Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| 10-K - FORM 10-K - MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORP /MI/ | k48985e10vk.htm |
| EX-31 - EX-31 - MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORP /MI/ | k48985exv31.htm |
| EX-21 - EX-21 - MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORP /MI/ | k48985exv21.htm |
| EX-23.1 - EX-23.1 - MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORP /MI/ | k48985exv23w1.htm |
| EX-32.2 - EX-32.2 - MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORP /MI/ | k48985exv32w2.htm |
| EX-32.1 - EX-32.1 - MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORP /MI/ | k48985exv32w1.htm |
Exhibit 13
2009
ANNUAL REPORT

Table of Contents
To Our Shareholders
|
1 | |||
Five-Year Overview
|
5 | |||
Regional Review
|
7 | |||
Selected Financial Highlights
|
13 | |||
Quarterly Financial Summary
|
14 | |||
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
|
15 | |||
Consolidated Balance Sheets
|
16 | |||
Consolidated Statements of Operations
|
17 | |||
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity
|
18 | |||
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
|
19 | |||
Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements
|
20 | |||
Selected Financial Data
|
45 | |||
Summary Quarterly Financial Information
|
46 | |||
Market Information
|
48 | |||
Shareholder Return Performance Graph
|
49 | |||
Forward-Looking Statements
|
50 | |||
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial
Condition and Results of Operations
|
51 | |||
Directors and Officers
|
72 |
BUSINESS OF THE CORPORATION
Mackinac Financial Corporation is a registered bank holding company formed under the Bank Holding
Company Act of 1956 with assets in excess of $500 million and whose common stock is traded on the
NASDAQ stock market as “MFNC.” The principal subsidiary of the Corporation is mBank.
Headquartered in Manistique, Michigan, mBank has 10 branch locations; six in the Upper Peninsula,
three in the Northern Lower Peninsula and one in Oakland County, Michigan. The newest branch,
located in Escanaba, opened on March 24, 2009. The Company’s banking services include commercial
lending and treasury management products and services geared toward small to mid-sized businesses,
as well as a full array of personal and business deposit products and consumer loans.
FORM 10-K
A copy of the Annual Report to the Securities and Exchange Commission on Form 10-K is available
without charge by writing the Shareholders’ Relations Department, Mackinac Financial Corporation,
130 South Cedar Street, Manistique, Michigan, 49854.
MARKET SUMMARY
The Corporation’s common stock is traded on the Nasdaq Capital Market under the symbol MFNC. The
Corporation had 1,228 shareholders of record as of March 30, 2010.
To Our Shareholders

March 30, 2010
Dear Fellow Shareholders:
This letter will provide you with a review of the performance of Mackinac Financial Corporation
through the end of 2009 and our thoughts about business strategy as we move through 2010. In
addition, we have included an overview of our five year performance since the recapitalization of
the company in December of 2004, and a regional market performance review to better detail the
progress of the company during this period of economic turmoil in the State of Michigan and
national markets.
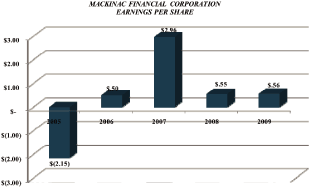
The company reported net income of $1.907 million, or $.56 per share, for the year ended December
31, 2009, compared to a net income of $1.872 million, or $.55 per share, for 2008. The 2009
results include $1.208 million of gains related to the sale of two branch offices and $1.471
million of security gains. The 2008 results include the positive effect, $3.475 million, of a
lawsuit settlement and the negative effect, $.425 million, of a severance agreement. Shareholders’
equity totaled $55.299 million at December 31, 2009, compared to $41.552 million at the end of
2008, an increase of $13.747 million. This increase includes $10.5 million of preferred stock that
was issued by MFNC as a TARP recipient, consolidated net income of $1.907 million noted above, the
capital contribution impact of stock options and also the increase in equity due to the increase in
the market value of held-for-sale investments, which amounted to $.648 million.
In 2009, we continued to focus our efforts to improve the overall operation and value of the
company. These included core deposit generation through our branch network to offset reliance on
wholesale funding sources, originating new loans through various government guaranteed loan
programs with good risk / return pricing, and noninterest expense management and proper allocation
of personnel and capital resources to make the company more efficient.
Noted below are some highlighted 2009 achievements as they relate to these initiatives;
| • | The increase in new core deposits of approximately $55 million net of the sale of the two noted branches above with approximately $29 million in deposits. We experienced deposit growth in all of our markets, with $26 million in Northern Lower Michigan, $20 million in Southeast Michigan and $10 million in the Upper Peninsula. Most of our 2009 deposit growth occurred in low cost transactional accounts which grew by $41 million. | ||
| • | In April of 2009, the Corporation, in an abundance of caution, decided to participate in the TARP program and issued $11 million of preferred stock. In order to offset the cost of the preferred, we infused a portion of the TARP proceeds, $3 million, into the Bank and leveraged this excess capital by purchasing approximately $40 million of investment securities. We funded the purchase of these investments by issuing brokered deposits. In December, we began the process of deleveraging this position in anticipation of narrowing spreads and recognized a fourth quarter security gain of $.827 million. This strategy has resulted in overall security gains in excess of $1 million. | ||
| • | Steady loan demand with approximately $88 million of new loan production with a $14 million increase in loans outstanding, after reductions for amortization and payoffs. After the receipt of the TARP funds in April of 2009, we originated over $74 million of new loans and through February of 2010 that number is approximately $85 million. We were successful in producing loans in all of our markets in 2009, but were less aggressive in Southeast Michigan where the recession remains severe. Loan production for 2009 totaled $44 million in the Upper Peninsula, $35 million in Northern Lower Michigan and $9 million in Southeast Michigan. | ||
| • | Continued development of our government SBA/USDA lending programs to become a leader state wide in these initiatives to mitigate credit risk substantially when new loans are originated, along with positively augmenting non-interest income though the sale of the guaranteed portion of the loan for a premium gain. |
1
To Our Shareholders
| • | Divesting of two outlier branches with a pretax gain to the company of approximately $1.2 million which also decreases operating expenses and results in a more manageable footprint for the company. | ||
| • | Enhancing our core earnings by controlling noninterest expense, increasing noninterest income and net interest margin improvement. The combination of these three factors resulted in an improved efficiency ratio from 86% in 2008 to 73% in 2009. In addition for future margin improvement in this low interest rate environment, we continued to use interest rate floors for the majority of all new and renewed variable rate loans. | ||
| • | Prudent and proactive credit administration practices to quickly identify any potential problem assets to better monitor our portfolio given the recession which continues to put substantial pressure on many businesses’ cash flow and overall operations. |
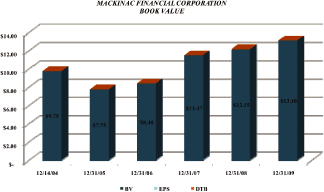
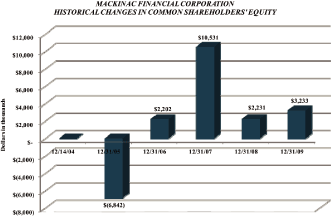
The book value per share of the company increased by $.95 to $13.10 (excluding TARP proceeds). This
marks the fourth consecutive year of increased shareholder value and a cumulative book value
increase of $3.35 per share since the December 2004 recapitalization at $9.75 per share. The chart
below is a recap of various balances and book value per share as of the end of the last three years
(dollars in thousands, except per share data):
| 2009/2008 | 2008/2007 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| As of December 31, | Increase (Decrease) | Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | Dollars | Percentage | Dollars | Percentage | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Loans |
$ | 384,310 | $ | 370,280 | $ | 355,079 | $ | 14,030 | 3.79 | % | $ | 15,201 | 4.28 | % | ||||||||||||||
Assets |
515,452 | 451,431 | 408,880 | 64,021 | 14.18 | 42,551 | 10.41 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Deposits |
421,389 | 371,097 | 320,827 | 50,292 | 13.55 | 50,270 | 15.67 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Borrowings |
36,140 | 36,210 | 45,949 | (70 | ) | (0.19 | ) | (9,739 | ) | (21.20 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Shareholders’ equity |
55,299 | 41,552 | 39,321 | 13,747 | 33.08 | 2,231 | 5.67 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Book vaue per share |
13.10 | 12.15 | 11.47 | .95 | 7.82 | .68 | 5.93 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Credit Quality
Nonperforming assets increased in 2009 as the economy continued to weaken, especially in Southeast
Michigan. Nonperforming loans totaled $15.237 million, or 3.96% of total loans at December 31,
2009. Nonperforming assets at December 31, 2009 were $21.041 million, 4.08% of total assets,
compared to $7.076 million or 1.57% of total assets at December 31, 2008. The elevated level of
nonperforming assets, while still below peers and manageable, does concern us given the challenges
throughout the state. However; we do not have a systematic problem with our overall loan portfolio
as approximately 75% of these totals are centered around 5-6 customer relationships. The increase
in these problem assets did hamper overall earnings with higher than anticipated provision charges,
carrying costs and legal expense. The nonperforming assets by region are as follows; $13 million
in Southeast Michigan, $6 million in Northern Lower Michigan and $2 million in the Upper Peninsula.
We continue to devote significant management attention to the administration of these problem
assets and hope to have resolution in the first half of 2010 on several of these. The increased
stress in our loan portfolio resulting from the ongoing troubles in the state has led us to a very
cautious approach in all markets, but particularly in Southeast Michigan. This approach includes
an emphasis on smaller more granular loans. We will continue
to focus on early identification and resolution of all our problem credits to minimize carrying
costs, collateral deterioration, and overall risk exposure of capital loss to the company.
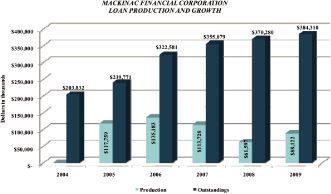
Loan Growth/Production
Loan growth in 2009 occurred in a challenging and tough Michigan economic climate with loans
increasing by $14.030 million in 2009, despite accelerated levels of loan pay-downs and runoff
totaling $60.415 million. Total bank wide new loan production equated to $88.122 million. Through
an annual credit process review, we continue to evaluate and adjust underwriting standards to keep
pace with the changing risk issues presented by the market. A good portion of loan runoff in 2009
was due to our discipline in re-qualifying renewal loans and repricing to garner acceptable returns
adjusted for risk. The majority of the loan growth was centered in the commercial real estate,
construction, and 1-4 family residential loan
2
To Our Shareholders
portfolios. We have purposely avoided the subprime lending opportunities in these sectors, and
do not offer any subprime lending products within any of our product lines of business.
Loan production in our three geographical regions is shown below.
| For the Year Ending December 31, | ||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||
REGION |
||||||||||||
Upper Peninsula |
43,777 | 37,040 | $ | 40,876 | ||||||||
Northern Lower Peninsula |
35,027 | 14,183 | 22,448 | |||||||||
Southeast Michigan |
9,318 | 10,374 | 50,404 | |||||||||
TOTAL |
$ | 88,122 | $ | 61,597 | $ | 113,728 | ||||||
Government Guaranteed Lending Programs
In 2007, the company made a concerted effort to become a premier SBA/USDA lender throughout the
State of Michigan and separate ourselves from our local competition in terms of the adjudication of
these types of loans to minimize credit risk and increase noninterest income through the sale of
the guaranteed portion of the loans for a premium. As you will note from the chart shown below, we
have had success due to the strong competencies of our lenders and credit personnel. For the SBA
fiscal year ended September 30, 2009, we ranked 3rd in the entire State of Michigan in
dollar volume of SBA loans processed at $13.214 million and 7th in number of loans
processed at 36. In addition to the level of SBA production generated, the Corporation recorded
$.498 million in fees for 2009, for a total of $.813 million over the last three years. The company
does not sell all the loan guarantees from every credit, only those where acceptable market rates
are paid above par that warrant recognizing the income now, and where the company feels that the
reinvestment of the monies paid can be lent out again in sufficient time to exceed the lost
interest income from the loan sold.
| SBA Loans Originated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For the Year Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| # Loans | SBA Amount | Premium | # Loans | SBA Amount | Premium | # Loans | SBA Amount | Premium | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
UP |
32 | $ | 6,797 | $ | 373 | 2 | $ | 386 | $ | 18 | 4 | $ | 1,879 | $ | 141 | |||||||||||||||||||||
NLP |
10 | 5,829 | 125 | 6 | 1,009 | 5 | 5 | 2,837 | 116 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
SEM |
— | — | — | 3 | 572 | 3 | 3 | 952 | 32 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total |
42 | $ | 12,626 | $ | 498 | 11 | $ | 1,967 | $ | 26 | 12 | $ | 5,668 | $ | 289 | |||||||||||||||||||||
mBank is being presented with two awards for SBA fiscal year 2009, “Business Development
Lender of the Year”, (2nd year in a row we have won that award), as mBank had the
largest percentage increase in of approvals from 2008 to 2009. In addition, we have been awarded
the “Community Lender of the Year” as mBank had the best overall performance among MI based, non
“Preferred Lender Program” lenders, with criteria including total new volume, new market activity,
and comparison with historical performance. We are pleased with the progress we have made here;
first in terms to the benefit of the company, but also for the many local businesses in these
markets that through these programs are provided the capital to grow their organizations to help
rebuild the economic base of the State.
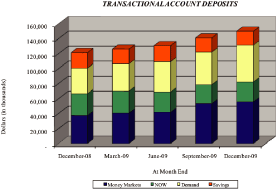
Deposit Growth
We continue to have success in growing core bank deposits, which we define as demand deposits,
interest bearing checking accounts, money market savings accounts and certificates of deposit less
than $100,000. In 2009, we increased core deposits by $14 million, net of the $30 million in
deposits sold.
3
To Our Shareholders
Shown below is the mix of our deposits for the three most recent years.
| DEPOSIT MIX | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| As of December 31, | Percent Change | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | Mix | 2008 | Mix | 2007 | Mix | 2009/2008 | 2008/2007 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
CORE DEPOSITS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Transactional accounts: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Noninterest bearing |
$ | 35,878 | 8.51 | % | $ | 30,099 | 8.11 | % | $ | 25,557 | 7.97 | % | 19.20 | % | 17.77 | % | ||||||||||||||||
NOW, money market, checking |
95,790 | 22.73 | 70,584 | 19.02 | 81,160 | 25.30 | 35.71 | (13.03 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Savings |
18,207 | 4.32 | 20,730 | 5.59 | 12,485 | 3.89 | (12.17 | ) | 66.04 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Total transactional accounts |
149,875 | 35.57 | 121,413 | 32.72 | 119,202 | 37.15 | 23.44 | 1.85 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Certficates of deposit <$100,000 |
59,953 | 14.23 | 73,752 | 19.87 | 80,607 | 25.12 | (18.71 | ) | (8.50 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total core deposits |
209,828 | 49.79 | 195,165 | 52.59 | 199,809 | 62.28 | 7.51 | (2.32 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
NONCORE DEPOSITS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Certificates of deposit >$100,000 |
36,385 | 8.63 | 25,044 | 6.75 | 22,355 | 6.97 | 45.28 | 12.03 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Brokered CDs |
175,176 | 41.57 | 150,888 | 40.66 | 98,663 | 30.75 | 16.10 | 52.93 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total noncore deposits |
211,561 | 50.21 | 175,932 | 47.41 | 121,018 | 37.72 | 20.25 | 45.38 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
TOTAL DEPOSITS |
$ | 421,389 | 100.00 | % | $ | 371,097 | 100.00 | % | $ | 320,827 | 100.00 | % | 13.55 | 15.67 | % | |||||||||||||||||
We have been successful in improving our mix of core deposits to wholesale funding sources with the
introduction of new and innovative products to meet the needs of our markets. Contributing to this
success is a proactive top down sales and service incentive program, along with a culture that
rewards sales personnel throughout the company for the procurement of new core deposits into the
bank based on targeted goals achieved. The combination of products, service and culture, will
continue to be the driver of this initiative given it is the most competitive business line that
most banks are trying to retain, and hardest to get customers to want to move over from another
financial institution, given the uncertainty of the financial markets in the short-term.
Building Franchise Value since the Recapitalization
As mentioned earlier, with this letter are various charts and graphs which track the performance of
the company through the challenging economic times of the last five years in terms of key
shareholder metrics and operating performance levels. Over this period the Corporation has
increased its common stock book value of stock by $3.35 or 34.5%. During this five year period, we
significantly increased total assets, loans, and core deposits which provides the foundation that
will lead to future increases in common shareholders’ equity. Following this letter is a
descriptive overview which provides a snapshot of how the three distinctively different regions of
our franchise, (Upper Peninsula “UP”, Northern Lower Peninsula, and Southeast Michigan) have
performed in relation to the market specific challenges, lines of business, and opportunities that
each region provides the company.
Looking Forward
In 2010, we remain faced with the challenges of a State economy still in turmoil and we have modest
expectations for the improvement of the overall economy and real estate values in the near term.
We believe that in economic times such as these, it becomes especially important to focus on
principal business objectives that preserve and increase bank franchise value; the “blocking and
tackling” of banking. In 2010 we intend to originate well priced, well structured loans, funded
with low cost in market deposits, while we control our expense base. The Corporation is, and will
remain dedicated to the primary strategic objective of enhancing franchise and shareholder value by
building a strong banking franchise in our local markets and serving the communities that provide
the business opportunities for the company to prosper.
We sincerely thank you for your continued support during these difficult times and we will work
diligently and prudently to provide improved shareholder results in the years to come.
|
 |
|
Paul D. Tobias
|
Kelly W. George | |
Chairman and CEO
|
President and CEO | |
Mackinac Financial Corporation
|
mBank |
4
Five Year Overview
|
 |
|
Since the recapitalization, which occurred in
December 2004, the book value of MFNC stock has
increased by $3.35, or 34.5%. |
|
 |
|
Since the recapitalization, common shareholders’ equity
has increased by a total of $11 million.
|
In April 2009, MFNC participated in the TARP program, receiving $11 million. |
5
Five Year Overview
|
 |
|
| Through 2009, MFNC has achieved total loan production of $516 million, which contributed to overall net growth of $180 million, or 88% since the recapitalization in 2004. |
|
 |
|
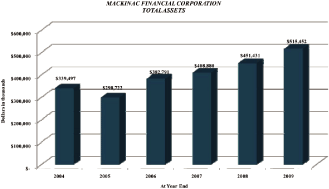
Total assets have increased $176 million or 52% since the
recapitalization. Since the Corporation’s lowest level of
assets, $299 million in 2005, we have grown assets by $216 million
through 2009 year end.
|
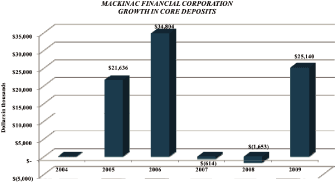
Since the recapitalization, core deposits have grown a total of $79 million. Adjusting for the branch sales in 2007 and 2009, core deposit growth amounted to $118 million through 2009 year end. |
6
Regional Review – Upper Peninsula
Jack C. Frost – Regional President, UP
BRANCH LOCATIONS
ESCANABA
|
NEWBERRY |  |
||
Located at Menards
|
414 Newberry Avenue | |||
3300 Ludington Street
|
Newberry, MI 49868 | |||
Escanaba, MI 49829
|
(906) 293-5165 | |||
(906) 233-9443
|
Manager: Michael A. Slaght | |||
Manager: Scott A. Ravet |
||||
MANISTIQUE
|
SAULT STE. MARIE | |||
130 South Cedar Street
|
138 Ridge Street | |||
Manistique, MI 49854
|
Sault Ste. Marie, MI 49783 | |||
(906) 341-2413
|
(906) 635-3992 | |||
Manager: Gregory D. Schuetter
|
Manager: Herbert C. Maloney | |||
MARQUETTE
|
STEPHENSON | |||
300 North McClellan
|
S216 Menominee Street | |||
Marquette, MI 49855
|
Stephenson, MI 49887 | |||
(906) 226-5000
|
(906) 753-2225 | |||
Manager: Teresa M. Same
|
Manager: Barbara A. Parrett |
|
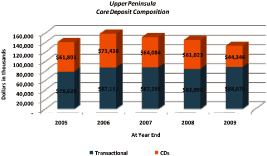 |
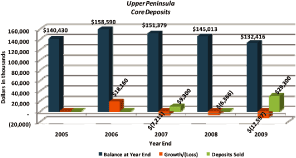
Excluding the branch sales, which were predominantly transactional accounts, total
deposits grew $30.6 million
in the five year period, with transactional deposits comprising roughly $21.1 million of that
growth.
Core deposits are defined as demand deposits, interest bearing checking accounts, money
markets, savings and CDs less than $100,000.
|
 |
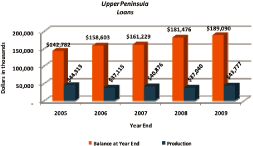
Total loan production over the five year period amounted to $203.1 million.
7
Regional Review – Upper Peninsula
MARKET COMMENTARY
In the five years since the recapitalization of mBank in December of 2004, the Bank’s Upper
Peninsula (UP) has made steady progress, both in terms of growing its loan and deposit base and
maneuvering through very difficult previous reputational issues as a result of the former company’s
troubles. This negative publicity made it difficult to both attract new business as well as talent
to the bank. However, the tarnished past is now just that, and the UP region continues to be the
largest market footprint of the institution in terms of geography, branches, and loan and deposit
footings. Similar to the other regions, we have implemented various new deposit and treasury
management products which continue to set us ahead of our competition in terms of delivery of
cutting edge technology and convenience to our customers. We have also been able to procure some
talented local bankers that are deep rooted into their communities that have spurred the consistent
growth of core loans and deposit accounts.
In recent years, we formulated a plan to strategically realign our branch footprint to better match
our business model in the region. This has been accomplished by reallocating our personnel and
capital resources into targeted “commerce center hub” markets of the UP and divesting of outlier
branches located in small markets with declining populations. Specifically in 2007, we sold our
Ripley location which allowed the bank to divest of a longer term fixed asset issue and in 2009 we
sold two additional locations in South Range and Ontonagon. The sale of the latter two locations
provided a gain of approximately $1.2M to the bank. These divestitures also provided significant
cost savings throughout the company and enabled management to focus on the growth and development
of our remaining network. mBank also strategically reentered the Delta County Market by opening a
small full service branch in the new Menards store located in Escanaba in 2009 which is the second
largest business center in the UP footprint. Lastly, in 2009 we converted our banking center in
Marquette Presque Isle from a full service branch operation to a Mortgage and Consumer Lending
Division to provide a more centralized approach to operating this portion of the company. In doing
this we were able to procure a highly talented veteran banker who had been the top residential
mortgage producer in the UP for many years to oversee and grow this line of business.
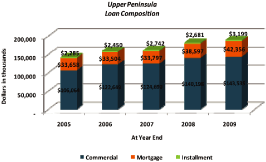
Our commercial loan portfolio includes a diverse mix of industries that represents an inclusive
sampling of the economic platform of the UP. These business sectors include various retail and
office space in addition to professional, medical and hospitality entities which are similar to
those found in the other regions of mBank. However, it is the industries that are more indigenous
to the UP that add even further variety and stability to the overall risk matrix of the portfolio.
Bank clients in the timber, light non-auto manufacturing and service industries have both
alleviated some of the general downward fiscal pressure of the state and lessened the indirect
impact of the auto industry on the overall loan portfolio. We also continue to add value to our
clients with our knowledge and understanding of government guaranteed loans from the Small Business
Administration (SBA) and United States Department of Agriculture. This core competency was very
evident in 2009 when mBank not only led all UP institutions in number of SBA loans closed – 27 –
but also in total dollar amount of SBA loans originated – $7.4 million. We are very proud of this
achievement not only for the success of the organization, but also for being a catalyst for
promoting economic stimulus through helping small businesses get the capital that is essential to
their success, as well as the communities they operate in, within these under developed areas of
the state.
Given some of the aforementioned industrial diversity, the UP economy continues to perform better
than the state as a whole. Although unemployment is somewhat elevated on a normalized scale and
pockets of comparatively high jobless claims remain, many of our markets are trending near
historical levels. Given that it is not atypical for the unemployment rate in the UP to be higher
than the remainder of the state, the experience of operating in this environment provides for a
more stable economic base which seldom experiences the severe highs or lows in times of changing
economic conditions. Furthermore, real estate values have experienced a very modest decrease on
average in the UP markets compared to much larger decreases in the Southern part of the state. Our
markets continue to see growth opportunities with the development of several successful large
projects throughout the UP over the past several years including new construction as well as
expansions of existing hospitals, hotels, schools, and retail centers. This steady and methodical
economic progress and the ability to successfully function in a difficult national financial
environment has allowed the UP region of mBank continued growth through prudent banking activities
and our proactive sales and serviced based culture. We thank you for your business and for
supporting mBank endeavors and look forward to continuing to serve our clients and communities in
2010.
8
Regional Review – Northern Lower Peninsula
Andrew P. Sabatine, Regional President – NLP
BRANCH LOCATIONS
GAYLORD
|
KALEVA |  |
||
1955 South Otsego Avenue
|
14429 Wuoksi Avenue | |||
Gaylord, MI 49735
|
Kaleva, MI | |||
(989) 732-3750
|
(231)362-3223 | |||
Manager: Nicole Shelters
|
Manager: Barb J. Miller | |||
TRAVERSE CITY |
||||
3530 North Country Drive |
||||
Traverse City, MI 49684 |
||||
(231) 929-5600 |
||||
Manager: Andrea Pease |
|
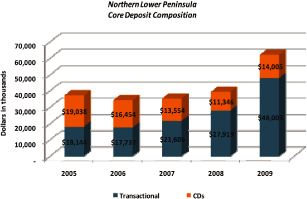 |
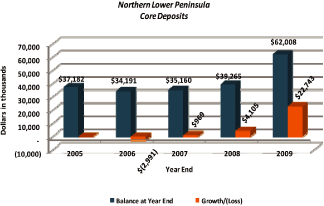
Total deposit growth amounted to $24.8 million over the five year period, largely in
transactional accounts.
