Attached files
| file | filename |
|---|---|
| EX-21 - India Globalization Capital, Inc. | ex21.htm |
| EX-23.1 - India Globalization Capital, Inc. | ex23-1.htm |
As
filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission on March
9, 2010
Registration
No. 333-163867
UNITED
STATES
SECURITIES
AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
WASHINGTON,
D.C. 20549
Amendment
No. 1 to
FORM
S-1
REGISTRATION
STATEMENT
UNDER
THE
SECURITIES ACT OF 1933
INDIA
GLOBALIZATION CAPITAL, INC.
(Exact
Name of Registrant as Specified in Its Charter)
|
Maryland
|
1600
|
20-2760393
|
||
|
(State
or Other Jurisdiction of
Incorporation
or Organization)
|
(Primary
Standard Industrial
Classification
Code Number)
|
(I.R.S.
Employer
Identification
Number)
|
4336
Montgomery Ave.
Bethesda, Maryland
20814
(301) 983-0998
(Address,
Including Zip Code, and Telephone Number,
Including
Area Code, of Registrant’s Principal Executive Offices)
Ram
Mukunda
Chief
Executive Officer and President
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
4336
Montgomery Ave.
Bethesda,
Maryland, 20814
(301) 983-0998
(Name,
Address, Including Zip Code, and Telephone Number,
Including
Area Code, of Agent for Service)
Copies
to:
Stanley
S. Jutkowitz, Esq.
Seyfarth
Shaw LLP
975
F Street, N.W.
Washington,
D.C. 20004
Telephone:
(202) 463-2400
Facsimile:
(202) 828-5393
Approximate date of commencement of
proposed sale to public: As soon as practicable after this
registration statement becomes effective.
If any of
the securities being registered on this form are to be offered on a delayed or
continuous basis pursuant to Rule 415 under the Securities Act of 1933,
check the following box: o
If this
form is filed to register additional securities for an offering pursuant to
Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act, please check the following box and
list the Securities Act registration statement number of the earlier effective
registration statement for the same offering: o
If this
form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(c) under the
Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration
statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same
offering: o
If this
Form is a post-effective amendment filed pursuant to Rule 462(d) under the
Securities Act, check the following box and list the Securities Act registration
statement number of the earlier effective registration statement for the same
offering: o
Indicate
by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an
accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See
the definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer” and “smaller
reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check
one):
|
Large
accelerated filer o
|
Accelerated
filer o
|
Non-accelerated
filer o
(Do
not check if a smaller reporting company)
|
Smaller
reporting company þ
|
CALCULATION
OF REGISTRATION FEE
|
Proposed
Maximum
|
||||||||||
|
Title
of Each Class of
|
Aggregate
Offering
|
Amount
of
|
||||||||
|
Securities
to be Registered
|
Price
|
Registration
Fee
|
||||||||
|
Common
Stock, $0.0001 par value per share
|
(1)
|
$
|
4,000,000
|
(1)
|
$
|
223.20
|
||||
|
(1)
|
Estimated
solely for purposes of calculating the registration fee in accordance with
Rule 457(o) under the Securities Act of 1933, as
amended.
|
The Registrant hereby amends this
Registration Statement on such date or dates as may be necessary to delay its
effective date until the Registrant shall file a further amendment which
specifically states that this Registration Statement shall thereafter become
effective in accordance with Section 8(a) of the Securities Act of 1933 or
until the Registration Statement shall become effective on such date as the
Commission, acting pursuant to said Section 8(a), may
determine.
|
The
information in this Prospectus is not complete and may be changed. We may
not sell these securities until the registration statement filed with the
Securities and Exchange Commission is effective. This prospectus is not an
offer to sell these securities and is not soliciting an offer to buy these
securities in any state where the offer or sale is not
permitted.
|
SUBJECT
TO COMPLETION, DATED [ ]
[ ], 2010
PROSPECTUS
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
Common
Stock
This
prospectus relates to the offering of
[ ] shares of common
stock of India Globalization Capital, Inc. (“IGC” or “the Company”), par value
$0.0001 per share. We have retained ___________ as
underwriter in connection with this offering, which is made on a ______
basis.
Our units, shares of common stock and warrants are
currently traded on the NYSE Amex Equities (“NYSE Amex”) under the symbols
“IGC.U,” “IGC” and “IGC.WS,” respectively. As of March 8, 2010, the closing sale
price of our common stock was $1.26, the closing sale price of our units was
$1.30 (the last trade
having occurred on March 2), and the closing sale price of our
warrants was $0.05.
In
reviewing this prospectus, you should carefully consider the matters described
under the heading “Risk Factors” beginning on page 4.
| Per Share |
Total
|
|||||||
|
Price
to public
|
$ | $ | ||||||
|
Underwriting
discount
|
$ | $ | ||||||
|
Proceeds,
before expenses, to India Globalization
Capital, Inc.
|
$ | $ | ||||||
We
have granted the underwriter a 30-day option to purchase up to
[ • ] additional shares of common
stock at the same price, and on the same terms, solely to cover over-allotments,
if any.
Neither
the Securities and Exchange Commission nor any state securities commission has
approved or disapproved these securities or determined if this prospectus is
truthful or complete. Any representation to the contrary is a criminal
offense.
The date
of this prospectus is __________, 2010.
|
1
|
|
|
4
|
|
|
11
|
|
|
12
|
|
|
12
|
|
|
12
|
|
|
12
|
|
|
15
|
|
|
19
|
|
|
33
|
|
|
40
|
|
|
47
|
|
|
51
|
|
|
51
|
|
|
53
|
|
|
56
|
|
|
59
|
|
|
59
|
|
|
59
|
|
|
60
|
All
references to “IGC,” “we,” “our,” “us,” and similar terms in this prospectus
refer to India Globalization Capital, Inc.
Some of
the industry data contained in this prospectus are derived from data from
various third-party sources. While we are not aware of any misstatements
regarding any industry data presented herein, such data is subject to change
based on various factors, including those discussed under the heading “Risk
Factors” in this prospectus.
ABOUT
THIS PROSPECTUS
This
prospectus is part of a registration statement that we have filed with the
Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC” or the “Commission”) utilizing a
shelf registration process. Under this shelf registration process, we may, from
time to time, offer and sell shares of the common stock of the Company pursuant
to this prospectus. It is important for you to read and consider all of the
information contained in this prospectus and any applicable prospectus
supplement before making a decision whether to invest in the common stock. You
should also read and consider the information contained in the documents that we
have incorporated by reference as described in “Where You Can Find More
Information” and “Incorporation of Certain Documents by Reference” in this
prospectus.
You
should rely only on the information contained in this prospectus and any
applicable prospectus supplement, including the information incorporated by
reference. We have not authorized anyone to provide you with different
information. We are not offering to sell or soliciting offers to buy, and will
not sell, any securities in any jurisdiction where it is unlawful. You should
assume that the information contained in this prospectus or any prospectus
supplement, as well as information contained in a document that we have
previously filed or in the future will file with the SEC and incorporate by
reference into this prospectus or any prospectus supplement, is accurate only as
of the date of this prospectus, the applicable prospectus supplement or the
document containing that information, as the case may be.
The
following is a summary of some of the information contained in this prospectus.
In addition to this summary, we urge you to read the entire prospectus
carefully, especially the risks relating to our business and common stock
discussed under the heading “Risk Factors” and our financial
statements.
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
Our
Business
Background of India Globalization
Capital, Inc. (IGC)
IGC, a
Maryland corporation, was organized on April 29, 2005 as a blank check
company formed for the purpose of acquiring one or more businesses with
operations primarily in India through a merger, capital stock exchange, asset
acquisition or other similar business combination or acquisition. On March 8,
2006, we completed an initial public offering. On February 19, 2007,
we incorporated India Globalization Capital, Mauritius, Limited (IGC-M), a
wholly owned subsidiary, under the laws of Mauritius. On March 7,
2008, we consummated the acquisition of 63% of the equity of Sricon
Infrastructure Private Limited (Sricon) and 77% of the equity of Techni Bharathi
Limited (TBL). The shares of the two Indian companies, Sricon and TBL, are held
by IGC-M.
Most of
the shares of Sricon and TBL acquired by IGC were purchased directly from the
companies. IGC purchased a portion of the shares from the existing owners of the
companies. The founders and management of Sricon own 78% of Sricon
(after giving effect to the deconsolidation described below) and the founders
and management of TBL own 23% of TBL.
In
connection with the acquisitions, IGC borrowed approximately $17 million from
Sricon. According to the original purchase agreement, if the
loan is not repaid, then the result could be a reduction in IGC’s ownership
percentage of Sricon.
The
acquisitions were accounted for under the purchase
method of accounting. Under this method of accounting, for accounting
and financial purposes, IGC-M, Limited was treated as the acquiring entity and
TBL as the acquired entity
Effective
October 1, 2009 we decreased our ownership in Sricon Infrastructure from 63% to
22.3%. As described earlier, on March 7, 2008 we consummated the
Sricon Acquisition by purchasing 63% for about $29 million (based on an exchange
rate of 40 INR for $1 USD). We subsequently borrowed around $17.9
million (based on 40 INR for 1 USD) from Sricon. Through 2008 and
2009 we expanded our business offerings beyond construction to include a rapidly
growing materials business. We have successfully repositioned the company as a
materials and construction company; with construction activity in our TBL
subsidiary and materials activity in our other subsidiaries. Rather
than continue to owe Sricon $17.9 million, and more importantly, continue to
fund two construction companies, we decreased our ownership in Sricon by an
amount proportionate to the loan. The impact of this is that we no
longer owe Sricon $17.9 million and our corresponding ownership is a
non-controlling interest. The deconsolidation of Sricon from the
balance sheet of IGC, resulted in shrinkage of the IGC balance sheet,
compared to March 31, 2009, and a one-time charge on the P&L in the quarter
ended December 31, 2009. Post deconsolidation, earnings and losses
from Sricon are accounted for using the equity method of
accounting.
The consolidated IGC financial statements provided after the date
of deconsolidation (October 1, 2009) do not include a line by line consolidation
of Sricon. However, the consolidated IGC financials before
October 1, 2009 include a line by line consolidation of
Sricon.
Unless the context requires otherwise, all references in this
report to the “Company”, “IGC”, “we”, “our”, and “us” refer to India
Globalization Capital, Inc, together with its wholly owned subsidiary IGC-M, and
its subsidiaries and non-controlling interests (TBL, IGC-MPL, IGC-LPL, IGC IMT
and Sricon,).
Background
of India based Subsidiaries
Techni
Bharathi Limited (“TBL”) was incorporated as a public (but not listed on the
stock market) limited company on June 19, 1982 in Cochin, India. TBL
is an engineering and construction company engaged in the execution of civil
construction and structural engineering projects. TBL has a focus in
the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Assam and Tamil Nadu. Its
present and past clients include various Indian government
organizations.
IGC
Materials, Private Limited (“IGC-MPL”) and IGC Logistics, Private
Limited (“IGC-LPL”), are based in Nagpur India and were incorporated in June
2009. The two companies focus on infrastructure materials like rock
aggregate, bricks, concrete and other material as well as the logistical support
for the transportation of infrastructure material. IGC India Mining
and Trading (“IGC-IMT”) was incorporated in December 2008 in Chennai,
India. IGC-IMT is involved in the
export of iron ore to China. IGC-MPL, IGC-LPL and IGC-IMT are all wholly owned
subsidiaries of IGC-M.
Our
approach is to offer a suite of services to customers involving construction as
well as sale and transportation of materials.
Core Business
Competencies
We offer
an integrated approach in our customer service delivery based on core
competencies that we have demonstrated over the years. This
integrated approach provides us with an advantage over our
competitors.
Our core
business competencies include the following:
|
1)
|
Highway
and heavy construction
|
|
2)
|
Mining
and Quarrying
|
|
3)
|
Construction
and maintenance of high temperature
plants
|
Our
Growth Strategy and Business Model
Our
growth strategy and business model is the following:
|
1)
|
Deepen
our relationships with our existing construction customers by providing
them infrastructure materials like iron ore, rock aggregate, concrete,
coal and associated logistical
support.
|
|
2)
|
Expand
our materials offering by expanding the number of rock aggregate quarries
and other material infrastructure.
|
|
3)
|
Leverage
our expertise in the logistics and supply of iron ore by increasing the
number of shipping hubs we operate from and expand our offering into China
and other Asian countries to take advantage of the infrastructure growth
in India, China and other Asian
countries.
|
|
4)
|
Expand
the number of recurring contracts for infrastructure build out to
customers that can benefit from our portfolio of
offerings.
|
|
5)
|
As
part of our financing plan, aggressively pursue the collection of delay
claims in past projects.
|
Please
see the “Risk Factors” section commencing on page 4 for more information
concerning the risks of investing in our company.
Where
You Can Find More Information
We have
three securities listed on the NYSE Amex: (1) common stock, $.0001 par value
(ticker symbol: IGC), (2) redeemable warrants to purchase common stock (ticker
symbol: IGC.WS) and (3) units consisting of one share of common stock and two
redeemable warrants to purchase common stock (ticker symbol:
IGC.U).
We will
make available on our website, www.indiaglobalcap.com,
our annual reports, quarterly reports, proxy statements as well as up to- date
investor presentations. The registration statement and its exhibits, as
well as our other reports filed with the SEC, can be inspected and copied at the
SEC’s public reference room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, D.C.
20549. The public may obtain information about the operation of the public
reference room by calling the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330. In addition, the SEC
maintains a web site at http://www.sec.gov which contains
the Form S-1 and other reports, proxy and information statements and
information regarding issuers that file electronically with the
SEC.
We have
filed a registration statement on Form S-1 with the SEC registering under
the Securities Act the common stock that may be distributed under this
prospectus. This prospectus, which is a part of such registration statement,
does not include all of the information contained in the registration statement
and its exhibits. For further information regarding us and our common stock, you
should consult the registration statement and its exhibits.
Statements
contained in this prospectus concerning the provisions of any documents are
summaries of those documents, and we refer you to the documents filed with the
SEC for more information. The registration statement and any of its amendments,
including exhibits filed as a part of the registration statement or an amendment
to the registration statement, are available for inspection and copying as
described above.
The
Offering
We are
offering ____________ shares of our common stock pursuant to this
prospectus.
|
Issuer
|
India
Globalization Capital, Inc., a Maryland corporation
|
|
|
Shares
Offered
|
[ ]
shares
|
|
|
Shares
Outstanding
|
12,898,291 shares
|
|
|
Use
of Proceeds
|
We
expect proceeds from this offering to us to be approximately
$[ ], after underwriters’ discounts and before
deducting the estimated expenses for the offering. We intend to use
the proceeds for working capital, operating expenses and other general
corporate purposes. We may also use the proceeds to repay
indebtedness.
|
|
|
NYSE
Amex Symbol for Common Stock:
|
IGC
|
|
|
Risk
Factors
|
You
should carefully consider the matters discussed under the heading “Risk
Factors”
|
You
should carefully consider the following risk factors, together with all of the
other information included in this prospectus in evaluating us and our common
stock and other securities. If any of the following risks and uncertainties
develop into actual events, they could have a material adverse effect on our
business, financial condition or results of operations. In that case, the
trading price of our common stock and other securities also could be
adversely affected. We make various
statements in this section, which constitute “forward-looking statements.” See
“Forward-Looking Statements.”
RISKS
ASSOCIATED WITH OUR INDUSTRY AND DOING BUSINESS IN INDIA
Any downgrading
of India’s debt rating by an international rating agency, or an increase in
interest rates in India, could have a negative impact on our ability to borrow
in India.
As we
scale our operations we may increase the amount of money we borrow for working
capital and leasing of equipment. Any adverse revisions to India’s credit
ratings for domestic and international debt by international rating agencies as
well as an increase in Indian interest rates may adversely impact our ability to
finance growth through debt and could lead to a tightening of our margins,
adversely affecting our operating income.
A
change in government policy, a down turn in the Indian economy or a natural
disaster could adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of
operations and future prospects.
Our
construction business is dependent on the government of India as well as the
state governments for contracts. Their operations and financial
results may be affected by changes in the government’s policy towards building
infrastructure. In addition, the slow down in the Indian economy has
caused the government to slow down the pace of infrastructure building, which if
unchanged could adversely affect our future performance. We foresee
no immediate changes to government policy or market conditions that would
adversely affect our ability to conduct business other than limited access to
credit.
Political,
economic, social and other factors in India may adversely affect
business.
Our
ability to grow our business may be adversely affected by political, economic,
social and religious factors, changes in Indian law or regulations and the
status of India’s relations with other countries. In addition, the economy of
India may differ favorably or unfavorably from the U.S. economy in such respects
as the rate of growth of gross domestic product, the rate of inflation, capital
reinvestment, resource self-sufficiency and balance of payments position.
According to the World Factbook published by the United States Central
Intelligence Agency, the Indian government has exercised and continues to
exercise significant influence over many aspects of the economy, and
privatization of government-owned industries proceeds at a slow pace.
Accordingly, Indian government actions in the future could have a significant
effect on the Indian economy, which could have a material adverse affect on our
ability to achieve our business objective.
Since
mid-1991, the Indian government has committed itself to implementing an economic
structural reform program with the objective of liberalizing India’s exchange
and trade policies, reducing the fiscal deficit, controlling inflation,
promoting a sound monetary policy, reforming the financial sector, and placing
greater reliance on market mechanisms to direct economic activity. A significant
component of the program is the promotion of foreign investment in key areas of
the economy and the further development of, and the relaxation of restrictions
in, the private sector. These policies have been coupled with the express
intention to redirect the government’s central planning function away from the
allocation of resources and toward the issuance of indicative guidelines. While
the government’s policies have resulted in improved economic performance, there
can be no assurance that the economic improvement will be sustained. Moreover,
there can be no assurance that these economic reforms will persist, and that any
newly elected government will continue the program of economic liberalization of
previous governments. Any change may adversely affect Indian laws and policies
with respect to foreign investment and currency exchange. Such changes in
economic policies could negatively affect the general business and economic
conditions in India, which could in turn adversely affect our
business.
Terrorist
attacks and other acts of violence or war within India or involving India and
other countries could adversely affect the financial markets and our
business.
Terrorist
attacks and other acts of violence could have the direct effect of destroying
our plant and property causing a loss and interruption of
business. According to the World Factbook, religious and border
disputes persist in India and remain pressing problems. For example, India has
from time to time experienced civil unrest and hostilities with neighboring
countries such as Pakistan. The longstanding dispute with Pakistan over the
border Indian states of Jammu and Kashmir, a majority of whose population is
Muslim, remains unresolved. If the Indian government is unable to control the
violence and disruption associated with these tensions, the results could
destabilize the economy and, consequently, adversely affect our
business.
Since
early 2003, there have also been military hostilities and civil unrest in
Afghanistan, Iraq, Pakistan and other Asian countries. These events could
adversely influence the Indian economy and, as a result, negatively affect our
business.
While we
may have insurance to cover some of these risks and can file claims against the
contracting agencies, there can be no guarantee that we will be able to collect
in a timely manner. Further, India has seen an increase in
politically motivated insurgencies and a fairly active communist
following. Any uprising from these groups can delay our roadwork and
disrupt our business. Terrorist attacks, insurgencies or the threat
of violence could slow down road building activity and acquisition of materials
which could adversely affect our business.
Exchange controls
that exist in India may limit our ability to utilize our cash flow
effectively.
We are
subject to India’s rules and regulations on currency conversion. In India, the
Foreign Exchange Management Act or FEMA, regulates the conversion of the Indian
rupee into foreign currencies. However, comprehensive amendments have
been made to FEMA to support the economic liberalization. Companies
are now permitted to operate in India without any special restrictions,
effectively placing them on par with wholly Indian owned companies. In addition,
foreign exchange controls have been substantially relaxed. Notwithstanding these
changes, the Indian foreign exchange market is not yet fully developed and we
cannot assure that the Indian authorities will not revert back to regulating
companies and imposing new restrictions on the convertibility of the Indian
rupee. Any future restrictions on currency exchanges may limit our ability to
use our cash flow for the distribution of dividends to our stockholders or to
fund operations we may have outside of India.
Changes in the
exchange rate of the Indian rupee may negatively impact our revenues and
expenses.
Our
operations are primarily located in India and we receive payment in Indian
rupees. As the results of operations are reported in US dollars, to
the extent that there is a decrease in the exchange rate of Indian rupees into
US dollars, such a decrease could have a material impact on our operating
results or financial condition.
Returns
on investment in Indian companies may be decreased by withholding and other
taxes.
Our
investments in India will incur tax risk unique to investment in India and in
developing economies in general. Income that might otherwise not be subject to
withholding of local income tax under normal international conventions may be
subject to withholding of Indian income tax. Under treaties with
India and under local Indian income tax law, income is generally sourced in
India and subject to Indian tax if paid from India. This is true whether or not
the services or the earning of the income would normally be considered as from
sources outside India in other contexts. Additionally, proof of payment of
withholding taxes may be required as part of the remittance procedure. Any
withholding taxes paid by us on income from our investments in India may or may
not be creditable on our income tax returns.
We intend
to avail ourselves of income tax treaties with India and minimize any Indian
withholding tax or local taxes. However, there is no assurance that
the Indian tax authorities will always recognize such treaties and its
applications. We have also created a foreign subsidiary in Mauritius, in
order to limit the potential tax exposure.
RISKS
ASSOCIATED WITH OUR BUSINESS
The
cost of obtaining bank financing may reduce our income.
TBL has restructured some
of its bank debt and may, in the future, face higher interest rates or will
require higher collateral with the banks. This increases the
cost of money for the construction business and could decrease our
margins. IGC expects to provide collateral support for two to three
years, by which time we expect the credit worthiness of the construction
business to increase to adequate levels. Further, collateral that has
been provided to the banks consists mostly of real estate, which has fallen in
value, thus reducing our ability to borrow.
Availability
of raw materials at competitive prices.
Construction
contracts are primarily dependent on adequate and timely supply of raw
materials, such as cement, steel and aggregates, at competitive prices. As the
demand from competing larger and well-established firms increases for procuring
raw materials, we could face an increase in the price of raw materials that may
negatively impact profitability.
Some
of our business is dependent on contracts awarded by the Government and its
agencies.
The
construction business is dependent on central and state budget allocations to
the infrastructure sector. We derive the bulk of our construction revenue from
contracts awarded by the central and state governments of India and their
agencies. If there are delays in the payment of invoices by the
government, our working capital requirements could increase.
Compliance
with the Foreign Corrupt Practices Act could adversely impact our competitive
position. Failure to comply could subject us to penalties and other adverse
consequences.
We are
subject to the United States Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, which generally
prohibits United States public companies from engaging in bribery of or other
prohibited payments to foreign officials to obtain or retain business. While we
will take precautions to educate the employees of our subsidiaries of the
Foreign Corrupt Practices Act, there can be no assurance that we or the
employees or agents of our subsidiaries will not engage in such conduct, for
which we might be held responsible. We could suffer penalties that may have a
material adverse effect on our business, financial condition and results of
operations.
We may issue shares of our capital
stock, including through convertible debt securities, which would reduce the
equity interest of our stockholders and likely cause a change in control of our
ownership.
Our
certificate of incorporation authorizes the issuance of up to
75,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $.0001 per share and
1,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $.0001 per share. There
are currently approximately 47,000,000 authorized but unissued shares of our
common stock available for issuance (after appropriate reservation for the
issuance of shares upon full exercise of our outstanding warrants and the
purchase option granted to Ferris, Baker Watts, Inc. and shares authorized for
issuance under our 2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan, including outstanding options
issued there under) and all of the 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock
available for issuance. We have recently issued 1,060,000 shares of our common
stock in connection with a private placement of debt securities and an exchange
of previously issued debt securities for new debt securities and the common
stock and may engage in similar private placements in the future. The
issuance of additional shares of our common stock including upon conversion of
any debt securities:
|
·
|
may
significantly reduce the equity interest of our existing shareholders;
and
|
|
·
|
may
adversely affect prevailing market prices for our common stock, warrants
or units.
|
We
may issue notes or other debt securities, which may adversely affect our
leverage and financial condition.
During
each of 2008 and 2009, we sold debt securities in the principal amount of
$2,000,000 in a private placement and may engage in similar private
placements in the future. The incurrence of this debt:
|
·
|
may
lead to default and foreclosure on our assets if our operating
revenues are insufficient to pay our debt
obligations;
|
|
·
|
may
cause an acceleration of our obligations to repay the debt even if we make
all principal and interest payments when due if we breach the covenants
contained in the terms of the debt
documents;
|
|
·
|
may
create an obligation to immediately repay all principal and accrued
interest, if any, upon demand to the extent any debt securities are
payable on demand; and
|
|
·
|
may
hinder our ability to obtain additional financing, if necessary, to the
extent any debt securities contain covenants restricting our ability to
obtain additional financing while such security is outstanding, or to the
extent our existing leverage discourages other potential
investors.
|
Additional
capital may be costly or difficult to obtain.
Additional
capital, whether through the offering of equity or debt securities, may not be
available on reasonable terms or at all, especially in light of the recent
downturn in the economy and dislocations in the credit and capital markets. If
we are unable to obtain required additional capital, we may have to curtail our
growth plans or cut back on existing business and, further, we may not be able
to continue operating if we do not generate sufficient revenues from operations
needed to stay in business. We may incur substantial costs in
pursuing future capital financing, including investment banking fees, legal
fees, accounting fees, securities law compliance fees, printing and distribution
expenses and other costs. We may also be required to recognize non-cash expenses
in connection with certain securities we issue, such as convertible notes and
warrants, which may adversely impact our financial condition.
Leveled
penalties for time overruns may adversely affect our economic
performance.
TBL
executes construction contracts primarily in the roads and infrastructure
development sectors. TBL typically enters into high value contracts for these
activities, which impose penalties if contracts are not executed in a timely
manner. If TBL is unable to meet the performance criteria
as prescribed by respective contracts, then levied penalties may adversely
affect our financial performance.
Our
business is dependent on continuing relationships with clients and strategic
partners.
Our
business is dependent on developing and maintaining strategic alliances with
contractors that undertake turnkey contracts for infrastructure development
projects as well as government organizations. The business and our
results could be adversely affected if we are unable to maintain continuing
relationships and pre-qualified status with key clients and strategic
partners.
Our
business model relies heavily on our management team and any
unexpected loss of key officers may adversely affect our
operations
The
continued success of our business is largely dependent on the continued services
of key employees. The loss of the services of certain key personnel,
without adequate replacement, could have an adverse effect on our performance.
Our senior management as well as the senior management of our subsidiaries have
played a significant role in developing and executing the overall business plan,
maintaining client relationships, proprietary processes and
technology. While no one is irreplaceable, the loss of the
services of any would be disruptive to our business. Our
strategy, management, financial and operational oversight are heavily dependent
on our Founder and CEO. The loss of our CEO could have a significant adverse
effect on our business. In order to mitigate these risk factors we
are recruiting professional managers and expanding the executive ranks as well
as pursuing succession-planning initiatives, but this will take time and
there can be no guarantees that these mitigation efforts will be
successful.
Quarterly financial
results will vary.
Factors
that may contribute to the variability of quarterly revenue, operating results
or profitability include:
|
·
|
Fluctuations
in revenue due to seasonality: For example, during the monsoon
season, the heavy rains slow down construction work resulting
in an overall slow down of the supply of materials as well as construction
activity. This results in uneven revenue and operating results
through the quarters. In general, the months between June
and September are the rainy seasons and these tend to be slower quarters
than the others.
|
Our
future operating results and the market price of our common stock could be
materially adversely affected if we are required to write down the carrying
value of goodwill associated with any of our businesses in the
future.
We review
our goodwill balance for impairment on at least an annual basis through the
application of a fair value-based test. Our estimate of fair value is based
primarily on projected future results and cash flows and other assumptions. In
addition, we review long-lived assets whenever events or changes in
circumstances indicate that its carrying amount may not be recoverable. In the
fourth quarter of our 2009 fiscal year, we performed our annual test for
goodwill impairment and determined that our goodwill was not impaired. In the
future, if our projected discounted cash flows associated with our businesses do
not exceed the carrying value of their net assets, we may be required to record
write downs of the carrying value of goodwill or other long-lived assets
associated with any of our businesses and our operating results and the market
price of our common stock may be materially adversely affected.
As of March 31 2009 our goodwill balance was $17.5 million and as
of December 31 2009 our goodwill balance
was $6.9 million respectively . We perform an annual goodwill impairment
test during the fourth quarter of each fiscal year, or more frequently if an
event occurs or circumstances change between annual tests that would more likely
than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying amount.
The 2008-2009 recession has impacted our financial results and has reduced
near-term purchases from certain of our key customers. We may determine that our
expectations of future financial results and cash flows from one or more of our
businesses has decreased or a decrease in stock valuation may occur, which could
result in a review of our goodwill associated with these businesses. Since a
large portion of the value of our intangibles has been ascribed to projected
revenues from certain key customers, a change in our expectation of future cash
from one or more of these customers could indicate potential impairment to the
carrying value of our assets.
Our
subsidiaries may become involved in litigation in the future.
Our
subsidiaries are fairly large companies and may have to initiate actions in the
Indian Courts to enforce their rights and may also be drawn into legal
litigation. The expenses of litigation and any judgments against us
could have a material adverse effect on us.
We
face competition in the Indian infrastructure industry.
The
Indian real estate and infrastructure industries are increasingly attracting
foreign capital. We currently have competition from international as
well as domestic companies that operate at the national
level. Smaller localized contractors and companies are also competing
in their respective regions. If we are unable to offer competitive
prices and obtain contracts, there could be a significant reduction in our
revenue.
A
down turn in the economy could adversely affect our business, financial
condition, results of operations and future prospects.
A
generally adverse financial global economy or a regional recession
including one in India and or China could adversely affect commodity prices and
infrastructure build out in Asia, which in turn could adversely affect our
future performance and result in a drop in our stock price.
Our
operations are sensitive to weather conditions.
Our
business activities in India could be materially and adversely affected by
severe weather conditions. Severe weather conditions may require us to evacuate
personnel or curtail services and may result in damage to a portion of our fleet
of equipment or to our facilities, resulting in the suspension of operations,
and may further prevent us from delivering materials to project sites in
accordance with contract schedules or generally reduce our
productivity. Difficult working conditions and extremely high
temperatures also adversely affect our operations during summer months and
during monsoon season, which restrict our ability to carry on construction and
mining activities and fully utilize our resources.
Depending
on the onset of the monsoons, revenue recorded in the first half of our fiscal
year, particularly between June through September, is traditionally lower than
revenue recorded during the second half of our fiscal year. During
periods of curtailed activity due to adverse weather conditions, we may continue
to incur operating expenses as well as build material reserves reducing
profitability.
We incur costs as a result of
operating as a public company. Our management is required to
devote substantial time to new compliance initiatives. Because we
report in USGAAP, we may experience untimely close of our books and records, in
India, and delays in the preparation of financial statements and related
disclosures.
As part
of a public company with substantial operations, we are experiencing an
increase in legal, accounting and other expenses. In addition the
Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (the “SOX” act), as well as new rules subsequently
implemented by the SEC and the NYSE Amex, have imposed various requirements on
public companies, including requiring changes in corporate governance
practices. Our management and other personnel need to devote a
substantial amount of time to these compliance initiatives. We have
completed the testing of internal controls in all our
subsidiaries. We expect to carry out the evaluations
and install systems and processes as required. However, we cannot be
certain as to the timing of completion of evaluation testing and remediation
actions or the impact of the same on our operations. Further, it is
difficult to hire personnel in India that are familiar with
USGAAP. However, we have hired several reputed consultants to help
review internal reporting and disclosures as well as train our India based staff
in the rigors of SEC reporting and USGAAP. We currently, do not
foresee a problem other than the time required to adequately train and
streamline the processes.
The
audit report provided by Yoganandh and Ram will require a review by a US
firm.
While our
audit firm, Yoganandh & Ram, is registered with the Public Company
Accounting Oversight Board (the “PCAOB”), the SEC requires that the audits
conducted by Yoganandh & Ram, be reviewed by another PCAOB registered
firm. If the review identifies changes to an audit, we will be
required to amend our annual report as filed on Form 10-K incorporating the
audited financial statements. The requirement of the review is
expected to increase our legal, accounting and other
expenses.
RISKS
RELATED TO OUR SECURITIES
The
Company has warrants outstanding, which could dilute the number of shares
outstanding.
At the
time the warrants are exercised, the company will get the exercise price, unless
the exercise is cashless. In either case, such an exercise will
also increase the number of shares outstanding. This may adversely
affect the share price as the supply of shares eligible for sale in the public
market will increase. The increased number of shares offered for sale
in the public market may exceed the public demand to buy shares at a given
market price resulting in the market price adjusting downward to equalize supply
and demand.
Although
we are required to use our best efforts to have an effective registration
statement covering the issuance of the shares underlying the public warrants at
the time that our warrant holders exercise their public warrants, we cannot
guarantee that a registration statement will be effective, in which case our
warrant holders may not be able to exercise our public warrants and such
warrants may expire worthless.
Holders
of our public warrants will be able to exercise the warrants only if a current
registration statement under the Securities Act of 1933 relating to the shares
of our common stock underlying the warrants is then effective. Although we have
undertaken in the warrant agreement, and therefore have a contractual
obligation, to use our best efforts to maintain a current registration statement
covering the shares underlying the public warrants to the extent required by
federal securities laws, and we intend to comply with such undertaking, with
such a registration statement currently effective, we cannot assure you that we
will be able to do so. In no event shall we be liable for, or any registered
holder of any warrant be entitled to receive, (a) physical settlement in
securities unless the conditions and requirements set forth in the warrant
agreement have been satisfied or (b) any net-cash settlement or other
consideration in lieu of physical settlement in securities. The value of the
public warrants may be greatly reduced if a registration statement covering the
shares issuable upon the exercise of the warrants is not kept current. Such
warrants may expire worthless.
Because
the warrants sold in the private placements were originally issued pursuant to
an exemption from registration requirements under the federal securities laws,
the holders of the warrants sold in the private placement will be able to
exercise their warrants even if, at the time of exercise, a prospectus relating
to the common stock issuable upon exercise of such warrants is not current. As a
result, the holders of the warrants purchased in the private placements will not
have any restrictions with respect to the exercise of their warrants. As
described above, the holders of the public warrants will not be able to exercise
them unless we have a current registration statement covering the shares
issuable upon their exercise.
If
equity research analysts do not publish research or reports about our business
or if they issue unfavorable commentary or downgrade our common stock, the price
of our common stock could decline.
The
trading market for our common stock will rely in part on the research and
reports that equity research analysts publish about our business and us. We do
not control these analysts. The price of our stock could decline if one or more
equity analysts downgrade our stock or if those analysts issue other unfavorable
commentary or cease publishing reports about our business or us.
We
do not currently intend to pay dividends, which may limit the return on your
investment in us.
We
currently intend to retain all available funds and any future earnings for use
in the operation and expansion of our business and do not anticipate paying any
cash dividends in the foreseeable future.
We
believe that some of the information in this prospectus constitutes
forward-looking statements within the definition of the Private Securities
Litigation Reform Act of 1995. You can identify these statements by
forward-looking words such as “may,” “should,” “believes,” “expects,” “intends,”
“anticipates,” “thinks,” “plans,” “estimates,” “seeks,” “predicts,” “potential”
or similar words or the negative of these words or other variations on these
words or comparable terminology. You should read statements that contain these
words carefully because they discuss future expectations, contain projections of
future results of operations or financial conditions or state or other forward
looking information.
While we
believe it is important to communicate our expectations to our stockholders,
there may be events in the future that we are not able to accurately predict or
over which we have no control. The risk factors and cautionary language
discussed in this prospectus provide examples of risks, uncertainties and events
that may cause actual results to differ materially from the expectations
described by us in our forward-looking statements, including among other
things:
· Competition in the road building
sector.
· Legislation by the government of
India.
· General economic conditions and the
Indian growth rates.
· Our ability to win licenses, contracts
and execute.
You
should be aware that the occurrence of the events described in these risk
factors and elsewhere in this prospectus could have a material adverse effect on
our business, financial condition and results of operations.
You are
cautioned not to place undue reliance on these forward-looking statements, which
speak only as of the date of this prospectus.
All
forward-looking statements included herein attributable to us or any person
acting on either party’s behalf are expressly qualified in their entirety by the
cautionary statements contained or referred to in this section. Except to the
extent required by applicable laws and regulations, we undertake no obligation
to update these forward-looking statements to reflect events or circumstances
after the date of this prospectus or to reflect the occurrence of unanticipated
events.
Before
you decide to invest in our securities, you should be aware that the occurrence
of the events described in the “Risk Factors” section and elsewhere in this
prospectus could have a material adverse effect on us.
We expect
proceeds from this offering to us to be approximately
$[ ], after underwriters’ discounts and before deducting
the estimated expenses for the offering. We are contractually required to
use 40% of the net proceeds of this offering in excess of $500,000 to repay two
outstanding promissory notes in the principal amount of $2,120,000 and
$2,000,000, respectively. The notes bear no interest and are due and
payable on October 5, 2010 and October 16, 2010 respectively or earlier upon a
change in control of the company or an event of default as set forth in the
notes. The proceeds of the notes were used for general working
capital purposes, primarily for our iron ore export business in the case of the
$2,000,000 note. We intend to use the balance of the proceeds for
working capital, operating expenses and other general corporate purposes. We may
also use the balance of the proceeds to further repay outstanding indebtedness,
although we do not currently expect to do so.
We have
not paid any cash dividends on its common stock to date. It is the
present intention of the board of directors to retain all earnings, if any, for
use in the business operations, and consequently, the board does not anticipate
declaring any dividends in the foreseeable future. The payment of any
dividends will be with the discretion of the board of directors and will be
contingent upon our financial condition, results of operations, capital
requirements and other factors our board deems relevant.
The
following table shows, for the last eight fiscal quarters, the high and low
closing prices per share of the Common Stock, Warrants and Units as quoted on
the NYSE Amex:
|
Common
Stock
|
Warrants
|
Units
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Quarter
Ended
|
High
|
Low
|
High
|
Low
|
High
|
Low
|
||||||||||||||||||
|
December
31, 2007
|
$ | 5.94 | $ | 5.69 | $ | 0.59 | $ | 0.34 | $ | 6.90 | $ | 6.35 | ||||||||||||
|
March
31, 2008
|
$ | 5.90 | $ | 3.60 | $ | 0.73 | $ | 0.25 | $ | 7.45 | $ | 4.15 | ||||||||||||
|
June
30, 2008
|
$ | 5.90 | $ | 3.81 | $ | 1.30 | $ | 0.58 | $ | 8.80 | $ | 5.28 | ||||||||||||
|
September
30, 2008
|
$ | 4.99 | $ | 4.50 | $ | 1.00 | $ | 0.55 | $ | 6.86 | $ | 5.65 | ||||||||||||
|
December
31, 2008
|
$ | 4.78 | $ | 0.70 | $ | 0.53 | $ | 0.01 | $ | 5.75 | $ | 0.01 | ||||||||||||
|
March
31, 2009
|
$ | 1.10 | $ | 0.33 | $ | 0.13 | $ | 0.02 | $ | 1.07 | $ | 0.40 | ||||||||||||
|
June
30, 2009
|
$ | 1.25 | $ | 1.12 | $ | 0.06 | $ | 0.06 | $ | 1.80 | $ | 1.02 | ||||||||||||
|
September
30, 2009
|
$ | 1.86 | $ | 0.88 | $ | 0.20 | $ | 0.05 | $ | 2.32 | $ | 1.00 | ||||||||||||
|
December
31, 2009
|
$ |
2.20
|
$ |
1.33
|
$ |
0.22
|
$ |
0.04
|
$ |
2.50
|
$ |
1.34
|
||||||||||||
A recent
reported closing price for our common stock, warrants and units is
set forth on the cover page of this prospectus. Continental Stock Transfer &
Trust Company is the transfer agent and registrar for our common stock. As of
September 30, 2009, we had 946 holders of record of
our common stock, 173 holders of record of our units and 1,054 holders of
record of our warrants.
Under the
terms and subject to the conditions contained in an underwriting agreement dated
____________ , 2010 , we have agreed to sell to
the underwriter, ____________, the following respective numbers of
shares of common stock:
|
Underwriter
|
Number
of Shares
|
|
The
underwriting agreement provides that the underwriters are obligated to purchase
all the shares of common stock in the offering if any are purchased, other than
those shares covered by the over-allotment option described below. The
underwriting agreement also provides that if an underwriter defaults, the
purchase commitments of non-defaulting underwriters will be
increased.
We have
granted to the underwriters a 30-day option to purchase up to ________
additional shares at the offering price less the underwriting discounts.
The option may be exercised only to cover any over-allotments of common
stock.
The
underwriters propose to offer the shares of common stock at the offering price
on the cover page of this prospectus supplement. After the offering,
_____________ may change the offering price and concession and discount to
broker/dealers.
The
following table summarizes the compensation and estimated expenses we will
pay:
|
Per
Share
|
Total
|
||||||
|
Without
Over-Allotment
|
With
Over-Allotment
|
Without
Over-Allotment
|
With
Over-Allotment
|
||||
|
Underwriting
discounts and commissions paid by us
|
|||||||
We have
agreed that during the period beginning from the date hereof and continuing to
and including the date __ days after the date of the prospectus supplement, we
will not offer, sell, contract to sell or otherwise dispose of any securities of
the Company which are substantially similar to our common stock (other than for
shares or stock options issued under employee stock plans, such plans as are
currently in existence and disclosed in the Prospectus), without the prior
written consent of _____________ (such consent not to be unreasonably
withheld or delayed) other than the sale of the shares to be sold by the Company
hereunder. During the period of __ days after the date of the prospectus
supplement, the Company will not file with the Commission or cause to become
effective any registration statement (other than a registration statement on
Form S-8 filed to register securities issued or to be issued under employee
stock option plans, each such plan as disclosed in the Prospectus) or prospectus
relating to any securities of the Company which are substantially similar to our
common stock without the prior written consent
of _____________
Our
executive officer and directors have agreed that they will not offer, sell,
contract to sell, pledge or otherwise dispose of, directly or indirectly, any
shares of our common stock or securities convertible into or exchangeable or
exercisable for any shares of our common stock, enter into a transaction that
would have the same effect, or enter into any swap, hedge or other arrangement
that transfers, in whole or in part, any of the economic consequences of
ownership of our common stock, whether any of these transactions are to be
settled by delivery of our common stock or other securities, in cash or
otherwise, or publicly disclose the intention to make any such offer, sale,
pledge or disposition, or to enter into any such transaction, swap, hedge or
other arrangement, without, in each case, the
prior written consent of _____________ for a period
__ days after the date of this prospectus supplement, provided, however, that
the foregoing shall not apply to a transfer of shares solely to the extent
necessary to satisfy federal income tax obligations with respect to any shares
of Common Stock issued prior to the date of this offering.
We have
agreed to indemnify the underwriters against liabilities under the Securities
Act, or contribute to payments that the underwriters may be required to make in
that respect.
