenue or market share, liability to customers or others, failure to achieve market acceptance or expansion, diversion of development resources, injury to our reputation, and increased costs. Defects or errors in our technology may discourage existing or potential customers from contracting with us. Correction of defects or errors could prove impossible or impracticable. The costs incurred in correcting any defects or errors or in responding to resulting claims or liability may be substantial and could adversely affect our operating results.
Disruptions in service or damage to the data center that hosts our data and our locations could adversely affect our business.
Our operations depend on our ability to maintain and protect our data servers and cloud applications, which are located in a data center operated for us by a third party. We cannot control or assure the continued or uninterrupted availability of this third-party data center. In addition, our information technologies and systems, as well as our data center, are vulnerable to damage or interruption from various causes, including natural disasters, war and acts of terrorism and power losses, computer systems failures, Internet and telecommunications or data network failures, operator error, losses of and corruption of data and similar events. Although we conduct business continuity planning and maintain certain insurance for certain events, the situations for which we plan, and the amount of insurance coverage we maintain, may prove inadequate in any particular case. In addition, the occurrence of any of these events could result in interruptions, delays or cessations in the delivery of the solutions we offer to our customers. Any of these events could impair or prohibit our ability to provide our solution, reduce the attractiveness of our solution to current or potential customers and adversely impact our financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, despite the implementation of security measures, our infrastructure, data center, operations and other centers or systems that we interface with, including the Internet and related systems, may be vulnerable to physical intrusions, hackers, improper employee or contractor access, computer viruses, programming errors, denial-of-service attacks or other attacks by third parties.
Any failure or interruptions in the Internet infrastructure, bandwidth providers, data center providers, other third parties or our own systems for providing our solution to customers could negatively impact our business.
Our ability to deliver our solution is dependent on the development and maintenance of the infrastructure of the Internet and other telecommunications services by third parties. Such services include maintenance of a
24
Table of Contents
reliable network backbone with the necessary speed, data capacity and security for providing reliable Internet access and services and reliable telecommunications systems that connect our global operations. While our solution is designed to operate without interruption, we have experienced and expect that we will in the future experience interruptions and delays in services and availability from time to time. We rely on internal systems as well as third-party vendors, including data center, bandwidth, and telecommunications equipment providers, to provide our solution. We do not maintain redundant systems or facilities for some of these services. In the event of a catastrophic event with respect to one or more of these systems or facilities, we may experience an extended period of system unavailability, which could negatively impact our relationship with our customers.
Additional government regulations may reduce the size of market for our solution, harm demand for our solution and increase our costs of doing business.
Any changes in government regulations that impact our customers or their end customers could have a harmful effect on our business by reducing the size of our addressable market or otherwise increasing our costs. For example, with respect to our technology-enabled healthcare and life sciences customers, any change in U.S. Food and Drug Administration or foreign equivalent regulation of, or denial, withholding or withdrawal of approval of, our customers’ products could lead to a lack of demand for service revenue management with respect to such products. Other changes in government regulations, in areas such as privacy, export compliance or anti-bribery statutes, such as the U.S. Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, could require us to implement changes in our services or operations that increase our cost of doing business and thereby hurt our financial performance.
The future success of our business depends upon the continued use of the Internet as a primary medium for commerce, communication and business applications. Federal, state or foreign government bodies or agencies have in the past adopted, and may in the future adopt, laws or regulations affecting data privacy and the use of the Internet as a commercial medium. In addition, government agencies or private organizations may begin to impose taxes, fees or other charges for accessing the Internet. These laws or charges could limit the growth of Internet-related commerce or communications generally, result in a decline in the use of the Internet and the viability of Internet-based applications such as ours and reduce the demand for our solution.
We operate and offer our services in many jurisdictions and, therefore, may be subject to state, local and foreign taxes that could harm our business.
We operate service sales centers in multiple locations. Some of the jurisdictions in which we operate, such as Ireland, give us the benefit of either relatively low tax rates, tax holidays or government grants, in each case that are dependent on how we operate or how many jobs we create and employees we retain. We plan on utilizing such tax incentives in the future as opportunities are made available to us. Any failure on our part to operate in conformity with applicable requirements to remain qualified for any such tax incentives or grants may result in an increase in our taxes. In addition, jurisdictions may choose to increase rates at any time due to economic or other factors, such as the current economic situation in Ireland. Any such rate increases may harm our results of operations.
In addition, we may lose sales or incur significant costs should various tax jurisdictions impose taxes on either a broader range of services or services that we have performed in the past. We may be subject to audits of the taxing authorities in any such jurisdictions that would require us to incur costs in responding to such audits. Imposition of such taxes on our services could result in substantial unplanned costs, would effectively increase the cost of such services to our customers and may adversely affect our ability to retain existing customers or to gain new customers in the areas in which such taxes are imposed.
We may choose to sell subscriptions to our cloud applications separately from our integrated solution, which may not be successful and could impact revenue from our existing solution.
We currently derive a small portion of our revenue from subscriptions to our cloud applications for a few customers, and we are exploring alternatives for packaging and pricing these applications to generate more
25
Table of Contents
revenues from them. In the event we choose to expand our technology subscriptions in this manner, we may not find a successful market for our applications. In addition, because we have limited prior experience selling technology subscriptions on a stand-alone basis, we may encounter technical and execution challenges that undermine the quality of the technology offering or cause us to fall short of customer expectations. We also have little experience in pricing our technology subscriptions separately, which could result in underpricing that damages our profit margins and other financial performance. It is also possible that selling a technology solution separate from our integrated solution will result in a reduction in sales of our current offerings that we might otherwise have sold. An unsuccessful expansion of our business to promote a stand-alone subscription model for any of the foregoing reasons or otherwise would lead to a diversion of financial and managerial resources from our existing business and an inability to generate sufficient revenue to offset our investment costs.
If we acquire companies or technologies in the future, they could prove difficult to integrate, disrupt our business, dilute stockholder value and adversely affect our operating results and the value of our common stock.
As part of our business strategy, we may acquire, enter into joint ventures with, or make investments in companies, services and technologies that we believe to be complementary. Acquisitions and investments involve numerous risks, including:
| • | difficulties in identifying and acquiring technologies or businesses that will help our business; |
| • | difficulties in integrating operations, technologies, services and personnel; |
| • | diversion of financial and managerial resources from existing operations; |
| • | the risk of entering new markets in which we have little to no experience; |
| • | risks related to the assumption of known and unknown liabilities; |
| • | potential litigation by third parties, such as claims related to intellectual property or other assets acquired or liabilities assumed; |
| • | the risk of write-offs of goodwill and other intangible assets; |
| • | delays in customer engagements due to uncertainty and the inability to maintain relationships with customers of the acquired businesses; |
| • | inability to generate sufficient revenue to offset acquisition or investment costs; |
| • | incurrence of acquisition-related costs; |
| • | harm to our existing business relationships with business partners and customers as a result of the acquisition; |
| • | the key personnel of the acquired entity or business may decide not to work for us or may not perform according to our expectations; and |
| • | use of substantial portions of our available cash or dilutive issuances of equity securities or the incurrence of debt to consummate the acquisition. |
As a result, if we fail to properly evaluate acquisitions or investments, we may not achieve the anticipated benefits of any such acquisitions, we may incur costs in excess of what we anticipate and management resources and attention may be diverted from other necessary or valuable activities.
Risks Relating to Owning Our Common Stock and this Offering
Our share price may be volatile, and you may be unable to sell your shares at or above the offering price.
Our common stock has no prior trading history, and an active public market for these shares may not develop or be sustained after this offering. The initial public offering price for our common stock was determined
26
Table of Contents
through negotiations with the representatives of the underwriters. This price does not necessarily reflect the price at which investors in the market will be willing to buy and sell our shares following this offering. In addition, the trading price of our common stock is likely to be highly volatile and could be subject to wide fluctuations in response to various factors. In addition to the risks described in this section, factors that may cause the market price of our common stock to fluctuate include:
| • | fluctuations in our quarterly financial results or the quarterly financial results of companies perceived to be similar to us as discussed in more detail elsewhere in “Risk Factors;” |
| • | failing to achieve our revenue or earnings expectations, or those of investors or analysts; |
| • | changes in estimates of our financial results or recommendations by securities analysts; |
| • | recruitment or departure of key personnel; |
| • | investors’ general perception of us; |
| • | volatility inherent in prices of technology company stocks; |
| • | adverse publicity; |
| • | the volume of trading in our common stock, including sales upon exercise of outstanding options; |
| • | regulatory developments in our target markets affecting us, our customers or our competitors; |
| • | terrorist attacks or natural disasters or other such events impacting countries where we or our customers have operations; and |
| • | actual or perceived changes in general economic, industry and market conditions. |
In addition, if the stock market in general experiences a loss of investor confidence, the trading price of our common stock could decline for reasons unrelated to our business, financial condition or results of operations.
Some companies that have had volatile market prices for their securities have had securities class actions filed against them. If a suit were filed against us, regardless of its merits or outcome, it would likely result in substantial costs and divert management’s attention and resources. This could have a material adverse effect on our business, operating results and financial condition.
No public market for our common stock currently exists, and an active trading market may not develop or be sustained following this offering.
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for shares of our common stock. Although we intend to apply for listing of our common stock on The Nasdaq Global Market, an active public trading market for our common stock may not develop or, if it develops, may not be maintained after this offering. For example, The Nasdaq Global Market imposes certain securities trading requirements, including minimum trading price, minimum number of stockholders and minimum market capitalization. Failure to meet those requirements for prolonged periods could result in delisting, which could further lower our stock price and trading volumes. We and the representatives of the underwriters negotiated to determine the initial public offering price. The initial public offering price may be higher than the trading price of our common stock following this offering.
Our actual results may differ significantly from any guidance that we may issue in the future.
From time to time, we may release earnings guidance or other forward looking statements in our earnings releases, earnings conference calls or otherwise, regarding our future performance that represent our management’s estimates as of the date of release. If given, this guidance will be based on forecasts prepared by our management. These forecasts are not prepared with a view toward compliance with published accounting guidelines, and neither our registered public accountants nor any other independent expert or outside party compiles or examines the forecasts and, accordingly, no such person expresses any opinion or any other form of
27
Table of Contents
assurance with respect to such forecasts. The principal reason that we may release guidance is to provide a basis for our management to discuss our business outlook with analysts and investors. We do not accept any responsibility for any projections or reports published by any such third persons. Guidance is necessarily speculative in nature, and it can be expected that some or all of the assumptions of any future guidance furnished by us may not materialize or may vary significantly from actual future results.
We will incur increased costs and demands upon management as a result of complying with the laws and regulations affecting public companies, which could adversely affect our operating results.
As a public company, we will incur significant legal, accounting and other expenses that we did not incur as a private company, and greater expenditures may be necessary in the future with the advent of new laws, regulations and stock exchange listing requirements pertaining to public companies. The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 and the Dodd-Frank Act of 2010, as well as rules subsequently implemented by the Securities and Exchange Commission and The Nasdaq Stock Market, impose various requirements on public companies, including establishing effective internal controls and certain corporate governance practices. Our management and other personnel have begun to devote a substantial amount of time to these compliance initiatives, and additional laws and regulations may divert further management resources. Moreover, if we are not able to comply with the requirements of new compliance initiatives in a timely manner, the market price of our stock could decline, and we could be subject to investigations and other actions by The Nasdaq Stock Market, the Securities and Exchange Commission, or other regulatory authorities, which would require additional financial and management resources.
In particular, we will be required to comply with the management certification requirements of Section 404 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 that will require us to report, among other things, control deficiencies that constitute a material weakness or changes in internal controls that, or that are reasonably likely to, materially affect internal controls over financial reporting. Failure to comply with Section 404 or the report by us of any material weakness may cause us to be subject to SEC investigation, and may lead to investors losing confidence in our financial statements. Also as a public company and to manage our growth, we will be required to implement and maintain various other control and business systems related to our equity, finance, treasury, information technology, other recordkeeping systems and other operations. As a result of any failure to remedy any material weakness in our internal controls or to implement or maintain other effective control or business systems, our financial statements may be inaccurate, we may face restricted access to the capital markets and our stock price may be adversely affected.
Concentration of ownership among our existing executive officers, directors and their affiliates may prevent new investors from influencing significant corporate decisions.
Upon the closing of this offering, our directors and executive officers and their affiliates will beneficially own, in the aggregate, approximately % of our outstanding common stock, assuming no exercise of the underwriters’ overallotment option. As a result, these stockholders will be able to determine substantially all matters requiring stockholder approval, including the election of directors and approval of significant corporate transactions, such as a merger or other sale of our company or its assets. This concentration of ownership could limit the ability of other stockholders to influence corporate matters and may have the effect of delaying or preventing a third party from acquiring control over us. For information regarding the ownership of our outstanding stock by our executive officers and directors and their affiliates, see “Principal and Selling Stockholders.”
Anti-takeover provisions contained in our certificate of incorporation, as well as provisions of Delaware law, could impair a takeover attempt.
Our certificate of incorporation and Delaware law contain provisions that could have the effect of rendering more difficult or discouraging an acquisition deemed undesirable by our board of directors. Our corporate governance documents include provisions:
| • | authorizing blank check preferred stock, which could be issued by our board of directors without stockholder approval, with voting, liquidation, dividend and other rights superior to our common stock; |
28
Table of Contents
| • | classifying our board of directors, staggered into three classes, only one of which is elected at each annual meeting; |
| • | limiting the liability of, and providing indemnification to, our directors and officers; |
| • | limiting the ability of our stockholders to call and bring business before special meetings and to take action by written consent in lieu of a meeting; |
| • | requiring advance notice of stockholder proposals for business to be conducted at meetings of our stockholders and for nominations of candidates for election to our board of directors; |
| • | controlling the procedures for the conduct and scheduling of stockholder meetings; |
| • | providing the board of directors with the express power to postpone previously scheduled annual meetings and to cancel previously scheduled special meetings; |
| • | limiting the determination of the number of directors on our board and the filling of vacancies or newly created seats on the board to our board of directors then in office; and |
| • | providing that directors may be removed by stockholders only for cause. |
These provisions, alone or together, could delay hostile takeovers and changes in control or changes in our management.
As a Delaware corporation, we are also subject to provisions of Delaware law, including Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation law, which limits the ability of stockholders owning in excess of 15% of our outstanding common stock to merge or combine with us.
Any provision of our certificate of incorporation or Delaware law that has the effect of delaying or deterring a change in control could limit the opportunity for our stockholders to receive a premium for their shares of our common stock, and could also affect the price that some investors are willing to pay for our common stock.
Future sales of our common stock in the public market could cause our share price to fall.
If our existing stockholders sell, or indicate an intent to sell, substantial amounts of our common stock in the public market, the trading price of our common stock may be adversely affected and our ability to raise capital through the issuance of equity securities may be impeded. Based on the number of shares outstanding as of September 30, 2010, upon the closing of this offering, we will have shares of our common stock outstanding, assuming no exercise of our outstanding options.
All of these shares will be immediately freely tradeable without restrictions or further registration under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, except for any shares held by our affiliates as defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act. As of September 30, 2010, our affiliates, which include GA SS Holding LLC, controlled by General Atlantic LLC, SSLLC Holdings, Inc., controlled by Benchmark Capital, certain entities affiliated with Housatonic Partners and our officers and directors beneficially owned in the aggregate 36,256,813 shares of common stock, representing an ownership interest of approximately 63%. Such equityholders will be able to sell their common stock in the public market from time to time without registering them, subject to the lock-up agreements and certain limitations on the timing, amount and method of those sales imposed by Rule 144 under the Securities Act. Most of the remaining shares will be restricted as a result of securities laws, lock-up agreements as described elsewhere in this prospectus or other contractual restrictions that restrict transfers for at least 180 days after the date of this prospectus subject to extension. However, these lock-up agreements are subject to various exceptions and in any event Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated may, in its sole discretion, release all or a portion of the shares subject to the lock-up agreements. See “Shares Eligible for Future Sale.”
Affiliates of Benchmark Capital, General Atlantic LLC and Housatonic Partners and certain other stockholders have contractual registration rights, subject to certain conditions, to require us to file registration
29
Table of Contents
statements covering all of the shares of common stock (including restricted shares) that they own or to include their common stock in registration statements that we may file for ourselves or other stockholders. Following their registration and sale under the applicable registration statement, those shares will become freely tradable. By exercising their registration rights and selling a large number of shares of common stock, these holders could cause the price of our common stock to decline. In addition, the perception in the public markets that sales by them might occur could also adversely affect the market price of our common stock.
Purchasers in this offering will experience immediate and substantial dilution in the book value of their investment.
The initial public offering price per share is substantially higher than the pro forma net tangible book value per share of our common stock outstanding prior to this offering. As a result, investors purchasing common stock in this offering will experience immediate dilution of $ per share. This dilution is due in large part to the fact that our earlier investors paid substantially less than the initial public offering price when they purchased their shares of common stock. In addition, we have issued options to acquire common stock at prices significantly below the initial public offering price. To the extent outstanding options are ultimately exercised, there will be further dilution to investors in this offering. In addition, if the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares from us or if we issue additional equity securities, you will experience additional dilution.
If securities or industry analysts do not publish or cease publishing research or reports about us, our business or our market, or if they change their recommendations regarding our stock, our stock price and trading volume could decline.
The trading market for our common stock will depend in part on the research and reports that securities or industry analysts publish about us or our business. If any of these analysts cease coverage of our company, the trading price and trading volume of our stock could be negatively impacted. If analysts downgrade our stock or publish unfavorable research about our business, our stock price would also likely decline.
Our management will have broad discretion over the use of the proceeds we receive in this offering and might not apply the proceeds in ways that increase the value of your investment.
We expect to use the net proceeds from this offering to repay debt and for general corporate purposes, including possible investments in, or acquisitions of, businesses, joint ventures, services or technologies, working capital and capital expenditures. Our management will have broad discretion in the use of the net proceeds from this offering, and you will be relying on the judgment of our management regarding the application of these proceeds. The net proceeds may be used for corporate purposes that ultimately fail to increase the value of our business, which could cause the price of our common stock to decline.
We do not expect to declare any dividends in the foreseeable future.
We do not expect to pay cash dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future following the closing of this offering. Any future dividend payments will be within the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on, among other things, our financial condition, results of operations, capital requirements, capital expenditure requirements, contractual restrictions, provisions of applicable law and other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant. We may not generate sufficient cash from operations in the future to pay dividends on our common stock. See “Dividend Policy.”
30
Table of Contents
This prospectus contains forward looking statements that are based on our management’s beliefs and assumptions and on information currently available to our management. The forward looking statements are contained principally in “Prospectus Summary,” “Risk Factors,” “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” “Business” and “Executive Compensation.” Forward looking statements include information concerning our possible or assumed future results of operations, estimates of service revenue opportunity under management, estimates of our customers’ and our renewal rates, business strategies, technology development, protection of our intellectual property, investment and financing plans, liquidity, competitive position, the effects of competition, industry environment and potential growth opportunities. Forward looking statements include all statements that are not historical facts and can be identified by terms such as “anticipates,” “believes,” “could,” “estimates,” “expects,” “intends,” “may,” “might,” “likely,” “plans,” “potential,” “predicts, “projects,” “seeks,” “should,” “will,” “would” or similar expressions and the negatives of those terms.
Forward looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors that may cause our actual results, performance or achievements to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward looking statements. We discuss these risks in greater detail in “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus. Given these uncertainties, you should not place undue reliance on these forward looking statements. Also, forward looking statements represent our management’s beliefs and assumptions only as of the date of this prospectus. You should read this prospectus and the documents that we have filed as exhibits to the registration statement, of which this prospectus is a part, completely and with the understanding that our actual future results may be materially different from what we expect.
Except as required by law, we assume no obligation to update these forward looking statements publicly, or to update the reasons actual results could differ materially from those anticipated in these forward looking statements, even if new information becomes available in the future.
In addition, projections, assumptions and estimates of our future performance and the future performance of the industry in which we operate is necessarily subject to a high degree of uncertainty and risk due to a variety of factors, including those described in “Risk Factors” and elsewhere in this prospectus. These and other factors could cause results to differ materially from those expressed in the estimates made by the independent parties and by us.
31
Table of Contents
We estimate that the net proceeds from our sale of shares of common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the front cover of this prospectus, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses, will be approximately $ million, or $ million if the underwriters’ option to purchase additional shares is exercised in full. A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price would increase (decrease) the net proceeds to us from this offering by $ million, assuming the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the front cover of this prospectus, remains the same and after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions.
We will not receive any proceeds from the sale of shares of common stock by the selling stockholders, including any shares of common stock sold by the selling stockholders in connection with the underwriters’ exercise of their option to purchase additional shares of common stock, although we will bear the costs, other than underwriting discounts and commissions, associated with the sale of these shares. The selling stockholders may include certain entities affiliated with or controlled by members of our board of directors.
We intend to use the net proceeds we receive from this offering to repay the loan balances outstanding under our credit facility. As of September 30, 2010, we had total indebtedness of $16.1 million outstanding under our term loan, consisting of $15.8 million in aggregate principal and $0.3 million in accrued and unpaid interest. The term loan has a maturity date of April 29, 2013. Borrowings under the term loan bear interest at a base LIBOR rate plus a margin. The annual interest rate was equal to 5.75% as of September 30, 2010.
We expect to use the remaining net proceeds from this offering for working capital and other general corporate purposes, which may include sales and marketing expenditures, general and administrative expenditures, developing new technologies and funding capital expenditures. In addition, if opportunities arise to acquire or invest in companies, businesses or technologies that we believe to be complementary, we may use a portion of the net proceeds for such acquisition or investment. However, we do not have agreements or commitments for any specific acquisitions at this time. The amount and timing of any of these expenditures could vary depending on a number of factors, including developments related to our business and events outside of our control. Pending their use, we plan to invest our net proceeds from this offering in short-term, interest-bearing obligations, investment-grade instruments, certificates of deposit or direct or guaranteed obligations of the U.S. government. This offering is also intended to facilitate our future access to public markets.
We currently intend to retain all available funds and any future earnings for use in the operation of our business and do not anticipate paying any dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future. Any future determination to declare dividends will be made at the discretion of our board of directors and will depend on our financial condition, operating results, capital requirements, general business conditions and other factors that our board of directors may deem relevant. In addition, our credit facility contains restrictions on our ability to declare and pay cash dividends on our capital stock.
32
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth our capitalization as of September 30, 2010 on:
| • | an actual basis; |
| • | a pro forma basis after giving effect to the Conversion; and |
| • | a pro forma as adjusted basis to reflect (i) the Conversion, (ii) our receipt of the net proceeds from our sale of shares of common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the front cover of this prospectus, after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us and (iii) the application of a portion of the net proceeds of this offering to repay the loan balances outstanding under our credit facility, as described under “Use of Proceeds.” |
The information below is illustrative only and our capitalization following the completion of this offering will be adjusted based on the actual initial public offering price and other terms of this offering determined at pricing. You should read this table together with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our financial statements and the related notes appearing elsewhere in this prospectus.
| As of September 30, 2010 | ||||||||||||
| Actual | Pro Forma | Pro Forma As Adjusted(1) |
||||||||||
| (in thousands, except share and per share data) |
||||||||||||
| Total debt, current and non-current |
$ | 17,790 | $ | $ | ||||||||
| Members’/stockholders’ equity |
||||||||||||
| Common shares: 99,000,000 shares authorized, 57,926,833 shares issued and 57,426,218 shares outstanding, actual; no shares authorized, issued or outstanding, pro forma; no shares authorized, issued or outstanding, pro forma as adjusted |
33,196 | — | — | |||||||||
| Preferred stock, $0.0001 par value; no shares authorized, issued or outstanding, actual or pro forma; 20,000,000 shares authorized, no shares issued or outstanding, pro forma as adjusted |
— | — | ||||||||||
| Common stock, $0.0001 par value; no shares authorized, issued or outstanding, actual; 1,000,000,000 shares authorized, shares issued and outstanding, pro forma; and 1,000,000,000 shares authorized, shares issued and outstanding, pro forma as adjusted |
— | |||||||||||
| Treasury stock |
(441 | ) | ||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
— | |||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
165 | |||||||||||
| Retained earnings |
— | |||||||||||
| Total members’/stockholders’ equity |
32,920 | |||||||||||
| Total capitalization |
$ | 50,710 | $ | $ | ||||||||
| (1) | A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) each of additional paid-in capital, total stockholders’ equity and total capitalization by $ million, assuming that the number of shares offered by us, as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus, remains the same, and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses payable by us. Each increase of 1.0 million shares in the number of shares offered by us would increase additional paid-in capital, total stockholders’ equity and total capitalization by approximately $ million. Similarly, each decrease of 1.0 million shares in the number of shares offered by us would decrease additional paid-in capital, total stockholders’ equity and total capitalization by approximately $ million. |
33
Table of Contents
The number of shares of our common stock to be outstanding following this offering is based on 57,426,218 shares of our common stock outstanding as of September 30, 2010 and excludes:
| • | 15,726,057 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of options outstanding as of September 30, 2010, with a weighted average exercise price of $4.09 per share; |
| • | 2,315,428 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of options granted after September 30, 2010, at an exercise price of $5.80 per share; and |
| • | shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan, which will become effective in connection with this offering. |
ServiceSource International, LLC may be required to make tax distributions to equityholders to the extent it has taxable income. Pursuant to the limited liability company agreement of ServiceSource International, LLC in existence prior to our conversion to a corporation, we were required to pay cash distributions to our equityholders to fund their tax obligations in respect of their equity interests in 2007, 2008 and the nine months ended September 30, 2010 in aggregate amounts of $5.1 million, $5.2 million, and $2.5 million, respectively. Apart from such obligations, our board of directors has sole discretion whether to make distributions to our equityholders. Based on the operating results of the limited liability company for the first nine months of 2010, we do not expect to make any further tax distributions for 2010. Distributions to equityholders in future periods are dependent on taxable income, if any, attributable to the equityholders for such periods.
34
Table of Contents
If you invest in our common stock, your interest will be diluted to the extent of the difference between the amount per share paid by purchasers of shares of common stock in this offering and the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share of common stock immediately after completion of this offering.
At September 30, 2010, our pro forma net tangible book value was approximately , or per share of common stock. Pro forma net tangible book value per share represents the amount of our tangible assets less our liabilities, divided by the shares of common stock outstanding at September 30, 2010 after giving effect to the Conversion. After giving effect to our sale of shares of common stock in this offering at an assumed initial public offering price of $ , the midpoint of the price range set forth on the front cover of this prospectus, and after deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses, our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value at September 30, 2010 would have been $ , or $ per share of common stock. This represents an immediate increase in pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value of $ per share to existing stockholders and immediate dilution of $ per share to new investors.
The following table illustrates this dilution:
| Initial public offering price per share |
$ | |||||||
| Pro forma net tangible book value per share as of September 30, 2010 |
$ | |||||||
| Increase per share attributed to this offering |
||||||||
| Pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share |
||||||||
| Dilution per share to new investors |
$ | |||||||
A $1.00 increase (decrease) in the assumed initial public offering price of $ per share, the midpoint of the price range set forth on the front cover of this prospectus, would increase (decrease) our pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share by $ , assuming the number of shares offered by us remains the same as set forth on the cover page of this prospectus and after deducting the underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses that we must pay.
If the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares of our common stock from us in full, the pro forma as adjusted net tangible book value per share would be $ , the increase in pro forma net tangible book value per share to existing stockholders would be $ and the dilution per share to new investors purchasing shares in this offering would be $ .
If all our outstanding options had been exercised, the pro forma net tangible book value as of September 30, 2010 would have been $ million, or $ per share, and the pro forma net tangible book value after this offering would have been $ million, or $ per share, causing dilution to new investors of $ per share.
The following table summarizes, on a pro forma as adjusted basis as of September 30, 2010, after giving effect to the Conversion, the total number of shares of common stock purchased from us, the total consideration paid to us and the average price per share paid to us by existing stockholders and by new investors purchasing shares in this offering at the initial public offering price of $ , the midpoint of the price range set forth on the front cover of this prospectus, before deducting underwriting discounts and commissions and estimated offering expenses:
| Shares Purchased | Total Consideration | Average Price Per Share |
||||||||||||||||||
| Number | Percent | Amount | Percent | |||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except percentage and per share data) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Existing stockholders |
% | $ | % | $ | ||||||||||||||||
| New public investors |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
100.0 | % | $ | 100.0 | % | |||||||||||||||
35
Table of Contents
The foregoing calculations are based on 57,426,218 shares of our common stock outstanding as of September 30, 2010 after giving effect to the Conversion and exclude:
| • | 15,726,057 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of options outstanding as of September 30, 2010, with a weighted average exercise price of $4.09 per share; |
| • | 2,315,428 shares of common stock issuable upon the exercise of options granted after September 30, 2010, at an exercise price of $5.80 per share; and |
| • | shares of common stock reserved for issuance under our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan, which will become effective in connection with this offering. |
To the extent any outstanding options are exercised, new investors will experience further dilution.
Sales by the selling stockholders in this offering will cause the number of shares owned by existing stockholders to be reduced to shares or % of the total number of shares of our common stock outstanding upon the closing of this offering. If the underwriters exercise their option to purchase additional shares in full, our existing stockholders would own % and our new public investors would own % of the total number of shares of our common stock outstanding upon the closing of this offering.
36
Table of Contents
SELECTED CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL DATA
We have derived the selected consolidated statements of operations data for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009 and selected consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2008 and 2009 from our audited consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus. We have derived the selected consolidated statements of operations data for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010 and the consolidated balance sheet data as of September 30, 2010 from our unaudited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus. We have prepared the unaudited consolidated financial statement data on a basis consistent with our audited consolidated financial statements, and, in the opinion of our management, the unaudited consolidated financial statements reflect all adjustments, consisting only of normal recurring adjustments necessary for a fair statement of such financial statements. We have derived the selected consolidated statements of operations data for the year ended December 31, 2006 and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2006 and 2007 from our audited consolidated financial statements not included in this prospectus. The consolidated statements of operations data for the year ended December 31, 2005 and the consolidated balance sheet data as of December 31, 2005 was derived from our unaudited consolidated financial statements not included in this prospectus. Our historical results are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for any future period, and the results for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected for the full year or for any other period. The following selected consolidated financial data should be read in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” and our consolidated financial statements and related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus.
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands, except per share amounts) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue |
$ | 29,624 | $ | 45,918 | $ | 75,189 | $ | 100,280 | $ | 110,676 | $ | 76,889 | $ | 108,468 | ||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue(1) |
9,875 | 22,442 | 39,224 | 56,965 | 58,877 | 41,577 | 63,841 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
19,749 | 23,476 | 35,965 | 43,315 | 51,799 | 35,312 | 44,627 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses(1) |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
2,739 | 6,107 | 13,119 | 20,486 | 23,182 | 16,802 | 25,640 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
— | — | — | 1,160 | 2,054 | 1,647 | 3,927 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
7,127 | 12,268 | 10,475 | 10,571 | 13,777 | 10,214 | 13,806 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
1,576 | 1,677 | 912 | 857 | 68 | 68 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
11,442 | 20,052 | 24,506 | 33,074 | 39,081 | 28,731 | 43,373 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Income from operations |
8,307 | 3,424 | 11,459 | 10,241 | 12,718 | 6,581 | 1,254 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(406 | ) | (2,060 | ) | (2,305 | ) | (2,209 | ) | (1,116 | ) | (772 | ) | (940 | ) | ||||||||||||||
| Loss on extinguishment of debt |
— | — | — | (561 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expenses), net |
— | (33 | ) | (118 | ) | (1,497 | ) | 639 | 465 | (202 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) before provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
7,901 | 1,331 | 9,036 | 5,974 | 12,241 | 6,274 | 112 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax (benefit) provision |
— | — | (632 | ) | 1,153 | 1,866 | 730 | 1,368 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 7,901 | $ | 1,331 | $ | 9,668 | $ | 4,821 | $ | 10,375 | $ | 5,544 | $ | (1,256 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) per common share(2): |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.70 | $ | 0.03 | $ | 0.17 | $ | 0.09 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.10 | $ | (0.02 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.15 | $ | 0.02 | $ | 0.16 | $ | 0.08 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.09 | $ | (0.02 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Cash distributions per common share(3) |
$ | — | $ | 0.43 | $ | 0.09 | $ | 0.09 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 0.04 | ||||||||||||||
| Weighted-average shares used in computing net income (loss) per common share(2): |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
10,548 | 45,908 | 55,936 | 56,209 | 56,750 | 56,702 | 57,167 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
53,730 | 56,461 | 58,706 | 58,733 | 58,912 | 58,510 | 57,167 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma net income (loss) per common share(4): |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
$ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma weighted-average shares used in computing net income (loss) per common share(4): |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements
37
Table of Contents
| (1) | Effective January 1, 2006, we adopted FASB ASC Topic 718, Accounting for Stock-Based Compensation. Reported balances include stock-based compensation expense as follows: |
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine
Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | — | $ | 114 | $ | 1,096 | $ | 1,271 | $ | 914 | $ | 672 | $ | 843 | ||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
— | 264 | 1,100 | 1,570 | 2,340 | 1,706 | 2,214 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
— | — | — | — | 541 | 399 | 598 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
— | 383 | 1,680 | 2,608 | 2,265 | 1,663 | 2,362 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total stock-based compensation |
$ | — | $ | 761 | $ | 3,876 | $ | 5,449 | $ | 6,060 | $ | 4,440 | $ | 6,017 | ||||||||||||||
| (2) | Our basic net income (loss) per common share is calculated by dividing the net income (loss) by the weighted-average number of shares of common stock outstanding for the period. |
| (3) | Pursuant to our limited liability company agreement, we were required to pay cash distributions to our members to fund their tax obligations in respect of their equity interests. All other distributions are determined by our directors in their sole discretion. Tax distributions to members were $4.9 million, $5.1 million, $5.2 million and $0 in 2006, 2007, 2008 and 2009, and $0 and $2.5 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively. In 2006, the directors approved an additional $15.0 million distribution to all members. |
| (4) | Our pro forma net income (loss) per common share gives effect to the Conversion and to an assumed issuance of only that number of shares that would have been required to be issued to repay the loan balances outstanding under our credit facility as of September 30, 2010 assuming the issuance of such shares at an initial offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus). The diluted pro forma net income (loss) per common share calculation also assumes the conversion, exercise, or issuance of all potential common shares, unless the effect of inclusion would result in the reduction of a loss or the increase in net income per common share. |
| As of December 31, | As of September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2005 | 2006 | 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated Balance Sheet Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 3,960 | $ | 4,491 | $ | 13,147 | $ | 3,780 | $ | 13,169 | $ | 10,807 | $ | 23,231 | ||||||||||||||
| Working capital(1) |
9,277 | 6,883 | 15,175 | 12,319 | 19,099 | 17,221 | 18,887 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total assets |
41,282 | 31,154 | 45,366 | 51,712 | 69,580 | 59,903 | 99,136 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Term loan, current and non-current |
3,726 | 20,069 | 20,000 | 19,625 | 16,835 | 17,418 | 15,834 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Obligations under capital leases, current and non-current |
133 | 113 | — | 151 | 773 | 786 | 1,956 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total stockholders’ equity (deficit) |
24,256 | (799 | ) | 7,937 | 13,482 | 30,331 | 23,875 | 32,920 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Working capital is defined as current assets less current liabilities. |
38
Table of Contents
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS OF FINANCIAL CONDITION
AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations should be read together with “Prospectus Summary—Summary Consolidated Financial Data,” “Selected Consolidated Financial Data” and our consolidated financial statements and accompanying notes included elsewhere within this prospectus. This discussion includes both historical information and forward-looking information that involves risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Our actual results may differ materially from management’s expectations as a result of various factors, including but not limited to those discussed in the sections titled “Risk Factors” and “Special Note Regarding Forward Looking Statements.” While our outstanding equity as a limited liability company prior to the Conversion was called “common shares,” unless otherwise indicated in this prospectus, we refer to such common shares in this prospectus as common stock for the periods prior to the Conversion for ease of comparison. Similarly, we refer to members’ equity in this prospectus as stockholders’ equity.
Overview
We manage the service contract renewals process for renewals of maintenance, support and subscription agreements on behalf of our customers. Our integrated solution consists of a suite of cloud applications, dedicated service sales teams working under our customers’ brands and a proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform. By integrating software, managed services and data, we address the critical steps of the renewals process including data management, quoting, selling and service revenue business intelligence. Our business is built on our pay-for-performance model, whereby our revenues are based on the service renewals customers achieve with our solution. As of September 30, 2010, we managed over 90 engagements across more than 50 customers, representing over $5 billion in service revenue opportunity under management. We had approximately 50, 60 and 80 engagements as of December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively, and over 90 engagements as of September 30, 2010.
We were formed in November 2002 as a limited liability company, and shortly thereafter we purchased certain assets of a business originally started by service sales representatives from a major technology company. Since then we have refined our business model, developed and expanded our service sales teams, our suite of cloud based applications and our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform, and opened additional sales centers in the United States, Europe and Asia and a global sales operations center in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. We broadened our customer focus from technology companies to also include technology-enabled healthcare and life sciences companies. We have experienced rapid growth in our operations in recent periods, as indicated by the following:
| • | Our revenue has increased from $45.9 million in 2006 to $110.7 million in 2009, representing a compound annual growth rate of 34%. For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, our revenue was $108.5 million, which represented an increase of 41% as compared to the nine months ended September 30, 2009. |
| • | Our engagements have grown from approximately 40 as of December 31, 2006 to more than 90 as of September 30, 2010. |
| • | As of September 30, 2010, we had more than 1,300 employees, with offices in Colorado, Tennessee, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Malaysia and Singapore in addition to our corporate headquarters in San Francisco. |
In 2010, Oracle acquired our then largest customer, Sun Microsystems, and terminated our contract with Sun Microsystems effective as of September 30, 2010. Sun Microsystems accounted for $17.9 million, or 17%, of our revenue for the nine months ended September 30, 2010. While the loss of revenues from Sun Microsystems is significant, we have added additional customers and engagements throughout 2010 and expect to continue to expand our business irrespective of the loss of Sun Microsystems. In the near term, however, we expect the loss of Sun Microsystems to have an adverse effect on our gross margins, operating margins and cash flows.
39
Table of Contents
We are currently in the midst of a significant investment cycle in which we have taken steps designed to drive our future growth and profitability. We plan to further build out our infrastructure, develop our technology, offer additional cloud based applications and hire additional sales, service sales and other personnel.
We initially funded our business primarily with investments from our founders, certain other small investors and the venture capital firm Housatonic Partners. As our business has grown, we have funded our business primarily with cash flows from operations, and returned capital to equityholders, including our founders. Affiliates of Benchmark Capital and General Atlantic Partners invested in our company in 2004 and 2007, respectively, and Housatonic made an additional investment in 2008. All of these investments involved the direct or indirect purchase of equity from our existing equityholders, including our founders. We drew down funds from a term loan in 2006, with the proceeds used primarily to fund tax distributions to our equityholders as required under our limited liability company agreement, and remaining proceeds used for general corporate purposes. In April 2008, we entered into a five year credit facility agreement with various financial institutions, the proceeds of which were primarily used to refinance outstanding debt under several prior debt agreements. We were originally formed as a Delaware limited liability company. Prior to the closing of this offering, we will complete the Conversion pursuant to which ServiceSource International, LLC will convert to ServiceSource International, Inc., a Delaware corporation.
Key Business Metrics
In assessing the performance of our business, we consider a variety of business metrics in addition to the financial metrics discussed below under “—Basis of Presentation.” These key metrics include service revenue opportunity under management and number of engagements.
Service Revenue Opportunity Under Management. Service revenue opportunity under management (“opportunity under management”) is our estimate, as of a given date, of the value of all end customer service contracts that we will have the opportunity to sell on behalf of our customers over the subsequent twelve-month period. Opportunity under management is not a measure of our expected revenue.
We estimate the value of such end customer contracts based on a combination of factors, including the value of end customer contracts made available to us by customers in past periods, the minimum value of end customer contracts that our customers are required to give us the opportunity to sell pursuant to the terms of their contracts with us, periodic internal business reviews of our expectations as to the value of end customer contracts that will be made available to us by customers, the value of end customer contracts included in the SPA and collaborative discussions with our customers assessing their expectations as to the value of service contracts that they will make available to us for sale. While the minimum value of end customer contracts that our customers are required to give us represents a portion of our estimated opportunity under management, a significant portion of the opportunity under management is estimated based on the other factors described above.
When estimating service revenue opportunity under management, we must, to a large degree, rely on the assumptions described above, which may prove incorrect. These assumptions are inherently subject to significant business and economic uncertainties and contingencies, many of which are beyond our control. Our estimates therefore may prove inaccurate, causing the actual value of end customer contracts delivered to us in a given twelve-month period to differ from our estimate of opportunity under management. These factors include:
| • | the extent to which customers deliver a greater or lesser value of end customer contracts than may be required or otherwise expected; |
| • | roll-overs of unsold service contract renewals from prior periods to the current period or future periods; |
| • | changes in the pricing or terms of service contracts offered by our customers; |
| • | increases or decreases in the end customer base of our customers; |
40
Table of Contents
| • | the extent to which the renewal rates we achieve on behalf of a customer early in an engagement affect the amount of opportunity that the customer makes available to us later in the engagement; |
| • | customer cancellations of their contracts with us due to acquisitions or otherwise; and |
| • | changes in our customers’ businesses, sales organizations, sales processes or priorities. |
In addition, opportunity under management reflects our estimate for a forward twelve-month period and should not be used to estimate our opportunity for any particular quarter within that period. The value of end customer contracts actually delivered during a twelve-month period should not be expected to occur in even quarterly increments due to seasonality and other factors impacting our customers and their end customers.
The actual value of qualified end customer contracts delivered to us by our customers affects the amount of revenue we can earn in a given period. Our revenue also depends upon our close rates and commissions. Our close rate is the percentage of our opportunity under management that we renew on behalf of our customers. Our commission rate is an agreed-upon percentage of the renewal value of end customer contracts that we sell on behalf of our customers.
Our close rate is impacted principally by our ability to successfully sell service contracts on behalf of our customers. Other factors impacting our close rate include: the manner in which our customers price their service contracts for sale to their end customers; the stage of life-cycle associated with the products and underlying technologies covered by the service contracts offered to the end customer; the extent to which our customers or their competitors introduce new products or underlying technologies; the nature, size and age of the service contracts; and the extent to which we have managed the renewals process for similar products and underlying technologies in the past.
In determining commission rates for an individual engagement, various factors, including our close rates, as described above, are evaluated. These factors include: historical, industry-specific and customer-specific renewal rates for similar service contracts; the magnitude of the opportunity under management in a particular engagement; the number of end customers associated with these opportunities; and the opportunity to receive additional performance commissions when we exceed certain renewal levels. We endeavor to set our commission rates at levels commensurate with these factors and other factors that may be relevant to a particular engagement. Accordingly, our commission rates vary, often significantly, from engagement to engagement. In addition, we sometimes agree to lower commission rates for engagements with significant opportunity under management.
Renewal Rates. Our ability to attract and retain new customers and add new engagements depends in part on the degree to which we improve renewal rates for our customers as compared to their historical renewal rates. In general, we calculate renewal rates for new customers or engagements by looking at the dollar value of end customer contracts delivered to us for renewal and the dollar value of the portion of those end customer contracts that were actually renewed. These renewals can occur over the course of several quarters. We then compare the renewal rates we generate to the renewal rates achieved over prior periods by the customer based on the data provided by the customer during the SPA.
To calculate the renewal rate for each customer, we take the value of the end customer contracts, including upsells, that were renewed and divide it by the value of contracts that were provided for renewal. The renewal rate can exceed 100% when an existing service contract is renewed for an amount greater than the original value of the contract. We calculate improvement in renewal rates for a given period by taking a simple average of the improvement in the renewal rate for each customer.
For example, for new engagements added in 2009, we generated renewal rates that increased by an average of over 15 percentage points over the renewal rates achieved by the customer based on the SPA data. This renewal rate increase is based on the value of end customer contracts delivered to us for renewal pursuant to such engagements during the first six months of 2010 and renewed in 2010.
41
Table of Contents
In calculating the historical renewal rates of customers, we rely on and cannot provide assurance as to the accuracy or completeness of the customer renewal data we receive during the SPA. In addition, changes in renewal rates may result from several external factors unrelated to our performance, including the nature of the contracts, the popularity of the products, and changing economic conditions, among others. To the extent that the actual data and information provided for the SPA by the customer is inaccurate or not representative of the contracts we actually receive for renewal in future periods, our calculation of the improvement in renewal rates may be inaccurate or not representative. While we believe the example provided above is representative of our renewal rate capabilities, changes in renewal rates have varied widely and will continue to vary widely from period to period and from customer to customer. We cannot assure you that similar improvements in renewal rates will occur in the future.
Number of Engagements. We track the number of engagements we have with our customers. We often have multiple engagements with a single customer, particularly where we manage the sales of service renewals relating to different product lines, technologies, types of contracts or geographies for the customer. When the set of renewals we manage on behalf of a customer is associated with a separate customer contract or a distinct product set, type of end customer contract or geography and therefore requires us to assign a dedicated service sales team to manage the renewals, we designate the set of renewals, and associated revenues and costs to us as a unique engagement. For example, we may have one engagement consisting of a dedicated service sales team selling maintenance contract renewals of a particular product for a customer in the United States and another engagement consisting of a dedicated sales team selling warranty contract renewals of a different product for the same customer in Europe. These would count as two engagements. We had approximately 50, 60 and 80 engagements as of December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively, and over 90 engagements as of September 30, 2010.
Transactions. Since our inception, we have managed over two million service renewal transactions. Our references to transactions in this prospectus include interactions with end customers that led to successful renewals and those that did not.
Factors Affecting our Performance
Sales Cycle. We sell our integrated solution to our customers through a sales organization. At the beginning of the sales process, our quota-carrying sales representatives contact prospective customers and educate them about our offerings. Educating prospective customers about the benefits of our solution can take time, as many of these prospects have not historically relied upon integrated solutions like ours for service revenue management, nor have they typically put out a formal request for proposal or otherwise made a decision to focus on this area. As part of the education process, we utilize our solutions design team to perform the SPA of our prospect’s service revenue. The SPA includes an analysis of best practices and benchmarks the prospect’s service revenue against industry peers. Through the SPA process, which typically takes several weeks, we are able to assess the characteristics and size of the prospect’s service revenue, identify potential areas of performance improvement and formulate our proposal for managing the prospect’s service revenue. The length of our sales cycle for a new customer, inclusive of the SPA process and measured from our first formal discussion with the customer until execution of a new customer contract, is typically longer than six months.
We generally contract with new customers to manage a specified portion of their service revenue opportunity, such as the opportunity associated with a particular product line or technology, contract type or geography. We negotiate the customized terms of our customer contracts, including commission rates, based on the output of the SPA, including the areas identified for improvement. Once we demonstrate success to a customer with respect to the opportunity under contract, we seek to expand the scope of our engagement to include other opportunities with the customer. For some customers, we manage all or substantially all of their service contract renewals.
42
Table of Contents
Implementation Cycle. After entering into an engagement with a new customer, and to a lesser extent after adding an engagement with an existing customer, we incur sales and marketing expenses related to the commissions owed to our sales personnel. The commissions are based on the estimated total contract value, a material portion of which is expensed upfront and the remaining portion of which is expensed over a period of eight to fourteen months, including commissions paid on multi-year contracts. We also make upfront investments in technology and personnel to support the engagement. These expenses are typically incurred one to three months before we begin generating sales and recognizing revenue. Accordingly, in a given quarter, an increase in new customers, and, to a lesser extent, an increase in engagements with existing customers, or a significant increase in the contract value associated with such new customers and engagements, will negatively impact our gross margin and operating margins until we begin to achieve anticipated sales levels associated with the new engagements.
Although we expect new customer engagements to contribute to our operating profitability over time, in the initial periods of a customer relationship, the near term impact on our profitability can be negative due to upfront costs we incur, the lower initial level of associated service sales team productivity and lack of mature data and technology integration with the customer. As a result, an increase in the mix of new customers as a percentage of total customers may initially have a negative impact on our operating results. Similarly, a decline in the ratio of new customers to total customers may positively impact our operating results. This is illustrated by our analysis of new customers signed in 2007, which generated a modest contribution margin (as defined below) of 1% for the 2007 fiscal year. However, for the nine months ended September 30, 2010, the same set of customers generated a contribution margin of 53%. The initial lower margin is attributable in large part to the fact that we incurred significant costs in 2007 to hire and train the service sales teams for the new customer engagements, in addition to paying commissions to our own sales representatives for signing the new customers, prior to generating meaningful revenues from these customer engagements. The improvement in contribution margin over time is due primarily to the ramping of service sales team productivity, the decrease or absence of additional sales representative commission payments, and, to a lesser extent, improvement in data accuracy through technology and automation of processes.
We define contribution margin for a period as the excess of the revenue recognized from the customer over the estimated expenses for the period associated with supporting the customer and managing the service contract renewals process for them, expressed as a percentage of associated revenue. The expenses allocated to the customer include personnel costs associated with the service sales teams who support that customer, such as salaries and benefits, allocated management overhead expenses based on a percentage of revenue and service sales commissions. These expenses exclude the allocation of costs associated with use of infrastructure, facilities and company-wide resources that are available to all service sales teams.
Although we believe the estimates and assumptions we used to estimate the expenses are reasonable, the estimated expenses and resulting contribution margin could vary significantly from the amounts disclosed above had we used different estimates and assumptions. Moreover, we cannot assure you that we will experience similar contribution margins from customers added in other years or in future periods. You should not rely on the estimated expenses or contribution margin as being indicative of our future performance. Because of our growing customer base, we expect that there will be times when large numbers of our customers are in the initial phases of their relationship with us or have a material expansion of their existing engagements with us. In these scenarios, our operating results will be negatively impacted over the near term.
Contract Terms. Under our pay-for-performance model, we earn commissions based on the value of service contracts we sell on behalf of our customers. In some cases, we earn additional performance-based commissions for exceeding pre-determined service renewal targets. These commissions, including performance-based commissions, represent substantially all of our revenue.
Since 2009, our new customer contracts have typically had a term of 36 months, although we sometimes have contract terms of up to 60 months. Older customer contracts typically have a term of 12 months. Our contracts generally require our customers to deliver a minimum value of qualifying service revenue contracts for
43
Table of Contents
us to renew on their behalf during a specified period. To the extent that our customers do not meet their minimum contractual commitments over a specified period, they may be subject to fees for the shortfall. Our customer contracts are cancelable on relatively short notice, subject in most cases to the payment of an early termination fee by the customer. The amount of this fee is based on the length of the remaining term and value of the contract.
We typically invoice our customers on a monthly basis based on commissions we earn during the prior month, and with respect to performance-based commissions, on a quarterly basis based on our overall performance during the prior quarter. Amounts invoiced to our customers are recognized as revenue in the period in which our services are performed or, in the case of performance commissions, when the performance condition is determinable. Because the invoicing for our services generally coincides with or immediately follows the sale of service contracts on behalf of our customers, we do not generate or report a significant deferred revenue balance. However, the combination of minimum contractual commitments, combined with our success in generating improved renewal rates for our customers, and our customers’ historical renewal rates, provides us with revenue visibility. In addition, the performance improvement potential identified by our SPA process provides us with revenue visibility for new customers.