Core deposits are defined as demand deposits, interest bearing checking accounts, money
markets, savings and CDs less than $100,000.
|
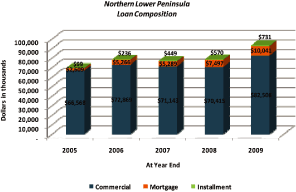 |
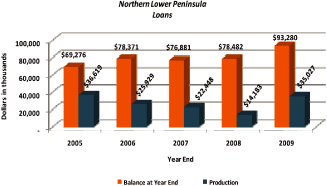
Total loan production over the five year period amounted to $134.2 million.
9
Regional Review – Northern Lower Peninsula
MARKET COMMENTARY
Since the late 2004 recapitalization and subsequent conversion to mBank, the Northern Lower
Peninsula region has experienced positive trends in both core depository and loan portfolio growth.
The positive growth in both loans and deposits is a direct result of mBank refining and augmenting
its products, services and staff within this region to better position itself to grow market share.
As demonstrated by our historical totals, core deposit generation in the Northern Lower Peninsula
region initially proved challenging due to having single, non-prime locations in the two largest
and most competitive markets (Traverse City & Gaylord). However, the poorly positioned Gaylord
branch was relocated in the summer of 2006 to a more visible and convenient placed bank branch
through the redesign of a piece of bank owned property (REO), which has proved to be a more
effective location to drive market growth. Additionally, courier service and remote deposit
capabilities were added to the Traverse City & Gaylord locations in mid 2007 providing customers
with convenient and electronic access to their accounts. Total deposit growth during this period
for the Gaylord branch was approximately $22.7 million ($10.3 to $33 million) and approximately
$19.4 million ($12.1 to $31.5 million) for the Traverse City branch, with the majority of the
growth for both branches in transactional core deposit accounts. As a result of offering clients
this option, it negated the need for the additional and expensive capital outlay of adding more
branches while neutralizing many logistical obstacles caused by location.
With regard to the aforementioned depository growth, the Smart Money Market Account was also
introduced to the Northern Lower Peninsula markets in early 2009 and was a main driver of the core
deposit success over the past 12 months. This account was designed as a market specific deposit
alternative to enhance mBank’s existing deposit product line and better service the needs of the
high balance consumer and business depositor. The resulting increase in core deposit base has been
very beneficial in providing a cost effective funding source to support loan portfolio growth.
The overall increase in the loan portfolio for the Northern Lower Peninsula region is represented
by steady new commercial and residential loan origination over the last five years. The industry
mix in the commercial area is well diversified among business sectors ranging from tourism &
hospitality to small business and various types of real estate. While the composition of the
portfolio mitigates some risk, the current economic downturn and the related decline in the housing
market has prompted a focus on lower risk loan structures. As a result of the challenging business
environment, new commercial loan production is centered on origination of loans guaranteed under
United States Small Business Administration (SBA) and United States Department of Agricultural
(USDA) loan programs. These guarantees, allow us to meet our client’s needs and also provide the
market with capital for economic stimulus while still significantly reducing portfolio risk.
Overall, we are satisfied with the performance of the Northern Lower Peninsula region given the
general condition of the Michigan economy over the past eighteen months, and we see signs of
gradual economic improvement and development throughout the region. Fortunately, the waterfront
housing market and tourism related businesses in the region have not experienced as severe of a
decline as other areas of the state. This is undoubtedly due to the popularity and relative
affordability of the region compared to other coastal markets in the U.S. This makes the region a
very competitive growth market and as a result it is anticipated that it will recover faster than
others as population and industry continue to migrate from other parts of Michigan and other
contiguous states. We are looking forward to another successful year with the general focus going
into 2010 being on continued core deposit growth, controlled opportunistic loan growth and
proactive portfolio management. If you are in the region, please stop by one of our locations and
experience the mBank difference!
10
Regional Review – Southeast Michigan
Jesse A. Deering, First VP/Southeast Michigan Executive
BRANCH LOCATION
BIRMINGHAM
|
 |
|
260 East Brown Street, Suite 300 |
||
Birmingham, MI 48009 |
||
(248) 290-5900 |
||
Manager: Elena Dritsas |
|
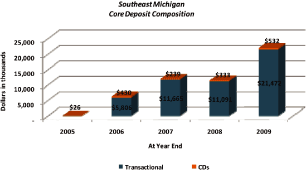 |
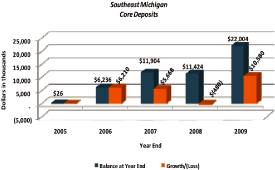
Total deposit growth amounted to $22.0 million over the five year period, almost solely in
transactional accounts.
Core deposits are defined as demand deposits, interest bearing checking accounts, money
markets, savings and CDs less than $100,000.
|
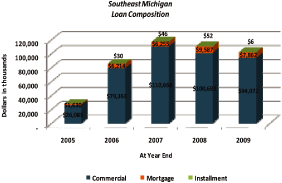 |
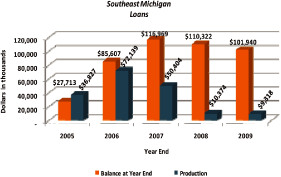
Total loan production over the five year period amounted to $179.1 million.
11
Regional Review – Southeast Michigan
MARKET COMMENTARY
The Southeast Michigan region of mBank opened in early 2005 and has grown to its current size
through two distinctly different phases of business initiatives. With the main initial focus being
asset growth through the origination of new credit facilities, the loan portfolio successfully grew
to roughly $117 million over the first three years of operation. Soon after the inaugural year of
existence, Oakland County added full service branch capabilities and a complete depository product
line to offer our clientele. This not only allowed Southeast Michigan to provide a full banking
experience, including treasury management options, to our growing portfolio of loan customers, but
also allowed us to focus on providing similar personalized products and services to deposit only
customers. This resulted in steady core deposit growth over the past three years with totals
nearly doubling from $11 million at year end 2008 to just over $22 million at year end 2009.
However, The Southeast Michigan region of mBank also experienced challenges resulting from the
inherent effects of the global economic downturn of late 2008. As a result of issues within the
automotive industry and the prolonged fiscal impact of the recent recession, the financial
condition of this region has negatively affected nearly all business sectors. In addition to
manufacturing and other operating entities, the market for commercial real estate is seeing drastic
downward pressure on lease rates caused by an increase in available space within the market.
Further, with the population of this region trending downward as residents relocate in search of
employment, the housing and residential development markets continue to be fundamentally weak. As
a result, mBank has taken a careful credit posture in Southeast Michigan over the past eighteen
months. This has allowed us to increase our level of monitoring and administration of the current
loan portfolio. Given the aforementioned market trends, this is deemed as a necessary and prudent
governance move at this time.
While the overall economic condition of Southeast Michigan poses challenges for us, it presents
opportunities as well. Specifically, the general change in lending posture by some regional banks
and their lack of desire to grow business in this particular region has allowed mBank to offer
competitive loan and deposit options to strong potential customers. These customers may no longer
fit their current bank’s ideal profile from an industry, geographic or relationship size
standpoint. Additionally, by utilizing the programs offered through the Small Business
Administration and the State of Michigan, the Southeast Michigan region has the opportunity and
desire to promote loans for qualified small businesses. The involvement of the SBA and other
government resources will increase the granularity of our loan portfolio. These small to midsized
loans will both mitigate risk and allow controlled and systematic loan production in this Region.
While evidence of economic recovery may begin to show throughout the next twelve months, it is
anticipated that 2010 will continue to be another challenging year for Metropolitan Detroit. As a
result, the direction of mBank’s business activities in this region will remain focused on
continued growth of core depository relationships and also the prudent underwriting and
administration of new and existing loan relationships. While the internal focus will center on
these initiatives, it remains the utmost importance to us to continue to provide the highest level
of customer service to our clientele and do everything within our ability to meet their banking
needs and expectations.
12
Selected Financial Highlights
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Per Share Data)
| For The Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
| (Unaudited) | (Unaudited) | |||||||
Selected Financial Condition Data (at end of period): |
||||||||
Assets |
$ | 515,377 | $ | 451,431 | ||||
Loans |
384,310 | 370,280 | ||||||
Investment securities |
46,513 | 47,490 | ||||||
Deposits |
421,389 | 371,097 | ||||||
Borrowings |
36,140 | 36,210 | ||||||
Shareholders’ equity |
55,299 | 41,552 | ||||||
Selected Statements of Income Data: |
||||||||
Net interest income |
$ | 16,287 | $ | 12,864 | ||||
Income before taxes |
3,536 | 2,659 | ||||||
Net income available to common shareholders |
1,907 | 1,872 | ||||||
Income per common share — Basic |
.56 | .55 | ||||||
Income per common share — Diluted |
.56 | .55 | ||||||
Weighted average shares outstanding |
3,419,736 | 3,422,012 | ||||||
Selected Financial Ratios and Other Data: |
||||||||
Performance Ratios: |
||||||||
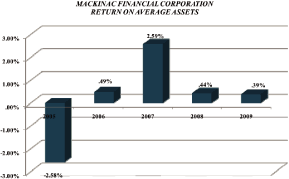
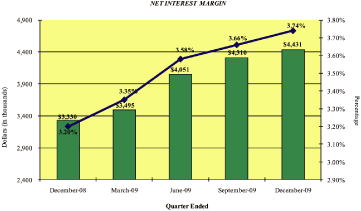
Net interest margin |
3.59 | % | 3.23 | % | ||||
Efficiency ratio |
73.37 | 85.51 | ||||||
Return on average assets |
.39 | .44 | ||||||
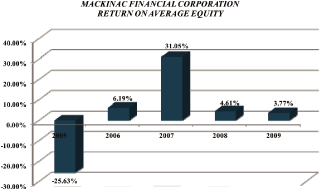
Return on average equity |
3.77 | 4.61 | ||||||
Average total assets |
$ | 493,652 | $ | 425,343 | ||||
Average total shareholders’ equity |
50,531 | 40,630 | ||||||
Average loans to average deposits ratio |
92.99 | % | 105.61 | % | ||||
Common Share Data at end of period: |
||||||||
Market price per common share |
$ | 4.64 | $ | 4.40 | ||||
Book value per common share |
$ | 13.10 | $ | 12.15 | ||||
Common shares outstanding |
3,419,736 | 3,419,736 | ||||||
Other Data at end of period: |
||||||||
Allowance for loan losses |
$ | 5,225 | $ | 4,277 | ||||
Non-performing assets |
$ | 21,041 | $ | 7,076 | ||||
Allowance for loan losses to total loans |
1.36 | % | 1.16 | % | ||||
Non-performing assets to total assets |
4.08 | % | 1.57 | % | ||||
Number of: |
||||||||
Branch locations |
10 | 12 | ||||||
FTE Employees |
100 | 100 | ||||||
The above summary should be read in connection with the related consolidated financial statements
and notes included elsewhere in this report.
13
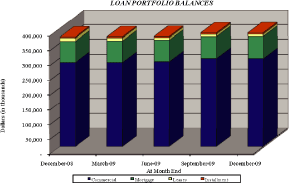
Quarterly Financial Summary
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION
QUARTERLY FINANCIAL SUMMARY
| Average | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average | Average | Average | Shareholders’ | Return on Average | Net Interest | Efficiency | Net Income | Book Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Quarter Ended | Assets | Loans | Deposits | Equity | Assets | Equity | Margin | Ratio | Per Share | Per Share | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2009 |
$ | 514,102 | $ | 386,203 | $ | 418,280 | $ | 55,665 | (.14) | % | (1.28 | )% | 3.74 | % | 71.03 | % | $ | (.05 | ) | $ | 13.10 | |||||||||||||||||||
September 30, 2009 |
513,687 | 370,310 | 419,102 | 54,594 | 1.19 | 11.16 | 3.66 | 70.09 | .45 | 13.25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
June 30, 2009 |
491,205 | 371,609 | 401,510 | 49,855 | .38 | 3.71 | 3.58 | 76.55 | .13 | 12.73 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
March 31, 2009 |
454,740 | 370,943 | 372,669 | 41,813 | .08 | 0.87 | 3.35 | 82.36 | .03 | 12.24 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2008 |
441,583 | 366,077 | 358,213 | 41,516 | (.23 | ) | (2.42 | ) | 3.20 | 80.30 | (.07 | ) | 12.15 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
September 30, 2008 |
423,702 | 358,844 | 341,377 | 41,097 | .20 | 2.08 | 3.39 | 79.12 | .06 | 12.11 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
June 30, 2008 |
418,246 | 362,574 | 332,725 | 40,399 | 1.70 | 17.62 | 3.19 | 88.45 | .52 | 11.98 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
March 31, 2008 |
417,682 | 357,778 | 336,016 | 39,491 | .13 | 1.42 | 3.13 | 95.34 | .04 | 11.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2007 |
406,308 | 350,050 | 324,194 | 38,973 | .51 | 5.36 | 3.55 | 78.02 | .15 | 11.47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
 |
14
 |
Plante & Moran,
PLLC Suite 500 2601 Cambridge Court Aubum Hills, MI 48326 Tel: 248 375 7100 Fax: 248 375 7101 plantemoran.com |
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
Board of Directors
Mackinac Financial Corporation, Inc.
We have audited the consolidated statement of financial condition of Mackinac Financial
Corporation, Inc. as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 and the related consolidated statements of
income, changes in stockholders’ equity, and cash flows for each year in the three-year period
ended December 31, 2009. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the
Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial
statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight
Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain
reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. The
Company is not required to have, nor were we engaged to perform, an audit of its internal control
over financial reporting. Our audits included consideration of internal control over financial
reporting as a basis for designing audit procedures that are appropriate in the circumstances, but
not for the purpose of expressing an opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control
over financial reporting. Accordingly, we express no such opinion. An audit also includes
examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial
statements, assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management,
as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits
provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all
material respects, the consolidated financial position of Mackinac Financial Corporation, Inc. as
of December 31, 2009 and 2008 and the consolidated results of their operations and their cash
flows for each year in the three-year period ended December 31, 2009, in conformity with
accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
| Auburn Hills, Michigan March 30, 2010 |
 |
15
Consolidated Balance Sheets
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
December 31, 2009 and 2008
(Dollars in Thousands)
December 31, 2009 and 2008
(Dollars in Thousands)
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
ASSETS |
||||||||
Cash and due from banks |
$ | 18,433 | $ | 10,112 | ||||
Federal funds sold |
27,000 | — | ||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
45,433 | 10,112 | ||||||
Interest-bearing deposits in other financial institutions |
678 | 582 | ||||||
Securities available for sale |
46,513 | 47,490 | ||||||
Federal Home Loan Bank stock |
3,794 | 3,794 | ||||||
Loans: |
||||||||
Commercial |
305,670 | 296,088 | ||||||
Mortgage |
74,350 | 70,447 | ||||||
Installment |
4,290 | 3,745 | ||||||
Total Loans |
384,310 | 370,280 | ||||||
Allowance for loan losses |
(5,225 | ) | (4,277 | ) | ||||
Net loans |
379,085 | 366,003 | ||||||
Premises and equipment |
10,165 | 11,189 | ||||||
Other real estate held for sale |
5,804 | 2,189 | ||||||
Other assets |
23,905 | 10,072 | ||||||
TOTAL ASSETS |
$ | 515,377 | $ | 451,431 | ||||
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
||||||||
Liabilities: |
||||||||
Non-interest-bearing deposits |
$ | 35,878 | $ | 30,099 | ||||
Interest-bearing deposits: |
||||||||
NOW, Money Market, Checking |
95,790 | 70,584 | ||||||
Savings |
18,207 | 20,730 | ||||||
CDs<$100,000 |
59,953 | 73,752 | ||||||
CDs>$100,000 |
36,385 | 25,044 | ||||||
Brokered |
175,176 | 150,888 | ||||||
Total deposits |
421,389 | 371,097 | ||||||
Borrowings: |
||||||||
Federal Home Loan Bank |
35,000 | 35,000 | ||||||
Other |
1,140 | 1,210 | ||||||
Total borrowings |
36,140 | 36,210 | ||||||
Other liabilities |
2,549 | 2,572 | ||||||
Total liabilities |
460,078 | 409,879 | ||||||
Shareholders’ equity: |
||||||||
Preferred stock — No par value: |
||||||||
Authorized 500,000 shares, 11,000 shares issued and outstanding |
10,514 | — | ||||||
Common stock and additional paid in capital — No par value
Authorized - 18,000,000 shares
Issued and outstanding — 3,419,736 shares |
43,493 | 42,815 | ||||||
Accumulated earnings (deficit) |
199 | (1,708 | ) | |||||
Accumulated other comprehensive income |
1,093 | 445 | ||||||
Total shareholders’ equity |
55,299 | 41,552 | ||||||
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
$ | 515,377 | $ | 451,431 | ||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
16
Consolidated Statements of Operations
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
Years Ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Per Share Data)
Years Ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Per Share Data)
| For The Years Ended December 31, | ||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
INTEREST INCOME: |
||||||||||||
Interest and fees on loans: |
||||||||||||
Taxable |
$ | 20,521 | $ | 22,555 | $ | 26,340 | ||||||
Tax-exempt |
292 | 404 | 533 | |||||||||
Interest on securities: |
||||||||||||
Taxable |
2,783 | 1,293 | 1,100 | |||||||||
Tax-exempt |
19 | 5 | — | |||||||||
Other interest income |
93 | 305 | 722 | |||||||||
Total interest income |
23,708 | 24,562 | 28,695 | |||||||||
INTEREST EXPENSE: |
||||||||||||
Deposits |
6,431 | 10,115 | 13,224 | |||||||||
Borrowings |
990 | 1,583 | 2,054 | |||||||||
Total interest expense |
7,421 | 11,698 | 15,278 | |||||||||
Net interest income |
16,287 | 12,864 | 13,417 | |||||||||
Provision for loan losses |
3,700 | 2,300 | 400 | |||||||||
Net interest income after provision for loan losses |
12,587 | 10,564 | 13,017 | |||||||||
OTHER INCOME: |
||||||||||||
Service fees |
1,023 | 838 | 688 | |||||||||
Net security gains |
1,471 | 64 | (1 | ) | ||||||||
Net gains on sale of secondary market loans |
830 | 120 | 498 | |||||||||
Proceeds from settlement of lawsuits |
— | 3,475 | 470 | |||||||||
Gain on sales of branch offices |
1,208 | — | 5 | |||||||||
Other |
219 | 156 | 346 | |||||||||
Total other income |
4,751 | 4,653 | 2,006 | |||||||||
OTHER EXPENSES: |
||||||||||||
Salaries and employee benefits |
6,583 | 6,886 | 6,757 | |||||||||
Occupancy |
1,385 | 1,374 | 1,272 | |||||||||
Furniture and equipment |
805 | 771 | 678 | |||||||||
Data processing |
862 | 844 | 785 | |||||||||
Professional service fees |
603 | 508 | 532 | |||||||||
Loan and deposit |
933 | 488 | 250 | |||||||||
FDIC insurance premiums |
839 | 81 | 35 | |||||||||
Other |
1,792 | 1,606 | 1,791 | |||||||||
Total other expenses |
13,802 | 12,558 | 12,100 | |||||||||
Income before provision for income taxes |
3,536 | 2,659 | 2,923 | |||||||||
Provision for (benefit of) income taxes |
1,120 | 787 | (7,240 | ) | ||||||||
NET INCOME |
$ | 2,416 | $ | 1,872 | $ | 10,163 | ||||||
Preferred dividend and accretion of discount |
509 | — | — | |||||||||
NET INCOME AVAILABLE TO COMMON SHAREHOLDERS |
$ | 1,907 | $ | 1,872 | $ | 10,163 | ||||||
INCOME PER COMMON SHARE |
||||||||||||
Basic |
$ | .56 | $ | .55 | $ | 2.96 | ||||||
Diluted |
$ | .56 | $ | .55 | $ | 2.96 | ||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
17
Consolidated Statements of Changes in Shareholders’ Equity
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
Years Ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(Dollars in Thousands)
Years Ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(Dollars in Thousands)
| Accumulated | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Shares of | Preferred | Common Stock | Other | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Common | Stock | and Additional | Accumulated | Comprehensive | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock | Series A | Paid in Capital | Deficit | Income (Loss) | Total | |||||||||||||||||||
Balance, January 1, 2007 |
3,428,695 | $ | — | $ | 42,722 | $ | (13,745 | ) | $ | (187 | ) | $ | 28,790 | |||||||||||
Net income |
— | — | — | 10,163 | — | 10,163 | ||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net unrealized loss on
securities available for sale |
— | — | — | — | 247 | 247 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total comprehensive income |
10,410 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock option compensation |
— | — | 121 | — | — | 121 | ||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2007 |
3,428,695 | — | 42,843 | (3,582 | ) | 60 | 39,321 | |||||||||||||||||
Purchase of oddlot shares |
(8,959 | ) | — | (110 | ) | — | — | (110 | ) | |||||||||||||||
Net income |
— | — | 1,872 | — | 1,872 | |||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net unrealized income on
securities available for sale |
— | — | — | — | 385 | 385 | ||||||||||||||||||
Other |
— | — | — | 2 | — | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total comprehensive income |
2,259 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock option compensation |
— | — | 82 | — | — | 82 | ||||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2008 |
3,419,736 | — | 42,815 | (1,708 | ) | 445 | 41,552 | |||||||||||||||||
Net income |
— | — | — | 2,416 | — | 2,416 | ||||||||||||||||||
Other comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net unrealized income on
securities available for sale |
— | — | — | — | 648 | 648 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total comprehensive income |
3,064 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
Stock option compensation |
— | — | 60 | — | 60 | |||||||||||||||||||
Dividend on preferred stock |
— | — | — | (377 | ) | — | (377 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Issuance of preferred stock, 11,000 shares |
— | 10,382 | — | — | — | 10,382 | ||||||||||||||||||
Issuance of common stock warrants |
— | — | 618 | — | — | 618 | ||||||||||||||||||
Accretion of preferred stock discount |
— | 132 | — | (132 | ) | — | — | |||||||||||||||||
Balance, December 31, 2009 |
3,419,736 | $ | 10,514 | $ | 43,493 | $ | 199 | $ | 1,093 | $ | 55,299 | |||||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
18
Consolidated Statements of Cash Flows
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
Years Ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(Dollars in Thousands)
Years Ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(Dollars in Thousands)
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Cash Flows from Operating Activities: |
||||||||||||
Net income |
$ | 2,416 | $ | 1,872 | $ | 10,163 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net net cash
provided by (used in) operating activities: |
||||||||||||
Depreciation and amortization |
2,027 | 1,355 | 942 | |||||||||
Provision for loan losses |
3,700 | 2,300 | 400 | |||||||||
Provision for (benefit of) income taxes |
1,120 | 787 | (7,240 | ) | ||||||||
(Gain) loss on sales/calls of securities available for sale |
(1,471 | ) | (64 | ) | 1 | |||||||
(Gain) on sales of branch offices |
(1,208 | ) | — | (5 | ) | |||||||
(Gain) loss on sale of premises, equipment, and other real estate |
23 | (77 | ) | (12 | ) | |||||||
Writedown of other real estate |
187 | 964 | 40 | |||||||||
Stock option compensation |
60 | 82 | 121 | |||||||||
Change in other assets |
(15,331 | ) | 367 | 12 | ||||||||
Change in other liabilities |
(22 | ) | (210 | ) | (491 | ) | ||||||
Net cash (used in) provided by operating activities |
(8,499 | ) | 7,376 | 3,931 | ||||||||
Cash Flows from Investing Activities: |
||||||||||||
Net (increase) in loans |
(21,218 | ) | (21,173 | ) | (35,043 | ) | ||||||
Net (increase) decrease in interest-bearing deposits in other financial institutions |
(96 | ) | 1,228 | (954 | ) | |||||||
Purchase of securities available for sale |
(50,113 | ) | (50,813 | ) | (25,556 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from maturities, sales, calls or paydowns of securities available for sale |
52,742 | 25,373 | 37,215 | |||||||||
Capital expenditures |
(679 | ) | (618 | ) | (1,516 | ) | ||||||
Proceeds from sale of premises, equipment, and other real estate |
581 | 1,956 | 323 | |||||||||
Net cash paid in connection with branch sales |
(28,578 | ) | — | (8,042 | ) | |||||||
Net cash (used in) investing activities |
(47,361 | ) | (44,047 | ) | (33,573 | ) | ||||||
Cash Flows from Financing Activities: |
||||||||||||
Net increase in deposits |
80,760 | 50,270 | 17,656 | |||||||||
Issuance of Series A Preferred Stock and common stock warrants |
11,000 | — | — | |||||||||
Dividend on preferred stock and discount accretion |
(509 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in federal funds purchased |
— | (7,710 | ) | 7,710 | ||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in lines of credit |
— | (1,959 | ) | — | ||||||||
Repurchase of common stock-oddlot shares |
— | (110 | ) | — | ||||||||
Principal payments on borrowings |
(70 | ) | (70 | ) | (68 | ) | ||||||
Net cash provided by financing activities |
91,181 | 40,421 | 25,298 | |||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents |
35,321 | 3,750 | (4,344 | ) | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period |
10,112 | 6,362 | 10,706 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period |
$ | 45,433 | $ | 10,112 | $ | 6,362 | ||||||
Supplemental Cash Flow Information: |
||||||||||||
Cash paid during the year for: |
||||||||||||
Interest |
$ | 7,584 | $ | 11,961 | $ | 13,609 | ||||||
Income taxes |
90 | 70 | — | |||||||||
Noncash Investing and Financing Activities: |
||||||||||||
Transfers of Foreclosures from Loans to Other Real Estate Held for Sale
(net of adjustments made through the allowance for loan losses) |
4,879 | 2,849 | 1,218 | |||||||||
Assets and Liabilities Divested in Branch Sales: |
||||||||||||
Loans |
31 | — | 27 | |||||||||
Premises and equipment |
651 | — | 1,181 | |||||||||
Deposits |
29,260 | — | 9,250 | |||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
19
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 1 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
The accounting policies of Mackinac Financial Corporation (the “Corporation”) and Subsidiaries
conform to accounting principles generally accepted in the United States and prevailing practices
within the banking industry. Significant accounting policies are summarized below.