In
connection with the offering the underwriters may engage in stabilizing
transactions, over-allotment transactions, syndicate covering transactions ad
penalty bids in accordance with Regulation M under the Exchange
Act.
|
|
·
Stabilizing transactions permit bids to purchase the underlying
security so long as the stabilizing bids do not exceed a specified
maximum.
|
|
|
|
|
|
·
Over-allotment involves sales by the underwriters of shares in
excess of the number of shares the underwriters are obligated to purchase,
which creates a syndicate short position. The short position may be
either a covered short position or a naked short position. In a
covered short position, the number of shares over-allotted by the
underwriters is not greater than the number of shares that they may
purchase in the over-allotment option. In a naked short position,
the number of shares involved is greater than the number of shares in the
over-allotment option. The underwriters may close out any covered
short position by exercising their over-allotment option and/or purchasing
shares in the open market.
|
|
|
|
|
|
·
Syndicate covering transactions involve purchases of the common
stock in the open market after the distribution has been completed in
order to cover syndicate short positions. In determining the source
of shares to close out the short position, the underwriters will consider,
among other things, the price of shares available for purchase in the open
market as compared to the price at which they may purchase shares through
the over-allotment option. If the underwriters sell more shares than
could be covered by the over-allotment option, a naked short position, the
position can only be closed out by buying shares in the open market.
A naked short position is more likely to be created if the underwriters
are concerned that there could be downward pressure on the price of the
shares in the open market after pricing that could adversely affect
investors who purchase in the
offering.
|
|
|
|
|
|
·
Penalty bids permit the representatives to reclaim a selling
concession from a syndicate member when the common stock originally sold
by the syndicate member is purchased in a stabilizing or syndicate
covering transaction to cover syndicate short
positions.
|
|
|
|
These
stabilizing transactions, syndicate covering transactions and penalty bids may
have the effect of raising or maintaining the market price of our common stock
or preventing or retarding a decline in the market price of the common
stock. As a result, the price of our common stock may be higher than the
price that might otherwise exist on the open market. These transactions
may be affected on the NYSE Amex or otherwise and if commenced, may be
discontinued at any time.
A
prospectus supplement and prospectus in electronic format may be made available
on the web sites maintained by one or more of the underwriters participating in
this offering.
IGC’s
historical information is derived from its audited financial statements for
the period from its inception (April 29, 2005) to March 31, 2006, for the fiscal
years ended March 31, 2007, 2008 and 2009. In addition, historical
information is derived from its unaudited financial statements for the 6 months
period ended September 30, 2009 and 2008. The information is only a
summary and should be read in conjunction with IGC’s historical financial
statements and related notes and IGC’s respective Management’s Discussion and
Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations contained elsewhere
herein. The historical results included below and elsewhere herein are not
indicative of the future financial performance of IGC.
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
Selected
Summary Statement of Income Data
(Audited)
Annual
results:
|
Selected
Statement of Operations Data:
|
Year
Ended
|
Year
Ended
|
Year
Ended
|
29-Apr-05
|
||||||||||||
|
31-Mar-09
|
31-Mar-08
|
31-Mar-07
|
To
March 31, 2006
|
|||||||||||||
|
Revenue
|
$
|
35,338,725
|
$
|
2,188,018
|
$
|
$
|
||||||||||
|
Other
Income-Interest, net
|
(577,934
|
)
|
471,698
|
3,171,818
|
210,584
|
|||||||||||
|
Net
Income (loss)
|
(521,576
|
)
|
(5,215,270
|
)
|
1,517,997
|
(443,840
|
)
|
|||||||||
|
Per
Share Data
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Earnings
per share – basic
|
$
|
(0.05
|
)
|
$
|
(0.61
|
)
|
$
|
0.11
|
$
|
(0.14
|
)
|
|||||
|
Earnings
per share - diluted
|
$
|
(0.05
|
)
|
$
|
(0.61
|
)
|
||||||||||
|
Weighted
Average Shares
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Basic
|
10,091,171
|
8,570,107
|
13,974,500
|
3,191,000
|
||||||||||||
|
Diluted
|
10,091,171
|
8,570,107
|
||||||||||||||
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
Selected
Summary Statement of Income Data
(unaudited)
Most
recent quarterly results:
|
Three
Months Ended
December
31, 2009
|
Three
Months Ended
December
31, 2008
|
Nine
Months Ended
December
31, 2009
|
Nine
Months Ended
December
31, 2008
|
|||||||||||||
|
Revenue:
|
$
|
5,909,024
|
$
|
3,836,428
|
13,994,503
|
$
|
32,263,680
|
|||||||||
|
Other
income (expense)
|
(389,953
|
)
|
(304,602
|
)
|
(1,051,428
|
)
|
(920,288
|
|||||||||
|
Equity
in (gain) loss of affiliates
|
16,446
|
16,446
|
||||||||||||||
|
Net
Income attributable to non-controlling interest
|
(7,574
|
)
|
550,207
|
(72,599
|
)
|
(936,996
|
||||||||||
|
Net
income (loss) attributed to controlling interest
|
$
|
(6,175,518
|
)
|
$
|
(1,734,078
|
)
|
$
|
(7,291,708
|
)
|
$
|
(374,835
|
|||||
|
Weighted
average number of shares outstanding:
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Basic
|
12,898,291
|
8,780,107
|
12,898,291
|
8,780,107
|
||||||||||||
|
Diluted
|
13,559,184
|
8,780,107
|
13,559,184
|
8,780,107
|
)
|
|||||||||||
|
Net
income per share:
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Basis
|
$
|
(0.48
|
)
|
$
|
(0.20
|
)
|
$
|
(0.56
|
)
|
$
|
(0.04
|
|||||
|
Diluted
|
$
|
(0.45
|
)
|
$
|
(0.20
|
)
|
$
|
(0.54
|
)
|
$
|
(0.04
|
|||||
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
Selected
Summary Balance Sheet Data
|
31-Dec-09
|
31-Mar-09
|
31-Mar-08
|
31-Mar-07
|
|||||||||||||
|
(unaudited)
|
(audited)
|
(audited)
|
(audited)
|
|||||||||||||
|
ASSETS
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Investments
held in trust fund
|
$
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
66,104,275
|
|||||||||
|
Total
Current Assets
|
15,946,918
|
19,498,584
|
32,896,447
|
70,385,373
|
||||||||||||
|
Total
Assets
|
35,965,433
|
51,832,513
|
67,626,973
|
70,686,764
|
||||||||||||
|
LIABILITIES
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Current
Liabilities
|
11,064,632
|
9,446,345
|
17,384,059
|
5,000,280
|
||||||||||||
|
Total
Liabilities
|
12,466,165
|
13,974,638
|
26,755,261
|
5,000,280
|
||||||||||||
|
Common
stock subject to possible conversion
|
12,762,785
|
|||||||||||||||
|
Total
stockholders’ equity
|
$
|
21,860,767
|
$
|
23,595,269
|
$
|
27,326,056
|
$
|
52,923,699
|
||||||||
The
following table sets forth certain selected financial data of Techni Bharathi Limited
(TBL). The selected financial data presented below was derived
from TBL’s audited consolidated financial statements for the
period April 1, 2007 through March 7, 2008 (date of acquisition) and for the
three year period ended March 31, 2007, and from TBL’s unaudited consolidated
financial statements for the year ended March 31, 2004. The
information is only a summary and should be read in conjunction with IGC’s
historical financial statements and related notes and our Management’s
Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations
contained elsewhere herein. Additional information regarding TBL’s historical
performance can be found in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-KSB for the
year ended March 31, 2008. The historical results included below and elsewhere
herein are not indicative of the future financial performance of IGC and its
subsidiaries.
Techni
Bharathi Limited (Predecessor)
Selected
Summary Statement of Income Data
|
(Amounts
in Thousand US Dollars, except share data and as stated
otherwise)
|
April
1 2007 to March 7, 2008
|
31-Mar-07
|
31-Mar-06
|
|||||||||
|
Revenue
|
$
|
5,321
|
$
|
4,318
|
$
|
2,285
|
||||||
|
Income
(loss) before income taxes
|
2,245
|
401
|
(2,369
|
)
|
||||||||
|
Income
taxes
|
(86
|
)
|
135
|
62
|
||||||||
|
Net
(loss)/income
|
1,988
|
536
|
(2,307
|
)
|
||||||||
|
Per
Share Data
|
||||||||||||
|
Basic
|
$
|
0.46
|
$
|
0.13
|
$
|
(0.54
|
)
|
|||||
|
Diluted
|
$
|
0.22
|
$
|
0.13
|
$
|
(0.54
|
)
|
|||||
|
Weighted
Average Shares
|
||||||||||||
|
Basic
|
4,287,500
|
4,287,500
|
4,287,500
|
|||||||||
|
Diluted
|
9,089,928
|
4,287,500
|
4,287,500
|
|||||||||
| (Amounts in Thousand US Dollars, except share data and as stated otherwise) |
31-Mar-05
|
Unaudited
31-Mar-04
|
|||||
|
Revenue
|
$
|
8,954
|
$
|
8,773
|
|||
|
Income
(loss) before income taxes
|
(3,823
|
)
|
(2,609
|
)
|
|||
|
Income
taxes
|
515
|
(63
|
)
|
||||
|
Net
(loss)/income
|
(3,308
|
)
|
(2,672
|
)
|
|||
|
Per
Share Data
|
|||||||
|
Basic
|
$
|
(0.77
|
)
|
$
|
(0.62
|
)
|
|
|
Diluted
|
$
|
(0.77
|
)
|
$
|
(0.62
|
)
|
|
|
Weighted
Average Shares
|
|||||||
|
Basic
|
4,287,500
|
4,287,500
|
|||||
|
Diluted
|
4,287,500
|
4,287,500
|
Techni
Bharathi Limited (Predecessor)
Selected
Summary Balance Sheet Data
|
(Amounts
in Thousand US Dollars)
|
7-Mar-08
|
31-Mar-07
|
31-Mar-06
|
|||||||||
|
ASSETS
|
||||||||||||
|
Cash
and cash equivalents
|
$
|
736
|
$
|
1,208
|
$
|
69
|
||||||
|
Inventories
|
1,428
|
1,284
|
4,182
|
|||||||||
|
Prepaid
and other assets
|
271
|
1,231
|
1,275
|
|||||||||
|
Property,
plant and equipment (net)
|
1,979
|
2,265
|
2,417
|
|||||||||
|
LIABILITIES
|
||||||||||||
|
Short
term borrowings and current portion of long-term loan
|
2,437
|
6,079
|
8,125
|
|||||||||
|
Trade
payable
|
2,222
|
1,502
|
987
|
|||||||||
|
Long
term debts, net of current portion
|
-
|
2,333
|
3,656
|
|||||||||
|
Advance
from customers
|
824
|
1,877
|
2,997
|
|||||||||
|
Total
Stockholders' equity
|
$
|
(397
|
)
|
$
|
(4,895
|
)
|
$
|
(5,438
|
)
|
|||
|
Unaudited
|
||||||||
|
(Amounts
in Thousand US Dollars)
|
31-Mar-05
|
31-Mar-04
|
||||||
|
ASSETS
|
||||||||
|
Cash
and cash equivalents
|
$ | 83 | $ | 107 | ||||
|
Inventories
|
4,459 | 4,922 | ||||||
|
Prepaid
and other assets
|
1,765 | 2,070 | ||||||
|
Property,
plant and equipment (net)
|
3,463 | 3,985 | ||||||
|
LIABILITIES
|
||||||||
|
Short
term borrowings and current portion of long-term loan
|
6,291 | 6,614 | ||||||
|
Trade
payable
|
3,341 | 2,738 | ||||||
|
Long
term debts, net of current portion
|
3,897 | 2,892 | ||||||
|
Advance
from customers
|
3,057 | 2,755 | ||||||
|
Total
Stockholders' equity
|
$ | (3,032 | ) | $ | 320 | |||
FINANCIAL
CONDITION AND RESULTS OF OPERATIONS
The
following discussion should be read in conjunction with the financial statements
and notes thereto included in this prospectus. Except for the historical
information contained herein, the discussion in this prospectus contains certain
forward-looking statements that involve risk and uncertainties, such as
statements of the Company’s plans, objectives, expectations and intentions as of
the date of this filing. The cautionary statements made in this document should
be read as being applicable to all related forward-looking statements wherever
they appear in this document. The Company’s actual results could differ
materially from those discussed here. Factors that could cause differences
include those discussed in the “Risk Factors” section as well as discussed
elsewhere herein.
Overview
In
response to India’s rapidly expanding economy, our primary focus is to
execute infrastructure projects through our subsidiaries such as
constructing interstate highways, rural roads, mining and quarrying, and
construction of high temperature cement and steel plants.
IGC, a
Maryland corporation was organized on April 29, 2005 as a blank check
company for the purpose of acquiring one or more businesses with operations
primarily in India through a merger, capital stock exchange, asset acquisition
or other similar business combination or acquisition. The operations of IGC are
based in India. IGC owns 100% of a subsidiary in Mauritius called IGC-Mauritius
(IGC-M). This company in turn operates through five subsidiaries in
India. We own twenty two (22.3%) percent of Sricon
Infrastructure Private Limited (“Sricon”) and seventy seven (77%) percent of
Techni Bharathi, Limited (“TBL”). We also beneficially own one
hundred percent of IGC India Mining and Trading, Private Limited, IGC Logistic,
Private Limited, and IGC Materials, Private Limited. Through our subsidiaries we
operate in the infrastructure industry. Operating as a fully
integrated infrastructure company, IGC, through its subsidiaries, has expertise
in road building, mining and quarrying and engineering of high temperature
plants. The Company’s medium term plans are to expand each of these core
competencies while offering an integrated suite of service offerings to our
customers.
The
financial statements provided after the date of deconsolidation (October 1,
2009) are the consolidated statements of IGC, which include IGC-M and our other
subsidiaries. Accordingly, the financial statements provided
prior to the date of deconsolidation (October 1, 2009) are the consolidated
statements of IGC, which include IGC-M, Sricon, TBL and our other
subsidiaries. However, historical description of our business for
periods and dates prior to March 7, 2008 (Acquisition Date) include information
on Sricon and TBL. The consolidated financial statements of our
business for periods prior to March 7, 2008 (acquisition date) do not
include information on Sricon and TBL.
On
February 19, 2009 IGC-M beneficially purchased 100% of IGC Mining and Trading,
Limited based in Chennai India. On July 4, 2009 IGC-M beneficially
purchased 100% of IGC Materials, Private Limited, and 100% of IGC Logistics,
Private Limited. Both these companies are based in Nagpur, India.
Indian IGC Materials, Private Limited (IGC-MPL) and IGC Logistics,
Private Limited (IGC-LPL), is also involved in the building of rock quarries,
the export of iron ore and the transport of materials.
As stated
above, IGC divested part of its interest in Sricon effective October 1,
2009. Its ownership share of Sricon effective October 1, 2009 is
22.3% and is considered a non-controlling interest.
The
financial statements provided here and going forward are the consolidated
statements of IGC, which includes all the aforementioned
subsidiaries.
Company
Overview
We are a
materials and construction company offering a suit of services including: 1)
civil construction of roads and highways, 2) the construction and maintenance of
high temperature cement and steel plants, 3) operations and supply of rock
aggregate and 4) the export of iron ore to China. Our present
and past clients include various Indian government organizations and steel mills
in China. Including our subsidiaries, we have approximately 400
employees and contractors. We are focused on winning construction
contracts, building out rock aggregate quarries and setting up relations and
export hubs for the export of iron ore to China.
The
Indian government has articulated plans to modernize the Indian
Infrastructure. It expects to spend around $22 billion in the next 12
months on roads and highways. We believe that these initiatives will continue to
be favorable to our business. Our model is three fold: 1) we bid on
construction and engineering contracts which provide us with a backlog which
translates into greater revenues and earnings, 2) we are in the process of
building rock quarries and selling rock aggregate to the infrastructure industry
and 3) we export iron ore to China. There is seasonality in our
business as outdoor construction activity slows down during the Indian
monsoons. The rains typically last intermittently from June through
September. Our expansion plans include 1) building out 10 rock
aggregate quarries to create a pure play one-stop shop for rock aggregate (a
business not prevalent in India), 2) obtaining licenses for the mining of iron
ore in India (to fill customer orders from China), and 3) win and execute
construction contracts.
Critical
Accounting Policies and Estimates
The
discussion and analysis of our financial condition and results of operations are
based upon our consolidated financial statements, which have been prepared in
accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of
America. The preparation of these financial statements requires us to make
significant estimates and judgments that affect the reported amounts of assets,
liabilities, revenues and expenses, and related disclosure of contingent assets
and liabilities. These items are regularly monitored and analyzed by management
for changes in facts and circumstances, and material changes in these estimates
could occur in the future. These estimates include, among others, our revenue
recognition policies related to the proportional performance and percentage of
completion methodologies of revenue recognition of contracts and assessing our
goodwill for impairment annually. Changes in estimates are recorded in the
period in which they become known. We base our estimates on historical
experience and various other assumptions that we believe are reasonable under
the circumstances. Actual results will differ and may differ materially from the
estimates if past experience or other assumptions do not turn out to be
substantially accurate.
Our
significant accounting policies are presented within Note 2 to our consolidated
financial statements and the following summaries should be read in conjunction
with the unaudited consolidated financial statements and the related notes
included in this Report. While all accounting policies impact the financial
statements, certain policies may be viewed as critical. Critical accounting
policies are those that are both most important to the portrayal of financial
condition and results of operations and that require management’s most
subjective or complex judgments and estimates. Our management believes the
policies that fall within this category are the policies on revenue recognition,
accounting for stock-based compensation, goodwill and income
taxes.
Revenue
Recognition
The
majority of the revenue recognized for three and nine month periods ended
December 31, 2009 was derived from the Company’s subsidiaries and as
accordingly:
Revenue
is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, the sales price
is fixed or determinable and collectability is reasonably
assured.
In
Government contracting we recognize revenue when a Government consultant
verifies and certifies an invoice for payment.
Revenue
from sale of goods is recognized when substantial risks and rewards of ownership
are transferred to the buyer under the terms of the
contract.
Revenue
from construction/project related activity and contracts for
supply/commissioning of complex plant and equipment is recognized as
follows:
|
|
a)
|
|
Cost
plus contracts: Contract revenue is determined by adding the aggregate
cost plus proportionate margin as agreed with the customer and expected to
be realized.
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
b)
|
|
Fixed
price contracts: Contract revenue is recognized using the percentage
completion method. Percentage of completion is determined as a proportion
of cost incurred-to-date to the total estimated contract cost. Changes in
estimates for revenues, costs to complete and profit margins are
recognized in the period in which they are reasonably
determinable
|
Full
provision is made for any loss in the period in which it is
foreseen.
Revenue
from property development activity is recognized when all significant risks and
rewards of ownership in the land and/or building are transferred to the customer
and a reasonable expectation of collection of the sale consideration from the
customer exists.
Revenue
from service related activities and miscellaneous other contracts are recognized
when the service is rendered using the proportionate completion method or
completed service contract method.
Employee
Stock Options or Share Based Payments
We grant
options to purchase our common stock and award restricted stock to our employees
and directors under our equity incentive plans. The benefits provided under
these plans are share-based payments subject to the provisions of SFAS No. 123R,
Share-Based Payment, and SEC Staff Accounting Bulletin 107, Share-Based
Payments. Effective April 1, 2009, we use the fair value method to apply the
provisions of FAS 123R with the modified prospective application, which provides
for certain changes to the method for valuing share-based
compensation. Share-based compensation expense recognized under FAS
123R for the 9-month period ended December 31, 2009 was $130,407. At
December 31, 2009, total unrecognized estimated compensation expense related to
non-vested awards granted prior to that date was zero. Stock options
vest immediately. At the close of this offering the Company
will grant options for the fiscal year 2010, which ends March 31. 2009, to
Directors, Employees and Advisors at a price that is at least a 10% premium to
the offering price. The number of options that will be granted will be
determined by the Compensation Committee and approved by the
Board.
As a
result of FAS 123R, we estimate the value of share-based awards on the date of
grant using a Black-Scholes option-pricing model. The determination
of the fair value of share-based payment awards on the date of grant using an
option-pricing model is affected by our stock price as well as assumptions
regarding a number of complex and subjective variables. These variables include
our expected stock price volatility over the term of the awards, actual and
projected employee stock option exercise behaviors, risk-free interest rate, and
expected dividends.
If
factors change and we employ different assumptions in the application of FAS
123R during future periods, the compensation expense that we record under FAS
123R may differ significantly from what we have recorded in the current period.
Therefore, we believe it is important for investors to be aware of the high
degree of subjectivity involved when using option-pricing models to estimate
share-based compensation under FAS 123R. Option-pricing models were developed
for use in estimating the value of traded options that have no vesting or
hedging restrictions, are fully transferable and do not cause dilution. Because
our share-based payments have characteristics significantly different from those
of freely traded options, and because changes in the subjective input
assumptions can materially affect our estimates of fair values, in our opinion,
existing valuation models, including the Black-Scholes Option Pricing model, may
not provide reliable measures of the fair values of our share-based
compensation. Consequently, there is a risk that our estimates of the fair
values of our share-based compensation awards on the grant dates may bear little
resemblance to the intrinsic values realized upon the exercise, expiration,
cancellation, or forfeiture of those share-based payments in the future. Certain
share-based payments, such as employee stock options, may expire worthless or
otherwise result in zero intrinsic value as compared to the fair values
originally estimated on the grant date and expensed in our financial statements.
Alternatively, value may be realized from these instruments that are
significantly in excess of the fair values originally estimated on the grant
date and expensed in our financial statements. There currently is neither a
market-based mechanism nor other practical application to verify the reliability
and accuracy of the estimates stemming from these valuation models, nor a way to
compare and adjust the estimates to actual values. Although the fair value of
employee share-based awards is determined in accordance with FAS 123R and SAB
107 using a qualified option-pricing model, that value may not be indicative of
the fair value observed in a willing buyer/willing seller market transaction.
Estimates of share-based compensation expenses are significant to our financial
statements, but these expenses are based on the aforementioned option valuation
model and will never result in the payment of cash by us.
Theoretical
valuation models and market-based methods are evolving and may result in lower
or higher fair value estimates for share-based compensation. The timing,
readiness, adoption, general acceptance, reliability, and testing of these
methods is uncertain. Sophisticated mathematical models may require voluminous
historical information, modeling expertise, financial analyses, correlation
analyses, integrated software and databases, consulting fees, customization, and
testing for adequacy of internal controls.
For
purposes of estimating the fair value of stock options granted during the nine
months ended December 31, 2009 using the Black-Scholes model, we used the
historical volatility of our stock for the expected volatility assumption input
to the Black-Scholes model, consistent with the guidance in FAS 123R and SAB
107. The risk-free interest rate is based on the risk-free zero-coupon rate for
a period consistent with the expected option term at the time of grant. We do
not currently pay nor do we anticipate paying dividends, but we are required to
assume a dividend yield as an input to the Black-Scholes model. As such, we use
a zero dividend rate. The expected option term is estimated using both
historical term measures and projected termination
estimates.
Goodwill
We
account for goodwill in accordance with SFAS No. 142, “Goodwill and Other Intangible
Assets” (“SFAS No. 142”). SFAS No. 142 requires the use of a
non-amortization approach to account for purchased goodwill and certain
intangibles. Under the non-amortization approach, goodwill and certain
intangibles are not amortized into results of operations, but instead are
reviewed for impairment at least annually and written down and charged to
operations only in the periods in which the recorded value of goodwill and
certain intangibles exceeds its fair value. We have elected
to perform our annual impairment test in the fourth quarter of each
calendar year . An interim goodwill impairment test would be performed if
an event occurs or circumstances change between annual tests that would more
likely than not reduce the fair value of a reporting unit below its carrying
amount. For purposes of performing the goodwill impairment test, we concluded
there is one reporting unit. During the fourth quarter of the year ending March
31, 2009, we completed the required annual test, which indicated there was no
impairment.
Accounting
for Income Taxes
In
connection with preparing our financial statements, we are required to estimate
our income taxes in each of the jurisdictions in which we operate. This process
involves the assessment of our net operating loss carry forwards and credits, as
well as estimating the actual current tax liability together with assessing
temporary differences resulting from differing treatment of items, such as
reserves and accrued liabilities, for tax and accounting purposes. We
then assess the likelihood that deferred tax assets will be recovered from
future taxable income, and to the extent we believe that recovery is not likely,
we must establish a valuation allowance. We expect to realize our differed tax
assets as we expect to generate revenue and profit at the parent level through
service fees charged to the subsidiaries and ore contracts obtained at the
parent level. We have therefore not provided an allowance against the
deferred tax asset.
Results
of Operations
Three
Months Ended December 31, 2009 Compared to Three Months Ended December 31,
2008
Revenue -
Total revenue was $5.9 million for the three months ended December
31, 2009, as compared $3.8 million for the three months ended December 31,
2008. The revenue reported in December 2009 does not include Sricon
revenue, due to the deconsolidation of Sricon. The revenue reported
in December 2008 however, includes revenue from Sricon. Despite
deconsolidation, the Company grew its top line, year over year, by
55%. The revenue reported in the quarter ended September 30, 2009 was
$5.36 million. This revenue also included Sricon. The quarter over
quarter growth is 10% despite the deconsolidation of Sricon. This
revenue growth is from the materials business as well as the construction
business.
Cost of Revenue
- Cost of revenue consists primarily of compensation and related fringe
benefits for project-related personnel, department management and all other
dedicated project related costs and indirect costs. It also includes
the cost associated with buying raw materials. Cost of revenue for
the quarter ended December 31, 2009 was $5.3 million compared to $2.9 million
for the quarter ended December 31, 2008. As a percentage of revenue,
the cost of revenue increased, primarily because the Company has contracts for
rock aggregate and iron ore that it is filling before its quarries become
operational. This practice will continue till our quarries and ore
mines are functional. At that point, we will fill orders for
infrastructure materials from a much-improved cost basis. We expect
two rock quarries to come on line in the quarter ending March 31, 2010 and the
ore mines to come on line towards the end of this calendar
year. In the mean time our strategy is to gain market
share, establish our brand, and expand the customer
base.
Selling,
General and Administrative - Selling, general and administrative expenses
were $3.0 million for the quarter ended December 31, 2009 compared to $2.1
million for the quarter ended December 31, 2008. The December
2009 SG&A has a total of $2.44 million of one time charges, about $1.85
million relating to the deconsolidation of Sricon, and $587 thousand relating to
the extinguishment of the debt. Adjusting for the one-time
charges the SG&A for the quarter ended December 31, 2009 would be around
$600 thousand, or around 10% of revenue, compared to $2.1 million, or around 55%
of revenue, incurred in the quarter ended December 31, 2008. The
SG&A for the quarter ended December 31, 2009 also had increased legal fees
from the capital raise as well as the
deconsolidation.
Operating Income (loss) - In
the quarter ended December 31, 2009, operating loss was $2.6 million compared to
an operating loss of $1.4 million for the quarter ended December 31,
2008. The operating loss in the quarter ended December 2009, stem
partly from a large one-time charge of $2.44 M in SG&A reflecting
the de consolidation of Sricon and the extinguishment of debt. With
an adjustment for one-time charges the operating loss for the quarter is around
$127 thousand. We expect operating income to increase as our revenue
ramps up and our quarries become operational.
Early
extinguishment of debt, interest expense, and amortization of debt discount –
the early extinguishment of debt resulted in a one-time charge of about
$586,785 thousand, that is included in the SG&A. The interest
expense and amortization of debt discount for the quarter ended December 31,
2009 was $430,837 compared to $442,265 for the quarter ended December 31,
2008. The interest expense and amortization of debt discount are for
$5.11 million of short and long term debt. The annual effective rate
of interest is 34%, albeit much of it non-cash. If the Company raises
equity and pays of some of the loans, it can potentially save around $400,000
per quarter, or $1.6 million a year, which would increase our bottom line
substantially.
AOCI & Loss on dilution of
Sricon – AOCI stands for Accumulated Other Comprehensive
Income. As a result of the deconsolidation of Sricon, we have taken a
one-time charge for about $2.1 million, which represents a portion of the Other
Comprehensive Income of Sricon that accumulated from the time that IGC acquired
63% of Sricon. We recorded a one-time loss of $1.1 million, as a result of
decreasing our ownership from 63% to 22.3% in Sricon and extinguishing the loan
of $17.9 million due to Sricon.
Inter Company
Loans- IGC borrowed $17.9 million from Sricon. As a result of
the decrease in ownership, this loan is
eliminated.
Consolidated
Net Income (loss) – Consolidated Net loss for the quarter ended December
31, 2009 was ($6.2) million compared to a consolidated net loss
of ($2.3) million for the quarter ended December 31,
2008. The net loss in the 2009 December quarter includes one-time and
non-cash charges of $6.0 million.
Cash, cash
equivalents, restricted cash and working capital – As on December 31,
2009 the company had $3.9 million of cash, cash equivalents and restricted
cash. Restricted cash is cash in a fixed deposit used to secure a
bank guarantee. For the quarter ended December 31, 2009 the Company
had about $4.9 million in working capital.
Stock holders
equity and Total Assets: Compared to March 31, 2009 our stock holders
equity decreased from $23.6 million to $21.9 million and our total assets
decreased from $51.8 million to $35.9 million, mostly based on the de
consolidation of Sricon. The decrease in the balance sheet ($15.9)
million is primarily due to elimination of debt ($17.9) million that was owed to
Sricon, along with accounting adjustments.
Nine
Months Ended December 31, 2009 Compared to Nine Months Ended December 31,
2008
Revenue -
Total revenue was $13.99 million for the nine months ended December
31, 2009, as compared to $32.3 million for the nine months ended December 31,
2008. The lower revenue for the nine months ended December 31, 2009
is from decreasing our contracts and backlog of work as a result of the
financial turmoil.
Cost of Revenue - Cost of
revenue consists primarily of compensation and related fringe benefits for
project-related personnel, department management and all other dedicated project
related costs and indirect costs. Cost of Revenue decreased by $12.1
million, compared to the nine-month period ended December 31,
2008. The decrease was caused by declining revenue and associated
costs.
Selling, General and Administrative
- Consists primarily of employee-related expenses, professional fees,
other corporate expenses and allocated overhead. Selling, general and
administrative expenses were $4.4 million for the nine-month period ended
December 31, 2009 compared to $4.2 million for the nine-month period ended
December 31, 2008, or 13.1% of revenue. The nine-month period ended
December 31, 2009 included $2.44 million of one time charges related to the
deconsolidation of Sricon. Net of deconsolidation charges the
SG&A was about $2.0 million or about 14.3% of the revenue for the nine month
period ended December 31, 2009.
Operating Income (loss) - In
the nine-month period ended December 31, 2009, operating loss was ($2.8)
million, compared to operating income of $3.4 million for the nine-month period
ending December 31, 2008.
Net Interest Income (Expense)
– Net interest expense decreased by $47 thousand compared to the nine-month
period ending December 31, 2008.
Consolidated Net Income (loss) –
Net loss for the nine months ended December 31, 2009 was ($7.2) million
compared to consolidated net income of $562 thousand for the nine months ended
December 31, 2008. As explained in the quarterly comparisons,
one-time charges were taken in the quarter ended December 31, 2009 for the
deconsolidation of Sricon as well as for the extinguishment of
debt.
Off-Balance
Sheet Arrangements
We do not
have any off-balance sheet arrangements as defined in Regulation S-K promulgated
under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934.
Liquidity
and Capital Resources
This
liquidity and capital resources discussion compares the consolidated company
results for nine months period ended December 31, 2009 and 2008.
Cash used
for operating activities from continuing operations is our net loss adjusted for
certain non-cash items and changes in operating assets and liabilities. During
the first nine months of 2009, cash used for operating activities was ($2.8)
million compared to cash used for operating activities of ($6.3) million during
the first nine months of 2008. The uses of cash in the first nine months of 2009
relate primarily to the payment of general operating expenses of our subsidiary
companies. The large change is due to less business
volume.
During
the first nine months of 2009, investing activities from continuing operations
used ($985) thousand of cash as compared to $2.6 million provided during the
comparable period in 2008.
Financing
cash flows from continuing operations consist primarily of transactions related
to our debt and equity structure. In the first nine months of 2009 there was
financing cash provided of approximately $3.7 million, compared to cash used of
approximately ($2.3) million for the first nine months of 2008. The
increase of cash from financing was due to the issuance of 1,599,000 shares of
stock.
Our
future liquidity needs will depend on, among other factors, stability of
construction costs, interest rates, and a continued increase in infrastructure
contracts in India. We believe that our current cash balances and anticipated
operating cash flow will be sufficient to fund our normal operating requirements
for at least the next 12 months. However, we may seek to secure additional
capital to fund further growth of our business, or the repayment of debt, in the
near term.
Annual Pro Forma and Adjusted Pro Forma Financial
Information
In prior
annual filings, we compared annual consolidated results of operations and cash
flows to the preceding year. Since we acquired both TBL and
Sricon at the close of year ending March 31, 2008, we believe a comparison of
the December 31, 2009 consolidated results of operations and cash flows to March
31, 2008 is not an adequate comparison. Only the operating results
for March 8, 2008 to March 31, 2008 are included in our 2008 consolidated
results of operations and cash flows. To reflect a better comparison
of operating results, we are presenting in this Management’s Discussion and
Analysis section, the Pro Forma results of operations for the
Company as if the acquisitions occurred on April 1, 2007 and April 1,
2008, respectively. We are basing our Pro Forma results of operations
from (1) the audited financial statements of Sricon for the period ended March
7, 2008, (2) the unaudited financial statements of Sricon for the period March
8, 2008 to March 31, 2008, (3) the audited financial statements of TBL for the
period ended March 7, 2008, (4) the unaudited financial statements of TBL for
the period March 8, 2008 to March 31, 2008, and (5) the audited consolidated
financial statements of the Company for the year ended March 31, 2009 and
2008.
We
believe that the presented Pro Forma financial statements and analysis is a more
meaningful comparison of our operating results.
The
following tables represent our Pro Forma Consolidated Financial
Statements.
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
Adjusted
Pro Forma Consolidated Statements of Operations
(unaudited)
|
Year
Ended
March
31, 2009
|
Year
Ended
March
31, 2008
|
Percentage
Increase (Decrease)
|
||||||||||
|
Revenue
|
$
|
35,338,725
|
$
|
30,123,348
|
$
|
17.3
|
%
|
|||||
|
Cost
of revenue
|
(27,179,494
|
)
|
(22,462,592
|
)
|
21.0
|
%
|
||||||
|
Gross
profit
|
8,159,231
|
7,660,756
|
6.5
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Selling,
general and administrative expenses
|
(4,977,815
|
)
|
(2,997,983
|
)
|
66.0
|
%
|
||||||
|
Depreciation
|
(873,022
|
)
|
(921,382
|
)
|
(5.2
|
%)
|
||||||
|
Operating
income
|
2,308,394
|
3,741,392
|
(38.3
|
%)
|
||||||||
|
Legal
and formation, travel and other start up costs
|
(5,765,620
|
)
|
(100.0
|
%)
|
||||||||
|
Interest
expense
|
(1,753,952
|
)
|
(3,411,357
|
)
|
48.6
|
%
|
||||||
|
Interest
income
|
1,176,018
|
319,984
|
267.5
|
%
|
||||||||
|
Other
Income
|
2,997,495
|
(100.0
|
%)
|
|||||||||
|
Income
/ (loss) before income taxes
|
1,730,461
|
(2,118,106
|
)
|
(181.7
|
%)
|
|||||||
|
Provision
for income taxes, net
|
(1,535,087
|
)
|
(946,939
|
)
|
(62.1
|
%)
|
||||||
|
Income
after Income Taxes
|
195,373
|
(3,065,046
|
)
|
106.4
|
%
|
|||||||
|
Provision
for Dividend on Preference Stock and its Tax
|
||||||||||||
|
Minority
interest
|
(716,950
|
)
|
(1,343,845
|
)
|
46.6
|
%
|
||||||
|
Net
income / (loss)
|
$
|
(521,576
|
)
|
$
|
(4,408,891
|
)
|
$
|
88.2
|
%
|
|||
|
Net
income / (loss) per share: basic and diluted
|
$
|
(0.05
|
)
|
|||||||||
|
Weighted
average number of shares outstanding-basic and diluted
|
10,091,171
|
|||||||||||
Pro Forma
Adjustments
The
Consolidated Pro Forma Statement of Operations contains US GAAP to Pro Forma
adjustments consisting of the elimination of interest income held in trust and
provision for income taxes. Had the merger occurred during April 1,
2007, interest income in the amount of $2,192,402 would not have been earned
because funds as reported in US GAAP results would have not been held in
trust. Therefore, we eliminate the applicable interest earned from
the Pro Forma statement of operations for the year ended March 31,
2008. Accordingly, the provision for income taxes is reduced by
$16,955.
Year
Ended March 31, 2009 and March 31, 2008
The
following discussion relates to IGC for the years ended March 31, 2009 and March
31, 2008:
Revenues
Total pro
forma revenue increased 17.1% from $35.3 million for the year ended March
31, 2009, as compared to $30.1 million for the year ended March 31,
2008. Due to increased liquidity requirements in maintaining a high
level of growth, we have curtailed the number of contracts we are working on by
sub-contracting some and cancelling others.
Cost
of Revenues
Costs of
revenue consists primarily of compensation and related fringe benefits for
project-related personnel, department management and all other dedicated project
related costs and indirect costs. Cost of revenue increased by 4.7 million
or 21.0%, compared to the year ended March 31, 2008. The increase was
due to the increase of construction material.
Selling,
General and Administrative Expenses
Consist
primarily of employee-related expenses, professional fees, other corporate
expenses and allocated overhead. Selling, general and administrative expenses
increased by $2 million or 67.5% for the year ended March 31, 2009,
compared to the year ended March 31, 2008. The increase in SG&A
stem partly from overheads related to US compliance, USGAAP filings with the
SEC, and legal costs associated with the warrant tender offer and general fund
raising activity.
Net Interest Income (Expense)
– Net interest expense increased by $484 thousand for the year ended March
31, 2009 compared to the year ended March 31, 2008. The main reason
is that the interest income from money in trust is not included in the pro forma
statements.
Net
Income (loss)
Net loss
for the years ended March 31, 2009 and March 31, 2008 was $522 thousand and $4.4
million, respectively. The 2008 net loss included compensation
expense, legal, interest expense, formation, travel, other and start-up
costs net of interest income related to the cash held in our trust
account. The 2009 loss includes approximately $1.5 million of one
time expenses related to fund raising and non cash expenses related to warrants,
as well as approximately $300,000 of losses due to a strengthening US dollar
against the Indian Rupee.
Impairment
of Goodwill
As a
result of our annual impairment tests which occurred during the fourth quarter,
we have not recorded an impairment adjustment to goodwill. Factors
that influence the analysis include, contracts, potential contracts, ability to
grow the quarry and ore business, among others. While there is
an overall liquidity constraint and we require more cash to grow, the market
potential for the infrastructure business in India remains
unabated.
Off-Balance
Sheet Arrangements
We do not
have any off-balance sheet arrangements as defined in Item 303(a) (4) (ii) of
Regulation S-K promulgated under the Securities Exchange Act of
1934.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Cash used
for operating activities from continuing operations is our net loss adjusted for
certain non-cash items and changes in operating assets and liabilities. During
the first three months of 2009, cash used for operating activities was $470
thousand compared to cash used for operating activities of $5.5 million during
the first three months of 2008. The uses of cash in the first three months of
2009 relates primarily to the payment of general operating expenses of our
subsidiary companies. The large change is due to less business
volume.
During
the first three months of 2009, investing activities from continuing operations
used $242 thousand of cash as compared to $5.3 million used during the
comparable period in 2008.
Financing
cash flows from continuing operations consist primarily of transactions related
to our debt and equity structure. In the first three months of 2009 there was
financing cash used of approximately $332 thousand, compared to cash provided of
approximately $4.1 million for the first three months of 2008. The cash
provided in 2009 was primarily due to use of bank credit lines. The
cash used in 2008 was primarily due to repayment of long-term
notes.
Our
future liquidity needs will depend on, among other factors, stability of
construction costs, interest rates, and a continued increase in infrastructure
contracts in India. We believe that our current cash balances and anticipated
operating cash flow, will be sufficient to fund our normal operating
requirements for at least the next 12 months. However, we may seek to secure
additional capital to fund further growth of our business, or the repayment of
debt, in the near term.
Quantitative
and Qualitative Disclosure about Market Risks
The
primary objective of the following information is to provide forward-looking
quantitative and qualitative information about our potential exposure to market
risks. Market risk is the sensitivity of income to changes in
interest rates, foreign exchanges, commodity prices, equity prices, and other
market-driven rates or prices. The disclosures are not meant to be
precise indicators of expected future losses, but rather, indicators of
reasonably possible losses. This forward-looking information provides
indicators of how we view and manage our ongoing market risk
exposures.
Customer
Risk
The
Company’s customers are the Indian government, state government, private
companies and Indian government owned companies. Therefore, our
business requires that we continue to maintain a pre-qualified status with our
clients so we are not disqualified from bidding on future
work. The loss of a significant client, like the National Highway
Authority of India (NHAI), may have an adverse effect on
Company. Disqualification can occur if, for example, we run out of
capital to finish contracts that we have undertaken.
Commodity
Prices and Vendor Risk
The
Company is affected by the availability, cost and quality of raw materials
including cement, asphalt, steel, rock aggregate and
fuel. The prices and supply of raw materials and fuel
depend on factors beyond the control of the Company, including general economic
conditions, competition, production levels, transportation costs and import
duties. The Company typically builds contingencies into the
contracts, including indexing key commodity prices into escalation
clauses. However, drastic changes in the global markets for raw
material and fuel could affect our vendors, which may create disruptions in
delivery schedules that could affect our ability to execute contracts in a
timely manner. We are taking steps to mitigate some of this risk by
attempting to control the supply of raw materials. We do
not currently hedge commodity prices on capital markets.
Labor
Risk
The
building boom in India and the Middle East (India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh
export labor to the Middle East) had created pressure on the availability of
skilled labor like welders, equipment operators, etc. While this has
recently changed with the shortage of financial liquidity and falling oil
prices, we expect a construction boom and although manageable, some regional
shortage of skilled labor.
Compliance,
Legal and Operational Risks
We
operate under regulatory and legal obligations imposed by the Indian
governments and U.S. securities regulators. Those obligations
relate, among other things, to the company’s financial reporting, trading
activities, capital requirements and the supervision of its
employees. For example, we file our financial statements in
three countries under three different Generally Accepted Accounting Standards,
(GAAP). Failure to fulfill legal or regulatory obligations can lead
to fines, censure or disqualification of management and/or staff and other
measures that could have negative consequences for our
subsidiaries’ activities and financial performance. We are mitigating
this risk by hiring local consultants and staff who can manage the compliance in
the various jurisdictions in which we operate. However, the cost of
compliance in various jurisdictions could have an impact on our future
earnings.
Interest
Rate Risk
The
infrastructure development industry is one in which leverage plays a large
role. A typical contract requires that we furnish an earnest money
deposit and a performance guaranty. Furthermore, most contracts
demand that we reserve between 7 and 11 percent of contract value in the form of
bank guaranties and/or deposits. Finally, as interest rates rise, our
cost of capital increases thus impacting our margins.
