Attached files
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
UNITED STATES
SECURITIES AND EXCHANGE COMMISSION
Washington, D. C. 20549
FORM 10-K
(Mark one)
| x | ANNUAL REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2009
or
| ¨ | TRANSITION REPORT PURSUANT TO SECTION 13 OR 15(d) OF THE SECURITIES EXCHANGE ACT OF 1934 |
Commission File Number: 1-8182
PIONEER DRILLING COMPANY
(Exact name of registrant as specified in its charter)
| TEXAS | 74-2088619 | |
| (State or other jurisdiction of incorporation or organization) |
(I.R.S. Employer Identification Number) | |
| 1250 N.E. Loop 410, Suite 1000 San Antonio, Texas |
78209 | |
| (Address of principal executive offices) | (Zip Code) | |
Registrant’s telephone number, including area code: (210) 828-7689
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(b) of the Act:
| Title of each class |
Name of each exchange on which registered | |
| Common Stock, $0.10 par value | NYSE Amex |
Securities registered pursuant to Section 12(g) of the Act: None
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is a well-known seasoned issuer, as defined in Rule 405 of the Securities Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark if the registrant is not required to file reports pursuant to Section 13 or Section 15(d) of the Act. Yes ¨ No x
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant: (1) has filed all reports required to be filed by Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934 during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to file such reports), and (2) has been subject to such filing requirements for the past 90 days. Yes x No ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the Registrant has submitted electronically and posted on its corporate Website, if any, every Interactive Data File required to be submitted and posted pursuant to Rule 405 of Regulation S-T during the preceding 12 months (or for such shorter period that the registrant was required to submit and post such files). Yes ¨ No ¨
Indicate by check mark if disclosure of delinquent filers pursuant to Item 405 of Regulation S-K is not contained herein, and will not be contained, to the best of registrant’s knowledge, in definitive proxy or information statements incorporated by reference in Part III of this Form 10-K or any amendment to this Form 10-K. ¨
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a large accelerated filer, an accelerated filer, a non-accelerated filer, or a smaller reporting company. See definitions of “large accelerated filer,” “accelerated filer,” and “smaller reporting company” in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act. (Check one):
| Large accelerated filer ¨ | Accelerated filer x | |||
| Non-accelerated filer ¨ | (Do not check if a smaller reporting company) | Smaller reporting company ¨ |
Indicate by check mark whether the registrant is a shell company (as defined in Rule 12b-2 of the Exchange Act). Yes ¨ No x
The aggregate market value of the registrant’s common stock held by nonaffiliates of the registrant on the last business day of the registrant’s most recently completed second fiscal quarter (based on the closing sales price on the American Stock Exchange (NYSE Amex on June 30, 2009) was approximately $243.8 million.
As of February 5, 2010, there were 54,119,952 shares of common stock, par value $0.10 per share, of the registrant issued and outstanding.
DOCUMENTS INCORPORATED BY REFERENCE
Portions of the proxy statement related to the registrant’s 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders are incorporated by reference into Part III of this report.
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Page | ||||
| PART I | ||||
| 1 | ||||
| Item 1. |
2 | |||
| Item 1A. |
20 | |||
| Item 1B. |
31 | |||
| Item 2. |
31 | |||
| Item 3. |
31 | |||
| Item 4. |
31 | |||
| PART II | ||||
| Item 5. |
32 | |||
| Item 6. |
34 | |||
| Item 7. |
Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
35 | ||
| Item 7A. |
59 | |||
| Item 8. |
61 | |||
| Item 9. |
Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
95 | ||
| Item 9A. |
95 | |||
| Item 9B. |
96 | |||
| PART III | ||||
| Item 10. |
96 | |||
| Item 11. |
96 | |||
| Item 12. |
Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters |
96 | ||
| Item 13. |
Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
96 | ||
| Item 14. |
96 | |||
| PART IV | ||||
| Item 15. |
97 | |||
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
SPECIAL NOTE REGARDING FORWARD-LOOKING STATEMENTS
From time to time, our management or persons acting on our behalf make forward-looking statements to inform existing and potential security holders about our company. These statements may include projections and estimates concerning the timing and success of specific projects and our future backlog, revenues, income and capital spending. Forward-looking statements are generally accompanied by words such as “estimate,” “project,” “predict,” “believe,” “expect,” “anticipate,” “plan,” “intend,” “seek,” “will,” “should,” “goal” or other words that convey the uncertainty of future events or outcomes. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date on which they are first made, which in the case of forward-looking statements made in this report is the date of this report. Sometimes we will specifically describe a statement as being a forward-looking statement and refer to this cautionary statement.
In addition, various statements contained in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, including those that express a belief, expectation or intention, as well as those that are not statements of historical fact, are forward-looking statements. Such forward-looking statements appear in Item 1—“Business” and Item 3—“Legal Proceedings” in Part I of this report; in Item 5—“Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Shareholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities,” Item 7—“Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations,” Item 7A—“Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk” and in the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements we have included in Item 8 of Part II of this report; and elsewhere in this report. These forward-looking statements speak only as of the date of this report. We disclaim any obligation to update these statements, and we caution you not to rely on them unduly. We have based these forward-looking statements on our current expectations and assumptions about future events. While our management considers these expectations and assumptions to be reasonable, they are inherently subject to significant business, economic, competitive, regulatory and other risks, contingencies and uncertainties, most of which are difficult to predict and many of which are beyond our control. These risks, contingencies and uncertainties relate to, among other matters, the following:
| • | general economic and business conditions and industry trends; |
| • | levels and volatility of oil and gas prices; |
| • | decisions about onshore exploration and development projects to be made by oil and gas producing companies; |
| • | risks associated with economic cycles and their impact on capital markets and liquidity; |
| • | the continued demand for drilling services or production services in the geographic areas where we operate; |
| • | the highly competitive nature of our business; |
| • | our future financial performance, including availability, terms and deployment of capital; |
| • | the supply of marketable drilling rigs, workover rigs and wireline units within the industry; |
| • | the continued availability of drilling rig, workover rig and wireline unit components; |
| • | the continued availability of qualified personnel; |
| • | the success or failure of our acquisition strategy, including our ability to finance acquisitions and manage growth; and |
| • | changes in, or our failure or inability to comply with, governmental regulations, including those relating to the environment. |
We believe the items we have outlined above are important factors that could cause our actual results to differ materially from those expressed in a forward-looking statement contained in this report or elsewhere. We
1
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
have discussed many of these factors in more detail elsewhere in this report. Unpredictable or unknown factors we have not discussed in this report could also have material adverse effects on actual results of matters that are the subject of our forward-looking statements. We do not intend to update our description of important factors each time a potential important factor arises, except as required by applicable securities laws and regulations. We advise our security holders that they should (1) be aware that unpredictable or unknown factors not referred to above could affect the accuracy of our forward-looking statements and (2) use caution and common sense when considering our forward-looking statements. Also, please read the risk factors set forth in Item 1A—“Risk Factors.”
| Item 1. | Business |
In December 2007, our Board of Directors approved a change in our fiscal year end from March 31st to December 31st. The fiscal year end change was effective December 31, 2007 and resulted in a nine month reporting period from April 1, 2007 to December 31, 2007. Fiscal years beginning with the year ended December 31, 2008, represent twelve month reporting periods. We implemented the fiscal year end change to align our United States reporting period with the required Colombian statutory reporting period as well as the reporting periods of peer companies in the industry.
General
Pioneer Drilling Company provides drilling services and production services to independent and major oil and gas exploration and production companies throughout much of the onshore oil and gas producing regions of the United States and internationally in Colombia. Pioneer Drilling Company was incorporated under the laws of the State of Texas in 1979 as the successor to a business that had been operating since 1968. Our business has grown through acquisitions and through organic growth. Over the last 10 years, we have significantly expanded our drilling rig fleet by adding 35 rigs through acquisitions and by adding 31 rigs through the construction of rigs from new and used components. On March 1, 2008, we significantly expanded our service offerings when we acquired the production services businesses of WEDGE Group Incorporated (“WEDGE”) for $314.7 million and Prairie Investors d/b/a Competition Wireline (“Competition”) for $30.0 million, which provide well services, wireline services and fishing and rental services. We funded the WEDGE acquisition primarily with $311.5 million of borrowings under our senior secured revolving credit facility. As of February 5, 2010, the senior secured revolving credit facility had an outstanding balance of $257.5 million, of which, $1.9 million is due by March 31, 2010 as a mandatory prepayment and the remaining $255.6 million is due by the maturity date on August 31, 2012. Drilling services and production services are fundamental to establishing and maintaining the flow of oil and natural gas throughout the productive life of a well site and enable us to meet multiple needs of our customers.
We currently conduct our operations through two operating segments: our Drilling Services Division and our Production Services Division. The following is a description of these two operating segments. Financial information about our operating segments is included in Note 11, Segment Information, of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, included in Part II Item 8, Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| • | Drilling Services Division—Our Drilling Services Division provides contract land drilling services with its fleet of 71 drilling rigs in the following locations: |
| Drilling Division Locations |
Rig Count | |
| South Texas |
15 | |
| East Texas |
19 | |
| North Dakota |
8 | |
| North Texas |
5 | |
| Utah |
5 | |
| Oklahoma |
6 | |
| Appalachia |
5 | |
| Colombia |
8 |
2
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
As of February 5, 2010, 34 drilling rigs are operating under drilling contracts. We have 31 drilling rigs that are idle and six drilling rigs have been placed in storage or “cold stacked” in our Oklahoma drilling division due to low demand for drilling rigs in that region. We are actively marketing all our idle drilling rigs both domestically and internationally in Latin America. During the second quarter of 2009, we established our Appalachian drilling division and now have four drilling rigs operating in the Marcellus Shale region. We are currently upgrading a fifth rig that is scheduled to begin operating under a drilling contract in the Marcellus Shale region in late February 2010. We have seven drilling rigs located in Colombia that are operating under drilling contracts, five of which are drilling and two of which have been moved to their initial well site locations and are expected to begin drilling in late February 2010. In March 2010, we plan to export an eighth rig to Colombia that will begin working under a drilling contract. In addition to our drilling rigs, we provide the drilling crews and most of the ancillary equipment needed to operate our drilling rigs. We obtain our contracts for drilling oil and natural gas wells either through competitive bidding or through direct negotiations with customers. Our drilling contracts generally provide for compensation on either a daywork, turnkey or footage basis. Contract terms generally depend on the complexity and risk of operations, the on-site drilling conditions, the type of equipment used and the anticipated duration of the work to be performed.
| • | Production Services Division—Our Production Services Division provides a broad range of well services to oil and gas drilling and producing companies, including workover services, wireline services, and fishing and rental services. Our production services operations are managed regionally and are concentrated in the major United States onshore oil and gas producing regions in the Gulf Coast, Mid-Continent, Rocky Mountain and Appalachian states. We provide our services to a diverse group of oil and gas companies. The primary production services we offer are the following: |
| • | Well Services. Existing and newly-drilled wells require a range of services to establish and maintain production over their useful lives. We use our fleet of 74 workover rigs in eight regional locations to provide these required services, including maintenance of existing wells, workover of existing wells, completion of newly-drilled wells, and plugging and abandonment of wells at the end of their useful lives. We have a premium workover rig fleet consisting of sixty-nine 550 horsepower rigs, four 600 horsepower rigs, and one 400 horsepower rig. The average age of our workover rig fleet is 2.4 years as of December 31, 2009. As of February 5, 2010, 68 workover rigs have crews assigned and are either operating or are being actively marketed. The remaining six workover rigs in our fleet are idle with no crews assigned. |
| • | Wireline Services. In order for oil and gas companies to better understand the reservoirs they are drilling or producing, they require logging services to accurately characterize reservoir rocks and fluids. When a producing well is completed, they also must perforate the production casing to establish a flow path between the reservoir and the wellbore. We use our fleet of 65 truck mounted wireline units in 19 division locations to provide these important logging and perforating services. We provide both open and cased-hole logging services, including the latest pulsed-neutron technology. In addition, we provide services which allow oil and gas companies to evaluate the integrity of wellbore casing, recover pipe, or install bridge plugs. Our wireline unit fleet has an average age of 4.3 years as of December 31, 2009. |
| • | Fishing and Rental Services. During drilling operations, oil and gas companies frequently need to rent unique equipment such as power swivels, foam air units, blow-out preventers, air drilling equipment, pumps, tanks, pipe, tubing, and fishing tools. We have approximately $13 million of fishing and rental tools that we provide out of four locations in Texas and Oklahoma. |
Pioneer Drilling Company’s corporate office is located at 1250 N.E. Loop 410, Suite 1000, San Antonio, Texas 78209. Our phone number is (210) 828-7689 and our website address is www.pioneerdrlg.com. We make available free of charge though our website our Annual Reports on Form 10-K, Quarterly Reports on Form 10-Q, Current Reports on Form 8-K, and all amendments to those reports as soon as reasonably practicable after such material is electronically filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”). Information on our website is not incorporated into this report or otherwise made part of this report.
3
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Industry Overview
Since late 2008, there has been substantial volatility and a decline in oil and natural gas prices due to the downturn in the global economic environment. In addition, there has been uncertainty in the capital markets and access to financing has been limited. These conditions have adversely affected our business environment. Our customers have curtailed their drilling programs and reduced their production activities, which has resulted in a decrease in demand for drilling and production services and a reduction in day rates and utilization. In addition, certain of our customers could experience an inability to pay suppliers in the event they are unable to access the capital markets to fund their business operations.
Demand for oilfield services offered by our industry is a function of our customers’ willingness to make operating and capital expenditures to explore for, develop and produce hydrocarbons, which in turn is affected by current and expected levels of oil and natural gas prices. From 2004 through 2008, domestic exploration and production spending increased as oil and natural gas prices increased. In response to the significant decline in oil and natural gas prices and the downturn in the global economic environment in late 2008, exploration and production companies announced cuts in their exploration budgets for 2009. These reductions in oil and gas exploration budgets resulted in a reduction in our rig utilization and revenue rates on new contracts during 2009. We believe exploration and production companies have modestly increased their exploration budgets for 2010 as compared to 2009. Industry rig utilization and revenue rates are expected to show modest improvements during 2010. For additional information concerning the effects of the volatility in oil and gas prices and uncertainty in capital markets, see Item 1A—“Risk Factors” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
On February 5, 2010, the spot price for West Texas Intermediate crude oil was $71.19, the spot price for Henry Hub natural gas was $5.61 and the Baker Hughes land rig count was 1,280, a 4% decrease from 1,330 on February 6, 2009. The average weekly spot prices of West Texas Intermediate crude oil and Henry Hub natural gas, the average weekly domestic land rig count per the Baker Hughes land rig count, and the average monthly domestic workover rig count for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, the nine months ended December 31, 2007, and the years ended March 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 were:
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 |
Years Ended March 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | ||||||||||||||
| Oil (West Texas |
||||||||||||||||||
| Intermediate) |
$ | 61.81 | $ | 99.86 | $ | 77.42 | $ | 64.96 | $ | 59.94 | $ | 45.04 | ||||||
| Natural Gas (Henry Hub) |
$ | 3.85 | $ | 8.81 | $ | 6.82 | $ | 6.53 | $ | 9.10 | $ | 5.99 | ||||||
| U.S. Land Rig Count |
1,035 | 1,792 | 1,684 | 1,589 | 1,329 | 1,110 | ||||||||||||
| U.S. Workover Rig Count |
1,735 | 2,514 | 2,394 | 2,376 | 2,271 | 2,087 | ||||||||||||
Increased expenditures for exploration and production activities generally lead to increased demand for our drilling services and production services. Between 2005 and late 2008, rising oil and natural gas prices and the corresponding increase in onshore oil and natural gas exploration and production spending led to expanded drilling and well service activity as reflected by the increases in the U.S. land rig counts and U.S. workover rig counts as noted in the table above. The decline in oil and natural gas prices since late 2008 has led to decreased oil and natural gas exploration and production spending and a corresponding decrease in drilling and well services activities as reflected by the decrease in the U.S. land rig counts and the U.S. workover rig counts as noted in the table above.
Our business is influenced substantially by both operating and capital expenditures by exploration and production companies. Exploration and production spending is generally categorized as either a capital expenditure or operating expenditure.
Capital expenditures by oil and gas companies tend to be relatively sensitive to volatility in oil or natural gas prices because project decisions are tied to a return on investment spanning a number of years. As such, capital
4
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
expenditure economics often require the use of commodity price forecasts which may prove inaccurate in the amount of time required to plan and execute a capital expenditure project (such as the drilling of a deep well). When commodity prices are depressed for long periods of time, capital expenditure projects are routinely deferred until prices return to an acceptable level.
In contrast, both mandatory and discretionary operating expenditures are more stable than capital expenditures for exploration. Mandatory operating expenditure projects involve activities that cannot be avoided in the short term, such as regulatory compliance, safety, contractual obligations and certain projects to maintain the well and related infrastructure in operating condition. Discretionary operating expenditure projects may not be critical to the short-term viability of a lease or field, but these projects are less sensitive to commodity price volatility as compared to capital expenditures for exploration. Discretionary operating expenditure work is evaluated according to a simple short-term payout criterion which is far less dependent on commodity price forecasts.
Our business is influenced substantially by both operating and capital expenditures by exploration and production companies. Because existing oil and natural gas wells require ongoing spending to maintain production, expenditures by exploration and production companies for the maintenance of existing wells are relatively stable and predictable. In contrast, capital expenditures by exploration and production companies for exploration and drilling are more directly influenced by current and expected oil and natural gas prices and generally reflect the volatility of commodity prices.
Competitive Strengths
Our competitive strengths include:
| • | One of the Leading Providers in the Most Attractive Basins. Our 71 drilling rigs operate in many of the most attractive producing basins in the Americas, including the Bakken, Marcellus and Eagle Ford shales, as well as Colombia. Our rigs are located in eight divisions throughout the United States and Colombia, diversifying our geographic exposure and limiting the impact of any regional slowdown. We believe the varied horsepower capabilities of our rigs (550 horsepower to 2000 horsepower) make them well suited to these various areas where the optimal rig configuration is dictated by local geology and market conditions. Furthermore, certain of our divisions, such as Colombia, North Dakota and parts of our South Texas division, are located in basins with oil-focused drilling, which reduces our relative exposure to changes in natural gas drilling activity. |
| • | High Quality Assets. We believe our drilling rig fleet is modern and well maintained, with 31 new-build rigs purchased since 2001, and the majority of these constructed from 2004 to 2006. The majority of our rig fleet has preferred equipment such as more efficient and lower emission engines, rounded bottom mud tanks, matched horsepower mud pumps and mobile or fast-paced substructure. In addition, 69% of our rig fleet has a horsepower rating of over 1000 horsepower and 30% has top drives. We estimate that more than 75% of our drilling rigs are capable of drilling in shale plays, which typically require higher specification rigs than traditional areas. Our wireline and well servicing assets are among the newest in the industry, with 56% having been built in 2007 or later and all but one of the well servicing rigs having at least 550 horsepower. We believe that our modern and well maintained fleet allows us to realize higher contract and utilization rates by being able to offer our customers equipment that is more reliable and requires less downtime than older equipment. |
| • | Provide Services Throughout the Well Life Cycle. By offering our customers drilling, production and related services, we capture revenue throughout the life cycle of a well and diversify our business. Our Drilling Services Division performs work prior to initial production, and our Production Services Division provides services such as logging, completion, perforation, workover and maintenance throughout the productive life of a well. We also provide certain end-of-well-life activities such as plugging and abandonment. Drilling and production services activity have historically exhibited |
5
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| different degrees of demand fluctuation, and we believe the diversity of our services reduces our exposure to decreases in demand for any single service activity. The diversity of our services also enhances customer revenues by allowing us to cross-sell services in our various business divisions. |
| • | Excellent Safety Record. We believe that our excellent safety record and reputation are critical to winning new business and expanding our relationships with existing customers. Our commitment to safety also reduces our business risk by keeping our employees safe and our equipment in good condition. We have consistently exceeded the International Association of Drilling Contractors, or IADC, average for recordable incidents and have achieved a 65% improvement in recordable incidents since 2005. Much of our equipment contains additional safety features such as the iron roughnecks we have installed on 62% of our drilling rigs. In July and November 2009, we received scores of 100% on health, safety, environment and quality audits by Ecopetrol S.A. (NYSE: EC), one of the leading oil companies in Latin America, for whom we currently operate seven drilling rigs in Colombia. We believe our strong performance on such measures has contributed significantly to our growing business with Ecopetrol. |
| • | Experienced Management Team. We believe that important competitive factors in establishing and maintaining long-term customer relationships include having an experienced and skilled management team and maintaining employee continuity. Our CEO, Wm. Stacy Locke, joined Pioneer in 1995 as President and has over 25 years of professional experience. Our two division presidents, F.C. “Red” West and Joe Eustace, have over 70 years of combined oilfield services experience. Our management team has operated through numerous oilfield services cycles and provides us with valuable long-term experience and a detailed understanding of customer requirements. We also seek to maximize employee continuity and minimize employee turnover by maintaining modern equipment, a strong safety record, ongoing growth and competitive compensation. We have devoted, and will continue to devote, substantial resources to our employee safety and training programs and maintaining low employee turnover. |
| • | Longstanding and Diversified Customers. We maintain long-standing, high quality customer relationships with a diverse group of major independent oil and gas companies including Anadarko Petroleum Corporation, Cabot Oil and Gas Corporation, Whiting Petroleum Corporation and Chesapeake Energy Corporation. We also maintain a high quality relationship with Ecopetrol, which accounted for approximately 16% of our 2009 consolidated revenues. No other single customer accounted for more than 6% of consolidated revenues during the same period. We believe our relationships with our customers are excellent and offer numerous opportunities for future growth. |
Strategy
In past years, our strategy was to become a premier land drilling and production services company through steady and disciplined growth. We executed this strategy by acquiring and building a high quality drilling rig fleet and production services business that operates in active drilling markets in the United States and Colombia. Our long-term strategy is to maintain and leverage our position as a leading land drilling and production services company, continue to expand our relationships with existing customers, acquire new customers in the areas in which we currently operate and further enhance our geographic diversification through selective international expansion. The key elements of this long-term strategy include:
| • | Further Strengthen our Competitive Position in the Most Attractive Domestic Markets. Shale plays are expected to become increasingly important to domestic hydrocarbon production in the coming years and not all drilling rigs are capable of successfully drilling shale play opportunities. We estimate that more than 75% of our rigs are currently capable of shale drilling, and we intend to further develop our rig fleet to take advantage of the expected increase in shale activity, including furthering our investment in top drives and winterizing additional rigs in our fleet for markets such as the Marcellus Shale in the northeastern United States and the Bakken Shale in the upper mid-west United States. We also plan to invest in additional safety equipment, such as the installation of iron roughnecks on certain |
6
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| of our rigs. We also intend to selectively add capacity to our wireline and well servicing product offerings, which are well positioned to capitalize on increased shale development. |
| • | Increase our Exposure to Oil-Driven Drilling Activity. We have intentionally increased our exposure to oil-related activities by redeploying certain of our assets into predominately oil-producing regions and actively seeking contracts with oil-focused producers. We have 23% of our drilling rig fleet assigned to divisions in North Dakota and Colombia, both of which are predominately oil-producing regions, and we have 28% of our production services fleet assigned to predominately oil-producing districts in North Dakota, Kansas and Mississippi. We believe that by targeting a balanced mix of oil and natural gas oriented activities over time, we can lessen our exposure to fluctuations in capital spending associated with changes in any single commodity price. We believe that our flexible rig fleet and production services assets allow us to target both natural gas and oil-focused opportunities. |
| • | Selectively Expand our International Operations. In early 2007, we announced our intention to selectively expand internationally and began a relationship with Ecopetrol S.A. in Colombia after a comprehensive review of international opportunities wherein we determined that Colombia offered an attractive mix of favorable business conditions, political stability, and a long-term commitment to expanding national oil and gas production. We currently have seven drilling rigs located in Colombia and expect to export an eighth rig to Colombia that will begin working under a drilling contract in March 2010. We are continuously evaluating additional international expansion opportunities and intend to target international markets that share the favorable characteristics of our Colombian operations and which would allow us to deploy with sufficient scale to minimize regional management costs. |
| • | Continue Growth with Select Capital Deployment. We intend to invest in the growth of our business by continuing to strategically upgrade our existing assets, selectively engaging in new-build opportunities, and potentially making selective acquisitions. Our capital investment decisions are determined by an analysis of the projected return on capital employed. For significant capital expenditures, we have customarily identified the incremental revenue associated with the opportunity and secured use of the asset through contracts whenever possible. In addition to analyzing return on capital employed, we also require expenditures to be consistent with our strategic objectives. For example, we established our Appalachian division in 2009 to supply drilling rigs to the rapidly growing demand in the Marcellus Shale and began our operations in Colombia in 2007 to diversify our operations into the international market. |
Overview of Our Segments and Services
Drilling Services Division
A land drilling rig consists of engines, a hoisting system, a rotating system, pumps and related equipment to circulate drilling fluid, blowout preventers and related equipment.
Diesel or gas engines are typically the main power sources for a drilling rig. Power requirements for drilling jobs may vary considerably, but most land drilling rigs employ two or more engines to generate between 500 and 2,000 horsepower, depending on well depth and rig design. Most drilling rigs capable of drilling in deep formations, involving depths greater than 15,000 feet, use diesel-electric power units to generate and deliver electric current through cables to electrical switch gears, then to direct-current electric motors attached to the equipment in the hoisting, rotating and circulating systems.
Drilling rigs use long strings of drill pipe and drill collars to drill wells. Drilling rigs are also used to set heavy strings of large-diameter pipe, or casing, inside the borehole. Because the total weight of the drill string and the casing can exceed 500,000 pounds, drilling rigs require significant hoisting and braking capacities. Generally, a drilling rig’s hoisting system is made up of a mast, or derrick, a traveling block and hook assembly that attaches to the rotating system, a mechanism known as the drawworks, a drilling line and ancillary
7
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
equipment. The drawworks mechanism consists of a revolving drum, around which the drilling line is wound, and a series of shafts, clutches and chain and gear drives for generating speed changes and reverse motion. The drawworks also houses the main brake, which has the capacity to stop and sustain the weights used in the drilling process. When heavy loads are being lowered, a hydraulic or electric auxiliary brake assists the main brake to absorb the great amount of energy developed by the mass of the traveling block, hook assembly, drill pipe, drill collars and drill bit or casing being lowered into the well.
The rotating equipment from top to bottom consists of a top drive or a swivel, the kelly, and kelly bushing, the rotary table, drill pipe, drill collars and the drill bit. We refer to the equipment between the top drive or swivel and the drill bit as the drill stem. In a top drive system, the top drive hangs from a hook at the bottom of the traveling block. The top drive has a passageway for drilling mud to get into the drill pipe, and it has a heavy-duty electric motor connected to a threaded drive shaft which connects to and rotates the drill pipe. In a kelly drive system, the swivel assembly sustains the weight of the drill stem, permits its rotation and affords a rotating pressure seal and passageway for circulating drilling fluid into the top of the drill string. The swivel also has a large handle that fits inside the hook assembly at the bottom of the traveling block. Drilling fluid enters the drill stem through a hose, called the rotary hose, attached to the side of the swivel. The kelly is a triangular, square or hexagonal piece of pipe, usually 40 feet long, that transmits torque from the rotary table to the drill stem and permits its vertical movement as it is lowered into the hole. The bottom end of the kelly fits inside a corresponding triangular, square or hexagonal opening in a device called the kelly bushing. The kelly bushing, in turn, fits into a part of the rotary table called the master bushing. As the master bushing rotates, the kelly bushing also rotates, turning the kelly, which rotates the drill pipe and thus the drill bit. Drilling fluid is pumped through the kelly on its way to the bottom. The rotary table, equipped with its master bushing and kelly bushing, supplies the necessary torque to turn the drill stem. The drill pipe and drill collars are both steel tubes through which drilling fluid can be pumped. Drill pipe, sometimes called drill string, comes in 30-foot sections, or joints, with threaded sections on each end. Drill collars are heavier than drill pipe and are also threaded on the ends. Collars are used on the bottom of the drill stem to apply weight to the drilling bit. At the end of the drill stem is the bit, which chews up the formation rock and dislodges it so that drilling fluid can circulate the fragmented material back up to the surface where the circulating system filters it out of the fluid.
Drilling fluid, often called mud, is a mixture of clays, chemicals and water or oil, which is carefully formulated for the particular well being drilled. Drilling mud accounts for a major portion of the cost incurred and equipment used in drilling a well. Bulk storage of drilling fluid materials, the pumps and the mud-mixing equipment are placed at the start of the circulating system. Working mud pits and reserve storage are at the other end of the system. Between these two points, the circulating system includes auxiliary equipment for drilling fluid maintenance and equipment for well pressure control. Within the system, the drilling mud is typically routed from the mud pits to the mud pump and from the mud pump through a standpipe and the rotary hose to the drill stem. The drilling mud travels down the drill stem to the bit, up the annular space between the drill stem and the borehole and through the blowout preventer stack to the return flow line. It then travels to a shale shaker for removal of rock cuttings, and then back to the mud pits, which are usually steel tanks. The reserve pits, usually one or two fairly shallow excavations, are used for waste material and excess water around the location.
In a continuing effort to improve our rig fleet, we have installed top drives in 20 rigs (with one additional spare top drive available for installation), iron roughnecks in 44 rigs, walking / skidding systems on eight rigs and automatic catwalks in four rigs.
There are numerous factors that differentiate land drilling rigs, including their power generation systems and their drilling depth capabilities. The actual drilling depth capability of a rig may be less than or more than its rated depth capability due to numerous factors, including the size, weight and amount of the drill pipe on the rig. The intended well depth and the drill site conditions determine the amount of drill pipe and other equipment needed to drill a well. Generally, land rigs operate with crews of five to six persons.
We have 71 drilling rigs in our fleet. As of February 5, 2010, 34 drilling rigs are operating under drilling contracts. We have 31 drilling rigs that are idle and six drilling rigs have been placed in storage or “cold stacked”
8
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
in our Oklahoma drilling division due to low demand for drilling rigs in that region. We are actively marketing all our idle drilling rigs both domestically and internationally in Latin America. During the second quarter of 2009, we established our Appalachian drilling division and now have four drilling rigs operating in the Marcellus Shale region. We are currently upgrading a fifth rig that is scheduled to begin operating under a drilling contract in the Marcellus Shale region in late February 2010. We have seven drilling rigs located in Colombia that are operating under drilling contracts, five of which are drilling and two of which have been moved to their initial well site locations and are expected to begin drilling in late February 2010. In March 2010, we plan to export an eighth rig to Colombia that will begin working under a drilling contract.
The following table sets forth historical information regarding utilization for our drilling rig fleet:
| Years ended December 31, | Nine months ended December 31, 2007 |
Years ended March 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | ||||||||||||||
| Average number of operating rigs for the period |
70.7 | 67.4 | 66.7 | 60.8 | 52.3 | 40.1 | ||||||||||||
| Average utilization rate |
41 | % | 89 | % | 89 | % | 95 | % | 95 | % | 96 | % | ||||||
We believe that our drilling rigs and other related equipment are in good operating condition. Our employees perform periodic maintenance and minor repair work on our drilling rigs. We rely on various oilfield service companies for major repair work and overhaul of our drilling equipment when needed. We also engage in periodic improvement of our drilling equipment. In the event of major breakdowns or mechanical problems, our rigs could be subject to significant idle time and a resulting loss of revenue if the necessary repair services are not immediately available.
As of February 5, 2010, we owned a fleet of 78 trucks and related transportation equipment that we use to transport our drilling rigs to and from drilling sites. By owning our own trucks, we reduce the overall cost of rig moves and reduce downtime between rig moves.
As a provider of contract land drilling services, our business and the profitability of our operations depend on the level of drilling activity by oil and gas exploration and production companies operating in the geographic markets where we operate. The oil and gas exploration and production industry is a historically cyclical industry characterized by significant changes in the levels of exploration and development activities. During periods of reduced drilling activity or excess rig capacity, price competition tends to increase and the profitability of daywork contracts tends to decrease. In this competitive price environment, we may be more inclined to enter into turnkey contracts that expose us to greater risk of loss without commensurate increases in potential contract profitability.
We obtain our contracts for drilling oil and gas wells either through competitive bidding or through direct negotiations with customers. Our drilling contracts generally provide for compensation on either a daywork, turnkey or footage basis. The contract terms we offer generally depend on the complexity and risk of operations, the on-site drilling conditions, the type of equipment used and the anticipated duration of the work to be performed. Generally, our contracts provide for the drilling of a single well and typically permit the customer to terminate on short notice. However, we have entered into more longer-term drilling contracts during periods of high rig demand. In addition, we generally construct new drilling rigs once we have entered into longer-term drilling contracts for such rigs. As of February 5, 2010, we had 11 contracts with terms of six months to three years in duration, of which one will expire by August 5, 2010, three have a remaining term of six to 12 months and seven have a remaining term in excess of 18 months.
9
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
The following table presents, by type of contract, information about the total number of wells we completed for our customers during each of the last three fiscal years.
| Years ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 | |||||
| Type of Contract |
2009 | 2008 | ||||
| Daywork |
323 | 828 | 606 | |||
| Turnkey |
14 | 10 | 5 | |||
| Footage |
1 | 71 | 66 | |||
| Total number of wells |
338 | 909 | 677 | |||
Daywork Contracts. Under daywork drilling contracts, we provide a drilling rig and required personnel to our customer who supervises the drilling of the well. We are paid based on a negotiated fixed rate per day while the rig is used. Daywork drilling contracts specify the equipment to be used, the size of the hole and the depth of the well. Under a daywork drilling contract, the customer bears a large portion of the out-of-pocket drilling costs and we generally bear no part of the usual risks associated with drilling, such as time delays and unanticipated costs.
Turnkey Contracts. Under a turnkey contract, we agree to drill a well for our customer to a specified depth and under specified conditions for a fixed price, regardless of the time required or the problems encountered in drilling the well. We provide technical expertise and engineering services, as well as most of the equipment and drilling supplies required to drill the well. We often subcontract for related services, such as the provision of casing crews, cementing and well logging. Under typical turnkey drilling arrangements, we do not receive progress payments and are paid by our customer only after we have performed the terms of the drilling contract in full.
The risks to us under a turnkey contract are substantially greater than on a well drilled on a daywork basis. This is primarily because under a turnkey contract we assume most of the risks associated with drilling operations generally assumed by the operator in a daywork contract, including the risk of blowout, loss of hole, stuck drill pipe, machinery breakdowns, abnormal drilling conditions and risks associated with subcontractors’ services, supplies, cost escalations and personnel. We employ or contract for engineering expertise to analyze seismic, geologic and drilling data to identify and reduce some of the drilling risks we assume. We use the results of this analysis to evaluate the risks of a proposed contract and seek to account for such risks in our bid preparation. We believe that our operating experience, qualified drilling personnel, risk management program, internal engineering expertise and access to proficient third-party engineering contractors have allowed us to reduce some of the risks inherent in turnkey drilling operations. We also maintain insurance coverage against some, but not all, drilling hazards. However, the occurrence of uninsured or under-insured losses or operating cost overruns on our turnkey jobs could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations.
Footage Contracts. Under footage contracts, we are paid a fixed amount for each foot drilled, regardless of the time required or the problems encountered in drilling the well. We typically pay more of the out-of-pocket costs associated with footage contracts as compared to daywork contracts. Similar to a turnkey contract, the risks to us on a footage contract are greater because we assume most of the risks associated with drilling operations generally assumed by the operator in a daywork contract, including loss of hole, stuck drill pipe, machinery breakdowns, abnormal drilling conditions and risks associated with subcontractors’ services, supplies, cost escalation and personnel. As with turnkey contracts, we manage this additional risk through the use of engineering expertise and bid the footage contracts accordingly. However, the occurrence of uninsured or under-insured losses or operating cost overruns on our footage jobs could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations.