Principles of Consolidation
The consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Corporation and its wholly owned
subsidiaries, mBank (the “Bank”) and other minor subsidiaries, after elimination of intercompany
transactions and accounts.
Nature of Operations
The Corporation’s and the Bank’s revenues and assets are derived primarily from banking activities.
The Bank’s primary market area is the Upper Peninsula, the northern portion of the Lower Peninsula
of Michigan, and Oakland County in Lower Michigan. The Bank provides to its customers commercial,
real estate, agricultural, and consumer loans, as well as a variety of traditional deposit
products. A portion, approximately 2.0%, of the Bank’s commercial loan portfolio consists of leases
to commercial and governmental entities, which are secured by various types of equipment. These
leases are dispersed geographically throughout the country. Less than 1.0% of the Corporation’s
business activity is with Canadian customers and denominated in Canadian dollars.
While the Corporation’s chief decision makers monitor the revenue streams of the various
Corporation products and services, operations are managed and financial performance is evaluated on
a Corporation-wide basis. Accordingly, all of the Corporation’s banking operations are considered
by management to be aggregated in one reportable operating segment.
Use of Estimates in Preparation of Financial Statements
The preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles generally accepted
in the United States requires management to make estimates and assumptions that affect the reported
amounts of assets and liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date
of the financial statements, and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during the period.
Actual results could differ from those estimates.
Material estimates that are particularly susceptible to significant change in the near term relate
to the determination of the allowance for loan losses, the valuation of investment securities, the
valuation of foreclosed real estate, deferred tax assets, and impairment of intangible assets.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of reporting cash flows, cash and cash equivalents include cash on hand,
noninterest-bearing deposits in correspondent banks, and federal funds sold. Generally, federal
funds are purchased and sold for one-day periods.
Securities
The Corporation’s securities are classified and accounted for as securities available for sale.
These securities are stated at fair value. Premiums and discounts are recognized in interest income
using the interest method over the period to maturity. Unrealized holding gains and losses on
securities available for sale are reported as accumulated other comprehensive income within
shareholders’ equity until realized. When it is determined that securities or other investments
are impaired and the impairment is other than temporary, an impairment loss is recognized in
earnings and a new basis in the affected security is established. Gains and losses on the sale of
securities are recorded on the trade date and determined using the specific-identification method.
20
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 1 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
Federal Home Loan Bank Stock
As a member of the Federal Home Loan Bank (FHLB) system, the Bank is required to hold stock in the
FHLB based on the anticipated level of borrowings to be advanced. This stock is recorded at cost,
which approximates fair value. Transfer of the stock is substantially restricted.
Interest Income and Fees on Loans
Interest on loans is accrued and credited to income based on the principal amount outstanding.
The accrual of interest on loans is discontinued when, in the opinion of management, it is
probable that the borrower may be unable to meet payments as they become due. Upon such
discontinuance, all unpaid accrued interest is reversed. Loans are returned to accrual status
when all principal and interest amounts contractually due are brought current and future payments
are reasonably assured. Interest income on impaired and nonaccrual loans is recorded on a cash
basis. Loan-origination fees and allocated costs of originating loans are deferred and recognized
over the term of the loan as an adjustment to yield.
Allowance for Loan Losses
The allowance for loan losses includes specific allowances related to commercial loans, when they
have been judged to be impaired. A loan is impaired when, based on current information, it is
probable that the Corporation will not collect all amounts due in accordance with the contractual
terms of the loan agreement. These specific allowances are based on discounted cash flows of
expected future payments using the loan’s initial effective interest rate or the fair value of the
collateral if the loan is collateral dependent.
The Corporation continues to maintain a general allowance for loan losses for loans not considered
impaired. The allowance for loan losses is maintained at a level which management believes is
adequate to provide for possible loan losses. Management periodically evaluates the adequacy of
the allowance using the Corporation’s past loan loss experience, known and inherent risks in the
portfolio, composition of the portfolio, current economic conditions, and other factors. The
allowance does not include the effects of expected losses related to future events or future
changes in economic conditions. This evaluation is inherently subjective since it requires
material estimates that may be susceptible to significant change. Loans are charged against the
allowance for loan losses when management believes the collectability of the principal is
unlikely. In addition, various regulatory agencies periodically review the allowance for loan
losses. These agencies may require additions to the allowance for loan losses based on their
judgments of collectability.
In management’s opinion, the allowance for loan losses is adequate to cover probable losses
relating to specifically identified loans, as well as probable losses inherent in the balance of
the loan portfolio as of the balance sheet date.
Other Real Estate Held for Sale
Other real estate held for sale consists of assets acquired through, or in lieu of, foreclosure
and other long-lived assets to be disposed of by sale, whether previously held and used or newly
acquired. Other real estate held for sale is initially recorded at the lower of cost or fair
value, less costs to sell, establishing a new cost basis. Valuations are periodically performed
by management, and the assets’ carrying values are adjusted to the lower of cost basis or fair
value less costs to sell. Impairment losses are recognized for any initial or subsequent
write-downs. Net revenue and expenses from operations of other real estate held for sale are
included in other expense.
21
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 1 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
Premises and Equipment
Premises and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Maintenance and repair
costs are charged to expense as incurred. Gains or losses on disposition of premises and
equipment are reflected in income. Depreciation is computed on the straight-line method over the
estimated useful lives of the assets.
Stock Option Plans
The Corporation sponsors three stock option plans. One plan was approved during 2000 and applies
to officers, employees, and nonemployee directors. This plan was amended as a part of the December
2004 stock offering and recapitalization. The amendment, approved by shareholders, increased the
shares available under this plan by 428,587 shares from the original 25,000 (adjusted for the 1:20
reverse stock split), to a total authorized share balance of 453,587. This plan expires on
February 15, 2010. The other two plans, one for officers and employees and the other for
nonemployee directors, were approved in 1997. A total of 30,000 shares (adjusted for the 1:20
split), were made available for grant under these plans. These two 1997 plans expired early in
2007. Options under all of the plans are granted at the discretion of a committee of the
Corporation’s Board of Directors. Options to purchase shares of the Corporation’s stock are
granted at a price equal to the market price of the stock at the date of grant. The committee
determines the vesting of the options when they are granted as established under the plan.
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Comprehensive income (loss) consists of net income (loss) and other comprehensive income (loss).
Other comprehensive income (loss) includes unrealized gains and losses on securities available for
sale, which are recognized as a separate component of equity and accumulated other comprehensive
income (loss).
Earnings per Common Share
Basic earnings per common share is net income divided by the weighted average number of common
shares outstanding during the period. Diluted earnings per common share includes the dilutive
effect of additional potential common shares issuable under stock option agreements and the common
stock warrants issued as a part of the Corporation’s participation in the TARP Capital Purchase
Program.
Earnings per share are based upon the weighted average number of shares outstanding. The following
shows the computation of basic and diluted income per share for the years ended December 31
(dollars in thousands, except per share data):
| Net Income | Weighted | |||||||||||
| Available to Common | Average | Income | ||||||||||
| Shareholders | Number of Shares | per Share | ||||||||||
2009 |
||||||||||||
Income per share — basic and diluted |
$ | 1,907 | 3,419,736 | $ | .56 | |||||||
2008 |
||||||||||||
Income per share — basic and diluted |
$ | 1,872 | 3,422,012 | $ | .55 | |||||||
2007 |
||||||||||||
Income per share — basic and diluted |
$ | 10,163 | 3,428,695 | $ | 2.96 | |||||||
22
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 1 — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES (CONTINUED)
In the above disclosure the dilutive effect of additional shares outstanding, as a result of stock
options and warrants exercisable, was not taken into account since the additional shares issued as
a result of vested options under the Company’s option plans and common stock warrants issued under
the TARP Capital Purchase Program would not have a dilutive effect on the earnings calculated per
share.
Income Taxes
Deferred income taxes have been provided under the liability method. Deferred tax assets and
liabilities are determined based upon the difference between the financial statement and tax bases
of assets and liabilities as measured by the enacted tax rates which will be in effect when these
differences are expected to reverse. Deferred tax expense (credit) is the result of changes in the
deferred tax asset and liability. A valuation allowance is provided against deferred tax assets
when it is more likely than not that some or all of the deferred asset will not be realized. In
2009, the Corporation recorded a current tax provision of $1.120 million and a current tax
provision of $.787 million in 2008. The Corporation recorded a $.260 million current tax provision
in the fourth quarter of 2007. In the third quarter of 2007, the Corporation reversed a portion of
the valuation allowance that pertained to the deferred tax benefit of NOL and tax credit
carryforwards. This valuation adjustment, $7.500 million, was recorded as a current period income
tax benefit. The recognition of the deferred tax benefit in 2007 and was in accordance with
generally accepted accounting principles, and considered, among other things, the probability of
utilizing the NOL and credit carryforwards. Further discussion on the NOL carryforward and future
benefits is presented in the “Management’s Discussion and Analysis” section of this report.
Off-Balance-Sheet Financial Instruments
In the ordinary course of business, the Corporation has entered into off-balance-sheet financial
instruments consisting of commitments to extend credit, commitments under credit card arrangements,
commercial letters of credit, and standby letters of credit. For letters of credit, the
Corporation recognizes a liability for the fair market value of the obligations it assumes under
that guarantee.
Reclassifications
Certain amounts in the 2008 and 2007 consolidated financial statements have been reclassified to
conform to the 2009 presentation.
NOTE 2 — RESTRICTIONS ON CASH AND CASH EQUIVALENTS
Cash and cash equivalents in the amount of $1.372 million were restricted on December 31, 2009 to
meet the reserve requirements of the Federal Reserve System.
In the normal course of business, the Corporation maintains cash and due from bank balances with
correspondent banks. Balances in these accounts may exceed the Federal Deposit Insurance
Corporation’s insured limit of $250,000, which was increased from $100,000 under certain provisions
of the Troubled Asset Relief Program (“TARP”).
Management believes that these financial institutions have strong credit ratings and the credit
risk related to these deposits is minimal.
23
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 3 – SECURITIES AVAILABLE FOR SALE
The carrying value and estimated fair value of securities available for sale are as follows
(dollars in thousands):
| Gross | Gross | |||||||||||||||
| Amortized | Unrealized | Unrealized | Estimated | |||||||||||||
| Cost | Gains | Losses | Fair Value | |||||||||||||
December 31, 2009 |
||||||||||||||||
US Agencies — MBS |
$ | 43,651 | $ | 1,642 | $ | (55 | ) | $ | 45,238 | |||||||
Obligations of states and political subdivisions |
1,207 | 68 | — | 1,275 | ||||||||||||
Total securities available for sale |
$ | 44,858 | $ | 1,710 | $ | (55 | ) | $ | 46,513 | |||||||
December 31, 2008 |
||||||||||||||||
US Agencies — MBS |
$ | 46,316 | $ | 632 | $ | (7 | ) | $ | 46,941 | |||||||
Obligations of states and political subdivisions |
498 | 51 | — | 549 | ||||||||||||
Total securities available for sale |
$ | 46,814 | $ | 683 | $ | (7 | ) | $ | 47,490 | |||||||
Following is information pertaining to securities with gross unrealized losses at December 31,
2009 and 2008 aggregated by investment category and length of time these individual securities
have been in a loss position (dollars in thousands):
| Less Than Twelve Months | Over Twelve Months | |||||||||||||||
| Gross | Gross | |||||||||||||||
| Unrealized | Fair | Unrealized | Fair | |||||||||||||
| Losses | Value | Losses | Value | |||||||||||||
December 31, 2009 |
||||||||||||||||
US Agencies — MBS |
$ | (55 | ) | $ | 3,309 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
Total securities available for sale |
$ | (55 | ) | $ | 3,309 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
December 31, 2008 |
||||||||||||||||
US Agencies — MBS |
$ | (7 | ) | $ | 5,106 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
Total securities available for sale |
$ | (7 | ) | $ | 5,106 | $ | — | $ | — | |||||||
The gross unrealized losses in the current portfolio are considered temporary in nature and
related to interest rate fluctuations. The Corporation has both the ability and intent to hold
the investment securities until their respective maturities and therefore does not anticipate the
realization of the temporary losses.
24
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 3 – SECURITIES AVAILABLE FOR SALE (CONTINUED)
Following is a summary of the proceeds from sales and calls of securities available for sale, as
well as gross gains and losses for the years ended December 31 (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Proceeds from sales and calls |
$ | 44,611 | $ | 12,047 | $ | 6,579 | ||||||
Gross gains on sales |
1,472 | 65 | — | |||||||||
Gross (losses) on sales and calls |
(1 | ) | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | ||||||
The carrying value and estimated fair value of securities available for sale at December 31, 2009,
by contractual maturity, are shown below (dollars in thousands):
| Amortized | Estimated | |||||||
| Cost | Fair Value | |||||||
Due in one year or less |
$ | 6 | $ | 6 | ||||
Due after one year through five years |
409 | 469 | ||||||
Due after five years through ten years |
2,330 | 2,298 | ||||||
Due after ten years |
42,113 | 43,740 | ||||||
Total |
$ | 44,858 | $ | 46,513 | ||||
Contractual maturities may differ from expected maturities because issuers may have the right to
call or prepay obligations with or without call or prepayment penalties. See Note 8 for
information on securities pledged to secure borrowings from the Federal Home Loan Bank.
NOTE 4 — LOANS
The composition of loans at December 31 is as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Commercial real estate |
$ | 208,895 | $ | 185,241 | ||||
Commercial, financial, and agricultural |
72,184 | 79,734 | ||||||
One to four family residential real estate |
67,232 | 65,595 | ||||||
Construction : |
||||||||
Consumer |
7,118 | 4,852 | ||||||
Commerical |
24,591 | 31,113 | ||||||
Consumer |
4,290 | 3,745 | ||||||
Total loans |
$ | 384,310 | $ | 370,280 | ||||
25
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 4 – LOANS (CONTINUED)
An analysis of the allowance for loan losses for the years ended December 31 is as follows (dollars
in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Balance, January 1 |
$ | 4,277 | $ | 4,146 | $ | 5,006 | ||||||
Recoveries on loans previously charged off |
66 | 121 | 50 | |||||||||
Loans charged off |
(2,818 | ) | (2,290 | ) | (1,310 | ) | ||||||
Provision |
3,700 | 2,300 | 400 | |||||||||
Balance, December 31 |
$ | 5,225 | $ | 4,277 | $ | 4,146 | ||||||
In 2009, net charge off activity was $2.752 million, or .73% of average loans outstanding compared
to net charge-offs of $2.169 million, or .60% of average loans, in the same period in 2008 and
$1.260 million, or .38% of average loans, in 2007. During 2009, a provision of $3.700 million
was made to increase the reserve. This provision was made in accordance with the Corporation’s
allowance for loan loss reserve policy, which calls for a measurement of the adequacy of the
reserve at each quarter end. This process includes an analysis of the loan portfolio to take into
account increases in loans outstanding and portfolio composition, historical loss rates, and
specific reserve requirements of nonperforming loans. The allowance for loan losses and current
provisions are discussed in more detail under “Management’s Discussion and Analysis.”
Impaired Loans
Nonperforming loans are those which are contractually past due 90 days or more as to interest or
principal payments, on nonaccrual status, or loans, the terms of which have been renegotiated to
provide a reduction or deferral on interest or principal. The interest income recorded, and that
which would have been recorded had nonaccrual and renegotiated loans been current or not troubled,
was not material to the consolidated financial statements for the years ended December 31, 2009 and
2008.
A loan is considered impaired, based on current information and events, if it is probable that the
Bank will be unable to collect the scheduled payments of principal or interest when due, according
to the contractual terms of the loan agreement.
26
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 4 – LOANS (CONTINUED)
The following is a summary of impaired loans and their effect on interest income (dollars in
thousands):
| Impaired Loans | Valuation Reserve | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| December 31, | December 31, | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | |||||||||||||||||||
Balances, at period end |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Impaired loans with valuation reserve |
$ | 11,348 | $ | 3,730 | $ | 3,639 | $ | 2,705 | $ | 994 | $ | 1,320 | ||||||||||||
Impaired loans with no valuation
reserve |
3,889 | 1,157 | 369 | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Total impaired loans |
$ | 15,237 | $ | 4,887 | $ | 4,008 | $ | 2,705 | $ | 994 | $ | 1,320 | ||||||||||||
Impaired loans on nonaccrual basis |
$ | 14,368 | $ | 4,887 | $ | 3,298 | $ | 2,705 | $ | 994 | $ | 1,219 | ||||||||||||
Impaired loans on accrual basis |
869 | — | 710 | — | — | 101 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total impaired loans |
$ | 15,237 | $ | 4,887 | $ | 4,008 | $ | 2,705 | $ | 994 | $ | 1,320 | ||||||||||||
Average investment in impaired loans |
$ | 10,449 | $ | 4,834 | $ | 4,135 | ||||||||||||||||||
Interest income recognized during
impairment |
40 | 60 | 129 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Interest income that would have been
recognized on an accrual basis |
700 | 377 | 391 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Cash-basis interest income recognized |
— | 60 | 84 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Insider Loans
The Bank, in the ordinary course of business, grants loans to the Corporation’s executive officers
and directors, including their families and firms in which they are principal owners. Activity in
such loans is summarized below (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Loans outstanding, January 1 |
$ | 6,516 | $ | 1,720 | ||||
New loans |
2,160 | 372 | ||||||
Net activity on revolving lines of credit |
1,189 | 2,378 | ||||||
Change in related party interest |
297 | 2,733 | ||||||
Repayment |
(1,610 | ) | (687 | ) | ||||
Loans outstanding, December 31 |
$ | 8,552 | $ | 6,516 | ||||
There were no loans to related-parties classified substandard as of December 31, 2009 and 2008. In
addition to the outstanding balances above, there were unfunded commitments of $1.222 million to
related parties at December 31, 2009.
27
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 5 – PREMISES AND EQUIPMENT
Details of premises and equipment at December 31 are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Land |
$ | 1,811 | $ | 2,042 | ||||
Buildings and improvements |
11,816 | 12,545 | ||||||
Furniture, fixtures, and equipment |
4,346 | 4,261 | ||||||
Construction in progress |
84 | 70 | ||||||
Total cost basis |
18,057 | 18,918 | ||||||
Less — accumulated depreciation |
7,892 | 7,729 | ||||||
Net book value |
$ | 10,165 | $ | 11,189 | ||||
The construction in progress at the end of 2009 pertains to ATM installation at a branch location,
improvements to an existing branch location, and costs associated with the establishment of a new
branch location.
In August 2009, the Bank sold its Ontonagon and South Range branch offices, with deposits of
approximately $29.300 million, premises and equipment with a net book value of $.600 million, and
loans totaling approximately $31,000.
Depreciation of premises and equipment charged to operating expenses amounted to $1.050 million in
2009, $1.035 million in 2008, and $.891 million in 2007.
NOTE 6 – OTHER REAL ESTATE HELD FOR SALE
An analysis of other real estate held for sale for the years ended December 31 is as follows
(dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Balance, January 1 |
$ | 2,189 | $ | 1,226 | ||||
Other real estate transferred from loans due to foreclosure |
4,879 | 2,849 | ||||||
Reclassification of redemption ORE |
(475 | ) | — | |||||
Other real estate sold / written down |
(768 | ) | (1,886 | ) | ||||
Loss on ORE |
(21 | ) | — | |||||
Balance, December 31 |
$ | 5,804 | $ | 2,189 | ||||
28
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 7 – DEPOSITS
The distribution of deposits at December 31 is as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Noninterest bearing |
$ | 35,878 | $ | 30,099 | ||||
NOW, money market, checking |
95,790 | 70,584 | ||||||
Savings |
18,207 | 20,730 | ||||||
CDs <$100,000 |
59,953 | 73,752 | ||||||
CDs >$100,000 |
36,385 | 25,044 | ||||||
Brokered |
175,176 | 150,888 | ||||||
Total deposits |
$ | 421,389 | $ | 371,097 | ||||
Maturities of non-brokered time deposits outstanding at December 31, 2009, are as follows (dollars
in thousands):
2010 |
$ | 76,257 | ||
2011 |
11,551 | |||
2012 |
5,457 | |||
2013 |
2,133 | |||
2014 |
374 | |||
Thereafter |
566 | |||
Total |
$ | 96,338 | ||
Brokered deposits of $101.708 million mature in 2010, $70.739 million mature in 2011, and $2.729
million matures thereafter.
NOTE 8 – FEDERAL HOME LOAN BANK BORROWINGS
Federal Home Loan Bank borrowings consist of the following at December 31 (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Federal Home Loan Bank fixed rate advances at rates ranging from 4.98% to 5.16%
maturing in 2010 |
$ | 15,000 | $ | 15,000 | ||||
Federal Home Loan Bank variable rate advances at rates ranging from .298% to .304%
maturing in 2011 |
20,000 | 20,000 | ||||||
| $ | 35,000 | $ | 35,000 | |||||
The Federal Home Loan Bank borrowings are collateralized at December 31, 2009 by the following: a
collateral agreement on the Corporation’s one to four family residential real estate loans with a
book value of approximately $29.275 million; mortgage related and municipal securities with an
amortized cost and estimated fair value of $16.224 million and $17.077
million, respectively; and Federal Home Loan Bank stock owned by the Bank totaling $3.794 million.
Prepayment of the remaining advances is subject to the provisions and conditions of the credit
policy of the Federal Home Loan Bank of Indianapolis in effect as of December 31, 2009.
29
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 8 – FEDERAL HOME LOAN BANK BORROWINGS (CONTINUED)
The $35.000 million FHLB borrowings are comprised of both fixed and variable rate borrowings as
shown in the above table. The FHLB has the option to convert the $15.000 million of fixed rate
advances to adjustable rate advances, repricing quarterly at three month LIBOR flat, on the
original call date and thereafter.
NOTE 9– OTHER BORROWINGS
Other borrowings consist of the following at December 31 (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Farmers Home Administration, fixed-rate note payable, maturing August 24, 2024
interest payable at 1% |
$ | 1,140 | $ | 1,210 | ||||
The U.S.D.A. Rural Development borrowing is collateralized by loans totaling $.269 million
originated and held by the Corporation’s wholly owned subsidiary, First Rural Relending and an
assignment of a demand deposit account in the amount of $.954 million, and guaranteed by the
Corporation.
Maturities of long-term borrowings outstanding at December 31, 2009 are as follows (dollars in
thousands):
2010 |
$ | 15,071 | ||
2011 |
20,072 | |||
2012 |
72 | |||
2013 |
73 | |||
2014 |
74 | |||
Thereafter |
778 | |||
Total |
$ | 36,140 | ||
NOTE 10 – INCOME TAXES
The components of the federal income tax provision (credit) for the years ended December 31 are as
follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Current tax expense (credit) |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | 15 | ||||||
Change in valuation allowance |
— | — | (8,136 | ) | ||||||||
Deferred tax expense |
1,120 | 787 | 881 | |||||||||
Total provision (credit) for income taxes |
$ | 1,120 | $ | 787 | $ | (7,240 | ) | |||||
30
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 10 – INCOME TAXES (CONTINUED)
A summary of the source of differences between income taxes at the federal statutory rate and the
provision (credit) for income taxes for the years ended December 31 is as follows (dollars in
thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Tax expense at statutory rate |
$ | 1,202 | $ | 904 | $ | 993 | ||||||
Increase (decrease) in taxes resulting from: |
||||||||||||
Tax-exempt interest |
(106 | ) | (137 | ) | (181 | ) | ||||||
Change in valuation allowance |
— | — | (8,136 | ) | ||||||||
Other |
24 | 20 | 84 | |||||||||
Provision for (benefit of) income taxes |
$ | 1,120 | $ | 787 | $ | (7,240 | ) | |||||
Deferred income taxes are provided for the temporary differences between the financial reporting
and tax bases of the Corporation’s assets and liabilities. The major components of net deferred tax
assets at December 31 are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Deferred tax assets: |
||||||||
Allowance for loan losses |
$ | 1,776 | $ | 1,454 | ||||
Deferred compensation |
273 | 310 | ||||||
Intangible assets |
112 | 129 | ||||||
Alternative Minimum Tax Credit |
1,463 | 1,463 | ||||||
NOL carryforward |
9,520 | 10,924 | ||||||
Depreciation |
72 | 131 | ||||||
Tax credit carryovers |
672 | 672 | ||||||
Stock option compensation |
196 | 175 | ||||||
Other |
129 | 40 | ||||||
Total deferred tax assets |
14,213 | 15,298 | ||||||
Valuation allowance |
$ | (8,146 | ) | $ | (8,146 | ) | ||
Deferred tax liabilities: |
||||||||
FHLB stock dividend |
(128 | ) | (128 | ) | ||||
Unrealized gain (loss) on securities |
(563 | ) | (229 | ) | ||||
Other |
(95 | ) | (61 | ) | ||||
Total deferred tax liabilities |
(786 | ) | (418 | ) | ||||
Net deferred tax asset |
$ | 5,281 | $ | 6,734 | ||||
A valuation allowance is provided against deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not that
some or all of the deferred tax asset will not be realized. At December 31, 2009 and 2008, the
Corporation evaluated the valuation allowance against the net deferred tax asset which would
require future taxable income in order to be utilized. The Corporation, as of December 31, 2009
had a net operating loss and tax credit carryforwards for tax purposes of approximately $28.0
million, and $2.1 million, respectively.