M&A Activity. Our customers in the technology sector participate in an active environment for mergers and acquisitions. Large technology companies have maintained active acquisition programs to increase the breadth and depth of their product and service offerings and small and mid-sized companies have combined to better compete with large technology companies. A number of our customers have merged, purchased other companies or been acquired by other companies. We expect merger and acquisition activity to continue to occur in the future.
The impact of these transactions on our business can vary. Acquisitions of other companies by our customers can provide us with the opportunity to pursue additional business to the extent the acquired company is not already one of our customers. Similarly, when a customer is acquired, we may be able to use our relationship with the acquired company to build a relationship with the acquirer. In some cases we have been able to maintain our relationship with an acquired customer even where the acquiring company handles its other service contract renewals through internal resources. In other cases, however, acquirers have elected to terminate or not renew our contract with the acquired company. For example, Oracle terminated our contracts with Sun Microsystems effective as of September 30, 2010, as discussed in more detail under “—Results of Operations—Nine Months Ended September 30, 2010 and 2009—Net Revenue,” and had previously terminated our contract with another customer, BEA Systems, in April 2008 .
Economic Conditions. An improving economic outlook generally has a positive, but mixed, impact on our business. As with most businesses, improved economic conditions can lead to increased end customer demand and sales. In particular, within the technology sector, we believe that the recent economic downturn led many companies to cut their expenses by choosing to let their existing maintenance, support and subscription agreements lapse. An improving economy may have the converse effect.
However, an improving economy may also cause companies to purchase new hardware, software and other technology products, which we generally do not sell on behalf of our customers, instead of purchasing maintenance, support and subscription services for existing products. To the extent this occurs, it would have a negative impact on our opportunities in the near term that would partially offset the benefits of an improving economy.
Adoption of “Software-as-a-Service” Solutions. Within the software industry, there is a growing trend toward providing software to customers using a software-as-a-service model. Under this model, software-as-a-service companies provide access to software applications to customers on a remote basis, and provide their customers with a subscription to use the software, rather than licensing software to their customers. Software-as-a-service companies face a distinct set of challenges with respect to customer renewals, given the potentially
44
Table of Contents
lower switching costs for customers utilizing their solutions, and are more reliant on renewals for their long-term revenues than traditional software companies. Given the strategic importance of renewals to their model, software-as-a-service companies may be less inclined than traditional software companies to rely on third-party solutions such as ours to manage the sale of renewals of subscription contracts. We have tailored our solution to address the needs of software-as-a-service companies in this area and expect to continue to develop and enhance our solution as this market grows.
Basis of Presentation
Net Revenue
Substantially all of our net revenue is attributable to commissions we earn from the sale of renewals of maintenance, support and subscription agreements on behalf of our customers. We generally invoice our customers for our services in arrears on a monthly basis for sales commissions, and on a quarterly basis for certain performance sales commissions; accordingly, we typically have no deferred revenue related to these services. We do not set the price, terms or scope of services in the service contracts with end customers and do not have any obligations related to the underlying service contracts between our customers and their end customers.
For a limited number of historical engagements, our services included the sale of service contracts as well as the related invoicing and cash collections on behalf of customers. Under these arrangements, commissions are considered earned when we receive cash payment from end customers. As of September 30, 2010, we no longer had any such customer engagements.
We also earn revenue from the sale of subscriptions to our cloud based applications. To date, subscription revenue has been insignificant. Subscription fees are accounted for separately from commissions and they are billed on either a monthly or quarterly basis in advance and revenue is recognized ratably over the related subscription term.
We have generated a significant portion of our revenue from a limited number of customers. For the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008, 2009 and for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, our top ten customers in each period accounted for 76%, 72%, 64%, 66% and 57% of our net revenue, respectively. In addition, during the same periods, Sun Microsystems accounted for 22%, 23%, 24%, 24% and 17% of our net revenue, respectively. As discussed above, Oracle terminated our contracts with Sun Microsystems effective as of September 30, 2010. We will not recognize additional revenue from Sun Microsystems in future periods other than fees associated with the transition of certain end user contracts to Oracle, the amount and timing of which has not yet been finalized.
Our business is geographically diversified. For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, 67% of our net revenue was earned in North America and Latin America (“NALA”), 28% in Europe, Middle East and Africa (“EMEA”) and 5% in Asia Pacific Japan (“APJ”). Net revenue for a particular geography generally reflects commissions earned from sales of service contracts managed from our sales center in that geography. Predominantly all of the service contracts sold and managed by our sales centers relate to end customers located in the same geography.
Cost of Revenue and Gross Profit
Our cost of revenue consists primarily of compensation, which includes salary, bonuses, benefits and stock-based compensation related to our service sales teams. Costs of revenue also includes allocated overhead costs for facilities, information technology and depreciation, including amortization of internal-use software associated with our service revenue technology platform and cloud applications. Allocated costs for facilities consist of rent, maintenance and compensation of personnel in our facilities departments. Our allocated costs for information technology include costs associated with a third-party data center where we maintain our data servers,
45
Table of Contents
compensation of our information technology personnel and the cost of support and maintenance contracts associated with computer hardware and software. Our overhead costs are allocated to all departments based on headcount. To the extent our customer base or opportunity under management expands, we may need to hire additional service sales personnel and invest in infrastructure to support such growth. We currently expect that our cost of revenue will fluctuate significantly and may increase on an absolute basis and as a percentage of revenue in the near term, including for the reasons discussed above under “—Factors Affecting Our Performance—Implementation Cycle.”
Operating Expenses
Sales and Marketing. Sales and marketing expenses are the largest component of our operating expenses and consist primarily of compensation and sales commissions for our sales and marketing staff, allocated expenses and marketing programs and events. We sell our solutions through our global sales organization, which is organized across three geographic regions: NALA, EMEA and APJ. Our commission plans provide that payment of commissions to our sales representatives is contingent on their continued employment and we recognize expense over a period that is generally between eight and fourteen months following the execution of the applicable contract. We currently expect sales and marketing expense to increase on an absolute basis and as a percentage of revenue in the near term based on commissions earned on customer contracts entered into in prior periods, as well as continued investments in sales and marketing personnel and programs as we expand our business domestically and internationally.
Research and Development. Research and development expenses consist primarily of compensation, allocated costs and the cost of third-party service providers. We focus our research and development efforts on developing new products and adding new features to our existing technology platform. In addition, we capitalize certain expenditures related to the development and enhancement of internal-use software related to our technology platform, as discussed in more detail under “—Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates—Capitalized Internal-Use Software” below. We expect research and development spending, and the related expenses and capitalized costs, to increase on an absolute basis as a percentage of revenue in the near term as we continue to invest in our technology platform and cloud applications.
General and Administrative. General and administrative expenses consist primarily of compensation for our executive, human resources, finance and legal functions, and related expenses for professional fees for accounting, tax and legal services, as well as allocated expenses. We expect that our general and administrative expenses will increase on an absolute basis and as a percentage of revenue in the near term as our operations continue to expand and as a result of incremental costs associated with being a publicly-traded company.
Amortization of Intangible Assets. Our intangible assets consist of goodwill, customer contracts and related relationships, trademarks and trade names and a non-competition agreement. Except for goodwill, which is not amortized, all of our intangible assets were fully amortized as of March 31, 2009.
Other Income (Expense)
Other income (expense) consists primarily of interest expense associated with borrowings under our credit facility and foreign exchange transaction gains and losses, partially offset by interest income, which has been insignificant in recent periods.
Income Tax (Benefit) Provision
Since inception through December 31, 2007 we conducted our U.S. operations through ServiceSource International, LLC (“LLC”), a pass-through entity for tax purposes that files its income tax return as a partnership for federal and state income tax purposes. The LLC is not subject to income taxes other than annual California limited liability company fees based on revenue. The members of the LLC, not the LLC itself, are
46
Table of Contents
subject to income taxes on their allocated share of the LLC’s earnings. The LLC is required to pay cash distributions to the members to fund members’ tax obligations in respect of the members’ allocated share of the LLC’s net income, if applicable. Effective January 1, 2008, the LLC transferred a significant portion of its U.S. operations to a wholly-owned U.S. taxable subsidiary. We also have several subsidiaries formed in foreign jurisdictions, which are subject to local income taxes.
For a description of our accounting practices relating to income taxes, see “—Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates—Income Taxes” below.
Results of Operations
The table below sets forth our consolidated results of operations for the periods presented. The period-to-period comparison of financial results presented below is not necessarily indicative of financial results to be achieved in future periods, and the results for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 are not necessarily indicative of results to be expected for the full year or for any other period.
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Consolidated statement of operations data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue |
$ | 75,189 | $ | 100,280 | $ | 110,676 | $ | 76,889 | $ | 108,468 | ||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
39,224 | 56,965 | 58,877 | 41,577 | 63,841 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
35,965 | 43,315 | 51,799 | 35,312 | 44,627 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
13,119 | 20,486 | 23,182 | 16,802 | 25,640 | |||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
— | 1,160 | 2,054 | 1,647 | 3,927 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
10,475 | 10,571 | 13,777 | 10,214 | 13,806 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
912 | 857 | 68 | 68 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
24,506 | 33,074 | 39,081 | 28,731 | 43,373 | |||||||||||||||
| Income from operations |
11,459 | 10,241 | 12,718 | 6,581 | 1,254 | |||||||||||||||
| Other expense, net |
(2,423 | ) | (4,267 | ) | (477 | ) | (307 | ) | (1,142 | ) | ||||||||||
| Income (loss) before provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
9,036 | 5,974 | 12,241 | 6,274 | 112 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax (benefit) provision |
(632 | ) | 1,153 | 1,866 | 730 | 1,368 | ||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 9,668 | $ | 4,821 | $ | 10,375 | $ | 5,544 | $ | (1,256 | ) | |||||||||
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Includes stock-based compensation of: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 1,096 | $ | 1,271 | $ | 914 | $ | 672 | $ | 843 | ||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
1,100 | 1,570 | 2,340 | 1,706 | 2,214 | |||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
— | — | 541 | 399 | 598 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
1,680 | 2,608 | 2,265 | 1,663 | 2,362 | |||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 3,876 | $ | 5,449 | $ | 6,060 | $ | 4,440 | $ | 6,017 | ||||||||||
47
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth our operating results as a percentage of net revenue:
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (as % of net revenue) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue |
100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
52 | % | 57 | % | 53 | % | 54 | % | 59 | % | ||||||||||
| Gross profit |
48 | % | 43 | % | 47 | % | 46 | % | 41 | % | ||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
17 | % | 20 | % | 21 | % | 22 | % | 24 | % | ||||||||||
| Research and development |
0 | % | 1 | % | 2 | % | 2 | % | 4 | % | ||||||||||
| General and administrative |
14 | % | 11 | % | 12 | % | 13 | % | 12 | % | ||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
1 | % | 1 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
33 | % | 33 | % | 35 | % | 37 | % | 40 | % | ||||||||||
| Income from operations |
15 | % | 10 | % | 11 | % | 9 | % | 1 | % | ||||||||||
Nine Months Ended September 30, 2010 and 2009
Net Revenue
| Nine Months Ended September 30, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue by geography: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NALA |
$ | 54,594 | 71 | % | $ | 72,776 | 67 | % | 18,182 | 33 | % | |||||||||||||
| EMEA |
21,490 | 28 | % | 30,599 | 28 | % | 9,109 | 42 | % | |||||||||||||||
| APJ |
805 | 1 | % | 5,093 | 5 | % | 4,288 | 533 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total net revenue |
$ | 76,889 | 100 | % | $ | 108,468 | 100 | % | $ | 31,579 | 41 | % | ||||||||||||
The 41% increase in net revenue for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 reflects an increase in the number and value of service contracts sold on behalf of our customers. The actual value of qualified end customer contracts available for us to sell in 2010 was greater than in 2009, resulting from new customers, expanded engagements with existing customers and the ramp of customers from prior periods. We increased our number of engagements from approximately 80 as of December 31, 2009 to over 90 as of September 30, 2010. Our largest customer in both the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010 was Sun Microsystems, which represented $18.7 million and $17.9 million of our net revenue, respectively. Revenue from Sun Microsystems decreased following its acquisition by Oracle in the first quarter of 2010. Net revenue for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 included $3.8 million in fees resulting from the termination of the Sun Microsystems contracts. When expressed as a percentage of net revenue, Sun Microsystems decreased from 24% for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 to 17% for the nine months ended September 30, 2010, which reflects the offset of revenue growth from both new and existing engagements. International revenue increased 60% during the nine months ended September 30, 2010 as compared to the same period in 2009 with this growth supported by the addition of new service sales centers in APJ and EMEA.
48
Table of Contents
Cost of Revenue and Gross Profit
| Nine Months Ended September 30, |
Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 41,577 | $ | 63,841 | $ | 22,264 | 54 | % | ||||||||
| Includes stock-based compensation of: |
672 | 843 | 171 | 25 | % | |||||||||||
| Gross profit |
35,312 | 44,627 | 9,315 | 26 | % | |||||||||||
| Gross profit percentage |
46 | % | 41 | % | (5 | )% | ||||||||||
The 54% increase in our cost of revenue in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 reflected an increase in the number of service sales personnel, primarily in NALA and APJ, resulting in a $16.6 million increase in compensation, a $2.9 million increase in allocated costs for facilities (due to opening of new offices in EMEA and APJ) information technology and depreciation and a $0.7 million increase in outside fees primarily due to the recruitment of service sales personnel. Gross profit percentage decreased from 46% in the nine months ended September 30, 2009 to 41% for the nine months ended September 30, 2010. The decrease in gross profit percentage reflects additional compensation associated with staffing new and expanded engagements which typically have minimal revenue during the initial start-up phase and facility costs associated with the opening of two new international sales centers, partially offset by the favorable gross margin impact resulting from the Sun Microsystems termination fees.
Operating Expenses
| Nine Months Ended September 30, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
$ | 16,802 | 22 | % | $ | 25,640 | 24 | % | $ | 8,838 | 53 | % | ||||||||||||
| Research and development |
1,647 | 2 | % | 3,927 | 4 | % | 2,280 | 138 | % | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
10,214 | 13 | % | 13,806 | 13 | % | 3,592 | 35 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
68 | 0 | % | — | 0 | % | (68 | ) | (100 | )% | ||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
$ | 28,731 | 37 | % | $ | 43,373 | 40 | % | $ | 14,642 | 51 | % | ||||||||||||
| Includes stock-based compensation of: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
$ | 1,706 | $ | 2,214 | $ | 508 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
399 | 598 | 199 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
1,663 | 2,362 | 699 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 3,768 | $ | 5,174 | $ | 1,406 | ||||||||||||||||||
Sales and marketing expenses
The 53% increase in sales and marketing expenses for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 reflected an increase in the number of sales and marketing personnel, primarily in NALA and APJ, and higher sales commissions for new multi-year customer engagements, resulting in a $6.2 million increase in compensation, a $0.7 million increase in travel expenses and a $0.6 million increase in allocated costs. The increase in headcount reflected our investment in sales and marketing resources aimed at expanding our customer base.
49
Table of Contents
Research and development expenses
The 138% increase in research and development expense in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 reflected an increase in the number of research and development personnel in NALA, resulting in a $1.2 million increase in compensation, a $0.1 million increase in consulting services related to contract research and development services and a $0.2 million increase in allocated costs. The increase is a result of our continued investment in the development of additional cloud based applications to enable greater operational efficiencies and enhanced functionality for our customers.
General and administrative expenses
The 35% increase in general and administrative expense in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 reflected a $1.9 million increase in compensation due to an increase in headcount in the general and administrative function, primarily in NALA, a $0.4 million lease termination fee and a $0.2 million increase in professional fees.
Amortization of intangible assets
The decrease in amortization of intangible assets is a result of the related assets being fully amortized as of March 31, 2009.
Other Expense, Net
| Nine Months Ended September 30, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of Net Revenue |
Amount | % of Net Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other expense, net |
$ | 307 | 0 | % | $ | 1,142 | 1 | % | $ | 835 | 272 | % | ||||||||||||
The increase in other expense in the nine months ended September 30, 2010 primarily resulted from a $0.7 million increase in losses on foreign exchange transactions due in part to a decline in the value of the U.S. dollar relative to international currencies, most notably the Canadian dollar. Also contributing to the year-over-year rise in other expense was a $0.1 million increase in interest expense on our term loan as a result of higher interest rates and a $0.1 million increase in interest expense related to our capital lease obligations.
Income Tax Provision
| Nine Months Ended September 30, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2010 | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision |
$ | 730 | $ | 1,368 | $ | 638 | 87 | % | ||||||||
Our effective tax rate for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 was 12% due to a portion of our income allocated to the non-taxable limited liability parent company and a taxable subsidiary subject to a lower tax rate. Because our income tax provision exceeded our consolidated pre-tax income for the nine months ended September 30, 2010, the effective tax rate for such period is not comparable to the prior period. For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, we had taxable income at our taxable subsidiaries and losses incurred by the non-taxable limited liability parent company that do not result in a tax benefit for us.
50
Table of Contents
Years Ended December 31, 2009 and 2008
Net Revenue
| Years Ended December 31, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue by geography: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NALA |
$ | 70,177 | 70 | % | $ | 77,283 | 70 | % | $ | 7,106 | 10 | % | ||||||||||||
| EMEA |
30,103 | 30 | % | 31,995 | 29 | % | 1,892 | 6 | % | |||||||||||||||
| APJ |
— | 0 | % | 1,398 | 1 | % | 1,398 | * | ||||||||||||||||
| Total net revenue |
$ | 100,280 | 100 | % | $ | 110,676 | 100 | % | $ | 10,396 | 10 | % | ||||||||||||
| * | Not meaningful. |
The 10% increase in net revenue in 2009 reflects an increase in the number and value of service contracts sold on behalf of our customers. The actual value of qualified end customer contracts available for us to sell in 2009 was greater than in 2008, resulting from new customers and expanded engagements with existing customers. We increased our number of engagements from approximately 60 as of December 31, 2008 to approximately 80 as of December 31, 2009. In 2009, we opened a sales service center in APJ which contributed to our international growth.
Cost of Revenue and Gross Profit
| Years Ended December 31, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 56,965 | $ | 58,877 | $ | 1,912 | 3 | % | ||||||||
| Includes stock-based compensation of: |
1,271 | 914 | (357 | ) | (28) | % | ||||||||||
| Gross profit |
43,315 | 51,799 | 8,484 | 20 | % | |||||||||||
| Gross profit percentage |
43 | % | 47 | % | 4 | % | ||||||||||
The 3% increase in our cost of revenue in 2009 reflected an increase in the number of service sales personnel, resulting in a $1.9 million increase in compensation across all geographic segments and a $0.7 million increase in allocated costs. The increase was partially offset by a $0.4 million decrease in start-up costs and a $0.3 million decrease in travel expenses associated with a new sales center opened in 2008. The higher gross profit percentage of 47% in 2009 as compared with the 43% in 2008 resulted from a shift of our service sales personnel to sales service centers in Denver and Nashville with lower costs relative to San Francisco.
51
Table of Contents
Operating Expenses
| Years Ended December 31, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
$ | 20,486 | 20 | % | $ | 23,182 | 21 | % | $ | 2,696 | 13 | % | ||||||||||||
| Research and development |
1,160 | 1 | % | 2,054 | 2 | % | 894 | 77 | % | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
10,571 | 11 | % | 13,777 | 12 | % | 3,206 | 30 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
857 | 1 | % | 68 | 0 | % | (789 | ) | (92 | )% | ||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
$ | 33,074 | 33 | % | $ | 39,081 | 35 | % | $ | 6,007 | 18 | % | ||||||||||||
|
Includes stock-based compensation of: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
$ | 1,570 | $ | 2,340 | $ | 770 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
— | 541 | 541 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
2,608 | 2,265 | (343 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 4,178 | $ | 5,146 | $ | 968 | ||||||||||||||||||
Sales and marketing expenses
The 13% increase in sales and marketing expenses in 2009 reflected an increase in the number of sales and marketing personnel, resulting in a $0.9 million increase in compensation, a $0.3 million increase in allocated costs, and a $0.1 million increase in travel expenses associated with our global expansion, particularly in APJ.
Research and development expenses
The 77% increase in research and development expenses in 2009 reflected an increase in the number of research and development personnel in NALA, resulting in a $0.3 million increase in compensation, a $0.3 million increase in allocated cost and a $0.2 million increase in travel expenses.
General and administrative expenses
The 30% increase in general and administrative expenses in 2009 reflected an increase in headcount in the general and administrative functions, resulting in a $3.5 million increase in compensation and a $0.2 million increase in travel expenses, partially offset by a $0.5 million decrease in bad debt expense.
Amortization of intangible assets
The decrease in amortization of intangible assets resulted from the related assets being fully amortized as of March 31, 2009.
Other Expense, Net
| Years Ended December 31, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of Net Revenue |
Amount | % of Net Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other expense, net |
$ | 4,267 | 4 | % | $ | 477 | 0 | % | $ | (3,790 | ) | (89 | )% | |||||||||||
The decrease in other expense in 2009 primarily resulted from a $2.1 million decrease in losses on foreign currency transactions, as well as a $1.1 million decrease in interest expense due to lower average balances
52
Table of Contents
outstanding under our term loan. Other expense in 2008 also included $0.6 million relating to a loss on extinguishment of debt recorded in connection with refinancing our long-term debt.
Income Tax Provision
| Years Ended December 31, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Income tax provision |
$ | 1,153 | $ | 1,866 | $ | 713 | 62 | % | ||||||||
Our effective tax rate for 2008 and 2009 was 19% and 15%, respectively. In 2009, our effective tax rate decreased as a result of higher income related to the non-taxable LLC which is not subject to taxes.
Years Ended December 31, 2008 and 2007
Net Revenue
| Years Ended December, 31 | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue by geography: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| NALA |
$ | 60,314 | 80 | % | $ | 70,177 | 70 | % | $ | 9,863 | 16 | % | ||||||||||||
| EMEA |
14,875 | 20 | % | 30,103 | 30 | % | 15,228 | 102 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Total net revenue |
$ | 75,189 | 100 | % | $ | 100,280 | 100 | % | $ | 25,091 | 33 | % | ||||||||||||
The 33% increase in net revenue in 2008 reflects an increase in the number and value of service contracts sold on behalf of our customers, as well as higher performance commissions as a result of our performance on larger contracts. The value of service contracts available for us to sell in 2008 was greater than in 2007, which resulted from new customers and expanded engagements with existing customers, partially offset by lower commission rates upon contract renewal in June 2008 by our then-largest customer. We experienced our largest growth in EMEA, reflecting expansion of our global customer base.
Cost of Revenue and Gross Profit
| Years Ended December 31, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 39,224 | $ | 56,965 | $ | 17,741 | 45 | % | ||||||||
| Includes stock-based compensation of: |
1,096 | 1,271 | 175 | 16 | % | |||||||||||
| Gross profit |
35,965 | 43,315 | 7,350 | 20 | % | |||||||||||
| Gross profit percentage |
48 | % | 43 | % | (5 | )% | ||||||||||
The 45% increase in our cost of revenue in 2008 reflected an increase in the number of service sales personnel, resulting in an $12.3 million increase in compensation and sales staffing costs related to the opening of our Denver service sales office in NALA and a $3.5 million increase in allocated costs. The lower gross profit percentage in 2008 of 43% as compared to the 48% achieved in 2007 reflected lower commission rates with our then-largest customer upon contract renewal in June 2008 and higher start-up costs associated with new engagements in 2008 for which little or no revenue was earned during the start-up phase.
53
Table of Contents
Operating Expenses
| Years Ended December 31, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
$ | 13,119 | 17 | % | $ | 20,486 | 20 | % | $ | 7,367 | 56 | % | ||||||||||||
| Research and development |
— | 0 | % | 1,160 | 1 | % | 1,160 | * | ||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
10,475 | 14 | % | 10,571 | 11 | % | 96 | 1 | % | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
912 | 1 | % | 857 | 1 | % | (55 | ) | (6 | )% | ||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
$ | 24,506 | 33 | % | $ | 33,074 | 33 | % | $ | 8,568 | 35 | % | ||||||||||||
| Includes stock-based compensation of: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
$ | 1,100 | $ | 1,570 | $ | 470 | ||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
1,680 | 2,608 | 928 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 2,780 | $ | 4,178 | $ | 1,398 | ||||||||||||||||||
| * | Not meaningful. |
Sales and marketing expenses
The 56% increase in sales and marketing expenses in 2008 is due to increased sales commissions earned from new customer engagements and an increase in the number of sales and marketing personnel, primarily in NALA, resulting in a $6.4 million increase in compensation, a $0.9 million increase in allocated costs and a $0.2 million increase in travel expenses, partially offset by a $0.1 million decrease in professional fees.
Research and development expenses
In 2008, we hired engineering and other personnel in NALA to expand the development of our technology which today is our service revenue performance management suite of applications. These costs consisted primarily of $1.1 million in compensation and $0.1 million in allocated costs.
General and administrative expenses
The 1% increase in general and administrative expenses in 2008 reflected a $3.1 million increase in compensation, primarily in NALA, a $0.4 million increase in local taxes, a $0.2 million increase in bad debt expense, partially offset by a reduction in allocated costs.
Amortization of intangible assets
The decrease in amortization of intangible assets in 2008 resulted from certain assets having been fully amortized in early 2008.
Other Expense, Net
| Years Ended December 31, | Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
Amount | % of
Net Revenue |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Other expense, net |
$ | 2,423 | 3 | % | $ | 4,267 | 4 | % | $ | 1,844 | 76 | % | ||||||||||||
The 76% increase in other expense in 2008 primarily resulted from foreign currency transaction losses of $0.7 million and a $0.6 million loss on the extinguishment of debt.
54
Table of Contents
Income Tax (Benefit) Provision
| Years Ended December 31, |
Change | % Change |
||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||
| Amount | Amount | |||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||
| Income tax (benefit) provision |
$ | (632 | ) | $ | 1,153 | $ | 1,785 | * | ||||||||
| * | Not meaningful |
Our effective tax rate for 2007 and 2008 was (7)% and 19%, respectively. In 2007, the income tax benefit resulted from the release of our valuation allowance against net operating loss carryforwards in a foreign subsidiary. In 2008, our effective tax rate increased from 2007 as a result of higher taxable income from the transfer of certain U.S. operations from our non-taxable LLC to our U.S. taxable subsidiary, partially offset by a one-time income tax benefit of $0.8 million on the date of the transfer.
Quarterly Results of Operations
The following table sets forth our unaudited quarterly consolidated statements of operations during each of the quarters in the year ended December 31, 2009 and in the nine months ended September 30, 2010. In management’s opinion, the data below has been prepared on the same basis as the audited consolidated financial statements included elsewhere in this prospectus, and reflects all recurring adjustments necessary for the fair statement of this data. The period-to-period comparison of financial results is not necessarily indicative of future results and should be read in conjunction with our audited annual financial statements and the related notes included elsewhere in this prospectus:
| Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mar. 31, 2009 |
June 30, 2009 |
Sept. 30, 2009 |
Dec 31, 2009 |
Mar. 31, 2010 |
June 30, 2010 |
Sept. 30, 2010 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue |
$ | 22,209 | $ | 27,472 | $ | 27,208 | $ | 33,787 | $ | 32,176 | $ | 37,976 | $ | 38,316 | ||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
12,250 | 13,940 | 15,387 | 17,300 | 20,771 | 21,175 | 21,895 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
9,959 | 13,532 | 11,821 | 16,487 | 11,405 | 16,801 | 16,421 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
5,652 | 5,247 | 5,903 | 6,380 | 7,604 | 8,340 | 9,696 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
621 | 584 | 442 | 407 | 1,018 | 1,490 | 1,419 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
3,713 | 3,211 | 3,290 | 3,563 | 3,970 | 4,392 | 5,444 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
68 | — | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
10,054 | 9,042 | 9,635 | 10,350 | 12,592 | 14,222 | 16,559 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(95 | ) | 4,490 | 2,186 | 6,137 | (1,187 | ) | 2,579 | (138 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense), net |
(667 | ) | 338 | 22 | (170 | ) | (406 | ) | (136 | ) | (600 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) before provision for (benefit from) for income taxes |
(762 | ) | 4,828 | 2,208 | 5,967 | (1,593 | ) | 2,443 | (738 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Income tax (benefit) provision |
(146 | ) | 924 | (48 | ) | 1,136 | 177 | 926 | 265 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | (616 | ) | $ | 3,904 | $ | 2,256 | $ | 4,831 | $ | (1,770 | ) | $ | 1,517 | $ | (1,003 | ) | |||||||||||
|
Includes stock-based compensation of: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 219 | $ | 222 | $ | 231 | $ | 242 | $ | 274 | $ | 299 | $ | 270 | ||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
490 | 599 | 617 | 634 | 703 | 742 | 769 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
131 | 130 | 138 | 143 | 149 | 144 | 305 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
549 | 542 | 572 | 601 | 845 | 733 | 784 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 1,389 | $ | 1,493 | $ | 1,558 | $ | 1,620 | $ | 1,971 | $ | 1,918 | $ | 2,128 | ||||||||||||||
55
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth our unaudited quarterly consolidated statements of operations as a percentage of revenue:
| Three Months Ended | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Mar. 31, 2009 |
June 30, 2009 |
Sept. 30, 2009 |
Dec. 31 2009 |
Mar. 31, 2010 |
June 30, 2010 |
Sept. 30, 2010 |
||||||||||||||||||||||
| (as % of net revenue) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue |
100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
55 | % | 51 | % | 57 | % | 51 | % | 65 | % | 56 | % | 57 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
45 | % | 49 | % | 43 | % | 49 | % | 35 | % | 44 | % | 43 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
25 | % | 19 | % | 22 | % | 19 | % | 24 | % | 22 | % | 25 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
3 | % | 2 | % | 2 | % | 1 | % | 3 | % | 4 | % | 4 | % | ||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
17 | % | 12 | % | 12 | % | 11 | % | 12 | % | 12 | % | 14 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | 0 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
45 | % | 33 | % | 35 | % | 31 | % | 39 | % | 37 | % | 43 | % | ||||||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(0 | )% | 16 | % | 8 | % | 18 | % | (4 | )% | 7 | % | (0 | )% | ||||||||||||||
We have generally experienced growth in quarterly revenue resulting from an increase in new engagements with new and existing customers. Quarterly revenue is directly correlated with the value of service contracts provided to us by our customers for a given quarterly period. Many of our customers operate on a calendar year basis and, because of the seasonal nature of their revenue and the propensity for many of their end customers to make IT and other technology purchases and renewals during the fourth quarter, have a greater proportion of contract renewals in the fourth quarter as compared to the first three quarters of the year. As a result, revenue earned in our fourth quarter has historically represented a larger portion of our annual revenue as compared to the other three quarters of the year and has typically exceeded revenue in the first quarter of the following year. Revenue in the fourth quarter of 2009 represented 30% of our annual revenue. In addition, our third quarter revenue is affected by the slowed economic activity in the summer, particularly in Europe.
Our quarterly gross profit percentage in 2009 and the first three quarters of 2010 has varied from 35% to 49% and is impacted by a number of factors, including: the hiring of service sales personnel to support new engagements ahead of recognizing revenue from those engagements, the number and size of engagements in start-up phase, during which we earn minimal revenue, and the opening of new facilities in Liverpool and Kuala Lumpur. In addition, our gross profit percentage is impacted by the seasonality of our revenue, as discussed above.
Our operating expenses have increased in each of the past several quarters and reflect increased expenses associated with hiring additional sales and marketing personnel to support our global expansion, sales commission expense related to multi-year customer contracts, increased spending to hire research and development personnel related to the development of cloud applications, and increased costs for facilities, information technology and administrative functions to support this growth. We experienced a net loss in the first quarters of 2009 and 2010, and we currently expect that our cost of revenue and operating expenses will fluctuate from quarter to quarter and may increase on an absolute basis and as a percentage of revenue in future periods.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
As of September 30, 2010, our principal sources of liquidity were our cash of $23.2 million and $13.4 million available under our revolving credit facility. Our primary operating cash requirements include the payment of compensation and related costs, working capital requirements related to advances and accrued payables to customers, as well as costs for our facilities and information technology infrastructure. Historically, we have financed our operations principally from cash provided by our operating activities and to a lesser extent from borrowings under our credit facility.
56
Table of Contents
In April 2008, we entered into a five year credit facility with various financial institutions. The credit facility initially provided for a $20.0 million term loan and a $25.0 million revolving credit facility, which includes letters of credit in a face amount up to $7.5 million. The proceeds from the term loan were used primarily to fund tax distributions to our equityholders as required under our limited liability company agreement and the remaining proceeds were used for general corporate purposes. Borrowing under the revolving credit facility is subject to limitations imposed by collateral agreements and certain other conditions in the credit facility. The credit facility expires in April 2013 and is secured by substantially all of our assets. Availability under the revolving credit facility is subject to certain limitations related to our consolidated revenues and bank reserves, as defined in the agreement.
In March 2010, we obtained a waiver from the requirement to make additional principal payments in 2010 based on 2009 excess cash flow levels as defined in the credit facility. The credit facility was amended in April 2010 to, among other things, reduce the commitment amount of the revolving credit facility to $15.0 million and to change the borrowing base calculation. In December 2010, the credit facility was amended to reduce the maximum amount available for borrowing under the revolving credit facility from $15.0 million to $7.5 million, subject to certain limitations related to our consolidated revenues and bank reserves, and to ease a financial covenant applicable as of December 31, 2010. We also amended our fee arrangement with the lenders such that any termination of or prepayment in full of the obligations under the credit facility on or prior to December 31, 2011, would result in us being subject to a prepayment premium based on the sum of the maximum revolver amount, as defined in the agreement, and the then-outstanding principal balance on the term loan. In January 2011, the credit facility was amended to (i) increase the maximum commitment amount under the revolving credit facility from $7.5 million to $12.5 million, (ii) eliminate the fixed charge coverage ratio test for the twelve month period ending March 31, 2011 only, (iii) require the Company to maintain a minimum liquidity level of $10 million based on unrestricted cash balances held in the U.S. and available borrowings under the revolving credit facility, as defined therein, from and after May 15, 2011, and (iv) allow for the planned conversion to a taxable corporation, initial public offering of the Company’s stock and other specified transactions related to us.
The credit facility also has various restrictive financial covenants, which include maintaining a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio, a maximum consolidated leverage ratio and restrictions, subject to certain exceptions, under which we can make distributions to our equityholders. Distributions to fund tax obligations of our equityholders are permitted so long as there are no events of default, including compliance with financial covenants, immediately prior to or after giving effect to any such distribution. Distributions other than those to fund our equityholders’ tax obligations are, among other things, subject to us achieving specified levels of earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization or maintaining minimum levels of cash as defined in the credit facility.
We intend to use a portion of the net proceeds we receive from this offering to repay the loan balances outstanding under the credit facility but leave the revolving credit facility in place. As of September 30, 2010, we had $15.8 million outstanding under our term loan, no balance was outstanding under the revolving credit facility, $13.4 million was available for borrowing under the revolving credit facility and we were in compliance with all covenants. Additionally, as of September 30, 2010 we had a $1.6 million letter of credit outstanding relating to our office space at our San Francisco headquarters.
We believe our existing cash, cash flows from operating activities, our currently available credit facility and proceeds from this offering will be sufficient to meet our working capital and capital expenditure needs for at least the next eighteen months. Continued availability of borrowings under our current or any future credit facilities will be dependent upon our compliance with the applicable financial covenants and other contractual terms under such facilities. Our future capital requirements will depend on many factors, including revenue growth, costs incurred to support new customers and new engagements from existing customers, the timing and extent of spending to support development and expansion into new territories, continued investment in our technology platform and increased general and administrative expenses to support the anticipated growth in our operations. Our capital expenditures in future periods are expected to grow in line with our business. To the
extent that proceeds resulting from this offering, together with existing cash and cash from operations, are not
57
Table of Contents
sufficient to fund our future operations, we may need to raise additional funds through public or private equity or additional debt financing.
For a limited number of historical customer arrangements that include both sales of customer service contracts and other account management services, we record advances to and accrued payables to customers to account for the timing differences between when we collect cash from end customers and when we make payments to our customers. The $26.2 million balance at September 30, 2010 consists primarily of net payments due to Sun Microsystems from end customers renewing their service contracts with Sun Microsystems through us. Oracle terminated our contracts with Sun Microsystems effective as of September 30, 2010 and we are currently in discussions to achieve final resolution relating to the timing and amount of the payment we anticipate making to Sun Microsystems, net of amounts owed to us. We expect to pay Oracle a net amount ranging from $16 million to $18 million, which will result in a $12 million decrease in our accounts receivables and will be funded from our existing cash balances. We do not currently record a material amount of advances or payables to our other customers pursuant to such arrangements.
Although we are currently not a party to any agreement or letter of intent with respect to potential investments in, or acquisitions of, businesses or technologies, we may enter into these types of arrangements in the future, which could also require us to seek additional equity or debt financing. Additional funds may not be available on terms favorable to us or available at all.
Summary Cash Flows
The following table sets forth a summary of our cash flows for the periods indicated:
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
$ | 17,182 | $ | 3,232 | $ | 19,504 | $ | 14,490 | $ | 21,137 | ||||||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(3,182 | ) | (6,806 | ) | (7,476 | ) | (5,540 | ) | (7,427 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(5,254 | ) | (5,951 | ) | (2,379 | ) | (1,795 | ) | (3,740 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash, net of impact of exchange rate change on cash |
8,656 | (9,367 | ) | 9,389 | 7,027 | 10,062 | ||||||||||||||
Operating Activities
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, cash inflows from our operating activities were $21.1 million. Our net loss during the period was $1.3 million, adjusted by non-cash charges of $4.4 million for depreciation and amortization and $6.0 million for stock-based compensation. Additional sources of net cash inflows were from changes in our working capital, including a $19.2 million increase in accrued payables to customers, consisting of amounts owed to Oracle from end customers with respect to our Sun Microsystems engagements that terminated effective September 30, 2010, and a $2.7 million increase in accrued compensation and benefits, partially offset by a $13.2 million increase in accounts receivable and a $1.3 million decrease in prepaid expenses.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2009, cash inflows from our operating activities were $14.5 million. Our net income during the period was $5.5 million, adjusted by non-cash charges of $2.4 million for depreciation and amortization and $4.4 million for stock-based compensation. The remainder of our sources of net cash inflows was from changes in our working capital, including a $2.0 million decrease in accrued taxes and a $3.2 million decrease in accounts receivable.
In 2009, cash inflows from our operating activities of $19.5 million primarily resulted from our net income of $10.4 million, adjusted by non-cash charges of $6.1 million for stock-based compensation and $3.5 million for depreciation and amortization. The remainder of our sources of net cash inflows was from changes in our working capital, including a decrease in advances to customers of $3.6 million and an increase in accrued payables to customers of $3.5 million, partially offset by an increase in accounts receivable of $4.5 million and a decrease in accrued taxes of $1.9 million. The decrease in our advances to customers was due to the loss of a
58
Table of Contents
significant customer with whom this type of arrangement was agreed upon, hence fewer payments were due to customers before the receipt of the related amounts due from end customers. The increase in accrued payables to customers, which are reported net of our commissions, was due to an increase in the amounts of payments received from end customers which we had not yet remitted to our customers at year end. The increase in our accounts receivable reflects growth in our service revenue in the fourth quarter of 2009 as compared to the fourth quarter in 2008.
In 2008, cash inflows from our operating activities of $3.2 million primarily resulted from our net income of $4.8 million, adjusted by non-cash charges of $5.4 million for stock-based compensation and $3.4 million for depreciation and amortization. The sources of net cash inflows were partially offset by an increase in accounts receivable of $6.4 million and an increase in advances to customers of $3.2 million.
In 2007, cash inflows from our operating activities of $17.2 million primarily resulted from our net income of $9.7 million, adjusted by $3.9 million of stock-based compensation and $2.6 million of depreciation and amortization. The remainder of our sources of net cash inflows was from an increase in other accrued liabilities of $3.7 million and an increase in accrued compensation and benefits of $1.9 million, partially offset by an increase in accounts receivable of $3.3 million.
Investing Activities
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009, cash used in investment activities was $7.4 million and $5.5 million, respectively, and related to the acquisition of property and equipment, including costs capitalized for development of internal-use software.
In 2009, 2008 and 2007, net cash used in investing activities was $7.5 million, $6.8 million and $3.2 million, respectively, and related to the purchase of property and equipment, including costs capitalized for development of internal-use software.
Financing Activities
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010 and 2009, cash used in financing activities was $3.7 million and $1.8 million, respectively, primarily resulting from principal payments on our term loan. Additionally, during 2010 we had a $2.5 million cash distribution to members.
In 2009, cash used in financing activities was $2.4 million, primarily resulting from principal payments related to our long term obligations. In 2008 and 2007, cash used in financing activities was $6.0 million and $5.3 million, respectively, resulting primarily from cash distributions to members. During 2008, we entered into a new credit facility and used the proceeds to retire several prior debt agreements.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not have any relationships with other entities or financial partnerships, such as entities often referred to as structured finance or special-purpose entities, that have been established for the purpose of facilitating off-balance sheet arrangements or other contractually narrow or limited purposes.
59
Table of Contents
Contractual Obligations and Commitments
Our principal commitments consist of obligations under operating leases for office space and computer equipment. At December 31, 2009, the future minimum payments under these commitments, as well as repayments of our term loan, were as follows:
| Contractual Obligations | Payments Due by Period | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Less than 1 year |
1-3 years | 3-5 years | More than 5 years |
||||||||||||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Term loan |
$ | 16,835 | $ | 3,251 | $ | 13,584 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
| Expected interest payments on term loan(1) |
2,737 | 879 | 1,858 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Obligations under capital leases |
773 | 71 | 238 | 158 | 306 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating lease obligations |
22,106 | 3,307 | 11,111 | 5,851 | 1,837 | |||||||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 42,451 | $ | 7,508 | $ | 26,791 | $ | 6,009 | $ | 2,143 | ||||||||||
| (1) | We have calculated the expected interest payments on our term loan based on an interest rate of 5.25% in effect at December 31, 2009 applied to the principal balance of the term loan scheduled to be outstanding during the relevant interest period. |
The contractual commitment amounts in the table above are associated with agreements that are enforceable and legally binding, which specify significant terms including payment terms, related services and the approximate timing of the transaction. Obligations under contracts that we can cancel without a significant penalty are not included in the table above.
Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risk
We have operations both within the United States and internationally, and we are exposed to market risks in the ordinary course of our business. These risks primarily include foreign currency exchange and inflation risks, as well as risks relating to changes in the general economic conditions in the countries where we conduct business. To date, we have not used derivative instruments to mitigate the impact of our market-risk exposures. We have also not used, nor do we intend to use, derivatives for trading or speculative purposes.
Foreign Currency Exchange Risk
Our results of operations and cash flows are subject to fluctuations due to changes in foreign currency exchange rates, particularly changes in the euro, British pound, Canadian dollar, Singapore dollar and Japanese Yen. To date, we have not entered into any foreign currency hedging contracts, but may consider entering into such contracts in the future. We believe our operating activities act as a natural hedge for a substantial portion of our foreign currency exposure because we typically collect revenue and incur costs in the currency in the location in which we provide our solution from our sales centers. However, our global sales operations center in Kuala Lumpur incurs costs in the Malaysian Ringgit but we do not generate revenue or cash proceeds in this currency and, as a result, have some related foreign currency risk exposure. As our international operations grow, we will continue to reassess our approach to managing our risk relating to fluctuations in currency rates.
Inflation Risk
We do not believe that inflation has had a material effect on our business, financial condition or results of operations. Nonetheless, if our costs were to become subject to significant inflationary pressures, we may not be able to fully offset such higher costs through price increases. Our inability or failure to do so could harm our business, financial condition and results of operations.
60
Table of Contents
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Revenue Recognition
Substantially all of our revenue is generated from commissions earned from selling renewals of maintenance, support and subscription agreements on behalf of our customers. We recognize revenue upon acceptance of end customer purchase orders by our customers.
We recognize revenue when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, services have been provided, the sales price is fixed and determinable and collectability is reasonably assured from our customer and no significant obligations remain unfulfilled. Customer contracts are generally used to determine the existence of an arrangement. Under the terms of our customer contracts, our service obligations are completed when end customer purchase orders are accepted by our customers. We assess whether our fee is fixed or determinable based on the payment terms with our customers and whether any part of our fee is subject to refund or adjustment. We assess collectability based primarily on the creditworthiness of the customer as determined by credit checks and analysis as well as the customer’s payment history.
Our revenue management services are limited to renewing contracts on behalf of our customers. Therefore, we have no other obligations or responsibilities to our customers after they accept purchase orders from end customers. Moreover, we do not set the sales price, terms or scope of services contained in the service contracts we sell on behalf of our customers to their end customers, and we are not a party to contracts between our customers and their end customers.
Some of our customer agreements include performance-based commissions that we earn for exceeding pre-determined performance targets, including the achievement of renewal rates for contracts in excess of specified targets. Our customer arrangements also entitle us to fees and adjustments which are invoked in various circumstances, including the failure of our customers to provide us with a specified minimum value of service contracts. Our agreements generally contain early termination fees. Revenue related to performance-based commissions, adjustments and early termination fees is recorded when the performance criteria have been met, or the triggering event has occurred, and the amount earned is not subject to claw-back or future adjustment.
For multiple element arrangements, including deliverables such as sales of service contracts, account management services and/or subscriptions to our hosted technology platform, we separate each revenue stream at the inception of the arrangement on a relative fair value basis, provided that each service element meets the criteria for treatment as a separate unit of accounting. An item is considered a separate unit of accounting if it has value to the customer on a stand-alone basis and there is objective and reliable fair value of the undelivered services. The fair value of the undelivered elements is determined by the price charged when the element is sold separately, or in the cases where the item is not sold separately, by using other acceptable objective evidence.
We have a limited number of multiple-element arrangements where we are responsible for selling service contracts and we provide a subscription to our cloud applications. In these limited instances, our service sales revenue is recognized on a monthly basis as services are performed while subscription revenue is recognized ratably over the subscription term, generally a year. To date, subscription revenue earned from access to our cloud applications has been insignificant.
Under a limited number of historical customer engagements, we were responsible for selling service contracts and the related invoicing and cash collections from end customers. Under these arrangements, we collected the gross amount of payment due from end customers and remitted to our customers an amount equal to the gross billing less our sales commission and sales taxes or other indirect taxes invoiced to the end customers. Under these arrangements, revenue is recognized when the service has been delivered and the fee is fixed or determinable, which is upon receipt of cash payment from the end customer.
61
Table of Contents
Stock-Based Compensation
We measure and recognize compensation expense for all stock-based payment made to employees and directors based on the grant date fair values of the awards. For stock–based awards with service-based vesting conditions, the fair value is estimated using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The value of awards that are ultimately expected to vest is recognized as expense on a straight-line basis, net of estimated forfeitures, over the requisite service period. Stock-based compensation expenses are classified in the statements of operations based on the functional area to which the related recipients belong.
The Black-Scholes option pricing model requires management to make assumptions and to apply judgment in determining the fair value of our awards. The most significant assumptions and judgments include estimating the fair value of our common stock, expected volatility of our common stock and estimated term between the grant date and settlement date, as discussed below. In addition, the recognition of stock-based compensation expense is impacted by estimated forfeiture rates. We estimated the fair value of each stock option granted for 2007, 2008 and 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2010 using the following assumptions:
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, 2010 | |||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||||||
| Expected term (in years) |
4.8 | 4.6 | 4.8 | 5.4 | ||||
| Expected volatility |
74% | 55% | 56% | 54% | ||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
3.57 - 4.68% | 2.45 – 3.07% | 2.17 – 2.68% | 1.75 – 2.43% | ||||
| Expected dividend yield |
— | — | — | — | ||||
The expected option term was estimated by analyzing the historical period from grant to settlement of the stock option. This analysis includes exercise and forfeitures and also gives consideration to the expected holding period for those options that are still outstanding. The risk-free interest rate is based on a daily treasury yield curve rate that has a term consistent with the expected life of the stock option. We have not paid and do not anticipate paying cash dividends on our common stock, and therefore our expected dividend yield is assumed to be zero. We are required to estimate forfeiture rates at the time of grant and such estimates are revised in subsequent periods if actual forfeitures differ from those estimates. We apply an estimated forfeiture rate based on our historical forfeiture experience, which has been stratified into two relatively homogeneous groups.
As there has been no public market for our common stock prior to this offering, and therefore a lack of company-specific historical and implied volatility data, we have determined the share price volatility for options granted based on an analysis of reported data for a self-designated peer group of companies that grant options with substantially similar terms and conditions. The expected volatility of options granted has been determined using a simple average of the historical volatility measures of this peer group of companies for a period equal to the expected life of the option. We intend to continue to consistently apply this process using the same or similar entities until a sufficient amount of historical information regarding the volatility of our own common stock share price becomes available, or unless circumstances change such that the identified entities are no longer similar to us, in which case, more suitable entities whose share prices are publicly available would be utilized in the calculation.
We have historically granted stock options at exercise prices equal to the fair market value as determined by our board of directors on the date of grant, with input from management. Because our common stock is not publicly traded, our board of directors exercises significant judgment in determining the fair value of our common stock on the date of grant based on a number of objective and subjective factors. Factors considered by our board of directors included:
| • | contemporaneous independent valuations performed at periodic intervals by outside firms; |
| • | our performance, our financial condition and future financial projections at the approximate time of the option grant; |
62
Table of Contents
| • | trends in the technology and technology-enabled service company industries; |
| • | the value of companies that we consider peers based on a number of factors including, but not limited to, similarity to us with respect to industry, business model, stage of growth, geographic diversification, profitability, company size, financial risk or other factors; |
| • | changes since the last time the board of directors approved option grants and made a determination of fair value, including changes in planned business from new engagements and anticipated business from existing engagements; |
| • | amounts paid by investors for our common stock in arm’s-length purchases from our founders and employees; |
| • | the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event, such as an initial public offering or sale given prevailing market conditions and the nature and history of our business; and |
| • | any adjustment necessary to recognize a lack of marketability for our common stock. |
The valuation of our common stock was performed in accordance with the guidelines outlined in the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants Practice Aid, Valuation of Privately-Held-Company Equity Securities Issued as Compensation. In order to value our common stock, we first determined our business enterprise value and then allocated this business enterprise value to our common stock and common stock equivalents. Our business enterprise value was estimated using a combination of two generally accepted approaches: the income approach and the market-based approach. The income approach estimates enterprise value based on the estimated present value of future net cash flows the business is expected to generate over its remaining life. The estimated present value is calculated using a discount rate reflective of the risks associated with an investment in a similar company in a similar industry. The market approach measures the value of a business through an analysis of recent sales or offerings of comparable investments or assets, and in our case, focused on comparing us to the group of peer companies described above. In applying this method, valuation multiples are derived from historical operating data of the peer company group. We then apply multiples to our operating data to arrive at a range of indicated values of the company.
For each valuation, we prepared a financial forecast to be used in the computation of the value of invested capital for both the market approach and income approach. The financial forecast took into account our past results and expected future financial performance. The risk associated with achieving this forecast was assessed in selecting the appropriate discount rate. There is inherent uncertainty in these estimates as the assumptions used are highly subjective and subject to changes as a result of new operating data and economic and other conditions that impact our business.