10
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Production Services Division
Well Services. We provide rig-based well services, including maintenance of existing wells, workover of existing wells, completion of newly-drilled wells, and plugging and abandonment of wells at the end of their useful lives.
Regular maintenance is generally required throughout the life of a well to sustain optimal levels of oil and gas production. We believe regular maintenance comprises the largest portion of our work in this business segment. Common maintenance services include repairing inoperable pumping equipment in an oil well and replacing defective tubing in a gas well. Our maintenance services involve relatively low-cost, short-duration jobs which are part of normal well operating costs. The need for maintenance does not directly depend on the level of drilling activity, although it is somewhat impacted by short-term fluctuations in oil and gas prices. Accordingly, maintenance services generally experience relatively stable demand; however, when oil or gas prices are too low to justify additional expenditures, operating companies may choose to temporarily shut in producing wells rather than incur additional maintenance costs.
In addition to periodic maintenance, producing oil and gas wells occasionally require major repairs or modifications called workovers, which are typically more complex and more time consuming than maintenance operations. Workover services include extensions of existing wells to drain new formations either through perforating the well casing to expose additional productive zones not previously produced, deepening well bores to new zones or the drilling of lateral well bores to improve reservoir drainage patterns. Our workover rigs are also used to convert former producing wells to injection wells through which water or carbon dioxide is then pumped into the formation for enhanced oil recovery operations. Workovers also include major subsurface repairs such as repair or replacement of well casing, recovery or replacement of tubing and removal of foreign objects from the well bore. These extensive workover operations are normally performed by a workover rig with additional specialized auxiliary equipment, which may include rotary drilling equipment, mud pumps, mud tanks and fishing tools, depending upon the particular type of workover operation. All of our well servicing rigs are designed to perform complex workover operations. A workover may require a few days to several weeks and generally requires additional auxiliary equipment. The demand for workover services is sensitive to oil and gas producers’ intermediate and long-term expectations for oil and gas prices.
Completion services involve the preparation of newly drilled wells for production. The completion process may involve selectively perforating the well casing in the productive zones to allow oil or gas to flow into the well bore, stimulating and testing these zones and installing the production string and other downhole equipment. We provide well service rigs to assist in this completion process. Newly drilled wells are frequently completed by well servicing rigs to minimize the use of higher cost drilling rigs in the completion process. The completion process typically requires a few days to several weeks, depending on the nature and type of the completion, and generally requires additional auxiliary equipment. Accordingly, completion services require less well-to-well mobilization of equipment and generally provide higher operating margins than regular maintenance work. The demand for completion services is directly related to drilling activity levels, which are sensitive to changes in oil and gas prices.
Well servicing rigs are also used in the process of permanently closing oil and gas wells no longer capable of producing in economic quantities. Many well operators bid this work on a “turnkey” basis, requiring the service company to perform the entire job, including the sale or disposal of equipment salvaged from the well as part of the compensation received, and complying with state regulatory requirements. Plugging and abandonment work can provide favorable operating margins and is less sensitive to oil and gas pricing than drilling and workover activity since well operators must plug a well in accordance with state regulations when it is no longer productive. We perform plugging and abandonment work throughout our core areas of operation in conjunction with equipment provided by other service companies.
11
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
When we provide well services, we typically bill customers on an hourly basis during the period that the rig providing services is actively working. As of December 31, 2009, our fleet of well service rigs totaled 74 rigs. These rigs are located mostly in Texas, serving the Gulf Coast and ArkLaTex regions, though we also have six rigs in Louisiana and six rigs in North Dakota. Our fleet is one of the youngest in the industry, consisting primarily of premium, 550 horsepower rigs capable of working at depths of 20,000 feet.
Wireline Services. We provide both open and cased-hole wireline services with our fleet of 65 wireline units. We provide these services in Texas, Kansas, Colorado, Utah, Montana, North Dakota, Louisiana and certain Appalachian states. Wireline services typically utilize a single truck equipped with a spool of wireline that is used to lower and raise a variety of specialized tools in and out of the wellbore. These tools can be used to measure pressures and temperatures as well as the condition of the casing and the cement that holds the casing in place. Other applications for wireline tools include placing equipment in or retrieving equipment from the wellbore, or perforating the casing and cutting off pipe that is stuck in the well so that the free section can be recovered. Electric wireline contains a conduit that allows signals to be transmitted to or from tools located in the well. Wireline trucks are often used in place of a well servicing rig when there is no requirement to remove tubulars from the well in order to make repairs. Wireline trucks, like well servicing rigs, are utilized throughout the life of a well.
Fishing and Rental Services. Our rental and fishing tool business provides a range of specialized services and equipment that are utilized on a non-routine basis for both drilling and well servicing operations. Drilling and well servicing rigs are equipped with a complement of tools to complete routine operations under normal conditions for most projects in the geographic area where they are employed. When downhole problems develop with drilling or servicing operations, or conditions require non-routine equipment, our customers will usually rely on a provider of rental and fishing tools to augment equipment that is provided with a typical drilling or well servicing rig package. The important rental tools that we offer include air drilling equipment, foam units, power swivels, and blowout preventers.
The term “fishing” applies to a wide variety of downhole operations designed to correct a problem that has developed when drilling or servicing a well. Often, the problem involves equipment that has become lodged in the well and cannot be removed without special equipment. Our customers employ our technicians and our tools that are specifically suited to retrieve the trapped equipment, or “fish,” in order for operations to resume.
Our Production Services operations are impacted by seasonal factors. Our business can be negatively impacted during the winter months due to inclement weather, fewer daylight hours, and holidays. Because our well service rigs and wireline units are mobile, during periods of heavy snow, ice or rain, we may not be able to move our equipment between locations.
12
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Customers
We provide drilling services and production services to numerous major and independent oil and gas companies that are active in the geographic areas in which we operate. The following table shows our three largest customers as a percentage of our total revenue for each of our last three fiscal years.
| Customer |
Total Revenue Percentage |
||
| Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2009: |
|||
| Ecopetrol |
16.2 | % | |
| Anadarko Petroleum Corporation |
5.9 | % | |
| Cabot Oil and Gas Corporation |
5.6 | % | |
| Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2008: |
|||
| EOG Resources, Inc. |
10.0 | % | |
| Ecopetrol |
7.4 | % | |
| Anadarko Petroleum Corporation |
6.4 | % | |
| Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007: |
|||
| EOG Resources, Inc. |
13.1 | % | |
| Anadarko Petroleum Corporation |
8.8 | % | |
| Chesapeake Operating Inc. |
7.7 | % | |
We continued to provide drilling services and production services to EOG Resources, Inc. during the year ended December 31, 2009, however, EOG Resources, Inc. was no longer one of our three largest customers due to the expiration of term contracts that were in place during the year ended December 31, 2008 for seven drilling rigs. We had term contracts in place with EOG Resources, Inc. during the nine months ended December 31, 2007 for six drilling rigs.
Competition
Drilling Services Division
We encounter substantial competition from other drilling contractors. Our primary market areas are highly fragmented and competitive. The fact that drilling rigs are mobile and can be moved from one market to another in response to market conditions heightens the competition in the industry.
The drilling contracts we compete for are usually awarded on the basis of competitive bids. Our principal competitors are Helmerich & Payne, Inc., Precision Drilling Trust, Patterson-UTI Energy, Inc. and Nabors Industries, Ltd. In addition to pricing and rig availability, we believe the following factors are also important to our customers in determining which drilling contractors to select:
| • | the type and condition of each of the competing drilling rigs; |
| • | the mobility and efficiency of the rigs; |
| • | the quality of service and experience of the rig crews; |
| • | the safety records of the rigs; |
| • | the offering of ancillary services; and |
| • | the ability to provide drilling equipment adaptable to, and personnel familiar with, new technologies and drilling techniques. |
While we must be competitive in our pricing, our competitive strategy generally emphasizes the quality of our equipment, the safety record of our rigs and the experience of our rig crews to differentiate us from our competitors.
Contract drilling companies compete primarily on a regional basis, and the intensity of competition may vary significantly from region to region at any particular time. If demand for drilling services improves in a
13
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
region where we operate, our competitors might respond by moving in suitable rigs from other regions. An influx of rigs from other regions could rapidly intensify competition and make any improvement in demand for drilling rigs in a particular region short-lived.
Some of our competitors have greater financial, technical and other resources than we do. Their greater capabilities in these areas may enable them to:
| • | better withstand industry downturns; |
| • | compete more effectively on the basis of price and technology; |
| • | better retain skilled rig personnel; and |
| • | build new rigs or acquire and refurbish existing rigs so as to be able to place rigs into service more quickly than us in periods of high drilling demand. |
Production Services Division
The market for production services is highly competitive. Competition is influenced by such factors as price, capacity, availability of work crews, type and condition of equipment and reputation and experience of the service provider. We believe that an important competitive factor in establishing and maintaining long-term customer relationships is having an experienced, skilled and well-trained work force. In recent years, many of our larger customers have placed increased emphasis on the safety performance and quality of the crews, equipment and services provided by their contractors. We have devoted, and will continue to devote, substantial resources toward employee safety and training programs. Although we believe customers consider all of these factors, price is generally the primary factor in determining which service provider is awarded the work. However, we believe that most customers are willing to pay a slight premium for the quality and efficient service we provide.
The largest well service providers that we compete with are Key Energy Services, Basic Energy Services, Nabors Industries, Complete Production Services and CC Forbes. In addition, there are numerous smaller companies that compete in our well service markets.
The wireline market is dominated by Schlumberger Ltd. and Halliburton Company. These companies have a substantially larger asset base than we do and operate in all major U.S. oil and natural gas producing basins. Other competitors include Weatherford International, Baker Atlas, Superior Energy Services, Basic Energy Services, and Key Energy Services. The market for wireline services is very competitive, but historically we have competed effectively with our competitors based on performance and strong customer service.
The fishing and rental tools market is fragmented compared to our other product lines. Companies which provide fishing services generally compete based on the reputation of their fishing tool operators and their relationships with customers. Competition for rental tools is sometimes based on price; however, in most cases, when a customer chooses a specific fishing tool operator for a particular job, then the necessary rental equipment will be part of that job as well. Our primary competitors include: Baker Oil Tools, Weatherford International, Basic Energy Services, Key Energy Services, Quail Tools (owned by Parker Drilling) and Knight Oil Tools.
The need for well servicing, wireline, and fishing and rental services fluctuates, primarily, in relation to the price (or anticipated price) of oil and natural gas, which, in turn, is driven by the supply of and demand for oil and natural gas. Generally, as supply of those commodities decreases and demand increases, service and maintenance requirements increase as oil and natural gas producers attempt to maximize the productivity of their wells in a higher priced environment.
The level of our revenues, earnings and cash flows are substantially dependent upon, and affected by, the level of domestic and international oil and gas exploration and development activity, as well as the equipment capacity in any particular region. For a more detailed discussion, see Item 7. “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations.”
14
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Raw Materials
The materials and supplies we use in our drilling and production services operations include fuels to operate our drilling and well service equipment, drilling mud, drill pipe, drill collars, drill bits and cement. We do not rely on a single source of supply for any of these items. While we are not currently experiencing any shortages, from time to time there have been shortages of drilling equipment and supplies during periods of high demand. Shortages could result in increased prices for drilling equipment or supplies that we may be unable to pass on to customers. In addition, during periods of shortages, the delivery times for equipment and supplies can be substantially longer. Any significant delays in our obtaining drilling equipment or supplies could limit drilling operations and jeopardize our relations with customers. In addition, shortages of drilling equipment or supplies could delay and adversely affect our ability to obtain new contracts for our rigs, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Operating Risks and Insurance
Our operations are subject to the many hazards inherent in the contract land drilling business, including the risks of:
| • | blowouts; |
| • | fires and explosions; |
| • | loss of well control; |
| • | collapse of the borehole; |
| • | lost or stuck drill strings; and |
| • | damage or loss from natural disasters. |
Any of these hazards can result in substantial liabilities or losses to us from, among other things:
| • | suspension of drilling operations; |
| • | damage to, or destruction of, our property and equipment and that of others; |
| • | personal injury and loss of life; |
| • | damage to producing or potentially productive oil and gas formations through which we drill; and |
| • | environmental damage. |
We seek to protect ourselves from some but not all operating hazards through insurance coverage. However, some risks are either not insurable or insurance is available only at rates that we consider uneconomical. Those risks include pollution liability in excess of relatively low limits. Depending on competitive conditions and other factors, we attempt to obtain contractual protection against uninsured operating risks from our customers. However, customers who provide contractual indemnification protection may not in all cases maintain adequate insurance to support their indemnification obligations. Our insurance or indemnification arrangements may not adequately protect us against liability or loss from all the hazards of our operations. The occurrence of a significant event that we have not fully insured or indemnified against or the failure of a customer to meet its indemnification obligations to us could materially and adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition. Furthermore, we may not be able to maintain adequate insurance in the future at rates we consider reasonable.
Our current insurance coverage includes property insurance on our rigs, drilling equipment and real property. Our insurance coverage for property damage to our rigs and to our drilling equipment is based on our estimates of the cost of comparable used equipment to replace the insured property. The policy provides for a deductible on rigs of $250,000 per occurrence ($500,000 deductible for rigs with an insured value greater than $10 million). Our third-party liability insurance coverage is $51 million per occurrence and in the aggregate, with a deductible of $260,000 per occurrence. We believe that we are adequately insured for public liability and
15
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
property damage to others with respect to our operations. However, such insurance may not be sufficient to protect us against liability for all consequences of well disasters, extensive fire damage or damage to the environment.
In addition, we generally carry insurance coverage to protect against certain hazards inherent in our turnkey contract drilling operations. This insurance covers “control-of-well,” including blowouts above and below the surface, redrilling, seepage and pollution. This policy provides coverage of $3 million, $5 million, $10 million, $15 million or $20 million depending on the area in which the well is drilled and its target depth, subject to a deductible of the greater of 15% of the well’s anticipated dry hole cost or $150,000. This policy also provides care, custody and control insurance, with a limit of $1 million, subject to a $100,000 deductible.
Employees
We currently have approximately 1,700 employees. Approximately 200 of these employees are salaried administrative or supervisory employees. The rest of our employees are working in operations for our Drilling Services Division and Production Services Division and are primarily compensated on an hourly basis. The number of employees in operations fluctuates depending on the utilization of our drilling rigs, workover rigs and wireline units at any particular time. None of our employment arrangements are subject to collective bargaining arrangements.
Our operations require the services of employees having the technical training and experience necessary to obtain proper operational standards. As a result, our operations depend, to a considerable extent, on the continuing availability of such personnel. Although we have not encountered material difficulty in hiring and retaining employees in our operations, shortages of qualified personnel have occurred in our industry. If we should suffer any material loss of personnel to competitors or be unable to employ additional or replacement personnel with the requisite level of training and experience to adequately operate our equipment, our operations could be materially and adversely affected. While we believe our wage rates are competitive and our relationships with our employees are satisfactory, a significant increase in the wages paid by other employers could result in a reduction in our workforce, increases in wage rates, or both. The occurrence of either of these events for a significant period of time could have a material and adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Facilities
Our corporate office facilities are located at 1250 N.E. Loop 410, Suite 1000 San Antonio, Texas 78209 and are leased with costs escalating from $27,360 per month to $29,316 per month with a non-cancelable lease term expiring in December 2013.
We conduct our business operations through 47 other real estate locations in the United States (Texas, Oklahoma, Colorado, Utah, Montana, North Dakota, Pennsylvania, West Virginia, Louisiana and Kansas) and internationally in Colombia. These real estate locations are primarily used for regional offices and storage and maintenance yards. We own 10 of these real estate locations and the remaining 37 real estate locations are leased with costs ranging from $240 per month to $12,402 per month with non-cancelable lease terms expiring through October 2014.
Governmental Regulation
Our operations are subject to stringent laws and regulations relating to containment, disposal and controlling the discharge of hazardous oilfield waste and other non-hazardous waste material into the environment, requiring removal and cleanup under certain circumstances, or otherwise relating to the protection of the environment. In addition, our operations are often conducted in or near ecologically sensitive areas, such as wetlands, which are subject to special protective measures and which may expose us to additional operating costs and liabilities for accidental discharges of oil, natural gas, drilling fluids or contaminated water, or for noncompliance with other
16
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
aspects of applicable laws. We are also subject to the requirements of the federal Occupational Safety and Health Act (“OSHA”) and comparable state statutes. The OSHA hazard communication standard, the Environmental Protection Agency (“EPA”) “community right-to-know” regulations under Title III of the Federal Superfund Amendment and Reauthorization Act and comparable state statutes require us to organize and report information about the hazardous materials we use in our operations to employees, state and local government authorities and local citizens.
Environmental laws and regulations are complex and subject to frequent change. In some cases, they can impose liability for the entire cost of cleanup on any responsible party, without regard to negligence or fault, and can impose liability on us for the conduct of others or conditions others have caused, or for our acts that complied with all applicable requirements when we performed them. We may also be exposed to environmental or other liabilities originating from businesses and assets that we purchased from others. Compliance with applicable environmental laws and regulations has not, to date, materially affected our capital expenditures, earnings or competitive position, although compliance measures have added to our costs of operating drilling equipment in some instances. We do not expect to incur material capital expenditures in our next fiscal year in order to comply with current environment control regulations. However, our compliance with amended, new or more stringent requirements, stricter interpretations of existing requirements or the future discovery of contamination may require us to make material expenditures or subject us to liabilities that we currently do not anticipate.
There are a variety of regulatory developments, proposals or requirements and legislative initiatives that have been introduced in the United States and international regions in which we operate that are focused on restricting the emission of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases. Among these developments are the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, also known as the “Kyoto Protocol” (an internationally applied protocol, which has been ratified in Columbia, one of our reporting segments), the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative or “RGGI” in the Northeastern United States, and the Western Regional Climate Action Initiative in the Western United States, including partners states New Mexico, Utah, and Montana and observer states Colorado and Wyoming.
The U.S. Congress has been actively considering legislation to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases, primarily through the development of greenhouse gas cap and trade programs. In June of 2009, the U.S. House of Representatives passed a cap and trade bill known as the American Clean Energy and Security Act of 2009, which is now being considered by the U.S. Senate, among other alternative bills. In addition, more than one-third of the states already have begun implementing legal measures to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases.
In 2007, the United States Supreme Court in Massachusetts, et al. v. EPA, held that carbon dioxide may be regulated as an “air pollutant” under the federal Clean Air Act. On December 7, 2009, the EPA responded to the Massachusetts, et al. v. EPA decision and issued a finding that the current and projected concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere threaten the public health and welfare of current and future generations, and that certain greenhouse gases from new motor vehicles and motor vehicle engines contribute to the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases and hence to the threat of climate change.
On September 22, 2009, EPA finalized a rule requiring nation-wide reporting of greenhouse gas emissions beginning January 1, 2010. The rule applies primarily to large facilities emitting 25,000 metric tons or more of carbon dioxide-equivalent greenhouse gas emissions per year, and to most upstream suppliers of fossil fuels and industrial greenhouse gas, as well as to manufacturers of vehicles and engines. In addition, EPA recently proposed a rule that would, in general, require facilities that emit more than 25,000 tons per year of greenhouse gas equivalents to obtain permits to demonstrate that best practices and technology are being used to minimize greenhouse gas emissions.
Although it is not possible at this time to predict whether proposed legislation or regulations will be adopted as initially written, if at all, or how legislation or new regulations that may be adopted to address greenhouse gas emissions would impact our business, any such future laws and regulations could result in increased compliance
17
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
costs or additional operating restrictions. Any additional costs or operating restrictions associated with legislation or regulations regarding greenhouse gas emissions could have a material adverse effect on our operating results and cash flows. In addition, these developments could curtail the demand for fossil fuels such as oil and gas in areas of the world where our customers operate and thus adversely affect demand for our services, which may in turn adversely affect our future results of operations. Finally, we cannot predict with any certainty whether changes to temperature, storm intensity or precipitation patterns as a result of climate change will have a material impact on our operations.
In addition, our business depends on the demand for land drilling services from the oil and gas industry and, therefore, is affected by tax, environmental and other laws relating to the oil and gas industry generally, by changes in those laws and by changes in related administrative regulations. It is possible that these laws and regulations may in the future add significantly to our operating costs or those of our customers, or otherwise directly or indirectly affect our operations.
Our wireline operations involve the use of radioactive isotopes along with other nuclear, electrical, acoustic, and mechanical devices. Our activities involving the use of isotopes are regulated by the U.S. Nuclear Regulatory Commission and specified agencies of certain states. Additionally, we use high explosive charges for perforating casing and formations, and we use various explosive cutters to assist in wellbore cleanout. Such operations are regulated by the U.S. Department of Justice, Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms, and Explosives and require us to obtain licenses or other approvals for the use of densitometers as well as explosive charges. We have obtained these licenses and approvals when necessary and believe that we are in substantial compliance with these federal requirements.
Among the services we provide, we operate as a motor carrier and therefore are subject to regulation by the U.S. Department of Transportation and by various state agencies. These regulatory authorities exercise broad powers, governing activities such as the authorization to engage in motor carrier operations and regulatory safety. There are additional regulations specifically relating to the trucking industry, including testing and specification of equipment and product handling requirements. The trucking industry is subject to possible regulatory and legislative changes that may affect the economics of the industry by requiring changes in operating practices or by changing the demand for common or contract carrier services or the cost of providing truckload services. Some of these possible changes include increasingly stringent environmental regulations, changes in the hours of service regulations which govern the amount of time a driver may drive in any specific period, onboard black box recorder devices or limits on vehicle weight and size.
Interstate motor carrier operations are subject to safety requirements prescribed by the U.S. Department of Transportation. To a large degree, intrastate motor carrier operations are subject to state safety regulations that mirror federal regulations. Such matters as weight and dimension of equipment are also subject to federal and state regulations.
From time to time, various legislative proposals are introduced, including proposals to increase federal, state, or local taxes, including taxes on motor fuels, which may increase our costs or adversely impact the recruitment of drivers. We cannot predict whether, or in what form, any increase in such taxes applicable to us will be enacted.
Available Information
Our Website address is www.pioneerdrlg.com. Our annual reports on Form 10-K, quarterly reports on Form 10-Q, current reports on Form 8-K and amendments to those reports, are available free of charge through our Website as soon as reasonably practicable after we electronically file those materials with, or furnish those materials to, the Securities and Exchange Commission. The public may read and copy these materials at the Securities and Exchange Commission’s Public Reference Room at 100 F Street, N.E., Washington, DC 20549. For additional information on the Securities and Exchange Commission’s Public Reference Room, please call
18
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
1-800-SEC-0330. In addition, the Securities and Exchange Commission maintains an Internet site at www.sec.gov that contains reports, proxy and information statements and other information regarding issuers that file electronically. We have also posted on our Website our: Charters for the Audit, Compensation, and Nominating and Corporate Governance Committees of our Board; Code of Conduct and Ethics; Rules of Conduct; and Company Contact Information.
19
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Item 1A. | Risk Factors |
The information set forth in this Item 1A should be read in conjunction with the rest of the information included in this report, including “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in Item 7 and the historical financial statements and related notes this report contains. While we attempt to identify, manage and mitigate risks and uncertainties associated with our business to the extent practical under the circumstances, some level of risk and uncertainty will always be present. Additional risks and uncertainties not presently known to us or that we currently believe are immaterial also may negatively impact our business, financial condition or operating results.
Set forth below are various risks and uncertainties that could adversely impact our business, financial condition, results of operations and cash flows.
Risks Relating to the Oil and Gas Industry
We derive all our revenues from companies in the oil and gas exploration and production industry, a historically cyclical industry with levels of activity that are significantly affected by the levels and volatility of oil and gas prices.
As a provider of contract land drilling services and oil and gas production services, our business depends on the level of exploration and production activity by oil and gas companies operating in the geographic markets where we operate. The oil and gas exploration and production industry is a historically cyclical industry characterized by significant changes in the levels of exploration and development activities. Oil and gas prices, and market expectations of potential changes in those prices, significantly affect the levels of those activities. Worldwide political, economic, and military events as well as natural disasters have contributed to oil and gas price volatility and are likely to continue to do so in the future. Any prolonged reduction in the overall level of exploration and development activities, whether resulting from changes in oil and gas prices or otherwise, could materially and adversely affect us in many ways by negatively impacting:
| • | our revenues, cash flows and profitability; |
| • | the fair market value of our drilling rig fleet and production service assets; |
| • | our ability to maintain or increase our borrowing capacity; |
| • | our ability to obtain additional capital to finance our business and make acquisitions, and the cost of that capital; and |
| • | our ability to retain skilled rig personnel whom we would need in the event of an upturn in the demand for our services. |
Depending on the market prices of oil and gas, oil and gas exploration and production companies may cancel or curtail their drilling programs and may lower production spending on existing wells, thereby reducing demand for our services. Oil and gas prices have been volatile historically and, we believe, will continue to be so in the future. Many factors beyond our control affect oil and gas prices, including:
| • | the cost of exploring for, producing and delivering oil and gas; |
| • | the discovery rate of new oil and gas reserves; |
| • | the rate of decline of existing and new oil and gas reserves; |
| • | available pipeline and other oil and gas transportation capacity; |
| • | the levels of oil and gas storage; |
| • | the ability of oil and gas companies to raise capital; |
| • | economic conditions in the United States and elsewhere; |
20
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| • | actions by OPEC, the Organization of Petroleum Exporting Countries; |
| • | political instability in the Middle East and other major oil and gas producing regions; |
| • | governmental regulations, both domestic and foreign; |
| • | domestic and foreign tax policy; |
| • | weather conditions in the United States and elsewhere; |
| • | the pace adopted by foreign governments for the exploration, development and production of their national reserves; |
| • | the price of foreign imports of oil and gas; and |
| • | the overall supply and demand for oil and gas. |
As a result of declines in oil and natural gas prices and uncertainty in the capital markets due to the downturn in the global economic environment that began in late 2008 and a continued sluggish economy during 2009, our customers have reduced spending on exploration and production and this has resulted in a decrease in demand for our services. We are unable to determine whether customers and/or vendors and suppliers will be able to access financing necessary to sustain or increase their current level of operations, fulfill their commitments and/or fund future operations and obligations. The sluggish global economic environment may impact industry fundamentals, and the potential resulting continued sluggish demand for drilling and production services could adversely affect our business.
Oil and natural gas prices, and market expectations of potential changes in these prices, significantly impact the level of worldwide drilling and production services activities. Oil and natural gas prices are significantly below the levels seen in late 2008 due to a deteriorating global economic environment which remained sluggish during 2009. The lower oil and natural gas prices, as well as the slow recovery in the global credit markets, have caused exploration and production companies to reduce their overall level of drilling and production services activity and spending. When drilling and production activity and spending declines, both day rates and utilization have historically declined. As a result, the declines in oil and natural gas prices and the sluggish economy have adversely affected our business and operating results. Continued declines in oil and natural gas prices and a continued sluggish economy could materially and adversely affect our business and financial results.
Moreover, the sluggish global economic environment may continue to impact fundamentals that are critical to our industry, such as the global demand for, and consumption of, oil and natural gas. Reduced demand for oil and natural gas generally results in lower prices for these commodities and may impact the economics of planned drilling projects and ongoing production projects, resulting in the curtailment, reduction, delay or postponement of such projects for an indeterminate period of time. Companies that planned to finance exploration, development or production projects through the capital markets may be forced to curtail, reduce, postpone or delay drilling or production services activities, and also may experience an inability to pay suppliers. The sluggish global economic environment could also impact our vendors and suppliers’ ability to meet obligations to provide materials and services in general. If any of the foregoing were to occur, it could have a material adverse effect on our business and financial results.
Risks Relating to Our Business
Reduced demand for or excess capacity of drilling services or production services could adversely affect our profitability.
Our profitability in the future will depend on many factors, but largely on pricing and utilization rates for our drilling and production services. A reduction in the demand for drilling rigs or an increase in the supply of drilling rigs, whether through new construction or refurbishment, could decrease the dayrates and utilization rates for our drilling services, which would adversely affect our revenues and profitability. An increase in supply of
21
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
well service rigs, wireline units and fishing and rental tools equipment, without a corresponding increase in demand, could similarly decrease the pricing and utilization rates of our production services, which would adversely affect our revenues and profitability. We experienced a substantial decrease in revenue and utilization rates during the last quarter of 2008 and during 2009.
We operate in a highly competitive, fragmented industry in which price competition could reduce our profitability.
We encounter substantial competition from other drilling contractors and other oilfield service companies. Our primary market areas are highly fragmented and competitive. The fact that drilling, workover and well-servicing rigs are mobile and can be moved from one market to another in response to market conditions heightens the competition in the industry and may result in an oversupply of rigs in an area. Contract drilling companies and other oilfield service companies compete primarily on a regional basis, and the intensity of competition may vary significantly from region to region at any particular time. If demand for drilling or production services improves in a region where we operate, our competitors might respond by moving in suitable rigs from other regions. An influx of rigs from other regions could rapidly intensify competition, reduce profitability and make any improvement in demand for drilling or production services short-lived.
Most drilling services contracts and production services contracts are awarded on the basis of competitive bids, which also results in price competition. In addition to pricing and rig availability, we believe the following factors are also important to our customers in determining which drilling services or production services provider to select:
| • | the type and condition of each of the competing drilling, workover and well-servicing rigs; |
| • | the mobility and efficiency of the rigs; |
| • | the quality of service and experience of the rig crews; |
| • | the safety records of the rigs; |
| • | the offering of ancillary services; and |
| • | the ability to provide drilling and production equipment adaptable to, and personnel familiar with, new technologies and drilling and production techniques. |
While we must be competitive in our pricing, our competitive strategy generally emphasizes the quality of our equipment, the safety record of our rigs, our ability to offer ancillary services and the quality of service and experience of our rig crews to differentiate us from our competitors. This strategy is less effective as lower demand for drilling and production services or an oversupply of drilling, workover and well-servicing rigs intensifies price competition and makes it more difficult for us to compete on the basis of factors other than price. In all of the markets in which we compete, an oversupply of rigs can cause greater price competition, which can reduce our profitability.
We face competition from many competitors with greater resources.
Some of our competitors have greater financial, technical and other resources than we do. Their greater capabilities in these areas may enable them to:
| • | better withstand industry downturns; |
| • | compete more effectively on the basis of price and technology; |
| • | retain skilled rig personnel; and |
| • | build new rigs or acquire and refurbish existing rigs so as to be able to place rigs into service more quickly than us in periods of high drilling demand. |
22
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Additionally, although we take measures to ensure that we use advanced technologies for drilling and production services equipment, changes in technology or improvements in our competitors’ equipment could make our equipment less competitive or require significant capital investments to keep our equipment competitive.
Unexpected cost overruns on our turnkey drilling jobs and our footage contracts could adversely affect our financial position and our results of operations.
We have historically derived a portion of our revenues from turnkey drilling contracts, and we expect turnkey contracts will continue to represent a component of our future revenues. The occurrence of uninsured or under-insured losses or operating cost overruns on our turnkey jobs could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations. Under a typical turnkey drilling contract, we agree to drill a well for our customer to a specified depth and under specified conditions for a fixed price. We provide technical expertise and engineering services, as well as most of the equipment and drilling supplies required to drill the well. We often subcontract for related services, such as the provision of casing crews, cementing and well logging. Under typical turnkey drilling arrangements, we do not receive progress payments and are paid by our customer only after we have performed the terms of the drilling contract in full. For these reasons, the risk to us under a turnkey drilling contract is substantially greater than for a well drilled on a daywork basis because we must assume most of the risks associated with drilling operations that the operator generally assumes under a daywork contract, including the risks of blowout, loss of hole, stuck drill pipe, machinery breakdowns, abnormal drilling conditions and risks associated with subcontractors’ services, supplies, cost escalations and personnel. Similar to our turnkey contracts, under a footage contract we assume most of the risks associated with drilling operations that the operator generally assumes under a daywork contract. In addition, since we are only paid by our customers after we have performed the terms of the drilling contract in full, our liquidity can be affected by the number of turnkey and footage contracts that we enter into.
Although we attempt to obtain insurance coverage to reduce certain of the risks inherent in our turnkey drilling operations, adequate coverage may be unavailable in the future and we might have to bear the full cost of such risks, which could have an adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our operations involve operating hazards, which, if not insured or indemnified against, could adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition.
Our operations are subject to the many hazards inherent in the drilling, workover and well-servicing industries, including the risks of:
| • | blowouts; |
| • | cratering; |
| • | fires and explosions; |
| • | loss of well control; |
| • | collapse of the borehole; |
| • | damaged or lost drilling equipment; and |
| • | damage or loss from natural disasters. |
Any of these hazards can result in substantial liabilities or losses to us from, among other things:
| • | suspension of operations; |
| • | damage to, or destruction of, our property and equipment and that of others; |
| • | personal injury and loss of life; |
23
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| • | damage to producing or potentially productive oil and gas formations through which we drill; and |
| • | environmental damage. |
We seek to protect ourselves from some but not all operating hazards through insurance coverage. However, some risks are either not insurable or insurance is available only at rates that we consider uneconomical. Those risks include, among other things, pollution liability in excess of relatively low limits. Depending on competitive conditions and other factors, we attempt to obtain contractual protection against uninsured operating risks from our customers. However, customers who provide contractual indemnification protection may not in all cases maintain adequate insurance or otherwise have the financial resources necessary to support their indemnification obligations. Our insurance or indemnification arrangements may not adequately protect us against liability or loss from all the hazards of our operations. The occurrence of a significant event that we have not fully insured or indemnified against or the failure of a customer to meet its indemnification obligations to us could materially and adversely affect our results of operations and financial condition. Furthermore, we may be unable to maintain adequate insurance in the future at rates we consider reasonable.
We could be adversely affected if shortages of equipment, supplies or personnel occur.
From time to time there have been shortages of drilling and production services equipment and supplies during periods of high demand which we believe could recur. Shortages could result in increased prices for drilling and production services equipment or supplies that we may be unable to pass on to customers. In addition, during periods of shortages, the delivery times for equipment and supplies can be substantially longer. Any significant delays in our obtaining drilling and production services equipment or supplies could limit drilling and production services operations and jeopardize our relations with customers. In addition, shortages of drilling and production services equipment or supplies could delay and adversely affect our ability to obtain new contracts for our rigs, which could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our strategy of constructing drilling rigs during periods of peak demand requires that we maintain an adequate supply of drilling rig components to complete our rig building program. Our suppliers may be unable to continue providing us the needed drilling rig components if their manufacturing sources are unable to fulfill their commitments.
Our operations require the services of employees having the technical training and experience necessary to obtain the proper operational results. As a result, our operations depend, to a considerable extent, on the continuing availability of such personnel. Shortages of qualified personnel have occurred in our industry. If we should suffer any material loss of personnel to competitors or be unable to employ additional or replacement personnel with the requisite level of training and experience to adequately operate our equipment, our operations could be materially and adversely affected. A significant increase in the wages paid by other employers could result in a reduction in our workforce, increases in wage rates, or both. The occurrence of either of these events for a significant period of time could have a material and adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
Our acquisition strategy exposes us to various risks, including those relating to difficulties in identifying suitable acquisition opportunities and integrating businesses, assets and personnel, as well as difficulties in obtaining financing for targeted acquisitions and the potential for increased leverage or debt service requirements.
As a key component of our business strategy, we have pursued and intend to continue to pursue acquisitions of complementary assets and businesses. For example, over the last 10 years, we have significantly expanded our drilling rig fleet by adding 35 rigs through acquisitions and by adding 31 rigs through the construction of rigs from new and used components. In addition, during the first quarter of 2008, we completed the acquisition of the production services businesses of WEDGE and Competition.