31
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 10 — INCOME TAXES (CONTINUED)
The Corporation utilized NOL carryforwards to offset taxable income for the first nine months of
2007. In the third quarter of 2007, the Corporation reversed a portion of the valuation allowance,
$7.500 million that pertained to the deferred tax benefit of NOL and tax credit carryforwards.
This valuation adjustment was recorded as a current period income tax benefit. The recognition of
the deferred tax benefit in 2007 was in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles,
and considered among other things, the probability of utilizing the NOL and credit carryforwards.
The Corporation recorded the future benefits from these carryforwards at such time as it became
“more likely than not” that they would be utilized prior to expiration. Please refer to further
discussion on income taxes contained in “Management’s Discussion and Analysis.” The net operating
loss carryforwards expire twenty years from the date they originated. These carryforwards, if not
utilized, will begin to expire in the year 2023. A portion of the NOL, approximately $18 million,
and all of the credit carryforwards are subject to the limitations for utilization as set forth in
Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code. The annual limitation is $1.400 million for the NOL and
the equivalent value of tax credits, which is approximately $.477 million. These limitations for
use were established in conjunction with the recapitalization of the Corporation in December 2004.
NOTE 11 — OPERATING LEASES
The Corporation currently maintains two operating leases for branch office locations. The first
operating lease, for our location in Birmingham, was originated in September 2005 and had an
original term of 66 months with an option to renew for an additional five year period.
The second operating lease, for our new location in Escanaba, was executed in December 2008, the
terms of which began in April 2009. The original term of this lease is three years and will
automatically renew and extend for four additional consecutive terms of two years each. The
additional terms call for a lease adjustment based on the Consumer Price Index at time of renewal.
Future minimum payments, by year and in the aggregate, under the initial terms of the operating
lease agreements, consist of the following (dollars in thousands):
2010 |
$ | 209 | ||
2011 |
82 | |||
2012 |
10 | |||
Total |
$ | 301 | ||
Rent expense for all operating leases amounted to $207,000 in 2009, $195,000 in 2008, and $141,000
in 2007.
NOTE 12 — RETIREMENT PLAN
The Corporation has established a 401(k) profit sharing plan. Employees who have completed three
months of service and attained the age of 18 are eligible to participate in the plan. Eligible
employees can elect to have a portion, not to exceed 80%, of their annual compensation paid into
the plan. In addition, the Corporation may make discretionary contributions into the plan.
Retirement plan contributions charged to operations totaled $120,000, $90,000, and $112,000 in
2009, 2008, and 2007, respectively.
32
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 13 — DEFERRED COMPENSATION PLAN
As an incentive to retain key members of management and directors, the Corporation established a
deferred compensation plan, with benefits based on the number of years the individuals have served
the Corporation. This plan was discontinued and no longer applies to current officers and
directors. A liability was recorded on a present value basis and discounted using the rates in
effect at the time the deferred compensation agreement was entered into. The liability may change
depending upon changes in long-term interest rates. The liability at December 31, 2009 and 2008,
for vested benefits under this plan, was $.815 million and $.912 million respectively. These
benefits were originally contracted to be paid over a ten to fifteen-year period. The final
payment is scheduled to occur in 2023. The deferred compensation plan is unfunded; however, the
Bank maintains life insurance policies on the majority of the plan participants. The cash
surrender value of the policies was $1.464 million and $1.384 million at December 31, 2009 and
2008, respectively. Deferred compensation expense for the plan was $72,000, $84,000, and $90,000
for 2009, 2008, and 2007 respectively.
NOTE 14 — REGULATORY MATTERS
The Corporation is subject to various regulatory capital requirements administered by the federal
banking agencies. Failure to meet minimum capital requirements can initiate certain mandatory—and
possibly additional discretionary—actions by regulators that, if undertaken, could have a direct
material effect on the Corporation’s consolidated financial statements. Under capital adequacy
guidelines and the regulatory framework for prompt corrective action, the Corporation must meet
specific capital guidelines that involve quantitative measures of the Corporation’s assets,
liabilities, and certain off-balance-sheet items as calculated under regulatory accounting
practices. The Corporation’s capital amounts and classification are also subject to qualitative
judgments by the regulators about components, risk weightings, and other factors.
Quantitative measures established by regulation to ensure capital adequacy require the Corporation
to maintain minimum amounts and ratios (set forth in the table below) of total and Tier 1 capital
to risk-weighted assets and of Tier 1 capital to average assets. Management has determined that,
as of December 31, 2009, the Corporation is well capitalized.
To be categorized as well capitalized, the Bank must maintain minimum total risk-based, Tier 1
risk-based, and Tier 1 leverage ratios as set forth in the table. In addition, federal banking
regulators have established capital classifications beyond the minimum requirements in order to
risk-rate deposit insurance premiums and to provide trigger points for prompt corrective action.
33
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 14 — REGULATORY MATTERS (CONTINUED)
The Corporation’s and the Bank’s actual and required capital amounts and ratios as of December 31
are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| To Be Well | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Capitalized Under | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| For Capital | Prompt Corrective | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Actual | Adequacy Purposes | Action Provisions | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | Amount | Ratio | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
2009
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total capital to risk
weighted assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consolidated |
$ | 54,587 | 13.2 | % | ³ | $ | 33,155 | ³ 8.0 | % | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||
mBank |
$ | 47,630 | 11.5 | % | ³ | $ | 33,166 | ³ 8.0 | % | ³ | $ | 41,458 | 10.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 capital to
risk weighted assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consolidated |
$ | 49,406 | 11.9 | % | ³ | $ | 16,578 | ³ 4.0 | % | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||
mBank |
$ | 42,446 | 10.2 | % | ³ | $ | 16,583 | ³ 4.0 | % | ³ | $ | 24,875 | 6.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 capital to
average assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consolidated |
$ | 49,406 | 9.8 | % | ³ | $ | 20,272 | ³ 4.0 | % | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||
mBank |
$ | 42,446 | 8.4 | % | ³ | $ | 20,261 | ³ 4.0 | % | ³ | $ | 25,326 | 5.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
2008
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total capital to risk
weighted assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consolidated |
$ | 39,138 | 10.4 | % | ³ | $ | 30,158 | ³ 8.0 | % | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||
mBank |
$ | 39,428 | 10.4 | % | ³ | $ | 30,202 | ³ 8.0 | % | ³ | $ | 37,752 | 10.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 capital to
risk weighted assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consolidated |
$ | 34,861 | 9.3 | % | ³ | $ | 15,079 | ³ 4.0 | % | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||
mBank |
$ | 35,192 | 9.3 | % | ³ | $ | 15,101 | ³ 4.0 | % | ³ | $ | 22,651 | 6.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 capital to
average assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Consolidated |
$ | 34,861 | 8.0 | % | ³ | $ | 17,407 | ³ 4.0 | % | N/A | ||||||||||||||||||||||
mBank |
$ | 35,192 | 8.1 | % | ³ | $ | 17,393 | ³ 4.0 | % | ³ | $ | 21,741 | 5.0 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
At December 31, 2009, the Bank was not authorized to pay dividends to the Corporation without
prior regulatory approval because of a negative retained earnings balance due to cumulative losses.
NOTE 15 — STOCK OPTION PLANS
The Corporation sponsors three stock option plans. All historical information presented below has
been adjusted to reflect the 1 for 20 reverse stock split which occurred on December 16, 2004. One
plan was approved during 2000 and applies to officers, employees, and non-employee directors. A
total of 25,000 shares were made available for grant under this plan. This plan was amended as a
part of the recapitalization to provide for additional authorized shares equal to 12.50% of all
outstanding shares subsequent to the recapitalization, which amounted to 428,587 shares. This plan
expires on February 15, 2010. The other two plans, one for officers and employees and the other
for non-employee directors, were approved in 1997 and expired in 2007. A total of 30,000 shares
were made available for grant under these plans. Options under all of
the plans are granted at the discretion of a committee of the Corporation’s Board of Directors.
Options to purchase shares of the Corporation’s stock are granted at a price equal to the market
price of the stock at the date of grant. The committee determines the vesting of the options when
they are granted as established under the plan.
34
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 15 — STOCK OPTION PLANS (CONTINUED)
A summary of stock option transactions for the years ended December 31 is as follows:
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Outstanding shares at beginning of year |
446,237 | 446,417 | ||||||
Granted during the year |
— | — | ||||||
Expired / forfeited during the year |
(35,180 | ) | (180 | ) | ||||
Outstanding shares at end of year |
411,057 | 446,237 | ||||||
Exercisable shares at end of year |
157,266 | 164,446 | ||||||
Weighted average exercise price per share
at end of year |
$ | 12.03 | $ | 12.14 | ||||
Shares available for grant at end of year |
24,780 | 18,488 | ||||||
There were no options granted in 2009 and in 2008.
Following is a summary of the options outstanding and exercisable at December 31, 2009:
| Weighted | ||||||||||||||||
| Average | Weighted | |||||||||||||||
| Remaining | Average | |||||||||||||||
| Exercise | Number of Shares | Contractual | Exercise | |||||||||||||
| Price Range | Outstanding | Exercisable | Life-Years | Price | ||||||||||||
$9.16 |
12,500 | 5,000 | 5.96 | $ | 9.16 | |||||||||||
$9.75 |
257,152 | 120,861 | 4.96 | 9.75 | ||||||||||||
$10.65 |
57,500 | 11,500 | 6.96 | 10.65 | ||||||||||||
$11.50 |
40,000 | 8,000 | 5.75 | 11.50 | ||||||||||||
$12.00 |
40,000 | 8,000 | 5.46 | 12.00 | ||||||||||||
$156.00 — $240.00 |
3,545 | 3,545 | 1.23 | 186.75 | ||||||||||||
$300.00 — $400.00 |
360 | 360 | .29 | 300.00 | ||||||||||||
| 411,057 | 157,266 | 5.36 | $ | 12.03 | ||||||||||||
Options issued since the Corporation’s recapitalization in December of 2004 call for 20% immediate
vesting upon issue and subsequent vesting to occur over a two to five year period, based upon the
market value appreciation of the underlying Corporation’s stock. Compensation related to these
options is expensed based upon the vesting period without
consideration given to market value appreciation. Future compensation for all outstanding options
is projected to total $29,000 in 2010 and none thereafter.
35
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 16 — OTHER COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
Other comprehensive income (loss) components and related taxes for the years ended December 31 are
as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Unrealized holding gains on
available for sale securities |
$ | 2,451 | $ | 681 | $ | 246 | ||||||
Less reclassification adjustments for gains (losses)
later recognized in income |
1,471 | 64 | (1 | ) | ||||||||
Net unrealized gains |
980 | 617 | 247 | |||||||||
Tax effect |
331 | 232 | — | |||||||||
Other comprehensive income |
$ | 649 | $ | 385 | $ | 247 | ||||||
NOTE 17 — SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY
Participation in the TARP Capital Purchase Program
On April 24, 2009, the Corporation entered into and closed a Letter Agreement, including the
Securities Purchase Agreement-Standard Terms (collectively, the “Securities Purchase Agreement”),
related to the CPP. Pursuant to the Securities Purchase Agreement, the Corporation issued and sold
to the Treasury (i) 11,000 shares of the Corporation’s Series A Preferred Shares, and (ii) the
Warrant to purchase 379,310 shares of the Corporation’s Common Shares, at an exercise price of
$4.35 per share (subject to certain anti-dilution and other adjustments), for an aggregate purchase
price of $11.000 million in cash. The Warrant has a ten-year term.
As a result of the CPP transaction, the Corporation is required to take certain actions, for so
long as the Treasury holds any securities acquired from the Corporation pursuant to the CPP
(excluding any period in which the Treasury holds only the Warrant to purchase Common Shares of the
Corporation) (the “CPP Period”), to ensure that its executive compensation and benefit plans with
respect to Senior Executive Officers (as defined in the relevant agreements) comply with Section
111(b) of Emergency Economic Stabilization Act of 2008 (“EESA”), as implemented by any guidance or
regulations issued under Section 111(b) of EESA, and not adopt any benefit plans with respect to,
or which cover, the Corporation’s Senior Executive Officers that do not comply with EESA, as
amended by the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (the “ARRA”), which was passed by
Congress and signed by the President on February 17, 2009. The applicable executive compensation
standards generally remain in effect during the CPP Period and apply to the Corporation’s Senior
Executive Officers (which for purposes of the ARRA and the CPP agreements, includes the
Corporation’s Chief Executive Officer, its Chief Financial Officer, and the next three most
highly-compensated executive officers, even though the Corporation’s senior executive officers
consist of a smaller group of executives for purposes of the other compensation disclosures in this
proxy statement).
Amounts recorded for Preferred Stock and Warrant Common Stock were estimated based on an allocation
of the total proceeds from the issuance on the relative fair values of both instruments. Fair
value of the Preferred Stock was determined based on assumptions regarding the discount rate
(market rate) on the Preferred Stock (estimated 12%). Fair value of the
Warrant Common Stock is based on the value of the underlying Preferred Stock based on an estimate
for a three year term. The allocation of the proceeds received resulted in the recording of a
discount on the Preferred Stock and a premium on the Warrant Common Stock. The discount on the
preferred will be accreted on an effective yield basis over a three-year term. The allocated
carrying value of the Preferred Stock and Warrant Common Stock on the date of issuance (based on
their relative fair values) was $10.382 million and $.618 million, respectively. Cumulative
dividends on the Preferred Stock are payable at 5% annum for the first five years and at a rate of
9% per annum thereafter on the liquidation preference of
36
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 17 — SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY (CONTINUED)
$1,000 per share. The Company is prohibited from paying any dividend with respect to shares of
common stock unless all accrued and unpaid dividends are paid in full on the Preferred Stock for
all past dividend periods. The Preferred Stock is non-voting, other than class voting rights on
matters that could adversely affect the Preferred Stock. The Preferred Stock may be redeemed at
any time with regulatory approval. The Treasury may also transfer the Preferred Stock to a third
party at any time. The preferred stock qualifies as Tier 1 Capital for regulatory purposes at the
holding company.
The Corporation has the right to redeem the Series A Preferred Shares at any time after consulting
with its primary regulator, in which case the executive compensation standards would no longer
apply to the Corporation.
This capital will be used to increase the strong capital position of the Bank. The Bank will use
the capital to grow loans. In addition, the capital will allow the Corporation to consider
acquisitions of deposit franchisees that would enhance our funding mix.
NOTE 18 — COMMITMENTS, CONTINGENCIES, AND CREDIT RISK
Financial Instruments with Off-Balance-Sheet Risk
The Corporation is a party to financial instruments with off-balance-sheet risk in the normal
course of business to meet the financing needs of its customers. These financial instruments
include commitments to extend credit and standby letters of credit. Those instruments involve, to
varying degrees, elements of credit risk in excess of the amount recognized in the consolidated
balance sheets.
The Corporation’s exposure to credit loss, in the event of nonperformance by the other party to the
financial instrument for commitments to extend credit and standby letters of credit, is represented
by the contractual amount of those instruments. The Corporation uses the same credit policies in
making commitments and conditional obligations as it does for on-balance-sheet instruments. These
commitments at December 31 are as follows (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
Commitments to extend credit: |
||||||||
Variable rate |
$ | 24,839 | $ | 40,036 | ||||
Fixed rate |
6,039 | 4,487 | ||||||
Standby letters of credit — Variable rate |
1,279 | 1,838 | ||||||
Credit card commitments — Fixed rate |
2,714 | 2,438 | ||||||
| $ | 34,871 | $ | 48,799 | |||||
Commitments to extend credit are agreements to lend to a customer as long as there is no violation
of any condition established in the contract. Commitments generally have fixed expiration dates or
other termination clauses and may require payment of a fee. Since many of the commitments are
expected to expire without being drawn upon, the total commitment amounts do not necessarily
represent future cash requirements. The Corporation evaluates each customer’s creditworthiness on
a case-by-case basis. The amount of collateral obtained, if deemed necessary by the Corporation
upon extension of credit, is based on management’s credit evaluation of the party. Collateral held
varies, but may include accounts receivable, inventory, property, plant and equipment, and
income-producing commercial properties.
Standby letters of credit are conditional commitments issued by the Corporation to guarantee the
performance of a customer to a third party. Those guarantees are primarily issued to support
public and private borrowing arrangements. The credit risk involved in issuing letters of credit
is essentially the same as that involved in extending loan facilities to customers. The
commitments are structured to allow for 100% collateralization on all standby letters of credit.
Credit card commitments are commitments on credit cards issued by the Corporation’s subsidiary and
serviced by other companies. These commitments are unsecured.
37
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 18 — COMMITMENTS, CONTINGENCIES, AND CREDIT RISK (CONTINUED)
Contingencies
In the normal course of business the Corporation is involved in various legal proceedings.
Concentration of Credit Risk
The Bank grants commercial, residential, agricultural, and consumer loans throughout Michigan. The
Bank’s most prominent concentration in the loan portfolio relates to commercial real estate loans
to operators of nonresidential buildings. This concentration at December 31, 2009 represents
$48.689 million, or 15.93%, compared to $41.299 million, or 13.95%, of the commercial loan
portfolio on December 31, 2008. The remainder of the commercial loan portfolio is diversified in
such categories as hospitality and tourism, real estate agents and managers, new car dealers,
gaming, petroleum, forestry, agriculture, and construction. Due to the diversity of the Bank’s
locations, the ability of debtors of residential and consumer loans to honor their obligations is
not tied to any particular economic sector.
NOTE 19 — FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
Fair value estimates, methods, and assumptions are set forth below for the Corporation’s financial
instruments:
Cash, cash equivalents, and interest-bearing deposits — The carrying values approximate the fair
values for these assets.
Securities — Fair values are based on quoted market prices where available. If a quoted market
price is not available, fair value is estimated using quoted market prices for similar securities.
Federal Home Loan Bank stock — Federal Home Loan Bank stock is carried at cost, which is
its redeemable value and approximates its fair value, since the market for this stock is limited.
Loans — Fair values are estimated for portfolios of loans with similar financial characteristics.
Loans are segregated by type such as commercial, residential mortgage, and other consumer. The
fair value of loans is calculated by discounting scheduled cash flows using discount rates
reflecting the credit and interest rate risk inherent in the loan.
The methodology in determining fair value of nonaccrual loans is to average them into the blended
interest rate at 0% interest. This has the effect of decreasing the carrying amount below the
risk-free rate amount and, therefore, discounts the estimated fair value.
Impaired loans are measured at the estimated fair value of the expected future cash flows at the
loan’s effective interest rate or the fair value of the collateral for loans which are collateral
dependent. Therefore, the carrying values of impaired loans approximate the estimated fair values
for these assets.
Deposits — The fair value of deposits with no stated maturity, such as noninterest-bearing demand
deposits and savings, is equal to the amount payable on demand at the reporting date. The fair
value of time deposits is based on the discounted value of contractual cash flows applying interest
rates currently being offered on similar time deposits.
Borrowings — Rates currently available for debt with similar terms and remaining maturities are
used to estimate the fair value of existing debt. The fair value of borrowed funds due on demand
is the amount payable at the reporting date.
Accrued interest — The carrying amount of accrued interest approximates fair value.
Off-balance-sheet instruments — The fair value of commitments is estimated using the fees currently
charged to enter into similar agreements, taking into account the remaining terms of the
agreements, the current interest rates, and the present creditworthiness of the counterparties.
Since the differences in the current fees and those reflected to the off-balance-sheet instruments
at year-end are immaterial, no amounts for fair value are presented.
38
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 19 — FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS (CONTINUED)
The following table presents information for financial instruments at December 31 (dollars in
thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||
| Carrying | Estimated | Carrying | Estimated | |||||||||||||
| Amount | Fair Value | Amount | Fair Value | |||||||||||||
Financial assets: |
||||||||||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 45,433 | $ | 45,433 | $ | 10,112 | $ | 10,112 | ||||||||
Interest-bearing deposits |
678 | 678 | 582 | 582 | ||||||||||||
Securities available for sale |
46,513 | 46,513 | 47,490 | 47,490 | ||||||||||||
Federal Home Loan Bank stock |
3,794 | 3,794 | 3,794 | 3,794 | ||||||||||||
Net loans |
379,085 | 382,352 | 366,003 | 372,080 | ||||||||||||
Other real estate owned |
5,804 | 5,804 | 2,189 | 2,189 | ||||||||||||
Cash surrender value — life insurance |
1,485 | 1,485 | 1,397 | 1,397 | ||||||||||||
Accrued interest receivable |
1,413 | 1,413 | 1,457 | 1,457 | ||||||||||||
Total financial assets |
$ | 484,205 | $ | 487,472 | $ | 433,024 | $ | 439,101 | ||||||||
Financial liabilities: |
||||||||||||||||
Deposits |
$ | 421,389 | $ | 421,124 | $ | 371,097 | $ | 371,434 | ||||||||
Borrowings |
36,140 | 36,447 | 36,210 | 36,846 | ||||||||||||
Directors deferred compensation |
815 | 815 | 912 | 912 | ||||||||||||
Accrued interest payable |
325 | 325 | 488 | 488 | ||||||||||||
Total financial liabilities |
$ | 458,669 | $ | 458,711 | $ | 408,707 | $ | 409,680 | ||||||||
Limitations - Fair value estimates are made at a specific point in time based on relevant market
information and information about the financial instrument. These estimates do not reflect any
premium or discount that could result from offering for sale at one time the Corporation’s entire
holdings of a particular financial instrument. Because no market exists
for a significant portion of the Corporation’s financial instruments, fair value estimates are
based on judgments regarding future expected loss experience, current economic conditions, risk
characteristics of various financial instruments, and other factors. These estimates are
subjective in nature and involve uncertainties and matters of significant judgment and therefore
cannot be determined with precision. Changes in assumptions could significantly affect the
estimates. Fair value estimates are based on existing on-and off-balance-sheet financial
instruments without attempting to estimate the value of anticipated future business and the value
of assets and liabilities that are not considered financial instruments. Significant assets and
liabilities that are not considered financial assets or liabilities include premises and equipment,
other assets, and other liabilities. In addition, the tax ramifications related to the realization
of the unrealized gains and losses can have a significant effect on fair value estimates and have
not been considered in the estimates.
39
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 19 — FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS (CONTINUED)
The following tables present information about the Corporation’s assets and liabilities measured at
fair value on a recurring basis at December 31, 2009, and the valuation techniques used by the
Corporation to determine those fair values.
Level 1: In general, fair values determined by Level 1 inputs use quoted prices in active markets
for identical assets or liabilities that the Corporation has the ability
to access.
Level 2: Fair values determined by Level 2 inputs use other inputs that are observable, either
directly or indirectly. These Level 2 inputs include quoted prices for similar assets and
liabilities in active markets, and other inputs such as interest rates and yield curves that are
observable at commonly quoted intervals.
Level 3: Level 3 inputs are unobservable inputs, including inputs available in situations where
there is little, if any, market activity for the related asset or liability.
In instances where inputs used to measure fair value fall into different levels in the above fair
value hierarchy, fair value measurements in their entirety are categorized based on the lowest
level input that is significant to the valuation. The Corporation’s assessment of the significance
of particular inputs to these fair value measurements requires judgment and considers factors
specific to each asset or liability.
Disclosures concerning assets and liabilities measured at fair value are as follows (dollars in
thousands):
Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis at December 31, 2009
| Quoted Prices in Active | Significant Other | Significant | ||||||||||||||
| Markets for Identical | Observable Inputs | Unobservable Inputs | Balance at | |||||||||||||
| Assets (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | December 31, 2009 | |||||||||||||
Assets |
||||||||||||||||
Investment securities — available for sale |
$ | — | $ | 46,513 | $ | — | $ | 46,513 | ||||||||
Liabilities |
||||||||||||||||
None |
||||||||||||||||
Assets and Liabilities Measured at Fair Value on a Recurring Basis at December 31, 2008
| Quoted Prices in Active | Significant Other | Significant | ||||||||||||||
| Markets for Identical | Observable Inputs | Unobservable Inputs | Balance at | |||||||||||||
| Assets (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | December 31, 2008 | |||||||||||||
Assets |
||||||||||||||||
Investment securities — available for sale |
$ | 47,422 | $ | 68 | $ | — | $ | 47,490 | ||||||||
Liabilities |
||||||||||||||||
None |
||||||||||||||||
The Corporation had no Level 3 assets or liabilities on a recurring basis as of December 31, 2009
or 2008.