Exchange
Rate Sensitivity
Our
Indian subsidiaries conduct all business in Indian Rupees with the exception of
foreign equipment that is purchased from the U.S. or Europe. Exchange
rates have an insignificant impact on our financial results. However,
as we convert from Indian Rupees to USD and subsequently report in U.S. dollars,
we may see an impact on translated revenue and
earnings. Essentially, a stronger USD decreases our reported earnings
and a weakening USD increases our reported earnings.
Accounting
Developments and their impact
In
December 2007, the FASB issued ASC 810-10-65 “Consolidation — Transition
and Open Effective Date Information” (previously referred to as SFAS
No. 160, “Non-controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements,
an amendment of ARB No. 51”). ASC 810-10 establishes accounting and
reporting standards for a non-controlling interest in a subsidiary and for the
deconsolidation of a subsidiary. ASC 810-10-65 establishes accounting and
reporting standards that require (i) the ownership interest in subsidiaries
held by parties other than the parent to be clearly identified and presented in
the consolidated balance sheet within equity, but separate from the parent’s
equity, (ii) the amount of consolidated net income attributable to the
parent and the non-controlling interest to be clearly identified and presented
on the face of the consolidated statements of income, and (iii) changes in
a parent’s ownership interest while the parent retains its controlling financial
interest in its subsidiary to be accounted for consistently. Effective
April 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC 810-10-65. See “Consolidated Balance
Sheets”, “Consolidated Statements of Income”, “Consolidated Statements of
Shareholders’ Equity and Comprehensive Income (Loss)”, and note 2 for
information and related disclosures regarding non-controlling
interest.
In
December 2007, the FASB issued ASC 805 “Business Combinations” (previously
referred to as SFAS No. 141 (revised 2007), “Business Combinations”, which
was a revision of SFAS No. 141, “Business Combinations”). This Statement
establishes principles and requirements for how an acquirer recognizes and
measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the
liabilities assumed and any non-controlling interest in an acquiree; recognizes
and measures the goodwill acquired in the business combination or a gain from a
bargain purchase; and determines what information to disclose to enable users of
the financial statements to evaluate the nature and financial effects of the
business combination. Effective April 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC 805
and the adoption did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated
results of operations, cash flows or financial position.
In
February 2008, the FASB approved ASC 820-10 “Fair Value Measurements and
Disclosures” (previously referred to as FASB Staff Position FAS No.157-2,
“Effective Date of FASB statement No. 157” (FSP FAS 157-2), which grants a
one-year deferral of SFAS No. 157’s fair-value measurement requirements for
non-financial assets and liabilities, except for items that are measured or
disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a recurring basis).
Effective April 1, 2009, the Company has adopted ASC 820-10 for
non-financial assets and liabilities. The adoption of ASC 820-10 for
non-financial assets and liabilities did not have a material impact on the
Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or financial
position.
In
November 2008, the FASB’s Emerging Issues Task Force reached a consensus on
ASC 323-10 “Investments-Equity Method and Joint Ventures” (previously referred
to as EITF Issue No. 08-6, “Equity Method Investment Accounting
Considerations”). ASC 323-10 continues to account for the initial carrying value
of equity method investments on a cost accumulation model, which generally
excludes contingent consideration. ASC 323-10 also specifies that
other-than-temporary impairment testing by the investor should be performed at
the investment level and that a separate impairment assessment of the underlying
assets is not required. An impairment charge by the investee should result in an
adjustment of the investor’s basis of the impaired asset for the investor’s
pro-rata share of such impairment. In addition, ASC 323-10 reached a consensus
on how to account for an issuance of shares by an investee that reduces the
investor’s ownership share of the investee. An investor should account for such
transactions as if it had sold a proportionate share of its investment with any
gains or losses recorded through earnings. ASC 323-10 also addresses the
accounting for a change in an investment from the equity method to the cost
method after adoption of ASC 810-10 (previously referred to as SFAS
No. 160). ASC 323-10 affirms existing guidance which requires cessation of
the equity method of accounting and application of ASC 320-10 (previously
referred to as FASB Statement No. 115, “Accounting for Certain Investments
in Debt and Equity Securities”), or the cost method under ASC 323-10-35, as
appropriate. Effective April 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC 323-10 and
the adoption did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated
results of operations, cash flows or financial position.
In
April 2009, the FASB issued ASC 805-20 “Business Combinations —
Identifiable Assets and Liabilities, and Any Non-controlling Interest”
(previously referred to as FASB Staff Position FAS No. 141R-1, “Accounting
for Assets Acquired and Liabilities Assumed in a Business Combination That Arise
from Contingencies” (FSP FAS No. 141R-1). ASC 805-20 eliminates the
distinction between contractual and non-contractual contingencies, including the
initial recognition and measurement criteria, in ASC 805 and instead carries
forward most of the provisions in FASB Statement No. 141, Business
Combinations, for acquired contingencies. ASC 805-20 is effective for contingent
assets or contingent liabilities acquired in business combinations for which the
acquisition date is on or after the beginning of the first annual reporting
period beginning on or after December 15, 2008. Effective April 1,
2009, the Company adopted ASC 805-20 and the adoption did not have a material
impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or
financial position.
In
April 2009, the FASB issued the following three ASCs intended to provide
additional application guidance and enhance disclosures regarding fair value
measurements and impairments of securities:
ASC
820-10-65 “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures — Transition and Open
Effective Date Information” (previously referred to as FASB Staff Positions FAS
157-4 “ Determining Fair Value When the Volume and Level of Activity for
the Asset or Liability Have Significantly Decreased and Identifying Transactions
That Are Not Orderly”) provides additional guidance for estimating fair value in
accordance with ASC 820-10 “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures” (previously
referred to as SFAS No. 157) when the volume and level of activity
for the asset or liability have decreased significantly. ASC 820-10-65 also
provides guidance on identifying circumstances that indicate a transaction is
not orderly. The provisions of ASC 820-10-65 are effective for the Company’s
interim period ending on June 30, 2009. Effective April 1, 2009, the
Company adopted ASC 820-10-65 and the adoption did not have a material impact on
the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or financial
position.
ASC
825-10-65 “Financial Instruments - Transition and Open Effective Date
Information” (previously referred to as FASB Staff Positions FAS 107-1 and APB
28-1, “Interim Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments”), requires
disclosures about the fair value of financial instruments in interim reporting
periods of publicly traded companies that were previously only required to be
disclosed in annual financial statements. The provisions of ASC 825-10-65 are
effective for the Company’s interim period ending on June 30, 2009.
Effective April 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC 825-10-65 and the adoption
did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated results of
operations, cash flows or financial position.
ASC
320-10-65 “Investments-Debt and Equity Securities - Transition and Open
Effective Date Information” (previously referred to as FASB Staff Positions FAS
115-2 and FAS 124-2, “Recognition and Presentation of Other-Than-Temporary
Impairments”) amends current other-than-temporary impairment guidance in U.S.
GAAP for debt securities to make the guidance more operational and to improve
the presentation and disclosure of other-than-temporary impairments on debt and
equity securities in the financial statements. This ASC does not amend existing
recognition and measurement guidance related to other-than-temporary impairments
of equity securities. The provisions of ASC 320-10-65 are effective for the
Company’s interim period ending on June 30, 2009. Effective April 1,
2009, the Company adopted ASC 320-10-65 and the adoption did not have a material
impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or
financial position.
In
May 2009, the FASB issued ASC 855-10 “Subsequent events” (previously
referred to as SFAS No. 165, “Subsequent Events” (“SFAS 165”)), which
provides guidance to establish general standards of accounting for and
disclosures of events that occur after the balance sheet date but before
financial statements are issued or are available to be issued. ASC 855-10 also
requires entities to disclose the date through which subsequent events were
evaluated as well as the rationale for why that date was selected. ASC 855-10 is
effective for interim and annual periods ending after June 15, 2009.
Effective April 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC 855-10 which only requires
additional disclosures and the adoption did not have any impact on its
consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. The
Company evaluated all events or transactions that occurred after
December 31, 2009 up through February 6, 2010. Based on this
evaluation, the Company is not aware of any events or transactions that would
require recognition or disclosure in the consolidated financial
statements.
In
June 2009, the FASB issued ASC 105-10 “Generally Accepted Accounting
Principles” (previously referred to as SFAS No. 168 “The FASB Accounting
Standards Codification and the Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting
Principles—a replacement of FASB Statement No. 162”). The FASB Accounting
Standards Codification (“Codification”) will be the single source of
authoritative nongovernmental U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Rules and interpretive releases of the SEC under authority of federal
securities laws are also sources of authoritative GAAP for SEC registrants. ASC
105-10 is effective for interim and annual periods ending after
September 15, 2009. All existing accounting standards are superseded as
described in ASC 105-10. Effective October 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC
105-10 and the adoption did not have any material impact on its consolidated
financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Recently
issued accounting pronouncements
In
October 2009, the FASB issued ASU 2009-13 (EITF No. 08-1) which amends
ASC 605-25 “Revenue Recognition—Multiple-Element Arrangements”. ASU 2009-13
amends ASC 605-25 to eliminate the requirement that all undelivered elements
have Vendor Specific Objective Evidence (VSOE) or Third Party Evidence (TPE)
before an entity can recognize the portion of an overall arrangement fee that is
attributable to items that already have been delivered. In the absence of VSOE
or TPE of the standalone selling price for one or more delivered or undelivered
elements in a multiple-element arrangement, the overall arrangement fee will be
allocated to each element (both delivered and undelivered items) based on their
relative estimated selling prices. Application of the “residual method” of
allocating an overall arrangement fee between delivered and undelivered elements
will no longer be permitted upon adoption of ASU 2009-13. The provisions of ASU
2009-13 will be effective prospectively for revenue arrangements entered into or
materially modified in fiscal years beginning on or after June 15, 2010.
Early adoption will be permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect
of adoption of the provisions of the ASU 2009-13 on the Company’s consolidated
financial Statements.
In
August 2009, the FASB issued ASU 2009-05 which amends Subtopic 820-10 “Fair
Value Measurements and Disclosures” for the fair value measurement of
liabilities. ASU 2009-05 provides clarification that in circumstances in which a
quoted price in an active market for the identical liability is not available,
an entity is required to measure fair value utilizing one or more of the
following techniques (1) a valuation technique that uses the quoted market
price of an identical liability or similar liabilities when traded as assets; or
(2) another valuation technique that is consistent with the principles of
Topic 820, such as a present value technique or a market approach. The
provisions of ASU No. 2009-05 are effective for the first reporting period
(including the interim periods) beginning after issuance. The provisions of ASU
No. 2009-05 will be effective for interim and annual periods beginning
after August 27, 2009. The Company is currently evaluating the effect of
the provisions of the ASU 2009-05 on the Company’s consolidated financial
statements.
Management
does not believe that any other recently issued, but not yet effective,
accounting standards if currently adopted would have a material effect on the
accompanying financial statements.
Background of India Globalization
Capital, Inc. (IGC)
IGC, a
Maryland corporation, was organized on April 29, 2005 as a blank check
company formed for the purpose of acquiring one or more businesses with
operations primarily in India through a merger, capital stock exchange, asset
acquisition or other similar business combination or acquisition. On March 8,
2006, we completed an initial public offering. On February 19, 2007,
we incorporated India Globalization Capital, Mauritius, Limited (IGC-M), a
wholly owned subsidiary, under the laws of Mauritius. On March 7,
2008, we consummated the acquisition of 63% of the equity of Sricon
Infrastructure Private Limited (Sricon) and 77% of the equity of Techni Bharathi
Limited (TBL). The shares of the two Indian companies, Sricon and TBL, are held
by IGC-M. Most of the shares of Sricon and TBL acquired by IGC were
purchased directly from the companies. IGC purchased a portion of the shares
from the existing owners of the companies. The founders and
management of Sricon own 78% of Sricon (after giving effect to the deconsolidation described
below) and the founders and management of TBL own 23% of
TBL.
The
acquisitions were accounted for under the purchase method of
accounting. Under this method of accounting, for accounting and
financial purposes, IGC-M, Limited was treated as the acquiring entity and
Sricon and TBL as the acquired entities.
On
February 19, 2009 IGC-M beneficially purchased 100% of IGC Mining and Trading,
Limited (IGC-IMT based in Chennai, India). IGC-IMT was formed on
December 16, 2008 as a privately held start-up company engaged in the business
of mining and trading. Its current activity is to operate a shipping
hub and export iron ore to China. On July 4, 2009, IGC-M beneficially
purchased 100% of IGC Materials, Private Limited (IGC-MPL based in Nagpur,
India), which will conduct IGC’s quarrying business, and 100% of IGC Logistics,
Private Limited (IGC-LPL based in Nagpur, India), which will be involved in the
transport and delivery of ore, cement, aggregate and other
material. Each of IGC-IMT, IGC-MPL and IGC-LPL were formed by
third parties at the behest of IGC-M to facilitate the creation of the
subsidiaries, and the purchase price paid for each of IGC-IMT. IGC-MPL and
IGC-LPL was equal to the expenses incurred in incorporating the respective
entities with no premium paid. No officer or director of IGC had a
financial interest in the subsidiaries at the time of their acquisition by
IGC-M. India Globalization Capital, Inc. (the Registrant, the
Company, or we) and its subsidiaries are significantly engaged in one segment,
infrastructure construction.
Effective
October 1, 2009 we decreased our ownership in Sricon Infrastructure from 63% to
22.3%. On March 7, 2008 we consummated the Sricon Acquisition by
purchasing a 63% interest for about $29 million (based on an exchange rate of 40
INR for $1 USD). We subsequently borrowed around $17.9 million (based
on 40 INR for 1 USD) from Sricon. Through 2008 and 2009 we expanded
our business offerings beyond construction to include a rapidly growing
materials business. We have successfully repositioned the company as a materials
and construction company; with construction activity in our TBL subsidiary and
materials activity in our other subsidiaries. Rather than continue to
owe Sricon $17.9 million, and more importantly, continue to fund two
construction companies, we decreased our ownership in Sricon by an amount
proportionate to the loan. The impact of this is that we no longer
owe Sricon $17.9 million and our corresponding ownership is a non-controlling
interest. The deconsolidation of Sricon from the balance sheet of
IGC, results in shrinking the IGC balance sheet and a one-time charge on the
P&L. Post deconsolidation, earnings and losses from Sricon are
accounted for using the equity method of accounting.
IGC’s
organizational structure is as follows:

Unless
the context requires otherwise, all references in this report to the “Company”,
“IGC”, “we”, “our”, and “us” refer to India Globalization Capital, Inc, together
with its wholly owned subsidiary IGC-M, its direct and indirect subsidiaries
(TBL, IGC-IMT, IGC-MPL and IGC-LPL) and Sricon, in which we hold a
non-controlling interest.
Overview
Techni
Bharathi Limited (“TBL”) was incorporated as a public (but not listed on the
stock market) limited company on June 19, 1982 in Cochin, India. TBL
is an engineering and construction company engaged in the execution of civil
construction and structural engineering projects. TBL has a focus in
the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Assam and Tamil Nadu. Its
present and past clients include various Indian government
organizations. The overall lack of liquidity led TBL to curtail its
construction contracts and cut its costs through layoffs. TBL is
re-focused on smaller construction contracts and the settlement of
claims.
IGC-Mauritius
(IGC-M), through its wholly owned Indian subsidiaries (IGC India Mining and
Trading (IGC-IMT), IGC Materials, Private Limited (IGC-MPL)
and IGC Logistics, Private Limited (IGC-LPL), is also involved in the
building of rock quarries, the export of iron ore and the transport of
materials. IGC-M operates a shipping hub in the Krishnapatnam port on
the west coast of India and one at Goa on the east coast of
India. We aggregate ore from smaller mines before shipping to
China. We are also engaged in the production of rock aggregate and
the development of rock quarries. Rock aggregate is used in the
construction of roads, railways, dams, and other infrastructure
development. We are in the process of developing several quarries
through partnerships with landowners. Iron ore is rock and minerals from which
metallic iron can be extracted. The primary form used in industry
today is hematite and is often the principle raw material used to make “pig
iron”, a material critical to the production of industrial steel.
Industry
Overview
The
Indian GDP surpassed $1 Trillion in fiscal 2007. According to the
World Bank, only nine economies at the close of 2005 generated more than $1
Trillion in GDP. According to the CIA World Fact Book, India’s growth
rates have been ranging from 6.2% to 9.6% since 2003. The GDP growth
rate for fiscal year ending March 31, 2008 was 7.4% (estimated). The
Indian stock markets experienced significant growth with the SENSEX peaking at
21,000 (January 8, 2008). The current global financial crisis
created a liquidity crunch starting in October 2008, which
continues.
India’s
GDP growth for fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 is estimated to be lower than
2008’s growth rate. The slowing of the GDP was caused by the global
financial crisis. However, it does indicate that India has withstood the global
downturn better than many nations. The factors contributing to maintaining the
relatively high growth included growth in the agriculture and service
industries, favorable demographic dynamics (India has a large youth population
that exceeds 550 Million), the savings rate and spending habits of the Indian
middle class. Other factors are attributed to changing investment patterns,
increasing consumerism, healthy business confidence, inflows of foreign
investment (India ranks #2 behind China in the A.T. Kearney “FDI Confidence
Index” for 2007) and improvements in the Indian banking system.
To
sustain India’s fast growing economy, the share of infrastructure investment in
India is expected to increase to 9 per cent of GDP by 2014, which is an
increase from 5 per cent in 2006-07. This forecast is based on The
Indian Planning Commission’s statement in its annual publication that for
the Eleventh Plan period (2007-12), a large investment of approximately
$494 Billion is required for Infrastructure build out and
modernization. This industry is one of the largest employers in the
country – the construction industry alone employs more than 30 million
people. According to the Business Monitor International (BMI), by
2012, the construction industry’s contribution to India’s GDP is forecasted to
be 16.98%.
This
ambitious infrastructure development mandate by the Indian Government will
require funding. The Government of India has already raised funds
from multi-lateral agencies such as the World Bank and the Asian Development
Bank. The India Infrastructure Company was set up to support
projects by guaranteeing up to $2 Billion annually. In addition,
the Indian Government has identified public-private partnerships (PPP) as the
cornerstone of its infrastructure development policy. The government
is also proactively seeking additional FDI and approval is not required for up
to 100% of FDI in most infrastructure areas. According to Indian
Prime Minister Dr. Manmohan Singh, addressing the Finance Ministers of ASEAN
countries, at the Indo ASEAN Summit at New Delhi, in August 2007, India
needs $150 billion at the rate of $15 billion per annum for the next 10
years.
The
Government of India is also permitting External Commercial Borrowings (ECB’s) as
a source of financing Indian Companies looking to expand existing
capacity as well as incubation for new startups. ECB’s
include commercial bank loans, buyers' credit, suppliers' credit, securitized
instruments such as Floating Rate Notes and Fixed Rate Bonds, credit from
official export credit agencies, and commercial borrowings from private sector
Multilateral Financial Institutions such as International Finance Corporation
(Washington), ADB, AFIC, CDC, etc. National credit policies seek to
keep an annual cap or ceiling on access to ECB, consistent with prudent debt
management. Also, these policies seek to encourage greater
emphasis on infrastructure projects and core sectors such as power,
oil exploration, telecom, railways, roads & bridges, ports, industrial
parks, urban infrastructure, and fosters exporting. Applicants will
be free to raise ECB from any internationally recognized source such as banks,
export credit agencies, suppliers of equipment, foreign collaborators, foreign
equity-holders, and international capital markets.
ECB can
be accessed in two methods, namely, the Automatic Route and the Approval
Route. The Automatic Route is primarily for investment in Indian
infrastructure, and will not require Reserve Bank of India (RBI)/Government
approval. The maximum amount of ECB’s under the Automatic Route raised by an
eligible borrower is limited to $500 million during any financial year. The
following are additional requirements under the Automatic route:
a) ECB up
to $20 million or equivalent with minimum average maturity of 3
years.
b) ECB
above $20 million and up to $500 million or equivalent with minimum average
maturity of 5 years.
Some of
the areas where ECB’s are utilized is the National Highway Development Project
and the National Maritime Development Program. In addition, the
following represent some of the major infrastructure projects planned for the
next five years:
|
1.
|
Constructing
dedicated freight corridors between Mumbai-Delhi and
Ludhiana-Kolkata.
|
|
2.
|
Capacity
addition of 485 million MT in Major Ports, 345 million MT in Minor
Ports.
|
|
3.
|
Modernization
and redevelopment of 21 railway
stations.
|
|
4.
|
Developing
16 million hectares through major, medium and minor irrigation
works.
|
|
5.
|
Modernization
and redevelopment of 4 metro and 35 non-metro
airports.
|
|
6.
|
Expansion
to six-lanes 6,500 km (4,038 Miles) of Golden Quadrilateral and selected
National Highways.
|
|
7.
|
Constructing
228,000 miles of new rural roads, while renewing and upgrading the
existing 230,000 miles covering 78,304 rural
habitations.
|
Our
operations are subject to certain risks and uncertainties, including among
others, dependency on the Indian and Asian economy and government policies,
competitively priced raw materials, dependence upon key members of the
management team and increased competition from existing and new
entrants.
Our
Securities
We have
three securities listed on the NYSE Amex: (1) common stock, $.0001 par value
(ticker symbol: IGC), (2) redeemable warrants to purchase common stock (ticker
symbol: IGC.WS) and (3) units consisting of one share of common stock and two
redeemable warrants to purchase common stock (ticker symbol:
IGC.U). On March 8, 2006, we sold 11,304,500 units in our initial
public offering. These 11,304,500 units include 9,830,000 units sold to
the public and the over-allotment option of 1,474,500 units exercised by the
underwriters of the public offering. The units may be separated into common
stock and warrants. Each warrant entitles the holder to purchase one
share of common stock at an exercise price of $5.00. The warrants
expire on March 3, 2011, or earlier upon redemption. The
registration statement for initial public offering was declared effective on
March 2, 2006. The warrants are exercisable and may be exercised by
contacting the Company or the transfer agent Continental Stock Transfer &
Trust Company. We have a right to call the warrants, provided the
common stock has traded at a closing price of at least $8.50 per share for any
20 trading days within a 30 trading day period ending on the third business day
prior to the date on which notice of redemption is given. If we call the
warrants, the holder will either have to redeem the warrants by purchasing the
common stock from us for $5.00 or the warrants will expire.
On March
7, 2008, we bought and redeemed a total of 6,159,346 shares. As a
result of the redemption and the subsequent issuance of 210,000 shares of common
stock in private placements, on September 30, 2008, we had 8,780,107 shares
outstanding (including shares sold to our founders in a private placement prior
to the public offering) and 24,874,000 shares of common stock were reserved for
issuance upon exercise of redeemable warrants and underwriters’ purchase
option.
On
January 9, 2009 we completed an exchange of 11,943,878 public and private
warrants for 1,311,064 new shares of common stock.
In
September 2009 we sold 1,599,000 shares of our common stock and warrants to
purchase an aggregate of 319,800 shares of our common stock (the “New Warrants”)
in a registered direct offering. Each warrant entitles the holder to
purchase one share of common stock at an exercise price of $1.60. The
warrants expire on September 18 2012. The New Warrants are
exercisable and may be exercised by contacting the Company or the transfer agent
Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company. We do not have a
right to call the New Warrants.
On
October 5, 2009, the Company issued 530,000 new shares of common stock as
partial consideration for the exchange of an outstanding promissory note for a
new note with an extended maturity date
On
October 16, 2009, the Company issued 530,000 new shares of common stock in a
private placement in connection with the sale of a promissory note to an
investor.
In
November 2009 we sold 3,300 shares of our common stock in a registered at the
market offering.
Following
the issuance of the shares in the preceding transactions, we have 12,898,291
shares of common stock outstanding, warrants to purchase 11,855,122 shares of
common stock outstanding and New Warrants to purchase 318,800 shares of common
stock outstanding.
Core Business
Competencies
We offer
an integrated approach in our customer service delivery based on core
competencies that we have demonstrated over the years. This
integrated approach provides us with an advantage over our
competitors.
Our core
business competencies include the following:
Highway and heavy
construction:
The
Indian government has articulated a plan to build and modernize Indian
infrastructure. The government’s plan, calls for spending over $475
billion over the next five years for the expansion and construction of rural
roads, major highways, airports, seaports, freight corridors, railroads and
townships. A significant number of our customers involve highway and
heavy construction contracts.
Mining
and Quarrying
As Indian
infrastructure modernizes, the demand for raw materials like stone aggregate,
coal, ore and similar resources is projected to increase. In 2006, according to
the Freedonia Group, India was the fourth largest stone aggregate market in the
world with demand of up to 1.1 billion metric tons. We are in the
process of teaming with landowners to build out rock quarries; in addition we
have licenses for the installation and production of rock aggregate
quarries. Our mining and trading activity centers on the export
of Iron ore to China. India is the fourth largest producer of
ore.
Construction
and maintenance of high temperature plants
We have
an expertise in the civil engineering, construction and maintenance of high
temperature plants. This requires specialized skills to build and maintain
high temperature chimneys and kilns.
Customers
Over the
past 10 years, Sricon has qualified in all states in India and has worked in
several, including Maharashtra, Gujarat, Orissa and Madhya
Pradesh. The National Highway Authority of India (NHAI) awards
interstate highway contracts on a national level, while intra-state contracts
are awarded by state agencies. The National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC)
awards contacts for civil work associated with power plants. The National
Coal Limited (NCL) awards large mining contracts. Our customers include, or have
included, NHAI, NTPC, and various state public works departments. Sricon
is registered across India and is qualified to bid on contracts anywhere in
India. For the export of iron ore from India, we are developing
customers in Asia including China.
Contract
bidding process
In order
to create transparency, the Indian government has centralized the contract
awarding process for building inter-state
roads. The new process is as follows: At the “federal” level, as an
example, NHAI publishes a Statement of Work for an interstate highway
construction project. The Statement of Work has a detailed
description of the work to be performed as well as the completion time frame.
The bidder prepares two proposals in response to the Statement of Work. The
first proposal demonstrates technical capabilities, prior work experience,
specialized machinery, and manpower required, and other criteria required to
complete the project. The second proposal includes a financial
bid. NHAI evaluates the technical bids and short lists technically
qualified companies. Next, the short list of technically qualified companies
are invited to place a detailed financial bid and show adequate
financial strength in terms of revenue, net worth, credit lines,
and balance sheets. Typically, the lowest bid wins the contract. Also,
contract bidders must demonstrate an adequate level of capital reserves such as
the following: 1) An earnest money deposit between 2% to 10%
of project costs, 2) performance guarantee of between 5% and 10%, 3)
adequate working capital and 4) additional capital for plant and
machinery. Bidding qualifications for larger NHAI projects
are set by NHAI which are imposed on each contractor. As the
contractor executes larger highway projects, the ceiling is increased by
NHAI.
Our
Growth Strategy and Business Model
Our
business model for the construction business is simple. We bid on
construction, over burden removal at mining sites and or maintenance
contracts. Successful bids increase our backlog of orders,
which favorably impacts our revenues and margins. The
contracting process typically takes approximately six months. Over the
years, we have been successful in winning one out of every seven bids on
average. We currently have one bid team. In the
next year we will focus on the following: 1) build out between two and five rock
quarries, begin production and obtain long term contracts for the sale of rock
aggregate, 2) leverage our shipping hub, develop a second shipping hub, obtain
long term contracts for the delivery and sale of iron ore, 3) execute and expand
recurring contracts for infrastructure build out, 4) aggressively pursue the
collection of accounts receivables and delay claims.
Competition
We
operate in an industry that is fairly competitive. However, there is
a large gap in the supply of well qualified and financed contractors and the
demand for contractors. Large domestic and international firms compete for
jumbo contracts over $250 million in size, while locally based contractors vie
for contracts less than $5 million. The recent capital markets crisis has made
it more difficult for smaller companies to maturate into mid-sized companies, as
their access to capital has been restrained. Therefore, we would like to be
positioned in the $5 million to $50 million contract range, above locally based
contractors and below the large firms, creating a distinct technical and
financial advantage in this market niche. Rock aggregate is supplied
to the industry through small crushing units, which supply low quality
material. Frequently, high quality aggregate is unavailable, or is
transported over large distances. We fill this gap by providing high
quality material in large quantities. We compete on price, quantity
and quality. Iron ore is produced in India where our core assets are
located, and exported to China. While this is a fairly established
business, we compete by aggregating ore from smaller suppliers who do not have
access to customers outside India. Further, at our second shipping hub we expect
to install a crusher that can grind ore pebbles into dust, again providing a
value added service to the smaller mine owners.
Seasonality
The
construction industry (road building) typically experiences recurring and
natural seasonal patterns throughout India. The North East Monsoons,
historically, arrive on June 1, followed by the South West Monsoons, which
usually lasts intermittently until September. Historically, the
monsoon months are slower than the other months because of the
rains. Activity such as engineering, maintenance of high temperature
plants, and export of iron ore are less susceptible to the rains. The
reduced paced in construction activity has historically been used to bid and win
contracts. The contract bidding activity is typically very high during the
monsoon season in preparation for work activity when the rains
abate. During the monsoon season the rock quarries operate to build
up and distribute reserves to the various construction sites.
Employees
and Consultants
As of
December 31, 2009, we employed a work force of
approximately 400 employees and contract workers worldwide. Employees
are typically skilled workers including executives, welders, drivers, and other
specialized experts. Contract workers require less specialized skills. We make
diligent efforts to comply with all employment and labor regulations, including
immigration laws in the many jurisdictions in which we operate. In
order to attract and retain skilled employees, we have implemented a performance
based incentive program, offered career development programs, improved
working conditions, and provided United States work assignments, technology
training, and other fringe benefits. We are hoping that our efforts will make
our companies more attractive. While we have not done so yet, we are
exploring adopting best practices for creating and providing vastly improved
labor camps for our labor force. We are hoping that our efforts will
make our companies “employers of choice” and best of breed. As of
March 31, 2009 our Executive Chairman, Chief Executive Officer is Ram
Mukunda and our Non Executive Chairman is Ranga Krishna. Our over all
Country Head in India is Mr. K. Parthasarathy. Our Managing Director
for Construction is Ravindra Lal Srivastava, our Managing Director for
Materials, Mining and Trading is P. M. Shivaraman. Our
Treasurer and Principal Accounting officer is John Selvaraj. Our
General Manager of Accounting based in India is Santhosh Kumar. We
also utilize the services of several consultants who provide USGAAP systems
expertise among others.
Environmental
Regulations
India has
very strict environmental, occupational, health and safety
regulations. In most instances, the contracting agency regulates and
enforces all regulatory requirements. We internally monitor and
manage regulatory issues on a continuous basis, and we believe that we are in
compliance in all material respects with the regulatory requirements of the
jurisdictions in which we operate. Furthermore, we do not believe that
compliance will have a material adverse effect on our business
activities.
Information
and timely reporting
Our
operations are located in India where the accepted accounting standards is
Indian GAAP, which in many cases, is not congruent to
USGAAP. Indian accounting standards are evolving towards adopting
IFRS (International Financial Reporting Standards). We
annually conduct PCAOB (USGAAP) audits for the company. We
acknowledge that this process is at times cumbersome and places significant
restraints on our existing staff. We believe we are still 6 to 12
months away from having processes and adequately trained personal in place to
meet the reporting timetables set out by the U.S. reporting
requirements. Until then we expect to file for extensions to meet the
reporting timetables. We will make available on our website, www.indiaglobalcap.com,
our annual reports, quarterly reports, proxy statements as well as up to- date
investor presentations. Our SEC filings are also available at
www.sec.gov.
Our
Directors, Executive Officers and Advisory Board Members
The board
of directors, executive officers, advisors and key employees of IGC, Sricon and
TBL are as follows:
Directors,
Executive Officers and Special Advisors of IGC
|
Name
|
Age
|
Position
|
|
Dr.
Ranga Krishna
|
45
|
Non Executive Chairman
|
|
Ram
Mukunda
|
51
|
Chief
Executive Officer, Executive Chairman, President and
Director
|
|
John
Selvaraj
|
65
|
Principal
Accounting Officer
|
|
Sudhakar
Shenoy
|
62
|
Director
|
|
Richard
Prins
|
52
|
Director
|
|
Suhail
Nathani
|
44
|
Director
|
|
Larry
Pressler
|
67
|
Special
Advisor
|
|
P.G.
Kakodkar
|
73
|
Special
Advisor
|
|
Shakti
Sinha
|
53
|
Special
Advisor
|
|
Dr.
Prabuddha Ganguli
|
60
|
Special
Advisor
|
|
Dr.
Anil K. Gupta
|
60
|
Special
Advisor
|
Directors
and Executive Officers of TBL
|
Name
|
Age
|
Position
|
|
Jortin
Antony
|
43
|
Director
|
|
M.
Santhosh Kumar
|
44
|
General
Manager of Accounting
|
|
Ram
Mukunda
|
51
|
Director
|
Ranga Krishna, has served as
our Chairman of the Board since December 15, 2005. Dr. Krishna previously served
as a Director from May 25, 2005 to December 15, 2005 and as our Special Advisor
from April 29, 2005 through June 29, 2005. In 1998, he founded Rising
Sun Holding, LLC, a $120 million construction and land banking
company. In September 1999, he co-founded Fastscribe, Inc., an
Internet-based medical and legal transcription company with its operations in
India with over 200 employees. He has served as a director of Fastscribe since
September 1999. He is currently the Managing Partner. In February
2003, Dr. Krishna founded International Pharma Trials, Inc., a company with
operations in India and over 150 employees, which assists U.S. pharmaceutical
companies performing Phase II clinical trials in India. He is currently the
Chairman and CEO of that company. In April 2004, Dr. Krishna founded
Global Medical Staffing Solutions, Inc., a company that recruits nurses and
other medical professionals from India and places them in U.S. hospitals. Dr.
Krishna is currently serving as the Chairman and CEO of that company. On
November 7, 2008 he joined the board of TransTech Service Partners, a SPAC which
initiated liquidation on May 23 rd, 2009. Dr. Krishna is a member of
several organizations, including the American Academy of Neurology and the
Medical Society of the State of New York. He is also a member of the Medical
Arbitration panel for the New York State Worker’s Compensation Board. Dr.
Krishna was trained at New York’s Mount Sinai Medical Center
(1991-1994) and New York University (1994-1996).
Ram Mukunda has served as our
Founder, Chief Executive Officer, President and a Director since our inception
on April 29, 2005 and was Chairman of the Board from April 29, 2005 through
December 15, 2005. Since September 2004 Mr. Mukunda has served as Chief
Executive Officer of Integrated Global Networks, LLC, a communications
contractor in the U.S. Government. From January 1990 to May 2004, Mr. Mukunda
served as Founder, Chairman and Chief Executive Officer of Startec Global
Communications, an international telecommunications carrier focused on providing
voice over Internet protocol (VOIP) services to the emerging economies. Startec
was among the first carriers to have a direct operating agreement with India for
the provision of telecom services. Mr. Mukunda was responsible for the
organizing, structuring, and integrating a number of companies owned by
Startec. Many of these companies provided strategic investments
in India-based operations or provided services to India-based
companies. Under Mr. Mukunda’s tenure at Startec, the company made an initial
public offering of its equity securities in 1997 and conducted a public
high-yield debt offering in 1998.
From June
1987 to January 1990, Mr. Mukunda served as Strategic Planning Advisor at
INTELSAT, a provider of satellite capacity. Mr. Mukunda serves on the Board of
Visitors at the University of Maryland School of Engineering. From 2001-2003, he
was a Council Member at Harvard’s Kennedy School of Government, Belfer Center of
Science and International Affairs. Mr. Mukunda is the recipient of several
awards, including the University of Maryland’s 2001 Distinguished Engineering
Alumnus Award and the 1998 Ernst & Young, LLP’s Entrepreneur of the Year
Award. He holds B.S. degrees in electrical engineering and mathematics and a MS
in Engineering from the University of Maryland.
John B. Selvaraj has served as our
Treasurer and Principal Accounting Officer since November 27,
2006. From November 15, 1997 to August 10, 2007, Mr. Selvaraj served
in various capacities with Startec, Inc., including from January 2001 to April
2006 as Vice President of Finance and Accounting where he was responsible for
SEC reporting and international subsidiary consolidation. Prior to
joining Startec, from July 1984 to December 1994, Mr. Selvaraj served as the
Chief Financial and Administration Officer for the US office of the European
Union. In 1969, Mr. Selvaraj received a BBA in Accounting from Spicer
Memorial College India, and an Executive MBA, in 1993, from Averette
University, Virginia. Mr. Selvaraj is a Charted Accountant (CA,
1971).
Sudhakar Shenoy, has served as
our Director since May 25, 2005. Since January 1981, Mr. Shenoy has been the
Founder, Chairman and CEO of Information Management Consulting, Inc., a business
solutions and technology provider to the government, business, health and life
science sectors. Mr. Shenoy is a member of the Non Resident Indian Advisory
Group that advises the Prime Minister of India on strategies for attracting
foreign direct investment. Mr. Shenoy was selected for the United States
Presidential Trade and Development Mission to India in 1995. From 2002 to June
2005 he served as the chairman of the Northern Virginia Technology
Council. In 1970, Mr. Shenoy received a B. Tech (Hons.) in electrical
engineering from the Indian Institute of Technology. In 1971 and 1973, he
received an M.S. in electrical engineering and an M.B.A. from the University of
Connecticut Schools of Engineering and Business Administration,
respectively.
Richard Prins, has served as our Director since May 2007 and as Lead Director since March 2010 .
Mr. Prins has 25 years of experience in all aspects of corporate
finance and has participated directly in more than 150 transactions with both
private and public companies across a number of industries in North America,
Europe, and Asia. Mr. Prins was the Director of Investment
Banking for Ferris, Baker Watts, Inc., or FBW, from 1996 until June of 2008
when FBW was acquired by Royal Bank of Canada. At FBW, he managed all of
the firm's industry groups and product offerings including public offerings,
mergers and acquisitions, private placements, restructurings, as well as other
corporate advisory services activities. He was also responsible for
executing a variety of financial and strategic transactions.
Mr. Prins served as a consultant to Royal Bank of Canada Capital
Markets through December 2008 to facilitate the post-acquisition
transition. Currently Mr. Prins is a private investor and involved in
various charitable organizations. Prior to FBW, Mr. Prins was a
Managing Director for eight years at Crestar Bank (now SunTrust Bank) in charge
of Mergers and Acquisitions. Mr. Prins began his career in 1983 as the Assistant
to the Chairman of the leverage buyout company, Tuscarora Corp. He
currently serves on the boards of directors of Amphastar Pharmaceutical,
Advancing Native Missions and The Hope Foundation. Mr. Prins received
a B.A. in liberal arts from Colgate University and an M.B.A. from Oral Roberts
University.
Suhail Nathani, has served as
our Director since May 25, 2005. Since September 2001, he has served as a
partner at the Economics Laws Practice in India, which he co-founded. The
25-person firm focuses on consulting, general corporate law, tax regulations,
foreign investments and issues relating to the World Trade Organization (WTO).
From December 1998 to September 2001, Mr. Nathani was the Proprietor of the
Strategic Law Group, also in India, where he practiced telecommunications law,
general litigation and licensing. Mr. Nathani currently serves on
the boards of the following companies based in India: BLA Industries
Pvt. Ltd, BLA Power Pvt. Ltd., Development Credit Bank Ltd., Phoenix Mills
Limited, Salaam Bombay Foundation, and Siddhesh Capital Market Services Pvt.
Ltd.
Mr.
Nathani earned a LLM in 1991 from Duke University School of Law. In 1990 Mr.
Nathani graduated from Cambridge University, in England, with a MA (Hons)
in Law. In 1987, he graduated from Sydenham College of Commerce and Economics,
Bombay, India.
Sricon
& TBL Management
Rabindralal B. Srivastava is
Founder and Chairman of Sricon. In 1974, he started his career at Larsen and
Toubro (L&T), one of India’s premier engineering and construction
companies. In 1994, his company, Vijay Engineering,
became a civil engineering sub-contractor to L&T. He worked as a
sub-contractor for L&T in Haldia, West Bengal and Tuticorin in South India
among others. Under his leadership, Vijay Engineering expanded to
include civil engineering and construction of power plants, water treatment
plants, steel mills, sugar plants and mining. In 1996, Mr. Srivastava
founded Srivastava Construction Limited, which in 2004 changed its name to
Sricon Infrastructure to address the larger infrastructure needs in India like
highway construction. He merged Vijay Engineering and Sricon in
2004. Mr. Srivastava graduated with a BS from Banaras University
in 1974. Mr. Srivastava founded Hi-tech Pro-Oil Complex in
1996. The company is involved in the extraction of soy bean
oil. He founded Aurobindo Laminations Limited in 2003. The
company manufactures laminated particleboards.
Jortin Antony, has been
a Director of TBL since 2000. Prior to that, he held
various positions at Bhagheeratha starting as a management trainee in
1991. From 1997 to 2000, he was the Director of Projects at
Bhagheeratha. In 2003, Mr. Jortin Antony was awarded the Young Entrepreneur
Award from the Rashtra Deepika. He graduated with a B.Eng, in 1991,
from Bangalore Institute of Technology, University of Bangalore.
M Santhosh Kumar, has been
with TBL since 1991. Since 2008 he has been the General Manager of
Accounting and Finance. From 2002 to January 2008 he has
been the Deputy Manager (Finance and Accounting). From 2000 to 2002,
he was the Marketing Executive for Techni Soft (India) Limited, a subsidiary of
Techni Bharathi Limited. From 1991 to 2000, he held various positions
at TBL in the Finance and Accounting department. From 1986 to 1991,
he worked as an accountant in the Chartered Account firm of Balan and
Company. In 1986 Mr. Santhosh Kumar graduated with a BA in Commerce
from, Gandhi University, Kerala, India.
Special
Advisors
Senator Larry Pressler has
served as our Special Advisor since February 3, 2006. Since leaving the U.S.
Senate in 1997, Mr. Pressler has been a combination of businessman, lawyer,
corporate board director and lecturer at universities. From March 2002 to
present, he has been a partner in the New York firm, Brock law Partners. He was
a law partner with O’Connor & Hannan from March 1997 to March
2002.
In
November 2009 President Obama appointed Mr. Pressler as a Member for the
Commission for the Preservation of America’s Heritage Abroad. From
1979 to 1997, Mr. Pressler served as a member of the United States Senate. He
served as the Chairman of the Senate Commerce Committee on Science and
Transportation, and the Chairman of the Subcommittee on Telecommunications (1994
to 1997). From 1995 to 1997, he served as a Member of the Committee on Finance
and from 1981 to 1995 on the Committee on Foreign Relations. From 1975 to 1979,
Mr. Pressler served as a member of the United States House
of Representatives. Among other bills, Senator Pressler authored the
Telecommunications Act of 1996. As a member of the Senate Foreign Relations
Committee, he authored the “Pressler Amendment,” which became the parity for
nuclear weapons in Asia from 1980 to 1996.
In 2000,
Senator Pressler accompanied President Clinton on a visit to India. He is a
frequent traveler to India where he lectures at universities and business
forums. He serves on the board of directors for The Philadelphia Stock Exchange
and Flight Safety Technologies, Inc. (FLST). From 2002 to 2005 he served on the
board of advisors at Chrys Capital, a fund focused on investments in India. He
was on the board of directors of Spectramind from its inception in 1999 until
its sale to WIPRO, Ltd (WIT) in 2003.