As an additional indicator of fair value, we considered arm’s-length transactions involving sales and purchases of our common stock occurring near the respective valuation dates. The most recent such transaction occurred in December 2008 when an existing stockholder purchased shares from our founders and certain employees at a price of $4.26 per share.
We also utilize a probability-weighted expected return method (“PWERM”) to estimate the fair value of our common stock using the methods discussed above. The recent growth and expansion of our business in 2009 and 2010, combined with a continuing trend of general improvement in the capital markets during the same period, provided us better visibility into the likelihood of achieving a liquidity event in the next one to two years.
Under the PWERM, the value of our common stock is estimated based upon an analysis of values for our common stock assuming the following possible future events for the company:
| • | initial public offering; |
| • | strategic merger or sale; |
63
Table of Contents
| • | remaining a private company; and |
| • | dissolution of the company. |
For each of the possible events, a range of future equity values is estimated, based on the market, income or cost approaches and over a range of possible event dates, all discounted for the time-value of money. The timing of these events is based on management’s estimates. For each future equity value scenario, we determine the appropriate allocation of value to holders of our shares of common stock. The value of each share of common stock is then multiplied by a discount factor derived from the calculated discount rate and the expected timing of the event. The value per share of common stock is then multiplied by an estimated probability for each of the possible events based on management’s estimates. The calculated value per share of common stock under each scenario is then discounted for a lack of marketability. A probability-weighted value per share of common stock is then determined.
When using the PWERM, a market-comparable approach and an income approach were used to estimate our aggregate enterprise value at each valuation date. When choosing the market-comparable companies to be used for the market-comparable approach, we focused on the peer group of comparable companies described above operating within the technology and technology-enabled service sectors. The income approach involves applying an appropriate risk-adjusted discount rate to our projected debt-free cash flows, based on forecasted revenue and costs.
We also prepared financial forecasts for each valuation report date used in the computation of the enterprise value for both the market-comparable approach and the income approach. The financial forecasts were based on assumed revenue growth rates that took into account our past experience and contemporaneous future expectations of revenue from new and existing engagements. The risks associated with achieving these forecasts were assessed in selecting the appropriate cost of capital, which ranged from 16% to 18%.
In identifying other indicators of fair value, we considered transactions involving purchases and sales of shares, with the most recent being the previously mentioned transaction in December 2008.
Since January 1, 2009 through December 16, 2010, we granted stock options with exercise prices as follows:
| Grant Date |
Number of Options Granted |
Exercise Price and Common Stock Fair Value at Grant Date |
||||||
| (in thousands) | ||||||||
| February 4, 2009 |
186 | $ | 4.26 | |||||
| February 27, 2009 |
1,695 | $ | 4.26 | |||||
| May 8, 2009 |
148 | $ | 4.26 | |||||
| July 28, 2009 |
638 | $ | 4.26 | |||||
| November 4, 2009 |
983 | $ | 4.60 | |||||
| January 27, 2010 |
284 | $ | 4.65 | |||||
| February 9, 2010 |
1,863 | $ | 4.65 | |||||
| May 7, 2010 |
854 | $ | 4.70 | |||||
| July 28, 2010 |
1,678 | $ | 4.95 | |||||
| December 16, 2010 |
2,315 | $ | 5.80 | |||||
64
Table of Contents
Common Stock Valuations
The most significant factors considered by our board of directors in determining the fair value of our common stock at these grant dates were as follows:
Grants on February 4, February 27, May 8 and July 28, 2009
| • | The most recent independent contemporaneous valuation report was prepared as of December 1, 2008 utilizing the PWERM approach resulting in an indicated fair value of $4.05 to $4.26 per share of our common stock. The high end of the indicated fair value range reflects the price paid in an arm’s-length sale of our common stock by founders and certain employees to an existing stockholder in December 2008. |
| • | The PWERM approach scenario probabilities used in the valuation report were based on our business outlook. Our management estimated a 25%-30% probability of an initial public offering, a 25%-30% probability of a sale or merger and a 40%-50% probability that we would continue as a private company. A bankruptcy scenario was deemed not probable and was assigned a 0% probability. In addition, our board recognized that management forecasts had not changed materially since the December 1, 2008 valuation report. |
| • | In determining the fair value of option awards on July 28, 2009, our board specifically considered the April 2009 public announcement by Oracle that it had entered into an agreement to acquire Sun Microsystems, our largest customer and the potential impact to our operations if this customer terminated its contracts with us. |
| • | Our board of directors determined the fair value of stock awards to be $4.26, the high end of the indicated range of value reflected in the valuation analysis. |
Grants on November 4, 2009
| • | The most recent independent contemporaneous valuation report was prepared as of September 30, 2009 utilizing the PWERM approach resulting in an indicated fair value of $4.55 to $4.75 per share of our common stock. |
| • | The PWERM approach scenario probabilities used in the valuation report were based on our business outlook. Our management estimated a 30%-35% probability of an initial public offering, an increase of five percentage points from the prior valuation; a 30%-35% probability of a sale or merger, also a five percentage point increase from the prior valuation; and a ten percentage decrease in the probability that we continue as a private company to an estimated range of 30%-40%. A bankruptcy scenario was deemed not probable and was assigned a 0% probability. In addition, our board recognized that management forecasts had not changed materially since the September 30, 2009 valuation report. |
| • | Management’s business outlook which considered the growth in revenue resulting from new customer arrangements as well as the potential impact to our business if Sun Microsystems were to terminate its relationship with us as a result of being acquired by Oracle. |
| • | The fair value of stock awards on November 4, 2009 was determined by our board to be $4.60 per share, the low end of the range of indicated fair value reflected in the valuation analysis. |
Grants on January 27 and February 9, 2010
| • | The most recent independent contemporaneous valuation report was prepared as of December 31, 2009 utilizing the PWERM approach resulting in an indicated fair value of $4.65 to $4.80 per share of our common stock. |
65
Table of Contents
| • | The PWERM approach scenario probabilities used in the valuation report were based on our business outlook. Management estimated a 30%-35% probability of an initial public offering, a 30%-35% probability of a sale or merger and a 30%-40% probability that we would continue as a private company. A bankruptcy scenario was deemed not probable and was assigned a 0% probability. In addition, our board recognized that management forecasts had not changed materially since the December 31, 2009 valuation report. |
| • | Management’s business outlook continued to reflect revenue growth anticipated from new customer engagements and expected revenue from existing engagements, as well as uncertainty surrounding continuation of the Sun Microsystems engagements. |
| • | Our board of directors determined the fair value of stock awards to be $4.65, the low end of the indicated range of fair value reflected in the valuation analysis, which reflected the continued uncertainty to our business following the acquisition of Sun Microsystems by Oracle. |
Grants on May 7, 2010
| • | The most recent independent contemporaneous valuation report was prepared as of March 31, 2010 utilizing the PWERM approach resulting in an indicated fair value of $4.70 per share of our common stock. |
| • | The PWERM approach scenario probabilities used in the valuation report were based on our business outlook. Management estimated a 33% probability of an initial public offering, a 33% probability of a sale or merger and a 33% probability that we would continue as a private company. A bankruptcy scenario was deemed not probable and was assigned a 0% probability. In addition, our board recognized that management forecasts had not changed materially since the March 31, 2010 valuation report. |
| • | Management’s business outlook continued to reflect revenue growth anticipated from new customer engagements and expected revenue from existing engagements, as well as uncertainty surrounding continuation of the Sun Microsystems engagements. |
| • | Our board of directors determined the fair value of stock awards to be $4.70, consistent with the indicated fair value reflected in the valuation analysis. |
Grants on July 28, 2010
| • | The most recent independent contemporaneous valuation report was prepared as of June 30, 2010 and indicated a fair value of $4.95 per share. |
| • | PWERM approach scenario probabilities used in the valuation report were based upon our business outlook. Our management estimated a 40% probability of an initial public offering, an increase from the 33% assumption in the prior valuation; a 30% probability of a sale or merger, down from a 33% probability used in the prior valuation; and a 30% probability that we would continue as a private company, a decrease from the 33% probability used in the prior valuation. A bankruptcy scenario was deemed not probable and was assigned a 0% probability. In addition, our board recognized that management forecasts had not changed materially since the June 30, 2010 valuation report. |
| • | While our financial forecast remained unchanged from the forecast utilized in the March 31, 2010 valuation, the increase in the fair value of our common stock as compared to the prior valuation resulted principally from the increased probability of an initial public offering as we undertook activities in this area. |
| • | Management’s business outlook continued to reflect revenue growth from new customer engagements and anticipated revenue from new engagements or revenue from expanded engagements with existing customers. Our financial forecast decreased as a result of the notice of cancellation of the Sun Microsystems contracts. |
66
Table of Contents
| • | Our board of directors determined the fair value of stock awards to be $4.95, consistent with the indicated fair value reflected in the valuation analysis. |
Grants on December 16, 2010
| • | The most recent independent contemporaneous valuation report was prepared as of September 30, 2010 and indicated a fair value of $5.80 per share. |
| • | PWERM approach scenario probabilities used in the valuation report were based upon our business outlook. Our management estimated a 50% probability of an initial public offering, an increase from the 40% assumption in the prior valuation; a 25% probability of a sale or merger, down from a 30% probability used in the prior valuation; and a 25% probability that we would continue as a private company, a decrease from the 30% probability used in the prior valuation. A bankruptcy scenario was deemed not probable and was assigned a 0% probability. |
| • | While our financial forecast remained unchanged from the forecast utilized in the March 31, 2010 valuation, the increase in the fair value of our common stock as compared to the prior valuation resulted principally from the increased probability of an initial public offering as we undertook activities in this area. |
| • | Our board of directors determined the fair value of stock awards to be $5.80, consistent with the indicated fair value reflected in the valuation analysis. |
Nonemployee Stock-Based Compensation
We account for stock options issued to nonemployees based on the estimated fair value of the awards using the Black-Scholes option pricing model. The measurement of stock based compensation is subject to periodic adjustments as the underlying equity instruments vest, and the resulting change in value, if any, is recognized in our consolidated statements of operations during the period the related services are rendered.
Stock-based compensation expense for options granted to nonemployees for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 was $0.1 million. The amount for 2008 was insignificant. There were no options granted to nonemployees in 2007 and 2009.
There is inherent uncertainty in these estimates and if different assumptions had been used, the fair value of the equity instruments issued to nonemployee consultants could have been significantly different.
Capitalized Internal-Use Software
Commencing in 2007, we began incurring costs related to the development of our technology platform. In connection with these efforts, we capitalized external costs as well as internal labor costs related to the development of internal-use software associated with our technology platform. During 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, we capitalized $0.7 million, $2.8 million, $5.0 million, $3.8 million and $3.1 million, respectively, primarily related to the development of our technology platform and cloud applications. Capitalized amounts included costs of internal labor totaling $0.9 million and $0.4 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively, while the remainder of amounts capitalized during the periods related to costs of third-party developers. The higher spending during the nine months ended September 30, 2009 relative to the same period in 2010 reflects increased costs related to the development of our channel sales and analytics and reporting applications.
We capitalize certain internal and external costs related to the development and enhancement of our internal-use software when we enter the application development stage and until software is substantially complete and is ready for its intended use. These capitalized costs include direct external costs of services utilized in developing or obtaining internal-use software, compensation and related expenses of employees who
67
Table of Contents
are directly associated with, and who devote time to, internal-use software projects. Capitalization of these costs ceases once the project is substantially complete and the software is ready for its intended use and the related costs are amortized over estimated useful lives ranging from 24 to 60 months. Post-implementation training and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred. We initiate our review of potential impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of the capitalized internal-use software may not be recoverable. Recoverability of assets is assessed by a comparison of the carrying amount of an asset to the expected future undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If it is determined that the carrying value of the internal-use software is not recoverable, an impairment loss is recorded in the amount by which the carrying amount of the asset exceeds the fair value of the asset. There were no impairments to internal-use software in 2007, 2008 or 2009, or during the nine months ended September 30, 2010.
Income Taxes
Since inception through December 31, 2007 we conducted our U.S. operations through the LLC, a pass-through entity for tax purposes. Under this structure, we file our income tax return as a partnership for federal and state income tax purposes. The LLC is not subject to income taxes other than annual California limited liability company fees based on revenues. The members of the LLC, not the LLC itself, are subject to income taxes on their allocated share of the LLC’s earnings. The LLC is required to pay cash distributions to the members to fund members’ tax obligations based on the members’ allocated share of the LLC’s net income, if applicable. Effective January 1, 2008, the LLC transferred a significant portion of its U.S. operations to a wholly-owned U.S. taxable subsidiary. We also have several subsidiaries formed in foreign jurisdictions, which are subject to local income taxes.
We account for income taxes for our taxable subsidiaries using an asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of taxes payable or refundable for the current year and deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences that currently exist between the tax basis and the financial reporting basis of our taxable subsidiaries’ assets and liabilities using the enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in operations in the period that includes the enactment date. The measurement of deferred tax assets is reduced, if necessary, by the amount of any tax benefits that, based on available evidence, are not expected to be realized.
We adopted FASB ASC Topic 740 (“ASC 740”) on unrecognized tax benefits on January 1, 2007. The adoption of ASC 740 did not have an impact on the January 1, 2007 stockholders’ equity because we believe there were no uncertain tax positions for tax years prior to 2007. As of December 31, 2009 and September 30, 2010, we did not have any unrecognized tax benefits that if recognized would impact our annual effective tax rate. We account for unrecognized tax benefits using a more-likely-than-not threshold for financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. We establish reserves for tax-related uncertainties based on estimates of whether, and the extent to which, additional taxes will be due. We record an income tax liability, if any, for the difference between the benefit recognized and measured and the tax position taken or expected to be taken on our tax returns. To the extent that the assessment of such tax positions change, the change in estimate is recorded in the period in which the determination is made. The reserves are adjusted in light of changing facts and circumstances, such as the outcome of a tax audit. The provision for income taxes includes the impact of reserve provisions and changes to reserves that are considered appropriate. As of December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010, we have not recorded any liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits.
Income Tax Accounting Related to the Conversion
We have prepared and provided unaudited pro forma disclosures in our consolidated statements of operations and consolidated balance sheets as if the entire company was taxable as a corporation since inception. The pro forma income tax expense was $ million for the nine months ended September 30, 2010, and the
68
Table of Contents
pro forma deferred tax liability on our balance sheet at September 30, 2010 was $ million. Upon our conversion from an LLC into a corporation in connection with the completion of this offering, we expect to record a non-cash income tax benefit equal to the amount of the net adjustment to the deferred tax balances, which would have been $ on a pro forma basis as of September 30, 2010.
Pro forma deferred income taxes reflect the net tax effects of temporary differences between the pro forma carrying amounts of our tax assets and liabilities calculated for financial reporting purposes and the amounts that would have been calculated for our income tax returns in accordance with tax regulations and the net pro forma tax effects of operating loss and tax credit carryforwards if we had been a taxable entity.
The ultimate realization of deferred tax assets depends on the generation of sufficient taxable income of the appropriate character and in the appropriate taxing jurisdictions during the future periods in which the related temporary differences become deductible. We determined the valuation allowance on our pro forma deferred tax assets is in accordance with the accounting standard for income taxes, which require weight of both positive and negative evidence in order to ascertain whether it is more likely than not that the pro forma deferred tax assets would be realized. We evaluated all significant available positive and negative evidence, including the existence of cumulative net income, benefits that could be realized from available tax strategies and forecasts of future taxable income, in determining the need for a valuation allowance on our pro forma deferred tax assets. After applying the evaluation guidance of the accounting standard for income taxes we determined that it was more likely than not that the pro forma deferred tax assets will be realized, and as such, a valuation allowance is not required.
Our pro forma gross, tax effected, deferred tax assets were approximately $ million as of September 30, 2010. Our pro forma net deferred tax liabilities were $ million as of September 30, 2010.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In October 2009, Financial Accounting Standards Board, (“FASB”) issued a new accounting standard that changes the accounting for arrangements with multiple deliverables. The new standard requires an entity to allocate arrangement consideration at the inception of an arrangement to all of its deliverables based on their relative selling prices. This standard will become effective for us beginning January 1, 2011. This Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) removed the previous separation criteria that objective and reliable evidence of the fair value of any undelivered items must exist for the delivered item to be considered a separate unit or units of accounting. Given our current contractual arrangements, the adoption of this standard is not expected to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In January 2010, the FASB issued amended guidance on fair value measurements and disclosures. The new guidance requires additional disclosures regarding fair value measurements, amends disclosures about postretirement benefit plan assets, and provides clarification regarding the level of disaggregation of fair value disclosures by investment class. This guidance is effective for interim and annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2009, except for certain Level 3 activity disclosure requirements that will be effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2010. Accordingly, we adopted this amendment for the nine month period ended September 30, 2010, except for the additional Level 3 requirements which will be adopted in 2011. Level 3 assets and liabilities are those whose fair market value inputs are unobservable and reflect management’s best estimate of what market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability at the measurement date. The adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In February 2010, the FASB issued ASU No. 2010-09 Subsequent Events (FASB ASC Topic 855): Amendments to Certain Recognition and Disclosure Requirements. ASU 2010-09 requires an entity that is a filer with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) to evaluate subsequent events through the date that the financial statements are issued and removes the requirement for an SEC filer to disclose a date, in both issued
69
Table of Contents
and revised financial statements, through which the filer had evaluated subsequent events. The adoption of this standard did not have a significant impact on our consolidated financial statements.
In April 2010, the FASB issued ASU No. 2010-13, Compensation—Stock Compensation (Topic 718)—Effect of Denominating the Exercise Price of a Share-Based Payment Award in the Currency of the Market in Which the Underlying Equity Security Trades. ASU 2010-13 provides amendments to Topic 718 to clarify that an employee share-based payment award with an exercise price denominated in the currency of a market in which a substantial portion of the entity’s equity securities trades should not be considered to contain a condition that is not a market, performance, or service condition. Therefore, an entity would not classify such an award as a liability if it otherwise qualifies as equity. The amendments in ASU 2010-13 are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning on or after December 15, 2010. The adoption of this standard is not expected to have a material impact on our consolidated financial statements.
70
Table of Contents
Overview
ServiceSource is a leader in service revenue management, providing solutions that drive increased renewals of maintenance, support and subscription agreements for technology companies. Our integrated solution consists of a suite of cloud applications, dedicated service sales teams working under our customers’ brands and a proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform. By integrating software, managed services and data, we provide end-to-end management and optimization of the service contract renewals process, including data management, quoting, selling and service revenue business intelligence. Our business is built on our pay-for-performance model, whereby customers pay us based on renewal sales that we generate on their behalf. As of September 30, 2010, we managed over 90 engagements across more than 50 customers, representing over $5 billion in service revenue opportunity under management. We had approximately 50, 60 and 80 engagements as of December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009.
We deploy our solution through offerings that provide end-to-end management of the renewals process or that are tailored to address specific challenges of this process. Our highly scalable solution allows us to sell in over 30 languages from six sales centers around the globe. It is designed to provide optimized service revenue performance irrespective of revenue models, distribution models, and segments within the technology and technology-enabled healthcare and life sciences industries, including hardware, software and software-as-a-service. Based on our analysis of customer renewal rates for new engagements added in 2009, we generated renewal rates on contracts delivered to us in the first half of 2010 that on a dollar value basis increased by an average of over 15 percentage points over historical customer renewal rates calculated in our Service Performance Analysis (“SPA”).
Our total revenue was $75.2 million, $100.3 million and $110.7 million for the years ended December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, respectively, and was $76.9 million and $108.5 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively. For summarized financial information by geographic area, see Note 13 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements.
For a discussion of the development of our business over the last five years, see “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations—Overview.”
Industry Background
The Importance of Service Revenue
As the technology industry matures and companies search for new drivers of growth and profitability, a new focus is emerging: service revenue. We define service revenue as the revenue companies earn from the sale of maintenance and support agreements, as well as subscription contracts. Service revenue has become increasingly important for technology companies as it represents a significant portion of total revenue, drives incremental profitability, can be highly recurring and correlates with customer satisfaction.
| • | Service revenue is a dramatically growing component of technology industry revenue. Over the last decade, service revenue has surpassed new product and license revenue for many technology companies. The advent of software-as-a-service and cloud based solutions has further increased the contribution of service revenue to technology industry revenue. According to Gartner, total spending on maintenance and support agreements across the technology sector is expected to total $141 billion in 2010, including approximately $84 billion on hardware and approximately $56 billion on software.1 |
| • | Service revenue can deliver enhanced profitability. Service revenue is a significant contributor to the profitability of technology companies. For example, one large technology company reported |
| 1 | Gartner, Inc., IT Services Market Metrics Worldwide: Forecast Database, Kathryn Hale et al., September 9, 2010 |
71
Table of Contents
| approximately 90% in gross margin from support and updates revenue compared to 43% gross margin for license and product revenue for its fiscal year 2010. We believe that the support costs associated with service revenue can be relatively fixed, which allows each incremental dollar generated from improved renewal rates to fall to the bottom line without significant cost. |
| • | Service revenue is predictable and recurring. Service revenue is typically based on annual or multi-year contracts to provide ongoing maintenance and support for existing technology investments or subscriptions for continued access to products and services. Continued successful renewal of service contracts provides technology companies with highly predictable service revenue streams as well as the ongoing opportunity to renew contracts. |
| • | Service relationships increase end customer satisfaction. Service relationships allow technology companies to maintain an active dialogue with their end customers. By regularly interacting with end customers, providing them with effective service, communicating to them the value of that service and better understanding their needs, companies can increase customer satisfaction and retention. Greater customer satisfaction increases the probability of future contract renewals and new product sales. |
Effective Service Revenue Management is Complex and Challenging
Just as service revenue has become increasingly important to technology companies, service revenue management has also become more complex and challenging. While technology companies have generally increased their focus on renewal rates associated with service contracts, we believe many have been unable to optimize their service revenue performance due to limited expertise in effective service revenue management and historical underinvestment in associated infrastructure. In addition, multiple factors have made effective service revenue management challenging for technology companies, including the following:
| • | Fragmented service revenue data. Effective service revenue management requires more extensive data management than new product or license sales. Service renewals utilize data from CRM, contract, quoting, entitlement, asset management and support systems, among others. The data is often duplicative, error prone, incomplete or simply outdated and it may be cobbled together from half a dozen or more enterprise systems. |
| • | Existing infrastructure ill-equipped to optimize service revenue. Many companies have not invested in the enterprise systems, data warehouses, analytical applications and sales teams needed to optimize service revenue performance. As service contract renewals often encompass different processes and rely on information attributes not typically captured by existing systems, such as aging, contract entitlements and warranty considerations, traditional business applications are not designed to support end-to-end service revenue management. Additionally, sales teams are often not effectively trained or sufficiently incentivized to drive sales of service contracts, and are focused instead on product or license sales. |
| • | Channel complexity and misaligned incentives. Many technology companies have hundreds, if not thousands, of channel partners across one or more distribution tiers. This structure increases management complexity and can be exacerbated by misalignment of incentives and limited channel transparency. For example, companies typically measure and incentivize channel partners based on new product and license sales, not service revenue renewals. Also, channel partners sometimes may be reluctant to share end customer information, making it difficult for technology companies to maximize service revenue through the channel. |
| • | Savvy IT buyers with limited budgets. The macroeconomic landscape has put significant pressure on enterprise technology budgets, causing IT buyers to push back on service contract pricing and seek discounts. Additionally, a new group of advisors has emerged to help IT buyers better negotiate service contracts with technology companies. Furthermore, the rise of third-party vendors who provide independent maintenance and support has put further pressure on renewals. |
72
Table of Contents
| • | Lack of industry standards and benchmarks. Consistent definitions for renewal rates and meaningful benchmarks are necessary for companies to determine how they are performing relative to industry peers and how they can employ best practices to improve their service revenue performance. However, there are currently no widely accepted industry metrics for service revenue management, nor is there easy access to best practices. |
| • | Complexity due to mergers and acquisitions and global scale. Mergers and acquisitions create a unique challenge for service revenue management as the complete view of the customer and its service contracts requires the integration of disparate systems and data between merging companies, which is often fraught with challenges. Optimizing service revenue requires overcoming these challenges to gain a complete and accurate view of the customer base and develop a consistent approach to selling renewals. The global scale of many technology companies adds further complexity, as effective service revenue management requires diverse strategies and tactics across different geographies. Maintaining a global service sales effort requires significant investment in infrastructure and personnel to have the language and local selling capabilities required to engage with and sell to end customers. |
Significant Opportunity for Service Revenue Management
According to Gartner, total spending on maintenance and support agreements across the technology sector will total $141 billion in 2010, including approximately $84 billion on hardware agreements and approximately $56 billion on software agreements.1 We believe the complexity of effective service revenue management, coupled with underinvestment in this area has led to suboptimal renewal rates on service contracts. Lower renewal rates result in significant lost revenue and may give the impression that products and services are not viewed positively by end customers.
Effective service revenue management requires a focused and differentiated approach as well as resources that many technology companies lack. These resources include enterprise systems built specifically for service revenue data management, analytical applications that monitor service revenue performance, sales processes tailored specifically to increase service contract renewals and global service sales teams with the expertise to sell service contracts.
Most technology companies focus their internal investments on developing and selling new products. The historical lack of investment in service revenue performance solutions presents a compelling opportunity for us. By improving renewal rates, technology companies can generate higher service revenue, profitability and end customer satisfaction. We believe optimized service revenue performance can be a powerful earnings growth engine for the technology industry.
Business Customers are Increasingly Turning to Cloud Based Technology and Performance Based Solutions
Companies are rapidly adopting cloud based solutions as management teams strive to reduce the risk of technology implementation, focus on core competencies and improve financial performance. Cloud based solutions refers to software applications and other services delivered over the Internet, typically in place of on-premise software applications.
Historically, enterprises have deployed home-grown or third-party software applications on site and managed business processes internally. More recently, however, businesses have become increasingly convinced that cloud based solutions are less expensive, can be deployed more rapidly and with less risk, and have increased data analysis capability and functionality.
Recently, companies are also realizing the value of solutions that integrate software, managed services and data to deliver a business outcome. Rather than investing in infrastructure based on an assumed return on
| 1 | Gartner, Inc., IT Services Market Metrics Worldwide: Forecast Database, Kathryn Hale et al., September 9, 2010 |
73
Table of Contents
investment or incurring significant fees that are not tied to performance, companies are recognizing the value of paying for solutions based on business outcomes. An example of this trend is the market for Internet search, in which companies pay for a combination of advertising services, data and a technology platform, and pay for this solution on a per-click or performance basis.
Our Solution
Our solution is based on nearly a decade of experience pioneering the service revenue management category and is designed to optimize service revenue performance for our customers. It addresses the critical elements of the renewals process, including data management, quoting, selling, and service revenue business intelligence. We believe our solution, which tightly integrates software, managed services and data, reflects the growing trend of delivering enterprise services via the cloud. We believe this approach is critical to addressing the unique requirements of effective service revenue management.
The components of our solution consist of our proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform, our suite of cloud applications, and our dedicated service sales teams. The foundation of our solution is our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform, a data warehouse of transactional, analytical and industry data that grows with each service renewal transaction and customer. Our suite of cloud applications increase visibility and control of service revenue management and are utilized by customers, channel partners, end customers and our service sales teams. Our dedicated service sales teams have specific expertise in our customers’ businesses, are deployed under our customers’ brands and follow a sales process tailored specifically to increase service contact renewals.
We deploy our solution through five offerings to address specific needs of our customers’ different business and selling models: Direct Sales, Channel Enablement, Reseller Sales, Subscription Lifecycle Management and Enterprise. For example, the Subscription Lifecycle Management solution incorporates critical product adoption business processes unique to the software-as-a-service market that have been effective in increasing renewal rates. Likewise, the Channel Enablement solution deploys a Channel Sales application and specialized channel enablement service sales teams to navigate the challenges associated with optimizing renewal rates in a complex, multi-tier channel distribution environment.
Key benefits of our solution include:
Financial Benefits
| • | Increased service revenue. Our solution is designed to increase customers’ service revenues. Each customer engagement begins with an in-depth analysis of customers’ current renewal rates, which we call our SPA. We actively monitor the service contract renewal rates we drive on behalf of our customers in each engagement. When we generate higher renewal rates, we not only drive incremental service revenue for the associated period, but also have a compounding effect in increasing the base number of contracts eligible for renewal in subsequent periods, which expands the opportunity to generate greater revenue in future periods. |
| • | Increased margin and profitability. We believe that the costs associated with delivering maintenance, support and subscription services by many of our customers can be relatively fixed, and thus growth of service revenue can benefit our customers’ bottom line. In addition, customers that deploy our solution can avoid infrastructure expenditures and personnel costs that would otherwise be associated with managing service renewals internally. As a result, each incremental dollar of service revenue generated by our solution can drive greater profitability for our customers. |
Operational Benefits
| • | Improved end customer satisfaction. Our regular dialogue with end customers allows us to communicate the value of our customers’ maintenance, support and subscription services, and capture and address questions and concerns about our customers’ products. |
74
Table of Contents
| • | Greater business insight and analytics. Our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform allows us to analyze our customers’ renewals against similar transactions and to identify areas for improvement, enabling greater insight into their renewals business. All transactions, whether or not resulting in a successful renewal by an end customer, are recorded in our intelligence platform. We leverage this platform to provide benchmarking, end customer metrics, sales efficiency data and insight into successful and unsuccessful renewal efforts. The breadth of our data allows us to provide powerful analysis across regions, industries, channel partners and product segments. |
| • | Greater visibility and forecasting tools. Our cloud applications deliver real-time analytics and visibility into a customer’s service revenue performance, sales efficiency and forecasts. We measure service revenue performance across over 100 Key Performance Indicators (“KPIs”) that are housed in our intelligence platform and provide real-time data to our customers through a clear and impactful web-based interface. CFOs and other executives utilize our applications to assist in forecasting their results and to measure progress against their forecasts on a real-time basis. |
| • | Strengthened channel loyalty. Our Channel Sales Cloud application and service sales teams empower our customers’ channel partners to generate higher sales by providing accurate, real-time data on their renewal opportunities and performance relative to quota as well as tools to sell more effectively to end customers. These cloud applications help our customers develop a closer relationship with their channel partners and enable our customers to increase renewals through the channel. |
| • | Global consistency. We are able to maintain a globally consistent renewals process for our customers as all of our six sales centers leverage a unified intelligence platform. Our solution automates the application of best practices to the service renewals process and provides all relevant constituencies with a consistent view of the data. This facilitates service renewals and provides reliable performance management and analytics. |
75
Table of Contents
Our Competitive Advantages
We believe our business is difficult to replicate, as it incorporates a combination of several important and differentiated elements, including:
| • | Proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform. We have built a proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform that aggregates the transactional, analytical and industry data we have gathered from over two million service renewal transactions. This information and associated business insight allows us to improve service revenue performance for each customer’s unique business. The intelligence platform powers substantially all of our business, including our SPA, the pricing and scoping of our solutions, performance optimization, customer benchmarking, and industry thought leadership, and influences the way in which we develop our cloud applications and our sales process tailored specifically to increase service contract renewals. We continue to enhance our intelligence platform as we grow our service revenue opportunity under management. |
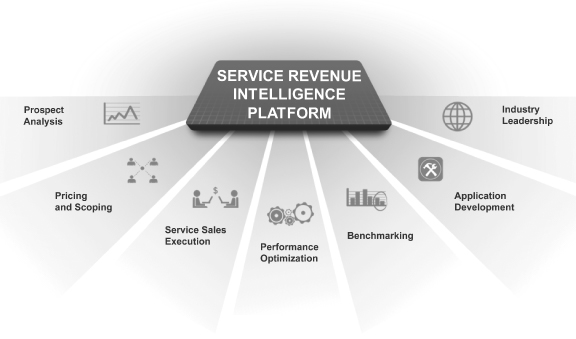
| • | Pay-for-performance business model. Our customers pay us based on the renewal sales that we generate on their behalf. Our business model directly aligns our interests with our customers’ interests to drive greater service revenue. This self-funding model also eliminates the need for our customers to make large upfront investments in infrastructure that offer no guarantee of improved service revenue performance. Our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform is the critical element that allows us to price effectively on a pay-for-performance basis. |
| • | Industry leadership. We were founded nearly a decade ago and we believe that we have more service revenue opportunity under management and more service revenue performance data than any other third-party provider. Our industry leadership enables us to innovate best practices, continue to enhance our intelligence platform and attract new customers. |
| • | Service revenue focused solution. Our entire solution is built from the ground up to deliver industry-leading service revenue performance across the key elements of the renewals process. We believe our combination of software, managed services and data is unmatched by any other third-party solution. |
76
Table of Contents
| • | Renewal sales methodology. Our service sales teams leverage our intelligence platform, sales processes and best practices to manage the end customer relationship and enhance service contract renewal rates. We engage in extensive ongoing training of our service sales teams to ensure consistency of execution across our entire organization. |
| • | Global scale and expertise. Our service sales teams sell in over 30 languages from six sales centers around the globe. Our sales footprint and localized capabilities enable us to better serve the increasingly global nature of our customers’ businesses. |
Our Strategy
We intend to continue our industry leadership in service revenue management with the following strategies:
| • | Expand customer base within existing industry verticals. We believe there is a significant opportunity to increase our service revenue opportunity under management. As of September 30, 2010, we had over $5 billion in service revenue opportunity under management. According to Gartner, total spending on maintenance and support agreements across the broader technology sector will total $141 billion in 2010.1 We intend to increase investment in our sales and marketing organization to win new customers in the technology and technology-enabled healthcare and life sciences industries. |
| • | Continue to build, deploy and increase the revenue we generate from our cloud applications. We intend to continue to invest in our cloud applications. We have created a variety of applications for channel partners, direct sellers and end customers that we provide as part of our offerings. In addition to extending and strengthening our suite of applications, we are exploring alternatives for packaging and pricing these applications to further monetize them. |
| • | Increase footprint with existing customers to drive greater revenue per customer. Our goal is to manage a greater portion of each customer’s service revenue. Typically, we initially manage one component of a customer’s service revenue, such as a specific product, market segment or geographic region. With our pay-for-performance model, we are able to quantify our results for the customer, frequently leading to an increase of service revenue opportunity under management for that customer, and ultimately greater revenue. |
| • | Increase our operating efficiency by developing additional technology. We have developed an intelligence platform and suite of applications that drive increases in efficiency and help to automate tasks associated with service revenue management. For example, we have created a quoting application to automate the service contract quoting process. By continuing to automate processes, we can lower operating costs, increase the efficiency of our solutions and ultimately enhance our profitability and cash flow. |
| • | Add new customers from additional industry verticals and geographic markets. We recognize that service revenue opportunities exist in sectors beyond the technology industry. We currently have a small number of technology-enabled healthcare and life sciences customers for whom we manage medical equipment maintenance and support contracts. We believe there are additional industry verticals and geographic markets that can benefit from our expertise and best practices, and we intend to pursue these opportunities. |
| 1 | Gartner, Inc., IT Services Market Metrics Worldwide: Forecast Database, Kathryn Hale et al., September 9, 2010 |
77
Table of Contents
The Components of Our Solution
Our solution consists of our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform, cloud applications and dedicated service sales teams. The following diagram illustrates the elements of our solution:
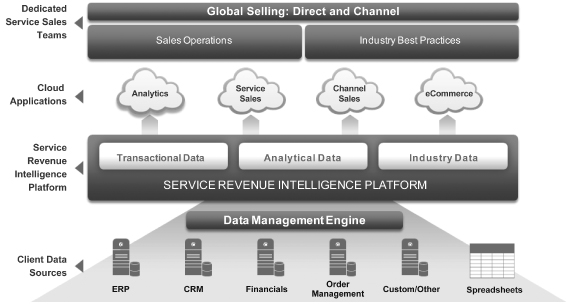
Service Revenue Intelligence Platform
Since our inception, we have developed and evolved our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform, a data warehouse of transactional, analytical and industry data that powers our solution, provides insight into the business we manage on behalf of our customers, and enables us to deliver higher performance for those customers.
| • | Transactional data. An integral part of our renewals process is the broad data capture we perform to ensure we have documented the important information about each transaction. With over two million transactions completed since inception, we have been able to build a robust data warehouse of service revenue and renewals information. |
| • | Analytical data. We track and leverage the 100 KPIs and benchmarks in our intelligence platform across our business. The data has been analyzed across a number of dimensions, such as by region, customer segment, and contract dollar value, among others. |
| • | Industry data. At the core of the intelligence platform is a service revenue-specific data model and benchmarking database that allows us to extract transactional data from customers and capture other structured and unstructured analytical data in a consistent manner. This allows us to benchmark performance across industries and perform cohort analyses to understand where we can apply best practices to increase performance. |
The intelligence platform improves with every renewal we manage, every customer we engage, and every benchmarking study we complete. We believe this is the most comprehensive data warehouse built exclusively for managing and optimizing service revenue from maintenance, support and subscription agreements on behalf of third-party customers.
Supporting the intelligence platform is our Data Management Engine. We have found that customer service renewals source data is almost universally embedded in fragmented information technology systems. Our Data
78
Table of Contents
Management Engine extracts data from enterprise systems, such as ERP, CRM, billing and order management. This data is typically contained in different formats with disparate levels of completeness, quality and freshness. After loading the data into our system, the Data Management Engine reconciles, cleanses and reorganizes our customers’ data providing our service sales teams with more accurate and relevant data, such as an inventory of the assets owned by end users, service quote history, and current service contract terms.
We leverage our Service Revenue Intelligence Platform across critical business processes, including:
| • | Service Performance Analysis. During the SPA process, we conduct interviews of our prospective customers, analyze their historical performance and future opportunity, and evaluate their service revenue business on a number of dimensions. The intelligence platform enables us to benchmark and identify service renewal opportunities and calculate our ability to improve performance based on our performance on similar types of businesses and opportunities. |
| • | Business Case, Pricing and Contract Structuring. We utilize our reservoir of data and benchmarks from the intelligence platform to estimate the critical components of the business case and pricing model that we use in discussions with prospective customers. This intelligence is fundamental to our pay-for-performance business model. |
| • | Service Revenue Performance. Once a partnership is in place with our customer, we leverage the intelligence platform to help enable, measure, analyze, benchmark, optimize, and continuously improve the performance of our service sales teams. |
| • | Customer Benchmarking and Continuous Improvement. Our intelligence platform serves as the foundation to benchmark our customers’ evolving service revenue performance against industry peers and previous period performance. As a component of our “Clients for Life” methodology, we convene quarterly business review meetings and annual partnership reviews with our customers to review performance, identify potential weaknesses and opportunities, and make recommendations that we believe will allow our customers and us to achieve higher levels of performance and efficiencies. |
| • | Developing and Delivering Applications. The intelligence platform includes the data warehouse that fuels the opportunity data, sales methodologies, metrics, and reporting dashboards that we engineer into our applications. Accordingly, we design our applications to leverage the transactional, analytical and industry data housed in our intelligence platform. |
Cloud Applications
We have developed a suite of applications designed to optimize specific elements of the renewals process. Our applications reflect our experience in optimizing service revenue and are tested for usability and impact inside our own operations. Our suite of applications includes:
| • | Analytics Cloud. Our Analytics Cloud serves as an analytics and reporting application. It provides customers with dashboards to view and analyze service revenue performance by customer, revenue tier, channel partner, product line and region. It also provides real-time visibility into expected results, conversion and up-sells, territory analysis, benchmarking and other trending reports. This tool enables the executive staff of our customers to identify trends and update sales strategies. |
| • | Service Sales Cloud. Our Service Sales Cloud provides renewals analytics and pipeline management used by our service sales teams. It includes an analytics dashboard for our teams to view their current sales pipeline, top deals and overall performance. It also includes an opportunity management view that incorporates our best practice renewal sales methodology to enable teams to focus on selling by quickly accessing quotes and customer information to maximize performance. |
| • | Channel Sales Cloud. Our Channel Sales Cloud provides channel partners and resellers with online access to their specific renewals opportunities and their performance. The application includes an executive dashboard that enables partners to view their renewals pipeline, their performance against |
79
Table of Contents
| key performance targets and how they are trending compared to previous quarters. In addition, an opportunity view allows partners to manage each upcoming renewal opportunity, find account, contact and asset information specific to that opportunity, download pre-built quotes and request assistance from ServiceSource to support the sales process. |
| • | eCommerce Cloud. Our eCommerce Cloud provides self-service capabilities to end customers through a secure, online portal. End customers can view their support contract information, modify their support coverage, obtain updated quotes and renew service contracts through online payment processes. In addition, it allows end customers to reach our service sales team should they require assistance or wish to make a purchase offline. |
Service Sales Teams
The service sales teams consist of individuals with specific expertise in our customers’ businesses, are deployed under our customers’ brand and follow sales processes tailored specifically to increase contract renewals, which is aimed at maximizing the value of the service revenue opportunity. These teams are deployed in direct sales or channel enablement models, and in each case manage the key components of the renewals process. Our service sales teams currently sell in over 30 languages from six sales centers around the globe. They are grouped into two primary areas:
| • | Global Selling. We employ service sales personnel that interact directly with end customers to sell service renewals. They also provide active sales enablement, support and management of channel partners. Our service sales teams act as an extension of our customers’ brands. |
| • | Sales Operations. We provide service revenue forecasting tailored to fit our customers’ bookings, revenue targets and specific reporting requirements. We supply a dedicated team of resources and tools to build and update customer and channel partner quotes and distribute them to the sales teams, channel partners and customers. Finally, we offer a business analytics team that provides analysis to maximize service revenue performance and provide insight into end customers, competitors and channel partners. |
Our Offerings
We deploy our solution through five offerings aimed at addressing specific industry needs. In each of these offerings, the specific deployment of software, managed services and data is tailored to address unique challenges. These offerings include:
| • | Direct Sales. Our direct sales offering is for customers who sell directly to their end customers. It includes teams skilled in sales of service contracts who are deployed under the customers’ brand and trained in the customers’ products, our data management infrastructure and applications to enable end customer self-service. Our dedicated service sales teams utilize sales process tailored specifically to increase contract renewals, as well as relevant best practices, to monitor each service revenue opportunity to drive higher service revenue renewals. |
| • | Channel Enablement. For customers who sell through single- or multi-tier channel distribution, our offering includes service sales teams skilled in channel enablement and management, and our Channel Sales Cloud. We help drive greater channel productivity and increased service revenue, while also enabling our customers to offload to us the complexity of managing service revenue through channel partners around the globe. |
| • | Reseller Sales. We manage service contract sales on behalf of large value-added resellers, such as leading telecom service providers responsible for selling products and services for multiple large technology vendors. We enable resellers to rely on us for sales and renewals of service contracts across their OEM partners, enabling the resellers to focus on their core business of providing services. An increase in renewal rates can impact the product discounts our resellers receive from OEMs in a financially meaningful way. |
80
Table of Contents
| • | Subscription Lifecycle Management. For software-as-a-service and other companies selling subscriptions, our offering includes custom applications and service sales teams focused not just on the renewal but on the adoption behavior critical to the renewal. Software-as-a-service companies face a distinct set of challenges with respect to customer renewals, given the lower switching cost and associated higher churn rates. Our service sales teams strive to improve customer adoption, reduce churn, increase cross-sell and up-sell opportunities and provide a detailed review of service revenue performance through our cloud based applications. |
| • | Enterprise. Our Enterprise solution typically encompasses a combination of all of our offerings listed above as a single package. For our Enterprise customers, we manage and sell all service revenue renewals for the customer on a global basis, which allows the customer to focus on product development and sales of new products and services. Our Enterprise engagements are often the result of our success in engaging with customers on one or more of the first four offerings, which may enable us to expand our service into a broader Enterprise relationship. In some instances, we may also enter directly into an Enterprise agreement without having previously provided a smaller set of solutions. |
How We Engage With Our Customers
The following illustrates the various elements of our customer engagement process:
| • | Service Performance Analysis. As part of our pre-sales process, our solution design team works with prospects to identify aspects of their service revenue performance where we can drive incremental revenue, visibility, efficiency and end customer and channel partner satisfaction. We do this through an SPA, which is a thorough and collaborative assessment of the prospect’s renewal data that leverages our proprietary intelligence platform. The SPA includes a comparative analysis against best practices and industry peers to better assess the prospect’s service revenue performance, identify recommendations and provide the foundation for a proposed solution and business case of how we might engage with the prospect to manage their service revenue. |
| • | Implementation of our solution. Once we have engaged a new customer, we implement our solution by building out a dedicated service sales team, integrating our customer’s enterprise systems and data into our systems, and deploying applications. We recruit our sales team members based on a refined set of attributes, competencies and characteristics that typically correlate with successful service sales personnel. We couple this knowledge with a global recruiting network to build out a team of service sales personnel that acts as an extension of our customers’ brands. Our project management organization works closely with our customers to consolidate, cleanse and manage customer data from disparate systems into our data warehouse. Our implementation team configures the applications for our customer, providing the reporting capabilities and systems access to enable our service sales team to start generating revenue for our customers as little as one month after entering into the engagement. |
| • | Account management. We provide active account management, including weekly forecast reviews, issue management, and quarterly forecast and performance reviews. We hold quarterly performance reviews with customer executives that include insights into channel performance, customer loss analytics and comparisons to benchmarks from our intelligence platform. We also regularly provide tailored recommendations for generating additional increases in service revenue, profitability, and end customer satisfaction. |
Customers
We sell our solutions to technology and technology-enabled healthcare and life sciences companies. As of September 30, 2010, we managed over 90 engagements across more than 50 customers, representing over $5 billion in service revenue opportunity under management.
Our top ten customers accounted for approximately 64% of our revenues in 2009. Sun Microsystems accounted for 24% of our revenue in 2009.
81
Table of Contents
Sales and Marketing
We sell our solutions through our global sales organization. Our sales representatives are organized by geographic regions, including NALA, EMEA and APJ, and by industry verticals. We deploy quota-carrying sales and solution design professionals to target specific regions and industry verticals.
We generate customer leads, accelerate sales opportunities and build brand awareness through our marketing programs. Our marketing programs target sales, services, and finance executives within technology and technology-enabled healthcare and life sciences industries. Our marketing teams and programs are organized by geography and industry segment to focus on the unique needs of customers within the specific target markets.
We host an annual executive summit in each of our three sales geographic regions where customers and industry players participate in a variety of programs designed to share information about the issues of service revenue performance. The summit features a variety of prominent keynote and customer speakers, panelists and presentations. The event also brings together partners, customers and other key participants in the service revenue management industry. Attendees gain insight into our technology roadmap and participate in interactive sessions that encourage them to express opinions on new features and functionality.
We are actively involved in the Service Executive Industry Board (“SEIB”), an independent industry board we founded to share best practices and address issues impacting the industry. The founding board members consist of 15 senior executives, including three of our executives, who manage and grow service revenue at leading technology-based hardware, software, and healthcare companies. SEIB meets regularly to establish industry standards and best practices for benchmarking and measuring the health of global maintenance, support and subscription service revenue and customer satisfaction.
Operations
Our cloud based solution is hosted in a secure third-party data center in the San Francisco Bay Area of California. Physical security features at this facility include 24x7 manned security with biometric access controls. Our technical redundancy features include redundant power, on-site backup generators, and environmental controls and monitoring. Our technology employs a wide range of security features, such as firewalls, server and user authentication access controls, data encryption, secured hosting, multi-tenant database, a global redundant network and secure encrypted offsite backup of sensitive data. We conduct regular security audits and tests for vulnerability and analysis of our infrastructure. We adhere to strict change management procedures and security policies when updating our technology. We proactively monitor and manage our infrastructure at all times for capacity, security and reliability. Our applications are secured via SSL protocols with data contained in a storage area network for high availability and security. Data backups are offsite, encrypted both during the transmission and at rest.
Research and Development
We focus our research and development efforts on enhancing our product and service offerings as well as complementary new capabilities as part of our proprietary solution. Our development strategy is to identify features, business intelligence, applications and other technology elements that are, or are expected to be, needed by service sales professionals, customers, channel partners and end customers to optimize service revenue performance. We are also investing in the development of additional cloud applications to serve our customers’ needs and enable greater operational efficiencies in our organization.
Our research and development expenses were $0 in 2007, $1.2 million in 2008, $2.1 million in 2009, and $3.9 million during the nine months ended September 30, 2010. In addition, we capitalize certain expenditures related to the development and enhancement of internal-use software. Capitalized software expenses were $0.7 million in 2007, $2.8 million in 2008, $5.0 million in 2009, and $3.1 million during the nine months ended September 30, 2010.
82
Table of Contents
Competition
The market for service revenue management is evolving. Historically, technology companies have managed their service renewals through internal personnel and relied upon technology ranging from Excel spreadsheets to internally-developed software to customized versions of traditional business intelligence tools and CRM or ERP software from vendors such as Oracle, SAP, salesforce.com and NetSuite. Some companies have made further investments in this area using firms such as Accenture and McKinsey for technology consulting and education services focused on service renewals. These internally-developed solutions represent the primary alternative to our integrated approach of combining software, managed services and data to provide end-to-end optimized service revenue performance.
We believe the principal competitive factors in our markets include the following:
| • | service revenue industry expertise, best practices, and benchmarks; |
| • | performance-based pricing of solutions; |
| • | ability to increase service revenue, renewal rates and close rates; |
| • | global capabilities; |
| • | completeness of solution; |
| • | ability to effectively represent customer brands to end customers and channel partners; |
| • | size of upfront investment; and |
| • | size and financial stability of operations. |
Although we believe we compete favorably with respect to many of these factors and currently have few direct competitors that offer integrated solutions at our scale, we believe that other competitors will emerge who have greater name recognition, longer operating histories, well-established relationships with customers in our markets and substantially greater financial, technical, personnel and other resources than we have. We expect competition and competitive pressure, from both new and existing competitors, to increase in the future.
Intellectual Property
We rely upon a combination of copyrights, trade secrets and trademarks, in addition to contractual restrictions such as confidentiality agreements, to establish and protect our proprietary rights. We currently have one registered copyright in the United States, and have registered trademarks for “ServiceSource” in the United States, the European Community, and Singapore. We also have pending trademark applications for the name ServiceSource in other locations and for other trade names in various locations.
Despite our efforts to protect our proprietary rights, unauthorized parties may attempt to copy or obtain and use our technology and/or brand names to develop products with the same functionality as our solution. Policing unauthorized use of our technology is difficult. The laws of other countries in which we market our solutions may offer little or no effective protection of our proprietary technology. Our competitors could also independently develop technologies equivalent to ours, and our intellectual property rights may not be broad enough for us to prevent competitors from selling products incorporating those technologies. Reverse engineering, unauthorized copying or other misappropriation of our proprietary technology could enable third parties to benefit from our technology without paying us for it, which would significantly harm our business.
We expect that technology solutions in our industry may be increasingly subject to third-party patent infringement claims as the number of competitors grows and the functionality of products in different industry segments overlaps. Such competitors could make a claim alleging that we infringe one or more of their patents, and we do not own any patents which could be asserted against them. Third parties may currently have, or may eventually be issued, patents upon which our current solution or future technology infringe. Any of these third parties might make a claim of infringement against us at any time.