24
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Our acquisition strategy in general, and our recent acquisitions in particular, involve numerous inherent risks, including:
| • | unanticipated costs and assumption of liabilities and exposure to unforeseen liabilities of acquired businesses, including environmental liabilities; |
| • | difficulties in integrating the operations and assets of the acquired business and the acquired personnel; |
| • | limitations on our ability to properly assess and maintain an effective internal control environment over an acquired business in order to comply with applicable periodic reporting requirements; |
| • | potential losses of key employees and customers of the acquired businesses; |
| • | risks of entering markets in which we have limited prior experience; and |
| • | increases in our expenses and working capital requirements. |
The process of integrating an acquired business may involve unforeseen costs and delays or other operational, technical and financial difficulties that may require a disproportionate amount of management attention and financial and other resources. Possible future acquisitions may be for purchase prices significantly higher than those we paid for previous acquisitions. Our failure to achieve consolidation savings, to incorporate the acquired businesses and assets into our existing operations successfully or to minimize any unforeseen operational difficulties could have a material adverse effect on our financial condition and results of operations.
In addition, we may not have sufficient capital resources to complete additional acquisitions. Historically, we have funded the growth of our rig fleet through a combination of debt and equity financing. We may incur substantial additional indebtedness to finance future acquisitions and also may issue equity securities or convertible securities in connection with such acquisitions. Debt service requirements could represent a significant burden on our results of operations and financial condition and the issuance of additional equity or convertible securities could be dilutive to our existing shareholders. Furthermore, we may not be able to obtain additional financing on satisfactory terms.
Even if we have access to the necessary capital, we may be unable to continue to identify additional suitable acquisition opportunities, negotiate acceptable terms or successfully acquire identified targets.
Our indebtedness could restrict our operations and make us more vulnerable to adverse economic conditions.
For several years, we have had little or no long-term debt. In connection with the acquisition of the production services businesses of WEDGE and Competition in March 2008, we entered into a senior secured revolving credit facility which was later amended in October 2009. As of December 31, 2009, our total debt was $262.1 million.
Our current and future indebtedness could have important consequences, including:
| • | impairing our ability to make investments and obtain additional financing for working capital, capital expenditures, acquisitions or other general corporate purposes; |
| • | limiting our ability to use operating cash flow in other areas of our business because we must dedicate a substantial portion of these funds to make principal and interest payments on our indebtedness; |
| • | making us more vulnerable to a downturn in our business, our industry or the economy in general as a substantial portion of our operating cash flow could be required to make principal and interest payments on our indebtedness, making it more difficult to react to changes in our business and in industry and market conditions; |
| • | limiting our flexibility in planning for, or reacting to, changes in our business and the industry in which we operate; |
25
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| • | limiting our ability to obtain additional financing that may be necessary to operate or expand our business; |
| • | putting us at a competitive disadvantage to competitors that have less debt; and |
| • | increasing our vulnerability to rising interest rates. |
We anticipate that our cash generated by operations and our ability to borrow under the currently unused portion of our senior secured revolving credit facility should allow us to meet our routine financial obligations for the foreseeable future. However, our ability to make payments on our indebtedness, and to fund planned capital expenditures, will depend on our ability to generate cash in the future. This, to a certain extent, is subject to conditions in the oil and gas industry, general economic and financial conditions, competition in the markets where we operate, the impact of legislative and regulatory actions on how we conduct our business and other factors, all of which are beyond our control. If our business does not generate sufficient cash flow from operations to service our outstanding indebtedness, we may have to undertake alternative financing plans, such as:
| • | refinancing or restructuring our debt; |
| • | selling assets; |
| • | reducing or delaying acquisitions or capital investments, such as refurbishments of our rigs and related equipment; or |
| • | seeking to raise additional capital. |
However, we may be unable to implement alternative financing plans, if necessary, on commercially reasonable terms or at all, and any such alternative financing plans might be insufficient to allow us to meet our debt obligations. If we are unable to generate sufficient cash flow or are otherwise unable to obtain the funds required to make principal and interest payments on our indebtedness, or if we otherwise fail to comply with the various covenants in our senior secured revolving credit facility or other instruments governing any future indebtedness, we could be in default under the terms of our senior secured revolving credit facility or such instruments. In the event of a default, the lenders under our senior secured revolving credit facility could elect to declare all the loans made under such facility to be due and payable together with accrued and unpaid interest and terminate their commitments thereunder and we or one or more of our subsidiaries could be forced into bankruptcy or liquidation. Any of the foregoing consequences could materially and adversely affect our business, financial condition, results of operations and prospects.
Our senior secured revolving credit facility imposes restrictions on us that may affect our ability to successfully operate our business.
Our senior secured revolving credit facility limits our ability to take various actions, such as:
| • | limitations on the incurrence of additional indebtedness; |
| • | restrictions on investments, capital expenditures, mergers or consolidations, asset dispositions, acquisitions, transactions with affiliates and other transactions without the lenders’ consent; and |
| • | limitation on dividends and distributions. |
In addition, our senior secured revolving credit facility requires us to maintain certain financial ratios and to satisfy certain financial conditions, which may require us to reduce our debt or take some other action in order to comply with them. The failure to comply with any of these financial conditions, several of which become more restrictive over time, such as financial ratios or covenants, would cause an event of default under our senior secured revolving credit facility. An event of default, if not waived, could result in acceleration of the outstanding indebtedness under our senior secured revolving credit facility, in which case the debt would become immediately due and payable. If this occurs, we may not be able to pay our debt or borrow sufficient funds to refinance it. Even if new financing is available, it may not be available on terms that are acceptable to us. These
26
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
restrictions could also limit our ability to obtain future financing, make needed capital expenditures, withstand a downturn in our business or the economy in general, or otherwise conduct necessary corporate activities. We also may be prevented from taking advantage of business opportunities that arise because of the limitations imposed on us by the restrictive covenants under our senior secured revolving credit facility.
Our international operations are subject to political, economic and other uncertainties not encountered in our domestic operations.
As we continue to implement our strategy of expanding into areas outside the United States, our international operations will be subject to political, economic and other uncertainties not generally encountered in our U.S. operations. These will include, among potential others:
| • | risks of war, terrorism, civil unrest and kidnapping of employees; |
| • | expropriation, confiscation or nationalization of our assets; |
| • | renegotiation or nullification of contracts; |
| • | foreign taxation; |
| • | the inability to repatriate earnings or capital due to laws limiting the right and ability of foreign subsidiaries to pay dividends and remit earnings to affiliated companies; |
| • | changing political conditions and changing laws and policies affecting trade and investment; |
| • | concentration of customers; |
| • | regional economic downturns; |
| • | the overlap of different tax structures; |
| • | the burden of complying with multiple and potentially conflicting laws; |
| • | the risks associated with the assertion of foreign sovereignty over areas in which our operations are conducted; |
| • | difficulty in collecting international accounts receivable; and |
| • | potentially longer payment cycles. |
Our international operations are concentrated in Colombia and our drilling contracts are currently with one customer, Ecopetrol. We believe our relationship with Ecopetrol is good; however, the loss of this large customer could have an adverse effect on our business, financial condition and result of operations.
Our international operations may also face the additional risks of fluctuating currency values, hard currency shortages and controls of foreign currency exchange. Additionally, in some jurisdictions, we may be subject to foreign governmental regulations favoring or requiring the awarding of contracts to local contractors or requiring foreign contractors to employ citizens of, or purchase supplies from, a particular jurisdiction. These regulations could adversely affect our ability to compete.
Our operations are subject to various laws and governmental regulations that could restrict our future operations and increase our operating costs.
Many aspects of our operations are subject to various federal, state and local laws and governmental regulations, including laws and regulations governing:
| • | environmental quality; |
| • | pollution control; |
| • | remediation of contamination; |
27
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| • | preservation of natural resources; |
| • | transportation, and |
| • | worker safety. |
Our operations are subject to stringent federal, state and local laws, rules and regulations governing the protection of the environment and human health and safety. Some of those laws, rules and regulations relate to the disposal of hazardous substances, oilfield waste and other waste materials and restrict the types, quantities and concentrations of those substances that can be released into the environment. Several of those laws also require removal and remedial action and other cleanup under certain circumstances, commonly regardless of fault. Our operations routinely involve the handling of significant amounts of waste materials, some of which are classified as hazardous substances. Planning, implementation and maintenance of protective measures are required to prevent accidental discharges. Spills of oil, natural gas liquids, drilling fluids and other substances may subject us to penalties and cleanup requirements. Handling, storage and disposal of both hazardous and non-hazardous wastes are also subject to these regulatory requirements. In addition, our operations are often conducted in or near ecologically sensitive areas, such as wetlands, which are subject to special protective measures and which may expose us to additional operating costs and liabilities for accidental discharges of oil, gas, drilling fluids, contaminated water or other substances, or for noncompliance with other aspects of applicable laws and regulations.
The federal Clean Water Act, as amended by the Oil Pollution Act, the federal Clean Air Act, the federal Resource Conservation and Recovery Act, the federal Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act, or CERCLA, the Safe Drinking Water Act, the Occupational Safety and Health Act, or OSHA, and their state counterparts and similar statutes are the primary statutes that impose the requirements described above and provide for civil, criminal and administrative penalties and other sanctions for violation of their requirements. The OSHA hazard communication standard, the Environmental Protection Agency “community right-to-know” regulations under Title III of the federal Superfund Amendment and Reauthorization Act and comparable state statutes require us to organize and report information about the hazardous materials we use in our operations to employees, state and local government authorities and local citizens. In addition, CERCLA, also known as the “Superfund” law, and similar state statutes impose strict liability, without regard to fault or the legality of the original conduct, on certain classes of persons who are considered responsible for the release or threatened release of hazardous substances into the environment. These persons include the current owner or operator of a facility where a release has occurred, the owner or operator of a facility at the time a release occurred, and companies that disposed of or arranged for the disposal of hazardous substances found at a particular site. This liability may be joint and several. Such liability, which may be imposed for the conduct of others and for conditions others have caused, includes the cost of removal and remedial action as well as damages to natural resources. Few defenses exist to the liability imposed by environmental laws and regulations. It is also common for third parties to file claims for personal injury and property damage caused by substances released into the environment.
Environmental laws and regulations are complex and subject to frequent change. Failure to comply with governmental requirements or inadequate cooperation with governmental authorities could subject a responsible party to administrative, civil or criminal action. We may also be exposed to environmental or other liabilities originating from businesses and assets which we acquired from others. Our compliance with amended, new or more stringent requirements, stricter interpretations of existing requirements or the future discovery of contamination or regulatory noncompliance may require us to make material expenditures or subject us to liabilities that we currently do not anticipate.
There are a variety of regulatory developments, proposals or requirements and legislative initiatives that have been introduced in the United States and international regions in which we operate that are focused on restricting the emission of carbon dioxide, methane and other greenhouse gases. Among these developments are the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change, also known as the “Kyoto Protocol” (an internationally applied protocol, which has been ratified in Columbia, one of our reporting segments), the Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative or “RGGI” in the Northeastern United States, and the Western Regional
28
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Climate Action Initiative in the Western United States, including partners states New Mexico, Utah, and Montana and observer states Colorado and Wyoming.
The U.S. Congress has been actively considering legislation to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases, primarily through the development of greenhouse gas cap and trade programs. In June of 2009, the U.S. House of Representatives passed a cap and trade bill known as the American Clean Energy and Security Act of 2009, which is now being considered by the U.S. Senate, among other alternative bills. In addition, more than one-third of the states already have begun implementing legal measures to reduce emissions of greenhouse gases.
In 2007, the United States Supreme Court in Massachusetts, et al. v. EPA, held that carbon dioxide may be regulated as an “air pollutant” under the federal Clean Air Act. On December 7, 2009, the EPA responded to the Massachusetts, et al. v. EPA decision and issued a finding that the current and projected concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere threaten the public health and welfare of current and future generations, and that certain greenhouse gases from new motor vehicles and motor vehicle engines contribute to the atmospheric concentrations of greenhouse gases and hence to the threat of climate change.
On September 22, 2009, EPA finalized a rule requiring nation-wide reporting of greenhouse gas emissions beginning January 1, 2010. The rule applies primarily to large facilities emitting 25,000 metric tons or more of carbon dioxide-equivalent greenhouse gas emissions per year, and to most upstream suppliers of fossil fuels and industrial greenhouse gas, as well as to manufacturers of vehicles and engines. In addition, EPA recently proposed a rule that would, in general, require facilities that emit more than 25,000 tons per year of greenhouse gas equivalents to obtain permits to demonstrate that best practices and technology are being used to minimize greenhouse gas emissions.
Although it is not possible at this time to predict whether proposed legislation or regulations will be adopted as initially written, if at all, or how legislation or new regulations that may be adopted to address greenhouse gas emissions would impact our business, any such future laws and regulations could result in increased compliance costs or additional operating restrictions. Any additional costs or operating restrictions associated with legislation or regulations regarding greenhouse gas emissions could have a material adverse effect on our operating results and cash flows. In addition, these developments could curtail the demand for fossil fuels such as oil and gas in areas of the world where our customers operate and thus adversely affect demand for our services, which may in turn adversely affect our future results of operations. Finally, we cannot predict with any certainty whether changes to temperature, storm intensity or precipitation patterns as a result of climate change will have a material impact on our operations.
In addition, our business depends on the demand for land drilling and production services from the oil and gas industry and, therefore, is affected by tax, environmental and other laws relating to the oil and gas industry generally, by changes in those laws and by changes in related administrative regulations. It is possible that these laws and regulations may in the future add significantly to our operating costs or those of our customers, or otherwise directly or indirectly affect our operations.
Among the services we provide, we operate as a motor carrier and therefore are subject to regulation by the U.S. Department of Transportation and by various state agencies. These regulatory authorities exercise broad powers, governing activities such as the authorization to engage in motor carrier operations and regulatory safety. There are additional regulations specifically relating to the trucking industry, including testing and specification of equipment and product handling requirements. The trucking industry is subject to possible regulatory and legislative changes that may affect the economics of the industry by requiring changes in operating practices or by changing the demand for common or contract carrier services or the cost of providing truckload services. Some of these possible changes include increasingly stringent environmental regulations, changes in the hours of service regulations which govern the amount of time a driver may drive in any specific period, onboard black box recorder devices or limits on vehicle weight and size.
29
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Interstate motor carrier operations are subject to safety requirements prescribed by the U.S. Department of Transportation. To a large degree, intrastate motor carrier operations are subject to state safety regulations that mirror federal regulations. Such matters as weight and dimension of equipment are also subject to federal and state regulations.
From time to time, various legislative proposals are introduced, including proposals to increase federal, state, or local taxes, including taxes on motor fuels, which may increase our costs or adversely impact the recruitment of drivers. We cannot predict whether, or in what form, any increase in such taxes applicable to us will be enacted.
Risk Relating to Our Capitalization and Organizational Documents
We do not intend to pay dividends on our common stock in the foreseeable future, and therefore only appreciation of the price of our common stock will provide a return to our shareholders.
We have not paid or declared any dividends on our common stock and currently intend to retain any earnings to fund our working capital needs and growth opportunities. Any future dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors after taking into account various factors it deems relevant, including our financial condition and performance, cash needs, income tax consequences and restrictions imposed by the Texas Business Corporation Act and other applicable laws and by our credit facilities. Our debt arrangements include provisions that generally prohibit us from paying dividends on our capital stock, including our common stock.
We may issue preferred stock whose terms could adversely affect the voting power or value of our common stock.
Our articles of incorporation authorize us to issue, without the approval of our shareholders, one or more classes or series of preferred stock having such designations, preferences, limitations and relative rights, including preferences over our common stock respecting dividends and distributions, as our board of directors may determine. The terms of one or more classes or series of preferred stock could adversely impact the voting power or value of our common stock. For example, we might grant holders of preferred stock the right to elect some number of our directors in all events or on the happening of specified events or the right to veto specified transactions. Similarly, the repurchase or redemption rights or liquidation preferences we might assign to holders of preferred stock could affect the residual value of the common stock.
Provisions in our organizational documents could delay or prevent a change in control of our company even if that change would be beneficial to our shareholders.
The existence of some provisions in our organizational documents could delay or prevent a change in control of our company even if that change would be beneficial to our shareholders. Our articles of incorporation and bylaws contain provisions that may make acquiring control of our company difficult, including:
| • | provisions regulating the ability of our shareholders to nominate candidates for election as directors or to bring matters for action at annual meetings of our shareholders; |
| • | limitations on the ability of our shareholders to call a special meeting and act by written consent; |
| • | provisions dividing our board of directors into three classes elected for staggered terms; and |
| • | the authorization given to our board of directors to issue and set the terms of preferred stock. |
We may continue to experience market conditions that could adversely affect the liquidity of our auction rate preferred security investment.
At December 31, 2009, we held $15.9 million (par value) of investments comprised of tax exempt, auction rate preferred securities (“ARPSs”), which are variable-rate preferred securities and have a long-term maturity
30
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
with the interest rate being reset through “Dutch auctions” that are held every 7 days. The ARPSs have historically traded at par because of the frequent interest rate resets and because they are callable at par at the option of the issuer. Interest is paid at the end of each auction period. Our ARPSs are AAA/Aaa rated securities, collateralized by municipal bonds and backed by assets that are equal to or greater than 200% of the liquidation preference. Until February 2008, the auction rate securities market was highly liquid. Beginning mid-February 2008, we experienced several “failed” auctions, meaning that there was not enough demand to sell all of the securities that holders desired to sell at auction. The immediate effect of a failed auction is that such holders cannot sell the securities at auction and the interest rate on the security resets to a maximum auction rate. We have continued to receive interest payments on our ARPSs in accordance with their terms. Unless a future auction is successful or the issuer calls the security pursuant to redemption prior to maturity, we may not be able to access the funds we invested in our ARPSs without a loss of principal. We have no reason to believe that any of the underlying municipal securities that collateralize our ARPSs are presently at risk of default. We believe we will ultimately recover the par value of the ARPSs without loss, primarily due to the collateral securing the ARPSs and our estimate of the discounted cash flows that we expect to collect. We do not currently intend to sell our ARPSs at a loss. Also, we believe it is more-likely-than-not that we will not have to sell our ARPSs prior to recovery, since our liquidity needs are expected to be met with cash flows from operating activities and borrowings under our senior secured revolving credit facility. Our ARPSs are designated as available-for-sale and are reported at fair market value with the related unrealized gains or losses, included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax, a component of shareholders’ equity. The estimated fair value of our ARPSs at December 31, 2009 was $13.2 million compared with a par value of $15.9 million. The $2.7 million difference represents a fair value discount due to the current lack of liquidity which is considered temporary and has been recorded as an unrealized loss, net of tax, in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). There was no portion of the fair value discount attributable to credit losses. We would recognize an impairment charge in our statement of operations if the fair value of our investments falls below the cost basis and is judged to be other-than-temporary. Our ARPSs are classified with other long-term assets on our condensed consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2009 because of our inability to determine the recovery period of our investments.
| Item 1B. | Unresolved Staff Comments |
Not applicable.
| Item 2. | Properties |
For a description of our significant properties, see “Business—Overview of Our Segments and Services” and “Business—Facilities” in Item 1 of this report. We consider each of our significant properties to be suitable for its intended use.
| Item 3. | Legal Proceedings |
Due to the nature of our business, we are, from time to time, involved in routine litigation or subject to disputes or claims related to our business activities, including workers’ compensation claims and employment-related disputes. In the opinion of our management, none of the pending litigation, disputes or claims against us will have a material adverse effect on our financial condition or results of operations.
| Item 4. | Submission of Matters to a Vote of Security Holders |
We did not submit any matter to a vote of our shareholders during the quarter ended December 31, 2009.
31
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Item 5. | Market for Registrant’s Common Equity, Related Shareholder Matters and Issuer Purchases of Equity Securities |
As of February 5, 2010, 54,119,952 shares of our common stock were outstanding, held by 532 shareholders of record. The number of record holders does not necessarily bear any relationship to the number of beneficial owners of our common stock.
Our common stock trades on the NYSE Amex under the symbol “PDC.” The following table sets forth, for each of the periods indicated, the high and low sales prices per share on the NYSE Amex:
| Low | High | |||||
| Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2009: |
||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 3.28 | $ | 6.70 | ||
| Second Quarter |
3.46 | 6.88 | ||||
| Third Quarter |
3.96 | 7.34 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter |
6.00 | 8.16 | ||||
| Fiscal Year Ended December 31, 2008: |
||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 10.59 | $ | 16.70 | ||
| Second Quarter |
15.29 | 20.64 | ||||
| Third Quarter |
12.49 | 18.82 | ||||
| Fourth Quarter |
4.85 | 13.09 | ||||
| Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007: |
||||||
| First Quarter |
$ | 12.69 | $ | 16.00 | ||
| Second Quarter |
11.81 | 14.88 | ||||
| Third Quarter |
11.49 | 12.49 | ||||
The last reported sales price for our common stock on the NYSE Amex on February 5, 2010 was $7.50 per share.
We have not paid or declared any dividends on our common stock and currently intend to retain earnings to fund our working capital needs and growth opportunities. Any future dividends will be at the discretion of our board of directors after taking into account various factors it deems relevant, including our financial condition and performance, cash needs, income tax consequences and the restrictions Texas and other applicable laws and our credit facilities then impose. Our debt arrangements include provisions that generally prohibit us from paying dividends, other than dividends on our preferred stock. We currently have no preferred stock outstanding.
No shares of our common stock were purchased by or on behalf of our company or any affiliated purchaser during the quarter ended December 31, 2009.
32
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Performance Graph
The following graph compares, for the periods from December 31, 2004 to December 31, 2009, the cumulative total shareholder return on our common stock with the cumulative total return on the companies that comprise the AMEX Composite Index and a peer group index that includes five companies that provide contract drilling services and / or production services. The companies that comprise the peer group index are Patterson-UTI Energy, Inc., Nabors Industries Ltd., Bronco Drilling Company, Precision Drilling Trust and Key Energy Services. The comparison assumes that $100 was invested on December 31, 2004 in our common stock, the companies that compose the AMEX Composite Index and the companies that compose the peer group index, and further assumes all dividends were reinvested.
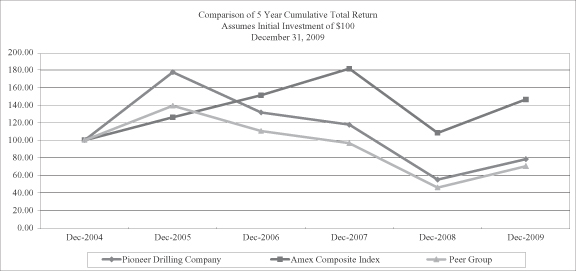
Equity Compensation Plan Information
The following table provides information on our equity compensation plans as of December 31, 2009:
| Plan category |
Number of securities to be issued upon exercise of outstanding options, warrants and rights |
Weighted-average exercise price per share of outstanding options, warrants and rights |
Number of securities remaining available for future issuance under equity compensation plans (1) | ||||
| Equity compensation plans approved by security holders |
5,055,613 | $ | 10.17 | 1,939,807 | |||
| Equity compensation plans not approved by security holders |
— | — | — | ||||
| Total |
5,055,613 | $ | 10.17 | 1,939,807 | |||
| (1) | Includes 514,401 shares that may be issued in the form of restricted stock or restricted stock units under the Amended and Restated Pioneer Drilling Company 2007 Incentive Plan. |
33
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Item 6. | Selected Financial Data |
The following information derives from our audited financial statements. You should review this information in conjunction with “Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations” in Item 7 of this report and the historical financial statements and related notes this report contains. The acquisitions of WEDGE and Competition, effective March 1, 2008, and the change in our fiscal year end, resulting in a nine month fiscal year ended December 31, 2007, affect the comparability from period to period of our historical results.
| Years Ended December 31, |
Nine months Ended December 31, 2007 |
Years Ended March 31, | ||||||||||||||||||
| 2009 (1) | 2008 (1)(2) | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands, except per share amounts) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Statement of Operations Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 325,537 | $ | 610,884 | $ | 313,884 | $ | 416,178 | $ | 284,148 | ||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(31,840 | ) | (43,954 | ) | 55,260 | 126,976 | 77,909 | |||||||||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
(40,172 | ) | (56,688 | ) | 57,774 | 130,789 | 79,813 | |||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) applicable to common stockholders |
(23,215 | ) | (62,745 | ) | 39,645 | 84,180 | 50,567 | |||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per common share-basic |
$ | (0.46 | ) | $ | (1.26 | ) | $ | 0.80 | $ | 1.70 | $ | 1.08 | ||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per common share-diluted |
$ | (0.46 | ) | $ | (1.26 | ) | $ | 0.79 | $ | 1.68 | $ | 1.06 | ||||||||
| Other Financial Data: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
$ | 123,313 | $ | 186,391 | $ | 115,455 | $ | 131,530 | $ | 97,084 | ||||||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(113,909 | ) | (505,615 | ) | (123,858 | ) | (137,960 | ) | (125,217 | ) | ||||||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities |
4,154 | 269,342 | 161 | 201 | 49,634 | |||||||||||||||
| Capital expenditures |
110,453 | 148,096 | 128,038 | 147,230 | 128,871 | |||||||||||||||
| As of December 31, | As of March 31, | ||||||||||||||
| 2009 (1) | 2008 (1) | 2007 | 2007 | 2006 | |||||||||||
| (In thousands) | |||||||||||||||
| Balance Sheet Data: |
|||||||||||||||
| Working capital |
$ | 90,336 | $ | 64,372 | $ | 99,807 | $ | 124,089 | $ | 106,904 | |||||
| Property and equipment, net |
637,022 | 627,562 | 417,022 | 342,901 | 260,783 | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt and capital lease obligations, excluding current installments |
258,073 | 262,115 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity |
421,448 | 414,118 | 471,072 | 428,109 | 340,676 | ||||||||||
| Total assets |
822,616 | 824,479 | 560,212 | 501,495 | 400,678 | ||||||||||
| (1) | The statement of operations data and other financial data for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 and the balance sheet data as of December 31, 2009 and 2008 include the impact of the acquisitions of WEDGE and Competition, both of which occurred on March 1, 2008. See Note 2 to Consolidated Financial Statements, included in Part II, Item 8, Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
| (2) | The statement of operations data and other financial data for the year ended December 31, 2008 reflect the impact of a goodwill impairment charge of $118.6 million and an intangible asset impairment charge of $52.8 million. See Note 1 to Consolidated Financial Statements, included in Part II, Item 8, Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K. |
34
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Item 7. | Management’s Discussion and Analysis of Financial Condition and Results of Operations |
Statements we make in the following discussion that express a belief, expectation or intention, as well as those that are not historical fact, are forward-looking statements that are subject to risks, uncertainties and assumptions. Our actual results, performance or achievements, or industry results, could differ materially from those we express in the following discussion as a result of a variety of factors, including general economic and business conditions and industry trends, the continued strength or weakness of the contract land drilling industry in the geographic areas in which we operate, decisions about onshore exploration and development projects to be made by oil and gas companies, the highly competitive nature of our business, the availability, terms and deployment of capital, the availability of qualified personnel, and changes in, or our failure or inability to comply with, government regulations, including those relating to the environment. We have discussed many of these factors in more detail elsewhere in this report, including under the headings “Special Note Regarding Forward-Looking Statements” in the Introductory Note to Part I and “Risk Factors” in Item 1A. These factors are not necessarily all the important factors that could affect us. Unpredictable or unknown factors we have not discussed in this report could also have material adverse effects on actual results of matters that are the subject of our forward-looking statements. All forward-looking statements speak only as the date on which they are made and we undertake no duty to update or revise any forward-looking statements. We advise our shareholders that they should (1) be aware that important factors not referred to above could affect the accuracy of our forward-looking statements and (2) use caution and common sense when considering our forward-looking statements.
Company Overview
Pioneer Drilling Company provides drilling services and production services to independent and major oil and gas exploration and production companies throughout much of the onshore oil and gas producing regions of the United States and internationally in Colombia. Pioneer Drilling Company was incorporated under the laws of the State of Texas in 1979 as the successor to a business that had been operating since 1968. Our business has grown through acquisitions and through organic growth. Over the last 10 years, we have significantly expanded our drilling rig fleet by adding 35 rigs through acquisitions and by adding 31 rigs through the construction of rigs from new and used components. On March 1, 2008, we significantly expanded our service offerings when we acquired the production services businesses of WEDGE Group Incorporated (“WEDGE”) for $314.7 million and Prairie Investors d/b/a Competition Wireline (“Competition”) for $30.0 million, which provide well services, wireline services and fishing and rental services. We funded the WEDGE acquisition primarily with $311.5 million of borrowings under our senior secured revolving credit facility. As of February 5, 2010, the senior secured revolving credit facility had an outstanding balance of $257.5 million, of which, $1.9 million is due by March 31, 2010 as a mandatory prepayment and the remaining $255.6 million is due by the maturity date on August 31, 2012. Drilling services and production services are fundamental to establishing and maintaining the flow of oil and natural gas throughout the productive life of a well site and enable us to meet multiple needs of our customers.
35
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Business Segments
We currently conduct our operations through two operating segments: our Drilling Services Division and our Production Services Division. The following is a description of these two operating segments. Financial information about our operating segments is included in Note 11, Segment Information, of the Notes to Consolidated Financial Statements, included in Part II, Item 8, Financial Statements and Supplementary Data, of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
| • | Drilling Services Division—Our Drilling Services Division provides contract land drilling services with its fleet of 71 drilling rigs in the following locations: |
| Drilling Division Locations |
Rig Count | |
| South Texas |
15 | |
| East Texas |
19 | |
| North Dakota |
8 | |
| North Texas |
5 | |
| Utah |
5 | |
| Oklahoma |
6 | |
| Appalachia |
5 | |
| Colombia |
8 |
As of February 5, 2010, 34 drilling rigs are operating under drilling contracts. We have 31 drilling rigs that are idle and six drilling rigs have been placed in storage or “cold stacked” in our Oklahoma drilling division due to low demand for drilling rigs in that region. We are actively marketing all our idle drilling rigs both domestically and internationally in Latin America. During the second quarter of 2009, we established our Appalachian drilling division and now have four drilling rigs operating in the Marcellus Shale region. We are currently upgrading a fifth rig that is scheduled to begin operating under a drilling contract in the Marcellus Shale region in late February 2010. We have seven drilling rigs located in Colombia that are operating under drilling contracts, five of which are drilling and two of which have been moved to their initial well site locations and are expected to begin drilling in late February 2010. In March 2010, we plan to export an eighth rig to Colombia that will begin working under a drilling contract. In addition to our drilling rigs, we provide the drilling crews and most of the ancillary equipment needed to operate our drilling rigs. We obtain our contracts for drilling oil and natural gas wells either through competitive bidding or through direct negotiations with customers. Our drilling contracts generally provide for compensation on either a daywork, turnkey or footage basis. Contract terms generally depend on the complexity and risk of operations, the on-site drilling conditions, the type of equipment used and the anticipated duration of the work to be performed.
| • | Production Services Division—Our Production Services Division provides a broad range of well services to oil and gas drilling and producing companies, including workover services, wireline services, and fishing and rental services. Our production services operations are managed regionally and are concentrated in the major United States onshore oil and gas producing regions in the Gulf Coast, Mid-Continent, Rocky Mountain and Appalachian states. We provide our services to a diverse group of oil and gas companies. The primary production services we offer are the following: |
| • | Well Services. Existing and newly-drilled wells require a range of services to establish and maintain production over their useful lives. We use our fleet of 74 workover rigs in eight regional locations to provide these required services, including maintenance of existing wells, workover of existing wells, completion of newly-drilled wells, and plugging and abandonment of wells at the end of their useful lives. We have a premium workover rig fleet consisting of sixty-nine 550 horsepower rigs, four 600 horsepower rigs, and one 400 horsepower rig. As of February 5, 2010, 68 workover rigs have crews assigned and are either operating or are being actively marketed. The remaining six workover rigs in our fleet are idle with no crews assigned. |
36
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| • | Wireline Services. In order for oil and gas companies to better understand the reservoirs they are drilling or producing, they require logging services to accurately characterize reservoir rocks and fluids. When a producing well is completed, they also must perforate the production casing to establish a flow path between the reservoir and the wellbore. We use our fleet of 65 truck mounted wireline units in 19 division locations to provide these important logging and perforating services. We provide both open and cased-hole logging services, including the latest pulsed-neutron technology. In addition, we provide services which allow oil and gas companies to evaluate the integrity of wellbore casing, recover pipe, or install bridge plugs. |
| • | Fishing and Rental Services. During drilling operations, oil and gas companies frequently need to rent unique equipment such as power swivels, foam air units, blow-out preventers, air drilling equipment, pumps, tanks, pipe, tubing, and fishing tools. We have approximately $13 million of fishing and rental tools that we provide out of four locations in Texas and Oklahoma. |
Market Conditions in Our Industry
Since late 2008, there has been substantial volatility and a decline in oil and natural gas prices due to the downturn in the global economic environment. In addition, there has been uncertainty in the capital markets and access to financing has been limited. These conditions have adversely affected our business environment. Our customers have curtailed their drilling programs and reduced their production activities, which has resulted in a decrease in demand for drilling and production services and a reduction in day rates and utilization. In addition, certain of our customers could experience an inability to pay suppliers in the event they are unable to access the capital markets to fund their business operations.
Demand for oilfield services offered by our industry is a function of our customers’ willingness to make operating and capital expenditures to explore for, develop and produce hydrocarbons, which in turn is affected by current and expected levels of oil and natural gas prices. From 2004 through 2008, domestic exploration and production spending increased as oil and natural gas prices increased. In response to the significant decline in oil and natural gas prices and the downturn in the global economic environment in late 2008, exploration and production companies announced cuts in their exploration budgets for 2009. These reductions in oil and gas exploration budgets resulted in a reduction in our rig utilization and revenue rates on new contracts during 2009. We believe exploration and production companies have modestly increased their exploration budgets for 2010 as compared to 2009. Rig utilization and revenue rates are expected to show modest improvements during 2010. In addition, we have experienced a shift to more turnkey drilling contracts from daywork drilling contracts during 2009 and we expect this shift to continue in 2010. For additional information concerning the effects of the volatility in oil and gas prices and uncertainty in capital markets, see Item 1A—“Risk Factors” in Part I of this Annual Report on Form 10-K.
On February 5, 2010, the spot price for West Texas Intermediate crude oil was $71.19, the spot price for Henry Hub natural gas was $5.61 and the Baker Hughes land rig count was 1,280, a 4% decrease from 1,330 on February 6, 2009. The average weekly spot prices of West Texas Intermediate crude oil and Henry Hub natural gas, the average weekly domestic land rig count per the Baker Hughes land rig count, and the average monthly domestic workover rig count for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, the nine months ended December 31, 2007, and years ended March 31, 2007, 2006 and 2005 were:
| Years Ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 |
Years Ended March 31, | ||||||||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | 2007 | 2006 | 2005 | ||||||||||||||
| Oil (West Texas |
||||||||||||||||||
| Intermediate) |
$ | 61.81 | $ | 99.86 | $ | 77.42 | $ | 64.96 | $ | 59.94 | $ | 45.04 | ||||||
| Natural Gas (Henry Hub) |
$ | 3.85 | $ | 8.81 | $ | 6.82 | $ | 6.53 | $ | 9.10 | $ | 5.99 | ||||||
| U.S. Land Rig Count |
1,035 | 1,792 | 1,684 | 1,589 | 1,329 | 1,110 | ||||||||||||
| U.S. Workover Rig Count |
1,735 | 2,514 | 2,394 | 2,376 | 2,271 | 2,087 | ||||||||||||
37
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Increased expenditures for exploration and production activities generally lead to increased demand for our drilling services and production services. Between 2005 and late 2008, rising oil and natural gas prices and the corresponding increase in onshore oil and natural gas exploration and production spending led to expanded drilling and well service activity as reflected by the increases in the U.S. land rig counts and U.S. workover rig counts as noted in the table above. The decline in oil and natural gas prices since late 2008 has led to decreased oil and natural gas exploration and production spending and a corresponding decrease in drilling and well services activities as reflected by the decrease in the U.S. land rig counts and the U.S. workover rig counts as noted in the table above.