The Corporation also has assets that under certain conditions are subject to measurement at fair
value on a non-recurring basis. These assets include loans and other real estate owned. The
Corporation has estimated the fair values of these assets using Level 3 inputs, specifically
discounted cash flow projections.
40
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 19 — FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS (CONTINUED)
Assets Measured at Fair Value on a Nonrecurring Basis at December 31, 2009
| Quoted Prices | Significant | Significant | ||||||||||||||||||
| in Active Markets | Other Observable | Unobservable | Total Losses for | |||||||||||||||||
| Balance at | for Identical Assets | Inputs | Inputs | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | December 31, 2009 | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | December 31, 2009 | |||||||||||||||
Assets |
||||||||||||||||||||
Impaired loans |
$ | 13,621 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 13,621 | $ | 1,300 | ||||||||||
Other real estate owned |
5,804 | — | — | 5,804 | 399 | |||||||||||||||
| $ | 1,699 | |||||||||||||||||||
Assets Measured at Fair Value on a Nonrecurring Basis at December 31, 2008
| Quoted Prices | Significant | Significant | ||||||||||||||||||
| in Active Markets | Other Observable | Unobservable | Total Losses for | |||||||||||||||||
| Balance at | for Identical Assets | Inputs | Inputs | Year Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | December 31, 2009 | (Level 1) | (Level 2) | (Level 3) | December 31, 2008 | |||||||||||||||
Assets |
||||||||||||||||||||
Impaired Loans |
$ | 1,030 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,030 | $ | 862 | ||||||||||
| $ | 862 | |||||||||||||||||||
The Corporation had no investments subject to fair value measurement on a nonrecurring basis.
Impaired loans categorized as Level 3 assets consist of non-homogeneous loans that are considered
impaired. The Corporation estimates the fair value of the loans based on the present value of
expected future cash flows using management’s best estimate of key assumptions. These assumptions
include future payment ability, timing of payment streams, and estimated realizable values of
available collateral (typically based on outside appraisals).
41
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 20 — PARENT COMPANY ONLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
BALANCE SHEETS
December 31, 2009 and 2008
(Dollars in Thousands)
December 31, 2009 and 2008
(Dollars in Thousands)
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
ASSETS |
||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 7,480 | $ | 413 | ||||
Investment in subsidiaries |
48,575 | 41,990 | ||||||
Other assets |
156 | 29 | ||||||
TOTAL ASSETS |
$ | 56,211 | $ | 42,432 | ||||
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
||||||||
Other liabilities |
$ | 912 | $ | 880 | ||||
Shareholders’ equity |
55,299 | 41,552 | ||||||
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
$56,211 | $ | 42,432 | |||||
42
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 20 — PARENT COMPANY ONLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (CONTINUED)
STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
Years Ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(Dollars in Thousands)
Years Ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(Dollars in Thousands)
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
INCOME: |
||||||||||||
Proceeds from settlement of lawsuits |
$ | — | $ | 3,475 | $ | 470 | ||||||
Other |
8 | 9 | 12 | |||||||||
Total income |
8 | 3,484 | 482 | |||||||||
EXPENSES: |
||||||||||||
Salaries and benefits |
250 | 265 | 300 | |||||||||
Interest |
— | 51 | 160 | |||||||||
Professional service fees |
196 | 55 | 96 | |||||||||
Other |
227 | 141 | 127 | |||||||||
Total expenses |
673 | 512 | 683 | |||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes and equity in undistributed net
income (loss) of subsidiaries |
(665 | ) | 2,972 | (201 | ) | |||||||
Provision for (benefit of) income taxes |
(226 | ) | 1,005 | (50 | ) | |||||||
Income (loss) before equity in undistributed net income (loss) of subsidiaries |
(439 | ) | 1,967 | (151 | ) | |||||||
Equity in undistributed net income (loss) of subsidiaries |
2,855 | (95 | ) | 10,314 | ||||||||
Net income |
2,416 | 1,872 | 10,163 | |||||||||
Preferred dividend and accretion of discount |
509 | — | — | |||||||||
NET INCOME AVAILABLE TO COMMON SHAREHOLDERS |
$ | 1,907 | $ | 1,872 | $ | 10,163 | ||||||
43
Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTE 20 — PARENT COMPANY ONLY FINANCIAL STATEMENTS (CONTINUED)
STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
Years Ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(Dollars in Thousands)
Years Ended December 31, 2009, 2008, and 2007
(Dollars in Thousands)
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Cash Flows from Operating Activities: |
||||||||||||
Net income
|
$ | 2,416 | $ | 1,872 | $ | 10,163 | ||||||
Adjustments to reconcile net income to net
cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
Equity in undistributed net (income) loss of subsidiaries
|
(2,855 | ) | 95 | (10,314 | ) | |||||||
Increase in capital from stock option compensation
|
60 | 82 | 121 | |||||||||
Change in other assets
|
(127 | ) | 49 | (15 | ) | |||||||
Change in other liabilities
|
32 | 765 | (59 | ) | ||||||||
Other
|
(19 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Net cash (used in) operating activities
|
(493 | ) | 2,863 | (104 | ) | |||||||
Cash Flows from Financing Activities: |
||||||||||||
Proceeds from issuance of Series A Preferred Stock and common stock warrants
|
11,000 | — | — | |||||||||
Dividend on preferred stock and discount accretion
|
(509 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
Net (decrease) in lines of credit
|
— | (1,959 | ) | — | ||||||||
Purchase of common stock — oddlot shares
|
— | (110 | ) | — | ||||||||
Payments from subsidiaries
|
69 | — | — | |||||||||
Investments in subsidiaries
|
(3,000 | ) | (500 | ) | — | |||||||
Net cash (used) provided by financing activities
|
7,560 | (2,569 | ) | — | ||||||||
Net increase (decrease) in cash and cash equivalents
|
7,067 | 294 | (104 | ) | ||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at beginning of period
|
413 | 119 | 223 | |||||||||
Cash and cash equivalents at end of period
|
$ | 7,480 | $ | 413 | $ | 119 | ||||||
44
Selected Financial Data
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
SELECTED FINANCIAL DATA
(Unaudited)
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Per Share Data)
(Unaudited)
(Dollars in Thousands, Except Per Share Data)
| Years Ended December 31 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | ||||||||||||||||
SELECTED FINANCIAL CONDITION DATA: |
||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets
|
$ | 515,377 | $ | 451,431 | $ | 408,880 | $ | 382,791 | $ | 298,722 | ||||||||||
Loans
|
384,310 | 370,280 | 355,079 | 322,581 | 239,771 | |||||||||||||||
Securities
|
46,513 | 47,490 | 21,597 | 32,769 | 34,210 | |||||||||||||||
Deposits
|
421,389 | 371,097 | 320,827 | 312,421 | 232,632 | |||||||||||||||
Borrowings
|
36,140 | 36,210 | 45,949 | 38,307 | 36,417 | |||||||||||||||
Total equity
|
55,299 | 41,552 | 39,321 | 28,790 | 26,588 | |||||||||||||||
SELECTED OPERATIONS DATA: |
||||||||||||||||||||
Interest income
|
$ | 23,708 | $ | 24,562 | $ | 28,695 | $ | 24,052 | $ | 16,976 | ||||||||||
Interest expense
|
(7,421 | ) | (11,698 | ) | (15,278 | ) | (12,459 | ) | (7,196 | ) | ||||||||||
Net interest income
|
16,287 | 12,864 | 13,417 | 11,593 | 9,780 | |||||||||||||||
Provision for loan losses
|
3,700 | 2,300 | 400 | (861 | ) | — | ||||||||||||||
Net security gains (losses)
|
1,471 | 64 | (1 | ) | (1 | ) | 95 | |||||||||||||
Other income
|
3,280 | 4,589 | 2,007 | 984 | 1,016 | |||||||||||||||
Other expenses
|
(13,802 | ) | (12,558 | ) | (12,100 | ) | (12,221 | ) | (18,255 | ) | ||||||||||
Income (loss) before income taxes
|
3,536 | 2,659 | 2,923 | 1,216 | (7,364 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Provision (credit) for income taxes
|
1,120 | 787 | (7,240 | ) | (500 | ) | — | |||||||||||||
Net income (loss)
|
2,416 | 1,872 | 10,163 | 1,716 | (7,364 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Preferred dividend and accretion of discount
|
509 | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Net income available to common shareholders
|
$ | 1,907 | $ | 1,872 | $ | 10,163 | $ | 1,716 | $ | (7,364 | ) | |||||||||
PER SHARE DATA: |
||||||||||||||||||||
Earnings (loss) — Basic
|
$ | .56 | $ | .55 | $ | 2.96 | $ | .50 | $ | (2.15 | ) | |||||||||
Earnings (loss) — Diluted
|
.56 | .55 | 2.96 | .50 | (2.15 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Cash dividends declared
|
— | — | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||
Book value
|
13.10 | 12.15 | 11.47 | 8.40 | 7.75 | |||||||||||||||
Market value — closing price at year end
|
4.64 | 4.40 | 8.98 | 11.50 | 9.10 | |||||||||||||||
FINANCIAL RATIOS: |
||||||||||||||||||||
Return on average equity
|
3.77 | % | 4.61 | % | 31.05 | % | 6.19 | % | (25.63 | )% | ||||||||||
Return on average assets
|
.39 | .44 | 2.59 | .49 | (2.58 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Dividend payout ratio
|
N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||
Average equity to average assets
|
10.24 | 9.55 | 8.34 | 7.97 | 10.05 | |||||||||||||||
Efficiency ratio
|
73.37 | 85.51 | 79.46 | 93.95 | 160.43 | |||||||||||||||
Net interest margin
|
3.59 | 3.23 | 3.60 | 3.51 | 3.64 | |||||||||||||||
45
Summary Quaterly Financial Information
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
SUMMARY QUARTERLY FINANCIAL INFORMATION
(Unaudited)
(Dollars in Thousands, Except per Share Data)
(Unaudited)
(Dollars in Thousands, Except per Share Data)
| FOR THE QUARTER ENDED | FOR THE QUARTER ENDED | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12/31 | 9/30 | 6/30 | 3/31 | 12/31 | 9/30 | 6/30 | 3/31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
BALANCE SHEET |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total loans
|
$ | 384,310 | $ | 384,100 | $ | 372,004 | $ | 370,776 | $ | 370,280 | $ | 361,521 | $ | 362,122 | $ | 360,056 | ||||||||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses
|
(5,225 | ) | (4,081 | ) | (4,119 | ) | (4,793 | ) | (4,277 | ) | (3,385 | ) | (3,585 | ) | (3,924 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Total loans, net
|
379,085 | 380,019 | 367,885 | 365,983 | 366,003 | 358,136 | 358,537 | 356,132 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intangible assets
|
— | — | 6 | 26 | 46 | 65 | 85 | 104 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets
|
515,377 | 513,180 | 506,304 | 466,375 | 451,431 | 440,953 | 437,327 | 417,175 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Core deposits
|
209,828 | 200,541 | 202,892 | 196,860 | 195,165 | 208,940 | 200,293 | 203,445 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Noncore deposits (1)
|
211,561 | 218,040 | 210,260 | 188,897 | 175,932 | 151,754 | 156,683 | 122,602 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total deposits
|
421,389 | 418,581 | 413,152 | 385,757 | 371,097 | 360,694 | 356,976 | 326,047 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total borrowings
|
36,140 | 36,140 | 36,210 | 36,210 | 36,210 | 36,210 | 36,280 | 48,849 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total shareholders’ equity
|
55,299 | 55,766 | 53,939 | 41,864 | 41,552 | 41,427 | 40,975 | 39,633 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total shares outstanding
|
3,419,736 | 3,419,736 | 3,419,736 | 3,419,736 | 3,419,736 | 3,419,736 | 3,419,736 | 3,428,695 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
AVERAGE BALANCE SHEET |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total loans
|
$ | 386,203 | $ | 370,310 | $ | 371,609 | $ | 370,943 | $ | 366,077 | $ | 358,844 | $ | 362,574 | $ | 357,778 | ||||||||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses
|
(3,872 | ) | (4,231 | ) | (4,847 | ) | (4,405 | ) | (3,530 | ) | (3,500 | ) | (3,886 | ) | (4,079 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
Total loans, net
|
382,331 | 366,079 | 366,762 | 366,538 | 362,547 | 355,344 | 358,688 | 353,699 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Intangible assets
|
— | 1 | 16 | 35 | 55 | 75 | 94 | 113 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total assets
|
514,102 | 513,687 | 491,205 | 454,740 | 441,583 | 423,702 | 418,246 | 417,682 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Core deposits
|
204,972 | 201,854 | 198,631 | 194,962 | 201,159 | 208,460 | 201,765 | 202,841 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Noncore deposits (1)
|
213,308 | 217,248 | 202,879 | 177,707 | 157,054 | 132,917 | 130,960 | 133,175 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total deposits
|
418,280 | 419,102 | 401,510 | 372,669 | 358,213 | 341,377 | 332,725 | 336,016 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total borrowings
|
36,140 | 36,194 | 36,376 | 36,648 | 37,969 | 37,245 | 42,430 | 39,382 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total shareholders’ equity
|
55,665 | 54,594 | 49,855 | 41,813 | 41,516 | 41,097 | 40,399 | 39,491 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
ASSET QUALITY RATIOS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nonperforming loans/total loans
|
3.96 | % | 3.00 | % | 2.66 | % | 3.52 | % | 1.32 | % | 1.29 | % | 1.27 | % | .94 | % | ||||||||||||||||
Nonperforming assets/total assets |
4.08 | 3.38 | 2.93 | 3.27 | 1.57 | 1.45 | 1.83 | 1.08 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses/total loans |
1.36 | 1.06 | 1.11 | 1.29 | 1.16 | .94 | .99 | 1.09 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Allowance for loan losses/nonperforming loans |
34.29 | 35.40 | 41.71 | 36.72 | 87.52 | 72.81 | 77.22 | 116.06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net charge-offs/average loans
|
.30 | .20 | .22 | .01 | .06 | .18 | .30 | .06 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
CAPITAL ADEQUACY RATIOS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 leverage ratio
|
9.75 | % | 9.74 | % | 9.65 | % | 7.86 | % | 8.01 | % | 8.31 | % | 8.56 | % | 7.85 | % | ||||||||||||||||
Tier 1 capital to risk
weighted assets
|
11.92 | 12.18 | 11.94 | 9.31 | 9.25 | 9.40 | 9.48 | 8.84 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total capital to risk weighted
assets
|
13.17 | 13.19 | 13.00 | 10.56 | 10.38 | 10.31 | 10.45 | 9.92 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average equity/average assets
|
10.83 | 10.63 | 10.15 | 9.19 | 9.40 | 9.70 | 9.66 | 9.45 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Tangible equity/tangible assets
|
10.83 | 10.87 | 10.65 | 8.97 | 9.20 | 9.38 | 9.35 | 9.48 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | Noncore deposits include brokered deposits and CDs greater than $100,000 |
46
Summary Quarterly Financial Information
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
SUMMARY QUARTERLY FINANCIAL INFORMATION
(Unaudited)
(Dollars in Thousands, Except per Share Data)
(Unaudited)
(Dollars in Thousands, Except per Share Data)
| FOR THE QUARTER ENDED 2009 | FOR THE QUARTER ENDED 2008 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 12/31 | 9/30 | 6/30 | 3/31 | 12/31 | 9/30 | 6/30 | 3/31 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
INCOME STATEMENT |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest income |
$ | 4,431 | $ | 4,310 | $ | 4,051 | $ | 3,495 | $ | 3,330 | $ | 3,371 | $ | 3,118 | $ | 3,045 | ||||||||||||||||
Provision for loan losses |
2,300 | 700 | 150 | 550 | 1,100 | 450 | 750 | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest income after
provision |
2,131 | 3,610 | 3,901 | 2,945 | 2,230 | 2,921 | 2,368 | 3,045 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total noninterest income |
1,503 | 2,418 | 439 | 391 | 308 | 288 | 3,747 | 310 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total noninterest expense |
3,650 | 3,443 | 3,470 | 3,239 | 2,961 | 2,935 | 3,471 | 3,191 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Income before taxes |
(16 | ) | 2,585 | 870 | 97 | (423 | ) | 274 | 2,644 | 164 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Provision for income taxes |
(22 | ) | 864 | 271 | 7 | (171 | ) | 58 | 875 | 25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income |
6 | 1,721 | 599 | 90 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Preferred dividend and
accretion of discount |
186 | 185 | 138 | — | — | — | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net income available to
common shareholders |
$ | (180 | ) | $ | 1,536 | $ | 461 | $ | 90 | $ | (252 | ) | $ | 216 | $ | 1,769 | $ | 139 | ||||||||||||||
PER SHARE DATA |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Earnings per share — basic |
$ | (.05 | ) | $ | .45 | $ | .13 | $ | .03 | $ | (.07 | ) | $ | .06 | $ | .52 | $ | .04 | ||||||||||||||
Earnings per share — diluted |
(.05 | ) | .45 | .13 | .03 | (.07 | ) | .06 | .52 | .04 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Book value per share |
13.10 | 13.25 | 12.73 | 12.24 | 12.15 | 12.11 | 11.98 | 11.56 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Market value per share |
4.64 | 4.10 | 4.50 | 4.00 | 4.40 | 5.26 | 7.00 | 8.50 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
PROFITABILITY RATIOS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Return on average assets |
(.14 | )% | 1.19 | % | .38 | % | .08 | % | (.23 | )% | .20 | % | 1.70 | % | .13 | % | ||||||||||||||||
Return on average equity |
(1.28 | ) | 11.16 | 3.71 | .87 | (2.42 | ) | 2.08 | 17.62 | 1.42 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest margin |
3.74 | 3.66 | 3.58 | 3.35 | 3.20 | 3.39 | 3.19 | 3.13 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Efficiency ratio |
71.03 | 70.09 | 76.55 | 82.36 | 80.30 | 79.12 | 88.45 | 95.34 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average loans/average deposits |
92.33 | 88.36 | 92.55 | 99.54 | 102.20 | 105.12 | 108.97 | 106.48 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
47
Market Information
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
MARKET INFORMATION
(Unaudited)
(Unaudited)
The Corporation’s common stock is traded on the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol MFNC. The
following table sets forth the range of high and low trading prices of the Corporation’s common
stock from January 1, 2008 through December 31, 2009, as reported by NASDAQ.
| For the Quarter Ended | ||||||||||||||||
| March 31 | June 30 | September 30 | December 31 | |||||||||||||
2009 |
||||||||||||||||
High |
$ | 4.72 | $ | 4.50 | $ | 6.37 | $ | 5.85 | ||||||||
Low |
2.45 | 3.76 | 4.00 | 4.00 | ||||||||||||
Close |
4.00 | 4.50 | 4.10 | 4.64 | ||||||||||||
Book value, at quarter end |
12.24 | 12.73 | 13.25 | 13.10 | ||||||||||||
2008 |
||||||||||||||||
High |
$ | 9.24 | $ | 8.50 | $ | 8.00 | $ | 5.95 | ||||||||
Low |
7.55 | 7.00 | 3.00 | 3.75 | ||||||||||||
Close |
8.50 | 7.00 | 5.26 | 4.40 | ||||||||||||
Book value, at quarter end |
11.56 | 11.98 | 12.11 | 12.15 | ||||||||||||
The Corporation had 1,228 shareholders of record as of March 30, 2010.
The holders of the Corporation’s common stock are entitled to dividends when, and if declared by
the Board of Directors of the Corporation out of funds legally available for that purpose. In
determining dividends, the Board of Directors considers the earnings, capital requirements and
financial condition of the Corporation and its subsidiary bank, along with other relevant factors.
The Corporation’s principal source of funds for cash dividends is the dividends paid by the Bank.
The ability of the Corporation and the Bank to pay dividends is subject to regulatory restrictions
and requirements. The Bank currently has a negative retained earnings position which precludes
payment of dividends. The Bank, in order to pay dividends, would need to seek regulatory approval
for the restatement of its equity to eliminate the negative retained earnings position. There were
no dividends declared or paid in 2007, 2008 and 2009. There were no sales of unregistered
securities in 2009, nor were there any repurchases of the Corporation’s common stock in 2009.
48
Shareholder Return Performance Graph
MACKINAC FINANCIAL CORPORATION AND SUBSIDIARIES
Set forth below is a line graph comparing the yearly percentage change in the cumulative total
shareholder return on the Corporation’s common stock with that of the cumulative total return on
the NASDAQ Bank Stocks Index and the NASDAQ Market Index for the five-year period ended December
31, 2009. The following information is based on an investment of $100, on December 31, 2004 in the
Corporation’s common stock, the NASDAQ Bank Stocks Index, and the NASDAQ Market Index, with
dividends reinvested. From August 31, 2001 to December 15, 2004, the Corporation’s common stock
traded on the NASDAQ Small Cap Market under the symbol “NCFC.” Effective with the recapitalization
and the 20:1 reverse stock split on December 16, 2004, the Corporation’s stock began trading on the
NASDAQ Small Cap Market, and later the NASDAQ Capital Market under the symbol “MFNC”.
This graph and other information contained in this section shall not be deemed to be “soliciting”
material or to be “filed” with the Securities and Exchange Commission or subject to Regulation 14A
or 14C, or to the liabilities of Section 18 of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended.
COMPARISON OF 5 YEAR CUMULATIVE TOTAL RETURN*
Among Mackinac Financial Corporation, The NASDAQ Composite Index
And The NASDAQ Bank Index
Among Mackinac Financial Corporation, The NASDAQ Composite Index
And The NASDAQ Bank Index
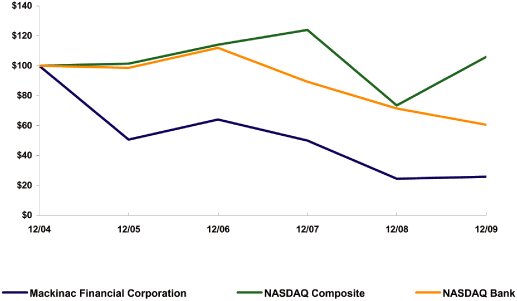
| * | $100 invested on 12/31/04 in stock or index, including reinvestment of dividends. Fiscal year ending December 31. |
49
Forward Looking Statements
This report contains certain forward-looking statements within the meaning of Section 27A of
the Securities Act of 1933, as amended, and Section 21E of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as
amended. The Corporation intends such forward-looking statements to be covered by the safe harbor
provisions for forward-looking statements contained in the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act
of 1995 and is including this statement for purposes of these safe harbor provisions.
Forward-looking statements which are based on certain assumptions and describe future plans,
strategies, or expectations of the Corporation, are generally identifiable by use of the words
“believe”, “expect”, “intend”, “anticipate”, “estimate”, “project”, or similar expressions. The
Corporation’s ability to predict results or the actual effect of future plans or strategies is
inherently uncertain. Factors that could cause actual results to differ from the results in
forward-looking statements include, but are not limited to:
| • | The highly regulated environment in which the Corporation operates could adversely affect its ability to carry out its strategic plan due to restrictions on new products, funding opportunities or new market entrances; | ||
| • | General economic conditions, either nationally or in the state(s) in which the Corporation does business; | ||
| • | Legislation or regulatory changes which affect the business in which the Corporation is engaged; | ||
| • | Changes in the level and volatility of interest rates which may negatively affect the Corporation’s interest margin; | ||
| • | Changes in securities markets with respect to the market value of financial assets and the level of volatility in certain markets such as foreign exchange; | ||
| • | Significant increases in competition in the banking and financial services industry resulting from industry consolidation, regulatory changes and other factors, as well as action taken by particular competitors; | ||
| • | The ability of borrowers to repay loans; | ||
| • | The effects on liquidity of unusual decreases in deposits; | ||
| • | Changes in consumer spending, borrowing, and saving habits; | ||
| • | Technological changes; | ||
| • | Acquisitions and unanticipated occurrences which delay or reduce the expected benefits of acquisitions; | ||
| • | Difficulties in hiring and retaining qualified management and banking personnel; | ||
| • | The Corporation’s ability to increase market share and control expenses; | ||
| • | The effect of compliance with legislation or regulatory changes; | ||
| • | The effect of changes in accounting policies and practices; | ||
| • | The costs and effects of existing and future litigation and of adverse outcomes in such litigation; | ||
| • | An increase in the Corporation’s FDIC insurance premiums, or the collection of special assessments by the FDIC. |
These risks and uncertainties should be considered in evaluating forward-looking statements.
Further information concerning the Corporation and its business, including additional factors that
could materially affect the Corporation’s financial results, is included in the Corporation’s
filings with the Securities and Exchange Commission. All forward-looking statements contained in
this report are based upon information presently available and the Corporation assumes no
obligation to update any forward-looking statements.
50
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following discussion will cover results of operations for 2007 through 2009 and asset
quality, financial position, liquidity, interest rate sensitivity, and capital resources for the
years 2008 and 2009. The information included in this discussion is intended to assist readers in
their analysis of, and should be read in conjunction with, the consolidated financial statements
and related notes and other supplemental information presented elsewhere in this report.
Throughout this discussion, the term “Bank” refers to mBank, the principal banking subsidiary of
the Corporation.
EXECUTIVE OVERVIEW
The purpose of this section is to provide a brief overview of the 2009 results of operations.
Additional detail of the balance sheet and Statement of Operations follows this summary.
The Corporation reported net income available to common shareholders of $1.907 million, or $.56 per
share for the year ended December 31, 2009, compared to net income available to common shareholders
of $1.872 million, or $.55 per share for 2008. Weighted average shares outstanding amounted to
3,419,736 in 2009 and 3,422,012 in 2008.