In 1971,
Mr. Pressler earned a Juris Doctor from Harvard Law School and a
Masters in Public Administration from the Kennedy School of Government at
Harvard. From 1964 to 1965 he was a Rhodes Scholar at Oxford University, England
where he earned a diploma in public administration. Mr. Pressler is a Vietnam
war veteran having served in the U.S. Army in Vietnam in 1967-68. He is an
active member of the Veterans of Foreign Wars Association.
P. G. Kakodkar has served as
our Special Advisor since February 3, 2006. Mr. Kakodkar serves on the boards of
several Indian companies, many of which are public in India. Since January of
2005 he has been a member of the board of directors of State Bank of India (SBI)
Fund Management, Private Ltd., which runs one of the largest mutual funds in
India. Mr. Kakodkar’s career spans 40 years at the State Bank of India. He
served as its Chairman from October 1995 to March 1997. Prior to his
Chairmanship, he was the Managing Director of State Bank of India (SBI) Fund
Management Private Ltd., which operates the SBI Mutual Fund.
Since
July 2005, he has served on the board of directors of the Multi Commodity
Exchange of India. Since April 2000, he has been on the board of Mastek, Ltd, an
Indian software house specializing in client server applications. In June 2001,
he joined the board of Centrum Capital Ltd, a financial services company. Since
March 2000, he has been on the board of Sesa Goa Ltd., the second largest mining
company in India. In April 2000, he joined the board at Uttam Galva Steel and in
April 1999 he joined the board of Goa Carbon Ltd, a manufacturer-exporter of
petcoke. Mr. Kakodkar received a BA from Karnataka University and an MA
from Bombay University in economics, in 1954 and 1956, respectively. Mr.
Kakodkar currently is an advisor to Societe Generale, India, which is an
affiliate of SG Americas Securities, LLC and one of the underwriters of the our
IPO.
Shakti Sinha, has served as
our Special Advisor since May 25, 2005. Since July 2004, Mr. Sinha has been
working as a Visiting Senior Fellow, on economic development, with the
Government of Bihar, India. From January 2000 to June 2004, he was a Senior
Advisor to the Executive Director on the Board of the World Bank. From March
1998 to November 1999, he was the Private Secretary to the Prime Minister of
India. He was also the Chief of the Office of the Prime Minister. Prior to that
he has held high level positions in the Government of India, including from
January 1998 to March 1998 as a Board Member responsible for Administration in
the Electricity Utility Board of Delhi. From January 1996 to January 1998, he
was the Secretary to the Leader of the Opposition in the lower house of the
Indian Parliament. From December 1995 to May 1996, he was a Director in the
Ministry of Commerce. In 2002, Mr. Sinha earned a M.S. in International Commerce
and Policy from the George Mason University, USA. In 1978 he earned a M.A. in
History from the University of Delhi and in 1976 he earned a BA (Honors) in
Economics from the University of Delhi.
Prabuddha Ganguli has served
as our Special Advisor since May 25, 2005. Since September 1996, Dr. Ganguli has
been the CEO of Vision-IPR. The company offers management consulting on the
protection of intellectual property rights. His clients include companies in the
pharmaceutical, chemical and engineering industries. He is an adjunct professor
of intellectual property rights at the Indian Institute of Technology, Bombay.
Prior to 1996, from August 1991 to August 1996, he was the Head of Information
Services and Patents at the Hindustan Lever Research Center. In
1986, he was elected as a fellow to the Maharashtra Academy of Sciences. In
1966, he received the National Science Talent Scholarship (NSTS). In 1977, he
was awarded the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation Fellow (Germany). He is
Honorary Scientific Consultant to the Principal Scientific Adviser to the
Government of India. He is a Member of the National Expert Group on Issues
linked to Access to Biological materials vis-à-vis TRIPS and CBD Agreements
constituted by the Indian Ministry of Commerce and Industry. He is also a Member
of the Editorial Board of the intellectual property rights journal “World Patent
Information” published by Elsevier Science Limited, UK. He is a Consultant to
the World Intellectual Property Organization (WIPO), Geneva in intellectual
property rights capability building training programs in various parts of the
world. In 1976, Dr. Ganguli received a PhD from the Tata Institute of
Fundamental Research, Bombay in chemical physics. In 1971, he received a M.Sc.
in Chemistry from the Indian Institute of Technology (Kanpur) and in 1969 he
earned a BS from the Institute of Science (Bombay University).
Anil K. Gupta has served as
our Special Advisor since May 25, 2005. Dr. Gupta has been Professor
of Strategy and Organization at the University of Maryland since
1986. He has been Chair of the Management & Organization
Department, Ralph J. Tyser Professor of Strategy and Organization, and Research
Director of the Dingman Center for Entrepreneurship at the Robert H. Smith
School of Business, The University of Maryland at College Park, since July
2003. Dr. Gupta earned a Bachelor of Technology from the Indian
Institute of Technology in 1970, an MBA from the Indian Institute of Management
in 1972, and a Doctor of Business Administration from the
Harvard Business School in 1980. Dr. Gupta has served on
the board of directors of NeoMagic Corporation (NMGC) since October 2000 and has
previously served as a director of Omega Worldwide (OWWP) from October 1899
through August 2003 and Vitalink Pharmacy Services (VTK) from July 1992 through
July 1999.
Board
of Directors
Our board
of directors is divided into three classes (Class A, Class B and Class C) with
only one class of directors being elected in each year and each class serving a
three-year term. The term of office of the Class A directors, consisting of Mr.
Nathani and Mr. Shenoy, will expire at our fourth annual meeting of
stockholders. The term of office of the Class B directors, consisting of Mr.
Prins and Dr. Krishna, will expire at the second annual meeting of stockholders.
The term of office of the Class C director, consisting of Mr. Mukunda, will
expire at the third annual meeting of stockholders. These individuals
have played a key role in identifying and evaluating prospective acquisition
candidates, selecting the target businesses, and structuring, negotiating and
consummating the acquisition. The NYSE Amex, where we are listed, has rules
mandating that the majority of the board be independent. Our board of
directors will consult with counsel to ensure that the boards of directors’
determinations are consistent with those rules and all relevant securities laws
and regulations regarding the independence of directors. The NYSE Amex listing
standards define an “independent director” generally as a person, other than an
officer of a company, who does not have a relationship with the company that
would interfere with the director’s exercise of independent judgment. Consistent
with these standards, the board of directors has determined that Messrs.
Krishna, Shenoy and Nathani are independent directors.
Committee
of the Board of Directors
Our Board
of Directors has established an Audit Committee currently composed of two
independent directors who report to the Board of Directors. Messrs.
Krishna and Shenoy, each of whom is an independent director under the NYSE
Amex’s listing standards, serve as members of our Audit Committee. In
addition, we have determined that Messrs. Krishna and Shenoy are “audit
committee financial experts” as that term is defined under Item 407 of
Regulation S-K of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as
amended. The Audit Committee is responsible for meeting with our
independent accountants regarding, among other issues, audits and adequacy of
our accounting and control systems. We intend to locate and appoint
at least one additional independent director to our Audit Committee to increase
the size of the Audit Committee to three members.
The Audit
Committee will monitor our compliance on a quarterly basis with the terms of our
initial pubic offering. If any noncompliance issues are identified,
then the Audit Committee is charged with the responsibility to take immediately
all action necessary to rectify such noncompliance or otherwise cause compliance
with our initial pubic offering. The Board currently does not have a
nominating and corporate governance committee. However, the majority of the
independent directors of the Board make all nominations.
Audit
Committee Financial Expert
The Audit
Committee will at all times be composed exclusively of “independent directors”
who are “financially literate” as defined under the NYSE Amex listing
standards. The NYSE Amex listing standards define “financially
literate” as being able to read and understand fundamental financial statements,
including a company’s balance sheet, income statement and cash flow
statement.
In
addition, we must certify to the NYSE Amex that the Audit Committee has, and
will continue to have, at least one member who has past employment experience in
finance or accounting, requisite professional certification in accounting, or
other comparable experience or background that results in the individual’s
financial sophistication. The Board of Directors has determined that
Messrs. Krishna and Shenoy satisfy the NYSE Amex’s definition of financial
sophistication and qualify as “audit committee financial experts,” as defined
under rules and regulations of the Securities and Exchange
Commission.
Compensation
Committee
Our Board
of Directors has established a Compensation Committee composed of two
independent directors, Messrs. Krishna and Shenoy and one non-independent
director Richard Prins. The Board determined that Richard Prins is not a
current officer or employee or an immediate family member of such
person. The Board deemed Mr. Prins to be non-independent because his
firm Ferris Baker Watts received compensation for the IPO and bridge
financing. The Board, however, determined that the best interests of
the Company and its shareholders require his membership on the compensation
committee, as Mr. Prins brings a great deal of prior experience with memberships
on public compensation committees. The Board used the exception
provided under Section 805(b) of the NYSE Amex Company Guide in appointing
Richard Prins to the Compensation Committee. The compensation
committee’s purpose will be to review and approve compensation paid to our
officers and directors and to administer the Stock Plan.
Nominating
and Corporate Governance Committee
We intend
to establish a nominating and corporate governance committee. The primary
purpose of the nominating and corporate governance committee will be to identify
individuals qualified to become directors, recommend to the board of directors
the candidates for election by stockholders or appointment by the board of
directors to fill a vacancy, recommend to the board of directors the composition
and chairs of board of directors committees, develop and recommend to the board
of directors guidelines for effective corporate governance, and lead an annual
review of the performance of the board of directors and each of its
committees.
We do not
have any formal process for stockholders to nominate a director for election to
our board of directors. Currently, nominations are selected or recommended by a
majority of the independent directors as stated in Section 804 (a) of the NYSE
Amex Company Guide. Any stockholder wishing to recommend an
individual to be considered by our board of directors as a nominee for election
as a director should send a signed letter of recommendation to the following
address: India Globalization Capital, Inc. c/o Corporate Secretary, 4336
Montgomery Avenue, Bethesda, MD 20817. Recommendation letters must state
the reasons for the recommendation and contain the full name and address of each
proposed nominee as well as a brief biographical history setting forth past and
present directorships, employments, occupations and civic activities. Any such
recommendation should be accompanied by a written statement from the proposed
nominee consenting to be named as a candidate and, if nominated and elected,
consenting to serve as a director. We may also require a candidate to furnish
additional information regarding his or her eligibility and qualifications. The
board of directors does not intend to evaluate candidates proposed by
stockholders differently than it evaluates candidates that are suggested by our
board members, execution officers or other sources.
Code of Conduct and Ethics
We have
adopted a code of conduct and ethics applicable to our directors, officers and
employees in accordance with applicable federal securities laws and the rules of
the NYSE Amex. We have filed the code of conduct and ethics as
Exhibit 99.1 to our Registration Statement on Form S-1/A, filed with the
Securities and Exchange Commission on March 2, 2006.
Board
Meetings
During
the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009, our board of directors held four meetings.
Although we do not have any formal policy regarding director attendance at our
annual meetings, we will attempt to schedule our annual meetings so that all of
our directors can attend. During the fiscal year ended March 31, 2009, all of
our directors attended 100% of the meetings of the board of
directors.
Compensation
of Directors
Our
directors do not currently receive any cash compensation for their service as
members of the board of directors. In 2009 all board members were awarded stock
options or restricted stock pursuant to our 2008 Omnibus Incentive
Plan. Messers. Prins, Shenoy and Nathani each received options
to purchase 125,000 shares of common stock at an exercise price of $1.00 per
share that were exercisable at the time of grant and which expire on May 13,
2014, five years from the date of grant. Mr. Mukunda and Dr. Krishna
each received grants of 39,410 shares of common stock which vest on December 31,
2009.
We pay
IGN, LLC, an affiliate of Mr. Mukunda, $4,000 per month for office space and
certain general and administrative services. Mr. Mukunda is the Chief
Executive Officer of IGN, LLC. We believe, based on rents and fees
for similar services in the Washington, DC metropolitan area that the fee
charged by IGN LLC was at least as favorable as we could have obtained from an
unaffiliated third party. The agreement is on a month-to-month basis and may be
terminated by the board with out notice.
Section
16 (a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance
Section
16(a) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, as amended, requires our
directors, executive officers and persons who beneficially own more than 10% of
our common stock to file reports of their ownership of shares with the
Securities and Exchange Commission. Such executive officers,
directors and stockholders are required by SEC regulation to furnish us with
copies of all Section 16(a) reports they file. Based solely upon
review of the copies of such reports received by us, our senior management
believes that all reports required to be filed under Section 16(a) for the
fiscal year ended March 31, 2009 were filed in a timely manner.
Compensation Discussion and
Analysis
Overview
of Compensation Policy
The
Company’s Compensation Committee is empowered to review and approve, or in some
cases recommend for the approval of the full Board of Directors the annual
compensation for the executive officers of the Company. This Committee has the
responsibility for establishing, implementing, and monitoring the Company’s
compensation strategy and policy. Among its principal duties, the Committee
ensures that the total compensation of the executive officers is fair,
reasonable and competitive.
Objectives
and Philosophies of Compensation
The
primary objective of the Company’s compensation policy, including the executive
compensation policy, is to help attract and retain qualified, energetic managers
who are enthusiastic about the Company’s mission and products. The policy is
designed to reward the achievement of specific annual and long-term strategic
goals aligning executive performance with company growth and shareholder value.
In addition, the Board of Directors strives to promote an ownership mentality
among key leaders and the Board of Directors.
Setting
Executive Compensation
The
compensation policy is designed to reward performance. In measuring executive
officers’ contribution to the Company, the Compensation Committee considers
numerous factors including the Company’s growth and financial performance as
measured by revenue, gross margin and net income before taxes among other key
performance indicators.
Regarding
most compensation matters, including executive and director compensation,
management provides recommendations to the Compensation Committee; however, the
Compensation Committee does not delegate any of its functions to others in
setting compensation. The Compensation Committee does not currently engage any
consultant related to executive and/or director compensation
matters.
Stock
price performance has not been a factor in determining annual compensation
because the price of the Company’s common stock is subject to a variety of
factors outside of management’s control. The Company does not subscribe to an
exact formula for allocating cash and non-cash compensation. However, a
significant percentage of total executive compensation is performance-based.
Historically, the majority of the incentives to executives have been in the form
of non-cash incentives in order to better align the goals of executives with the
goals of stockholders.
Elements
of Company’s Compensation Plan
The
principal components of compensation for the Company’s executive officers
are:
|
·
|
base
salary
|
|
|
·
|
performance-based
incentive cash compensation
|
|
|
·
|
right
to purchase the company’s stock at a preset price (stock
options)
|
|
|
·
|
retirement
and other benefits
|
Base Salary
The
Company provides named executive officers and other employees with base salary
to compensate them for services rendered during the fiscal year. Base salary
ranges for named executive officers are determined for each executive based on
his or her position and responsibility.
During
its review of base salaries for executives, the Committee primarily
considers:
|
·
|
market
data;
|
|
|
·
|
internal
review of the executives’ compensation, both individually and relative to
other officers; and
|
|
|
·
|
individual
performance of the executive.
|
Salary
levels are typically evaluated annually as part of the Company’s performance
review process as well as upon a promotion or other change in job
responsibility.
Performance-Based
Incentive Compensation
The
management incentive plan gives the Committee the latitude to design cash and
stock-based incentive compensation programs to promote high performance and
achievement of corporate goals, encourage the growth of stockholder value and
allow key employees to participate in the long-term growth and profitability of
the Company. So that stock-based compensation may continue to be a viable part
of the Company’s compensation strategy, management is currently seeking
shareholder approval of a proposal to increase the number of shares of Company
common stock reserved for issuance pursuant to the Company’s Stock
Plan.
Ownership
Guidelines
To
directly align the interests of the Board of Directors with the interests of the
stockholders, the Committee recommends that each Board member maintain a minimum
ownership interest in the Company. Currently, the Compensation Committee
recommends that each Board member own a minimum of 5,000 shares of the Company’s
common stock with such stock to be acquired within a reasonable time following
election to the Board.
Stock
Option Program
The Stock
Option Program assists the Company to:
|
·
|
enhance
the link between the creation of stockholder value and long-term executive
incentive compensation;
|
|
|
·
|
provide
an opportunity for increased equity ownership by executives;
and
|
|
|
·
|
maintain
competitive levels of total
compensation.
|
Stock
option award levels are determined based on market data and vary among
participants based on their positions within the Company and are granted at the
Committee’s regularly scheduled meeting. As of September 30, 2009, we had
granted 78,820 shares of common stock and 1,413,000 stock options under our
Stock Plan.
Perquisites
and Other Personal Benefits
The
Company provides some executive officers with perquisites and other personal
benefits that the Company and the Committee believe are reasonable and
consistent with its overall compensation program to better enable the Company to
attract and retain superior employees for key positions. The Committee
periodically reviews the levels of perquisites and other personal benefits
provided to named executive officers.
Some
executive officers are provided use of company automobiles, an
entertainment budget and assistants based in the US and in India to
alleviate the extensive overseas travel. All employees can
participate in the plans and programs described above.
Each
employee of the Company is entitled to term life insurance, premiums for which
are paid by the Company. In addition, each employee is entitled to receive
certain medical and dental benefits and part of the cost is funded by the
employee.
Accounting
and Tax Considerations
The
Company’s stock option grant policy will be impacted by the implementation of
SFAS No. 123R, which was adopted in the first quarter of fiscal year 2006. Under
this accounting pronouncement, the Company is required to value unvested stock
options granted prior to the adoption of SFAS 123 under the fair value method
and expense those amounts in the income statement over the stock option’s
remaining vesting period.
Section
162(m) of the Internal Revenue Code restricts deductibility of executive
compensation paid to the Company’s chief executive officer and each of the four
other most highly compensated executive officers holding office at the end of
any year to the extent such compensation exceeds $1,000,000 for any of such
officers in any year and does not qualify for an exception under Section 162(m)
or related regulations. The Committee’s policy is to qualify its executive
compensation for deductibility under applicable tax laws to the extent
practicable. In the future, the Committee will continue to evaluate the
advisability of qualifying its executive compensation for full
deductibility.
Compensation
for Executive Officers of the Company
Prior
March 8, 2008, we did not pay any cash compensation to our executive officers or
their affiliates except as follows. As described above in
“Directors, Executive Officers And Special Advisors of the Company – Director
Compensation”, we pay IGN, LLC, an affiliate of Mr. Mukunda, $4,000 per month
for office space and certain general and administrative services, an amount
which is not intended as compensation for Mr. Mukunda. On or
around November 27, 2006, we engaged SJS Associates, an affiliate of Mr.
Selvaraj, which provides the services of Mr. John Selvaraj as our
Treasurer. We have agreed to pay SJS Associates $5,000 per month for
these services. Mr. Selvaraj is the Chief Executive Officer of SJS
Associates. Effective November 1, 2007 the Company and SJS Associates
terminated the agreement. We subsequently entered into a new
agreement with SJS Associates on identical terms subsequent to the acquisition
of Sricon and TBL. On May 22, 2008, the
Company and its subsidiary India Globalization Capital
Mauritius (“IGC-M”) entered into an employment agreement (the
“Employment Agreement”) with Ram Mukunda, pursuant to which he will receive a
salary of $300,000 per year for services to IGC and IGC-M as Chief Executive
Officer. The Employment Agreement was approved in May 2008 and
made effective as of March 8, 2008. For fiscal year 2009, Mr. Mukunda
was paid $300,000.
The
annual executive compensation for the Chief Executive Officer and Chief
Financial Officer of the Company is set out below.
|
Summary
compensation
|
||||||||
|
FY
2008
|
FY
2009
|
|||||||
|
Ram
Mukunda
|
$
|
15,000
|
$
|
450,000
|
||||
|
John
Selvaraj
|
$
|
35,000
|
$
|
63,300
|
||||
Compensation
of Directors
No
compensation was paid to the Company’s Board of Directors for the one-year
period ended March 31, 2009.
Certain
Relationships and Related Transactions
As of
March 31, 2009, there were no related party transactions other than the
agreements with IGN, an affiliate of Ram Mukunda, and SJS Associates, an
affiliate of John Selvaraj, described above. We are party to indemnification
agreements with each of the executive officers and directors. Such
indemnification agreements require us to indemnify these individuals to the
fullest extent permitted by law.
Employment
Contracts
Ram
Mukunda has served as President and Chief Executive Officer of the Company since
its inception. The Company, IGC-M and Mr. Mukunda entered into an
Employment Agreement on May 22, 2008, which agreement was made effective as of
March 8, 2008, the date on which the Company completed its acquisition of Sricon
and TBL. Pursuant to the agreement, the Company pays Mr. Mukunda a base salary
of $300,000 per year. Mr. Mukunda is also entitled to receive bonuses of at
least $225,000 for meeting certain targets for net income (before one time
charges including charges for employee options, warrants and other items) for
fiscal year 2009
and $150,000 for meeting targets with respect to obtaining new
contracts. The Agreement further provides that the Board of Directors
of the Company may review and update the targets and amounts for the net revenue
and contract bonuses on an annual basis. The Agreement also provides
for benefits, including insurance, 20 days of paid vacation, a car (subject to
partial reimbursement by Mr. Mukunda of lease payments for the car) and
reimbursement of business expenses. The term of the Employment Agreement is five
years, after which employment will become at-will. The Employment Agreement is
terminable by the Company and IGC-M for death, disability and
cause. In the event of a termination without cause, the Company would
be required to pay Mr. Mukunda his full compensation for 18 months or until the
term of the Employment Agreement was set to expire, whichever is
earlier.
In
partial consideration for the equity shares in Sricon purchased by the Company,
pursuant to the terms of a Shareholders Agreement dated as of September 15, 2007
by and among IGC, Sricon and the Promoters or Sricon, the stockholders of Sricon
as of the date of the acquisition, including Ravindra Lal Srivastava, who
currently serves as the Chairman and Managing Director of Sricon, shall have the
right to receive up to an aggregate of 418,431 equity shares of Sricon over a
three-year period if Sricon achieves certain profit after tax targets for its
2008-2010 fiscal years. The maximum number of shares the Promoters
may receive in any given fiscal year is 139,477 shares. If Sricon’s
profits after taxes for a given fiscal year are less than 100% of the target for
that year but are equal to at least 85% of the target, the Promoters shall
receive a pro rated portion of the maximum share award for that fiscal
year. A copy of this agreement was filed with the SEC in the
Company’s definitive proxy statement filed February 8, 2008 and is incorporated
here by reference.
In
partial consideration for the equity shares in TBL purchased by the Company,
pursuant to the terms of a Shareholders Agreement dated as of September 16, 2007
by and among IGC, TBL and the Promoters of TBL, Jortin Anthony, who currently
serves as the Managing Director of TBL, shall have the right to
receive up to an aggregate of 1,204,000 equity shares of TBL over a
five-year period if TBL achieves certain profit after tax targets for its
2008-2012 fiscal years. The maximum number of shares Mr.
Anthony may receive is 140,800 shares for fiscal year 2008 and 265,800 shares
for each of the following fiscal years. If TBL’s profits after taxes
for a given fiscal year are less than 100% of the target for that year but are
equal to at least 85% of the target Mr. Anthony shall receive a pro rated
portion of the maximum share award for that fiscal year. A copy of
this agreement was filed with the SEC in the Company’s definitive proxy
statement filed February 8, 2008 and is incorporated here by
reference.
Compensation
Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation
A
Compensation Committee comprised of two independent members of the Board of
Directors, Ranga Krishna and Sudhakar Shenoy, and a non-independent director
Richard Prins, administer executive compensation. No executive
officer of the Company served as a director or member of the compensation
committee of any other entity.
Review,
Approval or Ratification of Related Party Transactions
We do not
maintain a formal written procedure for the review and approval of transactions
with related persons. It is our policy for the disinterested members
of our board to review all related party transactions on a case-by-case
basis. To receive approval, a related-party transaction must have a
business purpose for IGC and be on terms that are fair and reasonable to IGC and
as favorable to IGC as would be available from non-related entities in
comparable transactions.
Pursuant
to the terms of a registration rights agreement with the Company, the holders of
the majority of these shares issued to our officers and directors prior to our
initial public offering are be entitled to make up to two demands that we
register these shares. The holders of the majority of these shares can elect to
exercise these registration rights at any time after the date on which the
lock-up period expires. The lock-up period expired on September 8,
2008. In addition, these stockholders have certain “piggy-back”
registration rights on registration statements filed subsequent to such date. We
will bear the expenses incurred in connection with the filing of any such
registration statements. We have registered these shares for resale
on a registration statement on Form S-1 that was declared effective on November
12, 2008.
The
following table sets forth information regarding the beneficial ownership of our
common stock as of November 30, 2009 by:
• each person known by us to be the
beneficial owner of more than 5% of our outstanding shares of common
stock;
• each of our executive officers,
directors and our special advisors; and
• all of our officers and directors
as a group.
Beneficial
ownership is determined in accordance with the rules of the Securities and
Exchange Commission and does not necessarily indicate beneficial ownership for
any other purpose. Under these rules, beneficial ownership includes those shares
of common stock over which the stockholder has sole or shared voting or
investment power. It also includes shares of common stock that the stockholder
has a right to acquire within 60 days through the exercise of any option,
warrant or other right. The percentage ownership of the outstanding common
stock, which is based upon 12,898,291 shares of common stock outstanding as of
November 30, 2009, is based on the assumption, expressly required by the rules
of the Securities and Exchange Commission, that only the person or entity whose
ownership is being reported has converted options or warrants into shares of our
common stock.
Unless
otherwise indicated, we believe that all persons named in the table have sole
voting and investment power with respect to all shares of common stock
beneficially owned by them. Unless otherwise noted, the nature of the ownership
set forth in the table below is common stock of the Company.
The table
below sets forth as of November 30, 2009, except as noted in the footnotes to
the table, certain information with respect to the beneficial ownership of the
Company’s Common Stock by (i) all persons known by the Company to be the
beneficial owners of more than 5% of the outstanding Common Stock of the
Company, (ii) each director and director-nominee of the Company, (iii) the
executive officers named in the Summary Compensation Table, and (iv) all such
executive officers and directors of the Company as a group.
|
Shares
Owned
|
||||||||
|
Name and Address of Beneficial
Owner(1)
|
Number
of Shares
|
Percentage
of Class
|
||||||
|
Wachovia
Corporation (2)
One
Wachovia Center
Charlotte,
North Carolina 28288-0137
|
1,879,289
|
14.6
|
%
|
|||||
|
Sage
Master Investments Ltd (3)
500
Fifth Avenue, Suite 930
New
York, New York 10110
|
947,300
|
7.3
|
%
|
|||||
|
Brightline
Capital Management, LLC (4)
1120
Avenue of the Americas, Suite 1505
New
York, New York 10036
|
750,000
|
5.8
|
%
|
|||||
|
Ram
Mukunda (5)
|
1,449,914
|
10.6
|
%
|
|||||
|
Ranga
Krishna (6)
|
2,215,624
|
16.8
|
%
|
|||||
|
Richard
Prins (7)
|
196,250
|
1.5
|
%
|
|||||
|
Sudhakar
Shenoy(8)
|
175,000
|
1.4
|
%
|
|||||
|
Suhail
Nathani(9)
|
150,000
|
1.2
|
%
|
|||||
|
Larry
Pressler
|
25,000
|
*
|
||||||
|
Dr.
Anil K. Gupta
|
25,000
|
*
|
||||||
|
P.G.
Kakodkar
|
12,500
|
*
|
||||||
|
Shakti
Sinha
|
12,500
|
*
|
||||||
|
Dr.
Prabuddha Ganguli
|
12,500
|
*
|
||||||
|
All
Executive Officers and Directors as a group (5
Persons)(10)
|
4,186,788
|
29.0
|
%
|
|||||
*
Represents less than 1%
|
(1)
|
Unless
otherwise indicated, the address of each of the individuals listed in the
table is: c/o India Globalization Capital, Inc., 4336 Montgomery Avenue,
Bethesda, MD 20814.
|
|
(2)
|
Based
on a Schedule 13F filed with the SEC on March 31, 2009 by Wachovia
Corporation. Dr. Ranga Krishna is entitled to 100% of the
economic benefits of the shares.
|
|
(3)
|
Based
on a Schedule 13G filed with the SEC on June 1, 2009 by Sage Master
Investments Ltd., a Cayman Islands exempted company (“Sage Master”), Sage
Opportunity Fund (QP), L.P., a Delaware limited partnership (“QP Fund”),
Sage Asset Management, L.P., a Delaware limited partnership (“SAM”), Sage
Asset Inc., a Delaware corporation (“Sage Inc.”), Barry G. Haimes and
Katherine R. Hensel (collectively, the “Reporting Persons”). As
disclosed in the Schedule 13G, Each of the Reporting Persons’ beneficial
ownership of 947,300 shares of Common Stock constitutes 7.4% of all of the
outstanding shares of Common Stock. The address for each of the foregoing
parties is c/o 500 Fifth Avenue, Suite 930, New York, New York
10110.
|
|
(4)
|
Based
on an amended Schedule 13G jointly filed with the SEC on May 28, 2008 by
Brightline Capital Management, LLC (“Management”), Brightline Capital
Partners, LP (“Partners”), Brightline GP, LLC (“GP”), Nick Khera (“Khera”)
and Edward B. Smith, III (“Smith”). As disclosed in the amended
Schedule 13G, Management and Khera are each the beneficial owners of
750,000 shares of common stock (5.8%), Smith is the beneficial owner of
1,031,500 shares of common stock (8.0%) including 281,500 shares over
which he holds sole control of their voting and disposition, and Partners
and GP are each the beneficial owners of 592,560 shares of common stock
(4.6%), respectively. The address for
each of the foregoing parties is 1120 Avenue of the Americas, Suite 1505,
New York, New York 10036.
|
|
(5)
|
Includes(i)
245,175 shares of common stock directly owned by Mr. Mukunda, (ii) 425,000
shares of common stock owned by Mr. Mukunda’s wife Parveen Mukunda, (iii)
options to purchase 635,000 shares of common stock which are exercisable
within sixty (60) days of November 30, 2009, all of which are currently
exercisable and (iv) warrants to purchase 144,739 shares of common stock,
of which warrants to purchase 28,571 shares of common stock are owned by
Mr. Mukunda’s wife Parveen Mukunda and all which are
exercisable within sixty (60) days of November 30, 2009, all of which are
currently exercisable.
|
|
(6)
|
Includes warrants to
purchase 290,000 shares of common stock which are exercisable within sixty
(60) days of November 30, 2009, all of which are currently
exercisable. Includes 1,879,279 shares beneficially owned by
Wachovia Corporation, which has sole voting and dispositive control over
the shares. Dr. Krishna is entitled to 100% of the
economic benefits of the shares.
|
|
(7)
|
Based
on a Form 4 filed with the SEC on May 18, 2009 by Richard
Prins. Includes options to purchase 125,000 shares of common
stock and a unit purchase option to purchase 71,250 units, each consisting
of 1 share of common stock and 2 warrants to purchase a share of common
stock and does not include the warrants underlying the units that may be
acquired upon exercise of the unit purchase option. Both
the options, and the unit purchase option are both exercisable
within sixty (60) days of November 30, 2009 and currently
exercisable.
|
|
(8)
|
Based
on a Form 4 filed with the SEC on May 18, 2009 by Sudhakar
Shenoy. Includes options to purchase 125,000 shares of common
stock, which are both exercisable within sixty (60) days of November 30,
2009 and currently exercisable.
|
|
(9)
|
Based
on a Form 4 filed with the SEC on May 18, 2009 by Suhail
Nathani. Includes options to purchase 125,000 shares of common
stock, which are both exercisable within sixty (60) days of November 30,
2009 and currently exercisable.
|
|
(10)
|
Does
not include shares owned by our special advisors. Includes: (i)
2,654,464 shares of common stock, (ii) warrants to purchase 1,069,739
shares of common stock, (iii) options to purchase 375,000 shares of common
stock and (iv) a unit purchase option to purchase 71,250 units, each
consisting of 1 share of common stock and 2 warrants to purchase a share
of common stock and does not include the warrants underlying the units
that may be acquired upon exercise of the unit purchase
option. The warrants, options, and the unit purchase option are
all both exercisable within sixty (60) days of November 30, 2009 and
currently exercisable. Includes 1,879,289 shares
beneficially owned by Wachovia Corporation, which has sole voting and
dispositive control over the
shares.
|
Messrs.
Mukunda and Krishna may be deemed our “parent,” “founder” and “promoter,” as
these terms are defined under the Federal securities laws.
General
We are
authorized to issue 75,000,000 shares of common stock, par value $.0001,
and 1,000,000 shares of preferred stock, par value $.0001. As of November
30, 2009, 12,898,291 shares of common stock are outstanding, held
by 946 record holders and no shares of preferred stock are
outstanding.
Units
Each unit
consists of one share of common stock and two warrants. Each warrant entitles
the holder to purchase one share of common stock. Each of the common stock and
warrants can be traded separately.
Common
stock
Our
stockholders are entitled to one vote for each share held of record on all
matters to be voted on by stockholders.
Our board
of directors is divided into three classes (Class A, Class B and
Class C), each of which will generally serve for a term of three years with
only one class of directors being elected in each year. There is no cumulative
voting with respect to the election of directors, with the result that the
holders of more than 50% of the shares voted for the election of directors can
elect all of the directors.
Our
stockholders have no conversion, preemptive or other subscription rights and
there are no sinking fund or redemption provisions applicable to the common
stock.
Preferred
stock
Our
certificate of incorporation authorizes the issuance of 1,000,000 shares of
blank check preferred stock with such designation, rights and preferences as may
be determined from time to time by our board of directors. No shares of
preferred stock are being issued or registered in this offering. Accordingly,
our board of directors is empowered, without stockholder approval, to issue
preferred stock with dividend, liquidation, conversion, voting or other rights
which could adversely affect the voting power or other rights of the holders of
common stock. We may issue some or all of the preferred stock to
effect a business combination. In addition, the preferred stock could be
utilized as a method of discouraging, delaying or preventing a change in control
of us. Although we do not currently intend to issue any shares of preferred
stock, we cannot assure you that we will not do so in the future.
Dividends
We have
not paid any dividends on our common stock to date and do not intend to pay
dividends prior to the completion of a business combination. The payment of
dividends in the future will be contingent upon our revenues and earnings, if
any, capital requirements and general financial condition subsequent to
completion of a business combination. The payment of any dividends subsequent to
a business combination will be within the discretion of our then board of
directors. It is the present intention of our board of directors to retain all
earnings, if any, for use in our business operations and, accordingly, our board
does not anticipate declaring any dividends in the foreseeable
future.
Maryland
Anti-Takeover Provisions and Certain Anti-Takeover Effects of our Charter and
Bylaws
Business
Combinations
Under the
Maryland General Corporation Law, some business combinations, including a
merger, consolidation, share exchange or, in some circumstances, an asset
transfer or issuance or reclassification of equity securities, are prohibited
for a period of time and require an extraordinary vote. These transactions
include those between a Maryland corporation and the following persons (a
“Specified Person”):
•an interested stockholder, which is
defined as any person (other than a subsidiary) who beneficially owns 10% or
more of the corporation’s voting stock, or who is an affiliate or an associate
of the corporation who, at any time within a two-year period prior to the
transaction, was the beneficial owner of 10% or more of the voting power of the
corporation’s voting stock or
•an affiliate of an interested
stockholder.
A person
is not an interested stockholder if the board of directors approved in advance
the transaction by which the person otherwise would have become an interested
stockholder. The board of directors of a Maryland corporation also may exempt a
person from these business combination restrictions prior to the time the person
becomes a Specified Person and may provide that its exemption is subject to
compliance with any terms and conditions determined by the board of directors.
Transactions between a corporation and a Specified Person are prohibited for
five years after the most recent date on which such stockholder becomes a
Specified Person. After five years, any business combination must be recommended
by the board of directors of the corporation and approved by at least 80% of the
votes entitled to be cast by holders of voting stock of the corporation and
two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast by holders of shares other than
voting stock held by the Specified Person with whom the business combination is
to be effected, unless the corporation’s stockholders receive a minimum price as
defined by Maryland law and other conditions under Maryland law are
satisfied.
A
Maryland corporation may elect not to be governed by these provisions by having
its board of directors exempt various Specified Persons, by including a
provision in its charter expressly electing not to be governed by the applicable
provision of Maryland law or by amending its existing charter with the approval
of at least 80% of the votes entitled to be cast by holders of outstanding
shares of voting stock of the corporation and two-thirds of the votes entitled
to be cast by holders of shares other than those held by any Specified Person.
Our Charter does not include any provision opting out of these business
combination provisions.
Control
Share Acquisitions
The
Maryland General Corporation Law also prevents, subject to exceptions, an
acquiror who acquires sufficient shares to exercise specified percentages of
voting power of a corporation from having any voting rights except to the extent
approved by two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast on the matter not
including shares of stock owned by the acquiring person, any directors who are
employees of the corporation and any officers of the corporation. These
provisions are referred to as the control share acquisition
statute.
The
control share acquisition statute does not apply to shares acquired in a merger,
consolidation or share exchange if the corporation is a party to the
transaction, or to acquisitions approved or exempted prior to the acquisition by
a provision contained in the corporation’s charter or bylaws. Our Bylaws include
a provision exempting IGC from the restrictions of the control share acquisition
statute, but this provision could be amended or rescinded either before or after
a person acquired control shares. As a result, the control share acquisition
statute could discourage offers to acquire IGC stock and could increase the
difficulty of completing an offer.
Board
of Directors
The
Maryland General Corporation Law provides that a Maryland corporation which is
subject to the Exchange Act and has at least three outside directors (who are
not affiliated with an acquirer of the company) under certain circumstances may
elect by resolution of the board of directors or by amendment of its charter or
bylaws to be subject to statutory corporate governance provisions that may be
inconsistent with the corporation’s charter and bylaws. Under these provisions,
a board of directors may divide itself into three separate classes without the
vote of stockholders such that only one-third of the directors are elected each
year. A board of directors classified in this manner cannot be altered by
amendment to the charter of the corporation. Further, the board of directors
may, by electing to be covered by the applicable statutory provisions and
notwithstanding the corporation’s charter or bylaws:
• provide that a special meeting of
stockholders will be called only at the request of stockholders entitled to cast
at least a majority of the votes entitled to be cast at the
meeting,
• reserve for itself the right to fix the
number of directors,
• provide that a director may be removed
only by the vote of at least two-thirds of the votes entitled to be cast
generally in the election of directors and
• retain for itself sole authority to
fill vacancies created by an increase in the size of the board or the death,
removal or resignation of a director.
In
addition, a director elected to fill a vacancy under these provisions serves for
the balance of the unexpired term instead of until the next annual meeting of
stockholders. A board of directors may implement all or any of these provisions
without amending the charter or bylaws and without stockholder approval.
Although a corporation may be prohibited by its charter or by resolution of its
board of directors from electing any of the provisions of the statute, we have
not adopted such a prohibition. We have adopted a staggered board of directors
with 3 separate classes in our charter and given the board the right to fix the
number of directors, but we have not prohibited the amendment of these
provisions. The adoption of the staggered board may discourage offers
to acquire IGC stock and may increase the difficulty of completing an offer to
acquire our stock. If our board chose to implement the statutory provisions, it
could further discourage offers to acquire IGC stock and could further increase
the difficulty of completing an offer to acquire our stock.
Effect
of Certain Provisions of our Charter and Bylaws
In
addition to the Charter and Bylaws provisions discussed above, certain other
provisions of our Bylaws may have the effect of impeding the acquisition of
control of IGC by means of a tender offer, proxy fight, open market purchases or
otherwise in a transaction not approved by our board of directors. These
provisions of Bylaws are intended to reduce our vulnerability to an unsolicited
proposal for the restructuring or sale of all or substantially all of our assets
or an unsolicited takeover attempt which our board believes is otherwise unfair
to our stockholders. These provisions, however, also could have the effect of
delaying, deterring or preventing a change in control of IGC.
Stockholder Meetings; Advance Notice
of Director Nominations and New Business . Our Bylaws provide that with
respect to annual meetings of stockholders, (i) nominations of individuals for
election to our board of directors and (ii) the proposal of business to be
considered by stockholders may be made only:
• pursuant to IGC’s notice of the
meeting,
• by or at the direction of our board of
directors or
• by a stockholder who is entitled to
vote at the meeting and has complied with the advance notice procedures set
forth in our Bylaws.
Special
meetings of stockholders may be called only by the chief executive officer, the
board of directors or the secretary of IGC (upon the written request of the
holders of a majority of the shares entitled to vote). At a special meeting of
stockholders, the only business that may be conducted is the business specified
in IGC’s notice of meeting. With respect to nominations of persons for election
to our board of directors, nominations may be made at a special meeting of
stockholders only:
• pursuant to IGC’s notice of
meeting,
• by or at the direction of our board of
directors or
• if our board of directors has
determined that directors will be elected at the special meeting, by a
stockholder who is entitled to vote at the meeting and has complied with the
advance notice procedures set forth in our Bylaws.
These
procedures may limit the ability of stockholders to bring business before a
stockholders meeting, including the nomination of directors and the
consideration of any transaction that could result in a change in control and
that may result in a premium to our stockholders.
Our
Transfer Agent and Warrant Agent
The
transfer agent for our securities and warrant agent for our warrants is
Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company.
We have
an aggregate of 12,898,291 shares
of common stock outstanding. Of these shares, 9,333,191 shares
are either freely tradable without restriction or further registration under the
Securities Act of 1933, except for any shares purchased by one of our affiliates
within the meaning of Rule 144 under the Securities Act of 1933, or
registered for resale. Shares purchased by our affiliates include the
170,000 shares included in the units purchased in a private placement by
our officers and directors or their nominees, which were the subject of a
lock-up agreement with us and the representative of the underwriters until we
completed a business combination. Since we have completed a business
combination, the lock-up has terminated with respect to those
shares. All of the remaining 3,560,000 shares are restricted
securities under Rule 144, in that they were issued in private transactions
not involving a public offering. None of those will be eligible for sale under
Rule 144 until the one year holding period has elapsed with respect to each
purchase and the additional conditions described in “Restrictions on the Use of
Rule 144 by Shell Companies or Former Shell Companies” below are
satisfied.
Rule 144
In
general, under Rule 144 as currently in effect, a person (or persons whose
shares are aggregated) who is deemed to be an affiliate of ours at the time of
sale, or at any time during the preceding three months, and who has beneficially
owned restricted shares of our common stock for at least six months, would be
entitled to sell within any three-month period a number of shares that does not
exceed the greater of either of the following:
|
·
|
1%
of the number of shares of common stock then outstanding, which currently
equals
128,983 shares; and
|
|
·
|
the
average weekly trading volume of the common stock during the four calendar
weeks preceding the filing of a notice on Form 144 with respect to
the sale.
|
Sales
under Rule 144 are also limited by manner of sale provisions and notice
requirements and to the availability of current public information about
us.