Our business is influenced substantially by both operating and capital expenditures by exploration and production companies. Exploration and production spending is generally categorized as either a capital expenditure or operating expenditure.
Capital expenditures by oil and gas companies tend to be relatively sensitive to volatility in oil or natural gas prices because project decisions are tied to a return on investment spanning a number of years. As such, capital expenditure economics often require the use of commodity price forecasts which may prove inaccurate in the amount of time required to plan and execute a capital expenditure project (such as the drilling of a deep well). When commodity prices are depressed for even a short period of time, capital expenditure projects are routinely deferred until prices return to an acceptable level.
In contrast, both mandatory and discretionary operating expenditures are more stable than capital expenditures for exploration. Mandatory operating expenditure projects involve activities that cannot be avoided in the short term, such as regulatory compliance, safety, contractual obligations and certain projects to maintain the well and related infrastructure in operating condition. Discretionary operating expenditure projects may not be critical to the short-term viability of a lease or field, but these projects are less sensitive to commodity price volatility as compared to capital expenditures for exploration. Discretionary operating expenditure work is evaluated according to a simple short-term payout criterion which is far less dependent on commodity price forecasts.
Our business is influenced substantially by both operating and capital expenditures by exploration and production companies. Because existing oil and natural gas wells require ongoing spending to maintain production, expenditures by exploration and production companies for the maintenance of existing wells are relatively stable and predictable. In contrast, capital expenditures by exploration and production companies for exploration and drilling are more directly influenced by current and expected oil and natural gas prices and generally reflect the volatility of commodity prices.
Liquidity and Capital Resources
Sources of Capital Resources
Our principal liquidity requirements have been for working capital needs, capital expenditures and acquisitions. Our principal sources of liquidity consist of: (i) cash and cash equivalents (which equaled $40.4 million as of December 31, 2009); (ii) cash generated from operations; and (iii) the unused portion of our senior secured revolving credit facility, which has borrowing availability of $56.0 million as of February 5, 2010. On February 29, 2008, we entered into a credit agreement with Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. and a syndicate of lenders (the “Initial Credit Agreement”). On October 5, 2009, we entered into a First Amendment to the Initial Credit Agreement (the “Amended Credit Agreement”). There are no limitations on our ability to access the full borrowing availability under the senior secured revolving credit facility other than maintaining compliance with the covenants in the Amended Credit Agreement. Additional information regarding these covenants is provided in the Debt Requirements section below. We presently expect that cash and cash equivalents, cash generated from operations and available borrowings under our senior secured revolving credit facility are adequate to cover our liquidity requirements for at least the next 12 months.
In the future, we may consider equity or debt offerings, as appropriate, to meet our liquidity needs. In July 2009, we filed a shelf registration statement that permits us to sell equity or debt in one or more offerings up to a
38
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
total dollar amount of $300 million. In November 2009, we obtained $24.0 million in net proceeds when we sold 3,820,000 shares of our common stock at $6.75 per share, less underwriters’ commissions, pursuant to a public offering under the shelf registration statement. The remaining availability under the shelf registration statement for equity or debt offerings is $274.2 million as of February 5, 2010. Our prior public offering was in February 2006 when we obtained $61.7 million in proceeds when we sold 3,000,000 shares of our common stock at $20.63 per share, net of underwriters’ commissions.
Our Amended Credit Agreement provides for a senior secured revolving credit facility, with sub-limits for letters of credit and swing-line loans, of up to an aggregate principal amount of $325 million, all of which mature on August 31, 2012. The Amended Credit Agreement contains customary mandatory prepayments in respect of asset dispositions, debt incurrence and equity issuances, and commencing with the fiscal year ending December 31, 2009, if the senior consolidated leverage ratio is greater than 2.50 to 1.00 at the end of any fiscal year, the Amended Credit Agreement requires mandatory prepayments equal to 50% of our excess cash flows. Borrowings and commitments under the Amended Credit Agreement will be reduced concurrently with the application of certain mandatory prepayments by the amount of such mandatory prepayment, but in no event be reduced to less than $200,000,000 as a result of such mandatory prepayments. Our obligations under the Amended Credit Agreement are secured by substantially all of our domestic assets (including equity interests in Pioneer Global Holdings, Inc. and 65% of the outstanding equity interests of any first-tier foreign subsidiaries owned by Pioneer Global Holdings, Inc., but excluding any equity interest in, and any assets of, Pioneer Services Holdings, LLC) and are guaranteed by certain of our domestic subsidiaries, including Pioneer Global Holdings, Inc. Borrowings under the Amended Credit Agreement bear interest, at our option, at the bank prime rate or at the LIBOR rate, plus an applicable per annum margin in each case. The applicable per annum margin is determined based upon our leverage ratio in accordance with a pricing grid in the Amended Credit Agreement. The per annum margin for LIBOR rate borrowings ranges from 3.50% to 6.00% and the per annum margin for bank prime rate borrowings ranges from 2.50% to 5.00%. The LIBOR margin and bank prime rate margin in effect at February 5, 2010 are 3.5% and 2.5%, respectively. A commitment fee is due quarterly based on the average daily unused amount of the commitments of the lenders under the Amended Credit Agreement. In addition, a fronting fee is due for each letter of credit issued and a quarterly letter of credit fee is due based on the average undrawn amount of letters of credit outstanding during such period. Borrowings under the Amended Credit Agreement are available for acquisitions, working capital and other general corporate purposes.
At December 31, 2009, our senior consolidated leverage ratio was greater than 2.5 to 1.00 which resulted in a mandatory prepayment requirement (and corresponding reduction in the commitments under the Amended Credit Agreement) based on 50% of our excess cash flows, as defined in the Amended Credit Agreement, and due within 90 days of year end. We classified this mandatory prepayment of $1.9 million in the current portion of long-term debt as of December 31, 2009. After we pay the mandatory prepayment of $1.9 million, borrowing capacity under the Amended Credit Agreement will be reduced from $325 million to $323.1 million. We may choose to make additional principal payments to reduce the outstanding debt balance prior to maturity on August 31, 2012 when cash and working capital is sufficient.
At February 5, 2010, the borrowing capacity under our senior secured revolving credit facility is reduced by the outstanding balance of $257.5 million, and committed letters of credit of $11.5 million, which results in borrowing availability of $56.0 million. There are no limitations on our ability to access this borrowing capacity other than maintaining compliance with the covenants under the Amended Credit Agreement.
At December 31, 2009, we held $15.9 million (par value) of investments comprised of tax exempt, auction rate preferred securities (“ARPSs”), which are variable-rate preferred securities and have a long-term maturity with the interest rate being reset through “Dutch auctions” that are held every 7 days. The ARPSs have historically traded at par because of the frequent interest rate resets and because they are callable at par at the option of the issuer. Interest is paid at the end of each auction period. Our ARPSs are AAA/Aaa rated securities, collateralized by municipal bonds and backed by assets that are equal to or greater than 200% of the liquidation preference. Until February 2008, the auction rate securities market was highly liquid. Beginning mid-February 2008, we experienced several “failed” auctions, meaning that there was not enough demand to sell all of the
39
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
securities that holders desired to sell at auction. The immediate effect of a failed auction is that such holders cannot sell the securities at auction and the interest rate on the security resets to a maximum auction rate. We have continued to receive interest payments on our ARPSs in accordance with their terms. Unless a future auction is successful or the issuer calls the security pursuant to redemption prior to maturity, we may not be able to access the funds we invested in our ARPSs without a loss of principal. We have no reason to believe that any of the underlying municipal securities that collateralize our ARPSs are presently at risk of default. We believe we will ultimately recover the par value of the ARPSs without loss, primarily due to the collateral securing the ARPSs and our estimate of the discounted cash flows that we expect to collect. We do not currently intend to sell our ARPSs at a loss. Also, we believe it is more-likely-than-not that we will not have to sell our ARPSs prior to recovery, since our liquidity needs are expected to be met with cash flows from operating activities and borrowings under our senior secured revolving credit facility. Our ARPSs are designated as available-for-sale and are reported at fair market value with the related unrealized gains or losses, included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax, a component of shareholders’ equity. The estimated fair value of our ARPSs at December 31, 2009 was $13.2 million compared with a par value of $15.9 million. The $2.7 million difference represents a fair value discount due to the current lack of liquidity which is considered temporary and has been recorded as an unrealized loss, net of tax, in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). There was no portion of the fair value discount attributable to credit losses. We would recognize an impairment charge in our statement of operations if the fair value of our investments falls below the cost basis and is judged to be other-than-temporary. Our ARPSs are classified with other long-term assets on our condensed consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2009 because of our inability to determine the recovery period of our investments.
Uses of Capital Resources
For the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, our primary uses of capital resources were property and equipment additions that consisted of the following (amounts in thousands):
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||
| Drilling Services Division: |
||||||
| Routine |
$ | 13,853 | $ | 17,860 | ||
| Discretionary |
71,088 | 61,034 | ||||
| New-builds and acquisitions |
10,350 | 30,281 | ||||
| Total Drilling Services Division |
95,291 | 109,175 | ||||
| Production Services Division: |
||||||
| Routine |
5,314 | 4,740 | ||||
| Discretionary |
810 | 1,175 | ||||
| New-builds and acquisitions |
9,038 | 33,006 | ||||
| Total Production Services Division |
15,162 | 38,921 | ||||
| $ | 110,453 | $ | 148,096 | |||
We capitalized $0.3 million of interest costs in property and equipment during each of the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008.
We completed the construction of a 2000 horsepower drilling rig that was placed into service in June 2009 and incurred $13.7 million of rig construction costs for this drilling rig during the year ended December 31, 2009. Our Drilling Services Division had significant upgrade projects for seven drilling rigs during the year ended December 31, 2009 in connection with obtaining new drilling contracts in the Marcellus shale region and Colombia. In addition, we added 11 top drives to our drilling rigs during the year ended December 31, 2009. During the year ended December 31, 2008, our Drilling Services Division incurred $28.4 million of rig construction costs related to two new drilling rigs.
40
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Our Production Services Division acquired five wireline units and auxiliary equipment for workover rigs during the year ended December 31, 2009 which is reflected in the new-builds and acquisitions section of the table above. Our Production Services Division incurred $20.2 million acquiring 14 workover rigs and $5.0 million acquiring 10 wireline units during the year ended December 31, 2008.
For the fiscal year ending December 31, 2010, we budgeted capital expenditures of approximately $80.0 million, comprised of newly approved capital expenditures of approximately $61.0 million for our Drilling Services Division and approximately $19.0 million for our Production Services Division. In addition, previously approved capital expenditures from 2009 of approximately $17.1 million will be carried over and incurred in 2010. These 2010 capital expenditures will be made for routine capital expenditures, drilling rig upgrades (including top drives) and fleet additions. We expect to fund these capital expenditures primarily from operating cash flow in excess of our working capital and other normal cash flow requirements.
Working Capital
Our working capital was $90.3 million at December 31, 2009, compared to $64.4 million at December 31, 2008. Our current ratio, which we calculate by dividing our current assets by our current liabilities, was 2.9 at December 31, 2009 compared to 1.8 at December 31, 2008.
Our operations have historically generated cash flows sufficient to at least meet our requirements for debt service and normal capital expenditures. However, during periods when higher percentages of our drilling contracts are turnkey and footage contracts, our short-term working capital needs could increase.
The changes in the components of our working capital were as follows (amounts in thousands):
| December 31, 2009 |
December 31, 2008 |
Change | ||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 40,379 | $ | 26,821 | $ | 13,558 | ||||
| Receivables: |
||||||||||
| Trade, net of allowance for doubtful accounts |
26,648 | 76,176 | (49,528 | ) | ||||||
| Insurance recoveries |
5,107 | 5,951 | (844 | ) | ||||||
| Income taxes |
41,126 | 5,034 | 36,092 | |||||||
| Unbilled receivables |
8,586 | 12,262 | (3,676 | ) | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
5,560 | 6,270 | (710 | ) | ||||||
| Inventory |
5,535 | 3,874 | 1,661 | |||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current |
6,199 | 8,902 | (2,703 | ) | ||||||
| Current assets |
139,140 | 145,290 | (6,150 | ) | ||||||
| Accounts payable |
15,324 | 21,830 | (6,506 | ) | ||||||
| Current portion of long-term debt |
4,041 | 17,298 | (13,257 | ) | ||||||
| Prepaid drilling contracts |
408 | 1,171 | (763 | ) | ||||||
| Accrued expenses: |
||||||||||
| Payroll and related employee costs |
7,740 | 13,592 | (5,852 | ) | ||||||
| Insurance premiums and deductibles |
8,615 | 11,569 | (2,954 | ) | ||||||
| Insurance claims and settlements |
5,042 | 5,951 | (909 | ) | ||||||
| Other |
7,634 | 9,507 | (1,873 | ) | ||||||
| Current liabilities |
48,804 | 80,918 | (32,114 | ) | ||||||
| Working capital |
$ | 90,336 | $ | 64,372 | $ | 25,964 | ||||
The increase in cash and cash equivalents was primarily due to $123.3 million of cash provided by operating activities and $24.0 million in net proceeds from our equity offering in November 2009. The increase in cash and cash equivalents was partially offset by our use of $114.7 million for certain property and equipment expenditures, debt payments of $17.3 million and debt costs of $2.6 million incurred to amend our senior secured revolving credit facility.
41
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
The decreases in our trade receivables and unbilled revenues as of December 31, 2009 as compared to December 31, 2008 were primarily due to the decline in demand for drilling, workover, wireline and fishing and rental services. We experienced a decrease in revenues of $89.5 million, or 52%, for the quarter ended December 31, 2009 as compared to the quarter ended December 31, 2008.
Income taxes receivable increased $36.1 million as of December 31, 2009 as compared to December 31, 2008 primarily due to net operating losses recognized during 2009. We can carry-back our 2009 net operating losses and apply them against taxable income that we recognized in prior years; therefore, we expect to receive a federal income tax refund in 2010 relating to the carry-back of the 2009 net operating losses.
The increase in inventory at December 31, 2009 as compared to December 31, 2008 was primarily due to the expansion of our operations in Colombia from five drilling rigs at December 31, 2008 to seven drilling rigs at December 31, 2009. We maintain inventories of replacement parts and supplies for our drilling rigs operating in Colombia to ensure efficient operations in geographically remote areas.
The decrease in prepaid expenses and other current assets at December 31, 2009 as compared to December 31, 2008 was primarily due to a decrease of $1.6 million in prepaid insurance. We renew and prepay most of our insurance premiums in late October of each year and some in April of each year. Insurance premiums are based on certain types of estimates. For instance, general liability and workers compensation premiums are based on estimated payroll cost for the upcoming year, umbrella insurance premiums are based on estimated revenues for the upcoming year and property insurance is based on estimated fair market values of our property and equipment. Decreases in our prepaid insurance premiums were due to decreases in estimated payroll costs, revenues and fair values of our property and equipment made for our 2009 insurance policies as compared to estimates made for our 2008 insurance policies. In addition, prepaid expenses and other current assets decreased by $0.9 million relating to funds held in a trust account that were distributed to our former Chief Financial Officer on March 3, 2009 in accordance with the terms of the severance agreement.
The decrease in accounts payable at December 31, 2009 as compared to December 31, 2008 was due to the decline in demand for drilling, workover, wireline and fishing and rental services during the quarter ended December 31, 2009 as compared to the quarter ended December 31, 2008, which resulted in decreased purchases from vendors. Our operating costs decreased $40.7 million, or 42%, for the quarter ended December 31, 2009 as compared to the quarter ended December 31, 2008.
The outstanding balance under our senior secured revolving credit facility is not due until maturity on August 31, 2012. However, when cash and working capital are sufficient, we may make principal payments to reduce the outstanding debt balance prior to maturity. The current portion of long-term debt at December 31, 2008 included principal payments of $15 million that were made after December 31, 2008 to reduce the outstanding balance of our senior secured revolving credit facility. At December 31, 2009, our senior consolidated leverage ratio was greater than 2.5 to 1.00 which resulted in a mandatory prepayment requirement based on 50% of our excess cash flows, as defined in the Amended Credit Agreement, and due within 90 days of year end. Therefore, we classified this mandatory prepayment of $1.9 million in the current portion of long-term debt as of December 31, 2009. The remaining current portion of long-term debt at December 31, 2009 relates to $2.1 million of debt payments under our subordinated notes payable and other debt that are due within the next year.
The decrease in accrued expenses—payroll and related employee costs was primarily due to a decrease of $2.8 million in accrued employee bonuses and a decrease of $2.6 million in accrued payroll and as of December 31, 2009 as compared to December 31, 2008. The decrease in employee bonuses is primarily related to the overall decrease in operating results for 2009 as compared to 2008. Annual employee bonuses that are accrued at year end are paid in late February or early March. The decrease in accrued payroll is primarily due to workforce reductions that occurred during the year ended December 31, 2009.
42
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
The decrease in accrued expenses—insurance premiums and deductibles at December 31, 2009 as compared to December 31, 2008 is due to the declines in our drilling services and production services utilization and the resulting reduced workforce during the quarter ended December 31, 2009 as compared to the quarter ended December 31, 2008. The reduction in our workforce led to fewer workers compensation claims which reduced our obligations for the deductibles under these insurance policies.
The decrease in other accrued expenses at December 31, 2009 as compared to December 31, 2008 is primarily due to a decrease in accrued property taxes that resulted from reductions in the tax values of certain property and equipment for 2009 as compared to 2008.
Long-term Debt
Long-term debt as of December 31, 2009 consists of the following (amounts in thousands):
| Senior secured credit revolving facility |
$ | 257,500 | ||
| Subordinated notes payable |
4,387 | |||
| Other |
227 | |||
| 262,114 | ||||
| Less current portion |
(4,041 | ) | ||
| $ | 258,073 | |||
Contractual Obligations
The following table includes all our contractual obligations at December 31, 2009 (amounts in thousands):
| Payments Due by Period | |||||||||||||||
| Contractual Obligations |
Total | Less than 1 year |
2-3 years | 4-5 years | More than 5 years | ||||||||||
| Long-term debt |
$ | 262,114 | $ | 4,041 | $ | 257,423 | $ | 650 | $ | — | |||||
| Interest on long term debt |
26,132 | 9,931 | 16,179 | 22 | — | ||||||||||
| Purchase commitments |
30,667 | 30,667 | — | — | — | ||||||||||
| Operating leases |
6,003 | 2,119 | 2,723 | 1,161 | — | ||||||||||
| Restricted cash obligation |
2,600 | 650 | 1,300 | 650 | — | ||||||||||
| Total |
$ | 327,516 | $ | 47,408 | $ | 277,625 | $ | 2,483 | $ | — | |||||
Long-term debt consists of $257.5 million outstanding under our senior secured revolving credit facility, $4.4 million outstanding under subordinated notes payable to certain employees that are former shareholders of previously acquired production services businesses and other debt of $0.2 million. The outstanding balance under our senior secured revolving credit facility is not due until maturity on August 31, 2012; however, mandatory prepayments could be required by the Amended Credit Agreement in certain situations. At December 31, 2009, our senior consolidated leverage ratio was greater than 2.5 to 1.00 which resulted in a mandatory prepayment requirement that is based on 50% of our excess cash flows, as defined in the Amended Credit Agreement, and due within 90 days of year end. We classified this mandatory prepayment of $1.9 million in the current portion of long-term debt as of December 31, 2009. We may choose to make additional principal payments to reduce the outstanding debt balance prior to maturity on August 31, 2012 when cash and working capital is sufficient. The remaining current portion of long-term debt at December 31, 2009 relates to $2.1 million of debt payments under our subordinated notes payable and other debt that are due within the next year.
Interest payment obligations on our senior secured revolving credit facility are estimated based on (1) interest rates that are in effect on February 5, 2010, (2) $1.9 million of mandatory prepayments that will be made within 90 days of December 31, 2009 and (3) the remaining principal balance of $255.6 million to be paid
43
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
at maturity in August 2012. Interest payment obligations on our subordinated notes payable are based on interest rates ranging from 5.4% to 14%, with quarterly payments of principal and interest and final maturity dates ranging from January 2010 to March 2013.
Purchase commitments primarily relate to drilling rig and workover rig upgrades, acquisitions or new construction.
Operating leases consist of lease agreements with terms in excess of one year for office space, operating facilities, equipment and personal property.
As of December 31, 2009, we had restricted cash in the amount of $2.6 million held in an escrow account to be used for future payments in connection with the acquisition of Competition. The former owner of Competition will receive annual installments of $0.7 million payable over a five year term from the escrow account.
Debt Requirements
The financial covenants contained in our Amended Credit Agreement include the following:
| • | A maximum total consolidated leverage ratio that cannot exceed: |
| • | 4.25 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2009; |
| • | 5.00 to 1.00 as of the end of any fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2010 through June 30, 2011; |
| • | 4.75 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending September 30, 2011; |
| • | 4.50 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2011; |
| • | 4.25 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2012; and |
| • | 4.00 to 1.00 as of the end of any fiscal quarter ending June 30, 2012 and thereafter. |
| • | A maximum senior consolidated leverage ratio, which excludes unsecured and subordinated debt, that cannot exceed: |
| • | 4.25 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2009; |
| • | 5.00 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarters ending March 31, 2010 and June 30, 2010; |
| • | 4.75 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending September 30, 2010; |
| • | 4.50 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2010; |
| • | 4.25 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2011; |
| • | 4.00 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending June 30, 2011; |
| • | 3.75 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending September 30, 2011; |
| • | 3.50 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2011; |
| • | 3.25 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2012; and |
| • | 3.00 to 1.00 as of the end of any fiscal quarter ended June 30, 2012 and thereafter. |
| • | A minimum interest coverage ratio that cannot be less than: |
| • | 3.00 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2009; |
| • | 2.00 to 1.00 as of the end of any fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2010 through December 31, 2011; and |
| • | 3.00 to 1.00 as of the end of any fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2012 and thereafter. |
44
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| • | If our senior consolidated leverage ratio is greater than 2.25 to 1.00 at the end of any fiscal quarter, a minimum asset coverage ratio that cannot be less than 1.00 to 1.00 for any fiscal quarter ending on or before December 31, 2011, and 1.10 to 1.00 for any fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2012 and thereafter (as provided in the Amended Credit Agreement). If our senior consolidated leverage ratio is greater than 2.25 to 1.00 and our asset coverage ratio is less than 1.00 to 1.00, then borrowings outstanding under the Amended Credit Agreement will be limited to the sum of 80% of eligible accounts receivable, 80% of the orderly liquidation value of eligible equipment and 40% of the net book value of certain other fixed assets. |
The Amended Credit Agreement restricts capital expenditures unless (a) after giving effect to such capital expenditure, no event of default would exist under the Amended Credit Agreement and availability under the Amended Credit Agreement would be equal to or greater than $25 million and (b) if the senior consolidated leverage ratio as of the last day of the most recent reported fiscal quarter was equal to or greater than 2.50 to 1.00, such capital expenditure would not cause the sum of all capital expenditures to exceed:
| • | $52 million for the second half of fiscal year 2009; |
| • | $65 million for fiscal year 2010; and |
| • | $80 million for each fiscal year thereafter. |
The capital expenditure thresholds for each period noted above may be increased by:
| • | the first $25 million of any aggregate equity issuance proceeds received during such period and 25% of any equity issuance proceeds received in excess of $25 million during such period; and |
| • | 25% of any debt incurrence proceeds received during such period. |
In addition, any unused portion of the capital expenditure threshold up to $30 million can be carried over from the immediate preceding fiscal year.
At December 31, 2009, we were in compliance with our financial covenants. Our total consolidated leverage ratio was 3.3 to 1.0, our senior consolidated leverage ratio was 3.3 to 1.0, our interest coverage ratio was 9.0 to 1.0 and our asset coverage ratio was 1.6 to 1.0. The Amended Credit Agreement has additional restrictive covenants that, among other things, limit the incurrence of additional debt, investments, liens, dividends, acquisitions, redemptions of capital stock, prepayments of indebtedness, asset dispositions, mergers and consolidations, transactions with affiliates, hedging contracts, sale leasebacks and other matters customarily restricted in such agreements. In addition, the Amended Credit Agreement contains customary events of default, including without limitation, payment defaults, breaches of representations and warranties, covenant defaults, cross-defaults to certain other material indebtedness in excess of specified amounts, certain events of bankruptcy and insolvency, judgment defaults in excess of specified amounts, failure of any guaranty or security document supporting the credit agreement and change of control.
Critical Accounting Policies and Estimates
Revenue and cost recognition—Our Drilling Services Division earns revenues by drilling oil and gas wells for our customers under daywork, turnkey or footage contracts, which usually provide for the drilling of a single well. We recognize revenues on daywork contracts for the days completed based on the dayrate each contract specifies. We recognize revenues from our turnkey and footage contracts on the percentage-of-completion method based on our estimate of the number of days to complete each contract. Individual contracts are usually completed in less than 60 days. The risks to us under a turnkey contract and, to a lesser extent, under footage contracts, are substantially greater than on a contract drilled on a daywork basis. Under a turnkey contract, we assume most of the risks associated with drilling operations that are generally assumed by the operator in a
45
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
daywork contract, including the risks of blowout, loss of hole, stuck drill pipe, machinery breakdowns and abnormal drilling conditions, as well as risks associated with subcontractors’ services, supplies, cost escalations and personnel operations.
Our management has determined that it is appropriate to use the percentage-of-completion method, as defined in the Financial Accounting Standards Board (FASB) Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) Topic 605 (formerly American Institute of Certified Public Accountants’ Statement of Position 81-1), to recognize revenue on our turnkey and footage contracts. Although our turnkey and footage contracts do not have express terms that provide us with rights to receive payment for the work that we perform prior to drilling wells to the agreed-on depth, we use this method because, as provided in applicable accounting literature, we believe we achieve a continuous sale for our work-in-progress and believe, under applicable state law, we ultimately could recover the fair value of our work-in-progress even in the event we were unable to drill to the agreed-on depth in breach of the applicable contract. However, in the event we were unable to drill to the agreed-on depth in breach of the contract, ultimate recovery of that value would be subject to negotiations with the customer and the possibility of litigation.
If a customer defaults on its payment obligation to us under a turnkey or footage contract, we would need to rely on applicable law to enforce our lien rights, because our turnkey and footage contracts do not expressly grant to us a security interest in the work we have completed under the contract and we have no ownership rights in the work-in-progress or completed drilling work, except any rights arising under the applicable lien statute on foreclosure. If we were unable to drill to the agreed-on depth in breach of the contract, we also would need to rely on equitable remedies outside of the contract, including quantum meruit, available in applicable courts to recover the fair value of our work-in-progress under a turnkey or footage contract.
We accrue estimated contract costs on turnkey and footage contracts for each day of work completed based on our estimate of the total costs to complete the contract divided by our estimate of the number of days to complete the contract. Contract costs include labor, materials, supplies, repairs and maintenance, operating overhead allocations and allocations of depreciation and amortization expense. In addition, the occurrence of uninsured or under-insured losses or operating cost overruns on our turnkey and footage contracts could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations. Therefore, our actual results for a contract could differ significantly if our cost estimates for that contract are later revised from our original cost estimates for a contract in progress at the end of a reporting period which was not completed prior to the release of our financial statements.
With most drilling contracts, we receive payments contractually designated for the mobilization of rigs and other equipment. Payments received, and costs incurred for the mobilization services are deferred and recognized on a straight line basis over the contract term of certain drilling contracts. Costs incurred to relocate rigs and other drilling equipment to areas in which a contract has not been secured are expensed as incurred. Reimbursements that we receive for out-of-pocket expenses are recorded as revenue and the out-of-pocket expenses for which they relate are recorded as operating costs.
The asset “unbilled receivables” represents revenues we have recognized in excess of amounts billed on drilling contracts and production services in progress. The assets “prepaid expenses and other current assets” and “other long-term assets” include the current and long-term portions of deferred mobilization costs for certain drilling contracts. The liabilities “prepaid drilling contracts” and “other long-term liabilities” include the current and long-term portions of deferred mobilization revenues for certain drilling contracts and amounts collected on contracts in excess of revenues recognized.
Our Production Services Division earns revenues for well services, wireline services and fishing and rental services pursuant to master services agreements based on purchase orders, contracts or other persuasive evidence of an arrangement with the customer that include fixed or determinable prices. Production service revenue is recognized when the service has been rendered and collectability is reasonably assured.
46
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Long-lived Assets and Intangible Assets—We evaluate for potential impairment of long-lived assets and intangible assets subject to amortization when indicators of impairment are present, as defined in ASC Topic 360 (formerly SFAS No. 144). Circumstances that could indicate a potential impairment include significant adverse changes in industry trends, economic climate, legal factors, and an adverse action or assessment by a regulator. More specifically, significant adverse changes in industry trends include significant declines in revenue rates, utilization rates, oil and natural gas market prices and industry rig counts for drilling rigs and workover rigs. In performing the impairment evaluation, we estimate the future undiscounted net cash flows relating to long-lived assets and intangible assets grouped at the lowest level that cash flows can be identified. For our Production Services Division, our long-lived assets and intangible assets are grouped at the reporting unit level which is one level below the operating segment level. For our Drilling Services Division, we perform an impairment evaluation and estimate future undiscounted cash flows for individual drilling rig assets. If the sum of the estimated future undiscounted net cash flows is less than the carrying amount of the long-lived assets and intangible assets for these asset grouping levels, then we would recognize an impairment charge. The amount of an impairment charge would be measured as the difference between the carrying amount and the fair value of these assets. The assumptions used in the impairment evaluation for long-lived assets and intangible assets are inherently uncertain and require management judgment.
We performed an impairment analysis of our long-lived assets and intangible assets at December 31, 2008, due to significant adverse changes in the economic and business climate that resulted in decreases in estimated revenues, margins and cash flows. Essentially all our intangible assets were recorded in connection with the acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE, Competition, Pettus and Paltec when revenues, margins and cash flows were at historically high levels in early 2008. We determined that the sum of the estimated future undiscounted net cash flows was less than the carrying amount of the long-lived assets and intangible assets in each reporting unit at December 31, 2008. Our long-lived asset and intangible asset impairment analysis for the reporting units in our Production Services Division resulted in no impairment charge to property and equipment and a non-cash impairment charge of $52.8 million to the carrying value of our intangible assets for customers relationships for the year ended December 31, 2008. This impairment charge did not have an impact on our liquidity or debt covenants; however, it was a reflection of the overall downturn in our industry and decline in our projected cash flows. We did not record an impairment charge on any long-lived assets for our Production Services Division for the year ended December 31, 2009. For our Drilling Services Division, we did not record an impairment charge on any long-lived assets for the years ended December 31, 2009 or 2008. The assumptions used in the impairment evaluation for long-lived assets and intangible assets are inherently uncertain and require management judgment.
Goodwill—Goodwill results from business acquisitions and represents the excess of acquisition costs over the fair value of the net assets acquired. We account for goodwill and other intangible assets under the provisions of ASC Topic 350 (formerly SFAS No. 142), Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets. Goodwill is tested for impairment annually as of December 31 or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. Circumstances that could indicate a potential impairment include a significant adverse change in the economic or business climate, a significant adverse change in legal factors, an adverse action or assessment by a regulator, unanticipated competition, loss of key personnel and the likelihood that a reporting unit or significant portion of a reporting unit will be sold or otherwise disposed of. These circumstances could lead to our net book value exceeding our market capitalization which is another indicator of a potential impairment in goodwill. ASC Topic 350 requires a two-step process for testing impairment. First, the fair value of each reporting unit is compared to its carrying value to determine whether an indication of impairment exists. Second, if impairment is indicated, then the fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill is determined by allocating the unit’s fair value to its assets and liabilities (including any unrecognized intangible assets) as if the reporting unit had been acquired in a business combination on the impairment test date. The amount of impairment for goodwill is measured as the excess of the carrying value of the reporting unit over its fair value. Goodwill of $118.6 million was initially recorded in connection with the acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE, Competition, Pettus and Paltec, all of which occurred between March 1, 2008 and October 1, 2008, and was allocated to the three reporting units for our Production Services Division which are well services,
47
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
wireline services and fishing and rental services. We recorded a full impairment of this goodwill during the year ended December 31, 2008 as further described below.
When estimating fair values of a reporting unit for our goodwill impairment test, we use a combination of an income approach and a market approach which incorporates both management’s views and those of the market. The income approach provides an estimated fair value based on each reporting unit’s anticipated cash flows that are discounted using a weighted average cost of capital rate. The market approach provides an estimated fair value based on our market capitalization that was computed using the prior 30-day average market price of our common stock and the number of shares outstanding as of the impairment test date. The estimated fair values computed using the income approach and the market approach were then equally weighted and combined into a single fair value. The primary assumptions used in the income approach were estimated cash flows and weighted average cost of capital. Estimated cash flows were primarily based on projected revenues, operating costs and capital expenditures and are discounted based on comparable industry average rates for weighted average cost of capital. We utilized discount rates based on weighted average cost of capital ranging from 15.8% to 16.7% when we estimated fair values of our reporting units as of December 31, 2008. The primary assumptions used in the market approach were the allocation of total market capitalization to each reporting unit, which was based on projected EBITDA percentages for each reporting unit, and control premiums, which were based on comparable industry averages. We utilized a 30% control premium when we estimated fair values of our reporting units as of December 31, 2008. To ensure the reasonableness of the estimated fair values of our reporting units, we performed a reconciliation of our total market capitalization to the total estimated fair value of all our reporting units. The assumptions used in estimating fair values of reporting units and performing the goodwill impairment test are inherently uncertain and required management judgment.
Our common stock price per share declined in market value from $13.30 at September 30, 2008, to $5.57 at December 31, 2008, which resulted in our net book value exceeding our market capitalization during most of that time period. We concluded that the decline in the market price of our common stock resulted from a significant adverse change in the economic and business climate as financial markets reacted to the credit crisis facing major lending institutions and worsening conditions in the overall economy during the fourth quarter of the year ended December 31, 2008. During the same time, there were significant declines in oil and natural gas prices which led to declines in production service revenues, margins and cash flows. We considered the impact of these significant adverse changes in the economic and business climate as we performed our annual impairment assessment of goodwill as of December 31, 2008. The estimated fair values of our reporting units were negatively impacted by significant reductions in estimated cash flows for the income approach component and a significant reduction in our market capitalization for the market approach component of our fair value estimation process. Our goodwill was initially recorded in connection with the acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE, Competition, Pettus and Paltec, all of which occurred between March 1, 2008 and October 1, 2008, when production service revenues, margins and cash flows and our market capitalization were at historically high levels.
Our goodwill impairment analysis led us to conclude that there would be no remaining implied fair value attributable to our goodwill and, accordingly, we recorded a non-cash charge of $118.6 million to our operating results for the year ended December 31, 2008, for the full impairment of our goodwill. Our goodwill impairment analysis would have led to the same full impairment conclusion if we increased or decreased our discount rates or control premiums by 10% when estimating the fair values of our reporting units. This impairment charge did not have an impact on our liquidity or debt covenants; however, it was a reflection of the overall downturn in our industry and decline in our projected cash flows.
We had no goodwill additions during the year ended December 31, 2009, and consequently, have no goodwill reflected on our consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2009.