83
Table of Contents
Employees
As of September 30, 2010, we had 1,391 employees including 25 in research and development, 93 in sales and marketing, 1,200 in our service sales organization and 73 in a general and administrative capacity. As of September 30, 2010, we had 829 employees in the United States, 116 in Singapore, 27 in the United Kingdom, 53 in Malaysia and 366 in Ireland.
None of our employees is represented by a labor union with respect to his or her employment with us.
Facilities
Our corporate headquarters occupy approximately 45,800 square feet in San Francisco, California under a lease that expires in June 2015.
We also have six globally distributed sales centers. We have three sales centers in North America: one at our corporate headquarters in San Francisco, and one in each of Denver and Nashville. We have additional international sales centers in Dublin, Ireland; Liverpool, United Kingdom; and Singapore. As of September 30, 2010, we have leased approximately 46,100 square feet in Denver expiring in 2012; approximately 73,000 square feet in Nashville expiring in 2018; approximately 38,000 square feet in Dublin expiring in 2019; approximately 11,800 square feet in Liverpool expiring in 2012; and approximately 13,300 square feet in Singapore expiring in 2013.
We recently opened a global sales operations center in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia. We use this center to centralize key contract renewal processes that do not require regional expertise, such as customer data management and quoting. We have leased approximately 10,100 square feet in Kuala Lumpur under a lease expiring in 2011.
84
Table of Contents
The following table sets forth the names, ages and positions of our executive officers, other members of executive management and directors as of the date hereof:
| Name |
Age | Position | ||||
| Executive Officers: |
||||||
| Michael A. Smerklo |
41 | Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board | ||||
| Jeffrey M. Bizzack |
50 | President | ||||
| David S. Oppenheimer |
53 | Chief Financial Officer | ||||
| Robert J. Sturgeon |
49 | Chief Delivery Officer | ||||
| Ganesh Bell |
38 | Executive Vice President, Products | ||||
| Raymond M. Martinelli |
52 | Chief People Officer | ||||
| Natalie A. McCullough |
38 | Chief Marketing Officer | ||||
| Paul D. Warenski |
46 | Senior Vice President and General Counsel | ||||
| Other Executive Management: |
||||||
| Stephen M. Unterberger |
52 | Chief Solutions Officer | ||||
| Jay R. Ackerman |
43 | Chief Services Officer | ||||
| Matt Rosenberg |
39 | Senior Vice President, Worldwide Sales | ||||
| Non-Employee Directors: |
||||||
| Steven M. Cakebread(1) |
59 | Director | ||||
| Marc F. McMorris(1)(2) |
42 | Director | ||||
| Bruce W. Dunlevie |
54 | Director | ||||
| Anthony Zingale |
55 | Director | ||||
| James C. Madden, V(2) |
49 | Director | ||||
| Barry D. Reynolds(1) |
48 | Director | ||||
| (1) | Member of the Audit Committee |
| (2) | Member of the Compensation Committee |
Executive Officers
Michael A. Smerklo has served as our Chief Executive Officer since January 2003 and as Chairman of our board of directors since November 2008. Prior to joining us, Mr. Smerklo served as Director of Business Development at Opsware, Inc., a software company, from 2000 to 2001. From 1998 to 2000, he served as an Associate at Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated, a financial services firm. We believe that Mr. Smerklo possesses specific attributes that qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors. Specifically, as our founder and the longest serving member of our board of directors, Mr. Smerklo possesses a deep understanding of our business as it has evolved over time. Of particular value is the operational experience and perspective he brings as our Chief Executive Officer. We believe Mr. Smerklo is a highly regarded leader in the service revenue management industry and that his operational experience greatly enhances the overall skill set of our board.
Jeffrey M. Bizzack has served as our President since February 2009. Prior to joining us, Mr. Bizzack served as Managing Director and Chief Executive Officer for Finance, Accounting and Human Resources Outsourcing at Accenture BPO Services LLC, a management consulting, technology services and outsourcing company, from May 2006 to May 2008. From April 2004 to April 2006, he served as Chief Executive Officer of Savista LLC, an outsourcing firm that provides business process outsourcing services for the finance and accounting sectors. From October 1988, Mr. Bizzack served in various positions with ProBusiness Services Inc., a human resources business process outsourcing company, with his last position being its Executive Vice President, Sales and Services when it was acquired by Automatic Data Processing Inc. in early 2003.
David S. Oppenheimer has served as our Chief Financial Officer since July 2010. Prior to joining us, Mr. Oppenheimer served as Chief Financial Officer of Mindjet Corporation, a desktop software company, from
85
Table of Contents
July 2007 to July 2010. From July 2005 to January 2007, he served as Chief Financial Officer of Hands-On Mobile, Inc., a mobile content company. From July 1999 to May 2005, he served as Chief Financial Officer of Digital Impact, Inc., an internet marketing company prior to its acquisition by Acxiom Corporation.
Robert J. Sturgeon has served as our Chief Delivery Officer since November 2010. Prior to that, he served as our Executive Vice President, Client Delivery from January 2009. He has also served as our Worldwide Executive Vice President, Client Operations from October 2007 to December 2008. Prior to joining us, Mr. Sturgeon served as Executive Vice President and General Manager of the Security Products Group for Juniper Networks, Inc., an information technology and computer networking products company, from August 2005 to May 2007, and as Juniper Networks, Inc.’s Vice President, Worldwide Customer Service from December 2001 to August 2005. Mr. Sturgeon also served as Vice President of Customer Service for Lucent Technologies, Inc., a provider of solutions to deliver voice, data and video communication services, from May 2000 to December 2001.
Ganesh Bell has served as our Executive Vice President, Products since May 2010. Prior to joining us, Mr. Bell served in various management positions at SAP AG, an enterprise software company, from January 2006 to April 2010, including Vice President of Product Strategy & Management for the Business Intelligence & Technology Platform Group and Vice President of Portfolio Strategy. Prior to that, Mr. Bell served as Chief Technologist for PeopleSoft, Inc., a software company that was acquired by Oracle, and as Chief Software Architect for J.D. Edwards & Company, an enterprise resource planning software company that was acquired by PeopleSoft, Inc.
Raymond M. Martinelli has served as our Chief People Officer since November 2010. Prior to that, Mr. Martinelli was our Executive Vice President of Human Resources since April 2006. Prior to joining us, Mr. Martinelli served as the Senior Vice President of Human Resources for Macromedia, Inc., a provider of web publishing products and solutions, from 2005 to 2006, before it was acquired by Adobe Systems Incorporated. From 2000 to 2005, Mr. Martinelli served as the Vice President of Human Resources for Juniper Networks, Inc., an information technology and computer networking products company.
Natalie A. McCullough has served as our Chief Marketing Officer since November 2010. Prior to that, Ms. McCullough was our Executive Vice President of Marketing from June 2010. She has also served as our Senior Vice President, Go To Market, from June 2009 to June 2010, our Senior Vice President of Sales Effectiveness, from March 2008 to June 2009, our Vice President of Sales Effectiveness, from December 2007 to March 2008, and our Vice President of Strategy Operations from August 2006 to December 2007. Prior to joining us, Ms. McCullough served as an Associate Principal at McKinsey & Company, a management consulting firm, where she worked from August 2000 to December 2005.
Paul D. Warenski has served as our Senior Vice President and General Counsel since May 2008. Prior to joining us, Mr. Warenski served as Senior Vice President and General Counsel of BenefitStreet, Inc., a provider of solutions for corporate benefit plans, from June 2007 to November 2007. From March 2006 to May 2007, Mr. Warenski served as Senior Vice President and General Counsel of Intraware, Inc., a software-as-a-service company. Prior to that, Mr. Warenski served as Senior Vice President, General Counsel, and Secretary of Commerce One, Inc., an e-commerce software company, which filed a voluntary petition for bankruptcy under Chapter 11 of the United States Bankruptcy Code in October 2004, serving as the Responsible Person for Commerce One in its bankruptcy proceeding. Prior to becoming General Counsel of Commerce One in September 2004, Mr. Warenski served at Commerce One as Associate General Counsel and Senior Counsel, beginning in February 2001. Mr. Warenski also was an associate, and later a partner, at the law firm of Schachter, Kristoff, Orenstein and Berkowitz in San Francisco, from 1996 to 2000.
Other Executive Management
Stephen M. Unterberger has served as our Chief Solutions Officer since September 2007. Prior to joining us, Mr. Unterberger served as Vice President of HRO Strategy Services of Hewitt Associates, Inc., a provider of
86
Table of Contents
human resource business process outsourcing and consulting services, from October 2004 to April 2007. Mr. Unterberger has also served as the Business Model Architecture President for Exult, Inc., a provider of business services related to human resources and business process outsourcing, from June 2003 until it was acquired by Hewitt Associates, Inc. in October 2004. Prior to that, Mr. Unterberger served in various executive positions for Exult, Inc., including Corporate Executive Vice President, Business Model Operations from January 2003 to June 2003, Chief of Service Delivery from June 2001 to January 2003, and Executive Vice President and Chief Operating Officer from February 1999 to June 2001.
Jay R. Ackerman has served as our Chief Services Officer since December 2009. He has also served as our Executive Vice President of Client Care from December 2005 to November 2009. Prior to joining us, Mr. Ackerman served as Chief Executive Officer and President of WNS North America Inc., a business processing outsourcing company, from 2003 to 2005. From 1999 to 2003, Mr. Ackerman served as Vice President Client Accounts and Sales for Exult, Inc., a provider of business services related to human resource and business process outsourcing.
Matt Rosenberg has served as our Senior Vice President, Worldwide Sales since July 2010. Prior to that, he served as our Senior Vice President of North America Sales since December 2008, and our Vice President of Sales since March 2007. Prior to joining us, Mr. Rosenberg served as Vice President of Sales of Visage Mobile Inc., a wireless mobility management solutions provider that was acquired by Convergys Corporation, from August 2003 to March 2007. From June 2001 to July 2003, he served as Director, Sales and Strategic Alliances of Vividence Corporation, a provider of market information services and evaluation applications to e-businesses, before it was acquired by Keynote Systems, Inc. From May 1999 to June 2001, Mr. Rosenberg served as Senior Director, Sales and Business Development of PeoplePC Inc., an internet service provider, before it was acquired by Earthlink, Inc.
Non-Employee Directors
Steven M. Cakebread has served as a member of our board of directors since January 2010. Since March 2010, Mr. Cakebread has served as Chief Financial Officer of Pandora Media, Inc., a provider of personalized internet radio and music discovery services. He has also served as a member of the board of directors of Solar Winds, Inc., a provider of information technology management software, since January 2008, and as a member of the board of directors of eHealth, Inc., an online provider of health insurance for individuals, families and small businesses, since June 2006. From August 2009 to March 2010, Mr. Cakebread was a Principal with J. Stevens & Co. LLC, a consulting company. From February 2009 to December 2009, Mr. Cakebread served as Senior Vice President, Chief Accounting Officer and Chief Financial Officer of Xactly Corporation, a provider of on-demand sales performance management software. Mr. Cakebread also served as President and Chief Strategy Officer of salesforce.com, inc., a CRM service provider, from March 2008 to February 2009, and as salesforce.com, inc.’s Chief Financial Officer from May 2002 to March 2008. From April 1997 to April 2002, Mr. Cakebread served as Senior Vice President and Chief Financial Officer at Autodesk, a software company. We believe that Mr. Cakebread possesses specific attributes that qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors. In particular, Mr. Cakebread has deep experience in the software industry, including software-as-a-service, which gives him a strong expertise on our business model and a valuable understanding of a large segment of our customer base. Mr. Cakebread also possesses financial expertise due to his experience as Chief Financial Officer at several technology companies and his past service as director of other technology firms.
Marc F. McMorris has served as a member of our board of directors since January 2007. Since August 1999, Mr. McMorris has been a Managing Director of General Atlantic LLC, a private equity firm. He has also served as a member of the board of directors of SSA Global Technologies, Inc., an enterprise software company, from 2003 to 2006. From May 1998 to August 1999, Mr. McMorris served as a Vice President in the High Technology Group at Goldman Sachs & Co, an investment banking and securities firm, and as an Associate in the same group from June 1996 to May 1998. We believe Mr. McMorris possesses specific attributes that qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors, including his overall knowledge of public markets and the
87
Table of Contents
technology industry, and his experience as an investor in numerous other private and public companies on behalf of General Atlantic, including technology firms. Mr. McMorris also has many professional relationships in the technology industry, both individually and through his firm, General Atlantic LLC, and those relationships have proven highly valuable in providing us access to prospective customers.
Bruce W. Dunlevie has served as a member of our board of directors since December 2004. Since May 1995, Mr. Dunlevie has been a General Partner of Benchmark Capital, a venture capital firm. He has also served as a member of the board of directors of Rambus Inc., a technology licensing company, since March 1990. From October 2003 to October 2007, Mr. Dunlevie was a member of the board of directors of Palm, Inc., a provider of mobile products. We believe that Mr. Dunlevie possesses specific attributes that qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors. In particular, Mr. Dunlevie is a longstanding member of our board of directors with a deep understanding of our business and our customer base, and he has extensive experience as an investor in technology companies on behalf of Benchmark Capital. Mr. Dunlevie brings the experience of having served on the board of several other technology companies. In addition, his professional network has given us access to numerous prospective customers.
Anthony Zingale has served as a member of our board of directors since July 2009. Since April 2010, Mr. Zingale has served as Chief Executive Officer of Jive Software, Inc., an independent social business software company, and from February 2010 to April 2010 he served as Jive Software, Inc.’s Interim Chief Executive Officer. Mr. Zingale has also served as a member of the board of directors of McAfee, Inc., a supplier of computer security solutions, since May 2008. From November 2005 to November 2006, he served as President and Chief Executive Officer of Mercury Interactive Corporation, a provider of business technology optimization solutions that included the quality, performance, availability and governance of enterprise software applications, and as Mercury Interactive Corporation’s President and Chief Operating Officer from December 2004 to November 2005. From July 2002 to November 2006, Mr. Zingale served as a member of the board of directors of Mercury Interactive Corporation. We believe Mr. Zingale possesses specific attributes that qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors. Of particular value is Mr. Zingale’s operational experience, which he has obtained by leading and managing multiple technology firms, including publicly traded companies. Mr. Zingale has also served as a director of other private and publicly traded technology companies. We believe he is a highly regarded leader in the technology industry and that his operational experience greatly enhances the overall skill set of our board.
James C. Madden, V has served as a member of our board of directors since January 2007. Since January 2007, Mr. Madden has been a General Partner of Accretive LLC, a private equity firm. He has also served as a member of the board of directors of Genpact Limited, a business process and technology management provider, since January 2005. From January 2005 to January 2007, Mr. Madden was a Special Advisor to General Atlantic LLC, a private equity firm. Mr. Madden also served as Chief Executive Officer of Exult, Inc., a provider of outsourced human resource services, from November 1998 to October 2004, and as Exult, Inc.’s Chairman of the Board, from February 2000 to October 2004 and as its President, from November 1998 to May 2003. We believe that Mr. Madden possesses specific attributes that qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors. Specifically, as the founder, Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of Exult, Inc., Mr. Madden possesses valuable operational and director experience leading a publicly traded company, and also brings the important perspective of running a company that was an external service provider of key business processes. We believe that perspective complements the technology-oriented background of most of our other board members. Mr. Madden also provides a formidable professional network, which has served us well. We also value Mr. Madden’s perspective as a director of a business process and technology management company.
Barry D. Reynolds has served as a member of our board of directors since January 2003. Since January 1998, Mr. Reynolds has been a General Partner of Housatonic Partners, a private equity firm. We believe that Mr. Reynolds possesses specific attributes that qualify him to serve as a member of our board of directors. Mr. Reynolds has served as a member of our board of directors longer than any other non-management director and has a thorough understanding of our business as it has evolved over time. Mr. Reynolds also brings valuable
88
Table of Contents
insight as an experienced investor on behalf of his private equity firm, Housatonic Partners, and as a respected business leader.
There are no family relationships among any of our directors or executive officers.
Code of Business Conduct and Ethics
Our board of directors has adopted a code of business conduct and ethics that applies to all of our employees, officers and directors, including our chief executive officer, chief financial officer and other principal executive and senior financial officers. The code of business conduct and ethics will be available on our website at www.servicesource.com. We expect that any amendments to the code, or any waivers of its requirements, will be disclosed on our website.
Board Composition and Risk Oversight
Our board of directors is currently composed of seven members. Our bylaws permit our board of directors to establish by resolution the authorized number of directors, and nine directors are currently authorized.
As of the closing of this offering, our certificate of incorporation and bylaws will provide for a classified board of directors consisting of three classes of directors, each serving staggered three-year terms, as follows:
| • | the Class I directors will be Bruce Dunlevie and Barry Reynolds, and their terms will expire at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2012; |
| • | the Class II directors will be Anthony Zingale and James Madden, and their terms will expire at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2013; and |
| • | the Class III directors will be Steven Cakebread, Marc McMorris and Michael Smerklo, and their terms will expire at the annual meeting of stockholders to be held in 2014. |
Upon expiration of the term of a class of directors, directors for that class will be elected for three-year terms at the annual meeting of stockholders in the year in which that term expires. Each director’s term continues until the election and qualification of his successor, or his earlier death, resignation or removal. Any increase or decrease in the number of directors will be distributed among the three classes so that, as nearly as possible, each class will consist of one-third of the directors. This classification of our board of directors may have the effect of delaying or preventing changes in control of our company.
Our board of directors is responsible for, among other things, overseeing the conduct of our business, reviewing and, where appropriate, approving our long-term strategic, financial and organizational goals and plans, and reviewing the performance of our chief executive officer and other members of senior management. Following the end of each year, our board of directors will conduct an annual self-evaluation, which includes a review of any areas in which the board of directors or management believes the board of directors can make a better contribution to our corporate governance, as well as a review of the committee structure and an assessment of the board of directors’ compliance with corporate governance principles. In fulfilling the board of directors’ responsibilities, directors have full access to our management and independent advisors.
Our board of directors, as a whole and through its committees, has responsibility for the oversight of risk management. Our senior management is responsible for assessing and managing our risks on a day-to-day basis. Our audit committee oversees and reviews with management our policies with respect to risk assessment and risk management and our significant financial risk exposures and the actions management has taken to limit, monitor or control such exposures, and our compensation committee oversees risk related to compensation policies. Both our audit and compensation committees report to the full board of directors with respect to these matters, among others.
89
Table of Contents
Director Independence
We intend to list our common stock on The Nasdaq Global Market. Under the rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market, independent directors must comprise a majority of a listed company’s board of directors within a specified period of the completion of this offering. In addition, the rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market require that, subject to specified exceptions, each member of a listed company’s audit, compensation and nominating and governance committees be independent. Audit committee members must also satisfy the independence criteria set forth in Rule 10A-3 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended. Under the rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market, a director will only qualify as an “independent director” if, in the opinion of that company’s board of directors, that person does not have a relationship that would interfere with the exercise of independent judgment in carrying out the responsibilities of a director.
In order to be considered to be independent for purposes of Rule 10A-3, a member of an audit committee of a listed company may not, other than in his or her capacity as a member of the audit committee, the board of directors, or any other board committee: (1) accept, directly or indirectly, any consulting, advisory, or other compensatory fee from the listed company or any of its subsidiaries; or (2) be an affiliated person of the listed company or any of its subsidiaries.
In December 2010, our board of directors undertook a review of its composition, the composition of its committees and the independence of each director. Based upon information requested from and provided by each director concerning his background, employment and affiliations, including family relationships, our board of directors has determined that none of the non-employee directors has a relationship that would interfere with the exercise of independent judgment in carrying out the responsibilities of a director and that each of these directors is “independent” as that term is defined under the rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market. Our board of directors also determined that Messrs. Cakebread, McMorris and Reynolds, who compose our audit committee, and Messrs. McMorris and Madden, who comprise our compensation committee, satisfy the independence standards for those committees established by the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and The Nasdaq Stock Market. In making this determination, our board of directors considered the relationships that each non-employee director has with our company and all other facts and circumstances our board of directors deemed relevant in determining their independence, including the beneficial ownership of our capital stock by each non-employee director.
Committees of the Board of Directors
Our board of directors has established the following committees: an audit committee and a compensation committee. The composition and primary responsibilities of each committee are described below. Members serve on these committees until their resignation or until otherwise determined by our board of directors. In addition, our board of directors is considering forming a nominating and corporate governance committee prior to the closing of this offering.
Audit Committee
Our audit committee consists of Messrs. Cakebread, McMorris and Reynolds each of whom is a non-employee member of our board of directors. All members of our audit committee meet the requirements for financial literacy established by the applicable rules and regulations of the SEC and The Nasdaq Stock Market. Mr. Cakebread is the chairperson of our audit committee, is our audit committee financial expert, as that term is defined under the SEC rules implementing Section 407 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002, and possesses financial sophistication as defined under the rules of The Nasdaq Stock Market. Our audit committee oversees our corporate accounting and financial reporting process and is responsible for, among other things:
| • | evaluating our independent auditors’ qualifications, independence and performance and approving the audit and non-audit services to be performed by our independent auditors; |
| • | monitoring the integrity of our financial statements and our compliance with legal and regulatory requirements as they relate to financial statements or accounting matters; |
90
Table of Contents
| • | reviewing the adequacy and effectiveness of our internal control policies and procedures; |
| • | discussing the scope and results of the audit with the independent auditors and reviewing with management and the independent auditors our interim and year-end operating results; |
| • | preparing the audit committee report that the SEC requires in our annual proxy statement; and |
| • | reviewing annually the audit committee charter and the committee’s performance. |
The audit committee will operate under a written charter that satisfies the applicable standards of the SEC and The Nasdaq Stock Market.
Compensation Committee
Our compensation committee consists of Messrs. McMorris and Madden. Mr. McMorris is the chairperson of our compensation committee. All of the members of our compensation committee meet the definition of outside directors under Section 162(m) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended. Our compensation committee reviews and recommends policies relating to the compensation and benefits of our officers and employees and is responsible for, among other things:
| • | overseeing our compensation policies, plans and benefit programs; |
| • | reviewing and approving for our executive officers: the annual base salary, the annual incentive bonus, including the specific goals and amount, equity compensation, employment agreements, severance arrangements and change in control arrangements and any other benefits, compensation or arrangements; |
| • | preparing the compensation committee report that the SEC requires to be included in our annual proxy statement; |
| • | administering, reviewing and making recommendations with respect to our equity compensation plans; and |
| • | reviewing annually the compensation committee charter and the committee’s performance. |
Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
None of the members of our compensation committee is currently, or has been at any time, an officer or employee of ours. None of our executive officers currently serves or in the past year has served as a member of the board of directors or compensation committee of any entity that has one or more executive officers serving on our board of directors or compensation committee.
Director Compensation
Directors who are employees do not receive any compensation for their service on our board of directors. We currently pay each of Messrs. Dunlevie, Madden and Reynolds $5,000 per meeting of the board of directors for regularly scheduled quarterly meetings. We have a policy of reimbursing directors for travel, lodging and other reasonable expenses incurred in connection with their attendance at board or committee meetings.
During the year ended December 31, 2009, one of our non-employee directors received options to purchase shares of common stock under the 2008 Share Option Plan. In July 2009, we granted an option to purchase 284,481 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $4.26 per share to Mr. Zingale in connection with his appointment to the board of directors. This option vests as to twenty-five percent of the shares as of one year from the date of grant and then in equal monthly installments over the subsequent three years.
During the year ended December 31, 2010, two of our non-employee directors received options to purchase shares of common stock of ServiceSource International, LLC under the 2008 Share Option Plan. In January
91
Table of Contents
2010, we granted an option to purchase 284,147 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $4.65 per share to Mr. Cakebread in connection with his appointment to the board of directors. In December 2010, we granted an option to purchase 134,000 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $5.80 per share to Mr. Madden. These options vest as to twenty-five percent of the shares as of one year from the date of grant and then in equal monthly installments over the subsequent three years.
The 2008 Share Option Plan provides that in the event we merge with or into another corporation or undergo a change in control, as defined in the 2008 Share Option Plan, the successor corporation or its parent or subsidiary will assume or substitute an equivalent award for each outstanding award under the 2008 Share Option Plan. If there is no assumption or substitution of outstanding options, then such options will become fully vested and exercisable. In addition, the administrator will notify participants in writing or electronically that options under the 2008 Share Option Plan will be exercisable for a period of time determined by the administrator, and will terminate upon expiration of such period to the extent unexercised.
Prior to and effective upon this offering, we intend to implement standard director fees and possible equity grants to each non-employee director who is not affiliated with a significant stockholder.
The following table sets forth information regarding compensation earned or accrued by our non-employee directors during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2010.
| Name |
Year | Fees Earned or Paid in Cash |
Option Awards(1) |
Total | ||||||||||||
| Steven M. Cakebread(2) |
2010 | — | $ | 666,921 | $ | 666,921 | ||||||||||
| 2009 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Marc F. McMorris |
2010 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Bruce W. Dunlevie |
2010 | $ | 20,000 | — | $ | 20,000 | ||||||||||
| 2009 | $ | 20,000 | — | $ | 20,000 | |||||||||||
| Anthony Zingale |
2010 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | — | $ | 595,675 | $ | 595,675 | |||||||||||
| James C. Madden, V |
2010 | $ | 20,000 | $ | 392,620 | $ | 412,620 | |||||||||
| 2009 | $ | 20,000 | — | $ | 20,000 | |||||||||||
| Barry D. Reynolds |
2010 | $ | 20,000 | — | $ | 20,000 | ||||||||||
| 2009 | $ | 20,000 | — | $ | 20,000 | |||||||||||
| R. James Ellis(3) |
2010 | $ | 20,000 | — | $ | 20,000 | ||||||||||
| 2009 | $ | 20,000 | — | $ | 20,000 | |||||||||||
| David Kennedy(4) |
2009 | $ | 5,000 | — | $ | 5,000 | ||||||||||
| (1) | The amounts in this column represent the aggregate grant date fair value of the option awards computed in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718. See Note 10 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion of assumptions made in determining the grant date fair value and compensation expense of our stock options. |
| (2) | Mr. Cakebread joined our board of directors in February 2010. |
| (3) | Mr. Ellis resigned as a member of our board of directors in December 2010. |
| (4) | Mr. Kennedy resigned as a member of our board of directors in March 2009. |
92
Table of Contents
The following table lists all outstanding equity awards held by our non-employee directors as of the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2010.
| Name |
Year | Option Grant Date |
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options Exercisable |
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options Unexercisable |
Option Exercise Price |
Option Expiration Date |
||||||||||||||||||
| Steven M. Cakebread(1) |
2010 | 1/27/2010 | — | 284,147 | $ | 4.65 | 1/27/2020 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Marc F. McMorris |
2010 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Bruce W. Dunlevie |
2010 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Anthony Zingale(1) |
2010 | 7/28/2009 | 100,754 | 183,727 | $ | 4.26 | 7/28/2019 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 7/28/2009 | — | 284,481 | $ | 4.26 | 7/28/2019 | ||||||||||||||||||
| James C. Madden, V |
2010 | (2) | 8/1/2007 | 150,000 | — | $ | 4.26 | 8/1/2017 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2010 | (1) | 12/16/2010 | — | 134,000 | $ | 5.80 | 12/16/2020 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | (2) | 8/1/2007 | 150,000 | — | $ | 4.26 | 8/1/2017 | |||||||||||||||||
| Barry D. Reynolds |
2010 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| R. James Ellis(3) |
2010 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | — | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Twenty-five percent of the shares subject to the option shall vest on the one year anniversary of the grant date and one forty-eighth of the shares vest monthly thereafter, subject to continued service. |
| (2) | The option is subject to an early exercise provision and is immediately exercisable. Twenty-five percent of the shares subject to the option vested on August 1, 2008 and 2.03% of the shares vest monthly thereafter. As of December 31, 2009, 87,500 shares were fully vested and 62,500 shares vest monthly over the remainder of the vesting period subject to continued service. As of December 31, 2010, 125,000 shares were fully vested and 25,000 shares vest monthly over the remainder of the vesting period, subject to continued service. |
| (3) | Mr. Ellis resigned as a member of our board of directors in December 2010. |
93
Table of Contents
Compensation Discussion and Analysis
The following discussion and analysis of compensation arrangements of our named executive officers for 2009 and 2010 should be read together with the compensation tables and related disclosures presented below. This discussion contains forward looking statements that are based on our current plans, considerations, expectations and determinations regarding future compensation programs.
For 2009, our named executive officers were:
Michael A. Smerklo, our Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board;
Jeffrey M. Bizzack, who joined us in February 2009 as our President;
Charles D. Boynton, our Chief Financial Officer during 2009;
Robert J. Sturgeon, our Chief Delivery Officer;
Raymond M. Martinelli, our Chief People Officer; and
Crosbie Burns, our current Executive Vice President, EMEA, who held the position of Executive Vice President, Worldwide Sales in 2009.
For 2010, our named executive officers were:
Michael A. Smerklo, our Chief Executive Officer and Chairman of the Board;
Jeffrey M. Bizzack, our President;
David S. Oppenheimer, who joined us in July 2010 as our Chief Financial Officer;
Charles D. Boynton, our former Chief Financial Officer, who departed in June 2010;
Robert J. Sturgeon, our Chief Delivery Officer; and
Ganesh Bell, who joined us in May 2010 as our Executive Vice President, Products.
Objectives and Principles of Our Executive Compensation
Our compensation philosophy is based on the following objectives and principles:
| • | attract, retain and motivate top-level executive talent; |
| • | provide compensation levels and structures that are both fiscally responsible and competitive within our industry and geography; |
| • | create a culture in which executive compensation aligns with our overall philosophy and pay-for-performance business model; |
| • | maintain simplicity, transparency and ease of administration; and |
| • | align the interests of our management team and shareholders by providing equity incentives, while avoiding unreasonable levels of shareholder dilution. |
Compensation Decision Process
Role of the Board of Directors and Compensation Committee. We established our compensation committee several years ago to take on the responsibility of compensation matters for all of our employees, including our executives. Our board of directors formally approved a charter for our compensation committee in November
94
Table of Contents
2008, and we have adopted a new charter in connection with this offering to comply with the applicable rules and regulations of a public company listed on The Nasdaq Global Market. In the past several years, including 2009 and 2010, our compensation committee has met and approved compensation decisions with respect to our executive officers at the beginning of each year, typically in January or February, including approval of cash incentive bonus payments based on the results of the previously completed year. Our compensation committee deliberates with respect to compensation decisions and then recommends to the full board of directors the ratification of such compensation decisions. Our full board of directors has ratified all of such decisions to date. For a description of the composition of our compensation committee upon the completion of the offering, see “Management—Committees of the Board of Directors—Compensation Committee.” In December 2010, our compensation committee made certain decisions with respect to 2011 executive compensation, as described below.
Role of Executive Officers. Our compensation committee generally seeks input from our Chief Executive Officer and our Chief People Officer when discussing the performance of and compensation levels for named executive officers (other than their own compensation). Our Chief People Officer has the responsibility to advise the compensation committee and coordinate with third-party compensation advisors. The compensation committee also works with our Chief Financial Officer to evaluate the financial, accounting and tax implications, and with our general counsel to evaluate legal matters, all related to our various compensation programs. None of our named executive officers participates in deliberations regarding his or her own compensation. Our compensation committee charter also specifies that our compensation committee deliberates and determines compensation decisions related to our Chief Executive Officer in executive session, outside of the presence of our Chief Executive Officer.
Role of Compensation Advisors. For 2009 and 2010, we retained Syzygy Consulting Group, an independent compensation consulting firm, to provide advice with respect to executive compensation decisions and comparison benchmarking. Working with management, Syzygy met with our compensation committee and provided various data and recommendations. In 2010, our compensation committee retained Compensia, an independent compensation consulting firm. Compensia advised the compensation committee for the compensation decisions made in December 2010 with respect to 2011. Our compensation committee retains the authority to retain and dismiss any compensation consultants pursuant to its charter.
Benchmarking. Given that we compete for executive officer talent with companies in the technology sector and companies that provide other professional services, we rely on certain compensation benchmarking in making our compensation decisions. To determine what constitutes competitive compensation, we engaged Syzygy to benchmark our cash and equity compensation levels for each executive against data from market surveys. For the past two years we have used market compensation surveys from Aon Consulting, with its Radford Executive Compensation Survey, and Culpepper, with its Culpeper Executive Compensation Survey.
Using that market data, we then determined individual compensation for each executive. Although our practice has been to benchmark to the fiftieth percentile of market-data survey compensation, we did not automatically tie compensation to that benchmark level for each member of our executive management team. Rather, we considered a number of individualized factors that are unique to our business, including individual performance, skill set, industry knowledge and experience, prior employment history, compensation at previous companies, recruiting efforts and negotiations, retention risk and an executive’s overall compensation level relative to his or her peers. The specific compensation data upon which we relied for benchmarking in 2009 and 2010 are described in more detail below.
For 2009, Syzygy provided competitive total cash and stock compensation data for our executive positions using multiple published compensation surveys of comparable software, services and general high-technology companies. Syzygy furnished and analyzed cash and stock compensation data from its 2008 proprietary database of private companies that reflect the pay practices of a broad number of technology companies. The ultimate data
95
Table of Contents
used for comparison for 2009 consisted of total cash and stock compensation pay practices for executives of 164 software and services companies that:
| • | privately raised a median of $53 million in capital since formation; |
| • | generated a median of $122 million in annual revenues in the last year; and |
| • | reported a median market valuation of $270 million. |
In addition, for 2009 Syzygy sourced private company total cash and stock compensation data from the 2008 Culpepper Executive Compensation Survey, which consisted of survey results from a group of 146 private software companies with annual revenues from $60 million to $200 million. Syzygy also provided public company data for total cash and stock compensation from the 2008 Culpepper Executive Compensation Survey and the Aon Consulting 2008 Radford Executive Compensation Survey. For the 2008 Culpepper Executive Compensation Survey, the public company data that was benchmarked came from 63 domestic software companies with annual revenues from $60 million to $200 million. For the Aon Consulting 2008 Radford Executive Compensation Survey, the domestic public company data came from:
| • | 61 software companies with annual revenues less than $200 million; |
| • | 98 Northern California technology companies with annual revenues under $200 million; and |
| • | all technology companies with annual revenues from $50 million to $200 million, which comprised 126 companies. |
One of our named executive officers for 2009 was based in the United Kingdom. For this individual, Syzygy sourced total cash and stock compensation data using comparable Culpepper and Radford United Kingdom surveys.
In comparing the total market-based compensatory stock ownership data of our executives to the various surveys, we assumed one new-hire equity grant for each executive plus one follow-on equity grant for each 18 months of service of such executive, all measured as of July 1, 2009.
In recognition that we were growing in size and beginning to move closer to initiating an initial public offering, our initial benchmarking for 2010 compensation decisions was based upon placing each executive at the mid-point between private and public pay practices at the fiftieth percentile. As a result, for 2010, Syzygy also provided cash and stock compensation data using multiple published compensation surveys of comparable software, services and general high-technology companies. Private company compensation data was primarily sourced from Syzygy’s 2009 proprietary database of private companies. The data used for comparison consisted of total cash and stock compensation pay practices for executives of 178 software and professional services companies that:
| • | privately raised a median of $67.5 million in capital since formation; |
| • | generated a median of $127 million in annual revenue in the last year; and |
| • | reported a median market valuation of $272.5 million. |
In addition, for 2010, Syzygy used for benchmarking purposes the Culpepper Executive Compensation Survey, which consisted of survey results from a group of 146 private and 63 public software companies, and the Aon Consulting Radford Executive Compensation Survey, which consisted of survey results from a group of approximately 215 public companies. For the 2009 Culpepper Executive Compensation Survey, the public company data that was benchmarked came from domestic software companies with annual revenues from $60 million to $200 million. For the Aon Consulting 2009 Radford Executive Compensation Survey, the domestic public company data came from:
| • | software companies with annual revenues less than $200 million; |
96
Table of Contents
| • | all Northern California technology companies; |
| • | Northern California technology companies with annual revenues less than $200 million; and |
| • | all technology companies with annual revenues from $50 million to $200 million. |
The specific comparison data for cash and equity compensation for 2010 was measured using the same methodology as 2009, with the measurement dates as of July 1, 2010.
Our Compensation Programs
The four elements of our executive compensation package are base salary, variable incentive pay, equity-based rewards and employee-benefits programs. We view these components of compensation as related in reviewing the total compensation packages of our executive officers. We determine the appropriate level for each compensation component based in part, but not exclusively, on information from analysis of third-party compensation surveys consistent with our recruiting and retention goals, our view of internal equity and consistency and overall company and individual performance. We compete with many other companies in seeking to attract and retain a skilled workforce, particularly companies in the technology sector. We have not adopted any formal or informal policies or guidelines for allocating compensation between long-term and currently paid-out compensation, between cash and non-cash compensation or among different forms of non-cash compensation. However, in line with our overall pay-for-performance philosophy of rewarding our employees for results that benefit us and our customers, the compensation committee’s practice has been to make a significant portion of an employee’s total compensation performance-based, so that the employee will be rewarded through bonuses and equity if we perform well in the near term and over time. We also believe that, for technology companies, stock-based compensation continues to be a primary motivator in attracting employees.
On Target Earnings—Base Salary and Variable Incentive Compensation. When analyzing the cash compensation of our executive leadership team, we have viewed the total cash compensation of base salary plus the variable incentive plan compensation as the on target earnings for each of such executive officers. In analyzing this figure, we assume that we will meet the targets necessary for our executives to earn their on target bonuses. For 2009 and 2010, we analyzed these on target cash earnings as the benchmark by which to measure our named executive officers’ compensation compared to the comparable positions identified in the market surveys provided by Syzygy. While we target the fiftieth percentile of the compensation levels of the companies in such surveys, we find that the data sets for private and public technology companies vary. Overall, for 2009 and 2010, our named executive officers as a group have ranged from approximately the twentieth to the fiftieth percentiles when their on target cash earnings are compared to public companies in such surveys, but have ranged generally from the fiftieth to the one hundredth percentile compared to private companies in such surveys. Overall, the percentiles vary in range significantly based on the individual positions of our named executive officers. As noted above, given our age as a company, our size, our results and our plans to pursue our initial public offering, we believe that the on target earnings for our named executive officers have been reasonable and appropriate for 2009 and 2010.
Base Salary. We establish base pay that is both reasonable and competitive in relation to the market, including the benchmarking data described above. We regularly monitor competitive base pay levels and make adjustments to base pay as appropriate. In general, a named executive officer’s base pay level should reflect the executive’s overall performance and contribution to us over time. We also seek to structure competitive base pay for our named executive officers based upon applicable market data analysis. As described below, we design base pay to provide the ongoing reward for each named executive officer’s work and contribution and to be competitive in attracting or retaining the executive. We do not provide automatic salary increases for our executive team. Once base pay levels are initially determined, however, we conduct salary reviews each year based upon current market data and the executive’s specific performance achievements. We also take into account salary levels for their retention effect. Salaries are also determined based on negotiations with our executive officers. We believe this pay-for-performance approach reflects our cultural values and our business model.
97
Table of Contents
The following are the effective annual base salaries for each of our named executive officers for 2008, 2009, 2010 and 2011:
| Annual Base Salary(1) | ||||||||||||||||
| Executive Officer |
2008 | 2009 | 2010 | 2011 | ||||||||||||
| Michael A. Smerklo |
$ | 383,250 | $ | 393,000 | $ | 410,000 | $ | 450,000 | ||||||||
| Jeffrey M. Bizzack |
— | $ | 375,000 | $ | 375,000 | $ | 400,000 | |||||||||
| David S. Oppenheimer |
— | — | $ | 300,000 | $ | 307,500 | ||||||||||
| Charles D. Boynton |
$ | 275,000 | $ | 275,000 | $ | 295,000 | — | |||||||||
| Robert J. Sturgeon |
$ | 275,000 | $ | 275,000 | $ | 275,000 | $ | 275,000 | ||||||||
| Ganesh Bell |
— | — | $ | 260,000 | $ | 260,000 | ||||||||||
| Raymond M. Martinelli |
$ | 250,000 | $ | 250,000 | — | — | ||||||||||
| (1) | Reflects effective annual base salary. Actual amounts earned vary for those named executive officers that either joined or departed during the years specified as described above. Data not provided for any period in which an individual was not a named executive officer. |
For the 2009 base salary compensation decisions, as a result of company performance and the levels of base compensation in relation to the benchmarking of the on target cash earnings discussed above, the compensation committee and the board determined to keep most salaries flat, with a modest increase in base salary for Mr. Smerklo. For the 2010 compensation decisions, Messrs. Smerklo and Boynton received modest increases in their base salaries as a result of the compensation committee and board acknowledgement of a mix of continued effective performance and the benchmarking analysis reflected above. Also, as Mr. Bizzack started with us in 2009 and Messrs. Oppenheimer and Bell commenced employment in 2010, their initial base salary levels reflect market benchmarking and negotiations with these individuals prior to their agreement to join us. For the 2011 compensation decisions made in December 2010, the board of directors determined to make modest increases in the base salaries of Messrs. Smerklo, Bizzack and Oppenheimer as an acknowledgement of performance and to further adjust salaries based on benchmarking provided by Compensia to comparable pre-IPO and public companies, given the developing plans for this offering. In addition, Mr. Burns’ annual base salary was £200,000 for both 2008 and 2009, denominated in British pounds given his location in the United Kingdom.
Variable Pay. Consistent with our pay-for-performance philosophy, we link a significant portion of our named executive officers’ cash compensation to individual and company performance. We design our variable pay programs to provide reasonable and competitive earnings potential relative to our industry and geography. For most of our named executive officers, we have implemented our corporate incentive bonus program as a motivational tool to achieve and exceed individual and company goals by paying for outstanding results. For those named executive officers who are sales executives, we have sales commission plans that serve as the primary motivational tool for achieving our company goals. Our variable pay programs are typically based on a formulaic assessment of our financial performance, giving consideration to an assessment of each individual’s performance. Our programs are designed to avoid entitlements, and to align actual payouts with actual results based on clearly understood metrics.
Our compensation committee reviews the structure and design of our variable pay plans on an annual basis, typically at the beginning of each year. For 2009 and 2010, our variable pay plans have been designed to be evaluated in each half of the applicable year. The overall business plan and related goals of our variable pay plans will be determined at the start of the year, typically in January or February. Once first half results are available, our compensation committee and board review these results and approve any payout under each plan for such first half results, typically in July of each year. Once the full-year results are available, the compensation committee and board review and approve the final, second half payouts under each plan for the full year results, typically in January or February of the following year. The compensation committee and the board of directors have the discretion to increase or decrease a payout under the variable pay plans in the event that they determine that circumstances warrant adjustment. The compensation committee and the board did not exercise any such discretion with respect to 2009. As described below, the compensation committee and the board modified the
98
Table of Contents
design of our variable pay plans in connection with analyzing the results for the first half of 2010 and setting the goals for the full year 2010.
2009 Corporate Incentive Bonus Plan. For 2009, all of our named executive officers participated in our 2009 Corporate Incentive Bonus Plan, which we refer to as the 2009 CIP. The 2009 CIP was designed for non-commissioned employees, generally at the manager level and above. For the named executive officers, the 2009 CIP bonus targets are set forth as a percentage of base salary, which range from approximately 30% to approximately 45% for most executives. Mr. Burns’ variable pay was based 35% upon the 2009 CIP and 65% upon a sales commission plan tied to the amount of new projected revenue sold by our worldwide service sales team in 2009. The actual targets are reflected below under “Executive Compensation—Grants of Plan-Based Awards.”
The 2009 CIP was designed for semi-annual payments, with funding based upon the company achieving certain Adjusted EBITDA targets. The Adjusted EBITDA targets were set by our board of directors in early February 2009. For the six months ended June 30, 2009, the Adjusted EBITDA target was $5.9 million, which was derived from a targeted net income of $0.1 million. The following table reconciles targeted net income to the Adjusted EBITDA target for the 2009 CIP of $5.9 million for the six months ended June 30, 2009:
| Targeted Net income |
$ | 0.1 | million | |
| Adjusted for: |
||||
| Stock-based compensation |
3.2 | |||
| Deprecation and amortization |
1.8 | |||
| Interest expense |
0.8 | |||
| Adjusted EBITDA Target |
$ | 5.9 | million | |
The following table reconciles targeted net income to the Adjusted EBITDA target for the 2009 CIP as set by our board of directors in early February 2009 for the year ended December 31, 2009:
| Targeted Net income |
$ | 10.1 | million | |
| Adjusted for: |
||||
| Stock-based compensation |
6.4 | |||
| Deprecation and amortization |
3.8 | |||
| Interest expense |
1.5 | |||
| Other income |
0.1 | |||
| Adjusted EBITDA Target |
$ | 21.9 | million | |
In July 2009, in connection with our mid-year evaluation of our business and targets for the 2009 CIP, the board of directors set a revised full year 2009 Adjusted EBITDA target for the 2009 CIP of $23.0 million.
To fund the 2009 CIP, the company was required to meet 85% of its Adjusted EBITDA target for the applicable period. Upon reaching the 85% level, we would pay bonuses at 50% of target. Funding then increased as Adjusted EBIDTA achievement increased, as shown in the table below.
The 2009 CIP also provided upside potential if we exceeded our Adjusted EBITDA targets. If we achieved 110% of our Adjusted EBITDA target for the first half of the year, we would fund the 2009 CIP in full for the first half, and the remaining 10% over achievement would be available for payment at the end of the year provided that we met 100% of our Adjusted EBITDA target for the full year. Similarly, if we met our goal for the first half of the year, and then overachieved for the full year, we would fund the 2009 CIP based on the full year overachievement. To the extent we missed our Adjusted EBITDA target in the first half of the year, any overachievement for the full year would be
99
Table of Contents
offset by the amount of the first half shortfall. Funding for overachievement in any 2009 CIP bonus period was capped at 200% of target.
The following table illustrates potential payouts at different levels of achievement under the 2009 CIP.
| Adjusted EBITDA Target Achievement |
2009 CIP Funding Percentage | |
| Below 85% |
No Payout | |
| 85% |
50% | |
| 88% |
60% | |
| 91% |
70% | |
| 94% |
80% | |
| 97% |
90% | |
| 100% |
100% | |
| 110% |
133% | |
| 120% |
166% | |
| 130% and above |
200% |
Performance goals were assessed quarterly and paid semi-annually, subject to the company achieving the necessary Adjusted EBITDA targets to fund the 2009 CIP. Under the 2009 CIP, individual bonus payments were calculated as follows for each bonus period, with any payment for the first half of the year taken into account with respect to the payment for the full year:
(% Company Bonus Pool Funded) x (% Individual Performance Goals Achieved) x (Individual Salary x Individual Semi-Annual Bonus %) = Aggregate Employee Payment
We made semi-annual bonus payments to the participating named executive officers, and to other 2009 CIP participants, in August 2009 and February 2010 after we had results for the applicable bonus periods. For the first half of 2009 semi-annual bonus period, we achieved approximately 110% against the 2009 CIP targets, and funded the bonus pool at a 100% level, with possible upside potential that carried into the full year assessment. For the full year, we achieved approximately 88% of our Adjusted EBITDA target, and funded the bonus pool at an 80% level (based upon 60% achievement in the second half of 2009). In addition, the overachievement in the first half of 2009 did not result in any additional payments at the end of the 2009 CIP year because any overachievement payments arising from the first half year were dependent upon our achieving 100% of our Adjusted EBITDA target for the full year. As noted above, we only attained 88% of our Adjusted EBITDA target for the full year under the 2009 CIP, which negated the first-half overachievement. For the targets related to the specific named executive officers under the 2009 CIP, see “Executive Compensation—Grants of Plan-Based Awards,” and for total annual payments made under the 2009 CIP for each named executive officer, see “Executive Compensation—Summary Compensation Tables.”
2010 Corporate Incentive Bonus Plan. For 2010, all of our named executive officers are eligible to participate in the 2010 Corporate Incentive Plan, to which we refer as the 2010 CIP. Like the 2009 CIP, the 2010 CIP is designed for non-commissioned employees, generally at the manager level and above. Employees paid by commission are not eligible to participate in the 2010 CIP. For the named executive officers, the 2010 CIP bonus targets are set forth as a percentage of base salary, which range from approximately 37% to approximately 49% for most executives. Mr. Sturgeon’s variable compensation for 2010 is based on a mixed target in which 60% of his overall target bonus amount is tied to the 2010 CIP and 40% is tied to a separate measurement of performance described below.
The 2010 CIP was designed with semi-annual payments. Unlike the 2009 CIP, however, funding for the 2010 CIP was based upon our achieving certain revenue targets, subject to a minimum level of Adjusted EBITDA. Those targets were set by our board of directors in late January 2010 for the six months ended June 30, 2010, and in July 2010 for the full year. For the six months ended June 30, 2010, the revenue threshold was $63.5 million representing 95% of the 2010 first half target of $66.8
100
Table of Contents
million and the Adjusted EBITDA minimum was $4.5 million representing 80% of the 2010 first half target of $5.6 million. The following table reconciles our targeted net loss of $0.6 million to the Adjusted EBITDA target for the 2010 CIP of $5.6 million for the six months ended June 30, 2010:
| Targeted Net loss |
$ | (0.6) | million | |
| Adjusted for: |
||||
| Stock-based compensation |
3.2 | |||
| Deprecation and amortization |
2.4 | |||
| Interest expense |
0.6 | |||
| Adjusted EBITDA Target |
$ | 5.6 | million | |
For the year ending December 31, 2010, the revenue threshold was $140.6 million representing 95% of the annual target of $148.0 million and the Adjusted EBITDA minimum was $21.4 million, representing 80% of the annual target of $26.8 million. The following table reconciles our targeted net income of $9.1 million to the Adjusted EBITDA target for the 2010 CIP of $26.8 million for the year ending December 31, 2010:
| Targeted Net income |
$ | 9.1 | million | |
| Adjusted for: |
||||
| Stock-based compensation |
6.7 | |||
| Deprecation and amortization |
5.5 | |||
| Interest expense |
1.2 | |||
| Provision for income taxes |
4.3 | |||
| Adjusted EBITDA Target |
$ | 26.8 | million | |
For the full year 2010 target, the board determined in July 2010 that the payment of certain sales commissions to our sales force, which were resulting from increased commission rates due to increased performance of our overall business, and certain previously unplanned expenses attributable to the planning and preparation for our initial public offering, would not be included as expenses in calculating the Adjusted EBITDA target. This was based on the rationale that the named executive officers and other employees eligible for the 2010 CIP should not be penalized for an otherwise lower Adjusted EBITDA due to the increased commission rates due to sales overachievement or for the added costs of pursuing this offering.