A person
who has not been our affiliate at any time during the three months preceding a
sale, and who has beneficially owned his shares for at least six months, would
be entitled under Rule 144 to sell such shares without regard to any manner
of sale, notice provisions or volume limitations described above. Any such sales
must comply with the public information provision of Rule 144 until our
common stock has been held for one year.
Restrictions
on the Use of Rule 144 by Shell Companies or Former Shell Companies
Historically,
the SEC staff had taken the position that Rule 144 is not available for the
resale of securities initially issued by companies that are, or previously were,
blank check companies, like us. The SEC has codified and expanded this position
in recent amendments by prohibiting the use of Rule 144 for resale of securities
issued by any shell companies (other than business combination related shell
companies) or any issuer that has been at any time previously a shell
company. The SEC has provided an important exception to this
prohibition, however, if the following conditions are met:
|
·
|
the
issuer of the securities that was formerly a shell company has ceased to
be a shell company;
|
|
·
|
the
issuer of the securities is subject to the reporting requirements of
Section 13 or 15(d) of the Exchange
Act;
|
|
·
|
the
issuer of the securities has filed all Exchange Act reports and material
required to be filed, as applicable, during the preceding 12 months (or
such shorter period that the issuer was required to file such reports and
materials), other than Form 8-K reports;
and
|
|
·
|
at
least one year has elapsed from the time that the issuer filed current
Form 10 type information with the SEC reflecting its status as an entity
that is not a shell company.
|
We have satisfied the preceding
requirements and as a result, pursuant to Rule 144, our initial shareholders are
able to sell their initial shares freely without
registration.
SEC
Position on Rule 144 Sales
The SEC
has taken the position that promoters or affiliates of a blank check company and
their transferees, both before and after a business combination, would act as an
“underwriter” under the Securities Act of 1933 when reselling the securities of
a blank check company. Accordingly, the SEC believes that those securities can
be resold only through a registered offering and that Rule 144 would not be
available for those resale transactions despite technical compliance with the
requirements of Rule 144.
Registration Rights
The
officer, director and our special advisor holders of our 2,500,000 shares
of common stock that are issued and outstanding on the date of this prospectus
are entitled to registration rights pursuant to an agreement dated as of March
8, 2005. The 170,000 shares purchased by such persons in the private
placement are also be entitled to registration rights pursuant to the agreement.
Our Chairman, Dr. Ranga Krishna, also owns 446,226 shares of our common stock
that he acquired in a separate private placement in connection with his lending
money to us that are be entitled to registration rights pursuant to
the agreement The holders of the majority of these shares are entitled to
make up to two demands that we register these shares. The holders of the
majority of these shares can elect to exercise these registration rights at any
time after the date on which the lock-up period expires. In addition, these
stockholders have certain “piggy-back” registration rights on registration
statements filed subsequent to such date. We will bear the expenses incurred in
connection with the filing of any such registration statements.
Oliveira
Capital, LLC which acquired warrants to purchase 425,000 shares of our common
stock (at an initial exercise price of $5.00 per share) and 103,774 shares of
our common stock (at an initial exercise price of $5.00 per share) in two
private placements in connection with it lending money to us is entitled
to “piggy-back” registration rights for the shares, the warrants and
the warrants underlying the shares, pursuant to an agreement dated as of
February 5, 2007, on registration statements filed subsequent to such
date.
The
holders of an aggregate of 204,953 shares of our common stock acquired in a
private placement in connection with the purchase of promissory notes from the
Company entered into a registration rights agreement providing registration
rights similar to those provided to the Company’s founders except that they are
only entitled to one demand registration.
Steven M.
Oliveira 1998 Charitable Remainder Unitrust, the holder of an aggregate of
200,000 shares of our common stock acquired in a private placement in connection
with the purchase of a promissory note from the Company entered into a
registration rights agreement requiring the Company to file a registration
statement registering the shares for resale on or before November 14, 2008 and
to have that registration statement effective by December 14, 2008 (subject to
extension if certain conditions are met) If the Company fails to meet
those deadlines, the trust will be entitled to an additional 50,000 shares of
common stock and, if the deadline is unmet for 30 days, an additional 10,000
shares and a further 10,000 shares for each subsequent 30 day period such
deadline is unmet.
We satisfied the registration
rights described in the preceding paragraphs by registering all of the shares
and warrants described in the preceding paragraphs for resale on a registration
statement on Form S-1 that was declared effective on November 12,
2008.
Bricoleur
Partners, L.P., the holder of an aggregate of 530,000 shares of our common stock
acquired in a private placement in connection with the purchase of a promissory
note from the Company entered into a registration rights agreement requiring the
Company to file a registration statement registering the shares for resale on or
before November 30, 2009 and to have that registration statement effective by
December 30, 2009 (subject to extension if certain conditions are
met) If the Company fails to meet those deadlines, Bricoleur will be
entitled to an additional 50,000 shares of common stock and, if the deadline is
unmet for 60 days, an additional 10,000 shares and a further 10,000 shares for
each subsequent 60 day period such deadline is unmet. We satisfied the registration rights described in this paragraph
by registering all of the shares for resale on a registration statement on Form
S-3 that was declared effective on February 4, 2010.
Shares
Issuable Upon Default of Notes
Pursuant
to the terms of Note and Shares Purchase Agreements entered into by the Company
with each of Steven M. Oliveira 1998 Charitable Remainder Unitrust and Bricoleur
Partners, L.P., if an event of default occurs with respect to the promissory
notes issued by the Company to the Unitrust and Bricoleur and such default is
uncured for a period of 30 days, the Company is required to issue to the
Unitrust and/or Bricoleur, as applicable, 200,000 shares of the Company’s common
stock.
Employee
Stock Options
We intend
to file a registration statement on Form S-8 under the Securities Act to
register up to 1,869,083 shares of common stock that are issuable under our
2008 Omnibus Incentive Plan. Shares issued upon the exercise of options after
the effective date of such registration statement, when filed, other than shares
issued to affiliates, generally will be freely tradable without further
registration under the Securities Act.
The
validity of the securities offered in this prospectus is being passed upon for
us by Seyfarth Shaw LLP, Chicago, Illinois.
The
consolidated financial statements of IGC for the years ending March 31, 2009 and
March 31, 2008 included herein have been audited by Yoganandh & Ram, an
independent registered public accounting firm, as set forth in their report
appearing elsewhere herein, and are included in reliance upon such report given
on the authority of such firm as experts in accounting and
auditing.
This
prospectus, which is part of a registration statement filed with the SEC, does
not contain all of the information set forth in the registration statement or
the exhibits filed therewith. For further information with respect to us and the
common stock offered by this prospectus, please see the registration statement
and exhibits filed with the registration statement.
You may
also read and copy any materials we have filed with the SEC at the SEC’s public
reference room, located at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, DC 20549. Please call
the SEC at 1-800-SEC-0330 for further information on the public reference room.
In addition, our SEC filings, including reports, proxy statements and other
information regarding issuers that file electronically with the SEC, are also
available to the public at no cost from the SEC’s website at http://www.sec.gov.
No person
is authorized to give any information or to make any representation other than
those contained in this prospectus, and if made such information or
representation must not be relied upon as having been given or authorized. This
prospectus does not constitute an offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to
buy any security other than the securities offered by this prospectus, or an
offer to sell or a solicitation of an offer to buy any securities by anyone in
any jurisdiction in which the offer or solicitation is not authorized or is
unlawful. The delivery of this prospectus will not, under any circumstances,
create any implication that the information is correct as of any time subsequent
to the date of this prospectus.
|
Page
|
|
|
Index
to Consolidated Financial Statements and Audited Historical Financial
Statements
|
|
|
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
|
|
|
F-1
|
|
|
F-2
|
|
|
F-3
|
|
|
F-4
|
|
|
F-5
|
|
|
F-6
|
|
|
F-7
|
|
|
F-19
|
|
|
F-20
|
|
|
F-21
|
|
|
F-22
|
|
|
F-23
|
|
|
F-24
|
To the
Board of Directors and Stockholders
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
In our
opinion, the accompanying consolidated balance sheets and the related
consolidated statements of operations, shareholders' equity and comprehensive
loss, and of cash flows present fairly, in all material respects, the financial
position of India Globalization Capital, Incorporated and its subsidiaries at
March 31, 2009 and 2008, and the results of their operations and their cash
flows for each of the two years in the period ended March 31, 2009 in conformity
with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America.
These financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management.
Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these financial statements based
on our audits. We conducted our audits of these statements in accordance with
the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States).
Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable
assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material
misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting
the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements, assessing the
accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, and
evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our
audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
/s/
Yoganandh &
Ram
Independent
Auditors registered with
Public
Company Accounting Oversight Board (USA)
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
|
March
31, 2009
|
March
31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
ASSETS
|
||||||||
|
Current
Assets:
|
||||||||
|
Cash
and cash equivalents
|
$
|
2,129,365
|
$
|
8,397,441
|
||||
|
Accounts
Receivable
|
9,307,088
|
8,708,861
|
||||||
|
Unbilled
Receivables
|
2,759,632
|
5,208,722
|
||||||
|
Inventories
|
2,121,837
|
1,550,080
|
||||||
|
Interest
Receivable - Convertible Debenture
|
277,479
|
|||||||
|
Convertible
debenture in MBL
|
3,000,000
|
|||||||
|
Prepaid
taxes
|
88,683
|
49,289
|
||||||
|
Restricted
cash
|
6,257
|
|||||||
|
Short
term investments
|
671
|
|||||||
|
Prepaid
expenses and other current assets
|
2,801,148
|
4,324,201
|
||||||
|
Due
from related parties
|
290,831
|
1,373,446
|
||||||
|
Total
Current Assets
|
19,498,584
|
32,896,447
|
||||||
|
Property
and equipment, net
|
6,601,394
|
7,337,361
|
||||||
|
Accounts
Receivable – Long Term
|
2,769,196
|
3,519,965
|
||||||
|
Goodwill
|
17,483,501
|
17,483,501
|
||||||
|
Investment
|
70,743
|
1,688,303
|
||||||
|
Deposits
towards acquisitions
|
261,479
|
187,500
|
||||||
|
Restricted
cash, non-current
|
1,430,137
|
2,124,160
|
||||||
|
Deferred
tax assets - Federal and State, net of valuation allowance
|
898,792
|
1,013,611
|
||||||
|
Other
Assets
|
2,818,687
|
1,376,126
|
||||||
|
Total
Assets
|
$
|
51,832,513
|
$
|
67,626,973
|
||||
|
LIABILITIES
AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
Current
Liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Short-term
borrowings and current portion of long-term debt
|
$
|
3,422,239
|
$
|
5,635,408
|
||||
|
Trade
payables
|
462,354
|
1,771,151
|
||||||
|
Advance
from Customers
|
206,058
|
931,092
|
||||||
|
Accrued
expenses
|
555,741
|
1,368,219
|
||||||
|
Taxes
payable
|
76,569
|
58,590
|
||||||
|
Notes
Payable to Oliveira Capital, LLC
|
1,517,328
|
3,000,000
|
||||||
|
Due
to related parties
|
1,214,685
|
1,330,291
|
||||||
|
Other
current liabilities
|
1,991,371
|
3,289,307
|
||||||
|
Total
current liabilities
|
$
|
9,446,345
|
$
|
17,384,059
|
||||
|
Long-term
debt, net of current portion
|
1,497,458
|
1,212,841
|
||||||
|
Advance
from Customers
|
832,717
|
|||||||
|
Deferred
taxes on income
|
590,159
|
608,535
|
||||||
|
Other
liabilities
|
2,440,676
|
6,717,109
|
||||||
|
Total
Liabilities
|
$
|
13,974,638
|
$
|
26,755,261
|
||||
|
Minority
Interest
|
14,262,606
|
13,545,656
|
||||||
|
Common
stock subject to possible conversion, 11,855,122 shares at conversion
value
|
-
|
-
|
||||||
|
COMMITMENTS
AND CONTINGENCY
|
||||||||
|
STOCKHOLDERS’
EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
Preferred
stock $.0001 par value; 1,000,000 shares authorized; none issued and
outstanding
|
-
|
|||||||
|
Common
stock — $.0001 par value; 75,000,000 shares authorized; 10,091,171
issued
and
outstanding at March 31, 2009 and 8,570,107 issued and outstanding at
March 31, 2008.
|
1,009
|
857
|
||||||
|
Additional
paid-in capital
|
33,186,530
|
31,470,134
|
||||||
|
Retained
Earnings (Deficit)
|
(4,662,689
|
)
|
(4,141,113
|
)
|
||||
|
Accumulated
other comprehensive (loss) income
|
(4,929,581
|
)
|
(3,822
|
)
|
||||
|
Total
stockholders’ equity
|
23,595,269
|
27,326,056
|
||||||
|
Total
liabilities and stockholders’ equity
|
$
|
51,832,513
|
$
|
67,626,973
|
||||
The
accompanying notes should be read in connection with the financial
statements.
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
|
Year
Ended March 31, 2009
|
Year
Ended March 31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
Revenue
|
$
|
35,338,725
|
$
|
2,188,018
|
||||
|
Cost
of revenue
|
(27,179,494
|
)
|
(1,783,117
|
)
|
||||
|
Gross
profit
|
8,159,231
|
404,901
|
||||||
|
Selling,
general and administrative expenses
|
(4,977,815
|
)
|
(367,647
|
)
|
||||
|
Depreciation
|
(873,022
|
)
|
(58,376
|
)
|
||||
|
Operating
income
|
2,308,394
|
5,153
|
||||||
|
Legal
and formation, travel and other start up costs
|
(5,765,620
|
)
|
||||||
|
Interest
expense
|
(1,753,952
|
)
|
(1,944,660
|
)
|
||||
|
Interest
income
|
1,176,018
|
2,213,499
|
||||||
|
Other
Income
|
202,858
|
|||||||
|
Income
/ (loss) before income taxes
|
1,730,461
|
(5,315,044
|
)
|
|||||
|
Provision
for income taxes, net
|
(1,535,087
|
)
|
(76,089
|
)
|
||||
|
Income
after Income Taxes
|
195,373
|
(5,391,134
|
)
|
|||||
|
Provision
for Dividend on Preference Stock and its Tax
|
171,084
|
|||||||
|
Minority
interest
|
(716,950
|
)
|
4,780
|
|||||
|
Net
income / (loss)
|
$
|
(521,576
|
)
|
$
|
(5,215,270
|
)
|
||
|
Net
income / (loss) per share: basic and diluted
|
$
|
(0.05
|
)
|
$
|
(0.61
|
)
|
||
|
Weighted
average number of shares outstanding-basic and diluted
|
10,091,171
|
8,570,107
|
||||||
The
accompanying notes should be read in connection with the financial
statements.
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
|
Year
Ended March 31, 2009
|
Year
Ended March 31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
Net
income / (loss)
|
$
|
(521,576
|
)
|
$
|
(5,215,270
|
)
|
||
|
Foreign
currency translation adjustments
|
(4,925,759
|
)
|
(3,822
|
)
|
||||
|
Comprehensive
income (loss)
|
$
|
(5,447,335
|
)
|
$
|
(5,219,092
|
)
|
||
The
accompanying notes should be read in connection with the financial
statements.
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
|
Common
Stock
|
Additional
Paid-in
|
Accumulated
Earnings
|
Accumulated
Other Comprehensive Income
|
Total
Stockholders'
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Shares
|
Amount
|
Capital
|
(Deficit)
|
/
Loss
|
Equity
|
|||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance
at April 1, 2007
|
13,974,500 | $ | 1,397 | $ | 51,848,145 | $ | 1,074,157 | $ | $ | 52,923,699 | ||||||||||||||
|
Redemption
of 1,910,469 shares on March 7, 2008 and balance in shares subject to
possible conversion transferred to paid in capital
|
(1,910,469 | ) | (191 | ) | 1,689,164 | 1,688,973 | ||||||||||||||||||
|
Buyback
of 4,248,877 shares on March 7, 2008
|
(4,248,877 | ) | (425 | ) | (25,237,905 | ) | (25,238,330 | ) | ||||||||||||||||
|
"Issuance
of common stock to Bridge Investors at $.01 per share
|
754,953 | 76 | 3,170,730 | 3,170,805 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net
Loss for the year
|
- | - | - | (5,215,270 | ) | (3,822 | ) | (5,219,091 | ) | |||||||||||||||
|
Balance
at March 31, 2008
|
8,570,107 | $ | 857 | $ | 31,470,134 | $ | (4,141,113 | ) | $ | (3,822 | ) | $ | 27,326,056 | |||||||||||
|
Fair
value of 425,000 warrants issued to Oliveira Capital, LLC
|
403,750 | 403,750 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance
of common stock to RedChip Companies at $4.71 per share
|
10,000 | 1 | 47,098 | 47,099 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Fair
value of 200,000 common stock issued to Oliveira Trust
|
200,000 | 20 | 967,980 | 968,000 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Conversion
of Warrants to Equity shares – 1,311,064 shares
|
1,311,064 | 131 | 297,568 | 297,699 | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net
income / (Loss)
|
(521,576 | ) | (521,576 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Foreign
currency translation adjustments
|
(4,925,759 | ) | (4,925,759 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance
at March 31, 2009
|
10,091,171 | $ | 1,009 | $ | 33,186,530 | $ | (4,662,689 | ) | $ | (4,929,581 | ) | $ | 23,595,269 | |||||||||||
The
accompanying notes should be read in connection with the financial
statements.
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
|
Year
Ended March 31, 2009
|
Year
Ended March 31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
Cash
flows from operating activities:
|
||||||||
|
Net
income (loss)
|
$
|
(521,576
|
)
|
$
|
(5,215,270
|
)
|
||
|
Adjustment
to reconcile net income (loss) to net cash used in operating
activities:
|
||||||||
|
Interest
earned on Treasury Bills
|
(2,119,104
|
)
|
||||||
|
Non-cash
compensation expense
|
450,850
|
|||||||
|
Deferred
taxes
|
221,037
|
(743,652
|
)
|
|||||
|
Depreciation
|
873,022
|
58,376
|
||||||
|
Loss
/ (Gain) on sale of property, plant and equipment
|
211,509
|
29
|
||||||
|
Amortization
of debt discount on Oliveira debt
|
2,652
|
4,052,988
|
||||||
|
Amortization
of loan acquisition cost
|
250,000
|
|||||||
|
Changes
in:
|
||||||||
|
Accounts
receivable
|
(2,725,195
|
)
|
808,978
|
|||||
|
Unbilled
Receivable
|
1,484,960
|
(635,207
|
)
|
|||||
|
Inventories
|
(1,001,389
|
)
|
341,950
|
|||||
|
Prepaid
expenses and other current assets
|
1,099,188
|
(3,063,771
|
)
|
|||||
|
Trade
Payable
|
(1,033,319
|
)
|
(1,744,137
|
)
|
||||
|
Other
Current Liabilities
|
(832,556
|
)
|
(884,639
|
)
|
||||
|
Advance
from Customers
|
(1,311,200
|
)
|
(97,946
|
)
|
||||
|
Other
non-current liabilities
|
(3,155,767
|
)
|
3,050,821
|
|||||
|
Non-current
assets
|
(1,926,571
|
)
|
928,696
|
|||||
|
Accounts
receivable – Long Term
|
(50
|
)
|
||||||
|
Interest
receivable - convertible debenture
|
277,479
|
(240,000
|
)
|
|||||
|
Deferred
interest liability
|
(3,597,998
|
)
|
||||||
|
Accrued
expenses
|
(922,300
|
)
|
854,902
|
|||||
|
Prepaid
/ taxes payable
|
(21,415
|
)
|
(569,283
|
)
|
||||
|
Minority
Interest
|
716,950
|
(4,780
|
)
|
|||||
|
Net
cash used in operating activities
|
$
|
(8,113,641
|
)
|
$
|
(8,569,097
|
)
|
||
|
Cash
flows from investing activities:
|
||||||||
|
Purchase
of treasury bills
|
(585,326,579
|
)
|
||||||
|
Maturity
of treasury bills
|
653,554,076
|
|||||||
|
Purchase
of property and equipment
|
(2,493,417
|
)
|
(3,447
|
)
|
||||
|
Proceeds
from sale of property and equipment
|
488,886
|
(13,521
|
)
|
|||||
|
Purchase
of short term investments
|
698
|
(1
|
)
|
|||||
|
Non
Current Investments
|
1,395,444
|
(498,677
|
)
|
|||||
|
Restricted
cash
|
272,754
|
(1,714,422
|
)
|
|||||
|
Decrease
(increase) in cash held in trust
|
(4,116
|
)
|
||||||
|
Redemption
of convertible debenture
|
3,000,000
|
|||||||
|
Deposit
towards acquisitions, net of cash acquired
|
220,890
|
(6,253,028
|
)
|
|||||
|
Payment
of deferred acquisition costs
|
(2,482,431
|
)
|
||||||
|
Net
cash provided/(used) in investing activities
|
$
|
2,885,255
|
$
|
57,257,854
|
||||
|
Cash
flows from financing activities:
|
||||||||
|
Issuance
of common stock to founders
|
(541
|
)
|
||||||
|
Net
movement in cash credit and bank overdraft
|
(1,215,253
|
)
|
646,515
|
|||||
|
Proceeds
from other short-term borrowings
|
(275,114
|
)
|
||||||
|
Proceeds
from long-term borrowings
|
1,287,940
|
(3,075,012
|
)
|
|||||
|
Repayment
of long-term borrowings
|
(591,927
|
)
|
(1,023
|
)
|
||||
|
Due
to related parties, net
|
583,235
|
(255,093
|
)
|
|||||
|
Issue
of Equity Shares
|
297,699
|
0
|
||||||
|
Money
received pending allotment
|
(3,669,574
|
)
|
||||||
|
Proceeds
from notes payable to stockholders
|
(270,000
|
)
|
||||||
|
Proceeds
from notes payable to stockholders
|
(600,000
|
)
|
||||||
|
Gross
proceeds from initial public offering
|
(33,140,796
|
)
|
||||||
|
Proceeds
from note payable to Oliveira Capital, LLC
|
2,000,000
|
(769,400
|
)
|
|||||
|
Repayment
of note payable to Oliveira Capital, LLC
|
(2,517,324
|
)
|
||||||
|
Proceeds
from other financing
|
31,047
|
|||||||
|
Net
cash provided/(used) by financing activities
|
$
|
(155,630
|
)
|
$
|
(41,378,991
|
)
|
||
|
Effect
of exchange rate changes on cash and cash equivalents
|
(884,059
|
)
|
(81,747
|
)
|
||||
|
Net
increase/(decrease) in cash and cash equivalent
|
(6,268,075
|
)
|
7,228,019
|
|||||
|
Cash
and cash equivalent at the beginning of the period
|
8,397,440
|
1,169,422
|
||||||
|
Cash
and cash equivalent at the end of the period
|
$
|
2,129,365
|
$
|
8,397,441
|
||||
|
Supplemental
schedule of non cash financing activities:
|
||||||||
|
Accrual
of deferred acquisition costs
|
$
|
26,000
|
||||||
|
Accrual
of loan acquisition cost
|
$
|
250,000
|
||||||
|
Value
of Common Stock to Bridge Investors
|
$
|
3,170,806
|
||||||
The
accompanying notes should be read in connection with the financial
statements.
INDIA
GLOBALIZATION CAPITAL, INC. AND SUBSIDIARIES
For
the Years Ended March 31, 2009 and 2008
NOTE
A — BASIS OF PRESENTATION
The
financial statements for March 31, 2009 and 2008 are audited. The
statements ending March 31, 2009 and 2008 are consolidated with all of our
subsidiaries. Sricon and TBL were acquired on March 8, 2008. IGC
Mining and Trading, Limited (IGC-IMT) was formed beneficially by IGC India
Globalization Capital, Mauritius, Limited (IGC-M) on December 16,
2008. All our companies have financial years that end on March
31.
In the
opinion of management, all adjustments (consisting of normal accruals) have been
made that are necessary to present fairly the financial position of the Company
as of March 31, 2009 and the results of its operation and cash flows for the
three years ended March 31, 2009 and 2008.
These
financial statements should be read in conjunction with the financial statements
that were included in the Company’s Annual Report on Form 10-KSB for the year
ended March 31, 2008. The March 31, 2008 and 2009 balance sheets,
statements of operations, statements of cash flows, and the statements of
stockholders’ equity have been derived from the audited financial
statements.
NOTE
B — ORGANIZATION AND BUSINESS OPERATIONS
India
Globalization Capital, Inc. (the “Company” or “IGC”), a Maryland
corporation, was incorporated on April 29, 2005 as a blank check
company, formed for the purpose of acquiring one or more infrastructure
businesses with operations primarily in India through a merger, capital stock
exchange, asset acquisition or other similar business combination or
acquisition. On March 8, 2006 the Company completed an initial public
offering. On February 19, 2007 the Company incorporated India
Globalization Capital, Mauritius, Limited (IGC-M), a wholly owned subsidiary,
under the laws of Mauritius.
Through
its subsidiaries, the company’s primary focus is to execute
major infrastructure projects in India such as constructing interstate
highways, rural roads, mining and quarrying, and construction of high
temperature cement and steel plants. IGC-IMT has been contracted to operate a
shipping hub and export iron ore to China.
The
registration statement for the Company’s initial public offering (the “Public
Offering”) (as described in Note C) was declared effective March 2, 2006. The
Company consummated the Public Offering including the over allotment option on
March 8, 2006, and preceding the consummation of the Public Offering on March 2,
2006 certain of the officers and directors of the Company purchased an aggregate
of 170,000 units (the “Units”) from the Company in a private placement (the
“Private Placement”). The Units sold in the Private Placement were
identical to the 11,304,500 Units sold in the Public Offering, but the
purchasers in the Private Placement waived their rights to conversion and
receipt of the distribution on liquidation in the event the Company did not
complete a business combination (as described below). The Company received net
proceeds from the Private Placement and the Public Offering of approximately
$62,815,000 (Note C).
As
described in Note K, on March 7, 2008 following the stockholder approval of and
pursuant to the terms of the purchase agreement, the Company consummated the
acquisition of 63% of the equity of Sricon Infrastructure Private Limited
(Sricon) for approximately $28.75 Million. As also
described in Note K, the Company paid about $12.03 Million for the acquisition
of 77% of Techni Bharathi Limited (TBL). The shares of the two Indian
companies, Sricon and TBL, are held by IGC-M. The founders and
management of Sricon own 37% of Sricon and the founders and management of TBL
own 23% of TBL.
NOTE
C — INITIAL PUBLIC OFFERING
On March
8, 2006, the Company sold 11,304,500 Units in the Public Offering, including the
exercise by the Underwriter of the over-allotment in full. Each Unit
consists of one share of the Company’s common stock, $.0001 par value, and two
redeemable common stock purchase warrants (“Warrants”). Each Warrant entitles
the holder to purchase from the Company one share of common stock at an exercise
price of $5.00. The Company has a right to redeem the Warrants in the event that
the last sale price of the common stock is at least $8.50 per share for any 20
trading-days within a 30-trading day period ending on the third day prior to the
date on which notice of redemption is given. If the Company redeems
the Warrants, either the holder will have to exercise the Warrants by purchasing
the common stock from the Company for $5.00, or the Warrants will
expire. The Warrants expire on March 3, 2011, or earlier upon
redemption.
In
connection with the Public Offering, the Company issued an option, for $100, to
the Underwriter to purchase 500,000 Units at an exercise price of $7.50 per
Unit. The Company has accounted for the fair value of the option, inclusive of
the receipt of the $100 cash payment, as an expense of the Public Offering
resulting in a charge directly to stockholders’ equity. The Company estimated,
using the Black-Scholes method, the fair value of the option granted to the
Underwriter as of the date of grant was approximately $756,200 using the
following assumptions: (1) expected volatility of 30.1%, (2) risk-free interest
rate of 3.9% and (3) expected life of five years. The estimated volatility was
based on a basket of Indian companies that trade in the United States or the
United Kingdom. The option may be exercised for cash or on a
“cashless” basis, at the holder’s option, such that the holder may use the
appreciated value of the option (the difference between the exercise prices of
the option and the underlying Warrants and the market price of the Units and
underlying securities) to exercise the option without the payment of any cash.
The Warrants underlying such Units are exercisable at $6.25 per
share.
NOTE
D — SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles
of Consolidation:
The
consolidated financial statements include the accounts of the Company and its
wholly owned subsidiaries. All material intercompany balances and transactions
have been eliminated.
Minority
interest in subsidiaries consists of equity securities issued by a subsidiary of
the Company. No gain or loss was recognized as a result of the issuance of these
securities, and the Company owned a majority of the voting equity of the
subsidiary both before and after the transactions. The Company reflects the
impact of the equity securities issuances in its investment in subsidiary and
additional paid-in-capital accounts for the dilution or anti-dilution of its
ownership interest in the subsidiary.
Use
of estimates:
The
preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make
estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and
liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of
the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during
the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those
estimates.
Revenue
recognition:
Revenue
is recognized based on the nature of activity when consideration can be
reasonably measured and there exists reasonable certainty of its
recovery.
Revenue
from sale of goods is recognized when substantial risks and rewards of ownership
are transferred to the buyer under the terms of the contract.
Revenue
from construction/project related activity and contracts for
supply/commissioning of complex plant and equipment is recognized as
follows:
|
|
|
a)
|
Cost
plus contracts: Contract revenue is determined by adding the aggregate
cost plus proportionate margin as agreed with the customer and expected to
be realized.
|
|
|
|
b)
|
Fixed
price contracts: Contract revenue is recognized using the percentage
completion method. Percentage of completion is determined as a proportion
of cost incurred-to-date to the total estimated contract cost. Changes in
estimates for revenues, costs to complete and profit margins are
recognized in the period in which they are reasonably
determinable
|
Full
provision is made for any loss in the period in which it is
foreseen.
Revenue
from property development activity is recognized when all significant risks and
rewards of ownership in the land and/or building are transferred to the customer
and a reasonable expectation of collection of the sale consideration from the
customer exists.
Revenue
from service related activities and miscellaneous other contracts are recognized
when the service is rendered using the proportionate completion method or
completed service contract method.
Income
per common share:
Basic
earnings per share is computed by dividing net income (loss) applicable to
common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding
for the period. Diluted earnings per share reflect the additional dilution for
all potentially dilutive securities such as stock warrants and options. The
effect of the 23,374,000 warrants have been included in the diluted weighted
average shares. However, for the years ending March 31, 2008
and 2009, the weighted average price of the common stock was below the exercise
price of all outstanding warrants and therefore the warrants did not contribute
to the dilution of basic shares.
Income
taxes:
Deferred
income taxes are provided for the differences between the bases of assets and
liabilities for financial reporting and income tax purposes. A valuation
allowance is established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the
amount expected to be realized.
Cash
and Cash Equivalents:
For
financial statement purposes, the Company considers all highly liquid debt
instruments with maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash
equivalents. The company maintains its cash in bank accounts in the United
States of America and Mauritius, which at times may exceed applicable insurance
limits. The Company has not experienced any losses in such accounts. The Company
believes it is not exposed to any significant credit risk on cash and cash
equivalent. The company does not invest its cash in securities that
have an exposure to U.S. mortgages.
Restricted
cash:
Restricted
cash consists of deposits pledged with various government authorities and
deposits restricted as to usage under lien to banks for guarantees and letters
of credit given by the Company. The restricted cash is primarily invested in
time deposits with banks.
Accounts
receivable:
Accounts
receivables are recorded at the invoiced amount. Account balances are written
off when the company believes that the receivables will not be recovered. The
company’s bad debts are included in selling and general administrative expenses.
The company did not recognize any bad debts during the year ended March 31, 2009
and March 31, 2008, respectively.
Inventories:
Inventories
primarily comprise finished goods, raw materials, work in progress, stock at
customer site, stock in transit, components and accessories, stores and spares,
scrap, residue and real estate. Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or
estimated net realizable value.
The Cost
of various categories of inventories is determined on the following
basis:
Raw
Material are valued at weighted average of landed cost (Purchase price, Freight
inward and transit insurance charges), Work in progress is valued as confirmed,
valued & certified by the technicians & site engineers and Finished
Goods at material cost plus appropriate share of labor cost and production
overhead. Components and accessories, stores erection, materials, spares and
loose tools are valued on a First-in-First out basis. Real Estate is valued at
the lower of cost or net realizable value.
Accounts
Receivable – Long Term:
Known in
India as Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT). It is money due to the company by the
private or public sector to finance, design, construct, and operate a facility
stated in a concession contract over an extended period of time.
Investments:
Investments
are initially measured at cost, which is the fair value of the consideration
given for them, including transaction costs. Investments generally comprises of
fixed deposits with banks.
Property,
Plant and Equipment:
Property
and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation of
computers, construction, scrap processing and other equipments, buildings and
other assets are provided based on the Straight-line method over useful life of
the assets.
The value
of plant and equipment that are capitalized include the acquisition price and
other direct attributable expenses.
The
estimated useful life of various categories of assets are as
follows:
|
Category
|
Useful
Life (years)
|
|
|
Building
(Flat)
|
25
|
|
|
Plant
and Machinery
|
20
|
|
|
Computer
Equipment
|
3
|
|
|
Office
Equipment
|
5
|
|
|
Furniture
and Fixtures
|
5
|
|
|
Vehicles
|
5
|
|
|
Leasehold
Improvements
|
Over
the period of lease or useful life (if
less)
|
Upon
disposition, cost and related accumulated depreciation of the Property and
equipment are removed from the accounts and the gain or loss is reflected in the
results of operation. Cost of additions and substantial improvements to property
and equipment are capitalized in the books of accounts. The cost of maintenance
and repairs of the property and equipment are charged to operating
expenses.
Policy
for Goodwill / Impairment:
Goodwill
represents the excess cost of an acquisition over the fair value of the Group's
share of net identifiable assets of the acquired subsidiary at the date of
acquisition. Goodwill on acquisition of subsidiaries is disclosed
separately. Goodwill is stated at cost less accumulated amortization
and impairment losses, if any.
The
company adopted provisions of FAS No. 142, "Goodwill and Other Intangible
Assets" ('FAS 142') which sets forth the accounting for goodwill and intangible
assets subsequent to their acquisition. FAS142 requires that goodwill and
indefinite-lived intangible assets no longer be amortized, but instead tested
for impairment at least annually.
The
goodwill impairment test under FAS 142 is performed in two phases during the
fourth quarter of each year. The first step of the impairment test, used to
identify potential impairment compares the fair value of the reporting unit with
its carrying amount, including goodwill. If the carrying amount of the reporting
unit exceeds its fair value, goodwill of the reporting unit is considered
impaired, and step two of the impairment test must be performed. The second step
of the impairment test quantifies the amount of the impairment loss by comparing
the carrying amount of goodwill to the implied fair value. An impairment loss is
recorded to the extent the carrying amount of goodwill exceeds its implied fair
value .
Impairment
of long – lived assets and intangible assets:
The
company reviews its long-lived assets, including identifiable intangible
assets with finite lives, for impairment whenever events or changes in business
circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of assets may not be fully
recoverable. Such circumstances include, though are not limited to, significant
or sustained declines in revenues or earnings and material adverse changes in
the economic climate. For assets that the company intends to hold for
use, if the total of the expected future undiscounted cash flows produced by the
assets or subsidiary company is less than the carrying amount of the assets, a
loss is recognized for the difference between the fair value and carrying value
of the assets. For assets the company intends to dispose of by
sale, a loss is recognized for the amount by which the estimated fair value less
cost to sell is less than the carrying value of the assets. Fair
value is determined based on quoted market prices, if available, or other
valuation techniques including discounted future net cash flows.
Asset
retirement obligations:
Asset
retirement obligations associated with the Company’s leasehold land are subject
to the provisions of FAS No. 143 “Accounting for Asset Retirement Obligations”
and related interpretation, FIN No. 47, “Accounting for Conditional Asset
Retirement Obligations, an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 143” . The lease
agreements entered into by the Company may contain clauses requiring restoration
of the leased site at the end of the lease term and therefore create asset
retirement obligations. The Company records the fair value of a liability for an
asset retirement obligation in the period in which it is incurred and
capitalizes the cost by increasing the carrying amount of the related long-lived
asset. Over time, the liability is accreted to its present value of each period,
and the capitalized cost is depreciated over the estimated useful life of the
related asset. Upon settlement of the liability, the Company either settles the
obligation for its recorded amount or incurs a gain or loss upon
settlement.
Foreign
currency transactions:
Monetary
assets and liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are expressed in the
functional currency Indian Rupees at the rates of exchange in effect at the
balance sheet date. Transactions in foreign currencies are recorded at rates
ruling on the transaction dates. Adjustments resulting from the translation of
functional currency financial statements to reporting currency are accumulated
and reported as other comprehensive income/(loss), a separate component of
shareholders’ equity.
Operating
leases:
Lease
payments under operating leases are recognized as an expense on a straight-line
basis over the lease term.
Capital
leases:
Assets
acquired under capital leases are capitalized as assets by the Company at the
lower of the fair value of the leased property or the present value of the
related lease payments or where applicable, the estimated fair value of such
assets. Amortization of leased assets is computed on straight line basis over
the useful life of the assets. Amortization charge for capital leases is
included in depreciation expense.
Recent
Pronouncements:
The
Company adopted FASB Interpretation No. 48, “Accounting for Uncertainty in
Income Taxes,” an interpretation of FASB Statement No. 109 (“FIN 48”) on
April 1, 2007. FIN 48 clarifies the criteria for the recognition,
measurement, presentation and disclosure of uncertain tax positions. A tax
benefit from an uncertain position may be recognized only if it is “more likely
than not” that the position is sustainable based on its technical merits. FIN 48
also provides guidance on de-recognition, classification, interest and
penalties, accounting in interim periods, disclosure, and
transition. In May 2007, the FASB issued Staff Position, FIN 48-1,
“ Definition of Settlement in
FASB Interpretation No. 48 ” (FSP FIN 48-1) which provides guidance on
how an enterprise should determine whether a tax position is effectively settled
for the purpose of recognizing previously unrecognized tax
benefits. FSP FIN 48-1 was effective with the initial adoption
of FIN 48. The adoption of FIN 48 or FSP FIN 48-1 did not have a material
effect on the Company’s financial condition or results of
operations.
In
September 2006, the FASB issued FAS No.157, “Fair Value Measurements” (FAS No.
157). FAS No. 157 clarifies the principle that fair value should be based on the
assumptions market participants would use when pricing an asset or liability and
establishes a fair value hierarchy that prioritizes the information used to
develop those assumptions. The Company’s adoption of this Standard on January 1,
2008 did not have a material effect on its financial statements. Relative to FAS
157, the FASB issued FASB Staff Positions (FSP) FAS 157-1, FAS 157-2, and FAS
157-3. FSP FAS 157-1 amends SFAS 157 to exclude SFAS No. 13,“Accounting for
Leases” (SFAS 13), and its related interpretive accounting pronouncements that
address leasing transactions, while FSP FAS 157-2 delays the effective date of
the application of SFAS 157 to fiscal years beginning after November 15, 2008
for all nonfinancial assets and nonfinancial liabilities that are recognized or
disclosed at fair value in the financial statements on a non-recurring basis.
FSP FAS 157-3 clarifies the application of FAS 157 as it relates to the
valuation of financial assets in a market that is not active for those financial
assets. This FSP is effective immediately and includes those periods for which
financial statements have not been issued. We currently do not have any
financial assets that are valued using inactive markets, and as such are not
impacted by the issuance of this FSP.
In
February 2007, the FASB issued FAS No. 159, “The Fair Value Option for Financial
Assets and Financial Liabilities— Including an amendment of FASB Statement
No. 115” (FAS No. 159). FAS No. 159 provides companies with a choice to measure
certain financial assets and liabilities at fair value that are not currently
required to be measured at fair value (the “Fair Value Option”). Election of the
Fair Value Option is made on an instrument-by-instrument basis and is
irrevocable. The Company’s adoption of this Standard on January 1, 2008 did not
have a material effect on its financial statements.
In
December 2007, the Financial Accounting Standards Board released SFAS 160
“Non-controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements” that is
effective for annual periods beginning December 15, 2008. The pronouncement
resulted from a joint project between the FASB and the International Accounting
Standards Board and continues the movement toward the greater use of fair values
in financial reporting. Upon adoption of SFAS 160, the Company will re-classify
any non-controlling interests as a component of equity.
Management
does not believe that any other recently issued, but not yet effective,
accounting standards if currently adopted would have a material effect on the
accompanying financial statements.
Segment
and Geographic Reporting:
India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and its subsidiaries are significantly engaged in
one segment, infrastructure construction. Since there is no Chief
Officer who allocates resources as described in FAS No. 131, the Company is not
required to report its operations by business segment reporting. All
revenue reporting in the years ending March 31, 2009 and March 31, 2008 were
earned solely in India. Therefore, no disclosures indicating source
country revenue is provided in this annual report.
NOTE
E – SHORT TERM BORROWINGS & CURRENT PORTION OF LONG-TERM DEBT
(Amounts
in thousand US Dollars)
Short
term debt for the consolidated companies consists of the
following:
|
As
of March 31, 2009
|
As
of March 31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
Secured
|
$
|
2,502
|
$
|
4,556
|
||||
|
Unsecured
|
249
|
3,306
|
||||||
|
Total
|
2,751
|
7,862
|
||||||
|
Add:
|
||||||||
|
Current
portion of long term debt
|
671
|
773
|
||||||
|
Total
|
$
|
3,422
|
$
|
8,635
|
||||
The above
debt is secured by hypothecation of materials/stock of spares, Work in Progress,
receivables and property & equipment in addition to personal guarantee of
three directors & collaterally secured by mortgage of company’s land &
other immovable properties of directors and their relatives.
LONG
TERM DEBT:
(Amounts
in thousand US Dollars)
Long term
debt for the consolidated companies consists of the following:
|
As
March 31, 2009
|
As
of March 31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
Secured
|
$
|
-
|
$
|
-
|
||||
|
Term
loans
|
-
|
632
|
||||||
|
Loan
for assets purchased under capital lease
|
2,169
|
1,354
|
||||||
|
Total
|
2,169
|
1,986
|
||||||
|
Less:
Current portion (Payable within 1 year)
|
671
|
773
|
||||||
|
Total
|
$
|
1,498
|
$
|
1,213
|
||||
The
secured loans were collateralized by:
|
.
|
Unencumbered
Net Asset Block of the Company
|
|
.
|
Equitable
mortgage of properties owned by promoter directors/
guarantors
|
|
.
|
Term
Deposits
|
|
.
|
Hypothecation
of receivables, assignment of toll rights, machineries and vehicles and
collaterally secured by deposit of title deeds of
land
|
|
.
|
First
charge on Debt-Service Reserve
Account
|
NOTE
F — RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
From
inception to March 31, 2009, $50,000 was paid to SJS Associates for Mr.
Selvaraj’s services. We entered into an agreement with SJS Associates
on substantially the same terms subsequent to the stockholder’s approval of the
acquisitions of Sricon and TBL. As a result of the new agreement, an
additional $3,871 was accrued as due to SJS Associates for the period between
March 8, 2008 and March 31, 2008. This was paid to SJS Associates in
the Company’s 2009 fiscal year.