Deferred taxes—We provide deferred taxes for the basis differences in our property and equipment between financial reporting and tax reporting purposes and other costs such as compensation, foreign net operating loss carryforwards, employee benefit and other accrued liabilities which are deducted in different periods for financial
48
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
reporting and tax reporting purposes. For property and equipment, basis differences arise from differences in depreciation periods and methods and the value of assets acquired in a business acquisition where we acquire an entity rather than just its assets. For financial reporting purposes, we depreciate the various components of our drilling rigs, workover rigs and wireline units over 2 to 25 years and refurbishments over 3 to 5 years, while federal income tax rules require that we depreciate drilling rigs, workover rigs, wireline units and refurbishments over 5 years. Therefore, in the first 5 years of our ownership of a drilling rig, workover rig or wireline unit, our tax depreciation exceeds our financial reporting depreciation, resulting in our providing deferred taxes on this depreciation difference. After 5 years, financial reporting depreciation exceeds tax depreciation, and the deferred tax liability begins to reverse.
Accounting estimates—We consider the recognition of revenues and costs on turnkey and footage contracts to be critical accounting estimates. On these types of contracts, we are required to estimate the number of days needed for us to complete the contract and our total cost to complete the contract. Our actual costs could substantially exceed our estimated costs if we encounter problems such as lost circulation, stuck drill pipe or an underground blowout on contracts still in progress subsequent to the release of the financial statements. We receive payment under turnkey and footage contracts when we deliver to our customer a well completed to the depth specified in the contract, unless the customer authorizes us to drill to a more shallow depth. Since 1995, we have completed all our turnkey or footage contracts. Although our initial cost estimates for turnkey and footage contracts do not include cost estimates for risks such as stuck drill pipe or loss of circulation, we believe that our experienced management team, our knowledge of geologic formations in our areas of operations, the condition of our drilling equipment and our experienced crews have previously enabled us to make reasonable cost estimates and complete contracts according to our drilling plan. While we do bear the risk of loss for cost overruns and other events that are not specifically provided for in our initial cost estimates, our pricing of turnkey and footage contracts takes such risks into consideration. When we encounter, during the course of our drilling operations, conditions unforeseen in the preparation of our original cost estimate, we increase our cost estimate to complete the contract. If we anticipate a loss on a contract in progress at the end of a reporting period due to a change in our cost estimate, we accrue the entire amount of the estimated loss, including all costs that are included in our revised estimated cost to complete that contract, in our consolidated statement of operations for that reporting period. During the year ended December 31, 2009, we did not experience a loss on any turnkey and footage contracts completed. We are more likely to encounter losses on turnkey and footage contracts in periods in which revenue rates are lower for all types of contracts. During periods of reduced demand for drilling rigs, our overall profitability on turnkey and footage contracts has historically exceeded our profitability on daywork contracts.
Revenues and costs during a reporting period could be affected for contracts in progress at the end of a reporting period which have not been completed before our financial statements for that period are released. We had 2 turnkey and no footage contracts in progress at December 31, 2009. Our unbilled receivables totaled $8.6 million at December 31, 2009. Of that amount accrued, turnkey drilling contract revenues were $2.0 million. The remaining balance of unbilled receivables related to $6.2 million of the revenue recognized but not yet billed on daywork drilling contracts in progress at December 31, 2009 and $0.4 million related to unbilled receivables for our Production Services Division.
We estimate an allowance for doubtful accounts based on the creditworthiness of our customers as well as general economic conditions. We evaluate the creditworthiness of our customers based on commercial credit reports, trade references, bank references, financial information, production information and any past experience we have with the customer. Consequently, any change in those factors could affect our estimate of our allowance for doubtful accounts. In some instances, we require new customers to establish escrow accounts or make prepayments. We typically invoice our customers at 15-day intervals during the performance of daywork contracts and upon completion of the daywork contract. Turnkey and footage contracts are invoiced upon completion of the contract. Our typical contract provides for payment of invoices in 10 to 30 days. We generally do not extend payment terms beyond 30 days and have not extended payment terms beyond 90 days for any of our contracts in the last three fiscal years. We had an allowance for doubtful accounts of $0.3 million at December 31, 2009 and $1.6 million at December 31, 2008.
49
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Our determination of the useful lives of our depreciable assets, which directly affects our determination of depreciation expense and deferred taxes is also a critical accounting estimate. A decrease in the useful life of our property and equipment would increase depreciation expense and reduce deferred taxes. We provide for depreciation of our drilling, production, transportation and other equipment on a straight-line method over useful lives that we have estimated and that range from 2 to 25 years. We record the same depreciation expense whether a drilling rig, workover rig or wireline unit is idle or working. Our estimates of the useful lives of our drilling, production, transportation and other equipment are based on our more than 35 years of experience in the oilfield services industry with similar equipment.
As of December 31, 2009, we had foreign deferred tax assets consisting of foreign net operating losses and other tax benefits available to reduce future taxable income in a foreign jurisdiction. The foreign net operating loss is primarily due to the special income tax benefits permitted by the Colombian government that allows us to recover 140% of the cost of certain imported assets. In assessing the realizability of our foreign deferred tax assets, we only recognize a tax benefit to the extent of taxable income that we expect to earn in the foreign jurisdiction in future periods. With the downturn in the industry in late 2008, we recorded a valuation allowance of $5.4 million that fully offset our foreign deferred tax asset at December 31, 2008. In January 2010, we finalized drilling contracts for six drilling rigs located in Colombia that each have a three-year term. We estimate that these drilling contracts will result in taxable income in Colombia in excess of our foreign net operating losses. We expect to apply the foreign net operating losses against the current year taxable income and taxable income that we have estimated in these future periods. Therefore, we removed the valuation allowance that fully offset our foreign deferred tax assets which resulted in a tax benefit of $5.4 million that we recognized in the year ended December 31, 2009.
Our accrued insurance premiums and deductibles as of December 31, 2009 include accruals for costs incurred under the self-insurance portion of our health insurance of approximately $1.0 million and our workers’ compensation, general liability and auto liability insurance of approximately $7.0 million. We have a deductible of $125,000 per covered individual per year under the health insurance. We have a deductible of $500,000 per occurrence under our workers’ compensation insurance, except in North Dakota, where we have a $100,000 deductible. We have deductibles of $250,000 and $100,000 per occurrence under our general liability insurance and auto liability insurance, respectively. We accrue for these costs as claims are incurred based on historical claim development data, and we accrue the costs of administrative services associated with claims processing. We also evaluate our workers’ compensation claim cost estimates based on estimates provided by a professional actuary.
50
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Results of Operations
Effective March 1, 2008, we acquired the production services businesses of WEDGE and Competition which provide well services, wireline services and fishing and rental services. These acquisitions resulted in the formation of our new operating segment, the Production Services Division. We consolidated the results of these acquisitions from the day they were acquired. These acquisitions affect the comparability from period to period of our historical results, and our historical results may not be indicative of our future results.
Statements of Operations Analysis—Year Ended December 31, 2009 Compared with the Year Ended December 31, 2008
The following table provides information about our operations for the years ended December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 (amounts in thousands, except average number of drilling rigs, utilization rate and revenue day information).
| Years ended December 31, |
||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
| Drilling Services Division: |
||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 219,751 | $ | 456,890 | ||||
| Operating costs |
147,343 | 269,846 | ||||||
| Drilling Services Division margin |
$ | 72,408 | $ | 187,044 | ||||
| Average number of drilling rigs |
70.7 | 67.4 | ||||||
| Utilization rate |
41 | % | 89 | % | ||||
| Revenue days |
10,491 | 22,057 | ||||||
| Average revenues per day |
$ | 20,947 | $ | 20,714 | ||||
| Average operating costs per day |
14,045 | 12,234 | ||||||
| Drilling Services Division margin per day |
$ | 6,902 | $ | 8,480 | ||||
| Production Services Division: |
||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 105,786 | $ | 153,994 | ||||
| Operating costs |
68,012 | 80,097 | ||||||
| Production Services Division margin |
$ | 37,774 | $ | 73,897 | ||||
| Combined: |
||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 325,537 | $ | 610,884 | ||||
| Operating costs |
215,355 | 349,943 | ||||||
| Combined margin |
$ | 110,182 | $ | 260,941 | ||||
| EBITDA |
$ | 74,942 | $ | 214,766 | ||||
51
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
We present Drilling Services Division margin, Production Services Division margin, combined margin and earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, amortization and impairments (EBITDA) information because we believe it provides investors and our management additional information to assist them in assessing our business and performance in comparison to other companies in our industry. Since Drilling Services Division margin, Production Services Division margin, combined margin and EBITDA are “non-GAAP” financial measures under the rules and regulations of the SEC, we are providing the following reconciliation of combined margin and EBITDA to net (loss) earnings, which is the nearest comparable GAAP financial measure.
| Year ended December 31, |
||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||
| (amounts in thousands) | ||||||||
| Reconciliation of combined margin and |
||||||||
| Combined margin |
110,182 | 260,941 | ||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
(37,478 | ) | (44,834 | ) | ||||
| Bad debt recovery (expense) |
1,642 | (423 | ) | |||||
| Other income (expense) |
596 | (918 | ) | |||||
| EBITDA |
74,942 | 214,766 | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
(106,186 | ) | (88,145 | ) | ||||
| Impairment of goodwill |
— | (118,646 | ) | |||||
| Impairment of intangible assets |
— | (52,847 | ) | |||||
| Interest income (expense), net |
(8,928 | ) | (11,816 | ) | ||||
| Income tax benefit (expense) |
16,957 | (6,057 | ) | |||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
$ | (23,215 | ) | $ | (62,745 | ) | ||
Our Drilling Services Division’s revenues decreased by $237.1 million, or 52%, for the year ended December 31, 2009 as compared to the corresponding period in 2008, due to a 52% decrease in revenue days that resulted from a decline in our rig utilization rate from 89% to 41%. In contrast to the decrease in our Drilling Services Division’s revenues, our average contract drilling revenues per day increased by $233, or 1%. This increase in average drilling revenues per day is attributable to higher average drilling revenues per day for our Colombian operations which represented a larger portion of our drilling revenues for 2009 as compared to 2008. Our average drilling revenues per day for our domestic operations decreased by 8% for the year ended December 31, 2009, since the demand for drilling rigs decreased during 2009 as compared to 2008. The decrease in our average drilling revenues per day for our domestic operations is less than expected because a significant portion of our domestic drilling rigs were operating or were on standby under longer-term drilling contracts that were entered into when drilling rig demand was high and revenues per day were at historically high levels.
Demand for drilling rigs influences the types of drilling contracts we are able to obtain. As demand for drilling rigs decreases, daywork rates move down and we may switch to performing more turnkey drilling contracts to maintain higher utilization rates and improve our Drilling Services Division’s margins. We completed 14 turnkey drilling contracts during the year ended December 31, 2009 as compared to 10 turnkey drilling contracts completed during the year ended December 31, 2008. The following table provides percentages of our drilling revenues by drilling contract type for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008:
| Years ended December 31, |
||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||
| Daywork Contracts |
90 | % | 93 | % | ||
| Turnkey Contracts |
10 | % | 2 | % | ||
| Footage Contracts |
— | 5 | % | |||
52
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Our Drilling Services Division’s operating costs declined by $122.5 million, or 45%, for the year ended December 31, 2009 as compared to the corresponding period in 2008, primarily due to a 52% decrease in revenue days that resulted from a decline in our rig utilization rate from 89% to 41%. In contrast to the decrease in our Drilling Services Division’s operating costs, our average operating costs per day increased by $1,811, or 15%, primarily due to higher average drilling costs per day for our Colombian operations which represented a larger portion of our drilling costs for 2009 as compared to 2008. In addition, average operating costs per day increased due to a shift to more turnkey contracts and fixed overhead costs associated with division offices, supervisory level employees, insurance and property taxes. Since we had a significant decrease in revenue days, these fixed overhead costs result in an increase in average operating costs per revenue day.
For the year ended December 31, 2009, our Production Services Division’s revenue decreased by $48.2 million, or 31%, while operating costs decreased by $12.1 million, or 15%, as compared to the corresponding period in 2008. Our Production Services Division experienced decreases in its revenue and operating cost due to lower demand for well services, wireline services and fishing and rental services during the year ended December 31, 2009, as compared to the corresponding period in 2008. This decrease in revenues and operating costs that was due to lower demand was partially offset by the timing impact of the WEDGE and Competition acquisitions on March 1, 2008 which created our Production Services Division. A full year of Production Services Division operations are reflected in the operating results for the year ended December 31, 2009, as compared to ten months of operating results for the corresponding period in 2008.
Our selling, general and administrative expense for the year ended December 31, 2009 decreased by approximately $7.4 million, or 16%, as compared to the corresponding period in 2008. Professional and consulting expenses decreased by $5.2 million and compensation related expenses decreased by $2.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2009, as compared to the corresponding period in 2008. We incurred professional and consulting expenses in 2008 related to an investigation conducted by the special committee of our Board of Directors and for the acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE and Competition. The decrease in compensation related expenses is primarily to due to decreases in bonus compensation and salary compensation related to workforce reductions in 2009 as compared to 2008. The overall decrease in selling, general and administrative expense was partially offset by increases in insurance expenses and selling, general and administrative expenses relating to our Production Services Division. As noted above, a full year of Production Services Division operations are reflected in the results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2009, as compared to ten months of operating results for the year ended December 31, 2008.
The bad debt recovery during the year ended December 31, 2009 was primarily due to the collection of a customer’s past due account receivable balance for which we had previously established a $1.3 million allowance for doubtful accounts in December 2008.
Our other income for the year ended December 31, 2009 increased by $1.5 million as compared to the corresponding period in 2008, primarily due to foreign currency translation gains and losses relating to our operations in Colombia. We recorded foreign currency translation losses of $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2009, and foreign currency translation losses of $1.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2008.
Our depreciation and amortization expenses for the year ended December 31, 2009 increased by $18.0 million, or 20%, as compared to the corresponding period in 2008. This increase resulted primarily from the increase in the fleet size of our drilling rigs, workover rigs and wireline units. The 2009 additions to each fleet consisted primarily of newly constructed equipment. The increase also related to additional depreciation and amortization expense for our new Production Services Division. As noted above, a full year of Production Services Division operations are reflected in the results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2009, as compared to ten months of operating results for the year ended December 31, 2008.
Our interest expense is primarily related to interest due on the amounts outstanding under our senior secured revolving credit facility. Our interest expense decreased $3.9 million for the year ended December 31, 2009, as
53
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
compared to the corresponding period in 2008. This decrease is due to reductions in the amounts outstanding under our senior secured revolving credit facility and due to decreases in the LIBOR and bank prime base rates used to determine our effective borrowing rate per our senior secured revolving credit facility. Borrowings under the senior secured revolving credit facility were first used to fund the acquisitions of the production services businesses of WEDGE and Competition on March 1, 2008. Operating results for the year ended December 31, 2009 reflect a full year of interest expense as compared to ten months of interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2008.
Our effective income tax rate for the year ended December 31, 2009 differs from the federal statutory rate in the United States of 35% primarily due to pretax income recognized in foreign jurisdictions with a lower effective tax rate, the release of valuation allowance relating to foreign net operating loss carryforwards, state income taxes and other permanent differences.
Statements of Operations Analysis—Year Ended December 31, 2008 Compared with the Year Ended December 31, 2007
The following table provides information about our operations for the year ended December 31, 2008 and the twelve months ended December 31, 2007 (amounts in thousands, except average number of drilling rigs, utilization rate and revenue day information). In 2007, we changed our fiscal year end from March 31 to December 31. The 2007 results in the following table reflect the twelve months ended December 31, 2007. Our Production Services Division was created on March 1, 2008, when we acquired the production services businesses from WEDGE and Competition.
| Years ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||||
| (unaudited) | ||||||||
| Drilling Services Division: |
||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 456,890 | $ | 417,231 | ||||
| Operating costs |
269,846 | 250,564 | ||||||
| Drilling Services Division margin |
$ | 187,044 | $ | 166,667 | ||||
| Average number of drilling rigs |
67.4 | 66.1 | ||||||
| Utilization rate |
89 | % | 89 | % | ||||
| Revenue days |
22,057 | 21,492 | ||||||
| Average revenues per day |
$ | 20,714 | $ | 19,413 | ||||
| Average operating costs per day |
12,234 | 11,658 | ||||||
| Drilling Services Division margin per day |
$ | 8,480 | $ | 7,755 | ||||
| Production Services Division: |
||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 153,994 | $ | — | ||||
| Operating costs |
80,097 | — | ||||||
| Production Services Division margin |
$ | 73,897 | $ | — | ||||
| Combined: |
||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 610,884 | $ | 417,231 | ||||
| Operating costs |
349,943 | 250,564 | ||||||
| Combined margin |
$ | 260,941 | $ | 166,667 | ||||
| EBITDA |
$ | 214,766 | $ | 144,583 | ||||
54
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
We present drilling margin and earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation and amortization (EBITDA) information because we believe it provides investors and our management additional information to assist them in assessing our business and performance in comparison to other companies in our industry. Since drilling margin and EBITDA are “non-GAAP” financial measures under the rules and regulations of the SEC, we are providing the following reconciliation of drilling margin and EBITDA to net earnings, which is the nearest comparable GAAP financial measure.
| Year ended December 31, | ||||||||
| 2008 | 2007 | |||||||
| (amounts in thousands) | ||||||||
| Reconciliation of combined margin and |
||||||||
| Combined margin |
260,941 | 166,667 | ||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
(44,834 | ) | (19,608 | ) | ||||
| Bad debt expense |
(423 | ) | (2,612 | ) | ||||
| Other income (expense) |
(918 | ) | 136 | |||||
| EBITDA |
214,766 | 144,583 | ||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
(88,145 | ) | (63,588 | ) | ||||
| Impairment of goodwill |
(118,646 | ) | — | |||||
| Impairment of intangible assets |
(52,847 | ) | — | |||||
| Interest income (expense), net |
(11,816 | ) | 3,266 | |||||
| Income tax expense |
(6,057 | ) | (27,398 | ) | ||||
| Net (loss) earnings |
$ | (62,745 | ) | $ | 56,863 | |||
Our Drilling Services Division’s revenues increased by $39.7 million, or 10%, for the year ended December 31, 2008, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2007, due to an increase in average contract drilling revenues of $1,301 per day, or 7%, that resulted from an increased demand for drilling rigs and higher revenues per day earned by our Colombian operations that expanded significantly during 2008. The increase in Drilling Services Divisions revenues is also due to a 3% increase in revenue days that resulted from a slightly higher average number of drilling rigs.
Our Drilling Services Division’s operating costs grew by $19.3 million, or 8%, for the year ended December 31, 2008, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2007, due to an increase in average contract drilling operating costs of $576 per day, or 5%, that resulted primarily from higher operating costs per day for our Colombian operations which has higher labor and fuel costs when compared to drilling operations in the United States. This increase in our Drilling Services Division’s operating costs is also due to a 3% increase in revenue days that resulted from a slightly higher average number of drilling rigs.
Our Production Services Division’s revenue of $154.0 million and operating costs of $80.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 are based on the operating results for this new operating segment which was created on March 1, 2008 when we acquired the production services businesses of WEDGE and Competition.
Our selling, general and administrative expense for the year ended December 31, 2008 increased by approximately $25.2 million, or 129%, compared to the year ended December 31, 2007. The increase resulted from $4.4 million in additional compensation-related expenses incurred for existing and new employees in our corporate office which includes $0.9 million paid to our former Chief Financial Officer pursuant to a severance agreement. Professional and consulting expenses increased $5.2 million during the year ended December 31, 2008 which includes approximately $3.1 million due to an investigation conducted by the special subcommittee of our Board of Directors. In addition, we incurred $15.1 million and $0.7 million of additional selling, general and administrative expenses relating to our Production Service Division and our Colombian operations, respectively.
55
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Our bad debt expense decreased by $2.2 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, as compared to the year ended December 31, 2007, primarily due to a write-off of a trade receivable during the year ended December 31, 2007 for a former customer in bankruptcy.
Our other income for the year ended December 31, 2008 decreased by $1.0 million as compared to the year ended December 31, 2007, primarily due to foreign currency translation losses relating to our operations in Colombia.
Our depreciation and amortization expenses increased by $24.6 million, or 39%, for the year ended December 31, 2008, as compared to December 31, 2007. The increase resulted primarily from additional depreciation and amortization expense of $21.8 million for our Production Services Division acquisitions, which includes an increase in amortization expense of intangible assets of $8.3 million. The increase is also due to the increases in the average size of our drilling rig fleet, which consisted of newly constructed rigs. Partially offsetting the increase in depreciation and amortization expense was a decrease of $3.8 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, resulting from the change in the estimated useful lives of a group of 19 drilling rigs from an average useful life of 9 years to 12 years.
We recorded goodwill of $118.6 million in our Production Services Division operating segment in connection with the acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE, Competition, Pettus and Paltec, all of which occurred during the year ended December 31, 2008. On December 31, 2008, we performed an impairment analysis that led us to conclude that there would be no remaining implied value attributable to our goodwill, and, accordingly, we recorded a non-cash charge of $118.6 million for the full impairment of our goodwill. In addition, we performed an intangible asset impairment analysis on December 31, 2008, which resulted in a reduction to our intangible asset carrying value of customers’ relationships and a non-cash impairment charge of $52.8 million. These impairment charges did not have an impact on our liquidity or debt covenants; however, they were a reflection of the overall downturn in our industry and decline in our projected cash flows.
Interest expense for the year ended December 31, 2008 is primarily related to interest due on the amounts outstanding under our senior secured revolving credit facility which was primarily used to fund the acquisitions of the production services businesses of WEDGE and Competition on March 1, 2008.
Our income tax expense is $6.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2008, as compared to an expected income tax benefit of $19.8 million, based on the federal statutory rate of 35%, primarily due to the permanent differences between GAAP requirements and United States income tax regulations. Certain types of goodwill are not amortizable for income tax purposes. A significant portion of the goodwill impairment charge recorded for GAAP purposes during the year ended December 31, 2008, is not deductible for income tax purposes in the current year or in future years. Therefore, our results of operations reflect a pretax loss for GAAP purposes, but our results of operations will reflect pretax income for tax purposes. The increase in income tax expense was partially offset by tax benefits in foreign jurisdictions and other permanent differences.
Inflation
Due to the increased rig count in each of our market areas over the past several years, availability of personnel to operate our rigs was limited. In April 2005, January 2006, May 2006 and September 2008, we raised wage rates for our drilling rig personnel by an average of 6%, 6%, 14% and 6%, respectively. We were able to pass these wage rate increases on to our customers based on contract terms. In February 2009, we reduced wage rates for drilling rig personnel to offset the wage rate increases from September 2008. In September 2009, we had additional wage rate reductions for drilling rig personnel of approximately 15%.
56
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
During the fiscal years ended December 31, 2007 and 2008, we experienced increases in costs for rig repairs and maintenance and costs of rig upgrades and new rig construction, due to the increased industry-wide demand for equipment, supplies and service. We estimate these costs increased by 10% to 15% during the fiscal years ended December 31, 2007 and 2008. We have not experienced similar cost increases during 2009 and do not expect similar cost increases during the fiscal year ending December 31, 2010.
Off-Balance Sheet Arrangements
We do not currently have any off-balance sheet arrangements.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
Accounting Standards Codification. The Financial Accounting Standards Board’s (FASB) Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) became effective on July 1, 2009. At that date, the ASC became FASB’s officially recognized source of authoritative U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) applicable to all public and non-public non-governmental entities, superseding existing FASB Statements of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) and other authoritative guidance issued by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) and Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF). Rules and interpretive releases of the SEC under the authority of federal securities laws are also sources of authoritative GAAP for SEC registrants. All other accounting literature is considered non-authoritative. The switch to the ASC affects the way companies refer to U.S. GAAP in financial statements and accounting policies. Citing particular content in the ASC involves specifying the unique numeric path to the content through the Topic, Subtopic, Section and Paragraph structure.
Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements. In December 2007, the FASB issued new authoritative accounting guidance under FASB ASC Topic 810 (formerly SFAS No. 160) which establishes accounting and reporting standards for the non-controlling interest in a subsidiary and for the deconsolidation of a subsidiary. ASC Topic 810 clarifies that a non-controlling interest in a subsidiary, which is sometimes referred to as minority interest, is an ownership interest in the consolidated entity that should be reported as a component of equity in the consolidated financial statements. Among other requirements, ASC 810 requires consolidated net income to be reported at amounts that include the amounts attributable to both the parent and the non-controlling interest. It also requires disclosure, on the face of the consolidated income statement, of the amounts of consolidated net income attributable to the parent and to the non-controlling interest. ASC Topic 810 is effective for fiscal years beginning on or after December 15, 2008. The adoption of ASC topic 810 on January 1, 2009 did not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition.
Business Combinations. On January 1, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance became effective under ASC Topic 805 (formerly SFAS No. 141R) which applies to all transactions and other events in which one entity obtains control over one or more other businesses. ASC Topic 805 requires an acquirer, upon initially obtaining control of another entity, to recognize the assets, liabilities and any non-controlling interest in the acquiree at fair value as of the acquisition date. Contingent consideration is required to be recognized and measured at fair value on the date of acquisition rather than at a later date when the amount of that consideration may be determinable beyond a reasonable doubt. This fair value approach replaces the cost-allocation process required under the previous authoritative accounting guidance (formerly SFAS No. 141) whereby the cost of an acquisition was allocated to the individual assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair value. ASC Topic 805 requires acquirers to expense acquisition-related costs as incurred rather than allocating such costs to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed, as was previously the case under SFAS No. 141. Under ASC Topic 805, the requirements of ASC Topic 420 (formerly SFAS No. 146) relating to the accounting for costs associated with exit or disposal activities, would have to be met in order to accrue for a restructuring plan in purchase accounting. Pre-acquisition contingencies are to be recognized at fair value, unless it is a non-contractual contingency that is not likely to materialize, in which case, nothing should be recognized in purchase accounting and, instead, that contingency would be subject to the probable and estimable recognition criteria of ASC Topic
57
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
450 which provides accounting guidance for contingencies. ASC Topic 805 had no impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition, since we have not had any business combinations closing on or after the January 1, 2009 effective date.
Disclosures about Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities. On January 1, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance became effective under ASC Topic 815 (formerly SFAS No. 161) which changes the disclosure requirements for derivative instruments and hedging activities. Entities are required to provide enhanced disclosures about (a) how and why an entity uses derivative instruments, (b) how derivative instruments and related hedged items are accounted for under ASC Topic 815, and (c) how derivative instruments and related hedged items affect an entity’s financial position, financial performance, and cash flows. The guidance in ASC Topic 815 is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after November 15, 2008, with early application encouraged. This authoritative accounting guidance encourages, but does not require, comparative disclosures for earlier periods at initial adoption. We do not have any derivative instruments and the January 1, 2009 adoption of this new accounting guidance under ASC Topic 815 had no impact on our financial statement disclosures.
Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures. Effective for accounting periods ending after June 15, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 820 (formerly FASB Staff Position FAS 157-4) provides additional guidance for estimating fair value when the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability have significantly decreased and provides additional guidance on disclosure requirements. ASC Topic 820 also includes guidance on identifying circumstances that indicate a transaction is not orderly. The adoption of the new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 820 during our quarter ended June 30, 2009 did not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition.
Other-than-temporary Impairments. Effective for accounting periods ending after June 15, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 320 (formerly FASB Staff Position FAS 115-2 and 124-2) modifies the indicator of other-than-temporary impairment for debt securities. Additionally, ASC Topic 320 changes the amount of an other-than-temporary impairment that is recognized in earnings when there are credit losses on a debt security that management does not intend to sell and it is more-likely-than-not that the entity will not have to sell prior to recovery of the noncredit impairment. In those situations, the portion of the total impairment that is attributable to the credit loss would be recognized in earnings, and the remaining difference between the debt security’s amortized cost basis and its fair value would be included in other comprehensive income. The adoption of this new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 320 during our quarter ended June 30, 2009 did not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition.
Interim Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments. Effective for accounting periods ending after June 15, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 825 (formerly FASB Staff Position FAS 107-1 and APB 28-1) requires disclosures about fair value of financial instruments in quarterly reports as well as in annual reports and applies to certain investments and long-term debt. The adoption of this new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 825 during our quarter ended June 30, 2009 did not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition.
Subsequent Events. For accounting periods ending after June 15, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance became effective under ASC Topic 855 (formerly SFAS No. 165) which modifies the definition of what qualifies as a subsequent event—those events or transactions that occur following the balance sheet date, but before the financial statements are issued, or are available to be issued—and requires companies to disclose the date through which it has evaluated subsequent events and the basis for determining that date. The adoption of ASC Topic 855 during the quarter ended June 30, 2009 did not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition.
58
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Multiple Deliverable Revenue Arrangements. In October 2009, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update, 2009-13, Revenue Recognition (Topic 605) Multiple Deliverable Revenue Arrangements—A Consensus of the FASB Emerging Issues Task Force. This update provides application guidance on whether multiple deliverables exist, how the deliverables should be separated and how the consideration should be allocated to one or more units of accounting. This update establishes a selling price hierarchy for determining the selling price of a deliverable. The selling price used for each deliverable will be based on vendor-specific objective evidence, if available, third-party evidence if vendor-specific objective evidence is not available, or estimated selling price if neither vendor-specific or third-party evidence is available. We will be required to apply this guidance prospectively for revenue arrangements entered into or materially modified after January 1, 2011; however, earlier application is permitted. We do not expect the adoption of this new guidance to have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations.
| Item 7A. | Quantitative and Qualitative Disclosures About Market Risk |
Interest Rate Risk
We are subject to interest rate market risk on our variable rate debt. As of December 31, 2009, we had $257.5 million outstanding under our senior secured revolving credit facility subject to variable interest rate risk. The impact of a 1% increase in interest rates on this amount of debt would have resulted in increased interest expense of approximately $2.6 million and a decrease in net income of approximately $1.7 million during 2009.
At December 31, 2009, we held $15.9 million (par value) of investments comprised of tax exempt, auction rate preferred securities (“ARPSs”), which are variable-rate preferred securities and have a long-term maturity with the interest rate being reset through “Dutch auctions” that are held every 7 days. The ARPSs have historically traded at par because of the frequent interest rate resets and because they are callable at par at the option of the issuer. Interest is paid at the end of each auction period. Our ARPSs are AAA/Aaa rated securities, collateralized by municipal bonds and backed by assets that are equal to or greater than 200% of the liquidation preference. Until February 2008, the auction rate securities market was highly liquid. Beginning mid-February 2008, we experienced several “failed” auctions, meaning that there was not enough demand to sell all of the securities that holders desired to sell at auction. The immediate effect of a failed auction is that such holders cannot sell the securities at auction and the interest rate on the security resets to a maximum auction rate. We have continued to receive interest payments on our ARPSs in accordance with their terms. Unless a future auction is successful or the issuer calls the security pursuant to redemption prior to maturity, we may not be able to access the funds we invested in our ARPSs without a loss of principal. We have no reason to believe that any of the underlying municipal securities that collateralize our ARPSs are presently at risk of default. We believe we will ultimately recover the par value of the ARPSs without loss, primarily due to the collateral securing the ARPSs and our estimate of the discounted cash flows that we expect to collect. We do not currently intend to sell our ARPSs at a loss. Also, we believe it is more-likely-than-not that we will not have to sell our ARPSs prior to recovery, since our liquidity needs are expected to be met with cash flows from operating activities and our senior secured revolving credit facility. Our ARPSs are designated as available-for-sale and are reported at fair market value with the related unrealized gains or losses, included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax, a component of shareholders’ equity. The estimated fair value of our ARPSs at December 31, 2009 was $13.2 million compared with a par value of $15.9 million. The $2.7 million difference represents a fair value discount due to the current lack of liquidity which is considered temporary and has been recorded as an unrealized loss, net of tax, in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). There was no portion of the fair value discount attributable to credit losses. We would recognize an impairment charge in our statement of operations if the fair value of our investments falls below the cost basis and is judged to be other-than-temporary. Our ARPSs are classified with other long-term assets on our condensed consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2009 because of our inability to determine the recovery period of our investments.
59
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Foreign Currency Risk
While the U.S. dollar is the functional currency for reporting purposes for our Colombian operations, we enter into transactions denominated in Colombian pesos. Nonmonetary assets and liabilities are translated at historical rates and monetary assets and liabilities are translated at exchange rates in effect at the end of the period. Income statement accounts are translated at average rates for the period. As a result, Colombian Peso denominated transactions are affected by changes in exchange rates. We generally accept the exposure to exchange rate movements without using derivative financial instruments to manage this risk. Therefore, both positive and negative movements in the Colombian Peso currency exchange rate against the U.S. dollar has and will continue to affect the reported amount of revenues, expenses, profit, and assets and liabilities in the Company’s consolidated financial statements.
The impact of currency rate changes on our Colombian Peso denominated transactions and balances resulted in foreign currency losses of $0.1 million for the year ended December 31, 2009.
60
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Item 8. | Financial Statements and Supplementary Data |
INDEX TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| Page | ||
| 62 | ||
| Consolidated Balance Sheets as of December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 |
64 | |
| 65 | ||
| 66 | ||
| 67 | ||
| 68 | ||
61
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders
Pioneer Drilling Company:
We have audited the accompanying consolidated balance sheets of Pioneer Drilling Company and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the related consolidated statements of operations, shareholders’ equity and comprehensive income, and cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the nine months ended December 31, 2007. These consolidated financial statements are the responsibility of the Company’s management. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on these consolidated financial statements based on our audits.
We conducted our audits in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether the financial statements are free of material misstatement. An audit includes examining, on a test basis, evidence supporting the amounts and disclosures in the financial statements. An audit also includes assessing the accounting principles used and significant estimates made by management, as well as evaluating the overall financial statement presentation. We believe that our audits provide a reasonable basis for our opinion.
In our opinion, the consolidated financial statements referred to above present fairly, in all material respects, the financial position of Pioneer Drilling Company and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the results of their operations and their cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the nine months ended December 31, 2007, in conformity with U.S. generally accepted accounting principles.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), Pioneer Drilling Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO), and our report dated February 16, 2010 expressed an unqualified opinion on the effectiveness of the Company’s internal control over financial reporting.
/s/ KPMG LLP
San Antonio, Texas
February 16, 2010
62
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Report of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm
The Board of Directors and Shareholders
Pioneer Drilling Company:
We have audited Pioneer Drilling Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO). Pioneer Drilling Company’s management is responsible for maintaining effective internal control over financial reporting and for its assessment of the effectiveness of internal control over financial reporting, included in the accompanying Management’s Report on Internal Control over Financial Reporting. Our responsibility is to express an opinion on the Company’s internal control over financial reporting based on our audit.
We conducted our audit in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States). Those standards require that we plan and perform the audit to obtain reasonable assurance about whether effective internal control over financial reporting was maintained in all material respects. Our audit included obtaining an understanding of internal control over financial reporting, assessing the risk that a material weakness exists, and testing and evaluating the design and operating effectiveness of internal control based on the assessed risk. Our audit also included performing such other procedures as we considered necessary in the circumstances. We believe that our audit provides a reasonable basis for our opinion.
A company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of the company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements.
Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
In our opinion, Pioneer Drilling Company maintained, in all material respects, effective internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009, based on criteria established in Internal Control—Integrated Framework issued by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission.
We also have audited, in accordance with the standards of the Public Company Accounting Oversight Board (United States), the consolidated balance sheets of Pioneer Drilling Company and subsidiaries as of December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the related consolidated statements of operations, shareholders’ equity and comprehensive income, and cash flows for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, and the nine months ended December 31, 2007, and our report dated February 16, 2010 expressed an unqualified opinion on those consolidated financial statements.