To fund the 2010 CIP, we are required to meet at least 80% of the Adjusted EBITDA target for the applicable period. Assuming we reach 80% of the Adjusted EBITDA target, we would fund the bonus pool based upon the level of revenue achieved, as shown in the table below.
| Revenue Target Achievement |
2010 CIP Funding Percentage | |
| Below 95% |
No Payout | |
| ³ 95% |
50% | |
| ³ 96% |
60% | |
| ³ 97% |
70% | |
| ³ 98% |
80% | |
| ³ 99% |
90% | |
| 100% |
100% |
The 2010 CIP also allows for additional upside payments in the event that we exceed our targets for full year 2010, subject to the following conditions:
| • | we must have achieved 100% of our Adjusted EBITDA target for the full year in order to make any upside payments; |
| • | upside payments are capped at 200% of 2010 CIP; |
101
Table of Contents
| • | no more than 50% of Adjusted EBITDA overachievement could be spent on bonuses under the 2010 CIP; and |
| • | upside payments will be determined based on the full year 2010 results after the year is completed. |
Subject to those conditions, the potential upside payments under the 2010 CIP were as follows:
| Annual Revenue Target Overachievement |
Annual 2010 CIP Funding Percentage | |
| ³ 102% |
120% | |
| ³ 104% |
140% | |
| ³ 106% |
160% | |
| ³ 108% |
180% | |
| 110% and above |
200% |
For purposes of the 2010 CIP, performance goals are assessed quarterly and bonuses are paid semi-annually, subject to our achieving the necessary Adjusted EBITDA and revenue targets to fund the 2010 CIP. Under the 2010 CIP, individual bonus payments are calculated as follows for each bonus period, with any payment for the first half of the year taken into account with respect to the payment for the full year:
(% Company Bonus Pool Funded) x (% Individual Performance Goal Achieved) x (Individual Salary x Individual Semi-Annual Bonus %) = Employee Payment
Given Mr. Sturgeon’s role and responsibility as a key manager of our service sales teams, our compensation committee and board of directors determined that Mr. Sturgeon’s 2010 bonus structure would include a separate 40% pay-for-performance target component that was tied to his operating unit, while 60% of his target bonus would continue to be tied to overall corporate performance under the 2010 CIP. This 40% target component is measured based on a gross margin statistic applicable to the service sales teams. The gross margin statistic is determined as the revenue generated by the service sales teams minus all of the direct and management costs for the service sales teams. This specific gross margin statistic is an internal financial metric that we use for measuring the performance of our service sales teams. This metric is not disclosed publicly by us and is confidential financial information to us, such that the disclosure of this metric would cause competitive harm to us. We believe this gross margin element for Mr. Sturgeon is challenging but achievable if we have strong performance by our service sales teams for the full year 2010.
We made semi-annual bonus payments to the participating named executive officers, and to other 2010 CIP participants, in July 2010. For the first semi-annual bonus period, we achieved 138% against the 2010 CIP targets, and therefore funded the bonus pool at a 100% level. We also carried the upside into the full year bonus period. We have not yet completed our assessment of the full year bonus period for 2010. For the targets related to the specific named executive officers under the 2010 CIP, see “Executive Compensation—Grants of Plan-Based Awards,” and for the earned first half payments made under the 2010 CIP for each named executive officer, see “Executive Compensation—Summary Compensation Tables.”
2010 Incremental Incentive Bonus Plan. In addition to our 2010 CIP, our compensation committee and board of directors approved a one-time, special variable cash incentive plan for 2010 for certain of our named executive officers and a few other senior executives. This plan, which we refer to as the 2010 Incremental Bonus Plan, is designed to award exceptional corporate performance based on a stretch target measuring our success with customers in 2010. The specific target that we use as the measurement for the 2010 Incremental Bonus Plan is an internal financial metric that we use for measuring certain customer contractual commitments based on a net recurring revenue amount in which we measure customer revenue gains offset by losses in the given measurement period. This
102
Table of Contents
metric is not disclosed publicly by us and is confidential financial information to us, such that the disclosure of this metric would cause competitive harm to us. We believe this target is challenging because it requires achieving exceptional sales and revenue results for 2010. Of our 2010 named executive officers, Jeffrey Bizzack, David Oppenheimer, Robert Sturgeon and Ganesh Bell are eligible for the 2010 Incremental Bonus Plan. We implemented the 2010 Incremental Bonus Plan in order to incentivize these senior executives to drive strong financial performance. Payment under the 2010 Incremental Bonus Plan will be in a lump sum if the stretch target is achieved by us, which will be assessed after the results for year 2010 are available. For detailed targets of each of these named executive officers under the 2010 Incremental Bonus Plan, see “Executive Compensation—Grants of Plan-Based Awards.”
Equity-Based Rewards. We design our equity programs to be both responsible and competitive in relation to the market. We monitor the market and applicable laws and regulations and adjust our equity programs as appropriate. Stock options are designed to reflect and reward a high level of sustained individual performance over time, as reflected in improved overall company value. As described in more detail below, we design equity-based compensation to help retain talent over a period of time and to provide named executive officers with a long-term reward that aligns their interests with those of our stockholders.
We historically have used stock option grants as the primary vehicle for equity compensation to our named executive officers and other employees. In order to promote the long-term incentive and retention features of equity compensation, we have typically issued our stock option grants subject to our standard one-year cliff vesting and four year vesting schedule. Under the vesting schedule, 25% of the stock option becomes exercisable one year after a specified vesting commencement date, and then vesting occurs monthly thereafter over the remaining three year period, which we believe is a common default vesting term in the technology industry. On occasion, we have also granted stock options with non-standard vesting or early exercise features, mostly in case-by-case situations for senior and other employees or candidates in high demand.
We anticipate using restricted stock units in addition to stock options upon becoming a publicly traded company for equity compensation, primarily to reduce the dilution associated with our equity compensation programs. We will be able to grant fewer shares of stock but still incent our executive officers based on the fact that restricted stock units will have value to the recipients in the absence of stock price appreciation.
We consider a number of factors to determine the size of all grants, including competitive market factors, named executive officer performance, retention value and a review of the named executive officer’s overall compensation package. Traditionally, equity awards to our named executive officers have been recommended by the compensation committee to our board of directors, which then makes the final determination as to whether to grant any equity award to a named executive officer. We anticipate that after our initial public offering, our compensation committee will make all equity grants.
Initial option grants upon hire are generally designed to attract experienced executives with established records of success and help retain them over the long term. The size of new hire grants has been evaluated by our compensation committee in light of the Syzygy-provided benchmarking data, and as a result of the negotiations with potential executive officers. Mr. Bizzack in 2009 and Messrs. Oppenheimer and Bell in 2010 each received new hire grants as part of their compensation packages upon joining us, the terms of which are reflected in the “Grants of Plan-Based Awards” table below.
Subsequent grants to named executive officers are intended to ensure that equity compensation remains competitive within our industry group and geography. Named executive officers whose skills and results we deem essential to our long-term success are eligible to receive higher equity grants. The decision to make such refresh grants has traditionally been based on rewarding performance, consistent with our pay-for-performance philosophy, and the benchmarking position of equity ownership of our named executive officers against the market surveys, taking into account the number of vested stock options that our named executive officers hold and the situation of our company as a mature private company approaching its initial public offering. Based on
103
Table of Contents
the benchmarking data, we determined that certain of our named executive officers in 2009, including our Chief Executive Officer, Chief Financial Officer and Chief People Officer, held equity compensation positions that were below the fiftieth percentile of the benchmarking private company group, but were above the fiftieth percentile of the public company group. At that time in 2009, we determined not to make any additional refresh grants to those named executive officers. In connection with our 2010 compensation review for our named executive officers and other employees, our compensation committee and board of directors determined to implement an annual refresh review for all employees, with emphasis on our senior employees, in order to award future performance and potential for future contributions to our company. We also took into account the market benchmarking for private companies in evaluating the size of potential refresh grants for our executive officers, especially given our plans to pursue this offering. As a result, our compensation committee and board approved refresh stock option grants to Messrs. Smerklo and Sturgeon in February 2010, the terms of which are reflected on the “Grants of Plan-Based Awards” table below.
Currently, we do not have any policy in place that requires us to grant equity compensation on specified dates. As noted above, we have traditionally made our equity grants to our named executive officers at the next board meeting, in the case of new hires, and in our annual review of compensation by our compensation committee and our board of directors, typically in January or February of each year.
We traditionally have not had any equity security ownership guidelines or requirements for our executive officers or directors.
Benefits Programs. We provide our employees with retirement, health and welfare benefits, such as our group health insurance plans, 401(k) retirement plan, and life, disability and accidental death insurance plans. Those plans, which are available to all employees including our named executive officers, are designed to provide a stable array of support to our employees and their families and are not performance based. Our benefits programs are generally established and adjusted by our human resources department with approval, as necessary, from senior management, the compensation committee or the board of directors, as appropriate.
Employment Agreements and Post-Employment Compensation
We enter into employment agreements with certain of our named executive officers, sometimes as part of the hiring process, that provide for at-will employment, base salary, eligibility to participate in the executive incentive bonus plan, standard employee benefit plan participation and recommendations for initial stock option grants. These agreements are subject to our standard proprietary information and invention assignment terms. Certain of the employment agreements contain certain severance and change of control benefits in favor of certain named executive officers, including our most senior executives. These arrangements provide for payments and benefits upon termination of their employment in specified circumstances, including following a change of control. These arrangements (including potential payments and terms) are discussed in more detail in the “Executive Compensation—Employment Agreements and Potential Payments upon Termination or Change-in-Control” section below. We believe that these agreements are an important retention tool, and will incent the named executive officers to maintain continued focus and dedication to their assigned duties to maximize stockholder value. The terms of these agreements were determined after review by the compensation committee of our retention goals for each named executive officer, as well as analysis of market data, similar agreements established in our industry and as a result of negotiations with certain of the executives.
Other Compensation Matters and Policies
Tax and Accounting Considerations. Internal Revenue Code Section 162(m) limits the amount that we may deduct for compensation paid to our Chief Executive Officer and to each of our four most highly compensated officers to $1,000,000 per person, unless certain exemption requirements are met. Exemptions to this deductibility limit may be made for various forms of “performance-based” compensation. In addition to salary and bonus compensation, upon the exercise of stock options that are not treated as incentive stock options, the excess of the current market price over the option price, or option spread, is treated as compensation and
104
Table of Contents
accordingly, in any year, such exercise may cause an officer’s total compensation to exceed $1,000,000. Under certain regulations, option spread compensation from options that meet certain requirements will not be subject to the $1,000,000 cap on deductibility, and in the past, we have granted options that we believe satisfy those requirements. While the compensation committee cannot predict how the deductibility limit may impact our compensation program in future years, the compensation committee intends to maintain an approach to executive compensation that follows our pay-for-performance philosophy. While the compensation committee has not adopted a formal policy regarding tax deductibility of compensation paid to our Chief Executive Officer and our four most highly compensated officers, the compensation committee intends to consider tax deductibility under Section 162(m) as a factor in compensation decisions.
Section 409A of the Internal Revenue Code imposes additional significant taxes in the event that an executive officer, director or other service provider receives “deferred compensation” that does not satisfy the requirements of Section 409A. Although we do not maintain traditional nonqualified deferred compensation plans, Section 409A may apply to certain arrangements we enter into with our executive officers, including our change of control severance arrangements. Consequently, to assist in avoiding additional tax under Section 409A, our intent is to design any such arrangements in a manner to avoid the application of Section 409A.
Adjustment or Recovery of Compensation. We do not have a formal policy regarding adjustment or recovery of awards or payments if the relevant performance measures upon which they are based are restated or otherwise adjusted in a manner that would reduce the size of the award or payment.
Compensation Risk Assessment
The compensation committee believes that although a portion of compensation provided to our executive officers is performance-based, our compensation programs do not encourage excessive or unnecessary risk taking. In fact, the design of our compensation programs encourage our executives to remain focused on both short-term and long-term strategic goals, in particular in connection with our pay-for-performance business model.
Summary Compensation Tables
The following tables provide information regarding the compensation of our named executive officers during the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2010.
| Name and Principal Position |
Year | Salary | Option Awards(1) |
Non-Equity Incentive Plan Compensation(2) |
All Other Compensation |
Total | ||||||||||||||||||
| Michael A. Smerklo Chief Executive Officer |
|
2010 2009 |
|
$ $ |
410,000 393,300 |
|
$
|
2,122,250 — |
|
$ $ |
100,000 146,400 |
|
$ $ |
2,000 2,000 |
(3) (3) |
$ $ |
2,634,250 541,700 |
| ||||||
| Jeffrey M. Bizzack President |
|
2010 2009 |
|
$ $ |
375,000 313,942 |
(4) |
$ $ |
586,000 3,527,334 |
|
$ $ |
87,500 110,833 |
|
|
— — |
|
$ $ |
1,048,500 3,952,109 |
| ||||||
| David S. Oppenheimer Chief Financial Officer |
2010 | $ | 128,409 | (5) | $ | 1,696,025 | — | — | $ | 1,824,434 | ||||||||||||||
| Charles D. Boynton former Chief Financial Officer |
|
2010 2009 |
|
$ $ |
144,285 275,000 |
(6)
|
$
|
85,837 — |
(6)
|
$ $ |
66,000 100,000 |
|
$ $ |
215,500 2,000 |
(7) (3) |
$ $ |
511,622 377,000 |
| ||||||
| Robert J. Sturgeon Chief Delivery Officer |
|
2010 2009 |
|
$ $ |
275,000 275,000 |
|
$
|
482,750 — |
|
$ $ |
112,500 180,000 |
|
|
— — |
|
$ $ |
870,250 455,000 |
| ||||||
| Ganesh Bell Executive Vice President, Products |
2010 | $ | 157,576 | (8) | $ | 838,000 | — | — | $ | 995,576 | ||||||||||||||
| Raymond M. Martinelli Chief People Officer |
2009 | $ | 250,000 | — | $ | 60,000 | $ | 2,000 | (3) | $ | 312,000 | |||||||||||||
| Crosbie Burns(9) Executive Vice President, EMEA |
2009 | $ | 324,400 | (9) | — | $ | 292,878 | (9) | — | $ | 617,278 | (9) | ||||||||||||
| (1) | The amounts in this column represent the aggregate grant date fair value of the option awards computed in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718. See Note 10 of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements for a discussion of assumptions made in determining the grant date fair value and compensation expense of our stock options. |
105
Table of Contents
| (2) | For 2009, all amounts represent payments under either the 2009 CIP or our sales commission plan earned with respect to 2009, and paid in July 2009 and February 2010. For 2010, all amounts represent payments under the 2010 CIP or our sales commission plan earned with respect to the six months ended June 30, 2010. All potential awards under either the 2010 CIP or other plans for the second half of 2010 are expected to be determined and paid in January or February of 2011 once results are available. See the “Grants of Plan-Based Awards” table for additional information. |
| (3) | Represents matching contributions made by us with respect to the named executive officer’s 401(k) contributions. We match a maximum of $2,000 per year. |
| (4) | Mr. Bizzack joined us as our President in February 2009 and received a prorated base salary based on an annual base salary of $375,000. |
| (5) | Mr. Oppenheimer joined us as our Chief Financial Officer in July 2010 and received a prorated base salary based on an annual base salary of $300,000. |
| (6) | Mr. Boynton left the company in June 2010 and received a prorated base salary based on an annual base salary of $295,000. In June 2010, we modified the vesting of 260,416 options granted to Mr. Boynton such that the cancellation of the vested shares occurs twelve months after termination. |
| (7) | Includes a severance payment in the amount of $213,500 described further under “Executive Compensation—Employment Agreements and Potential Payments upon Termination or Change-in-Control” and 401(k) company matching contributions of $2,000. |
| (8) | Mr. Bell joined us as our Executive Vice President of Products in May 2010 and received a prorated base salary based on an annual base salary of $260,000. |
| (9) | Mr. Burns was a named executive officer for part of 2009 when he held the title of Executive Vice President of Worldwide Sales. Since 2009, he has been our Executive Vice President of EMEA. Mr. Burns receives his cash compensation in British pounds. The amounts reported above were converted to U.S. dollars using a rate of £1.00 per $1.622, which was the exchange rate as of December 31, 2009. |
Grants of Plan-Based Awards
The following table presents information concerning grants of plan-based awards to each of our named executive officers during the years ended December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2010.
| Estimated Future Payouts Under Non-Equity Incentive Plan Awards(1) |
All Other Option Awards: Number of Securities Underlying Options |
Exercise or Base Price of Option Awards |
Grant Date Fair Value Option Awards(2) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Name |
Grant Date | Threshold | Target | Maximum | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Michael A. Smerklo |
12/16/2010 | — | — | — | 325,000 | $ | 5.80 | $ | 952,250 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1/27/2010 | $ | 100,000 | $ | 200,000 | $ | 400,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2/4/2009 | $ | 91,500 | $ | 183,000 | $ | 366,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2/9/2010 | 500,000 | $ | 4.65 | $ | 1,170,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Jeffrey M. Bizzack |
12/16/2010 | — | — | — | 200,000 | $ | 5.80 | $ | 586,000 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1/27/2010 | $ | 87,500 | $ | 175,000 | $ | 350,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1/27/2010 | — | $ | 100,000 | (3) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2/11/2009 | $ | 87,500 | $ | 175,000 | $ | 350,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2/27/2009 | 1,695,372 | $ | 4.26 | $ | 3,527,334 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| David S. Oppenheimer(4) |
12/16/2010 | — | — | — | 35,000 | $ | 5.80 | $ | 102,550 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7/7/2010 | $ | 25,000 | $ | 50,000 | $ | 100,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/7/2010 | — | $ | 20,000 | (3) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/28/2010 | 650,000 | $ | 4.95 | $ | 1,593,475 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Charles D. Boynton(5) |
1/27/2010 | $ | 66,000 | $ | 132,000 | $ | 264,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| 1/27/2010 | — | $ | 50,000 | (3) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2/4/2009 | $ | 62,500 | $ | 125,000 | $ | 250,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 6/25/2010 | — | — | — | 260,416 | $ | 4.26 | $ | 85,837 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Robert J. Sturgeon(6) |
12/16/2010 | — | — | — | 25,000 | $ | 5.80 | $ | 73,250 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 1/27/2010 | $ | 112,500 | $ | 225,000 | $ | 450,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1/27/2010 | — | $ | 50,000 | (3) | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2/4/2009 | $ | 112,500 | $ | 225,000 | $ | 450,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2/9/2010 | 175,000 | $ | 4.65 | $ | 409,500 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Ganesh Bell |
12/16/2010 | — | — | — | 35,000 | $ | 5.80 | $ | 102,550 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 7/28/2010 | $ | 58,500 | $ | 117,000 | $ | 234,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| 7/28/2010 | — | $ | 30,000 | (3) | 300,000 | $ | 4.95 | $ | 735,450 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Raymond M. Martinelli |
2/4/2009 | $ | 37,500 | $ | 75,000 | $ | 150,000 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Crosbie Burns(7) |
2/4/2009 | $ | 121,650 | $ | 243,300 | $ | 486,600 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Represents awards granted under our 2009 CIP, 2010 CIP or 2010 Incremental Bonus Plan, which were or are based on achievement of certain levels of performance for 2009 and 2010. These columns show the awards that were possible at the threshold, target and maximum levels of performance to the extent applicable. |
106
Table of Contents
| (2) | Reflects the grant date fair value of each award computed in accordance with FASB ASC Topic 718. These amounts do not necessarily correspond to the actual value that will be recognized by the named executive officers. The assumptions used in the valuation of these awards are consistent with the valuation methodologies specified in the notes to our consolidated financial statements. |
| (3) | Reflects amount payable under the 2010 Incremental Bonus Plan. The target amount is a lump sum amount payable if certain financial goals are achieved as measured at the end of 2010. For a further discussion, see “Executive Compensation—Compensation Discussion and Analysis—Our Compensation Programs—Variable Pay—2010 Incremental Incentive Bonus Plan.” |
| (4) | Mr. Oppenheimer joined us as our Chief Financial Officer in July 2010 and the 2010 CIP amount is a pro rated amount given his partial year of service. |
| (5) | Mr. Boynton left the company in June 2010 and no longer qualifies for any further payments under the 2010 CIP or the 2010 Incremental Bonus Plan. In June 2010, we modified the post-termination exercise period of 260,416 options granted to Mr. Boynton such that the cancellation of the vested shares occurs twelve months after termination. |
| (6) | For the 2010 CIP, Mr. Sturgeon is subject to an allocation of 60% of his target bonus based on corporate performance under the 2010 CIP and 40% of his target bonus based on a gross margin statistic applicable to the inside sales organization. For further discussion, see “Executive Compensation—Compensation Discussion and Analysis—Our Compensation Programs—Variable Pay—2010 Corporate Incentive Bonus Plan.” |
| (7) | Mr. Burns receives his cash compensation in British pounds. The amounts reported were converted to U.S. dollars using a rate of £1.00 per $1.622, which was the exchange rate as of December 31, 2009. |
Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End
The following table presents certain information concerning equity awards held by our named executive officers at the end of 2009 and 2010.
| Name |
Year | Vesting Commencement Date |
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options Exercisable |
Number of Securities Underlying Unexercised Options Unexercisable |
Option Exercise Price |
Option Expiration Date |
||||||||||||||||||
| Michael A. Smerklo |
|
2010 2009 |
|
|
1/1/2007 1/27/2010 12/16/2010 1/1/2007 |
|
|
1,800,000 — — 1,800,000 |
(1)
(1) |
|
— 500,000 325,000 — |
(2) (2)
|
$ $ $ $ |
4.26 4.65 5.80 4.26 |
|
|
6/1/2014 2/9/2020 12/16/2020 6/1/2014 |
| ||||||
| Jeffrey M. Bizzack |
|
2010 2009 |
|
|
2/27/2009 12/16/2010 2/27/2009 |
|
|
518,030 — — |
(3)
|
|
1,177,342 200,000 1,695,372 |
(2) (3) |
$ $ $ |
4.26 5.80 4.26 |
|
|
2/27/2019 12/16/2020 2/27/2019 |
| ||||||
| David S. Oppenheimer |
|
2010 2009 |
|
|
7/28/2010 12/16/2010 — |
|
|
— — — |
|
|
650,000 35,000 — |
(2) (2)
|
$ $
|
4.95 5.80 — |
|
|
7/28/2020 12/16/2020 — |
| ||||||
| Charles D. Boynton |
|
2010 2009 |
|
|
4/28/2008 4/28/2008 |
|
|
260,416 208,333 |
(4) (2) |
|
— 291,667 |
|
$ $ |
4.26 4.26 |
|
|
6/1/2014 4/30/2018 |
| ||||||
| Robert J. Sturgeon |
|
2010 2009 |
|
|
10/1/2007 1/27/2010 12/16/2010 10/1/2007 |
|
|
525,000 — — 525,000 |
(5)
(5) |
|
— 175,000 25,000 — |
(2) (2)
|
$ $ $ $ |
4.26 4.65 5.80 4.26 |
|
|
11/7/2017 2/9/2020 12/16/2020 11/7/2017 |
| ||||||
| Ganesh Bell |
|
2010 2009 |
|
|
5/24/2010 12/16/2010 — |
|
|
— — — |
|
|
300,000 35,000 — |
(2) (2)
|
$ $
|
4.95 5.80 — |
|
|
7/28/2020 12/16/2010 — |
| ||||||
| Raymond M. Martinelli |
|
2009 |
|
|
5/1/2006 11/1/2006 1/1/2008 |
|
|
185,000 15,000 75,000 |
(6) (7) (8) |
|
— — — |
|
$ $ $ |
1.20 1.49 4.26 |
|
|
6/1/2014 6/1/2014 1/30/2018 |
| ||||||
| Crosbie Burns |
|
2009 |
|
|
6/1/2005 11/1/2006 1/1/2008 |
|
|
431,000 90,000 75,000 |
(6) (9) (10) |
|
— — — |
|
$ $ $ |
0.25 1.49 4.26 |
|
|
6/1/2014 6/1/2014 1/30/2018 |
| ||||||
| (1) | The option is subject to an early exercise provision and is immediately exercisable. Twenty-five percent of the shares subject to the option vested on January 1, 2008 and 2.083% of the shares vest monthly thereafter. As of December 31, 2010, 1,762,500 shares were fully vested and 37,500 shares vest ratably over the remainder of the vesting period, subject to continued service to us. As of December 31, 2009, 1,312,500 shares were fully vested and 487,500 shares vest ratably over the remainder of the vesting period, subject to continued service to us. |
107
Table of Contents
| (2) | One-fourth of the shares subject to the option shall vest on the one year anniversary of the vesting commencement date and one forty-eighth of the shares vest monthly thereafter, subject to continued service to us. |
| (3) | Of the shares awarded, 1,130,248 shares subject to the option vest over four years, with 25% of the shares subject to the option vesting on February 27, 2010 and the remainder vest ratably over the following 36 months, and 565,124 shares subject to the option vest over five years with 25% of the shares subject to the option vesting on February 27, 2011 and the remainder vest ratably over the following 36 months, in each case subject to continued service with us. |
| (4) | Mr. Boynton left the company in June 2010. Shares subject to the option no longer vest. As a result of his separation and pursuant to his release agreement with us, the option is exercisable until June 24, 2011. |
| (5) | The option is subject to an early exercise provision and is immediately exercisable. Twenty-five percent of the shares subject to the option vested on October 1, 2008 and 2.083% of the shares vest monthly thereafter. As of December 31, 2010, 415,625 shares were fully vested and 109,375 shares vest ratably over the remainder of the vesting period. As of December 31, 2009, 284,375 shares were fully vested and 240,625 shares vest ratably over the remainder of the vesting period, subject to continued service to us. |
| (6) | The option is subject to an early exercise provision and is immediately exercisable. Twenty-five percent of the shares subject to the option vested on May 1, 2007 and 2.083% of the shares vest monthly thereafter. As of December 31, 2009, 158,958 shares were fully vested and 26,042 shares vest ratably over the remainder of the vesting period, subject to continued service to us. |
| (7) | The option is subject to an early exercise provision and is immediately exercisable. Twenty-five percent of the shares subject to the option vested on November 1, 2007 and 2.083% of the shares vest monthly thereafter. As of December 31, 2009, 11,562 shares were fully vested and 3,438 shares vest ratably over the remainder of the vesting period, subject to continued service to us. |
| (8) | The option is subject to an early exercise provision and is immediately exercisable. Twenty-five percent of the shares subject to the option vested on January 1, 2009 and 2.083% of the shares vest monthly thereafter, subject to continued service to us. As of December 31, 2009, 35,937 shares were fully vested and 39,063 shares will vest ratably over the remainder of the vesting period, subject to continued service to us. |
| (9) | The option is subject to an early exercise provision and is immediately exercisable. Twenty-five percent of the shares subject to the option vested on November 1, 2007 and 2.083% of the shares vest monthly thereafter. As of December 31, 2009, 69,375 shares were fully vested and 20,625 shares vest monthly thereafter, subject to continued service to us. |
| (10) | The option is subject to an early exercise provision and is immediately exercisable. Twenty-five percent of the shares subject to the option vested on January 1, 2009 and 2.083% of the shares vest monthly thereafter. As of December 31, 2009, 35,937 shares were fully vested and 39,063 shares vest ratably over the remainder of the vesting period, subject to continued service to us. |
Option Exercises and Stock Vested at Fiscal Year-End
None of the named executive officers exercised options or vested in shares of our common stock during the specified years.
Other Plans
We do not have any qualified or non-qualified defined benefit plans, any traditional non-qualified deferred compensation plans or other deferred compensation plans.
Employment Agreements and Potential Payments upon Termination or Change-in-Control
Employment Agreements
We have entered into employment agreements with Messrs. Smerklo, Bizzack, Oppenheimer, Sturgeon, Bell and Martinelli that provide for certain severance payments and equity vesting upon termination of their employment in specified circumstances. We believe that these agreements are an important retention tool, and will incent the named executive officers to maintain continued focus and dedication to their assigned duties to maximize stockholder value. The terms of these agreements were determined after review by the compensation committee of our retention goals for each named executive officer, as well as analysis of market data, similar agreements established within our industry, and applicable law. The employment agreements for Messrs. Smerklo, Bizzack and Sturgeon were effective in 2009. The employment agreements for Mr. Oppenheimer and Mr. Bell became effective in 2010 upon their joining the company. In addition, we entered into a separation agreement with Mr. Boynton in connection with his cessation of employment from us.
Michael A. Smerklo. We have entered into an employment agreement, dated July 6, 2007, amended and restated June 8, 2010, with Michael A. Smerklo, our Chairman and Chief Executive Officer. The agreement sets forth Mr. Smerklo’s annual base salary of $410,000 and a target bonus of $200,000, both amounts to be reviewed
108
Table of Contents
annually and subject to adjustment by the board of directors. The agreement also sets forth a grant of options to purchase 1,800,000 shares of our common stock vesting over four years. Mr. Smerklo’s agreement provides further that if we terminate his employment without Cause, or if he terminates his employment with us for Good Reason, either prior to a Change of Control or within twelve months following a Change of Control, he will be entitled to a severance payment in the amount of his earned, but not-yet-paid, annual target bonus for the year in which his separation occurs. In addition, if Mr. Smerklo is terminated without Cause, or if he terminates his employment with us for Good Reason, within one year following a Change of Control, in addition to receiving his earned but not-yet-paid annual target bonus, Mr. Smerklo’s outstanding equity compensation awards will immediately become vested in full. The foregoing separation payments and benefits are conditioned on Mr. Smerklo executing a general release of claims in our favor. In the event any payment to Mr. Smerklo provided in the agreement would constitute a “parachute payment” as defined in 280G(b)(2) of the Internal Revenue Code, then Mr. Smerklo will be entitled to receive the amount of such payment that would provide him the greatest after-tax benefit of either the full payment or a lesser payment which would result in no portion of such severance benefits being subject to excise tax.
Jeffrey M. Bizzack. We have entered into an employment agreement, dated February 27, 2009, amended and restated December 8, 2010, with Jeffrey Bizzack, our President. The agreement sets forth Mr. Bizzack’s annual base salary of $375,000, target bonus of $175,000 and grant of options to purchase 1,695,372 shares of our common stock vesting as to 1,130,248 shares over four years and 565,124 shares over five years. If, during the first year of employment, we were to terminate Mr. Bizzack’s employment without Cause or he terminated his employment with us for Good Reason, then 282,562 shares subject to the foregoing option grant would become vested on the termination date; this provision was not triggered, however, as Mr. Bizzack has been employed with us for over a year. Mr. Bizzack’s agreement provides further that if we terminate his employment without Cause, or if he terminates his employment with us for Good Reason, either prior to a Change of Control or within twelve months following a Change of Control, he will be entitled to a lump-sum severance payment equal to six months of his then current base salary, as well as six months target bonus, if any (subject to applicable tax withholdings), and the payment of premiums for up to 12 months of group health plan coverage, assuming that Mr. Bizzack has timely elected COBRA continuation coverage. In addition, if we terminate Mr. Bizzack’s employment without Cause, or if he terminates his employment with us for Good Reason, within one year following a Change of Control, in addition to receiving the severance payments described above, Mr. Bizzack’s outstanding equity compensation awards will immediately become vested in full. The foregoing separation payments and benefits are conditioned on Mr. Bizzack executing a general release of claims in our favor. In the event any payment to Mr. Bizzack provided in the agreement would constitute a “parachute payment” as defined in 280G(b)(2) of the Internal Revenue Code, then Mr. Bizzack will be entitled to receive the amount of such payment that would provide him the greatest after-tax benefit of either the full payment or a lesser payment which would result in no portion of such severance benefits being subject to excise tax.
David S. Oppenheimer. We have entered into an employment agreement, dated July 7, 2010, with David Oppenheimer, our Chief Financial Officer, who commenced employment in July 2010. The agreement sets forth Mr. Oppenheimer’s annual base salary of $300,000, target bonus of 40% of his annual salary to be pro rated for 2010 based on actual length of service pursuant to the 2010 CIP, eligibility for participation in the one-time 2010 special incentive bonus plan up to a level of $20,000 and grant of options to purchase 650,000 shares of our common stock vesting over four years. Mr. Oppenheimer’s agreement provides that if we terminate his employment without Cause, or if he terminates his employment with us for Good Reason, he will be entitled to a lump-sum severance payment equal to six months of his then current base salary, as well as 50% of his target bonus, if any (subject to applicable tax withholdings), the payment of premiums for up to 12 months of group health plan coverage, assuming that Mr. Oppenheimer has timely elected COBRA continuation coverage, and up to nine months from his termination date to exercise any stock option in which he has vested as of his termination date (which is six months longer than his stock option agreement would otherwise permit). In addition, if we terminate Mr. Oppenheimer’s employment without Cause, or if he terminates his employment with us for Good Reason, within one year following a Change of Control, in addition to the severance payments described above, all of Mr. Oppenheimer’s outstanding equity compensation awards will immediately vest. The foregoing
109
Table of Contents
separation payments and benefits are conditioned on Mr. Oppenheimer executing a general release of claims in our favor. In the event any payment to Mr. Oppenheimer provided in the agreement would constitute a “parachute payment” as defined in 280G(b)(2) of the Internal Revenue Code, then Mr. Oppenheimer will be entitled to receive the amount of such payment that would provide him the greatest after-tax benefit of either the full payment or a lesser payment which would result in no portion of such severance benefits being subject to excise tax.
Robert J. Sturgeon. We have entered into an employment agreement, dated September 17, 2007, amended and restated December 8, 2010, with Robert Sturgeon, our Chief Delivery Officer. The agreement sets forth Mr. Sturgeon’s annual base salary of $275,000, target bonus of $225,000 and grant of options to purchase 525,000 shares of our common stock vesting over four years. Mr. Sturgeon’s agreement provides that if we terminate his employment without Cause, or if he terminates his employment with us for Good Reason, within one year following a Change of Control, his outstanding equity compensation awards will immediately become vested in full. The foregoing acceleration benefit is conditioned on Mr. Sturgeon executing a general release of claims in our favor. In the event any payment to Mr. Sturgeon provided in the agreement would constitute a “parachute payment” as defined in 280G(b)(2) of the Internal Revenue Code, then Mr. Sturgeon will be entitled to receive the amount of such payment that would provide him the greatest after-tax benefit of either the full payment or a lesser payment which would result in no portion of such severance benefits being subject to excise tax.
Ganesh Bell. We have entered into an employment agreement, dated April 13, 2010, with Ganesh Bell, our Executive Vice President, Products, who commenced employment in May 2010. The agreement sets forth Mr. Bell’s annual base salary of $260,000, target bonus of $117,000, to be pro rated based on actual length of service pursuant to the 2010 CIP, and grant of options to purchase 300,000 shares of our common stock vesting over four years. Mr. Bell’s agreement provides that if we terminate his employment without Cause, or if he terminates his employment with us for Good Reason, within one year following a Change of Control, his outstanding equity compensation awards will immediately become vested in full. The foregoing acceleration benefit is conditioned on Mr. Bell executing a general release of claims in our favor. In the event any payment to Mr. Bell provided in the agreement would constitute a “parachute payment” as defined in 280G(b)(2) of the Internal Revenue Code, then Mr. Bell will be entitled to receive the amount of such payment that would provide him the greatest after-tax benefit of either the full payment or a lesser payment which would result in no portion of such severance benefits being subject to excise tax.
Raymond M. Martinelli. We have entered into an employment agreement, dated April 19, 2006, amended and restated December 8, 2010, with Raymond M. Martinelli, our Chief People Officer. The agreement sets forth Mr. Martinelli’s annual base salary of $270,000, potential bonus of $100,000 annually and grant of options to purchase 250,000 shares of our common stock vesting over four years. Mr. Martinelli’s agreement provides that if we terminate his employment without Cause, or if he terminates his employment with us for Good Reason, within one year following a Change of Control, his outstanding equity compensation awards will immediately become vested in full. The foregoing acceleration benefit is conditioned on Mr. Martinelli executing a general release of claims in our favor. In the event any payment to Mr. Martinelli provided in the agreement would constitute a “parachute payment” as defined in 280G(b)(2) of the Internal Revenue Code, then Mr. Martinelli will be entitled to receive the amount of such payment that would provide him the greatest after-tax benefit of either the full payment or a lesser payment which would result in no portion of such severance benefits being subject to excise tax.
For purposes of the employment agreements described above, the following definitions apply:
“Change of Control” means the a sale of all or substantially all of our equity interests; a merger, consolidation or similar transaction involving us following which the persons entitled to elect a majority of the members of our board of directors immediately before the transaction are not entitled to elect a majority of the members of the board of directors of the surviving entity following the transaction; or a sale of all or substantially all of our assets.
110
Table of Contents
“Cause” means (1) the employee’s commission of any felony or any crime involving fraud or dishonesty under the laws of the United States or any state thereof; (2) the employee’s commission of, or participation in, a fraud or act of dishonesty against us; (3) the employee’s intentional, material violation of any contract or agreement between the employee and us or any statutory duty owed to us; (4) the employee’s unauthorized use or disclosure of Proprietary and Confidential Information; or (5) the employee’s gross misconduct.
“Good Reason” means the occurrence of any one of the following events without the employee’s written consent: (1) a material, adverse change in the employee’s job title; (2) a material, adverse change in the employee’s job responsibilities; (3) any reduction in the employees’ base salary, target bonus or aggregate level of benefits; or (4) in most cases, a relocation of the employee’s principal place of employment beyond a specified radius of between 30 and 50 miles from the company’s location at the time the agreement is entered into; provided that the employee has notified us in writing of the event described in (1), (2), (3) or (4) above and within 30 days thereafter we have to restore the executive to the appropriate job title, responsibility, compensation or location. In the case of severance or vesting following a Change of Control, “Good Reason” is determined based on a change to the above factors as in effect immediately prior to a Change of Control.
Charles D. Boynton. In connection with his separation of employment from us on June 25, 2010, we entered into a release agreement with Mr. Boynton. Pursuant to the release agreement, we paid Mr. Boynton a lump sum of $213,500, representing six months of base salary and target bonus under the 2010 CIP, six months of COBRA continuation coverage, payment of the first half component of the 2010 CIP as actually calculated and determined by our board of directors and an extension of the exercise period with respect to the portion of vested stock options held by Mr. Boynton as of his separation date to June 24, 2011. In exchange, Mr. Boynton executed a standard release in favor of us. Mr. Boynton had previously entered into an employment agreement with us on terms generally similar to those described above for Mr. Bizzack except as noted on the table below.
Potential Payments upon Termination or Change-in-Control
The following table summarizes the estimated payments and benefits that would be provided to our named executive officers upon termination or a change-in-control under our plans and arrangements with our named executive officers described above, assuming the triggering event took place on the last business day of 2009 or 2010. For purposes of the table below, a “Qualifying Termination” means termination of employment by us without Cause, or termination of employment with us by the named executive officer for Good Reason, all as described above.
| Name |
Year | Qualifying Termination— Cash Compensation |
Qualifying Termination— Health Care Benefits |
Qualifying Termination within one year of a Change of Control— Acceleration of Equity Vesting(1) |
||||||||||||
| Michael A. Smerklo |
2010 | $ | 100,000 | (2) | –– | $ | 632,750 | (3) | ||||||||
| 2009 | $ | 91,500 | (2) | –– | $ | 190,125 | (3) | |||||||||
| Jeffrey M. Bizzack |
2010 | $ | 275,000 | (2) | $ | 16,660 | (2) | $ | 1,813,107 | |||||||
| 2009 | $ | 275,000 | (2) | $ | 16,848 | (2) | $ | 661,195 | ||||||||
| David S. Oppenheimer |
2010 | $ | 175,000 | (4) | $ | 16,660 | (4) | $ | 552,500 | |||||||
| Robert J. Sturgeon |
2010 | — | — | $ | 369,368 | |||||||||||
| 2009 | — | — | $ | 93,844 | ||||||||||||
| Ganesh Bell |
2010 | — | — | $ | 255,000 | |||||||||||
| Raymond M. Martinelli |
2009 | — | — | $ | 115,944 | |||||||||||
| Charles D. Boynton |
2010 | $ | 213,500 | (5) | $ | 8,330 | (4) | — | ||||||||
| 2009 | $ | 200,000 | (2) | $ | 8,424 | (2) | $ | 113,750 | ||||||||
| (1) | The amounts in this column represent the intrinsic value of the unvested shares subject to full equity acceleration, calculated as the sum of fair market value minus the option exercise price, multiplied by the number of unvested shares. Fair market value is equal to the value of shares of our common stock on December 31, 2009, the last business day of 2009, which was $4.65 per share, and an estimated fair market value on December 31, 2010, the last business day of 2010, which we estimate to be $5.80. |
| (2) | Eligibility for the specified compensation and benefits occurs upon a Qualifying Termination prior to a Change of Control or within twelve months after a Change of Control. For Mr. Smerklo, the amount for 2010 represents the estimated remaining payment under his 2010 CIP bonus assuming that the target amount is paid out at 100% for the full year 2010. |
111
Table of Contents
| (3) | Represents acceleration of the unvested portion of the applicable stock option, regardless of the early exercise provision applicable to the stock option. See “Executive Compensation—Outstanding Equity Awards at Fiscal Year-End” for further explanation of the stock options. |
| (4) | Eligibility for the specified compensation and benefits occurs upon a Qualifying Termination at any time. |
| (5) | Represents actual severance paid in June 2010 as described above. |
Employee Benefit Plans
2011 Equity Incentive Plan
Our board of directors has adopted our 2011 Equity Incentive Plan (the “2011 Plan”). The 2011 Plan will be effective upon the completion of this offering. The 2011 Plan permits the grant of incentive stock options, within the meaning of Code Section 422, to our employees and any of our subsidiary corporations’ employees, and the grant of nonstatutory stock options, restricted stock, restricted stock units, stock appreciation rights, performance units, performance shares, deferred stock units or dividend equivalents to our employees, directors and consultants and our subsidiary corporations’ employees and consultants.
Shares Under the Plan. The maximum aggregate number of shares issuable under the 2011 Plan will be determined by our board of directors prior to this offering, and will equal approximately 9% of the estimated shares of common stock outstanding upon completion of this offering. In addition, shares issuable under the 2011 Plan will include (i) any shares that, as of the completion of this offering, have been reserved but not issued pursuant to awards granted under our 2004 Omnibus Share Plan (the “2004 Plan”) or 2008 Share Option Plan (the “2008 Plan”) and are not subject to any awards granted thereunder, (ii) any shares subject to stock options or similar awards granted under the 2004 Plan or 2008 Plan that expire or terminate without having been exercised in full and (iii) any unvested shares issued pursuant to awards granted under the 2004 Plan or 2008 Plan that are forfeited to or repurchased by us, with the maximum number of shares to be added to the 2011 Plan pursuant to (i) through (iii) above equal to a cap to be determined by our board of directors prior to this offering. In addition, the number of shares available for issuance under the 2011 Plan will be annually increased on the first day of each of our fiscal years, beginning with 2012, by an amount equal to the least of:
| • | a number of shares to be specified; |
| • | 4% of the outstanding shares of our common stock as of the last day of our immediately preceding fiscal year; or |
| • | such other amount as our board of directors may determine. |
Shares issued pursuant to awards under the 2011 Plan that we repurchase or that expire or are forfeited, as well as shares tendered in payment of the exercise price of an award or to satisfy the tax withholding obligations related to an award, will become available for future grant or sale under the 2011 Plan. In addition, to the extent that an award is paid out in cash rather than shares, such cash payment will not reduce the number of shares available for issuance under the 2011 Plan.
Plan Administration. The 2011 Plan will be administered by our board of directors which, at its discretion or as legally required, may delegate such administration to our compensation committee and/or one or more additional committees (referred to as the “Administrator”). In the case of awards intended to qualify as “performance-based compensation” within the meaning of Code Section 162(m), the committee will consist of two or more “outside directors” within the meaning of Code Section 162(m).
Subject to the provisions of the 2011 Plan, the Administrator has the power to determine the terms of awards, including the recipients, the exercise price, if any, the number of shares covering each award, the fair market value of a share of our common stock, the vesting schedule applicable to the awards, together with any vesting acceleration, the form of consideration, if any, payable upon exercise of the award and the terms of the award agreement for use under the 2011 Plan. The Administrator also has the authority, subject to the terms of the 2011 Plan, to amend existing awards to reduce or increase their exercise price, to allow participants the
112
Table of Contents
opportunity to transfer outstanding awards to a financial institution or other person or entity selected by the Administrator, to institute an exchange program by which outstanding awards may be surrendered in exchange for awards that may have different exercise prices and terms, to prescribe rules and to construe and interpret the 2011 Plan and awards granted under the 2011 Plan.
Stock Options. The Administrator may grant incentive and/or nonstatutory stock options under the 2011 Plan, provided that incentive stock options are only granted to employees. The exercise price of such options must equal at least the fair market value of our common stock on the date of grant. The term of an incentive stock option may not exceed ten years; provided, however, that an incentive stock option held by a participant who owns more than 10% of the total combined voting power of all classes of our common stock, or of certain of our subsidiary corporations, may not have a term in excess of five years and must have an exercise price of at least 110% of the fair market value of our common stock on the grant date. The Administrator will determine the methods of payment of the exercise price of an option, which may include cash, shares, broker-assisted cashless exercise or other consideration permitted by applicable law and acceptable to the Administrator. Subject to the provisions of the 2011 Plan, the Administrator determines the remaining terms of the options (e.g., vesting). After the termination of service of an employee, director or consultant, the participant may exercise his or her options, to the extent vested as of such date of termination, for the period of time stated in his or her award agreement. However, in no event may an option be exercised later than the expiration of its term. The specific terms will be set forth in an award agreement.
Restricted Stock. Restricted stock may be granted under the 2011 Plan. Restricted stock awards are grants of shares of our common stock that are subject to various restrictions, including restrictions on transferability and forfeiture provisions. Shares of restricted stock will vest, and the restrictions on such shares will lapse, in accordance with terms and conditions established by the Administrator. The Administrator, in its sole discretion, may accelerate the time at which any restrictions will lapse or be removed. Recipients of restricted stock awards generally will have voting and dividend rights with respect to such shares upon grant without regard to vesting, unless the Administrator provides otherwise. Shares of restricted stock that do not vest for any reason will be forfeited by the recipient and will revert to us. The specific terms will be set forth in an award agreement.
Restricted Stock Units. Restricted stock units may be granted under the 2011 Plan. Each restricted stock unit granted is a bookkeeping entry representing an amount equal to the fair market value of one share of our common stock. The Administrator determines the terms and conditions of restricted stock units including the vesting criteria, which may include achievement of specified performance criteria or continued service to us, and the form and timing of payment. The Administrator, in its sole discretion, may reduce or waive any vesting criteria that must be met to receive a payout. The Administrator determines in its sole discretion whether an award will be settled in stock, cash or a combination of both. The specific terms will be set forth in an award agreement.
Stock Appreciation Rights. Stock appreciation rights may be granted under the 2011 Plan. Stock appreciation rights allow the recipient to receive the appreciation in the fair market value of our common stock between the exercise date and the date of grant. Subject to the provisions of the 2011 Plan, the Administrator determines the terms of stock appreciation rights, including when such rights vest and become exercisable and whether to settle such awards in cash or with shares of our common stock, or a combination thereof, except that the per share exercise price for the shares to be issued pursuant to the exercise of a stock appreciation right will be no less than 100% of the fair market value per share on the date of grant. The specific terms will be set forth in an award agreement.
Performance Units/Performance Shares. Performance units and performance shares may be granted under our 2011 Plan. Performance units and performance shares are awards that will result in a payment to a participant only if performance goals established by the Administrator are achieved or the awards otherwise vest. The Administrator determines the terms and conditions of performance units and performance shares including the vesting criteria, which may include achievement of specified performance criteria or continued service, which, depending on the extent to which they are met, will determine the number and/or value of performance units and
113
Table of Contents
performance shares to be paid out to participants. After the grant of a performance unit or performance share, the Administrator, in its sole discretion, may reduce or waive any performance objectives or other vesting provisions for such performance units or performance shares. Performance units shall have an initial dollar value established by the Administrator prior to the grant date. Performance shares will have an initial value equal to the fair market value of our common stock on the grant date. The Administrator, in its sole discretion, may pay earned performance units or performance shares in the form of cash, in shares or in any combination thereof. The specific terms will be set forth in an award agreement.
Deferred Stock Units. Deferred Stock Units may be granted under the 2011 Plan. Deferred Stock Units are restricted shares, restricted stock units, performance shares or performance units granted under the 2011 Plan that the Administrator permits to be paid out on an installment or deferred basis, in accordance with rules and procedures determined by the Administrator.
Dividend Equivalents. Dividend Equivalents may be granted under the 2011 Plan. Dividend Equivalents are credits, paid in cash, equal to the amount of cash dividends paid on shares represented by awards held by participants. Dividend Equivalents may be subject to the same vesting restrictions as the shares subject to an award.
Transferability of Awards. Unless the Administrator provides otherwise, the 2011 Plan generally does not allow for the transfer of awards and only the recipient of an option or stock appreciation right may exercise such an award during his or her lifetime.
Certain Adjustments. In the event of certain changes in our capitalization, to prevent diminution or enlargement of the benefits or potential benefits available under the 2011 Plan, the Administrator will make adjustments to one or more of the number and class of shares that may be delivered under the 2011 Plan and/or the number, class and price of shares covered by each outstanding award. In the event of a proposed dissolution or liquidation, the Administrator will notify participants as soon as practicable prior to the effective date of such proposed transaction, and all awards, to the extent not previously exercised, will terminate immediately prior to the consummation of such proposed transaction.
Merger or Change in Control. The 2011 Plan provides that in the event of a merger or Change in Control, as defined under the 2011 Plan, each outstanding award will be treated as the Administrator determines, except that if a successor corporation or its parent or subsidiary does not assume or substitute an equivalent award for any outstanding award, then such award will fully vest, all restrictions on such award will lapse, all performance goals or other vesting criteria applicable to such award will be deemed achieved at 100% of target levels and such award will become fully exercisable, if applicable, for a specified period prior to the transaction. The award will then terminate to the extent unexercised upon the expiration of the specified period of time. If the service of an outside director is terminated on or following a merger or Change in Control, other than pursuant to a voluntary resignation, his or her awards will become fully vested and exercisable, and all performance goals or other vesting requirements will be deemed achieved at 100% of target levels.
Clawback Requirement. The 2011 Plan provides that if the company is required to restate its financial statements due to material noncompliance with financial reporting requirements under the securities laws, executive officers will be required to repay compensation received pursuant to awards under the 2011 Plan during the three years preceding the restatement that is in excess of the amount to which they would be entitled under the restated financial statements, in accordance with Section 10D of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Plan Amendment, Termination. Our board of directors has the authority to amend, alter, suspend or terminate the 2011 Plan provided such action does not impair the existing rights of any participant. The 2011 Plan will automatically terminate in 2021, unless terminated earlier by our board of directors.
114
Table of Contents
2008 Share Option Plan
The 2008 Plan was adopted by our board of directors in December 2008 and approved by our equityholders in December 2008. The 2008 Plan was most recently amended in February 2009 to permit transfers of options for estate planning purposes. The 2008 Plan provides for the grant of stock options to our employees, directors and consultants and any of our subsidiary’s employees and consultants. As of the effective date of this offering, the 2008 Plan will be terminated and we will not grant any additional awards under the 2008 Plan. However, the 2008 Plan will continue to govern the terms and conditions of outstanding awards granted thereunder.
Shares Under the Plan. As of September 30, 2010, there were 8,021,139 options to purchase shares of our common stock outstanding and 3,476,597 shares were available for future grant under the 2008 Plan. Shares subject to options that expire or become unexercisable without having been exercised in full, or that are used to pay the exercise price of an option or to satisfy the tax withholding obligations related to an option (including any shares subject to options or similar awards granted under our 2004 Plan that expire or terminate without having been forfeited to or repurchased by us), will become available for future grant under the 2008 Plan, or, following this offering, under the 2011 Plan.