The
Company had agreed to pay Integrated Global Network, LLC (“IGN, LLC”), an
affiliate of our Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Mukunda, an administrative fee of
$4,000 per month for office space and general and administrative services from
the closing of the Public Offering through the date of a Business
Combination. From inception to March 31, 2009, approximately $144,000 was
paid to IGN, LLC. During March of 2008, the Company and IGN, LLC
agreed to continue the agreement on a month-to-month basis.
The
Company uses the services of Economic Law Practice (ELP), a law firm in
India. A member of our Board Directors is a Partner with ELP.
Since inception to March 31, 2009, the Company has incurred $186,303 for legal
services provided by ELP.
NOTE
G — COMMON STOCK
On August
24, 2005, the Company’s Board of Directors authorized a reverse stock split of
one share of common stock for each two outstanding shares of common stock and
approved an amendment to the Company’s Certificate of Incorporation to decrease
the number of authorized shares of common stock to 75,000,000. All references in
the accompanying financial statements to the number of shares of stock have been
retroactively restated to reflect these transactions. On March 7,
2008 we redeemed and bought a total of 6,159,346 shares at $5.94 per
share. At March 31, 2008 and 2007 we had 8,570,107 and 13, 974,500
shares of common stock issued and outstanding respectively. At
March 31, 2008 and 2007, 24,874,000 shares of common stock, were reserved for
issuance upon exercise of redeemable warrants, underwriters’ purchase option and
warrants issued to Oliveira Capital, LLC. At March 31, 2009 we had
10,091,171shares of common stock issued and outstanding.
NOTE H
– INCOME TAXES
The
provision for income taxes for the year ended March 31, 2009 and the period
ended March 31, 2008 consists of the following:
|
March
31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Current:
|
||||||||
|
Federal
|
$
|
61,355
|
$
|
708,868
|
||||
|
Foreign
|
1,396,248
|
(370,355
|
)
|
|||||
|
State
|
0
|
-
|
||||||
|
Net
Current
|
1,457,603
|
338,513
|
||||||
|
Deferred:
|
||||||||
|
Federal
|
10,322
|
(748,894
|
)
|
|||||
|
Foreign
|
95,824
|
420,368
|
||||||
|
State
|
0
|
66,103
|
||||||
|
Net
Deferred
|
106,146
|
(262,424
|
)
|
|||||
|
Total
tax provision
|
$
|
1,563,750
|
$
|
76,089
|
||||
The total
tax provision for income taxes for year ended March 31, 2009 and the period
ended March 31, 2008 differs from that amount which would be computed by
applying the U.S. Federal income tax rate to income before provision for income
taxes as follows:
|
March
31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Statutory
Federal income tax rate
|
34
|
%
|
34
|
%
|
||||
|
State
tax benefit net of federal tax
|
0
|
%
|
(0.8
|
)%
|
||||
|
Increase
in state valuation allowance
|
0
|
%
|
0.8
|
%
|
||||
|
Effective
income tax rate
|
34
|
%
|
34.0
|
%
|
||||
|
March
31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Operating
costs deferred for income tax purposes
|
$
|
(183,129
|
)
|
$
|
184,570
|
|||
|
Interest
income deferred for reporting purposes
|
0
|
95,792
|
||||||
|
Difference
between accrual accounting for reporting purposes and cash accounting for
tax purposes
|
599,802
|
235,665
|
||||||
|
Less:
Valuation Allowance
|
(108,041
|
)
|
(110,951
|
)
|
||||
|
Net
deferred tax asset
|
$
|
309,252
|
$
|
405,076
|
||||
The
Company has recorded a valuation allowance against the state deferred tax asset
since they cannot determine realizability for tax purposes and therefore cannot
conclude that the deferred tax asset is more likely than not recoverable at this
time.
NOTE
I — COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCY
The
Founders will be entitled to registration rights with respect to their shares of
common stock acquired prior to the Public Offering and the shares of common
stock they purchased in the Private Placement pursuant to an agreement executed
on March 3, 2006. The holders of the majority of these shares are entitled
to make up to two demands that the Company register these shares at any time
after the date on which the lock-up period expires. In addition, the
Founders have certain “piggy-back” registration rights on registration
statements filed subsequent to the anniversary of the effective date of the
Public Offering.
NOTE
J – INVESTMENT ACTIVITIES
Contract
Agreement between IGC, CWEL, AMTL and MAIL
As
previously disclosed in our Form 8-K dated May 2, 2007 and Form 10-QSB for the
quarterly period ended June 30, 2007, on April 29, 2007, the Company entered
into a Contract Agreement Dated April 29, 2007 (“CWEL Purchase Agreement”) with
CWEL, Arul Mariamman Textiles Limited (AMTL), and Marudhavel Industries
Limited (MAIL), collectively CWEL. Pursuant to the CWEL Purchase Agreement, the
Company or its subsidiary in Mauritius will acquire 100% of a 24-mega watt wind
energy farm, consisting of 96 250-kilowatt wind turbines, located in Karnataka,
India to be manufactured by CWEL.
CWEL is a
manufacturer and supplier of wind operated electricity generators, towers and
turnkey implementers of wind energy farms. On May 22, 2007, the
Company made a down payment of approximately $250,000 to
CWEL. Pursuant to the First Amendment dated August 20, 2007 (as
previously disclosed in the Company’s Form 8-K dated August 22, 2007), if the
Company does not consummate the transaction with CWEL, approximately $187,500
will be returned to the Company.
The
Company is contemplating pursuing this and similar opportunities in the
alternative energy space if it is able to obtain adequate funding from the
exercise of warrants, debt or other means.
NOTE
K – BUSINESS COMBINATION
As
previously disclosed in our Form 8-K dated September 21, 2007 and Form 10-QSB
for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2007, on September 21, 2007, the Company
entered into a Share Subscription cum Purchase Agreement (the “Sricon
Subscription Agreement”) dated as of September 15, 2007 with Sricon
Infrastructure Private Limited (“Sricon”) and certain individuals
(collectively, the “Sricon Promoters”), pursuant to which the Company or its
subsidiary in Mauritius (IGC-M) will acquire (the “Sricon Acquisition”) 4,041,676 newly-issued
equity shares (the “New Sricon Shares”) directly from Sricon for
approximately $26 million and 351,840 equity shares from Mr. R. L. Srivastava
for approximately $3 million (both based on an exchange rate of INR 40 per USD)
so that at the conclusion of the transactions contemplated by the Sricon
Subscription Agreement the Company would own approximately 63% of the outstanding
equity shares of Sricon. Effectively, the purchase price of $26 million
was funded with approximately $8.1 million in cash and a note for $17.9 million
(computed at an exchange rate of approximately 40 INR to $1
USD). Failure to repay the note or negotiate a settlement could
result in IGC having to decrease its ownership in Sricon by tendering all or a
portion of the Sricon shares it owns to Sricon to repay the note. The Sricon
Acquisition was consummated on March 7, 2008.
As
previously disclosed in our Form 8-K dated September 21, 2007 and Form 10-QSB
for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2007, on September 21, 2007, the Company
entered into a Share Subscription Agreement (the “TBL Subscription
Agreement”) dated as of September 16, 2007 with Techni Bharathi Limited (“TBL”)
and certain individuals (collectively, the “TBL Promoters”), pursuant to which
the Company through its subsidiary in Mauritius (IGC-M) acquired (the “TBL
Acquisition”)
7,150,000 newly-issued company stock for approximately $6.9 million, 1,250,000
newly-issued convertible preference shares for approximately $3.13
million (both at an exchange rate of INR 40 per USD; collectively,
the “New Shares”) directly from TBL and 5,000,000 convertible preference shares
from Odeon, a Singapore based holder of TBL securities, for approximately $2
million. With the conclusion of this transaction, on March 7, 2008
the Company owns
approximately 77%, of the outstanding equity shares of TBL.
NOTE
L – PRIVATE PLACEMENT OF PROMISSORY NOTES
Private
Placement Offering of Secured Promissory Notes (the “Bridge
Offering”)
As
previously disclosed in our Form 8-K dated December 27, 2007, we conducted a
private placement offering of secured promissory notes (the “Notes”) for an
aggregate principal amount of $7,275,000 (the “Bridge Offering”). The Notes
bear interest at a rate equal to 5% per annum from the date of issuance (January
10, 2008) until paid in full. The Notes were repaid in
full on March 19, 2008.
On March
7, 2008 the Company, issued 754,953 shares of common stock to the holders
of the Notes on a pro rata basis and recorded the cost of the shares as an
expense based on the closing price of the company’s stock on March 7,
2008. The expense associated with the issuance of the shares is about
$3,170,806.
NOTE
M – VALUATION OF WARRANTS ISSUED TO OLIVEIRA CAPITAL, LLC
We
account for derivative instruments and embedded derivative instruments in
accordance with SFAS No. 133, Accounting for Derivative Instruments and Hedging
Activities, as amended. The amended standard requires an entity to recognize all
derivatives as either assets or liabilities in the statement of financial
position and measure these instruments at fair value. Fair value is estimated
using the Black-Scholes Pricing model. We also follow EITF Issue No. 00-19,
Accounting for Derivative Financial Instruments Indexed to and Potentially
Settled in, a Company’s Own Stock, which requires freestanding contracts that
are settled in a company’s own stock, including common stock warrants, to be
designated as an equity instrument, asset or a liability. Under the provisions
of EITF Issue No. 00-19, a contract designated as an asset or a liability must
be carried at fair value, with any changes in fair value recorded in the results
of operations. A contract designated as an equity instrument can be included in
equity, with no fair value adjustments are required.
As
previously disclosed, the Company sold a promissory note and 425,000 warrants to
Oliveira Capital, LLC for $3,000,000. Each warrant will entitle the holder
to purchase from the Company one share of common stock at an exercise price of
$5.00 and expires five years from the date of issuance. The Company has
determined, based upon a Black-Scholes model, that the fair value of the
warrants on the date of issuance would approximately be $1,235,000 using an
expected life of five years, volatility of 46% and a risk-free interest rate of
4.8%. This amount is accounted for as a discount of the notes payable to
Oliveira Capital, LLC.
We
computed volatility for a period of five years. For approximately the first
four years, we used the trading history of two representative companies that are
listed on the Indian Stock exchange. For approximately one year, the
trading history of the Company’s common stock was used. The average volatility
of the combined data extending over five years was calculated as
46%. Management believes that this volatility is a reasonable benchmark to
use in estimating the value of the warrants.
NOTE
N – SPAC RELATED EXPENSES
As of
March 31, 2008 we incurred about $5.765 Million of SPAC related expenses, and
about $1.9 Million of SPAC interest related expenses, mostly as one-time
expenses. The major expenses are as follows: 1) Approximately $3.1
Million was non-cash expenses associated with the award of stock to the Bridge
investors. 2) Approximately $1.5 Million was paid to Ferris Baker
Watts, of which $.9 Million was expensed as the services rendered by them
related to acquisitions that we did not close. 3) Approximately $.469
Million relates to the bridge loan from Oliveira Capital, LLC , and 5)
approximately $.5 Million was incurred for legal and professional fees for two
bridge loans and several acquisitions that we did not close. In
addition, we incurred about $1.23 Million in non-cash interest related expenses
for the warrants issued to Oliveira Capital.
NOTE O
– SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
IGC-Mauritius
has beneficially formed a company called IGC Materials, Private Limited based in
India. At the completion of the formalities, in the month
of July 2009, IGC-Mauritius will beneficially own 100% of the shares
of IGC Materials, Private Limited, which will conduct IGC’s rock aggregate and
materials business.
IGC India
Mining & Trading, a wholly owned subsidiary of IGC- Mauritius, has received
a line of credit from State Bank of Mysore with the following
parameters:
a) Letter
of Credit - USD 1 million (USD 1 = INR 50);
b)
Forward Contract - USD 1 million (USD 1 = INR 50); and
c)
Foreign Demand Bills Payable / Foreign Usance Bills Payable - USD 1 million (USD
1 = INR 50).
The line
of credit is secured by a corporate guarantee from IGC Mauritius,
V. C. Homes (an associate company of the promoters of TBL), and a
personal guarantee of Mr. Pious Abraham (associate of TBL promoters).
The rate of interest is 1.25% above bank’s prime lending rate with a minimum of
interest rate of 14.25%. The line is used to provide back to back letters
of credit for iron ore contracts.
PART
I - Financial Information
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
|
December 31,
2009
(unaudited)
|
March
31,
2009
(audited)
|
|||||||
|
ASSETS
|
||||||||
|
Current
Assets:
|
||||||||
|
Cash
and cash equivalents
|
$
|
2,079,706
|
$
|
2,129,365
|
||||
|
Accounts
Receivable
|
5,648,811
|
9,307,088
|
||||||
|
Unbilled
Receivables
|
0
|
2,759,632
|
||||||
|
Inventories
|
2,124,836
|
2,121,837
|
||||||
|
Prepaid
taxes
|
88,683
|
88,683
|
||||||
|
Restricted
cash
|
215,517
|
|||||||
|
Prepaid
expenses and other current assets
|
2,113,766
|
2,801,148
|
||||||
|
Due
from related parties
|
3,675,599
|
290,831
|
||||||
|
Total
Current Assets
|
15,946,918
|
19,498,584
|
||||||
|
Property
and equipment, net
|
1,141,709
|
6,601,394
|
||||||
|
Accounts
Receivable – Long Term
|
0
|
2,769,196
|
||||||
|
Goodwill
|
6,931,307
|
17,483,501
|
||||||
|
Investments
in Affiliates
|
8,172,475
|
0
|
||||||
|
Other
Investments
|
64,655
|
70,743
|
||||||
|
Deposits
towards acquisitions
|
334,236
|
261,479
|
||||||
|
Restricted
cash, non-current
|
1,627,656
|
1,430,137
|
||||||
|
Deferred
tax assets, net of valuation allowance
|
972,493
|
898,792
|
||||||
|
Other
Assets
|
773,984
|
2,818,687
|
||||||
|
Total
Assets
|
$
|
35,965,433
|
$
|
51,832,513
|
||||
|
LIABILITIES
AND STOCKHOLDERS’ EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
Current
Liabilities:
|
||||||||
|
Short-term
borrowings and current portion of long-term debt
|
$
|
924,495
|
$
|
3,422,239
|
||||
|
Trade
payables
|
4,020,618
|
462,354
|
||||||
|
Advance
from Customers
|
0
|
206,058
|
||||||
|
Accrued
expenses
|
469,806
|
555,741
|
||||||
|
Taxes
payable
|
76,569
|
76,569
|
||||||
|
Notes
Payable
|
4,120,000
|
1,517,328
|
||||||
|
Due
to related parties
|
1,339,010
|
1,214,685
|
||||||
|
Other
current liabilities
|
114,134
|
1,991,371
|
||||||
|
Total
current liabilities
|
$
|
11,064,632
|
$
|
9,446,345
|
||||
|
Long-term
debt, net of current portion
|
69,174
|
1,497,458
|
||||||
|
Deferred
taxes on income
|
0
|
590,159
|
||||||
|
Other
liabilities
|
1,332,359
|
2,440,676
|
||||||
|
Total
Liabilities
|
$
|
12,466,165
|
$
|
13,974,638
|
||||
|
COMMITMENTS
AND CONTINGENCY
|
||||||||
|
STOCKHOLDERS’
EQUITY
|
||||||||
|
Common
stock — $.0001 par value; 75,000,000 shares authorized; 12,898,291 issued
and outstanding at December 31, 2009 and issued and 10,091,171
outstanding at March 31, 2009.
|
1,291
|
1,009
|
||||||
|
Additional
paid-in capital
|
36,534,929
|
33,186,530
|
||||||
|
Retained
Earnings (Deficit)
|
(11,954,396
|
)
|
(4,662,689
|
)
|
||||
|
Accumulated
other comprehensive (loss) income (AOCI)
|
(2,721,057
|
)
|
(4,929,581
|
)
|
||||
|
Total
stockholders’ equity
|
21,860,767
|
23,595,269
|
||||||
|
Non-controlling
Interest
|
1,638,501
|
14,262,606
|
||||||
|
Total
liabilities and stockholders’ equity
|
$
|
35,965,433
|
$
|
51,832,513
|
||||
The
accompanying notes should be read in connection with the financial
statements.
India Globalization Capital,
Inc.
(unaudited)
|
Three
Months Ended
December
31, 2009
|
Three
Months Ended
December
31, 2008
|
Nine
Months Ended
December
31, 2009
|
Nine
Months Ended
December
31, 2008
|
|||||||||||||
|
Revenue:
|
$ | 5,909,024 | $ | 3,836,428 | 13,994,503 | $ | 32,263,680 | |||||||||
|
Cost
of revenue:
|
(5,326,393 | ) | (2,902,431 | ) | (11,829,440 | ) | (23,948,382 | ) | ||||||||
|
Gross
Profit
|
582,631 | 933,996 | 2,165,063 | 8,315,299 | ||||||||||||
|
Selling,
General and Administrative
|
(3,049,603 | ) | (2,135,267 | ) | (4,446,137 | ) | (4,224,524 | ) | ||||||||
|
Depreciation
|
(101,991 | ) | (212,527 | ) | (519,812 | ) | (679,835 | ) | ||||||||
|
Total
operating expenses
|
(3,151,594 | ) | (2,347,794 | ) | (4,965,949 | ) | (4,904,359 | ) | ||||||||
|
Operating
income (loss)
|
(2,568,963 | ) | (1,413,798 | ) | (2,800,886 | ) | 3,410,939 | |||||||||
|
Compensation
Expense
|
(123,139 | ) | (123,139 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
Other
income (expense):
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Interest
and other income
|
40,884 | 137,663 | 146,477 | 324,062 | ||||||||||||
|
Interest
expense
|
(252,619 | ) | (442,265 | ) | (1,019,687 | ) | (1,244,350 | ) | ||||||||
|
Amortization
of debt discount
|
(178,218 | ) | (178,218 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
Total
other income (expense)
|
(389,953 | ) | (304,602 | ) | (1,051,428 | ) | (920,288 | ) | ||||||||
|
Equity
in (gain) loss of affiliates
|
16,446 | 16,446 | ||||||||||||||
|
Income
before extraordinary items and income taxes
|
(3,065,609 | ) | (1,718,400 | ) | (3,959,007 | ) | 2,490,651 | |||||||||
|
(Provision)
benefit for income taxes
|
103,281 | (565,885 | ) | (54,486 | ) | (1,928,490 | ) | |||||||||
|
Income
before extraordinary items
|
(2,962,328 | ) | (2,284,285 | ) | (4,013,493 | ) | 562,161 | |||||||||
|
Extraordinary
items:
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Loss
on dilution of stake in Sricon
|
(3,205,616 | ) | (3,205,616 | ) | ||||||||||||
|
Consolidated
Net Income
|
(6,167,944 | ) | (2,284,285 | ) | (7,291,709 | ) | 562,161 | |||||||||
|
Net
Income attributable to non-controlling interest
|
(7,574 | ) | 550,207 | (72,599 | ) | (936,996 | ) | |||||||||
|
Net
income (loss) attributed to controlling interest
|
$ | (6,175,518 | ) | $ | (1,734,078 | ) | $ | (7,291,708 | ) | $ | (374,835 | ) | ||||
|
Weighted
average number of shares outstanding:
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Basic
|
12,898,291 | 8,780,107 | 12,898,291 | 8,780,107 | ||||||||||||
|
Diluted
|
13,559,184 | 8,780,107 | 13,559,184 | 8,780,107 | ||||||||||||
|
Net
income per share:
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Basis
|
$ | (0.48 | ) | $ | (0.20 | ) | $ | (0.56 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | ||||
|
Diluted
|
$ | (0.45 | ) | $ | (0.20 | ) | $ | (0.54 | ) | $ | (0.04 | ) | ||||
The
accompanying notes should be read in connection with the financial
statements
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
(unaudited)
|
Three
|
Three
|
Nine
|
Nine
|
|||||||||||||
|
Months
Ended
|
Months
Ended
|
Months
Ended
|
Months
Ended
|
|||||||||||||
|
31-Dec-09
|
31-Dec-08
|
31-Dec-09
|
30-Dec-08
|
|||||||||||||
|
Net
income / (loss)
|
$
|
(6,175,518
|
)
|
$
|
(1,734,078
|
)
|
$
|
(7,291,708
|
)
|
$
|
(374,835
|
)
|
||||
|
Foreign
currency translation adjustments
|
2,167,829
|
(746,217
|
)
|
3,357,114
|
(4,119,684
|
)
|
||||||||||
|
Deconsolidation
of Sricon
|
(1,148,591
|
)
|
(1,148,591
|
)
|
||||||||||||
|
Comprehensive
income (loss)
|
$
|
(5,156,280
|
)
|
$
|
(2,480,295
|
)
|
$
|
(5,083,185
|
)
|
$
|
(4,494,519
|
)
|
||||
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
(unaudited)
|
Common
Stock
|
Additional
Paid-in
|
Accumulated
Retained
Earnings
|
Accumulated
Other
Comprehensive
Income
|
Non
Controlling
|
Total
Stockholders'
|
Comprehensive
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Shares
|
Amount
|
Capital
|
(Deficit)
|
/
Loss
|
Interest
|
Equity
|
Income | |||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance
at March 31, 2009
|
$ |
10,091,171
|
$
|
1,009
|
$
|
33,186,530
|
$
|
(4,662,689
|
)
|
$
|
(4,929,581
|
)
|
$
|
14,262,606
|
$
|
37,857,875
|
$
|
|
|
|||||||
|
Stock
Option for 1,413,000 grants
|
90,997
|
90,997
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issue
of 78,820 common stock
|
78,820
|
8
|
39,402
|
39,410
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issue
of Common Stock for Red Chip
Companies
@ .88 per share in Sep 09
|
15,000
|
2
|
13,198
|
13,200
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issuance
of 1,599,000 shares @ 1.25 per share
|
1,599,000
|
160
|
1,638,690
|
1,638,850
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss
of translation
|
1,189,286
|
1,189,286
|
1,189,286
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net
Income for non controlling interest
|
65,025
|
65,025
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net
Income (Loss)
|
(1,116,189
|
)
|
(1,116,189
|
)
|
(1,116,189
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance
at September 30, 2009
|
11,783,991
|
1,179
|
34,968,817
|
(5,778,878
|
)
|
(3,740,295
|
)
|
14,327,631
|
39,778,454
|
73,097
|
||||||||||||||||
|
Issue
of 51,000 common stock @ 1.60 per share
|
51,000
|
5
|
81,595
|
81,600
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issue
of 3,300 common stock @ 1.58 per share
|
3,300
|
1
|
5,054
|
5,055
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issue
of 530,000 common stock to Bricoleur Capital
|
530,000
|
53
|
811,528
|
811,582
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Issue
of 530,000 common stock to Oliviera
|
530,000
|
53
|
667,936
|
667,989
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Loss
on translation
|
2,167,829
|
2,167,829
|
2,167,829
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Impact
of de-consolidation of Sricon
|
(1,148,591
|
)
|
(1,148,591
|
)
|
(1,148,591
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
|
Elimination
of non controlling interest pertaining to Sricon
|
(12,696,704
|
) |
|
(12,696,704
|
)
|
|||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net
Income for non controlling interest
|
7,574
|
|
7,574
|
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Net
/Income (Loss)
|
(6,175,518
|
)
|
(6,175,518
|
)
|
(6,175,518
|
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||
| Rounding Difference | (2 |
)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Balance
at December 31, 2009
|
$ |
12,898,291
|
$
|
1,291
|
$
|
36,534,930
|
$
|
(11,954,396
|
)
|
$
|
(2,721,057
|
)
|
$
|
1,638,501
|
$
|
23,499,270
|
$ |
(5,083,185
|
)
|
|||||||
The
accompanying notes should be read in connection with the financial
statements.
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
(unaudited)
|
Nine
months ended
|
||||||||
|
December
31, 2009
|
December
31, 2008
|
|||||||
|
Cash
flows from operating activities:
|
||||||||
|
Net
income
|
$
|
(7,291,708
|
)
|
$
|
(374,835
|
) | ||
|
Adjustment
to reconcile net income to net cash used in operating
activities:
|
||||||||
|
Non-cash
compensation & interest expense
|
375,758
|
450,850
|
||||||
|
Deferred
taxes
|
(68,699
|
) |
222,873
|
|||||
|
Depreciation
|
519,812
|
679,835
|
||||||
|
Loss/(Gain)
on sale of property, plant and equipment
|
0
|
(50,905
|
)
|
|||||
|
Amortization
of debt discount
|
178,219
|
2,652
|
||||||
|
Deferred
acquisition costs written-off
|
1,854,750
|
0
|
||||||
|
Loss
on dilution of stake
|
3,205,616
|
0
|
||||||
|
Loss
on extinguishment of loan
|
586,785
|
0
|
||||||
|
Non
controlling interest
|
72,599
|
0
|
||||||
|
Equity
in earnings of affiliates
|
(16,446)
|
0
|
||||||
|
Changes
in:
|
||||||||
|
Accounts
and unbilled receivable
|
(5,364,846
|
)
|
(5,693,844
|
)
|
||||
|
Inventories
|
(389,904
|
)
|
(436,945
|
)
|
||||
|
Prepaid
expenses and other assets
|
(94,307
|
)
|
730,991
|
|||||
|
Accrued
expenses
|
(85,935
|
)
|
(925,311
|
)
|
||||
|
Taxes
payable
|
0
|
87,497
|
||||||
|
Trade
Payable
|
3,621,690
|
243,425
|
||||||
|
Advance
from Customers
|
0
|
(1,347,958
|
)
|
|||||
|
Other liabilities
|
14,503
|
(2,005,072
|
)
|
|||||
|
Due
to / from related parties
|
118,344
|
2,124,212
|
||||||
|
Net
cash provided (used) in operating activities
|
(2,763,768
|
)
|
(6,292,536
|
)
|
||||
|
Cash
flows from investing activities:
|
||||||||
|
Net
proceeds from purchase and sale of property and
equipment
|
(123,450
|
)
|
(1,843,985
|
)
|
||||
|
Purchase
of investments
|
0
|
(85,116
|
) | |||||
|
Proceeds
from sale of investments
|
0
|
1,424,897
|
||||||
|
Restricted
Cash
|
(261,232
|
)
|
116,545
|
|||||
|
Deposit
towards acquisitions, net of cash acquired
|
(600,024
|
)
|
0
|
|||||
|
Redemption
of convertible debenture
|
3,000,000
|
|||||||
|
Net
cash provided (used) in investing activities
|
(984,706
|
)
|
2,612,341
|
|||||
|
Cash
flows from financing activities:
|
||||||||
|
Net
proceeds / repayment of cash credit and bank
overdraft
|
82,097
|
(2,153,085
|
)
|
|||||
|
Proceeds
from other short-term and long-term borrowings
|
(75,879
|
)
|
1,192,408
|
|||||
|
Repayment
of long-term borrowings
|
0
|
(569,372
|
)
|
|||||
|
Net
proceeds from issue of equity shares
|
1,777,939
|
|||||||
|
Repayment
of notes payable
|
(2,756,010
|
)
|
||||||
|
Proceeds
from notes acquired
|
2,000,000
|
2,000,000
|
||||||
|
Interest
paid
|
(72,710
|
)
|
0
|
|||||
|
Net
cash provided (used) by financing activities
|
3,711,447
|
(2,286,059
|
)
|
|||||
|
Effect
of exchange rate changes on cash and cash
equivalents
|
(12,632
|
)
|
(691,910
|
|||||
|
Net
increase in cash and cash equivalent
|
(49,659
|
)
|
(6,658,165
|
)
|
||||
|
Cash
and cash equivalent at the beginning of the period
|
2,129,365
|
8,397,440
|
||||||
|
Cash
and cash equivalent at the end of the period
|
$
|
2,079,706
|
$
|
1,739,275
|
||||
The
accompanying notes should be read in connection with the financial
statements.
Background
of India Globalization Capital, Inc. (IGC)
NOTE
1 – NATURE OF OPERATIONS AND BASIS OF PRESENTATION
The
operations of IGC are based in India. IGC owns 100% of a subsidiary in Mauritius
called IGC-Mauritius (IGC-M). This company in turn operates through
five subsidiaries in India. We own twenty two (22.3%) of
percent of Sricon Infrastructure Private Limited (“Sricon”) and seventy seven
percent of Techni Bharathi, Limited (“TBL”). We also beneficially own
one hundred percent of IGC India Mining and Trading, Private Limited, IGC
Logistic, Private Limited, and IGC Materials, Private Limited. Through our
subsidiaries we operate in the infrastructure industry. Operating as
a fully integrated infrastructure company, IGC, through its subsidiaries, has
expertise in road building, mining and quarrying and engineering of high
temperature plants. The Company’s medium term plans are to expand each of these
core competencies while offering an integrated suite of service offerings to our
customers.
The
Company’s operations are subject to certain risks and uncertainties, including
among others, dependency on India’s economy and government policies, seasonal
business factors, competitively priced raw materials, dependence upon key
members of the management team and increased competition from existing and new
entrants.
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
IGC, a
Maryland corporation, was organized on April 29, 2005 as a blank check
company formed for the purpose of acquiring one or more businesses with
operations primarily in India through a merger, capital stock exchange, asset
acquisition or other similar business combination or acquisition. On March 8,
2006, we completed an initial public offering. On February 19, 2007,
we incorporated India Globalization Capital, Mauritius, Limited (IGC-M), a
wholly owned subsidiary, under the laws of Mauritius. On March 7,
2008, we consummated the acquisition of 63% of the equity of Sricon
Infrastructure Private Limited (Sricon) and 77% of the equity of Techni Bharathi
Limited (TBL). On February 19, 2009 IGC-M beneficially
purchased 100% of IGC Mining and Trading, Limited based in Chennai
India.
On July
4, 2009 IGC-M beneficially purchased 100% of IGC Materials, Private Limited, and
100% of IGC Logistics, Private Limited. Both these companies are
based in Nagpur, India.
Effective
October 1, 2009 we decreased our ownership in Sricon Infrastructure from 63% to
22.3%. By way of background: As explained in Note 13
(Deconsolidation) on or about March 7, 2008 we consummated the Sricon
Acquisition by purchasing 63% for about $29 million (based on an exchange rate
of 40 INR for $1 USD). We subsequently borrowed around $17.9 million
(based on 40 INR for 1 USD) from Sricon. Through 2008 and 2009 we
expanded our business offerings beyond construction to include a rapidly growing
materials business. We have successfully repositioned the company as a materials
and construction company; with construction activity in our TBL subsidiary and
materials activity in our other subsidiaries. Rather than continue to
owe Sricon $17.9 million, and more importantly, continue to fund two
construction companies, we decreased our ownership in Sricon by an amount
proportionate to the loan. The impact of this is that we no longer
owe Sricon $17.9 million and our corresponding ownership is a non-controlling
interest. The deconsolidation of Sricon from the balance sheet of
IGC, results in shrinking the IGC balance sheet and a one-time charge on the
P&L.
Merger
and Accounting Treatment
Most of
the shares of Sricon and TBL acquired by IGC were purchased directly from the
companies. IGC purchased a portion of the shares from the existing
owners of the companies. The founders and management of Sricon own
77.7% of Sricon and the founders and management of TBL own 23% of
TBL.
Our
interest in Sricon and the ownership interest of the founders and management, of
TBL, is reflected in our financial statements as “Non-Controlling
Interest”.
Unless
the context requires otherwise, all references in this report to the “Company”,
“IGC”, “we”, “our”, and “us” refer to India Globalization Capital, Inc, together
with its wholly owned subsidiary IGC-M, and its direct and indirect subsidiaries
(Sricon, TBL IGC-IMT, IGC-LPL, and IGC-MPL).
IGC’s
organizational structure is as follows:
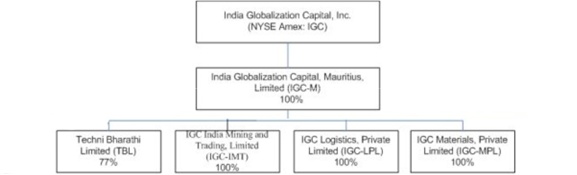
Securities
We have
three securities listed on NYSE Amex : (1) common stock, $.0001 par value
(ticker symbol: IGC), (2) redeemable warrants to purchase common stock (ticker
symbol: IGC.WS) and (3) units consisting of one share of common stock and two
redeemable warrants to purchase common stock (ticker symbol:
IGC.U). Each Unit consists of one share of common stock and two
warrants. The Units may be separated into common stock and
warrants. Each warrant entitles the holder to purchase one share of
common stock at an exercise price of $5.00. The warrants
expire on March 3, 2011, or earlier upon redemption. The
registration statement for initial public offering was declared effective on
March 2, 2006. The warrants may be exercised by contacting the
Company or the transfer agent Continental Stock Transfer & Trust
Company. We have a right to call the warrants, provided the common
stock has traded at a closing price of at least $8.50 per share for any 20
trading days within a 30 trading day period ending on the third business day
prior to the date on which notice of redemption is given. If we call the
warrants, the holder will either have to redeem the warrants by purchasing the
common stock from us for $5.00 or the warrants will expire.
On
January 9, 2009 we completed an exchange of 11,943,878 public and private
warrants for 1,311,064 new shares of common stock. Following the
issuance of the shares relating to the warrant exercise, we had 10,091,971
shares of common stock and 11,855,122 warrants outstanding as of March
31, 2009. On May 13, 2009, we issued 78,820 shares of common stock to
certain of our officers and directors pursuant to our 2008 Omnibus Incentive
Plan. Subsequent to this issuance, as of June 30, 2009 we had
10,169,991 shares of common stock issued and outstanding.
On July
13, 2009, we issued 15,000 shares of common stock to RedChip Companies Inc. for
services rendered.
On September 15,
2009, we entered into a securities purchase agreement (“Registered Direct”) with
institutional investors for the sale and issuance of an aggregate of 1,599,000
shares of our common stock and warrants to purchase up to 319,800 shares of our
common stock, for a total purchase price of $1,998,750. The common
stock and warrants were sold on a per unit basis at a purchase price of $1.25
per unit. The shares of common stock and warrants were issued
separately. Each investor received one warrant representing the right to
purchase, at an exercise price of $1.60 per share, a number of shares of common
stock equal to 20% of the number of shares of common stock purchased by the
investor in the offering. The sales were made pursuant to a shelf registration
statement. The warrants issued to the investors in the offering will
be exercisable any time on or after the date of issuance for a period of three
years from that date. The Black Scholes value of the warrants associated with
the Registered Direct is $71,411.
On
October 5, 2009, the Company issued 530,000 new shares of common stock as
partial consideration for the exchange of an outstanding promissory note for a
new interest free note of $2,120,000 with an extended due date of October 10,
2010.
On
October 13, 2009, the Company entered into an At The Market (“ATM”) Agency
Agreement with Enclave Capital LLC. Under the ATM Agency Agreement,
we may offer and sell shares of our common stock having an aggregate offering
price of up to $4 million from time to time. Sales of the shares, if
any, will be made by means of ordinary brokers’ transactions on the NYSE Amex at
market prices, or as otherwise agreed with Enclave. We estimate that
the net proceeds from the sale of the shares of common stock we are offering
will be approximately $3.73 million. We intend to use the net
proceeds from the sale of securities offered for working capital, repayment of
indebtedness and other general corporate purposes.
On
October 16, 2009, the Company issued 530,000 new shares of common stock in a
private placement in connection with the sale of an interest free, one year,
promissory note in the amount of $2,000,000 to an investor.
In
November 2009 we sold 3,300 shares of our common stock under the ATM Agency
Agreement.
Following
the issuance of the shares in the preceding transactions, we have 12,898,291
shares of common stock outstanding, warrants to purchase 11,855,122 shares of
common stock outstanding and new warrants to purchase 267,800 shares of common
stock outstanding.
Unaudited
Interim Financial Statements
The
unaudited consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2009, consolidated
statements of operations and cash flows for the three and nine months ended
December 31, 2009 and 2008 and consolidated statements of stockholders’ equity
(deficit) for the nine months ended December 31, 2009 include the accounts of
the Company and its subsidiaries. The unaudited interim consolidated financial
statements have been prepared in accordance with U.S. generally accepted
accounting principles for interim financial information and the rules and
regulations of the Securities and Exchange Commission for reporting on
Form 10-Q. Accordingly, they do not include certain information and
footnote disclosures required by generally accepted accounting principles for
annual financial reporting and should be read in conjunction with the
consolidated financial statements included in the Company’s Annual Report on
Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2009. The unaudited financial
statements include all adjustments (consisting of normal recurring adjustments)
which are, in the opinion of management, necessary for a fair presentation of
such financial statements. Operating results for the interim periods
presented are not necessarily indicative of the results to be expected for a
full fiscal year.
Prior
Pro Forma Results of Operations
We
previously disclosed Pro Forma results of Operations in our Quarterly Reports’
Management’s Discussion and Analysis sections. These Pro Forma statements were
reported as if the acquisition of Sricon and TBL occurred on April 1, 2007 and
April 1, 2008 respectively. We felt that this was a more meaningful
presentation of our results of operations since we acquired both Sricon and TBL
on March 7, 2008. Since the results from operations, for
Sricon and TBL, are included for the three and nine month periods ending
December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, we no longer believe that Pro Forma
results of operations as reported in filings prior to the June 30, 2009
quarterly filings present a meaningful discussion of our results of
operations. Therefore, the quarterly filing for the three and nine
month periods ended December 31, 2009 contains no pro forma
results.
NOTE
2 - SUMMARY OF SIGNIFICANT ACCOUNTING POLICIES
Principles
of Consolidation:
The accompanying unaudited
interim financial statements have been prepared on a consolidated basis and
reflect the unaudited interim financial statements of IGC and all of its
subsidiaries that are more than 50% owned and controlled. When the Company does
not have a controlling interest in an entity, but exerts a significant influence
on the entity, the Company applies the equity method of accounting. All
inter-company transactions and balances are eliminated in the consolidated
financial statements.
The
non-controlling interest disclosed in the accompanying unaudited interim
consolidated financial statements represents the non-controlling interest in
Techni Bharathi (TBL) and Sricon and the profits or losses associated with the
non-controlling interest in those operations.
The
adoption of Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) 810-10-65 “Consolidation —
Transition and Open Effective Date Information” (previously referred to as SFAS
No. 160, “Non-controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements,
an amendment of ARB No. 51”), has resulted in the reclassification of
amounts previously attributable to minority interest (now referred to as
non-controlling interest) to a separate component of Shareholders’ Equity on the
accompanying consolidated balance sheets and consolidated statements of
shareholders’ equity and comprehensive income (loss). Additionally, net income
attributable to non-controlling interest is shown separately from net income in
the consolidated statements of income. This reclassification had no effect on
our previously reported financial position or results of
operations.
Prior
period amounts related to non-controlling interest (previously referred to as
minority interest) have been reclassified to conform to the current period
financial statement presentation.
Reclassifications
Certain
prior year balances have been reclassified to the presentation of the current
year. Sales and services include adjustments made towards liquidated
damages, price variation and charges paid for discounting of receivables arising
from construction/project contracts on a non-recourse basis, wherever
applicable.
Use
of estimates:
The
preparation of financial statements in conformity with accounting principles
generally accepted in the United States of America requires management to make
estimates and assumptions that affect the reported amounts of assets and
liabilities and disclosure of contingent assets and liabilities at the date of
the financial statements and the reported amounts of revenue and expenses during
the reporting period. Actual results could differ from those
estimates.
Revenue
Recognition
The
majority of the revenue recognized for the three and nine month periods ended
December 31, 2009 was derived from the Company’s subsidiaries and as
follows:
Revenue
is recognized when persuasive evidence of an arrangement exists, the sales price
is fixed or determinable and collectability is reasonably
assured.
In
Government contracting we recognize revenue when a Government consultant
verifies and certifies an invoice for payment.
Revenue
from sale of goods is recognized when substantial risks and rewards of ownership
are transferred to the buyer under the terms of the
contract.
Revenue
from construction/project related activity and contracts for
supply/commissioning of complex plant and equipment is recognized as
follows:
|
a)
|
Cost
plus contracts: Contract revenue is determined by adding the aggregate
cost plus proportionate margin as agreed with the customer and expected to
be realized.
|
||
|
|
|||
|
b)
|
|
Fixed
price contracts: Contract revenue is recognized using the percentage
completion method. Percentage of completion is determined as a proportion
of cost incurred-to-date to the total estimated contract cost. Changes in
estimates for revenues, costs to complete and profit margins are
recognized in the period in which they are reasonably
determinable.
|
|
Full
provision is made for any loss in the period in which it is
foreseen.
Revenue
from property development activity is recognized when all significant risks and
rewards of ownership in the land and/or building are transferred to the customer
and a reasonable expectation of collection of the sale consideration from the
customer exists.
Revenue
from service related activities and miscellaneous other contracts are recognized
when the service is rendered using the proportionate completion method or
completed service contract method.
Income
per common share:
Basic
earnings per share is computed by dividing net income (loss) applicable to
common stockholders by the weighted average number of common shares outstanding
for the period. Diluted earnings per share reflect the additional dilution for
all potentially dilutive securities such as stock warrants and
options.
Income
taxes:
Deferred
income taxes are provided for the differences between the bases of assets and
liabilities for financial reporting and income tax purposes. A valuation
allowance is established when necessary to reduce deferred tax assets to the
amount expected to be realized. The IGC parent expects to
realize sufficient earnings and profits to utilize deferred tax assets as it
begins invoicing its subsidiaries for services and establishes iron sales
contracts with customers in China and other countries.
Cash
and Cash Equivalents:
For
financial statement purposes, the Company considers all highly liquid debt
instruments with maturity of three months or less when purchased to be cash
equivalents. The company maintains its cash in bank accounts in the United
States of America and Mauritius, which at times may exceed applicable insurance
limits. The Company has not experienced any losses in such accounts. The Company
believes it is not exposed to any significant credit risk on cash and cash
equivalent. The company does not invest its cash in securities that
have an exposure to U.S. mortgages.
Restricted
cash:
Restricted
cash consists of deposits pledged to various government authorities and deposits
used as collateral with banks for guarantees and letters of credit, given by the
Company to its customers or vendors.
Accounts
receivable:
Accounts
receivables are recorded at the invoiced amount, taking into consideration any
adjustments made by Government consultants that verify and certify construction
and material invoices. Account balances are written off when the
company believes that the receivables will not be recovered. The company did not
recognize any bad debt during the 9 month period ended December 31, 2009 and
December 31, 2008, respectively.
Inventories:
Inventories
primarily comprise of finished goods, raw materials, work in progress, stock at
customer site, stock in transit, components and accessories, stores and spares,
scrap and residue. Inventories are stated at the lower of cost or
estimated net realizable value.
The Cost
of various categories of inventories is determined on the following
basis:
Raw
Material are valued at weighed average of landed cost (purchase price, freight
inward and transit insurance charges), work in progress is valued as confirmed,
valued and certified by the technicians and site engineers and finished goods at
material cost plus appropriate share of labor cost and production overheads.
Components and accessories, stores erection, materials, spares and loose tools
are valued on a first-in-first out basis. Real Estate is valued at
the lower of purchase price or net realizable value.
Accounts
Receivable – Long Term:
This is
typically for Build-Operate-Transfer (BOT) contracts. It is money due
to the company by the private or public sector to finance, design, construct,
and operate a facility stated in a concession contract over an extended period
of time.