/s/ KPMG LLP
San Antonio, Texas
February 16, 2010
63
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
PIONEER DRILLING COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED BALANCE SHEET
| December 31, 2009 |
December 31, 2008 |
|||||||
| (In thousands, except share data) | ||||||||
| ASSETS |
||||||||
| Current assets: |
||||||||
| Cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 40,379 | $ | 26,821 | ||||
| Receivables: |
||||||||
| Trade, net of allowance for doubtful accounts |
26,648 | 76,176 | ||||||
| Insurance recoveries |
5,107 | 5,951 | ||||||
| Income taxes |
41,126 | 5,034 | ||||||
| Unbilled receivables |
8,586 | 12,262 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
5,560 | 6,270 | ||||||
| Inventory |
5,535 | 3,874 | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses and other current assets |
6,199 | 8,902 | ||||||
| Total current assets |
139,140 | 145,290 | ||||||
| Property and equipment, at cost |
967,893 | 858,491 | ||||||
| Less accumulated depreciation and amortization |
330,871 | 230,929 | ||||||
| Net property and equipment |
637,022 | 627,562 | ||||||
| Intangible assets, net of amortization |
25,393 | 29,969 | ||||||
| Other long-term assets |
21,061 | 21,658 | ||||||
| Total assets |
$ | 822,616 | $ | 824,479 | ||||
| LIABILITIES AND SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY |
||||||||
| Current liabilities: |
||||||||
| Accounts payable |
$ | 15,324 | $ | 21,830 | ||||
| Current portion of long-term debt |
4,041 | 17,298 | ||||||
| Prepaid drilling contracts |
408 | 1,171 | ||||||
| Accrued expenses: |
||||||||
| Payroll and related employee costs |
7,740 | 13,592 | ||||||
| Insurance premiums and deductibles |
8,615 | 11,569 | ||||||
| Insurance claims and settlements |
5,042 | 5,951 | ||||||
| Other |
7,634 | 9,507 | ||||||
| Total current liabilities |
48,804 | 80,918 | ||||||
| Long-term debt, less current portion |
258,073 | 262,115 | ||||||
| Other long-term liabilities |
6,457 | 6,413 | ||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
87,834 | 60,915 | ||||||
| Total liabilities |
401,168 | 410,361 | ||||||
| Commitments and contingencies (Note 12) |
||||||||
| Shareholders’ equity: |
||||||||
| Preferred stock, 10,000,000 shares authorized; none issued and outstanding |
— | — | ||||||
| Common stock $.10 par value; 100,000,000 shares authorized; 54,120,852 shares and 49,997,578 shares issued and outstanding at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively |
5,413 | 5,000 | ||||||
| Additional paid-in capital |
332,534 | 301,923 | ||||||
| Treasury stock, at cost; 5,174 shares and no shares at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, respectively |
(31 | ) | — | |||||
| Accumulated earnings |
85,225 | 108,440 | ||||||
| Accumulated other comprehensive loss |
(1,693 | ) | (1,245 | ) | ||||
| Total shareholders’ equity |
421,448 | 414,118 | ||||||
| Total liabilities and shareholders’ equity |
$ | 822,616 | $ | 824,479 | ||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
64
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
PIONEER DRILLING COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF OPERATIONS
| Years ended December 31, |
Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 |
|||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| (In thousands, except per share data) | ||||||||||||
| Revenues: |
||||||||||||
| Drilling services |
$ | 219,751 | $ | 456,890 | $ | 313,884 | ||||||
| Production services |
105,786 | 153,994 | — | |||||||||
| Total revenue |
325,537 | 610,884 | 313,884 | |||||||||
| Costs and expenses: |
||||||||||||
| Drilling services |
147,343 | 269,846 | 191,374 | |||||||||
| Production services |
68,012 | 80,097 | — | |||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
106,186 | 88,145 | 48,852 | |||||||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
37,478 | 44,834 | 15,786 | |||||||||
| Bad debt (recovery) expense |
(1,642 | ) | 423 | 2,612 | ||||||||
| Impairment of goodwill |
— | 118,646 | — | |||||||||
| Impairment of intangible assets |
— | 52,847 | — | |||||||||
| Total costs and expenses |
357,377 | 654,838 | 258,624 | |||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
(31,840 | ) | (43,954 | ) | 55,260 | |||||||
| Other income (expense): |
||||||||||||
| Interest expense |
(9,145 | ) | (13,072 | ) | (16 | ) | ||||||
| Interest income |
217 | 1,256 | 2,401 | |||||||||
| Other |
596 | (918 | ) | 129 | ||||||||
| Total other income (expense) |
(8,332 | ) | (12,734 | ) | 2,514 | |||||||
| Income (loss) before income taxes |
(40,172 | ) | (56,688 | ) | 57,774 | |||||||
| Income tax benefit (expense) |
16,957 | (6,057 | ) | (18,129 | ) | |||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
$ | (23,215 | ) | $ | (62,745 | ) | $ | 39,645 | ||||
| Earnings (loss) per common share—Basic |
$ | (0.46 | ) | $ | (1.26 | ) | $ | 0.80 | ||||
| Earnings (loss) per common share—Diluted |
$ | (0.46 | ) | $ | (1.26 | ) | $ | 0.79 | ||||
| Weighted average number of shares outstanding—Basic |
50,313 | 49,789 | 49,645 | |||||||||
| Weighted average number of shares outstanding—Diluted |
50,313 | 49,789 | 50,201 | |||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
65
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
PIONEER DRILLING COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF SHAREHOLDERS’ EQUITY AND COMPREHENSIVE INCOME
| Shares | Amount | Additional Paid In Capital |
Accumulated Earnings |
Accumulated Other Comprehensive Loss |
Total Shareholders’ Equity |
|||||||||||||||||||||||
| Common | Treasury | Common | Treasury | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of March 31, 2007 |
49,629 | — | 4,963 | — | 291,607 | 131,540 | — | 428,110 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive income: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net earnings |
— | — | — | — | — | 39,645 | — | 39,645 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive income |
— | — | — | — | — | — | — | 39,645 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of options and related income tax effect of $54 |
22 | — | 2 | — | 158 | — | — | 160 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | 3,157 | — | — | 3,157 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2007 |
49,651 | — | $ | 4,965 | $ | — | $ | 294,922 | $ | 171,185 | $ | — | $ | 471,072 | ||||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | (62,745 | ) | — | (62,745 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on securities |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (1,245 | ) | (1,245 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss |
(63,990 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Exercise of options and related income tax effect of $244 |
170 | — | 17 | — | 1,011 | — | — | 1,028 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of restricted stock |
177 | — | 18 | — | (34 | ) | — | — | (16 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | 6,024 | — | — | 6,024 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2008 |
49,998 | — | $ | 5,000 | $ | — | $ | 301,923 | $ | 108,440 | $ | (1,245 | ) | $ | 414,118 | |||||||||||||
| Comprehensive loss: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Net loss |
— | — | — | — | — | (23,215 | ) | — | (23,215 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Unrealized loss on securities |
— | — | — | — | — | — | (448 | ) | (448 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total comprehensive loss |
(23,663 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Sale of common stock, net of offering costs |
3,820 | — | 382 | — | 23,661 | — | — | 24,043 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Purchase of treasury stock |
— | (5 | ) | — | (31 | ) | — | — | — | (31 | ) | |||||||||||||||||
| Income tax effect of restricted stock vesting |
— | — | — | — | (235 | ) | — | — | (235 | ) | ||||||||||||||||||
| Issuance of restricted stock |
308 | — | 31 | — | (31 | ) | — | — | — | |||||||||||||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
— | — | — | — | 7,216 | — | — | 7,216 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Balance as of December 31, 2009 |
54,126 | (5 | ) | $ | 5,413 | $ | (31 | ) | $ | 332,534 | $ | 85,225 | $ | (1,693 | ) | $ | 421,448 | |||||||||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
66
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
PIONEER DRILLING COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
CONSOLIDATED STATEMENTS OF CASH FLOWS
| Years ended December 31, |
Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 |
|||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| (In thousands) | ||||||||||||
| Cash flows from operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Net (loss) earnings |
$ | (23,215 | ) | $ | (62,745 | ) | $ | 39,645 | ||||
| Adjustments to reconcile net (loss) earnings to net cash provided by operating activities: |
||||||||||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
106,186 | 88,145 | 48,852 | |||||||||
| Allowance for doubtful accounts |
(1,170 | ) | 1,591 | 2,612 | ||||||||
| (Gain) loss on dispositions of property and equipment |
56 | (805 | ) | 2,809 | ||||||||
| Stock-based compensation expense |
7,216 | 4,597 | 3,157 | |||||||||
| Impairment of goodwill and intangibles assets |
— | 171,493 | — | |||||||||
| Deferred income taxes |
28,400 | (2,310 | ) | 5,947 | ||||||||
| Change in other assets |
1,616 | 265 | (519 | ) | ||||||||
| Change in non-current liabilities |
(1,312 | ) | (621 | ) | (92 | ) | ||||||
| Changes in current assets and liabilities: |
||||||||||||
| Receivables |
18,180 | (24,867 | ) | 9,692 | ||||||||
| Inventory |
(1,661 | ) | (927 | ) | (1,180 | ) | ||||||
| Prepaid expenses & other current assets |
2,703 | (2,390 | ) | (1,420 | ) | |||||||
| Accounts payable |
(2,243 | ) | (2,610 | ) | 919 | |||||||
| Income tax payable |
— | 409 | — | |||||||||
| Prepaid drilling contracts |
(763 | ) | (762 | ) | 1,933 | |||||||
| Accrued expenses |
(10,680 | ) | 17,928 | 3,100 | ||||||||
| Net cash provided by operating activities |
123,313 | 186,391 | 115,455 | |||||||||
| Cash flows from investing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Acquisition of production services business of WEDGE |
— | (313,621 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Acquisition of production services business of Competition |
— | (26,772 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Acquisition of other production services businesses |
— | (9,301 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Purchases of property and equipment |
(114,712 | ) | (147,455 | ) | (126,158 | ) | ||||||
| Purchase of auction rate securities, net |
— | (15,900 | ) | — | ||||||||
| Proceeds from sale of property and equipment |
767 | 4,008 | 2,300 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from insurance recoveries |
36 | 3,426 | — | |||||||||
| Net cash used in investing activities |
(113,909 | ) | (505,615 | ) | (123,858 | ) | ||||||
| Cash flows from financing activities: |
||||||||||||
| Payments of debt |
(17,298 | ) | (87,767 | ) | — | |||||||
| Proceeds from issuance of debt |
— | 359,400 | — | |||||||||
| Debt issuance costs |
(2,560 | ) | (3,319 | ) | — | |||||||
| Proceeds from exercise of options |
— | 784 | 107 | |||||||||
| Proceeds from common stock, net of offering costs of $454 |
24,043 | — | — | |||||||||
| Purchase of treasury stock |
(31 | ) | — | — | ||||||||
| Excess income tax effect of stock option exercises |
— | 244 | 54 | |||||||||
| Net cash provided by financing activities |
4,154 | 269,342 | 161 | |||||||||
| Net decrease in cash and cash equivalents |
13,558 | (49,882 | ) | (8,242 | ) | |||||||
| Beginning cash and cash equivalents |
26,821 | 76,703 | 84,945 | |||||||||
| Ending cash and cash equivalents |
$ | 40,379 | $ | 26,821 | $ | 76,703 | ||||||
| Supplementary disclosure: |
||||||||||||
| Interest paid |
$ | 7,917 | $ | 12,468 | $ | 15 | ||||||
| Income tax (refunded) paid |
$ | (9,470 | ) | $ | 11,166 | $ | 9,473 | |||||
See accompanying notes to consolidated financial statements.
67
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
PIONEER DRILLING COMPANY AND SUBSIDIARIES
NOTES TO CONSOLIDATED FINANCIAL STATEMENTS
| 1. | Organization and Summary of Significant Accounting Policies |
Business and Principles of Consolidation
Pioneer Drilling Company and subsidiaries provide drilling and production services to our customers in select oil and natural gas exploration and production regions in the United States and Colombia. Our Drilling Services Division provides contract land drilling services with its fleet of 71 drilling rigs in the following locations:
| Drilling Division Locations |
Rig Count | |
| South Texas |
15 | |
| East Texas |
19 | |
| North Dakota |
8 | |
| North Texas |
5 | |
| Utah |
5 | |
| Oklahoma |
6 | |
| Appalachia |
5 | |
| Colombia |
8 |
As of February 5, 2010, 34 drilling rigs are operating under drilling contracts. We have 31 drilling rigs that are idle and six drilling rigs have been placed in storage or “cold stacked” in our Oklahoma drilling division due to low demand for drilling rigs in that region. We are actively marketing all our idle drilling rigs both domestically and internationally in Latin America. During the second quarter of 2009, we established our Appalachian drilling division and now have four drilling rigs operating in the Marcellus Shale region. We are currently upgrading a fifth rig that is scheduled to begin operating under a drilling contract in the Marcellus Shale region in late February 2010. We have seven drilling rigs located in Colombia that are operating under drilling contracts, five of which are drilling and two of which have been moved to their initial well site locations and are expected to begin drilling in late February 2010. In March 2010, we plan to export an eighth rig to Colombia that will begin working under a drilling contract. In addition to our drilling rigs, we provide the drilling crews and most of the ancillary equipment needed to operate our drilling rigs. We obtain our contracts for drilling oil and natural gas wells either through competitive bidding or through direct negotiations with customers. Our drilling contracts generally provide for compensation on either a daywork, turnkey or footage basis. Contract terms generally depend on the complexity and risk of operations, the on-site drilling conditions, the type of equipment used and the anticipated duration of the work to be performed.
Our Production Services Division provides a broad range of well services to oil and gas drilling and producing companies, including workover services, wireline services, and fishing and rental services. Our production services operations are managed regionally and are concentrated in the major United States onshore oil and gas producing regions in the Gulf Coast, Mid-Continent, and Rocky Mountain states. We have a premium fleet of 74 workover rigs consisting of sixty-nine 550 horsepower rigs, four 600 horsepower rigs, and one 400 horsepower rig. As of February 5, 2010, 68 workover rigs are operating and 6 workover rigs are idle with no crews assigned. We provide wireline services with a fleet of 65 wireline units and rental services with approximately $13 million of fishing and rental tools.
The accompanying consolidated financial statements include the accounts of Pioneer Drilling Company and our wholly owned subsidiaries. All intercompany balances and transactions have been eliminated in consolidation. In December 2007, our Board of Directors approved a change in our fiscal year end from March 31st to December 31st. The fiscal year end change was effective December 31, 2007 and resulted in a nine month reporting period from April 1, 2007 to December 31, 2007. We implemented the fiscal year end change to align our United States reporting period with the required Colombian statutory reporting period as well as the reporting periods of peer companies in the industry.
68
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
The accompanying consolidated financial statements have been prepared in accordance with accounting principles generally accepted in the United States of America. In preparing the accompanying consolidated financial statements, we make various estimates and assumptions that affect the amounts of assets and liabilities we report as of the dates of the balance sheets and income and expenses we report for the periods shown in the income statements and statements of cash flows. Our actual results could differ significantly from those estimates. Material estimates that are particularly susceptible to significant changes in the near term relate to our recognition of revenues and costs for turnkey contracts, our estimate of the allowance for doubtful accounts, our estimate of the self-insurance portion of our health and workers’ compensation insurance, our estimate of asset impairments, our estimate of deferred taxes and our determination of depreciation and amortization expense.
Recently Issued Accounting Standards
Accounting Standards Codification. The Financial Accounting Standards Board’s (FASB) Accounting Standards Codification (ASC) became effective on July 1, 2009. At that date, the ASC became FASB’s officially recognized source of authoritative U.S. generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) applicable to all public and non-public non-governmental entities, superseding existing FASB Statements of Financial Accounting Standards (SFAS) and other authoritative guidance issued by the American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA) and Emerging Issues Task Force (EITF). Rules and interpretive releases of the SEC under the authority of federal securities laws are also sources of authoritative GAAP for SEC registrants. All other accounting literature is considered non-authoritative. The switch to the ASC affects the way companies refer to U.S. GAAP in financial statements and accounting policies. Citing particular content in the ASC involves specifying the unique numeric path to the content through the Topic, Subtopic, Section and Paragraph structure.
Noncontrolling Interests in Consolidated Financial Statements. In December 2007, the FASB issued new authoritative accounting guidance under FASB ASC Topic 810 (formerly SFAS No. 160) which establishes accounting and reporting standards for the non-controlling interest in a subsidiary and for the deconsolidation of a subsidiary. ASC Topic 810 clarifies that a non-controlling interest in a subsidiary, which is sometimes referred to as minority interest, is an ownership interest in the consolidated entity that should be reported as a component of equity in the consolidated financial statements. Among other requirements, ASC 810 requires consolidated net income to be reported at amounts that include the amounts attributable to both the parent and the non-controlling interest. It also requires disclosure, on the face of the consolidated income statement, of the amounts of consolidated net income attributable to the parent and to the non-controlling interest. ASC Topic 810 is effective for fiscal years beginning on or after December 15, 2008. The adoption of ASC topic 810 on January 1, 2009 did not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition.
Business Combinations. On January 1, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance became effective under ASC Topic 805 (formerly SFAS No. 141R) which applies to all transactions and other events in which one entity obtains control over one or more other businesses. ASC Topic 805 requires an acquirer, upon initially obtaining control of another entity, to recognize the assets, liabilities and any non-controlling interest in the acquiree at fair value as of the acquisition date. Contingent consideration is required to be recognized and measured at fair value on the date of acquisition rather than at a later date when the amount of that consideration may be determinable beyond a reasonable doubt. This fair value approach replaces the cost-allocation process required under the previous authoritative accounting guidance (formerly SFAS No. 141) whereby the cost of an acquisition was allocated to the individual assets acquired and liabilities assumed based on their estimated fair value. ASC Topic 805 requires acquirers to expense acquisition-related costs as incurred rather than allocating such costs to the assets acquired and liabilities assumed, as was previously the case under SFAS No. 141. Under ASC Topic 805, the requirements of ASC Topic 420 (formerly SFAS No. 146) relating to the accounting for costs associated with exit or disposal activities, would have to be met in order to accrue for a restructuring plan in purchase accounting. Pre-acquisition contingencies are to be recognized at fair value, unless it is a non-contractual contingency that is not likely to materialize, in which case, nothing should be recognized in purchase accounting and, instead, that contingency would be subject to the probable and estimable recognition criteria of ASC Topic 450 which provides accounting guidance for contingencies. ASC Topic 805 had no impact on our financial
69
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
position or results of operations and financial condition, since we have not had any business combinations closing on or after the January 1, 2009 effective date.
Disclosures about Derivative Instruments and Hedging Activities. On January 1, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance became effective under ASC Topic 815 (formerly SFAS No. 161) which changes the disclosure requirements for derivative instruments and hedging activities. Entities are required to provide enhanced disclosures about (a) how and why an entity uses derivative instruments, (b) how derivative instruments and related hedged items are accounted for under ASC Topic 815, and (c) how derivative instruments and related hedged items affect an entity’s financial position, financial performance, and cash flows. The guidance in ASC Topic 815 is effective for financial statements issued for fiscal years and interim periods beginning after November 15, 2008, with early application encouraged. This authoritative accounting guidance encourages, but does not require, comparative disclosures for earlier periods at initial adoption. We do not have any derivative instruments and the January 1, 2009 adoption of this new accounting guidance under ASC Topic 815 had no impact on our financial statement disclosures.
Fair Value Measurements and Disclosures. Effective for accounting periods ending after June 15, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 820 (formerly FASB Staff Position FAS 157-4) provides additional guidance for estimating fair value when the volume and level of activity for the asset or liability have significantly decreased and provides additional guidance on disclosure requirements. ASC Topic 820 also includes guidance on identifying circumstances that indicate a transaction is not orderly. The adoption of the new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 820 during our quarter ended June 30, 2009 did not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition.
Other-than-temporary Impairments. Effective for accounting periods ending after June 15, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 320 (formerly FASB Staff Position FAS 115-2 and 124-2) modifies the indicator of other-than-temporary impairment for debt securities. Additionally, ASC Topic 320 changes the amount of an other-than-temporary impairment that is recognized in earnings when there are credit losses on a debt security that management does not intend to sell and it is more-likely-than-not that the entity will not have to sell prior to recovery of the noncredit impairment. In those situations, the portion of the total impairment that is attributable to the credit loss would be recognized in earnings, and the remaining difference between the debt security’s amortized cost basis and its fair value would be included in other comprehensive income. The adoption of this new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 320 during our quarter ended June 30, 2009 did not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition.
Interim Disclosures about Fair Value of Financial Instruments. Effective for accounting periods ending after June 15, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 825 (formerly FASB Staff Position FAS 107-1 and APB 28-1) requires disclosures about fair value of financial instruments in quarterly reports as well as in annual reports and applies to certain investments and long-term debt. The adoption of this new authoritative accounting guidance under ASC Topic 825 during our quarter ended June 30, 2009 did not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition.
Subsequent Events. For accounting periods ending after June 15, 2009, new authoritative accounting guidance became effective under ASC Topic 855 (formerly SFAS No. 165) which modifies the definition of what qualifies as a subsequent event—those events or transactions that occur following the balance sheet date, but before the financial statements are issued, or are available to be issued—and requires companies to disclose the date through which it has evaluated subsequent events and the basis for determining that date. The adoption of ASC Topic 855 during the quarter ended June 30, 2009 did not have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations and financial condition.
Multiple Deliverable Revenue Arrangements. In October 2009, the FASB issued Accounting Standards Update, 2009-13, Revenue Recognition (Topic 605) Multiple Deliverable Revenue Arrangements—A Consensus
70
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
of the FASB Emerging Issues Task Force. This update provides application guidance on whether multiple deliverables exist, how the deliverables should be separated and how the consideration should be allocated to one or more units of accounting. This update establishes a selling price hierarchy for determining the selling price of a deliverable. The selling price used for each deliverable will be based on vendor-specific objective evidence, if available, third-party evidence if vendor-specific objective evidence is not available, or estimated selling price if neither vendor-specific or third-party evidence is available. We will be required to apply this guidance prospectively for revenue arrangements entered into or materially modified after January 1, 2011; however, earlier application is permitted. We do not expect the adoption of this new guidance to have a material impact on our financial position or results of operations.
Drilling Contracts
Our drilling contracts generally provide for compensation on either a daywork, turnkey or footage basis. Contract terms generally depend on the complexity and risk of operations, the on-site drilling conditions, the type of equipment used and the anticipated duration of the work to be performed. Generally, our contracts provide for the drilling of a single well and typically permit the customer to terminate on short notice. However, we have entered into more longer-term drilling contracts during periods of high rig demand. In addition, we have entered into longer-term drilling contracts for our newly constructed rigs. As of February 5, 2010, we had 11 contracts with terms of six months to three years in duration, of which one will expire by August 5, 2010, three have a remaining term of six to 12 months and seven have a remaining term in excess of 18 months.
Foreign Currencies
Our functional currency for our foreign subsidiary in Colombia is the U.S. dollar. Nonmonetary assets and liabilities are translated at historical rates and monetary assets and liabilities are translated at exchange rates in effect at the end of the period. Income statement accounts are translated at average rates for the period. Gains and losses from remeasurement of foreign currency financial statements into U.S. dollars and from foreign currency transactions are included in other income or expense.
Revenue and Cost Recognition
Drilling Services—We earn revenues by drilling oil and natural gas wells for our customers under daywork, turnkey or footage contracts, which usually provide for the drilling of a single well. We recognize revenues on daywork contracts for the days completed based on the dayrate each contract specifies. We recognize revenues from our turnkey and footage contracts on the percentage-of-completion method based on our estimate of the number of days to complete each contract. With most drilling contracts, we receive payments contractually designated for the mobilization of rigs and other equipment. Payments received, and costs incurred for the mobilization services are deferred and recognized on a straight line basis over the contract term of certain drilling contracts. Costs incurred to relocate rigs and other drilling equipment to areas in which a contract has not been secured are expensed as incurred. Reimbursements that we receive for out-of-pocket expenses are recorded as revenue and the out-of-pocket expenses for which they relate are recorded as operating costs.
Our management has determined that it is appropriate to use the percentage-of-completion method, as defined in ASC Topic 605 (formerly American Institute of Certified Public Accountants’ Statement of Position 81-1), to recognize revenue on our turnkey and footage contracts. Although our turnkey and footage contracts do not have express terms that provide us with rights to receive payment for the work that we perform prior to drilling wells to the agreed-on depth, we use this method because, as provided in applicable accounting literature, we believe we achieve a continuous sale for our work-in-progress and we believe, under applicable state law, we ultimately could recover the fair value of our work-in-progress even in the event we were unable to drill to the agreed-on depth in breach of the applicable contract. However, in the event we were unable to drill to the agreed-on depth in breach of the contract, ultimate recovery of that value would be subject to negotiations with the customer and the possibility of litigation.
71
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
If a customer defaults on its payment obligation to us under a turnkey or footage contract, we would need to rely on applicable law to enforce our lien rights, because our turnkey and footage contracts do not expressly grant to us a security interest in the work we have completed under the contract and we have no ownership rights in the work-in-progress or completed drilling work, except any rights arising under the applicable lien statute on foreclosure. If we were unable to drill to the agreed-on depth in breach of the contract, we also would need to rely on equitable remedies outside of the contract, including quantum meruit, available in applicable courts to recover the fair value of our work-in-progress under a turnkey or footage contract.
We accrue estimated contract costs on turnkey and footage contracts for each day of work completed based on our estimate of the total costs to complete the contract divided by our estimate of the number of days to complete the contract. Contract costs include labor, materials, supplies, repairs and maintenance, operating overhead allocations and allocations of depreciation and amortization expense. We charge general and administrative expenses to expense as we incur them. Changes in job performance, job conditions and estimated profitability on uncompleted contracts may result in revisions to costs and income. When we encounter, during the course of our drilling operations, conditions unforeseen in the preparation of our original cost estimate, we immediately increase our cost estimate for the additional costs to complete the contract. If we anticipate a loss on a contract in progress at the end of a reporting period due to a change in our cost estimate, we immediately accrue the entire amount of the estimated loss including all costs that are included in our revised estimated cost to complete that contract in our consolidated statement of operations for that reporting period. We had two turnkey or footage contracts in progress as of December 31, 2009.
Production Services—We earn revenues for well services, wireline services and fishing and rental services based on purchase orders, contracts or other persuasive evidence of an arrangement with the customer, such as master service agreements, that include fixed or determinable prices. These production services revenues are recognized when the services have been rendered and collectability is reasonably assured.
The asset “unbilled receivables” represents revenues we have recognized in excess of amounts billed on drilling contracts and production services in progress. The assets “prepaid expenses and other current assets” and “other long-term assets” include the current and long-term portions of deferred mobilization costs for certain drilling contracts. The liabilities “prepaid drilling contracts” and “other long-term liabilities” include the current and long-term portions of deferred mobilization revenues for certain drilling contracts and amounts collected on contracts in excess of revenues recognized.
Cash and Cash Equivalents
For purposes of the statements of cash flows, we consider all highly liquid debt instruments purchased with a maturity of three months or less to be cash equivalents. Cash equivalents consist of investments in corporate and government money market accounts. Cash equivalents at December 31, 2009 and 2008 were $9.9 million and $23.4 million, respectively.
Restricted Cash
As of December 31, 2009, we had restricted cash in the amount of $2.6 million held in an escrow account to be used for future payments in connection with the acquisition of Prairie Investors d/b/a Competition Wireline (“Competition”). The former owner of Competition will receive annual installments of $0.7 million payable over a five year term from the escrow account. Restricted cash of $0.7 million and $1.9 million is recorded in other current assets and other-long term assets, respectively. The associated obligation of $0.7 million and $1.9 million is recorded in other accrued expenses and other long-term liabilities, respectively.
On August 28, 2008, we deposited $0.9 million into a trust account in accordance with the terms of the severance agreement in connection with the resignation of our former Chief Financial Officer. This balance was distributed to the former Chief Financial Officer on March 3, 2009.
72
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Trade Accounts Receivable
We record trade accounts receivable at the amount we invoice our customers. These accounts do not bear interest. The allowance for doubtful accounts is our best estimate of the amount of probable credit losses in our accounts receivable as of the balance sheet date. We determine the allowance based on the credit worthiness of our customers and general economic conditions. Consequently, an adverse change in those factors could affect our estimate of our allowance for doubtful accounts. We review our allowance for doubtful accounts on a monthly basis. Balances more than 90 days past due are reviewed individually for collectability. We charge off account balances against the allowance after we have exhausted all reasonable means of collection and determined that the potential for recovery is remote. We do not have any off-balance sheet credit exposure related to our customers.
The changes in our allowance for doubtful accounts consist of the following (amounts in thousands):
| Years ended December 31, |
Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 |
|||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| Balance at beginning of year |
$ | 1,574 | $ | — | $ | 1,000 | ||||||
| Increase (decrease) in allowance charged to expense |
(1,170 | ) | 1,591 | 2,612 | ||||||||
| Accounts charged against the allowance, net of recoveries |
(118 | ) | (17 | ) | (3,612 | ) | ||||||
| Balance at end of year |
$ | 286 | $ | 1,574 | $ | — | ||||||
The decrease in the allowance for doubtful accounts during the year ended December 31, 2009 is due to the recovery of a customer’s past due account receivable balance for which we had previously established a $1.3 million allowance for doubtful accounts in December 2008. The past due receivable was collected in October 2009.
Prepaid Expenses and Other Current Assets
Prepaid expenses and other current assets include items such as insurance, rent deposits and fees, and restricted cash. We routinely expense these items in the normal course of business over the periods these expenses benefit. Prepaid expenses and other current assets also include deferred mobilization costs for certain drilling contracts that are recognized on a straight line basis over the contract term.
Investments
Other long-term assets include investments in tax exempt, auction rate preferred securities (“ARPS”). Our ARPSs are classified with other long-term assets on our condensed consolidated balance sheet as of December 31, 2009 because of our inability to determine the recovery period of our investments.
At December 31, 2009, we held $15.9 million (par value) of ARPSs, which are variable-rate preferred securities and have a long-term maturity with the interest rate being reset through “Dutch auctions” that are held every 7 days. The ARPSs have historically traded at par because of the frequent interest rate resets and because they are callable at par at the option of the issuer. Interest is paid at the end of each auction period. Our ARPSs are AAA/Aaa rated securities, collateralized by municipal bonds and backed by assets that are equal to or greater than 200% of the liquidation preference. Until February 2008, the auction rate securities market was highly liquid. Beginning mid-February 2008, we experienced several “failed” auctions, meaning that there was not enough demand to sell all of the securities that holders desired to sell at auction. The immediate effect of a failed auction is that such holders cannot sell the securities at auction and the interest rate on the security resets to a maximum auction rate. We have continued to receive interest payments on our ARPSs in accordance with their terms. We may not be able to access the funds we invested in our ARPSs without a loss of principal, unless a
73
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
future auction is successful or the issuer calls the security pursuant to redemption prior to maturity. We have no reason to believe that any of the underlying municipal securities that collateralize our ARPSs are presently at risk of default. We believe we will ultimately recover the par value of the ARPSs without a loss, primarily due to the collateral securing the ARPSs and our estimate of the discounted cash flows that we expect to collect. We do not currently intend to sell our ARPSs at a loss. Also, we believe it is more-likely-than-not that we will not have to sell our ARPSs prior to recovery, since our liquidity needs are expected to be met with cash flows from operating activities and our senior secured revolving credit facility. See Note 3 “Long-term Debt” below regarding compliance with the covenants in our credit agreement.
Our ARPSs are reported at amounts that reflect our estimate of fair value. ASC Topic 820 (formerly SFAS No. 157), provides a hierarchal framework associated with the level of subjectivity used in measuring assets and liabilities at fair value. To estimate the fair values of our ARPSs, we used inputs defined by ASC Topic 820 as level 3 inputs which are unobservable for the asset or liability and are developed based on the best information available in the circumstances. We estimate the fair value of our ARPSs based on discounted cash flow models and secondary market comparisons of similar securities. In addition, during the quarter ended June 30, 2009, we adopted the new accounting guidance under ASC Topic 320 when we evaluated the fair value of our ARPS and evaluated whether the fair value discount represented an other-than-temporary impairment.
Our ARPSs are designated as available-for-sale and are reported at fair market value with the related unrealized gains or losses, included in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss), net of tax, a component of shareholders’ equity. The estimated fair value of our ARPSs at December 31, 2009 was $13.2 million compared with a par value of $15.9 million. The $2.7 million difference represents a fair value discount due to the current lack of liquidity which is considered temporary and has been recorded as an unrealized loss, net of tax, in accumulated other comprehensive income (loss). We recorded $2.0 million of this fair value discount during the year ended December 31, 2008 and the remaining $0.7 million was recorded during the year ended December 31, 2009. There was no portion of the fair value discount attributable to credit losses. We would recognize an impairment charge in our statement of operations if the fair value of our investments falls below the cost basis and is judged to be other-than-temporary.
Inventories
Inventories primarily consist of drilling rig replacement parts and supplies held for use by our Drilling Services Division’s operations in Colombia and supplies held for use by our Production Services Division’s operations. Inventories are valued at the lower of cost (first in, first out or actual) or market value.
Property and Equipment
Property and equipment are carried at cost less accumulated depreciation. Depreciation is provided for our assets over the estimated useful lives of the assets using the straight-line method. We record the same depreciation expense whether a rig is idle or working. We charge our expenses for maintenance and repairs to operating costs. We charge our expenses for renewals and betterments to the appropriate property and equipment accounts.
74
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
As of December 31, 2009, the estimated useful lives and costs of our asset classes are as follows:
| Lives | Cost | ||||
| (amounts in thousands) | |||||
| Drilling rigs and equipment |
3 - 25 | $ | 741,803 | ||
| Workover rigs and equipment |
5 - 20 | 119,605 | |||
| Wireline units and equipment |
2 - 10 | 47,808 | |||
| Fishing and rental tools equipment |
7 | 13,164 | |||
| Vehicles |
3 - 10 | 33,722 | |||
| Office equipment |
3 - 5 | 4,736 | |||
| Buildings and improvements |
3 - 40 | 6,447 | |||
| Land |
— | 608 | |||
| $ | 967,893 | ||||
We recorded gains (losses) on disposition of our property and equipment in contract drilling costs of ($0.1) million, $0.8 million and ($2.8) million for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 and the nine months ended December 31, 2007, respectively. During each of the years ended December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008, we capitalized $0.3 million of interest costs incurred during the construction periods of certain drilling equipment. We did not capitalize any interest costs during the nine months ended December 31, 2007. We had no drilling rigs under construction at December 31, 2009.
We evaluate for potential impairment of long-lived assets and intangible assets subject to amortization when indicators of impairment are present, as defined in ASC Topic 360 (formerly SFAS No. 144), Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets. Circumstances that could indicate a potential impairment include significant adverse changes in industry trends, economic climate, legal factors, and an adverse action or assessment by a regulator. More specifically, significant adverse changes in industry trends include significant declines in revenue rates, utilization rates, oil and natural gas market prices and industry rig counts for drilling rigs and workover rigs. In performing an impairment evaluation, we estimate the future undiscounted net cash flows from the use and eventual disposition of long-lived assets and intangible assets grouped at the lowest level that cash flows can be identified. For our Production Services Division, our long-lived assets and intangible assets are grouped at the reporting unit level which is one level below the operating segment level. For our Drilling Services Division, we perform an impairment evaluation and estimate future undiscounted cash flows for individual drilling rig assets. If the sum of the estimated future undiscounted net cash flows is less than the carrying amount of the long-lived assets and intangible assets for these asset grouping levels, then we would recognize an impairment charge. The amount of an impairment charge would be measured as the difference between the carrying amount and the fair value of these assets. As described in the Intangible Asset section of Note 1, our long-lived asset and intangible asset impairment analysis for the reporting units in our Production Services Division resulted in no impairment charge to property and equipment and a non-cash impairment charge of $52.8 million to the carrying value of our intangible assets for customers relationships for the year ended December 31, 2008. This impairment charge did not have an impact on our liquidity or debt covenants; however, it was a reflection of the overall downturn in our industry and decline in our projected cash flows. We did not record an impairment charge on any long-lived assets for our Production Services Division for the year ended December 31, 2009. For our Drilling Services Division, we did not record an impairment charge on any long-lived assets for the years ended December 31, 2009 or 2008. The assumptions used in the impairment evaluation for long-lived assets and intangible assets are inherently uncertain and require management judgment.