Plan Administration. Our board of directors or a committee appointed by our board of directors administers the 2008 Plan. Under the 2008 Plan, the administrator has the power to determine the terms of the options, including the recipients, the exercise price, the number of shares covering each option award, the fair market value of a share of our common stock, the form of consideration payable upon exercise of the option and the terms of the option agreement for use under the 2008 Plan. The administrator also has the authority, subject to the terms of the 2008 Plan, to amend existing options (including to reduce the option’s exercise price), to institute an exchange program by which outstanding options may be surrendered in exchange for options that may have different exercise prices and terms, to prescribe rules and to construe and interpret the 2008 Plan and options granted under the 2008 Plan.
Option Terms. The 2008 Plan permits the grant of stock options. The exercise price of such options must at least be equal to 100% of the fair market value of our common stock on the date of grant, and the term of the options may not exceed ten years. After termination of service of an employee, director or consultant, he or she may exercise his or her options, to the extent vested and exercisable as of such date of termination, for the period of time stated in the option agreement (which period of time must be at least three months). If termination is due to disability, or in the event of death, the options will remain exercisable for twelve months. However, in each case, an option may not be exercised later than the expiration of its term. The 2008 Plan generally does not allow for the transfer of options other than by will or the laws of descent and distribution, as permitted by Rule 701 under the Securities Act or into trust for estate planning purposes, unless the administrator otherwise determines.
Certain Adjustments. In the event of certain changes in our capitalization, the administrator will make adjustments to the number and class of shares and exercise price of shares subject to outstanding options and the number and class of shares that may be delivered under the 2008 Plan. In the event of a proposed liquidation or dissolution, the administrator will notify participants as soon as practicable and all options will terminate to the extent unexercised immediately prior to the consummation of such proposed transaction.
Merger or Change in Control. The 2008 Plan provides that in the event of our merger or change in control, the successor corporation or its parent or subsidiary will assume or substitute an equivalent award for each outstanding option. If there is no assumption or substitution of outstanding options, the options will become fully vested and exercisable. In addition, the administrator will notify participants in writing or electronically that options under the 2008 Plan will be exercisable for a period of time determined by the administrator, and will terminate to the extent unexercised upon expiration of such period.
Plan Amendment, Termination. Our board of directors has the authority to amend or terminate the 2008 Plan provided such action does not impair the rights of any participant, and subject to approval by our members, as
115
Table of Contents
defined in the LLC Agreement, if required by law. The 2008 Plan will terminate as of the effective date of this offering, unless terminated earlier by our board of directors.
2004 Omnibus Share Plan
The 2004 Plan was adopted by our Board of Directors and approved by our equityholders in May 2004. The 2004 Plan was most recently amended in February 2009 to permit transfers of options for estate planning purposes. The 2004 Plan expired in December 2008 upon adoption of the 2008 Plan. However, the 2004 Plan will continue to govern the terms and conditions of outstanding awards granted thereunder. The 2004 Plan provided for the grant of stock options and restricted stock to employees, officers, directors and consultants of us and our related companies.
Shares Under the Plan. As of September 30, 2010, there were 7,704,918 options to purchase shares of our common stock outstanding under the 2004 Plan. Shares subject to options or restricted stock that expire or otherwise terminate without having been forfeited to or repurchased by us will become available for future grant under the 2008 Plan, or, following this offering, under the 2011 Plan.
Plan Administration. Our board of directors or a committee appointed by our board of directors administered the 2004 Plan. Under the 2004 Plan, the administrator had the power to determine the terms and conditions of the awards, including the recipients, the exercise price, the number of shares covering each award and the vesting schedule of awards. The administrator also had the authority, subject to the terms of the 2004 Plan, to prescribe rules and to construe and interpret the 2004 Plan and awards granted under the 2004 Plan.
Option Terms. The 2004 Plan permitted the grant of stock options. The exercise price of such options had to be at least equal to 85% of the fair market value of a share of our common membership interests on the date of grant except that the price could not be less than 110% of such fair market value with respect to any person who owned securities of more than 10% of the total combined voting power of all classes of our securities and any securities of our subsidiaries. The option term may not exceed ten years.
After termination of continuous service with us or a related company, an optionee may exercise his or her option, to the extent vested as of such date of termination, for the period of time stated in the option agreement (which period of time must not be less than 30 days and will be three months if no period is specified). Generally, if termination is due to disability, or in the event of death, the options will remain exercisable for one year. However, an option may not be exercised later than the expiration of its term. The 2004 Plan generally does not allow for the transfer of options other than by will or the laws of descent and distribution, and during the optionee’s lifetime, may only be exercised by the optionee.
Restricted Stock. The 2004 Plan permitted the grant of restricted stock awards. After the administrator determined that it would grant a restricted stock award, the terms, conditions and restrictions related to the award were set forth in a restricted stock agreement. The 2004 Plan generally does not allow the transfer of restricted stock other than by will or the laws of descent and distribution, unless the administrator determines otherwise.
Certain Adjustments. In the event of certain changes in our capitalization, the administrator will make adjustments to the number and type of shares and exercise price of shares subject to outstanding options and the number and type of shares that may be delivered under the 2004 Plan. If we issue any of our shares as a share dividend while options are outstanding, then each optionee, upon exercising such outstanding option, will receive such share dividends that were declared or paid while the option was outstanding.
Merger or Other Transaction. The 2004 Plan provides that in the event of our merger into or consolidation with another entity in which we are not the surviving entity, or we are liquidated or we sell or dispose of all or substantially all of our assets to another entity, then the administrator will determine the treatment of awards, which may be any of the following: (i) subject to (iii) through (v) below, upon exercise of options, optionees may
116
Table of Contents
receive the same consideration as holders of our common stock receive pursuant to the transaction, (ii) all options will become fully vested, (iii) all optionees will be given a 30-day period prior to the transaction to exercise their options in full, subsequent to which all unexercised options will be cancelled, (iv) optionees may exercise their options prior to the transaction to the extent such options otherwise are exercisable according to their vesting schedule, and all options will be cancelled upon consummation of the transaction, or (v) all options are cancelled in exchange for payment of the value of the option minus the exercise price.
Plan Amendment, Termination. Our board of directors has the authority to amend or terminate the 2004 Plan provided such action does not adversely affect the rights of any award holder. The 2004 Plan terminated in December 2008 upon adoption of the 2008 Plan.
401(k) Plan
We have established a tax-qualified Section 401(k) retirement savings plan for all employees who satisfy certain eligibility requirements. Under this plan, participants may elect to make pre-tax contributions to the plan of up to a certain portion of their current compensation, not to exceed the applicable statutory income tax limitation. Currently, we match contributions made by participants in an amount up to $2,000 per annum. We intend for the plan to qualify under Section 401(a) of the Internal Revenue Code, such that contributions to the plan, and income earned on those contributions, are not taxable to participants until withdrawn from the plan.
Limitation on Liability and Indemnification Matters
Our certificate of incorporation, which will be in effect upon the completion of this offering, contains provisions that limit the liability of our directors for monetary damages to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law. Consequently, our directors will not be personally liable to us or our stockholders for monetary damages for any breach of fiduciary duties as directors, except liability for:
| • | any breach of the director’s duty of loyalty to us or our stockholders; |
| • | any act or omission not in good faith or that involves intentional misconduct or a knowing violation of law; |
| • | unlawful payments of dividends or unlawful stock repurchases or redemptions as provided in Section 174 of the Delaware General Corporation Law; or |
| • | any transaction from which the director derived an improper personal benefit. |
Our certificate of incorporation and bylaws to be in effect upon the completion of this offering provide that we are required to indemnify our directors and officers, in each case to the fullest extent permitted by Delaware law. Our bylaws also provide that we are obligated to advance expenses incurred by a director or officer in advance of the final disposition of any action or proceeding, and permit us to secure insurance on behalf of any officer, director, employee or other agent for any liability arising out of his or her actions in that capacity regardless of whether we would otherwise be permitted to indemnify him or her under the provisions of Delaware law. We have entered and expect to continue to enter into agreements to indemnify our directors, executive officers and other employees as determined by our board of directors. With specified exceptions, these agreements provide for indemnification for related expenses including, among other things, attorneys’ fees, judgments, fines and settlement amounts incurred by any of these individuals in any action or proceeding. We believe that these certificate of incorporation and bylaw provisions and indemnification agreements are necessary to attract and retain qualified persons as directors and officers. We also maintain directors’ and officers’ liability insurance.
The limitation of liability and indemnification provisions in our certificate of incorporation and bylaws may discourage stockholders from bringing a lawsuit against our directors and officers for breach of their fiduciary duty. They may also reduce the likelihood of derivative litigation against our directors and officers, even though
117
Table of Contents
an action, if successful, might benefit us and other stockholders. Further, a stockholder’s investment may be adversely affected to the extent that we pay the costs of settlement and damage awards against directors and officers as required by these indemnification provisions. At present, there is no pending litigation or proceeding involving any of our directors, officers or employees for which indemnification is sought, and we are not aware of any threatened litigation that may result in claims for indemnification.
118
Table of Contents
CERTAIN RELATIONSHIPS AND RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
The following is a description of certain relationships and transactions since January 1, 2007 involving our directors, executive officers, beneficial holders of more than 5% of our capital stock, or entities affiliated with them.
Conversion to a Corporation
We are currently a Delaware limited liability company. Prior to the issuance of any of our shares of common stock in this offering, we will convert into a Delaware corporation and change our name from ServiceSource International, LLC to ServiceSource International, Inc. This conversion to a corporate form in connection with this offering will occur pursuant to our Limited Liability Company Agreement (“LLC Agreement”) and has been approved by our board of directors. As a result, we will enter into a conversion agreement with certain of our equityholders that provides that the conversion to a corporation take the form of a statutory conversion, and also provides that the conversion shall occur immediately prior to the closing of this offering without any further action on the part of our board of directors or equityholders. In conjunction with the Conversion, all of our outstanding common shares will automatically be converted into shares of our common stock based on their relative rights as set forth in our LLC Agreement. See “Description of Capital Stock” for additional information regarding a description of the terms of our common stock following the Conversion and the terms of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws as will be in effect upon the closing of this offering. Also, as part of the Conversion and as contemplated by our LLC Agreement, two of our equityholders, GA SS Holding LLC, controlled by General Atlantic LLC, and SSLLC Holdings, Inc., controlled by Benchmark Capital, have each elected to merge with and into ServiceSource International, Inc. In the merger agreement, the companies that will be merged into us will represent and warrant that they do not have any liabilities, operations or businesses other than activities related to holding our common stock and other than liabilities for certain tax matters with respect to the periods prior to the merger which are not yet due and payable, and will provide us with certain indemnities. Concurrently with the consummation of the conversion to a corporation, the LLC Agreement will be terminated other than certain provisions relating to certain pre-termination tax matters and liabilities.
ServiceSource International, LLC may be required to make tax distributions to these equityholders with respect to 2010 and the portion of 2011 prior to the Conversion. These distributions would be made within 90 days after the end of 2010 and within 90 days after the Conversion, respectively.
Historical Transactions
Registration Rights Agreements
We have entered into a Registration and Information Rights Agreement with GA SS Holding LLC, controlled by General Atlantic, LLC, SSLLC Holdings, Inc., controlled by Benchmark Capital, and certain entities affiliated with Housatonic Partners, each a holder of our common stock. We have also entered into a securities purchase agreement that includes registration rights with certain of our stockholders. These agreements provide for certain rights relating to the registration of their shares of common stock. See “Description of Capital Stock—Registration Rights” below for additional information. In addition, these agreements provide for certain information rights. Following the completion of this offering, these agreements will continue in effect.
LLC Agreement
Our directors and members entered into the LLC Agreement which governs our operations. Upon the consummation of the Conversion, we will be converted into a corporation, and the LLC Agreement will no longer govern our operations and will not govern the rights of our stockholders.
ServiceSource International, LLC created a board of directors to manage our business affairs. Under the LLC Agreement, there shall be up to a maximum of nine directors of the board of directors and the specific
119
Table of Contents
number of directors shall be set by resolution of the board of directors. Pursuant to the LLC Agreement, each member shall vote to cause and to maintain the election to the board of directors one director selected by GA SS Holding LLC, one director selected by Housatonic Equity Investors SBIC, L.P. and Housatonic Micro Fund SBIC, L.P., and one director selected by SSLLC Holdings, Inc. or its affiliates. The remainder of the directors shall be selected by the holders of a majority of the then outstanding common shares.
Under the LLC Agreement, there is one class of shares designated as common shares. Each equityholder has one vote for each common share held. The LLC Agreement also sets forth the rights of and restrictions on common shareholders, including certain rights of first refusal in favor of us and our Chief Executive Officer with respect to proposed transfers of common shares held by any officer of ServiceSource International, LLC, and certain preemptive and co-sale rights in favor of each member holding at least 5% of the equity securities of ServiceSource International, LLC that are not subject to vesting forfeiture or repurchase conditions. In addition, the LLC Agreement places certain transfer restrictions on the holders of common shares. The LLC agreement also authorizes certain equity incentive plans pursuant to which unvested common shares have been granted. In accordance with the LLC Agreement, the common shares will be converted into shares of our common stock in connection with the Conversion. The LLC Agreement includes indemnification provisions obligating ServiceSource International, LLC to indemnify its board of directors, officers, members, employees and agents.
Concurrently with the consummation of the Conversion, the LLC Agreement will be terminated other than certain provisions relating to certain pre-termination tax matters and liabilities.
Policies and Procedures for Related Party Transactions
We have adopted a formal written policy that our executive officers, directors, holders of more than 5% of any class of our voting securities, and any member of the immediate family of and any entity affiliated with any of the foregoing persons, are not permitted to enter into a related party transaction with us without the prior consent of our audit committee, or other independent members of our board of directors in situations in which it is inappropriate for our audit committee to review such transaction due to a conflict of interest. Any request for us to enter into a transaction with an executive officer, director, principal stockholder, or any of their immediate family members or affiliates, in which the amount involved exceeds $120,000, must first be presented to our audit committee for review, consideration and approval. In approving or rejecting any such proposal, our audit committee is to consider the relevant facts and circumstances available and deemed relevant to the audit committee, including, but not limited to, whether the transaction is on terms no less favorable than terms generally available to an unaffiliated third party under the same or similar circumstances and the extent of the related party’s interest in the transaction. All of the transactions described above were entered into prior to the adoption of this policy.
120
Table of Contents
PRINCIPAL AND SELLING STOCKHOLDERS
The following table sets forth information regarding beneficial ownership of our common stock as of September 30, 2010, after giving effect to the Conversion, and as adjusted to reflect the shares of common stock to be issued and sold in the offering assuming no exercise of the underwriters’ overallotment option, by:
| • | each person or group of affiliated persons known by us to be the beneficial owner of more than 5% of our common stock; |
| • | each of our named executive officers; |
| • | each of our directors; |
| • | all executive officers and directors as a group; and |
| • | all selling stockholders. |
This beneficial ownership information is presented on the following bases:
We have determined beneficial ownership in accordance with SEC rules. The information does not necessarily indicate beneficial ownership for any other purpose. Under these rules, the number of shares of common stock deemed outstanding includes shares issuable upon exercise of options held by the respective person or group which may be exercised within 60 days after September 30, 2010. For purposes of calculating each person’s or group’s percentage ownership, stock options exercisable within 60 days after September 30, 2010 are included for that person or group. These shares are not deemed outstanding, however, for the purpose of calculating the percentage ownership of any other person or group.
Applicable percentage ownership is based on 57,426,218 shares of common stock outstanding at September 30, 2010 after giving effect to the Conversion. For purposes of the table below, we have assumed that shares of common stock will be outstanding upon completion of this offering.
121
Table of Contents
Unless otherwise indicated by the footnotes below and subject to applicable community property laws, to our knowledge, each stockholder named in the following table possesses sole voting and investment power over the shares listed. Unless otherwise indicated by the footnotes below, the address of each person listed in the table is c/o ServiceSource, 634 Second Street, San Francisco, California 94107.
| Shares beneficially owned prior to the offering |
Number of shares being offered |
Shares beneficially owned after the offering |
||||||||||||||||||
| Name of beneficial owner |
Number | Percentage | Number | Percentage | ||||||||||||||||
| 5% Stockholders: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| GA SS Holding LLC(1) |
15,286,453 | 26.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| SSLLC Holdings, Inc.(2) |
11,417,860 | 19.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Entities affiliated with Housatonic Partners(3) |
9,552,500 | 16.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Michael A. Smerklo(4) |
4,528,289 | 7.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Executive Officers and Directors: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Michael A. Smerklo(4) |
4,528,289 | 7.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Jeffrey M. Bizzack(5) |
494,483 | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| David S. Oppenheimer |
0 | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| Charles D. Boynton(6) |
260,416 | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| Robert J. Sturgeon(7) |
525,000 | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| Ganesh Bell |
0 | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| Steven M. Cakebread |
0 | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| Marc F. McMorris(8) |
15,286,453 | 26.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Bruce W. Dunlevie(9) |
11,417,860 | 19.9 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Anthony Zingale(10) |
94,827 | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| James C. Madden, V(11) |
150,000 | * | ||||||||||||||||||
| Barry D. Reynolds(12) |
9,552,500 | 16.6 | ||||||||||||||||||
| All executive officers and directors as a group (14 persons)(13) |
42,578,787 | 69.8 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Other Selling Stockholders: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| (*) | Less than 1%. |
| (1) | GA SS Holding LLC (“GA SS”) is wholly-owned by its sole member, GA SS Holding II, LLC (“GA SS II”). GA SS II is wholly-owned by investment funds affiliated with and controlled by General Atlantic LLC and/or certain of its managing directors. Mr. McMorris, one of the members of our board of directors, is a managing director of General Atlantic LLC and disclaims beneficial ownership of any shares listed in the table above as owned by GA SS except to the extent of his pecuniary interest therein. There are 28 other managing directors of General Atlantic LLC. Each of these managing directors disclaims ownership of the shares owned by GA SS except to the extent he or she has a pecuniary interest therein. Other than their interest in General Atlantic LLC and its investment entities, these individuals are not affiliated with us, our management or any of the named underwriters for this offering. The address for GA SS, GA SS II and General Atlantic LLC is c/o General Atlantic Service Company, LLC, 3 Pickwick Plaza, Greenwich, CT 06830. |
| (2) | Consists of shares held of record by SSLLC Holdings, Inc. (“SSLLC”), which is controlled by Benchmark Capital Partners V, L.P. (“BCP V”), as nominee for BCP V, Benchmark Founders’ Fund V, L.P., Benchmark Founders’ Fund V-A, L.P., Benchmark Founders’ Fund V-B, L.P. and related individuals. Benchmark Capital Management Co. V, L.P. is the general partner of BCP V and its managing members are Alexandre Balkanski, Bruce W. Dunlevie, J. William Gurley, Kevin R. Harvey, Robert C. Kagle, Steven M. Spurlock, Peter H. Fenton and Mitchell H. Lasky. These individuals may be deemed to have shared voting and dispositive power over all of the shares held by SSLLC. Each of these individuals disclaims beneficial ownership of such shares, except to the extent of his pecuniary interest therein. The address for these entities and individuals is 2480 Sand Hill Road, Suite 200, Menlo Park, California 94025. |
| (3) | Includes (i) 6,084,000 shares held of record by Housatonic Micro Fund SBIC, LP (“HMF SBIC”); (ii) 2,248,829 shares held of record by Housatonic Equity Investors IV, LP (“HEI IV”); (iii) 1,116,000 shares held of record by Housatonic Equity Investors SBIC, LP (“HEI SBIC”); and (iv) 103,671 shares held of record by Housatonic Equity Affiliates IV, LP (“HEA IV”). Housatonic Micro Partners SBIC, LLC is the General Partner of HMF SBIC; Housatonic Equity Partners IV, LLC is the General Partner of HEI IV and HEA IV; and Housatonic Equity Partners SBIC, LLC is the General Partner of HEI SBIC. William N. Thorndike, Jr., Barry D. Reynolds, Joseph M. Niehaus, Mark G. Hilderbrand, Jill A. Raimondi, James L. Wilder, III, Karen E. Liesching, Michael C. Jackson and Eliot Wadsworth, II are managing members of one or more of the entities, or general partners of the entities, that directly or indirectly hold such shares, and as such, may be deemed to have voting and investment power with respect to shares held by one or more of these entities. Each of these |
122
Table of Contents
| individuals disclaims beneficial ownership with respect to such shares except to the extent of their pecuniary interest therein. The address for these entities and individuals is 44 Montgomery Street, Suite 4010, San Francisco, California 94104. |
| (4) | Includes (i) 2,728,289 shares held of record by Michael A. Smerklo, Trustee of The True North Trust dated July 25, 2008; and (ii) 1,800,000 shares issuable upon exercise of options exercisable within 60 days of September 30, 2010, of which 1,725,000 are fully vested. |
| (5) | Consists of 494,483 shares issuable upon exercise of options exercisable within 60 days of September 30, 2010. |
| (6) | Consists of 260,416 shares issuable upon exercise of options exercisable within 60 days of September 30, 2010. |
| (7) | Consists of 525,000 shares issuable upon exercise of options exercisable within 60 days of September 30, 2010, of which 404,687 are fully vested. |
| (8) | Consists of the shares listed in footnote 1 above, which are held of record by GA SS. Mr. McMorris is a managing director of GA LLC and may be deemed to have shared voting and dispositive power over the shares held by GA SS. Mr. McMorris disclaims beneficial ownership of such shares, except to the extent of his individual pecuniary interest therein. |
| (9) | Consists of the shares listed in footnote 2 above, which are held of record by SSLLC. Mr. Dunlevie is a managing member of Benchmark Capital Management Co. V, L.P. and may be deemed to have shared voting and dispositive power over the shares held by SSLLC. Mr. Dunlevie disclaims beneficial ownership of such shares, except to the extent of his individual pecuniary interest therein. |
| (10) | Consists of 94,827 shares issuable upon exercise of options exercisable within 60 days of September 30, 2010. |
| (11) | Consists of 150,000 shares issuable to the James C. Madden, V Living Trust for which Mr. Madden serves as trustee, upon exercise of options exercisable within 60 days of September 30, 2010, of which 121,862 are fully vested. |
| (12) | Consists of the shares listed in footnote 3 above, which are held by entities affiliated with Housatonic Partners. Mr. Reynolds is a managing or general partner of the Housatonic entities that directly or indirectly hold such shares, and as such, may be deemed to have voting and investment power with respect to shares held by one or more of the entities affiliated with Housatonic Partners. Mr. Reynolds disclaims beneficial ownership of the shares held by the entities affiliated with Housatonic Partners, except to the extent of his individual pecuniary interest therein. |
| (13) | Includes (i) 3,593,685 shares issuable upon exercise of options held by our current executive officers and directors exercisable within 60 days of September 30, 2010, of which 3,342,525 are fully vested. |
123
Table of Contents
General
The following is a summary of our capital stock and certain provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws, as they will be in effect upon the closing of this offering. This summary does not purport to be complete and is qualified in its entirety by the provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws, copies of which have been filed as exhibits to the registration statement of which this prospectus is a part. The description of our common stock reflects the completion of the Conversion which will occur prior to the closing of this offering.
Upon the closing of this offering, our authorized capital stock will consist of 1,020,000,000 shares, with a par value of $0.0001 per share, of which:
| • | 1,000,000,000 shares are designated as common stock; and |
| • | 20,000,000 shares are designated as preferred stock. |
As of September 30, 2010, and after giving effect to the Conversion, we had outstanding 57,426,218 shares of common stock, held of record by 206 stockholders, and no shares of preferred stock were outstanding. In addition, as of September 30, 2010, and after giving effect to the Conversion, 15,726,057 shares of our common stock were subject to outstanding options. For more information on our capitalization, see “Capitalization” above.
Common Stock
The holders of our common stock are entitled to one vote per share on all matters submitted to a vote of our stockholders. Subject to preferences that may be applicable to any preferred stock outstanding at the time, the holders of outstanding shares of common stock are entitled to receive ratably any dividends declared by our board of directors out of assets legally available therefor. In the event that we liquidate, dissolve or wind up, holders of our common stock are entitled to share ratably in all assets remaining after payment of liabilities and the liquidation preference of any then outstanding shares of preferred stock. Holders of common stock have no preemptive or conversion rights or other subscription rights. There are no redemption or sinking fund provisions applicable to the common stock. All outstanding shares of common stock are, and all shares of common stock to be outstanding upon completion of this offering will be, fully paid and nonassessable.
Preferred Stock
After the closing of this offering, no shares of preferred stock will be outstanding. Pursuant to our certificate of incorporation, our board of directors will have the authority, without further action by our stockholders, to issue from time to time up to 20,000,000 shares of preferred stock in one or more series. Our board of directors may designate the rights, preferences, privileges and restrictions of the preferred stock, including dividend rights, conversion rights, voting rights, terms of redemption, liquidation preference, sinking fund terms and the number of shares constituting any series or the designation of any series. The issuance of preferred stock could have the effect of restricting dividends on our common stock, diluting the voting power of our common stock, impairing the liquidation rights of our common stock or delaying, deterring or preventing a change in control. Such issuance could have the effect of decreasing the market price of the common stock. The issuance of preferred stock or even the ability to issue preferred stock could also have the effect of delaying, deterring or preventing a change in control. We currently have no plans to issue any shares of preferred stock.
Registration Rights
GA SS Holding LLC, controlled by General Atlantic, LLC, SSLLC Holdings, Inc., controlled by Benchmark Capital, and certain entities affiliated with Housatonic Partners (together, the “Significant Holders”) and certain of our other stockholders (the “2003 Holders”) are entitled to the following rights with respect to the registration of their shares of our common stock under the Securities Act. For the Significant Holders, these
124
Table of Contents
rights are provided under the terms of a Registration and Information Rights Agreement (the “Registration Rights Agreement”). For the 2003 Holders, these rights are provided under the terms of a Registration Rights Schedule to a Securities Purchase Agreement (the “Registration Rights Schedule”). Both agreements include demand registration rights, piggyback registration rights and Form S-3 registration rights. For the 2003 Holders, registration rights are only granted to each 2003 Holder that would own at least 1% of our outstanding common stock after giving effect to this offering. We refer to these shares collectively as “registrable securities.” All fees, costs and expenses of underwritten registrations will be borne by us and all selling expenses, including underwriting discounts and selling commissions, will be borne by the holders of the shares being registered pro rata on the basis of the number of shares to be registered.
Demand Registration Rights. The Significant Holders and the 2003 Holders are entitled to demand registration rights. If the Significant Holders request in writing that we effect a registration that has an anticipated aggregate offering price to the public of at least $10 million or if the 2003 Holders request in writing a registration that has an anticipated aggregate offering price to the public of at least $7.5 million, then we will be required, at our expense, to register all registrable securities that these respective holders request to be registered. We are required to effect only two registrations for the Significant Holders pursuant to this provision of the Registration Rights Agreement and only two registrations for the 2003 Holders pursuant to this provision of the Registration Rights Schedule. Depending on certain conditions, however, we may defer such registration for a specified number of days. The underwriters of any underwritten offering have the right to limit the number of shares registered by these holders for marketing reasons, subject to certain limitations.
Piggyback Registration Rights. The Significant Holders and the 2003 Holders, respectively, are entitled to piggyback registration rights. If we register any of our securities either for our own account or for the account of other security holders, after the completion of this offering the Significant Holders and the 2004 Holders are entitled to include all or part of their shares in the registration at our expense. The underwriters of any underwritten offering have the right to limit the number of shares registered by these holders for marketing reasons, subject to certain limitations.
Form S-3 Registration Rights. The Significant Holders and the 2003 Holders, respectively, are also currently entitled to short-form registration rights. If we are eligible to file a registration statement on Form S-3, these holders have the right to have all or part of their shares registered by us at our expense, subject to certain exceptions. The underwriters of any underwritten offering have the right to limit the number of shares registered by these holders for marketing reasons, subject to certain limitations.
Anti-Takeover Effects of Delaware General Corporation Law and Our Certificate of Incorporation and Bylaws
Our certificate of incorporation and our bylaws contain certain provisions that could have the effect of delaying, deterring or preventing another party from acquiring control of us. These provisions and certain provisions of Delaware Law, which are referred to below, are expected to discourage coercive takeover practices and inadequate takeover bids. These provisions are also designed, in part, to encourage persons seeking to acquire control of us to negotiate first with our board of directors. We believe that the benefits of increased protection of our potential ability to negotiate more favorable terms with an unfriendly or unsolicited acquirer outweigh the disadvantages of potentially discouraging a proposal to acquire us.
Undesignated Preferred Stock. As discussed above, our board of directors has the ability to issue preferred stock with voting or other rights or preferences that could impede the success of any attempt to acquire control of our company. These and other provisions may have the effect of deterring hostile takeovers or delaying changes in control or management of our company.
Limits on Ability of Stockholders to Act by Written Consent or Call a Special Meeting. Our certificate of incorporation provides that our stockholders may not act by written consent, which may lengthen the amount of
125
Table of Contents
time required to take stockholder actions. As a result, a holder controlling a majority of our capital stock would not be able to amend our bylaws or remove directors without holding a meeting of our stockholders called in accordance with our bylaws.
In addition, our bylaws provide that special meetings of the stockholders may be called only by the chairperson of the board, the chief executive officer or our board of directors. Stockholders may not call a special meeting, which may delay the ability of our stockholders to force consideration of a proposal or for holders controlling a majority of our capital stock to take any action, including the removal of directors.
Requirements for Advance Notification of Stockholder Nominations and Proposals. Our bylaws establish advance notice procedures with respect to stockholder proposals and the nomination of candidates for election as directors, other than nominations made by or at the direction of our board of directors or a committee of our board of directors. These provisions may have the effect of precluding the conduct of certain business at a meeting if the proper procedures are not followed. These provisions may also discourage or deter a potential acquirer from conducting a solicitation of proxies to elect the acquirer’s own slate of directors or otherwise attempting to obtain control of our company.
Board Classification. Our board of directors is divided into three classes, one class of which is elected each year by our stockholders. The directors in each class will serve for a three-year term. For more information on the classified board, see “Management—Board Composition and Risk Oversight.” In addition, our certificate of incorporation and bylaws provide that directors may be removed only for cause. The classification of our board of directors and the limitations on the ability of our stockholders to remove directors could make it more difficult for a third party to acquire, or discourage a third party from seeking to acquire, control of our company.
No Cumulative Voting. Our certificate of incorporation and bylaws do not permit cumulative voting in the election of directors. Cumulative voting allows a stockholder to vote a portion or all of its shares for one or more candidates for seats on the board of directors. Without cumulative voting, a minority stockholder may not be able to gain as many seats on our board of directors as such stockholder would be able to gain if cumulative voting were permitted. The absence of cumulative voting makes it more difficult for a minority stockholder to gain a seat on our board of directors to influence our board of director’s decisions regarding a takeover or otherwise.
Amendment of Charter Provisions. The amendment of the above provisions of our certificate of incorporation and bylaws requires approval by holders of at least two-thirds of our outstanding capital stock entitled to vote generally in the election of directors.
Delaware Anti-Takeover Statute. Upon the completion of this offering, we will be subject to the provisions of Section 203 of the Delaware General Corporation Law regulating corporate takeovers. In general, Section 203 prohibits a publicly held Delaware corporation from engaging, under certain circumstances, in a business combination with an interested stockholder for a period of three years following the date the person became an interested stockholder unless:
| • | the transaction is approved by our board of directors prior to the date the interested stockholder obtained such status; |
| • | upon completion of the transaction that resulted in the stockholder becoming an interested stockholder, the interested stockholder owned at least 85% of the voting stock of the corporation outstanding at the time the transaction commenced, calculated as provided under Section 203; or |
| • | at or subsequent to the date of the transaction, the business combination is approved by our board of directors and authorized at an annual or special meeting of our stockholders, and not by written consent, by the affirmative vote of at least two-thirds of the outstanding voting stock which is not owned by the interested stockholder. |
126
Table of Contents
Generally, a business combination includes a merger, asset or stock sale, or other transaction resulting in a financial benefit to the interested stockholder. An interested stockholder is a person who, together with affiliates and associates, owns or, within three years prior to the determination of interested stockholder status, did own 15% or more of a corporation’s outstanding voting stock. We expect the existence of this provision to have an anti-takeover effect with respect to transactions our board of directors does not approve in advance. We also anticipate that Section 203 may discourage takeover attempts that might result in a premium over the market price for the shares of common stock held by our stockholders.
The provisions of Delaware law and our certificate of incorporation and bylaws, as amended upon the closing of this offering, could have the effect of discouraging others from attempting unsolicited takeovers and, as a consequence, they might also inhibit temporary fluctuations in the market price of our common stock that often result from actual or rumored unsolicited takeover attempts. These provisions might also have the effect of preventing changes in our management. It is possible that these provisions could make it more difficult to accomplish transactions that our stockholders might otherwise deem to be in their best interests.
Transfer Agent and Registrar
Upon the completion of this offering, the transfer agent and registrar for our common stock will be . The transfer agent’s address is , and its telephone number is .
Listing
We intend to apply to list our common stock for quotation on The Nasdaq Global Market under the trading symbol “ .”
127
Table of Contents
SHARES ELIGIBLE FOR FUTURE SALE
Before this offering, there has not been a public market for shares of our common stock. Future sales of substantial amounts of shares of our common stock, including shares issued upon the exercise of outstanding options, in the public market after this offering, or the possibility of these sales occurring, could cause the prevailing market price for our common stock to fall or otherwise impair our ability to raise equity capital in the future.
Upon the completion of this offering, based on shares outstanding on September 30, 2010, a total of shares of common stock will be outstanding. Of these shares, all shares of common stock sold in this offering, plus any shares sold upon exercise of the underwriters’ over-allotment option, will be freely tradable in the public market without restriction or further registration under the Securities Act, unless these shares are held by “affiliates,” as that term is defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act.
The remaining shares of common stock will be “restricted securities,” as that term is defined in Rule 144 under the Securities Act. These restricted securities are eligible for public sale only if they are registered under the Securities Act or if they qualify for an exemption from registration under Rules 144 or 701 under the Securities Act, which are summarized below.
As a result of the contractual 180-day lock-up period described below and under the section entitled “Underwriters,” and the provisions of Rules 144 and 701 under the Securities Act, these restricted securities will be available for sale in the public market as follows:
| Date |
Number of Shares |
|||
| On the date of this prospectus |
||||
| Between 90 and 180 days after the date of this prospectus |
||||
| At various times beginning more than 180 days after the date of this prospectus |
||||
In addition, of the 15,726,057 shares of our common stock that were subject to stock options outstanding as of September 30, 2010, options to purchase 7,206,370 shares of common stock were vested as of September 30, 2010 and will be eligible for sale following the effective date of this offering, subject to the lock-up agreements as described below and in the section titled “Underwriters.”
Lock-Up Agreements
The selling stockholders, all of our directors and executive officers and the holders of approximately % of our common stock on a fully-diluted basis have agreed, subject to limited exceptions, not to offer, pledge, sell, contract to sell, sell any option or contract to purchase, purchase any option or contract to sell, grant any option, right or warrant to purchase, or otherwise transfer or dispose of, directly or indirectly, or enter into any swap or other arrangement that transfers to another, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of ownership of any shares of common stock or any securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for shares of common stock for a period of 180 days after the date of this prospectus, without the prior written consent of Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated, subject to extension as described in the section titled “Underwriters.”
Rule 144
In general, under Rule 144 as currently in effect, once we have been subject to public company reporting requirements for at least 90 days, a person who is not deemed to have been one of our affiliates for purposes of the Securities Act at any time during the 90 days preceding a sale and who has beneficially owned the shares proposed to be sold for at least six months, including the holding period of any prior owner other than our affiliates, is entitled to sell such shares without complying with the manner of sale, volume limitation or notice provisions of Rule 144, subject to the availability of public information about us as required by Rule 144. If such
128
Table of Contents
a person has beneficially owned the shares proposed to be sold for at least one year, including the holding period of any prior owner other than our affiliates, then such person is entitled to sell such shares without complying with any of the requirements of Rule 144.
In general, under Rule 144, as currently in effect, our affiliates or persons selling shares on behalf of our affiliates will be entitled to sell within any three-month period beginning 90 days after the date of this prospectus, a number of shares that does not exceed the greater of:
| • | 1% of the number of shares of common stock then outstanding, which will equal approximately shares immediately after this offering; or |
| • | the average weekly trading volume of the common stock during the four calendar weeks preceding the filing of a notice on Form 144 with respect to such sale. |
Sales under Rule 144 by our affiliates or persons selling shares on behalf of our affiliates are also subject to certain manner of sale provisions and notice requirements and to the availability of current public information about us as required by Rule 144. The shares that may be sold in compliance with Rule 144 that are subject to lock-up agreements as described above and under the section titled “Underwriters” below, will not become eligible for sale until the expiration or waiver of the restrictions set forth in those agreements.
Rule 701
Rule 701 generally allows a stockholder who purchased shares of our common stock pursuant to a written compensatory plan or contract and who is not deemed to have been an affiliate of our company during the immediately preceding 90 days to sell these shares in reliance upon Rule 144, but without being required to comply with the public information, holding period, volume limitation, or notice provisions of Rule 144. Rule 701 also permits affiliates of our company to sell their Rule 701 shares under Rule 144 without complying with the holding period requirements of Rule 144. All holders of Rule 701 shares, however, are required to wait until 90 days after the date of this prospectus before selling such shares pursuant to Rule 701. The shares that may be sold in compliance with Rule 701 that are subject to lock-up agreements as described above and under the section titled “Underwriters” below will not become eligible for sale until expiration or waiver of the restrictions set forth in those agreements.
As of September 30, 2010, 2,074,711 shares of our outstanding common stock had been issued in reliance on Rule 701.
Stock Options
We intend to file a registration statement on Form S-8 under the Securities Act covering all of the shares of our common stock subject to options outstanding or reserved for issuance under our stock option plans and shares of our common stock issued upon the exercise of options by employees. We expect to file this registration statement as soon as practicable after this offering. Shares issuable upon exercise of the stock options that we have granted that are subject to lock-up agreements as described above and under the section titled “Underwriters” below will not become eligible for sale until the expiration or waiver of the restrictions set forth in those agreements.
Registration Rights
Upon completion of this offering, the holders of approximately 40 million shares of our common stock or their transferees will be entitled to various contractual registration rights with respect to the registration of these shares under the Securities Act. All of these shares are subject to certain restrictions including the lock-agreements as described above and under the section titled “Underwriters” below, and the holders of these shares will not be entitled to exercise their registration rights until the expiration or waiver of such restrictions. Registration of these shares under the Securities Act would result in these shares becoming fully tradable without restriction under the Securities Act immediately upon the effectiveness of the registration, except for shares purchased by affiliates. See “Description of Capital Stock — Registration Rights” for additional information.
129
Table of Contents
MATERIAL U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX CONSIDERATIONS FOR NON-U.S. HOLDERS
The following discussion is a summary of the material U.S. federal income tax consequences of the acquisition, ownership and disposition of our common stock to non-U.S. holders, but does not purport to be a complete analysis of all the potential tax considerations relating thereto. This summary is based upon the provisions of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986, as amended, or the Internal Revenue Code, Treasury Regulations promulgated thereunder, administrative rulings and judicial decisions, all as of the date hereof. These authorities may be changed, possibly retroactively, so as to result in U.S. federal income tax consequences different from those set forth below.
This summary is limited to non-U.S. holders who purchase our common stock pursuant to this offering and who hold our common stock as a capital asset within the meaning of Section 1221 of the Internal Revenue Code (generally, property held for investment). This summary does not address any U.S. federal non-income tax considerations or any tax considerations arising under the laws of any foreign, state or local jurisdiction. In addition, this discussion does not address tax considerations applicable to an investor’s particular circumstances or to investors that may be subject to special tax rules, including, without limitation:
| • | banks, insurance companies or other financial institutions; |
| • | persons subject to the alternative minimum tax; |
| • | tax-exempt organizations; |
| • | dealers in securities or currencies; |
| • | traders in securities that elect to use a mark-to-market method of accounting for their securities holdings; |
| • | persons that own, or are deemed to own, more than five percent of our capital stock (except to the extent specifically set forth below); |
| • | certain former citizens or long-term residents of the United States; |
| • | persons who hold our common stock as a position in a hedging transaction, “straddle,” “conversion transaction” or other risk reduction transaction; or |
| • | persons deemed to sell our common stock under the constructive sale provisions of the Internal Revenue Code. |
In addition, if a partnership holds our common stock, the tax treatment of a partner generally will depend on the status of the partner and upon the activities of the partnership. Accordingly, partnerships that hold our common stock, and partners in such partnerships, should consult their tax advisors regarding the specific U.S. federal income tax consequences to them of acquiring, owning or disposing of our common stock.
YOU ARE URGED TO CONSULT YOUR TAX ADVISOR WITH RESPECT TO THE APPLICATION OF THE U.S. FEDERAL INCOME TAX LAWS TO YOUR PARTICULAR SITUATION, AS WELL AS ANY TAX CONSEQUENCES OF THE ACQUISITION, OWNERSHIP OR DISPOSITION OF OUR COMMON STOCK ARISING UNDER THE U.S. FEDERAL NON-INCOME TAX RULES OR UNDER THE LAWS OF ANY STATE, LOCAL, FOREIGN OR OTHER TAXING JURISDICTION OR UNDER ANY APPLICABLE TAX TREATY.
Non-U.S. Holder Defined
For purposes of this discussion, you are a non-U.S. holder if you are a holder that, for U.S. federal income tax purposes, is not a U.S. person or a partnership or entity taxable as a partnership. For purposes of this discussion, you are a U.S. person if you are:
| • | an individual citizen or resident of the United States; |
130
Table of Contents
| • | a corporation or other entity taxable as a corporation for U.S. federal income tax purposes, created or organized in the United States or under the laws of the United States or any political subdivision thereof; |
| • | an estate whose income is subject to U.S. federal income tax regardless of its source; or |
| • | a trust (x) whose administration is subject to the primary supervision of a U.S. court and which has one or more U.S. persons who have the authority to control all substantial decisions of the trust or (y) which has made an election to be treated as a U.S. person for U.S. federal income tax purposes. |
Distributions
We have not made any distributions on our common stock, and we do not plan to make any distributions for the foreseeable future. However, if we do make distributions on our common stock, those payments will constitute dividends for U.S. tax purposes to the extent paid from our current or accumulated earnings and profits, as determined under U.S. federal income tax principles. To the extent those distributions exceed both our current and our accumulated earnings and profits, they will constitute a return of capital and will first reduce your basis in our common stock, but not below zero, and then will be treated as gain from the sale of stock.
Any dividend paid to you generally will be subject to U.S. withholding tax either at a rate of 30% of the gross amount of the dividend or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty. In order to receive a reduced treaty rate, you must provide us with an Internal Revenue Service (“IRS”) Form W-8BEN or other appropriate version of IRS Form W-8 certifying qualification for the reduced rate.
Dividends received by you that are effectively connected with your conduct of a U.S. trade or business and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, attributed to a permanent establishment in the United States, are exempt from such withholding tax. In order to obtain this exemption, you must provide us with an IRS Form W-8ECI properly certifying such exemption. Such effectively connected dividends, although not subject to withholding tax, are taxed at the same graduated rates generally applicable to U.S. persons, net of certain deductions and credits. In addition, if you are a corporate non-U.S. holder, dividends you receive that are effectively connected with your conduct of a U.S. trade or business may also be subject to a branch profits tax at a rate of 30% or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty.
If you are eligible for a reduced rate of withholding tax pursuant to a tax treaty, you may obtain a refund of any excess amounts currently withheld if you file an appropriate claim for refund with the IRS.
Gain on Disposition of Common Stock
You generally will not be required to pay U.S. federal income tax on any gain realized upon the sale or other disposition of our common stock unless:
| • | the gain is effectively connected with your conduct of a U.S. trade or business and, if required by an applicable income tax treaty, attributed to a permanent establishment in the United States; |
| • | you are an individual who is present in the United States for a period or periods aggregating 183 days or more during the calendar year in which the sale or disposition occurs and certain other conditions are met; or |
| • | our common stock constitutes a U.S. real property interest by reason of our status as a “United States real property holding corporation” for U.S. federal income tax purposes (a “USRPHC”) at any time within the shorter of the five-year period preceding the disposition or your holding period for our common stock. |
We believe that we are not currently and will not become a USRPHC. However, because the determination of whether we are a USRPHC depends on the fair market value of our U.S. real property relative to the fair
131
Table of Contents
market value of our other business assets, there can be no assurance that we will not become a USRPHC in the future. Even if we become a USRPHC, however, as long as our common stock is regularly traded on an established securities market, such common stock will be treated as U.S. real property interests only if you actually or constructively hold more than five percent of such regularly traded common stock at any time during the applicable period described above.
If you are a non-U.S. holder described in the first bullet above, you will generally be required to pay tax on the gain derived from the sale (net of certain deductions and credits) under regular graduated U.S. federal income tax rates, and corporate non-U.S. holders described in the first bullet above may be subject to branch profits tax at a 30% rate or such lower rate as may be specified by an applicable income tax treaty. If you are an individual non-U.S. holder described in the second bullet above, you will be required to pay a flat 30% tax on the gain derived from the sale, which tax may be offset by U.S. source capital losses (even though you are not considered a resident of the United States). You should consult any applicable income tax or other treaties that may provide for different rules.
Backup Withholding and Information Reporting
Generally, we must report annually to the IRS the amount of dividends paid to you, your name and address and the amount of tax withheld, if any. A similar report will be sent to you. Pursuant to applicable income tax treaties or other agreements, the IRS may make these reports available to tax authorities in your country of residence.
Payments of dividends or of proceeds on the disposition of stock made to you may be subject to additional information reporting and backup withholding at a current rate of 28% unless you establish an exemption, for example by properly certifying your non-U.S. status on a Form W-8BEN or another appropriate version of IRS Form W-8. Notwithstanding the foregoing, backup withholding and information reporting may apply if either we or our paying agent has actual knowledge, or reason to know, that you are a U.S. person.
Backup withholding is not an additional tax; rather, the U.S. income tax liability of persons subject to backup withholding will be reduced by the amount of tax withheld. If withholding results in an overpayment of taxes, a refund or credit may generally be obtained from the IRS, provided that the required information is furnished to the IRS in a timely manner.
New Legislation Relating to Foreign Accounts
Newly enacted legislation may impose withholding taxes on certain types of payments made to “foreign financial institutions” (as specially defined under these rules) and certain other non-U.S. entities. Under this legislation, the failure to comply with additional certification, information reporting and other specified requirements could result in withholding tax being imposed on payments of dividends and sales proceeds to foreign intermediaries and certain non-U.S. holders. The legislation imposes a 30% withholding tax on dividends on, or gross proceeds from the sale or other disposition of, our common stock paid to a foreign financial institution or to a foreign non-financial entity, unless (i) the foreign financial institution undertakes certain diligence and reporting obligations or (ii) the foreign non-financial entity either certifies it does not have any substantial U.S. owners or furnishes identifying information regarding each substantial U.S. owner. If the payee is a foreign financial institution, it must enter into an agreement with the U.S. Treasury requiring, among other things, that it undertake to identify accounts held by certain U.S. persons or U.S.-owned foreign entities, annually report certain information about such accounts, and withhold 30% on payments to account holders whose actions prevent it from complying with these reporting and other requirements. The legislation would apply to payments made after December 31, 2012. Prospective investors should consult their tax advisors regarding this legislation.
132
Table of Contents
Under the terms and subject to the conditions contained in an underwriting agreement dated the date of this prospectus, the underwriters named below, for whom Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated and Deutsche Bank Securities Inc. are serving as the representatives, have severally agreed to purchase, and we and the selling stockholders have agreed to sell to them, severally, the number of shares indicated below:
| Underwriters |
Number of Shares |
|||
| Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated |
||||
| Deutsche Bank Securities Inc. |
||||
| William Blair & Company, L.L.C. |
||||
| Lazard Capital Markets LLC |
||||
| Piper Jaffray & Co. |
||||
| JMP Securities LLC |
||||
| Total |
||||
The underwriters and the representatives are collectively referred to as the “underwriters” and the “representatives,” respectively. The underwriters are offering the shares of common stock subject to their acceptance of the shares from us and the selling stockholders and subject to prior sale. The underwriting agreement provides that the obligations of the several underwriters to pay for and accept delivery of the shares of common stock offered by this prospectus are subject to the approval of certain legal matters by their counsel and to certain other conditions. The underwriters are obligated to take and pay for all of the shares of common stock offered by this prospectus if any such shares are taken. However, the underwriters are not required to take or pay for the shares covered by the underwriters’ over-allotment option described below. If an underwriter defaults, the underwriting agreement provides that the purchase commitments of the non-defaulting underwriters may be increased.
The underwriters initially propose to offer part of the shares of common stock directly to the public at the initial public offering price listed on the cover page of this prospectus and part to certain dealers at a price that represents a concession not in excess of $ a share under the initial public offering price. Any underwriter may allow a concession not in excess of $ a share to other underwriters or to certain dealers. After the initial offering of the shares of common stock, the offering price and other selling terms may from time to time be varied by the representatives.
We and the selling stockholders have granted to the underwriters an option, exercisable for 30 days from the date of this prospectus, to purchase up to an aggregate of additional shares of our common stock at the public offering price listed on the cover page of this prospectus, less underwriting discounts and commissions. The underwriters may exercise this option solely for the purpose of covering over-allotments, if any, made in connection with the offering of the shares of common stock offered by this prospectus. To the extent the option is exercised, each underwriter will become obligated, subject to certain conditions, to purchase about the same percentage of the additional shares of common stock as the number listed next to the underwriter’s name in the preceding table bears to the total number of shares of common stock listed next to the names of all underwriters in the preceding table.
133
Table of Contents
The following table shows the per share and total public offering price, underwriting discounts and commissions, and proceeds before expenses to us and the selling stockholders. These amounts are set forth assuming both no exercise and full exercise of the underwriters’ option to purchase up to an additional shares of our common stock from us and the selling stockholders.
| Total | ||||||||||||
| Per Share | No Exercise | Full Exercise | ||||||||||
| Public offering price |
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
| Underwriting discounts and commissions to be paid by: |
||||||||||||
| Us |
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
| The selling stockholders |
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
| Proceeds before expenses, to us |
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
| Proceeds before expenses, to selling stockholders |
$ | $ | $ | |||||||||
The expenses of this offering payable by us, not including underwriting discounts and commissions, are estimated to be approximately $ , which includes legal, accounting and printing costs and various other fees associated with the registration and listing of our common stock.
The underwriters have informed us and the selling stockholders that they do not intend sales to discretionary accounts to exceed five percent of the total number of shares of common stock offered by them.
We intend to apply to have our common stock approved for quotation on The Nasdaq Global Market under the symbol “ .”