Investments
in Subsidiaries and Other Investments:
The
Company's equity in the earnings/(losses) of affiliates is included in the
statement of income and the Company's share of net assets of affiliates is
included in the balance sheet.
Other
Investments are initially measured at cost, which is the fair value of the
consideration given for them, including transaction
costs. Investments generally comprises of fixed deposits with
banks.
Property,
Plant and Equipment:
Property
and equipment are stated at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation of
computers, construction, scrap processing and other equipments, buildings and
other assets are provided based on the straight-line method over useful life of
the assets.
The value
of plant and equipment that are capitalized include the acquisition price and
other direct attributable expenses.
The
estimated useful life of various assets and associated historical costs are as
follows:
|
Category
|
Useful
Life (years)
|
As
of December 31, 2009
|
As
of March 31, 2009
|
||||||
|
Land
|
N/A
|
$
|
12,370
|
$
|
34,234
|
||||
|
Building
(Flat)
|
25
|
81,898
|
230,428
|
||||||
|
Plant
and Machinery
|
20
|
3,702,253
|
9,374,001
|
||||||
|
Computer
Equipment
|
3
|
233,317
|
261,099
|
||||||
|
Office
Equipment
|
5
|
179,329
|
160,728
|
||||||
|
Furniture
and Fixtures
|
5
|
97,376
|
127,680
|
||||||
|
Vehicles
|
5
|
786,531
|
740,886
|
||||||
|
Leasehold
Improvements
|
Over
the period of lease or useful life (if less)
|
0
|
139,185
|
||||||
|
Assets
under construction
|
N/A
|
0
|
13,063
|
||||||
|
Total
|
5,093,074
|
11,081,304
|
|||||||
|
Less:
Accumulated Depreciation
|
(3,951,365
|
)
|
(4,479,910
|
)
|
|||||
|
Net
Assets
|
$
|
1,141,709
|
$
|
6,601,394
|
Upon
disposition, cost and related accumulated depreciation of the Property and
equipment are removed from the accounts and the gain or loss is reflected in the
results of operation. Cost of additions and substantial improvements to property
and equipment are capitalized in the books of accounts. The cost of maintenance
and repairs of the property and equipment are charged to operating
expenses.
Policy
for Goodwill / Impairment
Goodwill
represents the excess cost of an acquisition over the fair value of the Group's
share of net identifiable assets of the acquired subsidiary at the date of
acquisition. Goodwill on acquisition of subsidiaries is disclosed
separately. Goodwill is stated at cost and adjusted for impairments
losses, if any.
The
company adopted provisions of Accounting Standards Codification (“ASC”) 350,
“Intangibles – Goodwill and Others”, (previously referred to as SFAS No. 142,
"Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets", which sets forth the accounting for
goodwill and intangible assets subsequent to their acquisition. ASC 350 requires
that goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible assets be allocated to the
reporting unit level, which the Group defines as each
circle.
ASC 350
also prohibits the amortization of goodwill and indefinite-lived intangible
assets upon adoption, but requires that they be tested for impairment at least
annually, or more frequently as warranted, at the reporting unit
level.
The
goodwill impairment test under ASC 350 is performed in two phases. The first
step of the impairment test, used to identify potential impairment, compares the
fair value of the reporting unit with its carrying amount, including goodwill.
If the carrying amount of the reporting unit exceeds its fair value, goodwill of
the reporting unit is considered impaired, and step two of the impairment test
must be performed. The second step of the impairment test quantifies the amount
of the impairment loss by comparing the carrying amount of goodwill to the
implied fair value. An impairment loss is recorded to the extent the carrying
amount of goodwill exceeds its implied fair value.
Impairment
of long – lived assets and intangible assets
The
company reviews its long-lived assets, including identifiable intangible
assets with finite lives, for impairment whenever events or changes in business
circumstances indicate that the carrying amount of assets may not be fully
recoverable. Such circumstances include, though are not limited to, significant
or sustained declines in revenues or earnings and material adverse changes in
the economic climate. For assets that the company intends to hold for
use, if the total of the expected future undiscounted cash flows produced by the
assets or subsidiary company is less than the carrying amount of the assets, a
loss is recognized for the difference between the fair value and carrying value
of the assets. For assets the company intends to dispose of by
sale, a loss is recognized for the amount by which the estimated fair value less
cost to sell is less than the carrying value of the assets. Fair
value is determined based on quoted market prices, if available, or other
valuation techniques including discounted future net cash
flows.
Asset
retirement obligations:
Asset
retirement obligations associated with the Company’s leasehold land are subject
to the provisions of ASC 410, “Asset Retirement and Environmental
Obligations”, (previously referred to as SFAS No. 143 “Accounting for Asset
Retirement Obligations” and related interpretation, FIN No. 47, “Accounting for
Conditional Asset Retirement Obligations, an interpretation of FASB Statement
No. 143”).The lease agreements entered into by the Company may contain clauses
requiring restoration of the leased site at the end of the lease term and
therefore create asset retirement obligations. The Company records the fair
value of a liability for an asset retirement obligation in the period in which
it is incurred and capitalizes the cost by increasing the carrying amount of the
related long-lived asset. Over time, the liability is accreted to its present
value of each period, and the capitalized cost is depreciated over the estimated
useful life of the related asset. Upon settlement of the liability, the Company
either settles the obligation for its recorded amount or incurs a gain or loss
upon settlement.
Foreign
currency transactions:
Our
functional currency is Indian Rupees (INR, or Rs). Our financial
statements reporting currency is the United States Dollar. We refer to foreign
currency as currencies that are not US Dollars. Monetary assets and
liabilities denominated in foreign currencies are converted from the foreign
currency at the rate of exchange in effect at the close of the balance
sheet. A transaction in a foreign currency is recorded at the
exchange rate on the date of the transaction. Adjustments resulting
from the translation of financial statements in the functional currency to
financial statements in to the reporting currency are accumulated and reported
as other comprehensive income/(loss), a separate component of shareholders’
equity.
Operating
leases:
Lease
payments made for operating leases are recognized as expenses using a
straight-line over the term of the lease.
Capital
leases:
Assets
acquired under capital leases are capitalized as assets by the Company at the
lower of the fair value of the leased property or the present value of the
related lease payments or where applicable, the estimated fair value of such
assets. Amortization of leased assets is computed on straight line basis over
the useful life of the assets. The amortization charge for capital leases is
included in depreciation expense.
Recently
adopted accounting pronouncements
In
December 2007, the FASB issued ASC 810-10-65 “Consolidation — Transition
and Open Effective Date Information” (previously referred to as SFAS
No. 160, “Non-controlling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements,
an amendment of ARB No. 51”). ASC 810-10 establishes accounting and
reporting standards for a non-controlling interest in a subsidiary and for the
deconsolidation of a subsidiary. ASC 810-10-65 establishes accounting and
reporting standards that require (i) the ownership interest in subsidiaries
held by parties other than the parent to be clearly identified and presented in
the consolidated balance sheet within equity, but separate from the parent’s
equity, (ii) the amount of consolidated net income attributable to the
parent and the non-controlling interest to be clearly identified and presented
on the face of the consolidated statements of income, and (iii) changes in
a parent’s ownership interest while the parent retains its controlling financial
interest in its subsidiary to be accounted for consistently. Effective
April 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC 810-10-65. See “Consolidated Balance
Sheets”, “Consolidated Statements of Income”, “Consolidated Statements of
Shareholders’ Equity and Comprehensive Income (Loss)”, and note 2 for
information and related disclosures regarding non-controlling
interest.
In
December 2007, the FASB issued ASC 805 “Business Combinations” (previously
referred to as SFAS No. 141 (revised 2007), “Business Combinations”, which
was a revision of SFAS No. 141, “Business Combinations”). This Statement
establishes principles and requirements for how an acquirer recognizes and
measures in its financial statements the identifiable assets acquired, the
liabilities assumed and any non-controlling interest in an acquiree; recognizes
and measures the goodwill acquired in the business combination or a gain from a
bargain purchase; and determines what information to disclose to enable users of
the financial statements to evaluate the nature and financial effects of the
business combination. Effective April 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC 805
and the adoption did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated
results of operations, cash flows or financial position.
In
Fe bruary 2008,
the FASB approved ASC 820-10 “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures”
(previously referred to as FASB Staff Position FAS No.157-2, “Effective Date of
FASB statement No. 157” (FSP FAS 157-2), which grants a one-year deferral
of SFAS No. 157’s fair-value measurement requirements for non-financial
assets and liabilities, except for items that are measured or disclosed at fair
value in the financial statements on a recurring basis). Effective April 1,
2009, the Company has adopted ASC 820-10 for non-financial assets and
liabilities. The adoption of ASC 820-10 for non-financial assets and liabilities
did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated results of
operations, cash flows or financial position.
In
November 2008, the FASB’s Emerging Issues Task Force reached a consensus on
ASC 323-10 “Investments-Equity Method and Joint Ventures” (previously referred
to as EITF Issue No. 08-6, “Equity Method Investment Accounting
Considerations”). ASC 323-10 continues to account for the initial carrying value
of equity method investments on a cost accumulation model, which generally
excludes contingent consideration. ASC 323-10 also specifies that
other-than-temporary impairment testing by the investor should be performed at
the investment level and that a separate impairment assessment of the underlying
assets is not required. An impairment charge by the investee should result in an
adjustment of the investor’s basis of the impaired asset for the investor’s
pro-rata share of such impairment. In addition, ASC 323-10 reached a consensus
on how to account for an issuance of shares by an investee that reduces the
investor’s ownership share of the investee. An investor should account for such
transactions as if it had sold a proportionate share of its investment with any
gains or losses recorded through earnings. ASC 323-10 also addresses the
accounting for a change in an investment from the equity method to the cost
method after adoption of ASC 810-10 (previously referred to as SFAS
No. 160). ASC 323-10 affirms existing guidance which requires cessation of
the equity method of accounting and application of ASC 320-10 (previously
referred to as FASB Statement No. 115, “Accounting for Certain Investments
in Debt and Equity Securities”), or the cost method under ASC 323-10-35, as
appropriate. Effective April 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC 323-10 and
the adoption did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated
results of operations, cash flows or financial position.
In
April 2009, the FASB issued ASC 805-20 “Business Combinations —
Identifiable Assets and Liabilities, and Any Non-controlling Interest”
(previously referred to as FASB Staff Position FAS No. 141R-1, “Accounting
for Assets Acquired and Liabilities Assumed in a Business Combination That Arise
from Contingencies” (FSP FAS No. 141R-1). ASC 805-20 eliminates the
distinction between contractual and non-contractual contingencies, including the
initial recognition and measurement criteria, in ASC 805 and instead carries
forward most of the provisions in FASB Statement No. 141, Business
Combinations, for acquired contingencies. ASC 805-20 is effective for contingent
assets or contingent liabilities acquired in business combinations for which the
acquisition date is on or after the beginning of the first annual reporting
period beginning on or after December 15, 2008. Effective April 1,
2009, the Company adopted ASC 805-20 and the adoption did not have a material
impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or
financial position.
In
April 2009, the FASB issued the following three ASCs intended to provide
additional application guidance and enhance disclosures regarding fair value
measurements and impairments of securities:
ASC
820-10-65 “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures — Transition and Open
Effective Date Information” (previously referred to as FASB Staff Positions FAS
157-4 “ Determining Fair Value When the Volume and Level of Activity for
the Asset or Liability Have Significantly Decreased and Identifying Transactions
That Are Not Orderly”) provides additional guidance for estimating fair value in
accordance with ASC 820-10 “Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures” (previously
referred to as SFAS No. 157) when the volume and level of activity
for the asset or liability have decreased significantly. ASC 820-10-65 also
provides guidance on identifying circumstances that indicate a transaction is
not orderly. The provisions of ASC 820-10-65 are effective for the Company’s
interim period ending on June 30, 2009. Effective April 1, 2009, the
Company adopted ASC 820-10-65 and the adoption did not have a material impact on
the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or financial
position.
ASC
825-10-65 “Financial Instruments - Transition and Open Effective Date
Information” (previously referred to as FASB Staff Positions FAS 107-1 and APB
28-1, “Interim Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments”), requires
disclosures about the fair value of financial instruments in interim reporting
periods of publicly traded companies that were previously only required to be
disclosed in annual financial statements. The provisions of ASC 825-10-65 are
effective for the Company’s interim period ending on June 30, 2009.
Effective April 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC 825-10-65 and the adoption
did not have a material impact on the Company’s consolidated results of
operations, cash flows or financial position.
ASC
320-10-65 “Investments-Debt and Equity Securities - Transition and Open
Effective Date Information” (previously referred to as FASB Staff Positions FAS
115-2 and FAS 124-2, “Recognition and Presentation of Other-Than-Temporary
Impairments”) amends current other-than-temporary impairment guidance in U.S.
GAAP for debt securities to make the guidance more operational and to improve
the presentation and disclosure of other-than-temporary impairments on debt and
equity securities in the financial statements. This ASC does not amend existing
recognition and measurement guidance related to other-than-temporary impairments
of equity securities. The provisions of ASC 320-10-65 are effective for the
Company’s interim period ending on June 30, 2009. Effective April 1,
2009, the Company adopted ASC 320-10-65 and the adoption did not have a material
impact on the Company’s consolidated results of operations, cash flows or
financial position.
In
May 2009, the FASB issued ASC 855-10 “Subsequent events” (previously
referred to as SFAS No. 165, “Subsequent Events” (“SFAS 165”)), which
provides guidance to establish general standards of accounting for and
disclosures of events that occur after the balance sheet date but before
financial statements are issued or are available to be issued. ASC 855-10 also
requires entities to disclose the date through which subsequent events were
evaluated as well as the rationale for why that date was selected. ASC 855-10 is
effective for interim and annual periods ending after June 15, 2009.
Effective April 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC 855-10 which only requires
additional disclosures and the adoption did not have any impact on its
consolidated financial position, results of operations or cash flows. The
Company evaluated all events or transactions that occurred after
December 31, 2009 up through February 6, 2010. Based on this
evaluation, the Company is not aware of any events or transactions that would
require recognition or disclosure in the consolidated financial
statements.
In
June 2009, the FASB issued ASC 105-10 “Generally Accepted Accounting
Principles” (previously referred to as SFAS No. 168 “The FASB Accounting
Standards Codification and the Hierarchy of Generally Accepted Accounting
Principles—a replacement of FASB Statement No. 162”). The FASB Accounting
Standards Codification (“Codification”) will be the single source of
authoritative nongovernmental U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
Rules and interpretive releases of the SEC under authority of federal
securities laws are also sources of authoritative GAAP for SEC registrants. ASC
105-10 is effective for interim and annual periods ending after
September 15, 2009. All existing accounting standards are superseded as
described in ASC 105-10. Effective October 1, 2009, the Company adopted ASC
105-10 and the adoption did not have any material impact on its consolidated
financial position, results of operations or cash flows.
Recently
issued accounting pronouncements
In
October 2009, the FASB issued ASU 2009-13 (EITF No. 08-1) which amends
ASC 605-25 “Revenue Recognition—Multiple-Element Arrangements”. ASU 2009-13
amends ASC 605-25 to eliminate the requirement that all undelivered elements
have Vendor Specific Objective Evidence (VSOE) or Third Party Evidence (TPE)
before an entity can recognize the portion of an overall arrangement fee that is
attributable to items that already have been delivered. In the absence of VSOE
or TPE of the standalone selling price for one or more delivered or undelivered
elements in a multiple-element arrangement, the overall arrangement fee will be
allocated to each element (both delivered and undelivered items) based on their
relative estimated selling prices. Application of the “residual method” of
allocating an overall arrangement fee between delivered and undelivered elements
will no longer be permitted upon adoption of ASU 2009-13. The provisions of ASU
2009-13 will be effective prospectively for revenue arrangements entered into or
materially modified in fiscal years beginning on or after June 15, 2010.
Early adoption will be permitted. The Company is currently evaluating the effect
of adoption of the provisions of the ASU 2009-13 on the Company’s consolidated
financial Statements.
In
August 2009, the FASB issued ASU 2009-05 which amends Subtopic 820-10 “Fair
Value Measurements and Disclosures” for the fair value measurement of
liabilities. ASU 2009-05 provides clarification that in circumstances in which a
quoted price in an active market for the identical liability is not available,
an entity is required to measure fair value utilizing one or more of the
following techniques (1) a valuation technique that uses the quoted market
price of an identical liability or similar liabilities when traded as assets; or
(2) another valuation technique that is consistent with the principles of
Topic 820, such as a present value technique or a market approach. The
provisions of ASU No. 2009-05 are effective for the first reporting period
(including the interim periods) beginning after issuance. The provisions of ASU
No. 2009-05 will be effective for interim and annual periods beginning
after August 27, 2009. The Company is currently evaluating the effect of
the provisions of the ASU 2009-05 on the Company’s consolidated financial
statements.
NOTE
3 – PREPAID EXPENSES AND OTHER ASSETS
Prepaid
expenses and other current assets consist of the following:
| Description |
As
of
December
31, 2009
|
As
of
March
31, 2009
|
||||||
|
Advance
to suppliers & services
|
$ | 828,777 | $ | 1,831,998 | ||||
|
Security
& other Deposits
|
225,100 | 596,793 | ||||||
|
Discount
on issues of Debt
|
534,657 | 0 | ||||||
|
Prepaid
/ Preliminary Expenses
|
525,232 | 372,357 | ||||||
|
Total
|
$ | 2,113,766 | $ | 2,801,148 | ||||
Other
Assets consist of the following:
| Description |
As
of
December
31, 2009
|
As
of
March
31, 2009
|
||||||
|
Sr.
Debtors Pending more than 1 year
|
$ | 488,655 | $ | 771,076 | ||||
|
Advance
pending more than 1 year
|
285,329 | 2,047,611 | ||||||
|
Total
|
$ | 773,984 | $ | 2,818,687 | ||||
NOTE
4 – CURRENT AND LONG TERM LIABILITIES
Short
term debt for the consolidated companies consists of the
following:
|
As
of December 31, 2009 |
As
of March 31,2009 |
|||||||
|
Secured
|
$
|
869
|
$
|
2,502
|
||||
|
Unsecured
|
56
|
249
|
||||||
|
Total
|
925
|
2,751
|
||||||
|
Add:
|
||||||||
|
Current
portion of long term debt
|
0
|
671
|
||||||
|
Total
|
$
|
925
|
$
|
3,422
|
||||
Amounts
in thousand US Dollars
The above
debt is secured by hypothecation of materials, stock of spares, Work in
Progress, receivables and property & equipment in addition to personal
guarantee of three India based directors & collaterally secured by mortgage
of company’s land & other immovable properties of directors and their
relatives.
Long term
debt for the consolidated companies consists of the
following:
|
As
of December 31, 2009 |
As
of March 31, 2009 |
|||||||
|
Secured
|
$
|
$
|
-
|
|||||
|
Term
loans
|
69
|
|||||||
|
Loan
for assets purchased under capital lease
|
0
|
2,168
|
||||||
|
Total
|
69
|
2,168
|
||||||
|
Less:
Current portion (Payable within 1 year)
|
0
|
671
|
||||||
|
Total
|
$
|
69
|
$
|
1,497
|
||||
Amounts
in thousand US Dollars
The
secured loans were collateralized by:
|
•
|
The
unencumbered Net Asset Block of the Company,
|
|
|
•
|
property
owned by the India based promoter directors,
|
|
|
•
|
cash
term deposits,
|
|
|
•
|
Hypothecation
of receivables, assignment of toll rights, pledge of machineries, vehicles
and land,
|
|
|
•
|
First
charge on the Debt-Service Reserve
Account
|
Other
current liabilities consist of the following:
|
Description
|
As
of
December
31,2009
|
As
of
March
31, 2009
|
||||||
|
ITDS
payable
|
$ | 5,483 | $ | 0 | ||||
|
Payables
more than 1 year
|
0 | 860,819 | ||||||
|
Employees’
dues
|
74,666 | 0 | ||||||
|
Accrued
vacation
|
33,985 | 1,130,552 | ||||||
|
Total
|
$ | 114,134 | $ | 1,991,371 |
Other
liabilities consist of the following:
| Description |
As
of
December
31,2009
|
As
on
March
31, 2009
|
||||||
|
Sr.
Creditors pending more than 1 year
|
$ | 1,299,690 | $ | 1,188,480 | ||||
|
Provision
for Expenses
|
32,669 | 1,252,196 | ||||||
|
Total
|
$ | 1,332,359 | $ | 2,440,676 |
NOTE
5 – OTHER DEBT AND NOTES PAYABLE
As
previously disclosed in Form 8-K dated October 5, 2009, the Company on October
5, 2009, consummated the exchange of an outstanding promissory note in the total
principal amount of $2,000,000 (the “Original Note”) initially issued to the
Steven M. Oliveira 1998 Charitable Remainder Unitrust (“Oliveira”) for a new
promissory note (the “New Note”) on substantially the same terms as the original
note except that the principal amount of the New Note is $2,120,000 reflected
the accrued but unpaid interest on the Original Note. There is no interest
payable on the New Note and the New Note is due and payable on October 4, 2010
(the “Maturity Date”). As is the case with the Original Note, IGC can pre-pay
the New Note at any time without penalty or premium, and the New Note is
unsecured. The New Note is not convertible into IGC Common Stock (the “Common
Stock”) or other securities of the Company. However, under the Note and Share
Purchase Agreement (the “Note and Share Purchase Agreement”), effective as of
October 4, 2009, by and among IGC and Oliveira, as additional consideration for
the exchange of the Original Note, IGC agreed to issue 530,000 shares of Common
Stock to Oliveira.
The
exchange or modification of the old loan was a substantial modification
determined in accordance with ASC 470-50, “Modifications and Extinguishments”,
(previously referred to as EITF 96-19, Debtors Accounting for Modification or
Exchange of Debt Instruments). Thus the Company recorded $586,785 as loss on
exchange or extinguishment of the old debt in the income statement during the
period ended December 31, 2009.
As
previously disclosed in Form 8-K dated October 16, 2009, the Company on October
16, 2009 consummated the sale of a promissory note in the principal amount of
$2,000,000 (the “Note”) to Bricolueur Partners, L.P. (“Bricoleur”) for
$2,000,000. There is no interest payable on the Note and the Note is due and
payable on October 16, 2010 (the “Maturity Date”). The Company can pre-pay the
Note at any time without penalty or premium and the Note is unsecured. The Note
is not convertible into the Company’s Common Stock or other securities of the
Company. However, under the Note and Share Purchase Agreement (the “Note and
Share Purchase Agreement”), effective as of October 16, 2009, by and among IGC
and Bricoleur, as additional consideration for the investment in the Note, IGC
issued 530,000 shares of Common Stock to Bricoleur.
The
Company in accordance with ASC 835-30, “Imputation of Interest”, (previously
referred to as APB 21, Interest on Receivables and Payables), and drawing
inference from ASC 815-40, “Contracts in Entity’s Own Equity”, (previously
referred to as EITF 00-19, Accounting for Derivative Financial Instruments
Indexed to, and Potentially Settled in, a Company's Own Stock), allocated the
proceeds based on the relative fair value of the various components of the
transaction and allocated such proceeds on a pro-rata basis, based on those
separately determined fair values. Accordingly, the Company recorded
$712,872 as discount on issue of debt, which will be amortized over the period
of the loan. The Company amortized such discount amounting to $178,218 during
the the three month period ended December 31, 2009.
The
Company’s total interest expense was $1,019,687 for the nine months ended
December 31, 2009. No interest was capitalized by the Company for the
nine months ended December 31, 2009.
NOTE
6 – FAIR VALUE OF FINANCIAL INSTRUMENTS
The fair
value of the Company’s current assets and current liabilities approximate their
carrying value because of their short term maturity. Such financial instruments
are classified as current and are expected to be liquidated within the next
twelve months.
NOTE
7 – GOODWILL
The
change in goodwill balance is as follows::
|
December
31
2009
|
March
31
2009
|
|||||||
|
(Unaudited)
|
(Audited)
|
|||||||
|
Balance
at the beginning of the period
|
$ | 17,483,501 | $ | 17,483,501 | ||||
|
Elimination
on deconsolidation of Sricon
|
(10,552,194 | ) | - | |||||
|
Balance
at the end of the period
|
$ | 6,931,307 | $ | 17,483,501 | ||||
NOTE
8 - RELATED PARTY TRANSACTIONS
For the
three month period ended December 31, 2009, $8,000 was paid to SJS Associates
for Mr. Selvaraj’s consulting services.
The
Company had agreed to pay Integrated Global Network, LLC (“IGN, LLC”), an
affiliate of our Chief Executive Officer, Mr. Mukunda, an administrative fee of
$4,000 per month for office space and general and administrative
services. A total $8,000 was paid to IGN, LLC for the
period. The Company and IGN, LLC have agreed to continue the
agreement on a month-to-month basis.
NOTE
9 -COMMITMENTS AND CONTINGENCY
No
significant commitments and contingencies were made during the 3 month and 9
month periods ended December 31, 2009.
NOTE
10 - INVESTMENT ACTIVITIES
No
significant investment activities occurred during the 3 month and 9 month
periods ended December 31, 2009.
NOTE
11 - COMMON STOCK
See
Securities Section.
NOTE
12 – STOCK-BASED COMPENSATION
On April
1, 2009 the Company adopted ASC 718, “Compensation-Stock Compensation”,
(previously referred to as SFAS No. 123 (revised 2004), Share Based
Payment). ASC 718 requires all share-based payments to
employees, including grants of employee stock options, to be recognized in the
financial statements based on their fair values. No stock based compensation was
awarded during the 3 month period ended December 31, 2009. On
May 13, 2009, the Company granted 78,820 shares of common stock and 1,413,000
stock options, to its directors and employees. The options
vested immediately. The exercise price of the options was $1.00 per
share, and the options will expire on May 13, 2014. The fair value of
the stock was $39,410 on the date of grant and the fair value of the stock
options was $90,997. Total share-based compensation expense, related
to all of the Company’s share-based awards, recognized for the 9 month period
ended December 31, 2009 is $130,407. Under the 2008 Omnibus Plan, 457,408
options remain issuable under the plan.
The fair
value of stock option awards is estimated on the date of grant using a
Black-Scholes Pricing Model with the following assumptions for options awarded
during the three and nine months ended December 31, 2009:
|
Three
Months Ended
December
31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Expected
life of options (years)
|
None
|
None
|
||||||
|
Vested
Options
|
None
|
None
|
||||||
|
Risk
free interest rate
|
None
|
None
|
||||||
|
Expected
volatility of stock
|
None
|
None
|
||||||
|
Expected
dividend yield
|
None
|
None
|
||||||
|
Nine
Months Ended
December
31,
|
||||||||
|
2009
|
2008
|
|||||||
|
Expected
life of options (years)
|
5
|
None
|
||||||
|
Vested
Options
|
100
|
%
|
None
|
|||||
|
Risk
free interest rate
|
1.98
|
%
|
None
|
|||||
|
Expected
volatility of stock
|
35.35
|
%
|
None
|
|||||
|
Expected
dividend yield
|
None
|
None
|
||||||
The
volatility estimate was derived using historical data for the IGC stock and
for public companies in the infrastructure industry.
NOTE
13 - DECONSOLIDATION
As
previously disclosed in our Form 8-K dated September 21, 2007 and Form 10-QSB
for the quarterly period ended June 30, 2007, on September 21, 2007, the Company
entered into a Share Subscription cum Purchase Agreement (the “Sricon
Subscription Agreement”) dated as of September 15, 2007 with Sricon
Infrastructure Private Limited (“Sricon”) and certain individuals
(collectively, the “Sricon Promoters”), pursuant to which the Company or its
subsidiary in Mauritius (IGC-M) acquired (the “Sricon
Acquisition”) 4,041,676 newly-issued
equity shares (the “New Sricon Shares”) directly from Sricon for
approximately $26 million and 351,840 equity shares from Mr. R. L. Srivastava
for approximately $3 million (both based on an exchange rate of INR 40 per USD)
so that at the conclusion of the transactions contemplated by the Sricon
Subscription Agreement, the Company owned approximately 63% of the outstanding
equity shares of Sricon. We paid full price for the stock of Sricon, and
we subsequently borrowed $17.9 million (computed at an exchange rate of
approximately 40 INR to $1 USD) from Sricon. As
previously disclosed, failure to repay the note or negotiate a settlement could
result in IGC having to decrease its ownership in Sricon by tendering all or a
portion of the Sricon shares it owns to Sricon to repay the note. The
Sricon Acquisition was consummated on March 7, 2008.
Pursuant
to board resolutions dated February 8, 2010, effective as of October 1, 2009 we
decreased our ownership in Sricon Infrastructure from 63% to 22.3%. Rather than
continue to owe Sricon $17.9 million, and more importantly, continue to fund two
construction companies, we decreased our ownership in Sricon by an amount
proportionate to the loan. The impact is that we no longer owe Sricon
$17.9 million and our corresponding ownership is decreased. The
deconsolidation of Sricon from the balance sheet of IGC results in shrinking the
IGC balance sheet and a one-time charge on the P&L taken in the quarter
ended December 31, 2009. The equity dilution of 40.715% resulted in a
consideration of $17,900,000 adjusted primarily for the inter-company loan
provided by Sricon to the parent. Following the guidance under ASC 810-10, the parent
derecognized the assets, liabilities and equity components (including the
amounts previously recognized in other comprehensive income) related to
Sricon. IGC recorded a loss of $1,107,124 million and further
reclassified an accumulated AOCI loss of $2,098,492 million in the income
statement as a result of the dilution. Deferred acquisition costs
related to Sricon amounted to $1,854,750, which were subsequently recorded in
the income statement for the period ended December 31, 2009.
The
Company has accounted for its remaining 22.3% interest in Sricon by the equity
method. The
carrying value of the investment in Sricon as of December 31, 2009, was
$8,182,387. The Company’s equity in the income of Sricon for the three months
ended December 31, 2009 was $16,446.
NOTE
14 - INCOME TAXES
The
provision for income taxes decreased $1.9 million in the nine month period ended
December 31, 2009 compared to the same period in 2008. The decrease
in income taxes was primarily due to the decrease in income before income taxes
of $6.4 million for the same nine month period. Our effective tax rate was 1.3%
in the nine month period ending December 31, 2009 and 77% for the same period in
2008. The majority of the tax expense was incurred by our overseas subsidiaries
with Sricon having the bulk of the tax expense allocation. The decrease in our
effective tax rate was due to the sharp decrease in income before income
taxes.
NOTE
15 - RECONCILIATION OF EPS
For
December 31, 2009, the basic shares include founders shares, shares sold in the
private placement, shares sold in the IPO, shares sold in the registered direct,
shares arising from the exercise of warrants issued in the placement of debt and
the registered direct, shares issued in connection with debt and shares issued
to employees, directors and vendors. The fully diluted shares
include the basic shares plus warrants issued as part of the units sold in the
private placement and IPO, warrants sold as part of the units sold in the
registered direct and employee options. The UPO issued to the
underwriters (1,500,000 shares) is not considered as the strike price for the
UPO is “out of the money” at $6.50 per share. The historical weighted
average per share, for our shares, through December 31, 2009, was applied using
the treasury method of calculating the fully diluted shares. The
calculations for fully diluted shares include 660,893 shares and exclude
12,954,849 shares from the fully diluted EPS computations.
NOTE
16 - SUBSEQUENT EVENTS
As stated
in our 8-K dated January 6, 2010 we commissioned a
quarry for commercial production in Maharashtra, India and announced plans for
use of a second quarry.
[ ] Shares
of
India
Globalization Capital, Inc.
Common
Stock
PROSPECTUS
Until (25 days
after the date of this prospectus), all dealers that effect transactions in
these securities may be required to deliver this prospectus.
PART II
Information
not required in prospectus
|
Item 13.
|
Other
expenses of issuance and
distribution
|
The
following table sets forth all expenses payable in connection with registration
of the securities covered by this prospectus. All the amounts shown are
estimates, except the SEC registration fee. We will bear all costs,
fees and expenses listed below incurred in effecting the issuance and
registration of the shares covered by this prospectus.
|
Total
|
||||
|
SEC
registration fee
|
$
|
223.20 | ||
|
Printing
expenses
|
$
|
* | ||
|
Legal
fees and expenses
|
$
|
* | ||
|
Accounting
fees and expenses
|
$
|
* | ||
|
Miscellaneous
|
$
|
* | ||
|
Total
|
$
|
|||
* Estimated.
Item 14.
Indemnification of
officers and directors
Our
certificate of incorporation provides that all directors, officers, employees
and agents of the registrant shall be entitled to be indemnified by us to the
fullest extent permitted by Section 2-418 of the Maryland General
Corporation Law. Section 2-418 of the Maryland General Corporation Law
concerning indemnification of officers, directors, employees and agents is set
forth below.
“Section 2-418.
Indemnification of directors, officers, employees and agents.
(a) Definitions. — In
this section the following words have the meanings indicated.
(1) “Director” means any person who is or
was a director of a corporation and any person who, while a director of a
corporation, is or was serving at the request of the corporation as a director,
officer, partner, trustee, employee, or agent of another foreign or domestic
corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust, other enterprise, or employee
benefit plan.
(2) “Corporation”
includes any domestic or foreign predecessor entity of a corporation in a
merger, consolidation, or other transaction in which the predecessor’s existence
ceased upon consummation of the transaction.
(3) ”Expenses” includes attorney’s
fees.
(4) “Official capacity” means the
following:
(i) When used with respect to a director,
the office of director in the corporation; and
(ii) When
used with respect to a person other than a director as contemplated in
subsection (j), the elective or appointive office in the corporation held by the
officer, or the employment or agency relationship undertaken by the employee or
agent in behalf of the corporation.
(iii) “Official capacity” does not include
service for any other foreign or domestic corporation or any partnership, joint
venture, trust, other enterprise, or employee benefit plan.
(5) “Party” includes a person who was, is,
or is threatened to be made a named defendant or r respondent in a
proceeding.
(6) “Proceeding”
means any threatened, pending or completed action, suit or proceeding, whether
civil, criminal, administrative, or investigative.
(b) Permitted indemnification of
director. —
(1)
A corporation may indemnify any
director made a party to any proceeding by reason of service in that capacity
unless it is established that:
(i) The act or omission of the director was
material to the matter giving rise to the proceeding; and
1. Was committed in bad faith;
or
2. Was the result of active and deliberate
dishonesty; or
(ii) The director actually received an
improper personal benefit in money, property, or services;
or
(iii) In the case of any criminal proceeding,
the director had reasonable cause to believe that the act or omission was
unlawful.
(2)
(i)
Indemnification may be against
judgments, penalties, fines, settlements, and reasonable expenses actually
incurred by the director in connection with the proceeding.
(ii) However, if the proceeding was one by
or in the right of the corporation, indemnification may not be made in respect
of any proceeding in which the director shall have been adjudged to be liable to
the corporation.
(3)
(i) The termination of any proceeding by
judgment, order, or settlement does not create a presumption that the director
did not meet the requisite standard of conduct set forth in this
subsection.
(ii) The termination of any proceeding by
conviction, or a plea of nolo contendere or its equivalent, or an entry of an
order of probation prior to judgment, creates a rebuttable presumption that the
director did not meet that standard of conduct.
(4) A
corporation may not indemnify a director or advance expenses under this section
for a proceeding brought by that director against the corporation,
except:
(i) For a proceeding brought to enforce
indemnification under this section; or
(ii) If the charter or bylaws of the
corporation, a resolution of the board of directors of the corporation, or an
agreement approved by the board of directors of the corporation to which the
corporation is a party expressly provide otherwise.
(c) No indemnification of director
liable for improper personal benefit. — A director may not be
indemnified under subsection (b) of this section in respect of any
proceeding charging improper personal benefit to the director, whether or not
involving action in the director’s official capacity, in which the director was
adjudged to be liable on the basis that personal benefit was improperly
received.
(d) Required indemnification against
expenses incurred in successful defense — Unless limited by the
charter:
(1) A director who has been successful, on
the merits or otherwise, in the defense of any proceeding referred to in
subsection (b) of this section shall be indemnified against reasonable
expenses incurred by the director in connection with the
proceeding.
(2) A court of appropriate jurisdiction,
upon application of a director and such notice as the court shall require, may
order indemnification in the following circumstances:
(i) If it determines a director is entitled
to reimbursement under paragraph (1) of this subsection, the court shall
order indemnification, in which case the director shall be entitled to recover
the expenses of securing such reimbursement; or
(ii) If it determines that the director is
fairly and reasonably entitled to indemnification in view of all the relevant
circumstances, whether or not the director has met the standards of conduct set
forth in subsection (b) of this section or has been adjudged liable under
the circumstances described in subsection (c) of this section, the court
may order such indemnification as the court shall deem proper. However,
indemnification with respect to any proceeding by or in the right of the
corporation or in which liability shall have been adjudged in the circumstances
described in subsection (c) shall be limited to
expenses.
(3) A
court of appropriate jurisdiction may be the same court in which the proceeding
involving the director’s liability took place.
(e) Determination that indemnification
is proper. — (1) Indemnification under subsection (b) of
this section may not be made by the corporation unless authorized for a specific
proceeding after a determination has been made that indemnification of the
director is permissible in the circumstances because the director has met the
standard of conduct set forth in subsection (b) of this
section.
(2)
Such determination shall be
made:
(i) By the board of directors by a majority
vote of a quorum consisting of directors not, at the time, parties to the
proceeding, or, if such a quorum cannot be obtained, then by a majority vote of
a committee of the board consisting solely of two or more directors not, at the
time, parties to such proceeding and who were duly designated to act in the
matter by a majority vote of the full board in which the designated directors
who are parties may participate;
(ii) By special legal counsel selected
by the board of directors or a committee of the board by vote as set forth in
subparagraph (i) of this paragraph, or, if the requisite quorum of the full
board cannot be obtained therefor and the committee cannot be established, by a
majority vote of the full board in which directors who are parties may
participate; or
(iii) By the
stockholders.
(3) Authorization of indemnification and
determination as to reasonableness of expenses shall be made in the same manner
as the determination that indemnification is permissible. However, if the
determination that indemnification is permissible is made by special legal
counsel, authorization of indemnification and determination as to reasonableness
of expenses shall be made in the manner specified in subparagraph (ii) of
paragraph (2) of this subsection for selection of such
counsel.
(4) Shares
held by directors who are parties to the proceeding may not be voted on the
subject matter under this subsection.
(f) Payment of expenses in advance of
final disposition of action. — (1) Reasonable expenses incurred
by a director who is a party to a proceeding may be paid or reimbursed by the
corporation in advance of the final disposition of the proceeding upon receipt
by the corporation of:
(i) A written affirmation by the director
of the director’s good faith belief that the standard of conduct necessary for
indemnification by the corporation as authorized in this section has been met;
and
(ii) A written undertaking by or on behalf
of the director to repay the amount if it shall ultimately be determined that
the standard of conduct has not been met.
(2)
The undertaking required by
subparagraph (ii) of paragraph (1) of this subsection shall be an
unlimited general obligation of the director but need not be secured and may be
accepted without reference to financial ability to make the
repayment.
(3)
Payments under this subsection shall be
made as provided by the charter, bylaws, or contract or as specified in
subsection (e) of this section.
(g) Validity of indemnification
provision. — The indemnification and advancement of expenses
provided or authorized by this section may not be deemed exclusive of any other
rights, by indemnification or otherwise, to which a director may be entitled
under the charter, the bylaws, a resolution of stockholders or directors, an
agreement or otherwise, both as to action in an official capacity and as to
action in another capacity while holding such office.
(h) Reimbursement of director’s expenses
incurred while appearing as witness. — This section does not limit
the corporation’s power to pay or reimburse expenses incurred by a director in
connection with an appearance as a witness in a proceeding at a time when the
director has not been made a named defendant or respondent in the
proceeding.
(i) Director’s service to employee
benefit plan. — For purposes of this section:
(1) The corporation shall be deemed to have
requested a director to serve an employee benefit plan where the performance of
the director’s duties to the corporation also imposes duties on, or otherwise
involves services by, the director to the plan or participants or beneficiaries
of the plan;
(2) Excise
taxes assessed on a director with respect to an employee benefit plan pursuant
to applicable law shall be deemed fines; and
(3) Action
taken or omitted by the director with respect to an employee benefit plan in the
performance of the director’s duties for a purpose reasonably believed by the
director to be in the interest of the participants and beneficiaries of the plan
shall be deemed to be for a purpose which is not opposed to the best interests
of the corporation.
(j) Officer, employee or
agent. — Unless limited by the charter:
(1) An officer of the corporation shall be
indemnified as and to the extent provided in subsection (d) of this section
for a director and shall be entitled, to the same extent as a director, to seek
indemnification pursuant to the provisions of subsection
(d);
(2) A corporation may indemnify and advance
expenses to an officer, employee, or agent of the corporation to the same extent
that it may indemnify directors under this section; and
(3) A
corporation, in addition, may indemnify and advance expenses to an officer,
employee, or agent who is not a director to such further extent, consistent with
law, as may be provided by its charter, bylaws, general or specific action of
its board of directors, or contract.
(k) Insurance or similar
protection. — (1) A corporation may purchase and maintain
insurance on behalf of any person who is or was a director, officer, employee,
or agent of the corporation, or who, while a director, officer, employee, or
agent of the corporation, is or was serving at the request of the corporation as
a director, officer, partner, trustee, employee, or agent of another foreign or
domestic corporation, partnership, joint venture, trust, other enterprise, or
employee benefit plan against any liability asserted against and incurred by
such person in any such capacity or arising out of such person’s position,
whether or not the corporation would have the power to indemnify against
liability under the provisions of this section.
(2)
A corporation may provide similar
protection, including a trust fund, letter of credit, or surety bond, not
inconsistent with this section.
(3)
The insurance or similar protection may
be provided by a subsidiary or an affiliate of the
corporation.
(l) Report of indemnification to
stockholders. — Any indemnification of, or advance of expenses to, a
director in accordance with this section, if arising out of a proceeding by or
in the right of the corporation, shall be reported in writing to the
stockholders with the notice of the next stockholders’ meeting or prior to the
meeting.
Insofar
as indemnification for liabilities arising under the Securities Act may be
permitted to our directors, officers, and controlling persons pursuant to the
foregoing provisions, or otherwise, we have been advised that in the opinion of
the SEC such indemnification is against public policy as expressed in the
Securities Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event that a claim for
indemnification against such liabilities (other than the payment of expenses
incurred or paid by a director, officer or controlling person in a successful
defense of any action, suit or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer
or controlling person in connection with the securities being registered, we
will, unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by
controlling precedent, submit to the court of appropriate jurisdiction the
question whether such indemnification by it is against public policy as
expressed in the Securities Act and will be governed by the final adjudication
of such issue.
Paragraph B.
of Article Tenth of our amended and restated certificate of incorporation
provides:
“The
Corporation, to the full extent permitted by Section 2-418 of the MGCL, as
amended from time to time, shall indemnify all persons whom it may indemnify
pursuant thereto. Expenses (including attorneys’ fees) incurred by an officer or
director in defending any civil, criminal, administrative, or investigative
action, suit or proceeding or which such officer or director may be entitled to
indemnification hereunder shall be paid by the Corporation in advance of the
final disposition of such action, suit or proceeding upon receipt of an
undertaking by or on behalf of such director or officer to repay such amount if
it shall ultimately be determined that he or she is not entitled to be
indemnified by the Corporation as authorized hereby.”