The 2009 results include $1.208 million of gains related to branch office sales and $1.471 million
of security gains. The 2008 results included the positive effect, $3.475 million, of a lawsuit
settlement, and the negative effect, $.425 million, of a severance agreement.
Total assets of the Corporation at December 31, 2009, were $515.377 million, an increase of $63.946
million, or 14.17% from total assets of $451.431 million reported at December 31, 2008.
At December 31, 2009, the Corporation’s loans stood at $384.310 million, an increase of $14.030
million, or 3.79%, from 2008 year-end balances of $370.280 million. Total loan originations in
2009 amounted to $88.122 million, while we experienced significant reductions from loan
amortization and principal payoffs of $60.415 million. A good portion of these payoffs pertained
to loan relationships that no longer met our pricing or credit standards.
Nonperforming assets increased in 2009, as the economy continued to weaken, especially in Southeast
Michigan. Nonperforming loans totaled $15.237 million, or 3.96% of total loans at December 31,
2009. Nonperforming assets at December 31, 2009, were $21.041 million, 4.08% of total assets,
compared to $7.076 million or 1.57% of total assets at December 31, 2008.
Total deposits grew from $371.097 million at December 31, 2008, to $421.389 million at December 31,
2009, an increase of 13.55%. Core deposits increased by $14.663 million after the sale of $29.260
million of deposits in connection with branch office sales.
Shareholders’ equity totaled $55.299 million at December 31, 2009, compared to $41.552 million at
the end of 2008, an increase of $13.747 million. This increase reflects consolidated net income of
$1.907 million, the capital contribution impact of stock options of $.060 million and the increase
in equity due to the increase in the market value of available-for-sale investments, which amounted
to $.648 million. The increase also includes the issuance of Series A Preferred Stock and common
stock warrants and subsequent discount accretion totaling $11.132 million through the Corporation’s
participation in TARP. The book value per share at December 31, 2009, amounted to $13.10 compared
to $12.15 at the end of 2008.
51
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
FINANCIAL POSITION
Loans
In 2009, the Corporation increased loan balances by $14.030 million, or 3.79%, from 2008 year-end
loan balances of $370.280 million. The loan growth in 2009 compares to loan growth in 2008 of
$15.201 million, or 4.28% from 2007 year-end loan balances of $355.079 million. The loan growth in
2009 and 2008 was accomplished despite high loan amortization and principal payoffs on existing
portfolio loans of $60.4 million in 2009 and $51.2 million in 2008.
Management continues to actively manage the loan portfolio, seeking to identify and resolve problem
assets at an early stage. Management believes a properly positioned loan portfolio provides the
most attractive earning asset yield available to the Corporation and, with changes to the loan
approval process and exception reporting, management can effectively manage the risk in the loan
portfolio. Management intends to continue loan growth within its markets for mortgage, consumer,
and commercial loan products while concentrating on loan quality, industry concentration issues,
and competitive pricing.
Loans represented 74.57% of total assets at the end of 2009 compared to 82.02% at the end of 2008.
The loan to deposit ratio, at 91.2%, is higher than a peer average of approximately 82.7% due in
part to the Bank’s utilization of Federal Home Loan Bank long-term borrowings as a funding source.
Following is a summary of the Corporation’s loan balances at December 31 (dollars in thousands):
| Percent Change | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2009-2008 | 2008-2007 | ||||||||||||||||
Commercial real estate |
$ | 208,895 | $ | 185,241 | $ | 171,695 | 12.77 | % | 7.89 | % | ||||||||||
Commercial, financial, and agricultural |
72,184 | 79,734 | 78,192 | (9.47 | ) | 1.97 | ||||||||||||||
One-to-four family residential real estate |
67,232 | 65,595 | 57,613 | 2.50 | 13.85 | |||||||||||||||
Construction |
||||||||||||||||||||
Consumer |
7,118 | 4,852 | 5,090 | 46.70 | (4.68 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Commercial |
24,591 | 31,113 | 38,952 | (20.96 | ) | (20.12 | ) | |||||||||||||
Consumer |
4,290 | 3,745 | 3,537 | 14.55 | 5.88 | |||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 384,310 | $ | 370,280 | $ | 355,079 | 3.79 | % | 4.28 | % | ||||||||||
The above table more clearly illustrates the growth of the loan portfolio from 2007 through 2009
year end. The Corporation continues to feel that a properly positioned loan portfolio is the most
attractive earning asset available. The Corporation is highly competitive in structuring loans to
meet borrowing needs and satisfy strong underwriting requirements.
Our commercial real estate loan portfolio predominantly relates to owner occupied real estate, and
our loans are generally secured by a first mortgage lien. Commercial real estate market conditions
continued to be under stress in 2009, and we
expect this trend to continue. These conditions may negatively affect our commercial real estate
loan portfolio in future periods. We make commercial loans for many purposes, including: working
capital lines, which are generally renewable annually and supported by business assets, personal
guarantees and additional collateral. Commercial business lending is generally considered to
involve a higher degree of risk than traditional consumer bank lending.
Looking forward, based upon the current economic outlook for the Michigan economy, management
believes there will be limited opportunity for loan growth in the near term. The Corporation will
continue to use a demanding pricing model for all new credit opportunities and existing loan
renewals.
52
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Following is a table showing the significant industry types in the commercial loan portfolio
as of December 31 (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| % of | % of | % of | % of | % of | % of | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance | Loans | Capital | Balance | Loans | Capital | Balance | Loans | Capital | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Real estate — operators of nonres bldgs |
$ | 48,689 | 15.93 | % | 88.05 | % | $ | 41,299 | 13.95 | % | 99.39 | % | $ | 41,597 | 14.40 | % | 105.79 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Hospitality and tourism |
45,315 | 14.82 | 81.95 | 35,086 | 11.85 | 84.44 | 37,604 | 13.02 | 95.63 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Real estate agents and managers |
24,242 | 7.93 | 43.84 | 29,292 | 9.89 | 70.50 | 29,571 | 10.24 | 75.20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other |
187,424 | 61.32 | 338.93 | 190,411 | 64.31 | 458.25 | 180,067 | 62.34 | 457.94 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total |
$ | 305,670 | 100.00 | % | $ | 296,088 | 100.00 | % | $ | 288,839 | 100.00 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Management recognizes the additional risk presented by the concentration in certain segments of the
portfolio. On a historical basis, the Corporation’s highest concentration of credit risk was the
hospitality and tourism industry. Management does not consider the current loan concentrations in
hospitality and tourism to be problematic, and has no intention of further reducing loans to this
industry segment. Management does not believe that its current portfolio composition has increased
exposure related to any specific industry concentration as of 2009 year-end. The current
concentration of real estate related loans represents a broad customer base composed of a high
percentage of owner-occupied developments.
Our residential real estate portfolio predominantly includes one-to-four family adjustable rate
mortgages that have repricing terms generally from one to three years, construction loans to
individuals and bridge financing loans for qualifying customers. As of December 31, 2009, our
residential loan portfolio totaled $74.350 million, or 19.35% of our total outstanding loans.
The Corporation has also extended credit to governmental units, including Native American
organizations. Tax-exempt loans and leases decreased from $5.589 million at the end of 2008 to
$3.184 million at 2009 year-end. The Corporation has elected to reduce its tax-exempt portfolio,
since it provides no current tax benefit, due to tax net operating loss carryforwards.
Due to the seasonal nature of many of the Corporation’s commercial loan customers, loan payment
terms provide flexibility by structuring payments to coincide with the customer’s business cycle.
The lending staff evaluates the collectability of the past due loans based on documented collateral
values and payment history. The Corporation discontinues the accrual of interest on loans when, in
the opinion of management, there is an indication that the borrower may be unable to meet the
payments as they become due. Upon such discontinuance, all unpaid accrued interest is reversed.
Loans are returned to accrual status when all principal and interest amounts contractually due are
brought current and future payments are reasonably assured.
Credit Quality
The table below shows balances of nonperforming assets for the three years ended December 31
(dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Nonperforming Assets: |
||||||||||||
Nonaccrual loans |
$ | 14,368 | $ | 4,887 | $ | 3,298 | ||||||
Accruing loans past due 90 days or more |
— | — | 710 | |||||||||
Restructured Loans |
869 | — | — | |||||||||
Total nonperforming loans |
15,237 | 4,887 | 4,008 | |||||||||
Other real estate owned |
5,804 | 2,189 | 1,226 | |||||||||
Total nonperforming assets |
$ | 21,041 | $ | 7,076 | $ | 5,234 | ||||||
Nonperforming loans as a % of loans |
3.96 | % | 1.32 | % | 1.13 | % | ||||||
Nonperforming assets as a % of assets |
4.08 | % | 1.57 | % | 1.28 | % | ||||||
Reserve for Loan Losses: |
||||||||||||
At period end |
$ | 5,225 | $ | 4,277 | $ | 4,146 | ||||||
As a % of loans |
1.36 | % | 1.16 | % | 1.17 | % | ||||||
As a % of nonperforming loans |
34.29 | % | 87.52 | % | 103.44 | % | ||||||
As a % of nonaccrual loans |
36.37 | % | 87.52 | % | 125.71 | % | ||||||
53
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Management continues to address market issues impacting its loan customer base. In
conjunction with the Corporation’s senior lending staff and the bank regulatory examinations,
management reviews the Corporation’s loans, related collateral evaluations, and the overall lending
process. The Corporation also utilizes a loan review consultant to perform a review of the loan
portfolio. The opinion of this consultant upon completion of the 2009 independent review provided
findings similar to management on the overall adequacy of the reserve. The Corporation will
utilize this same consultant for loan review in 2010.
The following table details the impact of nonperforming loans on interest income for the three
years ended December 31 (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Interest income that would have
been recorded at original rate |
$ | 700 | $ | 377 | $ | 391 | ||||||
Interest income that was
actually recorded |
40 | 60 | 129 | |||||||||
Net interest lost |
$ | 660 | $ | 317 | $ | 262 | ||||||
Allowance for Loan Losses
Management analyzes the allowance for loan losses on a quarterly basis to determine whether the
losses inherent in the portfolio are properly reserved for. Net charge-offs in 2009 amounted to
$2.752 million, or .73% of average loans outstanding, compared to $2.169 million, or .60% of loans
outstanding in 2008. In 2009, $1.400 million of these charge-offs resulted from three credit
relationships in Southeast Michigan. The current reserve balance is representative of the relevant
risk inherent within the Corporation’s loan portfolio. Additions or reductions to the reserve in
future periods will be dependent upon a combination of future loan growth, nonperforming loan
balances and charge-off activity.
A three year history of the Corporation’s credit quality is displayed in the following table (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Allowance for Loan Losses |
||||||||||||
Balance at beginning of period |
$ | 4,277 | $ | 4,146 | $ | 5,006 | ||||||
Loans charged off: |
||||||||||||
Commercial, financial &
agricultural |
2,465 | 2,062 | 1,148 | |||||||||
One-to-four family residential real estate |
282 | 157 | 89 | |||||||||
Consumer |
71 | 71 | 73 | |||||||||
Total loans charged off |
2,818 | 2,290 | 1,310 | |||||||||
Recoveries of loans previously charged off: |
||||||||||||
Commercial, financial & agicultural |
38 | 114 | 15 | |||||||||
One-to-four family residential real estate |
16 | — | — | |||||||||
Consumer |
12 | 7 | 35 | |||||||||
Total recoveries of loans previously charged off |
66 | 121 | 50 | |||||||||
Net loans charged off |
2,752 | 2,169 | 1,260 | |||||||||
Provision for loan losses |
3,700 | 2,300 | 400 | |||||||||
Balance at end of period |
$ | 5,225 | $ | 4,277 | $ | 4,146 | ||||||
Total loans, period end |
$ | 384,310 | $ | 370,280 | $ | 355,079 | ||||||
Average loans for the year |
374,796 | 361,324 | 333,415 | |||||||||
Allowance to total loans at end of year |
1.36 | % | 1.16 | % | 1.17 | % | ||||||
Net charge-offs to average loans |
.73 | .60 | .38 | |||||||||
Net charge-offs to beginning allowance balance |
64.34 | 52.32 | 25.17 | |||||||||
54
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The computation of the required allowance for loan losses as of any point in time is one of
the critical accounting estimates made by management in the financial statements. As such, factors
used to establish the allowance could change significantly from the assumptions made and impact
future earnings positively or negatively. The future of the national and local economies and the
resulting impact on borrowers’ ability to repay their loans and the value of collateral are
examples of areas where assumptions must be made for individual loans, as well as the overall
portfolio.
The Corporation’s computation of the allowance for loan losses follows the Interagency Policy
Statement on Allowance for Loan and Lease Losses Methodologies and Documentation for Banks and
Savings Associations issued by the Federal Financial Institutions Examination Council (FFIEC) in
July 2001. The computation of the allowance for loan losses considers prevailing local and
national economic conditions as well as past and present underwriting practices.
As part of the management of the loan portfolio, risk ratings are assigned to all commercial loans.
Through the loan review process, ratings are modified as believed to be appropriate to reflect
changes in the credit. Our ability to manage credit risk depends in large part on our ability to
properly identify and manage problem loans. To do so, we operate a credit risk rating system under
which our credit management personnel assign a credit risk rating to each loan at the time of
origination and review loans on a regular basis to determine each loan’s credit risk rating on a
scale of 1 through 8, with higher scores indicating higher risk. The credit risk rating structure
used is shown below. In the context of the credit risk rating structure, the term Classified is
defined as a problem loan which may or may not be in a nonaccrual status, dependent upon current
payment status and collectability.
Excellent (1)
Borrower is not vulnerable to sudden economic or technological changes and is in a non-seasonal
business or industry. These loans generally would be characterized by having good experienced
management and a strong liquidity position with minimal leverage.
Good (2)
Borrower shows limited vulnerability to sudden economic change with modest seasonal effect.
Borrower has “above average” financial statements and an acceptable repayment history with minimal
leverage and a profitability that exceeds peers.
Average (3)
Generally, a borrower rated as average may be susceptible to unfavorable changes in the economy and
somewhat effected by seasonal factors. Some product lines may be affected by technological change.
Borrowers in this category exhibit stable earnings, with a satisfactory payment history.
Acceptable (4)
The loan is an otherwise acceptable credit that warrants a higher level of administration due to
various underlying weaknesses. These weaknesses, however, have not and may never deteriorate to
the point of a Special Mention rating or Classified status. This rating category may include new
businesses not yet having established a firm performance record.
Special Mention (5)
The loan is not considered as a Classified status, however may exhibit material weaknesses that, if
not corrected, may cause future problems. Borrowers in this category warrant special attention but
have not yet reached the point of concern for loss. The borrower may have deteriorated to the
point that they would have difficulty refinancing elsewhere. Similarly, purchasers of these
businesses would not be eligible for bank financing unless they represent a significantly stronger
credit risk.
Substandard (6)
The loan is Classified and exhibits a number of well-defined weaknesses that jeopardize normal
repayment. The assets are no longer adequately protected due to declining net worth, lack of
earning capacity or insufficient collateral offering the distinct possibility of the loss of a
portion of the loan principal. Loans within this category clearly represent troubled and
deteriorating credit situations requiring constant supervision and an action plan must be developed
and approved by the appropriate officers to mitigate the risk.
55
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Doubtful (7)
Loans in this category exhibit the same weaknesses used to describe the substandard credit;
however, the traits are more pronounced. Loans are frozen with collection improbable. Such loans
are not yet rated as Charge-off because certain actions may yet occur which would salvage the loan.
Charge-off/Loss (8)
Loans in this category are largely uncollectible and should be charged against the loan loss
reserve immediately.
General Reserves:
For loans with a credit risk rating of 5 or better and any loans with a risk rating of 6 or 7 with
no specific reserve, reserves are established based on the type of loan collateral, if any, and the
assigned credit risk rating. Determination of the allowance is inherently subjective as it
requires significant estimates, including the amounts and timing of expected future cash flows on
impaired loans, estimated losses on pools of homogenous loans based on historical loss experience,
and consideration of current environmental factors and economic trends, all of which may be
susceptible to significant change.
Using a historical average loss by loan type as a base, each loan graded as higher risk is assigned
a specific percentage. Within the commercial loan portfolio, the historical loss rates are used
for specific industries such as hospitality, gaming, petroleum, and forestry. The residential real
estate and consumer loan portfolios are assigned a loss percentage as a homogenous group. If,
however, on an individual loan the projected loss based on collateral value and payment histories
are in excess of the computed allowance, the allocation is increased for the higher anticipated
loss. These computations provide the basis for the allowance for loan losses as recorded by the
Corporation.
Following is a table showing the specific loan allocation of the allowance for loan losses at
December 31, 2009 (dollars in thousands):
Commercial, financial and agricultural loans |
$ | 4,805 | ||
One-to-four family residential real estate loans |
23 | |||
Consumer loans |
13 | |||
Unallocated and general reserves |
384 | |||
Total |
$ | 5,225 | ||
At the end of 2009, the allowance for loan losses represented 1.36% of total loans. In
management’s opinion, the allowance for loan losses is adequate to cover probable losses related to
specifically identified loans, as well as probable losses inherent in the balance of the loan
portfolio.
As part of the process of resolving problem credits, the Corporation may acquire ownership of real
estate collateral which secured such credits. The Corporation carries this collateral in other
real estate on the balance sheet.
The following table represents the activity in other real estate (dollars in thousands):
Balance at January 1, 2008 |
$ | 1,226 | ||
Other real estate transferred from loans due to foreclosure |
2,849 | |||
Other real estate transferred to premises and equipment |
— | |||
Other real estate sold / written down |
(1,886 | ) | ||
Balance at December 31, 2008 |
2,189 | |||
Other real estate transferred from loans due to foreclosure |
4,879 | |||
Reclassification of redemption ORE |
(475 | ) | ||
Other real estate transferred to premises and equipment |
— | |||
Other real estate sold / written down |
(789 | ) | ||
Balance at December 31, 2009 |
$ | 5,804 | ||
56
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
During 2009, the Corporation received real estate in lieu of loan payments of $4.879 million.
In determining the carrying value of other real estate, the Corporation generally starts with a
third party appraisal of the underlying collateral and then deducts estimated selling costs to
arrive at a net asset value. After the initial receipt, management periodically re-evaluates the
recorded balance and any additional reductions in the fair value result in a write-down of other
real estate.
Securities
The securities portfolio is an important component of the Corporation’s asset composition to
provide diversity in its asset base and provide liquidity. Securities decreased $.977 million in
2009, from $47.490 million at December 31, 2008 to $46.513 million at December 31, 2009.
The carrying value of the Corporation’s securities is as follows at December 31 (dollars in
thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
US Agencies — MBS |
$ | 45,238 | $ | 46,941 | ||||
Obligations of states and political subdivisions |
1,275 | 549 | ||||||
Total securities |
$ | 46,513 | $ | 47,490 | ||||
The Corporation’s policy is to purchase securities of high credit quality, consistent with its
asset/liability management strategies. In 2009, a net gain of $1.471 million was recorded in
connection with the sale of approximately $45 million of investments. These investments were
purchased early in 2009 as a short-term “leveraging” program in the deployment of a portion of the
proceeds from the issuance of preferred stock in conjunction with the Corporation’s participation
in TARP. This “leveraging” program to increase investment securities was intended to offset the
relatively high cost of the preferred stock. Management, along with the concurrence of the Board
of Directors, deleveraged this position late in 2009.
All of the bank’s current investments are highly marketable investments guaranteed by the U.S.
government. The Corporation classifies all securities as available for sale, in order to maintain
adequate liquidity and to maximize its ability to react to changing market conditions. At December
31, 2009, investment securities with an estimated fair market value of $17.077 million were
pledged.
Deposits
Total deposits at December 31, 2009 were $421.389 million, an increase of $50.292 million, or
13.55% from December 31, 2008 deposits of $371.097 million. The table below shows the deposit mix
for the periods indicated (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | Mix | 2008 | Mix | 2007 | Mix | |||||||||||||||||||
Non-interest-bearing |
$ | 35,878 | 8.51 | % | $ | 30,099 | 8.11 | % | $ | 25,557 | 7.97 | % | ||||||||||||
NOW, money market, checking |
95,790 | 22.73 | 70,584 | 19.02 | 81,160 | 25.30 | ||||||||||||||||||
Savings |
18,207 | 4.32 | 20,730 | 5.59 | 12,485 | 3.89 | ||||||||||||||||||
Certificates of Deposit <$100,000 |
59,953 | 14.23 | 73,752 | 19.87 | 80,607 | 25.12 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total core deposits |
209,828 | 49.79 | 195,165 | 52.59 | 199,809 | 62.28 | ||||||||||||||||||
Certificates of Deposit >$100,000 |
36,385 | 8.63 | 25,044 | 6.75 | 22,355 | 6.97 | ||||||||||||||||||
Brokered CDs |
175,176 | 41.57 | 150,888 | 40.66 | 98,663 | 30.75 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total non-core deposits |
211,561 | 50.21 | 175,932 | 47.41 | 121,018 | 37.72 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total deposits |
$ | 421,389 | 100.00 | % | $ | 371,097 | 100.00 | % | $ | 320,827 | 100.00 | % | ||||||||||||
The increase in deposits, as illustrated above, is composed of an increase in noncore deposits of
$35.629 million, with wholesale brokered deposits increasing by $24.288 million. Core deposits
increased by $14.663 million in 2009. In August 2009, the Bank sold two branch offices with core
deposits of approximately $29 million. This strategic decision was in conjunction the bank’s
overall strategy to tighten its existing geographical footprint and concentrate its resources in
the commercial hubs of the Upper Peninsula. The additional wholesale brokered deposits were in
part utilized to enhance
57
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
balance sheet liquidity and to fund the acquisition of investments purchased in the TARP
leveraging program discussed earlier in this management discussion, the Corporation expects near
term reduction of wholesale deposits to a level of approximately $100 million as current issues
mature.
Although the Corporation has been successful in growing core deposits, the high level of funding
required by loan growth has resulted in increased reliance upon brokered deposits. As of December
31, 2009, non-core deposits amounted to 50.21% of total deposits, an increase from 47.41% at 2008
year-end. A portion, approximately $40.000 million, of the increase in brokered deposits was used
to augment liquidity through the purchase of investment securities. The Bank had $175.176 million
in brokered deposits at December 31, 2009, 41.57% of total deposits.
Management continues to monitor existing deposit products in order to stay competitive, both as to
terms and pricing. It is the intent of management to be aggressive in its markets to grow core
deposits with an emphasis placed on transactional accounts.
Borrowings
The Corporation historically used alternative funding sources to provide long-term, stable sources
of funds. Current borrowings total $35.000 million with stated maturities ranging through 2011.
Borrowings at year end include $20.000 million with adjustable rates that reprice quarterly based
upon the three month LIBOR. The FHLB has the option to convert the remaining $15.000 million
fixed-rate advances to adjustable rate advances on the original call date and quarterly thereafter.
Shareholders’ Equity
Changes in shareholders’ equity are discussed in detail in the “Capital and Regulatory” section of
this report.
RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
Summary
The Corporation reported net income available to common shareholders of $1.907 million in 2009,
compared to net income of $1.872 million in 2008 and a net income of $10.163 million in 2007. As
previously mentioned, the 2009 results include $1.208 million of gains related to branch office
sales and $1.471 million of security gains. The 2008 operating results include the positive
effect, $3.475 million of a lawsuit settlement, and the negative effect, $.425 million of a
severance agreement. The 2007 results of operations include the $7.500 million recognition of a
deferred tax benefit pertaining to
NOL and tax credit carryforwards. Also included in the 2007 results is $.470 million from the
settlement of the lawsuit against the Corporation’s former accountants.
