Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 10-K - FORM 10-K - STRATTEC SECURITY CORP | c59996e10vk.htm |
| EX-32 - EX-32 - STRATTEC SECURITY CORP | c59996exv32.htm |
| EX-31.1 - EX-31.1 - STRATTEC SECURITY CORP | c59996exv31w1.htm |
| EX-31.2 - EX-31.2 - STRATTEC SECURITY CORP | c59996exv31w2.htm |
| EX-23.2 - EX-23.2 - STRATTEC SECURITY CORP | c59996exv23w2.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - STRATTEC SECURITY CORP | c59996exv23w1.htm |
Exhibit 13

| The Trusted Leader in Automotive Access Control Products 2010 ANNUAL REPORT |

| The Trusted Leader in Automotive Access Control Products STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION is a direct descendant of a company founded in 1908 to produce automobiles and automotive components. While the production of automobiles was a very small and brief part of our heritage, automotive components, particularly security products, became the foundation for a century of leadership. We have provided quality locks and keys for cars and light trucks to our three largest customers and their predecessors for 90 years. That longevity is a good indication of the level of trust placed in us by our customers. Over the past 15 years, STRATTEC has been hard at work diversifying our product offerings. In addition to our traditional products, we now supply ignition lock housings, latches for the access points around a vehicle, and power access devices for sliding side doors, liftgates, trunk lids and even mobility ramps. Through a joint venture with ADAC Automotive, we also supply door handle components and related vehicle access hardware. Building on our heritage, we continually strive to develop the products and services that will keep us the trusted leader in automotive access products for years to come. |
 |
2010 ANNUAL REPORT
STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION designs, develops, manufactures and markets automotive
security products including mechanical locks and keys, electronically enhanced locks and keys,
steering column and instrument panel ignition lock housings; and access control products
including latches, power sliding side door systems, power lift gate systems, power deck lid
systems, door handles and related access control products for North American automotive
customers. We also supply global automotive manufacturers through the VAST Alliance in which we
participate with WITTE Automotive of Velbert, Germany and ADAC Automotive of Grand Rapids,
Michigan. Our products are shipped to customer locations in the United States, Canada, Mexico,
Europe, South America, Korea and China, and we provide full service and aftermarket support.
CONTENTS
LETTER TO THE SHAREHOLDERS |
2 | |||
FINANCIAL HIGHLIGHTS |
4 | |||
COMPANY DESCRIPTION |
5 | |||
STRATTEC EQUIPPED VEHICLE LIST |
12 | |||
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS |
13 | |||
FINANCIAL STATEMENTS |
25 | |||
REPORT OF MANAGEMENT |
44 | |||
REPORTS OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM |
45 | |||
FINANCIAL SUMMARY |
47 | |||
PERFORMANCE GRAPH |
48 | |||
DIRECTORS / OFFICERS / SHAREHOLDERS’ INFORMATION |
49 |
PROSPECTIVE INFORMATION
A number of the matters and subject areas discussed in this Annual Report (see above
“Contents” section) contain “forward-looking statements” within the meaning of the Private
Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These statements may be identified by the use of
forward-looking words or phrases such as “anticipate,” “believe,” “would,” “expect,” “intend,”
“may,” “planned,” “potential,” “should,” “will,” and “could.” These include expected future
financial results, product offerings, global expansion, liquidity needs, financing ability, planned
capital expenditures, management’s or the Company’s expectations and beliefs, and similar matters
discussed in the Letter to the Shareholders, Company’s Management’s Discussion and Analysis, and
other sections of this Annual Report. The discussions of such matters and subject areas are
qualified by the inherent risks and uncertainties surrounding future expectations generally, and
also may materially differ from the Company’s actual future experience.
The Company’s business, operations and financial performance are subject to certain risks and
uncertainties, which could result in material differences in actual results from the Company’s
current expectations. These risks and uncertainties include, but are not limited to, general
economic conditions, in particular relating to the automotive industry, customer demand for the
Company’s and its customers’ products, competitive and technological developments, customer
purchasing actions, foreign currency fluctuations, costs of operations and other matters described
under “Risk Factors” in the Management’s Discussion and Analysis section of this report. In
addition, such uncertainties and other operational matters are discussed further in the Company’s
quarterly and annual report filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
Shareholders, potential investors and other readers are urged to consider these factors
carefully in evaluating the forward-looking statements and are cautioned not to place undue
reliance on such forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements made herein are only
made as of the date of this Annual Report and the Company undertakes no obligation to publicly
update such forward-looking statements to reflect subsequent events or circumstances occurring
after the date of this Annual Report.

LETTER TO THE SHAREHOLDERS
AUGUST, 2010
Fellow Shareholders:
The difference between our fiscal years 2009 and 2010 is positively amazing. One year ago as
I wrote the Letter to Shareholders for 2009, we were coming off of the bankruptcies of our two
largest customers. The future of these customers and the U.S. auto industry was very uncertain.
Economic forecasts for auto production were very low compared to pre-2009 levels, and industry
analysts were in general agreement that any recovery would be long and slow.
Despite the dismal conditions at the time and our poor 2009 financial results, we had
demonstrated STRATTEC’s ability to weather the auto industry’s near death experience. We therefore
entered fiscal 2010 with the conviction that we were in a position to improve as the industry
recovered, and that the recovery would happen, though slowly and with different dynamics than in
the past. Consequently, we built our fiscal 2010 budget around the industry forecasts we thought
to be reasonable and achievable. The result was that we expected to finish 2010 with only a small
profit, but still a major improvement over the losses of fiscal 2009.
Our fiscal 2010 proved to be substantially better than our expectations and resulted in the
second best sales year in our history.
The auto industry benefited from the painful restructuring it went through during the first
half of calendar 2009. During the second half of the calendar year, the industry also benefited
from the federal government’s “Cash for Clunkers” program, greater availability of consumer credit,
an improvement in consumer confidence, and a modest release of pent-up demand for vehicles.
STRATTEC directly benefited from the resulting resumption of vehicle production. Although we can’t
claim we are back to normal, we certainly have achieved a level of encouraging normalcy. Our
customers are experiencing sales momentum and production schedules are stabilizing. New product
programs, which had all but stopped at General Motors and Chrysler for most of our fiscal 2009, are
once again moving ahead.
With the resumption of vehicle production, sales of all of our products improved
significantly over our fiscal 2009 levels, including those of ADAC-STRATTEC LLC, our joint venture
with ADAC Automotive. Sales of our STRATTEC POWER ACCESS products experienced the greatest
improvement and contributed nearly 28% of total net sales for fiscal 2010. Sales of our
traditional lock products have continued to decline as a portion of our overall product sales mix.
In addition to increased sales of our other products, the decline is a result of the technology
shift away from mechanical security devices toward electro-mechanical or electronic systems.
However, our market share for lock products remains stable. Additionally, we continue to gain some
content in the electro-mechanical/electronic replacements for our mechanical locks. We therefore
believe the growth of these and other non-traditional security or access control products will
largely offset the reduction in mechanical locks and keys within our mix.
While the increased sales story for fiscal 2010 was very positive, we were not able to deliver
as much profit to the bottom line as would have normally been the case. There were two main factors
for this. First, the return of vehicle production occurred faster than forecasted and caught
several of our component suppliers off guard. Their slow reaction to the production ramp-up caused
us to experience an excessive amount of inbound and outbound premium freight charges, and caused an
increase in assembly costs as we were forced to do many special production runs of the products
that utilize the delayed components. Some of the freight costs were recoverable from the suppliers
who caused the issues, but the majority were not. Second, our EVA® performance on a
year-over-year basis improved by $8.8 million. This improvement drove our EVA®-based
bonus compensation to a higher level than had been budgeted at the beginning of the fiscal year.
Our bonus plan is based on a formula that pays when the Economic Value generated by the business
improves beyond an established threshold. The plan covers virtually all our U.S. based hourly and
salaried associates, many associates in our Mexican operations and the independent members of the
Board of Directors. Our accruals to cover the bonuses earned under the EVA® formula
increased, particularly in our third and fourth quarters, as the financial results of our business
continued to improve. The total value of bonuses earned
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 2 |
LETTER TO THE SHAREHOLDERS
under the plan in 2010 appears disproportionately higher than normal due to the level of
improvement in EVA® resulting from the dramatic difference between our losses in fiscal
2009 (a year in which no bonuses were earned) and the success we achieved in fiscal 2010.
In addition to the positive financial outcome of 2010, other important developments improved
our outlook for the future. We won new conquest business for our driver control and latch
products, booked increased penetration of electronically-enhanced security products and received
demonstrations of real customer interest in some of our advanced development projects. We also
indirectly increased our financial interest in the China operations of Vehicle Access Systems
Technology LLC (VAST LLC), the joint venture we own equally with WITTE Automotive and ADAC
Automotive. Last November, VAST LLC acquired the portion of VAST China it did not already own from
our former partners there. VAST LLC now has complete control of VAST China, and we look forward to
participating in this important market through our 1/3 interest in VAST LLC.
VAST is the key to our globalization strategy. Along with WITTE and ADAC, we are redefining
how we work together to establish VAST as a global brand. VAST China currently represents the base
of our efforts in Asia, and is growing along with the Chinese market. VAST China recently began
construction of a new manufacturing plant and offices on a green-field site outside of Shanghai
that will be a world-class facility for the production of all the products offered by the VAST
members. This new facility will position us for greater growth in the future. I encourage you to
read more about VAST in the Company Description section of this report.
On January 1, 2010 Frank J. Krejci became STRATTEC’s President and Chief Operating Officer. I
remain Chairman and Chief Executive Officer, but dropped the additional title of President, which I
have held since October, 2004. The Company’s Board of Directors believe that due to the growth in
size and complexity of the business with the addition of ADAC-STRATTEC, STRATTEC POWER ACCESS, and
the VAST interests, it is both appropriate and desirable to return to the executive management
structure we had previously in which the position of President was separated from the position of
Chairman. With this action, Frank transitions from an independent Board member to a Company board
member. His extensive background as a former employee of Briggs & Stratton Technologies (our
predecessor company), a venture capitalist, a business owner, and an independent member of the
STRATTEC Board of Directors since its inception 15 years ago, makes Frank an excellent addition to
our full time management group.
Following the fiscal year-end financial review, our Board of Directors declared a special
dividend of $1.20 per share payable on October 29, 2010 to shareholders of record as of October 8,
2010. In coming to its decision to declare this special dividend, the Board considered the current
economic climate and performance of the auto industry, the forecasts for the auto industry going
forward, the resulting expectations for STRATTEC’s financial performance going forward, the
Company’s anticipated cash needs and its cash flow projections. Further, the Board believes that
given the increase in tax rates on dividends currently scheduled for calendar 2011, a special
dividend payable before the end of calendar 2010 is not only appropriate, but a tax efficient
method of transferring meaningful economic value directly to you.
To those shareholders who have invested in STRATTEC since the beginning of fiscal 2010,
welcome. We appreciate your confidence in STRATTEC as an investment. To those shareholders who
have been with us for a long time, and especially through the rough times of the past few years, I
would again like to offer my sincere thanks for your support. We look forward to justifying that
support.
Sincerely,
Harold M. Stratton II
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
Harold M. Stratton II
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 3 |

FINANCIAL HIGHLIGHTS
(IN MILLIONS)
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
Net Sales |
$ | 208.0 | $ | 126.1 | $ | 159.6 | ||||||
Gross Profit |
33.0 | 13.2 | 24.8 | |||||||||
Income (Loss) from Operations |
4.4 | (12.7 | ) | .8 | ||||||||
Net Income (Loss) |
3.4 | (6.1 | ) | 2.8 | ||||||||
Total Assets |
145.0 | 128.2 | 144.2 | |||||||||
Total Debt |
— | — | — | |||||||||
Shareholders’ Equity |
74.1 | 71.4 | 98.0 | |||||||||
ECONOMIC VALUE ADDED (EVA ®)
All U.S. associates and many of our Mexico-based salaried associates participate in incentive
plans that are based upon our ability to add economic value to the enterprise. During 2008, our
EVA® Plan was modified to include cash and cash equivalents as part of the Company’s net
capital employed in the business. Because cash and cash equivalents were a significant component of
the capital employed in the business again in 2010 this increased the capital charge, thereby
contributing to our negative EVA. The EVA® performance for 2010 was a negative $4.9
million which represents an $8.8 million improvement from 2009. We believe that EVA®
represents an accurate measure of STRATTEC’s overall performance and shareholder value. (For
further explanation of our EVA® Plan and the effect negative EVA® has on
awards granted under our incentive plans, see our 2010 definitive Proxy Statement.)
Net Operating Profit After Cash-Basis Taxes |
$ | 3.1 | ||||||
Average Monthly Net Capital Employed |
$ | 80.0 | ||||||
Cost of Capital |
10 | % | ||||||
Capital Charge |
8.0 | |||||||
Economic Value Added |
$ | (4.9 | ) | |||||
EVA® is not a traditional financial measurement under U.S. GAAP and may not be
similar to EVA® calculations used by other companies. However, STRATTEC believes the
reporting of EVA® provides investors with greater visibility of economic profit. The
following is a reconciliation of the relevant GAAP financial measures to the non-GAAP measures
used in the calculation of STRATTEC’s EVA®.
Net Operating Profit After Cash-Basis Taxes:
2010 Net Income as Reported |
$ | 3.4 | ||
Deferred Tax Provision |
3.4 | |||
Other |
(3.7 | ) | ||
Net Operating Profit After
Cash-Basis Taxes |
$ | 3.1 | ||
Average Monthly Net Capital Employed:
Total Shareholders’ Equity as Reported at June 27, 2010 |
$ | 74.1 | ||
Long-Term Liabilities |
23.0 | |||
Deferred Tax Asset |
(11.9 | ) | ||
Other |
(2.5 | ) | ||
Net Capital Employed at June 27, 2010 |
$ | 82.7 | ||
Impact of 12 Month Average |
(2.7 | ) | ||
Average Monthly Net Capital Employed |
$ | 80.0 | ||
EVA® is a registered trademark of Stern, Stewart & Co.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 4 |
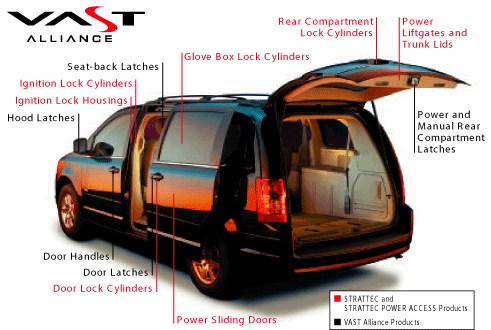
COMPANY DESCRIPTION
BASIC BUSINESS
STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION designs, develops, manufactures and markets automotive security
products including mechanical locks and keys, electronically enhanced locks and keys, steering
column and instrument panel ignition lock housings; and access control products including latches,
power sliding side door systems, power lift gate systems, power deck lid systems, door handles and
related access control products for North American automotive customers. We also supply global
automotive manufacturers through the VAST Alliance in which we participate with WITTE Automotive of
Velbert, Germany and ADAC Automotive of Grand Rapids, Michigan. Our products
are shipped to customer locations in the United States, Canada,
Mexico, Europe, South America, Korea and China, and we provide
full service and aftermarket support.

HISTORY
STRATTEC formerly was a division of Briggs & Stratton
Corporation. In 1995, STRATTEC was spun off from Briggs & Stratton
through a tax-free distribution to the then-existing Briggs &
Stratton shareholders and has been an independent public company
for fifteen years.
Our history in the automotive security business spans
over 100 years. STRATTEC has been the world’s largest producer of automotive locks and keys since
the late 1920s, and we currently maintain a dominant share of the North American markets for these
products.
PRODUCTS
Our traditional products are locks and keys for cars and light
trucks. A typical new car uses a set of two to three locks. A typical
3-way lockset contains a steering column/ignition lock, a
driver’s door lock
and a rear compartment (trunk, hatch or liftgate) lock.
Pickup trucks
also use
two to three locks, while sport utility vehicles and vans use three to five locks.
Some vehicles have additional locks for consoles, storage compartments or folding rear seats.
Pickup truck tailgate locks and spare tire locks are offered as options. Usually, two keys are
provided with each vehicle lockset. Many of the vehicles we currently supply are using keys with
sophisticated radio frequency identification technology for theft prevention.
However, keys with remote entry devices integrated into a single unit have been added to
our product line and are gaining in popularity.

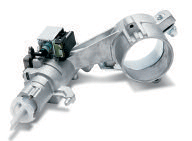
A
growing product line for us is ignition lock housings. These
housings are the mating part for our
ignition locks and typically are part of the steering
column structure, although there are instrument
panel-mounted versions for certain vehicle applications.
These housings are either zinc or magnesium die castings, or
plastic and can include electronic components for theft
deterrent systems.
We are also developing business for additional
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 5 |

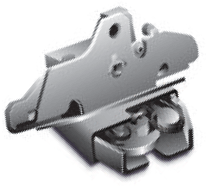
COMPANY DESCRIPTION
access control products, including trunk latches, liftgate
latches, tailgate latches, hood latches, side door latches and related hardware
for this product category. With our completed acquisition of Delphi
Corporation’s Power Products Group in fiscal 2009, we are now supplying
power access devices for sliding side doors, liftgates and trunk lids.
Through a joint venture formed with ADAC
Automotive during fiscal 2007, we also supply door handle components and
related vehicle access hardware.
STRATTEC’s products are supported by an extensive staff of experienced product engineers. This
staff, which includes product design, quality and manufacturing engineers, is
capable of providing complete design, development and testing
of new products for our customers. This
staff also is available for customer
problem solving, warranty
analysis, and other activities that arise during a product’s
life cycle. Our customers receive after-sales support in
the form of special field service kits, service manuals,
and specific in-plant production repair programs.


MARKETS
We are a direct supplier to OEM auto and light truck manufacturers as well as other
transportation-related manufacturers. Our largest customers are General Motors Company, Chrysler
Group LLC and Ford Motor Company. Our product mix varies by customer, but generally our sales
tend to be highest in lock and key products, followed by power access products, ignition lock
housings, the door handle and trim products produced by ADAC-STRATTEC de Mexico and latch
products.
Direct sales to various OEMs represented approximately 79% of our total sales for fiscal
2010. The remainder of our revenue is received primarily through sales to the OEM service
channels, the aftermarket and Tier 1 automotive supplier customers.
Sales to our major automotive customers, both OEM and Tier 1, are coordinated through direct
sales personnel located in our Detroit-area office. Sales are also facilitated
through daily interaction between our customer Program
Managers and Application Engineers located in Detroit, and
other product engineering personnel. Sales to other OEM
customers are accomplished through a combination of our own
sales personnel located in Detroit and personnel in our
Milwaukee headquarters office.

The majority of our OEM products are sold in North
America. While a modest amount of exporting is done to Tier 1
and automotive assembly plants in
Europe, Asia and South America, we are in the process of expanding our presence in these
markets and elsewhere through our Vehicle Access Systems Technology (VAST)
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 6 |
COMPANY DESCRIPTION
Alliance with WITTE Automotive and ADAC Automotive. This Alliance is described in more
detail on page 9.
OEM service and replacement parts are sold to the OEM’s own service operations. In addition,
we distribute our components and security products to the automotive aftermarket through
approximately 50 authorized wholesale distributors, as well as other marketers and users of
component parts, including export customers. Increasingly, our products find their way into the
retail channel, specifically the hardware store channel. Our ability to provide a full line of
keys to that channel has been accomplished
through the introduction of the STRATTEC “XL” key line.
This extension to
our line includes keys that we currently do not supply on an OE
basis, including keys for Toyota, Honda and other popular domestic and
import vehicles. This extended line of keys enable automotive repair
specialists to satisfy consumer needs
for repair or replacement parts. Our aftermarket activities are
serviced through a warehousing operation integral to our
Milwaukee headquarters and manufacturing
facility.


CUSTOMER FOCUS
To bring the proper focus to the
relationships with our major customers, we have seven
customer-focused teams, each with a Director of Sales, one or two
Engineering Program Managers and Customer Application Engineers. In
addition to customer teams for General Motors,
Ford and Chrysler, we currently have teams for New Domestic Vehicle Manufacturers, Driver
Control/Ignition Lock Housing customers, Tiered Products, and Service and Aftermarket customers.
Sales and engineering for ADAC-STRATTEC LLC are supported by our JV partner, ADAC Automotive.
Each Sales Director is responsible for the overall relationship between STRATTEC and a
specific customer group. Program Managers report to their respective customer teams and are
responsible for coordinating cross functional activities while managing new product programs for
their customers.
To serve our customers’ product needs, STRATTEC’s engineering resources are organized by
product type. We currently have four product groups: Locks and Keys, Latches
and Power Access Devices, Driver Control/Ignition Lock Housings and

The Aston Martin DBS uses an electronic key fob and mating docking station developed by
STRATTEC
exclusively for Aston Martin.


| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 7 |

COMPANY DESCRIPTION
Electrical. Each group has a Product Business Manager, Engineering Manager and a complement
of skilled engineers who design and develop products for specific applications. In doing this,
each engineering group works closely with the Customer teams, Engineering Program Managers, and
application engineers.
Underlying this organization is a formalized product development process to identify and meet
customer needs in the shortest possible time. By following this streamlined
development system, we shorten product lead times,
tighten our response to market changes and provide our
customers with the optimum value solution to their
security/access control requirements. STRATTEC is also
ISO/TS 16949 and ISO 14001 certified. This means we
embrace the philosophy that quality should exist not
only in the finished product, but in every step of our
processes as well.

OPERATIONS
A significant number of the components that go into our products are manufactured at our main
facility and headquarters in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. This facility produces zinc die cast components,
stampings and milled key blades. We have two owned production facilities in Juarez, Mexico
operating as STRATTEC de Mexico. Plant No. 1 houses assembly
operations for locksets and ignition
lock housings. Plant No. 2 is a new
facility we built during fiscal 2009 to
replace a leased facility. Plant No. 2
houses our key finishing operations as
well as dedicated space for the
assembly operations of STRATTEC
POWER ACCESS de Mexico and
ADAC-STRATTEC de Mexico.