We, the selling stockholders, all of our directors and executive officers and the holders of approximately % of our outstanding stock on a fully diluted basis immediately prior to this offering have agreed that, subject to certain exceptions, without the prior written consent of Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated on behalf of the underwriters, we and they will not, during the period ending 180 days after the date of this prospectus:
| • | offer, pledge, sell, contract to sell, sell any option or contract to purchase, purchase any option or contract to sell, grant any option, right or warrant to purchase, lend, or otherwise transfer or dispose of, directly or indirectly, any shares of our common stock or any securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for our common stock; |
| • | enter into any swap or other arrangement that transfers to another, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of ownership of our common stock; or |
| • | in the case of us, file any registration statement with the SEC relating to the offering of any shares of our common stock or any securities convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for our common stock; |
whether any such transaction described in the first two bullet points above is to be settled by delivery of shares of common stock or such other securities, in cash or otherwise. In addition, we and each such person agree that, without the prior written consent of Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated on behalf of the underwriters, it will not, during the period ending 180 days after the date of this prospectus, make any demand for, or exercise any right with respect to, the registration of any shares of common stock or any security convertible into or exercisable or exchangeable for common stock.
The restrictions described in the immediately preceding paragraph do not apply to:
| • | transactions relating to shares of common stock or other securities acquired in open market transactions after the completion of the offering, provided that no filing under Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act shall be required or shall be voluntarily made in connection with subsequent sales of common stock or other securities acquired in such open market transactions; |
134
Table of Contents
| • | transfers of shares of common stock or any security convertible into common stock as a bona fide gift or gifts or to any trust for the direct or indirect benefit of the holder or the immediate family of the holder; |
| • | distributions of shares of common stock or any security convertible into common stock to limited partners or stockholders of the holder or to the holder’s affiliates or to any investment fund or other entity controlled or managed by the holder; |
| • | transfers or distributions of shares of common stock to a corporation or other entity of which the holder and/or the holder’s immediate family are at all times the direct or indirect legal and beneficial owners of all the outstanding equity securities or similar interests of such corporation or other entity; provided that in the case of any transfer or distribution pursuant to this exception or the prior two exceptions above, (i) each donee or distributee shall sign and deliver a lock-up letter agreement and (ii) no filing under Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, reporting a reduction in beneficial ownership of shares of common stock, shall be required or shall be voluntarily made during the restricted period; |
| • | dispositions to us pursuant to our right to repurchase from the holder (or the obligation of the holder to sell or transfer to us) shares of common stock issued under the our equity incentive plans or under agreements pursuant to which such shares were issued, provided that no filing under Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act, reporting a reduction in beneficial ownership of shares of common stock, shall be required or shall be voluntarily made during the restricted period referred to in the foregoing sentence; |
| • | the receipt by the holder from us of shares of common stock upon the exercise of an option or warrant, provided that no filing under Section 16(a) of the Exchange Act shall be required or shall be voluntarily made; |
| • | the establishment of a trading plan pursuant to Rule 10b5-1 under the Exchange Act for the transfer of shares of common stock, provided that such plan does not provide for the transfer of common stock during the restricted period and no public announcement or filing under the Exchange Act regarding the establishment of such plan shall be required of or voluntarily made by or on behalf of the holder or ServiceSource; |
| • | our issuance of shares of common stock, or other securities convertible into or exercisable for shares of common stock, in connection with acquisitions, joint ventures, commercial relationships or other strategic transactions, in an aggregate number of shares not to exceed 5% of the total number of shares of common stock outstanding immediately following the completion of this offering, provided that each recipient of these shares of common stock shall be subject to the lock-up restrictions described herein; or |
| • | in the case of GA SS Holding LLC, pledges of up to 5% of the shares held by GA SS Holding LLC in favor of the lenders under its credit facility as existing on the date hereof, or any transfer of such shares in connection with such pledge. |
The 180-day restricted period described in the preceding paragraphs will be extended if:
| • | during the last 17 days of the 180-day restricted period, we issue an earnings release or material news or a material event relating to our company occurs; or |
| • | prior to the expiration of the 180-day restricted period, we announce that we will release earnings results during the 16-day period beginning on the last day of the 180-day period; |
in which case the restrictions described in the preceding paragraphs will continue to apply until the expiration of the 18-day period beginning on the issuance of the earnings release or the occurrence of the material news or material event.
In order to facilitate this offering of the common stock, the underwriters may engage in transactions that stabilize, maintain or otherwise affect the price of the common stock. Specifically, the underwriters may sell
135
Table of Contents
more shares than they are obligated to purchase under the underwriting agreement, creating a short position. A short sale is covered if the short position is no greater than the number of shares available for purchase by the underwriters under the over-allotment option. The underwriters can close out a covered short sale by exercising the over-allotment option or purchasing shares in the open market. In determining the source of shares to close out a covered short sale, the underwriters will consider, among other things, the open market price of shares compared to the price available under the over-allotment option. The underwriters may also sell shares in excess of the over-allotment option, creating a naked short position. The underwriters must close out any naked short position by purchasing shares in the open market. A naked short position is more likely to be created if the underwriters are concerned that there may be downward pressure on the price of the common stock in the open market after pricing that could adversely affect investors who purchase in this offering. In addition, to stabilize the price of the common stock, the underwriters may bid for, and purchase, shares of common stock in the open market. The underwriting syndicate may also reclaim selling concessions allowed to an underwriter or a dealer for distributing the common stock in this offering if the syndicate repurchases previously distributed common stock to cover syndicate short positions or to stabilize the price of the common stock. These activities may raise or maintain the market price of the common stock above independent market levels or prevent or retard a decline in the market price of the common stock. The underwriters are not required to engage in these activities and may end any of these activities at any time.
We, the selling stockholders and the underwriters have agreed to indemnify each other against certain liabilities, including liabilities under the Securities Act, or to contribute to payments required in connection with such liabilities.
A prospectus in electronic format may be made available on the websites maintained by one or more underwriters. The underwriters may agree to allocate a number of shares to underwriters for sale to their online brokerage account holders. Internet distributions will be allocated by Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated to underwriters that may make Internet distributions on the same basis as other allocations.
Lazard Frères & Co. LLC referred this transaction to Lazard Capital Markets LLC and will receive a referral fee from Lazard Capital Markets LLC in connection therewith.
Pricing of the Offering
Prior to this offering, there has been no public market for our common stock. The initial public offering price will be determined by negotiations among us, the selling stockholders and the representatives of the underwriters. Among the factors to be considered in determining the initial public offering price will be our future prospects and those of our industry in general, our sales, earnings and certain other financial and operating information in recent periods, and the price earnings ratios, price sales ratios and market prices of securities and certain financial and operating information of companies engaged in activities similar to ours. The estimated initial public offering price range set forth on the cover page of this preliminary prospectus is subject to change as a result of market conditions and other factors.
Directed Share Program
At our request, the underwriters have reserved percent of the shares of common stock to be issued by us and offered by this prospectus for sale, at the initial public offering price, to directors, officers, employees, business associates, customers and related persons of ServiceSource International, Inc. If purchased by these persons, these shares will be subject to a 180-day lock-up restriction. The number of shares of our common stock available for sale to the general public will be reduced to the extent these individuals purchase such reserved shares. Any reserved shares that are not so purchased will be offered by the underwriters to the general public on the same basis as the other shares offered by this prospectus. We have agreed to indemnify the underwriters against certain liabilities and expenses, including liabilities under the Securities Act, in connection with the sales of directed shares.
136
Table of Contents
Other Relationships
Certain of the underwriters and their respective affiliates may in the future perform various financial advisory services for us.
European Economic Area
In relation to each Member State of the European Economic Area which has implemented the Prospectus Directive (each, a “Relevant Member State”) an offer to the public of any shares which are the subject of the offering contemplated by this Prospectus (the “Shares”) may not be made in that Relevant Member State, except that an offer to the public in that Relevant Member State of any Shares may be made at any time under the following exemptions under the Prospectus Directive, if they have been implemented in that Relevant Member State:
| • | to any legal entity which is a qualified investor as defined in the Prospectus Directive; |
| • | to fewer than 100 or, if the Relevant Member State has implemented the relevant provision of the 2010 PD Amending Directive, 150, natural or legal persons (other than qualified investors as defined in the Prospectus Directive), as permitted under the Prospectus Directive, subject to obtaining the prior consent of Morgan Stanley & Co. Incorporated for any such offer; or |
| • | in any other circumstances falling within Article 3(2) of the Prospectus Directive, provided that no such offer of Shares shall result in a requirement for the publication by us or any of the underwriters of a prospectus pursuant to Article 3 of the Prospectus Directive. |
For the purposes of this provision, the expression an “offer to the public” in relation to any Shares in any Relevant Member State means the communication in any form and by any means of sufficient information on the terms of the offer and any Shares to be offered so as to enable an investor to decide to purchase any Shares, as the same may be varied in that Member State by any measure implementing the Prospectus Directive in that Member State, the expression “Prospectus Directive” means Directive 2003/71/EC (and amendments thereto, including the 2010 PD Amending Directive, to the extent implemented in the Relevant Member State), and includes any relevant implementing measure in the Relevant Member State, and the expression “2010 PD Amending Directive” means Directive 2010/73/EU.
United Kingdom
Each underwriter has represented and agreed that:
| • | it has only communicated or caused to be communicated and will only communicate or cause to be communicated an invitation or inducement to engage in investment activity (within the meaning of Section 21(1) of the FSMA) received by it in connection with the issue or sale of the Shares in circumstances in which Section 21(I) of the FSMA does not apply to us; and |
| • | it has complied and will comply with all applicable provisions of the FSMA with respect to anything done by it in relation to the Shares in, from or otherwise involving the United Kingdom. |
137
Table of Contents
The validity of the shares of common stock offered hereby will be passed upon for us by Wilson Sonsini Goodrich & Rosati, Professional Corporation, Palo Alto, California. Davis Polk & Wardwell LLP, Menlo Park, California, is acting as counsel to the underwriters.
The consolidated financial statements as of December 31, 2008 and 2009 and for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009 included in this prospectus have been so included in reliance on the report of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, an independent registered public accounting firm, given on the authority of said firm as experts in auditing and accounting.
WHERE YOU CAN FIND MORE INFORMATION
We have filed with the SEC a registration statement on Form S-1 under the Securities Act with respect to the shares of common stock offered hereby. This prospectus, which constitutes a part of the registration statement, does not contain all of the information set forth in the registration statement or the exhibits and schedules filed therewith. For further information about us and the common stock offered hereby, we refer you to the registration statement and the exhibits and schedules filed therewith. Statements contained in this prospectus regarding the contents of any contract or any other document that is filed as an exhibit to the registration statement are not necessarily complete, and each such statement is qualified in all respects by reference to the full text of such contract or other document filed as an exhibit to the registration statement. Following this offering, we will be required to file periodic reports, proxy statements, and other information with the SEC pursuant to the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. You may read and copy this information at the Public Reference Room of the SEC, 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C. 20549. You may obtain information on the operation of the Public Reference Room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. The SEC also maintains a website that contains registration statements, reports, proxy statements and other information filed electronically with the SEC. The address of that site is www.sec.gov.
138
Table of Contents
SERVICESOURCE INTERNATIONAL, LLC
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Page | ||
| F-2 | ||
| F-3 | ||
| F-4 | ||
| Consolidated Statements of Members’ Equity and Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
F-5 | |
| F-6 | ||
| F-7 | ||
F-1
Table of Contents
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
To the Board of Directors and Members of
ServiceSource International, LLC and Subsidiaries
In our opinion, the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and the related consolidated statements of operations, of members’ equity and comprehensive income (loss) and of cash flows present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of ServiceSource International, LLC and its subsidiaries at December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for each of the three years in the period ended December 31, 2009 in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audits. We conducted our audits of these statements in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/ PRICEWATERHOUSECOOPERS LLP
March 29, 2010, except for net income (loss) per common share information discussed in Note 3, the 2010 amendments to the credit facility discussed in Note 7, the adoption of the accounting standard on unrecognized tax benefits discussed in Note 12 and segment information discussed in Note 13, as to which the date is December 20, 2010.
San Francisco, California
F-2
Table of Contents
ServiceSource International, LLC and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Balance Sheets
(In thousands, except per share amounts)
| December 31, | September 30, 2010 |
Pro Forma | ||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | September 30, 2010 |
||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets |
||||||||||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||||||||||
| Cash |
$ | 3,780 | $ | 13,169 | $ | 23,231 | $ | |||||||||
| Accounts receivable, net |
23,369 | 28,015 | 41,222 | |||||||||||||
| Advances to customers |
4,303 | 741 | 207 | |||||||||||||
| Current portion of deferred income taxes |
469 | 713 | 1,171 | |||||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other |
1,551 | 1,087 | 2,319 | |||||||||||||
| Total current assets |
33,472 | 43,725 | 68,150 | |||||||||||||
| Property and equipment, net |
9,073 | 14,001 | 18,496 | |||||||||||||
| Goodwill |
6,334 | 6,334 | 6,334 | |||||||||||||
| Deferred debt issuance costs, net |
585 | 423 | 449 | |||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes, net of current portion |
2,101 | 2,882 | 4,350 | |||||||||||||
| Other assets, net |
147 | 2,215 | 1,357 | |||||||||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 51,712 | $ | 69,580 | $ | 99,136 | $ | |||||||||
| Liabilities and Members’/Stockholders’ Equity |
||||||||||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 2,063 | $ | 1,124 | $ | 2,310 | $ | |||||||||
| Accrued taxes |
4,561 | 2,679 | 2,686 | |||||||||||||
| Accrued compensation and benefits |
6,849 | 7,780 | 10,514 | |||||||||||||
| Accrued payables to customers |
3,509 | 6,998 | 26,160 | |||||||||||||
| Other accrued liabilities |
1,230 | 2,723 | 5,533 | |||||||||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt |
2,941 | 3,322 | 2,060 | |||||||||||||
| Total current liabilities |
21,153 | 24,626 | 49,263 | |||||||||||||
| Long-term debt, net of current portion |
16,835 | 14,286 | 15,730 | |||||||||||||
| Other long-term liabilities |
242 | 337 | 1,223 | |||||||||||||
| Total liabilities |
38,230 | 39,249 | 66,216 | |||||||||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Notes 7 and 8) |
||||||||||||||||
| Members’/stockholders’ equity: |
||||||||||||||||
| Common shares: 99,000 authorized; 56,841, 57,299 and 57,927 issued; 56,461, 56,885 and 57,426 outstanding as of December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010 (unaudited), respectively zero authorized, issued and outstanding, pro forma (unaudited) |
13,357 | 30,506 | 33,196 | |||||||||||||
| Common stock; $0.0001 par value; 1,000,000 shares authorized, shares issued and outstanding, pro forma (unaudited) |
— | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Treasury shares/stock |
— | (126 | ) | (441 | ) | |||||||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
— | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Retained earnings |
— | — | — | |||||||||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive income (loss) |
125 | (49 | ) | 165 | ||||||||||||
| Total members’/stockholders’ equity |
13,482 | 30,331 | 32,920 | |||||||||||||
| Total liabilities and members’/stockholders’ equity |
$ | 51,712 | $ | 69,580 | $ | 99,136 | $ | |||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-3
Table of Contents
ServiceSource International, LLC and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Operations
(In thousands, except per share amounts)
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue |
$ | 75,189 | $ | 100,280 | $ | 110,676 | $ | 76,889 | $ | 108,468 | ||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
39,224 | 56,965 | 58,877 | 41,577 | 63,841 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
35,965 | 43,315 | 51,799 | 35,312 | 44,627 | |||||||||||||||
| Operating expenses |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
13,119 | 20,486 | 23,182 | 16,802 | 25,640 | |||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
— | 1,160 | 2,054 | 1,647 | 3,927 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
10,475 | 10,571 | 13,777 | 10,214 | 13,806 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of intangible assets |
912 | 857 | 68 | 68 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Total operating expenses |
24,506 | 33,074 | 39,081 | 28,731 | 43,373 | |||||||||||||||
| Income from operations |
11,459 | 10,241 | 12,718 | 6,581 | 1,254 | |||||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(2,305 | ) | (2,209 | ) | (1,116 | ) | (772 | ) | (940 | ) | ||||||||||
| Loss on extinguishment of debt |
— | (561 | ) | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
| Other income (expense), net |
(118 | ) | (1,497 | ) | 639 | 465 | (202 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Income before provision for (benefit from) income taxes |
9,036 | 5,974 | 12,241 | 6,274 | 112 | |||||||||||||||
| Income tax (benefit) provision |
(632 | ) | 1,153 | 1,866 | 730 | 1,368 | ||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 9,668 | $ | 4,821 | $ | 10,375 | $ | 5,544 | $ | (1,256 | ) | |||||||||
| Pro forma (loss) before income taxes (Note 4, unaudited) |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma provision for income taxes (Note 4, unaudited) |
— | — | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma net loss (Note 4, unaudited) |
$ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) per common share: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.17 | $ | 0.09 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.10 | $ | (0.02 | ) | |||||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.16 | $ | 0.08 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.09 | $ | (0.02 | ) | |||||||||
| Weighted-average shares used in computing net income (loss) per common share: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
55,936 | 56,209 | 56,750 | 56,702 | 57,167 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
58,706 | 58,733 | 58,912 | 58,510 | 57,167 | |||||||||||||||
| Pro forma net income (loss) per common share (unaudited) (Note 4): |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
$ | $ | ||||||||||||||||||
| Pro forma weighted-average shares used in computing net income (loss) per common share (unaudited) (Note 4): |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Diluted |
||||||||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-4
Table of Contents
ServiceSource International, LLC and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Members’ Equity and Comprehensive Income (Loss)
(In thousands)
| Common Shares | Treasury Shares | Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income (Loss) |
Total | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares | Amount | Shares | Amount | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2006 |
55,521 | $ | (782 | ) | — | $ | — | $ | (17 | ) | $ | (799 | ) | |||||||||||
| Repurchase of common shares |
— | — | (15,286 | ) | (65,113 | ) | — | (65,113 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares |
— | — | 15,286 | 65,113 | — | 65,113 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cash distributions to members |
— | (5,109 | ) | — | — | — | (5,109 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares from exercise of share options |
208 | 100 | — | — | — | 100 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of share options subject to repurchase |
364 | 134 | — | — | — | 134 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation expense |
— | 3,876 | — | — | — | 3,876 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | 9,668 | — | — | — | 9,668 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments |
— | — | — | — | 67 | 67 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income |
9,735 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2007 |
56,093 | 7,887 | — | — | 50 | 7,937 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Cash distributions to members |
— | (5,201 | ) | — | — | — | (5,201 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares from exercise of share options |
305 | 207 | — | — | — | 207 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Vesting of share options subject to repurchase |
63 | 16 | — | — | — | 16 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation expense |
— | 5,449 | — | — | — | 5,449 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefits from exercise of share options |
— | 178 | — | — | — | 178 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | 4,821 | — | — | — | 4,821 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | 75 | 75 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income |
4,896 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2008 |
56,461 | 13,357 | — | — | 125 | 13,482 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares from exercise of share options |
459 | 585 | — | — | — | 585 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of common share |
— | — | (35 | ) | (126 | ) | — | (126 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation expense |
— | 6,060 | — | — | — | 6,060 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefits from exercise of share options |
— | 129 | — | — | — | 129 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income |
— | 10,375 | — | — | — | 10,375 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of tax |
— | — | — | — | (174 | ) | (174 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income |
10,201 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at December 31, 2009 |
56,920 | 30,506 | (35 | ) | (126 | ) | (49 | ) | 30,331 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash distributions to members (unaudited) |
— | (2,517 | ) | — | — | (2,517 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of common shares from exercise of share options (unaudited) |
627 | 415 | — | — | — | 415 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Repurchase of common shares (unaudited) |
— | — | (86 | ) | (315 | ) | — | (315 | ) | |||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation expense (unaudited) |
— | 6,017 | — | — | — | 6,017 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Excess tax benefits from exercise of share options (unaudited) |
— | 31 | — | — | — | 31 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss (unaudited) |
— | (1,256 | ) | — | — | — | (1,256 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
| Foreign currency translation adjustments, net of tax (unaudited) |
— | — | — | — | 214 | 214 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss (unaudited) |
(1,042 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balances at September 30, 2010 (unaudited) |
57,547 | $ | 33,196 | (121 | ) | $ | (441 | ) | $ | 165 | $ | 32,920 | ||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-5
Table of Contents
ServiceSource International, LLC and Subsidiaries
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
(In thousands)
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 9,668 | $ | 4,821 | $ | 10,375 | $ | 5,544 | $ | (1,256 | ) | |||||||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
2,596 | 3,356 | 3,527 | 2,367 | 4,436 | |||||||||||||||
| Amortization of deferred financing costs |
237 | 172 | 162 | 124 | 124 | |||||||||||||||
| Loss on extinguishment of debt |
— | 561 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
(689 | ) | (1,881 | ) | (1,025 | ) | (3,368 | ) | (960 | ) | ||||||||||
| Share-based compensation |
3,876 | 5,449 | 6,060 | 4,440 | 6,017 | |||||||||||||||
| Changes in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Accounts receivable |
(3,259 | ) | (6,408 | ) | (4,494 | ) | 3,200 | (13,207 | ) | |||||||||||
| Advances to customers |
(1,118 | ) | (3,185 | ) | 3,562 | 969 | 534 | |||||||||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other |
283 | (757 | ) | (1,665 | ) | 113 | (1,338 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Accounts payable |
984 | 938 | (1,063 | ) | (415 | ) | 1,186 | |||||||||||||
| Accrued taxes |
(1,000 | ) | 1,571 | (1,872 | ) | (1,992 | ) | 7 | ||||||||||||
| Accrued compensation and benefits |
1,859 | 1,198 | 930 | (831 | ) | 2,734 | ||||||||||||||
| Accrued payables to customers |
— | (2,077 | ) | 3,489 | 1,295 | 19,162 | ||||||||||||||
| Other accrued liabilities |
3,745 | (526 | ) | 1,518 | 3,044 | 3,698 | ||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
17,182 | 3,232 | 19,504 | 14,490 | 21,137 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of property and equipment |
(3,182 | ) | (6,806 | ) | (7,476 | ) | (5,540 | ) | (7,427 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(3,182 | ) | (6,806 | ) | (7,476 | ) | (5,540 | ) | (7,427 | ) | ||||||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Proceeds from revolving credit facility |
— | 3,500 | 10,600 | 10,600 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Repayments of revolving credit facility |
— | (3,500 | ) | (10,600 | ) | (10,600 | ) | — | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of long-term debt |
— | 17,500 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Repayments on long-term debt |
(113 | ) | (18,048 | ) | (2,967 | ) | (2,356 | ) | (1,204 | ) | ||||||||||
| Payments of deferred debt issuance costs |
(132 | ) | (587 | ) | — | — | (150 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Cash distributions to members |
(5,109 | ) | (5,201 | ) | — | — | (2,517 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from option exercises |
100 | 207 | 585 | 561 | 415 | |||||||||||||||
| Repurchases of common shares |
(65,113 | ) | — | (126 | ) | — | (315 | ) | ||||||||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of common shares |
65,113 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Tax benefit from share-based compensation |
— | 178 | 129 | — | 31 | |||||||||||||||
| Net cash used in financing activities |
(5,254 | ) | (5,951 | ) | (2,379 | ) | (1,795 | ) | (3,740 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net increase (decrease) in cash |
8,746 | (9,525 | ) | 9,649 | 7,155 | 9,970 | ||||||||||||||
| Effect of exchange rate changes on cash |
(90 | ) | 158 | (260 | ) | (128 | ) | 92 | ||||||||||||
| Cash at beginning of period |
4,491 | 13,147 | 3,780 | 3,780 | 13,169 | |||||||||||||||
| Cash at end of period |
$ | 13,147 | $ | 3,780 | $ | 13,169 | $ | 10,807 | $ | 23,231 | ||||||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of cash flow information |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Cash paid for interest |
$ | 2,110 | $ | 1,835 | $ | 1,038 | $ | 754 | $ | 692 | ||||||||||
| Cash paid for income taxes |
— | 110 | 5,627 | 4,452 | 2,686 | |||||||||||||||
| Supplemental disclosure of noncash investing and financing activities |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of property and equipment under capital leases |
— | 324 | 785 | 804 | 1,388 | |||||||||||||||
| Acquisition of property and equipment through accounts payable |
169 | — | 102 | 271 | 464 | |||||||||||||||
| Vesting of share options subject to repurchase |
134 | 16 | — | — | 35 | |||||||||||||||
The accompanying notes are an integral part of these consolidated financial statements.
F-6
Table of Contents
ServiceSource International, LLC and Subsidiaries
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
(Information as of September 30, 2010 and for the nine-month periods ended
September 30, 2009 and 2010 is unaudited)
1. The Company
ServiceSource International, LLC (the “Company,” “LLC” or “ServiceSource”) manages the service contract renewals process of maintenance, support and subscription agreements on behalf of its customers. The Company’s integrated solution consists of a suite of cloud applications, dedicated service sales teams working under its customers’ brands and a proprietary Service Revenue Intelligence Platform. The Company’s corporate headquarters are located in San Francisco, California. The Company has additional offices in Colorado, Tennessee, the United Kingdom, Ireland, Malaysia and Singapore.
The Company is currently established as a limited liability company and the members’ units of interest are defined as shares or common shares in the limited liability company agreement.
2. Summary of Significant Accounting Policies
Basis of Consolidation
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of ServiceSource International, LLC and its wholly-owned subsidiaries. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation.
Use of Estimates
The preparation of consolidated financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America (“GAAP”) requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of the consolidated financial statements and the reported amount of net revenue and expenses during the reporting period.
The Company’s significant accounting judgments and estimates include: revenue recognition; the determination and assessment of fair value of the Company’s common shares and related share-based compensation expense, realizability of deferred tax assets and uncertain tax positions, and capitalization of internal-use software.
The Company bases its estimates and judgments on historical experience and on various assumptions that it believes are reasonable under the circumstances. However, future events are subject to change and estimates and judgments routinely require adjustment. Actual results may differ from these estimates, and these differences may be material.
Unaudited Interim Financial Statements
The accompanying interim consolidated balance sheet at September 30, 2010, the interim consolidated statements of operations and cash flows for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010 and the interim consolidated statement of members’ equity and comprehensive income (loss) for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 are unaudited. The unaudited interim consolidated financial statements have been prepared on the same basis as the annual financial statements and, in the opinion of management, reflect all adjustments, which include only normal recurring adjustments, necessary for the fair statement of the Company’s consolidated financial position as of September 30, 2010 and the results of its consolidated operations and cash flows for the
F-7
Table of Contents
nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010. The financial data and the other financial information disclosed in these notes to the consolidated financial statements related to the nine-month periods are unaudited. The results of the Company’s operations for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for the year ending December 31, 2010 or for any other future year or interim period.
Segments
The Company defines an operating segment on the same basis that it uses internally to evaluate performance. Management has determined that the Company operates in three segments, as it reports financial information across three geographic regions to its chief executive officer, who is the Company’s chief operating decision maker. The Company’s three operating and reportable segments are NALA (North America and Latin America), EMEA (Europe and Middle East) and APJ (Asia Pacific and Japan).
Significant Risks and Uncertainties
The Company is subject to certain risks and uncertainties that could have a material and adverse effect on its future financial position or results of operations. The Company’s customers are primarily high technology companies and any downturn in these industries, changes in customers’ sales strategies, or widespread shift away from end customers purchasing maintenance and support contracts could have an adverse impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations and financial condition.
Financial instruments that potentially subject the Company to concentration of credit risk consist principally of cash, accounts receivable and advances to customers. The Company is also exposed to a variety of market risks, including the effects of changes in foreign currency exchange rates and interest rates.
Cash is maintained in demand accounts at U.S., European and Asian financial institutions that management believes are credit worthy. Deposits in these institutions may exceed the amount of insurance provided on these deposits.
Accounts receivable are derived from services performed for customers located primarily in the U.S., Europe and Asia. The Company attempts to mitigate the concentration of credit risk in its trade receivables through its ongoing credit evaluation process and historical collection experience. The Company maintains an allowance for doubtful accounts based upon the expected collectibility of all accounts receivable, which takes into consideration an analysis of historical bad debts and other available information.
The following table summarizes net revenue and accounts receivable from customers, as included in the NALA and EMEA geographic segments (Note 13), in excess of 10% of total net revenue and accounts receivable, respectively:
| Net Revenue | Accounts Receivable | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Years
Ended December 31, |
Nine Months
Ended September 30, |
December 31, | September
30, 2010 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | 2008 | 2009 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | (unaudited) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sun Microsystems, Inc. |
22 | % | 23 | % | 24 | % | 24 | % | 17 | % | 33 | % | 19 | % | 15 | % | ||||||||||||||||
The following table summarizes advances to customers and accrued payables to customers in excess of 10% of total advances and accrued payables to customers, respectively:
| Advances to Customers | Accrued Payables to Customers | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | September
30, 2010 |
December 31, | September
30, 2010 |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | (unaudited) |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sun Microsystems, Inc. |
100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | 99 | % | 99 | % | 100 | % | ||||||||||||
F-8
Table of Contents
In January 2010, Oracle Corporation (“Oracle”) acquired the Company’s then-largest customer, Sun Microsystems, Inc. (“Sun”). In July 2010, Oracle notified the Company that it was terminating the Sun agreements with the Company, effective in the third quarter of 2010. As of September 30, 2010, the Sun agreements were terminated.
Fair Value Measurements
Effective January 1, 2008, the Company adopted Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 820, Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures. Under this standard, fair value is defined as the price that would be received by selling an asset or paid by transferring a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement date. The fair value hierarchy requires an entity to maximize the use of the observable inputs and minimize the use of unobservable inputs when measuring fair value. The three levels of the hierarchy are as follows:
| Level 1 | Quoted prices in active markets that are accessible at the measurement date for identical, unrestricted assets or liabilities. | |
| Level 2 | Quoted prices for similar assets and liabilities in active markets; quoted prices for identical or similar assets and liabilities in markets that are not active; and model-derived valuations in which all significant inputs and significant value drivers are observable in active markets. | |
| Level 3 | Unobservable inputs that are supported by little or no market activity and that are significant to the fair value of the assets or liabilities. Level 3 assets and liabilities include financial instruments whose value is determined using pricing models, discounted cash flow methodologies, or similar techniques, as well as instruments for which the determination of fair value requires significant management judgment or estimation. | |
A financial instrument’s level within the fair value hierarchy is based on the lowest level of input that is significant to the fair value measurement.
The adoption of ASC 820 had no impact on members’ equity as of January 1, 2008.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments
The carrying amounts of certain financial instruments, which include cash, restricted cash, accounts receivable, accounts payable, advances to customers, accrued payables to customers and other accrued liabilities approximates fair value due to their short-term nature. Based on borrowing rates currently available to the Company for loans with similar terms, the carrying value of long-term debt approximates fair value, assuming minimal credit risk and nonperformance risk.
Foreign Currency Translation and Remeasurement
Assets and liabilities of non-U.S. subsidiaries that operate in a local currency environment, where that local currency is the functional currency, are translated to U.S. dollars at exchange rates in effect at the balance sheet date. Net revenue and expenses are translated at monthly average exchange rates. The Company accumulates net translation adjustments in members’ equity as a component of accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). For non-U.S. subsidiaries whose functional currency is the U.S. dollar, transactions that are denominated in foreign currencies have been remeasured in U.S. dollars, and any resulting gains and losses are reported in the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Foreign currency transaction (losses) gains of $(0.1) million, $(1.5) million, $0.6 million, $0.3 million and $(0.3) million were included in other income (expense), net during 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively.
F-9
Table of Contents
Cash, Cash Equivalents and Restricted Cash
Cash and cash equivalents include highly liquid investments with an original maturity of ninety days or less at the time of purchase. The Company did not have any cash equivalents at December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010. The Company had $0.1 million in cash held as collateral at a major financial institution which has been classified as restricted cash at December 31, 2008 and 2009. The balance of restricted cash was not significant at September 30, 2010. The restricted cash included in prepaid expenses and other on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets represented cash held for collateral pledged for corporate credit cards.
Accounts Receivable and Allowance for Doubtful Accounts
Accounts receivable consist of receivables from the Company’s customers and are stated at their carrying values net of an allowance for doubtful accounts. The Company evaluates the ongoing collectibility of its accounts receivable based on a number of factors such as the credit quality of its customers, the age of accounts receivable balances, collections experience and current economic conditions that may affect a customer’s ability to pay. In circumstances where the Company is aware of a specific customer’s inability to meet its financial obligations to the Company, a specific allowance for doubtful accounts is estimated and recorded, which reduces the recognized receivable to the estimated amount that management believes will ultimately be collected. Account balances are charged off against the allowance when it is probable that receivable will not be recovered.
The following are changes in the allowance for doubtful accounts during 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010 (in thousands):
| December 31, | Nine Months
Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance, beginning of period |
$ | 601 | $ | 879 | $ | 673 | $ | 673 | $ | 79 | ||||||||||
| Additions |
336 | 313 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
| Write-offs, net of adjustments |
(58 | ) | (519 | ) | (594 | ) | (498 | ) | (2 | ) | ||||||||||
| Balance, end of period |
$ | 879 | $ | 673 | $ | 79 | $ | 175 | $ | 77 | ||||||||||
Advances and Accrued Payables to Customers
For customer contracts that include both sales of customer service contracts and other account management services, the Company collects the gross amount of payment due from the end customers’ contracts and then remits such payment to the customer, net of the commissions and fees earned by the Company. An advance to customers is recorded in instances where the Company has remitted the net payment due to the customer before the receipt of the related gross amount due under the customer contract from the end customer. An accrued payables to customers is recorded by the Company for the net amount due to the customer when it has received the related gross payment from the end customer, but has not yet remitted the corresponding net payment to the customer.
Property and Equipment
The Company records property and equipment at cost less accumulated depreciation and amortization. Depreciation is recorded using the straight-line method over estimated useful lives of seven years for office furniture and equipment, two to three years for computer hardware and two to five years for software. Leasehold improvements are amortized on a straight-line basis over the lesser of the lease term or the estimated useful life of the related assets, ranging from three to eight years.
Upon retirement or sale, the cost of assets and the related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts and any resulting gain or loss is credited or charged to the consolidated statement of operations. Repairs and maintenance costs are expensed as incurred.
F-10
Table of Contents
Capitalized Internal-Use Software
Expenditures for software purchases and software developed or obtained for internal use are capitalized and amortized over a period of two to five years on a straight-line basis. For software developed or obtained for internal use, the Company capitalizes direct external costs associated with developing or obtaining internal-use software. In addition, the Company also capitalizes certain payroll and payroll-related costs for employees who are directly associated with the development of such applications. Costs associated with preliminary project stage activities, training, maintenance and all other post-implementation stage activities are expensed as incurred and are recorded in research and development on the accompanying consolidated statements of operations. Capitalized costs related to internal-use software under development are treated as construction-in-progress until the program, feature or functionality is ready for its intended use, at which time amortization commences.
Goodwill and Intangible Assets
In connection with an acquisition in 2003 the Company acquired certain intangible assets consisting of goodwill, customer contracts and related relationships, trade names and noncompete agreements. Goodwill is not amortized. Intangible assets are carried at cost, less accumulated amortization. Intangible assets are amortized using the straight-line method over estimated useful lives of six years for customer contracts and related relationships, and five years for trade name and noncompete agreements. The net carrying value of intangible assets included in other assets in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets was $0.1 million at December 31, 2008 and $0 each at December 31, 2009 and September 30, 2009 and 2010.
Goodwill is tested for impairment annually in the fourth quarter or whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate the carrying value of goodwill may not be recoverable. Triggering events that may indicate impairment include, but are not limited to, a significant adverse change in customer demand or business climate that could affect the value of an asset or a significant decrease in expected cash flows at a reporting unit. When impaired, the carrying value of goodwill is written down to fair value. The goodwill impairment test involves a two-step process. The first step, identifying a potential impairment, compares the fair value of a reporting unit with its carrying amount, including goodwill. If the carrying value of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, the second step would need to be conducted; otherwise, no further steps are necessary as no potential impairment exists. The second step, measuring the impairment loss, compares the implied fair value of the reporting unit goodwill with the carrying amount of that goodwill. Any excess of the reporting unit goodwill carrying value over the respective implied fair value is recognized as an impairment loss. The entire goodwill balance is associated with the NALA reporting unit. There was no impairment of goodwill identified during 2007, 2008, 2009, or the nine months ended September 30, 2010.
Impairment of Long-Lived Assets
The Company’s long-lived assets consist of property and equipment, including internal-use software, and intangible assets. The Company initiates its review of potential impairment whenever events or changes in circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of a long-lived asset may not be recoverable. Conditions that may indicate impairment include, but are not limited to, significant negative industry or economic trends which may affect operating income. Determination of recoverability of long-lived assets is based on an estimate of the undiscounted future cash flows resulting from the use of the asset and its eventual disposition. Measurement of an impairment loss for long-lived assets that management expects to hold and use is based on the difference between the fair value of the asset and its carrying value. Long-lived assets to be disposed of are reported at the lower of carrying amount or fair value, less costs to sell. No impairment charge was recorded for long-lived assets in 2007, 2008, 2009, or the nine months ended September 30, 2010.
Operating Leases
The Company’s operating lease agreements include provisions for certain rent holidays, tenant incentives and escalations in the base price of the rent payment. The Company records rent holidays and rent escalations on
F-11
Table of Contents
a straight-line basis over the lease term and records the difference between expense and payment as deferred rent. The tenant incentives are recorded as deferred rent and amortized on a straight-line basis over the lease term. Deferred rent is included in other accrued liabilities on the accompanying consolidated balance sheets.
Deferred Debt Issuance Costs
The Company defers debt issuance costs, which consist primarily of bank and legal fees. Such costs related to the term loan (Note 7) are amortized using the effective-interest method over the term of the debt agreement. Costs related to the revolving credit facility (Note 7) are amortized using the straight-line method over the term of the credit facility. The amortization of deferred debt issuance costs is recorded as interest expense. Unamortized deferred debt issuance costs were $0.6 million, $0.4 million and $0.4 million at December 31, 2008, 2009 and September 30, 2010, respectively. Amortization of deferred debt issuance costs was $0.2 million, $0.2 million, $0.2 million, $0.1 million and $0.1 million in 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively. Estimated future amortization of deferred debt issuance costs expense will approximate $0.1 million in each of the years 2010 through 2013.
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Comprehensive income (loss) consists of two components, net income (loss) and other comprehensive income (loss). Other comprehensive income (loss) refers to revenue, expenses, gains and losses recorded as an element of members’ equity but are excluded from net income (loss). The Company’s other comprehensive income (loss) consists of foreign currency translation adjustments from those subsidiaries not using the U.S. dollar as their functional currency. The Company has disclosed accumulated comprehensive other income (loss) as a separate component of members’ equity.
Revenue Recognition
Substantially all of the Company’s revenue is generated from commissions earned from sales of renewals of maintenance, support and subscription contracts on behalf of its customers. Commissions are generally a fixed percentage of the overall sales value associated with the service revenue contracts sold by the Company on behalf of its customers. Revenue is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, services have been provided, the sales price is fixed or determinable and collectibility is reasonably assured from customers and no significant obligations remain unfulfilled by the Company. Customer contracts are used to determine the existence of an arrangement. Under the terms of the Company’s customer contracts, the Company’s service obligations are completed when the Company’s customers accept purchase orders from their end customers and no significant post-delivery obligations of the Company remain unfulfilled. The Company assesses whether the fee is fixed or determinable based on the payment terms with customers and whether any part of the fee is subject to refund or adjustment. The Company assesses collectibility based primarily on the creditworthiness of customers as determined by credit checks and analyses as well as the payment history of its customers. Revenue is recognized on a net basis primarily because the Company is not a party to the contracts between the customers and the end customers and does not provide actual services to the end customers. Also, the Company does not set the price, terms or scope of services in the contracts with end customers.
Some customer agreements include performance-based commissions based on attainment of certain performance targets, including the achievement of contract renewal rates in excess of specified targets. Certain customer arrangements also entitle the Company to fees and adjustments which are invoked in various circumstances, including the failure of customers to provide the Company with a specified minimum value of service contracts to sell on their behalf. The Company’s contracts generally contain termination fees should customers elect to cancel agreements prior to their expiration. Revenue related to commissions incentives and early termination fees are recorded in the period when the performance criteria have been met, or the triggering event has occurred, and the amount earned is not subject to claw-back or future adjustment. Some customers may cancel their contracts if the Company is out of compliance with certain performance obligations, as defined in
F-12
Table of Contents
the relevant customer agreement. In addition, the Company estimates an allowance for potential cancellation of service contracts and unpaid invoices from end customers, which is calculated based on historical results and the aging of the outstanding invoices and constitutes a reduction of the revenue recorded upon the sale of service contracts.
For multiple element arrangements including deliverables such as sales of service contracts, account management services and subscriptions to the Company’s service revenue management solutions, the Company separates each revenue stream at the inception of the arrangement on a relative fair value basis, provided that each service element meets the criteria for treatment as a separate unit of accounting. An item is considered a separate unit of accounting if it has value to the customer on a stand-alone basis and there is objective and reliable fair value of the undelivered services. The fair value of the undelivered elements is determined by the price charged when the element is sold separately, or in cases where the item is not sold separately, by using other acceptable objective evidence.
For a limited number of customer arrangements, the Company is responsible for selling service contracts and for providing account management services such as invoicing and cash collections from end customers. Under these arrangements, revenue is recognized when the service has been delivered and the fee is fixed or determinable, which is upon receipt of cash payment from the end customer. Revenue is also reported net of sales taxes collected from end customers and remitted to state and local government authorities.
For a limited number of customer engagements that include sales of service contracts and subscription fees to the Company’s hosted technology platform, fees earned for selling service contracts are recognized as revenue as services are performed, while hosting revenue is recognized ratably over the subscription term, which term is generally one year.
Cost of Revenue
Cost of revenue includes compensation and related personnel expenses directly related to service contract sales and account management services personnel. The Company allocates overhead expenses related to facilities, information technology and depreciation, including amortization of internal-use software to all departments based on headcount. As a result, allocated overhead costs are reflected in cost of revenues, sales and marketing, research and development and general administrative expenses.
Sales Commissions
Sales commissions earned by the Company’s sales representatives are generally paid in two or three installments with an initial payment shortly after entering into a new customer agreement and a final payment approximately twelve months after the Company begins to sell service contracts on behalf of the customer. Commission payments are contingent upon continued employment by the sales representatives and subject to adjustments during the service period based on the estimated value of service contracts received from the customer for sale. Commission expense is recognized over the employment service period, generally eight to fourteen months. At the time of each payment, sales commission expense recorded is in excess of each payment.
Advertising Costs
The Company expenses advertising costs as incurred. Advertising expenses were insignificant for all periods presented.
Income Taxes
ServiceSource International, LLC (“LLC”), as the parent company, files its income tax return as a partnership for federal and state income tax purposes. The LLC recognizes no federal, state, or local income
F-13
Table of Contents
taxes, as the members of the LLC, and not the LLC itself, are subject to income tax on their allocated share of the LLC’s earnings. The Company’s taxable subsidiaries are included in the provision for income taxes in the accompanying consolidated financial statements as further described below. The Company is subject to an annual California LLC registration fee based on revenue. The Company generally makes an annual distribution to its limited liability company members for their estimated tax liability on allocated net income under the terms of the limited liability company agreement.
Income taxes for the Company’s taxable subsidiaries, consisting of ServiceSource International, Inc and several subsidiaries formed in foreign jurisdictions are accounted for using an asset and liability method, which requires the recognition of taxes payable or refundable for the current year and deferred tax assets and liabilities for the expected future tax consequences of temporary differences that currently exist between the tax basis and the financial reporting basis of the Company’s taxable subsidiaries’ assets and liabilities using the enacted tax rates in effect for the year in which the differences are expected to reverse. The effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities is recognized in operations in the period that includes the enactment date. The measurement of deferred tax assets is reduced, if necessary, by the amount of any tax benefits that, based on available evidence, are not expected to be realized.
The Company accounts for unrecognized tax benefits using a more-likely-than-not threshold for financial statement recognition and measurement of tax positions taken or expected to be taken in a tax return. The Company establishes reserves for tax-related uncertainties based on estimates of whether, and the extent to which, additional taxes will be due. The Company records an income tax liability, if any, for the difference between the benefit recognized and measured and the tax position taken or expected to be taken on the Company’s tax returns. To the extent that the assessment of such tax positions changes, the change in estimate is recorded in the period in which the determination is made. The reserves are adjusted in light of changing facts and circumstances, such as the outcome of a tax audit. The provision for income taxes includes the impact of reserve provisions and changes to reserves that are considered appropriate. As of December 31, 2008, 2009 and September 30, 2010, the Company has not recorded any liabilities for unrecognized tax benefits.
The Company recognizes interest accrued related to unrecognized tax benefits in interest expense and tax penalties in general and administrative expense in the consolidated statements of operations. The Company did not accrue or pay any interest or penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits during 2007, 2008, and 2009, or the nine months ended September 30, 2010.
In general, it is the practice and intention of the Company to permanently reinvest the undistributed earnings of its non-US subsidiaries. Should the Company repatriate undistributed earnings, such amounts become subject to U.S. taxation giving recognition to current tax expense and foreign tax credits upon remittance of dividends and under certain other circumstances. As of December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010, the Company did not have any significant undistributed earnings from its foreign subsidiaries.
The Company’s provisions for income taxes for interim reporting periods are based on estimates of the annual effective tax rate for the full fiscal year. The computation of the annual effective tax rate includes a forecast of the Company’s estimated ordinary income (loss), which is the annual income (loss) from operations before tax, excluding unusual or infrequently occurring (or discrete) items. Significant management judgment is required in the projection of ordinary income (loss) in order to determine the estimated annual effective tax rate.
Share-Based Compensation
The Company measures and recognizes compensation expense for all share-based awards made to employees and directors based on estimated fair values. The fair value of employee and director options is estimated on the date of grant using the Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The value of awards that are ultimately expected to vest is recognized as expense over the requisite service periods. Since share-based compensation expense is based on awards ultimately expected to vest, it is reduced for expected forfeitures.
F-14
Table of Contents
For awards that are expected to result in a tax deduction, a deferred tax asset is established as the Company recognizes compensation expense. If the tax deduction exceeds the cumulative recorded compensation expense, the tax benefit associated with the excess deduction is considered a windfall benefit. The excess tax benefit from share compensation plans is recorded in members’ equity and classified as a financing cash flow on the consolidated statements of cash flows. The Company has elected to use the short-cut method for determining the historical pool of windfall tax benefits that accumulated prior to January 1, 2006.
Net Income (Loss) Per Common Share
Basic net income (loss) per common share is computed using the weighted-average number of common shares outstanding during the period. Diluted net income (loss) per common share is computed using the weighted-average number of common shares and potentially dilutive common shares outstanding during the period. Potential diluted shares include the dilutive effect of in-the-money options. The dilutive effect of such equity awards is calculated based on the average share price for each period using the treasury-stock method. Under the treasury-stock method, the amount the employee must pay for exercising options, the amount of compensation cost for future service that the Company has not yet recognized, and the amount of tax benefits that would be recorded in members’ equity when the award becomes deductible, are collectively assumed to be used to repurchase shares.
Recent Accounting Pronouncements
In October 2009, Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued a new accounting standard that changes the accounting for arrangements with multiple deliverables. The new standard requires an entity to allocate arrangement consideration at the inception of an arrangement to all of its deliverables based on their relative selling prices. This standard will be effective for the Company beginning January 1, 2011. This Accounting Standards Update (“ASU”) removed the previous separation criteria that objective and reliable evidence of the fair value of any undelivered items must exist for the delivered item to be considered a separate unit or units of accounting. Given the Company’s current contractual arrangements, the adoption of this standard is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In January 2010, the FASB issued amended guidance on fair value measurements and disclosures. The new guidance requires additional disclosures regarding fair value measurements, amends disclosures about postretirement benefit plan assets, and provides clarification regarding the level of disaggregation of fair value disclosures by investment class. This guidance is effective for interim and annual reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2009, except for certain Level 3 activity disclosure requirements that will be effective for reporting periods beginning after December 15, 2010. Accordingly, the Company adopted this amendment for the nine month period ended September 30, 2010, except for the additional Level 3 requirements which will be adopted in 2011. Level 3 assets and liabilities are those whose fair market value inputs are unobservable and reflect management’s best estimate of what market participants would use in pricing the asset or liability at the measurement date. The adoption of this guidance did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In February 2010, the FASB issued ASU No. 2010-09 Subsequent Events (ASC Topic 855): Amendments to Certain Recognition and Disclosure Requirements. ASU 2010-09 requires an entity that is a filer with the Securities and Exchange Commission (“SEC”) to evaluate subsequent events through the date that the financial statements are issued and removes the requirement for an SEC filer to disclose a date, in both issued and revised financial statements, through which the filer had evaluated subsequent events. The adoption of this standard did not have a significant impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
In April 2010, the FASB issued ASU No. 2010-13, Compensation—Stock Compensation (Topic 718)—Effect of Denominating the Exercise Price of a Share-Based Payment Award in the Currency of the Market in Which the Underlying Equity Security Trades. ASU 2010-13 provides amendments to Topic 718 to clarify that an
F-15
Table of Contents
employee share-based payment award with an exercise price denominated in the currency of a market in which a substantial portion of the entity’s equity securities trades should not be considered to contain a condition that is not a market, performance, or service condition. Therefore, an entity would not classify such an award as a liability if it otherwise qualifies as equity. The amendments in ASU 2010-13 are effective for fiscal years, and interim periods within those fiscal years, beginning on or after December 15, 2010. The adoption of this standard is not expected to have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
3. Net Income (Loss) Per Common Share
The basic and diluted net income per share calculations are presented below (in thousands, except for per share amounts):
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic net income (loss) per common share | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 9,668 | $ | 4,821 | $ | 10,375 | $ | 5,544 | $ | (1,256 | ) | |||||||||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding(1) |
55,936 | 56,209 | 56,750 | 56,702 | 57,167 | |||||||||||||||
| Basic net income (loss) per common share |
$ | 0.17 | $ | 0.09 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.10 | $ | (0.02 | ) | |||||||||
| (1) | Outstanding unvested common shares purchased by employees are subject to repurchase by the Company and therefore are not included in the calculation of the weighted-average shares outstanding for basic net income (loss) per common share. |
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Diluted net income (loss) per common share | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net income (loss) used to determine diluted net income (loss) per common share |
$ | 9,668 | $ | 4,821 | $ | 10,375 | $ | 5,544 | $ | (1,256 | ) | |||||||||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding |
55,936 | 56,209 | 56,750 | 56,702 | 57,167 | |||||||||||||||
| Adjustment for incremental shares arising from assumed exercise of options |
2,770 | 2,524 | 2,162 | 1,808 | — | |||||||||||||||
| Weighted-average common shares for diluted net income (loss) per share |
58,706 | 58,733 | 58,912 | 58,510 | 57,167 | |||||||||||||||
| Diluted net income (loss) per common share(1) |
$ | 0.16 | $ | 0.08 | $ | 0.18 | $ | 0.09 | $ | (0.02 | ) | |||||||||
| (1) | As the Company was in a net loss position for the nine months ended September 30, 2010, there was no dilutive effect on net loss per common share. Therefore, both basic and diluted net loss per common share were $(0.02) for the nine months ended September 30, 2010. |
4. Pro forma information (unaudited)
The pro forma information has been computed to give effect to the pro forma adjustments discussed below:
Pro forma stockholders’ equity and pro forma deferred income tax assets and liabilities as of September 30, 2010 have been computed to give effect to the conversion of the Company’s common shares into shares of common stock and repayment of the loan balances using proceeds from the offering of common stock and accordingly reflect:
| • | the reclassification of the balance of members’ interests in common shares to common stock and additional paid-in capital upon a reorganization of the Company from a Delaware limited liability company to a Delaware corporation and the conversion of common shares into common stock in a ratio of 1:1 based on amounts outstanding as of September 30, 2010; |
F-16
Table of Contents
| • | adjustments to deferred income tax assets and deferred income tax liabilities in connection with the Company’s reorganization from a limited liability company to a Delaware corporation, with a resulting net adjustment of $ to stockholders’ equity; |
| • | the write-off of deferred debt issuance costs of $ and repayment of the loan balances of $ outstanding under the Credit Facility based on amounts outstanding as of September 30, 2010; and |
| • | the issuance of shares of common stock at the assumed initial offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus) net of offering costs of $ , where the proceeds of such issuance of shares would have been sufficient to repay outstanding loan balances as of September 30, 2010. |
All of the aforementioned adjustments have been reflected in the pro forma balance sheet as if these events all occurred on September 30, 2010.