58
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following table details changes in earnings and earnings per share for the three years
ended December 31 (dollars in thousands, except for per share data):
| Income/Expense | Change | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2009-2008 | 2008-2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Dollars | Dollars | Dollars | Dollars | Per Share | Dollars | Per Share | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest Income |
$ | 23,708 | $ | 24,562 | $ | 28,695 | $ | (854 | ) | $ | (.25 | ) | $ | (4,133 | ) | $ | (1.21 | ) | ||||||||||
Interest Expense |
7,421 | 11,698 | 15,278 | (4,277 | ) | (1.25 | ) | (3,580 | ) | (1.05 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
Net Interest Income |
16,287 | 12,864 | 13,417 | 3,423 | 1.00 | (553 | ) | (.16 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Provision for loan losses |
3,700 | 2,300 | 400 | 1,400 | .41 | 1,900 | .56 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest income after provision |
12,587 | 10,564 | 13,017 | 2,023 | .59 | (2,453 | ) | (.72 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Noninterest Income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Service fees |
1,023 | 838 | 688 | 185 | .05 | 150 | .04 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net gains on sale of secondary market loans |
737 | 120 | 498 | 617 | .18 | (378 | ) | (.11 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Proceeds from settlement of lawsuits |
— | 3,475 | 470 | (3,475 | ) | (1.01 | ) | 3,005 | .88 | |||||||||||||||||||
Other |
2,991 | 220 | 350 | 2,771 | .81 | (130 | ) | (.04 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Total noninterest income |
4,751 | 4,653 | 2,006 | 98 | .04 | 2,647 | .77 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Noninterest Expense: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Salaries and employee benefits |
6,583 | 6,886 | 6,757 | (303 | ) | (.09 | ) | 129 | .04 | |||||||||||||||||||
Occupancy |
1,385 | 1,374 | 1,272 | 11 | .00 | 102 | .03 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Furniture and equipment |
805 | 771 | 678 | 34 | .01 | 93 | .03 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Data processing |
862 | 844 | 785 | 18 | .01 | 59 | .02 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Professional services: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Accounting |
261 | 254 | 308 | 7 | .00 | (54 | ) | (.02 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Legal |
95 | 41 | 42 | 54 | .02 | (1 | ) | .00 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Consulting and other |
247 | 213 | 182 | 34 | .01 | 31 | .01 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Loan and deposit |
933 | 488 | 250 | 445 | .13 | 238 | .07 | |||||||||||||||||||||
FDIC insurance premiums |
839 | 81 | 35 | 758 | .22 | 46 | .01 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Telephone |
187 | 170 | 228 | 17 | .00 | (58 | ) | (.02 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Advertising |
322 | 305 | 370 | 17 | .00 | (65 | ) | (.02 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Other |
1,283 | 1,131 | 1,193 | 152 | .05 | (62 | ) | (.02 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Total noninterest expense |
13,802 | 12,558 | 12,100 | 1,244 | .36 | 458 | .13 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Income (loss) before provision for income taxes |
3,536 | 2,659 | 2,923 | 877 | .26 | (264 | ) | (.08 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Provision (credit) for income taxes |
1,120 | 787 | (7,240 | ) | 333 | .10 | 8,027 | 2.34 | ||||||||||||||||||||
Net Income |
2,416 | 1,872 | 10,163 | 544 | .16 | (8,291 | ) | (2.42 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||
Preferred dividend and accretion of discount |
509 | — | — | 509 | .15 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||
Net income available to common
shareholders, current period |
$ | 1,907 | $ | 1,872 | $ | 10,163 | $ | 35 | $ | .16 | $ | (8,291 | ) | $ | (2.42 | ) | ||||||||||||
Net Interest Income
Net interest income is the Corporation’s primary source of core earnings. Net interest income
represents the difference between the average yield earned on interest-earning assets and the
average rate paid on interest-bearing obligations. The net interest income is impacted by economic
and competitive factors that influence rates, loan demand, and the availability of funding.
Net interest income increased $3.423 million to $16.287 million, in 2009. In 2009, the Corporation
benefited from low interest rates prevalent on wholesale deposit instruments. The interest rates
in the wholesale environment were significantly more attractive than offering rates by competitors
in local markets. In addition to the benefits derived from lower rates or wholesale deposit
instruments a number of new or rewritten loans were structured with interest rate floors that
locked in a near term favorable interest rate spread.
Net interest income decreased $.553 million to $12.864 million, in 2008. The decrease in net
interest income for 2008 was primarily the result of prime rate reductions that translated into
lower yields on the Corporation’s earning assets, specifically variable rate commercial loans and
short-term investments which reprice immediately. Offering rates on
brokered certificates of deposit are influenced by other factors, such as overall market liquidity.
During most of 2008, rates on brokered deposits were high due to overall liquidity issues
prevalent in the financial markets. Throughout 2008, as interest rates continued to decline and
economic conditions deteriorated, management evaluated new and existing credit
59
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
relationships to ensure proper pricing. Floors were established on the majority of new loans
and renewals to mitigate interest rate risk going forward.
The Corporation’s net interest margin, on a fully taxable equivalent basis, was 3.62% in 2009
compared to 3.28% in 2008.
During 2008, the prime rate decreased from 7.25% to 3.25%, which created significant margin
pressure since a majority of the commercial loan portfolio repriced downward with each prime rate
change, and the majority of the bank’s funding sources had significant lag time in repricing. We
experienced additional margin pressure due to our brokered deposits, which did not reprice in line
with prime rate reduction, due to the overall market liquidity crisis. Management remains diligent
in its efforts to reduce margin pressure in this decreasing rate environment.
The following table details sources of net interest income for the three years ended December 31,
2009 (dollars in thousands):
| 2009 | Mix | 2008 | Mix | 2007 | Mix | |||||||||||||||||||
Interest Income |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loans |
$ | 20,813 | 87.79 | % | $ | 22,959 | 93.48 | % | $ | 26,873 | 93.65 | % | ||||||||||||
Funds sold |
— | — | 96 | .39 | 391 | 1.36 | ||||||||||||||||||
Taxable securities |
2,783 | 11.74 | 1,293 | 5.26 | 1,100 | 3.83 | ||||||||||||||||||
Nontaxable securities |
19 | .08 | 5 | .02 | — | — | ||||||||||||||||||
Other interest-earning assets |
93 | .39 | 209 | .85 | 331 | 1.15 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total earning assets |
23,708 | 100.00 | % | 24,562 | 100.00 | % | 28,695 | 100.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
Interest Expense |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOW, money markets, checking |
809 | 10.90 | % | 1,284 | 10.98 | % | 2,668 | 17.46 | % | |||||||||||||||
Savings |
142 | 1.92 | 193 | 1.65 | 199 | 1.30 | ||||||||||||||||||
CDs <$100,000 |
1,857 | 25.02 | 3,181 | 27.19 | 4,490 | 29.39 | ||||||||||||||||||
CDs >$100,000 |
633 | 8.53 | 1,037 | 8.86 | 1,183 | 7.74 | ||||||||||||||||||
Brokered deposits |
2,990 | 40.29 | 4,420 | 37.79 | 4,684 | 30.66 | ||||||||||||||||||
Borrowings |
990 | 13.34 | 1,583 | 13.53 | 2,054 | 13.44 | ||||||||||||||||||
Total interest-bearing funds |
7,421 | 100.00 | % | 11,698 | 100.00 | % | 15,278 | 100.00 | % | |||||||||||||||
Net interest income |
$ | 16,287 | $ | 12,864 | $ | 13,417 | ||||||||||||||||||
Average Rates |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Earning assets |
5.22 | % | 6.16 | % | 7.71 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing funds |
1.82 | 3.32 | 4.62 | |||||||||||||||||||||
Interest rate spread |
3.40 | 2.84 | 3.09 | |||||||||||||||||||||
While a majority of the Corporation’s loan portfolio, approximately 65%, is repriced with each
prime rate change due to floating rate loans, interest paid on similar rate changes does not impact
the pricing of interest-bearing liabilities to nearly the same degree. The mix of time deposits
reflects the Corporation’s need to utilize the brokered certificate of deposit markets for loan
funding when core deposits did not provide adequate sources. The Corporation has placed a high
priority on gathering in-market core deposits in order to reduce funding costs and reduce the risk
associated with non-core funding.
The current low interest rate environment has translated into lower yields on the Corporation’s
earning assets, specifically variable rate commercial loans and short-term investments which
reprice immediately. Offering rates on brokered certificates of deposit are influenced by other
factors, such as overall market liquidity. Reliance upon wholesale funding and further rate
reductions in the near term will unfavorably impact the net interest margin of the Corporation.
60
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following table presents the amount of taxable equivalent interest income from average
interest-earning assets and the yields earned on those assets, as well as the interest expense on
average interest-bearing obligations and the rates paid on those obligations. All average balances
are daily average balances.
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Average | Average | Average | Average | Average | Average | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (dollars in thousands) | Balance | Interest | Rate | Balance | Interest | Rate | Balance | Interest | Rate | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ASSETS: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loans (1,2,3) |
$ | 374,796 | $ | 20,964 | 5.59 | % | $ | 361,324 | $ | 23,166 | 6.41 | % | $ | 333,415 | $ | 27,146 | 8.14 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Taxable securities |
74,005 | 2,782 | 3.76 | 28,766 | 1,293 | 4.49 | 25,061 | 1,100 | 4.39 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nontaxable securities (2) |
571 | 28 | 4.90 | 69 | 8 | 11.59 | 5 | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Federal Funds sold |
74 | — | — | 4,101 | 96 | 2.34 | 7,515 | 391 | 5.20 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other interest-earning assets |
4,415 | 93 | 2.11 | 4,318 | 209 | 4.84 | 6,358 | 332 | 5.22 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total earning assets |
453,861 | 23,867 | 5.26 | 398,578 | 24,772 | 6.22 | 372,354 | 28,969 | 7.78 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Reserve for loan losses |
(4,337 | ) | (3,747 | ) | (4,881 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Cash and due from banks |
19,397 | 6,901 | 6,266 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fixed assets |
10,839 | 11,453 | 12,276 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other assets |
13,892 | 12,158 | 6,298 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 39,791 | 26,765 | 19,959 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TOTAL ASSETS |
$ | 493,652 | $ | 425,343 | $ | 392,313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOW and Money Markets |
$ | 73,003 | $ | 665 | .91 | % | $ | 77,997 | $ | 1,245 | 1.60 | % | $ | 77,942 | $ | 2,669 | 3.42 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Interest checking |
7,735 | 143 | 1.85 | 1,501 | 39 | 2.60 | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Savings deposits |
20,179 | 142 | .70 | 15,963 | 193 | 1.21 | 13,013 | 199 | 1.53 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CDs <$100,000 |
67,356 | 1,858 | 2.76 | 78,755 | 3,181 | 4.04 | 91,313 | 4,490 | 4.92 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CDs >$100,000 |
26,906 | 633 | 2.35 | 27,079 | 1,037 | 3.83 | 23,879 | 1,183 | 4.95 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Brokered deposits |
176,017 | 2,990 | 1.70 | 111,482 | 4,420 | 3.96 | 85,703 | 4,683 | 5.46 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Borrowings |
36,338 | 990 | 2.72 | 39,248 | 1,583 | 4.03 | 38,949 | 2,054 | 5.27 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total interest-bearing liabilities |
407,534 | 7,421 | 1.82 | % | 352,025 | 11,698 | 3.32 | 330,799 | 15,278 | 4.62 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Demand deposits |
31,864 | 29,348 | 25,860 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other liabilities |
3,723 | 3,340 | 2,923 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Shareholders’ equity |
50,531 | 40,630 | 32,731 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 86,118 | 73,318 | 61,514 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TOTAL LIABILITIES AND
SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
$ | 493,652 | $ | 425,343 | $ | 392,313 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rate spread |
3.44 | 2.90 | % | 3.16 | % | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Net interest margin/revenue, tax
equivalent basis |
$ | 16,446 | 3.62 | % | $ | 13,074 | 3.28 | % | $ | 13,691 | 3.68 | % | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (1) | For purposes of these computations, non-accruing loans are included in the daily average loan amounts outstanding. | |
| (2) | The amount of interest income on nontaxable securities and loans has been adjusted to a tax equivalent basis, using a 34% tax rate. | |
| (3) | Interest income on loans includes loan fees. |
61
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following table presents the dollar amount, in thousands, of changes in taxable equivalent
interest income and interest expense for major components of interest-earning assets and
interest-bearing obligations. It distinguishes between changes related to higher or lower
outstanding balances and changes due to the levels and fluctuations in interest rates. For each
category of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing obligations, information is provided for
changes attributable to (i) changes in volume (i.e. changes in volume multiplied by prior period
rate) and (ii) changes in rate (i.e., changes in rate multiplied by prior period volume). For
purposes of this table, changes attributable to both rate and volume are shown as a separate
variance.
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | vs. | 2008 | 2008 | vs. | 2007 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Increase (Decrease) | Increase (Decrease) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Due to | Due to | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Total | Total | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume | Increase | Volume | Increase | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Volume | Rate | and Rate | (Decrease) | Volume | Rate | and Rate | (Decrease) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest earning assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Loans |
$ | 863 | $ | (2,955 | ) | $ | (110 | ) | $ | (2,202 | ) | $ | 2,271 | $ | (5,768 | ) | $ | (483 | ) | $ | (3,980 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Taxable securities |
2,033 | (212 | ) | (332 | ) | 1,489 | 163 | 26 | 4 | 193 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Nontaxable securities |
58 | (5 | ) | (33 | ) | 20 | — | 1 | 7 | 8 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Federal funds sold |
(94 | ) | (96 | ) | 94 | (96 | ) | (178 | ) | (215 | ) | 98 | (295 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Other interest earning assets |
5 | (118 | ) | (3 | ) | (116 | ) | (107 | ) | (24 | ) | 8 | (123 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total interest earning assets |
$ | 2,865 | $ | (3,386 | ) | $ | (384 | ) | $ | (905 | ) | $ | 2,149 | $ | (5,980 | ) | $ | (366 | ) | $ | (4,197 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Interest bearing obligations |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NOW and money market deposits |
$ | (80 | ) | $ | (535 | ) | $ | 35 | $ | (580 | ) | $ | 2 | $ | (1,425 | ) | $ | (1 | ) | $ | (1,424 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Interest checking |
162 | (11 | ) | (47 | ) | 104 | — | — | 39 | 39 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Savings deposits |
51 | (81 | ) | (21 | ) | (51 | ) | 45 | (42 | ) | (9 | ) | (6 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
CDs <$100,000 |
(460 | ) | (1,010 | ) | 147 | (1,323 | ) | (617 | ) | (802 | ) | 110 | (1,309 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
CDs >$100,000 |
(7 | ) | (400 | ) | 3 | (404 | ) | 159 | (269 | ) | (36 | ) | (146 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Brokered deposits |
2,559 | (2,526 | ) | (1,463 | ) | (1,430 | ) | 1,409 | (1,285 | ) | (387 | ) | (263 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Borrowings |
(117 | ) | (514 | ) | 38 | (593 | ) | 16 | (483 | ) | (4 | ) | (471 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||
Total interest bearing obligations |
$ | 2,108 | $ | (5,077 | ) | $ | (1,308 | ) | $ | (4,277 | ) | $ | 1,014 | $ | (4,306 | ) | $ | (288 | ) | $ | (3,580 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Net interest income, tax equivalent basis |
$ | 3,372 | $ | (617 | ) | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Provision for Loan Losses
The Corporation records a provision for loan losses when it believes it is necessary to adjust the
allowance for loan losses to maintain an adequate level after considering factors such as loan
charge-offs and recoveries, changes in identified levels of risk in the loan portfolio, changes in
the mix of loans in the portfolio, loan growth, and other economic factors. During 2009, the
Corporation recorded a provision for loan loss of $3.700 million, compared to a provision of $2.300
million in 2008. In the third quarter of 2007, the Corporation recorded a $.400 million provision
in order to provide for the potential loss related to a commercial loan.
Noninterest Income
Noninterest income was $4.751 million, $4.653 million, and $2.006 million in 2009, 2008, and 2007,
respectively. The principal recurring sources of noninterest income are the gains on the sale of
secondary market loans and fees for services related to deposit and loan accounts. In 2009, the
Corporation recorded a gain on the sale of two branch offices, $1.208 million, and a gain on
security sales of $1.471 million. In 2008, the Corporation recorded the benefit of proceeds
received, $3.475 million, from the settlement of a lawsuit. In 2007, the Corporation recognized
$.470 million of income from the settlement of a lawsuit against its former accountants. Service
fees were $1.023 million in 2009, while other noninterest income was $.219 million.
62
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following table details noninterest income for the three years ended December 31 (dollars
in thousands):
| % Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2009-2008 | 2008-2007 | ||||||||||||||||
Deposit service charges |
$ | 116 | $ | 101 | $ | 92 | 14.85 | % | 9.78 | % | ||||||||||
NSF Fees |
907 | 737 | 597 | 23.07 | 23.45 | |||||||||||||||
Gain on sale of secondary market loans |
224 | 107 | 261 | 109.35 | (59.00 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Secondary market fees generated |
93 | 34 | 41 | 173.53 | (17.07 | ) | ||||||||||||||
SBA Fees |
513 | 12 | 237 | 4,175.00 | (94.94 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Proceeds from settlement of lawsuits |
— | 3,475 | 470 | (100.00 | ) | 639.36 | ||||||||||||||
Other |
1,427 | 123 | 309 | 1,060.16 | (60.19 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Subtotal |
3,280 | 4,589 | 2,007 | (28.52 | ) | 128.65 | ||||||||||||||
Net security gains |
1,471 | 64 | (1 | ) | 2,198.44 | N/A | ||||||||||||||
Total noninterest income |
$ | 4,751 | $ | 4,653 | $ | 2,006 | 2.11 | % | 131.95 | % | ||||||||||
Net gains on loan sales increased from $.119 million in 2008 to $.737 million. Net gains on loan
sales is comprised of the gains recognized on the sale of secondary market mortgage loans, which
totaled $.224 million in 2009 and the sale of SBA loans, which totaled $.513 million in 2009. The
Corporation anticipates increased revenues from these activities in future periods. Late in 2009,
we increased our capacity for secondary market activities. We hired a primary producer of
secondary market mortgage loans in the Upper Peninsula as well as additional staff in order to
support increased volume. We are also considering additions of other mortgage loan producers to
enhance our revenue stream from this activity. We are also increasing our SBA and USDA lending
activities as these types of government sponsored programs become more advantageous to borrowers.
We do anticipate increased fee income in future periods as the housing market improves and home
buyers look to more traditional lenders for their borrowing needs. We did realize increased income
from service fees related to our deposit products. Management initiated several changes in fees
associated with various deposit products, to better align services and costs.
Noninterest Expense
Noninterest expense was $13.802 million in 2009, compared to $12.558 million and $12.100 million in
2008 and 2007, respectively. In 2009, the increase in noninterest expense totaled $1.244 million,
or 9.91%. Salaries and employee benefits decreased in 2009 by $.303 million to $6.583 million,
compared to 2008 expense of $6.886 million. During 2008, the Corporation recorded a $.425 million
expense related to a severance payment. Excluding this item, the Corporation had an increase in
salaries and employee benefits of $.122 million from 2008.
The largest increase in noninterest expense for 2009 occurred in loan and deposit expense, which
increased from $.488 million in 2008 to $.933 million in 2009. This increase was due in part to
increased costs associated with a higher level of nonperforming assets. Management expects that
costs associated with carrying nonperforming loans will continue to be above historical norms. The
most significant noninterest expense increase was in FDIC insurance assessment premiums which
totaled $.081 million in 2008 and increased to $.839 million in 2009. FDIC insurance costs are
also expected to increase in future periods based upon the need to replenish the deposit insurance
fund for charges due to increased bank failures.
Management will continue to review all areas of noninterest expense in order to evaluate where
opportunities may exist which could reduce expenses without compromising service to customers.
63
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following table details noninterest expense for the three years ended December 31 (dollars
in thousands):
| % Increase (Decrease) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2009 - 2008 | 2008 - 2007 | ||||||||||||||||
Salaries and benefits |
$ | 6,583 | $ | 6,886 | $ | 6,757 | (4.40) | % | 1.91 | % | ||||||||||
Occupancy |
1,385 | 1,374 | 1,272 | .80 | 8.02 | |||||||||||||||
Furniture and equipment |
805 | 771 | 678 | 4.41 | 13.72 | |||||||||||||||
Data processing |
862 | 844 | 785 | 2.13 | 7.52 | |||||||||||||||
Professional service fees: |
||||||||||||||||||||
Accounting |
261 | 254 | 308 | 2.76 | (17.53 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Legal |
95 | 41 | 42 | 131.71 | (2.38 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Consulting and other |
247 | 213 | 182 | 15.96 | 17.03 | |||||||||||||||
Total professional service fees |
603 | 508 | 532 | 18.70 | (4.51 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Loan and deposit |
933 | 488 | 250 | 91.19 | 95.20 | |||||||||||||||
FDIC insurance premiums |
839 | 81 | 35 | 935.80 | 131.43 | |||||||||||||||
Telephone |
187 | 170 | 228 | 10.00 | (25.44 | ) | ||||||||||||||
ORE writedowns/impairment |
187 | — | 40 | N/A | N/A | |||||||||||||||
(Gain) loss on sale of premises, equipment
branch and other real estate |
23 | 77 | (17 | ) | (70.13 | ) | (552.94 | ) | ||||||||||||
Advertising |
322 | 305 | 370 | 5.57 | (17.57 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Amortization of intangibles |
46 | 78 | 82 | (41.03 | ) | (4.88 | ) | |||||||||||||
Other operating expenses |
1,027 | 976 | 1,088 | 5.23 | (10.29 | ) | ||||||||||||||
Total noninterest expense |
$ | 13,802 | $ | 12,558 | $ | 12,100 | 9.91 | % | 3.79 | % | ||||||||||
Federal Income Taxes
Current Federal Tax Provision
The Corporation recorded a current period federal tax provision of $1.120 million in 2009, compared
to a $.787 million provision in the same period a year earlier due to increased income.
Deferred Tax Benefit
The Corporation recognized a federal deferred tax benefit of $7.500 million in the third quarter of
2007. The recognition of this deferred tax benefit relates to the generally accepted accounting
principles applicable to the probability of utilizing the NOL and tax credit carryforwards of the
Corporation. The Corporation, based upon current profitability trends largely supported by
expansion of the net interest margin and controlled expenses, determined that the utilization of
the NOL
carryforward was probable. This tax benefit was recorded by reducing the valuation allowance that
was recorded against the deferred tax assets of the Corporation. The $7.500 million recognition is
based upon assumptions of a sustained level of taxable income within the NOL carryforward period
and takes into account Section 382, establishing annual limitations. A valuation allowance is
provided against deferred tax assets when it is more likely than not that some or all of the
deferred tax assets will not be realized. As of December 31, 2009, the Corporation had an NOL
carryforward of approximately $28.0 million along with various credit carryforwards of $2.136
million. This NOL and credit carryforward benefit is dependent upon the future profitability of
the Corporation. A portion of the NOL, approximately $18.0 million, and all of the tax credit
carryforwards are also subject to the limitations of Section 382 of the Internal Revenue Code since
they originated prior to the December 2004 recapitalization of the Corporation. The Corporation
intends to further evaluate the utilization of the NOL and credit carryforwards in subsequent
periods to determine if any further adjustment to the valuation allowance is necessary. The
determination criteria for recognition of deferred tax benefits will include the assumption of
future period taxable income based upon the projected profitability of the Corporation.
64
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
QUANTITATIVE AND QUALITATIVE DISCLOSURES ABOUT MARKET RISK
Interest Rate Risk
In general, the Corporation attempts to manage interest rate risk by investing in a variety of
assets which afford it an opportunity to reprice assets and increase interest income at a rate
equal to or greater than the interest expense associated with repricing liabilities.
Interest rate risk is the exposure of the Corporation to adverse movements in interest rates. The
Corporation derives its income primarily from the excess of interest collected on its
interest-earning assets over the interest paid on its interest-bearing obligations. The rates of
interest the Corporation earns on its assets and owes on its obligations generally are established
contractually for a period of time. Since market interest rates change over time, the Corporation
is exposed to lower profitability if it cannot adapt to interest rate changes. Accepting interest
rate risk can be an important source of profitability and shareholder value; however, excess levels
of interest rate risk could pose a significant threat to the Corporation’s earnings and capital
base. Accordingly, effective risk management that maintains interest rate risk at prudent levels
is essential to the Corporation’s safety and soundness.
Loans are the most significant earning asset. Management offers commercial and real estate loans
priced at interest rates which fluctuate with various indices, such as the prime rate or rates paid
on various government issued securities. When loans are made with longer-term fixed rates, the
Corporation attempts to match these balances with sources of funding with similar maturities in
order to mitigate interest rate risk. In addition, the Corporation prices loans so it has an
opportunity to reprice the loan within 12 to 36 months.
The Bank has $46.513 million of securities, with a weighted average maturity of 22 months. The
investment portfolio is intended to provide a source of liquidity to the Corporation with limited
interest rate risk. The Corporation may also elect to sell monies as investments in federal funds
sold to correspondent banks, and has other interest bearing deposits with correspondent banks.
These funds are generally repriced on a daily basis.
The Corporation offers deposit products with a variety of terms ranging from deposits whose
interest rates can change on a weekly basis to certificates of deposit with repricing terms of up
to five years. Longer-term deposits generally include penalty provisions for early withdrawal.
Beyond general efforts to shorten the loan pricing periods and extend deposit maturities,
management can manage interest rate risk by the maturity periods of securities purchased, selling
securities available for sale, and borrowing funds with targeted maturity periods, among other
strategies. Also, the rate of interest rate changes can impact the actions taken, since the speed
of change affects borrowers and depositors differently.
Exposure to interest rate risk is reviewed on a regular basis. Interest rate risk is the potential
of economic losses due to future interest rate changes. These economic losses can be reflected as
a loss of future net interest income and/or a loss of current fair market values. The objective is
to measure the effect of interest rate changes on net interest income and to structure the
composition of the balance sheet to minimize interest rate risk and, at the same time, maximize
income.
Management realizes certain risks are inherent and that the goal is to identify and minimize the
risks. Tools used by management include maturity and repricing analysis and interest rate
sensitivity analysis. The Bank has monthly asset/ liability (“ALCO”) meetings, whose membership
includes senior management, board representation and third party investment consultants. During
these monthly meetings, we review the current ALCO position and strategize about future
opportunities on risks relative to pricing and positioning of assets and liabilities.
The difference between repricing assets and liabilities for a specific period is referred to as the
gap. An excess of repricable assets over liabilities is referred to as a positive gap. An excess
of repricable liabilities over assets is referred to as a
negative gap. The cumulative gap is the summation of the gap for all periods to the end of the
period for which the cumulative gap is being measured.
Assets and liabilities scheduled to reprice are reported in the following timeframes. Those
instruments with a variable interest rate tied to an index and considered immediately repricable
are reported in the 1 to 90 day timeframe. The
65
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
estimates of principal amortization and prepayments are assigned to the following time frames.