Article XI
of our Bylaws provides for indemnification of any of our directors, officers,
employees or agents for certain matters in accordance with Section 2-418 of
the Maryland General Corporation Law.
|
Item 15.
|
Recent
sales of unregistered securities
|
Set forth
below is information regarding shares of common stock and preferred stock
issued, and options and warrants granted, by us within the past three years.
Also included is the consideration, if any, received by us for such shares,
options and warrants and information relating to the section of the Securities
Act, or rule of the SEC under which exemption from registration was
claimed.
On
February 3, 2006, the Company sold 200,000 shares of common stock for an
aggregate consideration of $2,000 in cash at a price of approximately $.01 per
share as follows:
|
Name
|
|
Number
of Shares
|
|
Relationship
to the Company at the Time of Acquisition
|
|
|
Dr.
Ranga Krishna
|
100,000
|
Chairman
of the Board
|
|||
|
John
Cherin
|
37,500
|
Chief
Financial Officer, Treasurer
|
|||
|
and
Director
|
|||||
|
Larry
Pressler
|
25,000
|
Special
Advisor
|
|||
|
P.G.
Kakodkar
|
12,500
|
Special
Advisor
|
|||
|
Sudhakar
Shenoy
|
12,500
|
Director
|
|||
|
Suhail
Nathani
|
12,500
|
Director
|
|||
These
shares were issued in connection with our organization pursuant to the exemption
from registration contained in Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933,
as they were sold to sophisticated, wealthy individuals. No underwriting
discounts or commissions were paid with respect to such sales.
In March,
2006, immediately prior to the initial public offering of the Company’s units,
in a private placement, the Company sold an aggregate of 170,000 units, with
each unit consisting of 1 share of Common Stock and 2 warrants, each exercisable
to purchase 1 share of common stock (at an initial exercise price of $5.00 per
share) at a price equal to the offering price of the Company’s initial public
offering, $6.00 per unit. These shares were issued in connection with
our organization pursuant to the exemption from registration contained in
Section 4(2) of the Securities Act of 1933, as they were sold to
sophisticated, wealthy individuals. No underwriting discounts or commissions
were paid with respect to such sales. The units were sold as
follows:
|
Name
|
|
Number
of Units
|
|
Relationship
to the Company at the Time of Acquisition
|
|
|
Dr.
Ranga Krishna
|
120,000
|
Chairman
of the Board
|
|||
|
John
Cherin
|
16,666
|
Chief
Financial Officer, Treasurer and Director
|
|||
|
Ram
Mukunda
|
33,334
|
Chief
Executive Officer, President and
Director
|
|||
On
February 5, 2007, the Company entered into a Note and Warrant Purchase Agreement
with Oliveira Capital, LLC (“Oliveira”) pursuant to which the Company sold
Oliveira a Promissory Note in the principal amount of $3,000,000 and a warrant
to purchase up to 425,000 shares of common stock of the Company (at an initial
exercise price of $5.00 per share) in a private placement. The Note
became due on February 5, 2008. As provided in the Note and Warrant
Purchase Agreement, the Company requested an extension of the term of the Note
and issued to Oliveira an additional warrant to purchase up to 425,000 shares of
common stock of the Company (at an initial exercise price of $5.00 per
share). These transactions were exempt from registration under the
Securities Act pursuant to Section 4(2) of the Securities Act, which
exempts private issuances of securities in which the securities are not offered
or advertised to the general public. No underwriting discounts or
commissions were paid with respect to such sales.
On
December 24, 2007, the Company sold Promissory Notes and shares of the Company’s
common stock in a private placement as follows:
|
Name
|
|
Principal
Amount of
Promissory
Note
|
|
Number
of Shares
of
Common Stock
|
Relationship
to the Company
at
the Time of Acquisition
|
|||
|
Dr.
Ranga Krishna
|
$4,300,000
|
446,226
|
Chairman
of the Board
|
|||||
|
Oliveira
Capital, LLC
|
$1,000,000
|
103,774
|
None
|
|||||
On
January 10, 2008, the Company sold Promissory Notes and shares of the Company’s
common stock in a private placement as follows:
|
Name
|
Principal
Amount of
Promissory
Note
|
Number
of Shares
of
Common Stock
|
Relationship
to the Company
at
the Time of Acquisition
|
||||||
|
Funcorp
Associates
|
$
|
50,000
|
5,189
|
None
|
|||||
|
Trufima
NV
|
$
|
50,000
|
5,189
|
None
|
|||||
|
Geri
Investments NV
|
$
|
100,000
|
10,377
|
None
|
|||||
|
Harmon
Corp NV
|
$
|
50,000
|
5,189
|
None
|
|||||
|
La
Legetaz
|
$
|
100,000
|
10,377
|
None
|
|||||
|
Arterio,
Inc.
|
$
|
50,000
|
5,189
|
None
|
|||||
|
Domanco
Venture Capital Find
|
$
|
50,000
|
5,189
|
None
|
|||||
|
Anthony
Polak
|
$
|
75,000
|
7,783
|
None
|
|||||
|
Anthony
Polak “S”
|
$
|
50,000
|
5,189
|
None
|
|||||
|
Jamie
Polak
|
$
|
50,000
|
5,189
|
None
|
|||||
|
RL
Capital Partners LP
|
$
|
250,000
|
25,943
|
None
|
|||||
|
Ronald
M. Lazar, IRA
|
$
|
50,000
|
5,189
|
None
|
|||||
|
White
Sand Investor Group
|
$
|
500,000
|
51,887
|
None
|
|||||
|
MLR
Capital Offshore Master Fund, Ltd.
|
$
|
550,000
|
57,075
|
None
|
|||||
The
December 2007 and January 2008 transactions were exempt from registration under
the Securities Act pursuant to Section 4(2) of the Securities Act, which
exempts private issuances of securities in which the securities are not offered
or advertised to the general public. No underwriting discounts or
commissions were paid with respect to such sales. These
Promissory Notes have been repaid in full Pursuant to the terms of
the Note Purchase Agreement between the Company and the purchasers of the
Promissory Notes and shares, the shares of common stock were issued to the
purchasers subsequent to the Company’s acquisition of a controlling interest in
Sricon and TBL
On August
15, 2008, the Company issued 10,000 shares of its common stock to RedChip
Companies, Inc. in a private placement as payment for
services . This transaction was exempt from registration under
the Securities Act pursuant to Section 4(2) of the Securities Act, which
exempts private issuances of securities in which the securities are not offered
or advertised to the general public. No underwriting discounts or
commissions were paid with respect to such sale.
On
September 30, 2008, the Company entered into a Note and Share Purchase Agreement
with Steven M. Oliveira 1998 Charitable Remainder Unitrust (“Oliveira Trust”)
pursuant to which the Company sold the Oliveira Trust a Promissory Note in the
principal amount of $2,000,000 (the “Original Olivera Trust Note”) and 200,000
shares of common stock of the Company . The Original Olivera Trust
Note was due and payable on September 30, 2009, or upon an earlier change in
control of the Company, and bears interest at a rate of 6% per
annum. The Note and Share Purchase Agreement provided for the
issuance by the Company of additional shares of its Common Stock to the Oliveira
Trust for no additional consideration as follows: if an event of
default under the Promissory Note remains uncured for a period of more than 30
days, the Company would issue to the Oliveira Trust an additional 10,000 shares
of Common Stock for each $100,000 of outstanding principal amount of the
Original Olivera Trust Note and if the Company failed to file a registration
statement covering the resale Common Stock within 45 days after the sale of the
Original Olivera Trust Note and Common Stock to the Oliveira Trust or such
registration statement is not declared effective within 150 days after filing
(subject to certain exceptions and extensions) the Company would issue to the
Oliveira Trust an additional 25,000 shares of Common Stock for each $100,000 of
outstanding principal amount of the “Original Olivera Trust Note and an
additional 5,000 shares for each $100,000 of outstanding principal
amount of the Promissory Note for each subsequent 30 day period such
registration statement is not declared effective, These transactions
were exempt from registration under the Securities Act pursuant to Regulation D
promulgated under the Securities Act, which exempts private issuances of
securities in which the securities are not offered or advertised to the general
public. No underwriting discounts or commissions were paid with
respect to such sales.
On July 13, 2009, the Company issued 15,000 shares of common
stock to RedChip Companies Inc. in a private placement as payment for
services. This transaction was exempt from registration under the
Securities Act pursuant to Section 4(2) of the Securities Act, which
exempts private issuances of securities in which the securities are not offered
or advertised to the general public. No underwriting discounts or
commissions were paid with respect to such sale.
On
October 5, 2009, the Company entered into a new Note and Share Purchase
Agreement (the “New Oliveira Purchase Agreement”) with the Oliveira Trust
pursuant to which the Oliveria Trust exchanged the Original Olivera Trust Note
for a new promissory note (the “New Note”) on substantially the same terms as
the Original Olivera Trust Note except that the principal amount of the New Note
is $2,120,000, which reflects the accrued but unpaid interest on the Original
Olivera Trust Note. There is no interest payable on the New Note and the New
Note is due and payable on October 4, 2010 (the “Maturity Date”). As
is the case with the Original Olivera Trust Note, the Company can pre-pay the
New Note at any time without penalty or premium, and the New Note is
unsecured.
The New
Note is not convertible into Common Stock) or other securities of the Company.
However, under the New Oliveira Purchase Agreement, as additional consideration
for the exchange of the Original Olivera Trust Note, the Company agreed to issue
530,000 shares of Common Stock to the Oliveira Trust. If the Company
fails to repay the Notes by the Maturity Date, the Oliveira Trust would be
entitled to receive an additional 200,000 shares of Common Stock.
Pursuant
to the New Oliveira Purchase Agreement, which supercedes the original Note and
Warrat Purcahse Agreement, the Company has also agreed that if the Note is not
repaid by the Maturity Date it will use reasonable best efforts to ensure that
no later than October 4, 2010, it will have a registration statement
effective with a sufficient number of shares of Common Stock based on the then
fair market value of the shares registered in excess of the amount due under the
New Note. The securities sold in this transaction have not been
registered under the Securities Act of 1933, as amended (the “Act”) and may not
be offered or sold in the United States in the absence of an effective
registration statement or exemption from the registration requirements under the
Act. The issuance of the foregoing securities was exempt from
registration under Section 3(a)(9) of the Act as an exchange of securities
solely with an existing securityholder where no commission or other remuneration
was paid or given directly or indirectly for soliciting such
exchange.
On
October 16, 2009, the Company entered into a Note and Share Purchase Agreement
with Bricoleur Partners, L.P. (“Bricoleur”) pursuant to which the
Company sold Bricoleur a Promissory Note in the principal amount of $2,000,000
and 530,000 shares of common stock of the Company . The Promissory
Note is due and payable on October 16, 2010, or upon an earlier change in
control of the Company, and bears no interest. The Note and
Share Purchase Agreement, provides for the issuance by the Company of additional
shares of its Common Stock to Bricoleur for no additional consideration as
follows: if an event of default under the Promissory Note remains
uncured for a period of more than 30 days, the Company shall issue to Bricoleur
an additional 10,000 shares of Common Stock for each $100,000 of outstanding
principal amount of the Promissory Note and if the Company fails to file a
registration statement covering the resale Common Stock within 45 days after the
sale of the Promissory Note and Common Stock to Bricoleur or such registration
statement is not declared effective within 150 days after filing (subject to
certain exceptions and extensions) the Company shall issue to Bricoleur an
additional 25,000 shares of Common Stock for each $100,000 of outstanding
principal amount of the Promissory Note and an additional 5,000
shares for each $100,000 of outstanding principal amount of the
Promissory Note for each subsequent 30 day period such registration statement is
not declared effective, These transactions were exempt from
registration under the Securities Act pursuant to Section 4(2) of the Act, which
exempts private issuances of securities in which the securities are not offered
or advertised to the general public. No underwriting discounts or
commissions were paid with respect to such sales.
On May
13, 2009, the Company granted 39,410 shares of its common stock to each of Ram
Mukunda and Dr. Ranga Krishna. These transactions were exempt from
registration under the Securities Act pursuant to Section 4(2) of the Act, which
exempts private issuances of securities in which the securities are not offered
or advertised to the general public. No underwriting discounts or
commissions were paid with respect to such sales.
In March
2010, the Company issued 9,135 shares of common stock to RedChip Companies
Inc. in a private placement as payment for services. This
transaction was exempt from registration under the Securities Act pursuant to
Section 4(2) of the Securities Act, which exempts private issuances of
securities in which the securities are not offered or advertised to the general
public. No underwriting discounts or commissions were paid with
respect to such sale.
|
Item 16.
|
Exhibits
and financial statement schedules
|
|
(a)
|
Exhibits
|
|
Exhibit
No.
|
Description
|
|
| 1.1 |
Underwriting
Agreement between the Registrant and ____________ dated ________,
2010.*
|
|
|
3.1
|
Amended
and Restated Articles of Incorporation. (1)
|
|
|
3.2
|
By-laws.
(2)
|
|
|
4.1
|
Specimen
Unit Certificate. (3)
|
|
|
4.2
|
Specimen
Common Stock Certificate. (3)
|
|
|
4.3
|
Specimen
Warrant Certificate. (3)
|
|
|
4.4
|
Form
of Warrant Agreement between Continental Stock Transfer & Trust
Company and the Registrant. (1)
|
|
|
4.5
|
Form
of Purchase Option to be granted to Ferris, Baker Watts, Inc..
(1)
|
|
|
5.1
|
Opinion
of Seyfarth Shaw LLP *
|
|
|
10.1
|
Amended
and Restated Letter Agreement between the Registrant, Ferris, Baker Watts,
Inc. and Ram Mukunda. (4)
|
|
|
10.2
|
Amended
and Restated Letter Agreement between the Registrant, Ferris, Baker Watts,
Inc. and John Cherin. (4)
|
|
|
10.3
|
Amended
and Restated Letter Agreement between the Registrant, Ferris, Baker Watts,
Inc. and Ranga Krishna. (4)
|
|
|
10.4
|
Form
of Investment Management Trust Agreement between Continental Stock
Transfer & Trust Company and the Registrant. (5)
|
|
|
10.5
|
Promissory
Note issued by the Registrant to Ram Mukunda. (2)
|
|
|
10.5.1
|
Extension
of Due Date of Promissory Note issued to Ram Mukunda.
(2)
|
|
|
10.6
|
Form
of Stock and Unit Escrow Agreement among the Registrant, Ram Mukunda, John
Cherin and Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company.
(2)
|
|
|
10.7
|
Form
of Registration Rights Agreement among the Registrant and each of the
existing stockholders. (3)
|
|
|
10.8
|
Form
of Unit Purchase Agreement among Ferris, Baker Watts, Inc. and one or more
of the Initial Stockholders. (5)
|
|
|
10.9
|
Form
of Office Service Agreement between the Registrant and Integrated Global
Networks, LLC. (5)
|
|
|
10.10
|
Amended
and Restated Letter Advisory Agreement between the Registrant, Ferris,
Baker Watts, Inc. and SG Americas Securities, LLC. (5)
|
|
|
10.11
|
Form
of Letter Agreement between Ferris, Baker Watts, Inc. and certain officers
and directors of the Registrant. (4)
|
|
|
10.12
|
Form
of Letter Agreement between Ferris, Baker Watts, Inc. and each of the
Special Advisors of the Registrant. (4)
|
|
|
10.13
|
Form
of Letter Agreement between the Registrant and certain officers and
directors of the Registrant. (4)
|
|
|
10.14
|
Form
of Letter Agreement between the Registrant and each of the Special
Advisors of the Registrant. (4)
|
|
|
10.15
|
Promissory
Note issued by the Registrant to Ranga Krishna. (2)
|
|
|
10.15.1
|
Extension
of Due Date of Promissory Note issued to Ranga Krishna.
(2)
|
|
|
10.16
|
Form
of Promissory Note to be issued by the Registrant to Ranga Krishna.
(2)
|
|
|
10.17
|
Share
Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement dated February 2, 2007 by and
among India Globalization Capital, Inc., MBL Infrastructures Limited and
the persons “named as Promoters therein”. (6)
|
|
|
10.18
|
Debenture
Subscription Agreement dated February 2, 2007 by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc., MBL Infrastructures Limited and the persons
named as Promoters therein. (6)
|
|
|
10.19
|
Note
and Warrant Purchase Agreement dated February 5, 2007 by and among
India Globalization Capital, Inc. and Oliveira Capital, LLC.
(6)
|
|
|
10.20
|
Promissory
Note dated February 5, 2007 in the initial principal amount for
$3,000,000 issued by India Globalization Capital, Inc. to Oliveira
Capital, LLC. (6)
|
|
|
10.21
|
Warrant
to Purchase Shares of Common Stock of India Globalization Capital, Inc.
issued by India Globalization Capital, Inc. to Oliveira Capital, LLC.
(6)
|
|
|
10.22
|
First
Amendment to Share Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement dated February 2,
2007 by and among India Globalization Capital, Inc., MBL Infrastructures
Limited and the persons named as Promoters therein. (7)
|
|
|
10.23
|
First
Amendment to the Debenture Subscription Agreement dated February 2, 2007
by and among India Globalization Capital, Inc., MBL Infrastructures
Limited and the persons named as Promoters therein. (7)
|
|
|
10.24
|
Contract
Agreement dated April 29, 2007 between IGC, CWEL, AMTL and MAIL.
(7)
|
|
|
10.25
|
First
Amendment dated August 20, 2007 to Agreement dated April 29, 2007 between
IGC, CWEL, AMTL and MAIL. (8)
|
|
|
10.26
|
Share
Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement dated September 16, 2007 by and among
India Globalization Capital, Inc., Techni Bharathi Limited and the persons
named as Promoters therein (9).
|
|
|
10.27
|
Shareholders
Agreement dated September 16, 2007 by and among India Globalization
Capital, Inc., Techni Bharathi Limited and the persons named as Promoters
therein. (9)
|
|
|
10.28
|
Share
Purchase Agreement dated September 21, 2007 by and between India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and Odeon Limited. (9)
|
|
|
10.29
|
Share
Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement dated September 15, 2007 by and among
India Globalization Capital, Inc., Sricon Infrastructure
Private Limited and the persons named as Promoters therein.
(9)
|
|
|
10.30
|
Shareholders
Agreement dated September 15, 2007 by and among India Globalization
Capital, Inc., Sricon Infrastructure Private Limited and the
persons named as Promoters therein. (9)
|
|
|
10.31
|
Form
of Amendment to the Share Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement Dated
September 15, 2007, entered into on December 19, 2007 by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc., Sricon Infrastructure Private Limited and the
persons named as Promoters therein. (10)
|
|
|
10.32
|
Form
of Amendment to the Share Subscription Agreement Dated September 16, 2007,
entered into on December 21, 2007 by and among India Globalization
Capital, Inc., Techni Bharathi Limited and the persons named as Promoters
therein. (10)
|
|
|
10.33
|
Note
Purchase Agreement, effective as of December 24, 2007, by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and the persons named as Lenders therein.
(10)
|
|
|
10.34
|
Form
of India Globalization Capital, Inc. Promissory Note.
(10)
|
|
10.35
|
Form
of Registration Rights Agreement by and among India Globalization Capital,
Inc. and the persons named as Investors therein. (10)
|
|
|
10.36
|
Form
of Pledge Agreement, effective as of December 24, 2007, by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and the persons named as
Secured Parties therein. (10)
|
|
|
10.37
|
Form
of Lock up Letter Agreement, dated December 24, 2007 by and between India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and Dr. Ranga Krishna.
(10)
|
|
|
10.38
|
Form
of Letter Agreement, dated December 24, 2007, with Dr. Ranga Krishna.
(10)
|
|
|
10.39
|
Form
of Letter Agreement, dated December 24, 2007, with Oliveira Capital, LLC.
(10)
|
|
|
10.40
|
Form
of Warrant Clarification Agreement, dated January 4, 2008, by and between
the Company and Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company.
(11)
|
|
|
10.41
|
Form
of Amendment to Unit Purchase Options, dated January 4, 2008, by and
between the Company and the holders of Unit Purchase Options.
(11)
|
|
|
10.42
|
Second
Amendment to the Share Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement Dated September
15, 2007, entered into on January 14, 2008 by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc., Sricon Infrastructure Private Limited and the
persons named as Promoters therein. (12)
|
|
|
10.43
|
Letter
Agreement dated January 8, 2008 by and among India Globalization Capital,
Inc., Odeon Limited, and Techni Bharathi Limited with respect to the Share
Purchase Agreement dated September 21, 2007 by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and Odeon Limited.
(12)
|
|
|
10.44
|
Employment
Agreement between India Globalization Capital, Inc., India Globalization
Capital Mauritius and Ram Mukunda dated as of March 8, 2008.
(13)
|
|
|
10.45
|
2008
Omnibus Incentive Plan. (14)
|
|
|
10.46
|
Note
and Share Purchase Agreement dated as of September 30, 2008, by and among
India Globalization Capital, Inc. and Steven M. Oliveira 1998
Charitable Remainder Unitrust (15)
|
|
|
10.47
|
Registration
Rights Agreement dated September 30, 2008 by and among India Globalization
Capital, Inc. and the persons named as Investors therein.
(15)
|
|
|
10.48
|
Note
and Share Purchase Agreement dated as of October 5, 2009, by and among
India Globalization Capital, Inc. and Steven M. Oliveira 1998
Charitable Remainder Unitrust (16)
|
|
|
10.49
|
Unsecured
Promissory Note dated as of October 5, 2009 in the principal amount of
$2,120,000 issued by the Company to the Steven M. Oliveira 1998 Charitable
Remainder Unitrust. (16)
|
|
|
10.50
|
Note
and Share Purchase Agreement dated as of October 16, 2009 between the
Company and Bricoleur Partners, L.P. (17)
|
|
|
10.51
|
Unsecured
Promissory Note dated as of October 16, 2009 in the principal amount of
$2,000,000 issued by the Company to Bricoleur Partners, L.P.
(17)
|
|
|
10.52
|
Registration Rights Agreement dated as of October
16, 2009 between the Company and Bricoleur Partners, L.P.
(17)
|
|
|
10.53
|
Form
of Securities Purchase Agreement dated as of September 14, 2009 by and
among India Globalization Capital, Inc. and the investors named therein
(18)
|
|
|
10.54
|
Amendment
No. 1 dated as of October 30, 2009 to Securities Purchase Agreement by and
among India Globalization Capital, Inc. and the investors named
therein .**
|
|
|
10.55
|
ATM
Agency Agreement, dated as of October 13, 2009, by and between India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and Enclave Capital LLC
(19)
|
|
|
21
|
||
|
23.1
|
||
|
23.2
|
Consent
of Seyfarth Shaw LLP (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 5.1) *
|
|
|
23.3
|
Consent
of Mega Ace Consultancy. (4)
|
|
|
24
|
Power
of Attorney. **
|
|
|
99.1
|
Code
of Ethics. (5)
|
| * | To be filed by amendment. | |
| ** |
Previously
filed as an exhibit to this Registration
Statement.
|
|
|
(1)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC
File No. 333-124942), as amended and filed on November 2,
2005.
|
|
|
(2)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC
File No. 333-124942), as amended and filed on February 14,
2006.
|
|
|
(3)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC
File No. 333-124942), as originally filed on May 13,
2005.
|
|
|
(4)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC
File No. 333-124942), as amended and filed on July 11,
2005.
|
|
(5)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC
File No. 333-124942), as amended and filed on March 2,
2006.
|
|
|
(6)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on February 12, 2007.
|
|
|
(7)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on May 2, 2007.
|
|
|
(8)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on August 23, 2007.
|
|
|
(9)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on September 27, 2007.
|
|
|
(10)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on December 27, 2007.
|
|
|
(11)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on January 7, 2008.
|
|
|
(12)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on January 16, 2008.
|
|
|
(13)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on May 23, 2008.
|
|
|
(14)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule
14A (SEC File No. 333-124942), as originally filed on February 8,
2008.
|
|
|
(15)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on October 6,
2008.
|
|
|
(16)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on October 8, 2009.
|
|
|
(17)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on October 21,
2009.
|
|
(18)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on September 17, 2009.
|
|
|
(19)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on October 13,
2009.
|
|
(b)
|
Financial
Statement Schedules
|
All
financial statement schedules are omitted because they are not applicable, not
required or the information is indicated elsewhere in the financial statements
or the notes thereto.
|
Item 17.
|
Undertakings
|
(a) The
undersigned registrant hereby undertakes:
(1) To
file, during any period in which offers or sales are being made, a
post-effective amendment to this registration statement:
(i) To
include any prospectus required by section 10(a)(3) of the Securities
Act;
(ii) To
reflect in the prospectus any facts or events arising after the effective date
of the registration statement (or the most recent post-effective amendment
thereof) which, individually or in the aggregate, represent a fundamental change
in the information set forth in the registration statement. Notwithstanding the
foregoing, any increase or decrease in volume of securities offered (if the
total dollar value of securities offered would not exceed that which was
registered) and any deviation from the low or high end of the estimated maximum
offering range may be reflected in the form of prospectus filed with the SEC
pursuant to Rule 424(b) if, in the aggregate, the changes in volume and
price represent no more than a 20 percent change in the maximum aggregate
offering price set forth in the “Calculation of Registration Fee” table in the
effective registration statement; and
(iii) To
include any material information with respect to the plan of distribution not
previously disclosed in the registration statement or any material change to
such information in the registration statement.
(2) That,
for the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act of 1933,
each such post-effective amendment shall be deemed to be a new registration
statement relating to the securities offered therein, and the offering of such
securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial bona fide offering
thereof.
(3) To
remove from registration by means of a post-effective amendment any of the
securities being registered which remain unsold at the termination of the
offering.
(4) That,
for the purpose of determining liability under the Securities Act to any
purchaser, each prospectus filed pursuant to Rule 424(b) as part of a
registration statement relating to an offering, other than registration
statements relying on Rule 430B or other than prospectuses filed in
reliance on Rule 430A, shall be deemed to be part of and included in the
registration statement as of the date it is first used after effectiveness.
Provided, however, that no statement made in a registration statement or
prospectus that is part of the registration statement or made in a document
incorporated or deemed incorporated by reference into the registration statement
or prospectus that is part of the registration statement will, as to a purchaser
with a time of contract of sale prior to such first use, supersede or modify any
statement that was made in the registration statement or prospectus that was
part of the registration statement or made in any such document immediately
prior to such date of first use.
(5) That,
for the purpose of determining liability of the registrant under the Securities
Act to any purchaser in the initial distribution of the securities:
The
undersigned registrant undertakes that in a primary offering of securities of
the undersigned registrant pursuant to this registration statement, regardless
of the underwriting method used to sell the securities to the purchaser, if the
securities are offered or sold to such purchaser by means of any of the
following communications, the undersigned registrant will be a seller to the
purchaser and will be considered to offer or sell such securities to such
purchaser:
(i) Any
preliminary prospectus or prospectus of the undersigned registrant relating to
the offering required to be filed pursuant to Rule 424;
(ii) Any
free writing prospectus relating to the offering prepared by or on behalf of the
undersigned registrant or used or referred to by the undersigned
registrant;
(iii) The
portion of any other free writing prospectus relating to the offering containing
material information about the undersigned registrant or its securities provided
by or on behalf of the undersigned registrant; and
(iv) Any
other communication that is an offer in the offering made by the undersigned
registrant to the purchaser.
(b) The
undersigned registrant hereby further undertakes that,
(i) For
purposes of determining any liability under the Securities Act, the information
omitted from the form of prospectus filed as part of the registration statement
in reliance upon Rule 430A and contained in the form of prospectus filed by
the registrant pursuant to Rule 424(b)(1) or (4) or 497(h) under the
Securities Act shall be deemed to be part of the registration statement as of
the time it was declared effective; and
(ii) For
the purpose of determining any liability under the Securities Act, each
post-effective amendment that contains a form of prospectus shall be deemed to
be a new registration statement relating to the securities offered therein, and
the offering of such securities at that time shall be deemed to be the initial
bona fide offering
thereof.
(c) Insofar as indemnification for liabilities
arising under the Securities Act may be permitted to directors, officers, and
controlling persons of the registrant pursuant to the foregoing provisions, or
otherwise, the registrant has been advised that in the opinion of the Securities
and Exchange Commission such indemnification is against public policy as
expressed in the Securities Act and is, therefore, unenforceable. In the event
that a claim for indemnification against such liabilities (other than the
payment by the registrant of expenses incurred or paid by a director, officer,
or controlling person of the registrant in the successful defense of any action,
suit, or proceeding) is asserted by such director, officer, or controlling
person in connection with the securities being registered, the registrant will,
unless in the opinion of its counsel the matter has been settled by controlling
precedent, submit to a court of appropriate jurisdiction the question whether
such indemnification by it is against public policy as expressed in the
Securities Act and will be governed by the final adjudication of such
issue.
Signatures
Pursuant
to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, the registrant has duly
caused this registration statement to be signed on its behalf by the
undersigned, thereunto duly authorized, in the City of Bethesda, State of
Maryland, on March 9, 2010 .
|
INDIA
GLOBALIZATION CAPITAL, INC.
|
|||
|
By:
|
/s/ Ram
Mukunda
|
||
|
Name:
|
Ram
Mukunda
|
||
|
Title:
|
President
and Chief Executive Officer
|
||
Each
person whose signature appears below constitutes and appoints Ram
Mukanda his or her true and lawful attorneys-in-fact and agents, with
full power of substitution and resubstitution, for him or her and in his or her
name, place and stead, in any and all capacities, to sign any and all amendments
(including post-effective amendments) to this registration statement and any
additional registration statement to be filed pursuant to
Rule 462(b) under the Securities Act of 1933, and to file the same,
with all exhibits thereto and other documents in connection therewith, with the
Commission, granting unto said attorneys-in-fact and agents, and each of them,
full power and authority to do and perform each and every act and thing
requisite and necessary to be done in connection therewith, as fully to all
intents and purposes as he or she might or could do in person, hereby ratifying
and confirming all that said attorneys-in-fact and agents or any of them, or
their or his or her substitute or substitutes, may lawfully do or cause to be
done by virtue hereof.
Pursuant
to the requirements of the Securities Act of 1933, this Registration Statement
has been signed by the following persons in the capacities and on the dates
indicated. This document may be executed by the signatories hereto on any number
of counterparts, all of which shall constitute one and the same
instrument.
|
Name
|
Position
|
Date
|
||
|
/s/ Ram
Mukunda
|
|
President
and Chief Executive Officer
|
March 9, 2010
|
|
|
Ram
Mukunda
|
|
(Principal Executive
Officer)
|
||
|
/s/*
|
|
Chairman
|
March 9, 2010
|
|
|
Ranga
Krishna
|
|
|||
|
/s/ John
Selvaraj
|
|
Treasurer
|
March 9, 2010
|
|
|
John
Selvaraj
|
|
(Principal
Financial and Accounting Officer)
|
||
|
/s/*
|
|
Director
|
March 9, 2010
|
|
|
Suhail
Nathani
|
|
|||
|
/s/*
|
|
Director
|
March 9, 2010
|
|
|
Sudhakar
Shenoy
|
|
|||
|
/s/*
|
|
Director
|
March 9, 2010
|
|
|
Richard
Prins
|
|
|||
EXHIBIT INDEX
|
Exhibit
No.
|
Description
|
|
| 1.1 |
Underwriting
Agreement between the Registrant and ____________ dated ________,
2010.*
|
|
|
3.1
|
Amended
and Restated Articles of Incorporation. (1)
|
|
|
3.2
|
By-laws.
(2)
|
|
|
4.1
|
Specimen
Unit Certificate. (3)
|
|
|
4.2
|
Specimen
Common Stock Certificate. (3)
|
|
|
4.3
|
Specimen
Warrant Certificate. (3)
|
|
|
4.4
|
Form
of Warrant Agreement between Continental Stock Transfer & Trust
Company and the Registrant. (1)
|
|
|
4.5
|
Form
of Purchase Option to be granted to Ferris, Baker Watts, Inc..
(1)
|
|
|
5.1
|
Opinion
of Seyfarth Shaw LLP *
|
|
|
10.1
|
Amended
and Restated Letter Agreement between the Registrant, Ferris, Baker Watts,
Inc. and Ram Mukunda. (4)
|
|
|
10.2
|
Amended
and Restated Letter Agreement between the Registrant, Ferris, Baker Watts,
Inc. and John Cherin. (4)
|
|
|
10.3
|
Amended
and Restated Letter Agreement between the Registrant, Ferris, Baker Watts,
Inc. and Ranga Krishna. (4)
|
|
|
10.4
|
Form
of Investment Management Trust Agreement between Continental Stock
Transfer & Trust Company and the Registrant. (5)
|
|
|
10.5
|
Promissory
Note issued by the Registrant to Ram Mukunda. (2)
|
|
|
10.5.1
|
Extension
of Due Date of Promissory Note issued to Ram Mukunda.
(2)
|
|
|
10.6
|
Form
of Stock and Unit Escrow Agreement among the Registrant, Ram Mukunda, John
Cherin and Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company.
(2)
|
|
|
10.7
|
Form
of Registration Rights Agreement among the Registrant and each of the
existing stockholders. (3)
|
|
|
10.8
|
Form
of Unit Purchase Agreement among Ferris, Baker Watts, Inc. and one or more
of the Initial Stockholders. (5)
|
|
|
10.9
|
Form
of Office Service Agreement between the Registrant and Integrated Global
Networks, LLC. (5)
|
|
|
10.10
|
Amended
and Restated Letter Advisory Agreement between the Registrant, Ferris,
Baker Watts, Inc. and SG Americas Securities, LLC. (5)
|
|
|
10.11
|
Form
of Letter Agreement between Ferris, Baker Watts, Inc. and certain officers
and directors of the Registrant. (4)
|
|
|
10.12
|
Form
of Letter Agreement between Ferris, Baker Watts, Inc. and each of the
Special Advisors of the Registrant. (4)
|
|
|
10.13
|
Form
of Letter Agreement between the Registrant and certain officers and
directors of the Registrant. (4)
|
|
|
10.14
|
Form
of Letter Agreement between the Registrant and each of the Special
Advisors of the Registrant. (4)
|
|
|
10.15
|
Promissory
Note issued by the Registrant to Ranga Krishna. (2)
|
|
|
10.15.1
|
Extension
of Due Date of Promissory Note issued to Ranga Krishna.
(2)
|
|
|
10.16
|
Form
of Promissory Note to be issued by the Registrant to Ranga Krishna.
(2)
|
|
|
10.17
|
Share
Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement dated February 2, 2007 by and
among India Globalization Capital, Inc., MBL Infrastructures Limited and
the persons “named as Promoters therein”. (6)
|
|
|
10.18
|
Debenture
Subscription Agreement dated February 2, 2007 by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc., MBL Infrastructures Limited and the persons
named as Promoters therein. (6)
|
|
|
10.19
|
Note
and Warrant Purchase Agreement dated February 5, 2007 by and among
India Globalization Capital, Inc. and Oliveira Capital, LLC.
(6)
|
|
|
10.20
|
Promissory
Note dated February 5, 2007 in the initial principal amount for
$3,000,000 issued by India Globalization Capital, Inc. to Oliveira
Capital, LLC. (6)
|
|
|
10.21
|
Warrant
to Purchase Shares of Common Stock of India Globalization Capital, Inc.
issued by India Globalization Capital, Inc. to Oliveira Capital, LLC.
(6)
|
|
|
10.22
|
First
Amendment to Share Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement dated February 2,
2007 by and among India Globalization Capital, Inc., MBL Infrastructures
Limited and the persons named as Promoters therein. (7)
|
|
|
10.23
|
First
Amendment to the Debenture Subscription Agreement dated February 2, 2007
by and among India Globalization Capital, Inc., MBL Infrastructures
Limited and the persons named as Promoters therein. (7)
|
|
|
10.24
|
Contract
Agreement dated April 29, 2007 between IGC, CWEL, AMTL and MAIL.
(7)
|
|
|
10.25
|
First
Amendment dated August 20, 2007 to Agreement dated April 29, 2007 between
IGC, CWEL, AMTL and MAIL. (8)
|
|
|
10.26
|
Share
Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement dated September 16, 2007 by and among
India Globalization Capital, Inc., Techni Bharathi Limited and the persons
named as Promoters therein (9).
|
|
|
10.27
|
Shareholders
Agreement dated September 16, 2007 by and among India Globalization
Capital, Inc., Techni Bharathi Limited and the persons named as Promoters
therein. (9)
|
|
|
10.28
|
Share
Purchase Agreement dated September 21, 2007 by and between India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and Odeon Limited. (9)
|
|
|
10.29
|
Share
Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement dated September 15, 2007 by and among
India Globalization Capital, Inc., Sricon Infrastructure
Private Limited and the persons named as Promoters therein.
(9)
|
|
|
10.30
|
Shareholders
Agreement dated September 15, 2007 by and among India Globalization
Capital, Inc., Sricon Infrastructure Private Limited and the
persons named as Promoters therein. (9)
|
|
|
10.31
|
Form
of Amendment to the Share Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement Dated
September 15, 2007, entered into on December 19, 2007 by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc., Sricon Infrastructure Private Limited and the
persons named as Promoters therein. (10)
|
|
|
10.32
|
Form
of Amendment to the Share Subscription Agreement Dated September 16, 2007,
entered into on December 21, 2007 by and among India Globalization
Capital, Inc., Techni Bharathi Limited and the persons named as Promoters
therein. (10)
|
|
|
10.33
|
Note
Purchase Agreement, effective as of December 24, 2007, by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and the persons named as Lenders therein.
(10)
|
|
|
10.34
|
Form
of India Globalization Capital, Inc. Promissory Note.
(10)
|
|
10.35
|
Form
of Registration Rights Agreement by and among India Globalization Capital,
Inc. and the persons named as Investors therein. (10)
|
|
|
10.36
|
Form
of Pledge Agreement, effective as of December 24, 2007, by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and the persons named as
Secured Parties therein. (10)
|
|
|
10.37
|
Form
of Lock up Letter Agreement, dated December 24, 2007 by and between India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and Dr. Ranga Krishna.
(10)
|
|
|
10.38
|
Form
of Letter Agreement, dated December 24, 2007, with Dr. Ranga Krishna.
(10)
|
|
|
10.39
|
Form
of Letter Agreement, dated December 24, 2007, with Oliveira Capital, LLC.
(10)
|
|
|
10.40
|
Form
of Warrant Clarification Agreement, dated January 4, 2008, by and between
the Company and Continental Stock Transfer & Trust Company.
(11)
|
|
|
10.41
|
Form
of Amendment to Unit Purchase Options, dated January 4, 2008, by and
between the Company and the holders of Unit Purchase Options.
(11)
|
|
|
10.42
|
Second
Amendment to the Share Subscription Cum Purchase Agreement Dated September
15, 2007, entered into on January 14, 2008 by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc., Sricon Infrastructure Private Limited and the
persons named as Promoters therein. (12)
|
|
|
10.43
|
Letter
Agreement dated January 8, 2008 by and among India Globalization Capital,
Inc., Odeon Limited, and Techni Bharathi Limited with respect to the Share
Purchase Agreement dated September 21, 2007 by and among India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and Odeon Limited.
(12)
|
|
|
10.44
|
Employment
Agreement between India Globalization Capital, Inc., India Globalization
Capital Mauritius and Ram Mukunda dated as of March 8, 2008.
(13)
|
|
|
10.45
|
2008
Omnibus Incentive Plan. (14)
|
|
|
10.46
|
Note
and Share Purchase Agreement dated as of September 30, 2008, by and among
India Globalization Capital, Inc. and Steven M. Oliveira 1998
Charitable Remainder Unitrust (15)
|
|
|
10.47
|
Registration
Rights Agreement dated September 30, 2008 by and among India Globalization
Capital, Inc. and the persons named as Investors therein.
(15)
|
|
|
10.48
|
Note
and Share Purchase Agreement dated as of October 5, 2009, by and among
India Globalization Capital, Inc. and Steven M. Oliveira 1998
Charitable Remainder Unitrust (16)
|
|
|
10.49
|
Unsecured
Promissory Note dated as of October 5, 2009 in the principal amount of
$2,120,000 issued by the Company to the Steven M. Oliveira 1998 Charitable
Remainder Unitrust. (16)
|
|
|
10.50
|
Note
and Share Purchase Agreement dated as of October 16, 2009 between the
Company and Bricoleur Partners, L.P. (17)
|
|
|
10.51
|
Unsecured
Promissory Note dated as of October 16, 2009 in the principal amount of
$2,000,000 issued by the Company to Bricoleur Partners, L.P.
(17)
|
|
|
10.52
|
Registration Rights Agreement dated as of October
16, 2009 between the Company and Bricoleur Partners, L.P.
(17)
|
|
|
10.53
|
Form
of Securities Purchase Agreement dated as of September 14, 2009 by and
among India Globalization Capital, Inc. and the investors named therein
(18)
|
|
|
10.54
|
Amendment
No. 1 dated as of October 30, 2009 to Securities Purchase Agreement by and
among India Globalization Capital, Inc. and the investors named
therein .**
|
|
|
10.55
|
ATM
Agency Agreement, dated as of October 13 2009, by and between India
Globalization Capital, Inc. and Enclave Capital LLC
(19)
|
|
|
21
|
||
|
23.1
|
||
|
23.2
|
Consent
of Seyfarth Shaw LLP (incorporated by reference from
Exhibit 5.1) *
|
|
|
23.3
|
Consent
of Mega Ace Consultancy. (4)
|
|
|
24
|
Power
of Attorney. **
|
|
|
99.1
|
Code
of Ethics. (5)
|
| * | To be filed by amendment. | |
| ** | To be filed by amendment. | |
| *** | Previously filed as an exhibit to this Registration Statement. | |
|
(1)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC
File No. 333-124942), as amended and filed on November 2,
2005.
|
|
|
(2)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC
File No. 333-124942), as amended and filed on February 14,
2006.
|
|
|
(3)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC
File No. 333-124942), as originally filed on May 13,
2005.
|
|
|
(4)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC
File No. 333-124942), as amended and filed on July 11,
2005.
|
|
(5)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Registration Statement on Form S-1 (SEC
File No. 333-124942), as amended and filed on March 2,
2006.
|
|
|
(6)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on February 12, 2007.
|
|
|
(7)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on May 2, 2007.
|
|
|
(8)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on August 23, 2007.
|
|
|
(9)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on September 27, 2007.
|
|
|
(10)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on December 27, 2007.
|
|
|
(11)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on January 7, 2008.
|
|
|
(12)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on January 16, 2008.
|
|
|
(13)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on May 23, 2008.
|
|
|
(14)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule
14A (SEC File No. 333-124942), as originally filed on February 8,
2008.
|
|
|
(15)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on October 6,
2008.
|
|
|
(16)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on October 8, 2009.
|
|
|
(17)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on October 21,
2009.
|
|
(18)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on September 17, 2009.
|
|
|
(19)
|
Incorporated
by reference to the Registrant’s Current Report on Form 8-K (SEC File No.
333-124942), as originally filed on October 13,
2009.
|