Goodwill
Goodwill results from business acquisitions and represents the excess of acquisition costs over the fair value of the net assets acquired. We account for goodwill and other intangible assets under the provisions of ASC Topic 350 (formerly SFAS No. 142), Goodwill and Other Intangible Assets. Goodwill is tested for impairment
75
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
annually as of December 31 or more frequently if events or changes in circumstances indicate that the asset might be impaired. Circumstances that could indicate a potential impairment include a significant adverse change in the economic or business climate, a significant adverse change in legal factors, an adverse action or assessment by a regulator, unanticipated competition, loss of key personnel and the likelihood that a reporting unit or significant portion of a reporting unit will be sold or otherwise disposed of. These circumstances could lead to our net book value exceeding our market capitalization which is another indicator of a potential impairment in goodwill. ASC Topic 350 requires a two-step process for testing impairment. First, the fair value of each reporting unit is compared to its carrying value to determine whether an indication of impairment exists. All our goodwill was related to our Production Services Division operating segment and was allocated to its three reporting units which are well services, wireline services and fishing and rental services. Second, if impairment is indicated, then the fair value of the reporting unit’s goodwill is determined by allocating the unit’s fair value to its assets and liabilities (including any unrecognized intangible assets) as if the reporting unit had been acquired in a business combination on the impairment test date. The amount of impairment for goodwill is measured as the excess of the carrying value of the reporting unit over its fair value. Goodwill of $118.6 million was initially recorded in connection with the acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE, Competition, Pettus and Paltec, all of which occurred between March 1, 2008 and October 1, 2008, and was allocated to the three reporting units for our Production Services Division which are well services, wireline services and fishing and rental services. We recorded a full impairment of this goodwill during the year ended December 31, 2008 as further described below.
When estimating fair values of a reporting unit for our goodwill impairment test, we use a combination of an income approach and a market approach which incorporates both management’s views and those of the market. The income approach provides an estimated fair value based on each reporting unit’s anticipated cash flows that are discounted using a weighted average cost of capital rate. The market approach provides an estimated fair value based on our market capitalization that was computed using the prior 30-day average market price of our common stock and the number of shares outstanding as of the impairment test date. The estimated fair values computed using the income approach and the market approach were then equally weighted and combined into a single fair value. The primary assumptions used in the income approach were estimated cash flows and weighted average cost of capital. Estimated cash flows were primarily based on projected revenues, operating costs and capital expenditures and are discounted based on comparable industry average rates for weighted average cost of capital. We utilized discount rates based on weighted average cost of capital ranging from 15.8% to 16.7% when we estimated fair values of our reporting units as of December 31, 2008. The primary assumptions used in the market approach were the allocation of total market capitalization to each reporting unit, which was based on projected EBITDA percentages for each reporting unit, and control premiums, which were based on comparable industry averages. We utilized a 30% control premium when we estimated fair values of our reporting units as of December 31, 2008. To ensure the reasonableness of the estimated fair values of our reporting units, we performed a reconciliation of our total market capitalization to the total estimated fair value of all our reporting units. The assumptions used in estimating fair values of reporting units and performing the goodwill impairment test are inherently uncertain and required management judgment.
Our common stock price per share declined in market value from $13.30 at September 30, 2008, to $5.57 at December 31, 2008, which resulted in our net book value exceeding our market capitalization during most of that time period. We concluded that the decline in the market price of our common stock resulted from a significant adverse change in the economic and business climate as financial markets reacted to the credit crisis facing major lending institutions and worsening conditions in the overall economy during the fourth quarter of the year ended December 31, 2008. During the same time, there were significant declines in oil and natural gas prices which led to declines in production service revenues, margins and cash flows. We considered the impact of these significant adverse changes in the economic and business climate as we performed our annual impairment assessment of goodwill as of December 31, 2008. The estimated fair values of our reporting units were negatively impacted by significant reductions in estimated cash flows for the income approach component and a significant reduction in our market capitalization for the market approach component of our fair value estimation process. Our goodwill was initially recorded in connection with the acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE,
76
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Competition, Pettus and Paltec, all of which occurred between March 1, 2008 and October 1, 2008, when production service revenues, margins and cash flows and our market capitalization were at historically high levels.
Our goodwill impairment analysis led us to conclude that there would be no remaining implied fair value attributable to our goodwill and, accordingly, we recorded a non-cash charge of $118.6 million to our operating results for the year ended December 31, 2008, for the full impairment of our goodwill. Our goodwill impairment analysis would have led to the same full impairment conclusion if we increased or decreased our discount rates or control premiums by 10% when estimating the fair values of our reporting units. This impairment charge did not have an impact on our liquidity or debt covenants; however, it was a reflection of the overall downturn in our industry and decline in our projected cash flows.
Changes in the carrying amount of goodwill by operating segment are as follows (amounts in thousands):
| Drilling Services Division |
Production Services Division |
Total | |||||||||
| Goodwill balance at January 1, 2008 |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
| Goodwill relating to acquisitions |
— | 118,646 | 118,646 | ||||||||
| Impairment |
— | (118,646 | ) | (118,646 | ) | ||||||
| Goodwill balance at December 31, 2008 |
$ | — | $ | — | $ | — | |||||
We had no goodwill additions during the year ended December 31, 2009, and consequently, have no goodwill reflected on our consolidated balance sheet at December 31, 2009.
Intangible Assets
All our intangible assets are subject to amortization and consist of customers relationships, non-compete agreements and trade names. Essentially all of our intangible assets were recorded in connection with the acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE, Competition, Pettus and Paltec, all of which occurred between March 1, 2008 and October 1, 2008 as described in Note 2. Intangible assets consist of the following components (amounts in thousands):
| December 31, 2009 |
December 31, 2008 |
|||||||
| Cost: |
||||||||
| Customer Relationships |
$ | 32,039 | $ | 87,316 | ||||
| Non-compete |
2,304 | 2,304 | ||||||
| Trade marks |
143 | 1,656 | ||||||
| Accumulated amortization: |
||||||||
| Customer Relationships |
(7,509 | ) | (6,069 | ) | ||||
| Non-compete |
(1,584 | ) | (791 | ) | ||||
| Trade marks |
— | (1,600 | ) | |||||
| Impairment: |
||||||||
| Customer Relationships |
— | (52,847 | ) | |||||
| $ | 25,393 | $ | 29,969 | |||||
We evaluate for potential impairment of long-lived assets and intangible assets subject to amortization when indicators of impairment are present, as defined in ASC Topic 360 (formerly SFAS No. 144), Accounting for the Impairment or Disposal of Long-Lived Assets. Circumstances that could indicate a potential impairment include significant adverse changes in industry trends, economic climate, legal factors, and an adverse action or
77
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
assessment by a regulator. More specifically, significant adverse changes in industry trends include significant declines in revenue rates, utilization rates, oil and natural gas market prices and industry rig counts for drilling rigs and workover rigs. In performing the impairment evaluation, we estimate the future undiscounted net cash flows relating to long-lived assets and intangible assets grouped at the lowest level that cash flows can be identified. Our long-lived assets and intangible assets for our Production Services Division are grouped one level below the operating segment in the three reporting units which are well services, wireline services and fishing and rental services. If the sum of the estimated future undiscounted net cash flows is less than the carrying amount of the long-lived assets and intangible assets in each reporting unit, then we would recognize an impairment charge. The amount of an impairment charge would be measured as the difference between the carrying amount and the fair value of these assets. The assumptions used in the impairment evaluation for long-lived assets and intangible assets are inherently uncertain and require management judgment.
We performed an impairment analysis of our long-lived assets and intangible assets at December 31, 2008, due to significant adverse changes in the economic and business climate that resulted in decreases in estimated revenues, margins and cash flows. Essentially all our intangible assets were recorded in connection with the acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE, Competition, Pettus and Paltec when revenues, margins and cash flows were at historically high levels in early 2008. We determined that the sum of the estimated future undiscounted net cash flows was less than the carrying amount of the long-lived assets and intangible assets in each reporting unit at December 31, 2008. Our impairment analysis resulted in a reduction to our intangible asset carrying value of customers relationships and a non-cash impairment charge of $52.8 million recorded to our operating results for the year ended December 31, 2008.
The cost of our customer relationships is amortized using the straight-line method over their respective estimated economic useful lives which range from seven to eight years. Amortization expense for our non-compete agreements are calculated using the straight-line method over the period of the agreements which range from one to five years. Amortization expense was $4.7 million for the year ended December 31, 2009, $8.4 million for the year ended December 31, 2008 and $34,000 for the nine month period ended December 31, 2007. Amortization expense is estimated to be approximately $4.5 million, $4.0 million, $3.9 million, $3.9 million and $3.9 million for the years ending December 31, 2010, 2011, 2012, 2013 and 2014, respectively. These future amortization amounts are estimates and reflect the impact of the $52.8 million impairment charge to intangible assets recorded in the year ended December 31, 2008. Actual amortization amounts may be different due to future acquisitions, impairments, changes in amortization periods, or other factors.
Other Long-Term Assets
Other long-term assets consist of our investment in ARPSs, restricted cash held in an escrow account, cash deposits related to the deductibles on our workers’ compensation insurance policies, the long-term portion of deferred mobilization costs and loan fees, net of amortization. Loan fees are being amortized over the 35 month term of the related senior secured revolver credit facility described in Note 3.
Treasury Stock
Treasury stock purchases are accounted for under the cost method whereby the cost of the acquired common stock is recorded as treasury stock. Gains and losses on the subsequent reissuance of treasury stock shares are credited or charged to additional paid in capital using the average cost method.
Income Taxes
Pursuant to ASC Topic 740 (formerly SFAS No. 109), we follow the asset and liability method of accounting for income taxes, under which we recognize deferred tax assets and liabilities for the future tax consequences attributable to differences between the financial statement carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and their respective tax basis. We measure our deferred tax assets and liabilities by using the enacted
78
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
tax rates we expect to apply to taxable income in the years in which we expect to recover or settle those temporary differences. Under ASC Topic 740, we reflect in income the effect of a change in tax rates on deferred tax assets and liabilities in the period during which the change occurs.
Comprehensive Income (Loss)
Comprehensive income (loss) is comprised of net income (loss) and other comprehensive loss. Other comprehensive loss includes the change in the fair value of our ARPSs, net of tax, for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008. We did not have other comprehensive income (loss) for the nine months ended December 31, 2007. The following table sets forth the components of comprehensive income (loss):
| Years ended December 31, |
Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 | ||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
| (amounts in thousands) | |||||||||||
| Net income (loss) |
$ | (23,215 | ) | $ | (62,745 | ) | $ | 39,645 | |||
| Other comprehensive loss—unrealized loss on securities |
(448 | ) | (1,245 | ) | — | ||||||
| Comprehensive income (loss) |
$ | (23,663 | ) | $ | (63,990 | ) | $ | 39,645 | |||
Earnings Per Common Share
We compute and present earnings per common share in accordance with ASC Topic 260 (formerly SFAS No. 128), Earnings per Share. This standard requires dual presentation of basic and diluted earnings per share on the face of our statement of operations.
Stock-based Compensation
We recognize compensation cost for stock-based compensation based on the grant-date fair value estimated in accordance with ASC Topic 718 (formerly SFAS No. 123R) and we utilize the graded vesting method. Compensation costs of approximately $4.3 million and $1.0 million for stock options were recognized in selling, general and administrative expense and operating costs, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2009. Compensation costs of approximately $3.1 million and $0.9 million for stock options were recognized in selling, general and administrative expense and operating costs, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2008. Compensation costs of approximately $2.5 million and $0.7 million for stock options were recognized in selling, general and administrative and operating costs, respectively, for the nine months ended December 31, 2007.
We receive a tax deduction for certain stock option exercises during the period the options are exercised, generally for the excess of the market price of our common stock on the exercise date over the exercise price of the stock options. In accordance with ASC Topic 718, we reported all excess tax benefits resulting from the exercise of stock options as financing cash flows in our consolidated statement of cash flows. There were no stock options exercised during the year ended December 31, 2009. During the year ended December 31, 2008, there were 170,054 stock options exercised.
Restricted stock awards consist of our common stock that vest over a 3 year period. The fair value of restricted stock is based on the closing price of our common stock on the date of the grant. We amortize the fair value of the restricted stock awards to compensation expense using the graded vesting method. For the year ended December 31, 2009, 326,748 restricted stock awards were granted with a weighted-average grant date price of $4.23 and for the year ended December 31, 2008, 178,261 restricted stock awards were granted with a weighted-average grant date price of $17.07. Compensation costs of approximately $1.6 million and $0.3 million for restricted stock awards were recognized in selling, general and administrative expense and operating costs,
79
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2009. Compensation costs of approximately $0.5 million and $0.1 million for restricted stock awards were recognized in selling, general and administrative expense and operating costs, respectively, for the year ended December 31, 2008.
Related-Party Transactions
Our Chief Executive Officer, President of Drilling Services Division, Senior Vice President of Drilling Services Division—Marketing, and a Vice President of Drilling Services Division—Operations occasionally acquire at fair value a 1% to 5% minority working interest in oil and natural gas wells that we drill for one of our customers. These individuals did not own a working interest in any wells that we drilled for this customer during the year ended December 31, 2009. Our President of Drilling Services Division acquired a minority working interest in two wells that we drilled for this customer during the year ended December 31, 2008. These individuals acquired minority working interests in four wells that we drilled for this customer during the nine months ended December 31, 2007. We recognized drilling services revenues of $2.0 million and $1.6 million on these wells during the year ended December 31, 2008 and the nine months ended December 31, 2007, respectively.
In connection with the acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE Group Incorporated (“WEDGE”) and Competition on March 1, 2008, we have leases for various operating and office facilities with entities that are owned by former WEDGE employees and Competition employees that are now employees of our company. Rent expense for the year ended December 31, 2009 was approximately $0.7 million for these related party leases. In addition, we have non-compete agreements with several former WEDGE employees that are now employees of our company. These non-compete agreements are recorded as intangible assets with a cost, net of accumulated amortization, of $0.7 million at December 31, 2009. See note 2 for further information regarding the acquisitions.
We had aggregate purchases of $0.6 million of goods and services during the year ended December 31, 2009 from twelve vendors that are owned by company employees or family members of company employees.
Reclassifications
Certain amounts in the financial statements for the prior years have been reclassified to conform to the current year’s presentation.
| 2. | Acquisitions |
On March 1, 2008, we acquired the production services business from WEDGE which provided well services, wireline services and fishing and rental services with a fleet of 62 workover rigs, 45 wireline units and approximately $13 million of fishing and rental equipment through its facilities in Texas, Kansas, North Dakota, Colorado, Utah and Oklahoma. The aggregate purchase price for the acquisition was approximately $314.7 million, which consisted of assets acquired of $340.8 million and liabilities assumed of $26.1 million. The aggregate purchase price includes $3.4 million of costs incurred to acquire the production services business from WEDGE. We financed the acquisition with approximately $3.2 million of cash on hand and $311.5 million of debt incurred under our senior secured revolving credit facility described in Note 3.
80
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
The following table summarizes the allocation of the purchase price and related acquisition costs to the estimated fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed as of the date of acquisition (amounts in thousands):
| Cash acquired |
$ | 1,168 | |
| Other current assets |
22,102 | ||
| Property and equipment |
138,493 | ||
| Intangibles and other assets |
66,118 | ||
| Goodwill |
112,869 | ||
| Total assets acquired |
$ | 340,750 | |
| Current liabilities |
$ | 10,655 | |
| Long-term debt |
1,462 | ||
| Other long term liabilities |
13,949 | ||
| Total liabilities assumed |
$ | 26,066 | |
| Net assets acquired |
$ | 314,684 | |
The following unaudited pro forma consolidated summary financial information gives effect of the acquisition of the production services business from WEDGE as though it was effective as of the beginning of the year ended December 31, 2008. Pro forma adjustments primarily relate to additional depreciation, amortization and interest costs. The pro forma information reflects our company’s historical data and historical data from the acquired production services business from WEDGE for the periods indicated. The pro forma data may not be indicative of the results we would have achieved had we completed the acquisition on January 1, 2008, or what we may achieve in the future and should be read in conjunction with the accompanying historical financial statements.
| Pro Forma Year Ended December 31, 2008 |
||||
| (in thousands) | ||||
| Total revenues |
$ | 634,535 | ||
| Net (loss) earnings |
$ | (62,514 | ) | |
| (Loss) earnings per common share |
||||
| Basic |
$ | (1.26 | ) | |
| Diluted |
$ | (1.26 | ) | |
On March 1, 2008, immediately following the acquisition of the production services business from WEDGE, we acquired the production services business from Competition which provided wireline services with a fleet of 6 wireline units through its facilities in Montana. The aggregate purchase price for the Competition acquisition was approximately $30.0 million, which consisted of assets acquired of $30.1 million and liabilities assumed of $0.1 million. The aggregate purchase price includes $0.4 million of costs incurred to acquire the production services business from Competition. We financed the acquisition with $26.7 million cash on hand and a note payable due to the prior owner for $3.3 million. Goodwill of $5.3 million and intangible assets and other assets of $18.0 million were recorded in connection with the acquisition.
On August 29, 2008, we acquired the wireline services business from Paltec, Inc. The aggregate purchase price was $7.8 million which we financed with $6.5 million in cash and a sellers note of $1.3 million. Intangible and other assets of $4.3 million and goodwill of $0.1 million were recorded in connection with the acquisition.
81
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
On October 1, 2008, we acquired the well services business from Pettus Well Service. The aggregated purchase price was $3.0 million which we financed with $2.8 million in cash and a sellers note of $0.2 million. Intangible and other assets of $1.2 million and goodwill of $0.1 million were recorded in connection with the acquisition.
The acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE, Competition, Paltec and Pettus were accounted for as acquisitions of businesses. The purchase price allocations for these production services businesses were finalized as of December 31, 2008. Goodwill was recognized as part of the WEDGE, Competition, Paltec and Pettus acquisitions since the purchase price exceeded the estimated fair value of the assets acquired and liabilities assumed. We believed that the goodwill was related to the acquired workforces, future synergies between our existing Drilling Services Division and our new Production Services Division and the ability to expand our service offerings. These acquisitions occurred between March 1, 2008 and October 1, 2008, when production service revenues, margins and cash flows and our market capitalization were at historically high levels. As described in Note 1, our goodwill impairment analysis performed at December 31, 2008 led us to conclude that there would be no remaining implied value attributable to our goodwill and accordingly, we recorded a non-cash charge of $118.6 million for a full impairment of goodwill relating to these acquisitions. We also performed an impairment analysis which resulted in an impairment charge of $52.8 million and reduction in the intangible asset carrying value of customer relationships relating to these acquisitions. These impairment charges were primarily related to significant adverse changes in the economic and business climate that occurred during the fourth quarter of the year ended December 31, 2008.
| 3. | Long-term Debt, Subordinated Debt and Note Payable |
Long-term debt as of December 31, 2009 consists of the following (amounts in thousands):
| Senior secured credit revolving facility |
$ | 257,500 | ||
| Subordinated notes payable |
4,387 | |||
| Other |
227 | |||
| 262,114 | ||||
| Less current portion |
(4,041 | ) | ||
| $ | 258,073 | |||
Senior Secured Revolving Credit Facility
On February 29, 2008, we entered into a credit agreement with Wells Fargo Bank, N.A. and a syndicate of lenders (the “Initial Credit Agreement”). On October 5, 2009, we entered into a First Amendment to the Initial Credit Agreement (the “Amended Credit Agreement”).
Initial Credit Agreement—The Initial Credit Agreement provided for a senior secured revolving credit facility, with sub-limits for letters of credit and swing-line loans, of up to an aggregate principal amount of $400 million, all of which would have matured on February 28, 2013. The Initial Credit Agreement contained customary mandatory prepayments in respect of asset dispositions, debt incurrence and equity issuances which prepayments were applied to reduce outstanding revolving and swing-line loans and letter of credit exposure without a permanent reduction of commitments. Our obligations under the Initial Credit Agreement were secured by substantially all of our domestic assets (excluding any equity interests in, and any assets of, Pioneer Global Holdings, Inc. and its subsidiaries, which are the entities that comprise our international operations) and were guaranteed by certain of our domestic subsidiaries (excluding Pioneer Global Holdings, Inc.). Borrowings under the Initial Credit Agreement bore interest, at our option, at the bank prime rate or at the LIBOR rate, plus an applicable per annum margin in each case. The applicable per annum margin was determined based upon our leverage ratio in accordance with a pricing grid in the Initial Credit Agreement. The per annum margin for LIBOR rate borrowings ranged from 1.50% to 2.50% and the per annum margin for bank prime rate borrowings
82
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
ranged from 0.50% to 1.50%. A commitment fee was due quarterly based on the average daily unused amount of the commitments of the lenders under the Initial Credit Agreement. In addition, a fronting fee was due for each letter of credit issued and a quarterly letter of credit fee was due based on the average undrawn amount of letters of credit outstanding during such period. Borrowings under the Initial Credit Agreement were used to fund the WEDGE acquisition and were available for acquisitions, working capital and other general corporate purposes.
Amended Credit Agreement—Effective October 5, 2009, our Amended Credit Agreement provides for a senior secured revolving credit facility, with sub-limits for letters of credit and swing-line loans, of up to an aggregate principal amount of $325 million, all of which mature on August 31, 2012. The Amended Credit Agreement contains customary mandatory prepayments in respect of asset dispositions, debt incurrence and equity issuances, and commencing with the fiscal year ending December 31, 2009, if the senior consolidated leverage ratio is greater than 2.50 to 1.00 at the end of any fiscal year, the Amended Credit Agreement requires mandatory prepayments equal to 50% of our excess cash flows. Borrowings and commitments under the Amended Credit Agreement will be reduced concurrently with the application of certain mandatory prepayments by the amount of such mandatory prepayment, but in no event be reduced to less than $200,000,000 as a result of such mandatory prepayments. Our obligations under the Amended Credit Agreement are secured by substantially all of our domestic assets (including equity interests in Pioneer Global Holdings, Inc. and 65% of the outstanding equity interests of any first-tier foreign subsidiaries owned by Pioneer Global Holdings, Inc., but excluding any equity interest in, and any assets of, Pioneer Services Holdings, LLC) and are guaranteed by certain of our domestic subsidiaries, including Pioneer Global Holdings, Inc. Borrowings under the Amended Credit Agreement bear interest, at our option, at the bank prime rate or at the LIBOR rate, plus an applicable per annum margin in each case. The applicable per annum margin is determined based upon our leverage ratio in accordance with a pricing grid in the Amended Credit Agreement. The per annum margin for LIBOR rate borrowings ranges from 3.50% to 6.00% and the per annum margin for bank prime rate borrowings ranges from 2.50% to 5.00%. The LIBOR margin and bank prime rate margin in effect at February 5, 2010 are 3.5% and 2.5%, respectively. A commitment fee is due quarterly based on the average daily unused amount of the commitments of the lenders under the Amended Credit Agreement. In addition, a fronting fee is due for each letter of credit issued and a quarterly letter of credit fee is due based on the average undrawn amount of letters of credit outstanding during such period. Borrowings under the Amended Credit Agreement are available for acquisitions, working capital and other general corporate purposes.
At December 31, 2009, our senior consolidated leverage ratio was greater than 2.5 to 1.00 which resulted in a mandatory prepayment requirement (and corresponding reduction in the commitments under the Amended Credit Agreement) based on 50% of our excess cash flows, as defined in the Amended Credit Agreement, and due within 90 days of year end. We classified this mandatory prepayment of $1.9 million in the current portion of long-term debt as of December 31, 2009. After we pay the mandatory prepayment of $1.9 million, borrowing capacity under the Amended Credit Agreement will be reduced from $325 million to $323.1 million. We may choose to make additional principal payments to reduce the outstanding debt balance prior to maturity on August 31, 2012 when cash and working capital is sufficient.
At February 5, 2010, the borrowing capacity under our senior secured revolving credit facility is reduced by the outstanding balance of $257.5 million, and committed letters of credit of $11.5 million, which results in borrowing availability of $56.0 million. There are no limitations on our ability to access this borrowing capacity other than maintaining compliance with the covenants under the Amended Credit Agreement.
The financial covenants contained in our Amended Credit Agreement include the following:
| • | A maximum total consolidated leverage ratio that cannot exceed: |
| • | 4.25 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2009; |
| • | 5.00 to 1.00 as of the end of any fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2010 through June 30, 2011; |
| • | 4.75 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending September 30, 2011; |
83
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| • | 4.50 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2011; |
| • | 4.25 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2012; and |
| • | 4.00 to 1.00 as of the end of any fiscal quarter ending June 30, 2012 and thereafter. |
| • | A maximum senior consolidated leverage ratio, which excludes unsecured and subordinated debt, that cannot exceed: |
| • | 4.25 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2009; |
| • | 5.00 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarters ending March 31, 2010 and June 30, 2010; |
| • | 4.75 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending September 30, 2010; |
| • | 4.50 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2010; |
| • | 4.25 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2011; |
| • | 4.00 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending June 30, 2011; |
| • | 3.75 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending September 30, 2011; |
| • | 3.50 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2011; |
| • | 3.25 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2012; and |
| • | 3.00 to 1.00 as of the end of any fiscal quarter ended June 30, 2012 and thereafter. |
| • | A minimum interest coverage ratio that cannot be less than: |
| • | 3.00 to 1.00 as of the end of the fiscal quarter ending December 31, 2009; |
| • | 2.00 to 1.00 as of the end of any fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2010 through December 31, 2011; and |
| • | 3.00 to 1.00 as of the end of any fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2012 and thereafter. |
| • | If our senior consolidated leverage ratio is greater than 2.25 to 1.00 at the end of any fiscal quarter, a minimum asset coverage ratio that cannot be less than 1.00 to 1.00 for any fiscal quarter ending on or before December 31, 2011, and 1.10 to 1.00 for any fiscal quarter ending March 31, 2012 and thereafter (as provided in the Amended Credit Agreement). If our senior consolidated leverage ratio is greater than 2.25 to 1.00 and our asset coverage ratio is less than 1.00 to 1.00, then borrowings outstanding under the Amended Credit Agreement will be limited to the sum of 80% of eligible accounts receivable, 80% of the orderly liquidation value of eligible equipment and 40% of the net book value of certain other fixed assets. |
The Amended Credit Agreement restricts capital expenditures unless (a) after giving effect to such capital expenditure, no event of default would exist under the Amended Credit Agreement and availability under the Amended Credit Agreement would be equal to or greater than $25 million and (b) if the senior consolidated leverage ratio as of the last day of the most recent reported fiscal quarter was equal to or greater than 2.50 to 1.00, such capital expenditure would not cause the sum of all capital expenditures to exceed:
| • | $52 million for the second half of fiscal year 2009; |
| • | $65 million for fiscal year 2010; and |
| • | $80 million for each fiscal year thereafter. |
The capital expenditure thresholds for each period noted above may be increased by:
| • | the first $25 million of any aggregate equity issuance proceeds received during such period and 25% of any equity issuance proceeds received in excess of $25 million during such period; and |
| • | 25% of any debt incurrence proceeds received during such period. |
84
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
In addition, any unused portion of the capital expenditure threshold up to $30 million can be carried over from the immediate preceding fiscal year.
At December 31, 2009, we were in compliance with our financial covenants. Our total consolidated leverage ratio was 3.3 to 1.0, our senior consolidated leverage ratio was 3.3 to 1.0, our interest coverage ratio was 9.0 to 1.0 and our asset coverage ratio was 1.6 to 1.0. The Amended Credit Agreement has additional restrictive covenants that, among other things, limit the incurrence of additional debt, investments, liens, dividends, acquisitions, redemptions of capital stock, prepayments of indebtedness, asset dispositions, mergers and consolidations, transactions with affiliates, hedging contracts, sale leasebacks and other matters customarily restricted in such agreements. In addition, the Amended Credit Agreement contains customary events of default, including without limitation, payment defaults, breaches of representations and warranties, covenant defaults, cross-defaults to certain other material indebtedness in excess of specified amounts, certain events of bankruptcy and insolvency, judgment defaults in excess of specified amounts, failure of any guaranty or security document supporting the credit agreement and change of control.
Subordinated Notes Payable and Other
In addition to amounts outstanding under the senior secured revolving credit facility, long-term debt includes subordinated notes payable to certain employees that are former shareholders of the production services businesses that were acquired by WEDGE prior to our acquisition of WEDGE on March 1, 2008, a subordinated note payable to an employee that is a former shareholder of Competition, two subordinated notes payable to certain employees that are former shareholders of Paltec, Inc. and Pettus Well Service. These subordinated notes payable have interest rates ranging from 5.4% to 14%, require quarterly or annual payments of principal and interest and have final maturity dates ranging from November 2010 to March 2013. The aggregate outstanding balance of these subordinated notes payable was $4.4 million as of December 31, 2009.
Other debt represents a financing arrangement for computer software with an outstanding balance of $0.2 million at December 31, 2009.
| 4. | Leases |
We lease our corporate office facilities in San Antonio, Texas at a cost escalating from $27,360 per month to $29,316 per month pursuant to a lease extending through December 2013. We recognize rent expense on a straight line basis for our corporate office lease. In addition, we lease real estate at 37 other locations under non-cancelable operating leases at costs ranging from $240 per month to $12,402 per month, pursuant to leases expiring through October 2014. These real estate locations are used primarily for division offices and storage and maintenance yards. We also lease office equipment under non-cancelable operating leases expiring through November 2012.
Future lease obligations required under non-cancelable operating leases as of December 31, 2009 were as follows (amounts in thousands):
| Years Ended December 31, |
|||
| 2010 |
$ | 2,119 | |
| 2011 |
1,554 | ||
| 2012 |
1,169 | ||
| 2013 |
935 | ||
| 2014 |
226 | ||
| Thereafter |
— | ||
| $ | 6,003 | ||
Rent expense under operating leases for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, was $2.1 million and $1.4 million, respectively. Rent expense for the nine months ended December 31, 2007 was $0.3 million.
85
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| 5. | Income Taxes |
The jurisdictional components of income (loss) before income taxes consist of the following (amounts in thousands):
| Year Ended December 31, 2009 |
Year Ended December 31, 2008 |
Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 | |||||||||
| Domestic |
$ | (46,221 | ) | $ | (62,388 | ) | $ | 55,752 | |||
| Foreign |
6,049 | 5,700 | 2,022 | ||||||||
| Income (loss) before income tax |
$ | (40,172 | ) | $ | (56,688 | ) | $ | 57,774 | |||
The components of our income tax expense (benefit) consist of the following (amounts in thousands):
| Year Ended December 31, 2009 |
Year Ended December 31, 2008 |
Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 |
||||||||||
| Current tax: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
$ | (46,073 | ) | $ | 3,777 | $ | 10,587 | |||||
| State |
(2,969 | ) | 1,181 | 1,593 | ||||||||
| Foreign |
1,087 | 348 | — | |||||||||
| (47,955 | ) | 5,306 | 12,180 | |||||||||
| Deferred taxes: |
||||||||||||
| Federal |
31,740 | 476 | 6,533 | |||||||||
| State |
3,390 | (211 | ) | (100 | ) | |||||||
| Foreign |
(4,132 | ) | 486 | (484 | ) | |||||||
| 30,998 | 751 | 5,949 | ||||||||||
| Income tax expense (benefit) |
$ | (16,957 | ) | $ | 6,057 | $ | 18,129 | |||||
The difference between the income tax expense and the amount computed by applying the federal statutory income tax rate 35% to income (loss) before income taxes consist of the following (amounts in thousands):
| Years ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 |
|||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| Expected tax expense (benefit) |
$ | (14,060 | ) | $ | (19,840 | ) | $ | 20,221 | ||||
| State income taxes |
274 | 556 | 971 | |||||||||
| Incentive stock options |
243 | 508 | 538 | |||||||||
| Goodwill impairment |
— | 26,752 | — | |||||||||
| Tax benefits in foreign jurisdictions |
(5,162 | ) | (1,377 | ) | (1,191 | ) | ||||||
| Domestic production activities deduction |
1,130 | (457 | ) | (729 | ) | |||||||
| Tax-exempt interest income |
(33 | ) | (219 | ) | (475 | ) | ||||||
| Non deductible items for tax purposes |
218 | 247 | 61 | |||||||||
| Uncertain tax positions |
— | — | (717 | ) | ||||||||
| Other, net |
433 | (113 | ) | (550 | ) | |||||||
| $ | (16,957 | ) | $ | 6,057 | $ | 18,129 | ||||||
86
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
Income tax expense (benefit) was allocated as follows (amounts in thousands):
| Years ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 |
|||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| Results of operations |
$ | (16,957 | ) | $ | 6,057 | $ | 18,129 | |||||
| Stockholders’ equity |
(26 | ) | (963 | ) | (54 | ) | ||||||
| $ | (16,983 | ) | $ | 5,094 | $ | 18,075 | ||||||
Deferred income taxes arise from temporary differences between the tax bases of assets and liabilities and their reported amounts in the consolidated financial statements. The components of our deferred income tax assets and liabilities were as follows (amounts in thousands):
| December 31, 2009 |
December 31, 2008 |
||||||
| Deferred tax assets: |
|||||||
| Auction rate preferred securities |
$ | 983 | $ | 719 | |||
| Intangibles |
22,365 | 23,207 | |||||
| Employee benefits and insurance claims accruals |
3,338 | 4,963 | |||||
| Accounts receivable reserve |
99 | 600 | |||||
| Employee stock based compensation |
4,439 | 2,222 | |||||
| Accrued expenses not deductible for tax purposes |
1,919 | 1,730 | |||||
| Accrued revenue not income for book purposes |
1,649 | 1,784 | |||||
| Federal and state net operating loss and AMT credit carryforward |
4,718 | — | |||||
| Foreign net operating loss carryforward |
4,071 | 4,705 | |||||
| 43,581 | 39,930 | ||||||
| Valuation allowance |
— | (5,382 | ) | ||||
| Total deferred tax assets |
43,581 | 34,548 | |||||
| Deferred tax liabilities: |
|||||||
| Property and equipment |
125,855 | 89,193 | |||||
| Total deferred tax liabilities |
125,855 | 89,193 | |||||
| Net deferred tax liabilities |
$ | 82,274 | $ | 54,645 | |||
In assessing the realizability of deferred tax assets, we consider whether it is more likely than not that some portion or all of the deferred tax assets will not be realized. Based on the expectation of future taxable income and that the deductible temporary differences will offset existing taxable temporary differences, we believe it is more likely than not that we will realize the benefits of these deductible temporary differences.