The following is the Corporation’s repricing opportunities at December 31, 2009 (dollars in
thousands):
| 1-90 | 91-365 | >1-5 | Over 5 | |||||||||||||||||
| Days | Days | Years | Years | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Interest-earning assets: |
||||||||||||||||||||
Loans |
$ | 251,756 | $ | 18,278 | $ | 27,326 | $ | 86,950 | $ | 384,310 | ||||||||||
Securities |
— | 11,272 | 34,441 | 800 | 46,513 | |||||||||||||||
Other (1) |
27,678 | — | — | 3,794 | 31,472 | |||||||||||||||
Total interest-earning assets |
279,434 | 29,550 | 61,767 | 91,544 | 462,295 | |||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing obligations: |
||||||||||||||||||||
NOW, money market, savings and interest checking |
113,997 | — | — | — | 113,997 | |||||||||||||||
Time deposits |
33,701 | 42,554 | 19,514 | 569 | 96,338 | |||||||||||||||
Brokered CDs |
43,593 | 58,116 | 70,739 | 2,728 | 175,176 | |||||||||||||||
Borrowings |
20,000 | 15,000 | — | 1,140 | 36,140 | |||||||||||||||
Total interest-bearing obligations |
211,291 | 115,670 | 90,253 | 4,437 | 421,651 | |||||||||||||||
Gap |
$ | 68,143 | $ | (86,120 | ) | $ | (28,486 | ) | $ | 87,107 | $ | 40,644 | ||||||||
Cumulative gap |
$ | 68,143 | $ | (17,977 | ) | $ | (46,463 | ) | $ | 40,644 | ||||||||||
| (1) | includes Federal Home Loan Bank stock |
The above analysis indicates that at December 31, 2009, the Corporation had a cumulative liability
sensitivity GAP position of $17.977 million within the one-year timeframe. The Corporation’s
cumulative liability sensitive GAP suggests that if market interest rates were to increase in the
next twelve months, the Corporation has the potential to earn less net interest income since more
liabilities would reprice at higher rates than assets. Conversely, if market interest rates
decrease in the next twelve months, the above GAP position suggests the Corporation’s net interest
income would increase. A limitation of the traditional GAP analysis is that it does not consider
the timing or magnitude of non-contractual repricing or unexpected prepayments. In addition, the
GAP analysis treats savings, NOW and money market accounts as repricing within 90 days, while
experience suggests that these categories of deposits are actually comparatively resistant to rate
sensitivity
At December 31, 2008, the Corporation had a cumulative liability sensitivity gap position of
$47.708 million within the one-year time frame.
The borrowings in the gap analysis include $15 million of FHLB advances as fixed-rate advances.
These advances actually give the FHLB the option to convert from a fixed-rate advance to an
adjustable rate advance with quarterly repricing at three month LIBOR Flat. The exercise of this
conversion feature by the FHLB would impact the repricing dates currently assumed in the analysis.
The Corporation’s primary market risk exposure is interest rate risk and, to a lesser extent,
liquidity risk and foreign exchange risk. The Corporation has no market risk sensitive instruments
held for trading purposes. The Corporation has limited agricultural-related loan assets, and
therefore, has minimal significant exposure to changes in commodity prices. Any impact that
changes in foreign exchange rates and commodity prices would have on interest rates are assumed to
be insignificant.
Evaluating the exposure to changes in interest rates includes assessing both the adequacy of the
process used to control interest rate risk and the quantitative level of exposure. The
Corporation’s interest rate risk management process seeks to ensure that appropriate policies,
procedures, management information systems, and internal controls are in place to maintain interest
rate risk at prudent levels with consistency and continuity. In evaluating the quantitative level
of interest rate risk, the Corporation assesses the existing and potential future effects of
changes in interest rates on its financial
66
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
condition, including capital adequacy, earnings, liquidity, and asset quality. In addition to
changes in interest rates, the level of future net interest income is also dependent on a number of
variables, including: the growth, composition and levels of loans, deposits, and other earning
assets and interest-bearing obligations, and economic and competitive conditions; potential changes
in lending, investing, and deposit strategies; customer preferences; and other factors.
The table below measures current maturity levels of interest-earning assets and interest-bearing
obligations, along with average stated rates and estimated fair values at December 31, 2009
(dollars in thousands). Nonaccrual loans of $14.368 million are included in the table at an
average interest rate of 0.00% and a maturity greater than five years.
| Principal/Notional Amount Maturing/Repricing In: | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Fair Value | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 2010 | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | Thereafter | Total | 12/31/2009 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Rate Sensitive Assets |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fixed interest rate
securities |
$ | 11,272 | $ | 23,267 | $ | 7 | $ | 10,327 | 840 | $ | 800 | $ | 46,513 | $ | 46,513 | |||||||||||||||||
Average interest rate |
3.85 | % | 4.22 | % | 5.48 | % | 5.48 | % | 6.42 | % | 3.26 | % | 4.44 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Fixed interest rate loans |
41,686 | 21,974 | 23,910 | 6,445 | 17,455 | 17,180 | 128,650 | 129,165 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average interest rate |
6.68 | 7.42 | 6.99 | 6.89 | 6.16 | 5.58 | 6.66 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Variable interest rate loans |
255,660 | 255,660 | 258,412 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average interest rate |
5.00 | — | — | — | — | — | 5.00 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Other assets |
27,678 | — | — | — | — | 3,794 | 31,472 | 31,472 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average interest rate |
.24 | — | — | — | — | 2.00 | .45 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total rate sensitive assets |
$ | 336,296 | $ | 45,241 | $ | 23,917 | $ | 16,772 | $ | 18,295 | $ | 21,774 | $ | 462,295 | $ | 465,562 | ||||||||||||||||
Average interest rate |
4.78 | % | 5.78 | % | 6.99 | % | 6.02 | % | 6.17 | % | 5.35 | % | 4.87 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Rate Sensitive Liabilities |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Interest-bearing savings,
NOW, MMAs, interest checking |
113,997 | — | — | — | — | — | 113,997 | 113,997 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average interest rate |
1.24 | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | — | % | 1.24 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Time deposits |
177,963 | 82,290 | 5,457 | 2,132 | 374 | 3,298 | 271,514 | 271,249 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average interest rate |
1.45 | 2.15 | 3.00 | 3.53 | 6.04 | 3.57 | 1.74 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Fixed interest rate
borrowings |
15,000 | — | — | — | — | 1,140 | 16,140 | 16,437 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average interest rate |
5.10 | — | — | — | — | 1.00 | 4.81 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Variable interest rate
borrowings |
— | 20,000 | — | — | — | — | 20,000 | 20,010 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
Average interest rate |
— | .30 | .30 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Total rate sensitive
liabilities |
$ | 306,960 | $ | 102,290 | $ | 5,457 | $ | 2,132 | $ | 374 | $ | 4,438 | $ | 421,651 | $ | 421,693 | ||||||||||||||||
Average interest rate |
1.55 | % | 1.79 | % | 3.00 | % | 3.53 | % | 6.04 | % | 2.91 | % | 1.62 | % | ||||||||||||||||||
Foreign Exchange Risk
In addition to managing interest rate risk, management also actively manages risk associated with
foreign exchange. The Corporation provides foreign exchange services, makes loans to, and accepts
deposits from, Canadian customers primarily at its banking office in Sault Ste. Marie. To protect
against foreign exchange risk, the Corporation monitors the volume of Canadian deposits it takes in
and then invests these Canadian funds in Canadian commercial loans and securities. As of December
31, 2009, the Corporation had excess Canadian liabilities of $51,000 (or $53,000 in U.S. dollars).
Management believes the exposure to short-term foreign exchange risk is minimal and at an
acceptable level for the Corporation. Management intends to limit the Corporation’s foreign
exchange risk by acquiring deposit liabilities approximately equal to its Canadian assets.
67
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Off-Balance-Sheet Risk
Derivative financial instruments include futures, forwards, interest rate swaps, option contracts
and other financial instruments with similar characteristics. The Corporation currently does not
enter into futures, forwards, swaps or options. However, the Corporation is party to financial
instruments with off-balance-sheet risk in the normal course of business to meet the financing
needs of its customers. These financial instruments include commitments to extend credit and
standby letters of credit and involve to varying degrees, elements of credit and interest rate risk
in excess of the amount recognized in the consolidated balance sheets. Commitments to extend
credit are agreements to lend to a customer as long as there is no violation of any condition
established in the contract. Commitments generally have fixed expiration dates and may require
collateral from the borrower if deemed necessary by the Corporation. Standby letters of credit are
conditional commitments issued by the Corporation to guarantee the performance of a customer to a
third party up to a stipulated amount and with specified terms and conditions.
Commitments to extend credit and standby letters of credit are not recorded as an asset or
liability by the Corporation until the instrument is exercised. See Note 18 to the consolidated
financial statements for additional information.
LIQUIDITY
Liquidity is defined as the ability to generate cash at a reasonable cost to fulfill lending
commitments and support asset growth, while satisfying the withdrawal demands of customers and make
payments on existing borrowing commitments. The Bank’s principal sources of liquidity are core
deposits and loan and investment payments and prepayments. Providing a secondary source of
liquidity is the available for sale investment portfolio. As a final source of liquidity, the Bank
can exercise existing credit arrangements.
During 2009, the Corporation increased cash and cash equivalents by $35.321 million. As shown on
the Corporation’s consolidated statement of cash flows, liquidity was primarily impacted by cash
provided by investing activities, a net increase in loans of $21.218 million and a “net” decrease
in securities available for sale of $2.629 million. The net increases in assets were offset by a
similar increase in deposit liabilities of $79.552 million. This increase in deposits was
composed of an increase in non-core deposits of $35.629 million combined with an increase in bank
deposits of $14.663 million. The management of bank liquidity for funding of loans and
deposit maturities and withdrawals includes monitoring projected loan fundings and scheduled
prepayments and deposit maturities within a 30 day period, a 30 to 90 day period and from 90 days
until the end of the year. This funding forecast model is completed weekly.
The Bank’s investment portfolio, most of which are guaranteed by the U.S. government, provide added
liquidity during periods of market turmoil and overall liquidity concerns in the financial markets.
As of December 31, 2009, $29.436 million of the Bank’s investment portfolio was unpledged, which
makes them readily available for sale to address any short
term liquidity needs.
It is anticipated that during 2010, the Corporation will fund anticipated loan production with a
combination of core-deposit growth and noncore funding, primarily brokered CDs.
The Corporation’s primary source of liquidity on a stand-alone basis is dividends from the Bank.
The Bank is currently prohibited from paying dividends because of a deficit in retained earnings.
The Bank, in order to pay dividends in future periods, will need to restate its capital accounts,
which requires the approval of the Office of Financial and Insurance Services of the State of
Michigan. The Corporation is currently exploring alternative opportunities for longer term
sources of liquidity and permanent equity to support projected asset growth.
Liquidity is managed by the Corporation through its Asset and Liability Committee (“ALCO”). The
ALCO Committee meets monthly to discuss asset and liability management in order to address
liquidity and funding needs to provide a process to seek the best alternatives for investments of
assets, funding costs, and risk management. The liquidity position of the Bank is managed daily,
thus enabling the Bank to adapt its position according to market fluctuations. Core deposits are
important in maintaining a strong liquidity position as they represent a stable and relatively low
cost source of funds. The Bank’s liquidity is best illustrated by the mix in the Bank’s core and
non-core funding dependency ratio, which explains the degree of reliance on non-core liabilities to
fund long-term assets. Core deposits are herein defined as demand deposits, NOW (negotiable order
withdrawals), money markets, savings and certificates of deposit under $100,000. Non-core funding
consists of certificates of deposit greater than $100,000, brokered deposits, and FHLB and other
borrowings. At December 31, 2009, the Bank’s core deposits in relation to total funding was 45.86%
compared to 47.92% in 2008. These ratios indicated at December 31, 2009, that the Bank has
decreased its reliance on non-core deposits and borrowings to fund the Bank’s long-term assets,
namely loans and investments. The Bank believes that by maintaining adequate volumes of short-term
investments and implementing competitive pricing strategies on deposits, it can ensure adequate
liquidity to support future growth. The Bank also has correspondent lines of credit available to
meet unanticipated short-
68
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
term liquidity needs. As of December 31, 2009, the Bank had $15.875
million of unsecured lines available and another $7.085 million available if secured. Management
believes that its liquidity position remains strong to meet both present and future financial
obligations and commitments, events or uncertainties that have resulted or are reasonably likely to
result in material changes with respect to the Bank’s liquidity.
From a long-term perspective, the Corporation’s liquidity plan for 2010 includes strategies to
increase core deposits in the Corporation’s local markets and will continue to augment local
deposit growth efforts with wholesale CD funding, to the extent necessary.
CONTRACTUAL OBLIGATIONS AND COMMITMENTS
As disclosed in the Notes to the Consolidated Financial Statements, the Corporation has certain
obligations and commitments to make future payments under contracts. At December 31, 2009, the
aggregate contractual obligations and commitments are:
| Payments Due by Period | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Less than 1 | 1 to 3 | 4 to 5 | After 5 | |||||||||||||||||
| Year | Years | Years | Years | Total | ||||||||||||||||
Contractual Obligations |
||||||||||||||||||||
Total deposits |
$ | 327,838 | $ | 87,747 | $ | 2,506 | $ | 3,298 | $ | 421,389 | ||||||||||
Federal Home Loan Bank borrowings |
15,000 | 20,000 | — | — | 35,000 | |||||||||||||||
Preferred stock (1) |
— | — | 11,000 | — | 11,000 | |||||||||||||||
Other borrowings |
— | — | — | 1,140 | 1,140 | |||||||||||||||
Directors’ deferred compensation |
132 | 246 | 237 | 424 | 1,039 | |||||||||||||||
Annual rental / purchase commitments
under noncancelable leases / contracts |
209 | 92 | — | — | 301 | |||||||||||||||
TOTAL |
$ | 343,179 | $ | 108,085 | $ | 13,743 | $ | 4,862 | $ | 469,869 | ||||||||||
Other Commitments |
||||||||||||||||||||
Letters of credit |
$ | 1,279 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 1,279 | ||||||||||
Commitments to extend credit |
30,878 | — | — | — | 30,878 | |||||||||||||||
Credit card commitments |
2,714 | — | — | — | 2,714 | |||||||||||||||
TOTAL |
$ | 34,871 | $ | — | $ | — | $ | — | $ | 34,871 | ||||||||||
| (1) | The Corporation issued preferred stock in April of 2009 as part of its participation in TARP. The initial term of this preferred stock is five years with an interest rate of 5%, which increases to 9% after the initial term. Although there is no contractual obligation to do so, the Corporation intends to repay this obligation within the initial term. |
CAPITAL AND REGULATORY
As a bank holding company, the Corporation is required to maintain certain levels of capital under
government regulation. There are several measurements of regulatory capital, and the Corporation
is required to meet minimum requirements under each measurement. The federal banking regulators
have also established capital classifications beyond the minimum requirements in order to risk-rate
deposit insurance premiums and to provide trigger points for prompt corrective action in the event
an institution becomes financially troubled. As of December 31, 2009, the Corporation and the Bank
were well capitalized. The Corporation is currently exploring its alternatives for the possible
issuance of equity or debt in order to provide a broader base to support future asset growth.
During 2009, total capitalization increased by $13.747 million from the issuance of preferred stock
and common stock warrants in conjunction with the Corporation’s participation in TARP. Other
increases in total capital occurred from recognition of net income and market value increase of the
Corporation’s investment securities. During 2009, risk based capital increased by $15.449 million,
while Tier 1 Capital increased by $14.545 million.
69
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
The following table details sources of capital for the three years ended December 31 (dollars
in thousands):
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | ||||||||||
Capital Structure |
||||||||||||
Shareholders’ equity |
$ | 55,299 | $ | 41,552 | $ | 39,321 | ||||||
Total capitalization |
$ | 55,299 | $ | 41,552 | $ | 39,321 | ||||||
Tangible capital |
$ | 55,299 | $ | 41,507 | $ | 39,197 | ||||||
Intangible Assets |
||||||||||||
Subsidiaries: |
||||||||||||
Core deposit premium |
$ | — | $ | 46 | $ | 124 | ||||||
Other identifiable intangibles |
— | — | — | |||||||||
Total intangibles |
$ | — | $ | 46 | $ | 124 | ||||||
Risk-Based Capital |
||||||||||||
Tier 1 capital: |
||||||||||||
Shareholders’ equity |
$ | 55,299 | $ | 41,552 | $ | 39,321 | ||||||
Net unrealized (gains) losses on |
||||||||||||
available for sale securities |
(1,093 | ) | (445 | ) | (60 | ) | ||||||
Less: disallowed deferred tax asset |
(4,800 | ) | (6,200 | ) | (6,990 | ) | ||||||
Less: intangibles |
— | (46 | ) | (124 | ) | |||||||
Total Tier 1 capital |
$ | 49,406 | $ | 34,861 | $ | 32,147 | ||||||
Tier 2 Capital: |
||||||||||||
Allowable reserve for loan losses |
$ | 5,181 | $ | 4,277 | $ | 4,146 | ||||||
Qualifying long-term debt |
— | — | — | |||||||||
Total Tier 2 capital |
5,181 | 4,277 | 4,146 | |||||||||
Total risk-based capital |
$ | 54,587 | $ | 39,138 | $ | 36,293 | ||||||
Risk-weighted assets |
$ | 414,440 | $ | 376,986 | $ | 358,410 | ||||||
Capital Ratios: |
||||||||||||
Tier 1 Capital to average assets |
9.75 | % | 8.01 | % | 8.05 | % | ||||||
Tier 1 Capital to risk-weighted assets |
11.92 | % | 9.25 | % | 8.97 | % | ||||||
Total Capital to risk-weighted assets |
13.17 | % | 10.38 | % | 10.13 | % | ||||||
Regulatory capital is not the same as shareholders’ equity reported in the accompanying condensed
consolidated financial statements. Certain assets cannot be considered assets for regulatory
purposes. The Corporation’s acquisition intangibles and a portion of the deferred tax asset are
examples of such assets.
70
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Financial Condition and Results of Operations
Presented below is a summary of the Corporation’s and Bank’s capital position in comparison to
generally applicable regulatory requirements:
| Tangible | Tier 1 | Tier 1 | Total | |||||||||||||||||
| Equity to | Equity to | Capital to | Capital to | Capital to | ||||||||||||||||
| Year-end | Year-end | Average | Risk Weighted | Risk Weighted | ||||||||||||||||
| Assets | Assets | Assets | Assets | Assets | ||||||||||||||||
Regulatory minimum for capital adequacy purposes |
N/A | N/A | 4.00 | % | 4.00 | % | 8.00 | % | ||||||||||||
Regulatory defined well capitalized guideline |
N/A | N/A | 5.00 | % | 6.00 | % | 10.00 | % | ||||||||||||
The Corporation: |
||||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2009 |
10.73 | % | 10.73 | % | 9.75 | % | 11.92 | % | 13.17 | % | ||||||||||
December 31, 2008 |
9.21 | % | 9.20 | % | 8.01 | % | 9.25 | % | 10.38 | % | ||||||||||
The Bank: |
||||||||||||||||||||
December 31, 2009 |
9.38 | % | 9.38 | % | 8.38 | % | 10.24 | % | 11.49 | % | ||||||||||
December 31, 2008 |
9.25 | % | 9.24 | % | 8.09 | % | 9.32 | % | 10.44 | % | ||||||||||
The Corporation intends to maintain the Bank’s Tier I Capital at 8% and total capital to
risk-weighted assets at a minimum of 10.00% in order to qualify for reduced FDIC deposit based
insurance.
IMPACT OF INFLATION AND CHANGING PRICES
The accompanying financial statements have been prepared in accordance with generally accepted
accounting principles, which require the measurement of financial position and results of
operations in historical dollars without considering the change in the relative purchasing power of
money over time due to inflation. The impact of inflation is reflected in the increased cost of
the Corporation’s operations. Nearly all the assets and liabilities of the Corporation are
financial, unlike industrial or commercial companies. As a result, the Corporation’s performance
is directly impacted by changes in interest rates, which are indirectly influenced by inflationary
expectations. The Corporation’s ability to match the interest sensitivity of its financial assets
to the interest sensitivity of its financial liabilities tends to minimize the effect of changes in
interest rates on the Corporation’s performance. Changes in interest rates do not necessarily move
to the same extent as changes in the prices of goods and services.
71
Directors and Officers
DIRECTORS
Mackinac Financial Corporation and mBank
Walter J. Aspatore — Lead Director
|
Robert H. Orley | |
Chairman
|
Vice President and Secretary | |
Amherst Partners
|
Real Estate Interests Group, Inc. | |
Director Since: 2004
|
Director Since: 2004 | |
Dennis B. Bittner
|
L. Brooks Patterson | |
Owner and President
|
County Executive | |
Bittner Engineering, Inc.
|
Oakland County | |
Director Since: 2001
|
Director Since: 2006 | |
Joseph D. Garea
|
Randolph C. Paschke | |
Managing Partner
|
Chairman, Department of Accounting | |
Hancock Securities
|
Wayne State University, School of Business Administration | |
Director Since: 2007
|
Director Since: 2004 | |
Kelly W. George
|
Paul D. Tobias | |
President, Mackinac Financial Corporation
|
Chairman and CEO, Mackinac Financial Corporation | |
President and CEO, mBank
|
Chairman, mBank | |
Director Since: 2006
|
Director Since: 2004 | |
Robert E. Mahaney |
||
Sole Proprietor |
||
Veridea Group, LLC |
||
Director Since: 2008 |
OFFICERS
Mackinac Financial Corporation
| Name | Title | Location | ||
Paul D. Tobias
|
Chairman and Chief Executive Officer | Birmingham | ||
Kelly W. George
|
President | Manistique | ||
Ernie R. Krueger
|
EVP — Chief Financial Officer | Manistique |
mBank
| Name | Title | Location | ||
Bernadette C. Beaudre
|
AVP — Deposit Compliance Officer | Manistique | ||
Shelby J. Bischoff
|
AVP — Business Development Officer | Marquette | ||
Linda K. Bolda
|
VP — Human Resources Manager | Manistique | ||
Jesse A. Deering
|
First VP — SEM Executive | Birmingham | ||
Kevin D. Evans
|
SVP — Retail Sales Management | Newberry | ||
Jeremy W. Flodin
|
AVP — Sr. Credit Admin/Credit Risk Analyst | Manistique | ||
Jack C. Frost
|
Regional President — UP | Marquette | ||
Laura L. Garvin
|
VP — Commercial Banking Officer | Birmingham | ||
Kelly W. George
|
President and CEO | Manistique | ||
Clarice A. Ghiardi
|
VP — Mortgage/Consumer Banking Officer | Marquette | ||
Robert C. Henry
|
VP — Commercial Banking Officer | Traverse City | ||
Ernie R. Krueger
|
EVP — Chief Financial Officer | Manistique | ||
Jake D. Martin
|
SVP — IT Manager | Manistique | ||
Boris Martysz
|
VP — Commercial Banking Officer | Marquette | ||
Tamara R. McDowell
|
SVP — Sernior Credit/Operations Officer | Manistique | ||
Jacquelyn R. Menhennick
|
SVP — Mortgage and Consumer Lending Manager | Marquette | ||
Barbara A. Parrett
|
AVP — Branch Sales Manager/Retail Banking Officer | Stephenson | ||
Scott A. Ravet
|
VP — Commercial Banking Officer | Manistique/Escanaba | ||
Kimberly R. Robinson
|
VP — New Business Development | Birmingham | ||
Jason J. Rolling
|
AVP — Commercial Banking Officer | Marquette | ||
Andrew P. Sabatine
|
Regional President — NLP | Traverse City | ||
Gregory D. Schuetter
|
VP — Commercial Banking Officer | Manistique | ||
Joanna B. Slaght
|
SVP — Compliance/Risk Manager/BSA Officer | Manistique | ||
Michael A. Slaght
|
VP — Branch Sales Manager/Retail Banking Officer | Newberry | ||
Jennifer A. Stempki
|
VP — Assistant Controller | Manistique | ||
Ann M. Stepp
|
SVP — Branch Administration | Gaylord | ||
David R. Thomas
|
VP — Commercial Banking Officer | Sault Ste. Marie | ||
Timothy J. Timmer
|
VP — Commercial Banking Officer | Gaylord | ||
Paul D. Tobias
|
Chairman | Birmingham | ||
Janet M. Willbee
|
AVP — Mortgage Loan Officer | Gaylord |
72
Corporate Information
CORPORATE HEADQUARTERS
|
TRANSFER AGENT | |
Mackinac Financial Corporation
|
Registrar and Transfer Company | |
130 South Cedar Street
|
10 Commerce Drive | |
Manistique, Michigan 49854
|
Cranford, NJ 07016 | |
(888) 343-8147
|
(800) 368-5948 | |
INVESTOR RELATIONS
|
WEBSITE | |
(888) 343-8147
|
www.bankmbank.com | |
INDEPENDENT REGISTERED PUBLIC ACCOUNTING FIRM
|
STOCK LISTING AND SYMBOL | |
Plante and Moran, PLLC
|
NASDAQ Capital Market | |
Auburn Hills, Michigan
|
Symbol: MFNC |
SHAREHOLDER INFORMATION
Copies of the Corporation’s 10-K and 10-Q reports as filed with the Securities and Exchange
Commission are available upon request from the Corporation.
ANNUAL SHAREHOLDERS’ MEETING
The 2010 Annual Meeting of the Shareholders of Mackinac Financial Corporation will be held on
Wednesday May 26, 2010.
Visit our website, www.bankmbank.com, for updated news releases, financial reports, SEC filings,
corporate governance and other investor information.
73