ADVANCED DEVELOPMENT
Research and development activities
are centered around a dedicated research
engineering staff we call our Advanced
Development Group. This group has the
responsibility for developing future products
and
processes that will keep us in the forefront of the markets we serve. Projects we are pursuing
focus on electronic and mechanical access control products, modularization of related
access/security control components and new manufacturing processes to reduce costs for ourselves
and our customers. Once our Advanced Development Group establishes a proof-of-concept product
utilizing new technology, further product development shifts to our engineering groups for
commercialization and product applications.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 8 |
COMPANY DESCRIPTION
VAST ALLIANCE
In fiscal 2001, we entered into a formal Alliance with WITTE-Velbert GmbH, an automotive
supplier based in Germany which designs, develops, manufactures and markets automotive access
control products for European-based customers. This Alliance consisted of two initiatives. The
first was a cross licensing agreement which allowed STRATTEC to manufacture and market WITTE’s
core products in North America, and WITTE to manufacture and market STRATTEC’s core products
in Europe. The second initiative was a 50-50 joint venture to invest in operations with local
partners in strategic markets outside of Europe and North America.
In February of 2006, we announced the expansion of the Alliance and related joint
venture with the addition of ADAC Plastics, Inc. ADAC, of Grand Rapids, Michigan adds North
American expertise in door handles, a part of WITTE’s core product line that STRATTEC did not
support, and an expertise in color-matched painting of these components.
With the expansion of the Alliance, we now have a full range of access control related
products available on a global basis to support customer programs. To identify this powerful
combination of independent companies focused on working together, we renamed the joint venture
Vehicle Access Systems Technology LLC, and the Alliance is now called the VAST Alliance. WITTE
is now called WITTE Automotive, and ADAC is now doing business as ADAC Automotive. We have
adopted a common graphic image in which we share a logo mark and colors, and a specific logo
for the Alliance itself to be used on the partners’ printed and electronic presentation
materials. What is now VAST LLC made investments with a local partner in Brazil in September,
2001, and local partners in China in March, 2002. VAST do Brasil remains a joint venture with
our local partners there. However, during fiscal 2010, VAST LLC purchased the remaining 40
percent interest of its local partners in the China venture, and VAST China is now wholly
owned by VAST LLC. This was an important step which gives STRATTEC a one-third interest in
China’s activities in the important growing Chinese/Asia market.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 9 |

COMPANY DESCRIPTION
ADAC-STRATTEC de MEXICO
During fiscal 2007, we formed a joint venture (JV) with ADAC Automotive called ADAC-STRATTEC
LLC including a wholly owned Mexican subsidiary ADAC-STRATTEC de Mexico (ASdM). The purpose of this
joint venture is to produce certain ADAC and STRATTEC products utilizing ADAC’s plastic molding
expertise and STRATTEC’s assembly capability. ASdM currently operates out of defined space in one
of STRATTEC’s manufacturing facilities located in Juarez, Mexico. Initial products from this joint
venture include door handle components and exterior trim components for customers producing in
Mexico. Financial results for this JV are consolidated into STRATTEC’s financial statements. As a
start-up operation, ASdM had a minimal financial impact on STRATTEC’s fiscal 2007 through 2009
operating results. However, in our fiscal 2010, ASdM represented $13.3 million of our
consolidated net sales.
STRATTEC POWER ACCESS LLC
During fiscal year 2009, we formed a new subsidiary with WITTE Automotive called STRATTEC
Power Access LLC (SPA) to acquire the North American business of the Delphi Power Products Group.
WITTE is a minority owner. SPA in turn owns a Mexican subsidiary, STRATTEC Power Access de Mexico.
The purpose of this subsidiary is to produce power access devices for sliding side doors, liftgates
and trunk lids. SPA de Mexico currently operates out of defined space in one of STRATTEC’s
manufacturing facilities located in Juarez, Mexico. Financial results for SPA are consolidated in
STRATTEC’s financial statements. As a new operation effective November 30, 2008, SPA had a negative
impact on STRATTEC’s fiscal 2009 operating results due to the
overall economic
slowdown that was experienced throughout the global economy.
Beginning with our first full year
of operation in fiscal 2010, SPA represented $58.5 million
of our consolidated net sales.
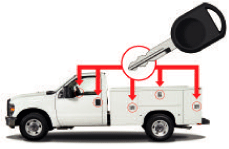

STRATTEC has just introduced BOLT,
the world’s first codeable padlock. In a simple one-step process, users can code the padlock to
their vehicle key. This provides significant convenience by reducing the number of keys users need to secure their lockers,
storage sheds and vehicle accessories such as tool boxes, trailer hitches, etc. You can buy this product direct at
www.boltlock.com
SEASONAL NATURE OF THE BUSINESS
The manufacturing of components used in automobiles is driven by the normal peaks and
valleys associated with the automotive industry. Typically, the months of July and August are
relatively slow as summer vacation shutdowns and model year changeovers occur at the automotive
assembly plants. September volumes increase rapidly as each new model year begins. This volume
strength continues through October and into early November. As the holiday and winter seasons
approach, the demand for automobiles slows as does production.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 10 |
COMPANY DESCRIPTION
March usually brings a major sales and production increase, which then continues through
most of June. This results in our first fiscal quarter (ending in September) sales and operating
results typically being our weakest, with the remaining quarters being more consistent. The
recession of 2008-2009 abnormally altered this pattern resulting in dramatically reduced
production levels throughout the period. We believe the more normal peaks and valleys are
returning as the economy emerges from recession.
GLOBAL PRESENCE
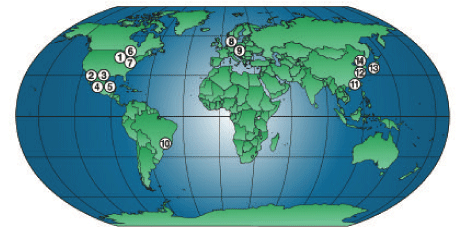
1. STRATTEC — Milwaukee, Wisconsin1
2. STRATTEC de Mexico — Juarez, Mexico1
3. STRATTEC de Mexico — Key Finishing — Juarez, Mexico1
4. ADAC-STRATTEC de Mexico — Juarez, Mexico
5. STRATTEC Power Access de Mexico — Juarez, Mexico
6. ADAC Automotive — Grand Rapids and Muskegan, Michigan1
7. ADAC Automotive, STRATTEC and STRATTEC POWER ACCESS
(Sales/Engineering Offices — Detroit, Michigan1
8. WITTE Automotive — Velbert, Germany1
9. WITTE Automotive — Nejdek, Czech Republic1
10. VAST do Brasil — Sao Paulo, Brazil2
11. VAST Fuzhou — Fuzhou, China2
12. VAST Great Shanghai Co. — Shanghai, China2
13. VAST Japan — Tokyo, Japan (Branch Office)2
14. VAST Korea — Anyang, Korea (Branch Office)2
2. STRATTEC de Mexico — Juarez, Mexico1
3. STRATTEC de Mexico — Key Finishing — Juarez, Mexico1
4. ADAC-STRATTEC de Mexico — Juarez, Mexico
5. STRATTEC Power Access de Mexico — Juarez, Mexico
6. ADAC Automotive — Grand Rapids and Muskegan, Michigan1
7. ADAC Automotive, STRATTEC and STRATTEC POWER ACCESS
(Sales/Engineering Offices — Detroit, Michigan1
8. WITTE Automotive — Velbert, Germany1
9. WITTE Automotive — Nejdek, Czech Republic1
10. VAST do Brasil — Sao Paulo, Brazil2
11. VAST Fuzhou — Fuzhou, China2
12. VAST Great Shanghai Co. — Shanghai, China2
13. VAST Japan — Tokyo, Japan (Branch Office)2
14. VAST Korea — Anyang, Korea (Branch Office)2
| 1 | Members of the VAST Alliance. 2 Units of VAST LLC joint venture. |
ECONOMIC VALUE COMMITMENT
The underlying philosophy of our business, and the means by which we measure our performance,
is Economic Value Added (EVA®). Simply stated, economic value is created when our
business enterprise yields a return greater than the cost of capital we and our shareholders have
invested in STRATTEC. The amount by which our return exceeds the cost of our capital is
EVA®. In line with this philosophy, EVA® bonus plans are in effect for all
our U.S. associates, outside directors and many of our Mexico-based salaried associates as an
incentive to help positively drive the business.
STRATTEC’s significant market presence is the result of a 100-year commitment to creating
quality products and systems that are responsive to changing needs. As technologies advance and
markets grow, STRATTEC retains that commitment to meeting and exceeding the expectations of our
customers, and providing economic value to our shareholders.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 11 |

| VEHICLE LIST 2011 VEHICLES We are proud to be associated with many of the quality vehicles produced in North America and elsewhere. The following model year 2011 cars and light trucks are equipped with STRATTEC products. CARS AND CAR BASED UTILITY VEHICLES Aston Martin DB9 * Chevrolet Impala Ford Taurus Aston Martin DBS * Chevrolet Malibu GMC Acadia Aston Martin Rapide * Chevrolet Orlando * GMC Terrain Aston Martin V8 Vantage * Chevrolet Traverse Holden Commodore * Aston Martin V12 Vantage * Chevrolet Volt Honda Civic Buick Excelle * Chrysler 300 Hyundai Veracruz * Buick Enclave Chrysler Sebring (Nassau) Jeep Compass Buick LaCrosse * Daewoo Gentra * Jeep Patriot Buick Lucerne Dodge Avenger Lincoln MKS Buick Regal * Dodge Caliber Lincoln MKT Cadillac CTS Dodge Challenger Lincoln MKX Cadillac DTS Dodge Charger Lincoln MKZ Cadillac SRX Dodge Journey Lincoln Town Car Cadillac STS * Ford Crown Victoria Opel Astra * Chevrolet Aveo * Ford Edge Opel Astra Van * Chevrolet Camaro Ford Fiesta Opel Insignia * Chevrolet Cruze * Ford Flex Opel Zafira * Chevrolet Equinox Ford Focus Saab 9-4X Chevrolet Corvette Ford Fusion Saab 9-5 * Chevrolet HHR Ford Mustang LIGHT TRUCKS, VANS AND SPORT UTILITY VEHICLES Buick GL8 * Dodge Dakota Pickup GMC Sierra Pickup Cadillac Escalade Dodge Durango GMC Yukon Cadillac Escalade ESV Dodge Nitro Jeep Grand Cherokee Cadillac Escalade EXT Dodge Ram Pickup Jeep Liberty Chevrolet Avalanche Ford Expedition Jeep Wrangler/Wrangler Chevrolet Express Van Ford Explorer Unlimited Chevrolet Silverado Pickup Ford Explorer Sport Trac Kia Sedona Chevrolet Suburban Ford F-Series Pickup Lincoln Mark LT Chevrolet Tahoe Ford F-Series Super Duty Lincoln Navigator Chrysler Town & Country * Ford Ranger Pickup Nissan Titan Dodge Grand Caravan GMC Savana Volkswagen Routan * Vehicles produced outside of North America, or both in and outside North America. |
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 12 |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
The following Discussion and Analysis should be read in conjunction with STRATTEC
SECURITY CORPORATION’s Financial Statements and Notes thereto. Unless otherwise indicated, all
references to years or quarters refer to fiscal years or fiscal quarters.
Purchase of Delphi Power Products Business
Effective November 30, 2008, STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION, in combination with WITTE
Automotive of Velbert, Germany, completed the acquisition of certain assets, primarily equipment
and inventory, and assumption of certain employee liabilities of Delphi Corporation’s Power
Products business for approximately $7.3 million. For the purposes of owning and operating the
North American portion of this acquired business, STRATTEC established a new subsidiary, STRATTEC
POWER ACCESS LLC (“SPA”), which is 80 percent owned by STRATTEC and 20 percent owned by WITTE. The
purchase price of the North American portion of the acquired business totaled approximately $4.4
million, of which STRATTEC paid approximately $3.5 million. WITTE acquired the European portion of
the business for approximately $2.4 million. Effective February 12, 2009, SPA acquired the Asian
portion of the business for approximately $500,000.
The acquisition of the North American and Asian portions of this business by SPA was not
material to STRATTEC’s consolidated financial statements. Amortizable intangible assets acquired
totaled $890,000 and are subject to amortization over a period of nine years. In addition,
goodwill of approximately $223,000 was recorded as part of the transaction. The amortizable
intangibles are included in Other Long-Term Assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Refer to
discussion of goodwill impairment under Analysis of Results of Operations below.
The financial results of SPA are consolidated with the financial results of STRATTEC and
resulted in increased net income to STRATTEC of approximately $545,000 during fiscal 2010 and
decreased net income to STRATTEC of approximately $2.1 million during fiscal 2009.
SPA designs, develops, tests, manufactures, markets and sells power systems to operate
vehicle sliding side doors and rear compartment access points such as liftgates and trunk lids.
In addition, the product line includes power cinching latches and cinching strikers used in these
systems. Current customers for these products supplied from North America are Chrysler Group LLC,
Hyundai Kia Automotive Group (Korea), General Motors Company, Ford Motor Company and Yulon Group
(Taiwan).
EXECUTIVE OVERVIEW
Historically, a significant portion of our total net sales are to domestic automotive OEM’s
(General Motors, Ford and Chrysler). During the past several years these customers continued to
lose North American vehicle production market share to the New Domestic automotive manufacturers
(primarily the Japanese and Korean automotive manufacturers). Therefore, our financial performance
depends, in large part on conditions in the automotive industry, which in turn, are dependent upon
the U.S. and global economies. During fiscal years 2010, 2009 and 2008, the domestic automotive
OEMs together represented 67 percent, 66 percent and 66 percent, respectively, of our total sales.
During the summer of 2008, the price of oil significantly escalated with the resultant run up
of gas prices to $4.00 plus per gallon which caused a major shift in consumer preferences away
from mid and full size trucks and SUV’s to smaller, more fuel efficient vehicles. This change had
a significant impact on STRATTEC, since our book of business was heavily weighted towards trucks
and SUV’s at that time.
In late 2008, our U.S. customers met with the U.S. Government to discuss the precarious
state of the auto industry. General Motors, Chrysler and Ford presented long-term viability plans
to the U.S. Government. Their plans focused on reducing North American production capacity,
closing facilities, eliminating certain vehicle models and brands and reducing overall structural
costs to operate profitably at a 10 million vehicle production build level in North America.
General Motors and Chrysler sought and received emergency funding from the U.S. Government. Ford
did not request emergency funding. On April 30, 2009, Chrysler filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy
protection and General Motors, filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection on June 1, 2009. The
reorganized entities emerged from bankruptcy for both Chrysler and General Motors on June 10, 2009
and July 10, 2009, respectively. The majority of our pre- and post petition accounts receivable
were paid in accordance with payment terms existing prior to the bankruptcy filing.
Our financial results for fiscal year 2009, reflected the overall weakness in the U.S. economy
and in particular the sharp decline in vehicle sales and production caused by the economic
recession, fluctuating fuel prices and a lack of credit for both consumers and commercial lending
markets, especially lending to the automotive supply base. During fiscal 2009, we reacted to the
unprecedented 27 year low in North American vehicle production in several ways. First of all, we
reduced our productive workforce at both our Milwaukee, Wisconsin and Juarez, Mexico facilities
through a combination of temporary and permanent layoffs. In January 2009, we reduced our U.S.
salaried workforce by approximately 10 percent, temporarily reduced our Company 401(k) match, and
instituted several unpaid work furlough days. We also renegotiated certain terms of our current
labor agreement, and restructured our benefit plans to reduce future expenses.
On November 30, 2008 STRATTEC, in combination with WITTE Automotive of Velbert, Germany,
completed the acquisition of certain assets, primarily equipment and inventory of Delphi
Corporation’s Power Products business. This acquisition expanded our product capabilities in our
access controls related to power sliding side door systems, power lift gate systems and power deck
lids. In addition, this acquisition expanded our customer base with two Asian OEMs. In conjunction
with this acquisition, we vacated two leased facilities, one in Juarez
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 13 |

MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
Mexico utilized by STRATTEC, and one in Matamoros, Mexico formerly utilized by Delphi which
we assumed as part of the acquisition. These two facilities were combined into a newly constructed
STRATTEC owned facility in Juarez during February 2009, saving approximately $500,000 annually.
Late in our fiscal 2009, a large volume of ignition lock housings sold to a Tier 1
customer, primarily for General Motors’ global passenger cars, was sourced to us, providing
additional sales and increased production of this product line at both our Milwaukee and Juarez
facilities. We anticipate that there will be further positive results from this additional
business experienced in fiscal 2011 and 2012, and therefore further diversification within our
product mix.
Our financial results for fiscal year 2010 reflected a significant improvement compared to
fiscal 2009, the worst year of operating results in our history. Fiscal 2010 sales were $208
million versus $126 million and net income of $3.4 million versus a net loss of $6.1 million. At
the beginning of fiscal 2010, our two largest customers, General Motors and Chrysler, emerged from
bankruptcy. During August 2009, the automotive industry was positively impacted by the U.S.
Government “Cash for Clunkers” rebate program designed to increase consumer spending. The
resultant effect was to significantly increase demand on the supply base as automakers increased
production to replenish U.S. automotive retail inventories after this program ended. Certain of
our suppliers that cut capacity in early 2009 struggled to regain that capacity during fiscal 2010
causing disruptions in the supply of components to us, and late shipments of our products to our
customers. As a result, we incurred approximately $3 million in expedited freight costs.
During November 2009, VAST LLC acquired the remaining 40 percent interests in its two
Chinese joint ventures located in Shanghai and Fuzhou. As a result of our 1/3 interest in VAST
LLC, STRATTEC’s equity earnings of VAST LLC positively impacted our 2010 operating results and
added approximately $1 million to pre-tax earnings.
Fiscal year 2010 also represented our first full year of operating results from the Power
Products business acquired from Delphi. Now called STRATTEC POWER ACCESS, this business
contributed $58.5 million in net sales during fiscal 2010. In addition, this product line of power
actuators for sliding doors, lift gates and deck lids provided additional vehicle content to help
offset our traditional lock business that over the past several years has been de-contented by our
major customers.
Prior to 2009, the normal yearly vehicle production build in North America ranged from 15
to 16 million vehicles. As we look out into the future, the July 2010 projections from our
third-party forecasting service indicates the North American light vehicle production will show
gradual improvement for the next five years. By model year, we are expecting a 2010 build of 11.1
million vehicles, 12.1 million vehicles for 2011, 13.0 million vehicles for 2012, 14.1 million
vehicles for 2013 and 15.1 million vehicles for 2014. General Motors Company and Ford Motor
Company are expected to experience increases in their production levels during this time period.
Chrysler Group LLC is expected to increase production in model year 2011, but decline starting in
model year 2012, primarily due to the forecasting uncertainty and risk in Fiat’s future vehicle
plans for the Chrysler Group. Of course all of these forecasts are subject to variability based on
what happens in the overall economy, especially as it relates to the current level of high
unemployment, continued tight credit markets, relatively low home equity values, fluctuating fuel
prices and other key factors we believe determine whether consumers can or will purchase new
vehicles.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The following is a discussion and analysis of our financial position and results of
operations for the periods ended June 27, 2010 and June 28, 2009. As of the fourth quarter of
2009, we changed our method of accounting for inventory from the LIFO method to the FIFO method.
Certain 2008 amounts referred to below have been restated to reflect the LIFO to FIFO inventory
costing change. See further discussion of the accounting change in Notes to Financial Statements.
2010 Compared to 2009
Net sales were $208.0 million in 2010 compared to $126.1 million in 2009. Sales to our largest
customers overall increased in the current year compared to the prior year period primarily due to
higher vehicle production volumes. Sales to General Motors Company in the current year were $51.7
million compared to $39.2 million in the prior year. Included in the current year sales to General
Motors were $5.0 million of sales to Nexteer Automotive, formerly a unit of Delphi Corporation,
which is now owned by General Motors. Sales to Chrysler Group LLC were $68.2 million in the current
year compared to $31.9 million in the prior year and sales to Ford Motor Company were $18.4 million
in the current year compared to $12.6 million in the prior year. In the current year, sales
generated by SPA to Hyundai Kia were $13.2 million. Also, in the current period historical customer
pricing issues were resolved which increased our sales by approximately $1.2 million. The pricing
issues related to a specific vehicle program and were fully resolved during fiscal 2010.
Gross profit as a percentage of net sales was 15.9 percent in the current year compared
to 10.5 percent in the prior year. The improvement in the gross profit margin was primarily the
result of higher customer vehicle production volumes compared to the prior year, which increased
overhead absorption of our manufacturing costs, partially offset by expense provisions for the
accrual of bonuses earned under our Economic Value Added (EVA®) Incentive Bonus Plans,
the increased warranty costs and expedited freight and overtime costs incurred to meet
significantly increased production requirements from our largest customers. Also impacting the
current year were lower purchased raw material costs for zinc. During 2010, we significantly
exceeded our
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 14 |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
planned financial targets on which payouts under our incentive bonus plans are based. Our
operating results therefore reflect incentive bonus expense provisions of $5.2 million in the
current year of which $2.6 million impacted our gross profit. No bonuses were provided for or paid
in the prior fiscal year. Warranty provisions totaled $2.6 million in the current year compared to
$362,000 in the prior year. Historically, we have experienced relatively low warranty charges from
our customers due to our contractual arrangements and improvements in the quality, reliability and
durability of our products. Recently, our largest customers have extended their warranty protection
for their vehicles and are demanding higher warranty cost sharing arrangements from suppliers. The
current year warranty provisions include additional accruals to address the warranty exposure
related to the demand for higher warranty cost sharing. Expedited freight and overtime costs
incurred to meet significantly increased production requirements from our largest customers totaled
$5.0 million in the current year compared to $1.1 million in the prior year. The average zinc price
paid per pound decreased to $1.03 in the current year from $1.21 in the prior year. During the
current year, we used approximately 8.6 million pounds of zinc. This resulted in decreased zinc
costs of approximately $1.5 million in the current year compared to the prior year. Also impacting
the current period gross margin was a curtailment loss related to our qualified defined benefit
pension plan. An amendment to this plan, which became effective January 1, 2010, discontinued the
benefit accruals for salary increases and credited service rendered after December 31, 2009. As a
result of the amendment, a curtailment loss related to unrecognized prior service cost of $505,000
was recorded, of which approximately $375,000 increased cost of goods sold and approximately
$130,000 increased engineering, selling and administrative expenses. Additionally, the 2009 year
was negatively impacted by approximately $205,000 of relocation costs related to the move from our
leased facility in Juarez, Mexico to our new owned manufacturing facility in Juarez, a
non-recurring inventory adjustment of $152,000 and severance costs of $154,000 relating to a work
force reduction in Mexico in January 2009. Construction of our new facility was completed in
November 2008, and the move from our leased facility in Juarez to our new facility was completed in
February 2009. The non-recurring inventory adjustment resulted from finished goods inventory that
was acquired in the Delphi Power Products business acquisition. The value of the finished goods
inventory acquired was adjusted to its selling price less costs to sell, and gross profit was
negatively impacted by the inventory that was sold during the year.
Engineering, selling and administrative expenses were $29.9 million in the current year,
compared to $25.5 million in the prior year. The increase is primarily attributable to the current
period including twelve months of expenses for SPA engineering and administrative personnel
compared to only seven months in the prior year period as a result of the timing of the
acquisition of this business and to the EVA® incentive bonus expense provisions
described above. EVA® incentive bonus expense provisions impacting engineering, selling
and administrative expenses totaled $2.6 million during 2010 compared to no provision in 2009.
Also, as previously discussed, included in the current year expense was a curtailment loss of
$130,000.
An annual goodwill impairment analysis was completed during 2010 related to the
goodwill recorded as part of the acquisition of SPA in November 2008. A $223,000 impairment charge
to write off the goodwill balance was recorded as a result of this analysis.
In 1995, we recorded a provision of $3 million for estimated costs to remediate a site at our
Milwaukee facility. The site was contaminated by a solvent spill, which occurred in 1985, from a
former above ground solvent storage tank located on the east side of the facility. The reserve was
originally established based on estimates to adequately cover the cost for active remediation of
the contamination. Due to changing technology and related costs associated with active remediation
of the contamination, an updated analysis and estimate was obtained during 2010. The reserve was
reduced by approximately $1.1 million to reflect the revised monitoring and remediation cost
estimate. As of June 27, 2010, costs of approximately $400,000 have been incurred to date related
to the installation of monitoring wells on the property and other ongoing monitoring costs.
In 2009, we recorded a $500,000 provision for doubtful accounts in connection with Chrysler
LLC’s filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection for certain of their U.S. legal entities on
April 30, 2009. All uncollectible receivables related to the bankruptcy were written off against
the $500,000 reserve during the current year. However, as a result of subsequent payments
received from Chrysler, $421,000 of the $500,000 provision was recorded as a recovery of
allowance for doubtful accounts during the current year.
Income from operations in the current year was $4.4 million compared to a loss from
operations of $12.7 million in the prior year. This improvement was the result of the increase
in sales and gross profit margin as discussed above.
Interest income was $86,000 in the current year compared to $731,000 in the prior
year. The decrease was due to both lower invested cash and cash equivalent balances and lower
investment returns on these assets in the current year compared to the prior year.
Equity earnings of joint ventures increased to $1.0 million in 2010 from $245,000 in
2009. The improvement in equity earnings of joint ventures is primarily due to the favorable
economic conditions in China and an increase in our ownership percentage resulting from the
November 20, 2009 purchase by VAST LLC of the non-controlling interest of its two Chinese joint
ventures, VAST Fuzhou and VAST Great Shanghai.
Net other income was $312,000 in the current year compared to $804,000 in the prior year.
The decrease was primarily due to transaction losses resulting from foreign currency transactions
entered into by our Mexican subsidiaries of $283,000 in the current year compared to transaction
gains of $918,000 in the prior year. The foreign currency transaction impact was partially offset
by
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 15 |

MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
gains on the Rabbi Trust which funds our supplemental executive retirement plan totaling
$431,000 in the current year compared to losses of $393,000 in the prior year. The investments
held in the Rabbi Trust are considered trading securities.
Our effective income tax rate for 2010 was 29.7 percent compared to 38.0 percent in 2009. The
2010 tax rate was impacted by a lower effective tax rate for income subject to tax in Mexico as
compared to the effective tax rate for income subject to tax in the U.S. The 2009 tax rate was
impacted by a higher U.S. effective tax rate applied to pre-tax U.S. losses and a lower Mexican
tax rate being applied to pre-tax income in Mexico. The overall U.S. effective tax rate differed
from the Federal statutory tax rate primarily due to the lower Mexican tax rate. As of June 27,
2010, a valuation allowance of $152,000 was recorded due to our assessment of the future
realization of certain capital loss carryforward benefits.
2009 Compared to 2008
Net sales were $126.1 million in 2009 compared to $159.6 million in 2008. The sales
decreases in 2009 were experienced across all of our largest customers. Sales to General Motors
Corporation in 2009 were $39.2 million compared to $45.0 million in 2008 due to lower vehicle
production volumes on the vehicles we supply. The impact of the lower volumes was partially offset
by the takeover of certain passenger car lockset production from another supplier and $800,000 of
sales generated by SPA primarily relating to products supplied on the Buick minivan produced in
China. 2008 sales to General Motors were impacted by production reductions as a direct result of a
strike called by the UAW against a major General Motors supplier. Sales to Chrysler LLC were $31.9
million in 2009 compared to $40.2 million in 2008. This sales reduction was due to a combination of
lower vehicle production volumes and reduced component content in the security products we supply,
offset by $9.8 million of sales generated by SPA relating primarily to the products supplied on the
Dodge, Chrysler and Volkswagen minivans. Sales to Ford Motor Company were $12.6 million in 2009
compared to $19.4 million in 2008 and sales to Delphi Corporation were $6.3 million in 2009
compared to $14.9 million in 2008. Included in 2009 Ford sales were $800,000 of sales generated by
SPA primarily relating to products supplied on the Lincoln Town Car. The lower sales to Ford and
Delphi were primarily due to lower vehicle production volumes. The impact of the above mentioned
strike in 2008 reduced sales to General Motors and Delphi Corporation by approximately $3.5 million
in 2008.
Gross profit as a percentage of net sales was 10.5 percent in 2009 compared to 15.5 percent in
2008. The decrease in the gross profit margin was primarily attributed to our customers’ reduced
vehicle production volumes, which lowered the absorption of our fixed manufacturing costs. The
impact of the reduced production volumes was partially offset by lower purchased material costs for
zinc and brass along with a favorable Mexican peso to U.S. dollar exchange rate affecting our
operations in Mexico. 2009 was also negatively impacted by approximately $205,000 of relocation
costs related to the move from our leased facility in Juarez, Mexico to our new owned manufacturing
facility in Juarez, a non-recurring inventory adjustment of $152,000 and severance costs of
$154,000 relating to a work force reduction in Mexico in January 2009. Construction of our new
facility was completed in November 2008, and the move from our leased facility in Juarez to our new
facility was completed in February 2009. The non-recurring inventory adjustment resulted from
finished goods inventory that was acquired in the Delphi Power Products business acquisition. The
value of the finished goods inventory acquired was adjusted to its selling price less costs to
sell, and gross profit was negatively impacted by the inventory that was sold during the year. The
2008 year was also negatively impacted by non-recurring items including a lump sum bonus totaling
$243,000 paid to our Milwaukee represented hourly workers resulting from a new four-year labor
contract ratified on June 22, 2008 as well as the disposal of a customer specific fixed asset
resulting in a fixed asset disposal loss of $382,000.
The average zinc price paid per pound decreased to $1.21 in 2009 from $1.53 in 2008.
During 2009, we used approximately 5.3 million pounds of zinc. This resulted in decreased zinc
costs of approximately $1.7 million in 2009 compared to 2008. The average brass price paid per
pound decreased to $3.05 in 2009 from $3.84 in 2008. During 2009, we used approximately 830,000
pounds of brass. This resulted in decreased brass costs of approximately $655,000 in 2009 compared
to 2008.
The inflation rate in Mexico for the twelve months ended June 28, 2009 was approximately
5.6 percent and increased our operating costs by approximately $880,000 in 2009 over 2008. The
average U.S. dollar/Mexican peso exchange rate increased to approximately 12.75 pesos to the
dollar in 2009 from approximately 10.75 pesos to the dollar in 2008. This resulted in decreased
costs related to our Mexican operations of approximately $2.7 million in 2009 compared to 2008.
Engineering, selling and administrative expenses were $25.5 million in 2009, compared to
$24.0 million in 2008. The increase was primarily attributed to hiring SPA engineering personnel,
contracting with Delphi for temporary transition services related to the acquisition, outside
legal costs incurred to defend a STRATTEC patent net of a recovery from a third party and a charge
of $350,000 for severance and outplacement costs relating to a 10 percent reduction in our U.S.
salaried work force on January 15, 2009. These added costs were partially offset by the cost
savings from the salary work force reduction, reduced 401(k) match for salaried associates
implemented in January 2009 and a salary reduction and temporary work furloughs for our U.S.
salaried associates, each of which were implemented in May 2009.
The provision for bad debts of $500,000 in 2009 was recorded in connection with Chrysler’s
filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection for certain of their U.S. legal entities on April 30,
2009. The Chrysler and General Motors bankruptcy filings had little affect on our receivables with
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 16 |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
Chrysler and General Motors, as both companies were able to continue making payments to
suppliers for parts they had purchased prior to their bankruptcy filings. We increased our reserve
for doubtful accounts at the end of our fiscal 2009 third quarter by $500,000 in anticipation of
difficulties collecting on our receivables from Chrysler. As of June 2009, a majority of our
pre-bankruptcy receivables from both Chrysler and General Motors had been paid under normal terms.
However, there remained some minor pre-bankruptcy past-due receivable balances outstanding.
Subsequently, both companies emerged from bankruptcy and started to resume production in July.
The loss from operations in 2009 was $12.7 million compared to income from operations of
$805,000 in 2008. This reduction was the result of the decrease in sales and gross profit margin,
the increase in operating expenses and the provision for doubtful accounts as discussed above.
Interest income was $731,000 in 2009 compared to $2.7 million in 2008. The decrease was
due to both lower invested cash and cash equivalent balances and lower investment returns on these
assets in the current year compared to the prior year.
Net other income was $804,000 in 2009 compared to net other expense of $300,000 in 2008.
The change was primarily due to favorable gains resulting from foreign currency transactions
entered into by our Mexican subsidiaries of $918,000 in 2009 compared to transaction losses of
$320,000 in 2008. The foreign currency transaction gains were offset by increased losses on
the Rabbi Trust which funds our supplemental executive retirement plan totaling $393,000 in
2009 compared to $174,000 in 2008. The investments held in the Rabbi Trust are considered
trading securities.
Our effective income tax rate for 2009 was 38.0 percent compared to 25.8 percent in 2008.
The 2009 tax rate was impacted by a higher U.S. effective tax rate applied to pre-tax U.S. losses
and a lower Mexican tax rate being applied to pre-tax income in Mexico. The overall U.S. effective
tax rate differed from the Federal statutory tax rate primarily due to the lower Mexican tax rate.
The 2008 provision included a favorable tax adjustment primarily related to Mexican tax benefits
allowed for our Mexican subsidiaries. The favorable adjustment totaled $573,000. In addition,
reduced 2008 earnings resulted in a larger percentage of our consolidated taxable income being
taxed in Mexico, which has a lower effective rate as compared to the U.S. rate. At June 28, 2009,
we had deferred tax assets resulting from unused operating losses and unused tax credits that we
are allowed to carry-forward to future years. The deferred tax asset relating to these losses and
credit carry-forwards totaled approximately $3.3 million at June 28, 2009. The loss and credit
carry-forwards expire in years 2017 through 2029. We evaluated the need to maintain a valuation
allowance against our deferred tax assets. Based on this evaluation, which included a review of
recent profitability and projections of future profitability, we concluded that a valuation
allowance was not necessary.
LIQUIDITY AND CAPITAL RESOURCES
Our primary source of cash flow is from our major customers, which include General Motors
Company, Ford Motor Company and Chrysler Group LLC. As of the date of filing this Annual Report
with the Securities and Exchange Commission, all of our customers are making payments on their
outstanding accounts receivable in accordance with the payment terms included on their purchase
orders. A summary of our outstanding receivable balances from our major customers as of June 27,
2010 is as follows (in thousands of dollars):
| U.S. | Canada | Mexico | Total | |||||||||||||
General Motors |
$ | 5,779 | $ | 1,231 | $ | 1,115 | $ | 8,125 | ||||||||
Ford |
$ | 2,430 | $ | 165 | $ | 123 | $ | 2,718 | ||||||||
Chrysler |
$ | 4,634 | $ | 6,808 | $ | 789 | $ | 12,231 | ||||||||
On April 30, 2009, Chrysler LLC filed for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection for certain of
their U.S. legal entities. During the quarter ended March 29, 2009, we increased our provision for
bad debts by $500,000 to cover the portion of the pre-bankruptcy receivable balances which we
believed could be uncollectible. As of June 27, 2010, all uncollectible amounts related to the
bankruptcy filings were written off against the reserve and $421,000 of amounts previously
written-off were paid by Chrysler LLC during the year ended June 27, 2010.
Cash flow provided by operating activities was $10.1 million in 2010 compared to cash
used in operating activities of $6.8 million in 2009. The improvement in operating cash flow was
primarily due to the improvement in our overall financial results. In addition, 2009 operating
cash flow was negatively impacted by the initial funding of working capital related to the SPA
operations. Pension contributions to our qualified plan totaled $4 million in 2010 and $3 million
in 2009.
On February 26, 2009, our Board of Directors took action to suspend payment of our
quarterly dividend to conserve cash. No dividends were paid during fiscal 2010. During the first
three quarters of fiscal 2009 approximately $1.5 million of cash dividends were paid to our
shareholders. On August 4, 2010, our Board of Directors declared a special one-time cash
dividend of $1.20 per common share payable October 29, 2010 to shareholders of record as of
October 8, 2010. The special dividend will total approximately $4.0 million and will be funded
with current cash balances. The company does not intend to reinstate the quarterly dividend in
the near future.
Our accounts receivable balance increased approximately $18.8 million and our accounts
payable balance increased approximately $9.8 million in 2010. The increases are primarily the
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 17 |

MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
result of the increased sales and production activity experienced in 2010 as discussed
under Results of Operations herein. The accrued payroll and benefits balance increased
approximately $7.3 million in fiscal 2010 primarily due to the accrual for our incentive bonus
payments as discussed under Results of Operations herein.
The accrued pension obligations balance includes our qualified plan and our supplemental
executive retirement plan (SERP). The change in the accrued pension obligations balance during
2010 is the result of the net impact of pension contributions, the actuarially calculated pension
expense and the impact of the change in the funded status of the plans. The 2010 pre-tax funded
status adjustment increased our liability position by $7.4 million at June 27, 2010. We anticipate
voluntary pension contributions to our qualified plan will be approximately $2 million in 2011.
The change in the accrued postretirement obligations balance during 2010 is also the net impact of
contributions, benefit payments, the actuarially calculated pension expense and the impact of the
change in the funded status of the plan. The 2010 pre-tax funded status adjustment decreased our
liability position by approximately $5.2 million and was primarily due to a plan amendment which
limits the maximum annual benefit amount for each participant to $4,000 during the maximum five
year benefit period.
Capital expenditures were $6.9 million in 2010 compared to $12.5 million in 2009.
Expenditures were primarily in support of requirements for new product programs and the upgrade
and replacement of existing equipment. Capital expenditures during the prior year included
approximately $5.7 million for the construction of a new facility in Juarez, Mexico, to replace
an existing leased facility. The construction of the new facility was completed in fiscal 2009.
We anticipate capital expenditures will be approximately $6 million in fiscal 2011 in support of
requirements for new product programs and the upgrade and replacement of existing equipment.
Our Board of Directors has authorized a stock repurchase program to buy back outstanding
shares of our common stock. Shares authorized for repurchase under the program totaled 3,839,395
at June 27, 2010. Over the life of the repurchase program through June 27, 2010, a total of
3,655,322 shares have been repurchased at a cost of approximately $136.4 million. During fiscal
year 2010, no shares were repurchased. Additional repurchases may occur from time to time and are
expected to continue to be funded by cash flow from operations and current cash balances. Based on
the current economic environment and our preference to conserve cash, we anticipate minimal or no
stock repurchase activity in fiscal year 2011.
We have a $20 million unsecured line of credit (“Line of Credit”) with M&I Marshall &
Ilsley Bank, which expires October 30, 2010. This unsecured line of credit replaced a $50.0
million unsecured line of credit with M&I Marshall & Ilsley Bank which terminated on October 31,
2009. Interest on borrowings under our line of credit is at varying rates based on the London
Interbank Offering Rate with a minimum annual rate of 4 percent. The Line of Credit is not
subject to any covenants. There were no outstanding borrowings at June 27, 2010 or June 28, 2009.
There were no borrowings under any third party debt facilities during 2010, 2009 or 2008. We
believe that the Line of Credit is adequate, along with existing cash balances and cash flow from
operations, to meet our anticipated capital expenditure, working capital and operating
expenditure requirements.
Over the past several years, we have been impacted by rising health care costs, which have
increased our cost of employee medical coverage. A portion of these increases have been offset by
plan design changes and employee wellness initiatives. We have also been impacted by increases in
the market price of zinc and brass and inflation in Mexico, which impacts the U.S. dollar costs of
our Mexican operations. We have negotiated raw material price adjustment clauses with certain
customers to offset some of the market price fluctuations. We do not hedge against our Mexican
peso exposure.
OFF-BALANCE SHEET ARRANGEMENTS
Contractual obligations are as follows as of June 27, 2010 (thousands of dollars):
| Payments Due By Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Less Than | More Than | |||||||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligation | Total | 1 Year | 1-3 Years | 3-5 Years | 5 Years | |||||||||||||||
Operating Leases |
$ | 1,732 | $ | 508 | $ | 771 | $ | 453 | $ | — | ||||||||||
Other Purchase Obligations |
24,154 | 9,849 | 14,305 | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Pension and Postretirement
Obligations(a) |
6,293 | 6,293 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 32,179 | $ | 16,650 | $ | 15,076 | $ | 453 | $ | — | ||||||||||
| (a) | As disclosed in our Notes to Financial Statements, estimated cash funding related to our pension and postretirement benefit plans is expected to total $6.3 million in 2011. Because the timing of funding related to these plans beyond 2011 is uncertain, and is dependent on future movements in interest rates and investment returns, changes in laws and regulations, and other variables, pension and postretirement outflows beyond 2011 have not been included in the table above. |
Liabilities recognized for uncertain tax benefits of $1.2 million are not presented in
the table above due to uncertainty as to amounts and timing regarding future payments.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 18 |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
JOINT VENTURES
We participate in certain Alliance Agreements with WITTE Automotive (“WITTE”) and ADAC
Automotive (“ADAC”). WITTE, of Velbert, Germany, is a privately held automotive supplier. WITTE
designs, manufactures and markets components including locks and keys, hood latches, rear
compartment latches, seat back latches, door handles and specialty fasteners. WITTE’s primary
market for these products has been Europe. ADAC, of Grand Rapids, Michigan, is a privately held
automotive supplier and manufactures engineered products, including door handles and other
automotive trim parts, utilizing plastic injection molding, automated painting and various assembly
processes.
The Alliance provides a set of cross-licensing agreements for the manufacture,
distribution and sale of WITTE products by STRATTEC and ADAC in North America, and the
manufacture, distribution and sale of STRATTEC and ADAC products by WITTE in Europe. Additionally,
a joint venture company, Vehicle Access Systems Technology LLC (“VAST LLC”), in which WITTE,
STRATTEC and ADAC each hold a one-third interest, exists to seek opportunities to manufacture and
sell the companies’ products in areas of the world outside of North America and Europe.
VAST do Brasil, a joint venture between VAST LLC and Ifer do Brasil Ltda., was formed
to service customers in South America. VAST Fuzhou and VAST Great Shanghai (collectively known as
VAST China), began as joint ventures between VAST LLC and a Taiwanese partner to provide a base of
operations to service our automotive customers in the Asian market. Effective November 20, 2009,
VAST LLC purchased the remaining 40 percent of these two Chinese joint ventures for $9.6 million.
VAST LLC now owns 100 percent of VAST Fuzhou and VAST Great Shanghai. VAST LLC also maintains
branch offices in South Korea and Japan in support of customer sales and engineering requirements.
The VAST LLC investments are accounted for using the equity method of accounting. The
activities related to the VAST LLC joint ventures resulted in equity in earnings of joint
ventures to STRATTEC of approximately $1.0 million during 2010 and $245,000 during 2009. During
the current year, the VAST partners made capital contributions to VAST totaling $300,000 in
support of general operating expenses. STRATTEC’s portion of the capital contributions totaled
$100,000.
In fiscal year 2007, we entered into a joint venture with ADAC, in which STRATTEC holds a
50.1 percent interest and ADAC holds a 49.9 percent interest. The joint venture, ADAC-STRATTEC
LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, was formed on October 27, 2006. In addition, a Mexican
entity, ADAC-STRATTEC de Mexico, which is wholly owned by ADAC-STRATTEC LLC, was formed on
February 21, 2007 to establish injection molding and assembly operations for door handle
components. ADAC-STRATTEC LLC’s financial results are consolidated with the financial results of
STRATTEC and resulted in increased net income to STRATTEC of approximately $114,000 in 2010 and no
change in net income to STRATTEC in 2009.
Effective November 30, 2008, STRATTEC established a new entity, STRATTEC POWER ACCESS LLC
(“SPA”), which is 80 percent owned by STRATTEC and 20 percent owned by WITTE. SPA operates the
North American portion of the Power Products business which was acquired from Delphi Corporation.
The financial results of SPA are consolidated with the financial results of STRATTEC and resulted
in increased net income to STRATTEC of approximately $545,000 in 2010 and decreased net income to
STRATTEC of approximately $2.1 million during 2009.
OTHER MATTERS
Health care reform legislation was recently enacted by the Federal government. We are
currently evaluating the legislation to determine its effects on our plan structure, future
operating results and financial position.
RECENTLY ISSUED ACCOUNTING STANDARDS
In June 2009, the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) issued authoritative guidance
which amends the consolidation guidance applicable to variable interest entities. The guidance
will affect the overall consolidation analysis under the current authoritative guidance for
consolidation of variable interest entities and is effective for us as of the beginning of the
first quarter of fiscal year 2011. We are currently evaluating the impact that the guidance may
have on our consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
In January 2010, the FASB issued guidance that requires reporting entities to make new
disclosures about recurring or nonrecurring fair value measurements, including significant
transfers into and out of Level 1 and Level 2 fair value measurements and information on
purchases, sales, issuances, and settlements on a gross basis in the reconciliation of Level 3
fair value measurements. The guidance is effective for interim and annual reporting periods
beginning after December 15, 2009, except for Level 3 reconciliation disclosures that are
effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2010. We do not expect these new
disclosure provisions to have a significant impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
CRITICAL ACCOUNTING POLICIES
We believe the following represents our critical accounting policies:
Pension and Postretirement Health Benefits — Pension and postretirement health
obligations and costs are developed from actuarial valuations. The determination of the obligation
and expense for pension and postretirement health benefits is dependent on the selection of
certain
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 19 |

MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
assumptions used by actuaries in calculating such amounts. Those assumptions are described in
the Notes to Financial Statements and include, among others, the discount rate, expected long-term
rate of return on plan assets, retirement age and rates of increase in compensation and health
care costs. We evaluate and update all of the assumptions annually on June 30, the measurement
date. Refer to Notes to Financial Statements for the impact of the pension and postretirement
plans on the financial statements.
We determine the discount rate used to measure plan liabilities using prevailing
market rates of a large population of high-quality, non-callable, corporate bonds currently
available that, if the obligation was settled at the measurement date, would provide the
necessary future cash flows to pay the benefit obligation when due. Using this methodology, we
determined a discount rate of 5.41 percent to be appropriate as of June 30, 2010, which is a
decrease of 1.45 percentage points from the rate used at June 30, 2009. The impact of this change
increased our year-end 2010 projected pension benefit obligations by approximately $13.5 million,
the year-end 2010 accumulated pension benefit obligations by approximately $13.5 million and the
year-end 2010 accumulated postretirement obligation by approximately $252,000. This change is
also expected to increase our 2011 pension expense by $1.1 million and decrease our
postretirement expense by $35,000.
As of June 30, 2010, we updated the termination rates for the qualified pension plan and
the postretirement plan. The impact of this change decreased our year-end 2010 projected pension
benefit obligations by approximately $513,000 and our year end accumulated postretirement
obligation by approximately $38,000. This change is also expected to increase our 2011 pension
expense by approximately $130,000 and postretirement expense by approximately $6,000.
As of January 1, 2010, the qualified defined benefit pension plan was amended
discontinuing the benefit accrual for salary increases and credited service rendered after
December 31, 2009. As a result, a curtailment loss related to the unrecognized prior service cost
of $505,000 was recorded during fiscal 2010. The impact of this change decreased our year-end 2010
projected pension benefit obligations by approximately $850,000 and our year-end 2010 accumulated
pension benefit obligations by approximately $800,000. This change is also expected to decrease
our 2011 pension expense by $2 million.
As of June 30, 2009, we decreased the salary scale from 3.5% to 3%. The impact of this change
decreased our year-end 2009 projected pension benefit obligations by approximately $652,000 and
increased our year-end 2009 accumulated pension benefit obligations by approximately $253,000. This
change decreased our 2010 pension expense by $179,000.
A significant element in determining the pension expense is the expected return on plan
assets. Our assumption for the expected return on plan assets is based on historical results for
similar allocations among asset classes and was 8.5 percent for 2008, 8.25 percent for 2009 and 8.0
percent for 2010. This reduced the expected return on plan assets by approximately $200,000 in both
2009 and 2010. Refer to Notes to Financial Statements for additional information on how this rate
was determined.
The difference between the expected return and actual return on plan assets is deferred
and, under certain circumstances, amortized over future years of service. Therefore, the deferral
of past asset gains and losses ultimately affects future pension expense. This is also the case
with changes to actuarial assumptions. As of June 30, 2010, we had $44.1 million of net
unrecognized pension actuarial losses, which included deferred asset losses of $13.2 million. As
of June 30, 2010, we had unrecognized postretirement actuarial losses of $7.9 million. These
amounts represent potential future pension and postretirement expenses that would be amortized
over average future service periods. The average remaining service period is about 9 years for the
pension plans and 11 years for the postretirement plan.
During fiscal years 2010, 2009 and 2008, we voluntarily contributed $4 million, $3
million and $5 million, respectively, to our qualified pension plan. Future pension contributions
are expected to be approximately $2 million annually depending on market conditions. We have
evaluated the potential impact of the Pension Protection Act (the “Act”), which was passed into
law on August 17, 2006, on future pension plan funding requirements based on current market
conditions. The Act has not had and is not anticipated to have in future periods a material
effect on our level of future funding requirements or on our liquidity and capital resources.
A significant element in determining the postretirement health expense is the health care
cost trend rates. We develop these rates based on historical cost data, the near-term outlook and
an assessment of likely long-term trends. Changes in the health care cost trend rate assumption
will have a significant effect on the postretirement benefit amounts reported. Refer to Notes to
Financial Statements for an analysis of the impact of a one percent change in the trend rate.
As of January 1, 2010, the postretirement health care benefit plan was amended to
limit future eligible retirees’ benefits under the plan to $4,000 per year for a maximum of five
years. This change decreased the year-end 2010 postretirement benefit obligation by approximately
$3.4 million and is expected to decrease 2011 postretirement expense by approximately $645,000.
While we believe that the assumptions used are appropriate, significant differences in
the actual experience or significant changes in the assumptions may materially affect our pension
and postretirement health obligations and future expense.
Other Reserves — We have reserves such as an environmental reserve, a warranty reserve,
an incurred but not reported claim reserve for self-insured health plans, a workers’ compensation
reserve, an allowance for doubtful accounts related to trade accounts receivable and a repair and
maintenance supply parts reserve. These reserves require the use of estimates and judgment with
regard to risk exposure, ultimate liability and net realizable value.
Environmental Reserve — We have a liability recorded related to the estimated costs to
remediate a site at our Milwaukee facility, which was contaminated by a solvent spill from a
former above ground solvent storage tank occurring in 1985. The recorded environmental liability
balance involves judgment
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 20 |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
and estimates. Our reserve estimate is based on an updated analysis of the costs to
adequately cover the cost of active remediation of the contamination at this site. Actual costs
might vary from this estimate for a variety of reasons including changes in laws and changes in
the assessment of the level of remediation actually required at this site. Therefore, future
changes in laws or the assessment of the level of remediation required could result in changes in
our estimate of the required liability. Refer to the discussion of Commitments and Contingencies
included in the Notes to Financial Statements on page 37 of this 2010 Annual Report.
Warranty Reserve — We have a warranty liability recorded related to our exposure to
warranty claims in the event our products fail to perform as expected, and we may be required to
participate in a recall of such products. The recorded warranty liability balance involves judgment
and estimates. Our liability estimate is based on an analysis of historical warranty data as well
as current trends and information, including our customers’ recent extension of their warranty
programs. Actual warranty costs might vary from estimates due to the level of actual claims varying
from our claims experience and estimates. Therefore, future actual claims experience could result
in changes in our estimate of the required liability. Refer to the discussion of Warranty Reserve
under Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies included in the Notes to
Financial Statements on page 34 of this 2010 Annual Report.
Incurred But Not Reported Claim Reserve for Self-Insured Health plans and Workers’
Compensation Reserve — We have self-insured medical and dental plans covering all eligible U.S.
associates. We also maintain an insured workers’ compensation program covering all U.S.
associates. The insurance is renewed annually and may be covered under a loss sensitive plan.
Under a loss sensitive plan, the ultimate cost is dependent upon losses incurred during the policy
period. The incurred loss amount for loss sensitive policies will continue to change as claims
develop and are settled in future periods. The expected ultimate cost of claims incurred under
these plans is subject to judgment and estimation. We estimate the ultimate expected cost of
claims incurred under these plans based upon the aggregate liability for reported claims and an
estimated additional liability for claims incurred but not reported. Our estimate of claims
incurred but not reported is based on an analysis of historical data, current trends related to
claims and health care costs and information available from the insurance carrier. Actual ultimate
costs may vary from estimates due to variations in actual claims experience from past trends and
large unexpected claims being filed. Therefore, changes in claims experience and large unexpected
claims could result in changes to our estimate of the claims incurred but not reported
liabilities. Refer to the discussion of Self Insurance and Loss Sensitive Plans under Organization
and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies included in Notes to Financial Statements on page
33 of this 2010 Annual Report.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Related to Trade Accounts Receivable — Our trade accounts
receivable consist primarily of receivables due from Original Equipment Manufacturers in the
automotive industry and locksmith distributors relating to our service and aftermarket business.
Our evaluation of the collectability of our trade accounts receivable involves judgment and
estimates and includes a review of past due items, general economic conditions and the economic
climate of the industry as a whole. The estimate of the required reserve involves uncertainty as
to future collectability of receivable balances. This uncertainty is magnified by the financial
difficulty currently experienced by our customers as discussed under Risk-Factors-Loss of
Significant Customers, Vehicle Content, Vehicle Models and Market Share on page 22 of this 2010
Annual Report. Refer to the discussion of Receivables under Organization and Summary of
Significant Accounting Policies included in Notes to Financial Statements on page 30 of this 2010
Annual Report. We increased our allowance for uncollectible trade accounts receivable by $500,000
during 2009 in connection with Chrysler LLC’s filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection for
certain of their U.S. legal entities on April 30, 2009. General Motors filed for Chapter 11
bankruptcy protection for their U.S. legal entities on June 1, 2009. The bankruptcy filings did
not significantly impact the collection of pre-bankruptcy receivable balances as both Companies
were able to continue to make payments to suppliers for parts they had purchased prior to their
bankruptcy filings. All receivables related to the bankruptcy filings which we assumed to be
uncollectible were written off against the $500,000 reserve. However, as a result of subsequent
payments received from Chrysler as of December 2009, $421,000 of the $500,000 provision was
recorded as a recovery of allowance for doubtful accounts during 2010.
Repair and Maintenance Supply Parts Reserve — We maintain an inventory of repair and
maintenance parts in support of operations. The inventory includes critical repair parts for all
production equipment as well as general maintenance items. The inventory of critical repair parts
is required to avoid disruptions in our customers’ just-in-time production schedules due to lack
of spare parts when equipment break-downs occur. Depending on maintenance requirements during the
life of the equipment, excess quantities of repair parts arise. A repair and maintenance supply
parts reserve is maintained to recognize the normal adjustment of inventory for obsolete and
slow-moving repair and maintenance supply parts. Our evaluation of the reserve level involves
judgment and estimates, which are based on a review of historical obsolescence and current
inventory levels. Actual obsolescence may differ from estimates due to actual maintenance
requirements differing from historical levels. This could result in changes to our estimated
required reserve. Refer to the discussion of Repair and Maintenance Supply Parts under
Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies included in the Notes to Financial
Statements on page 31 of this 2010 Annual Report.
We believe the reserves discussed above are estimated using consistent and
appropriate methods. However, changes to the assumptions could materially affect the
recorded reserves.
Stock-Based Compensation — Stock-based compensation cost is measured at the grant date based
on the value of the award and is recognized as expense over the vesting period. Determining the
fair value of stock-based awards at the grant date requires judgment, including estimating future
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 21 |

MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
volatility of our stock, the amount of stock-based awards that are expected to be forfeited
and the expected term of awards granted. We estimate the fair value of stock options granted using
the Black-Scholes option valuation model. We amortize the fair value of all awards on a
straight-line basis over the vesting periods. The expected term of awards granted represents the
period of time they are expected to be outstanding. We determine the expected term based on
historical experience with similar awards, giving consideration to the contractual terms and
vesting schedules. We estimate the expected volatility of our common stock at the date of grant
based on the historical volatility of our common stock. The volatility factor used in the
Black-Scholes option valuation model is based on our historical stock prices over the most recent
period commensurate with the estimated expected term of the award. We base the risk-free interest
rate used in the Black-Scholes option valuation model on the implied yield currently available on
U.S. Treasury zero-coupon issues with a remaining term commensurate with the expected term of the
award. We use historical data to estimate pre-vesting option forfeitures. We record stock-based
compensation only for those awards that are expected to vest. If actual results differ
significantly from these estimates, stock-based compensation expense and our results of operations
could be materially impacted.
RISK FACTORS
We recognize we are subject to the following risk factors based on our operations and
the nature of the automotive industry in which we operate:
Loss of Significant Customers, Vehicle Content, Vehicle Models and Market Share —
Sales to General Motors Company, Ford Motor Company and Chrysler Group LLC represented
approximately 67 percent of our annual net sales (based on fiscal 2010 results) and, accordingly,
these customers account for a significant percentage of our outstanding accounts receivable. The
contracts with these customers provide for supplying the customer’s requirements for a particular
model. The contracts do not specify a specific quantity of parts. The contracts typically cover
the life of a model, which averages approximately four to five years. Components for certain
customer models may also be “market tested” annually. Therefore, the loss of any one of these
customers, the loss of a contract for a specific vehicle model, reduction in vehicle content,
early cancellation of a specific vehicle model, technological changes or a significant reduction
in demand for certain key models could occur, and if so, could have a material adverse effect on
our existing and future revenues and net income.
On April 27, 2009, General Motors announced certain aspects of its Revised Viability Plan
including reduced production volumes for calendar year 2009 and the subsequent five years. The
announcement indicated that certain vehicle brands, including Pontiac, Saturn, Hummer and Saab,
would be discontinued or sold. In addition, subsequent to Chrysler LLC’s filing for Chapter 11
bankruptcy protection on April 30, 2009, they announced certain vehicle models planned for
discontinuation (including Jeep Commander, Jeep Compass, Jeep Patriot, Dodge Nitro, Dodge Avenger,
Dodge Caliber, Dodge Durango, Dodge Dakota, Dodge Viper, Chrysler Sebring, Chrysler Aspen etc.).
Subsequently, certain models have been reaffirmed for continued production over the next two years.
We will continue to evaluate the impact these evolving plans have on our business as more details
become available.
Our major customers also have significant under-funded legacy liabilities related to pension
and postretirement health care obligations. The future impact of these items along with a
continuing loss in their North American automotive market share to the “New Domestic” automotive
manufacturers (primarily the Japanese automotive manufacturers) and/or a significant decline in
the overall market demand for new vehicles may ultimately result in severe financial difficulty
for these customers, including bankruptcy. If our major customers cannot fund their operations, we
may incur significant write-offs of accounts receivable, incur impairment charges or require
additional restructuring actions. For example, on October 8, 2005, Delphi Corporation filed for
Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection. As a result, we wrote-off $1.6 million of uncollectible
pre-petition Chapter 11 accounts receivable due from Delphi Corporation. This directly reduced our
pre-tax net income during fiscal 2006. On April 30, 2009, Chrysler LLC filed for Chapter 11
bankruptcy protection for certain of their U.S. legal entities. As discussed under Critical
Accounting Policies — Other Reserves — Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Related to Trade Accounts
Receivable herein, during fiscal year 2009 we recorded a provision for bad debts of $500,000
related to this filing, of which we subsequently recovered $421,000 of the $500,000 provision
during fiscal 2010. This directly reduced our pre-tax net income during 2009 by $500,000 and
increased our pre-tax net income during 2010 by $421,000.
Production Slowdowns for Customers — Our major customers and many of their suppliers have
been significantly impacted by the recession of 2008/2009. Many of our major customers have
instituted production cuts during fiscal 2009 and fiscal 2010 as a result of this recession.
Moreover, certain of our major customers have announced plans to continue these production cuts
into future fiscal years. For example, during April 2009, General Motors Corporation announced
assembly plant downtime for the months of May through July in order to reduce excess inventories
at their dealer locations. Consequently, this downtime reduced our production schedules and
affected both our sales and profitability for our fiscal fourth quarter ending June 28, 2009 and
our fiscal 2010 first quarter ending September 27, 2009. Additionally, on April 27, 2009, General
Motors announced some aspects of its Revised Viability Plan including reduced production volumes
for the remainder of calendar 2009 and the subsequent five calendar years. The continuation of
these production cuts could have a material adverse effect on our existing and future revenues and
net income.
Financial Distress of Automotive Supply Base — Automotive industry conditions have adversely
affected STRATTEC and our supply base. Lower production levels at our major customers, volatility
in certain raw material and energy costs and the global credit market crisis have resulted in
severe financial distress among many companies within the automotive supply base. During calendar
year 2009, several automotive suppliers filed for bankruptcy protection or ceased operations. The
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 22 |
MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
continuation of financial distress within the supply base and suppliers’ inability to obtain
credit from lending institutions may lead to commercial disputes and possible supply chain
interruptions. In addition, the adverse industry environment may require us to take measures to
ensure uninterrupted production. The continuation or worsening of these industry conditions could
have a material adverse effect on our existing and future revenues and net income.
Shortage of Raw Materials or Components Supply — In the event of a rapid increase in
production demands, either we or our customers or other suppliers may experience supply shortages
of raw materials or components. This could be caused by a number of factors, including a lack of
production line capacity or manpower or working capital constraints. In order to manage and reduce
the cost of purchased goods and services, we and others within our industry have been
rationalizing and consolidating our supply base. In addition, due to the recent turbulence in the
automotive industry, several suppliers have initiated bankruptcy proceedings or ceased operations.
As a result, there is greater dependence on fewer sources of supply for certain components and
materials, which could increase the possibility of a supply shortage of any particular component.
If any of our customers experience a material supply shortage, either directly or as a result of a
supply shortage at another supplier, that customer may halt or limit the purchase of our products.
Similarly, if we or one of our own suppliers experience a supply shortage we may become unable to
produce the affected products if we cannot procure the components from another source. Such
production interruptions could impede a ramp-up in vehicle production and could have a material
adverse effect on our business, results of operations and financial condition.
We consider the production capacities and financial condition of suppliers in our
selection process, and expect that they will meet our delivery requirements. However, there can be
no assurance that strong demand, capacity limitations, shortages of raw materials or other
problems will not result in any shortages or delays in the supply of components to us.
Cost Reduction — There is continuing pressure from our major customers to reduce the prices
we charge for our products. This requires us to generate cost reductions, including reductions in
the cost of components purchased from outside suppliers. If we are unable to generate sufficient
production cost savings in the future to offset pre-programmed price reductions, our gross margin
and profitability will be adversely affected.
Cyclicality and Seasonality in the Automotive Market — The automotive market is cyclical and
is dependent on consumer spending, on the availability of consumer credit and, to a certain
extent, on customer sales incentives. Economic factors adversely affecting consumer demand for
automobiles and automotive production, such as rising fuel costs, could adversely impact our net
sales and net income. We typically experience decreased sales and operating income during the
first fiscal quarter of each year due to the impact of scheduled customer plant shut-downs in July
and new model changeovers.
Foreign Operations — As discussed under “Joint Ventures,” we have joint venture
investments in Mexico, Brazil and China. As these operations continue to expand, their success
will depend, in part, on our and our partners’ ability to anticipate and effectively manage
certain risks inherent in international operations including: enforcing agreements and collecting
receivables through certain foreign legal systems, payment cycles of foreign customers, compliance
with foreign tax laws, general economic and political conditions in these countries and compliance
with foreign laws and regulations.
Currency Exchange Rate Fluctuations — We incur a portion of our expenses in
Mexican pesos. Exchange rate fluctuations between the U.S. dollar and the Mexican peso could
have an adverse effect on our financial results.
Sources of and Fluctuations in Market Prices of Raw Materials — Our primary raw materials
are high-grade zinc, brass, magnesium, aluminum, steel and plastic resins. These materials are
generally available from a number of suppliers, but we have chosen to concentrate our sourcing
with one primary vendor for each commodity or purchased component. We believe our sources of raw
materials are reliable and adequate for our needs. However, the development of future sourcing
issues related to using existing or alternative raw materials and the global availability of these
materials as well as significant fluctuations in the market prices of these materials may have an
adverse affect on our financial results if the increased raw material costs cannot be recovered
from our customers.
Given the significant financial impact on us relating to changes in the cost of our primary
raw materials, commencing with fiscal 2008, we began quoting quarterly material price adjustments
for changes in our raw material costs in our negotiations with our customers. Our success in
obtaining these quarterly price adjustments in our customer contracts is dependent on separate
negotiations with each customer. It is not a standard practice for our customers to include such
price adjustments in their contracts. We have been successful in obtaining quarterly price
adjustments in some of our customer contracts. However, we have not been successful in obtaining
the adjustments with all of our customers.
Disruptions Due to Work Stoppages and Other Labor Matters — Our major customers and
many of their suppliers have unionized work forces. Work stoppages or slow-downs experienced by our
customers or their suppliers could result in slow-downs or closures of assembly plants where our
products are included in assembled vehicles. For example, strikes at a critical supplier called by
the United Auto Workers led to extended shut-downs of most of General Motors’ North American
assembly plants in February 2008 and in 1998. A material work stoppage experienced by one or more
of our customers could have an adverse effect on our business and our financial results. In
addition, all production associates at our Milwaukee facility are unionized. A sixteen-day strike
by these associates in June 2001 resulted in increased costs as all salaried associates worked with
additional outside
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 23 |

MANAGEMENT’S DISCUSSION AND ANALYSIS
resources to produce the components necessary to meet customer requirements. The current
contract with the unionized associates is effective through June 29, 2014. We may encounter
further labor disruption after the expiration date of this contract and may also encounter
unionization efforts in our other plants or other types of labor conflicts, any of which could
have an adverse effect on our business and our financial results.
Environmental and Safety Regulations — We are subject to Federal, state, local and
foreign laws and other legal requirements related to the generation, storage, transport, treatment
and disposal of materials as a result of our manufacturing and assembly operations. These laws
include the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act (as amended), the Clean Air Act (as amended)
and the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation and Liability Act (as amended). We have
an environmental management system that is ISO-14001 certified. We believe that our existing
environmental management system is adequate for current and anticipated operations and we have no
current plans for substantial capital expenditures in the environmental area. An environmental
reserve was established in 1995 for estimated costs to remediate a site at our Milwaukee facility.
The site was contaminated by a former above-ground solvent storage tank, located on the east side
of the facility. The contamination occurred in 1985. The site is being monitored in accordance
with Federal, state and local requirements. Refer to discussion under Analysis of Results of
Operations for additional information on this environmental reserve. We do not currently
anticipate any material adverse impact on our results of operations, financial condition or
competitive position as a result of compliance with Federal, state, local and foreign
environmental laws or other legal requirements. However, risk of environmental liability and
changes associated with maintaining compliance with environmental laws is inherent in the nature
of our business and there is no assurance that material liabilities or changes could not arise.
Highly Competitive Automotive Supply Industry — The automotive component supply
industry is highly competitive. Some of our competitors are companies, or divisions or
subsidiaries of companies, that are larger than STRATTEC and have greater financial and technology
capabilities. Our products may not be able to compete successfully with the products of these
other companies, which could result in loss of customers and, as a result, decreased sales and
profitability. Some of our major customers have also announced that they will be reducing their
supply base. This could potentially result in the loss of these customers and consolidation within
the supply base. The loss of any of our major customers could have a material adverse effect on
our existing and future net sales and net income.
In addition, our competitive position in the North American automotive component supply
industry could be adversely affected in the event that we are unsuccessful in making strategic
acquisitions, alliances or establishing joint ventures that would enable us to expand globally. We
principally compete for new business at the beginning of the development of new models and upon
the redesign of existing models by our major customers. New model development generally begins two
to five years prior to the marketing of such new models to the public. The failure to obtain new
business on new models or to retain or increase business on redesigned existing models could
adversely affect our business and financial results. In addition, as a result of relatively long
lead times for many of our components, it may be difficult in the short-term for us to obtain new
sales to replace any unexpected decline in the sale of existing products. Finally, we may incur
significant product development expense in preparing to meet anticipated customer requirements
which may not be recovered.
Program Volume and Pricing Fluctuations — We incur costs and make capital expenditures for
new program awards based upon certain estimates of production volumes over the anticipated program
life for certain vehicles. While we attempt to establish the price of our products for variances
in production volumes, if the actual production of certain vehicle models is significantly less
than planned, our net sales and net income may be adversely affected. We cannot predict our
customers’ demands for the products we supply either in the aggregate or for particular reporting
periods.
Investments in Customer Program Specific Assets — We make investments in machinery and
equipment used exclusively to manufacture products for specific customer programs. This machinery
and equipment is capitalized and depreciated over the expected useful life of each respective
asset. Therefore, the loss of any one of our major customers, the loss of specific vehicle models
or the early cancellation of a vehicle model could result in impairment in the value of these
assets which may have a material adverse effect on our financial results.
Financial Industry / Credit Market Risk — The U.S. capital and credit markets have been
experiencing volatility and disruption for over a year. In many cases this has resulted in
pressures on borrowers and reduced credit availability from certain issuers without regard to the
underlying financial strength of the borrower or issuer. If current levels of financial market
disruption and volatility continue or worsen, there can be no assurance that such conditions will
not have an effect on the Company’s ability to access debt and, in turn, result in a material
adverse effect on the Company’s business, financial condition and results of operations.
Warranty Claims — We are exposed to warranty claims in the event that our products fail
to perform as expected, and we may be required to participate in a recall of such products. Our
largest customers have recently extended their warranty protection for their vehicles. Other OEMs
have similarly extended their warranty programs. This trend will put additional pressure on the
supply base to improve quality systems. This trend may also result in higher cost recovery claims
by OEM’s from suppliers whose products incur a higher rate of warranty claims. Historically, we
have experienced relatively low warranty charges from our customers due to our commercial
arrangements and improvements in the quality, reliability and durability of our products. If our
customers demand higher warranty-related cost recoveries, or if our products fail to perform as
expected, it could have a material adverse impact on our results of operations and financial
condition.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 24 |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT PER SHARE AMOUNTS)
| Years Ended | ||||||||||||
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | June 29, 2008 | ||||||||||
NET SALES |
$ | 207,964 | $ | 126,097 | $ | 159,642 | ||||||
Cost of goods sold |
174,922 | 112,857 | 134,875 | |||||||||
GROSS PROFIT |
33,042 | 13,240 | 24,767 | |||||||||
Engineering, selling, and administrative expenses |
29,939 | 25,480 | 23,962 | |||||||||
Impairment charge |
223 | — | — | |||||||||
Environmental Reserve Adjustment |
(1,125 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
(Recovery of) Provision for doubtful accounts |
(421 | ) | 500 | — | ||||||||
INCOME (LOSS) FROM OPERATIONS |
4,426 | (12,740 | ) | 805 | ||||||||
Interest income |
86 | 731 | 2,749 | |||||||||
Equity earnings of joint ventures |
1,008 | 245 | 561 | |||||||||
Interest expense-related parties |
(225 | ) | (164 | ) | (31 | ) | ||||||
Other income (expense), net |
312 | 804 | (300 | ) | ||||||||
INCOME (LOSS) BEFORE PROVISION FOR INCOME
TAXES AND NON-CONTROLLING INTEREST |
5,607 | (11,124 | ) | 3,784 | ||||||||
Provision (benefit) for income taxes |
1,666 | (4,222 | ) | 977 | ||||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) |
3,941 | (6,902 | ) | 2,807 | ||||||||
Net (income) loss attributable to non-controlling
interest |
(520 | ) | 780 | (26 | ) | |||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) ATTRIBUTABLE TO
STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION |
$ | 3,421 | $ | (6,122 | ) | $ | 2,781 | |||||
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS): |
||||||||||||
NET INCOME (LOSS) |
$ | 3,941 | $ | (6,902 | ) | $ | 2,807 | |||||
Change in cumulative translation adjustments |
503 | (2,505 | ) | 717 | ||||||||
Pension funded status adjustment, net of tax |
(1,346 | ) | (11,114 | ) | (3,868 | ) | ||||||
TOTAL OTHER COMPREHENSIVE LOSS |
(843 | ) | (13,619 | ) | (3,151 | ) | ||||||
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS) |
3,098 | (20,521 | ) | (344 | ) | |||||||
Comprehensive (income) loss attributed to
non controlling interest |
(525 | ) | 800 | (29 | ) | |||||||
COMPREHENSIVE INCOME (LOSS)
ATTRIBUTABLE TO STRATTEC
SECURITY CORPORATION |
$ | 2,573 | $ | (19,721 | ) | $ | (373 | ) | ||||
EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE: |
||||||||||||
BASIC |
$ | 1.05 | $ | (1.87 | ) | $ | 0.80 | |||||
DILUTED |
$ | 1.04 | $ | (1.86 | ) | $ | 0.80 | |||||
AVERAGE SHARES OUTSTANDING: |
||||||||||||
BASIC |
3,271 | 3,280 | 3,487 | |||||||||
DILUTED |
3,280 | 3,284 | 3,494 | |||||||||
The year ended June 29, 2008 has been retrospectively adjusted for our change in 2009 from
the last-in, first-out method of inventory accounting to the first-in, first-out method.
Additional details are available in Notes to Financial Statements.
The accompanying Notes to Financial Statements are an integral part of these Consolidated
Statements of Operations and Comprehensive Income (Loss).
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 25 |

CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT SHARE AMOUNTS AND PER SHARE AMOUNTS)
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | |||||||
ASSETS |
||||||||
CURRENT ASSETS: |
||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 21,867 | $ | 22,764 | ||||
Receivables, less allowance for doubtful accounts
of $400 at June 27, 2010 and $750 at June 28, 2009 |
36,084 | 17,235 | ||||||
Restricted cash |
2,100 | — | ||||||
Inventories |
17,086 | 16,589 | ||||||
Customer tooling in progress |
3,439 | 1,714 | ||||||
Deferred income taxes |
2,133 | 2,124 | ||||||
Income taxes recoverable |
— | 1,181 | ||||||
Other current assets |
7,299 | 10,951 | ||||||
Total current assets |
90,008 | 72,558 | ||||||
DEFERRED INCOME TAXES |
10,534 | 13,143 | ||||||
INVESTMENT IN JOINT VENTURES |
5,176 | 4,483 | ||||||
LOAN TO JOINT VENTURE |
1,500 | — | ||||||
OTHER LONG-TERM ASSETS |
733 | 1,069 | ||||||
PROPERTY, PLANT AND EQUIPMENT, NET |
37,051 | 36,936 | ||||||
| $ | 145,002 | $ | 128,189 | |||||
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
||||||||
CURRENT LIABILITIES: |
||||||||
Accounts payable |
$ | 21,192 | $ | 11,369 | ||||
Loans from related parties |
3,000 | 3,225 | ||||||
Accrued liabilities: |
||||||||
Payroll and benefits |
15,496 | 8,232 | ||||||
Environmental |
1,497 | 2,636 | ||||||
Income taxes |
63 | — | ||||||
Other |
4,983 | 5,386 | ||||||
Total current liabilities |
46,231 | 30,848 | ||||||
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES — see note on page 37 |
||||||||
BORROWINGS UNDER LINE OF CREDIT |
— | — | ||||||
ACCRUED PENSION OBLIGATIONS |
18,492 | 15,183 | ||||||
ACCRUED POSTRETIREMENT OBLIGATIONS |
4,490 | 9,601 | ||||||
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY: |
||||||||
Common stock, authorized 12,000,000 shares, $.01 par value,
issued 6,909,357 shares at June 27, 2010 and
6,897,957 shares at June 28, 2009 |
69 | 69 | ||||||
Capital in excess of par value |
79,339 | 79,247 | ||||||
Retained earnings |
162,706 | 159,285 | ||||||
Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(31,941 | ) | (31,094 | ) | ||||
Less: Treasury stock at cost (3,633,402 shares at
June 27, 2010 and 3,635,989 shares at June 28, 2009) |
(136,047 | ) | (136,089 | ) | ||||
Total STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION shareholders’ equity |
74,126 | 71,418 | ||||||
Non-controlling interest |
1,663 | 1,139 | ||||||
Total shareholders’ equity |
75,789 | 72,557 | ||||||
| $ | 145,002 | $ | 128,189 | |||||
The accompanying Notes to Financial Statements are an integral part of these Consolidated
Balance Sheets.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 26 |
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
(IN THOUSANDS, EXCEPT PER SHARE AMOUNTS)
| Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capital in | Other | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common | Excess of | Retained | Comprehensive | Treasury | Non-controlling | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Stock | Par Value | Earnings | Loss | Stock | Interest | ||||||||||||||||||||||
BALANCE JULY 1, 2007 |
$ | 106,529 | $ | 69 | $ | 78,122 | $ | 168,922 | $ | (14,341 | ) | $ | (126,818 | ) | $ | 575 | ||||||||||||
Net Income |
2,807 | — | — | 2,781 | — | — | 26 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Translation adjustments |
717 | — | — | — | 714 | — | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Contribution from
non-controlling interest |
349 | — | — | — | — | — | 349 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Pension and postretirement
funded status adjustment,
net of tax of $2,371 |
(3,868 | ) | — | — | — | (3,868 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of common stock |
(3,109 | ) | — | — | — | — | (3,109 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Cash dividends declared
($1.60 per share) |
(5,652 | ) | — | — | (5,652 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation,
including tax benefit on
restricted stock dividends
of $13 |
745 | — | 745 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Adoption of accounting for
uncertain tax positions |
346 | — | — | 346 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Employee stock purchases |
29 | — | 18 | — | — | 11 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
BALANCE JUNE 29, 2008 |
$ | 98,893 | $ | 69 | $ | 78,885 | $ | 166,397 | $ | (17,495 | ) | $ | (129,916 | ) | $ | 953 | ||||||||||||
Net loss |
(6,902 | ) | — | — | (6,122 | ) | — | — | (780 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Translation adjustments |
(2,505 | ) | — | — | — | (2,485 | ) | — | (20 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
Contribution from
non-controlling interest |
986 | — | — | — | — | — | 986 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Pension and postretirement
funded status adjustment,
net of tax of $6,812 |
(11,114 | ) | — | — | — | (11,114 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Purchase of common stock |
(6,214 | ) | — | — | — | — | (6,214 | ) | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Cash dividends declared
($0.30 per share) |
(990 | ) | — | — | (990 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock-Based Compensation,
including tax benefit on
restricted stock dividends
of $5 |
363 | — | 363 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Employee stock purchases |
40 | — | (1 | ) | — | — | 41 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||
BALANCE June 28, 2009 |
$ | 72,557 | $ | 69 | $ | 79,247 | $ | 159,285 | $ | (31,094 | ) | $ | (136,089 | ) | $ | 1,139 | ||||||||||||
Net income |
3,941 | — | — | 3,421 | — | — | 520 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Translation adjustments |
503 | — | — | — | 499 | — | 4 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Pension and postretirement
funded status adjustment,
net of tax of $825 |
(1,346 | ) | — | — | — | (1,346 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Share of premium on
equity method ownership |
(409 | ) | — | (409 | ) | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based compensation |
464 | — | 464 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Stock Option Exercises |
35 | — | 35 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Employee stock purchases |
44 | — | 2 | — | — | 42 | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
BALANCE June 27, 2010 |
$ | 75,789 | $ | 69 | $ | 79,339 | $ | 162,706 | $ | (31,941 | ) | $ | (136,047 | ) | $ | 1,663 | ||||||||||||
The year ended June 29, 2008 has been retrospectively adjusted for our change in
2009 from the last-in, first-out method of inventory accounting to the first-in,
first-out method. Additional details are available in Notes to Financial Statements.
The accompanying Notes to Financial Statements are an integral part of these
Consolidated Statements of Shareholders’ Equity.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 27 |

CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
(IN THOUSANDS)
| Years Ended | ||||||||||||
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | June 29, 2008 | ||||||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM OPERATING ACTIVITIES |
||||||||||||
Net Income (Loss) |
$ | 3,421 | $ | (6,122 | ) | $ | 2,781 | |||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income (loss) to
net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
Non-controlling interest |
520 | (780 | ) | 26 | ||||||||
Equity earnings in joint ventures |
(1,008 | ) | (245 | ) | (561 | ) | ||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
7,143 | 6,264 | 6,830 | |||||||||
Foreign currency transaction loss (gain) |
283 | (918 | ) | 320 | ||||||||
Loss on disposition of property, plant and
equipment |
50 | 39 | 434 | |||||||||
Deferred income taxes |
3,428 | (2,986 | ) | 622 | ||||||||
Stock-based compensation expense |
468 | 419 | 741 | |||||||||
(Recovery) provision for doubtful accounts |
(421 | ) | 500 | — | ||||||||
Impairment charge |
223 | — | — | |||||||||
Environmental reserve adjustment |
(1,125 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Loss on curtailment of employee benefits |
505 | — | — | |||||||||
Change in operating assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
Receivables |
(18,301 | ) | 5,235 | 3,465 | ||||||||
Inventories |
(497 | ) | 1,033 | (2,319 | ) | |||||||
Other assets |
3,181 | (1,966 | ) | (8,413 | ) | |||||||
Accounts payable and accrued liabilities |
12,192 | (7,326 | ) | 163 | ||||||||
Other, net |
3 | 17 | (271 | ) | ||||||||
Net cash provided (used) by operating activities |
10,065 | (6,836 | ) | 3,818 | ||||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM INVESTING ACTIVITIES |
||||||||||||
Investment in joint ventures |
(100 | ) | (551 | ) | — | |||||||
Restricted cash |
(2,100 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Loan to joint venture |
(2,500 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Proceeds from repayment of loan to joint venture |
1,000 | — | — | |||||||||
Additions to property, plant and equipment |
(6,903 | ) | (12,492 | ) | (10,930 | ) | ||||||
Purchase of Delphi Power Products |
— | (4,931 | ) | — | ||||||||
Proceeds received on sale of property, plant and equipment |
21 | 8 | — | |||||||||
Net cash used in investing activities |
(10,582 | ) | (17,966 | ) | (10,930 | ) | ||||||
CASH FLOWS FROM FINANCING ACTIVITIES |
||||||||||||
Purchase of common stock |
— | (6,214 | ) | (3,109 | ) | |||||||
Exercise of stock options and employee stock
purchases |
72 | 40 | 29 | |||||||||
Excess tax benefits from stock-based compensation |
9 | — | — | |||||||||
Dividends paid |
— | (1,511 | ) | (5,133 | ) | |||||||
Loan from related parties |
— | 2,175 | 1,050 | |||||||||
Repayment of loan from related parties |
(225 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Contribution from minority interest |
— | 986 | 349 | |||||||||
Net cash used in financing activities |
(144 | ) | (4,524 | ) | (6,814 | ) | ||||||
FOREIGN CURRENCY IMPACT ON CASH |
(236 | ) | 589 | (64 | ) | |||||||
NET DECREASE IN CASH
AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
(897 | ) | (28,737 | ) | (13,990 | ) | ||||||
CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS |
||||||||||||
Beginning of year |
22,764 | 51,501 | 65,491 | |||||||||
End of year |
$ | 21,867 | $ | 22,764 | $ | 51,501 | ||||||
SUPPLEMENTAL DISCLOSURE OF
CASH FLOW INFORMATION |
||||||||||||
Income taxes (recovered) paid |
$ | (2,963 | ) | $ | (1,869 | ) | $ | 3,238 | ||||
Interest paid — related parties |
250 | 107 | 13 | |||||||||
The year ended June 29, 2008 has been retrospectively adjusted for our change in 2009 from the
last-in, first-out method of inventory accounting to the first-in, first-out method. Additional
details are available in Notes to Financial Statements.
The accompanying Notes to Financial Statements are an integral part of these Consolidated
Statements of Cash Flows.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 28 |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
ORGANIZATION AND SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION designs, develops, manufactures and markets automotive
security products including mechanical locks and keys, electronically enhanced locks and keys, and
ignition lock housings; and access control products including latches, power sliding side door
systems, power lift gate systems, power deck lid systems, door handles and related access control
products for North American automotive customers. We also supply global automotive manufacturers
through the VAST Alliance (“VAST ALLIANCE”) in which we participate with WITTE Automotive of
Velbert, Germany and ADAC Automotive of Grand Rapids, Michigan. Our products are shipped to
customer locations in the United States, Canada, Mexico, Europe, South America, Korea and China,
and we provide full service and aftermarket support.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements reflect the consolidated results of
STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION, its wholly owned Mexican subsidiary, STRATTEC de Mexico, and its
majority owned subsidiaries, ADAC-STRATTEC, LLC and STRATTEC POWER ACCESS LLC. STRATTEC SECURITY
CORPORATION is located in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. STRATTEC de Mexico is located in Juarez, Mexico.
ADAC-STRATTEC, LLC and STRATTEC POWER ACCESS LLC have operations in El Paso, Texas and Juarez,
Mexico. Equity investments in Vehicle Access Systems Technology LLC (“VAST LLC”) for which we
exercise significant influence but do not control and are not the primary beneficiary, are
accounted for using the equity method. VAST LLC consists primarily of two wholly owned
subsidiaries in China and one joint venture in Brazil. STRATTEC has only one reporting segment.
The significant accounting policies followed in the preparation of these financial
statements, as summarized in the following paragraphs, are in conformity with accounting
principles generally accepted in the United States of America (U.S. GAAP).
Purchase of Delphi Power Products Business: Effective November 30, 2008, STRATTEC
SECURITY CORPORATION, in combination with WITTE Automotive of Velbert, Germany, completed the
acquisition of certain assets, primarily equipment and inventory, and assumption of certain
employee liabilities of Delphi Corporation’s Power Products business for approximately $7.3
million. For purposes of owning and operating the North American portion of this acquired business,
STRATTEC established a new subsidiary, STRATTEC POWER ACCESS LLC (“SPA”), which is 80 percent owned
by STRATTEC and 20 percent owned by WITTE. The purchase price of the North American portion of the
acquired business totaled approximately $4.4 million, of which STRATTEC paid approximately $3.5
million. WITTE acquired the European portion of the business for approximately $2.4 million.
Effective February 12, 2009, SPA acquired the Asian portion of the business for approximately
$500,000.
The acquisition of the North American and Asian portions of this business by SPA was not
material to STRATTEC’s consolidated financial statements. Amortizable intangible assets acquired
totaled $890,000 and are subject to amortization over a period of nine years. In addition,
goodwill of approximately $223,000 was recorded as part of the transaction. The amortizable
intangibles and goodwill are included in Other Long-Term Assets in the Consolidated Balance
Sheets. Refer to Goodwill and Other Intangibles discussed on page 31 of this 2010 Annual Report.
The financial results of SPA are consolidated with the financial results of STRATTEC
and resulted in increased net income to STRATTEC of approximately $545,000 during fiscal 2010
and decreased net income to STRATTEC of approximately $2.1 million during fiscal 2009.
SPA designs, develops, tests, manufactures, markets and sells power systems to operate
vehicle sliding side doors and rear compartment access points such as liftgates and trunk lids.
In addition, the product line includes power cinching latches and cinching strikers used in
these systems. Current customers for these products supplied from North America are Chrysler
Group LLC, Hyundai Kia Automotive Group, General Motors Company, Ford Motor Company and Yulon
Group.
Principles of Consolidation and Presentation: The accompanying consolidated financial
statements include the accounts of STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION, its wholly owned Mexican
subsidiaries, and its majority owned subsidiaries. Equity investments for which STRATTEC exercises
significant influence but does not control and is not the primary beneficiary are accounted for
using the equity method. All significant inter-company transactions and balances have been
eliminated.
Reclassifications: Certain reclassifications have been made to the 2008 and 2009
financial statements to conform to the 2010 presentation, including the adoption of a new
accounting standard issued by the Financial Accounting Standards Board (“FASB”) related to
non-controlling interests in consolidated financial statements, which required retrospective
adjustment to the presentation of prior year financial information and disclosures, and separate
presentation of components of other income (expense), net. These reclassifications did not impact
previously reported net income (loss) or retained earnings amounts. In addition, reclassifications
have been made to the 2008 financial statements as a result of our change in accounting for
inventories from the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method to the first-in, first-out (FIFO) method.
Additional details are included under “Inventories” herein. The FASB Accounting Standards
Codification (“ASC”) was also adopted during fiscal 2010. The adoption of the ASC did not result
in any restatements of previously reported financial statements.
Fiscal Year: Our fiscal year ends on the Sunday nearest June 30. The years ended June 27,
2010, June 28, 2009 and June 29, 2008 are each comprised of 52 weeks.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 29 |

NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Use of Estimates: The preparation of financial statements in conformity with U.S. GAAP
requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets,
liabilities, revenues and expenses for the periods presented. These estimates and assumptions could
also affect the disclosure of contingencies. Actual results and outcomes may differ from
management’s estimates and assumptions.
Cash and Cash Equivalents: Cash and cash equivalents include all short-term investments with
an original maturity of three months or less due to the short-term nature of the instruments.
Excess cash balances are placed in a money market account at a high quality financial institution
and in short-term commercial paper.
Restricted Cash: Restricted cash consists of STRATTEC’s commercial guarantee of a $2.1
million stand-by letter of credit that was issued by VAST LLC related to future installment
payments for the November 2009 purchase of the remaining 40 percent interest of VAST China.
Fair Value of Financial Instruments: The fair value of our cash and cash equivalents,
accounts receivable, accounts payable and loans from related parties approximated book value as of
June 27, 2010 and June 28, 2009. Fair Value is defined as the exchange price that would be received
for an asset or paid for a liability (an exit price) in the principal or most advantageous market
for the asset or liability in an orderly transaction between market participants on the measurement
date. Valuation techniques used to measure fair value must maximize the use of observable inputs
and minimize the use of unobservable inputs. There is an established fair value hierarchy based on
three levels of inputs, of which the first two are considered observable and the last unobservable.
Level 1 — Quoted prices in active markets for identical assets or liabilities. These are typically
obtained from real-time quotes for transactions in active exchange markets involving identical
assets. Level 2 — Inputs, other than quoted prices included within Level 1, which are observable
for the asset or liability, either directly or indirectly. These are typically obtained from
readily-available pricing sources for comparable instruments. Level 3 — Unobservable inputs, where
there is little or no market activity for the asset or liability. These inputs reflect the
reporting entity’s own assumptions of the data that market participants would use in pricing the
asset or liability, based on the best information available in the circumstances. The following
table summarizes our financial assets and liabilities measured at fair value on a recurring basis
as of June 27, 2010 (thousands of dollars):
| Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | |||||||||||||
Rabbi Trust assets |
$ | 3,965 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 3,965 | ||||||||
The Rabbi Trust assets fund our supplemental executive retirement plan and are included
in Other Current Assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. Assets held in the Trust include U.S.
Treasury Securities, intermediate bond fund and large, medium and small-cap index funds.
Receivables: Receivables consist primarily of trade receivables due from Original
Equipment Manufacturers in the automotive industry and locksmith distributors relating to our
service and aftermarket business. We evaluate the collectability of receivables based on a number
of factors. An allowance for doubtful accounts is recorded for significant past due receivable
balances based on a review of the past due items, general economic conditions and the industry as
a whole. In 2009, we recorded a $500,000 provision for doubtful accounts in connection with
Chrysler LLC’s filing for Chapter 11 bankruptcy protection for certain of their U.S. legal
entities on April 30, 2009. All uncollectible receivables related to the bankruptcy were written
off against the $500,000 reserve during the current year. However, as a result of subsequent
payments received from Chrysler, $421,000 of the $500,000 provision was recorded as a recovery of
allowance for doubtful accounts during the current year. Changes in the allowance for doubtful
accounts are as follows (thousands of dollars):
| Balance, | (Recovery) Provision | Balance, | ||||||||||||||
| Beginning | for Doubtful | Net | End of | |||||||||||||
| of Year | Accounts | Recoveries | Year | |||||||||||||
Year ended June 27, 2010 |
$ | 750 | $ | (421 | ) | $ | 71 | $ | 400 | |||||||
Year ended June 28, 2009 |
$ | 250 | $ | 500 | $ | — | $ | 750 | ||||||||
Year ended June 29, 2008 |
$ | 250 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 250 | ||||||||
Inventories: Inventories are comprised of material, direct labor and manufacturing
overhead, and are stated at the lower of cost or market using the first-in, first-out (“FIFO”)
cost method of accounting. Prior to the fourth quarter of 2009, the majority of the inventories
were accounted for using the last-in, first-out (“LIFO”) method of accounting. During 2009, we
changed the method of accounting for this inventory from the LIFO method to the FIFO method. We
believe the FIFO method is a preferable method which better reflects the current cost of inventory
on our Consolidated Balance Sheets. After this change, all our inventories have a consistent
inventory costing method. All periods have been retrospectively adjusted on a FIFO basis.
Inventories consist of the following on a FIFO basis (thousands of dollars):
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | |||||||
Finished products |
$ | 3,653 | $ | 3,812 | ||||
Work in process |
4,260 | 3,432 | ||||||
Purchased materials |
9,173 | 9,345 | ||||||
| $ | 17,086 | $ | 16,589 | |||||
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 30 |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The following table summarizes the effect of the accounting change on our consolidated
financial statements for 2008 (thousands of dollars):
| 2008 | ||||||||
| Originally | As Computed | |||||||
| Reported | Under FIFO | |||||||
Consolidated Statement of Operations: |
||||||||
Cost of goods sold |
$ | 134,091 | $ | 134,875 | ||||
Provision for income taxes |
1,225 | 927 | ||||||
Net income attributable to STRATTEC |
||||||||
SECURITY CORPORATION |
3,267 | 2,781 | ||||||
Basic earnings per share |
0.94 | 0.80 | ||||||
Diluted earnings per share |
0.94 | 0.80 | ||||||
Consolidated Balance Sheet: |
||||||||
Inventories |
10,269 | 14,314 | ||||||
Deferred income taxes — current |
3,252 | 1,715 | ||||||
Retained earnings |
163,889 | 166,397 | ||||||
Consolidated Statement of Cash Flows: |
||||||||
Deferred income taxes |
920 | 622 | ||||||
Change in inventories |
(3,103 | ) | (2,319 | ) | ||||
Customer Tooling in Progress: We incur costs related to tooling used in component
production and assembly. Costs for development of certain tooling, which will be directly
reimbursed by the customer whose parts are produced from the tool, are accumulated on the balance
sheet and are then billed to the customer. The accumulated costs are billed upon formal acceptance
by the customer of products produced with the individual tool. Other tooling costs are not
directly reimbursed by the customer. These costs are capitalized and amortized over the life of
the related product based on the fact that the related tool will be used over the life of the
supply arrangement. To the extent that estimated costs exceed expected reimbursement from the
customer we will recognize a loss.
Repair and Maintenance Supply Parts: We maintain an inventory of repair and maintenance supply
parts in support of operations. This inventory includes critical repair parts for all production
equipment as well as general maintenance items. The inventory of critical repair parts is required
to avoid disruptions in our customers’ just-in-time production schedules due to a lack of spare
parts when equipment break-downs occur. All required critical repair parts are on hand when the
related production equipment is placed in service and maintained to satisfy the customer model life
production and service requirements, which may be 12 to 15 years. As repair parts are used,
additional repair parts are purchased to maintain a minimum level of spare parts inventory.
Depending on maintenance requirements during the life of the equipment, excess quantities of repair
parts arise. Excess quantities are kept on hand and are not disposed of until the equipment is no
longer in service. A repair and maintenance supply parts reserve is maintained to recognize the
normal adjustment of inventory for obsolete and slow moving supply and maintenance parts. The
adequacy of the reserve is reviewed periodically in relation to the repair parts inventory
balances. The gross balance of the repair and maintenance supply parts inventory was approximately
$2.0 million at June 27, 2010 and $1.9 million at both June 28, 2009 and June 29, 2008. The repair
and maintenance supply parts inventory balance is included in Other Current Assets in the
Consolidated Balance Sheets. The activity related to the repair and maintenance supply parts
reserve is as follows (thousands of dollars):
| Balance, | Provision | Balance, | ||||||||||||||
| Beginning | Charged to | Amounts | End of | |||||||||||||
| of Year | Expense | Written Off | Year | |||||||||||||
Year ended June 27, 2010 |
$ | 630 | $ | 78 | $ | 28 | $ | 680 | ||||||||
Year ended June 28, 2009 |
$ | 650 | $ | 80 | $ | 100 | $ | 630 | ||||||||
Year ended June 29, 2008 |
$ | 640 | $ | 145 | $ | 135 | $ | 650 | ||||||||
Goodwill and Other Intangibles: Goodwill is tested for impairment at least annually on
the last day of the second fiscal quarter and more frequently if an event occurs which indicates
the asset may be impaired. Based upon the goodwill impairment review completed during 2010, we
determined that goodwill related to SPA, which resulted from the purchase of Delphi Power Products
in 2009, was impaired. Accordingly, a non-cash impairment charge of $223,000 was recognized to
write-off the related goodwill amount.
Intangible assets that have defined useful lives acquired in the purchase of Delphi
Power products in 2009 consist of patents, engineering drawings and software. The carrying value
and accumulated amortization are as follows (thousands of dollars):
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | |||||||
Patents, engineering drawings
and software |
$ | 890 | $ | 890 | ||||
Less: accumulated amortization |
(157 | ) | (58 | ) | ||||
| $ | 733 | $ | 832 | |||||
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 31 |

NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The remaining useful life of the intangible assets in the table above is approximately
7.4 years. Intangible amortization expense for the years ended June 27, 2010 and June 28, 2009
totaled $99,000 and $58,000, respectively. There was no amortization expense for the year ended
June 29, 2008. Estimated intangible amortization expense for each of the next five fiscal years
is $99,000.
Property, Plant and Equipment: Property, plant and equipment are stated at cost.
Property, plant and equipment are depreciated on a straight-line basis over the estimated useful
lives of the assets as follows:
| Classification | Expected Useful Lives | |
Land improvements
|
20 years | |
Buildings and improvements
|
20 to 35 years | |
Machinery and equipment
|
3 to 10 years |
Property, plant and equipment consist of the following (thousands of dollars):
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | |||||||
Land and improvements |
$ | 2,919 | $ | 2,841 | ||||
Buildings and improvements |
18,337 | 17,862 | ||||||
Machinery and equipment |
115,472 | 110,799 | ||||||
| 136,728 | 131,502 | |||||||
Less: accumulated
depreciation |
(99,677 | ) | (94,566 | ) | ||||
| $ | 37,051 | $ | 36,936 | |||||
Depreciation expense for the years ended June 27, 2010, June 28, 2009 and June 29,
2008 totaled approximately $7.0 million, $6.2 million and $6.8 million, respectively.
Long-lived assets are reviewed for impairment whenever events or changes in
circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of an asset may not be recoverable.
Recoverability of assets to be held and used is measured by a comparison of the carrying amount
of an asset to future net undiscounted cash flows expected to be generated by the asset. If such
assets are considered to be impaired, the impairment recognized is measured by the excess of the
carrying amount of the assets over the fair value of the assets. Assets to be disposed of are
reported at the lower of the carrying amount or fair value, less estimated costs to sell. In
2008, a loss was recognized for a customer program specific fixed asset in the amount of
$382,000.
Expenditures for repairs and maintenance are charged to expense as incurred.
Expenditures for major renewals and betterments, which significantly extend the useful lives of
existing plant and equipment, are capitalized and depreciated. Upon retirement or disposition of
plant and equipment, the cost and related accumulated depreciation are removed from the accounts
and any resulting gain or loss is recognized in income.
Supplier Concentrations: The following inventory purchases were made from major
suppliers during each fiscal year noted:
| Percentage of | Number of | |||||||
| Fiscal Year | Inventory Purchases | Suppliers | ||||||
2010 |
34 | % | 8 | |||||
2009 |
24 | % | 4 | |||||
2008 |
25 | % | 3 | |||||
We have long-term contracts or arrangements with most of our suppliers to guarantee
the availability of merchandise.
Labor Concentrations: We had approximately 2,280 full-time employees of which
approximately 208 or 9.1 percent were represented by a labor union at June 27, 2010. The employees
represented by a labor union account for all production associates at our Milwaukee facility. The
current contract with the unionized associates is effective through June 29, 2014.
Revenue Recognition: Revenue is recognized upon the shipment of products, which is
when title passes, payment terms are final, we have no remaining obligations and the customer is
required to pay. Revenue is recognized net of estimated returns and discounts, which is
recognized as a deduction from revenue at the time of the shipment.
Research and Development Costs: Expenditures relating to the development of new products and
processes, including significant improvements and refinements to existing products, are expensed as
incurred. Research and development expenditures were approximately $900,000 in 2010, $670,000 in
2009, and $1.9 million in 2008.
Other Income, Net: Net other income included in the Consolidated Statements of
Operations primarily includes foreign currency transaction gains and losses and Rabbi Trust
gains and losses.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 32 |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Foreign currency transaction gains are the result of foreign currency transactions
entered into by our Mexican subsidiaries and foreign currency cash balances. The Rabbi Trust funds
our supplemental executive retirement plan. The investments held in the trust are considered
trading securities. The impact of these items for the periods presented is as follows (thousands
of dollars):
| Years Ended | ||||||||||||
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | June 29, 2008 | ||||||||||
Foreign currency
transaction (loss)
gain |
$ | (283 | ) | $ | 918 | $ | (320 | ) | ||||
Rabbi Trust gain (loss) |
431 | (393 | ) | (174 | ) | |||||||
Other |
164 | 279 | 194 | |||||||||
| $ | 312 | $ | 804 | $ | (300 | ) | ||||||
Self Insurance and Loss Sensitive Plans: We have self-insured medical and dental plans
covering all eligible U.S. associates. The claims handling process for the self-insured plans are
managed by a third party administrator. Stop-loss insurance coverage limits our liability on a per
individual per calendar year basis. The per individual per calendar year stop-loss limit was
$150,000 in each calendar year 2007 through 2009. Each covered individual can receive up to $2
million in total benefits during his or her lifetime. Once an individual’s medical claims reach $2
million, we are no longer liable for any additional claims for that individual. Effective January
1, 2011, under Health Care Reform, there will be no lifetime maximum for overall benefits.
We maintain an insured workers’ compensation program covering all U.S. associates. The
insurance is renewed annually, with a renewal date of February 27. The policy may be a guaranteed
cost policy or a loss sensitive policy. Under a guaranteed cost policy, the ultimate cost is known
at the beginning of the policy period and is subject to change only as a result of changes in
payrolls. Under a loss sensitive policy, the ultimate cost is dependent upon losses incurred
during each policy period. The incurred loss amount for loss sensitive policies will continue to
change as claims develop and are settled in future reporting periods.
The expected ultimate cost for claims incurred under the self-insured medical and dental
plans and loss sensitive workers’ compensation plan as of the balance sheet date is not discounted
and is recognized as an expense. The expected ultimate cost of claims is estimated based upon the
aggregate liability for reported claims and an estimated liability for claims incurred but not
reported, which is based on analysis of historical data, current trends and information available
from the insurance carrier. The expected ultimate cost for claims incurred under the self-insured
medical and dental plans that has not been paid as of the balance sheet date is included in the
accrued payroll and benefits liabilities amount in our Consolidated Balance Sheets. The schedule
of premium payments due under the workers compensation plan requires a larger percentage of the
estimated premium dollars to be paid during the beginning of the policy period. The excess of the
premium payments over the expected ultimate cost for claims incurred as of the balance sheet date
is included in other current assets in our Consolidated Balance Sheets.
Changes in the balance sheet amounts for self-insured and loss sensitive plans are
as follows (thousands of dollars):
| Balance, | Provision | Balance, | ||||||||||||||
| Beginning | Charged to | End of | ||||||||||||||
| of Year | Expense | Payments | Year | |||||||||||||
Year ended June 27, 2010
|
||||||||||||||||
Incurred but not reported claims
reserve for self insured plans |
$ | 300 | $ | 3,041 | $ | 3,021 | $ | 320 | ||||||||
Workers’ Compensation |
(78 | ) | 259 | 366 | (185 | ) | ||||||||||
Year ended June 28, 2009
|
||||||||||||||||
Incurred but not reported claims
reserve for self insured plans |
$ | 300 | $ | 2,468 | $ | 2,468 | $ | 300 | ||||||||
Workers’ Compensation |
(140 | ) | 208 | 146 | (78 | ) | ||||||||||
Year ended June 29, 2008
|
||||||||||||||||
Incurred but not reported claims
reserve for self insured plans |
$ | 300 | $ | 2,408 | $ | 2,408 | $ | 300 | ||||||||
Workers’ Compensation |
(251 | ) | 254 | 143 | (140 | ) | ||||||||||
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 33 |

NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
Warranty: We are exposed to warranty claims in the event that our products fail to
perform as expected, and we may be required to participate in a recall of such products.
Historically, we have experienced relatively low warranty charges from our customers due to our
commercial arrangements and improvements in the quality, reliability and durability of our
products. Recently, our largest customers have extended their warranty protection for their
vehicles and are demanding higher warranty cost sharing arrangements from suppliers. As a result
of these actions, during 2010 we increased our provision to cover these exposures. Our reserve is
based on an analysis of historical warranty data as well as current trends and information,
including our customers’ recent extension of their warranty programs and current warranty sharing
arrangements.
Changes in the warranty reserve which is included in current liabilities are as follows
(thousands of dollars):
| Balance, | Provision | Balance, | ||||||||||||||
| Beginning | Charged to | End of | ||||||||||||||
| of Year | Expense | Payments | Year | |||||||||||||
Year ended June 27, 2010 |
$ | 221 | $ | 2,560 | $ | 1,063 | $ | 1,718 | ||||||||
Year ended June 28, 2009 |
$ | 390 | $ | 362 | $ | 531 | $ | 221 | ||||||||
Year ended June 29, 2008 |
$ | 390 | $ | 267 | $ | 267 | $ | 390 | ||||||||
Foreign Currency Translation: The financial statements of our foreign subsidiaries and
equity investees are translated into U.S. dollars using the exchange rate at each balance sheet
date for assets and liabilities and the average exchange rate for each applicable period for
sales, costs and expenses. Foreign currency translation adjustments are included as a component
of other accumulated comprehensive loss. Foreign currency transaction gains and losses are
included in other income, net in the Consolidated Statement of Operations.
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss: Accumulated other comprehensive loss is
comprised of the following (thousands of dollars):
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | June 29, 2008 | ||||||||||
Unrecognized pension and
postretirement
benefit liabilities, net of tax |
$ | 28,222 | $ | 26,876 | $ | 15,762 | ||||||
Foreign currency translation |
3,719 | 4,218 | 1,733 | |||||||||
| $ | 31,941 | $ | 31,094 | $ | 17,495 | |||||||
| Deferred taxes have not been provided for the foreign currency translation adjustments. |
Accounting For Stock-Based Compensation: We maintain an omnibus stock incentive plan.
This plan provides for the granting of stock options, shares of restricted stock and stock
appreciation rights. The Board of Directors has designated 1,700,000 shares of common stock
available for the grant of awards under the plan. Remaining shares available to be granted under
the plan as of June 27, 2010 were 250,893. Awards that expire or are cancelled without delivery of
shares become available for re-issuance under the plan. We issue new shares of common stock to
satisfy stock option exercises.
Nonqualified and incentive stock options and shares of restricted stock have been granted
to our officers and specified employees under the stock incentive plan. Stock options granted
under the plan may not be issued with an exercise price less than the fair market value of the
common stock on the date the option is granted. Stock options become exercisable as determined at
the date of grant by the Compensation Committee of the Board of Directors. The options expire 5 to
10 years after the grant date unless an earlier expiration date is set at the time of grant. The
options vest 1 to 4 years after the date of grant. Shares of restricted stock granted under the
plan are subject to vesting criteria determined by the Compensation Committee of the Board of
Directors at the time the shares are granted. Restricted shares granted have voting and dividend
rights. The restricted stock granted vests 3 years after the date of grant.
The fair value of each stock option grant was estimated as of the date of grant using the
Black-Scholes pricing model. The resulting compensation cost for fixed awards with graded vesting
schedules is amortized on a straight-line basis over the vesting period for the entire award. The
expected term of awards granted is determined based on historical experience with similar awards,
giving consideration to the expected term and vesting schedules. The expected volatility is
determined based on our historical stock prices over the most recent period commensurate with the
expected term of the award. The risk-free interest rate is based on U.S. Treasury zero-coupon
issues with a remaining term commensurate with the expected term of the award. Expected pre-vesting
option forfeitures are based primarily on historical data. The fair value of each restricted stock
grant was based on the market price of the underlying common stock as of the date of grant. The
resulting compensation cost is amortized on a straight line basis over the vesting period. We
record stock based compensation only for those awards that are expected to vest.
As of June 27, 2010, there was $835,000 of total unrecognized compensation cost related
to stock options granted under the plan. This cost is expected to be recognized over a weighted
average period
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 34 |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
of 1.6 years. As of June 27, 2010, there was $218,000 of total unrecognized compensation
cost related to restricted stock grants under the plan. This cost is expected to be recognized
over a weighted average period of 9 months. Total unrecognized compensation cost will be adjusted
for any future changes in estimated and actual forfeitures.
Cash received from option exercises during fiscal 2010 was $26,000. The related income
tax benefit was $13,000.
The intrinsic value of stock options exercised and the fair value of stock options vested
are as follows (in thousands of dollars):
| Years Ended | ||||||||||||
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | June 29, 2008 | ||||||||||
Intrinsic value of options exercised |
$ | 35 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||
Fair value of stock options vesting |
$ | 114 | $ | 469 | $ | 273 | ||||||
Nonqualified stock options were granted to certain of our key employees during 2010 and
2009. No options were granted during 2008. The grant date fair values and assumptions used to
determine compensation expense in 2010 and 2009 are as follows:
| Options Granted During | 2010 | 2009 | ||||||
Weighted average grant date fair value: |
||||||||
Options issued at grant date market value |
$ | 8.95 | $ | 3.80 | ||||
Options issued above grant date market value |
n/a | n/a | ||||||
Assumptions: |
||||||||
Risk free interest rates |
3.14 | % | 2.22 | % | ||||
Expected volatility |
49.73 | % | 32.96 | % | ||||
Expected dividend yield |
— | 1.67 | % | |||||
Expected term (in years) |
6.0 | 5.5 | ||||||
No dividends were assumed in the grant date fair value calculations in 2010 as we did not
intend to pay cash dividends on our common stock as of the grant date.
| The range of options outstanding as of June 27, 2010 is as follows: |
| Weighted Average Remaining | ||||||||||||
| Number of Options | Weighted Average Exercise | Contractual Life Outstanding | ||||||||||
| Outstanding/Exercisable | Price Outstanding/Exercisable | (In Years) | ||||||||||
$10.92-$18.49 |
170,000/21,700 | $14.62/$12.23 | 9.0 | |||||||||
$31.95-$44.93 |
5,100/5,100 | $39.25/$39.25 | 1.7 | |||||||||
$53.07-$63.25 |
122,550/122,550 | $58.25/$58.25 | 2.6 | |||||||||
| $33.01/$50.92 | ||||||||||||
Recent Accounting Pronouncements: In June 2009, the FASB issued authoritative guidance which
amends the consolidation guidance applicable to variable interest entities. The guidance will
affect the overall consolidation analysis under the current authoritative guidance for
consolidation of variable interest entities and is effective for us as of the beginning of the
first quarter of fiscal year 2011. We are currently evaluating the impact that the guidance may
have on our consolidated financial statements and disclosures.
In January 2010, the FASB issued guidance that requires reporting entities to make new
disclosures about recurring or nonrecurring fair value measurements, including significant
transfers into and out of Level 1 and Level 2 fair value measurements and information on
purchases, sales, issuances, and settlements on a gross basis in the reconciliation of Level 3
fair value measurements. The guidance is effective for interim and annual reporting periods
beginning after December 15, 2009, except for Level 3 reconciliation disclosures that are
effective for annual periods beginning after December 15, 2010. We do not expect the disclosure
provisions to have a significant impact on our Consolidated Financial Statements.
SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
On August 4, 2010, our Board of Directors declared a special one-time cash dividend of
$1.20 per common share payable October 29, 2010 to shareholders of record as of October 8, 2010.
The dividend will total approximately $4.0 million and will be funded with current cash balances.
No additional subsequent events impacting the financial statements or disclosure items were
identified.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 35 |

NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
INVESTMENT IN JOINT VENTURES
We participate in certain Alliance Agreements with WITTE Automotive (“WITTE”) and ADAC
Automotive (“ADAC”). WITTE, of Velbert, Germany, is a privately held automotive supplier. WITTE
designs, manufactures and markets components including locks and keys, hood latches, rear
compartment latches, seat back latches, door handles and specialty fasteners. WITTE’s primary
market for these products has been Europe. ADAC, of Grand Rapids, Michigan, is a privately held
automotive supplier and manufactures engineered products, including door handles and other
automotive trim parts, utilizing plastic injection molding, automated painting and various
assembly processes.
The Alliance provides a set of cross-licensing agreements for the manufacture,
distribution and sale of WITTE products by STRATTEC and ADAC in North America, and the manufacture,
distribution and sale of STRATTEC and ADAC products by WITTE in Europe. Additionally, a joint
venture company, Vehicle Access Systems Technology LLC (“VAST LLC”), in which WITTE, STRATTEC and
ADAC each hold a one-third interest, exists to seek opportunities to manufacture and sell the
companies’ products in areas of the world outside of North America and Europe.
VAST do Brasil, a joint venture between VAST LLC and Ifer do Brasil Ltda., was formed to
service customers in South America. VAST Fuzhou and VAST Great Shanghai (collectively known as
VAST China), began as joint ventures between VAST LLC and a Taiwanese partner to provide a base of
operations to service our automotive customers in the Asian market. Effective November 20, 2009,
VAST LLC purchased the remaining 40 percent interest of these two Chinese joint ventures for $9.6
million. VAST LLC now owns 100 percent of VAST Fuzhou and VAST Great Shanghai. Initially, a loan
of $2.5 million was made from STRATTEC to VAST LLC related to the purchase of the remaining 40
percent interest in the Chinese joint ventures. As of June 27, 2010, $1 million of the loan has
been repaid. VAST LLC also maintains branch offices in South Korea and Japan in support of
customer sales and engineering requirements.
The VAST LLC investments are accounted for using the equity method of accounting. The
activities related to the VAST LLC joint ventures resulted in equity in earnings of joint ventures
to STRATTEC of approximately $1.0 million during 2010 and $245,000 during 2009. During the current
year, the VAST partners made capital contributions to VAST totaling $300,000 in support of general
operating expenses. STRATTEC’s portion of the capital contributions totaled $100,000.
In fiscal year 2007, we entered into a joint venture with ADAC, in which STRATTEC holds a
50.1 percent interest and ADAC holds a 49.9 percent interest. The joint venture, ADAC-STRATTEC
LLC, a Delaware limited liability company, was formed on October 27, 2006. In addition, a Mexican
entity, ADAC-STRATTEC de Mexico, which is wholly owned by ADAC-STRATTEC LLC, was formed on
February 21, 2007 to establish injection molding and assembly operations for door handle
components. ADAC-STRATTEC LLC’s financial results are consolidated with the financial results of
STRATTEC and resulted in increased net income to STRATTEC of approximately $114,000 in 2010 and no
change in net income to STRATTEC in 2009.
Effective November 30, 2008, STRATTEC established a new entity, STRATTEC POWER ACCESS
LLC (“SPA”), which is 80 percent owned by STRATTEC and 20 percent owned by WITTE. SPA operates
the North American portion of the Power Products business which was acquired from Delphi
Corporation. The financial results of SPA are consolidated with the financial results of STRATTEC
and resulted in increased net income to STRATTEC of approximately $545,000 in 2010 and decreased
net income to STRATTEC of approximately $2.1 million during 2009.
LOANS FROM RELATED PARTIES
At June 27, 2010 and June 28, 2009, loans from related parties (ADAC Automotive and WITTE
Automotive) totaled $3.0 million and $3.2 million, respectively, and consisted of loans to
ADAC-STRATTEC LLC and STRATTEC POWER ACCESS LLC to fund working capital requirements of these
entities. Working capital loans to these entities are made by each partner based on each partner’s
ownership percentage in the entity. The weighted average interest rate was approximately 7.2
percent in 2010 and in 2009.
LINE OF CREDIT
We have a $20 million unsecured line of credit (“Line of Credit”) with M&I Marshall &
Ilsley Bank which expires October 30, 2010. Interest on borrowings under the Line of Credit is at
varying rates based on the London Interbank Offering Rate with a minimum annual rate of 4 percent.
The Line of Credit is not subject to any covenants. There were no outstanding borrowings under the
Line of Credit at June 27, 2010 or June 28, 2009. There were no borrowings under any third party
debt facilities during 2010, 2009 or 2008.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 36 |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCIES
In 1995, we recorded a provision of $3.0 million for estimated costs to remediate a site
at our Milwaukee facility. The site was contaminated by a solvent spill, which occurred in 1985,
from a former above-ground solvent storage tank located on the east side of the facility. The
environmental reserve was originally established based on estimates to adequately cover the cost
for active remediation of the contamination. Due to changing technology affecting the cost
associated with active remediation of the contamination, an updated analysis and cost estimate was
obtained during 2010. The environmental reserve was reduced by approximately $1.1 million, to $1.5
million, to reflect the result of the updated monitoring and remediation cost estimate. As of June
27, 2010, costs of approximately $400,000 have been incurred related to the installation of
monitoring wells on the property and ongoing monitoring costs. We continue to monitor and evaluate
the site with the use of groundwater monitoring wells that are installed on the property. A third
party environmental consultant samples these wells one to two times a year to determine the status
of the contamination and the potential for remediation of the contamination by natural attenuation,
the dissipation of the contamination over time to concentrations below applicable standards. If
such sampling evidences a sufficient degree of and trend toward natural attenuation of the
contamination, we may be able to obtain a closure letter from the regulatory authorities resolving
the issue without the need for active remediation. If a sufficient degree and trend toward natural
attenuation is not evidenced by sampling, a more active form of remediation beyond natural
attenuation may be required. The sampling has not yet satisfied all of the requirements for closure
by natural attenuation. As a result, sampling continues and the environmental reserve remains at an
amount estimated to cover the cost of active remediation. The reserve is not measured on a
discounted basis. We believe, based upon findings-to-date and known environmental regulations, that
the environmental reserve at June 27, 2010, is adequate.
At June 27, 2010, we had purchase commitments for zinc, aluminum, other purchased parts and
natural gas totaling approximately $9.8 million payable in 2011, $7.6 million payable in 2012 and
$6.7 million payable in 2013. Minimum rental commitments under all non-cancelable operating
leases with a term in excess of one year are payable as follows: 2011-$508,000; 2012-$472,000;
2013-$299,000; 2014-$301,000; 2015-$152,000. Rental expense under all non-cancelable operating
leases totaled approximately $553,000 in 2010, $516,000 in 2009 and $622,000 in 2008.
INCOME TAXES
The provision for income taxes data presented below for 2009 and 2008 has been
retrospectively adjusted for the adoption of a new accounting standard issued by the FASB related
to non-controlling interests in consolidated financial statements. The provision for income taxes
and deferred tax asset data presented below for 2008 has been retrospectively adjusted for our
change in 2009 from the last-in, first-out
method of inventory accounting to the first-in, first-out method.
The provision (benefit) for income taxes consists of the following (thousands of dollars):
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
Currently (refundable) payable: |
||||||||||||
Federal |
$ | (2,745 | ) | $ | (1,747 | ) | $ | 62 | ||||
State |
230 | 150 | 226 | |||||||||
Foreign |
753 | 361 | 67 | |||||||||
| (1,762 | ) | (1,236 | ) | 355 | ||||||||
Deferred tax (benefit) provision |
3,428 | (2,986 | ) | 622 | ||||||||
| $ | 1,666 | $ | (4,222 | ) | $ | 977 | ||||||
The items accounting for the difference between income taxes computed at the Federal statutory
tax rate and the provision for income taxes are as follows:
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
U.S. statutory rate |
34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | 34.0 | % | ||||||
State taxes, net of Federal tax benefit |
4.1 | 1.2 | 4.6 | |||||||||
Foreign subsidiaries |
(4.1 | ) | 4.3 | (9.6 | ) | |||||||
Non-controlling interest |
(3.5 | ) | (2.3 | ) | .7 | |||||||
Valuation allowance |
2.8 | — | — | |||||||||
Other |
(3.6 | ) | .8 | (3.9 | ) | |||||||
| 29.7 | % | 38.0 | % | 25.8 | % | |||||||
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 37 |

NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The 2008 income tax provision includes favorable tax benefits related to the
operation of our Mexican subsidiaries as Maquiladora entities.
The components of deferred tax assets and (liabilities) are as follows (thousands of
dollars):
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | |||||||
Deferred income taxes—current: |
||||||||
Repair and maintenance supply parts reserve |
$ | 258 | $ | 239 | ||||
Payroll-related accruals |
1,028 | 814 | ||||||
Environmental reserve |
569 | 1,002 | ||||||
Inventory reserve |
475 | 371 | ||||||
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts |
152 | 285 | ||||||
Accrued customer pricing |
— | 934 | ||||||
Accrued Warranty |
436 | 54 | ||||||
Method change for inventory valuation |
(919 | ) | (1,317 | ) | ||||
Other |
288 | (258 | ) | |||||
| 2,287 | 2,124 | |||||||
Valuation allowance |
(154 | ) | — | |||||
| $ | 2,133 | $ | 2,124 | |||||
Deferred income taxes—noncurrent: |
||||||||
Accrued pension obligations |
$ | (8,634 | ) | $ | (7,384 | ) | ||
Unrecognized pension and postretirement
benefit plan liabilities |
17,297 | 16,472 | ||||||
Accumulated depreciation |
(2,001 | ) | (1,807 | ) | ||||
Stock-based compensation |
740 | 707 | ||||||
Postretirement obligations |
1,651 | 1,625 | ||||||
NOL/credit carry-forwards |
273 | 3,259 | ||||||
Other |
1,208 | 271 | ||||||
| $ | 10,534 | $ | 13,143 | |||||
Deferred income tax balances reflect the effects of temporary differences between the
carrying amounts of assets and liabilities and their tax basis and are stated at enacted tax
rates expected to be in effect when taxes are actually paid or recovered.
State operating loss and credit carry-forwards at June 27, 2010 result in future benefits
of approximately $217,000 and begin to expire in 2024. A valuation allowance of $154,000 has been
recorded as of June 27, 2010, due to our assessment of the future realization of certain capital
loss carry-forward benefits. We do not currently anticipate having sufficient future capital gains
to offset these capital losses. We believe that it is more likely than not that the results of
future operations will generate sufficient taxable income and foreign source income to realize the
remaining deferred tax assets. During 2010, the available Federal operating loss carry-back period
changed from 2 years to 5 years. As a result, approximately $2.8 million of the non-current
deferred tax asset balance related to Federal operating loss carry-forwards as of June 28, 2009
were reclassified as current taxes recoverable during 2010. The total tax recoverable amount
resulting from losses generated in 2009 was received in April 2010.
Foreign income before the provision for income taxes was $2.9 million in 2010, $2.9 million
in 2009 and $1.6 million in 2008. No provision for Federal income taxes was made on earnings of
foreign subsidiaries and joint ventures that are considered permanently invested or that would be
offset by foreign tax credits upon distribution. Such undistributed earnings at June 27, 2010 were
approximately $17.4 million.
The total liability for unrecognized tax benefits was $1.2 million as of June 27, 2010 and
as of June 28, 2009. This liability includes approximately $1.1 million of unrecognized tax
benefits at June 27, 2010 and at June 28, 2009 and approximately $118,000 of accrued interest at
June 27, 2010 and at June 28, 2009. The liability does not include an amount for accrued penalties.
The amount of unrecognized tax benefits that, if recognized, would affect the effective tax rate
was approximately $863,000 at June 27, 2010 and $949,000 at June 28, 2009. We recognize interest
and penalties related to unrecognized tax benefits in the provision for income taxes.
A reconciliation of the beginning and ending amount of unrecognized tax benefits
is as follows (thousands of dollars):
Unrecognized tax benefits June 28, 2009 |
$ | 1,103 | ||
Gross increases — tax positions in prior years |
— | |||
Gross decreases — tax positions in prior years |
(29 | ) | ||
Gross increases — current period tax positions |
115 | |||
Tax Years Closed |
(64 | ) | ||
Unrecognized tax benefits June 27, 2010 |
$ | 1,125 | ||
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 38 |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
We or one of our subsidiaries files income tax returns in the United States (Federal),
Wisconsin (state), Michigan (state) and various other states, Mexico and other foreign
jurisdictions. We are currently not subject to income tax examinations in any of our significant
tax jurisdictions. Tax years open to examination by tax authorities under the statute of
limitations include fiscal 2006 through 2010 for Federal, fiscal 2006 through 2010 for most
states and calendar 2005 through 2009 for foreign jurisdictions.
RETIREMENT PLANS AND POSTRETIREMENT COSTS
We have a qualified, noncontributory defined benefit pension plan covering
substantially all U.S. associates. Benefits are based on years of service and final average
compensation. Our policy is to fund at least the minimum actuarially computed annual contribution
required under the Employee Retirement Income Security Act of 1974 (ERISA). Plan assets consist
primarily of listed equity and fixed income securities. Effective January 1, 2010, an amendment to
the qualified defined benefit pension plan discontinued the benefit accruals for salary increases
and credited service rendered after December 31, 2009. As a result of this action, a curtailment
loss related to unrecognized prior service cost of $505,000 was recorded during 2010, of which
approximately $375,000 increased cost of goods sold and approximately $130,000 increased
engineering, selling and administrative expenses.
We have a noncontributory supplemental executive retirement plan (“SERP”), which is a
nonqualified defined benefit plan. The SERP will pay supplemental pension benefits to certain key
employees upon retirement based upon the employees’ years of service and compensation. The SERP is
being funded through a Rabbi Trust with M&I Trust Company. The trust assets had a value of $4.0
million at June 27, 2010 and $3.5 million at June 28, 2009. The Rabbi Trust assets are included in
other current assets in the Consolidated Balance Sheets. The projected benefit obligation was $3.7
million at June 27, 2010 and $3.0 million at June 28, 2009. The SERP liabilities are included in
the pension tables below. However, the trust assets are excluded from the table as they do not
qualify as plan assets.
We also sponsor a postretirement health care plan for all U.S. associates hired prior to
June 1, 2001. The expected cost of retiree health care benefits is recognized during the years the
associates who are covered under the plan render service. Effective January 1, 2010, an amendment
to the postretirement health care plan limited the benefit for future eligible retirees to $4,000
per plan year and includes coverage to age 65, subject to a maximum coverage period of five years.
The benefit for eligible associates with a retirement date prior to January 1, 2010, is not
subject to an annual limit and includes coverage to age 65, subject to a maximum coverage period
of five years, for eligible unionized associates with a retirement date after June 27, 2005 and
eligible non-unionized associates with a retirement date after October 1, 2005. The coverage
period for eligible associates with a retirement date prior to either of the 2005 dates extended
to age 65 for primary coverage under the plan. The postretirement health care plan is unfunded.
Amounts included in accumulated other comprehensive loss, net of tax, at June 27,
2010, which have not yet been recognized in net periodic benefit cost are as follows (thousands
of dollars):
| Pension and SERP Benefits | Postretirement Benefits | |||||||
Prior service cost (credit) |
$ | 59 | $ | (4,083 | ) | |||
Net actuarial loss |
27,359 | 4,887 | ||||||
| $ | 27,418 | $ | 804 | |||||
Included in accumulated other comprehensive loss at June 27, 2010 are prior service
costs of $12,000 ($7,000 net of tax) and unrecognized net actuarial losses of $2.5 million ($1.6
million net of tax) expected to be recognized in pension and SERP net periodic benefit cost
during 2011.
Included in accumulated other comprehensive loss at June 27, 2010 are prior service
credits of $764,000 ($474,000 net of tax) and unrecognized net actuarial losses of $645,000
($400,000 net of tax) expected to be recognized in postretirement net periodic benefit cost
during 2011.
The following tables summarize the pension, SERP and postretirement plans’ income and
expense, funded status and actuarial assumptions for the years indicated (thousands of dollars).
We use a June 30 measurement date for our pension and postretirement plans.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 39 |

NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Pension and SERP Benefits | Postretirement Benefits | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||
COMPONENTS OF NET PERIODIC
BENEFIT COST: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Service cost |
$ | 1,006 | $ | 1,935 | $ | 2,018 | $ | 124 | $ | 191 | $ | 221 | ||||||||||||
Interest cost |
5,047 | 5,083 | 4,680 | 701 | 737 | 718 | ||||||||||||||||||
Expected return on plan assets |
(6,351 | ) | (6,562 | ) | (6,210 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Amortization of prior service cost |
45 | 79 | 64 | (388 | ) | (388 | ) | (378 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Amortization of unrecognized net loss |
727 | 255 | 643 | 685 | 695 | 702 | ||||||||||||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost |
474 | 790 | 1,195 | 1,122 | 1,235 | 1,263 | ||||||||||||||||||
Curtailment loss |
505 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Net benefit cost |
$ | 979 | $ | 790 | $ | 1,195 | $ | 1,122 | $ | 1,235 | $ | 1,263 | ||||||||||||
| Pension and SERP Benefits | Postretirement Benefits | |||||||||||||||
| June 27, | June 28, | June 27, | June 28, | |||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 | |||||||||||||
WEIGHTED-AVERAGE ASSUMPTIONS |
||||||||||||||||
Benefit Obligations: |
||||||||||||||||
Discount rate |
5.41 | % | 6.86 | % | 5.41 | % | 6.86 | % | ||||||||
Expected return on plan assets |
8.0 | % | 8.0 | % | n/a | n/a | ||||||||||
Rate of compensation increases |
3.0 | % | 3.0 | % | n/a | n/a | ||||||||||
Net Periodic Benefit Cost: |
||||||||||||||||
Discount rate |
6.86 | % | 7.13 | % | 6.86 | % | 7.13 | % | ||||||||
Expected return on plan assets |
8.0 | % | 8.25 | % | n/a | n/a | ||||||||||
Rate of compensation increases |
3.0 | % | 3.5 | % | n/a | n/a | ||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | 2010 | 2009 | |||||||||||||
CHANGE IN PROJECTED
BENEFIT OBLIGATION: |
||||||||||||||||
Benefit obligation at beginning of year |
$ | 78,058 | $ | 72,939 | $ | 10,812 | $ | 10,871 | ||||||||
Service cost |
1,006 | 1,935 | 124 | 191 | ||||||||||||
Interest cost |
5,047 | 5,083 | 701 | 737 | ||||||||||||
Plan amendments |
(3,982 | ) | — | (3,399 | ) | — | ||||||||||
Actuarial loss (gain) |
14,101 | 1,567 | (1,543 | ) | 502 | |||||||||||
Benefits paid |
(3,828 | ) | (3,466 | ) | (1,053 | ) | (1,489 | ) | ||||||||
Benefit obligation at end of year |
$ | 90,402 | $ | 78,058 | $ | 5,642 | $ | 10,812 | ||||||||
CHANGE IN PLAN ASSETS: |
||||||||||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at beginning
of year |
$ | 60,594 | $ | 70,996 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||
Actual return on plan assets |
7,783 | (9,936 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||
Employer contribution |
4,219 | 3,000 | 1,053 | 1,489 | ||||||||||||
Benefits paid |
(3,828 | ) | (3,466 | ) | (1,053 | ) | (1,489 | ) | ||||||||
Fair value of plan assets at end of
year |
68,768 | 60,594 | — | — | ||||||||||||
Funded status—accrued benefit
obligations |
$ | (21,634 | ) | $ | (17,464 | ) | $ | (5,642 | ) | $ | (10,812 | ) | ||||
AMOUNTS RECOGNIZED IN
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEETS: |
||||||||||||||||
Accrued payroll and benefits
(current liabilities) |
$ | (3,142 | ) | $ | (2,281 | ) | $ | (1,152 | ) | $ | (1,211 | ) | ||||
Accrued benefit obligations
(long-term liabilities) |
(18,492 | ) | (15,183 | ) | (4,490 | ) | (9,601 | ) | ||||||||
Net amount recognized |
$ | (21,634 | ) | $ | (17,464 | ) | $ | (5,642 | ) | $ | (10,812 | ) | ||||
CHANGES IN PLAN ASSETS AND
BENEFIT OBLIGATIONS RECOGNIZED
IN OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME: |
||||||||||||||||
Net periodic benefit cost |
$ | 979 | $ | 790 | $ | 1,122 | $ | 1,235 | ||||||||
Net actuarial loss (gain) |
8,686 | 18,065 | (1,543 | ) | 502 | |||||||||||
Prior service cost |
— | — | (3,399 | ) | — | |||||||||||
Amortization of prior service (cost)
credits |
(550 | ) | (79 | ) | 388 | 388 | ||||||||||
Amortization of unrecognized net loss |
(727 | ) | (255 | ) | (685 | ) | (695 | ) | ||||||||
Total recognized in other comprehensive
income, before tax |
7,409 | 17,731 | (5,239 | ) | (195 | ) | ||||||||||
Total recognized in net periodic
benefit
cost and other comprehensive income |
$ | 8,388 | $ | 18,521 | $ | (4,117 | ) | $ | 1,430 | |||||||
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 40 |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
The pension benefits have a separately determined accumulated benefit obligation,
which is the actuarial present value of benefits based on service rendered and current and past
compensation levels. This differs from the projected benefit obligation in that it includes no
assumptions about future compensation levels. The following table summarizes the accumulated
benefit obligations and projected benefit obligations for the pension and SERP (thousands of
dollars):
| Pension | SERP | |||||||||||||||
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | |||||||||||||
Accumulated benefit
obligation |
$ | 86,658 | $ | 71,167 | $ | 3,682 | $ | 2,826 | ||||||||
Projected benefit obligation |
$ | 86,658 | $ | 75,079 | $ | 3,744 | $ | 2,979 | ||||||||
For measurement purposes, an 8.0 percent annual rate increase in the per capita cost
of covered health care benefits was assumed for 2011; the rate was assumed to decrease gradually
to 5 percent by the year 2017 and remain at that level thereafter relating to retirees prior to
January 1, 2010.
The health care cost trend assumption has a significant effect on the postretirement
benefit amounts reported. A 1% change in the health care cost trend rates would have the following
effects (thousands of dollars):
| 1% Increase | 1% Decrease | |||||||
Effect on total of service and interest
cost components in fiscal 2010 |
$ | 7 | $ | (7 | ) | |||
Effect on postretirement benefit
obligation as of June 27, 2010 |
$ | 129 | $ | (124 | ) | |||
We employ a total return investment approach whereby a mix of equities and fixed income
investments are used to maximize the long-term return of plan assets for a prudent level of risk.
Risk tolerance is established through careful consideration of short and long-term plan
liabilities, plan funded status and corporate financial condition. The investment portfolio
contains a diversified blend of equity and fixed income investments. Furthermore, equity
investments are diversified across U.S. and non-U.S. stocks, as well as growth and value style
managers, and small, mid and large market capitalizations. The investment portfolio does not
include any real estate holdings. The investment policy of the plan prohibits investment in
STRATTEC stock. Investment risk is measured and monitored on an ongoing basis through periodic
investment portfolio reviews, annual liability measurements and periodic asset/liability studies.
The pension plan weighted-average asset allocations by asset category are as follows:
| Target Allocation | June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | ||||||||||
Equity investments |
65 | % | 56 | % | 61 | % | ||||||
Fixed-income investments |
35 | % | 44 | % | 39 | % | ||||||
Total |
100 | % | 100 | % | 100 | % | ||||||
The following is a summary, by asset category, of the fair value of pension plan assets at the
June 30, 2010 measurement date (thousands of dollars):
| Asset Category | Level 1 | Level 2 | Level 3 | Total | ||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 1,508 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,508 | ||||||||
Equity Securities: |
||||||||||||||||
Domestic |
4,067 | — | — | 4,067 | ||||||||||||
Foreign |
158 | — | — | 158 | ||||||||||||
Equity Funds: |
||||||||||||||||
Small Cap |
6,392 | — | — | 6,392 | ||||||||||||
Mid Cap |
4,727 | — | — | 4,727 | ||||||||||||
Large Cap |
17,060 | — | — | 17,060 | ||||||||||||
International |
5,970 | — | — | 5,970 | ||||||||||||
Marketable Limited
Partnership |
21 | — | — | 21 | ||||||||||||
Taxable Bond Funds |
28,865 | — | — | 28,865 | ||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 68,768 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 68,768 | ||||||||
The expected long-term rate of return on U.S. pension plan assets used to calculate the
2010 net periodic benefit cost was 8.0 percent. The target asset allocation is 65 percent public
equity and 35 percent fixed income. The 8.0 percent is approximated by applying returns of 10
percent on public equity and 6 percent on fixed income to the target allocation. The actual
historical returns are also relevant. Annualized returns for periods ended June 27, 2010 were
3.02 percent for 10 years, 6.80 percent for 15 years, 7.81 percent for 20 years, 9.22 percent for
25 years and 10.24 percent for 30 years.
We expect to contribute approximately $2 million to our qualified pension plan, $3.1
million to our SERP and $1.2 million to our postretirement health care plan in 2011. The
following benefit payments, which reflect expected future service, as appropriate, are expected
to be paid (thousands of dollars):
| Pension and SERP Benefits | Postretirement Benefits | |||||||
2011 |
$ | 7,425 | $ | 1,151 | ||||
2012 |
4,669 | 1,091 | ||||||
2013 |
4,884 | 975 | ||||||
2014 |
5,193 | 841 | ||||||
2015 |
5,279 | 597 | ||||||
2016-2020 |
29,089 | 1,185 | ||||||
All U.S. associates may participate in a 401(k) Plan. As of January 1, 2010, we
contribute 100 percent up to the first 5 percent of eligible compensation that a participant
contributes to the plan. Prior to January 1, 2010, we contributed a fixed percentage up to the
first 6 percent of eligible compensation that a participant contributed to the plan. Prior to
January 1, 2010, the fixed percentage contribution for
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 41 |

NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
all U.S. bargaining unit associates was 50 percent. The fixed percentage contribution for all
U.S. salaried associates was 50 percent prior to January 1, 2009 and 20 percent from January 1,
2009 through December 31, 2009. Our contributions totaled approximately $743,000 in 2010, $464,000
in 2009 and $613,000 in 2008.
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
We have 12,000,000 shares of authorized common stock, par value $.01 per share, with
3,275,955 and 3,261,968 shares outstanding at June 27, 2010 and June 28, 2009, respectively.
Holders of our common stock are entitled to one vote for each share on all matters voted on by
shareholders.
Our Board of Directors authorized a stock repurchase program to buy back up to
3,839,395 outstanding shares as of June 27, 2010. As of June 27, 2010, 3,655,322 shares have been
repurchased under this program at a cost of approximately $136.4 million.
EARNINGS (LOSS) PER SHARE (“EPS”) (“LPS”)
Basic earnings (loss) per share is computed on the basis of the weighted average number
of shares of common stock outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per share is computed on
the basis of the weighted average number of shares of common stock plus the dilutive potential
common shares outstanding during the period using the treasury stock method. Dilutive potential
common shares include outstanding stock options and restricted stock awards. The reconciliation of
the components of the basic and diluted per share computations that follows includes amounts for
2008 that have been retrospectively adjusted for our change in 2009 from the last-in, first-out
method of inventory accounting to the first-in, first-out method (in thousands, except per share
amounts):
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net | Per Share | Net | Per Share | Net | Per Share | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Income | Shares | Amount | Loss | Shares | Amount | Income | Shares | Amount | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Basic EPS (LPS) |
$ | 3,421 | 3,271 | $ | 1.05 | $ | (6,122 | ) | 3,280 | $ | (1.87 | ) | $ | 2,781 | 3,487 | $ | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||||
Stock-based
compensation |
9 | 4 | 7 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Diluted EPS
(LPS) |
$ | 3,421 | 3,280 | $ | 1.04 | $ | (6,122 | ) | 3,284 | $ | (1.86 | ) | $ | 2,781 | 3,494 | $ | 0.80 | |||||||||||||||||||
As of June 27, 2010, options to purchase 207,650 shares of common stock at a
weighted-average exercise price of $42.17 were excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings
per share because their inclusion would have been anti-dilutive. As of June 28, 2009, options to
purchase 227,240 shares of common stock at a weighted-average exercise price of $38.07 were
excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings per share because their inclusion would have been
anti-dilutive. As of June 29, 2008, options to purchase 184,680 shares of common stock at a
weighted-average exercise price of $59.13 were excluded from the calculation of diluted earnings
per share because their inclusion would have been anti-dilutive.
In June 2008, the FASB issued a new accounting standard that clarifies when instruments
granted in share-based payment transactions should be included in computing EPS. Under the new
standard, companies are required to include unvested share-based payment awards that contain
non-forfeitable rights to receive dividends in their calculation of basic EPS and are required to
calculate basic EPS using the “two-class method.” The two-class method of computing EPS is an
earnings allocation formula that determines EPS for each class of common stock and participating
securities according to dividends declared (or accumulated) and participation rights in
undistributed earnings. We adopted this new accounting standard on a retrospective basis in the
first quarter of fiscal 2010, and the adoption did not have an impact on EPS.
STOCK OPTION AND PURCHASE PLANS
A summary of stock option activity under the plan is as
follows:
| Weighted | Weighted Average | Aggregate | ||||||||||||||
| Average | Remaining | Intrinsic Value | ||||||||||||||
| Shares | Exercise Price | Contractual Term (in years) | (in thousands) | |||||||||||||
Balance at July 1, 2007 |
235,420 | $ | 58.71 | |||||||||||||
Granted |
— | $ | — | |||||||||||||
Exercised |
— | $ | — | |||||||||||||
Expired |
(47,640 | ) | $ | 58.59 | ||||||||||||
Terminated |
— | $ | — | |||||||||||||
Balance at June 29, 2008 |
187,780 | $ | 58.74 | |||||||||||||
Granted |
96,800 | $ | 11.80 | |||||||||||||
Exercised |
— | $ | — | |||||||||||||
Expired |
(52,340 | ) | $ | 61.68 | ||||||||||||
Terminated |
(5,000 | ) | $ | 58.55 | ||||||||||||
Balance at June 28, 2009 |
227,240 | $ | 38.07 | |||||||||||||
Granted |
80,000 | $ | 17.73 | |||||||||||||
Exercised |
(2,400 | ) | $ | 10.92 | ||||||||||||
Expired |
(2,790 | ) | $ | 61.22 | ||||||||||||
Terminated |
(4,400 | ) | $ | 10.92 | ||||||||||||
Balance at June 27, 2010 |
297,650 | $ | 33.01 | 6.2 | $ | 1,214 | ||||||||||
Exercisable as of: |
||||||||||||||||
June 27, 2010 |
149,350 | $ | 50.92 | 3.4 | $ | 212 | ||||||||||
June 28, 2009 |
130,440 | $ | 57.57 | 3.5 | $ | — | ||||||||||
June 29, 2008 |
148,440 | $ | 58.09 | 3.6 | $ | 3 | ||||||||||
Available for grant as of
June 27, 2010 |
250,893 | |||||||||||||||
No options included above were granted at a price greater than the market value on the date
of grant during 2010, 2009 or 2008.
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 42 |
NOTES TO FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
A summary of restricted stock activity under the plan is as follows:
| Weighted Average | ||||||||
| Grant Date | ||||||||
| Shares | Fair Value | |||||||
Nonvested Balance at July 1, 2007 |
19,400 | $ | 45.56 | |||||
Granted |
10,000 | $ | 47.78 | |||||
Vested |
— | $ | — | |||||
Forfeited |
— | $ | — | |||||
Nonvested Balance at June 29, 2008 |
29,400 | $ | 46.32 | |||||
Granted |
10,000 | $ | 29.00 | |||||
Vested |
(10,200 | ) | $ | 50.58 | ||||
Forfeited |
(1,000 | ) | $ | 46.22 | ||||
Nonvested Balance at June 28, 2009 |
28,200 | $ | 38.64 | |||||
Granted |
10,000 | $ | 14.75 | |||||
Vested |
(9,000 | ) | $ | 40.00 | ||||
Forfeited |
(1,700 | ) | $ | 32.28 | ||||
Nonvested Balance at June 27, 2010 |
27,500 | $ | 29.90 | |||||
We have an Employee Stock Purchase Plan to provide substantially all U.S. full-time
associates an opportunity to purchase shares of STRATTEC common stock through payroll deductions. A
participant may contribute a maximum of $5,200 per calendar year to the plan. On the last day of
each month, participant account balances are used to purchase shares of stock at the average of the
highest and lowest reported sales prices of a share of STRATTEC common stock on the NASDAQ Global
Market. A total of 100,000 shares may be issued under the plan. Shares issued from treasury stock
under the plan totaled 2,587 at an average price of $17.01 during 2010, 2,548 at an average price
of $15.63 during 2009 and 704 at an average price of $41.62 during 2008. A total of 78,080 shares
are available for purchase under the plan as of June 27, 2010.
EXPORT SALES
| Export sales are summarized below (thousands of dollars): |
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
Export Sales |
$ | 29,170 | $ | 28,050 | $ | 25,714 | ||||||
Percent of Net Sales |
14 | % | 22 | % | 16 | % | ||||||
These sales were primarily to automotive manufacturing assembly plants in Canada,
China, Mexico and Korea.
SALES AND RECEIVABLE CONCENTRATION
Sales to our largest customers were as follows (thousands of dollars and percent of total
net sales):
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sales | % | Sales | % | Sales | % | |||||||||||||||||||
General Motors
Company |
$ | 51,673 | 25 | % | $ | 39,156 | 31 | % | $ | 45,039 | 28 | % | ||||||||||||
Ford Motor Company |
18,435 | 9 | % | 12,575 | 10 | % | 19,419 | 12 | % | |||||||||||||||
Chrysler Group LLC |
68,216 | 33 | % | 31,864 | 25 | % | 40,209 | 25 | % | |||||||||||||||
| $ | 138,324 | 67 | % | $ | 83,595 | 66 | % | $ | 104,667 | 66 | % | |||||||||||||
Receivables from our largest customers were as follows (thousands of dollars and percent of
gross receivables):
| June 27, 2010 | June 28, 2009 | |||||||||||||||
| Receivables | % | Receivables | % | |||||||||||||
General Motors
Company |
$ | 8,125 | 22 | % | $ | 7,029 | 39 | % | ||||||||
Ford Motor Company |
2,718 | 7 | % | 2,376 | 13 | % | ||||||||||
Chrysler Group LLC |
12,231 | 34 | % | 2,627 | 15 | % | ||||||||||
| $ | 23,074 | 63 | % | $ | 12,032 | 67 | % | |||||||||
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 43 |

REPORTS
REPORT ON MANAGEMENT’S ASSESSMENT OF INTERNAL CONTROL OVER FINANCIAL REPORTING
STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION is responsible for the preparation, integrity, and fair
presentation of the consolidated financial statements included in this annual report. The
consolidated financial statements and notes included in this annual report have been prepared in
conformity with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America and
necessarily include some amounts that are based on management’s best estimates and judgments.
We, as management of STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION, are responsible for establishing and
maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting that is designed to produce
reliable financial statements in conformity with United States generally accepted accounting
principles. The system of internal control over financial reporting as it relates to the financial
statements is evaluated for effectiveness by management and tested for reliability through a
program of internal audits. Actions are taken to correct potential deficiencies as they are
identified. Any system of internal control, no matter how well designed, has inherent limitations,
including the possibility that a control can be circumvented or overridden and misstatements due
to error or fraud may occur and not be detected. Also, because of changes in conditions, internal
control effectiveness may vary over time. Accordingly, even an effective system of internal
control will provide only reasonable assurance with respect to financial statement preparation.
The Audit Committee of the Company’s Board of Directors, consisting entirely of independent
directors, meets regularly with management and the independent registered public accounting firm,
and reviews audit plans and results, as well as management’s actions taken in discharging
responsibilities for accounting, financial reporting, and internal control. Deloitte & Touche
LLP, independent registered public accounting firm, has direct and confidential access to the
Audit Committee at all times to discuss the results of their examinations.
Management assessed the Corporation’s system of internal control over financial reporting as
of June 27, 2010, in relation to criteria for effective internal control over financial reporting
as described in “Internal Control – Integrated Framework,” issued by the Committee of Sponsoring
Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Based on the assessment, management concludes
that, as of June 27, 2010, its system of internal control over financial reporting is effective and
meets the criteria of the “Internal Control – Integrated Framework.” Deloitte & Touche LLP,
independent registered public accounting firm, has issued an attestation report on the
Corporation’s internal control over financial reporting, which is included herein.
|
 |
|
Harold M. Stratton II
|
Patrick J. Hansen | |
Chairman and
|
Senior Vice President and | |
Chief Executive Officer
|
Chief Financial Officer |
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 44 |
REPORTS
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION:
We have audited the internal control over financial reporting of STRATTEC SECURITY
CORPORATION and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of June 27, 2010, based on criteria established
in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations
of the Treadway Commission. The Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective
internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal
control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal
Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s
internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting
Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to
obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was
maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal
control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, testing and
evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk,
and performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe
that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed by, or under the
supervision of, the company’s principal executive and principal financial officers, or persons
performing similar functions, and effected by the company’s board of directors, management, and
other personnel to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting
and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally
accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes
those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable
detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the
company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit
preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles,
and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with
authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance
regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the
company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of the inherent limitations of internal control over financial reporting, including
the possibility of collusion or improper management override of controls, material misstatements
due to error or fraud may not be prevented or detected on a timely basis. Also, projections of any
evaluation of the effectiveness of the internal control over financial reporting to future periods
are subject to the risk that the controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions,
or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, the Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal
control over financial reporting as of June 27, 2010, based on the criteria established in
Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring
Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting
Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated financial statements as of and for the year ended
June 27, 2010 of the Company and our report dated September 1, 2010 expressed an unqualified
opinion on those financial statements.
Deloitte & Touche LLP
Milwaukee, Wisconsin
September 1, 2010
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 45 |

REPORTS
REPORT OF INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
To the Board of Directors and Shareholders of STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheet of STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION
and subsidiaries (the “Company”) as of June 27, 2010, and the related consolidated statement of
operations and comprehensive income, shareholders’ equity, and cash flows for the year then ended.
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility
is to express an opinion on these financial statements based on our audit. The consolidated
financial statements of the Company as of June 28, 2009 and the two years in the period ended June
28, 2009 were audited by other auditors whose report dated August 24, 2009, September 1, 2010 as to
the effects of the adoption of new accounting guidance on the presentation of noncontrolling
interests as described in the “Organizational and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies”
footnote, expressed an unqualified opinion and included explanatory paragraphs on the Company’s
changes in accounting method of inventory and accounting for noncontrolling interests, on those
statements.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting
Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to
obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material
misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and
disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting
principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall
financial statement presentation. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our
opinion.
In our opinion, such consolidated financial statements present fairly, in all material
respects, the financial position of the Company as of June 27, 2010, and the results of their
operations and their cash flows for the year then ended in conformity with accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States of America.
We have also audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting
Oversight Board (United States), the Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of June
27, 2010, based on the criteria established in Internal Control — Integrated Framework issued by
the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission and our report dated September
1, 2010 expressed an unqualified opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial
reporting.
Deloitte & Touche LLP
Milwaukee, Wisconsin
September 1, 2010
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 46 |
FINANCIAL SUMMARY
FIVE-YEAR FINANCIAL SUMMARY
The financial data for each period presented below reflects the consolidated results of
STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION and its wholly owned subsidiaries. Fiscal years 2006 through 2009
have been retrospectively adjusted for the adoption of a new accounting standard issued by the
Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) related to non-controlling interests in consolidated
financial statements. Fiscal years 2006 through 2008 have been retrospectively adjusted for our
change in 2009 from the last-in, first-out method of inventory accounting to the first-in,
first-out method. Additional details are available in Notes to Financial Statements. The
information below should be read in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis,” and
the Financial Statements and Notes thereto included elsewhere herein. The following data are in
thousands of dollars except per share amounts.
| Fiscal Years | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | ||||||||||||||||
INCOME STATEMENT DATA |
||||||||||||||||||||
Net sales |
$ | 207,964 | $ | 126,097 | $ | 159,642 | $ | 167,707 | $ | 181,197 | ||||||||||
Gross profit |
33,042 | 13,240 | 24,767 | 26,520 | 38,354 | |||||||||||||||
Engineering, selling, and
administrative expenses |
29,939 | 25,480 | 23,962 | 20,189 | 22,067 | |||||||||||||||
Impairment charge |
223 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Environmental reserve
adjustment |
(1,125 | ) | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||
(Recovery of) provision for
doubtful accounts |
(421 | ) | 500 | — | — | 1,622 | ||||||||||||||
Income (loss) from operations |
4,426 | (12,740 | ) | 805 | 6,331 | 14,665 | ||||||||||||||
Interest income |
86 | 731 | 2,749 | 3,611 | 2,563 | |||||||||||||||
Equity earnings of joint
ventures |
1,008 | 245 | 561 | 394 | 188 | |||||||||||||||
Interest expense -
related parties |
(225 | ) | (164 | ) | (31 | ) | — | — | ||||||||||||
Other income, net |
312 | 804 | (300 | ) | 321 | 772 | ||||||||||||||
Income (loss) before taxes
and
non-controlling interest |
5,607 | (11,124 | ) | 3,784 | 10,657 | 18,188 | ||||||||||||||
Provision (benefit) for
income taxes |
1,666 | (4,222 | ) | 977 | 2,533 | 4,900 | ||||||||||||||
Net income (loss) |
3,941 | (6,902 | ) | 2,807 | 8,124 | 13,288 | ||||||||||||||
Net (income) loss
attributable to
non-controlling interest |
(520 | ) | 780 | (26 | ) | 75 | — | |||||||||||||
Net income (loss)
attributable to
STRATTEC SECURITY
CORPORATION |
$ | 3,421 | $ | (6,122 | ) | $ | 2,781 | $ | 8,199 | $ | 13,288 | |||||||||
Earnings (Loss) per share: |
||||||||||||||||||||
Basic |
$ | 1.05 | $ | (1.87 | ) | $ | 0.80 | $ | 2.31 | $ | 3.58 | |||||||||
Diluted |
1.04 | (1.86 | ) | 0.80 | 2.31 | 3.57 | ||||||||||||||
Cash dividends declared per share: |
$ | — | $ | 0.30 | $ | 1.60 | $ | — | $ | — | ||||||||||
BALANCE SHEET DATA |
||||||||||||||||||||
Net working capital |
$ | 43,777 | $ | 41,710 | $ | 72,835 | $ | 84,077 | $ | 83,242 | ||||||||||
Total assets |
145,002 | 128,189 | 144,221 | 151,440 | 157,270 | |||||||||||||||
Long-term liabilities |
22,982 | 24,784 | 12,389 | 13,431 | 10,510 | |||||||||||||||
Total STRATTEC SECURITY
CORPORATION
Shareholders’ equity |
74,126 | 71,418 | 97,940 | 105,954 | 113,253 | |||||||||||||||
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 47 |

FINANCIAL SUMMARY/PERFORMANCE GRAPH
QUARTERLY FINANCIAL DATA (UNAUDITED)
The following data are in thousands of dollars except per share amounts. Quarterly data
presented below for fiscal 2009 has been retrospectively adjusted for our change in 2009 from the
last-in, first-out method of inventory accounting to the first-in, first-out method.
| Cash | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | Earnings | Dividends | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Attributable to | (Loss) Per Share | Declared | Market Price Per Share | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quarter | Net Sales | Gross Profit | STRATTEC | Basic | Diluted | Per Share | High | Low | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2010 |
First | $ | 41,181 | $ | 6,798 | $ | 943 | $ | 0.29 | $ | 0.29 | $ | — | $ | 15.40 | $ | 13.03 | |||||||||||||||||
| Second | 52,540 | 7,653 | 844 | 0.26 | 0.26 | — | 18.50 | 13.29 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Third | 52,883 | 8,861 | 781 | 0.24 | 0.24 | — | 22.15 | 16.75 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fourth | 61,360 | 9,730 | 853 | 0.26 | 0.26 | — | 27.80 | 19.52 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| TOTAL | $ | 207,964 | $ | 33,042 | $ | 3,421 | $ | 1.05 | $ | 1.04 | $ | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||
2009 |
First | $ | 34,731 | $ | 5,424 | $ | 20 | $ | 0.01 | $ | 0.01 | $ | 0.15 | $ | 38.45 | $ | 25.63 | |||||||||||||||||
| Second | 33,799 | 2,911 | (1,202 | ) | (0.37 | ) | (0.37 | ) | 0.15 | 28.90 | 12.06 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Third | 29,348 | 2,063 | (2,822 | ) | (0.87 | ) | (0.87 | ) | — | 18.89 | 6.26 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fourth | 28,219 | 2,842 | (2,118 | ) | (0.65 | ) | (0.65 | ) | — | 16.03 | 7.40 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| TOTAL | $ | 126,097 | $ | 13,240 | $ | (6,122 | ) | $ | (1.87 | ) | $ | (1.86 | ) | $ | 0.30 | |||||||||||||||||||
Registered shareholders of record at June 27, 2010, were 2,142.
The chart below shows a comparison of the cumulative return since July 1, 2005 had $100 been
invested at the close of business on July 1, 2005 in STRATTEC Common Stock, the NASDAQ Composite
Index (all issuers), and the Dow Jones U.S. Auto Parts Index.
COMPARISON OF 5-YEAR CUMULATIVE TOTAL RETURN*
Among STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION, The NASDAQ Composite Index
And The Dow Jones U.S. Auto Parts Index
Among STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION, The NASDAQ Composite Index
And The Dow Jones U.S. Auto Parts Index
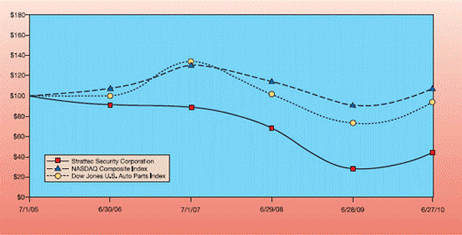
| 7/1/05 | 6/30/06 | 7/1/07 | 6/29/08 | 6/28/09 | 6/27/10 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
STRATTEC** |
100 | 93 | 87 | 67 | 27 | 43 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NASDAQ Composite Index |
100 | 107 | 131 | 114 | 90 | 106 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Dow Jones U.S. Auto Parts Index |
100 | 100 | 136 | 101 | 74 | 95 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| * | $100 invested on July 1, 2005 in stock or index-including reinvestment of dividends. Indexes calculated on a month-end basis. | |
| ** | The fiscal year end closing price of STRATTEC Common Stock on July 1, 2005 was $53.82, the closing price on June 30, 2006, was $49.81, the closing price on June 29, 2007 was $46.97, the closing price on June 27, 2008 was $34.99, the closing price on June 26, 2009 was $13.90 and the closing price on June 25, 2010 was $22.01. |
| 2010 STRATTEC Annual Report | 48 |

| DIRECTORS/OFFICERS/SHAREHOLDERS’ INFORMATION STRATTEC Board of Directors: (Left to Right) Frank J. Krejci, Michael J. Koss, Robert Feitler, Harold M. Stratton II, David R. Zimmer BOARD OF DIRECTORS Harold M. Stratton II, 62 Chairman and Chief Executive Officer Frank J. Krejci, 60 President and Chief Operating Officer Robert Feitler, 79 Former President and Chief Operating Officer of Weyco Group, Inc. Chairman of the Executive Committee and Director of Weyco Group, Inc. Michael J. Koss, 56 President and Chief Executive Officer of Koss Corporation Director of Koss Corporation David R. Zimmer, 64 Managing Partner of Stonebridge Business Partners CORPORATE OFFICERS Harold M. Stratton II, 62 Frank J. Krejci, 60 Patrick J. Hansen, 51 Senior Vice President-Chief Financial Officer, Treasurer and Secretary Dennis A. Kazmierski, 58 Vice President-Marketing and Sales Kathryn E. Scherbarth, 54 Vice President-Milwaukee Operations Rolando J. Guillot, 42 Vice President-Mexican Operations Brian J. Reetz, 52 Vice President-Security Products Richard P. Messina, 44 Vice President-Access Products SHAREHOLDERS’ INFORMATION Annual Meeting The Annual Meeting of Shareholders will convene at 8:00 a.m. (CDT) on October 5, 2010, at the Radisson Hotel, 7065 North Port Washington Road, Milwaukee, WI 53217 Common Stock STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION common stock is traded on the NASDAQ Global Market under the symbol: STRT. Form 10-K You may receive a copy of the STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION Form 10-K, filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission, by writing to the Secretary at STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION, 3333 W. Good Hope Road, Milwaukee, WI 53209. Corporate Governance To review the Company’s corporate governance, board committee charters and code of business ethics, please visit the “Corporate Governance” section of our Web site at www.strattec.com. Shareholder Inquiries Communications concerning the transfer of shares, lost certificates or changes of address should be directed to the Transfer Agent. Transfer Agent and Registrar Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. Shareholder Services P.O. Box 64854 St. Paul, MN 55164-0854 1.800.468.9716 |
49

| BOLT lear ns your vehicle key! Buy direct at www.boltlock.com A single turn is all it takes to enjoy single key convenience. STRATTEC SECURITY CORPORATION 3333 WEST GOOD HOPE ROAD MILWAUKEE, WI 53209 PHONE 414.247.3333 FAX 414.247.3329 www.strattec.com |