Based on operating results through September 30, 2010 in which the Company incurred a pre-tax loss, the Company does not expect to adjust its pro forma stockholders’ equity for any contingent distributions to members for potential tax obligations related to 2010 results.
The pro forma net income (loss) applied in computing the unaudited pro forma basic and diluted income (loss) per share for the year ended December 31, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2010 is based upon the Company’s historical net income (loss) as adjusted to reflect the following:
| • | The conversion of the Company’s LLC to a C corporation. Prior to such conversion, the LLC was treated as a partnership and generally not subject to income taxes. The pro forma net income (loss), therefore, includes adjustments for income tax expense (benefit) as if the LLC had been a corporation and subject to income taxes at an assumed combined federal, state, and local income tax rate of %. Upon the conversion of the LLC to a Delaware corporation, the Company expects to record a non-cash income tax benefit equal to the amount of the net adjustment to the deferred tax balances, which would have been $ on a pro forma basis as of September 30, 2010, which has not been reflected in the adjustment to pro forma net income (loss) for the year ended December 31, 2009 or the nine months ended September 30, 2010. |
| • | The elimination of historical interest expense, including the amortization of debt issuance costs, related to the loan balances under the Company’s credit facility which is assumed to be repaid using a portion of the net proceeds of the Company’s initial public offering of its common stock. |
F-17
Table of Contents
The basic and diluted pro forma per common share calculations are presented below (in thousands, except per share amounts). The calculation of weighted average common shares used in the calculation give effect on a pro forma basis to only that number of additional shares that would have been required to be issued to prepay the loan balances outstanding under the Company’s credit facility as of September 30, 2010 assuming the issuance of such shares at an initial offering price of $ per share (the midpoint of the range set forth on the cover page of this prospectus). The diluted pro forma per common share calculation also assumes the conversion, exercise, or issuance of all potential common shares, unless the effect of inclusion would result in the reduction of a net loss per common share or the increase in net income per common share.
| Year Ended December 31, 2009 |
Nine Months Ended
September 30, 2010 |
|||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||
| Basic pro forma net income (loss) per common share | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 10,375 | $ | (1,256 | ) | |||
| Adjustment for pro forma income tax expense |
||||||||
| Adjustment to interest expense related to prepayment of loan balances |
||||||||
| Pro forma net income (loss) |
$ | $ | ||||||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding |
56,750 | 57,167 | ||||||
| Adjustment to include the additional shares required to be issued to generate proceeds sufficient to prepay the outstanding loan balances |
||||||||
| Pro forma weighted-average common shares outstanding for basic net income (loss) per common share |
||||||||
| Basic pro forma net income (loss) per common share |
$ | $ | ||||||
| Diluted pro forma net income per common share | ||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | 10,375 | $ | (1,256 | ) | |||
| Adjustment for pro forma income tax expense |
||||||||
| Adjustment to interest expense related to prepayment of loan balances |
||||||||
| Pro forma net income (loss) |
$ | $ | ||||||
| Weighted-average common shares outstanding |
56,750 | 57,167 | ||||||
| Adjustment for additional shares arising from assumed exercise of options |
||||||||
| Adjustment to include the additional shares required to be issued to generate proceeds sufficient to prepay the outstanding loan balances |
||||||||
| Pro forma weighted-average common shares outstanding for diluted net income (loss) per common share |
||||||||
| Pro forma diluted net income (loss) per common share(1) |
$ | $ | ||||||
| (1) | As the Company was in a net loss position for the nine months ended September 30, 2010, there was no dilutive effect on pro forma net loss per common share. Therefore, both basic and diluted pro forma net loss per common share were $ for the nine months ended September 30, 2010. |
F-18
Table of Contents
5. Property and Equipment, Net
Property and equipment balances were comprised of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, | September
30, 2010 |
|||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||
| Computers and equipment |
$ | 4,403 | $ | 5,556 | $ | 7,337 | ||||||
| Software |
4,764 | 8,779 | 13,038 | |||||||||
| Furniture and fixtures |
2,445 | 3,986 | 5,125 | |||||||||
| Leasehold improvements |
1,265 | 1,646 | 2,676 | |||||||||
| 12,877 | 19,967 | 28,176 | ||||||||||
| Less: accumulated depreciation and amortization |
(4,494 | ) | (7,968 | ) | (12,286 | ) | ||||||
| 8,383 | 11,999 | 15,890 | ||||||||||
| Internal-use software development in process |
690 | 2,002 | 2,606 | |||||||||
| $ | 9,073 | $ | 14,001 | $ | 18,496 | |||||||
Depreciation expense related to property and equipment was $1.7 million, $2.5 million, $3.5 million, $2.3 million and $4.4 million during 2007, 2008, 2009, and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively. Property and equipment with a carrying value of $0.6 million, $1.3 million and $2.2 million, net of accumulated amortization of $0.2 million, $0.5 million and $0.9 million, were held under capital leases at December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010, respectively.
The Company capitalized $0.7 million, $2.8 million, $5.0 million, $3.8 million and $3.1 million during 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively, related to internal-use software development costs. As of December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010, the carrying value of capitalized costs related to internal-use software, net of accumulated amortization, was $3.4 million, $7.4 million and $8.4 million, respectively. Amortization of capitalized costs related to internal-use software was $0.2 million, $0.5 million, $1.1 million, $0.7 million, and $2.1 million during 2007, 2008 and 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively.
6. Other Accrued Liabilities
Other accrued liabilities balances were comprised of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, | September
30, 2010 |
|||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||
| Deferred rent obligations |
$ | 242 | $ | 3 | $ | 60 | ||||||
| Amounts refundable to end customers |
— | 600 | 2,118 | |||||||||
| Accrued professional fees |
565 | 553 | 735 | |||||||||
| Deferred revenue |
— | 608 | 690 | |||||||||
| Other |
423 | 959 | 1,930 | |||||||||
| $ | 1,230 | $ | 2,723 | $ | 5,533 | |||||||
F-19
Table of Contents
7. Long-Term Debt
Long-term debt balances were comprised of the following (in thousands):
| December 31, | September
30, 2010 |
|||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||
| Current: |
||||||||||||
| Term loan |
$ | 2,790 | $ | 3,251 | $ | 1,500 | ||||||
| Capital lease obligations |
151 | 71 | 560 | |||||||||
| 2,941 | 3,322 | 2,060 | ||||||||||
| Non-current: |
||||||||||||
| Term loan |
16,835 | 13,584 | 14,334 | |||||||||
| Capital lease obligations |
— | 702 | 1,396 | |||||||||
| 16,835 | 14,286 | 15,730 | ||||||||||
| Total long-term debt |
$ | 19,776 | $ | 17,608 | $ | 17,790 | ||||||
Term Loan and Revolving Credit Facility
In April 2008, the Company entered into a credit facility (the “Credit Facility”), with various financial institutions that replaced several prior debt agreements. The Credit Facility initially provided for (i) a $20.0 million term loan and (ii) a $25.0 million revolving credit facility consisting of direct loans, standby letters of credit and trade letters of credit. The Credit Facility expires in April 2013, and is collateralized by substantially all of the Company’s assets.
The repayment terms of the term loan require quarterly installments of specified amounts from June 30, 2008 to April 29, 2013. If the Company exceeds a certain level of excess cash flow, as defined in the Credit Facility, for the current year, then the Credit Facility requires additional principal payments in the next year. Such additional principal payments are classified in the current portion of long-term debt at each annual balance sheet date. The Company may prepay the principal of the term loan, in whole or in part, without premium or penalty. Each prepayment must be accompanied by the payment of accrued interest to the date of such payment on the amount prepaid.
Borrowing under the revolving credit facility is subject to limitations imposed by collateral agreements and certain other conditions in the Credit Facility. Availability under the revolving credit facility was subject to certain limitations related to the Company’s accounts receivable balance and bank product reserves, as defined in the Credit Facility. There was no amount outstanding under the revolving credit facility at December 31, 2008 and 2009 or at September 30, 2010. The maximum amount of outstanding letters of credit available under the revolving credit facility shall not exceed $7.5 million in the aggregate at any time. The Company had outstanding letters of credit amounting to $2.6 million, $1.6 million and $1.6 million at December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010, respectively, as required under certain operating lease agreements for office space.
The term loan and revolving credit facility bear interest at either: (i) the Base LIBOR Rate plus an additional margin; or, (ii) the Base Rate (i.e., prime rate) plus an additional margin. Prior to April 2010, the Company had elected to borrow at the Base Rate plus the additional margin as defined in the Credit Facility. In April 2010, the Company elected to borrow at the Base LIBOR Rate plus an additional margin. At December 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009, the applicable interest rate under the Credit Facility was 5.25%; and at September 30, 2010, the applicable interest rate was 5.75%. The Company is also required to pay a letter of credit fee calculated based upon 0.825% of the daily outstanding balance of letters of credit.
The Credit Facility also has various restrictive financial covenants, which include maintaining a minimum fixed charge coverage ratio, a maximum consolidated leverage ratio and restrictions, subject to certain exceptions, under which the Company can make distributions to its members. Distributions to fund tax
F-20
Table of Contents
obligations of members are permitted so long as there are no events of default, including compliance with financial covenants, immediately prior to or after giving effect to any such distribution. Distributions other than those to fund members’ tax obligations are subject to the Company achieving specified levels of earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization or maintaining minimum levels of cash, as defined in the Credit Facility. In March 2010, the Company obtained a waiver from the requirement to make additional principal payments in 2010 based on 2009 excess cash flow levels as defined in the Credit Facility. As of December 31, 2009 and September 30, 2010, the Company was in compliance with these financial covenants.
In April 2010, the Credit Facility was amended and the maximum commitment amount under the revolving credit facility was reduced to $15.0 million and the limitation on borrowing under the revolving credit facility was changed from accounts receivable balances to consolidated revenue. In connection with this amendment, the Base LIBOR Rate was revised to be equal to the greater of 2% or the published U.S. dollar LIBOR rate.
In December 2010, the Credit Facility was further amended to (i) reduce the maximum amount available for borrowing under the revolving credit facility from $15.0 million to $7.5 million and (ii) decrease the minimum fixed charge coverage ratio with respect to the calculation for the twelve-month period ending December 31, 2010. In addition, the Company also amended its fee arrangement with the lenders such that upon the termination of or prepayment in full of the obligations under the Credit Facility on or prior to December 31, 2011, the Company would be subject to a prepayment premium of 0.5% on the sum of the maximum revolver amount as defined in the agreement and the then-outstanding principal balance on the term loan.
Capital Leases
The Company has capital lease agreements that are collateralized by the underlying property and equipment and expire through September 2019. The weighted-average imputed interest rates for the capital lease agreements were 9.8%, 5.9%, and 5.6% at December 31, 2008, 2009 and September 30, 2010, respectively. There were no capital lease obligations outstanding during 2007.
The future contractual maturities of long-term debt, including the term loan and capital lease obligations, as of December 31, 2009 and September 30, 2010 are as follows (in thousands):
| December 31, 2009 |
September 30, 2010 |
|||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||
| 2010 |
$ | 3,322 | $ | 540 | ||||
| 2011 |
4,838 | 2,274 | ||||||
| 2012 |
5,824 | 1,983 | ||||||
| 2013 |
3,160 | 12,538 | ||||||
| 2014 |
79 | 74 | ||||||
| Thereafter |
385 | 381 | ||||||
| $ | 17,608 | $ | 17,790 | |||||
F-21
Table of Contents
8. Commitments and Contingencies
Operating Leases
The Company leases its office space under noncancelable operating lease agreements with various expiration dates through August 2018. As of December 31, 2009 and September 30, 2010, future minimum payments under operating leases were as follows (in thousands):
| December 31, 2009 |
September 30, 2010 |
|||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||
| 2010 |
$ | 3,307 | $ | 1,345 | ||||
| 2011 |
3,737 | 4,980 | ||||||
| 2012 |
3,780 | 4,839 | ||||||
| 2013 |
3,594 | 3,972 | ||||||
| 2014 |
3,640 | 3,884 | ||||||
| Thereafter |
4,048 | 5,162 | ||||||
| $ | 22,106 | $ | 24,182 | |||||
Rent expense during 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010 was $2.9 million, $4.2 million, $3.8 million, $2.7 million and $3.6 million, respectively.
For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, the Company entered into four new operating leases resulting in aggregate future lease commitments of $3.4 million over lease periods ranging from one to three years. For the nine months ended September 30, 2010, the Company recorded a $0.4 million charge to terminate an office lease prior to its expiration.
Other Matters
The Company may be subject to litigation or other claims in the normal course of business. In the opinion of management, the Company’s ultimate liability, if any, related to pending or threatened litigation or claims would not materially affect its consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
9. Members’ Equity
Members’ equity consists of one class of common shares. Income is allocated pro rata to members as defined in the limited liability company agreement. The holder of each common share is entitled to one vote. Members are entitled to mandatory distributions for their respective income tax expense resulting from the operations of the LLC and other distributions as and when declared by the Board of Directors.
In 2007, the Company repurchased 15,286,453 shares for $65.1 million from certain of its members and simultaneously issued such shares to an investor at the same share value in connection with a tender offer.
The Company repurchased 35,000 shares and 86,157 shares during 2009 and for the nine months ended September 30, 2010, respectively, at the then estimated fair value. There were no share repurchases in 2008 or the nine months ended September 30, 2009. All of the acquired shares are held as treasury shares on the accompanying statements of members’ equity and comprehensive income (loss).
Other than distributions upon a redemption or liquidation event, as defined in the Company’s limited liability company Agreement, funds and assets of the Company determined by the Company’s Board of Directors to be available for distribution shall be distributed to all of the members, pro rata in proportion to the number of vested common shares held by each member.
F-22
Table of Contents
10. Share-Based Compensation
Share Option Plans
The Company has granted options through two approved plans, the Company’s 2004 Omnibus Share Plan and the 2008 Option Plan (collectively, the “Option Plans”). The Company’s 2004 Omnibus Share Plan (the “2004 Plan”) authorizes the granting of options and restricted shares to directors, officers, employees and consultants of the Company. During 2008, the Board of Directors increased the number of authorized common shares under the 2004 Plan by 2,566,000 shares to a total of 12,950,000 shares. In December 2008, the Company adopted the 2008 Option Plan (the “2008 Plan”), and currently grants options only through the 2008 Plan. A total of 10,000,000 common shares have been reserved for issuance under the 2008 Plan. The Company’s Board of Directors administers the Option Plans and has authority to determine the directors, officers, employees and consultants to whom options or restricted shares may be granted, the option price or restricted share purchase price, the timing of when each share is exercisable and the duration of the exercise period and the nature of any restrictions or vesting periods applicable to an option or restricted share grant.
Under the Option Plans, options granted are generally subject to a four-year vesting period whereby options become 25% vested after a one-year period and then vest monthly through the end of the vesting period. Vested options may be exercised up to ten years from the vesting commencement date, as defined in the Option Plans. Vested but unexercised options expire three months after termination of employment with the Company. Certain grants are exercisable before becoming vested, but the unvested optioned shares are subject to a repurchase agreement in the event the employee is terminated either voluntarily or involuntarily whereby the repurchase price is equal to the option exercise price. Proceeds from the exercise of unvested options are classified as a liability upon exercise and are reclassified to equity as the underlying shares vest to the employee. The liability for exercises of unvested options was not significant for any of the periods reported on. There were 168,000 shares subject to repurchase outstanding at December 31, 2007 and none at December 31, 2008, 2009 or September 30, 2010.
There were no significant modifications or repurchases in 2007, 2008 or 2009. In June 2010, the Company modified the vesting of 260,416 share options granted to one employee such that the cancellation of the vested shares occurred 12 months after termination of the employee. This transaction was accounted for as a modification and total incremental compensation cost resulting from the modification amounted to $0.1 million.
The Company has elected to recognize the compensation cost of all share-based awards on a straight-line basis over the vesting period of the award. Further, the Company applied an estimated forfeiture rate to unvested awards when computing the share compensation expenses. The Company estimated the forfeiture rate for unvested awards based on its historical experience on employee turnover behavior and other factors during the preceding three calendar years.
Share Awards Issued to Non Employees
During 2008 and the nine months ended September 30, 2010, the Company granted share options to purchase 8,333, and 25,000 common shares, respectively, to non employees for professional services at exercise prices ranging from $4.26 to $4.95 per share under the 2008 Plan. Share-based compensation expense related to share options granted to non employees was $0.1 million for the nine months ended September 30, 2010 and insignificant in 2008. The weighted-average remaining contractual terms at September 30, 2010 for the two options grants was 7.3 years and 9.8 years, respectively.
Determining Fair Value of Share Options
The estimated fair value of share options granted during 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, was approximately $13.2 million, $6.6 million, $7.7 million and $5.6 million and $11.1 million, respectively. The fair value of the share options was estimated by using the Black-Scholes option-
F-23
Table of Contents
pricing model, which takes into account inputs such as the exercise price, the value of the underlying common shares at the grant date, expected term, expected volatility, risk-free interest rate and dividend yield. The fair market value of each grant of options during 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2010 was determined by the Company using the methods and assumptions discussed below. The Company stratifies its population of outstanding share options into two relatively homogeneous groups to estimate the expected term and forfeiture rate of options grants. Each of these inputs is subjective and generally requires significant judgment to determine.
Expected Term—The expected term represents the period that the Company’s share-based awards are expected to be outstanding. The Company calculated the expected term of share options using four data points: options exercised, options expired, options forfeited and options outstanding. The weighted-average of the four data points were used to calculate the expected term.
Expected Volatility—The expected volatility was based on the historical stock volatility of several of the Company’s self-designated publicly listed comparable companies over a period equal to the expected terms of the options, as the Company does not have any trading history to use the volatility of its own common shares.
Risk-Free Interest Rate—The risk-free interest rate was based on the implied yield on U.S. Treasury zero-coupon issues for each option grant date with maturities approximately equal to the option’s contractual term.
Expected Dividend Yield—The Company has not paid dividends on its common shares nor does it expect to pay dividends in the foreseeable future beyond annual tax distributions to LLC members.
Forfeiture Rate—The Company estimated its forfeiture rate based on an analysis of its actual forfeitures and will continue to evaluate the adequacy of the forfeiture rate based on actual forfeiture experience, analysis of employee turnover behavior, and other factors. The impact from a forfeiture-rate adjustment will be recognized in full in the period of adjustment, if the actual number of future forfeitures differs from that estimated by the Company.
Fair Value of Common Shares—The fair value of common shares underlying the share options has historically been determined by the Board of Directors. As there has been no public market for the Company’s common shares, the Board of Directors has determined the fair value of the common shares at the time of grant of the option by considering a number of objective and subjective factors, including valuation of comparable companies, the probability-weighted expected return under possible future events, such as an initial public offering, a strategic merger or sale, or remaining a private company, the Company’s operating and financial performance, the lack of liquidity of capital share and general and industry specific economic outlook, amongst other factors. The Board of Directors also considers work performed by valuation specialists engaged by the Company to determine the valuation of its common shares.
The following table reflects the weighted-average assumptions for options grants during 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010:
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Expected term (in years) |
4.8 | 4.6 | 4.8 | 4.8 | 5.4 | |||||||||||||||
| Expected volatility |
74 | % | 55 | % | 56 | % | 56 | % | 54 | % | ||||||||||
| Risk-free interest rate |
3.57 - 4.68 | % | 2.45 - 3.07 | % | 2.17 -2.68 | % | 2.17 - 2.68 | % | 1.75 - 2.43 | % | ||||||||||
| Expected dividend yield |
— | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
F-24
Table of Contents
Option activity under the Option Plans for 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2010 was as follows (shares in thousands):
| Options Outstanding | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares Available for Grant |
Number of Shares |
Weighted- Average Exercise Price |
Weighted- Average Remaining Contractual Life (Years) |
Aggregate Intrinsic Value |
||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding—January 1, 2007 |
980 | 4,907 | $ | 1.02 | ||||||||||||||||
| Additional shares authorized |
3,821 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Granted |
(4,983 | ) | 4,983 | 4.26 | ||||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
— | (208 | ) | 0.48 | ||||||||||||||||
| Forfeited |
398 | (398 | ) | 2.05 | ||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding—December 31, 2007 |
216 | 9,284 | 2.71 | |||||||||||||||||
| Additional shares authorized |
12,566 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
| Granted |
(3,214 | ) | 3,214 | 4.26 | ||||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
— | (305 | ) | 0.68 | ||||||||||||||||
| Forfeited |
1,886 | (1,886 | ) | 1.78 | ||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding—December 31, 2008 |
11,454 | 10,307 | 3.27 | |||||||||||||||||
| Granted |
(3,650 | ) | 3,650 | 4.35 | ||||||||||||||||
| Exercised |
— | (459 | ) | 1.27 | ||||||||||||||||
| Forfeited |
997 | (997 | ) | 3.10 | ||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding—December 31, 2009 |
8,801 | 12,501 | 3.67 | |||||||||||||||||
| Granted (unaudited) |
(4,678 | ) | 4,678 | 4.77 | ||||||||||||||||
| Exercised (unaudited) |
— | (627 | ) | 0.66 | ||||||||||||||||
| Forfeited (unaudited) |
826 | (826 | ) | 4.20 | ||||||||||||||||
| Outstanding—September 30, 2010 (unaudited) |
4,949 | 15,726 | 4.09 | |||||||||||||||||
| Options vested and expected to vest—December 31, 2009 |
11,783 | $ | 3.67 | 7.2 | $ | 11,578 | ||||||||||||||
| Options exercisable—December 31, 2009 |
5,982 | $ | 3.07 | 6.4 | 9,179 | |||||||||||||||
| Options vested and expected to vest—September 30, 2010 (unaudited) |
15,264 | $ | 4.07 | 7.6 | 13,375 | |||||||||||||||
| Options exercisable—September 30, 2010 (unaudited) |
7,206 | $ | 3.53 | 6.3 | 10,240 | |||||||||||||||
In December 2010, the Company granted 2,181,428 share options to employees and 134,000 share options to a member of the Company’s Board of Directors with an exercise price of $5.80 per share (unaudited).
The weighted-average grant date fair value of options granted during 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010 was $2.65, $2.05, $2.12, $2.08 and $2.38, respectively. The aggregate intrinsic value of options exercised under the Option Plans was $0.8 million, $1.1 million, $1.4 million, $1.3 million and $2.5 million in 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively, determined as of the date of option exercise. The intrinsic value is calculated as the difference between the fair value of the common shares on the exercise date and the exercise price of the option shares. The total estimated fair value of share options vested in 2007, 2008, 2009 and for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010 was $2.2 million, $6.6 million, $8.5 million, $6.9 million and $10.2 million, respectively.
Share-based compensation expense is based on applying calculated fair values determined at the grant date to those options granted in the year that are ultimately expected to vest. Accordingly, the fair values calculated on the total population of grants have been reduced for estimated forfeitures expected to occur in the future. The
F-25
Table of Contents
Company’s share-based compensation expense during 2007, 2008, 2009 and for the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010 was $3.9 million, $5.4 million, $6.1 million $4.4 million and $6.0 million, respectively. During 2008 and 2009, the tax benefit related to share-based compensation expense was $0.2 million, $0.1 million, respectively. The tax benefit related to share-based compensation during 2007 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010 was insignificant.
The table below summarizes share-based compensation expense as allocated within the Company’s consolidated statements of operations (in thousands):
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Cost of revenue |
$ | 1,096 | $ | 1,271 | $ | 914 | $ | 672 | $ | 843 | ||||||||||
| Sales and marketing |
1,100 | 1,570 | 2,340 | 1,706 | 2,214 | |||||||||||||||
| Research and development |
— | — | 541 | 399 | 598 | |||||||||||||||
| General and administrative |
1,680 | 2,608 | 2,265 | 1,663 | 2,362 | |||||||||||||||
| Total share-based compensation |
$ | 3,876 | $ | 5,449 | $ | 6,060 | $ | 4,440 | $ | 6,017 | ||||||||||
The following tables summarize information about share options outstanding at December 31, 2009 and September 30, 2010 (shares in thousands):
| December 31, 2009 | Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | ||||||||||||||||||
| Range of Exercise Prices |
Number of Shares Outstanding |
Weighted- Average Remaining Contract Life (in Years) |
Weighted- Average Exercise Price per Share |
Number of Shares Exercisable |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
|||||||||||||||
| $0.20 to $0.65 |
894 | 4.4 | $ | 0.35 | 894 | $ | 0.35 | |||||||||||||
| $1.20 to $1.49 |
1,425 | 4.4 | 1.33 | 1,240 | 1.32 | |||||||||||||||
| $4.26 to $4.60 |
10,182 | 7.6 | 4.29 | 3,848 | 4.26 | |||||||||||||||
| 12,501 | 7.0 | 3.67 | 5,982 | 3.07 | ||||||||||||||||
| September 30, 2010 (unaudited) | Options Outstanding | Options Exercisable | ||||||||||||||||||
| Range of Exercise Prices |
Number of Shares Outstanding |
Weighted- Average Remaining Contract Life (in Years) |
Weighted- Average Exercise Price per Share |
Number of Shares Exercisable |
Weighted Average Exercise Price |
|||||||||||||||
| $0.20 to $0.65 |
439 | 4.6 | $ | 0.44 | 439 | $ | 0.44 | |||||||||||||
| $1.20 to $1.49 |
1,238 | 5.5 | 1.31 | 1,230 | 1.31 | |||||||||||||||
| $4.26 to $4.95 |
14,049 | 8.0 | 4.45 | 5,537 | 4.27 | |||||||||||||||
| 15,726 | 7.7 | 4.09 | 7,206 | 3.53 | ||||||||||||||||
As of December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010, there was $11.9 million, $12.0 million and $16.3 million of unrecognized compensation expense related to nonvested share-based compensation arrangements granted under the Option Plans, which is expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.8 years, 1.7 years and 2.9 years, respectively.
F-26
Table of Contents
11. Employee Benefit Plan
The Company maintains a 401(k) defined contribution benefit plan that covers all eligible domestic employees who have attained 21 years of age and provide at least 20 hours of service per week. This plan allow U.S. employees to contribute up to 90% of their pre-tax salary in certain investments at the discretion of the employee, up to maximum annual contribution limits established by the U.S. Department of Treasury. During 2008 and 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2010, the Company matched, up to an annual limit of $2,000, the first 3% of a participant’s contributions. Matching contributions by the Company are fully vested upon completion of the first year of employment. Employer matching contributions, which may be discontinued at the Company’s discretion, amounted to $0.5 million, $0.6 million, $0.5 million and $0.6 million during 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively. There were no matching contributions by the Company in 2007.
12. Income Taxes
Income from continuing operations before provision for income taxes for the Company’s domestic and international operations was as follows (in thousands):
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||||||||||
| Domestic |
$ | 8,674 | $ | 4,295 | $ | 9,562 | ||||||
| International |
362 | 1,679 | 2,679 | |||||||||
| Income before provision for income taxes |
$ | 9,036 | $ | 5,974 | $ | 12,241 | ||||||
The income tax (benefit) provision consisted of the following (in thousands):
| Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||||||||||
| Current: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | — | $ | 2,431 | $ | 2,244 | ||||||
| Foreign |
37 | 32 | 280 | |||||||||
| State and local |
20 | 571 | 367 | |||||||||
| Total current income tax provision |
57 | 3,034 | 2,891 | |||||||||
| Deferred: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
— | (1,608 | ) | (585 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign |
(689 | ) | 514 | 264 | ||||||||
| State and local |
— | (787 | ) | (704 | ) | |||||||
| Total deferred income tax benefit |
(689 | ) | (1,881 | ) | (1,025 | ) | ||||||
| Income tax (benefit) provision |
$ | (632 | ) | $ | 1,153 | $ | 1,866 | |||||
F-27
Table of Contents
The following table provides the reconciliation between the statutory federal income tax rate and the effective tax rate:
| Years Ended December 31, |
||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | ||||||||||
| U.S. federal statutory rate for LLC |
— | % | — | % | — | % | ||||||
| U.S. federal statutory rate for taxable subsidiaries |
— | 34.0 | 34.0 | |||||||||
| Benefit from income attributable to LLC |
— | (2.0 | ) | (11.7 | ) | |||||||
| Benefit from change in tax status |
— | (13.5 | ) | — | ||||||||
| State income taxes, net of federal benefit |
0.2 | 4.7 | 2.0 | |||||||||
| Foreign tax rate differential |
2.3 | (4.4 | ) | (3.9 | ) | |||||||
| Permanent differences |
— | 5.0 | 2.3 | |||||||||
| State tax credits |
— | (4.2 | ) | (3.4 | ) | |||||||
| Change in valuation allowance |
(9.4 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Other, net |
— | (0.3 | ) | (4.1 | ) | |||||||
| (6.9 | )% | 19.3 | % | 15.2 | % | |||||||
At January 1, 2008, the Company transferred a significant portion of its U.S. operations from its LLC to a wholly-owned U.S. taxable subsidiary. As the companies are part of this consolidated group, the amounts were eliminated in consolidation and the transaction effectively was accounted for as a change in tax status in these consolidated financial statements. For tax purposes however, the assets were transferred to the U.S. taxable subsidiary at their current book and tax basis, thereby creating new net deferred tax assets at the U.S. taxable subsidiary. As such, deferred tax assets and liabilities were established on the basis of the transferred assets and liabilities and the Company recorded an income tax benefit of $0.8 million from the change in income tax status as of January 1, 2008.
The following table provides the effect of temporary differences that created deferred income taxes as of December 31, 2008 and 2009. Deferred tax assets and (liabilities) represent the future effects on income taxes resulting from temporary differences and carry-forwards at the end of the respective periods (in thousands):
| December 31, | ||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | |||||||
| Current |
||||||||
| Accrued liabilities |
$ | 253 | $ | 392 | ||||
| State taxes |
123 | 129 | ||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
93 | 192 | ||||||
| Current deferred tax assets |
469 | 713 | ||||||
| Non-current |
||||||||
| Share-based compensation expense |
1,690 | 2,546 | ||||||
| Tax credit carryforward |
275 | 609 | ||||||
| Net operating loss carryforward |
211 | — | ||||||
| Unrealized loss on foreign exchange transactions |
175 | 93 | ||||||
| Property & equipment |
(250 | ) | (366 | ) | ||||
| Non-current deferred tax assets, net |
2,101 | 2,882 | ||||||
| Total deferred tax assets, net |
$ | 2,570 | $ | 3,595 | ||||
As of December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010, management assessed the realizability of deferred tax assets and determined that based on the available evidence, including a history of taxable income and estimates of future taxable income, it is more likely than not that the deferred tax assets will be realized.
F-28
Table of Contents
During 2007, as a result of achieving a history of taxable income and estimates of future taxable income, the Company released the full valuation allowance of $847,000 that was recorded as of December 31, 2006 related to the Company’s Irish subsidiary.
The Company adopted ASC No. 740 on unrecognized tax benefits on January 1, 2007. The adoption of ASC 740 did not have an impact on the January 1, 2007 members’ equity because the Company believes there were no uncertain tax positions for tax years prior to 2007. As of December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010, the Company did not have any unrecognized tax benefits that if recognized would impact the annual effective tax rate.
The Company files U.S. federal and state and foreign income tax returns in jurisdictions with varying statutes of limitations. In the normal course of business the Company is subject to examination by taxing authorities throughout the world. These audits include questioning the timing and amount of deductions, the allocation of income among various tax jurisdictions and compliance with federal, state, local and foreign tax laws. In November 2010, the Company concluded an IRS audit of the 2008 tax year which resulted in a change to a temporary difference, without impact on the 2008 income tax provision as previously reported. The 2006 through 2009 tax years generally remain subject to examination by federal, state, and foreign tax authorities.
It is difficult to predict the final timing and resolution of any particular uncertain tax position. Based on the Company’s assessment of many factors, including past experience and complex judgments about future events, the Company does not expect that changes in the liability for unrecognized tax benefits during the next twelve months will have a significant impact on the Company’s consolidated financial position or results of operations.
13. Reportable Segments
The Company’s operations are principally managed on a geographic basis and are comprised of three reportable and operating segments: NALA, EMEA, and APJ.
The Company reports segment information based on the management approach. The management approach designates the internal reporting used by the Company’s Chief Operating Decision Maker (“CODM”), for making decisions and assessing performance as the source of the Company’s reportable segments. The CODM is the Company’s Chief Executive Officer. The CODM allocates resources to and assesses the performance of each of the operating segment using information about its revenue and direct profit contribution, which is management’s measure of segment profitability. Management has determined that the Company’s reportable and operating segments are as follows, based on the information used by the CODM:
NALA—Includes operations from offices in San Francisco, California; Denver, Colorado and Nashville, Tennessee related primarily to end customer in North America.
EMEA—Includes operations from offices in Liverpool, United Kingdom and Dublin, Ireland related primarily to end customers in Europe.
APJ—Includes operations from offices in Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia and Singapore related primarily to end customers in Asia Pacific and Japan.
The Company does not allocate sales and marketing, research and development, or general and administrative expenses to its geographic regions because management does not include the information in its measurement of the performance of the operating segments. The Company excludes certain items such as share-based compensation, overhead allocations and other items from direct profit contribution. Revenue for a particular geography reflects fees the Company earns from its customers for sales and renewals of maintenance, support and subscription contracts on their behalf and managed from the Company’s sales center in that geography.
F-29
Table of Contents
Summarized financial information by geographic location for 2007, 2008, 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, based on the Company’s internal management reporting and as utilized by the Company’s CODM, is as follows (in thousands):
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months
Ended September 30, |
|||||||||||||||||||
| 2007 | 2008 | 2009 | 2009 | 2010 | ||||||||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Net revenue |
||||||||||||||||||||
|
NALA(1) |
$ | 60,314 | $ | 70,177 | $ | 77,283 | $ | 54,594 | $ | 72,776 | ||||||||||
| EMEA |
14,875 | 30,103 | 31,995 | 21,490 | 30,599 | |||||||||||||||
| APJ |
— | — | 1,398 | 805 | 5,093 | |||||||||||||||
| Total net revenue |
75,189 | 100,280 | 110,676 | 76,889 | 108,468 | |||||||||||||||
| Direct profit contribution |
||||||||||||||||||||
| NALA |
38,256 | 42,179 | 49,561 | 34,927 | 41,188 | |||||||||||||||
| EMEA |
5,871 | 14,323 | 14,098 | 8,984 | 14,039 | |||||||||||||||
| APJ |
— | — | 696 | 543 | 1,662 | |||||||||||||||
| Total direct profit contribution |
44,127 | 56,502 | 64,355 | 44,454 | 56,889 | |||||||||||||||
| Adjustments: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Share-based compensation. |
1,096 | 1,271 | 914 | 672 | 843 | |||||||||||||||
| Overhead allocations |
6,435 | 11,792 | 10,568 | 7,651 | 10,350 | |||||||||||||||
| Other |
631 | 124 | 1,074 | 819 | 1,069 | |||||||||||||||
| Gross profit |
$ | 35,965 | $ | 43,315 | $ | 51,799 | $ | 35,312 | $ | 44,627 | ||||||||||
| (1) | Net revenue generated in the United States was $58.8 million, $68.9 million, $77.3 million, $54.6 million and $72.8 million for 2007, 2008 and 2009 and the nine months ended September 30, 2009 and 2010, respectively. |
The majority of the Company’s assets were attributable to its U.S. operations at December 31, 2008 and 2009 and September 30, 2010. Property and equipment information is based on the physical location of the assets. The following table presents the long-lived assets, consisting principally of property and equipment, by geographic location (in thousands):
| December 31, | September
30, 2010 |
|||||||||||
| 2008 | 2009 | |||||||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||||||
| NALA |
$ | 8,823 | $ | 12,658 | $ | 16,279 | ||||||
| EMEA |
250 | 1,123 | 1,314 | |||||||||
| APJ |
— | 220 | 903 | |||||||||
| Total property and equipment, net |
$ | 9,073 | $ | 14,001 | $ | 18,496 | ||||||
14. Subsequent Events
The Company evaluated subsequent events and transactions for potential recognition or disclosure through March 29, 2010, except for net income (loss) per common share information discussed in Note 3, the 2010 amendments to the credit facility discussed in Note 7, the adoption of the accounting standard on unrecognized tax benefits discussed in Note 12 and segment information discussed in Note 13, as to which the date is December 20, 2010, for the issuance of the 2009 consolidated financial statements. For the issuance of the consolidated financial statements for the nine months ended September 30, 2010, the unaudited interim period presented herein, such evaluation was performed through December 20, 2010.
F-30
Table of Contents
In January 2011, the Credit Facility was amended to (i) increase the maximum commitment amount under the revolving credit facility from $7.5 million to $12.5 million, (ii) eliminate the fixed charge coverage ratio test for the twelve month period ending March 31, 2011 only, (iii) require the Company to maintain a minimum liquidity level of $10 million based on unrestricted cash balances held in the U.S. and available borrowings under the revolving credit facility, as defined therein, from and after May 15, 2011, and (iv) allow for the planned conversion of the LLC to a taxable corporation, initial public offering of the Company’s stock and other specified transactions related to the Company (unaudited).
F-31
Table of Contents

Table of Contents
PART II
INFORMATION NOT REQUIRED IN THE PROSPECTUS
ITEM 13. OTHER EXPENSES OF ISSUANCE AND DISTRIBUTION.
Estimated expenses, other than underwriting discounts and commissions, payable by the Registrant in connection with the sale of the common stock being registered under this registration statement are as follows:
| SEC registration fee |
$ | 5,347.50 | ||
| FINRA filing fee |
$ | 8,000.00 | ||
| Listing fee |
* | |||
| Printing and engraving expenses |
* | |||
| Legal fees and expenses |
* | |||
| Accounting fees and expenses |
* | |||
| Blue Sky fees and expenses (including legal fees) |
* | |||
| Transfer agent and registrar fees and expenses |
* | |||
| Miscellaneous |
* | |||
| Total |
$ | * | ||
| * | To be filed by Amendment. |
ITEM 14. INDEMNIFICATION OF DIRECTORS AND OFFICERS.
On completion of this offering, the Registrant’s certificate of incorporation will contain provisions that eliminate, to the maximum extent permitted by the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware, the personal liability of the Registrant’s directors and executive officers for monetary damages for breach of their fiduciary duties as directors or officers. The Registrant’s certificate of incorporation and bylaws will provide that the Registrant must indemnify its directors and executive officers and may indemnify its employees and other agents to the fullest extent permitted by the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware.
Sections 145 and 102(b)(7) of the General Corporation Law of the State of Delaware provide that a corporation may indemnify any person made a party to an action by reason of the fact that he or she was a director, executive officer, employee or agent of the corporation or is or was serving at the request of a corporation against expenses (including attorneys’ fees), judgments, fines and amounts paid in settlement actually and reasonably incurred by him or her in connection with such action if he or she acted in good faith and in a manner he or she reasonably believed to be in, or not opposed to, the best interests of the corporation and, with respect to any criminal action or proceeding, had no reasonable cause to believe his or her conduct was unlawful, except that, in the case of an action by or in right of the corporation, no indemnification may generally be made in respect of any claim as to which such person is adjudged to be liable to the corporation.
The Registrant has entered into indemnification agreements with its directors and executive officers, in addition to the indemnification provided for in its certificate of incorporation and bylaws, and intends to enter into indemnification agreements with any new directors and executive officers in the future.
The Registrant has purchased and intends to maintain insurance on behalf of each person who is or was a director or officer of the Registrant against any loss arising from any claim asserted against him or her and incurred by him or her in any such capacity, subject to certain exclusions.
The underwriting agreement provides for indemnification by the underwriters of the Registrant and its executive officers and directors, and by the Registrant of the underwriters, for certain liabilities, including liabilities arising under the Securities Act.
See also the undertakings set out in response to Item 17 herein.
II-1
Table of Contents
ITEM 15. RECENT SALES OF UNREGISTERED SECURITIES.
Since January 1, 2007, the Registrant has sold the following unregistered securities:
(1) From January 1, 2007 through December 31, 2010, ServiceSource International, LLC sold and issued to its employees, non-employee directors, consultants and other service providers an aggregate of 1,664,995 common shares pursuant to option exercises under the 2004 Omnibus Share Plan at prices ranging from $0.20 to $4.26 per share for an aggregate purchase price of $1,425,142.
(2) From January 1, 2007 through December 31, 2010, ServiceSource International, LLC granted options under the 2004 Omnibus Share Plan to purchase 8,197,333 common shares to its employees, non-employee directors, consultants and other service providers, at a price of $4.26 per share for an aggregate purchase price of $34,920,638.
(3) From January 1, 2007 through December 31, 2010, ServiceSource International, LLC sold and issued to its employees, non-employee directors, consultants and other service providers an aggregate of 3,145 common shares pursuant to option exercises under the 2008 Share Option Plan at a price of $4.26 per share for an aggregate purchase price of $13,398.
(4) From January 1, 2007 through December 31, 2010, ServiceSource International, LLC granted options under the 2008 Share Option Plan to purchase 10,640,068 of its common shares to its employees, non-employee directors, consultants and other service providers, at prices ranging from $4.26 to $5.80 per share for an aggregate purchase price of $51,595,422.
(5) On January 12, 2007, ServiceSource International, LLC sold and issued 15,286,453 common shares to one accredited investor, at $4.2595 per share, for aggregate consideration of $65,112,646.
No underwriters were involved in the foregoing sales of securities. The issuances of the securities described above were deemed to be exempt from registration under the Securities Act in reliance on Section 4(2) of the Securities Act, Rule 701 promulgated under Section 3(b) of the Securities Act or Regulation S of the Securities Act. The recipients of securities in each such transaction represented their intention to acquire the securities for investment only and not with a view to or for sale in connection with any distribution thereof and appropriate legends were affixed to the stock certificates and option agreements issued in such transactions.
ITEM 16. EXHIBITS AND FINANCIAL STATEMENT SCHEDULES.
(a) Exhibits
See Exhibit Index immediately following the signature pages.
(b) Financial Statement Schedules.
All other schedules have been omitted because the information required to be presented in them is not applicable or is shown in the consolidated financials statements or related notes.
ITEM 17. UNDERTAKINGS.
Insofar as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, may be permitted to directors, officers and controlling persons of the Registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or otherwise, the Registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment by the Registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person of the Registrant in the successful defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, the Registrant will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter
II-2
Table of Contents
has been settled by controlling precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and will be governed by the final adjudication of such issue.
The undersigned Registrant hereby undertakes that:
(a) The Registrant will provide to the underwriters at the closing as specified in the underwriting agreement certificates in such denominations and registered in such names as required by the underwriters to permit prompt delivery to each purchaser.
(b) For purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the information omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of this registration statement in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in a form of prospectus filed by the Registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, shall be deemed to be part of this registration statement as of the time it was declared effective.
(c) For the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, each post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering thereof.
(d) For the purpose of determining liability under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, to any purchaser, if the Registrant is subject to Rule 430C, each prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a registration statement relating to an offering, other than registration statements relying on Rule 430B or other than prospectuses filed in reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in the registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness. Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser with a time of contract of sale prior to such first use, supersede or modify any statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately prior to such date of first use.
(e) For the purpose of determining liability of the registrant under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities, the Registrant undertakes that in a primary offering of securities of the Registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the following communications, the Registrant will be a seller to the purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such purchaser:
(i) any preliminary prospectus or prospectus of the undersigned registrant relating to the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424;
(ii) any free writing prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the Registrant or used or referred to by the Registrant;
(iii) the portion of any other free writing prospectus relating to the offering containing material information about the Registrant or its securities provided by or on behalf of the Registrant; and
(iv) any other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the Registrant to the purchaser.
II-3
Table of Contents
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, the registrant has duly caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of San Francisco, State of California, on January 28, 2011.
| SERVICESOURCE INTERNATIONAL, LLC | ||
| By: |
/s/ MICHAEL A. SMERKLO | |
| Michael A. Smerklo | ||
| Chief Executive Officer | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this registration statement has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates indicated below:
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||
| /S/ MICHAEL A. SMERKLO Michael A. Smerklo |
Chairman of the Board and Chief Executive Officer (Principal Executive Officer) |
January 28, 2011 | ||
| /S/ DAVID S. OPPENHEIMER David S. Oppenheimer |
Chief Financial Officer (Principal Accounting and Financial Officer) |
January 28, 2011 | ||
|
* Steven M. Cakebread |
Director |
January 28, 2011 | ||
|
* Marc F. McMorris |
Director |
January 28, 2011 | ||
|
* Bruce W. Dunlevie |
Director |
January 28, 2011 | ||
|
* Anthony Zingale |
Director |
January 28, 2011 | ||
|
* James C. Madden, V |
Director |
January 28, 2011 | ||
|
* Barry D. Reynolds |
Director |
January 28, 2011 | ||
| *By: /s/ DAVID S. OPPENHEIMER David S. Oppenheimer Attorney-in-Fact |
||||
II-4
Table of Contents
EXHIBIT INDEX
| Exhibit |
Exhibit Title | |
| 1.1* | Form of Underwriting Agreement | |
| 2.1* | Conversion Agreement dated as of , 2011, between the Registrant and the other parties thereto | |
| 2.2* | Agreement and Plan of Merger dated as of , 2011, between the Registrant and the other parties thereto | |
| 3.1# | Form of Certificate of Incorporation of the Registrant | |
| 3.2# | Form of Bylaws of the Registrant | |
| 3.3 | Fifth Amended and Restated Limited Liability Company Agreement | |
| 4.1* | Specimen Common Stock Certificate of the Registrant | |
| 4.2# | Registration and Information Rights Agreement dated as of December 8, 2006, between the Registrant and GA SS Holding LLC, SSLLC Holdings, Inc., Housatonic Micro Fund SBIC, LP and Housatonic Equity Investors SBIC, LP | |
| 4.3# | Securities Purchase Agreement and Registration Rights Schedule dated as of January 31, 2003, between the Registrant and the 2003 Holders | |
| 5.1* | Opinion of Wilson Sonsini Goodrich & Rosati, Professional Corporation | |
| 10.1# + | Form of Director and Executive Officer Indemnification Agreement | |
| 10.2# + | 2004 Omnibus Share Plan and forms of agreements thereunder | |
| 10.3# + | 2008 Share Option Plan and form of agreement thereunder | |
| 10.4# + | 2011 Equity Incentive Plan and forms of agreements thereunder to be in effect upon the closing of this offering | |
| 10.5# + | Amended and Restated Employment and Confidential Information Agreement dated as of June 8, 2010, between the Registrant and Michael A. Smerklo | |
| 10.6# + | Amended and Restated Employment and Confidential Information Agreement dated as of December 8, 2010, between the Registrant and Jeffrey M. Bizzack | |
| 10.7# + | Employment and Confidential Information Agreement dated as of July 7, 2010, between the Registrant and David Oppenheimer | |
| 10.8# + | Amended and Restated Employment and Confidential Information Agreement dated as of December 8, 2010, between the Registrant and Robert Sturgeon | |
| 10.9# + | Employment and Confidential Information Agreement dated as of April 13, 2010, between the Registrant and Ganesh Bell | |
| 10.10# + | Amended and Restated Employment and Confidential Information Agreement dated as of December 8, 2010, between the Registrant and Raymond M. Martinelli | |
| 10.11# + | Amended and Restated Employment Letter Agreement dated as of November 4, 2010, between the Registrant and Natalie A. McCullough | |
| 10.12+ | Amended and Restated Employment and Confidential Information Agreement dated as of December 8, 2010, between the Registrant and Paul D. Warenski | |
| 10.13# | Office Lease, dated as of October 31, 2007, between Registrant and Six Thirty-Four Second Street, LLC | |
| 10.14 | Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of April 29, 2008, between the Registrant, the Lenders named therein and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Administrative Agent | |
Table of Contents
| Exhibit |
Exhibit Title | |
| 10.15# | Amendment Number One dated as of May 19, 2009, to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of April 29, 2008, between the Registrant, the Lenders named therein and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Administrative Agent | |
| 10.16# | Amendment Number Two dated as of August 21, 2009, to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of April 29, 2008, between the Registrant, the Lenders named therein and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Administrative Agent | |
| 10.17# | Amendment Number Three dated as of April 30, 2010, to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of April 29, 2008, between the Registrant, the Lenders named therein and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Administrative Agent | |
| 10.18# | Amendment Number Four dated as of November 4, 2010, to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of April 29, 2008, between the Registrant, the Lenders named therein and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Administrative Agent | |
| 10.19 | Amendment Number Five dated as of December 17, 2010, to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of April 29, 2008, between the Registrant, the Lenders named therein and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Administrative Agent | |
| 10.20 | Amendment Number Six dated as of January 18, 2011, to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of April 29, 2008, between the Registrant, the Lenders named therein and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Administrative Agent | |
| 10.21 | Amendment Number Seven dated as of January 27, 2011, to the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement dated as of April 29, 2008, between the Registrant, the Lenders named therein and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Administrative Agent | |
| 10.22 | Amended and Restated Security Agreement dated as of April 29, 2008 between the Registrant, ServiceSource International Inc. and Wells Fargo Foothill, Inc. | |
| 10.23 | General Continuing Guaranty dated as of April 29, 2008 delivered by ServiceSource International Inc. in favor of Wells Fargo Foothill, Inc. | |
| 10.24 | Waiver dated as of March 19, 2010, between the Registrant, the Lenders named therein and Wells Fargo Capital Finance, LLC, as Administrative Agent | |
| 10.25+ | Employment and Confidential Information Agreement dated as of April 7, 2008, between the Registrant and Charles D. Boynton | |
| 10.26+ | Release Letter Agreement date as of June 25, 2010, between the Registrant and Charles D. Boynton | |
| 21.1# | List of subsidiaries of the Registrant | |
| 23.1 | Consent of PricewaterhouseCoopers LLP, Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm | |
| 23.2* | Consent of Wilson Sonsini Goodrich & Rosati, Professional Corporation (included in Exhibit 5.1) | |
| 24.1# | Power of Attorney (see page II-4 of the original filing) | |
| * | To be filed by amendment |
| # | Previously filed |
| + | Indicates a management contract or compensatory plan |