As of December 31, 2009, we had foreign deferred tax assets consisting of foreign net operating losses and other tax benefits available to reduce future taxable income in a foreign jurisdiction. The foreign net operating loss is primarily due to the special income tax benefits permitted by the Colombian government that allows us to recover 140% of the cost of certain imported assets. In assessing the realizability of our foreign deferred tax assets, we only recognize a tax benefit to the extent of taxable income that we expect to earn in the foreign jurisdiction in future periods. With the downturn in the industry in late 2008, we recorded a valuation allowance of $5.4 million that fully offset our foreign deferred tax asset at December 31, 2008. During 2009, our foreign operations generated taxable income, and in January 2010, we finalized drilling contracts for six drilling rigs located in Colombia that each have a three-year term. We estimate that these drilling contracts will result in taxable income in Colombia in excess of our foreign net operating losses. We expect to apply the foreign net
87
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
operating losses against the current year taxable income and taxable income that we have estimated in these future periods. Therefore, we removed the valuation allowance that fully offset our foreign deferred tax assets which resulted in a tax benefit of $5.4 million recognized in the year ended December 31, 2009.
Deferred income taxes have not been provided on the future tax consequences attributable to difference between the financial statements carrying amounts of existing assets and liabilities and the respective tax bases of our foreign subsidiary based on the determination that such differences are essentially permanent in duration in that the earnings of the subsidiary is expected to be indefinitely reinvested in foreign operations. As of December 31, 2009, the cumulative undistributed earnings of the subsidiary was approximately $3.7 million. If those earnings were not considered indefinitely reinvested, deferred income taxes would have been recorded after consideration of foreign tax credits. It is not practicable to estimate the amount of additional tax that might be payable on those earnings, if distributed.
We have no unrecognized tax benefits relating to ASC Topic 740 (formerly FIN No. 48) and no unrecognized tax benefit activity during the year ended December 31, 2009.
We adopted a policy to record interest and penalty expense related to income taxes as interest and other expense, respectively. At December 31, 2009, no interest or penalties have been or are required to be accrued. Our open tax years for our federal income tax returns in the United States are for the years ended March 31, 2007, December 31, 2007 and December 31, 2008. Our open tax years for our federal income tax returns in Colombia are for the years ended December 31, 2007 and December 31, 2008.
| 6. | Fair Value of Financial Instruments |
The carrying amounts of our cash and cash equivalents, trade receivables and payables approximate their fair values.
The fair value of our long-term debt is estimated using a discounted cash flow analysis, based on rates that we believe we would currently pay for similar types of debt instruments. This discounted cash flow analysis based on observable inputs for similar types of debt instruments represents level 2 inputs as defined by ASC Topic 820 (formerly SFAS No. 157). The following table presents the supplemental fair value information about long-term debt at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 (amounts in thousands):
| December 31, 2009 | December 31, 2008 | |||||||||||
| Carrying Amount |
Fair Value |
Carrying Amount |
Fair Value | |||||||||
| Total debt |
$ | 262,114 | $ | 262,429 | $ | 279,413 | $ | 250,943 | ||||
88
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| 7. | Earnings (loss) Per Common Share |
The following table presents a reconciliation of the numerators and denominators of the basic earnings (loss) per share and diluted earnings (loss) per share comparisons as required by ASC Topic 260 (amounts in thousands, except per share data):
| Years ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 | ||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | ||||||||||
| Basic |
|||||||||||
| Net (loss) earnings |
$ | (23,215 | ) | $ | (62,745 | ) | $ | 39,645 | |||
| Weighted average shares |
50,313 | 49,789 | 49,645 | ||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per share |
$ | (0.46 | ) | $ | (1.26 | ) | $ | 0.80 | |||
| Diluted |
|||||||||||
| Net (loss) earnings |
$ | (23,215 | ) | $ | (62,745 | ) | $ | 39,645 | |||
| Effect of dilutive securities |
— | — | — | ||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) available to common shareholders after assumed conversion |
$ | (23,215 | ) | $ | (62,745 | ) | $ | 39,645 | |||
| Weighted average shares: |
|||||||||||
| Outstanding |
50,313 | 49,789 | 49,645 | ||||||||
| Options |
— | — | 556 | ||||||||
| 50,313 | 49,789 | 50,201 | |||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per share |
$ | (0.46 | ) | $ | (1.26 | ) | $ | 0.79 | |||
Outstanding stock options and restricted common stock awards representing 279,949 and 546,429 shares of common stock were excluded from the diluted loss per share calculations for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008, respectively, because the effect of their inclusion would be anti-dilutive, or would decrease the reported loss per share.
| 8. | Equity Transactions |
On November 10, 2009, we sold 3,820,000 shares of our common stock at $6.75 per share, less underwriters’ commissions, pursuant to a public offering under a shelf registration statement.
Employees did not exercise any stock options during the year ending December 31, 2009. Employees exercised stock options for the purchase of 170,054 shares of common stock at prices ranging from $3.67 to $10.31 per share during the year December 31, 2008. Employees exercised stock options for the purchase of 22,500 shares of common stock at prices ranging from $4.52 to $4.77 per share during the nine months ended December 31, 2007.
Employees and directors were awarded 326,748 shares of restricted stock that vest over a three year period with a weighted-average grant date price of $4.23 during the year ended December 31, 2009. Employees and directors were awarded 178,261 shares of restricted stock that vest over a three year period with a weighted-average grant date price of $17.07 during the year ended December 31, 2008.
| 9. | Stock Option and Restricted Stock Plans |
We have stock based award plans that are administered by the Compensation Committee of our Board of Directors, which selects persons eligible to receive awards and determines the number of stock options or
89
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
restricted stock subject to each award and the terms, conditions and other provisions of the awards. Employee stock option awards generally become exercisable over three- to five-year periods, and generally expire 10 years after the date of grant. Stock option awards granted to outside directors vest immediately and expire five years after the date of grant. Our plans provide that all stock options must have an exercise price not less than the fair market value of our common stock on the date of grant. Restricted stock awards consist of our common stock that vest over a three year period. Total shares available for future stock option grants and restricted stock grants to employees and directors under existing plans were 1,939,807 at December 31, 2009. Of the total shares available, no more than 514,401 shares may be granted in the form of restricted stock.
We estimate the fair value of each stock option grant on the date of grant using a Black-Scholes options-pricing model. The following table summarizes the assumptions used in the Black-Scholes option-pricing model for the years ended December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 and for the nine months ended December 31, 2007:
| Years ended December 31, | Nine Months Ended December 31, 2007 |
|||||||||||
| 2009 | 2008 | |||||||||||
| Expected volatility |
58 | % | 44 | % | 46 | % | ||||||
| Weighted-average risk-free interest rates |
2.1 | % | 2.7 | % | 4.7 | % | ||||||
| Weighted-average expected life in years |
5.48 | 3.72 | 4.00 | |||||||||
| Weighted-average grant-date fair value |
$ | 2.09 | $ | 5.66 | $ | 5.84 | ||||||
The assumptions above are based on multiple factors, including historical exercise patterns of homogeneous groups with respect to exercise and post-vesting employment termination behaviors, expected future exercising patterns for these same homogeneous groups and volatility of our stock price. As we have not declared dividends since we became a public company, we did not use a dividend yield. In each case, the actual value that will be realized, if any, will depend on the future performance of our common stock and overall stock market conditions. There is no assurance the value an optionee actually realizes will be at or near the value we have estimated using the Black-Scholes options-pricing model.
At December 31, 2009, there was $3.0 million of unrecognized compensation cost relating to stock options which are expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 1.84 years.
The following table represents stock option activity from December 31, 2007 through December 31, 2009:
| Number of Shares |
Weighted-Average Exercise Price |
Weighted-Average Remaining Contract Life | ||||||
| Outstanding stock options as of December 31, 2007 |
2,800,499 | $ | 10.87 | |||||
| Granted |
1,460,764 | 15.89 | ||||||
| Exercised |
(170,054 | ) | 4.61 | |||||
| Forfeited |
(321,514 | ) | 13.74 | |||||
| Outstanding stock options as of December 31, 2008 |
3,769,695 | $ | 12.85 | |||||
| Granted |
1,526,550 | $ | 3.96 | |||||
| Forfeited |
(240,632 | ) | 12.88 | |||||
| Outstanding stock options as of December 31, 2009 |
5,055,613 | $ | 10.17 | 7.39 | ||||
| Stock options exercisable as of December 31, 2009 |
2,518,139 | $ | 11.58 | 5.95 | ||||
At December 31, 2009, the aggregate intrinsic value of stock options outstanding was $8.2 million and the aggregate intrinsic value of stock options exercisable was $2.3 million. Intrinsic value is the difference between
90
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
the exercise price of a stock option and the closing market price of our common stock, which was $7.90 on December 31, 2009.
The following table summarizes our nonvested stock option activity from December 31, 2007 through December 31, 2009:
| Number of Shares |
Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value | |||||
| Nonvested stock options as of December 31, 2007 |
1,503,841 | $ | 5.64 | |||
| Granted |
1,460,764 | 5.67 | ||||
| Vested |
(627,993 | ) | 5.63 | |||
| Forfeited |
(308,849 | ) | 5.17 | |||
| Nonvested stock options as of December 31, 2008 |
2,027,763 | $ | 5.74 | |||
| Granted |
1,526,550 | 2.09 | ||||
| Vested |
(831,539 | ) | 5.62 | |||
| Forfeited |
(185,300 | ) | 4.73 | |||
| Nonvested stock options as of December 31, 2009 |
2,537,474 | $ | 3.65 | |||
The following table summarizes our restricted stock activity from December 31, 2007 through December 31, 2009:
| Number of Shares |
Weighted-Average Grant-Date Fair Value per Share | |||||
| Nonvested restricted stock as of December 31, 2007 |
— | $ | — | |||
| Granted |
178,261 | 17.07 | ||||
| Vested |
(3,645 | ) | 17.07 | |||
| Forfeited |
(750 | ) | 17.07 | |||
| Nonvested restricted stock as of December 31, 2008 |
173,866 | $ | 17.07 | |||
| Granted |
326,748 | 4.23 | ||||
| Vested |
(54,956 | ) | 17.07 | |||
| Forfeited |
(18,300 | ) | 11.86 | |||
| Nonvested restricted stock as of December 31, 2009 |
427,358 | $ | 7.48 | |||
At December 31, 2009, there was $1.4 million of unrecognized compensation cost relating to restricted stock awards which are expected to be recognized over a weighted-average period of 2.07 years.
On February 2, 2010, our Board of Directors approved the grant of stock options representing 719,200 shares of common stock and the grant of restricted stock units representing 266,800 shares of common stock to officers and employees. The stock option awards and restricted stock unit awards will vest over a three year period.
| 10. | Employee Benefit Plans and Insurance |
We maintain a 401(k) retirement plan for our eligible employees. Under this plan, we may make a matching contribution, on a discretionary basis, equal to a percentage of each eligible employee’s annual contribution, which we determine annually. Our matching contributions for the years ended December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 and for the nine months ended December 31, 2007 were $0.7 million, $1.8 million and $0.8 million, respectively.
91
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
We maintain a self-insurance program, for major medical, hospitalization and dental coverage for employees and their dependents, which is partially funded by employee payroll deductions. We have provided for both reported and incurred but not reported medical costs in the accompanying consolidated balance sheets. We have a maximum liability of $125,000 per employee/dependent per year except for individuals employed by our Production Services Division where we had no deductible during the period ended December 31, 2008. Amounts in excess of the stated maximum are covered under a separate policy provided by an insurance company. Accrued expenses—payroll and employee related costs at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 include $1.0 million and $1.1 million, respectively, for our estimate of incurred but unpaid costs related to the self-insurance portion of our health insurance.
We are self-insured for up to $500,000 per incident for all workers’ compensation claims submitted by employees for on-the-job injuries, except in North Dakota where the deductible is $100,000. Our deductible under workers’ compensation insurance increased from $250,000 in October 2007. We have deductibles of $250,000 and $100,000 per occurrence under our general liability insurance and auto liability insurance, respectively. We accrue our workers’ compensation claim cost estimates based on historical claims development data and we accrue the cost of administrative services associated with claims processing. Accrued expenses—insurance premiums and deductibles at December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 include $7.0 million and $9.6 million, respectively, for our estimate of costs relative to the self-insured portion of our workers’ compensation, general liability and auto liability insurance. Based upon our past experience, management believes that we have adequately provided for potential losses. However, future multiple occurrences of serious injuries to employees could have a material adverse effect on our financial position and results of operations.
| 11. | Segment Information |
At December 31, 2009, we had two operating segments referred to as the Drilling Services Division and the Production Services Division which is the basis management uses for making operating decisions and assessing performance. Prior to our acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE and Competition on March 1, 2008, all our operations related to the Drilling Services Division and we reported these operations in a single operating segment. The acquisitions of the production services businesses from WEDGE and Competition resulted in the formation of our Production Services Division. See Note 2.
Drilling Services Division—Our Drilling Services Division provides contract land drilling services with its fleet of 71 drilling rigs in the following locations:
| Drilling Division Locations |
Rig Count | |
| South Texas |
15 | |
| East Texas |
19 | |
| North Dakota |
8 | |
| North Texas |
5 | |
| Utah |
5 | |
| Oklahoma |
6 | |
| Appalachia |
5 | |
| Colombia |
8 |
Production Services Division—Our Production Services Division provides a broad range of well services to oil and gas drilling and producing companies, including workover services, wireline services, and fishing and rental services. Our production services operations are managed regionally and are concentrated in the major United States onshore oil and gas producing regions in the Gulf Coast, Mid-Continent, Rocky Mountain and Appalachian states. We have a premium fleet of 74 workover rigs consisting of sixty-nine 550 horsepower rigs, four 600 horsepower rigs, and one 400 horsepower rig. We provide wireline services with a fleet of 65 wireline units and rental services with approximately $13 million of fishing and rental tools.
92
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
The following tables set forth certain financial information for our two operating segments and corporate as of and for the year ended December 31, 2009 (amounts in thousands):
| As of and for the Year Ended December 31, 2009 | ||||||||||||
| Drilling Services Division |
Production Services Division |
Corporate | Total | |||||||||
| Identifiable assets |
$ | 558,037 | $ | 232,155 | $ | 32,424 | $ | 822,616 | ||||
| Revenues |
$ | 219,751 | $ | 105,786 | $ | — | $ | 325,537 | ||||
| Operating costs |
147,343 | 68,012 | — | 215,355 | ||||||||
| Segment margin |
$ | 72,408 | $ | 37,774 | $ | — | $ | 110,182 | ||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
$ | 81,077 | $ | 23,603 | $ | 1,506 | $ | 106,186 | ||||
| Capital expenditures |
$ | 94,887 | $ | 15,162 | $ | 404 | $ | 110,453 | ||||
The following tables set forth certain financial information for our two operating segments and corporate as of and for the year ended December 31, 2008 (amounts in thousands):
| As of and for the Year Ended December 31, 2008 | ||||||||||||
| Drilling Services Division |
Production Services Division |
Corporate | Total | |||||||||
| Identifiable assets |
$ | 567,956 | $ | 232,063 | $ | 24,460 | $ | 824,479 | ||||
| Revenues |
$ | 456,890 | $ | 153,994 | $ | — | $ | 610,884 | ||||
| Operating costs |
269,846 | 80,097 | — | 349,943 | ||||||||
| Segment margin |
$ | 187,044 | $ | 73,897 | $ | — | $ | 260,941 | ||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
$ | 66,270 | $ | 21,441 | $ | 434 | $ | 88,145 | ||||
| Capital expenditures |
$ | 107,344 | $ | 38,921 | $ | 1,831 | $ | 148,096 | ||||
The following table reconciles the segment profits reported above to income from operations as reported on the condensed consolidated statements of operations for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 (amounts in thousands):
| Year Ended December 31, 2009 |
Year Ended December 31, 2008 |
|||||||
| Segment margin |
$ | 110,182 | $ | 260,941 | ||||
| Depreciation and amortization |
(106,186 | ) | (88,145 | ) | ||||
| Selling, general and administrative |
(37,478 | ) | (44,834 | ) | ||||
| Bad debt (expense) recovery |
1,642 | (423 | ) | |||||
| Impairment of goodwill |
— | (118,646 | ) | |||||
| Impairment of intangible assets |
— | (52,847 | ) | |||||
| Loss from operations |
$ | (31,840 | ) | $ | (43,954 | ) | ||
The following table sets forth certain financial information for our international operations in Colombia as of and for the years ended December 31, 2009 and 2008 which is included in our Drilling Services Division (amounts in thousands):
| As of and for the Year Ended December 31, 2009 |
As of and for the Year Ended December 31, 2008 | |||||
| Identifiable assets |
$ | 109,779 | $ | 107,927 | ||
| Revenues |
$ | 56,617 | $ | 51,414 | ||
93
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| 12. | Commitments and Contingencies |
In connection with our expansion into international markets, our foreign subsidiaries have obtained bonds for bidding on drilling contracts, performing under drilling contracts, and remitting customs and importation duties. We have guaranteed payments of $31.1 million relating to our performance under these bonds.
In addition, due to the nature of our business, we are, from time to time, involved in routine litigation or subject to disputes or claims related to our business activities, including workers’ compensation claims and employment-related disputes. Legal costs relating to these matters are expensed as incurred. In the opinion of our management, none of the pending litigation, disputes or claims against us will have a material adverse effect on our financial condition, results of operations or cash flow from operations and there is only a remote possibility that any such matter will require any additional loss accrual.
| 13. | Quarterly Results of Operations (unaudited) |
The following table summarizes quarterly financial data for the years ended December 31, 2009 and December 31, 2008 (in thousands, except per share data):
| Year Ended December 31, 2009 |
First Quarter |
Second Quarter |
Third Quarter |
Fourth Quarter |
Total | |||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 100,840 | $ | 69,120 | $ | 74,366 | $ | 81,211 | $ | 325,537 | ||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
2,857 | (9,273 | ) | (12,022 | ) | (13,402 | ) | (31,840 | ) | |||||||||||
| Income tax (expense) benefit |
180 | 3,547 | 4,406 | 8,824 | 16,957 | |||||||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
618 | (6,259 | ) | (9,190 | ) | (8,384 | ) | (23,215 | ) | |||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per share: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.01 | $ | (0.13 | ) | $ | (0.18 | ) | $ | (0.16 | ) | $ | (0.46 | ) | ||||||
| Diluted |
$ | 0.01 | $ | (0.13 | ) | $ | (0.18 | ) | $ | (0.16 | ) | $ | (0.46 | ) | ||||||
| Year Ended December 31, 2008 (1) (2) |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Revenues |
$ | 113,397 | $ | 152,547 | $ | 174,245 | $ | 170,695 | $ | 610,884 | ||||||||||
| Income (loss) from operations |
17,995 | 33,716 | 42,073 | (137,738 | ) | (43,954 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Income tax (expense) benefit |
(6,250 | ) | (9,609 | ) | (12,760 | ) | 22,562 | (6,057 | ) | |||||||||||
| Net earnings (loss) |
11,848 | 19,117 | 24,194 | (117,904 | ) | (62,745 | ) | |||||||||||||
| Earnings (loss) per share: |
||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic |
$ | 0.24 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.49 | $ | (2.37 | ) | $ | (1.26 | ) | ||||||||
| Diluted (3) |
$ | 0.24 | $ | 0.38 | $ | 0.48 | $ | (2.37 | ) | $ | (1.26 | ) | ||||||||
| (1) | Our quarterly results of operations for the year ended December 31, 2008 include the results of operations relating to acquisitions of WEDGE and Competition, both of which occurred on March 1, 2008. See note 2. |
| (2) | Our quarterly results of operations for the fourth quarter of the year ended December 31, 2008 reflect the impact of a goodwill impairment charge of $118.6 million and an intangible asset impairment charge of $52.8 million. See note 1. |
| (3) | Due to the effects of rounding, the sum of quarterly earnings per share does not equal total earnings per share for the fiscal year. |
94
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Item 9. | Changes in and Disagreements With Accountants on Accounting and Financial Disclosure |
Not applicable.
| Item 9A. | Controls and Procedures |
In accordance with Exchange Act Rules 13a-15 and 15d-15, we carried out an evaluation, under the supervision and with the participation of management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, of the effectiveness of our disclosure controls and procedures as of the end of the period covered by this report. Based upon that evaluation, our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer concluded that our disclosure controls and procedures were effective as of December 31, 2009, to ensure that information required to be disclosed in our reports filed or submitted under the Exchange Act is (1) recorded, processed, summarized and reported within the time periods specified in the Securities and Exchange Commission’s rules and forms and (2) accumulated and communicated to our management, including our Chief Executive Officer and Chief Financial Officer, as appropriate to allow timely decisions regarding required disclosure.
There has been no change in our internal control over financial reporting that occurred during the three months ended December 31, 2009 that has materially affected, or is reasonably likely to materially affect, our internal control over financial reporting.
Management’s Report on Internal Control Over Financial Reporting
The management of Pioneer Drilling Company is responsible for establishing and maintaining adequate internal control over financial reporting. Pioneer Drilling Company’s internal control over financial reporting is a process designed to provide reasonable assurance regarding the reliability of financial reporting and the preparation of financial statements for external purposes in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles. A company’s internal control over financial reporting includes those policies and procedures that: (1) pertain to the maintenance of records that, in reasonable detail, accurately and fairly reflect the transactions and dispositions of the assets of the company; (2) provide reasonable assurance that transactions are recorded as necessary to permit preparation of financial statements in accordance with generally accepted accounting principles, and that receipts and expenditures of Pioneer Drilling Company are being made only in accordance with authorizations of management and directors of the company; and (3) provide reasonable assurance regarding prevention or timely detection of unauthorized acquisition, use, or disposition of the company’s assets that could have a material effect on the financial statements. Because of its inherent limitations, internal control over financial reporting may not prevent or detect misstatements. Also, projections of any evaluation of effectiveness to future periods are subject to the risk that controls may become inadequate because of changes in conditions, or that the degree of compliance with the policies or procedures may deteriorate.
Pioneer Drilling Company’s management assessed the effectiveness of Pioneer Drilling Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009. In making this assessment, it used the criteria set forth by the Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) in Internal Control-Integrated Framework. Based on our assessment we have concluded that, as of December 31, 2009, Pioneer Drilling Company’s internal control over financial reporting was effective based on those criteria.
KPMG LLP, the independent registered public accounting firm that audited the consolidated financial statements of Pioneer Drilling Company included in this Annual Report on Form 10-K, has issued an attestation report on the effectiveness of Pioneer Drilling Company’s internal control over financial reporting as of December 31, 2009. This report appears on page 63.
95
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Item 9B. | Other Information |
Not applicable.
In Items 10, 11, 12, 13 and 14 below, we are incorporating by reference the information we refer to in those Items from the definitive proxy statement for our 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders. We intend to file that definitive proxy statement with the SEC on or about April 9, 2010.
| Item 10. | Directors, Executive Officers and Corporate Governance |
Please see the information appearing under the headings “Proposal 1—Election of Directors,” “Executive Officers,” “Information Concerning Meetings and Committees of the Board of Directors,” “Code of Conduct and Ethics” and “Section 16(a) Beneficial Ownership Reporting Compliance” in the definitive proxy statement for our 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders for the information this Item 10 requires.
| Item 11. | Executive Compensation |
Please see the information appearing under the headings “Compensation Discussion and Analysis,” “Compensation of Directors,” “Compensation of Executive Officers,” “Compensation Committee Interlocks and Insider Participation” and “Compensation Committee Report” in the definitive proxy statement for our 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders for the information this Item 11 requires.
| Item 12. | Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management and Related Shareholder Matters |
Please see the information appearing (1) under the heading “Equity Compensation Plan Information” in Item 5 of Part II of this report and (2) under the heading “Security Ownership of Certain Beneficial Owners and Management” in the definitive proxy statement for our 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders for the information this Item 12 requires.
| Item 13. | Certain Relationships and Related Transactions, and Director Independence |
Please see the information appearing under the headings “Proposal 1—Election of Directors” and “Certain Relationships and Related Transactions” in the definitive proxy statement for our 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders for the information this Item 13 requires.
| Item 14. | Principal Accountant Fees and Services |
Please see the information appearing under the heading “Proposal 2—Ratification of Appointment of Independent Auditors” in the definitive proxy statement for our 2010 Annual Meeting of Shareholders for the information this Item 14 requires.
96
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Item 15. | Exhibits and Financial Statement Schedules |
(1) Financial Statements.
See Index to Consolidated Financial Statements on page 61.
Financial Statement Schedules
No financial statement schedules are submitted because either they are inapplicable or because the required information is included in the consolidated financial statements or notes thereto.
97
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
(3) Exhibits. The following exhibits are filed as part of this report:
| Exhibit |
Description | |||
| 2.1* | - | Securities Purchase Agreement, dated January 31, 2008, by and among Pioneer Drilling Company, WEDGE Group Incorporated, WEDGE Energy Holdings, L.L.C., WEDGE Oil & Gas Services, L.L.C., Timothy Daley, John Patterson and Patrick Grissom (Form 8-K dated February 1, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 2.1)). | ||
| 2.2* | - | Letter Agreement, dated February 29, 2008, amending the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated January 31, 2008, by and among Pioneer Drilling Company, WEDGE Group Incorporated, WEDGE Energy Holdings, L.L.C., WEDGE Oil & Gas Services, L.L.C., Timothy Daley, John Patterson and Patrick Grissom (Form 8-K dated March 3, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 2.1)). | ||
| 3.1* | - | Restated Articles of Incorporation of Pioneer Drilling Company (Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 3.1)). | ||
| 3.2* | - | Amended and Restated Bylaws of Pioneer Drilling Company (Form 8-K dated December 15, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 3.1)). | ||
| 4.1* | - | Form of Certificate representing Common Stock of Pioneer Drilling Company (Form S-8 filed November 18, 2003 (Reg. No. 333-110569, Exhibit 4.3)). | ||
| 10.1+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Services, Ltd. Annual Incentive Compensation Plan dated August 5, 2005 (Form 8-K dated August 5, 2005 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | ||
| 10.2+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company Amended and Restated Key Executive Severance Plan dated December 10, 2007 (Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.4)). | ||
| 10.3+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company’s 1995 Stock Plan and form of Stock Option Agreement (Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2001 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.5)). | ||
| 10.4+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company’s 1999 Stock Plan and form of Stock Option Agreement (Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2001 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.7)). | ||
| 10.5+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company 2003 Stock Plan (Form S-8 filed November 18, 2003 (File No. 333-110569, Exhibit 4.4)). | ||
| 10.6+* | - | Amended and Restated Pioneer Drilling Company 2007 Incentive Plan adopted May 15, 2009 (Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A, filed April 10, 2009 (File No. 1-8182, Appendix A)). | ||
| 10.9+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company Form of Indemnification Agreement (Form 8-K dated August 8, 2007 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | ||
| 10.10+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company Employee Relocation Policy Executive Officers—Package A (Form 8-K dated August 8, 2007 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.3)). | ||
| 10.11* | Credit Agreement, dated February 29, 2008, among Pioneer Drilling Company, as Borrower, and Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, issuing lender, swing line lender and co-lead arranger, Fortis Bank SA/NV, New York Branch, as co-lead arranger, and each of the other parties listed therein (Form 8-K dated March 3, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
| 10.12* | First Amendment to Credit Agreement, dated as of October 5, 2009, among Pioneer Drilling Company, the lenders party thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, issuing lender and swing line lender (Form 8-K dated October 6, 2009 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)) | |||
| 10.13* | Waiver Agreement, dated as of June 9, 2008, among Pioneer Drilling Company, the guarantors party thereto, Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, issuing lender and swing line lender, and each of the other financial institutions party thereto (Form 8-K dated June 11, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
98
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Exhibit |
Description | |||
| 10.14+* | Employment Letter, effective March 1, 2008, from Pioneer Drilling Company to Joseph B. Eustace (Form 8-K dated March 5, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
| 10.15+* | Confidentiality and Non-Competition Agreement, dated February 29, 2008, by and between Pioneer Drilling Company, Pioneer Production Services, Inc. and Joe Eustace (Form 8-K dated March 5, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.2)). | |||
| 10.16+* | Agreement between Joyce M. Schuldt and Pioneer Drilling Company, dated August 20, 2008 (Form 8-K dated August 21, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
| 10.17* | Pioneer Drilling Company 2007 Incentive Plan Form of Stock Option Agreement (Form 8-K dated September 4, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
| 10.18* | Pioneer Drilling Company 2007 Incentive Plan Form of Employee Restricted Stock Award Agreement (Form 8-K dated September 4, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.2)). | |||
| 10.19* | Pioneer Drilling Company 2007 Incentive Plan Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Award Agreement (Form 8-K dated September 4, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.3)). | |||
| 10.20+* | Employment Letter Agreement, effective January 7, 2009, from Pioneer Drilling Company to Lorne E. Phillips (Form 8-K dated January 14, 2009 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
| 21.1 | - | Subsidiaries of Pioneer Drilling Company. | ||
| 23.1 | - | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | ||
| 31.1 | - | Certification by Wm. Stacy Locke, President and Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. | ||
| 31.2 | - | Certification by Lorne E. Phillips, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. | ||
| 32.1 | - | Certification by Wm. Stacy Locke, President and Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (Subsections (a) and (b) of Section 1350, Chapter 63 of Title 18, United States Code). | ||
| 32.2 | - | Certification by Lorne E. Phillips, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (Subsections (a) and (b) of Section 1350, Chapter 63 of Title 18, United States Code). | ||
| * | Incorporated by reference to the filing indicated. |
| + | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
99
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
SIGNATURES
Pursuant to the requirements of Section 13 or 15(d) of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, the registrant has duly caused this report to be signed on its behalf by the undersigned, thereunto duly authorized.
| PIONEER DRILLING COMPANY | ||
| February 16, 2010 |
BY: /S/ WM. STACY LOCKE | |
| Wm. Stacy Locke Chief Executive Officer and President | ||
Pursuant to the requirements of the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, this report has been signed below by the following persons on behalf of the registrant and in the capacities and on the dates indicated.
| Signature |
Title |
Date | ||
| /S/ DEAN A. BURKHARDT Dean A. Burkhardt |
Chairman | February 16, 2010 | ||
| /S/ WM. STACY LOCKE Wm. Stacy Locke |
President, Chief Executive Officer and Director (Principal Executive Officer) | February 16, 2010 | ||
| /S/ LORNE E. PHILLIPS Lorne E. Phillips |
Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer | February 16, 2010 | ||
| /S/ C. JOHN THOMPSON C. John Thompson |
Director | February 16, 2010 | ||
| /S/ JOHN MICHAEL RAUH John Michael Rauh |
Director | February 16, 2010 | ||
| /S/ SCOTT D. URBAN Scott D. Urban |
Director | February 16, 2010 | ||
100
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Exhibit Number |
Description | |||
| 2.1* | - | Securities Purchase Agreement, dated January 31, 2008, by and among Pioneer Drilling Company, WEDGE Group Incorporated, WEDGE Energy Holdings, L.L.C., WEDGE Oil & Gas Services, L.L.C., Timothy Daley, John Patterson and Patrick Grissom (Form 8-K dated February 1, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 2.1)). | ||
| 2.2* | - | Letter Agreement, dated February 29, 2008, amending the Securities Purchase Agreement, dated January 31, 2008, by and among Pioneer Drilling Company, WEDGE Group Incorporated, WEDGE Energy Holdings, L.L.C., WEDGE Oil & Gas Services, L.L.C., Timothy Daley, John Patterson and Patrick Grissom (Form 8-K dated March 3, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 2.1)). | ||
| 3.1* | - | Restated Articles of Incorporation of Pioneer Drilling Company (Form 10-K for the year ended December 31, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 3.1)). | ||
| 3.2* | - | Amended and Restated Bylaws of Pioneer Drilling Company (Form 8-K dated December 15, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 3.1)). | ||
| 4.1* | - | Form of Certificate representing Common Stock of Pioneer Drilling Company (Form S-8 filed November 18, 2003 (Reg. No. 333-110569, Exhibit 4.3)). | ||
| 10.1+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Services, Ltd. Annual Incentive Compensation Plan dated August 5, 2005 (Form 8-K dated August 5, 2005 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | ||
| 10.2+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company Amended and Restated Key Executive Severance Plan dated December 10, 2007 (Form 10-Q for the quarter ended March 31, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.4)). | ||
| 10.3+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company’s 1995 Stock Plan and form of Stock Option Agreement (Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2001 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.5)). | ||
| 10.4+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company’s 1999 Stock Plan and form of Stock Option Agreement (Form 10-K for the year ended March 31, 2001 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.7)). | ||
| 10.5+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company 2003 Stock Plan (Form S-8 filed November 18, 2003 (File No. 333-110569, Exhibit 4.4)). | ||
| 10.6+* | - | Amended and Restated Pioneer Drilling Company 2007 Incentive Plan adopted May 15, 2009 (Definitive Proxy Statement on Schedule 14A, filed April 10, 2009 (File No. 1-8182, Appendix A)). | ||
| 10.9+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company Form of Indemnification Agreement (Form 8-K dated August 8, 2007 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | ||
| 10.10+* | - | Pioneer Drilling Company Employee Relocation Policy Executive Officers—Package A (Form 8-K dated August 8, 2007 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.3)). | ||
| 10.11* | Credit Agreement, dated February 29, 2008, among Pioneer Drilling Company, as Borrower, and Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, issuing lender, swing line lender and co-lead arranger, Fortis Bank SA/NV, New York Branch, as co-lead arranger, and each of the other parties listed therein (Form 8-K dated March 3, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
| 10.12* | First Amendment to Credit Agreement, dated as of October 5, 2009, among Pioneer Drilling Company, the lenders party thereto, and Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, issuing lender and swing line lender (Form 8-K dated October 6, 2009 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)) | |||
| 10.13* | Waiver Agreement, dated as of June 9, 2008, among Pioneer Drilling Company, the guarantors party thereto, Wells Fargo Bank, N.A., as administrative agent, issuing lender and swing line lender, and each of the other financial institutions party thereto (Form 8-K dated June 11, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
101
Table of Contents
Index to Financial Statements
| Exhibit |
Description | |||
| 10.14+* | Employment Letter, effective March 1, 2008, from Pioneer Drilling Company to Joseph B. Eustace (Form 8-K dated March 5, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
| 10.15+* | Confidentiality and Non-Competition Agreement, dated February 29, 2008, by and between Pioneer Drilling Company, Pioneer Production Services, Inc. and Joe Eustace (Form 8-K dated March 5, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.2)). | |||
| 10.16+* | Agreement between Joyce M. Schuldt and Pioneer Drilling Company, dated August 20, 2008 (Form 8-K dated August 21, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
| 10.17* | Pioneer Drilling Company 2007 Incentive Plan Form of Stock Option Agreement (Form 8-K dated September 4, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
| 10.18* | Pioneer Drilling Company 2007 Incentive Plan Form of Employee Restricted Stock Award Agreement (Form 8-K dated September 4, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.2)). | |||
| 10.19* | Pioneer Drilling Company 2007 Incentive Plan Form of Non-Employee Director Restricted Stock Award Agreement (Form 8-K dated September 4, 2008 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.3)). | |||
| 10.20+* | Employment Letter Agreement, effective January 7, 2009, from Pioneer Drilling Company to Lorne E. Phillips (Form 8-K dated January 14, 2009 (File No. 1-8182, Exhibit 10.1)). | |||
| 21.1 | - | Subsidiaries of Pioneer Drilling Company. | ||
| 23.1 | - | Consent of Independent Registered Public Accounting Firm. | ||
| 31.1 | - | Certification by Wm. Stacy Locke, President and Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. | ||
| 31.2 | - | Certification by Lorne E. Phillips, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to Rule 13a-14(a) or Rule 15d-14(a) under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934. | ||
| 32.1 | - | Certification by Wm. Stacy Locke, President and Chief Executive Officer, pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (Subsections (a) and (b) of Section 1350, Chapter 63 of Title 18, United States Code). | ||
| 32.2 | - | Certification by Lorne E. Phillips, Executive Vice President and Chief Financial Officer, pursuant to Section 906 of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 (Subsections (a) and (b) of Section 1350, Chapter 63 of Title 18, United States Code). | ||
| * | Incorporated by reference to the filing indicated. |
| + | Management contract or compensatory plan or arrangement. |
102
